Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
|
|
|
- Harry Thomas
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Review Article *Hemali Soni 1, V. A. Patel 2 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. 2 Associate professor, Department of Pharmaceutics, A. R. College of Pharmacy, V. V. Nagar, Gujarat, India. *Corresponding author s get.hemalisoni@gmail.com Accepted on: ; Finalized on: ABSTRACT Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery (GRDDS) is most advantageous for increasing gastric residence time of drug and to achieve site specific drug delivery in upper GIT. GRDDS treats GI diseases by releasing the drug locally. This will leads to high concentration of drug at the gastric mucosa and sustain release of drug can be achieve. GRDDS empowers prolonged and continuous release of the drug to the upper GIT. Keywords: gastro retentive drug delivery system Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery INTRODUCTION Gastro retentive drug delivery system (GRDDS) is a site specific delivery It delivers the drug either in stomach or in intestine. The drug delivery is obtained by retention of dosage form in stomach and the drug is released in a controlled manner to the specific site either in stomach, duodenum or in intestine. Different Approaches of GRDDS 1 Figure 1 represents different approaches of GRDDS Non Effervescent 2 This system is also known as Hydrodynamically Balanced (HBS). This system remains buoyant by entrapment of air in the swelled polymer. When this system comes in contact with gastric fluid, the hydrocolloid starts to hydrate by first forming the gel at the surface of the dosage form and ultimately control the release of the drug. As the outer surface goes into the solution, the gel barrier is maintained by immediate adjacent hydrocolloid layer. Figure 2 represents overview of mechanism of non effervescent Approaches to GRDDS Floating Drug Delivery Mucoadhesive Raft Forming Expandable Super Porous Hydrogel Magnetic High Density Non Effervescent Effervescent Gas Generating Volatile Liquid/Vaccum Figure 1: Different approaches for GRDDS Floating Drug Delivery (Low Density ) 2 Floating drug delivery system (FDDS) possess bulk density lower than the gastric fluid and because of this reason it remains buoyant in the stomach without affecting gastric emptying time for an extended period of time.while the system is floating on the gastric content, the drug released slowly at a desired rate from system, which results in increase in gastric retention time and better control in fluctuation of plasma drug concentration. After complete release of the drug, the residual system is emptied from the stomach. Effervescent 2,3 Figure 2: Non Effervescent This system made to float in the stomach by incorporating floating chamber, which may be filled with vacuum, air or inert gas. This system uses matrices prepared with swellable polymer and effervescent components. The matrices are formulated in such a way that when they reach into the stomach carbon dioxide is liberated by acidity of gastric content. This carbon dioxide is entrapped in the hydrocolloid causes the upward 81
2 movements of the dosage form and maintain its buoyancy. This system is divided in to two classes: 1) volatile liquid containing system and 2) gas generating Volatile Liquid Containing 2 It is osmotically controlled floating This system consists of two chambers which are separated by pressure sensitive, impermeable, movable bladder and bio erodible plug which gradually release the gas. The drug and volatile liquid is placed in first and second chamber respectively. Upon administration, the drug is continuously released from the chamber into the gastric fluid. Figure 3 represents Volatile liquid containing residence time of the dosage form by binding them to the gastric mucosa. The adhesion is favored by rapid hydration. This mucoadhesive system is not that much feasible as the bond formation for mucoadhesion is prevented by the acidic environment and presence of thick mucus in the stomach. Polymers used for this purpose may include polycarbophil, carbopol, CMC, chitosan, lectin etc. Raft Forming 1,3,4,5 This system focus more for delivery of antacid and delivery of drugs used to treat gastrointestinal infection and disorders. The basic mechanism involves formation of viscous cohesive gel when the system comes in contact with gastric fluid. In this each portion of liquid swells and forms a continuous layer of gel known as raft. The raft floats because of buoyancy created by formation of CO 2. This raft acts as a physical barrier to prevent the reflex of gastric content into the esophagus. This system contains a gel forming agent and alkaline bicarbonates or carbonates responsible for making the system less dense than the gastric fluid and to float on the gastric fluid. Figure 5 represents raft forming system s mechanism. Figure 3: Volatile Liquid containing system Gas Generating 3 This system uses effervescent reaction between carbonate/bicarbonate salt and citric/tartaric acid which liberate carbon dioxide. This carbon dioxide gets entrapped in the hydrocolloid layer of the system and thus decreases the specific gravity of the system which makes it to float over the gastric fluid. Figure 4 represents general mechanism of Gas generating Figure 5: Raft Forming Effect of Sodium bicarbonate on the drug release from raft forming system Mucoadhesive 3,4 Figure 4: Gas Generating Mucoadhesion means attachment of the drug to the mucus coat. This approach helps to increase the gastric Sodium bicarbonate is used as a gas generating agent. Gas generating agent sodium bicarbonate interacts with the gastric acid and generates carbon dioxide which gets entrapped within the swellable matrix. Carbonate or bicarbonate may be present in the amount ranges from 5% to 50% and preferably from about 10% to 30% by weight of composition. Increasing the concentration of bicarbonate decreases the floating lag time because of faster and higher carbon dioxide generation. At higher concentration of effervescent agent, coating of the tablet becomes less stable. This is because of increase in the internal pressure and there by rupturing the polymer coating which ultimately results in sudden increase in drug release. 82
