Effect of Component Design in Retrieved Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty Systems
|
|
|
- Jean Hopkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Effect of Component Design in Retrieved Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty Systems Matthew D. Hess, MD; Erin A. Baker, MS; Meagan R. Salisbury, BS; Lige M. Kaplan, MD; Ryan T. Greene, BS; Perry W. Greene, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics. Search: Primary articulation of bipolar hemiarthroplasty systems is at the femoral head-liner interface. The purpose of this study was to compare observed damage modes on 36 retrieved bipolar systems with implant, demographic, intraoperative, and radiographic data to elucidate the effects of component design, specifically locking mechanism, on clinical performance. A Retrieved bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty systems of 3 different design types were obtained, disassembled, and evaluated macro- and microscopically for varying modes of wear, including abrasion, burnishing, embedding, scratching, and pitting. Clinical record review and radiographic analysis were performed by a senior orthopedic surgery resident. Average bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty system term of service was 46 months (range, months). All devices contained wear debris captured within the articulating space between the femoral head and liner. In 31% of patients without infection, lucency was observed on immediate prerevision radiographs. The system with a leaf locking mechanism showed significantly increased radiographically observed osteolysis (P5.03) compared with a system with a stopper ring locking mechanism. In addition, implant design and observed damage modes, including pitting and third-body particle embedding, were significantly associated with radiographically observed osteolysis. Figure: Captured debris from a retrieved MultiPolar (Zimmer, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana) bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty system, showing differential size in polyethylene wear debris generated in vivo (A, B). Scale bar, millimeters. B The authors are from the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery (MDH, LMK, PWG); and the Department of Orthopaedic Research (EAB, MRS, RTG), Beaumont Health System, Royal Oak, Michigan. The authors have a Stryker Corporation Rebate Agreement. A generous gift provided by Byron and Dorothy Gerson to establish the Byron and Dorothy Gerson Implant Analysis Fund supported this research. The Implant Retrieval Program at William Beaumont Hospital is partially funded by the Stryker Corporation. Other financial support was provided to the Beaumont Health System Department of Orthopaedic Research by the Stryker Corporation. This article is dedicated in memory of Harry N. Herkowitz, MD. Correspondence should be addressed to: Lige M. Kaplan, MD, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Beaumont Health System, Royal Oak, Michigan (ligekaplan@yahoo.com). doi: / e1180
2 Component Design in Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty Systems Hess et al According to the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 350,000 hospital admissions per year are due to hip fractures, a figure that is expected to double by the year Factors leading to this increase include rising rates of osteoporosis, an increase in the average lifespan, and an increase in the population of people older than 65 years. 1 Depending on the fracture type and comorbidities, treatment options include open reduction and internal fixation with cephalomedullary devices and joint replacement. Hemiarthroplasty is an accepted treatment option for displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients that decreases nonunion rates and eliminates avascular necrosis complications of the femoral head, both of which occur more frequently with internal fixation. 2,3 However, hemiarthroplasty is associated with complications, including increased risks of infection, dislocation, fracture, acetabular cartilage erosion, and implant loosening. 4 Acetabular cartilage erosion may lead to pain, component migration, acetabular protrusio, and eventually subsequent revision to total hip arthroplasty (THA). 5 The bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty (BHA) was developed to minimize acetabular wear, thereby reducing these complications. The BHA allowed 2 points of articulation, both between an outer shell and the acetabulum and between the inner femoral head and a polyethylene liner. 6 The BHA device is composed of a cobaltchromium-molybdenum (CoCrMo) alloy femoral head articulating against an ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene (UHMWPE) liner. The femoral head is subsequently locked into the liner, theoretically reducing the rate of dislocation. The liner is contained in a CoCrMo alloy shell that articulates with acetabular cartilage. The primary articulation of BHA devices is at the femoral head-liner interface, although in vivo evidence demonstrates motion between the CoCrMo alloy shell and acetabular cartilage. 7,8 Motion at the metal-polyethylene articulation may lead to generation of particulate debris, potentially leading to polyethylene wear induced osteolysis. 7 Although the CoCrMo-cartilage articulation is reduced in the BHA design, the constrained femoral head-liner articulation may promote polyethylene wear. Generation of polyethylene wear debris of a specific size range, morphology, and concentration is known to induce osteolysis, compromising the mechanical stability of implants. 9 Coleman et al 10 reported 31 consecutive BHAs converted to THAs, of which 56% showed radiographic evidence of osteolysis. Histologic investigation of tissues in these osteolytic zones demonstrated findings consistent with particle-induced osteolysis. 10 Tsumura et al 11 presented a mid-term follow-up of 30 patients with avascular necrosis treated with BHA, where 22.6% of the hips demonstrated osteolysis on the acetabular side and approximately 13% displayed osteolysis on the femoral side. Hips with osteolysis had a significantly greater amount of prosthesis migration compared with those without osteolysis, 11 which was consistent with findings described by Ishihara et al. 12 Other studies have shown that embedded periarticular wear debris induces osteolysis and the progression of femoroacetabular joint degeneration. 13,14 Despite numerous reported cases of osteolysis and subsequent loosening observed with BHA systems, no studies correlate radiographic findings and medical record review with ex vivo evaluation of implant damage. 10,15,16 Hara et al 17 performed an analysis of 23 retrieved BHA systems and reported mechanical damage and oxidation of the UHMWPE liners. Kusaba and Kuroki 18 performed an in situ radiographic analysis of total UHMWPE wear in uncemented BHAs. The authors measured penetration of the femoral head into the acetabular liner but did not compare linear wear measurements to damage on retrieved device components. 18 Kusaba and Kuroki 19 also analyzed the surface roughness of 40 retrieved bipolar femoral heads and measured the associated polyethylene wear to determine changes in surface configuration. However, no studies have characterized damage modes of all BHA system components to understand the relationships between polyethylene and metallic damage and radiographic findings, patient demographics, and surgical data, which may lead to clinical failure. The purpose of the current study was to compare damage modes observed on retrieved BHA components with implant design type and radiographic findings to elucidate the effects of component design (locking mechanism specifically) and material selection on clinical performance and failure. Materials and Methods Following institutional review board approval, 36 explanted BHA systems were obtained and disassembled between 2002 and Devices were obtained within 1 week of surgery and ultrasonically cleaned in a diluted Micro-90 solution (International Products Corporation, Burlington, New Jersey) for 5 minutes, followed by an ultrasonic bath in 85% (or greater) ethanol solution for 5 minutes. Devices were allowed to air dry and were vacuum-sealed to prevent oxidation, de-identified by labeling with an explant identification number, and entered into an electronic database. The 36 retrieved explanted BHA systems included the following 3 design types: 9 Centrax (CX; Stryker Orthopaedics, Mahwah, New Jersey), 20 Self-Centering (SC; DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana), and 7 MultiPolar (MP; Zimmer, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana) systems (Figure 1). Implant types differ mainly by the locking mechanism used to prevent dissociation of the femoral head from the UHMWPE liner. The CX design has a leaf locking mechanism, whereas the SC and MP designs have stopper ring locking mechanisms. Individual components included 36 CoCrMo shells, 36 UHMWPE liners, 36 SEPTEMBER 2013 Volume 36 Number 9 e1181
