Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular
|
|
|
- George Palmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Percutaneous treatment of displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures T. Schepers, I.B. Schipper, L.M.M. Vogels, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, M.J. Heetveld, P. Patka J Orthop Sci 2007;12(1):22-27
2 Abstract Background The outcome after displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures is influenced by the condition of the surrounding soft tissues. To avoid secondary soft tissue complications after surgical treatment, several less-invasive procedures for reduction and fixation have been introduced. The percutaneous technique according to Forgon and Zadravecz is suitable for all types of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures and was therefore introduced in our clinic. The aim of this study was to evaluate the long-term outcome of percutaneous treatment according to Forgon and Zadravecz in patients with displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Methods A cohort of patients with displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures treated with percutaneous surgery was retrospectively defined. Clinical outcome was evaluated by standardized physical examination, radiographs, three published outcome scores, and a visual analogue scale of patient satisfaction. Results Fifty patients with 61 calcaneal fractures were included. After a mean follow-up period of 35 months, the mean values of the Maryland foot score, the Creighton- Nebraska score, and the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score were 79, 76, and 83 points out of 100, respectively. The average visual analogue scale was 7.2 points out of 10. The average range of motion of the ankle joint was 90% of normal and subtalar joint movements were almost 70% compared with the healthy side or normal values. Superficial wound complications occurred in seven cases (11%) and deep infections in two (3%). A secondary arthrodesis of the subtalar joint was performed in five patients and was scheduled in four patients (15%). Conclusions Compared with the outcome of historic controls from randomized trials and metaanalyses, this study indicates favourable results for the percutaneous technique compared with the open technique. Despite similar rates of postoperative infection and secondary arthrodesis, the total outcome scores and preserved subtalar motion are overall good to excellent.
3 Introduction Owing to their complexity and the diverse treatment options, displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures remain a therapeutic challenge. The clinical evidence supporting operative treatment for selected patient groups is limited, whereas long-term complications and adverse outcomes are frequently documented. 1-3 One of the adverse effects of operative treatment is secondary damage to soft tissues after extensive surgical procedures. To avoid soft tissue complications, several lessinvasive procedures have been introduced. The most frequently used minimally invasive technique for the tongue-type fracture was proposed by Westhues in 1935, modified by Gissane, and propagated by Essex-Lopresti. 4 In 1983 Forgon and Zadravecz introduced a new minimally invasive technique using an external distractor applied percutaneously, followed by percutaneous fixation. 5,6 This technique applies the principle of distraction reduction (ligamentotaxis) of the fracture fragments and is suitable for all types of intra-articular fractures. 7 The aim of this study was to evaluate the long-term outcome of percutaneous treatment according to Forgon and Zadravecz in patients with displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Patients and methods Patient selection A study cohort was retrospectively defined to include all patients with displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures treated according to Forgon and Zadravecz 5,6 over a 5- year period at our institution. Approval for the study was obtained from the Institutional Reviewing Board (IRB). Patients who died (n = 2), had a spinalcord lesion (n = 1), moved to a foreign country (n = 4), or whose addresses were unknown (n = 5) were excluded. After a follow-up period of at least 12 months (mean 35 months, range months), patients were interviewed after informed consent was given and were evaluated for their functional outcome. Patients who had undergone secondary subtalar arthrodesis in the follow-up period were considered to have had a poor outcome for the primary surgery. Surgical procedure Surgical treatment according to the technique described by Forgon and Zadravecz 5,6 with three minor modifications was carried out by three staff trauma surgeons. The patient was placed in the prone position and received spinal analgesia and antibiotic
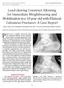
4 prophylaxis prior to the operation. Two fluoroscopes were installed to provide imaging in two orthogonal planes. Three 3-mm Kirschner wires were inserted from the lateral side through the calcaneal tuberosity, the cuboid, and the talar neck. The first modification concerned the placement of the distractors. These were positioned on both sides of the foot between the tuberosity of the calcaneus and talus and between the tuberosity and cuboid. Zadravecz et al. placed the latter between the cuboid and talus (Figure 1). Through the distracting force generated between the three pins, the tuber angle of Böhler can be restored. The second modification concerned the insertion of a blunt drifter introduced from the plantar side to unlock and push up any remaining depressed parts of the subtalar joint surface of the calcaneus; Forgon and colleagues used pin leveraging from the lateral side to manipulate these fragments. The third modification was the discarding of the Böhler bone press to reduce the width of the fractured calcaneus. When an acceptable reduction was achieved, two Kirschner wires or two cancellous screws were inserted from the posterior aspect of the tuberosity. If necessary, a third screw was inserted from the lateral side of the calcaneus toward the sustentaculum tali to reduce bulging of the lateral wall. Postoperatively, patients remained non-weight-bearing for 3 months. Figure 1. a Medial and lateral distractor in place during percutaneous surgery. b Fluoroscopic image showing the distractor and the osseous structures of the foot. The white arrows show the three Kirschner wires for distraction in the calcaneal tuberositas, the talus, and the cuboid. The black solid arrow shows a Kirschner wire inserted posteriorly for fixation. The black dotted arrow shows the contralateral foot in which the calcaneal fracture has already been distracted and fixated with two Kirschner wires Functional outcome
