Hand Injuries. SRPC Rural Critical Care Module. C. Stuart Johnston, M.B., Ch. B., M.Sc.(Civil Eng), C.C.F.P., FRRMS Associate Clinical Professor UBC
|
|
|
- Chastity Small
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Hand Injuries SRPC Rural Critical Care Module C. Stuart Johnston, M.B., Ch. B., M.Sc.(Civil Eng), C.C.F.P., FRRMS Associate Clinical Professor UBC THE MANGLED HAND Introduction Mangling injuries of the hand are defined as serious injuries involving multiple vital structures that often lead to significant physical and psychological disabilities later on. Multiple systems, including bones, muscles, tendons, vessels, nerves and skin, may be involved, and it has been found that the resulting scar formation extends from the skin down to the deepest damaged structures. This impacts significantly on the function and blood supply during and after the recovery process. (For example, the permanent sensitivity to the cold of a previously injured finger.) To minimise this scar formation it is imperative that the tissues are handled with care, cleaned well and the blood supply restored as soon as possible. Non-viable tissue should be removed, fractures stabilised and coverage of the exposed tissues attempted. Some basic principles when dealing with serious hand injuries 1. Preserve life. Treat the patient, not just the hand. There are often other life threatening injuries present which must be dealt with first ATLS approach with attention to the ABCs. 2. Preserve tissues. Be conservative, particularly in young patients, preserve viable tissue whenever possible. You can always take tissue away later, to replace tissue is much more difficult. Handle all tissues gently. 3. Preserve function. Try to maintain digit length, particularly the pincer grip function. Give realistic reassurances regarding recovery. 4. Be aware of the Zone of injury. This concept recognizes that the area of injury often extends well beyond the area of initial injury. For this reason it may be necessary to delay closure of large wounds until re-examinations of the wound at 24 to 48hrs post injury do not show any further tissue ischemia and necrosis. 5. Try not to hurt or frighten the patient. Once the sensation has been assessed and documented provide anesthesia before further examination of the injury. 6. Confer with specialist colleagues early if in doubt. The Dept. of Plastic Surgery at your nearest major hospital will usually be very helpful if your usual consultant is unavailable.
2 Dealing with the Mangled Hand as a GP surgeon Much of the management is no different than any other trauma case. However the following may be useful when dealing with hands. Initial evaluation ATLS approach and ABC s. Hemostasis becomes the priority if major bleeding is occurring. Look for other injuries associated with a significant injury force. History When did the injury occur? This is important because of ischemic tissue time. As a rule of thumb, bone may survive more than 6hrs without a blood supply, muscle about 4 to 6hrs and nerves 2 to 4hrs. This is temperature dependent, and the muscle can be revascularised up to 24hrs later if cooled. A finger has been successfully reattached after 94hrs with cooling. Where? Was it in a farming environment (usually highly contaminated and need extensive dibridement), or an industrial setting with oils or caustic substances contaminating the wound? Where does the patient come from? This impacts on the post-operative care plan. How? What was the mechanism of the injury? How much force was involved? Was it a sharp or a crushing type injury? High velocity, high-pressure, crushing or avulsion injuries have a much larger Zone of injury and require more extensive debridement, assessment of surrounding tissues and awareness of compartment syndrome. Examination After dealing with any life threatening injuries attention is turned to the hand. It may be easier to do this in an OR setting if the injury is substantial and wrapped in blood-soaked bandages. Usually an assessment of the vascular status, sensation, muscle and tendon function and X- Rays can be done in the ER. Vascular status is the primary concern. Traditionally nail bed capillary refill time is used, however this has been shown to be a very unreliable indicator of perfusion because blood simply moves laterally with compression of the nail, and returns to the center on release. A more accurate area is the dorsal paronychial tissue on the sides of the nail, which should be pink and spongy, with good turgor, compressing with pressure and refilling with release within about 4 seconds. A dusky color with exceptionally brisk refill can represent venous congestion. Have a high index of suspicion for compartment syndrome.
3 Skeletal injury is best determined by X-Rays after the initial assessment. It is unnecessary (and traumatic for the patient) to manipulate the limb to determine whether a fracture is present. Remember to take AP and Lateral views if possible to avoid missing hidden fractures or significant displacement. Muscle-tendon injury can be assessed by asking the patient to flex and extend the fingers and wrist. This may be difficult in the presence of pain. Additionally one can observe the movement (cascade) of all the fingers as the wrist is passively flexed and extended in the comatose or anesthetized patient. A relative weakness on testing flexion or extension of a digit, or a lag on full extension often indicates a partially transected tendon, or a completely lacerated extensor tendon with some extension function remaining from the cross-over extensor bands (Juncturae tendinum) on the dorsum of the hand. Nerve injury requires assessment of both the motor and sensory function. The motor function of the Median, Radial and Ulnar nerves is checked by testing both extrinsic and intrinsic muscle function. Three simple maneuvers test motor integrity: (1) resistance against palmar abduction of the thumb reflects the median nerve-innervated abductor pollicis brevis function; (2) resistance against flexion of the MCP joint of the little finger reflects the ulnar nerve-innervated flexor digiti quinti function; (3) resistance to extension of the MCP joint of the index reflects the radial nerveinnervated extensor digitorum communis and extensor indicus proprius. The sensory nerve function can be assessed by checking both sides of each finger if damage to the digital nerves is suspected, or more generally, the volar aspects of the index and middle fingers for the median nerve, the volar aspect of the little finger for ulnar supply and the dorsum of the first web space for Radial nerve supply. With sharp or penetrating injuries if you think the nerve is probably OK, it usually is not, and warrants exploration. Blunt trauma on the other hand may lead to neuropraxia with an intact nerve. Treatment Antibiotic cover The early administration of antibiotics is critical to their efficacy. Generally a first-generation cephalosporin is adequate (the most common organism is Staph aureus), with the addition of an aminoglycoside for farming or highly contaminated wounds. Tetanus prophylaxis Blood supply Avascular limb attempt to straighten the injured part to re-establish blood flow, or urgently refer to a hospital where revascularization can be attempted if blood flow cannot be re-established or the vessels have been severed ( tag the ends of identified arteries). Tissues may still be viable after up to 3 hours of ischemia depending on the ambient temperatures. This can be extended to about 7 hours if the affected limb is chilled on a bed of ice (with protection form frostbite) during transfer. Compartment syndrome this is a surgical emergency requiring decompression ASAP. Hemostasis use pressure or ligation of vessels under direct vision. Avoid using hemostat clamps blindly as this may lead to nerve damage. To improve visualization of a bleeding vessel use a running drip tube (opened fully) with N saline to provide continuous irrigation of the area.
