DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
|
|
|
- Stuart Jordan
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different dosage form. Oral route is considered most natural, uncomplicated, convenient and safe due to its ease of administration, patient acceptance, and cost-effective manufacturing process. 1 The dissolution rate of a drug from its dosage form is considered as an important parameter in the bio-availability. Dissolution is the rate limiting step in the absorption of drugs from solid dosage forms, especially when the drug is poorly soluble. DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION: The poor dissolution characteristics of relatively insoluble drugs have long been a problem to the pharmaceutical industry. When an insoluble or sparingly soluble drug is administered orally, the rate and extent of absorption are controlled by the dissolution rate in the gastrointestinal fluids. The process of dissolution is primarily dependent on pharmaceutical variables with the possible exception of ph dependency which may be patient variable. A quantitative description of dissolution rate is given by the Noyes-Whitney 2 equation based on diffusion layer model. dc DS ( CS C) dt h dc where, dt S D is the rate of diffusion, is the surface area, is the diffusion coefficient, h is the thickness of the diffusion layer, Cs C is the saturation solubility and is the concentration of the drug in the solvent at time t. In dissolution rate limited absorption C is negligible when compared to Cs. Under these conditions D and h remain constant and cannot be altered to any degree by the product formulation. Hence, dc dt = K.S.C S Thus, the dissolution rate of a poorly soluble drug can be increased by increasing either solubility or surface area or both.
2 STUDIES ON SOLUBILITY IMPROVEMENT 2, 6 : The most important property of a dosage form is its ability to deliver the active ingredient to its site of action at a rate and amount sufficient to elicit the desired pharmacological response. If the drug is administered by an extravascular route and acts systemically, its potency will be directly related to the amount of drug the dosage form delivers into the blood. Methods Used For Increasing the Dissolution Rate of Poorly Soluble Drugs: Poor aqueous solubility and/or slow dissolution rate in the biological fluids. 1. Poor stability of the dissolved drug at the physiologic ph. 2. Inadequate partition coefficient and thus poor permeation through the biomembrane. 3. Extensive presystemic metabolism. The three approaches in overcoming the bioavailability problems due to such causes are: 1. The Pharmaceutical Approach which involves modification of formulation, manufacturing, process or the physicochemical properties of drugs without changing the chemical structure 2. The Pharmacokinetic Approach in which the pharmacokinetics of drugs is altered by modifying its chemical structure. 3. The Biological Approach where by the route of drug administration may be changed such as changing from oral to parenteral route. The second approach of chemical structure modification has a number of draw backs like very expensive and time consuming, require repetition of studies and a long for regulatory approval. The attempts, whether optimizing the formulation, manufacturing process or physicochemical properties of the drug, are aimed at enhancement of dissolution rate. The methods are: 1. Micronization: The process involves reducing the size of the solid drug particles to 1 to 10 microns commonly by spray drying or by use of air attrition methods. Examples of drugs whose bioavailability have been increased by micronization include griesofulvin and several steroidal and sulfa drugs. 2. Use of surfactants: The surface-active agents enhance dissolution rate primarily by promoting wetting and penetration of dissolution fluid into the solid particles. They are generally used in concentration
3 below their (CMC) values since above CMC, the drug entrapped in the micelle structure fails to partition in the dissolution fluid. Nonionic surfactants like polysorbates are widely used. Examples of the drugs whose bioavailability have been increased by use of surfactants in the formulation include steroids like spironolactone. 3. Use of salt Forms: Salts have improved solubility and dissolution characteristics in comparison to the original drug. Alkali metal salts of acidic drugs like penicillins and strong acid salts of basic drugs like atropine are more water soluble than the parent drug. 4. Alteration of ph of the Drug Microenvironment: This can be achieved in two ways-in situ salt formation, and addition of buffers to the formulation. e.g. buffered aspirin tablets. 5. Use of Metastable polymorphs: A metastable polymorphs is more soluble than the stable polymorph of a drug that exhibit polymorphism for example, the B form of chloramphenicol palmitate is more soluble than A and C forms. 6. Solute-Solvent complexation: Solvates of drugs with organic solvents have higher aqueous solubility than their respective hydrates or the original drug. Much higher solubility can be attained by freeze drying such as solute in solution with an organic solvent with which it is known to form a solvate. E.g.1:2 griesofulvin-benzene solvate. 7. Solvent deposition: In this method, the poorly aqueous soluble drug such as nifedipine is dissolved in an organic solvent like alcohol and deposited on an inert, hydrophilic, solid matrix such as starch or micro-crystalline cellulose by evaporation of solvent. 8. Selective Adsorption on Insoluble Carriers: A highly active adsorbent such as the inorganic clays like bentonite can enhance the dissolution rate of poorly soluble drugs such as griesofulvin, indomethaciin and prednesolone by maintaining the concentration gradient at its maximum. The two reasons suggested for the rapid release of drugs from the surface of clay are- the weak physical bonding between the adsorbate and the adsorbent, and hydration and swelling of the clay in the aqueous media. 9. Solid solutions: The three means by which the particle size of a drug can be reduced to submicron level are a) Use of solid solution, b) Use of eutectic mixtures, and c) Use of solid dispersions.
