3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3
|
|
|
- Mariah Hunter
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 .5 Unit : Biology We need to understand how biological and environmental systems operate when they are working well in order to be able to intervene when things go wrong. Modern developments in biomedical and technological research allow us to do so. B.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells The cells, tissues and organs in plants and animals are adapted to take up and get rid of dissolved substances. Different conditions can affect the rate of transfer. Sometimes energy is needed for transfer to take place. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding to: evaluate the development and use of artificial aids to breathing, including the use of artificial ventilators evaluate the claims of manufacturers about sports drinks analyse and evaluate the conditions that affect water loss in plants. B.1.1 Dissolved substances a) Dissolved substances move by diffusion and by active transport. b) Water often moves across boundaries by osmosis. Osmosis is the diffusion of water from a dilute to a more concentrated solution through a partially permeable membrane that allows the passage of water molecules. Use of the terms turgor and plasmolysis is not required. c) Differences in the concentrations of the solutions inside and outside a cell cause water to move into or out of the cell by osmosis. d) Most soft drinks contain water, sugar and ions. e) Sports drinks contain sugars to replace the sugar used in energy release during the activity. They also contain water and ions to replace the water and ions lost during sweating. f) If water and ions are not replaced, the ion / water balance of the body is disturbed and the cells do not work as efficiently. 45
2 g) Substances are sometimes absorbed against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy from respiration. The process is called active transport. Active transport enables cells to absorb ions from very dilute solutions. h) Many organ systems are specialised for exchanging materials. The effectiveness of an exchange surface is increased by: having a large surface area being thin, to provide a short diffusion path (in animals) having an efficient blood supply (in animals, for gaseous exchange) being ventilated. i) Gas and solute exchange surfaces in humans and other organisms are adapted to maximise effectiveness. j) The size and complexity of an organism increases the difficulty of exchanging materials. k) In humans: the surface area of the lungs is increased by the alveoli the surface area of the small intestine is increased by villi. l) The villi provide a large surface area with an extensive network of capillaries to absorb the products of digestion by diffusion and active transport. B.1.2 Gaseous exchange a) The lungs are in the upper part of the body (thorax), protected by the ribcage and separated from the lower part of the body (abdomen) by the diaphragm. Candidates should be able to recognise these structures on a diagram. b) The breathing system takes air into and out of the body so that oxygen from the air can diffuse into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide can diffuse out of the bloodstream into the air. c) To make air move into the lungs the ribcage moves out and up and the diaphragm becomes flatter. These changes are reversed to make air move out of the lungs. The movement of air into and out of the lungs is known as ventilation. Candidates should be able to describe the mechanism by which ventilation takes place, including the relaxation and contraction of muscles leading to changes in pressure in the thorax. 46
3 B.1. Exchange systems in plants a) In plants: carbon dioxide enters leaves by diffusion most of the water and mineral ions are absorbed by roots. b) The surface area of the roots is increased by root hairs and the surface area of leaves is increased by the flattened shape and internal air spaces. c) Plants have stomata to obtain carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and to remove oxygen produced in photosynthesis. d) Plants mainly lose water vapour from their leaves. Most of the loss of water vapour takes place through the stomata. Evaporation is more rapid in hot, dry and windy conditions. If plants lose water faster than it is replaced by the roots, the stomata can close to prevent wilting. e) The size of stomata is controlled by guard cells, which surround them. Suggested ideas for practical work to develop skills and understanding include the following: use sensors, eg spirometers, to measure air flow and lung volume investigating potato slices in different concentrations of liquid in terms of mass gain and mass loss design an investigation to measure the mass change of potato when placed in a series of molarities of sucrose solution investigating the relationship between concentrations of sugar solution and change in length of potato strips placing shelled eggs in different concentrations of liquid to observe the effect placing slices of fresh beetroot in different concentrations of liquid to observe the effect, and then taking thin slices to observe the cells observing guard cells and stomata using nail varnish observing water loss from plants by placing in a plastic bag with cobalt chloride paper. 47
4 B.2 Transport systems in plants and animals Substances are transported around the body by the circulatory system (the heart, the blood vessels and the blood). They are transported from where they are taken into the body to the cells, or from the cells to where they are removed from the body. Modern developments in biomedical and technological research enable us to help when the circulatory system is not working well. Plants have separate transport systems for water and nutrients. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding to: evaluate data on the production and use of artificial blood products evaluate the use of artificial hearts and heart valves evaluate the use of stents. B.2.1 The blood system a) The circulatory system transports substances around the body. b) The heart is an organ and pumps blood around the body. Much of the wall of the heart is made from muscle tissue. Knowledge of the cardiac cycle is not required. c) There are four main chambers (left and right atria and ventricles) of the heart. d) Blood enters the atria of the heart. The atria contract and force blood into the ventricles. The ventricles contract and force blood out of the heart. Valves in the heart ensure that blood flows in the correct direction. Blood flows from the heart to the organs through arteries and returns through veins. There are two separate circulation systems, one for the lungs and one for all other organs of the body. Knowledge of the names of the heart valves is not required. Knowledge of the names of the blood vessels associated with the heart is limited to aorta, vena cava, pulmonary artery and pulmonary vein. e) Arteries have thick walls containing muscle and elastic fibres. Veins have thinner walls and often have valves to prevent back-flow of blood. f) If arteries begin to narrow and restrict blood flow stents are used to keep them open. Candidates should understand the importance of stents, particularly with reference to the coronary arteries. g) In the organs, blood flows through very narrow, thin-walled blood vessels called capillaries. Substances needed by the cells in body tissues pass out of the blood, and substances produced by the cells pass into the blood, through the walls of the capillaries. 48
5 B.2.2 The blood a) Blood is a tissue and consists of a fluid called plasma in which red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets are suspended. b) Blood plasma transports: carbon dioxide from the organs to the lungs soluble products of digestion from the small intestine to other organs urea from the liver to the kidneys. c) Red blood cells transport oxygen from the lungs to the organs. Red blood cells have no nucleus. They are packed with a red pigment called haemoglobin. In the lungs haemoglobin combines with oxygen to form oxyhaemoglobin. In other organs oxyhaemoglobin splits up into haemoglobin and oxygen. d) White blood cells have a nucleus. They form part of the body s defence system against microorganisms. e) Platelets are small fragments of cells. They have no nucleus. Platelets help blood to clot at the site of a wound. B.2. Transport systems in plants a) Flowering plants have separate transport systems: xylem tissue transports water and mineral ions from the roots to the stem and leaves the movement of water from the roots through the xylem and out of the leaves is called the transpiration stream phloem tissue carries dissolved sugars from the leaves to the rest of the plant, including the growing regions and the storage organs. 49
6 Suggested ideas for practical work to develop skills and understanding include the following: dissection of the heart use software simulations of the work of the heart and blood vessels observation of arteries and veins from slides observation of blood smears observation of valves in veins preventing backflow of blood using the athletic arm / prominent vein use sensors to measure blood pressure before, during and after exercise investigate flow rate in xylem using celery, which can include calculation of flow rate investigate the content of artificial phloem and xylem given knowledge of the appropriate tests plan an investigation using a potometer to measure the effect of temperature or wind speed on the transpiration rate. B. Homeostasis Humans need to remove waste products from their bodies to keep their internal environment relatively constant. People whose kidneys do not function properly may die because toxic substances accumulate in their blood. Their lives can be saved by using dialysis machines or having a healthy kidney transplanted. Water and ion content, body temperature and blood glucose levels must be kept within very narrow ranges. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding to: evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of treating kidney failure by dialysis or kidney transplant evaluate modern methods of treating diabetes. B..1 Removal of waste and water control a) Waste products that have to be removed from the body include: carbon dioxide, produced by respiration and removed via the lungs when we breathe out urea, produced in the liver by the breakdown of amino acids and removed by the kidneys in the urine, which is temporarily stored in the bladder. b) If the water or ion content of the body is wrong, too much water may move into or out of the cells and damage them. Water and ions enter the body when we eat and drink. 50
7 c) A healthy kidney produces urine by: first filtering the blood Knowledge of other parts of the urinary system, the structure of the kidney and the structure of a nephron is not required. reabsorbing all the sugar reabsorbing the dissolved ions needed by the body reabsorbing as much water as the body needs releasing urea, excess ions and water as urine. d) People who suffer from kidney failure may be treated either by using a kidney dialysis machine or by having a healthy kidney transplanted. e) Treatment by dialysis restores the concentrations of dissolved substances in the blood to normal levels and has to be carried out at regular intervals. f) In a dialysis machine a person s blood flows between partially permeable membranes. The dialysis fluid contains the same concentration of useful substances as the blood. This ensures that glucose and useful mineral ions are not lost. Urea passes out from the blood into the dialysis fluid. g) In kidney transplants a diseased kidney is replaced with a healthy one from a donor. However, the donor kidney may be rejected by the immune system unless precautions are taken. h) Antigens are proteins on the surface of cells. The recipient s antibodies may attack the antigens on the donor organ as they do not recognise them as part of the recipient s body. i) To prevent rejection of the transplanted kidney: a donor kidney with a tissue-type similar to that of the recipient is used Knowledge of the ABO blood grouping and compatibility tables is not required. the recipient is treated with drugs that suppress the immune system. 51