5 Patients completed three questionnaires: the Maryland foot score (MFS), the Creighton-Nebraska (CN) score, and the American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society (AOFAS) hindfoot score A modified visual analogue scale (VAS) was used to measure patient satisfaction on a scale of Patients with a bilateral fracture completed the questionnaire for the foot with the most complaints and functional disability. 6 For the purposes of comparison, the AOFAS scores were divided into the same groups used for the MFS: a score of was graded as an excellent result; as good; as fair, and less than 49 points was graded as a failure. 11,12 This differed slightly from the CN score, in which an excellent score is ; good is 80 89; fair is 65 79, and poor is a score of less than 64 points. 8 Physical examination Physical assessments (walking ability on heels and toes, heel width, calf circumference, stability and alignment of the heel) were performed in the outpatient clinic by the investigator (TS). The ranges of motion of the ankle and the subtalar joint were measured according to the Association for Osteosynthesis (AO) neutral zero method. The subtalar range of motion was measured with patients sitting on their knees to measure only the subtalar joint motion. 13 In patients with unilateral fractures, these measurements were compared with the values of the uninjured foot and ankle. In patients with bilateral fractures, standard normal values according to McMaster were used (inversion of 25 and 5 of eversion). 14 The mean normal sagittal (flexion and extension) range of motion of the ankle joint was set at Radiographic data The preoperative radiographs and computed tomography (CT) scans were classifi ed according to the classifications of Essex-Lopresti and Sanders, respectively, the latter without the use of subclasses. 10,15 Immediately after the operation, radiographs in the lateral and axial plane were obtained to show the status of fracture reduction. At the time of inclusion in this study additional weight-bearing lateral, axial, and 45 inverted foot (Anthonson) views of the calcaneocuboid joint were obtained for both feet. The angles of Böhler and Gissane on preoperative and immediate postoperative radiographs were compared with the follow-up values and with normal values in patients with a unilateral fracture. 15,16 The length, height, and width of the calcaneus were measured on the radiographs. The Zwipp score was used, in which the osteoarthrosis of the ankle joint, subtalar joint, and the calcaneocuboid joint, together with the difference in the Böhler s angle were scored. 17,18 A radiographic score of less
6 than 6 points was considered a poor result, 7 8 points fair, 9 10 a good result, and points an excellent result. 17,18 All radiographs were evaluated together with a radiologist. Results A total of 59 patients with 71 fractures were considered for analysis. Nine patients refused to participate (Figure 2). The remaining 50 patients, with a total of 61 fractures, showed a mean time from trauma to operation of 5 days (range 0 17 days) and a mean hospital stay of 8 days (range 1 77 days). The trauma mechanism was a traffic accident in 8 patients and a fall from height in 42 patients. In the latter group, 16 patients fell from stairs or a ladder and 5 had attempted suicide. A total of 60 additional injuries were found in 46% of the patients, of which ten patients had vertebral fractures. The patient demographics and fracture characteristics are shown in Table 1. Forty-two patients were seen at the outpatient clinic; eight did not attend but completed the questionnaire at home. Figure 2. Flowchart showing the process of inclusion of patients in the study. OPC, outpatient clinic; Q/A, questionnaires Infectious complications
7 The complications, related to the fractured calcaneus or the operation, were collected from medical records and the visits to the outpatient clinic. Infectious complications occurred in 9 of 61 (15%) feet that had undergone an operation. Seven patients had a superficial wound infection that was treated conservatively with antibiotics or operatively by removal of hardware. Two patients developed a deep infection: one osteomyelitis and one pin tract infection. One patient had an impingement of the peroneal tendon. Table 1. Patient demographics and fracture characteristics of 50 patients with 61 fractures Characteristic n = 50 patients with 61 fractures (%) Gender Male 36 (72) Female 14 (28) Age (years) 46 (range 16-65) Fracture side Right 21 (42) Left 18 (36) Bilateral 11 (22) Soft tissue Closed 57 (93) Open 4 (7) Essex-Lopresti classification Joint-depression 23 (38) Tongue-type 9 (15) Comminuted 27 (44) Unknown 2 (3) Sanders classification Type II 23 (38) Type III 17 (28) Type IV 17 (28) Unknown 4 (6) Calcaneocuboid joint Yes 27 (44) involvement No 29 (48) Unknown 5 (8) Outcome A total of five calcaneal fractures in five patients had been treated with a secondary (triple) arthrodesis and four patients had the procedure planned (total 9/61 feet; 15%) because of disabling residual pain. The five patients who had already undergone arthrodesis did not complete the questionnaire and were considered to have had a poor result from the primary treatment. The functional outcomes are presented in Table 2. A good to excellent result was found in 42% to 72% of patients, depending
8 on the outcome score used. Patient satisfaction, as represented by the VAS, was on average 7.2 (range 0 10). Five patients (two who had already retired) did not reach the level of activity they enjoyed prior to the accident and were not working at the time of the follow-up. The other patients (90%) were able to work. Eighty-two percent of patients were able to wear normal shoes. Physical examination The average sagittal range of motion of the ankle joint (plantar plus dorsiflexion) was 53 (range 25 75, n = 37), which represents 88% of the normal range of motion. The average range of motion of the subtalar joint was 20 (range 5 40 ), 67% of the normal value. There was an increase in heel width of almost 6% and a decrease in calf circumference of 5%. All feet showed a normal level of stability, and of the 61 fractured feet, three had a slight malalignment. Table 2. Outcome according to four scoring systems after percutaneous treatment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures Score Average ± SD Excellent (%) Good (%) Fair (%) Poor/Failure (%) n = 45 n = 50 AOFAS 83 ± MFS 79 ± CN 76 ± VAS 7.2 ± Outcome as measured by the scoring systems in percentages of 45 patients without an arthrodesis, using four different scores. Grouped outcome in which the patients with an arthrodesis were considered having a poor result of primary treatment. AOFAS: American Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Society score, CN: Creighton Nebraska score, MFS: Maryland Foot Score, VAS: Visual Analogue Scale, SD: standard deviation. Radiographic evaluation The results of the radiographic examination of the investigated feet at three different points in time are presented in Table 3. The Zwipp score for osteoarthritis was 8 points on average. A total of four patients scored 6 points or less, meaning a poor radiologic outcome.