4 In all these cases, the solute is frequently a poorly water soluble drug acting as the guest and the solvent is highly water-soluble compound or polymer acting as a host or carrier. a) A solid solution is the binary system comprising of a solid solute molecularly dispersed in a solid solvent. Since the two components crystallize together in a homogeneous one phase system, solid solutions are also called as molecular dispersions or mixed crystals. Because of reduction in particle size to the molecular level, solid solution show greater aqueous solubility and faster dissolution than eutectics and solid dispersion. They are generally prepared by fusion method where by a physical mixture of solute and solvent are melted together followed by rapid solidification. Such system, prepared by fusion, is often called as melts. E.g. griseofulvin-succinic acid, the griesofulvin from such solid solution dissolves 6 to 7 times faster than pure griesofulvin. The two mechanisms suggested for enhanced solubility and rapid dissolution of molecular dispersions are:- 1. When the binary mixture is exposed to the water, the soluble carrier dissolves rapidly leaving the insoluble drug in a state of micro-crystalline dispersion of very fine particles, 2. When the solid solution, which is said to be in a state of randomly, arranged solute and solvent molecules in the crystalline lattice, is exposed to dissolution fluid, the soluble carrier dissolves rapidly leaving the insoluble drug stranded at almost molecular level. b) Eutectic Mixture: These systems are also prepared by fusion method. Eutectic melts differ from solid solution in that the fused melt of solute-solvent show complete miscibility but negligible solid-solid solubility i.e. such systems are basically intimately blended physical mixture of two crystalline components. Examples of eutectics include paracetamol-urea, griesofulvin-urea, griseofulvin-succinic acid, etc. Solid solutions and eutectics, which are basically melts, are easy to prepare and economical with no solvents involved. The method however cannot be applied to: drugs which fail to crystallize from the mixed melt, themolabile drugs, and Carriers such as succinic acid that decompose at their melting point. The eutectic product is often tacky, intractable or irregular crystals. c) Solid dispersions: These are generally prepared by solvent or co-precipitation method where by both the guest solute and the solvent are dissolved in a common volatile liquid solvent such as alcohol. The liquid solvent is removed by evaporation under reduced pressure or by freeze drying which results in amorphous precipitation of guest in a crystalline carrier. Example is griesofulvin PVP.
5 10. Molecular Encapsulation with Cyclodextrins: 3,4,5 The beta- and gamma-cyclodextrins and several of their derivatives are unique in having the ability to form molecular inclusion complexes with hydrophobic drugs having poor aqueous solubility. These cyclodexrtin molecules are versatile in having a hydrophobic cavity of size suitable enough to accommodate the lipophilic drugs as guest; the outside of the host molecule is relatively hydrophilic. Thus molecularly encapsulated drug has greatly improved aqueous solubility and dissolution rate. Among the possibilities, the preparation of inclusion complexes with cyclodextrin is of particular interest. Gastroretentive Dosage Form (GRDF): 7,8 It is evident from the recent scientific and patient literature that an increased interest in novel dosage forms that are retained in stomach for a prolonged and predictable period of time exists today in academic and industrial research groups. One of the most feasible approaches for achieving a prolonged and predictable drug delivery in the GI tract is to control the gastric residence time (GRT), i.e. gastro retentive dosage form (GRDF or GRDS). GRDFs extend significantly the period of time over which the drugs may be released. They not only prolong dosing intervals, but also increase patient compliance beyond the level of existing controlled release dosage form. Dosage form with prolonged GRT, i.e. gastro retentive dosage form (GRDF), will bring about new and important therapeutic options such as 9 1) This application is especially effective in sparingly soluble and insoluble drugs. It is known that, as the solubility of a drug decreases, the time available for drug dissolution becomes less adequate and thus the transit time becomes a significant factor affecting drug absorption. To override this problem, erodible, gastroretentive dosage forms have been developed that provide continuous, controlled administration of sparingly soluble drugs at the absorption site. 2) GRDFs greatly improve the pharmacotherapy of the stomach through local drug release, leading to high drug concentration at the gastric mucosa. (For e.g. Eradicating Helicobacter pylori from the submucosal tissue of stomach) making it possible to treat stomach and duodenal ulcers, gastritis and oesophagitis, reduce the risk of gastric carcinoma and administer non-systemic controlled release antacid formulations (calcium carbonate). 3) GRDFs can be used as carriers for drugs with so-called absorption windows. These substances for e.g. antiviral, antifungal and antibiotic agents (sulphonamides, quinolones, penicillins, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, tetracyclines etc.), are taken up only from very specific sites of the GI mucosa.
6 APPROACHES TO GASTRIC RETENTION 10 A number of approaches have been used to increase the GRT of a dosage form in stomach by employing a variety of concepts. These include a) Floating Systems: Floating Drug Delivery Systems (FDDS) 11 have a bulk density lower than gastric fluids and thus remain buoyant in the stomach for a prolonged period of time, without affecting the gastric emptying rate. While the system is floating on the gastric contents, the drug is released slowly at a desired rate from the system. After the release of the drug, the residual system is emptied from the stomach. This results in an increase in the GRT and a better control of fluctuations in the plasma drug concentrations. Floating systems can be classified into two distinct categories, non-effervescent and effervescent systems. Fig.5: Graphic of Buoyant tablet that is less dense than the stomach fluid and therefore remains in b) Bio/Muco-adhesive Systems: 12 the fundus. Bio/muco-adhesive systems are those which bind to the gastric epithelial cell surface or mucin and serve as a potential means of extending the GRT of drug delivery system (DDS) in the stomach, by increasing the intimacy and duration of contact of drug with the biological membrane. The surface epithelial adhesive properties of mucin have been well recognized and applied to the development of GRDDS based on bio/muco-adhesive polymers. The ability to provide adhesion of a drug (or a delivery system) to the GI wall provides a longer residence time in a particular organ site, thereby producing an improved effect in terms of local action or systemic effect. Binding of polymers to the mucin/epithelial surface can be divided into three broad categories: Hydration-mediated adhesion. Bonding-mediated adhesion. Receptor-mediated adhesion.