3 CoCr femoral heads, and 26 titanium or CoCr alloy femoral stems. Nineteen femoral stems were cemented and 17 were uncemented. One stem (MP) was designed as press-fit but was cemented at implantation. Little evidence exists implicating cement fixation with improved or deficient clinical outcomes compared with press-fit fixation of femoral stems. 6 For all design types, the UHMWPE liner was composed of conventional UHMWPE, which was sterilized using gamma irradiation in an inert environment (eg, inert gas or vacuum). The UHMWPE was not subject to further cross-linking than the minimal amount that occurs during sterilization. Retrieved BHA components were first evaluated visually for damage. Five damage modes were identified, including abrasion, burnishing, third-body particle embedding, pitting, and scratching/grooving. 20 The components were also evaluated under light microscopy and scanning electron microscopy to further evaluate the extent of damage. Ultra-high-molecularweight polyethylene components were sputter-coated with gold palladium prior to evaluation under scanning electron microscopy to improve electron conduction. Medical record review was performed to collect pertinent clinical data, such as age at implantation and revision, body mass index (BMI), sex, implant term of service, and reason(s) for implantation and revision surgeries. Available serial radiographs were collected for the term of service of the implant (from immediately postimplantation to immediately prerevision) for analysis of device alignment, lucency, and the presence or absence of cement and/ or metallic debris. Radiographic analyses were performed by a senior orthopedic surgery resident (M.D.H.). The location(s) of loosening, characterized radiographically as the presence of lucency, was defined by zone, as established by Gruen et al. 21 Devices were further stratified by infected and noninfected cases to differentiate between septic vs aseptic loosening, and infected devices were excluded from radiographic analysis for osteolysis. Implant alignment was characterized as acceptable, varus, subsided, or retroverted. Statistical analyses were performed with SigmaPlot version 11.0 statistical software (Systat Software, Inc, Chicago, Illinois) to understand the relationships between patient populations, damage mode and radiographic observations, and implant designs. First, Mann-Whitney rank sum analysis was performed to compare the patient populations in each design cohort. Second, chi-square analysis was used to compare the proportion of each observed damage mode in each design cohort. A Spearman rank order analysis was performed to ascertain any correlations between patient factors (eg, BMI, age at implantation) and implant designs. To explore relationships between observed damage modes, intraoperative observations, and radiographic data by design type, an analysis of variance analysis model (a50.05) was performed for each component. 1A 1B 1C Figure 1: Photographs of 3 retrieved bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty design types: Centrax (Stryker Orthopaedics, Mahwah, New Jersey) (A), Self-Centering (DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana) (B), and MultiPolar (Zimmer, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana) (C). Finally, the designs were split into 2 groups, leaf locking and stopper ring locking mechanisms, and Spearman rank order analyses were performed to determine whether relationships between observed damage modes or radiographic data were associated with the locking mechanism. For the correlation analyses, correlation coefficients of 0.20 to 0.40 were considered weak, 0.40 to 0.60 were considered moderate, 0.60 to 0.80 were considered strong, and 0.80 to 1.00 were considered very strong. 22 Cases of confirmed infection were removed when analyzing intraoperative and radiographic observational data. Results Medical Record Review Patient demographic data were collected (Table 1). Reasons for implantation were femoral neck fracture (n535) and avascular necrosis (n51). Average implant term of service for aseptic and septic devices were 68 months (range, months) e1182
4 Component Design in Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty Systems Hess et al Table 1 Patient Demographics of Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty Revisions by Design Type and Locking Mechanism Demographic All SC MP CX: Leaf Locking SC & MP: Stopper Ring Patient sex, No. F/M 25/11 14/6 1/6 5/4 15/12 Side, No. L/R 22/14 11/9 5/2 6/3 16/11 Mean BMI, kg/m (16-47) Mean age at implant, y Mean age at revision, y (49-90) (56-93) 2665 (16-36) (54-90) (56-92) 3068 (25-47) (55-90) (57-90) 2463 (20-29) (49-84) 8069 (62-93) 2766 (16-47) (54-90) (56-92) Abbreviations: BMI, body mass index; CX, Centrax (Stryker Orthopaedics, Mahwah, New Jersey); F, female; L, left; M, male; MP, MultiPolar (Zimmer, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana); R, right; SC, Self-Centering (DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana). Table 2 Reasons for Revision of Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty No. (%) Reason for Revision All SC MP CX: Leaf Locking SC & MP: Stopper Ring Dislocation 2 (6) 2 (10) 0 (0) 0 (0) 2 (7) Fracture 3 (8) 0 (0) 0 (0) 3 (33) 0 (0) Infection 9 (25) 5 (25) 2 (29) 2 (22) 7 (26) Instability 3 (8) 1 (5) 0 (0) 2 (22) 1 (4) Leg-length discrepancy 1 (3) 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (11) 0 (0) Loosening 4 (11) 0 (0) 3 (43) 0 (0) 3 (11) Pain 20 (56) 13 (65) 3 (43) 3 (33) 16 (59) Abbreviations: CX, Centrax (Stryker Orthopaedics, Mahwah, New Jersey); MP, MultiPolar (Zimmer, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana); SC, Self-Centering (DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana). Table 3 Intraoperative Observations at Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty Revision No. (%) Observation All SC MP CX: Leaf Locking SC & MP: Stopper Ring Cemented 19 (53) 9 (45) 2 (29) 8 (89) 11 (41) Infection 18 (50) 13 (65) 3 (43) 2 (22) 16 (59) Instability 11 (31) 4 (20) 2 (29) 5 (56) 6 (22) Aseptic loosening 12 (33) 3 (15) 2 (29) 7 (78) 5 (19) Septic loosening 5 (14) 3 (15) 1 (14) 1 (11) 4 (15) Pain 35 (97) 19 (95) 7 (100) 9 (100) 26 (96) Abbreviations: CX, Centrax (Stryker Orthopaedics, Mahwah, New Jersey); MP, MultiPolar (Zimmer, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana); SC, Self-Centering (DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana). and 42 months (range, months), respectively, with an overall average of 55 months (range, months). Reasons for revision included pain (n520), infection (n59), loosening (n54), fracture (n53), instability (n53), dislocation (n52), and leg-length discrepancy (n51) (Table 2). Fixation and status of implant loosening, infection, stability, and patient pain were collected from operative notes (Table 3). Of the 36 devices, 47% (n517) demonstrated loosening, 33% (n512) of which were aseptic, as determined by records of intraoperative documentation by the surgeon. Radiographic Analysis Radiographic analysis determined the presence or absence and location of osteolysis, septic loosening, and metallosis, as well as implant alignment. Protrusio was not noted in any device. Femoral osteolysis was observed radiographically in 11 of 18 aseptic hips and categorized by Gruen zone. Acetabular osteolysis was observed medially in 1 MP device. Septic loosening was also observed in 5 of 18 infected hips and categorized by Gruen zone (Figure 2). Metallosis was noted in 1 SC device. More than 64% of the implants demonstrated acceptable positioning (Table 4). Damage Mode Analysis On disassembly, it was noted that biologic or wear debris was captured within the articulation between the femoral head and UHMWPE liner, as well as between the UHMWPE liner and CoCrMo alloy shell, in all BHA devices, regardless of design and cleaning methodology (Figure 3). None of the retrieved BHA components experienced catastrophic failure; however, laboratory analysis indicated both polyethylene and metallic components experienced damage, with 5 damage modes identified: abrasion, burnishing, embedding, pitting, and scratching/grooving (Figure 4). The UHMWPE liner components showed the greatest frequency of damage modes. Abrasion (n515 [52%]), embed- SEPTEMBER 2013 Volume 36 Number 9 e1183
