Investigating the effect of concentration of blackcurrant squash on osmosis in chipped potatoes
|
|
|
- Katherine Lisa Johnson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Investigating the effect of concentration of blackcurrant on osmosis in chipped potatoes The purpose of this investigation is:. to explore what happens to chipped potatoes in different concentrations of blackcurrant. to explain the outcomes in terms of osmosis. Procedure SAFETY: Do not drink the blackcurrant as it is not safe to drink anything in a laboratory. Take care when cutting the potato with the scalpel or the cork borer. Report any accidents to your teacher. PAGE 1
2 Concentration of blackcurrant (%) blackcurrant needed (cm 3 ) to make 10 (A) water needed (cm 3 ) to make 10 (B) blackcurrant needed to make 30 cm 3 of (= A x 3) water needed to make 30 (= B x 3) Final volume of made (cm 3 ) Preparation Label beakers/ boiling tubes with the concentrations of blackcurrant you will use. Measure out blackcurrant for the dilutions using the volumes shown in column 4 of the table. Measure out water using the volumes shown in column 5. (Columns 2 and 3 show the volumes needed to make 10, which is multiplied to get larger volumes in columns 4 and 5.) Collect some potato chips or a potato to cut up. Cut or trim your chips, if necessary to fit into your small beaker/ boiling tube. Cut off any potato skin. Investigation Dry the chips on a paper towel. Weigh the chips using a balance and record masses in an appropriately designed table. Place chips in a beaker/ boiling tube. The s should completely cover the chips. Leave for at least 15 minutes. Remove chips one at a time from the beakers/ boiling tubes. Dry the chips on paper towel. Reweigh chips and record results in the table. Calculate the change in mass and then the percentage change in mass of each set of potato chips. PAGE 2
3 Plot percentage change in mass (y axis) against concentration of blackcurrant (x axis). PAGE 3
4 QUESTIONS 1 Why is it a good idea to remove all the potato skin? 2 Why do we dry the chips on a paper towel before weighing them? 3 Does your graph show any anomalies or inconsistencies? 4 Explain in biological terms what is happening to the potato chips in the different blackcurrant s. 5 What do you think is the approximate concentration of the cell contents of the potatoes? 6 You could modify this investigation to find out how quickly osmosis happens. Write down a hypothesis you would be testing and a plan for how to do the experiment. Include the variables you would need to control to get reliable results. PAGE 4
5 ANSWERS 1 It is a good idea to remove all the potato skin in case the movement of through skin is at a different rate than through freshly cut tissue. 2 We dry the chips on a paper towel before weighing them so that we are sure that we are measuring change in mass of the potato chips. 3 The graph may show anomalies or inconsistencies explained by differences in individual procedures, or some other factors. 4 In dilute s, the potato chips are drawing water in by osmosis as their cell contents are more concentrated than the outside. In concentrated s, the potato chips lose water by osmosis as their cell contents are less concentrated than the outside. At one concentration the cell contents are in equilibrium with the outside and so there will be no change in the mass of the potato chips. 5 The approximate concentration of the cell contents of the potatoes is the same as the with no change in mass. 6 Depends on student answers. A good response will describe a reliable method with a number of variables controlled. PAGE 5
Q1.Cells, tissues and organs are adapted to take in different substances and get rid of different substances.
 OSMOSIS. Thnton College NAME.. Q.Cells, tissues and gans are adapted to take in different substances and get rid of different substances. The table shows the concentration of four ions outside cells and
OSMOSIS. Thnton College NAME.. Q.Cells, tissues and gans are adapted to take in different substances and get rid of different substances. The table shows the concentration of four ions outside cells and
Lab #2: Osmosis Pre-Lab Exercise
 Lab #2: Osmosis Pre-Lab Exercise Name 1. Using your own words, define the following terms: a. Osmosis b. Concentration gradient: c. Hypertonic solution: d. Isotonic solution: e. Hypotonic solution: 2.
Lab #2: Osmosis Pre-Lab Exercise Name 1. Using your own words, define the following terms: a. Osmosis b. Concentration gradient: c. Hypertonic solution: d. Isotonic solution: e. Hypotonic solution: 2.
Q1.Strawberries may be dehydrated by removing most of the water they contain. Dehydrated strawberries have many different uses in the food industry.
 St Joseph's College Q1.Strawberries may be dehydrated by removing most of the water they contain. Dehydrated strawberries have many different uses in the food industry. Food scientists investigated the
St Joseph's College Q1.Strawberries may be dehydrated by removing most of the water they contain. Dehydrated strawberries have many different uses in the food industry. Food scientists investigated the
Q1. (a) The diagrams show cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells.
