Module 11: Micronutrients - Minerals. LLiana Shanti, CN
|
|
|
- Hollie Stone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Module 11: Micronutrients - Minerals LLiana Shanti, CN
2 MINERALS Four elements compose 96% of the body s makeup: carbon hydrogen oxygen nitrogen The remaining 4% of the body s composition is mineral.
3 MACROMINERALS Calcium Chlorine Sodium Potassium Phosphorus Magnesium Sulfur
4 TRACE MINERALS Chromium Tin Zinc Vanadium Copper Silicon Manganese Nickel Iron Molybdenum Fluorine Iodine Cobalt Selenium
5 MINERALS Structural: bones, teeth, ligaments Solutes and electrolytes in the blood Enzyme actions Energy production from food breakdown Nerve transmission Muscle action
6 MINERALS Calcium: Muscle contraction, Bone building Sodium: Cell life, Waste removal Potassium: Nerve transmission, Cell life Normal blood pressure, Muscle contraction Phosphorus: Bone formation, Cell energy Magnesium: Muscle contraction, Nerve transmission Calcium metabolism, Enzyme cofactor
7 MINERALS Chlorine: Digestion, Normal blood pressure Sulfur: Protein synthesis, Collagen cross-linking, bone and ligament structure Copper: Immune system, Artery strength, Forms hemoglobin from iron Chromium: Insulin action, Immune function
8 MINERALS Iron: Hemoglobin formation, Immune function Zinc: antioxidant production, cofactor for over 80 enzymes, wound healing, fat metabolism, myelin insulin function, tissue repair, skin health Selenium: Immune stimulant, Fight free radicals Activates Vit E Nickel: Immune regulation, Brain development, DNA synthesis
9 MINERALS Iodine: Thyroid function Vanadium: Circulation, Sugar metabolism Molybdenum: Enzyme action Silicon: Enzyme action, Connective tissue Tin: Enzyme action Manganese: Enzyme action Fluorine: Teeth enamel
10 MINERALS Mineral Deficiency = Premature Aging and Cell Breakdown
11 MINERALS DEFICIENCIES % of U.S. Population Magnesium 75% Iron 58% Copper 81% Manganese 50% Chromium 90% Zinc 67% Selenium 60%
12 MINERALS Soil Depletion In 1900, forests covered 40% of the earth. By 1992, the figure was about 27%. (Relating Land Use and Global Land Cover, Turner) In the past 200 years, the U.S. alone has lost as much as 75% of its topsoil. (John Robbins in his Pulitzer-nominated work Diet for a New America). To replace one inch of topsoil may take anywhere from years, depending on climate.
13 MINERALS Soil Depletion The standard NPK (nitrogen-phosphorus-potassium) fertilizer farmers commonly use is able to restore the soil enough to grow fruits and vegetables which are healthy looking, but may be entirely lacking in trace minerals.
14 MINERALS Diet Refined foods inhibit mineral absorption, which then are not efficiently digested because of diminished enzyme activity. Blocked Colon Secondary Deficiency Drugs
15 MINERALS BIOAVAILABILITY Elemental versus Nutritional Minerals Over-Exposure
16 MINERALS Supplementation Elemental Ionic Colloidal Chelated
17 MINERALS Supplementation - Take only the minerals we absolutely need - Take the smallest amounts possible - Nothing left over (no metabolic residue)
18 BORON Used to help with menopausal symptoms as well as maintaining healthy bones, hence its affinity to calcium and magnesium. SOURCES: Green leafy vegetables, nuts, grains, prunes, dates, raisins, honey, nuts, fresh fruit such as grapes and pears, beans.
19 CALCIUM Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the human body and one of the most important. The calcium topic is huge and complex. This mineral constitutes about percent of our body weight. Almost all (98 percent) of our approximately three pounds of calcium is contained in our bones, about 1 percent in our teeth, and the rest in the other tissues and the circulation. SOURCES: Almonds, Brazil nuts, broccoli, cabbage, carob, collards, dandelion leaves, dulse, figs, filberts, green leafy vegetables, kale, kelp, molasses, mustard greens, oats, parsley, pau d'arco bark, prunes, sesame seeds, soybeans, tofu, turnip greens, valerian root, white oak bark.
20 CHLORIDE Production of stomach acid and the transmission of nerve impulses. Helps regulate water balance in cells, acid-base balance and electrolyte balance. Necessary for the production of hydrochloric acid in stomach acid. Required for the absorption of vitamin B12 and iron. Helps stop the growth of microorganisms that enter the stomach. Activates amylases. SOURCES: Sea salt, kelp, olives, tomatoes, celery.
21 CHROMIUM An essential element of glucose tolerance factor (GTF). GTF (and thus chromium) is a vital molecule in regulating carbohydrate metabolism by enhancing insulin function for proper use of glucose in the body. Chromium is an essential nutrient required for normal sugar and fat metabolism and works primarily by potentiating the action of insulin. It is present in the entire body but with the highest concentrations in the liver, kidneys, spleen and bone. SOURCES: Apple peel, banana, blackstrap molasses, beans, eggs, mushrooms, oatstraw, potatoes with skin, Stevia leaves, whole grains.
22 COBALT Cobalt is an important element in the formation of cobalamin or vitamin B12. It is not easily assimilated in the body and is stored in red blood cells, liver, plasma, spleen, kidney, and pancreas. Promotes RBC formation. Activates enzymes, replaces zinc in some enzymes. SOURCES: Beet greens, buckwheat, cabbage, dulse, figs, goldenseal kelp, lettuce, pau d'arco, sarsaparilla, spinach, watercress.
23 COPPER Copper is absorbed into the intestine and quickly moves to the blood stream. It is stored in the liver, kidneys, heart, brain, muscles, and bones. Copper aids in the formation of bones, conversion of iron into hemoglobin, and works with zinc and vitamin C for the production of elastrin. It is necessary for the production of RNA, phospholipids, protein metabolism and adenosine triphosphate (ATP). Copper helps convert tyrosine into a pigment that colors the skin and hair. It is involved in the healing process, taste, healthy nerves, and the formation of collagen. Copper imbalance raises cholesterol by destroying proper HDL to LDL balance. Critical for metabolizing iron; plays a role in connective tissue formation (ie-muscle and blood vessels); protein synthesis. Necessary for the absorption & utilization of Iron; helps oxidize Vitamin C and works with Vitamin C to form Elastin, a chief component of the Elastin muscle fibers throughout the body; aids in the formation of red blood cells; helps proper bone formation & maintenance.
24 COPPER Alfalfa, almonds, avocados, barley, beans, beet roots, black pepper, blackstrap molasses, Brazil nuts, broccoli, cashews, cacao, dandelion leaves, garlic, grapes, green leafy vegetables, green olives, hazelnuts, herring, honey, horsetail, lentils, molasses, mushrooms, mussels, nuts, oats, oranges, pecans, radishes, raisins, sage, skullcap, sesame seeds, soybeans, sunflower seeds, walnuts, white oak bark, yucca.
25 IODINE Iodine is important for the development and proper function of the thyroid. It helps to metabolize fats, promotes growth, and regulates the production of energy. It is absorbed in the intestinal tract and is transported through the bloodstream to the thyroid were it becomes iodized and converted into thyroxin. Iodine is essential for absorption of carbohydrates, hair, mental health, nails, proper balance of cholesterol, proper metabolism, skin, speech, teeth, the conversion of carotene to vitamin A, and the synthesis of protein by ribosomes. Asparagus, chard, dulse, garlic, kelp, lima beans, mushrooms, seaweed, sesame seeds, soybeans, spinach, squash, sunflower seeds, turnip greens.