5 2A Figure 2: Graphs showing the frequency of radiographically observed osteolysis (A) and septic loosening (B) by zone and bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty design. 2B ding (n517 [47%]), and pitting (n521 [58%]) were each documented in more than 40% of liners, while scratching/ grooving was observed on approximately 72% (n526) of liners. Of the observed damage modes, only 4 (grooving/scratching, burnishing, pitting, and embedding) were detected on the metallic components. Scanning electron microscopy revealed the extent of these damage modes on several explants (Figure 5). Centrax UHMWPE liners demonstrated the highest incidence of pitting corrosion (n57 [77%]) and the lowest incidences of abrasion (n51 [11%]), burnishing (n52 [22%]), and scratching/ grooving (n55 [56%]). Self-Centering UHMWPE liners exhibited the highest incidence of abrasion (n511 [55%]), burnishing (n510 [50%]), and embedding (n514 [70%]). MultiPolar UHM- WPE liners showed the highest incidence of scratching/grooving (n57 [100%]) and the lowest incidences of embedding (n50 [0%]) and pitting corrosion (n52 [29%]). MultiPolar metallic components (ie, femoral head, femoral stem, and shell) showed the highest incidences of scratching/grooving (n54 [57%], n55 [83%], and n54 [57%], respectively) and pitting corrosion (n55 [71%], n54 [67%], and n53 [43%], respectively) and the lowest incidences of burnishing (n51 [14%], n50 [0%], and n51 [14%], respectively) and embedding (n50 [0%] for all components). Self-Centering metallic components showed the highest incidence of burnishing (n511 [55%], n53 [27%], and n512 [60%], respectively). Analysis of the nonarticulating surface of the UHMWPE liner, which is in contact with the metallic shell, revealed additional damage, with 13 UHMWPE liners showing evidence of impingement (CX, n51; SC, n59; MP, n53). Table 4 Summary of Radiographic Analysis Data of BHA Systems Using Immediate Postimplantation and Prerevision Radiographs No. (%) Variable All SC MP CX: Leaf Locking SC & MP: Stopper Ring Metallosis 1 (3) 1 (5) 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (4) Osteolysis 11 (31) 2 (10) 3 (43) 6 (67) 5 (19) Lucency (septic hip) 4 (11) 2 (10) 0 (0) 2 (22) 2 (7) Cement extrusion 2 (6) 2 (10) 0 (0) 0 (0) 2 (7) Acceptable alignment 25 (69) 15 (75) 6 (86) 3 (33) 21 (78) Varus alignment 10 (28) 3 (15) 1 (14) 6 (67) 4 (15) Subsidence 1 (3) 1 (5) 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (4) Retroversion 1 (3) 1 (5) 0 (0) 0 (0) 1 (4) Abbreviations: BHA, bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty; CX, Centrax (Stryker Orthopaedics, Mahwah, New Jersey); MP, MultiPolar (Zimmer, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana); SC, Self-Centering (DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana). Statistical Analysis Patient demographics and surgical factors, including BMI, age at implantation, age at revision, surgical side, implant term of service, sex, fixation (ie, cemented or uncemented), and implant head size, were compared for each implant design cohort using the Mann-Whitney rank sum test. The significant differences were a greater average BMI in the MP than in the CX designs (P5.03) and an increased rate of cemented fixation in the CX than in the SC e1184
6 Component Design in Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty Systems Hess et al 3A 3B 3C 3D Figure 3: Captured debris from retrieved bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty systems, including Centrax (Stryker Orthopaedics, Mahwah, New Jersey) (A, B), Self- Centering (DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana) (C, D), and MultiPolar (Zimmer, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana) (E, F), showing differential sizes in polyethylene wear debris generated in vivo. Scale bar, millimeters. 3E 3F 4A 4B 4C Figure 4: Graphs showing damage mode analysis of retrieved bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty systems: all (A), Centrax (Stryker Orthopaedics, Mahwah, New Jersey) (B), Self-Centering (DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana) (C), and MultiPolar (Zimmer, Inc, Warsaw, Indiana) (D) implant designs. 4D SEPTEMBER 2013 Volume 36 Number 9 e1185
7 5A 5B 5C Figure 5: Scanning electron micrographs of damage on the retrieved bipolar hemiarthroplasty components, including pitting on the femoral head (original magnification 3250) (A), abrasion (original magnification 3370) (B) and scratching on the ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene liner (original magnification 3370) (C). (P5.03) or MP (P5.02) designs. In addition, the average implant head size of the CX design was significantly greater than that of the SC design (P5.03), which was significantly greater than that of the MP design (P5.02). A chi-square analysis compared the proportion of each observed damage mode in each design cohort and showed no significant variability in the proportions between damage mode observations in each implant design cohort. Several significant correlations were found between patient demographics, surgical data, and implant cohorts using a Spearman rank order analysis. Multipolar and SC designs were significantly less likely than the CX design to be cemented (r50.40; P5.02). Cement fixation was negatively moderately correlated with BMI (r520.46; P5.01) and positively moderately correlated with ages at implantation (r50.42; P5.01) and revision (r50.46; P5.01). A significant negative weak correlation was also found between BMI and age at revision (r520.34; P5.05). Centrax explants showed a significantly greater incidence of radiographically observed osteolysis (P5.03) compared with SC explants, when infected cases were excluded; however, no additional statistically significant associations existed between loosening (intraoperative observation) or radiographic osteolysis when comparing any of the other explants. Individual components were also analyzed to assess the relationship between component damage and radiographic observations. For the femoral head, damage modes of scratching/grooving (P5.01), burnishing (P5.01), and embedding (P,.001) were significantly associated with increased frequency of radiographically observed osteolysis in the CX vs the SC designs. For the UHMWPE liner, scratching/grooving (P,.01), burnishing (P5.01) and embedding (P,.01) damage were also significantly related to greater frequency of radiographically observed osteolysis in the CX vs the SC designs. Scratching/grooving (P,.01), burnishing (P,.001), pitting (P5.01) and embedding (P,.001) damage to the shell were associated with significantly greater frequency of radiographically observed osteolysis in the CX vs the SC designs. Finally, Spearman rank order analyses correlated the observed damage modes and radiographic data, based on 2 cohorts delineated by locking mechanism (ie, leaf locking [CX] and stopper ring [SC, MP]). Liner abrasion damage was weakly correlated to stopper ring implants (r50.36; P5.03). Several damage modes were more likely to occur in concert. Liner abrasion and third-body embedding damage were positively weakly correlated (r50.33; P5.05). Embedding and burnishing on the shell were positively moderately correlated (r50.50; P,.01). On the stem, scratching and pitting were positively moderately correlated (r50.54; P5.01). No significant correlations existed between locking mechanism (leaf locking or stopper ring) and radiographically observed osteolysis, metallosis, or cement extrusion. Discussion Understanding the mechanics and failure mechanisms of orthopedic devices is crucial to development of surgeon technique, patient treatment, and, ultimately, patient outcomes. Bipolar hemiarthroplasty is a viable treatment option for the growing number of femoral neck fractures in the elderly population. However, as with any metal-on-polyethylene articulation, polyethylene debris generation, subsequent osteolysis, and eventual loosening of the implant are potential detrimental consequences. In the current study, damage modes and rates of osteolysis and aseptic loosening for this series of 36 retrieved bipolar systems were identified and defined. To the authors knowledge, this is the first retrieval-based design study for BHA that evaluated all components of each BHA system and related the retrieval analysis to clinical and radiographic data. Due to the retrieval-based nature of this study, a control has not been established to validate revision rates of BHA systems with regard to the observed damage modes; however, sta- e1186
8 Component Design in Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty Systems Hess et al tistical analysis showed the demographics of the cohorts were approximately equivalent, with cemented fixation, implant size, and BMI as the only significantly different factors. A relationship between aseptic osteolysis and implant loosening has been established and is attributed to implant wear. 23,24 Delaminated polyethylene thirdbody wear particles collected during disassembly of the components (Figure 3), in concert with the observed damage on all of the components, may be a strong predictor of accelerated wear to BHA components. Altered kinematics of the system due to component wear and impingement, as well as the presence of particulate debris, may initiate an inflammatory response. 25,26 Microscopy confirmed the presence of bone cement particles and metallic wear debris embedded in numerous polyethylene liners. The accelerated wear by third-body particles may ultimately lead to early device failure or revision. 