 Q. (a) The diagrams show cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Into which cell, A, B, C or D, will oxygen move the fastest? Write your answer,
Q. (a) The diagrams show cells containing and surrounded by oxygen molecules. Oxygen can move into cells or out of cells. Into which cell, A, B, C or D, will oxygen move the fastest? Write your answer,
GCSE Biology Coursework Osmosis : - The Potato Experiment
 GCSE Biology Coursework Osmosis : - The Potato Experiment Background Information Osmosis can be defined as the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration
GCSE Biology Coursework Osmosis : - The Potato Experiment Background Information Osmosis can be defined as the movement of water across a semi-permeable membrane from a region of high water concentration
Catalase Lab - A Bio ENZYME ACTIVITY Investigation Created by Gen Nelson, modified by Dr G
 Catalase Lab - A Bio ENZYME ACTIVITY Investigation Created by Gen Nelson, modified by Dr G INTRODUCTION Hydrogen peroxide (H 2O 2) is a poisonous byproduct of metabolism that can damage cells if it is
Catalase Lab - A Bio ENZYME ACTIVITY Investigation Created by Gen Nelson, modified by Dr G INTRODUCTION Hydrogen peroxide (H 2O 2) is a poisonous byproduct of metabolism that can damage cells if it is
BIO 12 UNIT 04: The Cell Membrane BCLN Rev. July, 2015
 Project 1: Osmosis Lab Name: Potential Credits: /50 Project Goals: to gain and demonstrate a better understanding of osmosis Instructions Please read through the Unit 4 Lessons, paying particular attention
Project 1: Osmosis Lab Name: Potential Credits: /50 Project Goals: to gain and demonstrate a better understanding of osmosis Instructions Please read through the Unit 4 Lessons, paying particular attention
Investigating Osmosis Lab. Biology 12
 Investigating Osmosis Lab In this lab, students will investigate the properties of osmosis using potato slices. Biology 12 Curriculum Connections: BC Chemistry 12 (2006) B2 - describe the characteristics
Investigating Osmosis Lab In this lab, students will investigate the properties of osmosis using potato slices. Biology 12 Curriculum Connections: BC Chemistry 12 (2006) B2 - describe the characteristics
AP Biology Lab 1c Water Potential
 Page 1 of 9 AP Biology Lab 1c Water Potential In this part of the exercise you will use potato cores placed in different molar concentrations of sucrose in order to determine the water potential of potato
Page 1 of 9 AP Biology Lab 1c Water Potential In this part of the exercise you will use potato cores placed in different molar concentrations of sucrose in order to determine the water potential of potato
INVESTIGATION : Determining Osmolarity of Plant Tissue
 INVESTIGATION : Determining Osmolarity of Plant Tissue AP Biology This lab investigation has two main components. In the first component, you will learn about the osmolarity of plant tissues and the property
INVESTIGATION : Determining Osmolarity of Plant Tissue AP Biology This lab investigation has two main components. In the first component, you will learn about the osmolarity of plant tissues and the property
Name: Bio A.P. Lab Diffusion & Osmosis
 Name: Bio A.P. Lab Diffusion & Osmosis BACKGROUND: Many aspects of the life of a cell depend on the fact that atoms and molecules are constantly in motion (kinetic energy). This kinetic energy results
Name: Bio A.P. Lab Diffusion & Osmosis BACKGROUND: Many aspects of the life of a cell depend on the fact that atoms and molecules are constantly in motion (kinetic energy). This kinetic energy results
Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
 GCSE BIOLOGY Higher Tier Paper 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
GCSE BIOLOGY Higher Tier Paper 1H H Specimen 2018 Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a calculator. Instructions Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 1: OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION. READING: Please read pages & in your text prior to lab.
 BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 1: OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION READING: Please read pages 27-31 & 83-86 in your text prior to lab. INTRODUCTION: All living things depend on water. A water molecule is made up of an oxygen atom
BIOLOGY 1101 LAB 1: OSMOSIS & DIFFUSION READING: Please read pages 27-31 & 83-86 in your text prior to lab. INTRODUCTION: All living things depend on water. A water molecule is made up of an oxygen atom
Distilled Water Balance Ruler Plastic wrap
 The following lab taken from: http://www.utsouthwestern.edu/edumedia/edufiles/education_training/programs/stars/osmosis-demo-lab.pdf Background Osmosis is the process whereby water moves across a cell
The following lab taken from: http://www.utsouthwestern.edu/edumedia/edufiles/education_training/programs/stars/osmosis-demo-lab.pdf Background Osmosis is the process whereby water moves across a cell
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level
 Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/3 PAPER 3 Practical Test Candidates
Centre Number Candidate Number Candidate Name CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Advanced Subsidiary Level and Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/3 PAPER 3 Practical Test Candidates
DIFFUSON AND OSMOSIS INTRODUCTION diffusion concentration gradient. net osmosis water potential active transport
 DIFFUSON AND OSMOSIS NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The life of a cell is dependent on efficiently moving material into and out of the cell across the cell membrane. Raw materials such as oxygen and sugars needed
DIFFUSON AND OSMOSIS NAME DATE INTRODUCTION The life of a cell is dependent on efficiently moving material into and out of the cell across the cell membrane. Raw materials such as oxygen and sugars needed
Investigating the Effect of Time on the Plasmolysis of Potatoes
 Investigating the Effect of Time on the Plasmolysis of Potatoes Research Question What causes potatoes to go soft after being stored for a long time? Aim The aim of this experiment is to investigate how
Investigating the Effect of Time on the Plasmolysis of Potatoes Research Question What causes potatoes to go soft after being stored for a long time? Aim The aim of this experiment is to investigate how
AP Lab Four: Water Potential and Osmosis
 AP Biology AP Lab Four: Water Potential and Osmosis Name Atoms and molecules are constantly in motion, bumping off of membranes, barriers, each other, without end. The results of this among other phenomena
AP Biology AP Lab Four: Water Potential and Osmosis Name Atoms and molecules are constantly in motion, bumping off of membranes, barriers, each other, without end. The results of this among other phenomena
GCSE. Biology Practical Manual. Unit 3: Practical Skills CCEA GCSE TEACHER GUIDANCE. 2.1 Investigate the process of osmosis
 GCSE CCEA GCSE TEACHER GUIDANCE Biology Practical Manual Unit 3: Practical Skills 2.1 Investigate the process of osmosis For first teaching from September 2017 Practical 2.1 Investigate the process of
GCSE CCEA GCSE TEACHER GUIDANCE Biology Practical Manual Unit 3: Practical Skills 2.1 Investigate the process of osmosis For first teaching from September 2017 Practical 2.1 Investigate the process of
Biology Unit 5 Cancer, Lab Activity 5-2
 Biology Unit 5 Cancer, Lab Activity 5-2 The Plasma membrane serves as a barrier between the internal cell environment and the external world. The plasma membrane is a dynamic structure. It allows some
Biology Unit 5 Cancer, Lab Activity 5-2 The Plasma membrane serves as a barrier between the internal cell environment and the external world. The plasma membrane is a dynamic structure. It allows some
Biology Cell Unit Homework Packet #3
 Biology Cell Unit Homework Packet #3 Name DUE: Hour HW #5 Egg Demo Drawings Analysis HW #6 Elodea Drawings lab Analysis HW #7 Cell Questions Membrane and Transport HW #8 Questions / 5 possible points Homework
Biology Cell Unit Homework Packet #3 Name DUE: Hour HW #5 Egg Demo Drawings Analysis HW #6 Elodea Drawings lab Analysis HW #7 Cell Questions Membrane and Transport HW #8 Questions / 5 possible points Homework
To understand osmosis, we must focus on the behavior of the solvent, not the solute.