26 IRON Iron plays an important role in the production of hemoglobin with protein and copper and oxygenation of red blood cells and lymphocytes. Iron improves the function of enzymes in protein metabolism and enhances the functions of calcium and copper. It is absorbed in the small intestine and stored in the liver, spleen, bone marrow, and blood. Iron is needed to metabolize B vitamins. Almonds, avocados, beans, beets, blue cohosh, broccoli, butchers broom, cashews, chickweed, cacao, dates, devil's claw, dried fruit, dulse, egg yolk, garbanzo beans, green leafy vegetables, spinach, kelp, legumes, lentils, millet, molasses, mullein, parsley, peaches, pears, pennyroyal, pistachios, potatoes, prunes, pumpkins, raisins, rice, seaweed, sesame seeds, soybeans, sunflower seeds, walnuts.
27 MAGNESIUM THE MASTER MINERAL. Responsible for over 300 metabolic processes. Plays an important role in regulating the neuromuscular activity of the heart; maintains normal heart rhythm; necessary for proper calcium & Vitamin C metabolism; converts blood sugar into energy. Magnesium is vital for many metabolic functions such as the activation of enzymes for proper metabolism of protein and carbohydrates for energy production. It is a constituent of bones and teeth and is important for the metabolism of phosphorus, calcium, potassium, sodium, B-complex vitamins, and vitamins C and E. Magnesium is absorbed in the small intestine and vitamin D is necessary for proper utilization of the mineral. Necessary in the production of testosterone and progesterone. It is essential for normal heart beat, nerve transmission, bone growth, body temperature, and arterial health. Magnesium, in proper balance with calcium, is important for neuromuscular contractions and is vital for DNA and RNA production. Helpful in stroke prevention
28 MAGNESIUM Almonds, barley, blackstrap molasses, cacao, figs, garlic, green leafy vegetables, kelp, licorice, lima beans, millet, molasses, nettle, nuts, oat straw, oats, peaches, peas, perch, sesame seeds,, soybeans, sunflower seeds.
29 Mg Deficiency Changes is nerve & muscle function such as muscle weakness or spasm. Heart conditions such as arrhythmia, irregular contractions, and increased heart rate. Weakening of the bones Imbalanced blood sugar Elevated blood pressure High excitability Brain damage Unstable internal cell structure Inadequate hormone production Headaches Seizures Depression Nausea Vomiting Lack of appetite
30 MANGANESE A cofactor in many enzyme systems including those involved in bone formation, energy production, and metabolism of protein, carbohydrate, and fat. It is essential for the utilization of choline, thiamine, biotin, and vitamins C and E. It is absorbed in the small intestine and is stored in the bones, liver, kidney, pituitary gland, and pancreas. Manganese is required for choline acetylcholine transsfer, enhances smooth muscle relaxation. Promotes normal growth and development, cell function. Manganese helps produce mucopolysaccharides, stimulates the production of cholesterol and is a co-factor in many of the body's enzymes. Avocados, barley, beans, bilberry fruit, blackberries, blackstrap molasses, blueberries, bran, brown rice, buckwheat, buchu leaves, chestnuts, cloves, egg yolks, ginger, grapevine, green leafy vegetables, hazelnuts, kelp, legumes,nuts, oatmealpeas, pecans, pineapples, red raspberry leaves, rice bran, seaweed, seeds, spinach, walnuts, whole grain cereals.
31 MOLYBDENUM Molybdenum plays an important role in 2 enzymatic reactions. They include aldehyde oxidase which is necessary for the oxidation of fats, and xanthine oxidase necessary for the movement of iron from liver reserves and converting nucleic acid to uric acid (waste product eliminated in the urine). Molybdenum is absorbed through the intestines and stored in the liver, bones, and kidneys. It is required for proper growth and development, the metabolism of fats and nucleic acids, metabolism of nitrogen, copper, and sulfur, and normal cellular functions. Cofactor in enzymatic systems involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, sulfur-containing amino acids, nucleic acids (DNA, RNA) and iron. Helps prevent cavities. Cancer-preventative (esophagus, stomach), helps detoxify or eliminate harmful sulfites from the body. Barley, beans, buckwheat, cereal grains, green leafy vegetables, legumes, lentils, lima beans, peas, sunflower seeds, whole grains.
32 PHOSPHORUS Phosphorus is important to keep in balance with calcium and magnesium. It plays a role in every metabolic reaction in the body and is important for the metabolism of fats, carbohydrates, and protein for proper growth and production of energy. Phosphorus is absorbed through the intestines, transported in the bloodstream, and stored in the bones and teeth. 70% of ingested phosphorus is absorbed. Cabbage, corn, cacao, eggs, fruit, garlic, legumes,nuts, pumpkin seeds,, squash seeds, soybeans, sunflower seeds
33 POTASSIUM Potassium is important for chemical reactions within the cells, and regulates the transfer of nutrients to the cells. Potassium helps to regulate water balance in the body, and the distribution of fluids on both sides of the cell walls. It is an electrolyte needed to maintain fluid balance, normal heartbeat, and nerve transmission. Potassium is absorbed through the intestines and is stored in the cells and kidneys. It is necessary for adrenal glands. Potassium is important for proper muscle contractions, normal blood pressure, growth, nerve impulses, healthy skin, cell metabolism, and enzyme reactions. Potassium increases the metabolism. Helpful in stroke prevention. Antidepressant, antihypertensive, antispasmodic.
34 POTASSIUM Almonds, apricots, avocados, bananas, Brazil nuts, broccoli, brown rice, cabbage herb, cashews, celery herb, chard, citrus fruit, dates, figs, fruit, garlic, grapefruit juice, green leafy vegetables, guava, legumes, lentils, molasses, nectarine, nuts, oranges, parsley, parsnips, peaches, potatoes, raisins, rice bran, seaweed, seeds, soybeans, spinach (fresh), squash, sunflower seeds, tomato juice, walnuts, yams
35 SELENIUM Selenium is an antioxidant that protects vitamin E from degradation. It helps to build the immune system by destroying free radicals, and aid in the production of antibodies. Selenium is absorbed through the intestines and stored in the liver, kidneys, and muscles. The lower the selenium intake the higher the incidents of cancer. Selenium fortifies heart energy cells, making sure they get enough oxygen. Selenium helps eliminate arsenic. Helpful in stroke prevention. Helps protect against the effects from arsenic, cadmium and mercury. Component of glutathione peroxidase, protecting tissues from the effects of polyunsaturated fatty acid oxidation.
36 SELENIUM Barley, blackstrap molasses, bran, Brazil nuts, broccoli, brown rice, buchu leaves, cabbage, catnip, celery, cereals, cinnamon, cucumbers, garlic, grains, green leafy vegetables, hibiscus, ho shou wu root, milk thistle seeds, molasses, mushrooms, nutmeg, nuts, oats, onions, swiss chard, turnips, whole grains.
37 SILICON Anti-arteriosclerotic. Silicon is needed for bone structure, growth, and connective tissue production of collagen. Silicon is important for healthy nails, skin, hair, and bone formation. It is need to maintain healthy arteries and prevents cardiovascular disease. It counteracts the effects of aluminum toxicity and improves calcium intake. Alfalfa, beets, bell peppers, cucumber, brown rice, dulse, Echinacea root, eyebright herb, goldenseal root, green leafy vegetables, horsetail grass, mother's milk, soybeans, whole grains.
