Paravertebral calcification as a potential indicator for nonaccidental trauma
|
|
|
- Louise Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
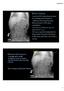
1 Paravertebral calcification as a potential indicator for nonaccidental trauma Katsuaki Kojima 1*, Jennifer Nimtz 1, Steven W Martin 1, Stephen R Guertin 1, Ellen C Cavenagh 2 1. Department of Pediatrics and Human Development, College of Human Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, USA 2. Department of Radiology, College of Human Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, USA * Correspondence: Katsuaki Kojima, Department of Pediatrics and Human Development, College of Human Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, Michigan, 48824, USA ( fi990071@gmail.com) :: DOI: /jrcr.v11i ABSTRACT We report a case of nonaccidental trauma (NAT) involving a 23-month-old boy who presented with seizures, acute subarachnoid hemorrhage, and acute subdural hemorrhage. Ophthalmologic examination showed bilateral intraretinal hemorrhages. Further evaluation revealed that he had bilateral thoracolumbar paravertebral calcifications. The Children's Protective Services agency was involved in the case. The child was discharged to an inpatient rehabilitation facility. Vertebral fracture associated with paravertebral calcification has been reported as a sign of NAT. This case was unique because our patient had paravertebral calcifications without vertebral fracture. Paravertebral calcification alone could serve as an indicator of NAT. CASE REPORT A 23-months-old previously healthy boy presented to the emergency department with status epilepticus. He had been examined at an emergency department 2 weeks prior, where he was diagnosed with viral gastroenteritis. At that time, it was noted that he also had bruises and a petechial rash of the left upper arm, right arm, and left ear. On the day of admission to the hospital, he had been found unconscious at home. He was brought to the emergency department via ambulance while still actively seizing. Lorazepam was administered to stop the seizure. Head computed tomography (CT) scan revealed acute subdural and subarachnoid hemorrhages (Figure 1). He was admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit for further management. CT scan of the chest and abdomen with contrast on day 2 of admission showed soft tissue calcifications posterior to and to the right of the spinous processes of the lower thoracic and upper lumbar spine. Alignment of the vertebral bodies was CASE REPORT normal, without evidence of acute or healing fractures. There were also linear soft tissue calcifications adjacent to the rib ends at the costovertebral junctions of the lower thoracic and upper lumbar spine (Figure 2). Brain magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) performed on day 3 revealed subdural hemorrhage and cerebral infarction in the left parietal/occipital cortex and in the posterior portions of the basal ganglia bilaterally (Figure 3). He was extubated on day 3 and he experienced another seizure on day 6. Levetiracetam was started. Electroencephalogram showed encephalopathy without epileptiform activities. His ophthalmologic evaluation revealed multiple bilateral intraretinal hemorrhages and left-sided preretinal hemorrhage. Skeletal survey did not reveal any fractures. He received physical therapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy during his hospital stay. Children s Protective Services obtained custody of the child. He was discharged to an inpatient rehabilitation facility on day 21 of admission to continue intensive inpatient rehabilitation. 8
2 DISCUSSION Etiology, Demographics & Imaging Findings: Nonaccidental trauma (NAT) is associated with high morbidity and mortality rates [1]. NAT that initially presents with minor trauma is referred to as a sentinel case [2]. It is important to correctly detect the underlying NAT in sentinel cases to protect children from subsequent, recurrent, and often worse trauma. We examined a complicated, albeit common, case of pediatric NAT with acute subarachnoid and subdural intracranial hemorrhages, seizures, bilateral multilayered retinal hemorrhages, and cerebral infarctions. The child was noted to have paravertebral calcifications around the lower thoracic and upper lumbar vertebral bodies without evidence of thoracolumbar fracture. Thoracolumbar fracture is a known radiological finding in NAT and often presents with paravertebral calcification [3]. However, paravertebral calcification without thoracolumbar fracture, which was observed in this case, has not been previously reported as a manifestation of NAT. Because our patient was a victim of child abuse, we speculated that the paravertebral calcifications in our case were secondary to previous NAT. We also speculated that the patient previously sustained minor injuries that caused soft tissue damage and subsequent calcifications, but that the injury was not significant enough to cause vertebral fracture or spinal injury. Irregularity and subtle adjacent calcifications of the posterior ribs noted on computed tomography (CT) scan also suggested previous NAT. It is possible that the child suffered vertebral fractures that completely healed by the time of this admission. However, we believe that this is unlikely given the absence of any signs of previous vertebral fractures on CT. He did not show neurological abnormalities suggestive of spinal injury at presentation or during his emergency department visit 2 weeks prior to presentation. This supports our speculation that he did not sustain a major spinal injury. MRI of the thoracic spine and lumbar spine was not performed. The mechanism of injury that causes paravertebral calcification is unclear. However, a possible mechanism of thoracolumbar fracture with listhesis is the combination of an axial load, flexion, and rotation [3, 4]. This combination could occur during an aggressive shaking episode. Just as the head moves during a shaking episode, so can the lower body and pelvis. Bleeding in these areas can be caused by the fingers of the abuser pushing deep into the paravertebral soft tissues or from tissue disruption during a shaking episode. Thereafter, calcification, just as is seen in myositis ossificans circumscripta, can result. Paravertebral calcifications are commonly seen with thoracolumbar fractures [3], and suggest an overlap in the mechanisms of injury. Chronic and less intense ligamentous and muscular injuries without vertebral fractures also may have resulted in