 GCC CHM 130LL Osmosis and Dialysis Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to observe the closely related phenomena of osmosis and diffusion as it relates to dialysis. It is hoped that you will be able
GCC CHM 130LL Osmosis and Dialysis Purpose: The purpose of this experiment is to observe the closely related phenomena of osmosis and diffusion as it relates to dialysis. It is hoped that you will be able
5 In fish and chip shops, potatoes are cut into chips several hours before they are cooked.
 8 Areas outside the box will not be scanned for marking 5 In fish and chip shops, potatoes are cut into chips several hours before they are cooked. The amount of water in the chips must be kept constant
8 Areas outside the box will not be scanned for marking 5 In fish and chip shops, potatoes are cut into chips several hours before they are cooked. The amount of water in the chips must be kept constant
The students measured the mass of four of the potato sticks using an electronic balance.
 1 Some students investigated osmosis in raw potato sticks. (a) Define the term osmosis. [3] (b) The students measured the mass of four of the potato sticks using an electronic balance. Fig. 4.1 shows an
1 Some students investigated osmosis in raw potato sticks. (a) Define the term osmosis. [3] (b) The students measured the mass of four of the potato sticks using an electronic balance. Fig. 4.1 shows an
Biology Cell Unit Homework Packet #3
 Biology Cell Unit Homework Packet #3 Name DUE: Hour HW #5 Egg Demo Drawings Analysis HW #6 Elodea Drawings lab Analysis HW #7 Cell Questions Membrane and Transport HW #8 Questions / 5 possible points Homework
Biology Cell Unit Homework Packet #3 Name DUE: Hour HW #5 Egg Demo Drawings Analysis HW #6 Elodea Drawings lab Analysis HW #7 Cell Questions Membrane and Transport HW #8 Questions / 5 possible points Homework
Measuring Osmotic Potential
 Measuring Osmotic Potential INTRODUCTION All cells require essential materials to ensure their survival. Chemical, physical, and biological processes are used to move these materials inside of cells. Similar
Measuring Osmotic Potential INTRODUCTION All cells require essential materials to ensure their survival. Chemical, physical, and biological processes are used to move these materials inside of cells. Similar
thebiotutor.com 2 D Movement of Molecules Time: 27 minutes Total marks available: 27 Total marks achieved: Andy Todd
 thebiotutor.com 2 D Movement of Molecules Time: 27 minutes Total marks available: 27 Total marks achieved: Andy Todd Q1. (a) The diagram shows a plant cell drawn by a student. (i) Label the diagram to
thebiotutor.com 2 D Movement of Molecules Time: 27 minutes Total marks available: 27 Total marks achieved: Andy Todd Q1. (a) The diagram shows a plant cell drawn by a student. (i) Label the diagram to
Investigation 5 (annotated)
 Investigating the Effect of Time on the Plasmolysis of Potatoes Research Question What causes potatoes to go soft after being stored for a long time? Aim The aim of this experiment is to investigate how
Investigating the Effect of Time on the Plasmolysis of Potatoes Research Question What causes potatoes to go soft after being stored for a long time? Aim The aim of this experiment is to investigate how
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 1 Q 154 minutes 154 marks Page 1 of 44 Q1. The table shows the percentage of some gases in the air a boy breathed in and out. Gases Air breathed
LAB 04 Diffusion and Osmosis
 LAB 04 Diffusion and Osmosis Objectives: Describe the physical mechanisms of diffusion and osmosis. Understand the relationship between surface area and rate of diffusion. Describe how molar concentration
LAB 04 Diffusion and Osmosis Objectives: Describe the physical mechanisms of diffusion and osmosis. Understand the relationship between surface area and rate of diffusion. Describe how molar concentration
LAB Potato Cores Honors Biology, Newton North High
 Name Date Block LAB Potato Cores Honors Biology, Newton North High BACKGROUND: Osmosis is a type of passive transport. No input of energy is needed in order for water to pass through a selectively permeable
Name Date Block LAB Potato Cores Honors Biology, Newton North High BACKGROUND: Osmosis is a type of passive transport. No input of energy is needed in order for water to pass through a selectively permeable
Egg-speriment With a Cell
 Name Date Class Cell Structure and Function Standards Investigation Overview S 7.1.a Standards Investigation Egg-speriment With a Cell One of the cell structures you will be learning about is the cell
Name Date Class Cell Structure and Function Standards Investigation Overview S 7.1.a Standards Investigation Egg-speriment With a Cell One of the cell structures you will be learning about is the cell
LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE
 LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE NAME: PERIOD: DATE: Building Background Knowledge: 1) SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE: Every cell is surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane
LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE NAME: PERIOD: DATE: Building Background Knowledge: 1) SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE: Every cell is surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane
GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper SPECIMEN
 GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper F Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical calculator
GCSE (9 1) Biology A (Gateway Science) J247/01 Paper 1 (Foundation Tier) Sample Question Paper F Date Morning/Afternoon Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes You may use: a scientific or graphical calculator