7 c) Swelling and Expanding Systems: 13 These are the dosage forms, which after swallowing; swell to an extent that prevents their exit from the pylorus. As a result, the dosage form is retained in the stomach for a long period of time. These systems may be named as plug type system, since they exhibit the tendency to remain logged at the pyloric sphincter if that exceed a diameter of approximately mm in their expanded state. The formulation is designed for gastric retention and controlled delivery of the drug into the gastric cavity. Such polymeric matrices remain in the gastric cavity for several hours even in the fed state. A balance between the extent and duration of swelling is maintained by the degree of crosslinking between the polymeric chains. A high degree of cross-linking retards the swelling ability ofa the system maintaining its physical integrity for prolonged period. d) High Density Systems:- 14 These systems with a density of about 3 g/cm 3 are retained in the rugae of the stomach and are capable of withstanding its peristaltic movements. A density of g/cm 3 acts as a threshold value after which such systems can be retained in the lower part of the stomach. High-density formulations include coated pellets. Coating is done by heavy inert material such as barium sulphate, zinc oxide, titanium dioxide, iron powder etc. e) Incorporation of Passage Delaying Food Agents: Food excipients like fatty acids e.g. salts of myristic acid change and modify the pattern of the stomach to a fed state, thereby decreasing gastric emptying rate and permitting considerable prolongation of release. The delay in the gastric emptying after meals rich in fats is largely caused by saturated fatty acids with chain length of C 10 -C 14. f) Ion Exchange Resins: A coated ion exchange resin bead formulation has been shown to have gastric retentive properties, which was loaded with bicarbonates. Ion exchange resins are loaded with bicarbonate and a negatively charged drug is bound to the resin. The resultant beads were then encapsulated in a semi-permeable membrane to overcome the rapid loss of carbon dioxide. Upon arrival in the acidic environment of the stomach, an exchange of chloride and bicarbonate ions take place. As a result of this reaction carbon dioxide was released and trapped in the membrane thereby carrying beads towards the top of gastric
8 content and producing a floating layer of resin beads in contrast to the uncoated beads, which will sink quickly. g) Osmotic Regulated Systems: 15 It is comprised of an osmotic pressure controlled drug delivery device and an inflatable floating support in a bioerodible capsule. In the stomach the capsule quickly disintegrates to release the intragastric osmotically controlled drug delivery device. The inflatable support inside forms a deformable hollow polymeric bag that contains a liquid that gasifies at body temperature to inflate the bag. The osmotic controlled drug delivery device consists of two components drug reservoir compartment and osmotically active compartment. TYPES OF FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS (FDDS) 16 Based on the mechanism of buoyancy, two distinctly different technologies have been utilized in development of FDDS that are: A. Effervescent System, and B. Non- Effervescent System. A. EFFERVESCENT SYSTEM: - Effervescent systems include use of gas generating agents, carbonates (ex. Sodium bicarbonate) and other organic acid (e.g. citric acid and tartaric acid) present in the formulation to produce carbon dioxide (CO 2 ) gas, thus reducing the density of the system and making it float on the gastric fluid. An alternative is the incorporation of matrix containing portion of liquid, which produce gas that evaporate at body temperature. These effervescent systems further classified into two types. I. Gas Generating systems II. Volatile Liquid/Vacuum Containing Systems. I. Gas Generating Systems: 8 1. Intra Gastric Single Layer Floating Tablets or Hydrodynamically Balanced Sysem (HBS): These are as shown in Fig.8 and formulated by intimately mixing the CO 2 generating agents and the drug with in the matrix tablet. These have a bulk density lower than gastric fluids and therefore remain floating in the stomach unflattering the gastric emptying rate for a prolonged period. The drug is
9 slowly released at a desired rate from the floating system and after the complete release the residual system is expelled from the stomach. This leads to an increase in the GRT and a better control over fluctuations in plasma drug concentration. 2. Intra Gastric Bilayer Floating Tablets: 17 These are also compressed tablet as shown in Fig 6 and containing two layer i.e., i. Immediate release layer and ii. Sustained release layer. 3. Multiple Unit type floating pills: 18 These systems consist of sustained release pills as seeds surrounded by double layers. The inner layer consists of effervescent agents while the outer layer is of swellable membrane layer. When the system is immersed in dissolution medium at body temp, it sinks at once and then forms swollen pills like balloons, which float as they have lower density. This lower density is due to generation and entrapment of CO 2 within the system. II. Volatile Liquid / Vacuum Containing Systems: 1. Intragastric Floating Gastrointestinal Drug Delivery System: These system can be made to float in the stomach because of floatation chamber, which may be a vacum or filled with air or a harmless gas, while drug reservoir is encapsulated inside a microprous compartment. 2. Inflatable Gastrointestinal Delivery Systems: In these systems an inflatable chamber is incorporated, which contains liquid ether that gasifies at body temperature to cause the chamber to inflate in the stomach. These systems are fabricated by loading the inflatable chamber with a drug reservoir, which can be a drug impregnated polymeric matrix, then encapsulated in a gelatin capsule. After oral administration, the capsule dissolves to release the drug reservoir together with the inflatable chamber. The inflatable chamber automatically inflates and retains the drug reservoir compartment in the stomach. The drug continuously released from the reservoir into the gastric fluid. 3. Intragastric Osmotically Controlled Drug Delivery System: It is comprised of an osmotic pressure controlled drug delivery device and an inflatable floating support in a biodegradable capsule. In the stomach, the capsule quickly disintegrates to release the intragastirc osmotically controlled drug delivery device. The inflatable support inside forms a deformable
