n Feature Article Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Intra-articular Hip Injections Performed in the Orthopedic Clinic Todd P. Balog, MD; Blair B. Rhodehou
|
|
|
- Audrey Irene Flynn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Intra-articular Hip Injections Performed in the Orthopedic Clinic Todd P. Balog, MD; Blair B. Rhodehouse, DO; Eric K. Turner, MD; John M. Slevin, PA; Lisabeth A. Bush, MD; Jason A. Grassbaugh, MD; Bryant G. Marchant, MD abstract Intra-articular hip injections have proven clinical value for both diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Historically, these injections have been performed by radiologists using fluoroscopic guidance. This necessitates a radiology referral, delays the injection, and represents lost productivity for the orthopedist. Ultrasound-guided intra-articular hip injections have been described in the radiology literature with excellent accuracy. These injections were performed by radiologists. The purpose of this study was to determine the accuracy of ultrasound-guided hip injections performed in the orthopedic clinic by orthopedic surgeons and orthopedic physician assistants. Fifty ultrasound-guided hip injections were performed using a standard technique. Contrast was included, and an anteroposterior pelvis radiograph was obtained immediately following injection. Diagnosis, body mass index, procedure time, and visual analog scale scores were recorded. Radiographs were reviewed independently by a musculoskeletal radiologist and an orthopedic surgeon to determine intra-articular placement of the injection. A total of 50 hips were injected. There was no identifiable contrast in 2 patients, leaving 48 hips for analysis. Of these, contrast was injected intra-articularly in 46 hips for an accuracy of 96%. Average procedural time was 2.6 minutes, and the average visual analog scale score was 1.9 during the procedure. Revenue value units ranged from for ultrasound-guided hip injections. These findings indicate ultrasound-guided intra-articular hip injections performed in the orthopedic clinic by surgeons or physician assistants are accurate, efficient, and patientfriendly. Additionally, they preserve patient continuity and maintain productivity within the orthopedic clinic. [Orthopedics. 2017; 40(2): ] Joint injections are some of the most commonly performed procedures in the orthopedic clinic. With the potential to provide both therapeutic and diagnostic value to patients and providers, many surgeons consider joint injections a valuable clinical tool. The knee and various locations around the shoulder remain the most commonly injected joints due to frequently occurring pathology, relatively superficial anatomic location, and palpable landmarks facilitating accurate injections. Hip pathology also is encountered frequently in the orthopedic clinic. Historically, hip pathology has been related mostly to degenerative joint disease, the incidence of which is expected to increase. 1 Recent developments in hip arthroscopy have led to a significant increase in the number of hip arthroscopies performed annually, many of which are performed for the treatment of femoro- The authors are from Blanchfield Army Community Hospital (TPB), Fort Campbell, Kentucky; and Madigan Army Medical Center (BBR, EKT, JMS, LAB, JAG, BGM), Tacoma, Washington. The authors have no relevant financial relationships to disclose. The views expressed in this manuscript are those of the authors and do not reflect the official policy of the Department of Army, Department of Defense, or US Government. All authors are employees of the US Government. This work was prepared as part of their official duties and as such, there is no copyright to be transferred. Correspondence should be addressed to: Todd P. Balog, MD, Blanchfield Army Community Hospital, 650 Joel Dr, Fort Campbell, KY (todd.p.balog.mil@mail.mil). Received: August 9, 2016; Accepted: October 31, doi: /
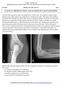
2 acetabular impingement (FAI). 2 As these numbers continue to increase, so will the number of patients evaluated in the orthopedic clinic for FAI. Similar to injections in other joints, intra-articular hip injections have been shown to have both diagnostic and therapeutic value for hip degenerative joint disease and FAI. 3-7 Unfortunately, blind intra-articular hip injections using anatomic landmarks are difficult, with success rates ranging from 60% to 80% in previously published studies. 4,5 As a result, most hip injections are performed by the orthopedic surgeon in the operating room (OR) using fluoroscopic guidance or are referred to radiology for fluoroscopic or ultrasound-guided injections. This article describes the current authors technique and results for ultrasound-guided intra-articular hip injections performed in the orthopedic clinic by either a surgeon or a physician assistant. Materials and Methods After receiving investigational review board approval, this prospective study included all patients who were indicated by orthopedic providers for a diagnostic or therapeutic intra-articular hip injection from March 2014 through May After patients were referred for an intraarticular hip injection, the study was explained and written consent was obtained. An ultrasound-guided injection then was performed by either a staff orthopedic surgeon or 1 of 2 orthopedic physician assistants. Injections were performed in the provider s standard clinic or in 1 of the physician assistant s weekly injection clinics. All injections were performed in the following standard fashion. The patient was given disposable shorts to wear and instructed to lie in the supine position with both legs extended. The shorts then were cut to expose the inguinal crease. The provider was positioned on the affected side with the ultrasound machine on the contralateral side (Figure 1). A 10-mL syringe was drawn up with 8 ml Figure 1: Photograph