4 Bone # Attempt to gently reduce fractures, and stabilize definitively (e.g. K-wires or a cast), or support the limb in a temporary splint until specialist care is available. Nerves Assess nerve damage, record the findings, and then anesthetize as required. If severed nerves are identified whilst debriding the wound, the ends should be tagged. Debridement The initial debridement is perhaps the single most important step that determines the functional outcome of mangling injuries. (Green s Operative Hand Surgery) There is good evidence that removing devitalized tissue early results in better outcomes. Meticulous cleaning of all foreign material from the wound must be done. With a mangling-type injury this is best done in the OR. Use mayonnaise or butter to emulsify petroleum products and tar on the skin. Gentle handling of the tissues with copious N saline irrigation minimizes further tissue trauma. Skin Preserve skin bridges whenever possible. Keep recovered skin in N saline gauze in a bag stored on ice for possible future use. Amputation In general if amputation is necessary it is best done at the time of the initial repair. That being said, the GP Surgeon needs to bear in mind a number of things: The thumb generally comprises 40% of hand function and the index and middle finger 20%. All traumatically amputated tissue including digits or limbs should be stored as per the transportation guidelines in the event that it may be reused/reattached at a later time. The decision to amputate or not may be tempered by such things as the patient s age, health status, smoking history and previous finger function. Remember that most open fingertip injuries without exposed bone will heal secondarily. Remember that there are ways of preserving finger length that can be safely done by the GP Surgeon, for example the V-Y Flap, the Wolfian graft, skin grafting using recovered tissues. Be aware that there are techniques that the specialist surgeons can use to preserve degloved limbs and digits. Reattachment of a digit below the level of the DIP is virtually impossible because of the diameter of the digital vessels. Tendons Primary repair of extensor tendons may be done after careful debridement. A simple figure 8 braided non- absorbable suture is ideal, but a nylon 6/0 will also work well. It is important that the ends of the tendon are healthy and have not been severely crushed and traumatized. If there is doubt then tag the ends of the tendons using nylon 6/0 and close the skin if possible. This facilitates later repair. Early repair helps restore function more quickly.
5 Flexor tendon repair depends on the experience of the GP Surgeon and the extent of other injuries. TRANSPORTATION OF HAND INJURIES Seek specialist advice early if a referral out looks likely. Analgesia Do not do local blocks until the sensation has been assessed. Provide good analgesia for any transfer as the movement will cause pain. Elevate the affected part above heart level. Gently stabilize fractures to minimize movement en route. Protect open wounds with saline soaked gauze (ABD pads also work well). I then wrap the whole hand in a plastic sheet (a clean blue pad is the simplest). Keep the parts. Store avulsed skin or amputated digits in normal saline-soaked gauze inside a plastic bag which is placed in another plastic bag containing ice and water. Record your findings and assessment in the referral letter. Include any blocks Chill ischemic tissues whilst waiting for re-establishment of a blood supply. EXTENSOR TENDON REPAIR. Repair of extensor tendons by rural physicians is considered to be an acceptable procedure to do, with adequate care and training. The post-operative care and follow up is important. There are some basic concepts to follow in repairing tendons, which if observed should reduce complications, and give good outcomes. Treat the patient not just the hand! Be conservative in dealing with tissue. Preserve viable tissue. Determine sensory status before anaesthetizing. Handle all Tissues gently. Don t clamp bleeders blindly. Keep the tissues well hydrated with normal saline. Use a 4/0 Ticron suture (or any non-absorbable 4/0 or 5/0 material) for the tendon repair, and a 6/0 nylon suture for the epitenon repair if needed. (The epitenon repair is usually unnecessary.)
6 Use a modified Kessler suture if possible, but even a simple figure 8 works well. Call your nearest Plastic or Orthopedic surgeon for advice if you have any concerns about the best way to proceed. If you are uncomfortable attempting the repair, close the skin or cover the wound ( after careful cleaning ) and ship the patient. Tagging the tendons with a suture prior to transfer to a specialist will facilitate subsequent repair Follow up at least weekly in the initial recovery phase. Protect the repair from tension with a splint for the first 3 weeks. Initiate physiotherapy early, and follow up to ensure good ROM. I routinely cover tendon repairs with an antibiotic if I suspect contamination may have occurred at the time of the injury. (Usually Keflex 500mg TID x 10 days). NAILBED INJURIES Provide a digital block to allow adequate cleaning and assessment. Remove the nail if a significant nail bed injury is present or suspected. Carefully reconstruct the damaged nail bed with 6/0 chromic sutures (5/0 will work). Cover the nail bed well with Polysporin Ointment. Replace the nail and suture with nylon sutures. Drill the holes in the nail for the sutures using an 18 G needle. If the nail is missing use a silastic sheet, a plastic nail, or cut out a nail shaped piece of foil from the suture packaging. Remove all sutures and the nail at two weeks. In children, because of the flexibility of the nail, it may be possible to bend the nail back enough to inspect and even repair a nail bed injury without removing the entire nail. Exercise the DIP, starting immediately after the repair.