38 SULFUR Sulfur is found in the amino acids cysteine, cystine and methionine. Sulfur is also found in cells, hemoglobin, collagen, keratin, insulin, heparin, hair, skin, nails, among many other biological structures. Sulfur is necessary for synthesizing collagen. It is required for the metabolism of several vitamins including thiamine, biotin and pantothenic acid. It is also required for cellular respiration. Sulfur is a component of biotin, insulin, glutathione, thiamine, coenzyme A. Helps in carbohydrate metabolism, helps detoxify by converting toxins to nontoxic forms. Sulfur aids in bile secretion in the liver. Beans, Brussels sprouts, cabbage, clams, eggs, onions, soybeans, taurine, turnips.
39 ZINC Zinc is important for absorption and action of B-complex vitamins. It is required for protein synthesis, collagen formation, healthy immune system, and the ability of the body to heal from wounds. Zinc is absorbed in the small intestine and is stored in the liver, eyes, kidneys, pancreas, bones, muscles, prostate gland, sperm, nails, skin, hair, and white blood cells. Zinc inhibits 5-alpha reductase from converting testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) a form of testosterone that promotes prostate growth. Zinc increases testosterone, and sperm count. If a zinc deficiency exists sex drive is reduced in order to conserve the zinc (zinc is concentrated in semen). Zinc is involved in protein synthesis, muscle contraction, formation of insulin, maintaining acid-base balance, synthesis of DNA, brain functions. Excessive sweating leads to loss of up to 3 mg per day.
40 ZINC Beans, bilberry fruit, black strap molasses, buchu leaves, capsicum fruit, legumes, maple syrup, pumpkin seeds, skullcap herb, sesame seeds, soybeans, sunflower seeds, whole grains. **Zinc is very hard to get in adequate amounts that are bioavailable to the body when consuming a plant based diet.
Macros and Micros. of a Healthy Diet. Macronutrients. Proteins
 Macros and Micros of a Healthy Diet Macronutrients Nutrients needed in large amounts in the body that provide energy Includes protein, carbohydrates, and fats Proteins Roles in the body: Develops, maintains,
Macros and Micros of a Healthy Diet Macronutrients Nutrients needed in large amounts in the body that provide energy Includes protein, carbohydrates, and fats Proteins Roles in the body: Develops, maintains,
Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals
 Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals A Beta-Carotene Thiamine (B 1 ) Riboflavin (B 2 ) Vitamin A is needed for new cell growth. Helps fight infection. Essential for healthy skin, good
Everything You Need to Know about Vitamins and Minerals A Beta-Carotene Thiamine (B 1 ) Riboflavin (B 2 ) Vitamin A is needed for new cell growth. Helps fight infection. Essential for healthy skin, good
F. To provide energy, to spare body protein, to prevent ketosis. G. Food sources include breads, vegetables, fruit, and milk.
 Nutrition: Nutrients for the Body Nutrients are chemical substances supplied by food that the body needs for growth, maintenance, and repair. The six nutrients are: 1. Carbohydrates. 2. Proteins. 3. Fats.
Nutrition: Nutrients for the Body Nutrients are chemical substances supplied by food that the body needs for growth, maintenance, and repair. The six nutrients are: 1. Carbohydrates. 2. Proteins. 3. Fats.
MACRO MINERALS Oct 13, 2015
 1 2 3 4 Macro Minerals Semester A: Basics Class # 3 Oct 13, 2015 Elements in Human Body 96% of Our Body is made of: - Oxygen - Hydrogen - Carbon - Nitrogen 4% is made of Minerals There are more than 100
1 2 3 4 Macro Minerals Semester A: Basics Class # 3 Oct 13, 2015 Elements in Human Body 96% of Our Body is made of: - Oxygen - Hydrogen - Carbon - Nitrogen 4% is made of Minerals There are more than 100
Chapter. The Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals. Images shutterstock.com
 Chapter 13 The Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Images shutterstock.com Objectives Differentiate between fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins. List functions and sources of major minerals
Chapter 13 The Micronutrients: Vitamins and Minerals Images shutterstock.com Objectives Differentiate between fat-soluble vitamins and water-soluble vitamins. List functions and sources of major minerals
6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health. By Dr. Isaac Eliaz
 6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health By Dr. Isaac Eliaz Minerals are essential micronutrients that are required in small amounts for the body to function properly. Untreated mineral deficiencies can
6 Essential Minerals for Women's Health By Dr. Isaac Eliaz Minerals are essential micronutrients that are required in small amounts for the body to function properly. Untreated mineral deficiencies can
NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS FAT SOLUBLE VITAMINS
 NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS Carbohydrates Found in breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, sugar and potatoes. good source of energy fiber in fruits and vegetables aid in eliminating wastes from the
NUTRITION CONCEPTS MACRONUTRIENTS Carbohydrates Found in breads, cereals, fruits, vegetables, sugar and potatoes. good source of energy fiber in fruits and vegetables aid in eliminating wastes from the
Demeka Scott. 6 Natural Foods to Boost Your Immune System. Natural Health Consultant.
 6 Natural Foods to Boost Your Immune System 1 Vitamin C. Vitamin C tops the list of immune boosters for many reasons. There has been more research about the immune-boosting effects of Vitamin C than perhaps
6 Natural Foods to Boost Your Immune System 1 Vitamin C. Vitamin C tops the list of immune boosters for many reasons. There has been more research about the immune-boosting effects of Vitamin C than perhaps
Nutrients. The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning.
 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to Provide energy. Build and repair
Six Essential Types of Nutrients: The human body needs a balanced mix of all seven essential nutrients to sustain its normal functions.
 Six Essential Types of Nutrients: The human body needs a balanced mix of all seven essential nutrients to sustain its normal functions. "Let thy food be thy medicine, and let thy medicine be thy food."
Six Essential Types of Nutrients: The human body needs a balanced mix of all seven essential nutrients to sustain its normal functions. "Let thy food be thy medicine, and let thy medicine be thy food."
Tends to lower blood cholesterol levels Found mostly in plant sources. (safflower, sunflower, soybean, corn, cottonseed)
 Calories Calories are needed to provide energy so the body functions properly. The number of calories in a food depends on the amount of energy the food provides. The number of calories a person needs
Calories Calories are needed to provide energy so the body functions properly. The number of calories in a food depends on the amount of energy the food provides. The number of calories a person needs
Vitamins and Minerals
 Eating Right Vitamins and Minerals Many claims about vitamins and minerals may be misleading and confusing. The following lists tell what vitamins and minerals do, where they are found and the current
Eating Right Vitamins and Minerals Many claims about vitamins and minerals may be misleading and confusing. The following lists tell what vitamins and minerals do, where they are found and the current
Nutrients in foods replace those used by the body
 Fundamentals of Nutrition Nutrition: those processes that allow the body to use food for energy, maintenance of health, and growth. Nutritional status: the state of one s nutrition Wellness: state of good
Fundamentals of Nutrition Nutrition: those processes that allow the body to use food for energy, maintenance of health, and growth. Nutritional status: the state of one s nutrition Wellness: state of good
Fiber In Your Diet. Provided by Hemorrhoid Centers of America Version Fiber
 In Your Diet The lack of dietary fiber and fluids is a contributing factor to the development of hemorrhoids and anal fissures. We recommend consuming 25-35 grams of fiber and drinking 7 glasses of fluids
In Your Diet The lack of dietary fiber and fluids is a contributing factor to the development of hemorrhoids and anal fissures. We recommend consuming 25-35 grams of fiber and drinking 7 glasses of fluids
Nutrition Essentials Improving your PKU diet through balanced nutrition
 Nutrition Essentials Improving your PKU diet through balanced nutrition Sharon L Ernst, MPH, RD, CSP, FAND Associate Professor Chief Metabolic Dietitian Division of Medical Genetics Department of Pediatrics
Nutrition Essentials Improving your PKU diet through balanced nutrition Sharon L Ernst, MPH, RD, CSP, FAND Associate Professor Chief Metabolic Dietitian Division of Medical Genetics Department of Pediatrics
Multivitamins are a mixture of vitamins and minerals which are essential for the body to work and stay healthy.