showing a patient with the affected hip exposed and the ultrasound screen on the contralateral side. of 1% lidocaine without epinephrine and was attached to an extension tubing line. A 22-gauge spinal needle then was attached and primed. A second 10-mL syringe was filled with 1% lidocaine without epinephrine, 0.5% bupivacaine, and 60 to 120 mg of triamcinolone for therapeutic injections. The low-frequency curved transducer was positioned in long axis parallel to the femoral neck, lateral to the femoral neurovascular structures, and just distal to the inguinal crease (Figure 2). Visualization of the head-neck junction was obtained and held. Excess gel was removed, and the injection site was prepped approximately 2 to 3 cm distal to the transducer. The 22-gauge spinal needle with extension tubing attached was inserted at an angle of approximately 45 to the horizontal skin plane, targeting the head-neck junction. The needle was visualized along its entire path, and 2 to 4 ml of 1% lidocaine was injected along the needle path by the assistant. After the needle tip was identified within the joint capsule near the head-neck junction, 1 to 2 ml of lidocaine was injected to verify placement by visualizing inflation of the capsule (Figure 3). The Figure 2: Photograph showing the position of the ultrasound transducer and the approximate needle entry site. Figure 3: Ultrasound image showing the spinal needle correctly positioned at the head-neck junction. assistant then switched syringes while the provider held the needle in place and in view on ultrasound. A mixture of 1 ml of 1% lidocaine and 1 ml of 0.5% bupivacaine was injected while visualizing capsular expansion and intra-articular flow. If the planned injection was therapeutic, 1.5 to 3 ml of triamcinolone (40 mg/ml) was included. For the purpose of this study, 2 ml of iohexol (Omnipaque; GE Healthcare, Chicago, Illinois) also was included in the injection. This was later increased to 5 ml to improve the ability to clearly visualize the contrast radiographically to determine whether the injection was intra-articular. MARCH/APRIL 2017 Volume 40 Number 2 97
3 Figure 4: Anteroposterior pelvis radiograph showing successful bilateral ultrasound-guided intraarticular hip injections. Following the injections, a single anteroposterior pelvis radiograph was obtained for all patients. Patient diagnosis, body mass index (BMI), procedural time, and visual analog scale (VAS) score were recorded for each patient. This concluded the patient s participation in the study. A senior orthopedic resident, a staff orthopedic surgeon, and a musculoskeletal radiologist reviewed the postinjection radiographs to determine the accuracy of the injection. Each injection was independently classified as clearly intra-articular, clearly extra-articular, or indeterminate. A final determination was assigned to each injection based on collaboration among the 3 independent reviewers, and the results were compared. Results Forty-three consecutive patients (25 men and 18 women) underwent ultrasound-guided hip injections. Seven patients underwent bilateral injections for a total of 50 hips injected. Average patient age was 47 years, and average BMI was 29.9 kg/m 2. Preinjection diagnoses included degenerative joint disease, FAI, labral tear, and hip pain of unknown origin. For 2 of the early study patients, there was no identifiable Omnipaque on their postinjection radiographs. Consequently, the amount of Omnipaque was increased for the remainder of the injections, and these 2 patients were discarded from further comparison, leaving 48 patients for final analysis. In 46 of the 48 hips, the injections were confirmed to be intra-articular for an accuracy of 96% (Figure 4). One injection was clearly extra-articular with contrast extravasating up the iliopsoas tendon sheath. One injection was indeterminate with contrast surrounding the capsule but not clearly in the capsule; this patient previously had undergone a hip arthroscopy with capsulotomy. The average procedural time was 2.6 minutes, and the average VAS score during the procedure was 1.9. Visual analog scale scores were not recorded prior to or after the injection. Discussion Hip pain is a common presentation in the orthopedic clinic and often is diagnosed as hip degenerative joint disease or FAI. The number of patients with these diagnoses can be expected to increase as the incidence and surgical treatment for both are predicted to steadily increase in the next decade. 1,2 Although surgical intervention will continue to be the definitive treatment, clinic-based injections can aid in the diagnostic process and also provide some level of therapeutic relief. Intra-articular hip injections have been shown to be of diagnostic value in hip degenerative joint disease and FAI, and of therapeutic value in degenerative joint disease. A retrospective review by Deshmukh et al 3 included 204 patients with atypical hip pain who underwent an intra-articular hip injection for diagnostic purposes. The authors reported a specificity and positive predictive value of 100% along with a negative predictive value of 84.6% for response to subsequent total hip arthroplasty. Of note, a radiologist performed all injections using fluoroscopy. 3 A prospective study by Ziv et al 7 included 52 patients under consideration for hip arthroscopy for FAI. All of the patients underwent an intra-articular hip injection performed by a radiologist, and patients relief after the injection was compared with functional scores recorded 6 months following surgery. The authors reported that a negative response to a hip injection may predict a higher likelihood of a negative result from surgery. Several studies have shown a short-term benefit to intra-articular hip injections in regard to pain and function when performed in patients with hip degenerative joint disease, and these studies also have shown a limited side-effect profile. 