7 HIGH PRESSURE PAINT OR GREASE GUN INJURIES Beware of the minimal damage present on initial presentation. The paint is injected at 1000 to 2000 psi and tracks extensively in the tissue. Refer immediately to a hand surgeon. This is a real emergency as there is a high risk of loss of digits. CLOSED MALLET FINGER Due to disruption of the extensor tendon mechanism of the DIP, usually caused by a sudden blow to the tip of the extended finger. This may be due to a tendon rupture or avulsion of a small bone fragment from distal phalanx. Must x-ray these. If the avulsed bone fragment involved > 1/3 of the articular surface, = surgery. If the avulsed bone fragment involved <1/3 of the articular surface, = splinting. Splinting for six to eight weeks, followed by two weeks of night splinting. Imperative joint is not allowed to flex at all in the six to eight weeks, else start again. Do not splint PIP; stiffness begins after as little as three days. SKIER S THUMB This is due to disruption of the ulna collateral ligament of the MCP joint of the thumb. Clinically there will be pain and swelling over the area with point tenderness. An x-ray is required to exclude fractures or an avulsion fracture. The thumb must be tested for complete or incomplete disruption of the ligament. This may require local anesthetic prior to testing. If the joint opens laterally >30 degrees then a complete tear is presumed and surgery is required. This must be done urgently as after two weeks, surgical repair is difficult. Incomplete tears should be immobilized in a hand-based thumb spica splint for four weeks. Thereafter a splint should be used for sporting activities for a further six to eight weeks.
8 BITES: N.B. Be very careful in following up bites in Diabetic, Splenectomised & immunocomprimised patients. Dog Bites: Tend to be crushing or tearing in nature Tetanus prophylaxis Vigorously scrub the wound with a surgical brush under LA followed by copious saline irrigation Antibiotic prophylaxis with a broad-spectrum drug, e.g. Amoxicillin/clavulanate is usually considered the first-line prophylactic antibiotic Inquire about the possibility of rabies Cat Bites: Tend to be a puncture wound injury with deceptively little damage Check carefully for signs of suppurative flexor teno-synovitis (fusiform swelling of the digit, tenderness along the flexor sheath, flexed posture, pain on passive extension) or septic arthritis (peri-articular pain increased with axial loading) Early infections should respond well to Amoxicillin and Clavulanic acid, otherwise I.V. antibiotics and drainage may be required Human Bites: Frequently seen with the punch injury over the MP joint X-ray must be taken to exclude tooth fragments or fractures Under local anesthetic the wound must be well cleaned and explored If there is evidence of joint involvement, then formal arthrotomy, irrigation of the MCP joint and I.V. antibiotics are required Antibiotic Cover: Orally PenVK, Amoxicillin, Cipro, Cloxacillin. I.V. Ancef and Flagyl VIGNETTES Frostbite Warm (in warm water 60 0 C.) for 20 to 30 minutes, if you are sure it won t refreeze. (E.g. mountain climbing situation.) Keep water circulating Do not burst blisters initially Aloe Vera (90% pure gel) topically for 24 hours, then Flamazine dressings Ibuprofen 400mg Q8h p.o. Pen VK p.o. prophylactically There is now evidence that using thrombolytics early can significantly reduce the extent of the ischemic damage. The current recommendations for this should be accessed Non-healing abrasion or laceration Look for a foreign body X-ray useful
9 Level of position of the digital neuro-vascular bundles on the fingers Flex the finger Mark a dot at the apex of each of the lateral flexion creases Straighten the finger and join the dots! A good approximation to the position of the digital neuro-vascular bundles is the line joining the PIP and DIP flexion crease apices on the lateral aspect of the fingers. The Wrinkle test To determine if sensory function is absent Method: Soak digit in warm water for 10 minutes. If no wrinkling occurs, this implies a disruption of sensory supply to the finger pad Burns Aloe Vera gel Q2H for 24 hours topically, then change to Flamazine Aloe Vera gel is bacteriostatic and a PGE2 inhibitor, this helps to reduce vasoconstriction Use Ibuprofen to reduce the inflammatory reaction and increase blood flow into the affected area REFERENCES 1. The Hand Examination and Diagnosis. Third Edition, American Society for Surgery of the Hand. ISBN N. Carr. Hands, Bites, Cuts and Sprains. The Canadian Journal of CME, March 1998, pp Kasdan MC, Amadio PC, Bowers WH, Technical Tips for Hand Surgery ISBN Green, Hotchkiss, Pederson & Wolfe, Green s Operative Hand Surgery, 5 th Edition, 2005.
Cheyenne Kate P. Rebosura, MD Clinical Associate Orthopaedic Surgery KhooTeck PuatHospital
 Cheyenne Kate P. Rebosura, MD Clinical Associate Orthopaedic Surgery KhooTeck PuatHospital Outline I. Principles of Assessment II. Flexor Tenosynovitis III. Fight Bite IV. Animal Bite V. Compartment Syndrome
Cheyenne Kate P. Rebosura, MD Clinical Associate Orthopaedic Surgery KhooTeck PuatHospital Outline I. Principles of Assessment II. Flexor Tenosynovitis III. Fight Bite IV. Animal Bite V. Compartment Syndrome
Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist. Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury
 Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury Disclosures We have no disclosures that are pertinent to this presentation Terminology Ring Long Index Small Thumb
Exam of the Injured Hand and Wrist Christina M. Ward, MD Regions Hospital TRIA Woodbury Disclosures We have no disclosures that are pertinent to this presentation Terminology Ring Long Index Small Thumb
Hand injuries. The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck.
 Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Hand injuries Metacarpal injuries The metacarpal bones may fracture through the base, shaft or the neck. Shaft fractures; these are caused by direct trauma which may cause transverse # of one or more metacarpal
Injuries to the Hands and Feet
 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 26 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. Death
THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HAND EMERGENCIES
 THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HAND EMERGENCIES Dr. Adel Abdel Aziz Senior Emergency Physician Honorary Senior Clinical Lecturer, University of Southampton Training Program Director Emergency Medicine/ Health Education
THE EPIDEMIOLOGY OF HAND EMERGENCIES Dr. Adel Abdel Aziz Senior Emergency Physician Honorary Senior Clinical Lecturer, University of Southampton Training Program Director Emergency Medicine/ Health Education
Initial care of amputations. Wendy Willmore
 Initial care of amputations Wendy Willmore Outline Initial care of the patient, stump and amputated part Indications and contraindications for replantation Initial care of the patient As necessitated by
Initial care of amputations Wendy Willmore Outline Initial care of the patient, stump and amputated part Indications and contraindications for replantation Initial care of the patient As necessitated by
Fig Fig Fig. 6-3
 CHAPTER 6 UPPER EXTREMITY The surgical treatment of hand problems is a specialized area of interest in plastic surgery. The hand is a unique organ which transmits sensations from the external environment
CHAPTER 6 UPPER EXTREMITY The surgical treatment of hand problems is a specialized area of interest in plastic surgery. The hand is a unique organ which transmits sensations from the external environment
A guide to help you survive nights and weekends
 A guide to help you survive nights and weekends General overview of service Expectations Hand Face Soft tissue injuries Decubitus ulcers V.A.C. system The make-up of the division of Plastic and Hand Surgery
A guide to help you survive nights and weekends General overview of service Expectations Hand Face Soft tissue injuries Decubitus ulcers V.A.C. system The make-up of the division of Plastic and Hand Surgery
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATIC HAND INJURIES IN SPORT. Katherine Katie Faust, MD
 MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATIC HAND INJURIES IN SPORT Katherine Katie Faust, MD None DISCLOSURES THE ATHLETE Children are hard to figure out Parents are not always better Don t Assume Maintain high index of suspicion
MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMATIC HAND INJURIES IN SPORT Katherine Katie Faust, MD None DISCLOSURES THE ATHLETE Children are hard to figure out Parents are not always better Don t Assume Maintain high index of suspicion
Practice Changes I Hope You Make
 Is that Bad? What PCPs (& Parents) Need to Know about Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein, MD Pediatric Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Assistant Professor, Orthopaedics Baylor College
Is that Bad? What PCPs (& Parents) Need to Know about Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein, MD Pediatric Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Assistant Professor, Orthopaedics Baylor College
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
FINGERTIP INJURIES ARE THEY REALLY THAT SIMPLE? SANJAY K SHARMA, MD, FACS INSTITUTE OF RECONSTRUCTIVE PLASTIC SURGERY
 FINGERTIP INJURIES ARE THEY REALLY THAT SIMPLE? SANJAY K SHARMA, MD, FACS INSTITUTE OF RECONSTRUCTIVE PLASTIC SURGERY Austin Trauma and Critical Care Conference 2018 May 31-June 1, 2018 Outline 1. Scope
FINGERTIP INJURIES ARE THEY REALLY THAT SIMPLE? SANJAY K SHARMA, MD, FACS INSTITUTE OF RECONSTRUCTIVE PLASTIC SURGERY Austin Trauma and Critical Care Conference 2018 May 31-June 1, 2018 Outline 1. Scope
1. A 40-year-old male has dislocated his right 2 nd MCP. You have pulled as hard as you can but cannot reduce the dislocation. The problem is likely:
 CHAPTER 50 HAND 2 OCTOBER 2013 1. A 40-year-old male has dislocated his right 2 nd MCP. You have pulled as hard as you can but cannot reduce the dislocation. The problem is likely: A. He is a gamer and
CHAPTER 50 HAND 2 OCTOBER 2013 1. A 40-year-old male has dislocated his right 2 nd MCP. You have pulled as hard as you can but cannot reduce the dislocation. The problem is likely: A. He is a gamer and
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers. Contusion Injuries to the Forearm. Forearm Fractures 12/11/2017. Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas
 The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
The Forearm, Wrist, Hand and Fingers Oak Ridge High School Conroe, Texas Contusion Injuries to the Forearm The forearm is constantly exposed to bruising and contusions in contact sports. The ulna receives
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
First Responders to Orthopaedic Emergencies
 First Responders to Orthopaedic Emergencies Tom McPartland MD FABOS, FAAP Assistant Clinical Professor Rutgers-RWJMS October 17,2018 Goals Review Epidemiology of School Injuries Review Definitions of Different
First Responders to Orthopaedic Emergencies Tom McPartland MD FABOS, FAAP Assistant Clinical Professor Rutgers-RWJMS October 17,2018 Goals Review Epidemiology of School Injuries Review Definitions of Different
Injuries to the Hands and Feet
 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 24 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. The
Injuries to the Hands and Feet Chapter 24 Injuries to the Hands and Feet Introduction Combat injuries to the hands and feet differ from those of the arms and legs in terms of mortality and morbidity. The
LRI Emergency Department
 LRI Emergency Department Guideline for the management of: Finger Tip Injuries in Children In the Paediatric Emergency Department (UHL Category C Guidance) Staff relevant to: ED Medical and Nursing staff
LRI Emergency Department Guideline for the management of: Finger Tip Injuries in Children In the Paediatric Emergency Department (UHL Category C Guidance) Staff relevant to: ED Medical and Nursing staff
Property Latmedical, LLC.
 Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine, bandaging, wound care and compression
Dr. Goed provides a complete and innovate product portfolio solution to the growing healthcare need within the field of non-invasive orthopedics, sports medicine, bandaging, wound care and compression
Evaluation of the Injured Hand. Sanjay K. Sharma, M.D., F.A.C.S Regional Trauma Conference June 2, 2016
 Evaluation of the Injured Hand 2016 Regional Trauma Conference June 2, 2016 Disclosures Nothing relevant Outline General overview of Hand Trauma Anatomy/Examination Selected Cases History of Hand Surgery
Evaluation of the Injured Hand 2016 Regional Trauma Conference June 2, 2016 Disclosures Nothing relevant Outline General overview of Hand Trauma Anatomy/Examination Selected Cases History of Hand Surgery
PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger A Patient's Guide to PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger
 PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger A Patient's Guide to PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger Introduction We use our hands constantly, placing them in harm's way continuously. Injuries to the finger joints are
PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger A Patient's Guide to PIP Joint Injuries of the Finger Introduction We use our hands constantly, placing them in harm's way continuously. Injuries to the finger joints are
Fractures and dislocations of the fingers
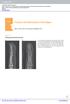 Chapter 1 Fractures and dislocations of the fingers Felix S. Chew, M.D., and Catherine Maldjian, M.D. Case 1 1 Phalangeal tuft avulsion fracture 31-year-old woman injured in a ground-level fall. Lateral
Chapter 1 Fractures and dislocations of the fingers Felix S. Chew, M.D., and Catherine Maldjian, M.D. Case 1 1 Phalangeal tuft avulsion fracture 31-year-old woman injured in a ground-level fall. Lateral
What you don t want to miss
 March 25, 2009 Vishal Michael Shah, M.D. What you don t want to miss Spectrum of Injuries Contusions Sprains Dislocations Fractures Lacerations Tendon Avulsions Ligament Tears Overuse Injuries FINGER
March 25, 2009 Vishal Michael Shah, M.D. What you don t want to miss Spectrum of Injuries Contusions Sprains Dislocations Fractures Lacerations Tendon Avulsions Ligament Tears Overuse Injuries FINGER
WRIST SPRAIN. Description
 WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
WRIST SPRAIN Description Other sports, such as skiing, bowling, pole vaulting Wrist sprain is a violent overstretching and tearing of one Poor physical conditioning (strength and flexibility) or more ligaments
Hand Trauma Update: Outline. Hand Surgeon s Area of Expertise. Orthopaedic Update 2015
 Hand Trauma Update: 2015 Orthopaedic Update 2015 March 21, 2015 Peter Tang, MD, MPH Director Hand, Upper Extremity & Microvascular Surgery Fellowship Associate Professor Drexel University College of Medicine
Hand Trauma Update: 2015 Orthopaedic Update 2015 March 21, 2015 Peter Tang, MD, MPH Director Hand, Upper Extremity & Microvascular Surgery Fellowship Associate Professor Drexel University College of Medicine
Common. Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes
 Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
Common Hand Problems in Elite Athletes Fred Corley M.D. Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UTHSCSA I have no disclosures concerning this talk. The University of Texas Health Science Center @ San Antonio - Orthopaedics
Common Hand Injuries Common Hand Infections. Braemar Hospital GPCME 1 November 2014
 Common Hand Injuries Common Hand Infections Braemar Hospital GPCME 1 November 2014 Waikato Hospital Tristram Clinic, 200 Collingwood Street, Hamilton P 07 838 1035 F 07 838 2032 E appts@tristramclinic.co.nz
Common Hand Injuries Common Hand Infections Braemar Hospital GPCME 1 November 2014 Waikato Hospital Tristram Clinic, 200 Collingwood Street, Hamilton P 07 838 1035 F 07 838 2032 E appts@tristramclinic.co.nz
A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Adult Finger Fractures 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
5/8/2017. Finger Injuries in Football. Tendon Injuries of the Hand and Wrist in Football Steve Kronlage, MD Andrews Institute Gulf Breeze, Florida
 Finger Injuries in Football Tendon Injuries of the Hand and Wrist in Football Steve Kronlage, MD Andrews Institute Gulf Breeze, Florida A jammed finger is an injury (at very least a torn ligament) A swollen
Finger Injuries in Football Tendon Injuries of the Hand and Wrist in Football Steve Kronlage, MD Andrews Institute Gulf Breeze, Florida A jammed finger is an injury (at very least a torn ligament) A swollen
OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries. Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department
 Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department Presented in Clinical Update Seminar January 15 th 2011 dr. Tedjo Rukmoyo, SpOT (K) Spine Initial Management ATLS Procedure A : airway
Principle Management of Wound and Fracture in Emergency Department Presented in Clinical Update Seminar January 15 th 2011 dr. Tedjo Rukmoyo, SpOT (K) Spine Initial Management ATLS Procedure A : airway
SPECIAL ARTICLE. Missed tendon injuries INTRODUCTION
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1991, 8, 87-91 SPECIAL ARTICLE Missed tendon injuries H. R. GULY Consultant in A & E, Derriford Hospital, Plymouth INTRODUCTION The timing of the repair of divided tendons
Primary Care Office Orthopedic Emergencies/ Urgencies
 Primary Care Office Orthopedic Emergencies/ Urgencies Joshua Crum M.D. Hill Country Sports Medicine San Marcos, TX Goals Define what constitutes and orthopedic emergency/urgency Know what conditions need
Primary Care Office Orthopedic Emergencies/ Urgencies Joshua Crum M.D. Hill Country Sports Medicine San Marcos, TX Goals Define what constitutes and orthopedic emergency/urgency Know what conditions need
POR4ULO Assessment. Low temperature thermoplastic orthoses for the Hand / Digit. Practical Guide
 POR4ULO Assessment Low temperature thermoplastic orthoses for the Hand / Digit Practical Guide Pattern Making for Upper Limb, Low Temperature Thermoplastic Orthoses The use of low temperature thermoplastics
POR4ULO Assessment Low temperature thermoplastic orthoses for the Hand / Digit Practical Guide Pattern Making for Upper Limb, Low Temperature Thermoplastic Orthoses The use of low temperature thermoplastics
Trigger Finger Release
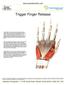 Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Trigger Finger Release Trigger finger, also known as stenosing tenosynovitis, occurs when one of the tendons responsible for bending a finger or the thumb develops a thickening, known as a nodule, and
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb
 Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
Trigger Finger and Trigger Thumb A Patient's Guide to Trigger Finger & Trigger Thumb Introduction Trigger finger and trigger thumb are conditions affecting the movement of the tendons as they bend the
What to expect after Dupuytren's surgery and what to do to get the best possible results.
 What to expect after Dupuytren's surgery and what to do to get the best possible results. Directly after surgery: You can expect a bulky bandage covering the palm and the fingers that were operated on.
What to expect after Dupuytren's surgery and what to do to get the best possible results. Directly after surgery: You can expect a bulky bandage covering the palm and the fingers that were operated on.
DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS
 YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
YOUR GUIDE TO DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Contents What is tendonitis and tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What is de Quervain s tenosynovitis?.............................. 3 What treatment
Chapter 39. Volar surface incisions
 Chapter 39 EXPLORATION OF AN INJURED HAND OR FOREARM KEY FIGURES: Tourniquet Midlateral finger incisions Brunner zigzag incisions Volar surface incisions Dorsal incisions Proximal and distal extension
Chapter 39 EXPLORATION OF AN INJURED HAND OR FOREARM KEY FIGURES: Tourniquet Midlateral finger incisions Brunner zigzag incisions Volar surface incisions Dorsal incisions Proximal and distal extension
INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT
 INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT An injury is damage to the body caused by external forces, which may be physical or chemical. 1) Incisions 2) Types of wounds and their closure
INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT INJURIES AND THEIR MANAGEMENT An injury is damage to the body caused by external forces, which may be physical or chemical. 1) Incisions 2) Types of wounds and their closure
HAND EXAMINATION & COMMON INJURIES OF THE HAND. Majoring in Minors Conference th January 2013 Derriford Hospital
 HAND EXAMINATION & COMMON INJURIES OF THE HAND Majoring in Minors Conference 16-17 th January 2013 Derriford Hospital Objectives Anatomy & Terminology History Examination Look Feel Move Investigations
HAND EXAMINATION & COMMON INJURIES OF THE HAND Majoring in Minors Conference 16-17 th January 2013 Derriford Hospital Objectives Anatomy & Terminology History Examination Look Feel Move Investigations
JuggerKnot Soft Anchor 1.0 mm Mini
 JuggerKnot Soft Anchor 1.0 mm Mini Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL) Repair of the Thumb Surgical Technique Surgical Protocols by Mark Rekant, M.D. A. Lee Osterman, M.D. One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1
JuggerKnot Soft Anchor 1.0 mm Mini Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL) Repair of the Thumb Surgical Technique Surgical Protocols by Mark Rekant, M.D. A. Lee Osterman, M.D. One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1
Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries of the Thumb Game Keeper s Thumb A Patient's Guide to Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries of the Thumb
 Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries of the Thumb Game Keeper s Thumb A Patient's Guide to Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries of the Thumb 1 Introduction Injury to the ulnar collateral ligament of the thumb
Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries of the Thumb Game Keeper s Thumb A Patient's Guide to Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries of the Thumb 1 Introduction Injury to the ulnar collateral ligament of the thumb
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure
 Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
Intrinsic muscles palsies of the hand Management of Thumb Opposition with BURKHALTER s Procedure TRUONG LE DAO, MD, IFAAD 1 Burkhalter W.E, Cristhensen R.C, Brown P.W, Extensor Indicis Proprius opponensplasty
FINGER INJURIES. Chapter 24, pgs ,
 FINGER INJURIES Chapter 24, pgs 727 730, 741 743 1. Demonstrate mastery of anatomical references to the hand and fingers. 2. Compare and contrast Mallet Finger, Swan Neck Deformity and Boutonnière Deformity.
FINGER INJURIES Chapter 24, pgs 727 730, 741 743 1. Demonstrate mastery of anatomical references to the hand and fingers. 2. Compare and contrast Mallet Finger, Swan Neck Deformity and Boutonnière Deformity.
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand. Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Kinesiology of The Wrist and Hand Cuneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University Bones The wrist and hand contain 29 bones including the radius and ulna. There are eight carpal bones in two rows of four to
Transfemoral Amputation
 Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Transfemoral Amputation Pre-Op: 42 year old male who sustained severe injuries in a motorcycle accident. Note: he is a previous renal transplant recipient and is on immunosuppressive treatments. His injuries
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Patient information Carpal Tunnel Syndrome i Important information for all patients having Carpal Tunnel surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
Patient information Carpal Tunnel Syndrome i Important information for all patients having Carpal Tunnel surgery. Golden Jubilee National Hospital Agamemnon Street Clydebank, G81 4DY (: 0141 951 5000 www.nhsgoldenjubilee.co.uk
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
MULTIMEDIA ARTICLES. Mary C. Burns & Brian Derby & Michael W. Neumeister
 HAND (2013) 8:17 22 DOI 10.1007/s11552-012-9488-z MULTIMEDIA ARTICLES Wyndell merritt immediate controlled active motion (ICAM) protocol following extensor tendon repairs in zone IV VII: review of literature,
HAND (2013) 8:17 22 DOI 10.1007/s11552-012-9488-z MULTIMEDIA ARTICLES Wyndell merritt immediate controlled active motion (ICAM) protocol following extensor tendon repairs in zone IV VII: review of literature,
Management of Fractures. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5
 Management of Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5 Common methods of fracture immobilization Plaster of Paris (POP): A high quality gypsum The standard method of external splinting
Management of Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5 Common methods of fracture immobilization Plaster of Paris (POP): A high quality gypsum The standard method of external splinting
Chapter 24. Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty. Introduction. Operative Technique. Patient Preparation and Positioning
 Chapter 24 Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty Introduction Osteoarthritis in the thumb carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is a common condition, especially in women over 60 years of
Chapter 24 Arthroscopic Thumb Carpometacarpal Interposition Arthroplasty Introduction Osteoarthritis in the thumb carpometacarpal (CMC) joint is a common condition, especially in women over 60 years of