10 hollow polymeric bag that contains a liquid that gasifies at body temperature to inflate the bag. The osmotic pressure controlled drug delivery devices consist of two components; drug reservoir compartment and an osmotically active compartment. The drug reservoir compartment is enclosed by a pressure responsive collapsible bag, which is impermeable to vapour and liquid and has a drug delivery orifice. The osmotically active compartment contains an osmotically active salt and is enclosed within a semipermeable housing. In the stomach, the water in the GI fluid is continuously absorbed through the semipermeable membrane into osmotically active compartment to dissolve the osmotically active salt. An osmotic pressure is thus created which acts on the collapsible bag and in turn forces the drug reservoir compartment to reduce its volume and activate the drug reservoir compartment to reduce its volume and activate the drug release of a drug solution formulation through the delivery orifice. The floating support is also made to contain a bioerodible plug that erodes after a predetermined time to deflate the support. The deflated drug delivery system is then emptied from the stomach. B. NON EFFERVESCENT SYSTEMS: The Non-effervescent FDDS based on mechanism of swelling of polymer or bioadhesion to mucosal layer in GI tract. The most commonly used excipients in non-effervescent FDDS are gel forming or highly swellable cellulose type hydrocolloids, polysaccharides and matrix forming material such as polycarbonate, polyacrylate, polymethacrylate, polystyrene as well as bioadhesive polymer such as chitosan and carbopol. The various types of this system are as: 1. Single Layer Floating Tablets: They are formulated by intimate mixing of drug with a gel-forming hydrocolloid, which swells in contact with gastric fluid and maintain bulk density of less than unity. The air trapped by the swollen polymer confers buoyancy to these dosage forms. 2. Bilayer Floating Tablets: A bilayer tablet contain two layer one immediate release layer which release initial dose from system while the another sustained release layer absorbs gastric fluid, forming an impermeable colloidal gel barrier on its surface, and maintain a bulk density of less than unity and thereby it remains buoyant in the stomach.
11 3. Alignate Beads: 19 Multi unit floating dosage forms were developed from freeze-dried calcium alginate. Spherical beads of approximately 2.5 mm diameter can be prepared by dropping a sodium alginate solution into aqueous solution of calcium chloride, causing precipitation of calcium alginate leading to formation of porous system, which can maintain a floating force for over 12 hours. When compared with solid beads, which gave a short residence, time of 1 hour, and these floating beads gave a prolonged residence time of more than 5.5 hour. 4. Hollow Microspheres: 20 Hollow microspheres (microballoons), loaded with drug in their outer polymer shells were prepared by a novel emulsion-solvent diffusion method. The ethanol:dichloromethane solution of the drug and an enteric acrylic polymer was poured into an agitated aqueous solution of PVA that was thermally controlled at 40 0 C. The gas phase generated in dispersed polymer droplet by evaporation of dichloromethane formed an internal cavity in microsphere of polymer with drug. The microballoons floated continuously over the surface of acidic dissolution media containing surfactant for more than 12 hours in vitro. Factors Controlling Gastric Retention Time of Dosage Form: 21 The gastric retention time (GRT) of dosage form is controlled by several factors that affect their efficacy as a gastroretentive system. Density GRT is a function of dosage form buoyancy that is dependent on the density. 22 Size Dosage form units with a diameter of more than 9.5mm are reported to have an increased GRT. Shape of dosage form Tetrahedron and ring-shaped devices with a flexural modulus of 48 and 22.5 kilopounds per square inch (KSI) are reported to have better GRT. 90% to 100% retention at 24 hours compared with other shapes. Single or multiple unit formulation Multiple unit formulations show a more predictable release profile and insignificant impairing of performance due to failure of units, allow co-administration of units with different release profiles or containing incompatible substances and permit a larger margin of safety against dosage form failure compared with single unit dosage forms. Nature of meal Feeding of indigestible polymers or fatty acid salts can change the motility pattern of the stomach to a fed state, thus decreasing the gastric emptying rate and prolonging drug release.
12 Caloric content GRT can be increased by four to 10 hours with a meal that is high in proteins and fats. Frequency of feed The GRT can increase by over 400 minutes when successive meals are given compared with a single meal due to the low frequency of MMC. Gender Mean ambulatory GRT in males ( hours) is less compared with their age and race-matched female counterparts ( hours), regardless of the weight, height and body surface. Age Elderly people, especially those over 70, have a significantly longer GRT. Posture GRT can vary between supine and upright ambulatory states of the patient. Biological factors Diabetes and Crohn s disease. 22, 23 Advantages of GDDS: Floating dosage systems form important technological drug delivery systems with gastric retentive behavior and offer several advantages in drug delivery. These advantages include: 1. Improved drug absorption, because of increased GRT and more time spent by the dosage form at its absorption site. 2. Controlled delivery of drugs. 3. Delivery of drugs for local action in the stomach. 4. Minimizing the mucosal irritation due to drugs, by drug releasing slowly at controlled rate. 5. Treatment of gastrointestinal disorders such as gastro-esophageal reflux. 6. Simple and conventional equipment for manufacture. 7. Ease of administration and better patient compliance. 8. Site-specific drug delivery. Disadvantages of GDDS: 1. Gastric retention is influenced by many factors such as gastric motility, ph and presence of food. These factors are never constant and hence the buoyancy cannot be predicted. 2. Drugs that cause irritation and lesion to gastric mucosa are not suitable to be formulated as floating drug delivery systems. 3. High variability in gastric emptying time due to its all or non-emptying process. 4. Gastric emptying of floating forms in supine subjects may occur at random and becomes highly dependent on the diametral size. Therefore patients should not be dosed with floating forms just before going to bed.
Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Biopharmaceutics. Lec: 4
 64 Biopharmaceutics Physicochemical Properties of Drugs Affecting Bioavailability Lec: 4 1 Assist. Lecturer Ali Yaseen Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School
64 Biopharmaceutics Physicochemical Properties of Drugs Affecting Bioavailability Lec: 4 1 Assist. Lecturer Ali Yaseen Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School
Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability.
 Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Suppository Chapter Content
 10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 4
 (A) (B) Figure 4-1 A, B (C) FIGURE 4-1C The active transport process moves particles against the concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Active transport
(A) (B) Figure 4-1 A, B (C) FIGURE 4-1C The active transport process moves particles against the concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Active transport
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Enhanced delivery methods for greater efficacy
 On-Line Formulation Training - Anywhere In The World - Enhanced delivery methods for greater efficacy Belinda Carli Director, Institute of Personal Care Science Image showing absorbance in the outer stratum
On-Line Formulation Training - Anywhere In The World - Enhanced delivery methods for greater efficacy Belinda Carli Director, Institute of Personal Care Science Image showing absorbance in the outer stratum
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug
 Chapter 5 Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug absorption. It is the study of the kinetics of absorption,
Chapter 5 Is the science that study relation of physicochemical properties of drug, dosage form, & route of administration on rate and extent of drug absorption. It is the study of the kinetics of absorption,
7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
 211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
211 7. SUMMARY, CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS Drug absorption from the gastro intestinal tract can be limited by various factors with the most common one being poor aqueous solubility and poor permeability
Topical Preparations
 Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels
 Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Determination of bioavailability
 Pharmaceutics 2 Bioavailability Bioavailability is the rate and extent to which an administered drug reaches the systemic circulation. For example, if 100 mg of a drug is administered orally and 70 mg
Pharmaceutics 2 Bioavailability Bioavailability is the rate and extent to which an administered drug reaches the systemic circulation. For example, if 100 mg of a drug is administered orally and 70 mg
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
 Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use
 Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
Pharmaceutical Preparation For Internal Use 1. Solid Preparations (Tablet, Capsule, Pill) 2. Liquid Preparations (Aqua, Syrup, Elixir, Extract, Liquor, Emulsion, Mixture, Infusion, Decoction). 3. Powder
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
Physical Pharmacy. Interfacial phenomena. Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department
 Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
Physical Pharmacy Interfacial phenomena Khalid T Maaroof MSc. Pharmaceutical sciences School of pharmacy Pharmaceutics department 1 Introduction The boundary between two phases is generally described as
Ph. D Synopsis. Mr. Mehul Pravinchandra Patel Page 1
 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Sustained Drug delivey: 1-6 It is defined as any drug or dosage form modification that prolongs the therapeutic activity of the drug. The amount of drug in the body decrease slowly
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release. Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy
 Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct ISSN APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS. Nalanda College of Pharmacy, Nalgonda, A.P.
 Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct -2010 ISSN 0976-4550 Review article APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS *Vinod K.R. 1, Santhosh Vasa 1, Anbuazaghan S 2, David Banji 1, Padmasri A 1, Sandhya
Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct -2010 ISSN 0976-4550 Review article APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS *Vinod K.R. 1, Santhosh Vasa 1, Anbuazaghan S 2, David Banji 1, Padmasri A 1, Sandhya
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester
 University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
University of Sulaimani School of Pharmacy Dept. of Pharmaceutics Third level - Second semester 5/21/2017 Pharmaceutical Compounding, Dr. rer. nat. Rebaz Ali 1 Outlines Why rectal or vaginal route? Suppository
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
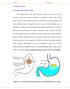 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE
 PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
PHARMA SCIENCE MONITOR AN INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY OF BICALUTAMIDE DRUG USING SOLID DISPERSION TECHNIQUE Kantilal B. Narkhede *1, R. B. Laware 2, Y. P.
Direct Compression. With the right ingredients it s a simple, cost-effective manufacturing process
 Direct With the right ingredients it s a simple, cost-effective manufacturing process TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow Speed and savings sounds good to us
Direct With the right ingredients it s a simple, cost-effective manufacturing process TM Trademark of The Dow Chemical Company ( Dow ) or an affiliated company of Dow Speed and savings sounds good to us
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
Pharmacokinetics I. Dr. M.Mothilal Assistant professor
 Pharmacokinetics I Dr. M.Mothilal Assistant professor DRUG TRANSPORT For a drug to produce a therapeutic effect, it must reach to its target and it must accumulate at that site to reach to the minimum
Pharmacokinetics I Dr. M.Mothilal Assistant professor DRUG TRANSPORT For a drug to produce a therapeutic effect, it must reach to its target and it must accumulate at that site to reach to the minimum
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS
 Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS K. P. R. Chowdary *, Tanniru Adinarayana, T. Vijay, Mercy. R. Prabhakhar
Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON THE ENHANCEMENT OF DISSOLUTION RATE OF KETOPROFEN BY SOLID DISPERSION IN COMBINED CARRIERS K. P. R. Chowdary *, Tanniru Adinarayana, T. Vijay, Mercy. R. Prabhakhar
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Ion Exchange Resins. Unique Solutions to Formulation Problems
 Ion Exchange Resins Unique Solutions to Formulation Problems Lyn Hughes Some of the common problems faced by formulators and how using ion exchange resins may be able to solve them are discussed. PHOTODISC,
Ion Exchange Resins Unique Solutions to Formulation Problems Lyn Hughes Some of the common problems faced by formulators and how using ion exchange resins may be able to solve them are discussed. PHOTODISC,
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms. prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy
 Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
APPLIED CHEMISTRY SURFACE TENSION, SURFACTANTS TYPES OF SURFACTANTS & THEIR USES IN TEXTILE PROCESSING
 APPLIED CHEMISTRY SURFACE TENSION, SURFACTANTS TYPES OF SURFACTANTS & THEIR USES IN TEXTILE PROCESSING Lecture No. 13 & 14 2 Surface Tension This property of liquids arises from the intermolecular forces
APPLIED CHEMISTRY SURFACE TENSION, SURFACTANTS TYPES OF SURFACTANTS & THEIR USES IN TEXTILE PROCESSING Lecture No. 13 & 14 2 Surface Tension This property of liquids arises from the intermolecular forces
Antacid therapy: Antacids side effects:
 Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
LAB.2. Tablet Production Methods
 LAB.2 Tablet Production Methods Dry methods Direct compression Dry granulation Wet methods Wet granulation Regardless whether tablets are made by direct compression or granulation, the first step, milling
LAB.2 Tablet Production Methods Dry methods Direct compression Dry granulation Wet methods Wet granulation Regardless whether tablets are made by direct compression or granulation, the first step, milling
New formulas for successful drug delivery Hot-melt extrusion for enhanced solubility and bioavailability
 New formulas for successful drug delivery Hot-melt extrusion for enhanced solubility and bioavailability Andreas Gryczke, an enabler in excipients Pharma Ingredients & Services. Welcome to more opportunities.