paravertebral calcifications. Risk factors for paravertebral calcification without thoracolumbar fracture are unknown. Risk factors for NAT include familial dysfunction, domestic violence, young maternal age, familial disruption and separation, male sex, history of abuse, and a nonbiologiccal parent. Previous case series of paravertebral calcification with thoracolumbar fracture have included children between 6 months and 7 years of age [3]. No treatment is needed for the calcification itself, but coexisting disabilities secondary to NAT must be addressed appropriately. The prognosis depends on the coexisting disabilities and whether a subsequent abusive event occurs. If NAT is not considered among the differential diagnoses as a cause of paravertebral calcification, then mistaken diagnoses will be made. A previous case of NAT involving thoracolumbar fracture with listhesis was misdiagnosed as neuroblastoma [3]. The consequences of missed NAT can be grave, leading to double or triple mortality rates for subsequent events [5]. We speculated that paravertebral calcification without listhesis was related to NAT in our case. Currently, there are no reports that definitively support this relationship, and we recognize that our speculation remains a hypothesis at this point. However, given the devastating prognosis for missed NAT, clinicians should be aware of any subtle signs of NAT. We believe that paravertebral calcification without listhesis, given the probable mechanisms of injury, should serve as a sign to clinicians that NAT may have occurred. Differential Diagnosis: The differential diagnoses for the cause of paravertebral calcification include trauma, infection, rheumatic disease, malignancy, and idiopathic hyperostosis (table 2). In addition to radiologic information, clinical information is helpful for differentiating each condition. The radiographic characteristics of paravertebral calcification observed in NAT have not been reported in detail. The presence of bony trabecular architecture in paravertebral calcification has been reported as an indicator of traumatic origin of the calcification [6]. X-rays are less sensitive for identifying paravertebral calcification compared to CT. Whether there is a thoracolumbar fracture or any other trauma, if a child has paravertebral calcification, then NAT must be suspected. In addition to NAT, ankylosing spondylitis and tuberculous spondylitis can be associated with reactive paravertebral calcification. Joint erosions, subchondral sclerosis, and bony ankyloses are characteristics of ankylosing spondylitis. Ossification of the paravertebral connective tissue and posterior interspinous ligament can be seen on CT scan. A Romanus lesion is a radiographic finding characterized by small erosions at the corners of vertebral bodies surrounded by reactive sclerosis. Abscess formation and vertebral changes such as ivory vertebrae, gibbus deformity, and vertebra plana suggest tuberculous spondylitis. Dracunculosis is characterized by linear irregular calcifications of the affected soft tissue. However, this finding is extremely rare outside of South Sudan, Mali, Ethiopia, and Chad [7]. 9
3 Furthermore, neuroblastoma can present as a heterogeneous soft tissue mass with calcification. If calcification is seen within mass lesions, then neuroblastoma and paraspinal ganglioneuroma should be suspected. Approximately 30% of neuroblastoma cases demonstrate calcification when X-rays are used and 80% demonstrate calcification on CT [8]. Paraspinal ganglioneuroma is a homogenous mass in the posterior mediastinum. Discrete and punctate calcifications are noted in 42-60% of cases when CT scan is used [8]. FIGURES Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis is typically found in elderly individuals and is characterized by idiopathic flowing ossification of the anterior aspect of the vertebral bodies. TEACHING POINT Paravertebral calcification without thoracolumbar fracture may be a sign of nonaccidental trauma (NAT). Because of the high morbidity and mortality rates associated with missed NAT, providers must be aware of the possible association between NAT and paravertebral calcification. REFERENCES 1. Roaten JB, Partrick DA, Nydam TL, et al Nonaccidental trauma is a major cause of morbidity and mortality among patients at a regional level 1 pediatric trauma center. Journal of pediatric surgery. 2006; 41: PMID: Lindberg DM, Beaty B, Juarez-Colunga E, et al Testing for Abuse in Children With Sentinel Injuries. Pediatrics. 2015; 136: PMID: Levin TL, Berdon WE, Cassell I, et al Thoracolumbar fracture with listhesis--an uncommon manifestation of child abuse. Pediatr Radiol. 2003; 33: PMID: Figure 1: 23-month-old boy with subdural hemorrhage and subarachnoid hemorrhage. Finding: Computed tomography on day 1 of admission. There is a hyperdensity of the posterior falx (white arrow) as well as sulcal effacement of the left posterior parietal lobe (block arrow). Technique: Axial CT, 150 ma, 100 kv, 3 mm slice thickness, no contrast. 4. Carrion WV, Dormans JP, Drummond DS, et al Circumferential growth plate fracture of the thoracolumbar spine from child abuse. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. 1996; 16: PMID: King WK, Kiesel EL, Simon HK Child abuse fatalities: are we missing opportunities for intervention? Pediatric emergency care. 2006; 22: PMID: Kleinman PK Diagnostic Imaging of Child Abuse. Cambridge University Press2015 ISBN: Menon B Serpentine calcification: A radiological stigma. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2011; 2: PMID: Lonergan GJ, Schwab CM, Suarez ES, et al Neuroblastoma, ganglioneuroblastoma, and ganglioneuroma: radiologicpathologic correlation. Radiographics : a review publication of the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. 2002; 22:
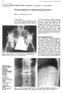
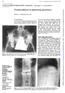
4 Figure 2: 23-month-old boy with paravertebral calcification. Finding: Computed tomography (CT) on day 2 of admission. (a) Soft tissue calcification noted posterior to and to the both sides of the spinous processes of the lower thoracic and upper lumbar spine (arrow). (b) Soft tissue calcification noted posterior to the spinous processes at the lower thoracic and upper lumbar spine including T11 through L1 (arrows). Normal alignment of the vertebral bodies without evidence of acute or healing fractures. (c) Linear soft tissue calcifications adjacent to the rib ends at the costovertebral junctions of the lower thoracic and upper lumbar spine (arrow). Technique: Axial CT (a), 93 ma, 100 kv, 0.5 mm slice thickness, no contrast; sagittal CT (b), 93 ma, 100 kv, 5 mm slice thickness, no contrast; coronal CT (c), 93 ma, 100 kv, 5mm slice thickness, no contrast. 11