8 B..2 Temperature control a) Sweating helps to cool the body. More water is lost when it is hot, and more water has to be taken as drink or in food to balance this loss. b) Body temperature is monitored and controlled by the thermoregulatory centre in the brain. This centre has receptors sensitive to the temperature of the blood flowing through the brain. c) Also temperature receptors in the skin send impulses to the thermoregulatory centre, giving information about skin temperature. The name of the centre in the brain (hypothalamus) is not required. d) If the core body temperature is too high: blood vessels supplying the skin capillaries dilate so that more blood flows through the capillaries and more heat is lost sweat glands release more sweat which cools the body as it evaporates. e) If the core body temperature is too low: blood vessels supplying the skin capillaries constrict to reduce the flow of blood through the capillaries muscles may shiver their contraction needs respiration, which releases some energy to warm the body. HT only FT candidates are not expected to describe details of changes in the blood vessels when the core body temperature is too high or too low but should understand that the skin looks red when we are hot due to increased blood flow. HT only B.. Sugar control a) The blood glucose concentration of the body is monitored and controlled by the pancreas. The pancreas produces the hormone insulin, which allows the glucose to move from the blood into the cells. b) A second hormone, glucagon, is produced in the pancreas when blood glucose levels fall. This causes glycogen to be converted into glucose and be released into the blood. HT only 52
9 c) Type 1 diabetes is a disease in which a person s blood glucose concentration may rise to a high level because the pancreas does not produce enough of the hormone insulin. d) Type 1 diabetes may be controlled by careful attention to diet, exercise, and by injecting insulin. Suggested ideas for practical work to develop skills and understanding include the following: use surface temperature sensors to monitor skin temperature in different conditions plan an investigation to measure the cooling effect of sweating demonstrate blood testing (using meters) dissect and make observations of a kidney design a model kidney dialysis machine using Visking tubing as the filter test urine from diabetic and non-diabetic people using Clinistix. B.4 Humans and their environment Humans often upset the balance of different populations in natural ecosystems, or change the environment so that some species find it difficult to survive. With so many people in the world, there is a serious danger of causing permanent damage not just to the local environments but also to the global environment unless our overall effect is managed carefully. Humans rely on ecosystems for food, water and shelter. Candidates should use their skills, knowledge and understanding to: analyse and interpret scientific data concerning Candidates will be given data to work from. environmental issues evaluate methods used to collect environmental data and consider their validity and reliability as evidence for environmental change evaluate the methods being used to feed and provide water to an increasing human population, both in terms of short term and long term effects evaluate the use of biogas generators evaluate the positive and negative effects of managing food production and distribution, and be able to recognise that practical solutions for human needs may require compromise between competing priorities. Candidates should have considered a number of biogas generator designs ranging from third-world generators supplying a single family to commercial generators. They should understand how the output from a biogas generator might be affected by climatic conditions. Candidates should consider: the differences in efficiency between producing food from animals and plants the pros and cons of factory farming of animals the implications of food miles. 5
10 B.4.1 Waste from human activity a) Rapid growth in the human population and an increase in the standard of living means that increasingly more waste is produced. Unless waste is properly handled, more pollution will be caused. b) Waste may pollute: water, with sewage, fertiliser or toxic chemicals air, with smoke and gases such as sulfur dioxide, which contributes to acid rain land, with toxic chemicals such as pesticides and herbicides, which may be washed from the land into waterways. c) Humans reduce the amount of land available for other animals and plants by building, quarrying, farming and dumping waste. B.4.2 Deforestation and the destruction of areas of peat a) Large-scale deforestation in tropical areas, for timber and to provide land for agriculture, has: increased the release of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere (because of burning and the activities of microorganisms) reduced the rate at which carbon dioxide is removed from the atmosphere and locked up for many years as wood. b) Deforestation leads to reduction in biodiversity. c) Deforestation has occurred so that: crops can be grown from which biofuels, based on ethanol, can be produced there can be increases in cattle and in rice fields to provide more food. These organisms produce methane and this has led to increases in methane in the atmosphere. d) The destruction of peat bogs and other areas of peat releases carbon dioxide into the atmosphere. Candidates should understand why peat free composts are of increasing importance. 54
11 B.4. Biofuels a) Levels of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere are increasing and contribute to global warming. An increase in the Earth s temperature of only a few degrees Celsius: may cause big changes in the Earth s climate may cause a rise in sea level may reduce biodiversity may cause changes in migration patterns, eg in birds may result in changes in the distribution of species. b) Carbon dioxide can be sequestered in oceans, lakes and ponds and this is an important factor in removing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. c) Biofuels can be made from natural products by fermentation. Biogas, mainly methane, can be produced by anaerobic fermentation of a wide range of plant products or waste material containing carbohydrates. B.4.4 Food production a) At each stage in a food chain, less material and less energy are contained in the biomass of the organisms. This means that the efficiency of food production can be improved by reducing the number of stages in food chains. b) The efficiency of food production can also be improved by restricting energy loss from food animals by limiting their movement and by controlling the temperature of their surroundings. c) Fish stocks in the oceans are declining. It is important to maintain fish stocks at a level where breeding continues or certain species may disappear altogether in some areas. Net size and fishing quotas play an important role in conservation of fish stocks. This is an example of sustainable food production. d) The fungus Fusarium is useful for producing mycoprotein, a protein-rich food suitable for vegetarians. The fungus is grown on glucose syrup, in aerobic conditions, and the biomass is harvested and purified. Suggested ideas for practical work to develop skills and understanding include the following: build a simple biogas generator to collect methane and demonstrate how the methane can be burned as a fuel investigate and design a way of measuring the gas output of a biogas generator and compare the amount of gas produced by different materials. 55
