This is the author s final accepted version.
|
|
|
- Betty Hodges
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Thomson, C. M., Esparon, T., Rea, P. M. and Jamal, B. (2016) Monoaxial external fixation of the calcaneus: an anatomical study assessing the safety of monoaxial pin insertion. Injury, 47(10), pp (doi: /j.injury ) This is the author s final accepted version. There may be differences between this version and the published version. You are advised to consult the publisher s version if you wish to cite from it. Deposited on: 13 September 2016 Enlighten Research publications by members of the University of Glasgow
2 Monoaxial External Fixation of the Calcaneus: An Anatomical Study Assessing the Safety of Monoaxial Pin Insertion Callum M Thomson a, Tom Esparon a, Paul M. Rea a, Bilal Jamal b a Laboratory of Human Anatomy, Thomson Building, School of Life Sciences, College of Medical, Veterinary and Life Sciences, Univeristy of Glasgow, UK b Department of Orhtopaedics, Glasgow Royal Infirmary, UK Authors: Callum M Thomson: BSc Anatomy Honours student at the University of Glasgow Tom Esparon: BSc Anatomy Honours student at the University of Glasgow Dr Paul M Rea: Senior University Teacher and Licensed Teacher of Anatomy at University of Glasgow Mr Bilal Jamal: Specialty Trainee Orthopaedic Surgeon Address for correspondence: Dr Paul M. Rea Laboratory of Human Anatomy Thomson Building School of Life Sciences College of Medical, Veterinary and Life Sciences University of Glasgow, UK [+44] [0] Paul.Rea@glasgow.ac.uk Keywords: External Fixation; Calcaneus; Heel Fractures; Monoaxial; Safe-Zone; Surgical Procedures
3 Abstract The use of external fixation for intra-articular calcaneal fractures is increasing in popularity. Studies have shown fine wire and monoaxial external fixation to be a viable surgical alternative to more invasive methods of open reduction and internal fixation of the calcaneus. However, there is an absence of literature that quantifies the risk of pin insertion for monoaxial fixation. This study aimed to determine the safety of inserting monoaxial pins within the calcaneus to house the Orthofix Calcaneal Mini-Fixator. Five formalin embalmed cadaveric ankle and lower leg specimens were inserted with six monoaxial pins. Careful dissection then revealed the presence of the tendons of peroneus longus and brevis, the sural nerve and the small saphenous vein in relation to these pins. Measurements from each pin to each of these structures were made as the structures transected lines drawn from each pin to two palpable bony landmarks: the inferior tip of the lateral malleolus and the posterosuperior calcaneus. In doing this, the risk posed by each pin could be evaluated. We found that two particular pins, those used to hold the articular surface of the subtalar joint in a reduced position, posed a larger risk of injury to surrounding structures than the remaining pins. These findings therefore suggest that monoaxial fixation of the calcaneus using a six pin approach is a relatively safe method of rectifying calcaneal fractures and thus may serve as a welcome alternative to other methods of calcaneal fixation.
4 Introduction Calcaneal fractures constitute 1-2% of all fractures [1]. By convention, due to improvements in computed tomography scanning and surgical techniques, open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) has been used extensively to reconstruct displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures [2,3,4]. Fine wire external fixation is one such method whereby the calcaneus can be effectively reduced without the need for open surgery [5]. As external fixation is respectful of the soft tissues, it does not rely on a delay to theatre to allow for soft tissue swelling to settle. It also permits almost immediate post-procedural weight bearing. Few complications occur with external fixation, such as minor infections at pin insertion sites [6]. As wires pass through the calcaneus percutaneously in external fixation, there is an indeterminate risk of damage to structures which traverse the calcaneus. To avoid this, there has been a variety of proposed safe zones within the calcaneus in the literature [7.8.9]. However, more emphasis has been placed on the medial side, perhaps as a consequence of a greater density of structures at risk. Of all the studies considered, a definite safe zone of the medial side of the calcaneus could not be identified, despite deploying several different techniques and taking variations in anatomy and gender into consideration. This may suggest that there is no medial safe zone that could eliminate the possibility of injury to neurovascular or tendinous structures. A more contemporary method utilizing monoaxial external fixation involves placing pins, instead of wires, only into the lateral side avoiding penetration through the calcaneus to the medial side [10]. Despite there being a number of studies that have attempted to evaluate the results of fine wire external fixation of the calcaneus, there is a paucity of anatomical studies evaluating the safety of moxoaxial fixation, and an absence of suggested safe zones for this approach. The aim of this study was to determine which structures, if any, have been impinged by the pins and also to determine how close these pins are to structures of interest. By doing this, the safety of the Orthofix Calcaneal Mini-Fixator in rectifying intra-articular calcaneal fractures could be evaluated.
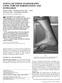
5 Materials and Methods Five formaldehyde embalmed ankle and lower leg cadaveric specimens were obtained from the regular stock in the Laboratory of Human Anatomy, University of Glasgow. All dissections were carried out under the Anatomy Act 1984 and the Human Tissue (Scotland) Act These specimens were from four different male individuals (four left specimens and one right specimen), with a mean age of 79 years (range 74-87). Six monoaxial pins were inserted into the lateral side of each of these specimens by an orthopaedic surgeon in line with the surgical technique for the Orthofix Calcaneal External Fixator [11]. In this study, these pins are numbered 1 to 6, from anterior to posterior. The middle pair of pins, pins 3 and 4, are used to hold the articular surface of the subtalar joint in a reduced position. The more anterior and posterior pins (pins 1, 2, 5 and 6) are used to maintain the length of the calcaneus and also serve to correct the varus angulation of the hindfoot following a fracture. However, when there is severe comminution of the anterior calcaneal apophysis, it may be necessary to insert pins 1 and 2 within the cuboid bone [11]. An incision was made down the midline anteriorly at the level approximately four finger breadths above the most inferior part of the lateral malleolus to the level of the base of the fifth metatarsal. This incision was continued laterally both proximally and distally to allow the skin to be carefully reflected to expose the area surrounding the pins. The subcutaneous fat was carefully removed so as not to damage any superficial structures. The sural nerve and small saphenous vein were first identified proximally and their course and distributions were revealed through blunt dissection. Care was taken not to disturb any soft tissue attachments of these structures to ensure their true anatomical positions were maintained. The tendons of peroneus brevis and peroneus longus muscles were then identified in close proximity to the lateral malleolus. Three easily palpable landmarks, the most inferior tip of the lateral malleolus, the posterosuperior tip of the calcaneus and the base of the fifth metatarsal were then revealed by dissection down to the level of bone. A photograph taken of one fully dissected specimen can be seen in figure 1.