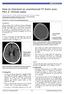
5 Figure 3: 23-month-old boy with left subdural hemorrhage and cerebral infarction in the left cerebral cortex and bilateral posterior basal ganglia. Finding: Brain magnetic resonance image (MRI) on day 3 of admission. (a, b) There is an area of restricted diffusion involving mainly the cortex in the left posterior parietal lobe extending into the left occipital lobe (arrow). (c, d) There is an area of restricted diffusion in the posterior basal ganglia bilaterally (arrow). (e, f) Signal loss on gradient echo images noted within the left posterior medulla (arrow). Given the clinical scenario, this probably reflects deoxyhemoglobin from recent injury. (g) Thin leftsided subdural hematoma overlying the left parietal occipital region (arrow). (i) Subdural hematoma extends medially to the falx and tentorium (arrow). Hyperintensity is noted in left medulla (block arrow). Technique: Brain MRI. 3 Tesla magnet, no contrast used. a. DWI, TR 8000, TE 100.8, no contrast; b. ADC, TR 8000, TE 100.8; c. DWI, TR 8000, TE 100.8; d. ADC, TR 8000, TE 100.8; e. axial T1, TR 616.7, TE 20; f. axial T2 MERGE, TR 600, TE 12.21; g. axial T2 MERGE, TR 600, TE 12.21; h. sagittal T1 BRAVO, TR 11.85, TE 4.8. Etiology Nonaccidental trauma (NAT). Exact mechanism is unknown, but proposed hypotheses include occult trauma causing soft tissue damage and subsequent calcification. Incidence Unknown. Paravertebral calcification with thoracolumbar fracture was previously reported. However, paravertebral calcification without thoracolumbar fracture previously has not been reported. Gender ratio Unknown. No gender difference expected. Age predilection Previous case series of paravertebral calcification with thoracolumbar fracture includes children between 6 months and 7 years of age. Risk factors Unknown. Risk factors of NAT should be considered, such as familial dysfunction, domestic violence, young maternal age, familial disruption and separation, and prior history of abuse. Treatment Treatment is not required for calcification itself, but coexisting disabilities secondary to NAT need to be addressed appropriately. Prognosis Prognosis depends on the coexisting disabilities secondary to NAT. Findings on Scattered calcification in paravertebral area without thoracolumbar fracture. Other finding suggestive of NAT Imaging may be identified. Table 1: Summary table of paravertebral calcification without thoracolumbar fracture. 12
6 Nonaccidental trauma Neuroblastoma Ankylosing spondylitis Tuberculous spondylitis Dracunculosis Diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis Paraspinal ganglioneuroma X-ray - Scattered paravertebral calcification may be observed. Less sensitive compared to CT. - Non-specific soft-tissue mass - Calcification may be noted in 30% of cases. - Small erosions at the corners of vertebral bodies surrounded by reactive sclerosis (Romanus lesion). - Ossification of the paravertebral connective tissue and posterior interspinous ligament. - Bamboo spine. - Irregularity of the anterior vertebral margin. - Ivory vertebrae, gibbus deformity, and vertebra plana. - Calcification can be seen. - Linear irregular calcifications of the affected soft tissue - Flowing syndesmophytes along, but separated from, the anterior aspect of the vertebral bodies. - Posterior mediastinal mass - Up to 30% may show calcification Table 2: Differential diagnosis table for paravertebral calcification. CT = Computed tomography NAT = Nonaccidental trauma ABBREVIATIONS KEYWORDS child abuse; seizure; subdural hemorrhage; subarachnoid hemorrhage; paravertebral calcification CT - Paravertebral calcification with or without signs of thoracolumbar fracture. - Bony trabecular architecture indicates traumatic origin. - Heterogeneous mass with calcification observed in 80% of cases. - Joint erosions, subchondral sclerosis, and bony ankyloses. - Ossification of the paravertebral connective tissue and posterior interspinous ligament. - Presence of pre- and paravertebral or intra-osseous abscess, and ivory vertebra. - Calcified paravertebral soft tissue. - Linear irregular calcifications of the affected soft tissue - Ossification along the anterior aspect of the vertebral bodies. - Homogeneous mass - Discrete and punctate calcification in 42-60% of cases. Online access This publication is online available at: Peer discussion Discuss this manuscript in our protected discussion forum at: Interactivity This publication is available as an interactive article with scroll, window/level, magnify and more features. Available online at Published by EduRad ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS We are grateful to Shiho Kutsuwada, MD for her assistance in collecting information relative to the case. 13
Spinal infection. Outline ANATOMY 6/2/2017. Anatomy Pathogen
 Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
Bilateral rib fractures 2 on right and 1 on left In different stages of healing, with left fracture older than right fractures
 More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
More history: Seen by PCP yesterday because of vomiting and fussinesss. Called by ED today because Mom presents with same complaints. ED found nothing but got an abdominal x ray. ED now wants kid admitted
Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient
 September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
Posterior Rectus Sheath Hernia Causing Intermittent Small Bowel Obstruction
 Posterior Rectus Sheath Hernia Causing Intermittent Small Bowel Obstruction Scott Lenobel 1*, Robert Lenobel 2, Joseph Yu 1 1. Department of Radiology, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center,
Posterior Rectus Sheath Hernia Causing Intermittent Small Bowel Obstruction Scott Lenobel 1*, Robert Lenobel 2, Joseph Yu 1 1. Department of Radiology, The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center,
HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE
 564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
564 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE HYPEROSTOSIS AND OSSIFICATION IN THE CERVICAL SPINE DONALD RESNICK A variety of diseases can produce hyperostosis or ossification in the cervical spine. Included among these are
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
The clinical scenario in this patient has been well reviewed by expert witnesses.