Year 11AA 11A1. Success criteria for all assessments (assessments will be every 6 weeks): A* = 90% + A = 80 89% B = 70 79% C = 60 69% D = 50 59%
 Year 11AA 11A1 Success criteria for all assessments (assessments will be every 6 weeks): A* = 90% + A = 80 89% B = 70 79% C = 60 69% D = 50 59% E = 40 49% Note: assessments are linear. For example, the
Year 11AA 11A1 Success criteria for all assessments (assessments will be every 6 weeks): A* = 90% + A = 80 89% B = 70 79% C = 60 69% D = 50 59% E = 40 49% Note: assessments are linear. For example, the
AQA GCSE Biology New Unit 3 Summary Notes
 AQA GCSE Biology New Unit 3 Summary Notes Page 1 11/15/2016 Unit 3 Summary We need to understand how biological and environmental systems operate when they are working well in order to be able to intervene
AQA GCSE Biology New Unit 3 Summary Notes Page 1 11/15/2016 Unit 3 Summary We need to understand how biological and environmental systems operate when they are working well in order to be able to intervene
Movement of substances
 1 How does oxygen move in and out of cells? 2 Name the enzyme produced in salivary glands. 3 How are cells found in salivary glands adapted to produce amylase? Diffusion Amylase Many ribosomes which produce
1 How does oxygen move in and out of cells? 2 Name the enzyme produced in salivary glands. 3 How are cells found in salivary glands adapted to produce amylase? Diffusion Amylase Many ribosomes which produce
alveoli high low blood concentration gradient diffusion low Thin high capillaries short membrane energy villi microvilli water dilute
 Unit 3: Movement in/out of cells Diffusion: the movement of particles from a high concentration to a low concentration, down a concentration gradient. Active transport: The movement of particles from a
Unit 3: Movement in/out of cells Diffusion: the movement of particles from a high concentration to a low concentration, down a concentration gradient. Active transport: The movement of particles from a
3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances
 3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances Substances are sometimes absorbed against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy from respiration. The process is called active transport.
3.5 Unit 3: Biology 3 B3.1.1 Dissolved Substances Substances are sometimes absorbed against a concentration gradient. This requires the use of energy from respiration. The process is called active transport.
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals
 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Transport Systems in Plants and Animals Bronze Level Mark Scheme Time
Exchange of materials
 Exchange of materials 1 During marathon races, athletes are advised to drink sports drinks. Choose the correct words from the list below to complete the sentences. alcohol fat ions protein starch sugar
Exchange of materials 1 During marathon races, athletes are advised to drink sports drinks. Choose the correct words from the list below to complete the sentences. alcohol fat ions protein starch sugar
B3 Essential Questions - Answers
 B3 Essential Questions - Answers M. any four from molecules / ions do not credit mineral salts move(d) through / across the cell wall / membrane against (a / the) concentration gradient by a series of
B3 Essential Questions - Answers M. any four from molecules / ions do not credit mineral salts move(d) through / across the cell wall / membrane against (a / the) concentration gradient by a series of
B3 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you)
 Name: B3 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you) Follow all the steps below... 1) Practice all the maths and working scientifically questions PRACTICE ALL THESE QUESTIONS! Maths and Science Skills
Name: B3 Revision Pack (Please keep this pack with you) Follow all the steps below... 1) Practice all the maths and working scientifically questions PRACTICE ALL THESE QUESTIONS! Maths and Science Skills
biologymaster Transporting materials AQA Biology B3 revision card: The heart
 Transporting materials AQA Biology B3 revision card: The heart The human body has two transport systems called double circulation. One carries blood from the heart to the lungs and back, the other carries
Transporting materials AQA Biology B3 revision card: The heart The human body has two transport systems called double circulation. One carries blood from the heart to the lungs and back, the other carries
1. understand that the internal skeleton of vertebrates is needed for support and movement
 B7.1 Peak performance movement and exercise 1. understand that the internal skeleton of vertebrates is needed for support and movement 2. understand that muscles can only move bones at a joint by contraction,
B7.1 Peak performance movement and exercise 1. understand that the internal skeleton of vertebrates is needed for support and movement 2. understand that muscles can only move bones at a joint by contraction,
Organisation. AQA Biology topic 2
 Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
Organisation AQA Biology topic 2 2.1 Principles of Organisation Cells, tissues, organs and systems Basically, all living things are made up of cells A group of CELLS makes up a TISSUE A group of TISSUES
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food.
 The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
The diagram below shows the parts of the body that digest and absorb food. It also shows some details about the structure of the stomach. (a) Complete the table to show whether each structure is an organ,
BL3FP. (Jun14BL3FP01) General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June Unit Biology B3 TOTAL. Time allowed 1 hour
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Biology Unit Biology B3 Tuesday 13 May 2014 For this paper you must have: a ruler.