Complex Limb Injury. Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered
 Complex Limb Injury Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Complex Limb Injuries Introduction This information booklet aims to help you to understand the nature, treatment and outcome of your limb
Complex Limb Injury Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Complex Limb Injuries Introduction This information booklet aims to help you to understand the nature, treatment and outcome of your limb
Open Fractures. Ria Dindial. Photo courtesy pic2fly.com
 Open Fractures Ria Dindial Photo courtesy pic2fly.com CLINICAL PEARL TYPE WOUND DESCRIPTION OTHER CRITERIA I < 1cm (puncture wounds) - II 1-10 cm - IIIA >10 cm, coverage available Segmental fractures,
Open Fractures Ria Dindial Photo courtesy pic2fly.com CLINICAL PEARL TYPE WOUND DESCRIPTION OTHER CRITERIA I < 1cm (puncture wounds) - II 1-10 cm - IIIA >10 cm, coverage available Segmental fractures,
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Skin Anatomy and Physiology
 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Body s largest organ Three layers: Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue 1 2 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Complex system, variety of functions Sensation Control of water loss
Skin Anatomy and Physiology Body s largest organ Three layers: Epidermis Dermis Subcutaneous tissue 1 2 Skin Anatomy and Physiology Complex system, variety of functions Sensation Control of water loss
JuggerKnot Soft Anchor 1.0 mm Mini
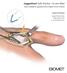 JuggerKnot Soft Anchor 1.0 mm Mini Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL) Repair of the Thumb Surgical Technique Surgical Protocols by Mark Rekant, M.D. A. Lee Osterman, M.D. One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1
JuggerKnot Soft Anchor 1.0 mm Mini Ulnar Collateral Ligament (UCL) Repair of the Thumb Surgical Technique Surgical Protocols by Mark Rekant, M.D. A. Lee Osterman, M.D. One Surgeon. One Patient. Over 1
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD
 Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Approach to traumatic hand injuries for primary care physicians
 Clinical Review Approach to traumatic hand injuries for primary care physicians Kevin Cheung MSc MD Alexandra Hatchell MSc Achilleas Thoma MD FRCSC FACS Abstract Objective To review the initial management
Clinical Review Approach to traumatic hand injuries for primary care physicians Kevin Cheung MSc MD Alexandra Hatchell MSc Achilleas Thoma MD FRCSC FACS Abstract Objective To review the initial management
with cross-finger pedicle grafts
 Salvage of digits with cross-finger pedicle grafts Robert I. Horner, MD and Floyd B. Bralliar, MD Mechanization in home and industry has brought to our emergency rooms an increasing number of patients
Salvage of digits with cross-finger pedicle grafts Robert I. Horner, MD and Floyd B. Bralliar, MD Mechanization in home and industry has brought to our emergency rooms an increasing number of patients
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy
 Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Hand Anatomy A Patient's Guide to Hand Anatomy Introduction Few structures of the human anatomy are as unique as the hand. The hand needs to be mobile in order to position the fingers and thumb. Adequate
Carpal tunnel decompression advice
 Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Service Carpal tunnel decompression advice SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 1 28/11/2018 09:16 SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 2 28/11/2018
Southend University Hospital NHS Foundation Trust Patient Information Service Carpal tunnel decompression advice SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 1 28/11/2018 09:16 SOU1277_120995_1018_V2.indd 2 28/11/2018
Hand & Wrist Casey G. Batten MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Sports Medicine
 Hand & Wrist Casey G. Batten MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Sports Medicine Topics: Scaphoid Fracture Scapholunate Separation TFCC Injury Thumb Ulnar Collateral Lig (UCL) Injury Extensor Injury /
Hand & Wrist Casey G. Batten MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF Sports Medicine Topics: Scaphoid Fracture Scapholunate Separation TFCC Injury Thumb Ulnar Collateral Lig (UCL) Injury Extensor Injury /
Orthoses for Orthoses for Hand & Finger Hand & Finger Living Proof m mediro oya al.se
 Orthoses for Hand & Finger mediroyal.se 2 Orthoses for Hand & Finger 502 EU 2010 X- Hard Art. 502, Coil-Extension Spring-PIP This spring provides an extra high degree of extension to the PIP joint. The
Orthoses for Hand & Finger mediroyal.se 2 Orthoses for Hand & Finger 502 EU 2010 X- Hard Art. 502, Coil-Extension Spring-PIP This spring provides an extra high degree of extension to the PIP joint. The
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Extensor Tendon Repair Zones II, III, IV
 Zones II, III, IV D. WATTS, MD Indications Lacerations to the central slip, lateral bends and/or triangular ligament Rupture of the central slip in association with a PIP joint volar dislocation Avulsion
Zones II, III, IV D. WATTS, MD Indications Lacerations to the central slip, lateral bends and/or triangular ligament Rupture of the central slip in association with a PIP joint volar dislocation Avulsion
Structure and Function of the Hand
 Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Structure and Function of the Hand Some say it takes a village to raise a child, but it takes 19 bones and 19 joints in the hand for it to function smoothly. The Hand Dorsal aspect 2 3 4 The digits are
Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction
 180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
180 Letter to Editor Revisiting the Curtis Procedure for Boutonniere Deformity Correction Lee Seng Khoo*, Vasco Senna-Fernandes Ivo Pitanguy Institute, Rua Dona Mariana 65, Botafogo, Rio De Janeiro, Brazil
Swan-Neck Deformity. Introduction. Anatomy
 Swan-Neck Deformity Introduction Normal finger position and movement occur from the balanced actions of many important structures. Ligaments support the finger joints. Muscles hold and move the fingers.
Swan-Neck Deformity Introduction Normal finger position and movement occur from the balanced actions of many important structures. Ligaments support the finger joints. Muscles hold and move the fingers.