 MULTIVITAMINS Multivitamins are a mixture of vitamins and minerals which are essential for the body to work and stay healthy. Vitamins are vital substances that are required for normal growth and functioning
MULTIVITAMINS Multivitamins are a mixture of vitamins and minerals which are essential for the body to work and stay healthy. Vitamins are vital substances that are required for normal growth and functioning
Nutrition and Energy 1
 Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
Nutrition and Energy 1 Food Energy The ingestion of food serves two primary functions: 1. it provides a source of energy 2. it provides raw materials the animal is unable to manufacture for itself. 2 Basal
STARCHES & GRAINS FATS FIBROUS VEGETABLES
 Thrive Staple Foods The tiers of the Thrive pyramid show a suggested ratio of each food group in your daily diet. This is not meant to suggest a hierarchy of nutritional value (that foods higher on the
Thrive Staple Foods The tiers of the Thrive pyramid show a suggested ratio of each food group in your daily diet. This is not meant to suggest a hierarchy of nutritional value (that foods higher on the
Principles of nutrition Lesson B
 Principles of nutrition Lesson B Sam - ID 38359016 Unit: Applying the principles of nutrition to a physical activity programme Learning outcomes & assessment criteria Learning outcome: The learner will:
Principles of nutrition Lesson B Sam - ID 38359016 Unit: Applying the principles of nutrition to a physical activity programme Learning outcomes & assessment criteria Learning outcome: The learner will:
A FULL SPECTRUM OF NUTRIENTS
 A FULL SPECTRUM OF NUTRIENTS All of us remember being told by our parents Eat your Vegetables. They re good for you. Fruits and vegetables are good for our Budgies too. Each color group has its own nutritional
A FULL SPECTRUM OF NUTRIENTS All of us remember being told by our parents Eat your Vegetables. They re good for you. Fruits and vegetables are good for our Budgies too. Each color group has its own nutritional
By Jacqueline Fields, MD and founder of Dr. Fields Sacred Skin August 14, 2014
 Osteoporosis By Jacqueline Fields, MD and founder of Dr. Fields Sacred Skin August 14, 2014 Osteoporosis is a significant problem in our culture and unfortunately is on the rise. One out of every two American
Osteoporosis By Jacqueline Fields, MD and founder of Dr. Fields Sacred Skin August 14, 2014 Osteoporosis is a significant problem in our culture and unfortunately is on the rise. One out of every two American
ADULTS: 550mg. MEN: 300mg WOMEN: 270mg
 Mineral WHY WHERE HOW MUCH RNI CALCIUM Essential for healthy, strong Milk ADULTS: 700 bones and teeth. If you don t cheese mg get enough in childhood it yogurt may lead to osteoporosis in fish with soft
Mineral WHY WHERE HOW MUCH RNI CALCIUM Essential for healthy, strong Milk ADULTS: 700 bones and teeth. If you don t cheese mg get enough in childhood it yogurt may lead to osteoporosis in fish with soft
Lecture 3. Nutrition
 Lecture 3 Nutrition, Part 1 1 Nutrition 1.Macronutrients a. Water b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Fats 2.Micronutrients a. Minerals b. Vitamins 2 1 Why is Nutrition Important? Your food choices each day
Lecture 3 Nutrition, Part 1 1 Nutrition 1.Macronutrients a. Water b. Carbohydrates c. Proteins d. Fats 2.Micronutrients a. Minerals b. Vitamins 2 1 Why is Nutrition Important? Your food choices each day
Chapter Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients
 Chapter 15.1 Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients Why do we eat? Physical Needs: Nutrients chemicals found in food, the body needs to function properly. Nutrition study of foods and the way your body
Chapter 15.1 Why do we eat & Nutrition and Nutrients Why do we eat? Physical Needs: Nutrients chemicals found in food, the body needs to function properly. Nutrition study of foods and the way your body
BHARATH ACADEMY VITAMINS AND MINERALS CHART
 VITAMINS AND MINERALS CHART Different types of vitamins and minerals enable healthy body function, such as cell and tissue repair, production of cells, and healthy brain function. Your body doesn t produce
VITAMINS AND MINERALS CHART Different types of vitamins and minerals enable healthy body function, such as cell and tissue repair, production of cells, and healthy brain function. Your body doesn t produce
VITAMIN BASICS VITAMIN WHAT IT DOES TOO LITTLE TOO MUCH SOURCES. Night blindness Total blindness Reduced resistance to infection Can lead to death
 VITAMIN BASICS VITAMIN WHAT IT DOES TOO LITTLE TOO MUCH SOURCES Fat-Soluble Vitamin A Maintains vision Maintains epithelial tissues (skin) Develops immune cells Bone growth Night blindness Total blindness
VITAMIN BASICS VITAMIN WHAT IT DOES TOO LITTLE TOO MUCH SOURCES Fat-Soluble Vitamin A Maintains vision Maintains epithelial tissues (skin) Develops immune cells Bone growth Night blindness Total blindness
Vitamins. Vitamin, Herb and Mineral Benefits
 Vitamins Vitamin A - promotes healthy vision and skin, and it also supports bone and tooth growth. In addition, vitamin A helps your immune system and is important in the reproductive process. Finally,
Vitamins Vitamin A - promotes healthy vision and skin, and it also supports bone and tooth growth. In addition, vitamin A helps your immune system and is important in the reproductive process. Finally,
Vitamin dan Mineral. Vitamin. General Concepts
 Vitamin dan Mineral Pengetahuan Bahan Agroindustri Vitamin Organic compound required in small amounts Divided into two major groups: fat soluble and water soluble fat soluble : Vitamin A, D, E, K water
Vitamin dan Mineral Pengetahuan Bahan Agroindustri Vitamin Organic compound required in small amounts Divided into two major groups: fat soluble and water soluble fat soluble : Vitamin A, D, E, K water
Nutrients Empty calorie foods DRI
 Nutrients are life-sustaining chemical substances that nourish and promote the growth of the human body. No one food contains all of the nutrients necessary for the body to function effectively; therefore,
Nutrients are life-sustaining chemical substances that nourish and promote the growth of the human body. No one food contains all of the nutrients necessary for the body to function effectively; therefore,
Information on vitamins. Good for eyes, sight, skin and growth. Excess is harmful to pregnant women who should avoid vitamin A rich foods.
 Information on vitamins. Vitamin A. Good for eyes, sight, skin and growth. Excess is harmful to pregnant women who should avoid vitamin A rich foods. Cod liver oil. Butter. Double cream. Cheese. Vitamin
Information on vitamins. Vitamin A. Good for eyes, sight, skin and growth. Excess is harmful to pregnant women who should avoid vitamin A rich foods. Cod liver oil. Butter. Double cream. Cheese. Vitamin
BUILD A HEALTHY EATING STYLE
 TASTE THE RAINBOW! BUILD A HEALTHY EATING STYLE Focus on healthy food and beverage choices of all five food groups including fruits, vegetables, grains, and proteins. Building a healthy diet can help you
TASTE THE RAINBOW! BUILD A HEALTHY EATING STYLE Focus on healthy food and beverage choices of all five food groups including fruits, vegetables, grains, and proteins. Building a healthy diet can help you
Food Introduction Schedule
 Six-Months Dr. Nadia Bakir, ND, Naturopathic Family Health Toronto/Niagara Falls, Ontario, Canada (877) 576-3192 reception@naturopathicpractice.com Food Introduction Schedule At six months of age, foods
Six-Months Dr. Nadia Bakir, ND, Naturopathic Family Health Toronto/Niagara Falls, Ontario, Canada (877) 576-3192 reception@naturopathicpractice.com Food Introduction Schedule At six months of age, foods
2002 Learning Zone Express
 1 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to 2 Fuel your energy. Help you grow.