9 Table 3. Parameters Radiographic data at follow-up Böhler angle in degrees (±SD) Gissane angle in degrees (±SD) Trauma (n = 61) (n = 61) Postoperatively Followup (n=37) Healthy side (n = 32) -2 (16) 19 (10) 14 (12) 31 (5) 116 (18) 114 (12) 113 (15) 109 (9) Height in mm (±SD) (5) 50 (3) Length in mm (±SD) (5) 83 (5) Width in mm (±SD) (5) 40 (3) Radiological follow-up data at time of the trauma, direct post-operatively and after a mean follow-up of 35 months. All measurements were compared in patients with unilateral fractures without an arthrodesis. SD: standard deviation. Discussion Various percutaneous and minimally invasive techniques have been introduced because of the skin and wound complications associated with open surgical techniques for the treatment of intra-articular calcaneal fractures. Forgon and Zadravecz combined several less invasive techniques for percutaneous reduction and fixation through the use of an external distractor. 4-6,19 In this study, the outcome of the percutaneous treatment according to Forgon and Zadravecz of patients with a displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture was evaluated over the long term. Patients in this study achieved a good to excellent result in 42% to 72% of cases, according to the use of three different outcome scores. The range of motion of the ankle joint was nearly normal, and the range of motion of the subtalar joint was approximately 70% compared with the uninjured side. A limitation of this study is the absence of a control group treated with a different method. In the level-1 setting where the study was conducted, no other technique was implemented, thus removing the possibility of a concurrent control group. Migrants, the homeless, and patients receiving psychiatric treatment were mostly lost to follow-up; however, their fracture characteristics and patient characteristics were not significantly different from the patients analyzed. Murnaghan showed an equivalent level of patients lost to follow-up, however they found that the attenders and nonattenders in a calcaneal fracture trial constituted two significantly different groups. It is therefore not prudent to extrapolate the results of this study to all patients who were treated in the study period; this constitutes a second limitation. 20
10 The largest published series of patients treated with the percutaneous distractor method comprised 265 cases and presented good to excellent results in approximately 85% of patients. 21 Differences in study parameters and outcome scores make it difficult to compare the results as presented by Forgon and Zadravecz and those of this study. The functional results presented in this study appear to be slightly less favorable than those reported for open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) groups in the literature, but appear to be better than those for conservatively treated patients. 10,19,22,23 The infection and wound complication rates in this study appear similar to those of ORIF and the infections that occurred at the insertion site of the traction pins were not severe. Historically complication rates as high as 30% 40% have been reported for ORIF. Reports from the last 5 to 10 years show a superficial skin infection or wound dehiscence rate of about 10%. Deep infections such as osteomyelitis occur at a lower rate. 24,25 The largest prospective, randomized multicenter study of Buckley et al. in 2002 showed a superficial infection and wound complication rate of 17% and a deep infection rate of 5% for ORIF. 2 With a 15% arthrodesis rate, our study results appear more favorable than those for conservatively treated patients, but less favorable than for open reduced and fixated fractures. 2 Buckley et al. showed that the need for arthrodesis was 4% in the ORIF group versus 20% in the conservatively treated group. 2 Many studies point out restrictions at the subtalar joint for both surgically and conservatively treated fractures. The average range of motion is approximately halved compared with the uninjured foot. 26 The more favorable results presented in this study are supported by the findings of other authors. 27 The percutaneous approach minimizes secondary trauma to the soft tissues, which may lead to less scar tissue formation around the ankle and subtalar joint and may thus lead to less stiffness of the joint. 19 In conclusion, this study confirms that the function of the calcaneus and subtalar joint can be restored by percutaneous reduction and fixation in patients with a displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture. Despite similar infectious complication rates and higher secondary arthrodesis rates compared with open procedures, the good outcome scores and the preservation of the subtalar range of motion at 3-year followup indicate little benefit of open procedures, as reported in the literature, over percutaneous reduction and fixation.
11 References 1. Bridgman SA, Dunn KM, McBride DJ, et al: Interventions for treating calcaneal fractures. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2000:CD Buckley R, Tough S, McCormack R, et al: Operative compared with nonoperative treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a prospective, randomized, controlled multicenter trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2002;84-A: Randle JA, Kreder HJ, Stephen D, et al: Should calcaneal fractures be treated surgically? A meta-analysis. Clin Orthop 2000: Tornetta P, 3rd: Percutaneous treatment of calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop 2000: Forgon M, Zadravecz G: Die Kalkaneusfraktur, in. Springer-Verlag Berlin, 1990, pp Zadravecz G, Szekeres P: [Late results of our treatment method in calcaneus fractures]. Aktuelle Traumatol 1984;14: Gill GG: A three pin method for treatment of severely comminuted fractures of the os calcis. Surg, Gynec and Obstet 1944;78: Crosby LA, Fitzgibbons T: Computerized tomography scanning of acute intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. A new classification system. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1990;72: Kitaoka HB, Alexander IJ, Adelaar RS, et al: Clinical rating systems for the anklehindfoot, midfoot, hallux, and lesser toes. Foot Ankle Int 1994;15: Sanders R, Fortin P, DiPasquale T, et al: Operative treatment in 120 displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Results using a prognostic computed tomography scan classification. Clin Orthop 1993: Ebraheim NA, Elgafy H, Sabry FF, et al: Sinus tarsi approach with trans-articular fixation for displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. Foot Ankle Int 2000;21: Follak N, Merk M: The benefit of gait analysis in functional diagnostics in the rehabilitation in patients after operative treatment of calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Surg 2003;9: Ryf C, Weymann A: The neutral zero method. Injury 1995;26: Sarrafian SK: Biomechanics of the subtalar joint complex. Clin Orthop 1993: Essex-Lopresti P: Mechanism, reduction technique and results in fractures of os calcis. Br J Surg. 1952;39: Böhler L: Diagnosis, pathology and treatment of fractures of the os calcis. J Bone Joint Surg 1931;13: Kennedy JG, Jan WM, McGuinness AJ, et al: An outcomes assessment of intraarticular calcaneal fractures, using patient and physician's assessment profiles. Injury 2003;34:
12 18. Siebert CH, Hansen M, Wolter D: Follow-up evaluation of open intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 1998;117: Gavlik JM, Rammelt S, Zwipp H: Percutaneous, arthroscopically-assisted osteosynthesis of calcaneus fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 2002;122: Murnaghan ML, Buckley RE: Lost but not forgotten: patients lost to follow-up in a trauma database. Can J Surg 2002;45: Forgon M: Closed reduction and percutaneous osteosynthesis: Technique and results in 265 calcaneal fractures. In: Tscherne H, Schatzker J, eds. Major fractures of the pilon, the talus, and the calcaneus. New York: Springer-Verlag 1993: Heier KA, Infante AF, Walling AK, et al: Open fractures of the calcaneus: soft-tissue injury determines outcome. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2003;85-A: Leung KS, Yuen KM, Chan WS: Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of the calcaneum. Medium-term results. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1993;75: Abidi NA, Dhawan S, Gruen GS, et al: Wound-healing risk factors after open reduction and internal fixation of calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Int 1998;19: Lim EVA, Leung JPE: Complications of intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Clin Orthop 2001: Barei DP, Bellabarba C, Sangeorzan BJ, et al: Fractures of the calcaneus. Orthop Clin North Am 2002;33: Kingwell S, Buckley R, Willis N: The association between subtalar joint motion and outcome satisfaction in patients with displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures. Foot Ankle Int 2004;25:
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular. calcaneal fractures
 Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Percutaneous calcaneal fracture surgery T. Schepers 1, I.B. Schipper 1, L.M.M. Vogels 1, A.Z. Ginai 2, P.G.H. Mulder 3, M.J. Heetveld
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Percutaneous calcaneal fracture surgery T. Schepers 1, I.B. Schipper 1, L.M.M. Vogels 1, A.Z. Ginai 2, P.G.H. Mulder 3, M.J. Heetveld
Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:22 27 DOI 10.1007/s00776-006-1076-z Original article Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Tim Schepers 1, Inger B. Schipper 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels
J Orthop Sci (2007) 12:22 27 DOI 10.1007/s00776-006-1076-z Original article Percutaneous treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures Tim Schepers 1, Inger B. Schipper 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure
 Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure T. Schepers, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, P. Patka Skeletal Radiol 2007;36(9):847-852 Abstract Objective The aim of this study
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures; To measure or not to measure T. Schepers, A.Z. Ginai, P.G.H. Mulder, P. Patka Skeletal Radiol 2007;36(9):847-852 Abstract Objective The aim of this study
Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure
 Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:847 852 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0330-6 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure T. Schepers & A. Z. Ginai & P. G. H. Mulder
Skeletal Radiol (2007) 36:847 852 DOI 10.1007/s00256-007-0330-6 SCIENTIFIC ARTICLE Radiographic evaluation of calcaneal fractures: to measure or not to measure T. Schepers & A. Z. Ginai & P. G. H. Mulder
Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures.