6 All measurements were taken using Clarke CM145 digital Vernier calipers in millimetres and repeated four times by two independent observers at different times. These calipers are accurate to within ±0.03 mm for measurements between 0 and mm. The distances between each of the three bony landmarks were then measured. Lines were drawn with a marker pen from each pin to both the most inferior part of the lateral malleolus and the posterosuperior tip of the calcaneus. The total distances from each pin to each of these landmarks were measured. Measurements were then taken from each pin to the sural nerve, small saphenous vein and the tendons of peroneus brevis and peroneus longus as they transected each of the drawn lines. Some structures did not transect every line due to both anatomical variation and the absence of structures at particular portions of the calcaneus such as the tendons of peroneus longus and brevis which were only present within the anterior portion of the calcaneus. The mean distances between all of the established palpable bony landmarks as well as the mean distances of each pin to structure measurement were calculated from the four independent measurements. The standard deviations between the four measurements of each distance were also calculated to assess inter/intra observer reliability. To combine data from all five specimens, an overall mean and standard deviation was calculated for each distance using the calculated mean distances from each specimen. Results In four out of the five specimens, the tendon of the peroneus longus muscle was impinged by pin 3. A calcaneal branch of the sural nerve was also impinged in one specimen by pin 5. The remaining pins; 1, 2, 4 and 6 did not impinge any structures in any of the specimens. Both the smallest mean distances obtained from individual specimens and the smallest combined mean measurements from all five specimens are given in table 1. It can be seen from this table, that pins 3 and 4 were the closest pins to anatomical structures and that pin 6 was the furthest away. This suggests that pins 3
7 and 4 pose the highest risk of injury to vulnerable anatomical structures and pin 6 poses the least risk of damage. Table 2 gives the mean measurements for each distance, which were calculated using four independent measurements from each specimen. A combined mean from all specimens as well as the 95% confidence interval and the standard deviation are also given for each distance. A traffic light labelling system is used to assess the danger of each pin of damaging each structure. Red is used to highlight structures that were impinged in any of the five specimens. Amber is used when the mean distance from all specimens between a pin and a structure is greater than 0 mm but less than or equal to 20.0 mm. Finally, green highlights structures that were a mean distance of 20.1 mm or greater away from each pin respectively. In some cases, certain structures were not visibly present on lines between each pin and the inferior tip of the lateral malleolus and the posterosuperior calcaneus and are labelled as N/A to show this. Larger standard deviations were observed in mean measurements from all specimens than those from individual specimens. This is likely to be due to variations between specimens, such as the individual s foot size. Large anatomical variation in the courses and distributions of structures, namely the sural nerve and the small saphenous vein may also have directly affected the increased spread of results for mean measurements. It can be deduced from table 2 that the pins which pose the greatest risk of neurological, vascular or tendinous damage are pins 3 and 4. There are no structures in relation to these pins that are highlighted as green, therefore all structures were present at a distance of 20.0 mm or less. This is to be expected however, as pins 3 and 4 are situated in the area of the calcaneus with the greatest density of structures vulnerable to damage. Pins which are placed both at the anterior and posterior margins of the calcaneus, pins 1 and 6, are the pins which were deemed to pose least risk of damage.
8 Figure 2 presents the combined results of the five specimens (as seen in table 2). Pins 3 and 4 are the closest pins to the subtalar joint and these are most closely related to structures that may well be injured. Discussion This study aimed to determine the risk of impingement upon anatomical structures when placing pins for the Orthofix Calcaneal Mini-Fixator. This was achieved by finding the smallest distances from each of the six pins to surrounding neurological, vascular and tendinous structures as they transected straight lines connecting each pin to two palpable bony landmarks. The results of this current study show that in five specimens inserted with six monoaxial pins, the tendon of the peroneus longus muscle was impinged in four out of the five specimens and a calcaneal branch of the sural nerve in one of the specimens. In clinical practice, a small incision is made over the subtalar joint and the tendons of peroneus longus and brevis are be retracted hence these tendons are not at risk [12]. The sural nerve is noticeably variable in its distribution [13,14,15]. Santi and Botte (1996) concluded in their study, which aimed to determine safe zones for wire insertion for external fixation, that the lateral calcaneal branches arising from the sural nerve were the structures most at risk of impingement by wires within the lateral calcaneus [7]. The calcaneal branches of the sural nerve supply exclusively sensory innervation to the lateral portion of the calcaneus and impingement of these branches would result in little clinical importance [16]. Painful neuroma formation does remain a possibility but this can be addressed surgically at a later sitting [17]. Percutaneous reduction and external fixation was used to treat 52 patients with closed articular displaced calcaneal fractures in a study by Magnan et al. (2006) [18]. For this study, the monoaxial Orthofix Mini-Fixator (series M300) was used. The authors reported an excellent Maryland foot score result in 26 out of 54 cases (48.1%). This score assesses pain, motion and stability, amongst other factors, of the foot post-operatively. Although a four-pin fixator was used in this study, no neurological, vascular or tendinous complications were reported.