1 Nutrients The food you eat is a source of nutrients. Nutrients are defined as the substances found in food that keep your body functioning. Your body needs nutrients to 2 Fuel your energy. Help you grow.
Essential Standard. 8.NPA.1 Apply tools (Body Mass Index, Dietary Guidelines) to plan healthy nutrition and fitness.
 Warm Up What vitamins and minerals can you name? How do people get the vitamins and minerals they need? What are health benefits that you know about vitamins and minerals? Why do some people take supplements?
Warm Up What vitamins and minerals can you name? How do people get the vitamins and minerals they need? What are health benefits that you know about vitamins and minerals? Why do some people take supplements?
Chewing the fat about fat!
 Chewing the fat about fat! When we talk about fat, most people think of fatty foods, like fries and fatty meats. But fat is an essential nutrient. It plays an important role in the many functions that
Chewing the fat about fat! When we talk about fat, most people think of fatty foods, like fries and fatty meats. But fat is an essential nutrient. It plays an important role in the many functions that
Nutrition for Health. Nutrients. Before You Read
 CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
CHAPTER 10 LESSON 2 Nutrition for Health Nutrients BIG Idea Each nutrient in your diet plays a unique and essential role in keeping you healthy. Before You Read Sometimes figuring out what to eat can be
Has agricultural intensification reduced the nutritional quality of food?
 Has agricultural intensification reduced the nutritional quality of food? Dr Anne-Marie Mayer Consultant on Nutrition and Agriculture Self-funded independent research Questions Has the nutrient composition
Has agricultural intensification reduced the nutritional quality of food? Dr Anne-Marie Mayer Consultant on Nutrition and Agriculture Self-funded independent research Questions Has the nutrient composition
Mineral Nutrients. NOW Guide to Mineral Nutrients
 Mineral Nutrients NOW Guide to Mineral Nutrients The Health Benefits of Mineral Nutrients Mineral nutrients (also called dietary elements and dietary minerals) are inorganic substances that are essential
Mineral Nutrients NOW Guide to Mineral Nutrients The Health Benefits of Mineral Nutrients Mineral nutrients (also called dietary elements and dietary minerals) are inorganic substances that are essential
Module Two: Detoxification Systems
 Module Two: Detoxification Systems Liana Shanti, CN www.healthmasteryinstitute.com Module 1 Who should detox and why What we are detoxing from Module 2 Now we look at the systems in the body that are responsible
Module Two: Detoxification Systems Liana Shanti, CN www.healthmasteryinstitute.com Module 1 Who should detox and why What we are detoxing from Module 2 Now we look at the systems in the body that are responsible
Macrominerals. Chloride. Potassium. Calcium. Hungry for more? Explore Healthy Living at plantsforhumanhealth.ncsu.edu. Sulfur. Phosphorus.
 acrominerals Cl Chloride eaweed, tomato, le,uce, celery, olives K Creates stomach acid and maintains proper fluid balance by ac:ng as an electrolyte. Potassium Banana, papaya, prune, mango, raisins, kiwi,
acrominerals Cl Chloride eaweed, tomato, le,uce, celery, olives K Creates stomach acid and maintains proper fluid balance by ac:ng as an electrolyte. Potassium Banana, papaya, prune, mango, raisins, kiwi,
The Cause of Disease
 Acid - Alkaline Balance The Cause of Disease Have you ever wondered if many of the diseases raging through our society have a common cause? Many doctors, herbalists and nutritionists believe that the explanation
Acid - Alkaline Balance The Cause of Disease Have you ever wondered if many of the diseases raging through our society have a common cause? Many doctors, herbalists and nutritionists believe that the explanation
Client will make 2 specific goals to decrease her potassium intake. Client will make 1 specific goal to decrease her fluid retention.
 Title: Renal Diet Target Audience: Renal Dialysis Patients LESSON PLAN Name: Heidi Washburn Terminal Objective Client will be able to plan an appropriate renal dialysis diet for him/herself. Domain Cognitive
Title: Renal Diet Target Audience: Renal Dialysis Patients LESSON PLAN Name: Heidi Washburn Terminal Objective Client will be able to plan an appropriate renal dialysis diet for him/herself. Domain Cognitive
Vitamin A. Vitamin D
 Vitamin A Fat Soluble Vitamin Maintains hair and skin cells. Helps prevent night blindness. Orange and dark green vegetables, dairy products, and fish oils Works with calcium to build and maintain healthy
Vitamin A Fat Soluble Vitamin Maintains hair and skin cells. Helps prevent night blindness. Orange and dark green vegetables, dairy products, and fish oils Works with calcium to build and maintain healthy
NUTRITION & DIETARY GUIDELINES. Ms. Panzica
 NUTRITION & DIETARY GUIDELINES Ms. Panzica DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR AMERICANS Federal Government s EVIDENCED-BASED nutritional guidance to Promote health Reduce the risk of chronic diseases Reduce the prevalence
NUTRITION & DIETARY GUIDELINES Ms. Panzica DIETARY GUIDELINES FOR AMERICANS Federal Government s EVIDENCED-BASED nutritional guidance to Promote health Reduce the risk of chronic diseases Reduce the prevalence
MORE THAN A MULTIVITAMIN!
 MORE THAN A MULTIVITAMIN! Double X provides 20 plant 900 mg of phytonutrients concentrates with more than the natural nutrients from plants. Between work, home, and social obligations, most of us struggle
MORE THAN A MULTIVITAMIN! Double X provides 20 plant 900 mg of phytonutrients concentrates with more than the natural nutrients from plants. Between work, home, and social obligations, most of us struggle
Potassium and Your CKD Diet
 A TO Z HEALTH GUIDE Potassium and Your CKD Diet What is potassium and why is it important to you? Potassium is a mineral found in many of the foods you eat. It plays a role in keeping your heartbeat regular
A TO Z HEALTH GUIDE Potassium and Your CKD Diet What is potassium and why is it important to you? Potassium is a mineral found in many of the foods you eat. It plays a role in keeping your heartbeat regular
6 Nutrients Essential for Life
 6 Nutrients Essential for Life Mind Moo-Ver SWBAT identify the 6 essential nutrients for life QOD: What does ph measure Give an example of an acidic substance, a basic substance and a neutral substance
6 Nutrients Essential for Life Mind Moo-Ver SWBAT identify the 6 essential nutrients for life QOD: What does ph measure Give an example of an acidic substance, a basic substance and a neutral substance
GREEN YELLOW RED PURPLE WHITE
 GREEN YELLOW RED PURPLE WHITE Broccoli, green cabbage, spinach, romaine lettuce, green peas, kiwi fruit, swiss chard Avoid cancer of the prostate and colon (large intestine) Develop and maintain healthy
GREEN YELLOW RED PURPLE WHITE Broccoli, green cabbage, spinach, romaine lettuce, green peas, kiwi fruit, swiss chard Avoid cancer of the prostate and colon (large intestine) Develop and maintain healthy
Electrolytes. Fat Soluble Vitamins. Minerals. Macro Nutrients. Water Soluble Vitamins. Know. Nutrients. Sodium Chloride Potassium
 Know Your Julie Gardner, MEd. Extension Program Specialist Healthy Lifestyles 4-H Youth Development Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Nutrients Reviewed By: Danielle Krueger, MPH, RD, LD Minerals Calcium Chromium
Know Your Julie Gardner, MEd. Extension Program Specialist Healthy Lifestyles 4-H Youth Development Texas A&M AgriLife Extension Nutrients Reviewed By: Danielle Krueger, MPH, RD, LD Minerals Calcium Chromium
Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water
 Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water 1. What is the main function of vitamins and minerals? To regulate body functions 2. What foods are a lot of the vitamins and minerals we need found in? Fruits and Vegetables
Intro to Vitamins, Minerals & Water 1. What is the main function of vitamins and minerals? To regulate body functions 2. What foods are a lot of the vitamins and minerals we need found in? Fruits and Vegetables
Vitamin A. What Is It Good For?