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2014), PP 100-107 Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures. (Dr.
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 13, Issue 9 Ver. III (Sep. 2014), PP 100-107 Study of Functional Outcome in Calcaneal Fractures. (Dr.
Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available evidence
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:36 41 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0160-2 EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Bondì R. Padua L. Bondì A. Battaglia E. Romanini A. Campi Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:36 41 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0160-2 EVIDENCE-BASED MEDICINE SECTION R. Bondì R. Padua L. Bondì A. Battaglia E. Romanini A. Campi Treatment of calcaneal fractures: the available
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks
 Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Calcaneus Fractures: My Small Incision Tricks Steven Steinlauf, MD The Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Institute of South Florida CSFA Tampa, February 2018 Disclosures Smith & Nephew Design surgeon, Royalties
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures. Kali Luker, PGY-1
 Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Radiographic Evaluation of Calcaneal Fractures Kali Luker, PGY-1 Anatomy Extraarticular Fractures Involve body, anterior process or tuberosity Treated with immobilization and NWB x 6 wks UNLESS Displaced
Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture
 Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture Sunghwan Byun, DPM, PGY-4 St. Luke s Hospital, Allentown, PA Sangbong Ko, MD Department of Orthopedic
Comparison of Functional Result and Prognostic Factors of Unilateral and Bilateral Calcaneal Fracture Sunghwan Byun, DPM, PGY-4 St. Luke s Hospital, Allentown, PA Sangbong Ko, MD Department of Orthopedic
My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
 PREOPERATIVE DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY IN DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES WITH AND WITHOUT COMPUTED-TOMOGRAPHY: COMPARISON OF POSTOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES USING NOVEL RADIOGRAPHIC SCORE
PREOPERATIVE DIGITAL RADIOGRAPHY IN DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES WITH AND WITHOUT COMPUTED-TOMOGRAPHY: COMPARISON OF POSTOPERATIVE RADIOGRAPHIC OUTCOMES USING NOVEL RADIOGRAPHIC SCORE
Functional outcome of intra-articular tongue type of calcaneus fractures treated with percutaneous technique
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Dalal BY et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):371-376 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164171
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Dalal BY et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2016 Dec;2(4):371-376 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20164171
Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures
 Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; Jan - March; 12(1):23-27 Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures Abhijit C Kawalkar¹, C M Badole² Abstract
Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; Jan - March; 12(1):23-27 Percutaneous Fixation of Displaced Intra-Articular Calcaneal Fractures Abhijit C Kawalkar¹, C M Badole² Abstract
Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(8):12372-12376 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0052574 Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator Binbin Li, Wen Chen, Taifang Gong,
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(8):12372-12376 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0052574 Original Article Treatment of open calcaneal fractures using a new external fixator Binbin Li, Wen Chen, Taifang Gong,
Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):144-8 Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures V Jain, R Kumar, DK Mandal Department of Orthopaedics, Lady Harding Medical College and Associated
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2007;15(2):144-8 Osteosynthesis for intra-articular calcaneal fractures V Jain, R Kumar, DK Mandal Department of Orthopaedics, Lady Harding Medical College and Associated
No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture
 CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
CALCANEUS FRACTURES No disclosures relevant to this topic Acknowledgement: some clinical pictures were obtained from the OTA fracture lecture series and AO fracture lecture series INCIDENCE 2% of all fractures
A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 26, 82, 779-786 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children Di Lu, Shao-Yu Zhu, Jie Yang, Hua
Acta Orthop. Belg., 26, 82, 779-786 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparison of two minimally invasive procedures for intra-articular displaced calcaneal fractures in older children Di Lu, Shao-Yu Zhu, Jie Yang, Hua
Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating
 Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; April - June; 12(2):13-17 Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating Yashwant J Mahale, Sagar
Original Article Journal of Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery 2017; April - June; 12(2):13-17 Study of Outcome of Intra-articular Fractures of Calcaneum Treated Surgically by Plating Yashwant J Mahale, Sagar
Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures
 Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures Gao Di, Zhang Yong, Li Zheng Lin, Jia Bin, Zheng Jie Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedics and Traumatology Hospital My disclosure
Comparative Study on Arthroscopic versus ORIF for Sanders Type II Calcaneus Fractures Gao Di, Zhang Yong, Li Zheng Lin, Jia Bin, Zheng Jie Shenzhen Pingle Orthopedics and Traumatology Hospital My disclosure
Functional outcomes of different modalities of fixation in intra-articular calcaneus fractures
 2018; 2(4): 199-204 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 199-204 Received: 25-08-2018 Accepted: 27-09-2018 Rajesh V Chawda Associate Professor,
2018; 2(4): 199-204 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 199-204 Received: 25-08-2018 Accepted: 27-09-2018 Rajesh V Chawda Associate Professor,
Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Introduction. Introduction 10/2/2009. Bryan Lapinski, MD
 Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Bryan Lapinski, MD Introduction The average person takes 1 million steps per year Approximately 30 bones in the foot and ankle are subjected to forces of 3 7 times body weight
Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Bryan Lapinski, MD Introduction The average person takes 1 million steps per year Approximately 30 bones in the foot and ankle are subjected to forces of 3 7 times body weight
Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile?