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Biology Unit Biology B3 Tuesday 13 May 2014 For this paper you must have: a ruler.
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT
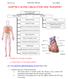 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING PLANTS Function of heart Wilting Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Transpiration: function
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
TRANSPORTATION IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS Circulatory system: organ system for the circulation of materials inside the body Materials transported in the body: Water, Oxygen, Carbon dioxide, Nutrients, Hormones
perfect practice makes perfect
 CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
CHAPTER 2: BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT HUMAN BEING BLOOD CIRCULATION AND TRANSPORT PLANTS Function of heart Structure of heart Blood vessels: characteristics and functions Wilting Transpiration: function
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Excretion (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Structure of the Kidney Excretion is the removal from organisms of toxic materials, the waste products of metabolism and substances in excess of requirements
Contact us:
 Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
Class X Chapter 6 Life Processes Science Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess
The function of the kidney
 Homeostasis Carbon dioxide must be removed because when it dissolves it makes an acidic solution which can affect enzymes working Carbon dioxide is removed by diffusing into the blood stream and being
Homeostasis Carbon dioxide must be removed because when it dissolves it makes an acidic solution which can affect enzymes working Carbon dioxide is removed by diffusing into the blood stream and being
(a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein.
 The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
The circulatory system contains arteries and veins. (a) (i) Describe how the structure of an artery is different from the structure of a vein. (2) A comparison is made between blood taken from an artery
Multicellular Organisms. Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals
 Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Multicellular Organisms Sub-Topic 2.6 Transport Systems in Animals On completion of this sub-topic I will be able to state that: In mammals a transport system is required to deliver essential substances
Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like
 Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
Page 95»Question» Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multi-cellular organisms like humans? Multicellular organisms such as humans possess complex body designs.
GCSE Biology. BL3HP Mark scheme June Version 1.0: Final Mark Scheme
 GCSE Biology BL3HP Mark scheme 440 June 206 Version.0: Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
GCSE Biology BL3HP Mark scheme 440 June 206 Version.0: Final Mark Scheme Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
UR Revision Guide. igcse Biology. Page 1
 UR Revision Guide igcse Biology 1 Photosynthesis Summary Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil.
UR Revision Guide igcse Biology 1 Photosynthesis Summary Green plants and algae use light energy to make their own food. They obtain the raw materials they need to make this food from the air and the soil.
M1. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine 1
 M. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted
M. (a) (concentration high) in the hepatic portal vein is blood with glucose absorbed from the intestine concentration is lower in the hepatic vein because insulin (has caused) glucose to be converted
Website: Page 1. Page 113»Exercise» Question 1:
 Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Page 113»Exercise» Question 1: The kidneys in human beings are a part of the system for (a) nutrition. (b) respiration. (c) excretion. (d) transportation. (c) In human beings, the kidneys are a part of
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans
 Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
Ch 9 Transport of substances in humans Think about (Ch 9, p.2) 1. Blood transports various substances and distributes heat around the body. It also plays a role in body defence. 2. Blood is a liquid tissue
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1
 AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1 176 minutes 176 marks Page 1 of 48 ## (a) The table shows the compounds and ions dissolved in a student s urine. Compound or ion Percentage of total urea 60 negative ions 25
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 1 176 minutes 176 marks Page 1 of 48 ## (a) The table shows the compounds and ions dissolved in a student s urine. Compound or ion Percentage of total urea 60 negative ions 25
LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS
 1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
1 LIFE PROCESSES TRANSPORT OF MATERIALS IN ANIMALS AND PLANTS I. Multiple choice questions: Tick ( ) the correct choice. 1. Human heart has (a) one auricle and one ventricle (b) two auricles and one ventricle
Movement of Substances in and out of cells
 Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Movement of Substances in and out of Cells Mark Scheme Level Subject Exam Board Unit Topic Difficulty Level Booklet GCSE Biology AQA B3 Movement of Substances in and out of cells Bronze Level Mark Scheme
Conditions inside the body must be kept constant. Urea must be removed from the body. Name the organ which makes urea.
 Conditions inside the body must be kept constant. (a) Urea must be removed from the body. (i) Name the organ which makes urea. () Which organ removes urea from the body? () (iii) What is urea made from?
Conditions inside the body must be kept constant. (a) Urea must be removed from the body. (i) Name the organ which makes urea. () Which organ removes urea from the body? () (iii) What is urea made from?
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 3
 AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 3 340 minutes 340 marks Page 1 of 49 Q1. To stay healthy, the amount of sodium in your body must not change very much. On average, a girl takes in 10 grams of sodium a day in
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 3 340 minutes 340 marks Page 1 of 49 Q1. To stay healthy, the amount of sodium in your body must not change very much. On average, a girl takes in 10 grams of sodium a day in
Life Processes. dronstudy.com
 Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
Human Circulatory System Life Processes Circulatory system is responsible for transportation of various substances in human beings. It is composed of heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. Blood
4.2.1 Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system
 GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
GCSE Biology (8461). For exams 2018 onwards. Version 1.0 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system
4.2 Organisation Principles of organisation Animal tissues, organs and organ systems The human digestive system.
 4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
4.2 Organisation In this section we will learn about the human digestive system which provides the body with nutrients and the respiratory system that provides it with oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
Y10 POS Combined BIOLOGY 3Y
 08-9 Y0 POS Combined BIOLOGY Y Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 7... Contraception Evaluate hormonal and non- hormonal contraception...6 Fertility hormones FSH & LH IVF Issues surrounding IVF...