 September 29, 2014 Michael J. Cronkright, Esq. Kronzek & Cronkight, PLLC 420 S. Waverly Road, Suite 100 Lansing, MI 48917 Re: Preliminary Report on Naomi Burns Dear Mr. Cronkright, I have reviewed all
September 29, 2014 Michael J. Cronkright, Esq. Kronzek & Cronkight, PLLC 420 S. Waverly Road, Suite 100 Lansing, MI 48917 Re: Preliminary Report on Naomi Burns Dear Mr. Cronkright, I have reviewed all
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
 A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH)
 A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
A Patient s Guide to Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis (DISH) 6565 Fannin Street Houston, TX 77030 Phone: 713-790-3333 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety of sources.
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies. Spondyloarthropathies
 Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Update - Imaging of the Spondyloarthropathies Donald J. Flemming, M.D. Dept of Radiology Penn State Hershey Medical Center Spondyloarthropathies Family of inflammatory arthritides of synovium and entheses
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADIOLOGY
 MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
MUSCULOSKELETAL RADOLOGY SECTON www.cambridge.org Achilles tendonopathy/rupture Characteristics Describes pathology of the combined tendon of the gastro-soleus complex, which inserts onto the calcaneum.
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D.
 Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Imaging of Cervical Spine Trauma Tudor H Hughes, M.D. General Considerations Most spinal fractures are due to a single episode of major trauma. Fatigue fractures of the spine are unusual except in the
Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging
 Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging Poster No.: C-1422 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Beretis, K. Giannaki, M. Fasoula, D. Kypriotis, T. Dagla, T.-P. Mantzouranis;
Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging Poster No.: C-1422 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Beretis, K. Giannaki, M. Fasoula, D. Kypriotis, T. Dagla, T.-P. Mantzouranis;
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know. 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012
 Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Overview of Abusive Head Trauma: What Everyone Needs to Know 11 th Annual Keeping Children Safe Conference Boise, ID October 17, 2012 Deborah Lowen, MD Associate Professor Pediatrics Director, Child Abuse
Accidental Concentrated Hydrogen Peroxide Ingestion Associated with Portal Venous Gas
 Accidental Concentrated Hydrogen Peroxide Ingestion Associated with Portal Venous Gas Eslam W Youssef 1,2*, Victor S Chukwueke 3, Lina Elsamaloty 3, Sherif Moawad 1,2, Haitham Elsamaloty 1 1. Department
Accidental Concentrated Hydrogen Peroxide Ingestion Associated with Portal Venous Gas Eslam W Youssef 1,2*, Victor S Chukwueke 3, Lina Elsamaloty 3, Sherif Moawad 1,2, Haitham Elsamaloty 1 1. Department
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam
 Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
Children diagnosed with skull fractures are often. Transfer of children with isolated linear skull fractures: is it worth the cost?
 clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:602 606, 2016 Transfer of children with isolated linear skull fractures: is it worth the cost? Ian K. White, MD, 1 Ecaterina Pestereva, BS, 1 Kashif A. Shaikh, MD,
clinical article J Neurosurg Pediatr 17:602 606, 2016 Transfer of children with isolated linear skull fractures: is it worth the cost? Ian K. White, MD, 1 Ecaterina Pestereva, BS, 1 Kashif A. Shaikh, MD,
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
ASJ. A Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia. Asian Spine Journal. Introduction
 sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
sian Spine Journal 126 Dong-Eun Case Shin Report et al. http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2013.7.2.126 Rare Hyperextension Injury in Thoracic Spine Presenting with Delayed Paraplegia Dong-Eun Shin, Ki-Sik
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES
 TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
TRAUMATIC CAROTID &VERTEBRAL ARTERY INJURIES ALBERTO MAUD, MD ASSOCIATE PROFESSOR TEXAS TECH UNIVERSITY HEALTH SCIENCES CENTER EL PASO PAUL L. FOSTER SCHOOL OF MEDICINE 18TH ANNUAL RIO GRANDE TRAUMA 2017
Spine. Neuroradiology. Spine. Spine Pathology. Distribution of fractures. Radiological algorithm. Role of radiology 18/11/2015
 Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spondyloarthritis: A Gouty Display
 Spondyloarthritis: A Gouty Display Preetam Gongidi 1*, Shawn Gough-Fibkins 2 1. Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA 2. Broward General Medical Center,
Spondyloarthritis: A Gouty Display Preetam Gongidi 1*, Shawn Gough-Fibkins 2 1. Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, FL, USA 2. Broward General Medical Center,
Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review
 Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Ankylosing spondylitis: A Pictorial Review Poster No.: P-0009 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. Acosta Batlle, B. Palomino Aguado, M. D. Lopez Parra, S. 1 2 3 2 4 1 2 Hernandez Muñiz,
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
MRI XR, CT, NM. Principal Modality (2): Case Report # 2. Date accepted: 15 March 2013
 Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
Radiological Category: Musculoskeletal Principal Modality (1): Principal Modality (2): MRI XR, CT, NM Case Report # 2 Submitted by: Hannah Safia Elamir, D.O. Faculty reviewer: Naga R. Chinapuvvula, M.D.
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Radiological investigations
 Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Nita Jain, MD, FRCPC The role of diagnostic imaging in the evaluation of child abuse Radiologists experienced in pediatric imaging can provide invaluable assistance to health care teams working to identify
Radiologic Pathologic Correlation of Intraosseous Lipomas. Tim Propeck 1, Mary Anne Bullard 1, John Lin 1, Kei Doi 2, William Martel 1
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 148.251.232.83 on 04/10/18 from IP address 148.251.232.83. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Radiologic Pathologic orrelation of Intraosseous
Small bowel perforation: a rare complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement
 Small bowel perforation: a rare complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement Kelsey Bourm 1*, Cory Pfeifer 2, Adam Zarchan 3 1. Department of Radiology, Wesley Medical Center, Wichita, KS, USA
Small bowel perforation: a rare complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement Kelsey Bourm 1*, Cory Pfeifer 2, Adam Zarchan 3 1. Department of Radiology, Wesley Medical Center, Wichita, KS, USA
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: Available online at: Case Study
 International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
International Journal of Research in Health Sciences ISSN: 2321-7251 Available online at: http://www.ijrhs.org/ Case Study Foreign body granuloma mimicking a soft tissue neoplasm *Rohan Sawant, Abhishek
Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A
 Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Clinical > Pediatric Imaging Case Report: Knee MR Imaging of Haemarthrosis in a Case of Haemophilia A M. A. Weber, J. K. Kloth University Hospital Heidelberg, Department of Diagnostic and Interventional
Paediatric post-traumatic osseous cystic lesion following a distal radial fracture
 Paediatric post-traumatic osseous cystic lesion following a distal radial fracture Joey Chan Yiing Beh 1*, Ehab Shaban Mahmoud Hamouda 1 1. Department of Diagnostic Imaging, KK Women's and Children's Hospital,
Paediatric post-traumatic osseous cystic lesion following a distal radial fracture Joey Chan Yiing Beh 1*, Ehab Shaban Mahmoud Hamouda 1 1. Department of Diagnostic Imaging, KK Women's and Children's Hospital,
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING. James Chen (MS IV)
 HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
HEAD AND NECK IMAGING James Chen (MS IV) Anatomy Course Johns Hopkins School of Medicine Sept. 27, 2011 OBJECTIVES Introduce cross sectional imaging of head and neck Computed tomography (CT) Review head
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive
 Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies: A Radiological Persepctive Poster No.: C-1816 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Shindi, H. Nejadhamzeeigilani, P. Nagtode, C. Nel ; 1 1 2 2 3
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Abstract. Aim. Materials and methods. Introduction. Results
 Is anatomical distribution helpful for differentiating TB spondylitis from neoplastic causes of extradural spinal cord compression in children? A pilot study Reena George, MD, MMed Rad, FRCR (UK) Savvas
Is anatomical distribution helpful for differentiating TB spondylitis from neoplastic causes of extradural spinal cord compression in children? A pilot study Reena George, MD, MMed Rad, FRCR (UK) Savvas
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE
 THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
THE ESSENTIAL BRAIN INJURY GUIDE Neuroanatomy & Neuroplasticity Section 2 Contributors Erin D. Bigler, PhD Michael R. Hoane, PhD Stephanie Kolakowsky-Hayner, PhD, CBIST, FACRM Dorothy A. Kozlowski, PhD
Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications
 Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications Poster No.: C-1536 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Veselova, V. Mazaev, M. Molodtsov; Moscow/RU Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications Poster No.: C-1536 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Veselova, V. Mazaev, M. Molodtsov; Moscow/RU Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing Spondylitis
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 590935, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/590935 Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 590935, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/590935 Case Report Traumatic Death due to Simultaneous Double Spine Fractures in Patient with Ankylosing
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type.