 Vitamin A What Is It Good For? Vitamin A is important for normal vision, your immune system, and to help your heart, lungs, kidneys, and other organs work properly. Where Can You Find It? Vitamin A is
Vitamin A What Is It Good For? Vitamin A is important for normal vision, your immune system, and to help your heart, lungs, kidneys, and other organs work properly. Where Can You Find It? Vitamin A is
Module Seven Macronutrients Continued
 Module Four: Module Seven Macronutrients Continued Liana Shanti, CN www.healthmasteryinstitute.com Proteins Where do we get protein from on a plant based diet? How Important is protein? What do our bodies
Module Four: Module Seven Macronutrients Continued Liana Shanti, CN www.healthmasteryinstitute.com Proteins Where do we get protein from on a plant based diet? How Important is protein? What do our bodies
Food & Mood. What we eat = How we feel
 Food & Mood Jennifer Adler, M.S., C.N. What we eat = How we feel Grown accustomed to being under the weather or not up to par What we eat can have a profound effect on how we feel now & later There is
Food & Mood Jennifer Adler, M.S., C.N. What we eat = How we feel Grown accustomed to being under the weather or not up to par What we eat can have a profound effect on how we feel now & later There is
Laura Kim, MGH Dietetic Intern March 17, 2015
 Laura Kim, MGH Dietetic Intern March 17, 2015 Introduction Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Understand basic functions of each nutrient Identify food sources of carbohydrates, fats, proteins Create balanced
Laura Kim, MGH Dietetic Intern March 17, 2015 Introduction Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Understand basic functions of each nutrient Identify food sources of carbohydrates, fats, proteins Create balanced
Ingredient List: Drs. Foster & Smith Chicken & Brown Rice Formula Hairball Control Dry Cat Food Drs. Foster & Smith Educational Staff
 Ingredient List: Drs. Foster & Smith Chicken & Brown Rice Formula Hairball Control Dry Cat Food Drs. Foster & Smith Educational Staff Drs. Foster & Smith Chicken & Brown Rice Formula Hairball Control dry
Ingredient List: Drs. Foster & Smith Chicken & Brown Rice Formula Hairball Control Dry Cat Food Drs. Foster & Smith Educational Staff Drs. Foster & Smith Chicken & Brown Rice Formula Hairball Control dry
Magnesium (Mg) is essential to all living cells. The earth metal plays important roles in the structure and the function of the human body.
 Magnesium AT A GLANCE Introduction Magnesium (Mg) is essential to all living cells. The earth metal plays important roles in the structure and the function of the human body. The adult human body contains
Magnesium AT A GLANCE Introduction Magnesium (Mg) is essential to all living cells. The earth metal plays important roles in the structure and the function of the human body. The adult human body contains
EASY WAYS TO EAT MORE FRUITS AND VEGETABLES AS PART OF A HEALTHY DIET.
 This is a text-only 508 accessible version for the visually impaired. For a full-color brochure, see: www.fruitsandveggiesmatter.gov/downloads/aa_womens_brochure.pdf Page 1- Left column (back cover) EASY
This is a text-only 508 accessible version for the visually impaired. For a full-color brochure, see: www.fruitsandveggiesmatter.gov/downloads/aa_womens_brochure.pdf Page 1- Left column (back cover) EASY
The Ins(tute of Transforma(onal Nutri(on
 SCIENCE MODULE 2 MINERALS MINERALS Chemical elements that are required by living organisms to survive Cannot be made by our bodies, but some are still considered essential Must be obtained through the
SCIENCE MODULE 2 MINERALS MINERALS Chemical elements that are required by living organisms to survive Cannot be made by our bodies, but some are still considered essential Must be obtained through the
4. Sulfur 5. Sodium. 8. Vanadium
 MINERALS The human body utilizes minerals for the proper composition of bone and blood, and maintenance of normal cell function. Minerals function along with vitamins as essential components in enzymes
MINERALS The human body utilizes minerals for the proper composition of bone and blood, and maintenance of normal cell function. Minerals function along with vitamins as essential components in enzymes
Six Nutrients. Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy. Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water
 Nutrients Six Nutrients Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water Water Function: most essential nutrient Helps digest and absorb
Nutrients Six Nutrients Nutrients: substances in food that your body needs to stay healthy Carbohydrates Protein Fat Minerals Vitamins Water Water Function: most essential nutrient Helps digest and absorb
Choosing Healthful Foods
 LESSON 25 Choosing Healthful Foods Before You Read List some of the healthful foods you eat. What makes these foods healthful choices? What You ll Learn the functions and sources of proteins, carbohydrates,
LESSON 25 Choosing Healthful Foods Before You Read List some of the healthful foods you eat. What makes these foods healthful choices? What You ll Learn the functions and sources of proteins, carbohydrates,
The Six Essential Nutrient Groups:
 The Six Essential Nutrient Groups: Water: Water transports other nutrients to cells, carries wastes away, aids digestion and more. It makes up more than half your weight. SOURCES: water; juices and
The Six Essential Nutrient Groups: Water: Water transports other nutrients to cells, carries wastes away, aids digestion and more. It makes up more than half your weight. SOURCES: water; juices and
FACTS ABOUT FIBER Dietary fiber is the part of a plant that provides and maintains the plant's structure. Cellulose, hemicellulose, polysaccharides,
 FACTS ABOUT FIBER Dietary fiber is the part of a plant that provides and maintains the plant's structure. Cellulose, hemicellulose, polysaccharides, pectins, gums, mucilages, and lignins are dietary fibers.
FACTS ABOUT FIBER Dietary fiber is the part of a plant that provides and maintains the plant's structure. Cellulose, hemicellulose, polysaccharides, pectins, gums, mucilages, and lignins are dietary fibers.