 28th Pak Orthocon 2014 S-161 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile? Syed Furqan Gilani, 1 Muhammad Suhail Amin 2 Abstract Objective:
28th Pak Orthocon 2014 S-161 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of displaced intra-articular fractures of Calcaneum: Is it worthwhile? Syed Furqan Gilani, 1 Muhammad Suhail Amin 2 Abstract Objective:
Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials
 British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published September 3, 2009 Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials Nikolaos Gougoulias, Anil Khanna, Donald J. McBride, and Nicola
British Medical Bulletin Advance Access published September 3, 2009 Management of calcaneal fractures: systematic review of randomized trials Nikolaos Gougoulias, Anil Khanna, Donald J. McBride, and Nicola
Session II 11:30 11:45 am. Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio. Disclosure: (n)
 Session II 11:30 11:45 am Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure: (n) Wound Complications after ORIF of Calcaneus Fractures and How to Prevent Them
Session II 11:30 11:45 am Wound Complications and How to Prevent Them Mark J. Berkowitz, MD Cleveland, Ohio Disclosure: (n) Wound Complications after ORIF of Calcaneus Fractures and How to Prevent Them
Radiological predictive factors for the outcome of surgically treated calcaneus fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 218-224 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiological predictive factors for the outcome of surgically treated calcaneus fractures Mário Baptista, Rui Pinto, João Torres From Faculdade de Medicina
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 218-224 ORIGINAL STUDY Radiological predictive factors for the outcome of surgically treated calcaneus fractures Mário Baptista, Rui Pinto, João Torres From Faculdade de Medicina
The optimal management of displaced
 Review Article Advances in Surgical Management of Intra-articular Calcaneus Fractures Abstract Andrew R. Hsu, MD Robert B. Anderson, MD Bruce E. Cohen, MD JAAOS Plus Webinar Join Dr. Cohen for the interactive
Review Article Advances in Surgical Management of Intra-articular Calcaneus Fractures Abstract Andrew R. Hsu, MD Robert B. Anderson, MD Bruce E. Cohen, MD JAAOS Plus Webinar Join Dr. Cohen for the interactive
Original Article The small dorsolateral incision approach for surgical treatment of sanders type III intra-articular fractures of the calcaneus
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):9261-9269 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017905 Original Article The small dorsolateral incision approach for surgical treatment of sanders type III intra-articular fractures
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(6):9261-9269 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0017905 Original Article The small dorsolateral incision approach for surgical treatment of sanders type III intra-articular fractures
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Fractures of the Calcaneus Anthony T. Sorkin, M.D. Rockford Orthopedic Trauma Service Rajeev Garapati, MD Illinois Bone and Joint Institute Assistant Clinical Professor University of Illinois at Chicago
Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture Dislocation Injuries
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 928938, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928938 Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2013, Article ID 928938, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/928938 Case Report A Novel Technique for Closed Reduction and Fixation of Paediatric Calcaneal Fracture
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Symptomatic nonunion after fracture of the calcaneum
 Symptomatic nonunion after fracture of the calcaneum DEMOGRAPHICS AND TREATMENT A. P. Molloy, M. S. Myerson, P. Yoon From Institute for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, USA
Symptomatic nonunion after fracture of the calcaneum DEMOGRAPHICS AND TREATMENT A. P. Molloy, M. S. Myerson, P. Yoon From Institute for Foot and Ankle Reconstruction, Mercy Medical Center, Baltimore, USA
AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING. Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion
 AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome
 Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome HY Wong, MD, AS Vivek*, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To, FRCS (Edin) Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Hospital
Conservative Management of Calcaneal Fractures. A Retrospective Review of Treatment Outcome HY Wong, MD, AS Vivek*, FRCS (Edin), BC Se To, FRCS (Edin) Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology, Hospital
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9): /ISSN: /IJCEM
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):18033-18039 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021277 Original Article Minimally invasive reduction of the medial wall shortening and misalignment in calcaneal fractures with
Int J Clin Exp Med 2016;9(9):18033-18039 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0021277 Original Article Minimally invasive reduction of the medial wall shortening and misalignment in calcaneal fractures with
Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: is bone grafting necessary?
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14:299 305 DOI 10.1007/s10195-013-0246-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: is bone grafting necessary? A. K. Singh K. Vinay
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2013) 14:299 305 DOI 10.1007/s10195-013-0246-y ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: is bone grafting necessary? A. K. Singh K. Vinay
Yanling Su, Wei Chen, Qi Zhang, Song Liu, Tao Zhang and Yingze Zhang *
 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bony destructive injuries of the calcaneus: long-term results of a minimally invasive procedure followed by early functional exercise: a retrospective
Su et al. BMC Surgery 2014, 14:19 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bony destructive injuries of the calcaneus: long-term results of a minimally invasive procedure followed by early functional exercise: a retrospective
The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-011-1223-9 REVIEW The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review Tim Schepers Received: 1 December 2010 / Accepted: 20 January 2011 #
DOI 10.1007/s00264-011-1223-9 REVIEW The sinus tarsi approach in displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a systematic review Tim Schepers Received: 1 December 2010 / Accepted: 20 January 2011 #
Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum
 JFAS JFAs (AP) How I Do It Minimally Invasive 10.5005/jp-journals-10040-1047 Management of Fracture Calcaneum Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum 1 Mandeep S Dhillon, 2 Sharad Prabhakar,
JFAS JFAs (AP) How I Do It Minimally Invasive 10.5005/jp-journals-10040-1047 Management of Fracture Calcaneum Minimally Invasive Management of Fracture Calcaneum 1 Mandeep S Dhillon, 2 Sharad Prabhakar,
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision
 Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Diagnosis and Treatment CARL E. HORN, M.D., Sacramento Good lateral, Anthonsen oblique, anterior-posterior, and axial roentgenograms are necessary to define the extent of fractures
Fractures of the Calcaneus Diagnosis and Treatment CARL E. HORN, M.D., Sacramento Good lateral, Anthonsen oblique, anterior-posterior, and axial roentgenograms are necessary to define the extent of fractures
Accepted: 3 April 2009
 Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
Open Access Case report Treatment of ipsilateral high energy tibial plateau and calcaneal fractures by a circular wire fixator: a case report Shabir Ahmed Dhar*, Mohammed Farooq Butt, Murtaza Fazal Ali,
Yanling Su, Wei Chen, Tao Zhang, Xingwang Wu, Zhanpo Wu and Yingze Zhang *
 Su et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:40 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bohler s angle s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal
Su et al. BMC Surgery 2013, 13:40 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Bohler s angle s role in assessing the injury severity and functional outcome of internal fixation for displaced intra-articular calcaneal
JMSCR Vol 07 Issue 04 Page April 2019
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.23 Sinus tarsi approach for displaced, Intra-articular Calcaneal
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v7i4.23 Sinus tarsi approach for displaced, Intra-articular Calcaneal
The fate of Böhler s angle in conservatively treated displaced intraarticular