BIOL 305L Spring 2019 Laboratory Six
 Please print Full name clearly: BIOL 305L Spring 2019 Laboratory Six Osmosis in potato and carrot samples Introduction Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane
Please print Full name clearly: BIOL 305L Spring 2019 Laboratory Six Osmosis in potato and carrot samples Introduction Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane
LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE
 LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE NAME: PERIOD: DATE: Building Background Knowledge: 1) SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE: Every cell is surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane
LAB: DIFFUSION ACROSS A SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE NAME: PERIOD: DATE: Building Background Knowledge: 1) SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE MEMBRANE: Every cell is surrounded by a selectively permeable membrane
Diffusion and Osmosis
 Diffusion and Osmosis During your first year of residency at Mountainside Hospital, you are treating a group of patients that exhibit signs of dehydration. You have to be sure to take note of all the solutes
Diffusion and Osmosis During your first year of residency at Mountainside Hospital, you are treating a group of patients that exhibit signs of dehydration. You have to be sure to take note of all the solutes
Osmosis in Potato Slices
 Osmosis in Potato Slices Vanderbilt Student Volunteers for Science Training Presentation 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural Important! Please use this resource to reinforce your understanding of the lesson! Make
Osmosis in Potato Slices Vanderbilt Student Volunteers for Science Training Presentation 2018-2019 VINSE/VSVS Rural Important! Please use this resource to reinforce your understanding of the lesson! Make
Ecology Pre-test (Middle School)
 Ecology Pre-test (Middle School) Science is easier to understand if you can make connections between what you know now and the new ideas that you are studying. This is a test that will help us to understand
Ecology Pre-test (Middle School) Science is easier to understand if you can make connections between what you know now and the new ideas that you are studying. This is a test that will help us to understand
Catalytic Activity of Enzymes
 Catalytic Activity of Enzymes Introduction Enzymes are biological molecules that catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions. You could call enzymes the Builders and Do-ers in the cell; without them, life could
Catalytic Activity of Enzymes Introduction Enzymes are biological molecules that catalyze (speed up) chemical reactions. You could call enzymes the Builders and Do-ers in the cell; without them, life could
BIO 322/122L Laboratory Plant Water Relations
 BIO 322/122L Laboratory Plant Water Relations I. Water Potential. The cytoplasm of the plant cell, with its enclosed vacuole, is contained within a membrane that is more permeable to water than to most
BIO 322/122L Laboratory Plant Water Relations I. Water Potential. The cytoplasm of the plant cell, with its enclosed vacuole, is contained within a membrane that is more permeable to water than to most
ENZYME CONCENTRATIONS AND ENZYME ACTIVITY: PLANNING SHEET
 Activity 2.11 Student Sheet ENZYME CONCENTRATIONS AND ENZYME ACTIVITY: PLANNING SHEET To investigate how enzyme concentration can affect the initial rate of reaction. Wear eye protection, lab coats and
Activity 2.11 Student Sheet ENZYME CONCENTRATIONS AND ENZYME ACTIVITY: PLANNING SHEET To investigate how enzyme concentration can affect the initial rate of reaction. Wear eye protection, lab coats and
Characteristics of Life. Problem: How does exercise affect a person's heart rate, breathing rate, and perspiration level? Pre-Lab:
 Pre-AP Homeostasis and Exercise Background: Homeostasis means maintaining a relatively constant state of the body s internal environment. Pulse rate is constantly checked by receptors throughout your body.
Pre-AP Homeostasis and Exercise Background: Homeostasis means maintaining a relatively constant state of the body s internal environment. Pulse rate is constantly checked by receptors throughout your body.
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3
 AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3 128 minutes 128 marks Page 1 of 29 Q1. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation
AQA B3.1 Movement of molecules in and out of cells LEVEL 3 128 minutes 128 marks Page 1 of 29 Q1. Plants need chemical energy for respiration and for active transport. (i) Write a balanced chemical equation
Osmosis and Diffusion: How biological membranes are important This page is a lab preparation guide for instructors.
 Osmosis and Diffusion: How biological membranes are important This page is a lab preparation guide for instructors. **All solutions and dialysis bags can easily be prepared prior to lab start to maximize
Osmosis and Diffusion: How biological membranes are important This page is a lab preparation guide for instructors. **All solutions and dialysis bags can easily be prepared prior to lab start to maximize
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department
 Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Investigating Cells Homework and Question Booklet 1 Investigating Cells (a) Investigating Living Cells... 2 Investigating Cells (b) Investigating Diffusion...
Hyndland Secondary School Biology Department Investigating Cells Homework and Question Booklet 1 Investigating Cells (a) Investigating Living Cells... 2 Investigating Cells (b) Investigating Diffusion...