Online Nutrition Training Course
 Expert advice, Excellent results Online Nutrition Training Course Module 5: Vitamins and Minerals www.diet-specialist.co.uk Notice of Rights All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
Expert advice, Excellent results Online Nutrition Training Course Module 5: Vitamins and Minerals www.diet-specialist.co.uk Notice of Rights All rights reserved. No part of this publication may be reproduced,
My Plate Healthy Eating 1
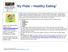 My Plate Healthy Eating 1 Learn more about healthy eating! Go to www.choosemyplate.gov Finding out how many calories YOU need for a day is a first step in managing your weight. Exercise is the key to any
My Plate Healthy Eating 1 Learn more about healthy eating! Go to www.choosemyplate.gov Finding out how many calories YOU need for a day is a first step in managing your weight. Exercise is the key to any
It is believed that a meal plan that includes low FODMAPs also may help ease symptoms from other health conditions, such as:
 If you have digestive issues, this could be why. You don't have to have IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) or Colitis (a chronically inflammed colon), to experience some of these symptoms. FODMAP The acronym
If you have digestive issues, this could be why. You don't have to have IBS (Irritable Bowel Syndrome) or Colitis (a chronically inflammed colon), to experience some of these symptoms. FODMAP The acronym
NUTRITION: THE STUDY OF HOW THE BODY UTILIZES THE FOOD WE EAT
 NUTRITION: THE STUDY OF HOW THE BODY UTILIZES THE FOOD WE EAT NUTRIENT: a chemical found in food that is needed for life and growth, & the building blocks to make your body function correctly! WHAT DO
NUTRITION: THE STUDY OF HOW THE BODY UTILIZES THE FOOD WE EAT NUTRIENT: a chemical found in food that is needed for life and growth, & the building blocks to make your body function correctly! WHAT DO
Understanding Nutrition A beginners guide
 Understanding Nutrition A beginners guide What is Nutrition? We refer best to nutrition as food food is composed of nutrients, the most well-known are macronutrients protein, carbohydrate and fats. Food
Understanding Nutrition A beginners guide What is Nutrition? We refer best to nutrition as food food is composed of nutrients, the most well-known are macronutrients protein, carbohydrate and fats. Food
Super Foods for a Super You Learning ZoneXpress
 Super Foods for a Super You 1 Whole New You The human body regenerates cells everyday It completely renews itself every 7 years To build the healthiest cells possible eat nutrient-rich foods everyday 2
Super Foods for a Super You 1 Whole New You The human body regenerates cells everyday It completely renews itself every 7 years To build the healthiest cells possible eat nutrient-rich foods everyday 2
The 12 Keys to Healthy Eating
 The 12 Keys to Healthy Eating What are the 12 Keys to Healthy Eating? #1 Digestion #7 Minerals #2 Balanced Plate & Blood Sugar #8 Water #3 Healthy Fats #9 Variety #4 Herbs & Spices #10 Organic Food #5
The 12 Keys to Healthy Eating What are the 12 Keys to Healthy Eating? #1 Digestion #7 Minerals #2 Balanced Plate & Blood Sugar #8 Water #3 Healthy Fats #9 Variety #4 Herbs & Spices #10 Organic Food #5
Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies
 Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies Introduction Nutrients Components of food required for the body s functioning Roles: Provide energy Building material Maintenance
Lisa Sasson Clinical Assistant Professor NYU Dept Nutrition and Food Studies Introduction Nutrients Components of food required for the body s functioning Roles: Provide energy Building material Maintenance
DR. SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGY UPM
 DR. SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGY UPM Mineral nutrients are inorganic elements found in food which the body cannot synthesis.
DR. SHAMSUL AZAHARI ZAINAL BADARI DEPARTMENT OF RESOURCES MANAGEMENT AND CONSUMER STUDIES FACULTY OF HUMAN ECOLOGY UPM Mineral nutrients are inorganic elements found in food which the body cannot synthesis.
Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance
 Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
Unit B Understanding Animal Body Systems Lesson 3 Understanding Nutrients and Their Importance 1 Terms Balanced ration Carbohydrates Complex carbohydrates Disaccharides Essential nutrients Ether Fat Fat-soluble
NUTRIENTS VS. CALORIES DIETARY GUIDELINES
 NUTRIENTS VS. CALORIES DIETARY GUIDELINES Nutrients: Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Vitamins Minerals Water Energy (calories) Problem in U.S.: Imbalance Nutrients vs. Calories Too many calories Not enough
NUTRIENTS VS. CALORIES DIETARY GUIDELINES Nutrients: Carbohydrates Fats Proteins Vitamins Minerals Water Energy (calories) Problem in U.S.: Imbalance Nutrients vs. Calories Too many calories Not enough
There are six general classes of nutrients needed in the horse s diet: water carbohydrates fats protein minerals vitamins.
 HORSE NUTRITION Nutrients A nutrient is defined as any feed constituent that is necessary to support life. The following is a list of functions that nutrients perform in the horse's body: source of energy
HORSE NUTRITION Nutrients A nutrient is defined as any feed constituent that is necessary to support life. The following is a list of functions that nutrients perform in the horse's body: source of energy
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013
 CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we will: Investigate the structure and function of molecules that are essential for life. Key Concepts Terminology A molecule is any
CHEMISTRY OF LIFE 30 JANUARY 2013 Lesson Description In this lesson, we will: Investigate the structure and function of molecules that are essential for life. Key Concepts Terminology A molecule is any
WHAT S INSIDE. Nutrient Institute LLC. All Rights Reserved
 WHAT S INSIDE Nutrient Institute LLC. All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Macronutrients PAGE 3-4 Micronutrients PAGE 5 Other Ingredients PAGE 5-6 Micronutrients PAGE 5 Bad Stuff PAGE 6-8 By Nutrients
WHAT S INSIDE Nutrient Institute LLC. All Rights Reserved Table of Contents Macronutrients PAGE 3-4 Micronutrients PAGE 5 Other Ingredients PAGE 5-6 Micronutrients PAGE 5 Bad Stuff PAGE 6-8 By Nutrients
Nutrition - What Should We Eat?
 Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans www.choosemyplate.gov Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans
Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans www.choosemyplate.gov Nutrition - What Should We Eat? Adapted from the 2010 USDA Dietary Guidelines for Americans
The Importance of an Alkaline Diet
 By Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo The Importance of an Alkaline Diet The internal environment of your body is maintained at a ph just above 7.0. Your blood ph must be maintained within a very narrow range or serious
By Dr. Ritamarie Loscalzo The Importance of an Alkaline Diet The internal environment of your body is maintained at a ph just above 7.0. Your blood ph must be maintained within a very narrow range or serious
Activity #4: Healthy Food Festival!
 Activity #4: Healthy Food Festival! Activity Overview In this activity, students apply their new learning to create fun ways to eat the rainbow during the week. Students are encouraged to consider the
Activity #4: Healthy Food Festival! Activity Overview In this activity, students apply their new learning to create fun ways to eat the rainbow during the week. Students are encouraged to consider the
Lesson 1 Carbohydrates, Fats & Proteins pages
 Lesson 1 Carbohydrates, Fats & Proteins pages 190-201 What are the 3 classes of nutrients that supply your body with energy and how does the body obtain the energy from foods? Describe the roles that carbohydrates,
Lesson 1 Carbohydrates, Fats & Proteins pages 190-201 What are the 3 classes of nutrients that supply your body with energy and how does the body obtain the energy from foods? Describe the roles that carbohydrates,
Super Foods for a Super You
 Super Foods for a Super You Presented by Jennifer Meachum RD, LD 1 Whole New You The human body regenerates cells everyday It completely renews itself every 7 years To build the healthiest cells possible
Super Foods for a Super You Presented by Jennifer Meachum RD, LD 1 Whole New You The human body regenerates cells everyday It completely renews itself every 7 years To build the healthiest cells possible
Nutrition During Pregnancy
 Nutrition During Pregnancy Nutrition is one of the most important factors in the health of both mother and baby before, during and after pregnancy. Be sure to eat a diet high in whole, organic, fresh foods.
Nutrition During Pregnancy Nutrition is one of the most important factors in the health of both mother and baby before, during and after pregnancy. Be sure to eat a diet high in whole, organic, fresh foods.