3 Advantages of Raft Forming It is used for the treatment of heartburn and oesophagitis. It is also useful to treat laryngo pharyngeal reflux (LPR) and gastro esophageal reflux disease. It does not interfere with activity of anti secretory agent e.g. cimetidine. Rapid and long duration of action can be achieved. It shows its action within seconds. It may not interfere with the function of pyloric sphincter. Improved patient compliance. Expandable 1 This system may be of two types: 1) unfoldable system and 2) swellable polymer. Unfoldable systems uses biodegradable polymer. This concept uses carrier such as capsule in which compressed system is incorporated which extends in the stomach. Swellable systems are retained due to their mechanical property. The swelling is resulted from absorption of water. sealed to prevent any direct contact of gastric fluid to the undissolved drug. As delivery system contains entrapped air chamber, when it reaches into the stomach, floating of the system on the gastric fluid takes place. Gastric fluid enters into the pores and dissolves the drug which causes release of dissolved drug. Magnetic 6,7 This approach of increased gastric retention time is base on the principle that dosage form contains a small internal magnet. A magnet is placed in abdomen over the position of stomach that retains dosage form in the gastric region. Figure 7 represents general situation for working of magnetic Disadvantages of this system are as follows: External magnet needs to be positioned with the degree of precision. Patient non compliance Due to these disadvantages this system is not commonly used. The resultant bulk enables gastric retention and maintains the stomach in the fed condition. The whole expandable system is coated with the polymeric membrane. This outer coat is permeable to both, drug and body fluid. This outer coat also controls the drug release. This system is gradually reduced in the size and rigidity. This results in reduction of drug and expanding This results in elimination of Superporous Hydrogel 1,6,7 Conventional hydrogel have pore size ranging from 10 mm to 10µm. This hydrogel possess very slow process of water absorption and require several hours to attain equilibrium state. High Density 1,6,7 Figure 6: Magnetic In contrast to conventional hydrogel, superporous hydrogel have average pore size >100µm. Superporous hydrogel swells to equilibrium size within minute. This occurs because of rapid water uptake by capillary wetting through numerous interconnected open pores. Superporous hydrogel swells to large size and have sufficient mechanical strength to withstand the pressure created by gastric contraction. This approach is based on the principle that encapsulation of drug within the microporous compartment which having pores on the top and on the bottom wall. Peripheral walls are completely This system possesses a density of about 3 g/cm 3 which are retained in the antrum part of the stomach and are capable of withstanding its peristaltic movements. This system is prepared by coating a drug on a heavy core or mixed with the inert material such as iron powder, barium sulphate, zinc oxide and titanium oxide etc. Figure 8 represents high density system in stomach. The major drawback with such system is that it is technically difficult to manufacture formulation with high amount of drug and to achieve density of about 2.8 g/cm 3. 83
4 Ability to float is depends upon the hydration state of the dosage form. This system is unsuitable for the drugs which have limited acid solubility. This system is also unsuitable for the drugs which are selectively absorbed from the stomach. Floating system is unsuitable for the drug which have stability problem in the stomach. Applications of GRDDS 2,8 Sustained drug delivery Advantages of GRDDS 1,2,3,6,7 Figure 7: High Density Floating dosage form remains in the stomach for longer period of time. Floating dosage form is advantageous for producing local action in the stomach. Controlled delivery of the drug is possible. Reduction in the mucosal irritation is possible by releasing drug slowly. Ease of administration Improved patient compliance can be achieved. Site specific drug delivery is possible. GRDDS is advantageous for the drug absorbed through the stomach. Bioavailability of therapeutic agents is significantly enhanced. For the drug with short half life, sustain release can be achieve and also reduce the frequency of the dosing. Gastro-retentive dosage form minimizes fluctuation of the drug concentration. GRDDS minimize counter activity of the body and ultimately increase the drug efficacy. Disadvantages of GRDDS 1,3,7,8 Bioadhesion in the acidic environment high mucus turn over may arise the question about the effectiveness of the system Not suitable for the drug which may produce gastric irritation. Mucus on the stomach wall is in continuous renewal state so unpredictable adherence may result. Retention time in the stomach is depends on the digestive state. So floating system should be administered after meal. Floating system remains in the stomach for longer period and release the drug over a prolong period of time. This system has bulk density less