08-9 Y0 POS Combined BIOLOGY Y Date Syllabus Ref Content Less Practical 7... Contraception Evaluate hormonal and non- hormonal contraception...6 Fertility hormones FSH & LH IVF Issues surrounding IVF...
PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark)
 1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
1 PART A: MULTIPLE CHOICE (100 questions 65% of exam mark) I: Wellness and Homeostasis 1. Determine the false statement about homeostasis. A) Homeostasis refers to the body s attempt to adjust to a fluctuating
The human digestive system
 Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
Cells A tissue Organs Organ systems Principles of organisation The basic building blocks of all living organisms. A group of cells with similar structure and function. Groups of tissues performing specific
KS4 Physical Education
 KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
KS4 Physical Education The Circulatory System These icons indicate that teacher s notes or useful web addresses are available in the Notes Page. This icon indicates that the slide contains activities created
Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology
 Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
Page1 Transportation and Excretion 7 th Biology William Harvey was an English physician was the first to give the details of blood circulation, the properties of blood and the pumping of blood by the heart.
NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes
 1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
1 NCERT SOLUTIONS OF Life Processes Question 1: Why is diffusion insufficient to meet the oxygen requirements of multicellular organisms like humans? Answer: The body structure of multicellular organism
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis
 CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
CIE Biology A-level Topic 14: Homeostasis Notes Communication is essential for the survival of organism as all living organisms must be able to detect and respond to changes in both their internal and
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System
 Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Unit 23.1: The Circulatory System This color-enhanced image was made with an electron microscope, so the objects it depicts are extremely small. Do you know what they are? This incredible photo shows red
Further Additional Science
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Further Additional Science Unit 1 Biology B3 Tuesday 12 May 2015 For this paper
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Further Additional Science Unit 1 Biology B3 Tuesday 12 May 2015 For this paper
International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
 www.xtremepapers.com International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice OTOER/NOVEMER SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials:
www.xtremepapers.com International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice OTOER/NOVEMER SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials:
Pre- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate assessment for each student
 Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
 Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Caledonia Science the system that circulates blood and lymph through the body, consisting of the heart, blood vessels, The is the muscle that moves the blood throughout the highway system of vessles. The
Chapter 1 : Respiration C D
 Name :. hapter 1 : Respiration Form :. ate :. 1. group of students built a model of the human respiratory system to investigate the mechanism of breathing in and breathing out. (2004) Which of the following
Name :. hapter 1 : Respiration Form :. ate :. 1. group of students built a model of the human respiratory system to investigate the mechanism of breathing in and breathing out. (2004) Which of the following
What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body.
 Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Excretion What is excretion? Excretion is the removal of metabolic waste from the body. Excretion in Plants Plants produce very little waste products. Plants lose oxygen and water vapour through the stomata.
Stem cells. Stem cells can be found in embryos, in adult animals and in the meristems in plants.
 Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Stem cells A stem cell is an undifferentiated cell of an organism which can produce more cells of the same type. Certain other cells can arise from stem cells when they differentiate. Stem cells can be
Page 2. Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer.
 Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
Q1.Substances can move into and out of cells. (a) (i) How does oxygen move into and out of cells? Draw a ring around one answer. diffusion digestion photosynthesis (ii) Diagram 1 shows the percentage concentration
National Know that stem cells in animals are cells which can divide.
 National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
National 5 Biology Multicellular Organisms Unit Success Criteria Success Criteria Multicellular Organisms National 5 Colour the box at the side of each objective: RED I don t know much about this or am
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system
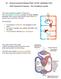 07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
07 Human transport Biology Notes IGCSE Cambridge 2014 #69 Transport in humans - the circulatory system The main transport system of human is the circulatory system, a system of tubes (blood vessels) with
Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
 The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
The diagram below shows the human digestive system. (a) (b) Label the stomach and pancreas on the diagram. Many people suffer from stomach ulcers caused by a species of bacteria called Helicobacter pylori.