BIOL 347L Laboratory Three
 Introduction BIOL 347L Laboratory Three Osmosis in potato and carrot samples Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration,
Introduction BIOL 347L Laboratory Three Osmosis in potato and carrot samples Osmosis is the movement of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration,
Diffusion and Osmosis
 Diffusion and Osmosis Introduction: In this exercise you will measure diffusion of small molecules through dialysis tubing, an example of a semi permeable membrane. The movement of a solute through a semi
Diffusion and Osmosis Introduction: In this exercise you will measure diffusion of small molecules through dialysis tubing, an example of a semi permeable membrane. The movement of a solute through a semi
Factors Affecting the Rate of Enzyme Activity NOTES
 Factors Affecting the Rate of Enzyme Activity NOTES I. Pepsin a) Pepsin is an released in the that breaks down the in food into its building blocks. b) Diagram: Pepsin c) Pepsin will ONLY break down the
Factors Affecting the Rate of Enzyme Activity NOTES I. Pepsin a) Pepsin is an released in the that breaks down the in food into its building blocks. b) Diagram: Pepsin c) Pepsin will ONLY break down the
Observing Osmosis Lab
 Observing Osmosis Lab Background Information: Molecules are in constant motion, and tend to move from areas of higher concentrations to areas of lower concentrations. Diffusion is defined as the movement
Observing Osmosis Lab Background Information: Molecules are in constant motion, and tend to move from areas of higher concentrations to areas of lower concentrations. Diffusion is defined as the movement
Name: Date: Solubility Lab - Worksheet #3 Level 1
 Name: Date: Solubility Lab - Worksheet #3 Level 1 In today s lab you will be working in groups to determine whether sugar or salt dissolves more quickly in water. The rate at which different substances
Name: Date: Solubility Lab - Worksheet #3 Level 1 In today s lab you will be working in groups to determine whether sugar or salt dissolves more quickly in water. The rate at which different substances
GCSE BIOLOGY. Materials For this paper you must have: a ruler a scientific calculator. Please write clearly in block capitals. Surname.
 Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE BIOLOGY Foundation Tier Paper 1F F Specimen 2018 (set 2) Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
Please write clearly in block capitals. Centre number Candidate number Surname Forename(s) Candidate signature GCSE BIOLOGY Foundation Tier Paper 1F F Specimen 2018 (set 2) Time allowed: 1 hour 45 minutes
Osmolarity Lab Sadhika Laxman HL1 Biology D
 Osmolarity Lab Sadhika Laxman HL1 Biology D 8.11.2017 1 Qualitative Data Below is two pictures, before and after leaving the potato chips in the sucrose water for approximately 72 hours. In both photos,
Osmolarity Lab Sadhika Laxman HL1 Biology D 8.11.2017 1 Qualitative Data Below is two pictures, before and after leaving the potato chips in the sucrose water for approximately 72 hours. In both photos,
Osmosis. Evaluation copy
 Osmosis Computer 1B In order to survive, all organisms need to move molecules in and out of their cells. Molecules such as gases (e.g., O 2, CO 2 ), water, food, and wastes pass across the cell membrane.
Osmosis Computer 1B In order to survive, all organisms need to move molecules in and out of their cells. Molecules such as gases (e.g., O 2, CO 2 ), water, food, and wastes pass across the cell membrane.
Big. Cellular Processes: Idea. Energy and Communication DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS. What causes my plants to wilt if I forget to water them?
 Big Cellular Processes: Idea 2 Energy and Communication INVESTIGATION 4 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS What causes my plants to wilt if I forget to water them? BACKGROUND Cells must move materials through membranes
Big Cellular Processes: Idea 2 Energy and Communication INVESTIGATION 4 DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS What causes my plants to wilt if I forget to water them? BACKGROUND Cells must move materials through membranes
2. Alcohol causes 2.5 million deaths in the world each year. In deaths of year olds, 9% of the time alcohol was involved.
 1 Drug classification Drugs change what is happening inside our bodies. Some drugs help our bodies to work properly. Some cause them damage. Draw lines to match each type of drug to some common names for
1 Drug classification Drugs change what is happening inside our bodies. Some drugs help our bodies to work properly. Some cause them damage. Draw lines to match each type of drug to some common names for
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *9531640679* BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical February/March 2017 1 hour Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *9531640679* BIOLOGY 0610/62 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical February/March 2017 1 hour Candidates
Running Head: ESTIMATING OSMOLARITY 1
 Running Head: ESTIMATING OSMOLARITY 1 Lab Report on Estimating Osmolarity of Potato cells by Change in weight Name Class Instructor Date ESTIMATING OSMOLARITY 2 Abstract This experiment was carried out
Running Head: ESTIMATING OSMOLARITY 1 Lab Report on Estimating Osmolarity of Potato cells by Change in weight Name Class Instructor Date ESTIMATING OSMOLARITY 2 Abstract This experiment was carried out
Name: NYS DIFFUSION LAB REVIEW Date: PACKET 1: Difusion Through a Membrane
 Name: NYS DIFFUSION LAB REVIEW Date: PACKET 1: Difusion Through a Membrane 1. The diagram below represents a laboratory setup used to demonstrate the movement of molecules across a selectively permeable
Name: NYS DIFFUSION LAB REVIEW Date: PACKET 1: Difusion Through a Membrane 1. The diagram below represents a laboratory setup used to demonstrate the movement of molecules across a selectively permeable
David Huang! AP Biology! Oct. 4,2013! AP Biology Osmosis Laboratory Analysis! Introduction:!! There are several different methods for the
 David Huang AP Biology Oct. 4,2013 AP Biology Osmosis Laboratory Analysis Introduction: There are several different methods for the transportation of molecules across the phospholipid bilayer. These transportation
David Huang AP Biology Oct. 4,2013 AP Biology Osmosis Laboratory Analysis Introduction: There are several different methods for the transportation of molecules across the phospholipid bilayer. These transportation
How do ph levels affect diffusion of starch in a sweet potato cell? A Great Student. Biology 111. October 12, Mrs. Stewart
 How do ph levels affect diffusion of starch in a sweet potato cell? A Great Student Biology 111 October 12, 2016 Mrs. Stewart Abstract The agriculture of sweet potatoes can be massively affected by the
How do ph levels affect diffusion of starch in a sweet potato cell? A Great Student Biology 111 October 12, 2016 Mrs. Stewart Abstract The agriculture of sweet potatoes can be massively affected by the
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 *2994000068* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates
*2994000068* Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education COMBINED SCIENCE 0653/63 Paper 6 Alternative to Practical May/June 2014 1 hour Candidates
Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane
 Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. What is/are the role(s) of structure A? (1) For cell recognition. (2) For carrying water-soluble substances across cell membrane. (3) For supporting
Topic 3: Movement of substances across cell membrane 1. What is/are the role(s) of structure A? (1) For cell recognition. (2) For carrying water-soluble substances across cell membrane. (3) For supporting
Lab #3 Potentiometric Titration of Soda Ash (after Christian, p , p ) (phenolphthalein)
 Lab #3 Potentiometric Titration of Soda Ash (after Christian, p.692-694, p.718-720) I: INTRODUCTION In this lab, an unknown sample of soda ash (a crude mixture of sodium carbonate) will be titrated with
Lab #3 Potentiometric Titration of Soda Ash (after Christian, p.692-694, p.718-720) I: INTRODUCTION In this lab, an unknown sample of soda ash (a crude mixture of sodium carbonate) will be titrated with