than 1 so it may float on the gastric content. Site specific drug delivery This system is particularly advantageous for the drugs which are absorbed from the stomach or proximal part of the small intestine. Absorption enhancement Drugs having a poor bioavailability are potential candidate for formulating as a floating system to enhance its absorption. Maintenance of constant blood flow This system provides an easy way for maintaining constant blood flow with relatively ease of administration. Comparison of GRDDS with the Conventional Dosage Form 1 Table 1 represents comparison of GRDDS and conventional dosage form Table 1: Comparison of GRDDS with conventional dosage form Conventional Drug Delivery High risk of toxicity Less patient compliance Not suitable for delivery of drugs with narrow absorption window in small intestine region Not much advantageous for -Drugs having rapid absorption through GIT -Drugs which degrade in the colon -Drugs acting locally in the stomach Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Very low risk of toxicity Improves patient compliance Suitable for delivery of drugs with narrow absorption window in small intestine region Very much advantageous for -Drugs acting locally in the stomach -Drugs which degrade in the colon Potential Drug Candidates for GRDDS 1,6,7 -Drugs having rapid absorption through GIT Drugs which are acting locally in the stomach. e.g. antacids. Drugs which are primarily absorbed in the stomach e.g. amoxicilline. 84
5 Drugs which are poorly soluble at alkaline ph. e.g. furosemide. Drugs having narrow absorption window. e.g. levodopa. Drugs that are absorbed rapidly from the stomach. e.g. tetracycline. Drug which are degrade in the stomach. e.g. ranitidine. Drugs those are unsuitable for GRDDS 6 Drugs which have very low acid solubility. e.g. phenytoin. Drugs which are unstable at lower ph. e.g. erythromycin. Drugs which are intended to be release in the colon. e.g. corticosteroids. Factors Affecting Efficacy of GRDDS 3,6,7,8 Particle size It should be in the range of 1 2 mm to pass through the pyloric valve into the small intestine. Density Density of the dosage form affects the gastric emptying rate. A buoyant dosage form has density less than the gastric fluid to float. Size Size of the system should be in greater than 7.5 mm in diameter. Shape Ring and tetrahedron shaped system shows better gastric retention compared with the other shapes. Single or multiple unit formulation Multiple unit formulation shows more predictable release profile. It also allows co-administration of the units with different release profile or containing incompatible substances. It also permit large margin of safety as compared to single unit formulation. Nature of the meal and caloric content Indigestible polymers, increased caloric content, fatty acid salt, increased acidity, fat and protein meal increase gastric retention time. Food intake Gastric retention time is increased in fed state. Posture Gastric retention time is different for inactive and active state of the patient. Gender Mean gastric retention time in male is less as compared to female regardless of weight, height and body surface. Age Age greater than 70 shows longer residence time. Biological factor Disease like gastroenteritis, gastric ulcer, diabetes, hypothyroidism retard gastric emptying rate while partial or total gastrectomy, duodenal ulcer promote gastric emptying rate. CONCLUSION GRDDS proves advantageous for the drugs having poor bioavailability. This system also provides an advantage for the drugs that are primarily absorb in upper GIT. Different approaches of GRDDS have their own advantages and disadvantages. REFERENCES 1. Bhavsar DN, Varde NM, Shah VH, Advances In Grdds: Raft Forming A Review, Journal of Drug Delivery & Therapeutics; 2(5), 2012, Kaur B, Sharma S, Sharma G, Saini R, Singh S, Nagpal M, Jain UK, Sharma M, A Review of Floating Drug Delivery, Asian Journal of Biomedical and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 3(24), 2013, Binoy B, Nair J, Floating Drug Delivery -A new Approach In Gastric Retention- A Review, Journal Of Drug Delivery Research, 1(3), 2012, Nayak KP, Upadhyay P, Deshpande J, Valera AR, Chauhan NP, Gastroretentive Drug Delivery s and Recent Approaches: A Review, Journal of Pharmaceutical Research and Opinion, 2(1), 2012, Chandel A, Floating drug delivery systems: A better approach, International Current Pharmaceutical Journal, 1(5), 2012, Nayak A, Maji R, Das B, Gastroretentive drug delivery systems: a Review, Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research, 3(1), 2010, Badoni A, Ojha A, GnanarajanI G, Kothiyal P, Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery, THE PHARMA INNOVATION, 1(8), 2012, Mishra A, Gupta P, Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery : A Review, International Journal of Drug Development & Research, October-December, 4(4), 2012, Source of Support: Nil, Conflict of Interest: None. 85
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
1 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 ORAL SUSTAINED RELEASE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS The oral route is the most promising and convenient route of drug administration. Conventional immediate release system achieves
SHRI JAGDISHPRASAD JHABARMAL TIBREWALA UNIVERSITY 1
 INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTRODUCTION Oral delivery of drugs is by far the most preferred route of drug delivery due to ease of administration, patient compliance and flexibility in formulation 1. Conventional oral dosage forms
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM AS A NOVEL VITAL CONCEPT BABITA SHARMA, NITAN BHARTI GUPTA Sri Sai College of Pharmacy, Pathankot, India.
Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review
 J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
J Chronother Drug Deliv Vol 5 Issue 1 2014: 1-7 Authors Journal of Chronotherapy and Drug Delivery REVIEW ARTICLE Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems: A Review Rupa Gupta 1 *, PK Sharma 1, Ashish Arora
Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Rev. Res., 27(2), July August 2014; Article No. 15, Pages: Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS)
 Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
Review Article Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System (GRDDS) Sachin A. Nitave*, Vishin A. Patil, Amrita A. Kagalkar Anil Alias Pintu Magdum Memorial Pharmacy College, Dharangutti, Shirol, Kolhapur,
1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small
 Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Lecture-5 1. Gastric Emptying Time Anatomically, a swallowed drug rapidly reaches the stomach. Eventually, the stomach empties its content in the small intestine. Because the duodenum has the greatest
Available Online through Research Article
 ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
ISSN: 0975-766X Available Online through Research Article www.ijptonline.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE TABLETS FOR CONTROLLED DELIVERY OF NORFLOXOCIN Ganesh Kumar Gudas*, Subal Debnath,
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW
 MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
MODIFIED DISSOLUTION APPARATUS FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: A REVIEW * Patel N. 1, Raiyani D. 1, Patel A. 1, Patel N. 1, Jain H. 1 and Upadhyay U. 1 Department of Pharmaceutics, Sigma Institute of
DISSOLUTION RATE LIMITED ABSORPTION:
 INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
INTRODUCTION Oral drug delivery is the most widely utilized route of administration among all the routes that have been explored for systemic delivery of drugs via pharmaceutical products of different
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF GASTRORETENTIVE FLOATING TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE Chandira. Margret R. *, Sahu Chandra Mohan and Jayakar B. Vinayaka Mission s College of Pharmacy Vinayaka Missions University,
DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE
 1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
1. Introduction: DESIGN AND DEVELOPMENT OF COLON TARGETED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM OF 5 FLUORURACIL & METRONIDAZOLE Oral controlled - release formulations for the small intestine and colon have received considerable
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium
 Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
Preparation and Evaluation of Gastro Retentive Floating Tablets of Atorvastatin Calcium Florida Sharmin 1, Md. Abdullah Al Masum 1, S. M. Ashraful Islam 1 and Md. Selim Reza 2 1 Department of Pharmacy,
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS. 6.7 Mathematical model fitting of obtained drug release data
 EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
EVALUATION OF EFFERVESCENT FLOATING TABLETS 6.1 Technological characteristics of floating tablets 6.2 Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR) 6.3 Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) 6.4 In
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY OF RANITIDINE HYDROCHLORIDE
 Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
Int. J. LifeSc. Bt & Pharm. Res. 2012 Varsha Deva and Manoj Kr Gautam, 2012 Research Paper ISSN 2250-3137 www.ijlbpr.com Vol. 1, No. 3, July 2012 2012 IJLBPR. All Rights Reserved FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review
 ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
ph Dependent Drug Delivery System: Review Korake.S.P. SVERI s College of Pharmacy (Poly.), Pandharpur The ph-dependent CTDDS exploit the generally accepted view that ph of the human GIT increases progressively
DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED RELEASE FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF METFORMIN HYDROCHLORIDE
 ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
ISSN: 0975-8232 IJPSR (2010), Vol. 1, Issue 8 (Research article) Received 11 April, 2010; received in revised form 17 June, 2010; accepted 13 July, 2010 DEVELOPMENT AND IN VITRO EVALUATION OF SUSTAINED
A. Incorrect! Histamine is a secretagogue for stomach acid, but this is not the only correct answer.
 Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
Pharmacology - Problem Drill 21: Drugs Used To Treat GI Disorders No. 1 of 10 1. Endogenous secretagogues for stomach acid include: #01 (A) Histamine (B) Gastrin (C) PGE1 (D) A and B (E) A, B and C Histamine
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research
 International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
International Journal of Medicine and Pharmaceutical Research Journal Home Page: www.pharmaresearchlibrary.com/ijmpr Research Article Open Access Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating
Volume 8, Issue 2, May June 2011; Article-029
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM: AN EMERGING APPROACH TO IMPROVE THE GASTRIC RESIDENCE TIME OF SOLID DOSAGE FORMS Manmohan *, Shukla T P, Mathur A, Upadhyay N, Sharma S
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems
 Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Effect of Polymer Concentration and Viscosity Grade on Atenolol Release from Gastric Floating Drug Delivery Systems 1 1 1 2 U.V. Bhosale*, V. Kusum Devi, Nimisha Jain and P.V. Swamy 1 Al-Ameen College
Chapter 2 Rationale and Objective
 Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Chapter 2 SPP School of Pharmacy & Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 44 2.0 Rationale Need for extended release drug delivery systems Over the past 50 years or so, substantial research in the
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5
 Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Biopharmaceutics Dosage form factors influencing bioavailability Lec:5 Ali Y Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School of Pharmacy University of Sulaimani 09/01/2019
Antacid therapy: Antacids side effects:
 Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
Antacids Lec:5 When the general public ask why it takes antacids, the answer will include: 1.that uncomfortable feeling from overeating. 2. heart burn. 3. a growing hungry feeling between meals. Antacids
2- Minimum toxic concentration (MTC): The drug concentration needed to just produce a toxic effect.
 BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
BIOPHARMACEUTICS Drug Product Performance Parameters: 1- Minimum effective concentration (MEC): The minimum concentration of drug needed at the receptors to produce the desired pharmacologic effect. 2-
Biswajit Biswal IRJP 2 (7)
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN 2230 8407 Available online http://www.irjponline.com Research Article DESIGN DEVELOPMENT AND EVALUATION OF TRIMETAZIDINE DIHYDROCHLORIDE FLOATING BILAYER
Topical Preparations
 Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
Topical Preparations One of the functions of the skin is to protect the internal body components against the external environment and thus to control the passage of chemicals into and out of the body.
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
Available on line www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research ISSN No: 975-7384 CODEN(USA): JCPRC5 J. Chem. Pharm. Res., 211, 3(2):786-791 Development and optimization of colon targeted
DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL COMPOSITE DESIGN
 Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
Academic Sciences Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical and Clinical Research Vol, Suppl 1, 2012 ISSN - 0974-2441 Research Article DESIGN AND OPTIMIZATION OF FLOATING MATRIX TABLETS OF FAMOTIDINE BY CENTRAL
LIST OF TABLES. Page No. No List of US Patents for FDDS Gastroretentive products available in the market
 LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
LIST OF TABLES Sl. Table Title of the table 1 3.01 List of US Patents for FDDS 27 2 3.02 List of drugs explored for various floating dosage forms 35 3 3.03 Gastroretentive products available in the market
Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche
 Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
Universita degli Studi di Milano Corso di Laurea Magistrale in Chimica e Tecnologia Farmaceutiche Tecnologia e Legislazione Farmaceutiche II- 9 CFU Prof. Andrea Gazzaniga Rilascio Modificato via Orale
EUDRATEC GRS. Your floating solution for an improved absorption in the stomach.