New formulas for successful drug delivery Hot-melt extrusion for enhanced solubility and bioavailability Andreas Gryczke, an enabler in excipients Pharma Ingredients & Services. Welcome to more opportunities.
CHAPTER-I DRUG CHARACTERIZATION & DOSAGE FORMS
 CHAPTER-I DRUG CHARACTERIZATION & DOSAGE FORMS by: j. jayasutha lecturer department of pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy srm university DRUG CHARACTERIZATION: Pre-formulation studies will attempt
CHAPTER-I DRUG CHARACTERIZATION & DOSAGE FORMS by: j. jayasutha lecturer department of pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy srm university DRUG CHARACTERIZATION: Pre-formulation studies will attempt
A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF IBUPROFEN BY β CYCLODEXTRIN AND SOLUTOL HS15
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF IBUPROFEN BY β CYCLODEXTRIN
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION RATE OF IBUPROFEN BY β CYCLODEXTRIN
Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating Tablets Using Different Polymers: Guargum, Sodium Alginate, Hpmc100cps and Carbopol940
 ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
ISSN 0976 3333 Available Online at www.ijpba.info International Journal of Pharmaceutical & Biological Archives 2011; 2(4):1146-1151 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ARTICLE Formulation and Evaluation of Atenolol Floating
Effect of Surfactants and Adjuvants on Postemergence Herbicide Efficacy
 Effect of Surfactants and Adjuvants on Postemergence Herbicide Efficacy Dr. William B. McCloskey Cooperative Extension Weed Specialist Department of Plant Sciences University of Arizona Herbicide Uptake
Effect of Surfactants and Adjuvants on Postemergence Herbicide Efficacy Dr. William B. McCloskey Cooperative Extension Weed Specialist Department of Plant Sciences University of Arizona Herbicide Uptake
CONTENTS PAGE. Please note: Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications
 Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
Hypromellose CONTENTS PAGE 2 Preface Matrix system Selection of METOLOSE grades Specifications Properties Powder Solution Application Related Patents 3 4-5 6 8 10 13 14 17 Please note: The information
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS OF LEVETIRACETAM
 DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS OF LEVETIRACETAM Dissertation submitted to The Tamilnadu Dr. M.G.R Medical University, Chennai -32 In partial fulfillment of the requirements For the award
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS OF LEVETIRACETAM Dissertation submitted to The Tamilnadu Dr. M.G.R Medical University, Chennai -32 In partial fulfillment of the requirements For the award
D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper
 D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper Introduction This background paper is intended to provide a basic rationale for initial formulation efforts, and define some of the terminology
D9G : Oro-Mucosal Dosage Forms Development Background Paper Introduction This background paper is intended to provide a basic rationale for initial formulation efforts, and define some of the terminology
LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY
 LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY The increasing demand for fresh and quality packaged food, consumer convenience and manufacturers concern for longer shelf life of the food products is driving the market
LECTURE 10. PACKAGING TECHNOLOGY The increasing demand for fresh and quality packaged food, consumer convenience and manufacturers concern for longer shelf life of the food products is driving the market
Chemate and Chowdary, IJPSR, 2012; Vol. 3(7): ISSN:
 IJPSR (2012), Vol. 3, Issue 07 (Research Article) Received on 18 March, 2012; received in revised form 25 April, 2012; accepted 22 June, 2012 A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION
IJPSR (2012), Vol. 3, Issue 07 (Research Article) Received on 18 March, 2012; received in revised form 25 April, 2012; accepted 22 June, 2012 A FACTORIAL STUDY ON ENHANCEMENT OF SOLUBILITY AND DISSOLUTION
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Assem Al Refaei. Sameer Emeish. Dr.Alia. Hodaifa Ababneh & Abdullah Shurafa
 8 Assem Al Refaei Sameer Emeish Hodaifa Ababneh & Abdullah Shurafa Dr.Alia Sheet Checklist Bioequivalence and Therapeutic equivalence. Factors Influencing Absorption. Revising Bioavailability. Factors
8 Assem Al Refaei Sameer Emeish Hodaifa Ababneh & Abdullah Shurafa Dr.Alia Sheet Checklist Bioequivalence and Therapeutic equivalence. Factors Influencing Absorption. Revising Bioavailability. Factors
REFERENCES OVERVIEW ADVANTAGES AEROSOLS. Aerosols. and Foams
 COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of Monash University pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968
COMMONWEALTH OF AUSTRALIA Copyright Regulations 1969 WARNING This material has been reproduced and communicated to you by or on behalf of Monash University pursuant to Part VB of the Copyright Act 1968
Edible Films, Coatings & Processing Aids
 Edible Films, Coatings & Processing Aids Mikal E. Saltveit Mann Laboratory, Department of Plant Sciences, University of California, Davis, CA 95616-8631 Use of Edible Films and Coatings Reduce water loss
Edible Films, Coatings & Processing Aids Mikal E. Saltveit Mann Laboratory, Department of Plant Sciences, University of California, Davis, CA 95616-8631 Use of Edible Films and Coatings Reduce water loss
Tablet is a major category of solid dosage forms which are widely used worldwide. Extensive information is required to prepare tablets with good
 TABLET PRODUCTİON Tablet is a major category of solid dosage forms which are widely used worldwide. Extensive information is required to prepare tablets with good quality at high standards. Based on preformulation