Food. Food Groups & Nutrients
 Food Food Groups & Nutrients Grains Group Grains Group Defined: Foods made from wheat, rice, oats, barley, etc. Grains Group Defined: Foods made from wheat, rice, oats, barley, etc. Examples: bread,
Food Food Groups & Nutrients Grains Group Grains Group Defined: Foods made from wheat, rice, oats, barley, etc. Grains Group Defined: Foods made from wheat, rice, oats, barley, etc. Examples: bread,
Walnuts // Chia seeds // Nutritional yeast // Pumpkin & Sesame seeds // Brazil nuts //
 BEAUTY FOODS LIST Skin, hair, and nail food! Many factors impact our skin heath, including lifestyle choices, hormonal balance, stress management, and of course what we put in our bodies. All of the foods
BEAUTY FOODS LIST Skin, hair, and nail food! Many factors impact our skin heath, including lifestyle choices, hormonal balance, stress management, and of course what we put in our bodies. All of the foods
IRON MANGANESE 6/6/2018. Minerals & Performance : Total Performance, Total Performance Plus
 Minerals & Performance : Total Performance, Total Performance Plus June Educational Webinar 2018 Dr Tania Cubitt Performance Horse Nutrition IRON Heme oxygen carrying capacity Iron deficiency rare Iron
Minerals & Performance : Total Performance, Total Performance Plus June Educational Webinar 2018 Dr Tania Cubitt Performance Horse Nutrition IRON Heme oxygen carrying capacity Iron deficiency rare Iron
Sample results. Actual results may vary. PATIENT INFORMATION DOB: AGE: GENDER: FASTING: Clinical Info: Test Name Result Flag Reference Range Lab
 Sample results. Actual results may vary. SPECIMEN INFORMATION SPECIMEN: REQUISITION: LAB REF NO: PATIENT INFORMATION DOB: AGE: GENDER: FASTING: REPORT STATUS: FINAL ORDERING PHYSICIAN CLIENT INFORMATION
Sample results. Actual results may vary. SPECIMEN INFORMATION SPECIMEN: REQUISITION: LAB REF NO: PATIENT INFORMATION DOB: AGE: GENDER: FASTING: REPORT STATUS: FINAL ORDERING PHYSICIAN CLIENT INFORMATION
MARINE PHYTOPLANKTON NUTRITIONAL ANALYSIS
 MARINE PHYTOPLANKTON NUTRITIONAL ANALYSIS Element Description Importance for / Helps to / Promotes: Lacking of increase risk of: Alanine Amino acid Forms proteins Hipertension Muscle formation Diabates
MARINE PHYTOPLANKTON NUTRITIONAL ANALYSIS Element Description Importance for / Helps to / Promotes: Lacking of increase risk of: Alanine Amino acid Forms proteins Hipertension Muscle formation Diabates
What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D.
 What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Primary source of nitrogen
What Are Proteins? Lecture 9: Proteins Nutrition 150 Shallin Busch, Ph.D. Proteins: large complex molecules composed of amino acids. Contain carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen Primary source of nitrogen
Proposed Revision or Revocation of Maximum Residue Limits for Discontinued Agricultural Pest Control Products: Update 2
 Proposed Maximum Residue Limit PMRL2018-44 Proposed Revision or Revocation of Maximum Residue Limits for Discontinued Agricultural Pest Control Products: Update 2 (publié aussi en français) 8 November
Proposed Maximum Residue Limit PMRL2018-44 Proposed Revision or Revocation of Maximum Residue Limits for Discontinued Agricultural Pest Control Products: Update 2 (publié aussi en français) 8 November
A Revolutionary Heavy Metal Detox Program HOW-TO GUIDE
 A Revolutionary Heavy Metal Detox Program HOW-TO GUIDE After Purify 2.0, my energy was better, I lost some weight, I felt less bloating and I was coping better with every day stressors. Kim C., Ohio WELCOME
A Revolutionary Heavy Metal Detox Program HOW-TO GUIDE After Purify 2.0, my energy was better, I lost some weight, I felt less bloating and I was coping better with every day stressors. Kim C., Ohio WELCOME
ENERGY NUTRIENTS: THE BIG PICTURE WHY WE EAT FUNCTIONS FATS FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN
 ENERGY NUTRIENTS: FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN Angeline B. David, DRPH, MHS NAD Health Summit March 14, 2013 The science of cooking is not a small matter.... This art should be regarded as the most valuable of
ENERGY NUTRIENTS: FAT, CARBS, PROTEIN Angeline B. David, DRPH, MHS NAD Health Summit March 14, 2013 The science of cooking is not a small matter.... This art should be regarded as the most valuable of
Eat Proteins with.. Acid Forming Proteins. Meats Meat Sub. Nuts (Raw) Oysters Poultry Scallops
 Proper combining of foods optimizes the digestive processes. It is possible to eat a variety of foods which interfere with the digestion of certain others. Likewise, it is possible to eat foods which enhance
Proper combining of foods optimizes the digestive processes. It is possible to eat a variety of foods which interfere with the digestion of certain others. Likewise, it is possible to eat foods which enhance
25* or higher Underweight. 240 mg/dl and above High (More than twice the risk as desirable level.) OK, but higher is better
 Biometrics Screening Biometric Health Indicators The charts below provide a summary of the ranges for each of the biometric screening tests. Be sure to check with your doctor if your results are outside
Biometrics Screening Biometric Health Indicators The charts below provide a summary of the ranges for each of the biometric screening tests. Be sure to check with your doctor if your results are outside
3.1.1 Water Soluble Vitamins
 3.1.1 Water Soluble Vitamins Overview of Vitamins essential for good health organic molecules individual units regulate body processes micronutrients solubility fat or water Water Soluble Vitamins B-complex;
3.1.1 Water Soluble Vitamins Overview of Vitamins essential for good health organic molecules individual units regulate body processes micronutrients solubility fat or water Water Soluble Vitamins B-complex;
in the form of carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, and minerals
 BCS_G8_U1C02_J15 5/23/06 11:45 AM Page 64 2.2 The Digestive and Excretory Systems A healthy body requires nutrients from five groups: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. There are four
BCS_G8_U1C02_J15 5/23/06 11:45 AM Page 64 2.2 The Digestive and Excretory Systems A healthy body requires nutrients from five groups: carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. There are four
Are You Eating Enough to Lose Weight?
 TM Are You Eating Enough to Lose Weight? The Full Plate Diet Slim Down, Look Great, Be Healthy! Full Plate Diet Weight Loss Program Stuart A. Seale, M.D. Teresa Sherard, M.D. Diana Fleming, Ph.D., LDN
TM Are You Eating Enough to Lose Weight? The Full Plate Diet Slim Down, Look Great, Be Healthy! Full Plate Diet Weight Loss Program Stuart A. Seale, M.D. Teresa Sherard, M.D. Diana Fleming, Ph.D., LDN
The food that we eat provides us with the energy we need to get us through the day. Our bodies also use that energy to perform necessary functions.
 The food that we eat provides us with the energy we need to get us through the day. Our bodies also use that energy to perform necessary functions. Breathe Maintain body temperature Heart rate Digestion
The food that we eat provides us with the energy we need to get us through the day. Our bodies also use that energy to perform necessary functions. Breathe Maintain body temperature Heart rate Digestion
OOO MICRONUTRIENTS. systemic diagnostics and treatment of mineral imbalances and intoxications. (Dr. Skalny's hair analyses )
 OOO MICRONUTRIENTS systemic diagnostics and treatment of mineral imbalances and intoxications Campus 8, build. 13, Perevedenovsky Lane Moscow, Russia, 105082 (Dr. Skalny's hair analyses ) Tel: 8-800-333-33-46,
OOO MICRONUTRIENTS systemic diagnostics and treatment of mineral imbalances and intoxications Campus 8, build. 13, Perevedenovsky Lane Moscow, Russia, 105082 (Dr. Skalny's hair analyses ) Tel: 8-800-333-33-46,
Nutrition. Metabolism. The study of how your body uses the food you eat.
 1 Nutrition The study of how your body uses the food you eat. Metabolism The speed at which your body uses energy to maintain its processes; vary by individual Nutrition Food- an edible, organic substance
1 Nutrition The study of how your body uses the food you eat. Metabolism The speed at which your body uses energy to maintain its processes; vary by individual Nutrition Food- an edible, organic substance