 The fate of Böhler s angle in conservatively treated displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures Berdine Bakker MSc, Jens A. Halm MD PhD, Esther M.M. Van Lieshout PhD, Tim Schepers MD PhD Erasmus MC,
The fate of Böhler s angle in conservatively treated displaced intraarticular calcaneal fractures Berdine Bakker MSc, Jens A. Halm MD PhD, Esther M.M. Van Lieshout PhD, Tim Schepers MD PhD Erasmus MC,
Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted intra-articular calcaneal fractures: a retrospective case analysis
 Shih et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:77 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1995-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted
Shih et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2018) 19:77 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-018-1995-9 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Modified Essex-Lopresti procedure with percutaneous calcaneoplasty for comminuted
Outcome of Internal Fixation of Comminuted Calcaneum Fractures
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. X (August. 2016), PP 29-35 www.iosrjournals.org Outcome of Internal Fixation of Comminuted
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 8 Ver. X (August. 2016), PP 29-35 www.iosrjournals.org Outcome of Internal Fixation of Comminuted
Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments -
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12 No1 January 1999 = Abstract = Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments - Seung-Rim
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12 No1 January 1999 = Abstract = Treatments of Intraarticular Calcaneal Fracture - Based on CT Classification and Comparison of Treatments - Seung-Rim
Or thopaedic Surger y
 Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
Article Medial external fixation for staged treatment of closed calcaneus fractures: Surgical technique and case series Journal of Or thopaedic Surger y Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 25(3) 1 8 ª The Author(s)
Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss
 Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 614 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2013, 7, 614-618 Open Access Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss Chad G. Williams,
Send Orders for Reprints to reprints@benthamscience.net 614 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2013, 7, 614-618 Open Access Staged Subtalar Fusion for Severe Calcaneus Fractures with Bone Loss Chad G. Williams,
Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients
 Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients Hirorfumi Tanaka 1)3), Tsutomu Motooka 2), Kyota Nishifuru 3) 1)Saga Social insulance Hospital 2)National Hospital Organization
Clinical result of plate fixation for calcaneal fractures in elderly patients Hirorfumi Tanaka 1)3), Tsutomu Motooka 2), Kyota Nishifuru 3) 1)Saga Social insulance Hospital 2)National Hospital Organization
Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal fractures
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(11):15782-15788 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0065292 Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal
Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(11):15782-15788 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0065292 Original Article Extensive lateral versus tarsal sinus approach to internal fixation for intra-articular calcaneal
Displaced Intra-articular Fractures of the Calcaneus with an emphasis on minimally invasive surgery
 Displaced Intra-articular Fractures of the Calcaneus with an emphasis on minimally invasive surgery Tim Schepers Displaced Intra-articular Fractures of the Calcaneus with an emphasis on minimally invasive
Displaced Intra-articular Fractures of the Calcaneus with an emphasis on minimally invasive surgery Tim Schepers Displaced Intra-articular Fractures of the Calcaneus with an emphasis on minimally invasive
Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:87 95 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0082-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach Mohamed F.
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:87 95 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0082-z ORIGINAL ARTICLE Surgical treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fracture using a single small lateral approach Mohamed F.
Calcaneal Fractures in Children
 Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 18:469-474 1998 Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphi a Calcaneal Fractures in Children Suguru Inokuchi, M.D., Norio Usami, M.D., Eiichi Hiraishi, M.D., and Takeshi
Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 18:469-474 1998 Lippincott-Raven Publishers, Philadelphi a Calcaneal Fractures in Children Suguru Inokuchi, M.D., Norio Usami, M.D., Eiichi Hiraishi, M.D., and Takeshi
SINUS TARSI APPROACH FOR TREATMENT OF DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2018 vol. 122, no. 2 SURGERY ORIGINAL PAPERS SINUS TARSI APPROACH FOR TREATMENT OF DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES B. Veliceasa 1, B. Puha 1*, D. Popescu
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2018 vol. 122, no. 2 SURGERY ORIGINAL PAPERS SINUS TARSI APPROACH FOR TREATMENT OF DISPLACED INTRA-ARTICULAR CALCANEAL FRACTURES B. Veliceasa 1, B. Puha 1*, D. Popescu
Peggers Super Summaries: Foot Injuries
 Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures
 FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
FOOT/ ANKLE RETROSPECTIVE STUDYIC S Retrospective Study of Surgical Outcomes for Combined Ankle and Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis, Cavovarus Deformity Correction and Ankle Fractures Adult & Pediatric Deformity
CALCANEAL FRACTURE. Romeo and Juliet, Ford Maddox Brown, oil on canvas, 1870 JULIET. Wilt thou be gone? It is not yet near day:
 CALCANEAL FRACTURE Romeo and Juliet, Ford Maddox Brown, oil on canvas, 1870 JULIET Wilt thou be gone? It is not yet near day: It was the nightingale, and not the lark, That pierced the fearful hollow of
CALCANEAL FRACTURE Romeo and Juliet, Ford Maddox Brown, oil on canvas, 1870 JULIET Wilt thou be gone? It is not yet near day: It was the nightingale, and not the lark, That pierced the fearful hollow of
Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures
 Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Page 1 of 8 Calcaneus (Heel Bone) Fractures A fracture of the calcaneus, or heel bone, can be a painful and disabling injury. This type of fracture commonly occurs during a high-energy event such as a
Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study
 CAIMS JOURNAL FINAL # 19 Original Article Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Ashok 2, Moorthy GVS 3, Rama Krishna G 4 1 Associate Professor
CAIMS JOURNAL FINAL # 19 Original Article Fracture Calcaneum, Open Reduction and Internal Fixation: A Prospective Study Nagamuneendrudu K 1, Ashok 2, Moorthy GVS 3, Rama Krishna G 4 1 Associate Professor
V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2008;16(2):215-9 V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet E Segev, E Ezra, M Yaniv, S Wientroub, Y Hemo Department of Pediatric Orthopaedics,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2008;16(2):215-9 V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet E Segev, E Ezra, M Yaniv, S Wientroub, Y Hemo Department of Pediatric Orthopaedics,
Open surgery vs minimal invasive methods for calcaneus fractures. Eur J Transl Myol 28 (2): , 2018
 Comparison of calcaneus joint internal and external fractures in open surgery and minimal invasive methods in patients Alireza Amani (1), Vahid Shakeri (1), Alireza Kamali (2) (1) Department of Orthopedic,
Comparison of calcaneus joint internal and external fractures in open surgery and minimal invasive methods in patients Alireza Amani (1), Vahid Shakeri (1), Alireza Kamali (2) (1) Department of Orthopedic,
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and
 This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
This article appeared in a journal published by Elsevier. The attached copy is furnished to the author for internal non-commercial research and education use, including for instruction at the authors institution
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
Diabetics. Referred for management of complex pilon fracture? 5/10/2017. Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?)
 Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?) Nirmal C Tejwani, MD Professor, NYU Langone Orthopedics Chief of Trauma, Bellevue Hospital, New York, NY 29 th Annual Orthopaedic Trauma Meeting May
Pilon Fractures: Exfix as definitive treatment (DM?) Nirmal C Tejwani, MD Professor, NYU Langone Orthopedics Chief of Trauma, Bellevue Hospital, New York, NY 29 th Annual Orthopaedic Trauma Meeting May
Calcaneal fractures: Where are we now?