TABLET PRODUCTİON Tablet is a major category of solid dosage forms which are widely used worldwide. Extensive information is required to prepare tablets with good quality at high standards. Based on preformulation
Industrial Pharmacy (3) Solutions as a dosage form. DR.Saad.M.YACOUB
 Industrial Pharmacy (3) Solutions as a dosage form DR.Saad.M.YACOUB Solutions: definition A solution is a homogenous one-phase system consisting of two or more components. The solvent, or mixture of solvents,
Industrial Pharmacy (3) Solutions as a dosage form DR.Saad.M.YACOUB Solutions: definition A solution is a homogenous one-phase system consisting of two or more components. The solvent, or mixture of solvents,
Introduction of emulsions Effect of polysaccharides on emulsion stability Use of polysaccharides as emulsifier. Polysaccharides in Food Emulsions
 1 Introduction of emulsions Effect of polysaccharides on emulsion stability Use of polysaccharides as emulsifier 2 Basic concepts of emulsions Interfacial tension (): the force that operates on an interface
1 Introduction of emulsions Effect of polysaccharides on emulsion stability Use of polysaccharides as emulsifier 2 Basic concepts of emulsions Interfacial tension (): the force that operates on an interface
PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION
 PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1 PHARMACEUTICS Pharmaceutics is the science of dosage form design. The general area of study concerned with the formulation, manufacture, stability, and
PHARMACEUTICS I صيدالنيات 1 UNIT 1 INTRODUCTION 1 PHARMACEUTICS Pharmaceutics is the science of dosage form design. The general area of study concerned with the formulation, manufacture, stability, and
Pharmacokinetics Dr. Iman Lec. 3
 Pharmacokinetics r. Iman Lec. 3 Pharmacokinetics A dequate drug doses must be delivered to the target organ to get therapeutic but not toxic levels. So, pharmacokinetic examines the movement of drug over
Pharmacokinetics r. Iman Lec. 3 Pharmacokinetics A dequate drug doses must be delivered to the target organ to get therapeutic but not toxic levels. So, pharmacokinetic examines the movement of drug over
Challenges and solutions for moisture sensitive API formulation
 Challenges and solutions for moisture sensitive API formulation Introduction Today, formulators are looking for alternative processes to reformulate existing products or to formulate New Chemical Entities
Challenges and solutions for moisture sensitive API formulation Introduction Today, formulators are looking for alternative processes to reformulate existing products or to formulate New Chemical Entities
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Encapsulation techniques
 Loughborough University Institutional Repository Encapsulation techniques This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation: VLADISAVLJEVIC, G.T.,
Loughborough University Institutional Repository Encapsulation techniques This item was submitted to Loughborough University's Institutional Repository by the/an author. Citation: VLADISAVLJEVIC, G.T.,
An introduction to Liposomal Encapsulation Technology
 An introduction to Liposomal Encapsulation Technology Mother Nature has the innate ability to solve problems through the most efficient and effective route possible. The problem of how to make an oil-soluble
An introduction to Liposomal Encapsulation Technology Mother Nature has the innate ability to solve problems through the most efficient and effective route possible. The problem of how to make an oil-soluble
Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems
 Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems November 16 th Prof. Gregory E. Amidon - University of Michigan What is an In vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) System? An IPD
Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems November 16 th Prof. Gregory E. Amidon - University of Michigan What is an In vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) System? An IPD
Innovations in Design: NIA-West. Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017
 Innovations in Design: NIA-West Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017 1 Innovations in Design: How Do You Stand Out? If all other competitors are the same
Innovations in Design: NIA-West Missy Lowery, MSc Head of Integrated Marketing Capsugel, now a Lonza company 11/13/2017 1 Innovations in Design: How Do You Stand Out? If all other competitors are the same
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4
 CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
PHARMACEUTICAL AID PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY
 PHARMACEUTICAL AID PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY Excipients are inactive ingredients used as carriers for the active ingredients in a pharmaceutical product. These may
PHARMACEUTICAL AID PREPARED BY B.KIRUTHIGA LECTURER DEPT OF PHARMACEUTICAL CHEMISTRY Excipients are inactive ingredients used as carriers for the active ingredients in a pharmaceutical product. These may
Cell membrane & Transport. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Ebneshahidi
 Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Cell membrane & Transport Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Cell Membrane To enclose organelles and other contents in cytoplasm. To protect the cell. To allow substances into and out of the cell. To have metabolic reactions
Easy, fast and reliable!
 Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. Tailormade formulated. s film coating products are one-step coating
Product Overview Easy, fast and reliable! Special easy-to-use preparations for film coating, sugar-coating, colouring and tabletting. Tailormade formulated. s film coating products are one-step coating
Parenteral products-definition
 Parenteral products-definition Parenteral preparations are sterile, pyrogen-free liquids (solutions, emulsions, or suspensions) or solid dosage forms packaged in either single-dose or multidose containers.