 Neurosurg Clin N Am 13 (2002) 259 264 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Abdominal injuries, in child abuse, 150, 159 Abrasions, in child abuse, 157 Abuse, child. See Child
Neurosurg Clin N Am 13 (2002) 259 264 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Abdominal injuries, in child abuse, 150, 159 Abrasions, in child abuse, 157 Abuse, child. See Child
Imaging of tuberculosis of the spine
 P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(9) : 439 CME Article Imaging of tuberculosis of the spine E L H J Teo, W C G Peh ABSTRACT Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of death worldwide
P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(9) : 439 CME Article Imaging of tuberculosis of the spine E L H J Teo, W C G Peh ABSTRACT Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of death worldwide
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
SPINAL PSEUDOARTHROSIS
 485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL SEPTEMBER 2013 NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE Claudia da Costa Leite, MD, PhD Thomas Bouldin, MD CASE 1 6 y-o female with headaches and vomiting
THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL SEPTEMBER 2013 NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE Claudia da Costa Leite, MD, PhD Thomas Bouldin, MD CASE 1 6 y-o female with headaches and vomiting
THORACO-LUMBAR SPINE TRAUMA NORDIC TRAUMA COURSE 2016, AARHUS
 THORACO-LUMBAR SPINE TRAUMA NORDIC TRAUMA COURSE 2016, AARHUS Ken F. Linnau, MD, MS Emergency Radiology Harborview Medical Center University of Washington Seattle, WA Thanks to Quynh T. Nguyen, MHS, PA-C
THORACO-LUMBAR SPINE TRAUMA NORDIC TRAUMA COURSE 2016, AARHUS Ken F. Linnau, MD, MS Emergency Radiology Harborview Medical Center University of Washington Seattle, WA Thanks to Quynh T. Nguyen, MHS, PA-C
Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review
 Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review M B Moss, MD; L Lanier, MD; R Slater; C L Sistrom, MD; R G Quisling, MD; I M Schmalfuss, MD; and D Rajderkar, MD Contact:
Neuroradiological Findings in Non- Accidental Trauma Educational Pictorial Review M B Moss, MD; L Lanier, MD; R Slater; C L Sistrom, MD; R G Quisling, MD; I M Schmalfuss, MD; and D Rajderkar, MD Contact:
Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury
 Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Isaac, P. A. Tyler; Stanmore/UK Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Isaac, P. A. Tyler; Stanmore/UK Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment
 Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. G. Trigo,
Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. G. Trigo,
41 year old female with headache. Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD
 41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
41 year old female with headache Elena G. Violari MD and Leo Wolansky MD ? Dural Venous Sinus Thrombosis with Hemorrhagic Venous Infarct Acute intraparenchymal hematoma measuring ~3 cm in diameter centered
Long Case Set 02. Dr Raviraj Uppoor. Dr Sameer Shamshuddin. Consultant Radiologist Cumberland Infirmary, Carlisle, UK
 Long Case Set 02 www.frcrtutorials.com Dr Raviraj Uppoor MBBS, DMRD, DNB, FRCR Consultant Radiologist Cumberland Infirmary, Carlisle, UK Dr Sameer Shamshuddin MBBS, DMRD, FRCR Consultant Radiologist Royal
Long Case Set 02 www.frcrtutorials.com Dr Raviraj Uppoor MBBS, DMRD, DNB, FRCR Consultant Radiologist Cumberland Infirmary, Carlisle, UK Dr Sameer Shamshuddin MBBS, DMRD, FRCR Consultant Radiologist Royal
Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures
 July 2006 Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures Denise De Las Nueces, Harvard Medical School Year IV General Overview Introduction
July 2006 Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures Denise De Las Nueces, Harvard Medical School Year IV General Overview Introduction
Case Report. Herpes simplex virus encephalitis presenting as frontal lobe hemorrhage
 1 Case Report Herpes simplex virus encephalitis presenting as frontal lobe hemorrhage Authors: Shila, MD, *Jessica Erfan, MPAS, PA-C, Ray Bogitch, MD, Jefferson T. Miley, MD Department of Neurology, Dell
1 Case Report Herpes simplex virus encephalitis presenting as frontal lobe hemorrhage Authors: Shila, MD, *Jessica Erfan, MPAS, PA-C, Ray Bogitch, MD, Jefferson T. Miley, MD Department of Neurology, Dell
Name : SK.Maibali Age : 24yrs Sex : Male occupation: labourer Residence : suryapet Date of admission : 8/5/17 IP no :
 Name : SK.Maibali Age : 24yrs Sex : Male occupation: labourer Residence : suryapet Date of admission : 8/5/17 IP no : 201715579 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : Complains of pain in the middle &lower 1/3 rd junction
Name : SK.Maibali Age : 24yrs Sex : Male occupation: labourer Residence : suryapet Date of admission : 8/5/17 IP no : 201715579 CHIEF COMPLAINTS : Complains of pain in the middle &lower 1/3 rd junction
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Introduction to Neuroimaging spine. John J. McCormick MD
 Introduction to Neuroimaging spine John J. McCormick MD Neuroanatomy Netter drawings Radiographic Anatomy Cervical Spine Cervical Spine Oblique View Cervical Spine Dens View Thoracic Spine Lumbar Spine
Introduction to Neuroimaging spine John J. McCormick MD Neuroanatomy Netter drawings Radiographic Anatomy Cervical Spine Cervical Spine Oblique View Cervical Spine Dens View Thoracic Spine Lumbar Spine
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint. Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital
 Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Imaging and intervention of sacroiliac joint Dr Ryan Lee Ka Lok Associate Consultant Prince of Wales Hospital Introduction 15%-25% of low back pain is related to sacroiliac joint (SIJ) pain SIJ pain is
Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in detecting posterior ligamentous complex injury in thoracolumbar vertebral fractures
 Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in detecting posterior ligamentous complex injury in thoracolumbar vertebral fractures Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Aguirre, P.