 EUDRATEC GRS Your floating solution for an improved absorption in the stomach. L+L 16-01-375 Flyer EUDRATEC GRS, 6 Seiten, DIN-A5.indd 02. Dec 2016; 11:44 Uhr EUDRATEC GRS unique gastro-retentive system
EUDRATEC GRS Your floating solution for an improved absorption in the stomach. L+L 16-01-375 Flyer EUDRATEC GRS, 6 Seiten, DIN-A5.indd 02. Dec 2016; 11:44 Uhr EUDRATEC GRS unique gastro-retentive system
Figure 1.1: (a) Drug release mechanism and (b) Floating drug delivery systems
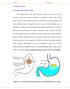 1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
1 1. INTRODUCTION 1.1. Floating drug delivery system Oral administration is the most convenient mode of drug delivery and is associated with superior patient compliance as compared to other modes of drug
Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery System
 ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 1 No. 8 2012 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery
ISSN: 2277-7695 CODEN Code: PIHNBQ ZDB-Number: 2663038-2 IC Journal No: 7725 Vol. 1 No. 8 2012 Online Available at www.thepharmajournal.com THE PHARMA INNOVATION Review on Gastro Retentive Drug Delivery
OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
 Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures Vol. 9, No. 3, July September 2014, p. 1077-1084 OPTIMIZATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE GASTRORETENTIVE BUOYANT TABLET WITH XANTHAN GUM AND POLYOX WSR 1105
What is Nanotechnology?
 Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
Use of Nanotechnology to Optimize Delivery of Probiotics and Prebiotics to Target Sites Ian G Tucker Professor of Pharmaceutical Sciences University of What is Nanotechnology? Some people say they have
Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability.
 Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
Pharmaceutics Reading Notes Define the terms biopharmaceutics and bioavailability. Biopharmaceutics: the area of study concerning the relationship between the physical, chemical, and biological sciences
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
A Review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Pranav Joshi*, Priyank Patel,Hiren Modi, Dr.M.R. Patel, Dr.K.R.Patel, Dr.N.M.Patel Department of pharmaceutics, Shri B.M.Shah College of Pharmaceutical
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN
 FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
FORMULATION AND EVALUATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF NORFLOXACIN Ms. Jyoti Rathore 1*, Mr. Hitesh Kumar Parmar 1 Ujjain Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Ujjain. Email- hkparmar7@rediffmail.com ABSTRACT
Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5): Research Article
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(5):1225-1231 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Formulation and evaluation of raft forming sustained
CHAPTER-I DRUG CHARACTERIZATION & DOSAGE FORMS
 CHAPTER-I DRUG CHARACTERIZATION & DOSAGE FORMS by: j. jayasutha lecturer department of pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy srm university DRUG CHARACTERIZATION: Pre-formulation studies will attempt
CHAPTER-I DRUG CHARACTERIZATION & DOSAGE FORMS by: j. jayasutha lecturer department of pharmacy practice Srm college of pharmacy srm university DRUG CHARACTERIZATION: Pre-formulation studies will attempt
Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist
 Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Human Journals Review Article January 2017 Vol.:8, Issue:2 All rights are reserved by Dharmendra Solanki et al. Floating Drug Delivery System Novel Tool for Delivering H 2 Antagonist Keywords: Floating
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage form of Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride.
 Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
Available online on www.ijcpr.com International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Review and Research, 3(4), 105-109 Research Article ISSN: 0976-822X Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Dosage
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS. Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4
 CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
CONTROLLED-RELEASE & SUSTAINED-RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS Pharmaceutical Manufacturing-4 The improvement in drug therapy is a consequence of not only the development of new chemical entities but also the combination
DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG
 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF RESEARCH IN PHARMACY AND CHEMISTRY Available online at www.ijrpc.com Research Article DESIGN AND CHARACTERIZATION OF FLOATING TABLETS OF ANTI-DIABETIC DRUG M Seth *, DS Goswami,
Digestive System Module 4: The Stomach *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
OpenStax-CNX module: m49286 1 Digestive System Module 4: The * Donna Browne Based on The by OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 4.0
Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets
 Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
Human Journals Research Article February 2015 Vol.:2, Issue:3 All rights are reserved by Anil Kumar R et al. Important Characterization of Nicorandil Buccal Tablets Keywords: Surface ph, Mucoadhesive strength,
A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
ISSN: 2230-7346 Suresh Rewar et al. / JGTPS / 6(1)-(2015) 2417 2422 (Review Article) Journal of Global Trends in Pharmaceutical Sciences Journal home page: www.jgtps.com A NOVEL APPROACH FOR FLOATING DRUG
FLOATING DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (FDDS): A REVIEW
 25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
25 P a g e International Standard Serial Number (ISSN): 2319-8141 International Journal of Universal Pharmacy and Bio Sciences 5(1): January-February 2016 INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF UNIVERSAL PHARMACY AND
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p.
 Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Cell Membranes, Epithelial Barriers and Drug Absorption p. 1 Introduction p. 2 The Plasma Membrane p. 2 The phospholipid bilayer p. 3 Dynamic behaviour of membranes p. 4 Modulation of membrane fluidity
Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research
 ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
ISSN: 2231-2560 Research Article Asian Journal of Biochemical and Pharmaceutical Research Design and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Tablets of Dipyridamole: Influence of Formulation Variables A.
Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct ISSN APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS. Nalanda College of Pharmacy, Nalgonda, A.P.
 Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct -2010 ISSN 0976-4550 Review article APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS *Vinod K.R. 1, Santhosh Vasa 1, Anbuazaghan S 2, David Banji 1, Padmasri A 1, Sandhya
Volume: I: Issue-2: Aug-Oct -2010 ISSN 0976-4550 Review article APPROACHES FOR GASTROTENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS *Vinod K.R. 1, Santhosh Vasa 1, Anbuazaghan S 2, David Banji 1, Padmasri A 1, Sandhya
A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES
 Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Review Article A REVIEW ON GASTRO RETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM (GRDDS) WITH SPECIAL EMPHASIS ON FORMULATION AND DEVELOPMENT OF FLOATING MICROSPHERES Kamini Vasava, Rajesh Ks, Lalit Lata Jha * Department
Fundamentals of Pharmacology for Veterinary Technicians Chapter 4
 (A) (B) Figure 4-1 A, B (C) FIGURE 4-1C The active transport process moves particles against the concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Active transport
(A) (B) Figure 4-1 A, B (C) FIGURE 4-1C The active transport process moves particles against the concentration gradient from a region of low concentration to a region of high concentration. Active transport
1 INTRODUCTION. 1.1 Oral Drug Delivery System: 1. Introduction
 1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Oral Drug Delivery System: The most widely utilized and preferred route of administration amongst all the routes that have been explored till date, is the oral route for the systemic
1 INTRODUCTION 1.1 Oral Drug Delivery System: The most widely utilized and preferred route of administration amongst all the routes that have been explored till date, is the oral route for the systemic
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet Formulation by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique
 Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Optimization of Valsartan SR Floating Tablet by 2 2 Factorial Design and Multiple Regression Technique K. Srinivasa Reddy 1, Surya Kanta Swain 2, K. P. R. Chowdary *3, S. V. U. M. Prasad 4 1 School of
Sphincters heartburn diaphragm The Stomach gastric glands pepsin, chyme The Small Intestine 1-Digestion Is Completed in the Small Intestine duodenum
 Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
Sphincters are muscles that encircle tubes and act as valves. The tubes close when the sphincters contract and they open when the sphincters relax. When food or saliva is swallowed, the sphincter relaxes
A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS
 WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACY AND PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES SJIF Impact Factor 5.210 Volume 4, Issue 11, 1313-1332 Review Article ISSN 2278 4357 A REVIEW ON GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEMS Sayyed Sarfaraz
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System
 Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
Swelling System: A Novel Approach Towards Gastroretentive Drug Delivery System Santosh Shep *, Sham Dodiya, Sandeep Lahoti, Rahul Mayee Dr. Vedprakash Patil Pharmacy College, Aurangabad, India INDO GLOBAL
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY. DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi
 KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE HUMAN ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY DIGESTIVE SYSTEM Dr.B.Jyothi Prof, Dept. Of Pharmacology KTPC The Digestive System Food undergoes six major processes: 1. Ingestion : process
Holistic Healing Professional Practitioner Diploma Course Sample Pages Page 1
 The last phase is called the intestinal phase and takes place about four hours after the gastric phase. The chyme passes through the small intestine, or duodenum, through the pyloric sphincter. This is
The last phase is called the intestinal phase and takes place about four hours after the gastric phase. The chyme passes through the small intestine, or duodenum, through the pyloric sphincter. This is
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
 BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
BUCCAL DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM Mr. Kambagiri Swamy M.Pharm.,(Ph.D) KRISHNA TEJA PHARMACY COLLEGE Introduction Novel drug delivery systems(ndds) are the system where the man searches for now method of entry
DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN
 Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 10(4), 2012, 2199-2208 ISSN 0972-768X www.sadgurupublications.com DESIGN AND EVALUATION OF CONTROLLED RELEASE MATRIX TABLETS OF FLURBIPROFEN K. V. R. N. S. RAMESH *, B. HEMA KIRNAMAYI
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms. prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy
 Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Formulation and evaluation of modified release oral solid dosage forms prof. dr. Saša Baumgartner University of Ljubljana Faculty of Pharmacy Content Terminology Why modified release? How to select appropriate
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin
 Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Development And Evaluation Of Gastroretentive Floating Tablet Of Rosuvastatin Amiya kumar Prusty, Archana P. Chand Institute of Pharmacy and Technology, salipur, Biju Patnaik University of technology,
Digestive System. - Food is ingested
 11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
11 V. Digestive Processes in the Mouth - Food is ingested - Mechanical digestion begins (chewing) - Salivary amylase begins chemical breakdown of starch - Propulsion is initiated by Deglutition (Swallowing)
EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH
 ejpmr, 2015,2(4), 185-203 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.ejpmr.com Vishvesh et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.026 Review Article ISSN 3294-3211 EJPMR RAFT FORMING TABLETS: A NOVEL
ejpmr, 2015,2(4), 185-203 EUROPEAN JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH www.ejpmr.com Vishvesh et al. SJIF Impact Factor 2.026 Review Article ISSN 3294-3211 EJPMR RAFT FORMING TABLETS: A NOVEL
University of Buea. Faculty of Health Sciences. Programme in Medicine
 Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Faculty of Health Sciences University of Buea Wednesday, 28 th January 2009 Time: 8 00-10 00 Programme in Medicine MED 303 (Gastrointestinal Physiology) EXAMS (2008-2009) Identify the letter of the choice
Factors responsible for the impaired bioavailability and instability rifampicin FDC
 Table of contents 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Oral multiparticulate drug delivery system...2 1.2 Methods of preparing pellets...3 1.3 Extrusion-spheronization...3 1.4 Theory of pellet formation and growth...4