9 A six pin Orthofix Calcaneal Mini-fixator was used in a study by Corina et al. (2014) [19]. This study aimed to demonstrate that use of the six pin Mini-fixator provides greater stability, better and more stable reduction and improved functional outcomes over the previous four pin series. Sixty-nine closed heel intra-articular displaced fractures were treated and an excellent score on the Maryland Foot Score was attained in 53.6% of interventions. There were no cases of hypoaesthesia of the sural nerve, however fifteen patients suffered algodystrophy. Whether this was caused by the initial trauma or as a consequence of surgery is unknown. The use of fine wire or monoaxial external fixation has been shown to result in minimal wound complications in comparison to ORIF. Benirschke et al. (1993) reported that following ORIF of the calcaneus in 80 patients, 16% experienced wound complications and deep infection was observed in two patients [20]. A wound complication rate of 25% was found in a study by Folk et al. (1999) in which 190 calcaneal fractures were treated with ORIF [21]. In comparison, a study by McGarvey et al. (2006) found that in 31 patients with 33 Sanders types II, III and IV fractures treated with external fixation, there was only one deep infection in a diabetic smoker [6]. Smoking however, is widely considered to be a risk factor for wound complications following calcaneal ORIF [22]. Despite this deep infection requiring secondary surgery, a considerably lower second-surgery rate was obtained than has been reported after ORIF. The results of our study in combination with the studies discussed above suggest that monoaxial external fixation of the calcaneus is a relatively safe method of reconstructing calcaneal fractures. The largest risk of damage to vulnerable structures appear to be via pins 3 and 4. Several limitations of this study are recognised. The cadaveric specimens used were embalmed in formalin. Fresh frozen cadavers would have provided a superior life-like representation of tissue in comparison. No female specimens were used and so it was not possible in this study to determine variations in measurements between male and female subjects. Furthermore, only five specimens within a narrow age range were investigated, a study which included a greater number of subjects,
10 within a wider age range, would perhaps provide more reproducible results. Larger standard deviations were observed with mean measurements in comparison to individual specimen measurements. This is likely to be due to a large variance in foot size used for the study in conjunction with a small number of specimens investigated; this is a noted limitation of the study. Cadaveric specimens that had no prior or existing calcaneal trauma were used in this study however, in subjects with trauma involving the calcaneus, the anatomical location of structures such as the sural nerve and small saphenous vein may become distorted. Additional study which further investigates the safety of monoaxial fixation of the calcaneus is advised. Studies which look at a greater number of both male and female specimens may be beneficial and help to delineate differences, if any, in anatomy between sexes. A study which perhaps investigates the safety of monoaxial pins inserted into specimens with existing trauma such as type II, III and IV Sander s type fractures of the calcaneus would help overcome the limitation of unpredictable anatomical variation that may occur after trauma, although it is understood that it may be difficult to obtain specimens to this specification. Despite these limitations, our results show that pins 3 and 4 pose a much greater risk of damage than the remaining pins. The use of a small incision centred over the subtalar joint combined with appropriate dissection and retraction eliminates the risk of injury to these tendons. Monoaxial external fixation of the calcaneus using the Orthofix Calcaneal Mini-Fixator appears to be a safe method of fixation of the calcaneus. Conclusions This study aimed to use cadaveric dissection to evaluate the risk of injury to anatomical structures with the use of monoaxial external fixation. The tendon of peroneus longus and the calcaneal branches of the sural nerve appear to be most at risk of impingement by monoaxial pins when a six pin approach is employed. However, as the tendons of the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis are retracted during surgery, these structures
11 will not be injured. Pins 3 and 4 should be inserted under direct vision to avoid pernennial tendon injury. The morphology of the calcaneal branches of the sural nerve were noticeably variable in the specimens studied. This therefore makes defining areas of the calcaneus which eliminate the risk of damage to these structures extremely difficult. Pin 5 can damage branches of the sural nerve but this is unlikely to be of great clinical significance given the limited distribution of these nerves.
12 Figure legends Figure 1: Photograph of one specimen showing the anatomical structures that were identified. The six monoaxial pins are also labelled, these are numbered in a clockwise fashion from pin 1 most anteriorly through to pin 6 most posteriorly. A = most inferior part of lateral malleolus; B = posterosuperior calcaneus. Figure 2: Scaled representation showing mean measurements from all five specimens from each of the six-monoaxial pins to the sural nerve, small saphenous vein and the tendons of the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis muscles. Structures are shown in relation to these pins as they transect lines from each pin to two palpable bony landmarks; the inferior tip of the lateral malleolus and the posterosuperior calcaneus.
13 Figure 1: Photograph of one specimen showing the anatomical structures that were identified. The six monoaxial pins are also labelled, these are numbered in a clockwise fashion from pin 1 most anteriorly through to pin 6 most posteriorly. A = most inferior part of lateral malleolus; B = posterosuperior calcaneus.
14 Table 1: Summary of Smallest Distances Measured Pin Smallest Mean Distances in any Specimen (structure: measurement ± S.D) (mm) Smallest Mean Distances from all Specimens (structure: measurement ± S.D) (mm) 1 TPL: 7.4 ± 0.9 SN: 16.3 ± TPL: 3.2 ± 0.2 SN: 8.3 ± SN: 1.6 ± 0.5 SSV: 8.2 ± SSV: 2.1 ± 0.3 SSV: 6.0 ± SSV: 8.6 ± 0.9 SN: 33.0 ± SN: 11.7 ± 0.4 SSV: 41.0 ± 4.0 TPL = tendon of the peroneus longus muscle; SN = sural nerve; SSV = small saphenous vein.
15 Table 2: Combined Monoaxial Measurements from all Five Specimens
16 Figure 2: Scaled representation showing mean measurements from all five specimens from each of the six monoaxial pins to the sural nerve, small saphenous vein and the tendons of the peroneus longus and peroneus brevis muscles. Structures are shown in relation to these pins as they transect lines from each pin to two palpable bony landmarks; the inferior tip of the lateral malleolus and the posterosuperior calcaneus.