24 When infected cases were excluded, CX explants showed a significantly greater incidence of radiographically observed osteolysis (n56 [86%]) compared with SC explants (n52 [29%]). Damage to the CX liners was also significantly associated with radiographically observed osteolysis. The leaf locking mechanism and slotted design of the CX polyethylene liner may create increased surface area and sharp corners, which may then act as locations for stress concentrations, allowing crack initiation and, ultimately, damage and wear of the liner. A statistically significant relationship between radiographically observed osteolysis and implant design was not demonstrated with the stopper ring locking mechanism explants; however, no definitive conclusions can be drawn to implicate design type alone as a generator of increased wear, due to the retrospective nature of this study and the small sample size. Kusaba and Kuroki 19 retrieved 40 bipolar femoral heads and observed increased polyethylene wear when the roughness of the femoral head increased. In their study, the bipolar femoral heads showed significantly greater surface roughness than the unconstrained THA femoral heads of the same material, which correlated with the amount of polyethylene wear. The current study also found damage to the femoral heads in the form of burnishing, embedding, scratching/grooving, and pitting in conjunction with adjacent liner damage. Kusaba and Kuroki 18 performed a radiographic wear analysis of 68 uncemented BHAs with Livermore s method and found that linear wear averaged 1.4 mm in situ (range, mm) and 0.17 mm per year (range, mm/year). They observed deep rim abrasion in osteolytic hips, whereas the current study found scratching/grooving, burnishing, and embedding of debris into the liner to be significantly related to radiographically observed osteolysis. A retrieval analysis of 24 UHMWPE liners by Hara et al 17 found that 92% of liners showed signs of neck-cup impingement. Although burnished surfaces were observed on all of the retrieved liners, the authors reported no other localized damage modes. Thus, the authors concluded that the primary cause of osteolysis in their study population was a direct result of the observed impingement and not due to wear debris generated from the bearing surface. The current study observed neckcup impingement in 13 of 36 retrievals (CX, n51; SC, n59; MP, n53), only 3 of which showed evidence of osteolysis or aseptic loosening radiographically (SC, n52; MP, n51). Conclusion Clinical failure of BHA is a multifactorial issue in which the ultimate performance of the implant is affected by patient factors, surgical elements, and implant characteristics. Eventually, component wear may lead to third-body wear particles, resulting in an inflammatory and osteolytic environment, and these elements become contributory factors to clinical failure. 27 The current study found that implant design and associated damage modes were significantly associated with the incidence of radiographically observed osteolysis but did not significantly affect the implant term of service. In general, the BHA implants with a leaf locking mechanism exhibited greater incidences of radiographically observed osteolysis and intraoperatively observed loosening than did BHAs with a stopper ring locking mechanism; however, the explants with a stopper ring locking mechanism demonstrated an increased incidence of neck-cup impingement. Bipolar hemiarthroplasty can provide satisfactory long-term results in the elderly patient population with femoral neck fractures. This study has shown that BHA systems are subject to both polyethylene and metallic component wear, which have been associated with inflammation and osteolysis. With polyethylene delamination encountered in all 3 implant designs, a role may exist for highly cross-linked polyethylene, which is associated with increased wear resistance and increased stability against oxidation, to reduce the wear and eventual migration of wear debris to the adjacent acetabular cartilage. 28,29 With currently available implants, consideration should be given to patient factors and implant design during hemiarthroplasty selection. References 1. Morris AH, Zuckerman JD. National consensus conference on improving the continuum of care for patients with hip fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84(4): Bhandari M, Devereaux PJ, Tornetta P III, et al. Operative management of displaced femoral neck fractures in elderly patients. An international survey. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(9): Frihagen F, Nordsletten L, Madsen JE. Hemiarthroplasty or internal fixation for intracapsular displaced femoral neck fractures: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2007; 335(7632): Kannan A, Kancherla R, McMahon S, Hawdon G, Soral A, Malhotra R. Arthroplasty options in femoral-neck fracture: answers from the national registries. Int Orthop. 2012; 36(1):1-8. SEPTEMBER 2013 Volume 36 Number 9 e1187
9 5. Hedbeck CJ, Blomfeldt R, Lapidus G, Tornkvist H, Ponzer S, Tidermark J. Unipolar hemiarthroplasty versus bipolar hemiarthroplasty in the most elderly patients with displaced femoral neck fractures: a randomised, controlled trial. Int Orthop. 2011; 35(11): Parker MJ, Gurusamy KS, Azegami S. Arthroplasties (with and without bone cement) for proximal femoral fractures in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010(6):CD Drinker H, Murray WR. The universal proximal femoral endoprosthesis. A shortterm comparison with conventional hemiarthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979; 61(8): Phillips TW. The Bateman bipolar femoral head replacement. A fluoroscopic study of movement over a four-year period. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987; 69(5): Harris WH. The problem is osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995; (311): Coleman SH, Bansal M, Cornell CN, Sculco TP. Failure of bipolar hemiarthroplasty: a retrospective review of 31 consecutive bipolar prostheses converted to total hip arthroplasty. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ). 2001; 30(4): Tsumura H, Torisu T, Kaku N, Higashi T. Five- to fifteen-year clinical results and the radiographic evaluation of acetabular changes after bipolar hip arthroplasty for femoral head osteonecrosis. J Arthroplasty. 2005; 20(7): Ishihara H, Matsui H, Ohmori K, Yoshino O. Rapidly progressive proximal migration of bipolar endoprosthesis due to osteolysis induced by polyethylene debris. Orthopedics. 2000; 23(10): Hansson U, Blunn G, Ryd L. Histologic reactions to particulate wear debris in different mesenchymal tissues: studies on the nonreplaced compartment from revised uni-knees. J Arthroplasty. 2004; 19(4): Amstutz HC, Campbell P, Kossovsky N, Clarke IC. Mechanism and clinical significance of wear debris-induced osteolysis. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1992; (276): Nakata K, Ohzono K, Masuhara K, Matsui M, Hiroshima K, Ochi T. Acetabular osteolysis and migration in bipolar arthroplasty of the hip: five- to 13-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997; 79(2): Kobayashi S, Takaoka K, Tsukada A, Ueno M. Polyethylene wear from femoral bipolar neck-cup impingement as a cause of femoral prosthetic loosening. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1998; 117(6-7): Hara K, Kaku N, Tsumura H, Torisu T. Analysis of wear and oxidation on retrieved bipolar polyethylene liner. J Orthop Sci. 2008; 13(4): Kusaba A, Kuroki Y. Wear of bipolar hip prostheses. J Arthroplasty. 1998; 13(6): Kusaba A, Kuroki Y. Femoral component wear in retrieved hip prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1997; 79(2): Hood RW, Wright TM, Burstein AH. Retrieval analysis of total knee prostheses: a method and its application to 48 total condylar prostheses. J Biomed Mater Res. 1983; 17(5): Gruen TA, McNeice GM, Amstutz HC. Modes of failure of cemented stem-type femoral components: a radiographic analysis of loosening. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1979; (141): Nam D, Kepler CK, Nho SJ, Craig EV, Warren RF, Wright TM. Observations on retrieved humeral polyethylene components from reverse total shoulder arthroplasty. J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2010; 19(7): Hozack WJ, Mesa JJ, Carey C, Rothman RH. Relationship between polyethylene wear, pelvic osteolysis, and clinical symptomatology in patients with cementless acetabular components. A framework for decision making. J Arthroplasty. 1996; 11(7): Hallab NJ, Jacobs JJ. Biologic effects of implant debris. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 2009; 67(2): Baxter RM, Freeman TA, Kurtz SM, Steinbeck MJ. Do tissues from THA revision of highly crosslinked UHMWPE liners contain wear debris and associated inflammation? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469(8): Kohilas K, Lyons M, Lofthouse R, Frondoza CG, Jinnah R, Hungerford DS. Effect of prosthetic titanium wear debris on mitogeninduced monocyte and lymphoid activation. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999; 47(1): Waddell J, Pritzker KP, Boynton EL. Increased cytokine secretion in patients with failed implants compared with patients with primary implants. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2005; (434): Kurtz SM, Muratoglu OK, Evans M, Edidin AA. Advances in the processing, sterilization, and crosslinking of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene for total joint arthroplasty. Biomaterials. 1999; 20(18): Martell JM, Verner JJ, Incavo SJ. Clinical performance of a highly cross-linked polyethylene at two years in total hip arthroplasty: a randomized prospective trial. J Arthroplasty. 2003; 18(7 suppl 1): e1188
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?
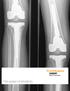
![Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis?](/thumbs/78/78456133.jpg) Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Case report: Pain L THR [ post THR 2 years; with history of trivial fall] Your Diagnosis? Diagnosis: Ceramic head fracture In the 1970 s, Boutin implemented ceramic in modern total hip arthroplasty (THA).
Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo?