Table of contents 1.0 Introduction 1.1 Oral multiparticulate drug delivery system...2 1.2 Methods of preparing pellets...3 1.3 Extrusion-spheronization...3 1.4 Theory of pellet formation and growth...4
REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS. Tablets
 March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
March 2011 REVISION OF MONOGRAPH ON TABLETS Final text for addition to The International Pharmacopoeia This monograph was adopted by the Forty-fourth WHO Expert Committee on Specifications for Pharmaceutical
Includes mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum, anus. Salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
 Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Chapter 14 The Digestive System and Nutrition Digestive System Brings Nutrients Into the Body The digestive system includes Gastrointestinal (GI) tract (hollow tube) Lumen: space within this tube Includes
Long-Term Care Updates
 Long-Term Care Updates May 2016 By Katee Miller, PharmD Candidate, Mohamed Jalloh, PharmD, & Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP Introduction Enteral nutrition (EN) through a tube is the preferred
Long-Term Care Updates May 2016 By Katee Miller, PharmD Candidate, Mohamed Jalloh, PharmD, & Zara Risoldi Cochrane, PharmD, MS, FASCP Introduction Enteral nutrition (EN) through a tube is the preferred
Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery Tablet
 International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
International Journal of Pharmacy and Medical Sciences (1): 01-06, 01 ISSN -5854 IDOSI Publications, 01 DOI: 10.589/idosi.ijpms.01..1.641 Formulation and Evaluation of Floating Mefenamic Acid Drug Delivery
Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual,
 Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual, buccal, GI, and rectal absorption. For most drugs,
Drug Absorption in the Gastrointestinal Tract Drugs may be absorbed by passive diffusion from all parts of the alimentary canal including sublingual, buccal, GI, and rectal absorption. For most drugs,
Tissues: systems of cells working together to perform specialized tasks. Ex muscles, nerves, blood
 Chapter 3 Cells: the smallest units in which independent life can exist. All living things are single cells or organisms made of cells. Need water and nutrients to survive Enzyme: any of the great working
Chapter 3 Cells: the smallest units in which independent life can exist. All living things are single cells or organisms made of cells. Need water and nutrients to survive Enzyme: any of the great working
Scholars Research Library. Formulation and evaluation of buccoadhesive tablet of Atenolol
 Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Available online at www.scholarsresearchlibrary.com Scholars Research Library Der Pharmacia Lettre, 2011, 3(2): 34-38 (http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html) ISSN 0975-5071 USA CODEN: DPLEB4
Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, ,
 IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
IDP Biological Systems Gastrointestinal System Section Coordinator: Jerome W. Breslin, PhD, Assistant Professor of Physiology, MEB 7208, 504-568-2669, jbresl@lsuhsc.edu Overall Learning Objectives 1. Characterize
Chapter 1 Introduction
 Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Chapter 1 SPP School of Pharmacy and Technology Management, SVKM s NMIMS, Mumbai 1.0 Extended release dosage form In the past few decades, significant advances have been made in the area of drug delivery
Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9.
 Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9. 1 9 8 2 7 3 4 5 6 Station 2. Identify/name the parts or structures labeled 10 20. 10. Is this the right or left lung? 15 13 14 16 11 12
Station 1. Identify (= name) the spaces or structures labeled 1 9. 1 9 8 2 7 3 4 5 6 Station 2. Identify/name the parts or structures labeled 10 20. 10. Is this the right or left lung? 15 13 14 16 11 12
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS. Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali
 GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS Submitted by: Shaema M. Ali GASTROINTESTINAL AND ANTIEMETIC DRUGS by: Shaema M. Ali There are four common medical conditions involving the GI system 1) peptic ulcers
Harvesting energy from food. Digestion: A Closer Look. Where digestion begins. Salivary Glands 4/17/13. Or how food gets from
 Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
Harvesting energy from food Or how food gets from to and body structures Cheese protein (a polymer of amino acids in a specific sequence) Breakdown of protein by human digestive system Amino acid monomer
DEVELOPMENT OF NON SODIUM EFFERVESCENT TABLET OF PARACETAMOL USING ARGININE CARBONATE
 IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 5 (Research Article) Received on 17 July, 2012; received in revised form, 23 February, 2013; accepted, 14 April, 2013 DEVELOPMENT OF NON SODIUM EFFERVESCENT TABLET OF PARACETAMOL
IJPSR (2013), Vol. 4, Issue 5 (Research Article) Received on 17 July, 2012; received in revised form, 23 February, 2013; accepted, 14 April, 2013 DEVELOPMENT OF NON SODIUM EFFERVESCENT TABLET OF PARACETAMOL
Formulation and Evaluation of Gastroretentive Floating Drug Delivery System of Atenolol
 DOI:10.2126/ijprhs.2016.0.06 H Kaur et al. CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-646 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article
DOI:10.2126/ijprhs.2016.0.06 H Kaur et al. CODEN (USA)-IJPRUR, e-issn: 2348-646 International Journal of Pharma Research and Health Sciences Available online at www.pharmahealthsciences.net Original Article
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release. Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy
 Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Principals and Dosage Forms in the Therapy Modified Drug Release Institute of Pharmaceutical Technology and Biopharmacy Dosage forms Definition: Dosage forms are the means by which drug molecules are delivered
Lipid Based Matrices as Colonic Drug Delivery System for Diflunisal (In-vitro, In-vivo study)
 Lipid Based Matrices as Colonic Drug Delivery System for Diflunisal (In-vitro, In-vivo study) Presented by Dr. AHMED ATEF DONIA, PH. D., Lecturer of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Tanta
Lipid Based Matrices as Colonic Drug Delivery System for Diflunisal (In-vitro, In-vivo study) Presented by Dr. AHMED ATEF DONIA, PH. D., Lecturer of Pharmaceutical Technology, Faculty of Pharmacy, Tanta
A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems
 29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
29 A review on Gastroretentive Drug Delivery Systems Hemendrasinh J Rathod*, Dhruti P. Mehta, Jitendra Singh Yadav Department of Pharmaceutics, Vidyabharti Trust College of Pharmacy, Umrakh, Gujarat, India.