17 References [1] Mitchell MJ, McKinley JC, Robinson CM. The epidemiology of calcaneal fractures. Foot 2009 Dec; 19(4): [2] Al-Ashhab MEA. ORIF for displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures in children. Foot 2015;25(2): [3] De Boer AS, Van Lieshout EMM, Den Hartog D, Weerts B, Verhofstad MHJ, Schepers T. Functional outcome and patient satisfaction after displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a comparison among open, percutaneous, and nonoperative treatment. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2015;54(3): [4] Yu G, Zhao H, Yang Y, Zhou J, Li H. Open reduction and internal fixation of intra-articular calcaneal fractures in children. Orthopedics 2012;35(6): [5] Zgonis T, Roukis TS, Polyzois VD. The use of Ilizarov technique and other types of external fixation for the treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Clin Podiatr Med Surg. 2006; 23(2): [6] McGarvey WC, Burris MW, Clanton TO, Melissinos EG. Calcaneal fractures: indirect reduction and external fixation. Foot Ankle Int. 2006;27(7): [7] Santi MD, Botte MJ. External fixation of the calcaneus and talus: an anatomical study for safe pin insertion. J Orthop Trauma 1996;10(7): [8] Langdon IJ, Harling R, Atkins RM, Nicholson H. A cadaveric study of the medial relations of the calcaneum. Foot Ankle Surg. 2000;6(3): [9] Casey D, McConnell T, Parekh S, Tornetta P. Percutaneous pin placement in the medial calcaneus: is anywhere safe? J Orthop Trauma 2002;16(1): 26-9.
18 [10] Rammelt S, Dürr C, Schneiders W, Zwipp H. Minimally invasive fixation of calcaneal fractures. Oper Orthop Traumatol 2012;24(4-5): [11] Orthofix. Orthofix Calcaneal External Fixator [Internet]. [place unknown]. Orthofix; 2010 Aug [cited 2015 Dec 21]. 9 p. Available from: E0%20OT%20Calcaneal%20Fixator.pdf. [12] Hoppenfeld S, Deboer P, Buckley R. Surgical Exposures in Orthopaedics: The Anatomic Approach. 4th rev. ed. USA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; p. [13] Apaydin N, Bozkurt M, Loukas M, Vefali H, Tubbs RS, Esmer AF. Relationships of the sural nerve with the calcaneal tendon: an anatomical study with surgical and clinical implications. Surg Radiol Anat 2009;31(10): [14] Kavyashree AN, Subhash LP, Asha KR, Bindu Rani MK. Anatomical variations in formation of sural nerve in adult Indian cadavers. J Clin Diagn Res 2013;7(9): [15] Seema SR. Study of sural nerve complex in human cadavers. ISRN Anat. 2013; Article ID [16] Aktan Ikiz ZA, Uçerler H, Bilge O. The anatomic features of the sural nerve with an emphasis on its clinical importance. Foot Ankle Int 2005;26(7): [17] Plotkin D, Patel D, Roberto T. Heel neuroma: a case study. J Foot Ankle Surg 2009;48(3): [18] Magnan B, Bortolazzi R, Marangon A, Marino M, Dall Oca C, Bartolozzi P. External fixation for displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum. J Bone Joint Surg Br 2006;88(11):
19 [19] Corina G, Mori C, Vicenti G, Galante VN, Conserva V, Speciale D, et al. Heel displaced intra-articular fractures treated with mini-calcaneal external fixator. Injury 2014;45 Suppl 6:S [20] Benirschke SK, Sangeorzan BJ. Extensive intraarticular fractures of the foot. Surgical management of calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1993;292: [21] Folk JW, Starr AJ, Early JS. Early wound complications of operative treatment of calcaneus fractures: analysis of 190 fractures. J Orthop Trauma 1999;13(5): [22] Abidi NA, Dhawan S, Gruen GS, Vogt MT, Conti SF. Wound-healing risk factors after open reduction and internal fixation of calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Int 1998;19(12):
This is the author s final accepted version.
 Esparon, T., Thomson, C. M., Rea, P. M. and Jamal, B. (2016) Circular frame fixation for calcaneal fractures risks injury to the medial neurovascular structures: a cadaveric description. Injury, 47(12),
Esparon, T., Thomson, C. M., Rea, P. M. and Jamal, B. (2016) Circular frame fixation for calcaneal fractures risks injury to the medial neurovascular structures: a cadaveric description. Injury, 47(12),
Session II 11:30 11:45 am. Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio. Disclosure: (n)
 Session II 11:30 11:45 am Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure: (n) Wound Complications after ORIF of Calcaneus Fractures and How to Prevent Them
Session II 11:30 11:45 am Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure: (n) Wound Complications after ORIF of Calcaneus Fractures and How to Prevent Them
Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures
 Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures Gao Di, Zhang Yong, Li Zheng Lin, Jia Bin, Zheng Jie Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedics and Traumatology Hospital My disclosure
Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures Gao Di, Zhang Yong, Li Zheng Lin, Jia Bin, Zheng Jie Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedics and Traumatology Hospital My disclosure
The myofascial compartments of the foot
 The myofascial compartments of the foot A CADAVER STUDY Z. X. Ling, V. P. Kumar From the National University of Singapore, Republic of Singapore Compartment syndrome of the foot requires urgent surgical
The myofascial compartments of the foot A CADAVER STUDY Z. X. Ling, V. P. Kumar From the National University of Singapore, Republic of Singapore Compartment syndrome of the foot requires urgent surgical
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks
 Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Posterior Malleolus Fractures and Iatrogenic Injuries: A Cadaveric Study
 Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Posterior Malleolus Fractures and Iatrogenic Injuries: A Cadaveric Study JOHN KARBASSI, MD, MPH ANDREW BRAZIEL, MD MICHAEL HEFFERNAN, MD ABHAY PATEL, MD UNIVERSITY OF
Open Reduction Internal Fixation of Posterior Malleolus Fractures and Iatrogenic Injuries: A Cadaveric Study JOHN KARBASSI, MD, MPH ANDREW BRAZIEL, MD MICHAEL HEFFERNAN, MD ABHAY PATEL, MD UNIVERSITY OF
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures. Kali Luker, PGY-1
 Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Anatomic Structures at Risk When Utilizing an Intramedullary Nail for Distal Fibular Fractures: A Cadaveric Study.