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners. Design Rationale Surgical Technique
 Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
Enhanced Stability Constrained Liners Design Rationale Surgical Technique The Pinnacle Acetabular Cup System was designed to maximize the number of options available to the surgeon, and provide those options
ESC. Enhanced Stability Liners. Design Rationale & Surgical Technique
 ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
ESC Enhanced Stability Liners Design Rationale & Surgical Technique Choice Without Compromise DePuy Synthes PINNACLE Hip Solutions are designed with a wide range of acetabular cup options, biological and
Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Duraloc CONSTRAINED LINER A COMPREHENSIVE ACETABULAR REVISION SYSTEM DURALOC CONSTRAINED LINER Introduction Dislocation is the most common postoperative complication in total hip reconstruction.
DISCLOSURE FNFX ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? 11/21/2016 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET
 FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? GEORGE HAIDUKEWYCH, MD ORLANDO, FLORIDA DISCLOSURE ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET CONSULTING DEPUY, SYNTHES, BIOMET, RESPONSIVE ORTHOPEDICS STOCK OWNERSHIP ORTHOPEDIATRICS
FEMORAL NECK FRACTURES: ORIF OR ARTHROPLASTY? GEORGE HAIDUKEWYCH, MD ORLANDO, FLORIDA DISCLOSURE ROYALTIES DEPUY, BIOMET CONSULTING DEPUY, SYNTHES, BIOMET, RESPONSIVE ORTHOPEDICS STOCK OWNERSHIP ORTHOPEDIATRICS
Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval
 Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval J. P. Collier,* M. B. Mayor,+ V. A. Surprenant,* H. P. Surprenant,* and R.E. Jensen* *Dartmouth Biomedical
Examination of Porous-Coated Patellar Components and Analysis of the Reasons for Their Retrieval J. P. Collier,* M. B. Mayor,+ V. A. Surprenant,* H. P. Surprenant,* and R.E. Jensen* *Dartmouth Biomedical
Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
 Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Mechanics of Contact and Lubrication, MTM G230 Department of Mechanical & Industrial Enineering Northeastern University Spring 2006 Wear Properties of UHMWPE in CHARITE Artificial Inter-vertebral Disc
Stability without compromise. Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert
 Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Stability without compromise Epsilon Durasul Constrained Insert History of Dislocation and Constrained Acetabular Inserts The Need for a Better Solution The Problem Dislocation is the second most common
Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric
 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (5): 493 498 493 Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures A cohort study with 5 11 year follow-up of 88 consecutive patients Anders
Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (5): 493 498 493 Hip arthroplasty after failed fixation of trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures A cohort study with 5 11 year follow-up of 88 consecutive patients Anders
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Poly Acetabular System Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell with X3 Poly insert Trident Hemispherical Acetabular
ARTICLE IN PRESS. Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction. Effects on Polyethylene Wear
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 00 No. 0 2008 Surface Oxidized Zirconium Total Hip Arthroplasty Head Damage Due to Closed Reduction Effects on Polyethylene Wear William L. Jaffe, MD,* Eric J. Strauss,
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
ACETABULAR CUP SURGICAL TECHNIQUE ACETABULAR CUP DEVICE INDICATIONS FOR USE The ICONACY I-Hip total hip replacement is indicated for the following conditions: 1. A severely painful and/or disabled hip
DePuy Orthopaedics, Inc. 700 Orthopaedic Drive Warsaw, IN USA Tel: +1 (800) Fax: +1 (574)
 References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
References 1. Sanchez-Sotelo J, Haidukewych GJ, Boberg CJ. Hospital Cost of Dislocation After Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg. 2006;88A:290-294. 2. Brodner W, Grübl A, Jankovsky R, Meisinger
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 22/ Mar 16, 2015 Page 3785
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FRACTURE NECK OF FEMUR TREATED WITH UNIPOLAR AND BIPOLAR HEMIARTHROPLASTY V. Nava Krishna Prasad 1, B. Mohammed Ghouse 2, B. Jaya Chandra Reddy 3, L. Abhishek 4 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE:
Hip Fracture Management. Product overview
 Hip Fracture Management Product overview Hip Fracture Management Intracapsular fractures Total hip replacement (THR) can offer clinical benefits over traditional internal fixation or hemiarthroplasty solutions
Hip Fracture Management Product overview Hip Fracture Management Intracapsular fractures Total hip replacement (THR) can offer clinical benefits over traditional internal fixation or hemiarthroplasty solutions
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital, Whitefield,
Positioning Sleeve Surgical Technique
 Positioning Sleeve Surgical Technique Surgical Technique The Comprehensive Fracture System offers a unique tool to evaluate and re-establish humeral height, which can be critical to restoring proper biomechanics
Positioning Sleeve Surgical Technique Surgical Technique The Comprehensive Fracture System offers a unique tool to evaluate and re-establish humeral height, which can be critical to restoring proper biomechanics
Bi-Polar 22.2mm & 28mm System - Operative technique
 Disclaimer Biomet UK Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend any particular surgical technique for use on a specific patient. The surgeon who performs
Disclaimer Biomet UK Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend any particular surgical technique for use on a specific patient. The surgeon who performs
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only.
 The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
The information contained in this document is intended for healthcare professionals only. Trident Hemispherical Acetabular Shell Trident PSL HA Acetabular Shell Featuring: The Trident Acetabular System
Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2. Preparation of the Acetabulum 4. Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5.
 Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
Surgical Technique Contents Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5 Cup Positioning 6 Joint Stability 7 Trial sizing and Impaction
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC.
 CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS HIP SYSTEMS Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS HIP SYSTEMS Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
Cement Polished Tapered Stems of 12/14 Taper. 96 mm 98 mm 104 mm 110 mm 116 mm 122 mm 128 mm. Ceramic Femoral Head. Outer Diameter
 Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Design Philosophy Cementless Stems of 12/14 Taper Stem Length Neck shaft Angle STEM-N3 STEM-N4 STEM-N5 STEM-N6 STEM-N7 STEM-N8 STEM-N9 123 mm 125 mm 130 mm 135 mm 140 mm 145 mm 150 mm 132 Cement Polished
Optimum implant geometry
 Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
Surgical Technique Optimum implant geometry Extending proven Tri-Lock heritage The original Tri-Lock was introduced in 1981. This implant was the first proximally coated tapered-wedge hip stem available
CAUTION: Ceramic liners are not approved for use in the United States.
 Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
Total Hip Prostheses, Self-Centering Hip Prostheses and Hemi-Hip Prostheses IMPORTANT: This essential product information sheet does not include all of the information necessary for selection and use of
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE CEMENTED & PRESS-FIT UNIFIED INSTRUMENTATION INTRAOPERATIVE FLEXIBILITY PROVEN BIOMECHANICS INTRODUCTION The Summit Tapered Hip System s comprehensive set of implants and instruments
National Joint Replacement Registry. Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement
 National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
National Joint Replacement Registry Lay Summary 2015 Annual Report Hip and Knee Replacement SUPPLEMENTARY REPORT 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS Introduction... 1 A brief history of the Registry origins... 1 The
Progeny Hip Stem. Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications
 Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Progeny Hip Stem Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Progeny Hip Stem Introduction With emphasis on maximum stability and ease of use, the StelKast ProgenyTM Hip System provides the surgeon with
Active Articulation E1
 Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Dual Mobility: Not a
Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Design Rationale Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Trauma Technology Active Articulation E1 Dual Mobility Hip System Dual Mobility: Not a
Poor mid-term results of total hip arthroplasty with use of a Hylamer liner
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 337-342 ORIGINAL STUDY Poor mid-term results of total hip arthroplasty with use of a Hylamer liner Adrian SKWARA, Simone STRACKE, Carsten O. TIBESKU, Susanne FUCHS-WINKELMANN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 74, 337-342 ORIGINAL STUDY Poor mid-term results of total hip arthroplasty with use of a Hylamer liner Adrian SKWARA, Simone STRACKE, Carsten O. TIBESKU, Susanne FUCHS-WINKELMANN
G7 ACETABULAR SYSTEM. beautifully. efficient.
