THE PROLAMIN STORAGE PROTEINS OF SORGHUM AND MILLETS
|
|
|
- Coral Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE PROLAMIN STORAGE PROTEINS OF SORGHUM AND MILLETS P R Shewry 1 and N G. Halford 2 1 Long Ashton Research Station, Long Ashton, Bristol BS41 9AF, UK, peter.shewry@bbsrc.ac.uk 2 Rothamsted Research, Harpenden, Herts AL5 2JQ, UK Most millets are classified with maize, sorghum and Coix (Job's tears) in the grass sub-family Panicoideae, but two species, tef and ragi (finger millet) are placed in a separate sub-family, the Chloridoideae. In all species the major storage proteins are alcohol-soluble prolamins, but their properties vary. For example, although the kafirins of sorghum are closely related to the zeins of maize, they differ in their solubility properties, being more efficiently extracted with 60% (v/v) tertiary butanol, a less polar solvent than propan-2-ol. Maize prolamins are classified into four groups, termed alpha-, beta-, gamma- and delta-zeins. Of these, the alpha-zeins are the major fraction but have low nutritional quality, with low contents of cysteine and methionine and no lysine or tryptophan. In contrast, the beta-zeins and delta-zeins contain about 11 mol% and over 20 mol% methionine, respectively. Alpha-type prolamins appear to be the major components in sorghum, Coix and all millet species which have been analysed in detail (pearl millet, foxtail millet, kodo millet, tef, ragi), with the exception of fonio (Digitaria exilis). Sorghum and Coix also contain homologues of the beta-and gamma-zeins of maize and sorghum homologues of delta-zein. Less well-characterized methionine-rich components have also been reported in foxtail millet and fonio, forming the major prolamin group in the latter species. INTRODUCTION The name millet is applied to a number of small seeded cereals, most of which are native to the tropics or sub-tropics. Most of these are classified with maize, sorghum and Coix (Job's tears) in the grass sub-family Panicoideae, but two species are placed in a separate sub-family, the Chloridoideae. These are ragi (Indian finger millet, Eleusine coracana) and tef (Eragrostis tef). Maize is one of the three most important crops in the world, the others being rice and wheat. Hence it has been the subject of a massive volume of research which provides a framework for more restricted studies of millets and sorghum. Prolamins The grain storage proteins of maize, millets and sorghum can be defined as prolamins in that they are soluble in alcohol/water mixtures. Although 60-70% (v/v) ethanol was initially used for extraction, it is now more usual to use 50% (v/v) propan-1-ol.
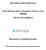
2 However, 60% (v/v) tertiary butanol (2-methyl-2-propanol) is a more efficient solvent for the prolamins (kafirins) of sorghum, which may indicate that they have a more hydrophobic nature. Furthermore, in all species some prolamins are only efficiently extracted if the solvent also contains a reducing agent, either dithiothreitol or 2-mercaptoethanol. This is because they form polymers stabilized by inter-chain disulphide bonds, with the reduced subunits but not the polymers being alcohol-soluble. Also, the alcoholsoluble fractions may contain disulphide-stabilized dimers and oligomers. Prolamins account for about half of the total grain proteins in all these species, the precise amounts being determined by the availability of nutrients (N and S). Prolamin groups SDS-PAGE of the prolamins (zeins) of maize shows a number of bands with apparent molecular masses ranging from about 27,000 to 10,000 (Figure 1). Detailed studies of purified proteins and cloned cdnas and genes have allowed these to be classified into four groups of proteins, called alpha-, beta-, gamma- and delta-zeins. These are discussed in detail below. Similar analyses of prolamin fractions from sorghum, Coix and millets show components with similar mobilities (Figure 1), which suggests that related proteins are present. Alpha-prolamins The alpha-zeins are the major components in maize, accounting for about 70% of the total prolamins. SDS-PAGE shows two broad bands of mass about 19,000 (Z19) and 22,000 (Z22) but isoelectric focusing shows that each of these comprises a number of components. In fact, up to 40 components can be resolved by 2-D electrophoresis 1 with 70 to 100 alpha-zein genes being present 2,3. Determination of amino acid sequences demonstrates that the true masses range from 23,000-24,000 for Z19 zeins and 26,500-27,000 for Z22 zeins 4. Alpha-zeins contain 0 or 1 cysteine residues and so are present as monomers or alcohol-soluble dimers. Their amino acid sequences contain peptide repeat motifs of about 20 residues, which are poorly conserved but tend to be rich in leucine, alanine and glutamine residues. Nine repeats are present in the Z19 and ten in the Z22 zeins 5. Alpha-type prolamins also form the major prolamin components in Coix and sorghum, and these appear to be more closely related in sequence to the Z22 than to the Z19 zeins 6,7. It has been proposed that the repeat units present in these proteins form alpha-helices which are arranged in antiparallel fashion to give a compact circular or hexagonal structure 5,8 but direct evidence for this structure is lacking. The low proportions of lysine and tryptophan in alpha-type prolamins contribute to the poor nutritional quality of the whole grain.