 Anatomic Structures at Risk When Utilizing an Intramedullary Nail for Distal Fibular Fractures: A Cadaveric Study. David A. Goss, Jr., DO Christopher W. Reb, DO Terrence M. Philbin, DO David A. Goss, Jr.,
Anatomic Structures at Risk When Utilizing an Intramedullary Nail for Distal Fibular Fractures: A Cadaveric Study. David A. Goss, Jr., DO Christopher W. Reb, DO Terrence M. Philbin, DO David A. Goss, Jr.,
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System
 Surgical Technique Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Endoscopic Plantar Fascia Release EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Arthrex has developed a comprehensive, completely disposable
Surgical Technique Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Endoscopic Plantar Fascia Release EndoBlade Soft Tissue Release System Endoscopic Gastroc Recession Arthrex has developed a comprehensive, completely disposable
Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study
 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1811.001 Risk of Axillary Nerve Injury in Standard Anterolateral Approach of Shoulder: Cadaveric Study Kongcharoensombat W, MD, Wattananon P, MD Department of Orthopaedics,
Anatomy MCQs Week 13
 Anatomy MCQs Week 13 1. Posterior to the medial malleolus of the ankle: The neurovascular bundle lies between Tibialis Posterior and Flexor Digitorum Longus The tendon of Tibialis Posterior inserts into
Anatomy MCQs Week 13 1. Posterior to the medial malleolus of the ankle: The neurovascular bundle lies between Tibialis Posterior and Flexor Digitorum Longus The tendon of Tibialis Posterior inserts into
Complication Rate and Pitfalls of Temporary Bridging External Fixator in Periarticular Communited Fractures
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:62-68 doi:10.4055/cios.2011.3.1.62 Complication Rate and Pitfalls of Temporary Bridging External Fixator in Periarticular Communited Fractures Jong-Keon
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:62-68 doi:10.4055/cios.2011.3.1.62 Complication Rate and Pitfalls of Temporary Bridging External Fixator in Periarticular Communited Fractures Jong-Keon
Anatomical Considerations Regarding the Posterior Interosseous Nerve During Posterolateral Approaches to the Proximal Part of the Radius *
 Anatomical Considerations Regarding the Posterior Interosseous Nerve During Posterolateral Approaches to the Proximal Part of the Radius * BY THOMAS DILIBERTI, M.D., MICHAEL J. BOTTE, M.D., AND REID A.
Anatomical Considerations Regarding the Posterior Interosseous Nerve During Posterolateral Approaches to the Proximal Part of the Radius * BY THOMAS DILIBERTI, M.D., MICHAEL J. BOTTE, M.D., AND REID A.
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision
 Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 04 Page April 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.23 Sinus tarsi approach for displaced, Intra-articular Calcaneal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.23 Sinus tarsi approach for displaced, Intra-articular Calcaneal
Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(8):12372-12376 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0052574 Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator Binbin Li, Wen Chen, Taifang Gong,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(8):12372-12376 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0052574 Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator Binbin Li, Wen Chen, Taifang Gong,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Osteochondral talar lesions and ankle biomechanics Zengerink, M. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Osteochondral talar lesions and ankle biomechanics Zengerink, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Zengerink, M. (2017). Osteochondral talar
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Osteochondral talar lesions and ankle biomechanics Zengerink, M. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Zengerink, M. (2017). Osteochondral talar
SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY
 Página 1 de 9 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "47 - ANKLE FRACTURES"
Página 1 de 9 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "47 - ANKLE FRACTURES"
Lateral femoral traction pin entry: risk to the. femoral artery and other medial neurovascular structures
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lateral femoral traction pin entry: risk to the femoral artery and other medial neurovascular structures John Y Kwon 1*, Catherine E Johnson 1, Paul Appleton 2, Edward K Rodriguez
RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lateral femoral traction pin entry: risk to the femoral artery and other medial neurovascular structures John Y Kwon 1*, Catherine E Johnson 1, Paul Appleton 2, Edward K Rodriguez
Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture Dislocation Injuries
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 928938, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928938 Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 928938, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928938 Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):18033-18039 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021277 Original Article Minimally invasive reduction of the medial wall shortening and misalignment in calcaneal fractures with
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):18033-18039 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021277 Original Article Minimally invasive reduction of the medial wall shortening and misalignment in calcaneal fractures with
Open Treatment and Internal Fixation of Displaced Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures in High-Risk Patients Utilizing the Sinus Tarsi Approach
 Open Treatment and Internal Fixation of Displaced Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures in High-Risk Patients Utilizing the Sinus Tarsi Approach W. Bret Smith, DO Steve Steinlauf, MD Greg E. Gaski, MD Disclosure
Open Treatment and Internal Fixation of Displaced Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures in High-Risk Patients Utilizing the Sinus Tarsi Approach W. Bret Smith, DO Steve Steinlauf, MD Greg E. Gaski, MD Disclosure
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Original article Journal of International Medicine and Dentistry 2014; 1 (1): 10-18
 Original article JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share ISSN 2350-045X Study of variations in medial sural cutaneous nerve, lateral sural cutaneous nerve and peroneal
Original article JOURNAL OF INTERNATIONAL MEDICINE AND DENTISTRY To search..to know...to share ISSN 2350-045X Study of variations in medial sural cutaneous nerve, lateral sural cutaneous nerve and peroneal
Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot)
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2007) 2:105 110 DOI 10.1007/s11751-007-0023-7 REVIEW Safe corridors in external fixation: the lower leg (tibia, fibula, hindfoot and forefoot) Selvadurai Nayagam Received: 9 August
FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]
![FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test] FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]](/thumbs/83/88335212.jpg) FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
ORIGINAL ARTICLE DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS
 DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS Peddi Manjunath 1, Ramesha K.T 2, Smitha S Segu 3, Jainath 4, Shankarappa M 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Peddi Manjunath, Ramesha KT, Smitha
DISTALLY BASED PERONEUS BREVIS MUSCLE FLAP FOR DISTAL LEG DEFECTS Peddi Manjunath 1, Ramesha K.T 2, Smitha S Segu 3, Jainath 4, Shankarappa M 5 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Peddi Manjunath, Ramesha KT, Smitha
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture
 Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture Sunghwan Byun, DPM, PGY-4 St. Luke s Hospital, Allentown, PA Sangbong Ko, MD Department of Orthopedic
Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture Sunghwan Byun, DPM, PGY-4 St. Luke s Hospital, Allentown, PA Sangbong Ko, MD Department of Orthopedic
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation *
 Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique. Description of Plate
 Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
Determination and classification of cutaneous innervation of dorsum of the foot in fetal cadavers
 Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is a provisional PDF only. Copyedited and fully formatted version will be made available soon. ONLINE FIRST ISSN: 0015-5659 e-issn: 1644-3284 Determination and classification
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org) This is a provisional PDF only. Copyedited and fully formatted version will be made available soon. ONLINE FIRST ISSN: 0015-5659 e-issn: 1644-3284 Determination and classification
Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials
 British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published September 3, 2009 Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials Nikolaos Gougoulias, Anil Khanna, Donald J. McBride, and Nicola
British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published September 3, 2009 Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials Nikolaos Gougoulias, Anil Khanna, Donald J. McBride, and Nicola
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular
 Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures T. Schepers, I.B. Schipper, L.M.M. Vogels, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, M.J. Heetveld, P. Patka J Orthop Sci 2007;12(1):22-27 Abstract
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures T. Schepers, I.B. Schipper, L.M.M. Vogels, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, M.J. Heetveld, P. Patka J Orthop Sci 2007;12(1):22-27 Abstract
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular. calcaneal fractures
 Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Percutaneous calcaneal fracture surgery T. Schepers 1, I.B. Schipper 1, L.M.M. Vogels 1, A.Z. Ginai 2, P.G.H. Mulder 3, M.J. Heetveld
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Percutaneous calcaneal fracture surgery T. Schepers 1, I.B. Schipper 1, L.M.M. Vogels 1, A.Z. Ginai 2, P.G.H. Mulder 3, M.J. Heetveld
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:22 27 DOI 10.1007/s00776-006-1076-z Original article Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Tim Schepers 1, Inger B. Schipper 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels
J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:22 27 DOI 10.1007/s00776-006-1076-z Original article Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Tim Schepers 1, Inger B. Schipper 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels
Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Introduction. Introduction 10/2/2009. Bryan Lapinski, MD
 Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Bryan Lapinski, MD Introduction The average person takes 1 million steps per year Approximately 30 bones in the foot and ankle are subjected to forces of 3 7 times body weight
Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Bryan Lapinski, MD Introduction The average person takes 1 million steps per year Approximately 30 bones in the foot and ankle are subjected to forces of 3 7 times body weight
Arthroscopy Of the Ankle.
 Arthroscopy Of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Arthroscopy Anatomy Patient setup Portal placement Procedures Complications Anatomy Portals Anterior Anteromedial Anterolateral Anterocentral Posterior
Arthroscopy Of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Arthroscopy Anatomy Patient setup Portal placement Procedures Complications Anatomy Portals Anterior Anteromedial Anterolateral Anterocentral Posterior
Case Report The Utility and Limitations of the Transfibular Approach in Ankle Trauma Surgery
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 234369, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/234369 Case Report The Utility and Limitations of the Transfibular Approach in Ankle Trauma Surgery Mustafa Yassin,
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 234369, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/234369 Case Report The Utility and Limitations of the Transfibular Approach in Ankle Trauma Surgery Mustafa Yassin,
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile?
 28th Pak Orthocon 2014 S-161 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile? Syed Furqan Gilani, 1 Muhammad Suhail Amin 2 Abstract Objective:
28th Pak Orthocon 2014 S-161 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile? Syed Furqan Gilani, 1 Muhammad Suhail Amin 2 Abstract Objective:
Midfoot - Reduction & Fixation - ORIF - screw fixation - AO Surgery Reference. ORIF - screw fixation
 Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
Midfoot - TMT (Lisfranc) injury 1. Diagnosis ORIF - screw fixation Authors Mechanism of the injury Tarso-metatarsal (Lisfranc) injuries may be caused by direct or indirect forces. Direct forces include
موسى صالح عبد الرحمن الحنبلي أحمد سلمان
 8 موسى صالح عبد الرحمن الحنبلي أحمد سلمان 1 P a g e Today we will talk about a new region, which is the leg. And as always, we will start with studying the sensory innervation of the leg. What is the importance
8 موسى صالح عبد الرحمن الحنبلي أحمد سلمان 1 P a g e Today we will talk about a new region, which is the leg. And as always, we will start with studying the sensory innervation of the leg. What is the importance
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
Versatility of Reverse Sural Artery Flap for Heel Reconstruction
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Introduction: The heel has two parts, weight bearing and non-weight bearing part. Soft tissue heel reconstruction has been a challenge due to its complex nature of anatomy, weight bearing
Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):144-8 Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures V Jain, R Kumar, DK Mandal Department of Orthopaedics, Lady Harding Medical College and Associated
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):144-8 Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures V Jain, R Kumar, DK Mandal Department of Orthopaedics, Lady Harding Medical College and Associated
Peggers Super Summaries: Foot Injuries
 Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG
 Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum
 JFAS JFAs (AP) How I Do It Minimally Invasive 10.5005/jp-journals-10040-1047 Management of Fracture Calcaneum Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum 1 Mandeep S Dhillon, 2 Sharad Prabhakar,
JFAS JFAs (AP) How I Do It Minimally Invasive 10.5005/jp-journals-10040-1047 Management of Fracture Calcaneum Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum 1 Mandeep S Dhillon, 2 Sharad Prabhakar,
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
The course of the superficial peroneal nerve in relation to the ankle position: anatomical study with ankle arthroscopic implications
 Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2010) 18:612 617 DOI 10.1007/s00167-010-1099-z ANKLE The course of the superficial peroneal nerve in relation to the ankle position: anatomical study with ankle arthroscopic
Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc (2010) 18:612 617 DOI 10.1007/s00167-010-1099-z ANKLE The course of the superficial peroneal nerve in relation to the ankle position: anatomical study with ankle arthroscopic
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique
 Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Surgical Technique Percutaneous Pinning Percutaneous Humeral Fracture Repair Closed reduction followed by percutaneous fixation reduces risk from soft tissue dissection
Safe Zone for the Plantar Portal: A Cadaveric Study
 Safe Zone for the Plantar Portal: A Cadaveric Study Shingo Maeda, Takaaki Hirano, Yui Akiyama, Hiroyuki Mitsui, Wataru Endo,Hisateru Niki Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Marianna University School
Safe Zone for the Plantar Portal: A Cadaveric Study Shingo Maeda, Takaaki Hirano, Yui Akiyama, Hiroyuki Mitsui, Wataru Endo,Hisateru Niki Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, St. Marianna University School
Leg. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
The Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System
 Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System VALUE ANALYSIS BRIEF Value Summary Calcaneal fractures are the most common fracture of the hindfoot, demanding individualized treatment. The Variable Angle
Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System VALUE ANALYSIS BRIEF Value Summary Calcaneal fractures are the most common fracture of the hindfoot, demanding individualized treatment. The Variable Angle
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
Thomas Zgonis a, *, Douglas T. Cromack b, Thomas S. Roukis c, Joann Orphanos d, Vasilios D. Polyzois e CASE REPORT. Introduction.