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2018) 13:1 11 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-017-0297-3 REVIEW Calcaneal fractures: Where are we now? Aisha Razik 1 Mark Harris 1 Alex Trompeter 1 Received: 21 August 2015 / Accepted:
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2018) 13:1 11 https://doi.org/10.1007/s11751-017-0297-3 REVIEW Calcaneal fractures: Where are we now? Aisha Razik 1 Mark Harris 1 Alex Trompeter 1 Received: 21 August 2015 / Accepted:
Primary Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis with Internal and External Fixation for the Repair of a Diabetic Comminuted Calcaneal Fracture
 Primary Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis with Internal and External Fixation for the Repair of a Diabetic Comminuted Calcaneal Fracture Zacharia Facaros, DPM a, Crystal L. Ramanujam, DPM b, Thomas Zgonis, DPM
Primary Subtalar Joint Arthrodesis with Internal and External Fixation for the Repair of a Diabetic Comminuted Calcaneal Fracture Zacharia Facaros, DPM a, Crystal L. Ramanujam, DPM b, Thomas Zgonis, DPM
Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report
 Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report John Y. Kwon, M.D., Mostafa M. Abousayed, M.D., Eric C. Fu,
Load-sharing Construct Allowing for Immediate Weightbearing and Mobilization in a 18 year old with Bilateral Calcaneus Fractures: A Case Report John Y. Kwon, M.D., Mostafa M. Abousayed, M.D., Eric C. Fu,
Prospective study of fracture calcaneus with Allan s procedure- bone grafting without implants
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Phadke VS et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):315-320 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop201808
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Phadke VS et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2018 Mar;4(2):315-320 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop201808
Traumatic Injuries to the Foot and Ankle
 Traumatic Injuries to the Foot and Ankle Dr. Joseph N. Daniel Clinical Associate Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Foot and Ankle Service, The Rothman Institute Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia,
Traumatic Injuries to the Foot and Ankle Dr. Joseph N. Daniel Clinical Associate Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Foot and Ankle Service, The Rothman Institute Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Philadelphia,
DEPARTMENT OF TRAUMATOLOGY AND HAND SURGERY INSTITUTE OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SURGERY ANKLE AND FOOT INJURIES
 DEPARTMENT OF TRAUMATOLOGY AND HAND SURGERY INSTITUTE OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SURGERY ANKLE AND FOOT INJURIES Presenter: Dr George Ayerh ENGLISH PROGRAM LECTURES EN_11/A - 2018 TOPICS I. Part: Ankle & Foot
DEPARTMENT OF TRAUMATOLOGY AND HAND SURGERY INSTITUTE OF MUSCULOSKELETAL SURGERY ANKLE AND FOOT INJURIES Presenter: Dr George Ayerh ENGLISH PROGRAM LECTURES EN_11/A - 2018 TOPICS I. Part: Ankle & Foot
Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2018;10:479-483 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2018.10.4.479 Modified Proximal Scarf Osteotomy for Hallux Valgus Ki Won Young, MD, Hong Seop Lee, MD, Seong
Talus Fractures: When and Why on Screws and Plates
 Talus Fractures: When and Why on Screws and Plates Frank A. Liporace, MD Associate Professor Director of Orthopaedic Research New York University / Hospital for Joint Diseases, NY, NY Director Orthopaedic
Talus Fractures: When and Why on Screws and Plates Frank A. Liporace, MD Associate Professor Director of Orthopaedic Research New York University / Hospital for Joint Diseases, NY, NY Director Orthopaedic
NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS. Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2
 NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY 2012-2013 CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS CONDITION PAGE(S) Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2 Fractures 3-4 Heel Pain (Posterior) Retrocalcaneal
NORTHEAST OHIO NEIGHBORHOOD HEALTH SERVICES, INC. PODIATRY 2012-2013 CLINICAL GUIDELINES TABLE OF CONTENTS CONDITION PAGE(S) Diabetes Mellitus and Podiatric Care 2 Fractures 3-4 Heel Pain (Posterior) Retrocalcaneal
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
NORTHERN OHIO FOUNDATION. ! The!Northern!Ohio!Foot!and!Ankle!Journal!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Official!Publication!of!the!NOFA!Foundation!! Calcaneal Fractures
 NORTHERN OHIO FOOT & ANKLE FOUNDATION! The!Northern!Ohio!Foot!and!Ankle!Journal!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Official!Publication!of!the!NOFA!Foundation!! Calcaneal Fractures by Chris Tyree DPM PGY-2 1 The Northern Ohio
NORTHERN OHIO FOOT & ANKLE FOUNDATION! The!Northern!Ohio!Foot!and!Ankle!Journal!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Official!Publication!of!the!NOFA!Foundation!! Calcaneal Fractures by Chris Tyree DPM PGY-2 1 The Northern Ohio
Displaced Intra-articular Calcaneal Fractures: Classification and Treatment
 Displaced Intra-articular Calcaneal Fractures: Classification and Treatment Ning Wei, MD; Yabin Zhou, MD; Wenli Chang, MD; Yingze Zhang, MD; Wei Chen, MD abstract The calcaneus is the most commonly fractured
Displaced Intra-articular Calcaneal Fractures: Classification and Treatment Ning Wei, MD; Yabin Zhou, MD; Wenli Chang, MD; Yingze Zhang, MD; Wei Chen, MD abstract The calcaneus is the most commonly fractured
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
The Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System
 Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System VALUE ANALYSIS BRIEF Value Summary Calcaneal fractures are the most common fracture of the hindfoot, demanding individualized treatment. The Variable Angle
Variable Angle Locking Calcaneal Plating System VALUE ANALYSIS BRIEF Value Summary Calcaneal fractures are the most common fracture of the hindfoot, demanding individualized treatment. The Variable Angle
Minimally invasive manipulative reduction with poking k-wire fixation in the treatment of various types of calcaneal fractures
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Minimally invasive manipulative reduction with poking k-wire fixation in the treatment of various types of calcaneal fractures B. LU 1, P. LIU 1,
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences Minimally invasive manipulative reduction with poking k-wire fixation in the treatment of various types of calcaneal fractures B. LU 1, P. LIU 1,
,
 , 49, 2013, 2 5 REVIEWS.,.,.,.,.,..,.. FRACTURES OF THE TALUS: COMPLICATIONS AND PROGNOSIS S. Asyov, V. Tzanov, K. Tzonkov, L. Zahariev, H. Stoychev, D. Pachev and M. Iliev Second Clinic of Orthopedic
, 49, 2013, 2 5 REVIEWS.,.,.,.,.,..,.. FRACTURES OF THE TALUS: COMPLICATIONS AND PROGNOSIS S. Asyov, V. Tzanov, K. Tzonkov, L. Zahariev, H. Stoychev, D. Pachev and M. Iliev Second Clinic of Orthopedic
Measurement of three-dimensional morphological characteristics of the calcaneus using CT image post-processing
 Qiang et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2014, 7:19 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Measurement of three-dimensional morphological characteristics of the calcaneus using
Qiang et al. Journal of Foot and Ankle Research 2014, 7:19 JOURNAL OF FOOT AND ANKLE RESEARCH RESEARCH Open Access Measurement of three-dimensional morphological characteristics of the calcaneus using
Minimally invasive, no hardware subtalar arthrodesis with autogenous posterior iliac bone graft