3 N-terminal amino acid sequences indicate that the major prolamins in pearl millet (pennisetin), tef and ragi are also alpha-type 9,10 but detailed information is not available on these components. Figure 1. SDS-PAGE of prolamin fractions from a pearl millet; b, maize; c, sorghum; d, Coix; e, tef; f, finger millet. α, β, γ and δ refer to the groups of zeins in track b. Taken from ref 23 Beta-, gamma- and delta-prolamins The minor prolamins of maize and related cereals all belong to a major family of plant proteins called the "prolamin superfamily". This includes the prolamins of the temperate cereals (wheat, barley, rye, oats) and a number of small sulphur-rich proteins, many of which are restricted to seeds. They include 2S storage albumins of dicotyledonous plants, non-specific lipid transfer proteins, and puroindolines, grain softness proteins and alpha-amylase/trypsin inhibitors of cereal seeds. The structural and evolutionary relationships of these proteins have been discussed in detail by Shewry et al. 11. The beta-, gamma- and delta-prolamins all form polymers stabilized
4 by inter-chain disulphide bonds and are predominantly, if not completely, insoluble in aqueous alcohols unless a reducing agent is included. The beta-zeins of maize have molecular masses of about 15,000 by SDS-PAGE with true masses of about 17,500. They comprise about 160 amino acids with 18 residues of methionine and 7 residues of cysteine 12. Shull et al. 13 proposed that M r 16,000, 18,000 and 20,000 kafirin bands corresponded to beta-kafirins, although only the M r 20,000 band reacted with an antiserum to beta-zein. This conclusion was supported by amino acid analysis of a fraction containing the M r 16,000 and 20,000 bands which showed 6 mol% methionine and 5 mol% cysteine. It is rather surprising that cloned cdnas or genes for beta-kafirin have not yet been reported, but a cloned cdna for beta-coixin from Coix lachryma-jobi showed high similarity to beta-zein 14. Gamma-zeins are the second most abundant group of proteins in maize, with two bands of M r about 27,000 (true mass about 22,000) and 16,000. They differ from all other zeins in being soluble in water as reduced subunits. Both sorghum and Coix contain prolamin bands of M r about 27,000-28,000 which react with gamma-zein antiserum and cloned cdnas and genes from both species encode proteins with high homology to gamma-zeins (Figure 2) All of the proteins have clear domain structures, with an N-terminal domain comprising repeats of the hexapeptide motif Pro.Pro.Pro.Val.His.Leu. Eight almost perfectly conserved repeats are present in the M r 27,000 gamma-zein, four in gamma-kafirin, two in gamma-coixin but only two incomplete copies in the M r 16,000 gamma-zein. The high histidine content may account for the solubility of the reduced subunits in water. All gamma-prolamins also contain ten conserved cysteine residues and are rich in proline, glutamine and nonpolar amino acids. The delta-zeins of maize comprise two minor components of M r about 10,000 and 18,000 with true masses of about 14,400 and 21, Both are methionine-rich, with the M r 18,000 component (26.9 mol% Met) having apparently been derived from the M r 10,000 protein (22.8 mol% Met) by duplication of part of the methionine-rich central region. A DNA-derived sequence for a delta-kafirin of sorghum shows high homology with the M r 10,000 delta-zein, except for the absence of part of the methionine-rich region (Figure 3). Consequently the methionine content is lower than that of the delta-zeins, with 18 residues out of a total of 114 (15.8 mol%). The minor prolamins of maize are encoded by small gene families, with one beta-zein gene, two or three gamma-zein genes and two delta-zein genes 21. Minor prolamins in millets It is likely that millets also contain prolamins related to the beta-, gamma- and deltaprolamins of maize and sorghum, but the only component which has been conclusively identified is from fonio (Digitaria exilis). The whole grain of fonio contains about 4.8 wt% methionine and this derives from the presence of two methionine-rich proteins which account for about 35% of the total prolamin fraction 20. These components have M r of about 19,000 (6.4 mol% Met, 6.4 mol% Cys) and
5 17,500 (7.8 mol% Met, 5.3 mol% Cys) and the former shows N-terminal amino acid sequence homology with the M r 10,000 delta-zein of maize. Naren and Vivupaksha 21 also prepared two methionine-rich prolamins from Italian or foxtail millet (Setaria italica), which had masses by SDS-PAGE of about 7,900 and 9,100. These proteins, called alpha- and beta-setarins, could also be related to the beta- or delta-zeins but the same authors showed that antibody to alpha-setarin did not react with prolamins from maize or sorghum 22. γ-zein THTSGGCGCQPPPPVHLPPPVHLPPPVHLPPPVHLPPPVHLPPPVHLPPP γ-kafirin TLTTGGCGCQTP...HLP...PPPVHLPPPVHLPPPVHLPPP γ-zein VHVPPPVHLPPPPCHYPTQPPRPQPHPQPHPCPCQQPHPSPCQ..LQGTC γ-kafirin VHVPP...PPPQCH...PHPTLPPHPHPCATYPPHPSPCHPGHPGSC γ-zein GVG...STPILGQCVEFLRHQCSPTATPYCSPQCQSLRQQCCQQLRQVE γ-kafirin GVGGGPVTPPILGQCIEFLRHQCSPAATPYCSPQCQALRQQCCQQLRQVE γ-zein PQHRYQAIFGLVLQSILQQQP..QSGQVAGLLAAQIAQQLTAMCGL..QQ γ-kafirin PLHRYQAIFGVVLQSIQQQQPQGQSSPLPALMAAQIAQQLTAMCGLGVGQ γ-zein PTPCPYAA..AGGVPH 204 γ-kafirin PSPCASCSPFAGGVHY Figure 2. Alignment of the amino acid sequences of the M r 27,000 gamma-zein of maize and gamma-kafirin of sorghum. The boxes indicate repeats of the conserved motif Pro.Pro.Pro.Val.His.Leu
6 δ-kafirin ATHIPGHL.PLVMPLGTMNPCTQYCMMQQRFARLLAWPIPMLQQLSLQPA 10 kd δ-zein ATHIPGHL.PPVMPLGTMNPCMQYCMMQQGLASLMACPSLMLQQLLALPL 18 kd δ-zein ATHIPGHLSPLLMPLATMNPWMQYCMKQQGVANLLAWPTLMLQQLLASPL δ-kafirin Y..QTPMTMPNMMP kd δ-zein Q..TMPVMMPQMMT kd δ-zein QPCQMPMMMPGMMPPMTMMPMPNMMPSMMVPTMMSPITIASMMPPMMMPN δ-kafirin...p..mt..mmpsmms...l...p 10 kd δ-zein...pnmmsplmmpsmmspmvlpsmmsqmmm...p 18 kd δ-zein MVSPMMMPSMMPSTMTPSMMPPIMMPSMIPPMMMPSMVSSMIMPNMMTVP δ-kafirin QCHCDAISQIMQQQQLPFMFNPTAMAIPPMFLQQPFVSSAF kd δ-zein QCHCDAVSQIMLQQQLPFMFNPMAMTIPPMFLQQPFVGAAF kd δ-zein QCYSDSISHIIQQQQLPFMFSPTAVAISPMFLQQPFVGAAF 191 Figure 3. Alignment of the amino acid sequences of M r 18,000 and M r 10,000 delta-zeins of maize and delta-kafirin of sorghum. Lines indicate residues in the delta-kafirin and M r 18,000 delta-zein that are identical to those in the M r 10,000 delta-zein. Methionine residues are shown in black boxes.