Diagnostic accuracy of MRI in detecting posterior ligamentous complex injury in thoracolumbar vertebral fractures Poster No.: C-1726 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: E. Aguirre, P.
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013
 Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR October 14, 2013 Disclosures I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest to report
Pediatric TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 14, 2013 Radiologic Presentation of Childhood TB Susan D. John, MD, FACR October 14, 2013 Disclosures I have no disclosures or conflicts of interest to report
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Neuroblastoma Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Neuroblastoma Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/18/2011 History 15 month old with anemia. Diagnosis Neuroblastoma Discussion Neuroblastic tumors derive from primordial neural crest cells destined for sympathetic
Neuroblastoma Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 03/18/2011 History 15 month old with anemia. Diagnosis Neuroblastoma Discussion Neuroblastic tumors derive from primordial neural crest cells destined for sympathetic
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines
 Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) PEDIATRIC Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma Center Medical Director/ Trauma
Trauma Center Practice Management Guideline Blank Children s Hospital (BCH) Des Moines Non-Accidental Trauma (NAT) PEDIATRIC Practice Management Guideline Contact: Trauma Center Medical Director/ Trauma
Paraspinal Venous Malformation Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Paraspinal Venous Malformation Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 06/04/2010 History 2 year old with history of fall. Rule out spinal injury. Diagnosis Paraspinal Venous Malformation Additional Clinical CT of the
Paraspinal Venous Malformation Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 06/04/2010 History 2 year old with history of fall. Rule out spinal injury. Diagnosis Paraspinal Venous Malformation Additional Clinical CT of the
Evaluation of Wedging of Lower Thoracic and Upper Lumbar Vertebral Bodies in the Pediatric Population
 Pediatric Imaging Original Research Gaca et al. Evaluation of Wedging of Lumbar Vertebral Bodies in Children Pediatric Imaging Original Research Ana Maria Gaca 1 Huiman X. Barnhart 2 George S. Bisset,
Pediatric Imaging Original Research Gaca et al. Evaluation of Wedging of Lumbar Vertebral Bodies in Children Pediatric Imaging Original Research Ana Maria Gaca 1 Huiman X. Barnhart 2 George S. Bisset,
CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May Leslie M. Quinn M.D.
 CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May 2012 - Leslie M. Quinn M.D. PHYSICAL ABUSE: For any child presenting with signs and or symptoms of an injury consider
CHILD MALTREATMENT- GUIDELINES FOR SUSPICION and INITIAL MEDICAL EVALUATION DRAFT May 2012 - Leslie M. Quinn M.D. PHYSICAL ABUSE: For any child presenting with signs and or symptoms of an injury consider
Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior Endplate Lesion after Recurrent Disc Herniation
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 5963924, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/5963924 Case Report A Rare Case of Progressive Palsy of the Lower Leg Caused by a Huge Lumbar Posterior
Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients
 Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Skeletal Radiol (1985) 14:159-163 Skeletal Radiology Magnetic resonance imaging of femoral head development in roentgenographically normal patients Peter J. Littrup, M.D. 1, Alex M. Aisen, M.D. 2, Ethan
Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures
 Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures C. Craig Blackmore, MD, MPH Professor of Radiology Adjunct Professor of Health Services Harborview Injury Prevention and Research Center University of Washington Outline Who
Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures C. Craig Blackmore, MD, MPH Professor of Radiology Adjunct Professor of Health Services Harborview Injury Prevention and Research Center University of Washington Outline Who
Calcification of the epiglottis presenting as foreign body sensation in the neck
 Calcification of the epiglottis presenting as foreign body sensation in the neck Sunil Jeph 1*, Michael Aidi 1, Ahmed Shah 2, Thu-Thao Ly 1, Oleg Bronov 1 1. Department of Radiology, Geisinger Medical
Calcification of the epiglottis presenting as foreign body sensation in the neck Sunil Jeph 1*, Michael Aidi 1, Ahmed Shah 2, Thu-Thao Ly 1, Oleg Bronov 1 1. Department of Radiology, Geisinger Medical
Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline
 Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline WHEN TO CONSIDER ABUSE Consider abuse on the differential Injuries to multiple organ systems Injuries in different stages of healing Patterned injuries
Suspected Physical Abuse Clinical Practice Guideline WHEN TO CONSIDER ABUSE Consider abuse on the differential Injuries to multiple organ systems Injuries in different stages of healing Patterned injuries
Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries
 Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries Paul Kleinman, M.D. Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, Ma. Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Kemp AM et. Al.
Common Abusive Skeletal Injuries Paul Kleinman, M.D. Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Boston, Ma. Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Rib fractures, especially posteromedial Kemp AM et. Al.