1. All cells have a that acts as a between the outside and inside of the cell.
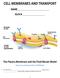 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cnbzdcibegy 1. All cells have a that acts as a between the outside and inside of the cell. 1 2. Cell membranes are primarily made of which are large molecules. 3. It is
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cnbzdcibegy 1. All cells have a that acts as a between the outside and inside of the cell. 1 2. Cell membranes are primarily made of which are large molecules. 3. It is
Quotes from Next Generation Science Standards, available at
 Teacher Preparation Notes for Diffusion across a Selectively Permeable Membrane Drs. Jennifer Doherty and Ingrid Waldron, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2015 1 Students investigate
Teacher Preparation Notes for Diffusion across a Selectively Permeable Membrane Drs. Jennifer Doherty and Ingrid Waldron, Department of Biology, University of Pennsylvania, 2015 1 Students investigate
COMBINED SCIENCE GCSE. Biology: Paper 1 Higher Tier. Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes. Materials. For this paper you must have: Instructions all
 GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE H Biology: Paper 1 Higher Tier Materials Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes For this paper you must have: Instructions all Information 70 Advice 01 Gonorrhoea is a disease caused by
GCSE COMBINED SCIENCE H Biology: Paper 1 Higher Tier Materials Time allowed: 1 hour 15 minutes For this paper you must have: Instructions all Information 70 Advice 01 Gonorrhoea is a disease caused by
Investigation 4: Diffusion and Osmosis Notes From the teacher
 Day 1: Investigation 4: Diffusion and Osmosis Notes From the teacher Before class: Read Learning Objectives through Procedure 1 and complete Day 1 Pre Lab. Pre-Lab: 1. What is diffusion? 2. What is kinetic
Day 1: Investigation 4: Diffusion and Osmosis Notes From the teacher Before class: Read Learning Objectives through Procedure 1 and complete Day 1 Pre Lab. Pre-Lab: 1. What is diffusion? 2. What is kinetic
Enzyme Reaction Rates Using TOOTHPICKASE
 Name Date Period Enzyme Reaction Rates Using TOOTHPICKASE INTRODUCTION: Enzymes are proteins that are used as catalysts in biochemical reactions. A catalyst is a factor that controls the rate of a reaction
Name Date Period Enzyme Reaction Rates Using TOOTHPICKASE INTRODUCTION: Enzymes are proteins that are used as catalysts in biochemical reactions. A catalyst is a factor that controls the rate of a reaction
Learning Outcomes. 2. Diffusion takes place through the cell membrane because it is selectively permeable.
 Diffusion Learning Outcomes 1. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration down a concentration gradient until evenly spread. 2. Diffusion takes place through
Diffusion Learning Outcomes 1. Diffusion is the movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration down a concentration gradient until evenly spread. 2. Diffusion takes place through
Introduction diffusion osmosis. imbibe Diffusion The Cell Membrane and Osmosis selectively permeable membrane Osmosis 1. Isotonic 2.
 Topic 6. Diffusion Introduction: This exercise explores the physical phenomenon of diffusion and osmosis. Osmosis is simply the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. We will also
Topic 6. Diffusion Introduction: This exercise explores the physical phenomenon of diffusion and osmosis. Osmosis is simply the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. We will also
Osmosis, Plasmolysis and Turgidity
 Osmosis, Plasmolysis and Turgidity Question Paper 2 Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet GCSE Biology CCEA Osmosis and plant transport Osmosis, plasmolysis and turgidity Question Paper Time
Osmosis, Plasmolysis and Turgidity Question Paper 2 Level Subject Exam Board Topic Sub-Topic Booklet GCSE Biology CCEA Osmosis and plant transport Osmosis, plasmolysis and turgidity Question Paper Time
Year 8 Assessment. Autumn Term Remember!
 Remember! Each section of questions gets harder as you go through (higher level questions at the end of each section). Try all questions. Write down an idea even if you re not sure you might get a mark!
Remember! Each section of questions gets harder as you go through (higher level questions at the end of each section). Try all questions. Write down an idea even if you re not sure you might get a mark!