7 CONCLUSIONS Although sorghum and millets appear to contain similar prolamin storage proteins to maize the amount of available information on these species is limited. Further detailed studies are clearly required, particularly of the minor millets. Of particular interest is the presence in most, if not all, of methionine-rich prolamins related to the beta- and delta-zeins of maize. The selection of genotypes containing high proportions of these proteins or the manipulation of their amounts by genetic engineering could lead to improved nutritional quality. REFERENCES 1. Wall, J.S., Fey, D.A. and Paulis, J.W. Improved two-dimensional electrophoretic separation of zein proteins: Application to study of zein inheritance in corn genotypes. Cereal Chemistry 33 (1984) Hagen, G. and Rubenstein, I. Complex organization of zein genes in maize. Gene 13 (1981) Wilson, D.R. and Larkins, B.A. Zein gene organization in maize and related grasses. Journal of Molecular Evolution 29 (1984) Coleman, C.E. and Larkins, B.A. Prolamins of maize. In 'Seed proteins', (P.R. Shewry and R. Casey, eds), Kluwer Academic Publishers, The Netherlands (1999) pp Garrat, R., Oliva, G., Caracelli, I., Leite, A. and Arruda, P. Studies of the zeinlike alpha-prolamins based on an analysis of amino acid sequences: implications for their evolution and three-dimensional structure. Proteins: Structure, Function and Genetics 15 (1993) Ottiboni, L.M.M., Leite, A., Yunes, J.A., Targon, M.L.P.N., Souza Filho, G.A. and Arruda, P. Sequence analysis of 22 kda-like alpha-coixin genes and their comparison with homologous zein and kafirin genes reveals highly conserved protein structure and regulatory elements. Plant Molecular Biology 21 (1993) DeRose, R., Ma, D-P., Kwon, I-S., Hasnain, S.E., Klassy, R.C. and Hall, T. Characterization of the kafirin gene family from sorghum reveals extensive homology with zein from maize. Plant Molecular Biology 12 (1989) Argos, P., Pedersen, K., Marks, M.S. and Larkins, B.A. A structural model for maize zein proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry 257 (1982) Bietz, J.A. Cereal prolamin evolution and homology revealed by sequence analysis. Biochemical Genetics 20 (1982) Tatham, A.S., Fido, R.J., Moore, C.M., Kasarda, D.D., Kuzmicky, D.D., Keen, J.N. and Shewry, P.R. Characterisation of the major prolamin of Tef (Eragrostis tef) and finger millet (Eleusine coracana). Journal of Cereal Science 24 (1996)
8 11. Shewry, P.R., Jenkins, J., Beaudoin, F. and Mills, E.N.C. The classification, functions and evolutionary relationships of plant proteins in relation to food allergens. In 'Plant Food Protein Allergens' (E.N.C. Mills and P.R. Shewry, eds) Blackwell Science Ltd. (2003) In press. 12. Pedersen, K., Argos, P., Naravana, S.V.L. and Larkins, B.A. Sequence analysis and characterization of a maize gene encoding a high-sulfur zein protein of M r 15,000. Journal of Biological Chemistry 261 (1986) Shull, J.M., Watterson, J.J. and Kirleis, A.W. Proposed nomenclature for the alcohol-soluble proteins (kafirins) of Sorghum bicolor (L. Moench) based on molecular weight, solubility and structure. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 39 (1991) Leite, A., Yunes, J.A., Turcinelli, S.R. and Arruda, P. Cloning and characterization of a cdna encoding a sulfur-rich coixin. Plant Molecular Biology 18 (1992) Leite, A., Ottoboni, L.M.M., Targon, M.L.P.N., Silva, M.J., Turcinelli, S.R. and Arruda, P. Phylogenetic relationship of zeins and coixins as determined by immunological cross-reactivity and Southern blot analysis. Plant Molecular Biology 14 (1990) Shull, J.M., Watterson, J.J. and Kirleis, A.W. Purification and immunocytochemical localization of kafirins in Sorghum bicolor (L. Moench) endosperm. Protoplasma 171 (1992) Watterson, J.J., Shull, J.M., Mohamed, A.A. and Kirleis, A.W. Isolation of a high-cysteine kafirin protein and its cross-reactivity with gamma-zein antiserum. Journal of Cereal Science 12 (1990) Barros, E.G., Takasaki, K., Kirleis, A.W. and Larkins, B.A. Nucleotide sequence of a cdna clone encoding gamma-kafirin protein from Sorghum biocolor. Plant Physiology 97 (1991) Leite, A., Freitas, F.A., Yunes, J.A. and Arruda, P. Nucleotide sequence of a cdna clone encoding gamma-coixin from Coix lacryma-jobi seeds. Plant Physiology 97 (1991) de Lumen, B.B., Thompson, S. and Odegard, W.J. Sulfur amino acid-rich proteins in aca (Digitaria exilis), a promising underutilized African cereal. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 41 (1993) Naren, A.P. and Virupaksha, T.K. Alpha- and beta-setarins: methionine-rich proteins of Italian millet (Setaria italica (L.) Beauv.). Cereal Chemistry 67 (1990a)
9 22. Naren, A.P. and Virupaksha, T.K. Effect of sulfur deficiency on the synthesis of alpha-setarin, a methionine-rich protein of Italian millet. Cereal Chemistry 67 (1990b) Shewry, P.R. The seed storage proteins of pseudocereals and minor cereals. In 'Pseudocereals and Less Well-known Cereals' (P. Belton and J. Taylor, eds) Springer-Verlag. (2002) pp
WHAT MAKES AMAZEIN TM DIFFERENT?
 ` Amazein TM is the trade name of a highly functional protein produced from raw whole corn (maize) by Prairie Gold Inc. The protein is zein (commonly pronounced zayne to rhyme with rain or cane), which
` Amazein TM is the trade name of a highly functional protein produced from raw whole corn (maize) by Prairie Gold Inc. The protein is zein (commonly pronounced zayne to rhyme with rain or cane), which
Functionality of Protein
 Protein Polymers of aa:20 different aa Primary structure aa sequence Secondary structure- chains take up conformations which may crosslink to form helices ie α helix and β pleated sheet Tertiary structure-
Protein Polymers of aa:20 different aa Primary structure aa sequence Secondary structure- chains take up conformations which may crosslink to form helices ie α helix and β pleated sheet Tertiary structure-
Comparison Properties of Adlay (Coix lachryma-jobi L.) Flour and Starch. Mayoongan Dechkunchon and Masubon Thongngam
 P-STARCH-2 Comparison Properties of Adlay (Coix lachryma-jobi L.) Flour and Starch Mayoongan Dechkunchon and Masubon Thongngam Department of Food Science and Technology, Faculty of Agro-industry, Kasetsart
P-STARCH-2 Comparison Properties of Adlay (Coix lachryma-jobi L.) Flour and Starch Mayoongan Dechkunchon and Masubon Thongngam Department of Food Science and Technology, Faculty of Agro-industry, Kasetsart
The source of protein structures is the Protein Data Bank. The unit of classification of structure in SCOP is the protein domain.