Parenteral products-definition Parenteral preparations are sterile, pyrogen-free liquids (solutions, emulsions, or suspensions) or solid dosage forms packaged in either single-dose or multidose containers.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT
 SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
SUMMARY OF PRODUCT CHARACTERISTICS 1 NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT "Carbellon" Tablets. 2. Qualitative and Quantitative Composition Active Constituents: Activated Charcoal Ph.Eur. Magnesium Hydroxide Ph.Eur.
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(1), 2012, 297-305 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF VALSARTAN TABLETS EMPLOYING CYCLODEXTRIN-POLOXAMER 407-PVP K30 INCLUSION COMPLEXES K. P.
PHAR 7632 Chapter 7. Table Market and Share of Pharmaceuticals by ROA Data from Viswanathan, 2004
 Student Objectives for this Chapter After completing the material in this chapter each student should:- be able to describe various routes of drug administration including the concentration versus time
Student Objectives for this Chapter After completing the material in this chapter each student should:- be able to describe various routes of drug administration including the concentration versus time
Chapter 3 Drug Absorption and Bioavailability
 Chapter 3 Drug Absorption and Bioavailability Debra Si Mui Sim Abstract Most drugs are prescribed as oral preparations or extravascular injections (other than intravenous injections) for the treatment
Chapter 3 Drug Absorption and Bioavailability Debra Si Mui Sim Abstract Most drugs are prescribed as oral preparations or extravascular injections (other than intravenous injections) for the treatment
International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage:
 Research Article CODEN: IJRPJK ISSN: 2319 9563 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage: www.ijrpns.com COMPARARISSION OF SOLUBILITY IMPROVEMENT OF CEFIXIME
Research Article CODEN: IJRPJK ISSN: 2319 9563 International Journal of Research in Pharmaceutical and Nano Sciences Journal homepage: www.ijrpns.com COMPARARISSION OF SOLUBILITY IMPROVEMENT OF CEFIXIME
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
DRUG DISTRIBUTION. Distribution Blood Brain Barrier Protein Binding
 DRUG DISTRIBUTION Distribution Blood Brain Barrier Protein Binding DRUG DISTRIBUTION Drug distribution is a reversible transport of drug through the body by the systemic circulation The drug molecules
DRUG DISTRIBUTION Distribution Blood Brain Barrier Protein Binding DRUG DISTRIBUTION Drug distribution is a reversible transport of drug through the body by the systemic circulation The drug molecules
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
Right time, right place: bioactive delivery systems
 Right time, right place: bioactive delivery systems Zhigao Niu, Alejandra Acevedo-Fani & Ali Rashidinejad Science of Food Team Riddet Institute, Massey University Developing High-Value Foods Food Systems
Right time, right place: bioactive delivery systems Zhigao Niu, Alejandra Acevedo-Fani & Ali Rashidinejad Science of Food Team Riddet Institute, Massey University Developing High-Value Foods Food Systems
Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems
 Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems November 16 th Prof. Gregory E. Amidon - University of Michigan What is an In vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) System? An IPD
Advantages and Limitations of In Vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) Systems November 16 th Prof. Gregory E. Amidon - University of Michigan What is an In vivo Predictive Dissolution (IPD) System? An IPD
FORMULATION CHOICE. How and why they are chosen. Dr Andy Fowles On behalf of ECPA Specification Expert Group
 FORMULATION CHOICE How and why they are chosen Dr Andy Fowles On behalf of ECPA Specification Expert Group Topics Why formulate? How to identify formulation options Drivers Principle formulation type overview
FORMULATION CHOICE How and why they are chosen Dr Andy Fowles On behalf of ECPA Specification Expert Group Topics Why formulate? How to identify formulation options Drivers Principle formulation type overview
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
NANO 243/CENG 207 Course Use Only
 L6. Drug Administration & Transport by Fluid Motion April 19, 2018 Part I: Drug Administration Routes of Drug Administration Topical: local effect, substance is applied directly where its action is desired.
L6. Drug Administration & Transport by Fluid Motion April 19, 2018 Part I: Drug Administration Routes of Drug Administration Topical: local effect, substance is applied directly where its action is desired.
Large scale production
 Large scale production Rotary capsule machine: This machine has two, side-by-side cylinders in each of which half-moulds are cut. These cylinders, like the rollers of a mangle, rotate in contrary direction
Large scale production Rotary capsule machine: This machine has two, side-by-side cylinders in each of which half-moulds are cut. These cylinders, like the rollers of a mangle, rotate in contrary direction
WHY... 8/21/2013 LEARNING OUTCOMES PHARMACOKINETICS I. A Absorption. D Distribution DEFINITION ADME AND THERAPEUIC ACTION
 PHARMACOKINETICS I Absorption & Distribution LEARNING OUTCOMES By the end of the lecture students will be able to.. Dr Ruwan Parakramawansha MBBS, MD, MRCP(UK),MRCPE, DMT(UK) (2013/08/21) Define pharmacokinetics,
PHARMACOKINETICS I Absorption & Distribution LEARNING OUTCOMES By the end of the lecture students will be able to.. Dr Ruwan Parakramawansha MBBS, MD, MRCP(UK),MRCPE, DMT(UK) (2013/08/21) Define pharmacokinetics,
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING
 SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
SUSTAINED RELEASE TABLETS USING A PVA DC FORMULATION RESISTANT TO ALCOHOL INDUCED DOSE DUMPING Dr. Dieter Lubda MilliporeSigma is a business of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany Agenda: Sustained release