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
 Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems David Julian McClements and Hang Xiao Department of Food Science University of Massachusetts Development of Nutrient Delivery Systems: Ingredients & Challenges
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY ISSN Review Article
 INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
INTERNATIONAL RESEARCH JOURNAL OF PHARMACY www.irjponline.com ISSN 2230 8407 Review Article AN OVERVIEW ON VARIOUS APPROACHES TO ORAL CONTROLLED DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM VIA GASTRORETENTIVE DRUG DELIVERY SYSTEM
January 07, ANIMALS Digestive System Stomach.notebook. The Stomach. (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb
 (cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
(cardiac sphincter) bbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbbb 1 Location: thoracic cavity Physical description: a "J" shaped organ with muscular walls lined with folds it is the widest part of the digestive tract has 2 muscular
Chapter 8: Digestion. Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes
 Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Chapter 8: Digestion Structure and Functions of Digestive Organs Macronutrients Digestive Enzymes What organisms need Digestion? Heterotrophs - rely on ingestion of organic molecules for production of
Ingestion Digestion- Absorption- Elimination
 DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM 1 FUNCTIONS Organization GI tract==mouth anus Accessory organs Salivary glands, liver, pancreas, gallbladder Major Functions: Ingestion-mouth, teeth, tongue Digestion- chemical and mechanical
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION
 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
SUMMARY AND CONCLUSION 8 SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS In spite of the many challenges faced by researchers while designing an effective, reproducible and stable dosage form, oral dosage forms continued to maintain
Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus
 Heartburn Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus Patient assessment with GERD 1-signs and symptoms The hallmark of typical symptom of GERD is heartburn (restrosternal),acid regurgitation,
Heartburn Reflux of gastric contents, particularly acid, into the esophagus Patient assessment with GERD 1-signs and symptoms The hallmark of typical symptom of GERD is heartburn (restrosternal),acid regurgitation,
Biopharmaceutics. Lec: 4
 64 Biopharmaceutics Physicochemical Properties of Drugs Affecting Bioavailability Lec: 4 1 Assist. Lecturer Ali Yaseen Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School
64 Biopharmaceutics Physicochemical Properties of Drugs Affecting Bioavailability Lec: 4 1 Assist. Lecturer Ali Yaseen Ali BSc Pharmacy MSc Industrial Pharmaceutical Sciences Dept. of Pharmaceutics School
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System
 MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
MCAT Biology Problem Drill 20: The Digestive System Question No. 1 of 10 Question 1. During the oral phase of swallowing,. Question #01 A. Initially, the food bolus is moved to the back of the tongue and
Dyspepsia. Dyspepsia covers upper abdominal pain, fullness, early satiety, bloating, and nausea.
 Antacids Hawler medical university Collage of pharmacy/ fourth year /pharmacy practice Sham A. Talat Shareef (B.Sc. Msc. clinical pharmacy) 2017-2018 Sham_talat@yahoo.com Head of Department Of Clinical
Antacids Hawler medical university Collage of pharmacy/ fourth year /pharmacy practice Sham A. Talat Shareef (B.Sc. Msc. clinical pharmacy) 2017-2018 Sham_talat@yahoo.com Head of Department Of Clinical
FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels
 Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
Seite 1 von 8 Share this story: Issue: April 2015, Posted Date: 3/30/2015 FORMULATION DEVELOPMENT - A QbD Approach to Develop Extended Release Softgels INTRODUCTION Soft gelatin capsules (softgels) continue
The Digestive System and Excretory System
 The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
The Digestive System and Excretory System By: Kay Foos, Amanda Smith, Joanna Dare, Lilli Blumkin Kay Digestive System The function of this system is to break down the food particles into materials the
The Digestive System. Prepares food for use by all body cells.
 The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
The Digestive System Prepares food for use by all body cells. Digestion The chemical breakdown of complex biological molecules into their component parts. Lipids to fatty acids Proteins to individual amino
This PDF is available for free download
 Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Research Paper Formulation Strategy for Low Absorption Window Antihypertensive Agent M. J. QURESHI, J. ALI*, ALKA AHUJA AND SANJULA BABOOTA Department of Pharmaceutics, Faculty of Pharmacy, Jamia Hamdard,
Suppository Chapter Content
 10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
10 min SUPPOSITORY Suppository Chapter Content 1. Suppositories and Factors Affecting Drug Absorption 2. Ideal Suppository and Different Types of Bases 3. Methods of Suppository Manufacturing Suppository