 UNIT 14 PROTEINS DEFINITION A large molecule composed of one or more chains of amino acids in a specific order; the order is determined by the base sequence of nucleotides in the gene that codes for the
UNIT 14 PROTEINS DEFINITION A large molecule composed of one or more chains of amino acids in a specific order; the order is determined by the base sequence of nucleotides in the gene that codes for the
Cereals and grains. Grain anatomy (APK) Simplified milling scheme for wheat 5/23/2012
 Cereals and grains Grain anatomy (APK) Bran -- contains much of the fiber and minerals of the grain Germ -- the part of the grain that would become the new plant if the seed were planted. High in protein
Cereals and grains Grain anatomy (APK) Bran -- contains much of the fiber and minerals of the grain Germ -- the part of the grain that would become the new plant if the seed were planted. High in protein
Nature s Neutraceuticals - Millets. * of corresponding author:
 Nature s Neutraceuticals - Millets M. Dhananivetha 1* and R. Gowthami 2 1 Ph. D Scholar, Department of Agronomy, AC and RI, Madurai 625 104 2 Ph. D Scholar, Department of Plant Breeding & Genetics, AC
Nature s Neutraceuticals - Millets M. Dhananivetha 1* and R. Gowthami 2 1 Ph. D Scholar, Department of Agronomy, AC and RI, Madurai 625 104 2 Ph. D Scholar, Department of Plant Breeding & Genetics, AC
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins
 Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Macromolecules of Life -3 Amino Acids & Proteins Shu-Ping Lin, Ph.D. Institute of Biomedical Engineering E-mail: splin@dragon.nchu.edu.tw Website: http://web.nchu.edu.tw/pweb/users/splin/ Amino Acids Proteins
Proteins. Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff. /3 rd class of pharmacy. PhD. Clinical Biochemistry
 Proteins /3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry a Greek word that means of first importance. It is a very important class of food molecules that provide organisms not
Proteins /3 rd class of pharmacy Dr. Basima Sadiq Jaff PhD. Clinical Biochemistry a Greek word that means of first importance. It is a very important class of food molecules that provide organisms not
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of
 Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Objective: You will be able to explain how the subcomponents of nucleic acids determine the properties of that polymer. Do Now: Read the first two paragraphs from enduring understanding 4.A Essential knowledge:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A
 Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Biological systems interact, and these systems and their interactions possess complex properties. STOP at enduring understanding 4A Homework Watch the Bozeman video called, Biological Molecules Objective:
Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals
 Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals Preben Bach Holm University of Aarhus Faculty of Agricultural Sciences Department of Genetics and Biotechnology
Amino acid composition and mineral bioavailability: Important feed quality traits in cereals Preben Bach Holm University of Aarhus Faculty of Agricultural Sciences Department of Genetics and Biotechnology
Gentilucci, Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins. Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds CH 3
 Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
Amino Acids Peptides and proteins are polymers of amino acids linked together by amide bonds Aliphatic Side-Chain Amino Acids - - H CH glycine alanine 3 proline valine CH CH 3 - leucine - isoleucine CH
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology:
 The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA Transcription RNA Translation Proteins DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is the genetic material It is an informational super polymer -think of it as the
The Basics: A general review of molecular biology: DNA Transcription RNA Translation Proteins DNA (deoxy-ribonucleic acid) is the genetic material It is an informational super polymer -think of it as the
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL
 Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
Multiple-Choice Questions Answer ALL 20 multiple-choice questions on the Scantron Card in PENCIL For Questions 1-10 choose ONE INCORRECT answer. 1. Which ONE of the following statements concerning the
I) Choose the best answer: 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine.
 1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
1- All of the following amino acids are neutral except: a) glycine. b) threonine. c) lysine. d) proline. e) leucine. 2- The egg white protein, ovalbumin, is denatured in a hard-boiled egg. Which of the
1.4. Lipids - Advanced
 1.4. Lipids - Advanced www.ck12.org In humans, triglycerides are a mechanism for storing unused calories, and their high concentration in blood correlates with the consumption of excess starches and other
1.4. Lipids - Advanced www.ck12.org In humans, triglycerides are a mechanism for storing unused calories, and their high concentration in blood correlates with the consumption of excess starches and other
Chemistry 121 Winter 17
 Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Chemistry 121 Winter 17 Introduction to Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry Instructor Dr. Upali Siriwardane (Ph.D. Ohio State) E-mail: upali@latech.edu Office: 311 Carson Taylor Hall ; Phone: 318-257-4941;
Proteins. Bởi: OpenStaxCollege
 Proteins Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living systems and have the most diverse range of functions of all macromolecules. Proteins may be structural, regulatory,
Proteins Bởi: OpenStaxCollege Proteins are one of the most abundant organic molecules in living systems and have the most diverse range of functions of all macromolecules. Proteins may be structural, regulatory,
Biochemistry - I. Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I
 Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Biochemistry - I Prof. S. Dasgupta Department of Chemistry Indian Institute of Technology, Kharagpur Lecture 1 Amino Acids I Hello, welcome to the course Biochemistry 1 conducted by me Dr. S Dasgupta,
Proteins and their structure
 Proteins and their structure Proteins are the most abundant biological macromolecules, occurring in all cells and all parts of cells. Proteins also occur in great variety; thousands of different kinds,
Proteins and their structure Proteins are the most abundant biological macromolecules, occurring in all cells and all parts of cells. Proteins also occur in great variety; thousands of different kinds,
Biology: Life on Earth Chapter 3 Molecules of life
 Biology: Life on Earth Chapter 3 Molecules of life Chapter 3 Outline 3.1 Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? p. 38 3.2 How Are Organic Molecules Synthesized? p. 38 3.3 What Are Carbohydrates?
Biology: Life on Earth Chapter 3 Molecules of life Chapter 3 Outline 3.1 Why Is Carbon So Important in Biological Molecules? p. 38 3.2 How Are Organic Molecules Synthesized? p. 38 3.3 What Are Carbohydrates?