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:39 45 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0081-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minimally invasive, no hardware subtalar arthrodesis with autogenous posterior iliac bone graft Mohamed A. M. Eid Maged
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2010) 5:39 45 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0081-0 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Minimally invasive, no hardware subtalar arthrodesis with autogenous posterior iliac bone graft Mohamed A. M. Eid Maged
Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture: an anatomical specimen study
 Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:78 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0580-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture:
Wang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:78 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0580-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Sustentacular screw placement with guidance during ORIF of calcaneal fracture:
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation *
 Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
Competence of the Deltoid Ligament in Bimalleolar Ankle Fractures After Medial Malleolar Fixation * BY PAUL TORNETTA, III, M.D. Investigation performed at Kings County Hospital, New York, N.Y. Abstract
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3
 OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
OUTCOME OF MANAGEMENT OF CLOSED PROXIMAL TIBIA FRACTURES IN TERTIARY HOSPITAL OF SURAT Karan Mehta 1, Prashanth G 2, Shiblee Siddiqui 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: Karan Mehta, Prashanth G. Shiblee Siddiqui,
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle
 Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Treatment of malunited fractures of the ankle A LONG-TERM FOLLOW-UP OF RECONSTRUCTIVE SURGERY I. I. Reidsma, P. A. Nolte, R. K. Marti, E. L. F. B. Raaymakers From Academic Medical Center, Amsterdam, Netherlands
Percutaneous Screw Fixation of Distal Tibia Fractures Functional Results in Sixteen Patients
 Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2014 Jun 15; 2(2):229-233. http://dx.doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2014.036 Clinical Science Percutaneous Screw Fixation of Distal Tibia Fractures Functional
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences. 2014 Jun 15; 2(2):229-233. http://dx.doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2014.036 Clinical Science Percutaneous Screw Fixation of Distal Tibia Fractures Functional
Conservative management of idiopathic clubfoot: Kite versus Ponseti method
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2009;17(1):67-71 Conservative management of idiopathic clubfoot: Kite versus Ponseti method AV Sanghvi, 1 VK Mittal 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2009;17(1):67-71 Conservative management of idiopathic clubfoot: Kite versus Ponseti method AV Sanghvi, 1 VK Mittal 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College
Complication Rate and Pitfalls of Temporary Bridging External Fixator in Periarticular Communited Fractures
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:62-68 doi:10.4055/cios.2011.3.1.62 Complication Rate and Pitfalls of Temporary Bridging External Fixator in Periarticular Communited Fractures Jong-Keon
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2011;3:62-68 doi:10.4055/cios.2011.3.1.62 Complication Rate and Pitfalls of Temporary Bridging External Fixator in Periarticular Communited Fractures Jong-Keon
ABC of Emergency Radiology
 l ja ) $% _2) < j> ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~foot ABC of Emergency Radiology THE FOOT D A Nicholson, D O'Keeffe, P A Driscoll Accurate clinical assessment of injuries to the foot will avoid unnecessary exposure
l ja ) $% _2) < j> ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~foot ABC of Emergency Radiology THE FOOT D A Nicholson, D O'Keeffe, P A Driscoll Accurate clinical assessment of injuries to the foot will avoid unnecessary exposure
X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Ankle.
 X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Complex hinge joint Articulations among: Fibula Tibia Talus Tibial plafond Distal tibial articular surface
X-Ray Rounds: (Plain) Radiographic Evaluation of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Complex hinge joint Articulations among: Fibula Tibia Talus Tibial plafond Distal tibial articular surface
Open Treatment and Internal Fixation of Displaced Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures in High-Risk Patients Utilizing the Sinus Tarsi Approach
 Open Treatment and Internal Fixation of Displaced Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures in High-Risk Patients Utilizing the Sinus Tarsi Approach W. Bret Smith, DO Steve Steinlauf, MD Greg E. Gaski, MD Disclosure
Open Treatment and Internal Fixation of Displaced Intraarticular Calcaneal Fractures in High-Risk Patients Utilizing the Sinus Tarsi Approach W. Bret Smith, DO Steve Steinlauf, MD Greg E. Gaski, MD Disclosure
Temporary bridge plating of the medial column in Chopart and Lisfranc injuries
 Temporary bridge plating of the medial column in Chopart and Lisfranc injuries by Alaa Mansour DPM 1*, Lawrence Fallat DPM, FACFAS 2 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal 10 (1): 5 Severe traumatic injuries
Temporary bridge plating of the medial column in Chopart and Lisfranc injuries by Alaa Mansour DPM 1*, Lawrence Fallat DPM, FACFAS 2 The Foot and Ankle Online Journal 10 (1): 5 Severe traumatic injuries
Case Report Lateral Subtalar Dislocation with Tarsometatarsal Dislocation: A Case Report of a Rare Injury
 Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 8090721, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8090721 Case Report Lateral Subtalar Dislocation with Tarsometatarsal Dislocation: A Case Report
Hindawi Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2017, Article ID 8090721, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/8090721 Case Report Lateral Subtalar Dislocation with Tarsometatarsal Dislocation: A Case Report
Lisfranc injuries. Mikko Kirjavainen, MD, PhD. Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki Finland
 Lisfranc injuries Mikko Kirjavainen, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki Finland Lisfranc injuries are midfoot fracture dislocations. The
Lisfranc injuries Mikko Kirjavainen, MD, PhD Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology Helsinki University Central Hospital, Helsinki Finland Lisfranc injuries are midfoot fracture dislocations. The
AVULSION FRACTURES OF THE CALCANEUS
 AVULSION FRACTURES OF THE CALCANEUS KEITH PROTHEROE, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The Royal Infirmary, Glasgov Fractures of the calcaneus [os calcis] have received much
AVULSION FRACTURES OF THE CALCANEUS KEITH PROTHEROE, GLASGOW, SCOTLAND From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The Royal Infirmary, Glasgov Fractures of the calcaneus [os calcis] have received much
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]
![FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test] FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]](/thumbs/83/88335212.jpg) FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate
 wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e Tornier WAVE Calcaneal fracture plate system surgical procedure Indications for Use: The Tornier Calcaneal Fracture Plate System is indicated
wave Calcaneal Fracture Plate s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e Tornier WAVE Calcaneal fracture plate system surgical procedure Indications for Use: The Tornier Calcaneal Fracture Plate System is indicated
Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