 G7 ACETABULAR SYSTEM beautifully efficient. HERITAGE MEETS MODERN DESIGN SIMPLICITY, EFFICIENCY AND PERFORMANCE The G7 System is a multi-bearing acetabular platform delivering simplicity, efficiency and
G7 ACETABULAR SYSTEM beautifully efficient. HERITAGE MEETS MODERN DESIGN SIMPLICITY, EFFICIENCY AND PERFORMANCE The G7 System is a multi-bearing acetabular platform delivering simplicity, efficiency and
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DePuy Synthes DURALOC Surgical Technique CONTENTS Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum
This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. SURGICAL TECHNIQUE DePuy Synthes DURALOC Surgical Technique CONTENTS Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum
TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT:
 THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
THR Prosthesis Design TOTAL HIP REPLACEMENT: PROSTHESIS DESIGN FEATURES JESS JOHNSTON & MELINDA ZIETH History of Hip Prosthesis Joint Replacement Registry Implant Design Technology & Future History and
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD
 UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
UHMWPE LONGEVITY: INFLUENCES OF THE ORTHOPAEDIC TRIAD AMERICAN ACADEMY OF ORTHOPAEDIC SURGEONS 66th Annual Meeting February 4-9, 1999 Anaheim, California COMMITTEE ON BIOMEDICAL ENGINEERING COMMITTEE ON
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
A NEW APPROACH TO BEARING SURFACES FOR TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY by Timothy McTighe, Exec. Dir., JISRF, Chagrin Falls, Ohio Ying Ko, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio Russell B. Bennett, Ph.D., Cincinnati, Ohio James
Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists
 : 31 35 doi 10.1308/1478708051450 Audit Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists Jac Ciampolini, Matthew JW Hubble Princess Elizabeth Orthopaedic Centre,
: 31 35 doi 10.1308/1478708051450 Audit Early failure of total hip replacements implanted at distant hospitals to reduce waiting lists Jac Ciampolini, Matthew JW Hubble Princess Elizabeth Orthopaedic Centre,
Wear Analysis of Second-generation Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty
 Wear Analysis of Second-generation Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Christopher Samujh, MD; Samrath Bhimani, MS; Langan Smith, BS; Arthur L. Malkani, MD abstract A major
Wear Analysis of Second-generation Highly Cross-Linked Polyethylene in Primary Total Hip Arthroplasty Christopher Samujh, MD; Samrath Bhimani, MS; Langan Smith, BS; Arthur L. Malkani, MD abstract A major
CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician.
 CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician. ENGLISH Mpact 3D Metal Implants and Augments 3D Metal INSTRUCTION FOR USE Important notice: the device(s) can
CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician. ENGLISH Mpact 3D Metal Implants and Augments 3D Metal INSTRUCTION FOR USE Important notice: the device(s) can
Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem
 Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem Clinical Results of the Tri-lock BPS Femoral Stem at One Year Follow-Up William L. Healy, M.D. Lahey Clinic Medical Center Burlington, Massachusetts Introduction Cementless
Tri-Lock Bone Preservation Stem Clinical Results of the Tri-lock BPS Femoral Stem at One Year Follow-Up William L. Healy, M.D. Lahey Clinic Medical Center Burlington, Massachusetts Introduction Cementless
Bipolar versus fixed-head hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients
 Strat Traum Limb Recon (2011) 6:1 6 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0100-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bipolar versus fixed-head hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients Mostafa Abdelkhalek Mohamed
Strat Traum Limb Recon (2011) 6:1 6 DOI 10.1007/s11751-010-0100-1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bipolar versus fixed-head hip arthroplasty for femoral neck fractures in elderly patients Mostafa Abdelkhalek Mohamed
Fracture of an Acetabular Component Inserted without Cement: A Case Report
 Syracuse University SURFACE Biomedical and Chemical Engineering College of Engineering and Computer Science 1997 Fracture of an Acetabular Component Inserted without Cement: A Case Report R T. Trousdale
Syracuse University SURFACE Biomedical and Chemical Engineering College of Engineering and Computer Science 1997 Fracture of an Acetabular Component Inserted without Cement: A Case Report R T. Trousdale
CeramTec Medical Products. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
CeramTec Medical Products BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less is more BIOLOX DUO is an alternative
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion. Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head
 Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
Enhancing stability and increasing range of motion Metasul LDH Large Diameter Head The Metasul large diameter head technology is the result of in-depth research, development and clinical experience that
Exeter. Designed for Anatomic Restoration. Clinical Evidence Education
 Exeter Designed for Anatomic Restoration Clinical Evidence Education Anatomic Restoration Exeter re-creating biomechanics In hip replacement, the smallest adjustment can make a big difference. Stryker
Exeter Designed for Anatomic Restoration Clinical Evidence Education Anatomic Restoration Exeter re-creating biomechanics In hip replacement, the smallest adjustment can make a big difference. Stryker
Scan Bi-Polar 22/28. Operative Technique
 Scan Bi-Polar 22/28 Operative Technique Disclaimer This publication and all content, artwork, photographs, names, logos and marks contained in it are protected by copyright, trademarks and other intellectual
Scan Bi-Polar 22/28 Operative Technique Disclaimer This publication and all content, artwork, photographs, names, logos and marks contained in it are protected by copyright, trademarks and other intellectual
Ceramic Femoral Heads and Acetabular Cup Liners
 Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution: Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The Surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique. Caution: Federal (U.S.A) law restricts this device to sale by or on the
Constrained Acetabular Insert
 Constrained Acetabular Insert Surgical Protocol Howmedica Osteonics Constrained Acetabular Insert Surgical Protocol Table of Contents Howmedica Osteonics Constrained Acetabular Insert..........................1
Constrained Acetabular Insert Surgical Protocol Howmedica Osteonics Constrained Acetabular Insert Surgical Protocol Table of Contents Howmedica Osteonics Constrained Acetabular Insert..........................1
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces
 Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
Systematic Review of Clinical Outcome using Titanium Fiber Mesh Porous Ingrowth Surfaces Timothy L. Tan, BS 1, Brenna C. Moeljadi, BS 2, Edward Ebramzadeh, PhD 3, Patricia Campbell, PhD 3, Sophia Nicole
Optimizing function Maximizing survivorship Accelerating recovery
 Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Surgical Technique Optimizing Function Maximizing Survivorship Accelerating Recovery The company believes in an approach to patient treatment that places equal importance on: Optimizing function Maximizing
Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using an Extensively Porous Coated Femoral Stem
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2009;1:105-109 doi:10.4055/cios.2009.1.2.105 Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using an Extensively Porous Coated Femoral Stem Kyoung Ho Moon, MD, Joon Soon
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2009;1:105-109 doi:10.4055/cios.2009.1.2.105 Revision Total Hip Arthroplasty Using an Extensively Porous Coated Femoral Stem Kyoung Ho Moon, MD, Joon Soon
Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
 M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
M Nomura, S The Journal et al. of International Medical Research Endovascular 2000; 28: Embolization 307 312 of Unruptured Results of Conversion Total Hip Prosthesis Performed Following Painful Hemiarthroplasty
Hip Fracture in the Elderly: Partial or Total Arthroplasty?
 3 Hip Fracture in the Elderly: Partial or Total Arthroplasty? Samo K. Fokter 1 and Nina Fokter 2 1 Celje General and Teaching Hospital 2 Maribor University Clinical Centre Slovenia 1. Introduction The
3 Hip Fracture in the Elderly: Partial or Total Arthroplasty? Samo K. Fokter 1 and Nina Fokter 2 1 Celje General and Teaching Hospital 2 Maribor University Clinical Centre Slovenia 1. Introduction The
Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System
 Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System Arcos System Simplify the Complex The Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System meets the demands of complex hip revision surgery by offering surgeons and OR staff the
Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System Arcos System Simplify the Complex The Arcos Modular Femoral Revision System meets the demands of complex hip revision surgery by offering surgeons and OR staff the
MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene
 MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene Fixation First... 1 Wear Reduction... 2 Oxidative Stability... 3 Mechanical Integrity... 4 Proven Technology...5-6 References... 7 Fixation First FIXATION FIRST Prodigy
MARATHON Cross-Linked Polyethylene Fixation First... 1 Wear Reduction... 2 Oxidative Stability... 3 Mechanical Integrity... 4 Proven Technology...5-6 References... 7 Fixation First FIXATION FIRST Prodigy
Zimmer TM. Continuum Acetabular System. Bringing together proven technologies.