 Injury Extra (2007) 38, 187 192 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Severe degloving injury of the sole and heel treated by a reverse flow sural artery neurofasciocutaneous flap and a modified off-loading
Injury Extra (2007) 38, 187 192 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Severe degloving injury of the sole and heel treated by a reverse flow sural artery neurofasciocutaneous flap and a modified off-loading
Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures
 FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
Yanling Su, Wei Chen, Tao Zhang, Xingwang Wu, Zhanpo Wu and Yingze Zhang *
 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:40 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bohler s angle s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal
Su et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:40 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bohler s angle s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal
The plantar aponeurosis
 Anatomy of the foot The plantar aponeurosis Is a triangular thickening of the deep fascia Its apex is attached to the medial and lateral tubercles of the calcaneum. The base of the aponeurosis divides
Anatomy of the foot The plantar aponeurosis Is a triangular thickening of the deep fascia Its apex is attached to the medial and lateral tubercles of the calcaneum. The base of the aponeurosis divides
Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(11):15782-15788 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0065292 Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(11):15782-15788 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0065292 Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
Technical Tip: A Simple Method for Proper Placement of an Intramedullary Nail Entry Point for Tibiotalocalcaneal or Tibiocalcaneal Arthrodesis
 Open Access Publication Technical Tip: A Simple Method for Proper Placement of an Intramedullary Nail Entry Point for Tibiotalocalcaneal or Tibiocalcaneal Arthrodesis by Ronald Belczyk, DPM 1, Wenjay Sung,
Open Access Publication Technical Tip: A Simple Method for Proper Placement of an Intramedullary Nail Entry Point for Tibiotalocalcaneal or Tibiocalcaneal Arthrodesis by Ronald Belczyk, DPM 1, Wenjay Sung,
A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 26, 82, 779-786 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children Di Lu, Shao-Yu Zhu, Jie Yang, Hua
Acta Orthop. Belg., 26, 82, 779-786 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children Di Lu, Shao-Yu Zhu, Jie Yang, Hua
AN ANATOMICAL STUDY OF MORPHOLOGY AND MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF CALCANEUM AND ITS TALAR ARTICULAR SURFACES
 Original Research Article AN ANATOMICAL STUDY OF MORPHOLOGY AND MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF CALCANEUM AND ITS TALAR ARTICULAR SURFACES Anbumani T L *, Sridharan R 2, Thamarai Selvi A 3. ABSTRACT Background
Original Research Article AN ANATOMICAL STUDY OF MORPHOLOGY AND MORPHOMETRIC ANALYSIS OF CALCANEUM AND ITS TALAR ARTICULAR SURFACES Anbumani T L *, Sridharan R 2, Thamarai Selvi A 3. ABSTRACT Background
Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available evidence
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:36 41 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0160-2 EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Bondì R. Padua L. Bondì A. Battaglia E. Romanini A. Campi Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:36 41 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0160-2 EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Bondì R. Padua L. Bondì A. Battaglia E. Romanini A. Campi Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available
Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 614 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2013, 7, 614-618 Open Access Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss Chad G. Williams,
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 614 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2013, 7, 614-618 Open Access Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss Chad G. Williams,
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-011-1223-9 REVIEW The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review Tim Schepers Received: 1 December 2010 / Accepted: 20 January 2011 #
DOI 10.1007/s00264-011-1223-9 REVIEW The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review Tim Schepers Received: 1 December 2010 / Accepted: 20 January 2011 #
Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture: an anatomical specimen study
 Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:78 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0580-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture:
Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:78 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0580-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture:
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY 3. TALRSALS = (FOOT BONES) Fibula. Frances Daly MSc 1 CALCANEUS 2. TALUS 3. NAVICULAR 4. CUBOID 5.
 ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate
 wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e Tornier WAVE Calcaneal fracture plate system surgical procedure Indications for Use: The Tornier Calcaneal Fracture Plate System is indicated
wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e Tornier WAVE Calcaneal fracture plate system surgical procedure Indications for Use: The Tornier Calcaneal Fracture Plate System is indicated
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Talex
 S U B TA L A R S TA B I L I Z AT I O N SY S T E M SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Talex S U B TA L A R S TA B I L I Z AT I O N SY S T E M Design Rationale The Talex Subtalar Stabilization System is the latest advancement
S U B TA L A R S TA B I L I Z AT I O N SY S T E M SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Talex S U B TA L A R S TA B I L I Z AT I O N SY S T E M Design Rationale The Talex Subtalar Stabilization System is the latest advancement
Superficial peroneal nerve (ISPN) is at risk During all inside arthroscopic brostrom procedures.