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 14
 BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 14 General topics for week 7 Session 14 Amino acids and proteins Students review the concepts learnt and answer the selected questions from the textbook. General
BIOB111 - Tutorial activity for Session 14 General topics for week 7 Session 14 Amino acids and proteins Students review the concepts learnt and answer the selected questions from the textbook. General
Ionization of amino acids
 Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
Amino Acids 20 common amino acids there are others found naturally but much less frequently Common structure for amino acid COOH, -NH 2, H and R functional groups all attached to the a carbon Ionization
a) The statement is true for X = 400, but false for X = 300; b) The statement is true for X = 300, but false for X = 200;
 1. Consider the following statement. To produce one molecule of each possible kind of polypeptide chain, X amino acids in length, would require more atoms than exist in the universe. Given the size of
1. Consider the following statement. To produce one molecule of each possible kind of polypeptide chain, X amino acids in length, would require more atoms than exist in the universe. Given the size of
RESEARCH OPINIONS IN ANIMAL & VETERINARY SCIENCES
 www.roavs.com EISSN: 2223-0343 RESEARCH OPINIONS IN ANIMAL & VETERINARY SCIENCES Seed proteins maneuver to improve cereals grain quality: A review Omid Pourzargham Faradonbeh 1, Reza Soleimani 2 and Hossein
www.roavs.com EISSN: 2223-0343 RESEARCH OPINIONS IN ANIMAL & VETERINARY SCIENCES Seed proteins maneuver to improve cereals grain quality: A review Omid Pourzargham Faradonbeh 1, Reza Soleimani 2 and Hossein
Lesson 5 Proteins Levels of Protein Structure
 Lesson 5 Proteins Levels of Protein Structure Primary 1º Structure The primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Chains of amino acids are written from the amino terminus (N-terminus)
Lesson 5 Proteins Levels of Protein Structure Primary 1º Structure The primary structure is simply the sequence of amino acids in a protein. Chains of amino acids are written from the amino terminus (N-terminus)
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5
 Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
Key Concepts: The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules Part 4: Proteins Chapter 5 Proteins include a diversity of structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins Enzymatic s
CS612 - Algorithms in Bioinformatics
 Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Spring 2016 Protein Structure February 7, 2016 Introduction to Protein Structure A protein is a linear chain of organic molecular building blocks called amino acids. Introduction to Protein Structure Amine
Most life processes are a series of chemical reactions influenced by environmental and genetic factors.
 Biochemistry II Most life processes are a series of chemical reactions influenced by environmental and genetic factors. Metabolism the sum of all biochemical processes 2 Metabolic Processes Anabolism-
Biochemistry II Most life processes are a series of chemical reactions influenced by environmental and genetic factors. Metabolism the sum of all biochemical processes 2 Metabolic Processes Anabolism-
SUMMARY OF DISCUSSIONS ARISING FROM PAPERS. AFRIPRO: DAY 1 (2 April 2003)
 SUMMARY OF S ARISING FROM PAPERS AFRIPRO: DAY 1 (2 April 2003) Overall Objectives of Workshop (PS Belton) Clear view of needs and opportunities in research towards improvement of quality of sorghum and
SUMMARY OF S ARISING FROM PAPERS AFRIPRO: DAY 1 (2 April 2003) Overall Objectives of Workshop (PS Belton) Clear view of needs and opportunities in research towards improvement of quality of sorghum and
The Building blocks of life. Macromolecules
 The Building blocks of life Macromolecules 1 copyright cmassengale 2 Organic Compounds Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. Macromolecules are large organic molecules. 3 LIFE ON EARTH IS CARBON-BASED
The Building blocks of life Macromolecules 1 copyright cmassengale 2 Organic Compounds Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. Macromolecules are large organic molecules. 3 LIFE ON EARTH IS CARBON-BASED
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges
 Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
Fundamentals of Organic Chemistry CHEM 109 For Students of Health Colleges Credit hrs.: (2+1) King Saud University College of Science, Chemistry Department CHEM 109 CHAPTER 9. AMINO ACIDS, PEPTIDES AND
Biomolecules: amino acids
 Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Biomolecules: amino acids Amino acids Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins They are also part of hormones, neurotransmitters and metabolic intermediates There are 20 different amino acids in
Extraction of kafirin and zein and their film properties
 Extraction of kafirin and zein and their film properties by Peter Jackson Muhiwa Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree Master of Science (MSc): Food Science In the Department
Extraction of kafirin and zein and their film properties by Peter Jackson Muhiwa Submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree Master of Science (MSc): Food Science In the Department
Methionine (Met or M)
 Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Fig. 5-17 Nonpolar Fig. 5-17a Nonpolar Glycine (Gly or G) Alanine (Ala or A) Valine (Val or V) Leucine (Leu or L) Isoleucine (Ile or I) Methionine (Met or M) Phenylalanine (Phe or F) Polar Trypotphan (Trp
Lecture 4. Grouping Amino Acid 7/1/10. Proteins. Amino Acids. Where Are Proteins Located. Nonpolar Amino Acids
 Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
Proteins Lecture 4 Proteins - Composition of Proteins (Amino Acids) Chapter 21 ection 1-6! Proteins are compounds of high molar mass consisting almost entirely of amino acid chain(s)! Molar masses range
The Structure and Func.on of Macromolecules Proteins GRU1L6
 The Structure and Func.on of Macromolecules Proteins GRU1L6 Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group Function: involved in almost everything enzymes (pepsin, DNA polymerase) structure
The Structure and Func.on of Macromolecules Proteins GRU1L6 Proteins Proteins Most structurally & functionally diverse group Function: involved in almost everything enzymes (pepsin, DNA polymerase) structure
Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids.
 Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Today we begin our discussion of the structure and properties of proteins. Proteins consist in whole or large part of amino acids. Simple proteins consist only of amino acids. Conjugated proteins contain
Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions. Proteins
 Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions Proteins Proteins Naturally occurring bioorganic polyamide polymers containing a sequence of various combinations of 20 amino acids. Amino acids contain the elements carbon,
Chapter 20 and GHW#10 Questions Proteins Proteins Naturally occurring bioorganic polyamide polymers containing a sequence of various combinations of 20 amino acids. Amino acids contain the elements carbon,
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules
 The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
The Structure and Function of Macromolecules Macromolecules are polymers Polymer long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks. Monomer the small building block molecules. Carbohydrates, proteins
NUTRITIONAL COMPOSITION AND HEALTH BENEFITS OF MILLETS
 NUTRITIONAL COMPOSITION AND HEALTH BENEFITS OF MILLETS Dr. S. Shobana SCIENTIST DEPARTMENT OF FOODS NUTRITION & DIETITICS RESEARCH MADRAS DIABETES RESEARCH FOUNDATION Millets Millet crops are minor cereals
NUTRITIONAL COMPOSITION AND HEALTH BENEFITS OF MILLETS Dr. S. Shobana SCIENTIST DEPARTMENT OF FOODS NUTRITION & DIETITICS RESEARCH MADRAS DIABETES RESEARCH FOUNDATION Millets Millet crops are minor cereals
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES
 3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
3. AMINO ACID AND PEPTIDES 3.1 Amino Acids and Peptides General structure - Only 20 amino-acids are found in proteins - Amino group and carboxyl group - α-carbon and side chain group 3.1 Amino Acids and
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London)
 BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
BIRKBECK COLLEGE (University of London) SCHOOL OF BIOLOGICAL SCIENCES M.Sc. EXAMINATION FOR INTERNAL STUDENTS ON: Postgraduate Certificate in Principles of Protein Structure MSc Structural Molecular Biology
The energy value of cereal grains, particularly wheat and sorghum, for poultry
 Proceedings of the Australian Poultry Science Symposium, (005), 17, 1-9. The energy value of cereal grains, particularly wheat and sorghum, for poultry J.L. Black 1, R.J. Hughes, S.G. Nielsen 3, A.M. Tredrea
Proceedings of the Australian Poultry Science Symposium, (005), 17, 1-9. The energy value of cereal grains, particularly wheat and sorghum, for poultry J.L. Black 1, R.J. Hughes, S.G. Nielsen 3, A.M. Tredrea
PHAR3316 Pharmacy biochemistry Exam #2 Fall 2010 KEY
 1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
1. How many protons is(are) lost when the amino acid Asparagine is titrated from its fully protonated state to a fully deprotonated state? A. 0 B. 1 * C. 2 D. 3 E. none Correct Answer: C (this question
Copyright 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings
 Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Concept 5.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 50% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage,
Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit
 Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit The primary sequence of a protein, composed of amino acids, determines the organization of the sequence into the secondary structure. There are two
Activities for the α-helix / β-sheet Construction Kit The primary sequence of a protein, composed of amino acids, determines the organization of the sequence into the secondary structure. There are two
So where were we? But what does the order mean? OK, so what's a protein? 4/1/11
 So where were we? We know that DNA is responsible for heredity Chromosomes are long pieces of DNA DNA turned out to be the transforming principle We know that DNA is shaped like a long double helix, with
So where were we? We know that DNA is responsible for heredity Chromosomes are long pieces of DNA DNA turned out to be the transforming principle We know that DNA is shaped like a long double helix, with
Amino acids. (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi
 Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Amino acids (Foundation Block) Dr. Essa Sabi Learning outcomes What are the amino acids? General structure. Classification of amino acids. Optical properties. Amino acid configuration. Non-standard amino
Proteases in germinating finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds
 Biosci., Vol. 5, Number 3, September 1983, pp. 219 224. Printed in India. Proteases in germinating finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds Introduction U. VIDYAVATHI, B. SHIVARAJ and T. N. PATTABIRAMAN
Biosci., Vol. 5, Number 3, September 1983, pp. 219 224. Printed in India. Proteases in germinating finger millet (Eleusine coracana) seeds Introduction U. VIDYAVATHI, B. SHIVARAJ and T. N. PATTABIRAMAN
1. Structure, classification, functions, properties of proteins
 1. Structure, classification, functions, properties of proteins Proteins are the major components of living organisms and perform a wide range of essential functions in cells. Proteins regulate metabolic
1. Structure, classification, functions, properties of proteins Proteins are the major components of living organisms and perform a wide range of essential functions in cells. Proteins regulate metabolic
1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids
 Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Amino acids 1-To know what is protein 2-To identify Types of protein 3- To Know amino acids 4- To be differentiate between essential and nonessential amino acids 5-To understand amino acids synthesis Amino
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD
 Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Protein conformation Many conformations are possible for proteins due to flexibility of amino acids linked by peptide
Nafith Abu Tarboush DDS, MSc, PhD natarboush@ju.edu.jo www.facebook.com/natarboush Protein conformation Many conformations are possible for proteins due to flexibility of amino acids linked by peptide
Amino Acids. Review I: Protein Structure. Amino Acids: Structures. Amino Acids (contd.) Rajan Munshi
 Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
Review I: Protein Structure Rajan Munshi BBSI @ Pitt 2005 Department of Computational Biology University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine May 24, 2005 Amino Acids Building blocks of proteins 20 amino acids
MBB 694:407, 115:511. Please use BLOCK CAPITAL letters like this --- A, B, C, D, E. Not lowercase!
 MBB 694:407, 115:511 First Test Severinov/Deis Tue. Sep. 30, 2003 Name Index number (not SSN) Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions
MBB 694:407, 115:511 First Test Severinov/Deis Tue. Sep. 30, 2003 Name Index number (not SSN) Row Letter Seat Number This exam consists of two parts. Part I is multiple choice. Each of these 25 questions
OPTION GROUP: BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 3 PROTEINS WORKBOOK. Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 3 PROTEINS WORKBOOK Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 1 Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 2 Instructions REVISION CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Regular
NAME: OPTION GROUP: BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 3 PROTEINS WORKBOOK Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 1 Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 2 Instructions REVISION CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Regular
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall Instructor: Professor Gopal. Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, Name: (print)
 Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
Moorpark College Chemistry 11 Fall 2013 Instructor: Professor Gopal Examination # 5: Section Five May 7, 2013 Name: (print) Directions: Make sure your examination contains TEN total pages (including this
AP Bio. Protiens Chapter 5 1
 Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
Concept.4: Proteins have many structures, resulting in a wide range of functions Proteins account for more than 0% of the dry mass of most cells Protein functions include structural support, storage, transport,
2.1 Development of high-lysine maize and sorghum
 1 INTRODUCTION Sorghum is a major subsistence cereal crop grown in Africa and Asia, due to its hardiness and drought-resistance, enabling its cultivation in semi-dry regions (FAO 1995, reviewed by Belton
1 INTRODUCTION Sorghum is a major subsistence cereal crop grown in Africa and Asia, due to its hardiness and drought-resistance, enabling its cultivation in semi-dry regions (FAO 1995, reviewed by Belton
Properties of amino acids in proteins
 Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Properties of amino acids in proteins one of the primary roles of DNA (but far from the only one!!!) is to code for proteins A typical bacterium builds thousands types of proteins, all from ~20 amino acids
Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics
 Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics Learning Objectives At the end of this assignment, you should be able to: 1. Draw the chemical structure of an amino acid and small peptide. 2. Describe the difference
Section 1 Proteins and Proteomics Learning Objectives At the end of this assignment, you should be able to: 1. Draw the chemical structure of an amino acid and small peptide. 2. Describe the difference
9/6/2011. Amino Acids. C α. Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups
 Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Amino Acids Side chains (R groups) vary in: size shape charge hydrogen-bonding capacity hydrophobic character chemical reactivity C α Nonpolar, aliphatic R groups Glycine (Gly, G) Alanine (Ala, A) Valine
Organic Compounds. Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. Macromolecules are large organic molecules.
 Macromolecules Organic Compounds Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. Macromolecules are large organic molecules. Carbon (C) Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent
Macromolecules Organic Compounds Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. Macromolecules are large organic molecules. Carbon (C) Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay
 Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Introduction to Proteomics Dr. Sanjeeva Srivastava Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering Indian Institute of Technology - Bombay Lecture 01 Introduction to Amino Acids Welcome to the proteomic course.