Beverage Density Lab
 Name: date: Beverage Density Lab Introduction: It is known that popular beverages often contain large amounts of. Nutritionists have raised concern in recent years as to the high levels of in these drinks
Name: date: Beverage Density Lab Introduction: It is known that popular beverages often contain large amounts of. Nutritionists have raised concern in recent years as to the high levels of in these drinks
Chapter MEMBRANE TRANSPORT
 Chapter 3 I MEMBRANE TRANSPORT The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It completely surrounds the protoplasm or living portion of the cell, separating the cell s interior
Chapter 3 I MEMBRANE TRANSPORT The cell membrane, or plasma membrane, is the outermost layer of the cell. It completely surrounds the protoplasm or living portion of the cell, separating the cell s interior
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/1 Paper Advanced Practical Skills 1 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level BIOLOGY 9700/1 Paper Advanced Practical Skills 1 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 40 Published This
Name : ( ) 4551/3 SMJK PEREMPUAN CHINA PULAU PINANG TRIAL EXAM 2012 BIOLOGY PAPER 3 1 HOUR 30 MINUTES DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED
 Name : ( ) 4551/3 Class : S5 BIOLOGY Paper 3 September 2012 1 ½ hours SMJK PEREMPUAN CHINA PULAU PINANG TRIAL EXAM 2012 BIOLOGY PAPER 3 1 HOUR 30 MINUTES DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED 1. This
Name : ( ) 4551/3 Class : S5 BIOLOGY Paper 3 September 2012 1 ½ hours SMJK PEREMPUAN CHINA PULAU PINANG TRIAL EXAM 2012 BIOLOGY PAPER 3 1 HOUR 30 MINUTES DO NOT OPEN THIS BOOKLET UNTIL INSTRUCTED 1. This
Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity
 Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity LabQuest 6A Many organisms can decompose hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) enzymatically. Enzymes are globular proteins, responsible for most of the chemical activities
Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity LabQuest 6A Many organisms can decompose hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) enzymatically. Enzymes are globular proteins, responsible for most of the chemical activities
Experimental Procedure
 1 of 7 9/12/2018, 2:19 PM https://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project-ideas/humbio_p043/human-biology-health/iron-rich-foods (http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects /project-ideas/humbio_p043/human-biology-health/iron-rich-foods)
1 of 7 9/12/2018, 2:19 PM https://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects/project-ideas/humbio_p043/human-biology-health/iron-rich-foods (http://www.sciencebuddies.org/science-fair-projects /project-ideas/humbio_p043/human-biology-health/iron-rich-foods)
TOXICOLOGY PROTOCOLS PROTOCOL 1. SERIAL DILUTIONS. Objective To make a serial dilution for use in dose/response bioassays.
 TOXICOLOGY PROTOCOLS PROTOCOL 1. SERIAL DILUTIONS Objective To make a serial dilution for use in dose/response bioassays. Background The idea behind a bioassay is that the test organism will respond in
TOXICOLOGY PROTOCOLS PROTOCOL 1. SERIAL DILUTIONS Objective To make a serial dilution for use in dose/response bioassays. Background The idea behind a bioassay is that the test organism will respond in
Passive Transport: Practice Problems PAP BIOLOGY
 Passive Transport: Practice Problems PAP BIOLOGY #1 Draw a diagram where the cell has low concentration of salt molecules and the environment it is in has a high concentration of salt molecules in a water
Passive Transport: Practice Problems PAP BIOLOGY #1 Draw a diagram where the cell has low concentration of salt molecules and the environment it is in has a high concentration of salt molecules in a water
4551/3 PP MARKING SCHEME PAPER 3 BIOLOGY
 Question 1 MARKING SCHEME PAPER BIOLOGY 1(a) [ KB060 Measuring Using Number ] Able to recd all 8 readings of initial mass and final mass of the potato slices in the spaces provided accurately. Concentration
Question 1 MARKING SCHEME PAPER BIOLOGY 1(a) [ KB060 Measuring Using Number ] Able to recd all 8 readings of initial mass and final mass of the potato slices in the spaces provided accurately. Concentration
Evaluation copy. Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity. Computer
 Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity Computer 6A Many organisms can decompose hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) enzymatically. Enzymes are globular proteins, responsible for most of the chemical activities
Enzyme Action: Testing Catalase Activity Computer 6A Many organisms can decompose hydrogen peroxide (H 2 O 2 ) enzymatically. Enzymes are globular proteins, responsible for most of the chemical activities
National 5 Biology Unit 1 Cell Biology Ink Exercise Two Cell Transport
 National 5 Biology Unit Cell Biology Ink Exercise Two Cell Transport Name: Class: . Four thin sections of onion tissue were immersed in 5% sugar solution. The sections were left for 5 minutes then viewed
National 5 Biology Unit Cell Biology Ink Exercise Two Cell Transport Name: Class: . Four thin sections of onion tissue were immersed in 5% sugar solution. The sections were left for 5 minutes then viewed
Osmosis. Computer OBJECTIVES
 Osmosis Computer 22 In order to survive, all organisms need to move molecules in and out of their cells. Molecules such as gases (e.g., O 2, CO 2 ), water, food, and wastes pass across the cell membrane.
Osmosis Computer 22 In order to survive, all organisms need to move molecules in and out of their cells. Molecules such as gases (e.g., O 2, CO 2 ), water, food, and wastes pass across the cell membrane.