Angel International School - Manipay
 c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
c Grade 10 Angel International School - Manipay 1 st Term Examination November 2016 Biology Duration: 3Hours Index No:- Choose the correct answer and underline it. (1) When a red stain is added to a culture
HSC Biology. Year 2016 Mark Pages 46 Published Jan 18, Biology Notes. By James (99.05 ATAR)
 HSC Biology Year 2016 Mark 93.00 Pages 46 Published Jan 18, 2017 Biology Notes By James (99.05 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, James. James achieved an ATAR of 99.05 in 2016 while
HSC Biology Year 2016 Mark 93.00 Pages 46 Published Jan 18, 2017 Biology Notes By James (99.05 ATAR) Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) Your notes author, James. James achieved an ATAR of 99.05 in 2016 while
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 2
 AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 2 89 minutes 88 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. Information is passed to target organs in the body by hormones. (a) (i) How do hormones travel around the body?... (ii) What name is given
AQA B3.3 Homeostasis LEVEL 2 89 minutes 88 marks Page 1 of 25 Q1. Information is passed to target organs in the body by hormones. (a) (i) How do hormones travel around the body?... (ii) What name is given
Glossary. Maintain keep up. Constant the same. Internal inside the body. Environment surroundings of the body.
 Homeostasis Glossary Maintain keep up. Constant the same. Internal inside the body. Environment surroundings of the body. What is Homeostasis? Body cells work best if they have the correct Temperature
Homeostasis Glossary Maintain keep up. Constant the same. Internal inside the body. Environment surroundings of the body. What is Homeostasis? Body cells work best if they have the correct Temperature
Book Second Term Test Model Answers. Page 84 to 87
 1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
1. Write the scientific term: a. Red blood cells b. Aorta c. Ball bearings d. Air resistance e. silt soil f. sand soil 2. Write a brief account: Book Second Term Test Model Answers Page 84 to 87 a. friction:
Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems
 Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
Table of Contents Chapter: Interactions of Human Systems Section 1: The Human Organism Section 2: How Your Body Works The Human Organism Organization in the Human Body Although your body is not made of
Life Functions Common to Living Things
 Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
Science 14 Unit C: From Life to Lifestyle Chapter 9 Life Functions Common to Living Things pp. 178-195 WORKBOOK Name: 9.1 Common Life Functions pp. 180-183 Read pp. 180-181 All things that are considered
UNIT 1: WELLNESS AND HOMEOSTASIS
 UNIT 1: WELLNESS AND HOMEOSTASIS WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN HEALTH AND WELLNESS? 5 FACTORS OF WELL-BEING PHYSICAL EMOTIONAL SPIRITUAL INTELLECTUAL SOCIAL WHAT IS BIOLOGY? BIOLOGY IS THE STUDY OF
UNIT 1: WELLNESS AND HOMEOSTASIS WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN HEALTH AND WELLNESS? 5 FACTORS OF WELL-BEING PHYSICAL EMOTIONAL SPIRITUAL INTELLECTUAL SOCIAL WHAT IS BIOLOGY? BIOLOGY IS THE STUDY OF
CIE Biology GCSE. 9: Transport in animals. Notes.
 CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
CIE Biology GCSE 9: Transport in animals Notes The circulatory system acts as the main transport system in animals. It is made up of blood vessels such as arteries, veins and capillaries, in which blood
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY. 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS Cambridge Ordinary Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2015 series 5090 BIOLOGY 5090/21 Paper 2 (Theory), maximum raw mark 80 This mark scheme is published as
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 4 3 2 5 2 H Signature Paper Reference(s) 4325/2H London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 2H Higher Tier Thursday 15 May 2008 Afternoon Time:
Centre No. Paper Reference Surname Initial(s) Candidate No. 4 3 2 5 2 H Signature Paper Reference(s) 4325/2H London Examinations IGCSE Biology Paper 2H Higher Tier Thursday 15 May 2008 Afternoon Time:
Unit 4: Summary. Similarities and Differences Between Living Things
 Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
Unit 4: Summary Similarities and Differences Between Living Things Review cell theory All living things made of cells Cells perform life functions Cells come from pre existing cells What are life functions?
International General Certificate of Secondary Education CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS
 International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice MY/JUNE SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials: Multiple hoice answer sheet
International General ertificate of Secondary Education MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS IOLOGY 0610/1 PPER 1 Multiple hoice MY/JUNE SESSION 2002 45 minutes dditional materials: Multiple hoice answer sheet
Biology Notes. Homeostasis
 Biology Notes Homeostasis Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of constant internal conditions within organisms. The principle can be developed in a wide range of contexts, including the maintenance
Biology Notes Homeostasis Homeostasis is defined as the maintenance of constant internal conditions within organisms. The principle can be developed in a wide range of contexts, including the maintenance
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System
 Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
Unit 4 Circulatory, Respiratory and Excretory System Test Date Project Due Lesson 1 The Cardiovascular System Homework: read pages 176-179 and take notes Warm up 1. 2. 3. 4. Finding Target Heart rate (220
By Helen and Mark Warner
 By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
By Helen and Mark Warner www.teachingpacks.co.uk Teaching Packs - The Human Body - Page 1 Image ThinkStock In this section, you will learn about... 1. The major systems and organs in the human body. 2.