 Superficial peroneal nerve (ISPN) is at risk During all inside arthroscopic brostrom procedures. Jae Hyuck Choi,M.D.,Kyung-tai Lee,M.D., Yeon soo Lee.PhD., Young koo Lee,M.D., Eui-Dong Yeo, M.D., Jaymes
Superficial peroneal nerve (ISPN) is at risk During all inside arthroscopic brostrom procedures. Jae Hyuck Choi,M.D.,Kyung-tai Lee,M.D., Yeon soo Lee.PhD., Young koo Lee,M.D., Eui-Dong Yeo, M.D., Jaymes
Bio-Tenodesis Screw Fixation
 Bio-Tenodesis Screw Fixation in Tendon Enhanced Ankle Ligament Reconstruction Surgical Technique Kevin O'Shea, M.D. with contributions from Thomas Clanton, M.D., and William McGarvey, M.D. Bio-Tenodesis
Bio-Tenodesis Screw Fixation in Tendon Enhanced Ankle Ligament Reconstruction Surgical Technique Kevin O'Shea, M.D. with contributions from Thomas Clanton, M.D., and William McGarvey, M.D. Bio-Tenodesis
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D
 Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Accepted: 3 April 2009
 Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
We investigated a new method of stress
 SUBTALAR STRESS RADIOGRAPHY USING FORCED DORSIFLEXION AND SUPINATION TOMOO ISHII, SHUMPEI MIYAGAWA, TORU FUKUBAYASHI, KOICHIRO HAYASHI From the University of Tsukuba, Japan We investigated a new method
SUBTALAR STRESS RADIOGRAPHY USING FORCED DORSIFLEXION AND SUPINATION TOMOO ISHII, SHUMPEI MIYAGAWA, TORU FUKUBAYASHI, KOICHIRO HAYASHI From the University of Tsukuba, Japan We investigated a new method
Talus Fractures: When and Why on Screws and Plates
 Talus Fractures: When and Why on Screws and Plates Frank A. Liporace, MD Associate Professor Director of Orthopaedic Research New York University / Hospital for Joint Diseases, NY, NY Director Orthopaedic
Talus Fractures: When and Why on Screws and Plates Frank A. Liporace, MD Associate Professor Director of Orthopaedic Research New York University / Hospital for Joint Diseases, NY, NY Director Orthopaedic
STS. Subtalar Spacer System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 STS Subtalar Spacer System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 4 Introduction 4 Device Description Chapter 2 5 Intended Use 5 Indications Chapter 3 6 Surgical Technique 9 Postoperative Protocol 9 Explant
STS Subtalar Spacer System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 4 Introduction 4 Device Description Chapter 2 5 Intended Use 5 Indications Chapter 3 6 Surgical Technique 9 Postoperative Protocol 9 Explant
Pilon fractures. Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota
 Pilon fractures Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota Disclosures Reviewer Foot and Ankle International Journal of the American Academy of
Pilon fractures Pat Yoon, MD Minneapolis Veterans Affairs Medical Center Associate Professor, University of Minnesota Disclosures Reviewer Foot and Ankle International Journal of the American Academy of
Surgical Technique. Calcaneal Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Calcaneal Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Calcaneal Locking Plate Surgical TechniqueCatalog Infor Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Surgical Technique Calcaneal Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Calcaneal Locking Plate Surgical TechniqueCatalog Infor Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
حسام أبو عوض. - Ahmad. 1 P a g e
 - 9 حسام أبو عوض - - Ahmad 1 P a g e In the last lecture, we finished discussing the superficial part of the posterior compartment and the popliteus muscle of the deep layer[reminder: The entire posterior
- 9 حسام أبو عوض - - Ahmad 1 P a g e In the last lecture, we finished discussing the superficial part of the posterior compartment and the popliteus muscle of the deep layer[reminder: The entire posterior
CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS
 CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Fix single column or both: Always fix both. A study by Svend-Hansen corroborated the poor results associated with isolated medial malleolar fixation in bimalleolar ankle fractures.
CURRENT TREATMENT OPTIONS Fix single column or both: Always fix both. A study by Svend-Hansen corroborated the poor results associated with isolated medial malleolar fixation in bimalleolar ankle fractures.
MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL
 C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
C H A P T E R 2 1 MULTIPLE APPLICATIONS OF THE MINIRAIL Thomas J. Merrill, DPM James M. Losito, DPM Mario Cala, DPM Victor Herrera, DPM Alan E. Sotelo, DPM INTRODUCTION The unilateral MiniRail External
Alan Cooney Northern Deanery Registrar Teaching June 2011
 Alan Cooney Northern Deanery Registrar Teaching June 2011 Introduction Anatomy Classification Surgical approaches What is the evidence? What are pilon fractures? Intra-articular # distal tibia Pilon (pestle)
Alan Cooney Northern Deanery Registrar Teaching June 2011 Introduction Anatomy Classification Surgical approaches What is the evidence? What are pilon fractures? Intra-articular # distal tibia Pilon (pestle)
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and
 Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2014), PP 100-107 Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures. (Dr.
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2014), PP 100-107 Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures. (Dr.
Technique for Single-Graft Lateral Ankle Stabilization: A Cadaveric Biomechanical Study
 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Technique for Single-Graft Lateral Ankle Stabilization: A Cadaveric Biomechanical Study by Craig E Clifford,
The Foot and Ankle Online Journal Official publication of the International Foot & Ankle Foundation Technique for Single-Graft Lateral Ankle Stabilization: A Cadaveric Biomechanical Study by Craig E Clifford,
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
Injuries to the Hands and Feet
 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
radiologymasterclass.co.uk
 http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures:
 Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Minimally Invasive Plating of Fractures: Advantages, Techniques and Trade-offs Matthew Garner, MD Created January 2016 OUTLINE Principles of fracture management The importance of vascular supply Equipment
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. Using pin clamps with outrigger posts.
 Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. Using pin clamps with outrigger posts. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. Using pin clamps with outrigger posts. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