Macromolecules. copyright cmassengale
 Macromolecules 1 Organic Compounds Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. Macromolecules are large organic molecules. 2 Carbon (C) Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent
Macromolecules 1 Organic Compounds Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. Macromolecules are large organic molecules. 2 Carbon (C) Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent
Proteins are sometimes only produced in one cell type or cell compartment (brain has 15,000 expressed proteins, gut has 2,000).
 Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Lecture 2: Principles of Protein Structure: Amino Acids Why study proteins? Proteins underpin every aspect of biological activity and therefore are targets for drug design and medicinal therapy, and in
Macromolecules Structure and Function
 Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Macromolecules Structure and Function Within cells, small organic molecules (monomers) are joined together to form larger molecules (polymers). Macromolecules are large molecules composed of thousands
Maha AbuAjamieh. Tamara Wahbeh. Mamoon Ahram
 12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
12 Maha AbuAjamieh Tamara Wahbeh Mamoon Ahram - - Go to this sheet s last page for definitions of the words with an asterisk above them (*) - You should memorise the 3-letter abbreviations, of all the
Supplementary Figure 1 Preparation, crystallization and structure determination of EpEX. (a), Purified EpEX and EpEX analyzed on homogenous 12.
 Supplementary Figure 1 Preparation, crystallization and structure determination of EpEX. (a), Purified EpEX and EpEX analyzed on homogenous 12.5 % SDS-PAGE gel under reducing and non-reducing conditions.
Supplementary Figure 1 Preparation, crystallization and structure determination of EpEX. (a), Purified EpEX and EpEX analyzed on homogenous 12.5 % SDS-PAGE gel under reducing and non-reducing conditions.
Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22
 Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22 Importance of Proteins Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in
Amino Acids and Proteins Hamad Ali Yaseen, PhD MLS Department, FAHS, HSC, KU Hamad.ali@hsc.edu.kw Biochemistry 210 Chapter 22 Importance of Proteins Main catalysts in biochemistry: enzymes (involved in
THE UNIVERSITY OF MANITOBA. DATE: Oct. 22, 2002 Midterm EXAMINATION. PAPER NO.: PAGE NO.: 1of 6 DEPARTMENT & COURSE NO.: 2.277/60.
 PAPER NO.: PAGE NO.: 1of 6 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS You must mark the answer sheet with pencil (not pen). Put your name and enter your student number on the answer sheet. The examination consists of multiple
PAPER NO.: PAGE NO.: 1of 6 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS You must mark the answer sheet with pencil (not pen). Put your name and enter your student number on the answer sheet. The examination consists of multiple
االمتحان النهائي لعام 1122
 االمتحان النهائي لعام 1122 Amino Acids : 1- which of the following amino acid is unlikely to be found in an alpha-helix due to its cyclic structure : -phenylalanine -tryptophan -proline -lysine 2- : assuming
االمتحان النهائي لعام 1122 Amino Acids : 1- which of the following amino acid is unlikely to be found in an alpha-helix due to its cyclic structure : -phenylalanine -tryptophan -proline -lysine 2- : assuming
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Biochemistry Lec #1 Dr. Nafith AbuTarboush- (30.6.2014) Amino Acids 1 Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 3 (pp.66-76) Introduction: Biochemistry is two courses; one is
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Biochemistry Lec #1 Dr. Nafith AbuTarboush- (30.6.2014) Amino Acids 1 Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapter 3 (pp.66-76) Introduction: Biochemistry is two courses; one is
Molecular Biology. general transfer: occurs normally in cells. special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions.
 Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Chapter 9: Proteins Molecular Biology replication general transfer: occurs normally in cells transcription special transfer: occurs only in the laboratory in specific conditions translation unknown transfer:
Amino acids. Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester,
 Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Amino acids Dr. Mamoun Ahram Summer semester, 2017-2018 Resources This lecture Campbell and Farrell s Biochemistry, Chapters 3 (pp.66-76) General structure (Chiral carbon) The amino acids that occur in
Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry
 Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
Biochemistry Department Date: 17/9/ 2017 Biomolecules Amino Acids & Protein Chemistry Prof.Dr./ FAYDA Elazazy Professor of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology Intended Learning Outcomes ILOs By the end
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Q1: the overall folding of a single protein subunit is called : -tertiary structure -primary structure -secondary structure -quaternary structure -all of the above Q2 : disulfide
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Q1: the overall folding of a single protein subunit is called : -tertiary structure -primary structure -secondary structure -quaternary structure -all of the above Q2 : disulfide
SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES
 1 SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES Proteins are important in food processing and food product development, as they are
1 SYNOPSIS STUDIES ON THE PREPARATION AND CHARACTERISATION OF PROTEIN HYDROLYSATES FROM GROUNDNUT AND SOYBEAN ISOLATES Proteins are important in food processing and food product development, as they are
Human Biochemistry Option B
 Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Human Biochemistry Option B A look ahead... Your body has many functions to perform every day: Structural support, genetic information, communication, energy supply, metabolism Right now, thousands of
Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes
 1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
1 2 Identification of free amino acids in several crude extracts of two legumes using Thin Layer Chromatography 3 Authors 4 5 6 7 8 9 Taghread Hudaib Key words 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Amino acids;
OPTION GROUP: BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 3 PROTEINS WORKBOOK. Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist
 NAME: OPTION GROUP: BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 3 PROTEINS WORKBOOK Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 1 Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 2 Instructions REVISION CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Regular
NAME: OPTION GROUP: BIOLOGICAL MOLECULES 3 PROTEINS WORKBOOK Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 1 Tyrone R.L. John, Chartered Biologist 2 Instructions REVISION CHECKLIST AND ASSESSMENT OBJECTIVES Regular
BIO 311C Spring Lecture 15 Friday 26 Feb. 1
 BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 15 Friday 26 Feb. 1 Illustration of a Polypeptide amino acids peptide bonds Review Polypeptide (chain) See textbook, Fig 5.21, p. 82 for a more clear illustration Folding and
BIO 311C Spring 2010 Lecture 15 Friday 26 Feb. 1 Illustration of a Polypeptide amino acids peptide bonds Review Polypeptide (chain) See textbook, Fig 5.21, p. 82 for a more clear illustration Folding and
PROTEINS. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins. Acid L-form * * Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 O = N -C -C-O.
 Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Proteins: Linear polymers of amino acids workhorses of the cell tools, machines & scaffolds Lecture 6 Macromolecules #2 PRTEINS 1 Enzymes catalysts that mediate reactions, increase reaction rate Structural
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids. Table of a-amino Acids Found in Proteins
 Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
Chemical Nature of the Amino Acids All peptides and polypeptides are polymers of alpha-amino acids. There are 20 a- amino acids that are relevant to the make-up of mammalian proteins (see below). Several
PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF DEGERMED FLOURS OF RICE (Oryza sativa), MILLET (Eleusine coracana) AND WHEAT Triticun aestivum)
 PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF DEGERMED FLOURS OF RICE (Oryza sativa), MILLET (Eleusine coracana) AND WHEAT Triticun aestivum) * 1 Oladebeye, A.A., 2 Amoo, I.A. and 3 Oladebeye, A.O. 1. Department of Food
PHYSICOCHEMICAL PROPERTIES OF DEGERMED FLOURS OF RICE (Oryza sativa), MILLET (Eleusine coracana) AND WHEAT Triticun aestivum) * 1 Oladebeye, A.A., 2 Amoo, I.A. and 3 Oladebeye, A.O. 1. Department of Food
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules
 Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Lipids: diverse group of hydrophobic molecules Lipids only macromolecules that do not form polymers li3le or no affinity for water hydrophobic consist mostly of hydrocarbons nonpolar covalent bonds fats
Structure and Function of Macromolecules Chapter 5 Macromolecules Macromolecules Multiple Units Synthesis of Dimers and Polymers
 Structure and Function of Macromolecules Chapter 5 Macromolecules Giant molecules weighing over 100,000 daltons Emergent properties not found in component parts Macromolecules Multiple Units meris = one
Structure and Function of Macromolecules Chapter 5 Macromolecules Giant molecules weighing over 100,000 daltons Emergent properties not found in component parts Macromolecules Multiple Units meris = one
Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS
 Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS The word "Protein" was coined by J.J. Berzelius in 1838 and was derived from the Greek word "Proteios" meaning the first rank. Proteins are macromolecular polymers composed
Lecture 11 AMINO ACIDS AND PROTEINS The word "Protein" was coined by J.J. Berzelius in 1838 and was derived from the Greek word "Proteios" meaning the first rank. Proteins are macromolecular polymers composed
Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene
 Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene YUELIN ZHANG, WEIHUA FAN, MARK KINKEMA, XIN LI, AND
Interaction of NPR1 with basic leucine zipper protein transcription factors that bind sequences required for salicylic acid induction of the PR-1 gene YUELIN ZHANG, WEIHUA FAN, MARK KINKEMA, XIN LI, AND
The building blocks of life.
 The building blocks of life. The 4 Major Organic Biomolecules The large molecules (biomolecules OR polymers) are formed when smaller building blocks (monomers) bond covalently. via anabolism Small molecules
The building blocks of life. The 4 Major Organic Biomolecules The large molecules (biomolecules OR polymers) are formed when smaller building blocks (monomers) bond covalently. via anabolism Small molecules
From Atoms to Cells: Fundamental Building Blocks. Models of atoms. A chemical connection
 From Atoms to Cells: A chemical connection Fundamental Building Blocks Matter - all materials that occupy space & have mass Matter is composed of atoms Atom simplest form of matter not divisible into simpler
From Atoms to Cells: A chemical connection Fundamental Building Blocks Matter - all materials that occupy space & have mass Matter is composed of atoms Atom simplest form of matter not divisible into simpler
Organic Compounds. Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. Macromolecules are large organic molecules.
 Macromolecules 1 Organic Compounds Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. Macromolecules are large organic molecules. 2 Carbon (C) Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent
Macromolecules 1 Organic Compounds Compounds that contain CARBON are called organic. Macromolecules are large organic molecules. 2 Carbon (C) Carbon has 4 electrons in outer shell. Carbon can form covalent
Introduction to proteins and nucleic acids. Basic biochemcial structure of these molecules. Important functions of these biomolecules in living cells
 Food Biotechnology (BIT-313) Lecture 3 Introduction to proteins and nucleic acids Basic biochemcial structure of these molecules Important functions of these biomolecules in living cells Industrial significance
Food Biotechnology (BIT-313) Lecture 3 Introduction to proteins and nucleic acids Basic biochemcial structure of these molecules Important functions of these biomolecules in living cells Industrial significance
Different types of proteins. The structure and properties of amino acids. Formation of peptide bonds.
 Introduction to proteins and amino acids Different types of proteins. The structure and properties of amino acids. Formation of peptide bonds. Introduction We tend to think of protein as a mass noun: a
Introduction to proteins and amino acids Different types of proteins. The structure and properties of amino acids. Formation of peptide bonds. Introduction We tend to think of protein as a mass noun: a
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011
 Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
Chapter 5: Structure and Function of Macromolecules AP Biology 2011 1 Macromolecules Fig. 5.1 Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Polymer - large molecule consisting of many similar building blocks
DECISION DOCUMENTAL. Food and feed safety assessment of maize event MIR604 OECD: SYN-IR6Ø4-5. Directorate of Agrifood Quality
 DECISION DOCUMENTAL Food and feed safety assessment of maize event MIR604 OECD: SYN-IR6Ø4-5 Directorate of Agrifood Quality Office of Biotechnology and Industrialized Agrifood Products INDEX SUMMARY AND
DECISION DOCUMENTAL Food and feed safety assessment of maize event MIR604 OECD: SYN-IR6Ø4-5 Directorate of Agrifood Quality Office of Biotechnology and Industrialized Agrifood Products INDEX SUMMARY AND
Chapter 3. Protein Structure and Function
 Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Chapter 3 Protein Structure and Function Broad functional classes So Proteins have structure and function... Fine! -Why do we care to know more???? Understanding functional architechture gives us POWER
Chemical Composition of the Cell. B. Balen
 Chemical Composition of the Cell B. Balen Table 2-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 1. Water the most abundant substance in the cell! Where did it come from? several hypothesis: -
Chemical Composition of the Cell B. Balen Table 2-2 Molecular Biology of the Cell ( Garland Science 2008) 1. Water the most abundant substance in the cell! Where did it come from? several hypothesis: -
Proteins * OpenStax. 1 Types and Functions of Proteins
 OpenStax-CNX module: m44402 1 Proteins * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
OpenStax-CNX module: m44402 1 Proteins * OpenStax This work is produced by OpenStax-CNX and licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution License 3.0 By the end of this section, you will be able to:
Macromolecules (Learning Objectives)
 Macromolecules (Learning Objectives) Recognize the role of water in synthesis and breakdown of polymers Name &recognize the monomer and the chemical bond that holds the polymeric structure of all biomolecules
Macromolecules (Learning Objectives) Recognize the role of water in synthesis and breakdown of polymers Name &recognize the monomer and the chemical bond that holds the polymeric structure of all biomolecules