Client centered approach to distal radius fracture management. Jared Rasmussen OTR
 Client centered approach to distal radius fracture management Jared Rasmussen OTR Disclosures Sadly, no financial disclosures Objectives Review of anatomy, common fractures of the distal radius, fixation
Client centered approach to distal radius fracture management Jared Rasmussen OTR Disclosures Sadly, no financial disclosures Objectives Review of anatomy, common fractures of the distal radius, fixation
Shaun P. Garff, DO Physician of Sports Medicine
 Shaun P. Garff, DO Physician of Sports Medicine Speaker Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest to disclose as it relates to this presentation. A little about me Born and raised
Shaun P. Garff, DO Physician of Sports Medicine Speaker Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflicts of interest to disclose as it relates to this presentation. A little about me Born and raised
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery
 Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville Trauma/Fractures
 WRIST/HAND PATHOLOGY Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Trauma/Fractures Hook of Hamate Fractures Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
WRIST/HAND PATHOLOGY Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Trauma/Fractures Hook of Hamate Fractures Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
Management of Penetrating Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department
 Management of Penetrating Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department Ioannis E. Bitzos, MD, and Mark S. Granick, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, New Jersey Medical School, University of Medicine and Dentistry
Management of Penetrating Wrist Injuries in the Emergency Department Ioannis E. Bitzos, MD, and Mark S. Granick, MD Division of Plastic Surgery, New Jersey Medical School, University of Medicine and Dentistry
Trauma/Fractures WRIST/HAND PATHOLOGY. TFCC Injury. Hook of Hamate Fracture. Property of VOMPTI, LLC
 WRIST/HAND PATHOLOGY Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Trauma/Fractures Hook of Hamate Fractures Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
WRIST/HAND PATHOLOGY Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Trauma/Fractures Hook of Hamate Fractures Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex (TFCC)
Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries. J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics
 Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics 10. Proximal Humerus Fractures Treatment Simple sling ICE, pain meds Button-down shirts Recliner to sleep in It will be up to the surgeon
Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics 10. Proximal Humerus Fractures Treatment Simple sling ICE, pain meds Button-down shirts Recliner to sleep in It will be up to the surgeon
WOUNDS. Emergency Procedures in PT
 WOUNDS Emergency Procedures in PT Types of Wounds Abrasions uppermost layer scraped away, minor capillary bleeding occurs, nerve endings exposed Lacerations skin tear with edges jagged and uneven Incisions
WOUNDS Emergency Procedures in PT Types of Wounds Abrasions uppermost layer scraped away, minor capillary bleeding occurs, nerve endings exposed Lacerations skin tear with edges jagged and uneven Incisions
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
Silicone Finger Implant
 Silicone Finger Implant Manufactured from high tear resistant implant grade silicone Surgical Technique Eleven, evenly scaled sizes for comprehensive anatomical fit Simple, precise instrumentation Designed
Silicone Finger Implant Manufactured from high tear resistant implant grade silicone Surgical Technique Eleven, evenly scaled sizes for comprehensive anatomical fit Simple, precise instrumentation Designed
Management of Wrist and Hand Injuries
 Sunday General Session Management of Wrist and Hand Injuries Shaun Garff, DO Sports Medicine Physician Methodist Health System Dallas, Texas Educational Objectives By the end of this educational activity,
Sunday General Session Management of Wrist and Hand Injuries Shaun Garff, DO Sports Medicine Physician Methodist Health System Dallas, Texas Educational Objectives By the end of this educational activity,
Hand and wrist emergencies
 Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
11/13/2017. Complications of Flexor Tendon Repair. Brandon E. Earp, M.D. How do we best get there?
 Complications of Flexor Tendon Repair Brandon E. Earp, M.D. Chief of Orthopaedic Surgery Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Vice-Chair of Clinical Operations Brigham and Women s Hospital Frontiers in
Complications of Flexor Tendon Repair Brandon E. Earp, M.D. Chief of Orthopaedic Surgery Brigham and Women s Faulkner Hospital Vice-Chair of Clinical Operations Brigham and Women s Hospital Frontiers in
CASE REPORT Compartment Syndrome of the Hand: Beware of Innocuous Radius Fractures
 CASE REPORT Compartment Syndrome of the Hand: Beware of Innocuous Radius Fractures Francesco Maria Egro, MBChB, BSc (Hons), MRCS, MSc, Matthew Robert Frederick Jaring, MBBS, BSc (Hons), and Asif Zafar
CASE REPORT Compartment Syndrome of the Hand: Beware of Innocuous Radius Fractures Francesco Maria Egro, MBChB, BSc (Hons), MRCS, MSc, Matthew Robert Frederick Jaring, MBBS, BSc (Hons), and Asif Zafar
HAND AND WRIST OWNER S MANUAL
 HAND AND WRIST OWNER S MANUAL Treatment for Common Hand and Wrist Problems Problems with the Hand and Wrist You depend on your hands and wrists every day. But an injury can make even simple tasks painful
HAND AND WRIST OWNER S MANUAL Treatment for Common Hand and Wrist Problems Problems with the Hand and Wrist You depend on your hands and wrists every day. But an injury can make even simple tasks painful
Duputytren's Contracture
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries
 MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
MR: Finger and Thumb Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Professor of Radiology University of Central Florida Florida State University Outline Normal anatomy of the fingers and thumb MR imaging protocols
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The information
A Patient s Guide to Adult Thumb Metacarpal Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The information
BCCH Emergency Department UPPER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: RENA HEATHCOTE RN
 - 1 - BCCH Emergency Department UPPER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: RENA HEATHCOTE RN - 2 - FRACTURES The shoulder Dislocation +/_ fracture of humeral head A dislocated shoulder generally follows
- 1 - BCCH Emergency Department UPPER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: RENA HEATHCOTE RN - 2 - FRACTURES The shoulder Dislocation +/_ fracture of humeral head A dislocated shoulder generally follows
Case 1. Your diagnosis
 Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
Case 1 44-year-old midwife presented with intermittent pins and needles in the little and ring fingers with blanching. Symptoms were exacerbated by cold exposure. Your diagnosis Diagnosis Hypothenar syndrome
PHYSIOTHERAPY PROTOCOLS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES
 PHYSIOTHERAPY PROTOCOLS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES Introduction As such, protocols in the management of brachial plexus injuries (BPI) are a bit of a misnomer. This
PHYSIOTHERAPY PROTOCOLS FOR THE MANAGEMENT OF DIFFERENT TYPES OF BRACHIAL PLEXUS INJURIES Introduction As such, protocols in the management of brachial plexus injuries (BPI) are a bit of a misnomer. This
How to Triage Orthopaedic Care. David W. Gray, M.D.
 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency Determine
How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency Determine
Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures
 Journal of the Accident and Medical Practitioners Association (JAMPA) 2006; Vol. 3 (No. 1) Accident and Medical Practitioners Association, New Zealand Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures Sarah Cooper, MBChB
Journal of the Accident and Medical Practitioners Association (JAMPA) 2006; Vol. 3 (No. 1) Accident and Medical Practitioners Association, New Zealand Volar Plate Avulsion Fractures Sarah Cooper, MBChB
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
A Patient's Guide to Ganglions of the Wrist
 Introduction A ganglion is a small, harmless cyst, or sac of fluid, that sometimes develops in the wrist. Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglions, but a ganglion that isn't painful and doesn't
Introduction A ganglion is a small, harmless cyst, or sac of fluid, that sometimes develops in the wrist. Doctors don't know exactly what causes ganglions, but a ganglion that isn't painful and doesn't
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME
 CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME Carpal tunnel syndrome results from the pinching or entrapping of the median nerve in the underside of the wrist. The actual pathology in most cases is due to either a decrease in