Chapter 10 EXCRETION
 Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
Chapter 10 EXCRETION Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance Control of Body Temperature and Water Balance as a part of homeostasis Homeostasis means Maintenance of steady internal conditions despite
3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human
 3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human Objectives What you will need to know from this section Explain the role of the excretory system in homeostasis -- the ability and necessity to maintain constancy
3.4.6 The Excretory System in the Human Objectives What you will need to know from this section Explain the role of the excretory system in homeostasis -- the ability and necessity to maintain constancy
Circulation, blood and heart
 Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
Circulation, blood and heart Name: Class: Date: Time: 35 minutes Marks: 35 marks Comments: Level,2 and 3. Increasing demand Q. (a) List A gives four structures in the human body. List B gives the functions
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Circulatory System Science Matters Chapter 8 Introduction Living things need a transport system to carry things around the body. In humans its called The Circulatory system. The parts of the system
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Blood flows away from the heart in arteries, to the capillaries and back to the heart in the veins
 Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
Cardiovascular System Summary Notes The cardiovascular system includes: The heart, a muscular pump The blood, a fluid connective tissue The blood vessels, arteries, veins and capillaries Blood flows away
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose. carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin
 1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
1 Which substances are dissolved in human blood plasma? carbon dioxide, haemoglobin and glucose carbon dioxide, oxygen and haemoglobin glucose, hormones and urea oxygen, urea and starch 2 Which chamber
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system.
 Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
Learning Objectives; 1. Identify the key features of the cardiovascular system. 2. Describe the function of the cardiovascular system. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yaxna8lmoiy The Circulatory System
The Function. To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body.
 The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
The Function To carry nutrients and oxygen to and remove waste from the cells of the body. What makes up the circulatory system? 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood vessels Blood travels from the heart to the body
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2012 45 minutes *8205284412* dditional Materials:
UNIVERSITY OF MRIGE INTERNTIONL EXMINTIONS International General ertificate of Secondary Education IOLOGY 0610/13 Paper 1 Multiple hoice October/November 2012 45 minutes *8205284412* dditional Materials:
Chapter 6---Life Processes
 Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Chapter 6---Life Processes 1. In Photosynthetic process, atmospheric carbon di oxide is to carbohydrates a) oxidised b) Reduced c) Neutralised d) Burnt 2. When water enters the guard cells the stomata
Revision Question Bank
 Revision Question Bank Life Processes 1. Name the passage in sequence through which urine passes from kidney to the outside in human. How is urine prevented from flowing back into the ureter? The passage
Revision Question Bank Life Processes 1. Name the passage in sequence through which urine passes from kidney to the outside in human. How is urine prevented from flowing back into the ureter? The passage
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY
 TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
TOPIC 6: HUMAN HEALTH AND PHYSIOLOGY 6.2 Transport System/Circulatory Draw and label a diagram of the heart showing the four chambers, associated blood vessels, valves and the route of blood through the
Page 2. Q1.Humans control their internal environment in many ways. Look at the diagram below. (a) Name organ A. ... (1) Organ A stores glucose.
 Q1.Humans control their internal environment in many ways. Look at the diagram below. (a) Name organ A.... (b) Organ A stores glucose. People with Type 1 diabetes cannot effectively control the levels
Q1.Humans control their internal environment in many ways. Look at the diagram below. (a) Name organ A.... (b) Organ A stores glucose. People with Type 1 diabetes cannot effectively control the levels
2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles:
 1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
1. Label these diagrams of cells: 2. Complete this table to give the function of the following organelles: Organelle Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chloroplast Mitochondria Vacuole 3. State 2 differences between
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus )
 Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
Transport in Animals (IGCSE Biology Syllabus 2016-2018) Blood o Red blood cells: heamoglobin and oxygen transport o White blood cells: phagocyte phagocytosis (engulf pathogen, vesicles fuse with vacuole,
The circulatory system
 The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
The circulatory system Key words Vessels heart blood plasma platelets haemoglobin To engulf arteries capillaries veins venules lymphocytes Atrium / - a ventricle tricuspid bicuspid cardiac coronary Humans
(a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. B... (2)
 1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
1 The diagrams show an animal cell and a bacterial cell. (a) (i) Structures A and B are found in both the animal cell and the bacterial cell. Use words from the box to name structures A and B. cell membrane
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium.
 CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
CONTEXT POINT 2: Plants and animals transport dissolved nutrients and gases in a fluid medium. Identify the form(s) in which each of the following is carried in mammalian blood: Carbon dioxide 70% as hydrogen
The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules.
 The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D, represents: (i)
The diagram shows four ways in which molecules may move into and out of a cell. The dots show the concentration of molecules. The cell is respiring aerobically. Which arrow, A, B, C or D, represents: (i)
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? The heart and blood vessels (arteries, veins & capillaries).
 Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
Q1: What is the word equation for aerobic respiration? Q2: What is the circulatory system composed of? Q3: How is glucose transported in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water The heart and blood
1. is used to decrease the effect of friction force between the internal moving parts of machines.
 1) Complete the following sentences : 1. is used to decrease the effect of friction force between the internal moving parts of machines. 2. Friction force has its effect in the direction of the objects
1) Complete the following sentences : 1. is used to decrease the effect of friction force between the internal moving parts of machines. 2. Friction force has its effect in the direction of the objects