Safety. What You Need. What to do... Neo/SCI Student s Guide Name... Teacher/Section... Date... Step 1. Step 2
 Diffusion & Osmosis Activity 1a Diffusion Lab 1 Background Diffusion occurs whenever concentrations of substances are not even throughout an area. This unequal distribution of particles is called a concentration
Diffusion & Osmosis Activity 1a Diffusion Lab 1 Background Diffusion occurs whenever concentrations of substances are not even throughout an area. This unequal distribution of particles is called a concentration
SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION AND PROCESS
 SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION AND PROCESS Open up to Scientific Process NOTE BLANKS 1) Read the introduction 2) Fill in the Scientific Process Skills using the reading 3) Complete the flow chart on page 2 using
SCIENTIFIC INVESTIGATION AND PROCESS Open up to Scientific Process NOTE BLANKS 1) Read the introduction 2) Fill in the Scientific Process Skills using the reading 3) Complete the flow chart on page 2 using
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport
 Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport 1 of 25 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 25 Boardworks Ltd 2012 Substances spread out by diffusion 3 of 25 Boardworks Ltd 2012 Particles in solutions and in gases move around
Diffusion, Osmosis and Active Transport 1 of 25 Boardworks Ltd 2012 2 of 25 Boardworks Ltd 2012 Substances spread out by diffusion 3 of 25 Boardworks Ltd 2012 Particles in solutions and in gases move around
Name: Date Block Selective Permeability
 LAB Name: Date Block Selective Permeability OBJECTIVES: Observe the selective permeability of an artificial membrane. Observe diffusion of substances across an artificial membrane. Devise a model for the
LAB Name: Date Block Selective Permeability OBJECTIVES: Observe the selective permeability of an artificial membrane. Observe diffusion of substances across an artificial membrane. Devise a model for the
LIFE SCIENCES: PAPER III
 NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2017 LIFE SCIENCES: PAPER III EXAMINATION NUMBER Time: 1½ hours 50 marks PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. Write your examination number
NATIONAL SENIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION NOVEMBER 2017 LIFE SCIENCES: PAPER III EXAMINATION NUMBER Time: 1½ hours 50 marks PLEASE READ THE FOLLOWING INSTRUCTIONS CAREFULLY 1. Write your examination number
Principles & Practice of Diffusion & Osmosis. Storage: Store entire experiment at room temperature. EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE
 The Biotechnology Education Company Storage: Store entire experiment at room temperature. 281 EDVO-Kit # Principles & Practice of Diffusion & Osmosis EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment
The Biotechnology Education Company Storage: Store entire experiment at room temperature. 281 EDVO-Kit # Principles & Practice of Diffusion & Osmosis EXPERIMENT OBJECTIVE The objective of this experiment
Passive Transport Lab: Diffusion and Osmosis
 Name Date Period Passive Transport Lab: Diffusion and Osmosis OBJECTIVE: Apply your understanding of the processes of diffusion and osmosis to explain observational data. PART A: Starch and Iodine MATERIALS
Name Date Period Passive Transport Lab: Diffusion and Osmosis OBJECTIVE: Apply your understanding of the processes of diffusion and osmosis to explain observational data. PART A: Starch and Iodine MATERIALS
Diffusion across a Selectively Permeable Membrane
 Diffusion across a Selectively Permeable Membrane Each cell is surrounded by a selectively permeable cell membrane Cell Membrane which regulates what gets into and out of the cell. A selectively permeable
Diffusion across a Selectively Permeable Membrane Each cell is surrounded by a selectively permeable cell membrane Cell Membrane which regulates what gets into and out of the cell. A selectively permeable
Name Date. In this lab investigation you will investigate the movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane.
 This lab will be hand-written in your data book AP Osmosis Labs Part A (was done in previous a previous class: Dialysis tube + Starch + Glucose) Part B: Osmosis Unknowns In this lab investigation you will
This lab will be hand-written in your data book AP Osmosis Labs Part A (was done in previous a previous class: Dialysis tube + Starch + Glucose) Part B: Osmosis Unknowns In this lab investigation you will
Diffusion and Osmosis Lab AP LAB 4
 Diffusion and Osmosis Lab AP LAB 4 Part 1: Surface Area and Cell Size Which do you think has a greater influence on the rate of diffusion in a cell surface area or volume? You will calculate surface are-to-volume
Diffusion and Osmosis Lab AP LAB 4 Part 1: Surface Area and Cell Size Which do you think has a greater influence on the rate of diffusion in a cell surface area or volume? You will calculate surface are-to-volume
Sc ienc e 10-Biology Ac t ivit y 6 Ex perim ent on Osm osis
 Sc ienc e 10-Biology Ac t ivit y 6 Ex perim ent on Osm osis Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Purpose: To observe cells in osmotic balance and osmotic imbalance. Introduction:
Sc ienc e 10-Biology Ac t ivit y 6 Ex perim ent on Osm osis Name Due Date 10 Show Me Hand In Correct and Hand In Again By Purpose: To observe cells in osmotic balance and osmotic imbalance. Introduction:
TITLE OF LAB: Effects of Temperature and Solvents on the Cell Membrane
 SOTM LAB: B14 12/99 I. TEACHER NOTES & GUIDELINES TITLE OF LAB: Effects of Temperature and Solvents on the Cell Membrane DEVELOPERS OF LAB: Adapted by James Kirby JD726, Jennifer Mortellaro JD449, and
SOTM LAB: B14 12/99 I. TEACHER NOTES & GUIDELINES TITLE OF LAB: Effects of Temperature and Solvents on the Cell Membrane DEVELOPERS OF LAB: Adapted by James Kirby JD726, Jennifer Mortellaro JD449, and
LAB #3 - DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS
 DIFFUSION EXPERIMENT - pg. 4-6 LAB #3 - DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS Definition of DIFFUSION - The natural tendency of particles to move from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration START
DIFFUSION EXPERIMENT - pg. 4-6 LAB #3 - DIFFUSION AND OSMOSIS Definition of DIFFUSION - The natural tendency of particles to move from areas of high concentration to areas of lower concentration START
The graph should contain 5 major parts: the title, the independent variable, the dependent variable, the scales for each variable, and a legend.
 BLIZZARD BAG #2 Please complete the activity below. You will need to print out this activity sheet (pages 2-5 only) OR Write out the answers on a separate piece of paper and graph on a piece of graphing
BLIZZARD BAG #2 Please complete the activity below. You will need to print out this activity sheet (pages 2-5 only) OR Write out the answers on a separate piece of paper and graph on a piece of graphing