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases
 How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
How to interpret an unenhanced CT brain scan. Part 2: Clinical cases Thomas Osborne a, Christine Tang a, Kivraj Sabarwal b and Vineet Prakash c a Radiology Registrar; b Radiology Foundation Year 1 Doctor;
Module 1: Basic Comprehensive Course
 The Hellenic Spine Society organize 5 modules according to the following program, which is based on the Eurospine program Module 1: Basic Comprehensive Course SESSION1: SPINE THE BIGGER PICTURE Evidence
The Hellenic Spine Society organize 5 modules according to the following program, which is based on the Eurospine program Module 1: Basic Comprehensive Course SESSION1: SPINE THE BIGGER PICTURE Evidence
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings
 Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
Osteonecrosis - Spectrum of imaging findings Poster No.: C-1861 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Ninitas, A. L. Amado Costa, A. Duarte, I. Távora ; Lisbon/ 1 1 2 1 1 2 PT, Costa
2/13/13. Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University
 Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University 3 month old, previously healthy infant, brought to the primary care physician due to a fall He was being carried by the father, who tripped over the family
Ann S. Botash, MD SUNY Upstate Medical University 3 month old, previously healthy infant, brought to the primary care physician due to a fall He was being carried by the father, who tripped over the family
Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C.
 Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
Role of Whole-body Diffusion MR in Detection of Metastatic lesions Prof. Dr. NAGUI M. ABDELWAHAB,M.D.; MARYSE Y. AWADALLAH, M.D. AYA M. BASSAM, Ms.C. Cancer is a potentially life-threatening disease,
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 3/12/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 11 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain. Dr Amy Davis
 An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
An Introduction to Imaging the Brain Dr Amy Davis Common reasons for imaging: Clinical scenarios: - Trauma (NICE guidelines) - Stroke - Tumours - Seizure - Neurological degeneration memory, motor dysfunction,
Lumbar puncture. Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml): <1h
 Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
Lumbar puncture Lumbar puncture Invasive procedure: diagnostic or therapeutic. The subarachnoid space 4-13 ys: 65-150ml Replenished: 4-6 h Routine LP (3-5 ml):
Case Report Hemoptysis as the Presenting Clinical Sign of a T8-T9 Spine Fracture with Diffuse Idiopathic Skeletal Hyperostosis Changes
 Case Reports in Emergency Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 7657652, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7657652 Case Report Hemoptysis as the Presenting Clinical Sign of a T8-T9 Spine Fracture with
Case Reports in Emergency Medicine Volume 2016, Article ID 7657652, 6 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/7657652 Case Report Hemoptysis as the Presenting Clinical Sign of a T8-T9 Spine Fracture with
JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22,
 JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22, 1990 16 SECTIONAL ANATOMY: STANDARDIZED METHODOLOGY Alexander Lane, Coordinator of Anatomy and Physiology, Triton College, Visiting Associate Professor, University of Illinois
JlntSocPlastination, Vol4:16-22, 1990 16 SECTIONAL ANATOMY: STANDARDIZED METHODOLOGY Alexander Lane, Coordinator of Anatomy and Physiology, Triton College, Visiting Associate Professor, University of Illinois
Spine MRI in Trauma Patients
 Spine MRI in Trauma Patients 4th Musculoskeletal MRI meeting 2017: Spine MRI 6th May, 2017 Gustav Andreisek, MD, MBA Ospedale Regionale di Lugano, Civico, Aula Magna Professor of Radiology, University
Spine MRI in Trauma Patients 4th Musculoskeletal MRI meeting 2017: Spine MRI 6th May, 2017 Gustav Andreisek, MD, MBA Ospedale Regionale di Lugano, Civico, Aula Magna Professor of Radiology, University
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma. Introduction. Anatomic Considerations 7/23/2018
 Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Subaxial Cervical Spine Trauma Sheyan J. Armaghani, MD Florida Orthopedic Institute Assistant Professor USF Dept of Orthopedics Introduction Trauma to the cervical spine accounts for 5 of all spine injuries
Popliteal vein aneurysm presenting as recurrent pulmonary embolism
 vein aneurysm presenting as recurrent pulmonary embolism Joel Lim 1*, Martin Marshall 2 1. Department of Clinical Services, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia 2. Department of Diagnostic and Radiology,
vein aneurysm presenting as recurrent pulmonary embolism Joel Lim 1*, Martin Marshall 2 1. Department of Clinical Services, Royal Perth Hospital, Perth, Australia 2. Department of Diagnostic and Radiology,
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA
 V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
V. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM TRAUMA I. Concussion - Is a clinical syndrome of altered consiousness secondary to head injury - Brought by a change in the momentum of the head when a moving head suddenly arrested
Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology
 Open Access Review Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2456 Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology MN Baig 1, Fergus Byrne 2, A Devitt 3, J P. McCabe 3 1. Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery, Galway University Hospital,
Open Access Review Article DOI: 10.7759/cureus.2456 Signs of Nature in Spine Radiology MN Baig 1, Fergus Byrne 2, A Devitt 3, J P. McCabe 3 1. Trauma & Orthopaedic Surgery, Galway University Hospital,
The role of CT and MRI in evaluation of Osteoid Oteoma
 The role of CT and MRI in evaluation of Osteoid Oteoma Elene Iordanishvili Tbilisi Sate Medical University Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ketevan Kotetishvili Department of Physics Georgian Technical University
The role of CT and MRI in evaluation of Osteoid Oteoma Elene Iordanishvili Tbilisi Sate Medical University Instructor: Prof. Dr. Ketevan Kotetishvili Department of Physics Georgian Technical University