 Zimmer TM Continuum Acetabular System Bringing together proven technologies. The power to meet individual patient needs. Zimmer Continuum Acetabular System provides highly flexible solutions for orthopaedic
Zimmer TM Continuum Acetabular System Bringing together proven technologies. The power to meet individual patient needs. Zimmer Continuum Acetabular System provides highly flexible solutions for orthopaedic
Document No Rev. B Pg. 1 of 5 Approvals / Date Title: INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE DJO SURGICAL MODULAR REVISION HIP SYSTEM AND ACETABULAR CAGE
 Document No. 0400-0205 Rev. B Pg. 1 of 5 Approvals / Date Title: INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE DJO SURGICAL MODULAR REVISION HIP SYSTEM AND ACETABULAR CAGE Revision ECO Date ECO Summary of Changes Deann Rector
Document No. 0400-0205 Rev. B Pg. 1 of 5 Approvals / Date Title: INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE DJO SURGICAL MODULAR REVISION HIP SYSTEM AND ACETABULAR CAGE Revision ECO Date ECO Summary of Changes Deann Rector
The power of simplicity
 The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
The power of simplicity The power of simplicity Consider the facts, and take a look at the future: Revision TKA procedures are projected to double between now and 2015. 1 Restoration of a normal joint
Design Rationale and Surgical Technique. *smith&nephew TANDEM. Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System
 Design Rationale and Surgical Technique *smith&nephew TANDEM Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System Maximizing performance from every angle Saving time in the operating room is one of the most valuable solutions
Design Rationale and Surgical Technique *smith&nephew TANDEM Bipolar and Unipolar Hip System Maximizing performance from every angle Saving time in the operating room is one of the most valuable solutions
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence.
 RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence RM Philosophy Innovation based on clinical evidence Design 1973 RM Classic Cup First uncoated RM Classic Cup out of Polyacetal was inserted by E. Morscher
Medical Products Division. BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System. Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion
 Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Medical Products Division BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Bone-sparing joint reconstruction with a maximum range of motion 2 BIOLOX DUO Keramisches Bipolarsystem BIOLOX DUO Ceramic Bipolar System Less
Revision hip arthroplasty with S-ROM prosthesis: a study of clinical outcomes and implant stability
 J Orthopaed Traumatol () 7:1 1 DOI 1.17/s1195--15- ORIGINAL M. El-Deen S. Zahid D.T. Miller A. Nargol R. Logishetty Revision hip arthroplasty with S-ROM prosthesis: a study of clinical outcomes and implant
J Orthopaed Traumatol () 7:1 1 DOI 1.17/s1195--15- ORIGINAL M. El-Deen S. Zahid D.T. Miller A. Nargol R. Logishetty Revision hip arthroplasty with S-ROM prosthesis: a study of clinical outcomes and implant
Malaysian Orthopaedic Journal 2011 Vol 5 No 1 doi: /MOJ
 doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
doi: 10.57704/MOJ.1103.001 Is there a Significant Difference in Surgery and Outcomes between Unipolar and Bipolar Hip Hemiarthroplasty? A Retrospective Study of a Single Institution in Singapore WL Loo,
FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY
 FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY Fixation First FIXATION FIRST 1958 Charnley Hip Over 1,000,000 implanted 1 96.2 percent survivorship at 32 years
FIXATION FIRST WEAR REDUCTION OXIDATIVE STABILITY MECHANICAL INTEGRITY PROVEN TECHNOLOGY Fixation First FIXATION FIRST 1958 Charnley Hip Over 1,000,000 implanted 1 96.2 percent survivorship at 32 years
The bi-metric XR series of Hip implants blends biomet s proven philosophy and tradition with Advanced technology. porous primary hip series
 The bi-metric XR series of Hip implants blends biomet s proven philosophy and tradition with Advanced technology porous primary hip series BI-METRIC XR SERIES implant technology The Bi-Metric XR Hip Series
The bi-metric XR series of Hip implants blends biomet s proven philosophy and tradition with Advanced technology porous primary hip series BI-METRIC XR SERIES implant technology The Bi-Metric XR Hip Series
Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Liner
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 27(4): 216-222, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.4.216 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Hip Pelvis 27(4): 216-222, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2015.27.4.216 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Total Hip Arthroplasty Using Metal Head on a Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation
 The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
The Leader in Orthopaedic Innovation Wright is a leading international manufacturer and distributor of superior, easy to use, and innovative orthopaedic implants and instrumentation. For over 50 years,
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. UNISYN HIP SYSTEM
 CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. UNISYN HIP SYSTEM Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. UNISYN HIP SYSTEM Instructions for Use (IFU) IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR
Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report
 Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 69 74 (2008) Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report W. Siebert, 1 S. Mai, 1 & S. Kurtz 2 1 Orthopädische Klinik
Journal of Long-Term Effects of Medical Implants, 18(1): 69 74 (2008) Retrieval Analysis of a Polycarbonate-Urethane Acetabular Cup: A Case Report W. Siebert, 1 S. Mai, 1 & S. Kurtz 2 1 Orthopädische Klinik
Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System
 Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System Simple. Versatile. The Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System is the next generation reverse shoulder prosthesis, offering unmatched
Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System Simple. Versatile. The Comprehensive Reverse Shoulder System is the next generation reverse shoulder prosthesis, offering unmatched
TriboFit Hip System. Issue 3 - August 2013 English
 Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique and all the information in this insert. Description: The TriboFit Hip
Important Information: Please read prior to use in a clinical setting. The surgeon should be familiar with the operative technique and all the information in this insert. Description: The TriboFit Hip
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement
 Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Femoral neck fractures Total hip replacement Subcapital hip fractures The use of THR Historical data RCT outcomes 3 groups of patients Displaced subcapital fractures Which method is best? Arthroplasty
Avascular necrosis of the hip treated with Metal-on-Metal. surface hip arthroplasty
 Avascular necrosis of the hip treated with Metal-on-Metal surface hip arthroplasty H Sharma ( ), C Watson, AC Campbell Department of Trauma and Orthopaedics, Monklands Hospital, Airdrie, Lanarkshire, ML6
Avascular necrosis of the hip treated with Metal-on-Metal surface hip arthroplasty H Sharma ( ), C Watson, AC Campbell Department of Trauma and Orthopaedics, Monklands Hospital, Airdrie, Lanarkshire, ML6
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System
 BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Technology Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Knees Hips Extremities Cement and Accessories PMI Technology Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
RECOVERY. P r o t r u s i o
 RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e RECOVERY P r o t r u s i o TM C a g e Design Features Revision acetabular surgery is a major challenge facing today s total joint revision surgeon. Failed endo/bi-polars,
StelKast Acetabular. Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications. Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems
 StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol Introduction StelKast offers
StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol and Product Specifications Including ProForm, Provident, Provident Apical Threaded Hole & Systems StelKast Acetabular Surgical Protocol Introduction StelKast offers
Cementless Acetabular Fixation With and Without Screws
 Cementless Acetabular Fixation With and Without Screws Analysis of Stability and Migration The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 2 2010 Richard Iorio, MD,* Brian Puskas, MD,y William L. Healy, MD,* John
Cementless Acetabular Fixation With and Without Screws Analysis of Stability and Migration The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 25 No. 2 2010 Richard Iorio, MD,* Brian Puskas, MD,y William L. Healy, MD,* John
BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement
 CASE REPORT Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement R. W. McCalden, K. D. Charron, R. D. Davidson, M. G. Teeter, D. W. Holdsworth From London Health
CASE REPORT Damage of an Oxinium femoral head and polyethylene liner following routine total hip replacement R. W. McCalden, K. D. Charron, R. D. Davidson, M. G. Teeter, D. W. Holdsworth From London Health
Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs: Report of Two Cases
 SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 519254, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/519254 Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs:
SAGE-Hindawi Access to Research Advances in Orthopedics Volume 2011, Article ID 519254, 4 pages doi:10.4061/2011/519254 Case Report Anterior Subluxation after Total Hip Replacement Confirmed by Radiographs:
HOSPITAL "A" (2007) ORTHOPEDIC JOINT IMPLANT COMPONENT MATRIX
 HOSPITAL "A" (2007) ORTHOPEDIC JOINT IMPLANT COMPONENT MATRIX HIP IMPLANTS TOTAL HIPS Ultra High Demand (metal on metal) Femur, ingrowth Femoral head, metal Acetabular shell, ingrowth Acetabular liner,
HOSPITAL "A" (2007) ORTHOPEDIC JOINT IMPLANT COMPONENT MATRIX HIP IMPLANTS TOTAL HIPS Ultra High Demand (metal on metal) Femur, ingrowth Femoral head, metal Acetabular shell, ingrowth Acetabular liner,
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe
 1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
1.1 Ceramic on Ceramic Bearings Used with Proximal Modular Stems in THA K. J. Keggi, J. M. Keggi, R. E. Kennon and T. McTighe Abstract Introduction: Osteolysis generated by wear debris remains a problem
Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination. Roberts, Garlick
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Increased Rate Of Dislocation Of Total Hip Arthroplasty With Cementless Implants: Accuracy Of Acetabular Inclination. Roberts, Garlick
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System. Product Features and Instructions for Use
 BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed of 75% aluminum oxide and approximately 25% zirconia.
BIOLOX delta Option Ceramic Femoral Head System Product Features and Instructions for Use Product Features BIOLOX delta ceramic heads are composed of 75% aluminum oxide and approximately 25% zirconia.
Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery
 Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
Mako TM Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery for Total Hip Replacement A Patient s Guide Causes of Your Hip Pain Your joints are involved in almost every activity you do. Movements such as walking, bending and
PINNACLE REVISION CUP SYSTEM
 PINNACLE REVISION CUP SYSTEM This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. DESIGN RATIONALE FLEXIBILITY. PRECISION. CONFIDENCE. DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction is proud to offer the
PINNACLE REVISION CUP SYSTEM This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. DESIGN RATIONALE FLEXIBILITY. PRECISION. CONFIDENCE. DePuy Synthes Joint Reconstruction is proud to offer the
Total Elbow Arthroplasty: an Update
 Total Elbow Arthroplasty: an Update Emilie Cheung, M.D. Associate Professor Chief, Shoulder and Elbow Service Stanford University Department of Orthopedic Surgery Procedure volumes and rates increased
Total Elbow Arthroplasty: an Update Emilie Cheung, M.D. Associate Professor Chief, Shoulder and Elbow Service Stanford University Department of Orthopedic Surgery Procedure volumes and rates increased
Dislocation of total hip replacement in patients with fractures of the femoral neck
 184 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 184 189 Dislocation of total hip replacement in patients with fractures of the femoral neck A prospective cohort study of 713 consecutive hips Anders Enocson 1, Carl-Johan
184 Acta Orthopaedica 2009; 80 (2): 184 189 Dislocation of total hip replacement in patients with fractures of the femoral neck A prospective cohort study of 713 consecutive hips Anders Enocson 1, Carl-Johan
Femoral Osteolysis Around the Unrevised Stem During Isolated Acetabular Revision
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2009) 467:1501 1506 DOI 10.1007/s11999-008-0499-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Femoral Osteolysis Around the Unrevised Stem During Isolated Acetabular Revision Byung-Woo Min MD, Kwang-Soon Song
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2009) 467:1501 1506 DOI 10.1007/s11999-008-0499-6 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Femoral Osteolysis Around the Unrevised Stem During Isolated Acetabular Revision Byung-Woo Min MD, Kwang-Soon Song
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene. Clinical Value Dossier - APAC
 Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier - APAC Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...................................................... 1 2 Burden of Illness........................................................
Zimmer Longevity Highly Cross-linked Polyethylene Clinical Value Dossier - APAC Table of Contents 1 Executive Summary...................................................... 1 2 Burden of Illness........................................................
AO Debate Controversies in Management
 46 AODIALOGUE 2 07 Jan Tidermark and Hans Törnqvist AO Debate Controversies in Management Case 1 A 72-year-old active lady (Fig 1). Sustained a displaced femoral neck fracture (Fig 2) after a simple fall.
46 AODIALOGUE 2 07 Jan Tidermark and Hans Törnqvist AO Debate Controversies in Management Case 1 A 72-year-old active lady (Fig 1). Sustained a displaced femoral neck fracture (Fig 2) after a simple fall.
Reflection. Constrained Liner
 Reflection Constrained Liner S u r g i c a l T e c h n i q u e S M I T H & N E P H E W R EFLECTION C ONSTRAINED L INER S URGICAL T ECHNIQUE Produced in conjunction with: Robert Barrack, M.D., Ph.D., Tulane
Reflection Constrained Liner S u r g i c a l T e c h n i q u e S M I T H & N E P H E W R EFLECTION C ONSTRAINED L INER S URGICAL T ECHNIQUE Produced in conjunction with: Robert Barrack, M.D., Ph.D., Tulane
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE. Pivot Bipolar Solitude Unipolar
 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Pivot Bipolar Solitude Unipolar The following technique is a general guide for the instrumentation of the Pivot Bipolar and Solitude Unipolar systems. It is expected that the surgeon
SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Pivot Bipolar Solitude Unipolar The following technique is a general guide for the instrumentation of the Pivot Bipolar and Solitude Unipolar systems. It is expected that the surgeon
The Treatment of Pelvic Discontinuity During Acetabular Revision
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 20 No. 4 Suppl. 2 2005 The Treatment of Pelvic Discontinuity During Acetabular Revision Scott M. Sporer, MD, MS,*y Michael O Rourke, MD,z and Wayne G. Paprosky, MD, FACS*y
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 20 No. 4 Suppl. 2 2005 The Treatment of Pelvic Discontinuity During Acetabular Revision Scott M. Sporer, MD, MS,*y Michael O Rourke, MD,z and Wayne G. Paprosky, MD, FACS*y
Is there a significant difference in surgery and outcomes between unipolar and bipolar hip hemiarthroplasty? - A Prospective Study
 Mohammad Faisal and Prithviraj Nistane / International Journal of Biomedical Research 2016; 7(10): 708-712. 708 International Journal of Biomedical Research ISSN: 0976-9633 (Online); 2455-0566 (Print)
Mohammad Faisal and Prithviraj Nistane / International Journal of Biomedical Research 2016; 7(10): 708-712. 708 International Journal of Biomedical Research ISSN: 0976-9633 (Online); 2455-0566 (Print)
Instructions for use for ADLER Cemented Bipolar hemi-arthroplasty Prosthesis
 Page 1 of 8 Instructions use Important Inmation on For use by an Accredited Orthopaedic Surgeon only 1. Device Description: ADLER Cemented Bipolar hemi-arthroplasty implants are used during a surgical
Page 1 of 8 Instructions use Important Inmation on For use by an Accredited Orthopaedic Surgeon only 1. Device Description: ADLER Cemented Bipolar hemi-arthroplasty implants are used during a surgical
Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 5 Number 1 Use Of A Long Femoral Stem In The Treatment Of Proximal Femoral Fractures: A Report Of Four Cases C Yu, V Singh Citation C Yu, V Singh..
DURALOC. Acetabular Cup System. Surgical Technique
 DURALOC Acetabular Cup System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Surgical Technique Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5
DURALOC Acetabular Cup System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Surgical Technique Templating and Pre Operative Planning 2 Preparation of the Acetabulum 4 Trial Sizing and Impaction of the Shell 5
Important notice: the device(s) can be prescribed and implanted only by a doctor legally authorized to perform this type of surgery.
 rev.10 CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician. ENGLISH - EVOLIS/GMK KNEE PROSTHESIS - INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Important notice: the device(s) can be prescribed
rev.10 CAUTION Federal law (USA) restricts this device to sale, by or on the order of a physician. ENGLISH - EVOLIS/GMK KNEE PROSTHESIS - INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE Important notice: the device(s) can be prescribed