4-6 Krych et al 6 performed a prospective study of 54 patients in which the therapeutic value of intra-articular hip injections was investigated in patients with FAI. The authors concluded that the injections provided little therapeutic value but did highlight the diagnostic value of hip injections in these patients. 6 These studies indicate significant clinical value in intra-articular hip injections in patients presenting with hip pain. Blind intra-articular hip injections have been studied with less-than-optimal results. A cadaver study by Leopold et al 4 in 2001 tested both an anterior and lateral approach using palpable anatomic landmarks to guide the injections. The authors reported a 60% success rate using the anterior approach and an 80% success rate using the lateral approach. They also reported that the needle either pierced or was within 5 mm of the femoral nerve in 87% of the anterior injections. Kurup and Ward 5 used an anterolateral injection technique based on palpable anatomic landmarks in 40 consecutive patients. The authors injected radiographic dye and used fluoroscopy to judge intraarticular location. They reported a success rate of 65%. Ziv et al 7 reported an intraarticular accuracy rate of 77.5% in 40 consecutive patients using a blind direct lateral approach. These studies indicate the requirement for some form of imaging assistance to improve the accuracy and safety of intra-articular hip injections. Most recently, Masoud and Said 8 reported a 95% success rate using a blind anterolateral injection technique based on palpable landmarks. No data were given 98
4 regarding patient BMI, and success was based on the anatomic location of the needle under fluoroscopy and not with the use of radiographic contrast. 8 Although these authors had comparable success, the current authors recommend using some form of imaging assistance. Historically, the use of ultrasound to guide intra-articular hip injections has been reported in the radiology literature. In a 2005 study performed by radiologists, computed tomography was used to determine the location of the needle tip for 30 consecutive ultrasound-guided hip injections; the authors reported a 100% accuracy rate with this technique. 3 In a 2009 study also performed by radiologists, fluoroscopy was used to determine the accuracy of 30 consecutive intra-articular hip injections performed under ultrasound guidance; the authors reported a 97% accuracy rate. 9 No complications were reported in either study. In the current study, the accuracy rate of 96% is comparable with that reported in the radiology literature. One of the injections was clearly extra-articular, with contrast observed tracking up the iliopsoas tendon sheath; it is believed that the needle may have been slightly withdrawn during the injection process. A second injection in a patient with a prior hip arthroscopy with capsulotomy was indeterminate. It is unknown whether the prior capsulotomy may have led to extravasation of injection contrast. However, even with this considered to be a miss, the accuracy rate of 96% for the current study is comparable with that reported in the radiology literature and supports the performance of these injections in the orthopedic clinic. The current study is the second study to report on the use of ultrasound-guided hip injections in the orthopedic clinic. Byrd et al 10 recently reported on a large series of hip injections performed by a nurse practitioner. A total of 206 patients underwent hip injections, including a cohort of 50 patients who previously had undergone a fluoroscopic-guided hip injection. They reported a 98% accuracy rate, and 49 of the 50 patients in the previous fluoroscopicguided injection cohort preferred the ultrasound-guided injection. 10 The advantages of the current study include the use of radiographic contrast to determine accuracy versus visualization of capsular distension via ultrasound, independent evaluation of success by a musculoskeletal radiologist, and the use of multiple providers to perform the injections. However, both studies showed comparable accuracy of hip injections performed in the orthopedic clinic vs radiologist-performed injections and highlight the use of physician extenders to perform the injections. There are multiple advantages to performing hip injections in the orthopedic clinic. A continuous relationship is maintained between the orthopedic provider and the patient without the requirement for an outside provider. Potential delays associated with referring a patient to a radiology department or scheduling a patient for an open OR date also are avoided. In the current study, 72% of patients had their injections performed either on the same day as the decision to perform an injection or within 6 days. Injections in the clinic allow the OR support staff and OR time to be used more efficaciously, which can help reduce cost as OR time has been estimated to cost approximately $62 per minute. 11 Performing injections in the clinic also allows immediate feedback to the orthopedic provider regarding symptom relief and facilitates communication for maintenance of a pain diary in the days and weeks following the injection. Finally, performing hip injections in the orthopedic clinic allows the clinic to capture the productivity and financial benefit associated with these procedures. The facility revenue value unit (RVU) in 2015 was 1.72 for an ultrasoundguided hip injection compared with 2.55 for the nonfacility RVU. 12 These RVUs represent lost productivity when these injections are referred to a radiology department. The current authors clinic has established a weekly physician assistant halfday injection clinic to which hip injections often are referred internally. This provides the patients with greater continuity as they do not have to see another provider at a different facility or from a different specialty. It also frees up additional clinic time for surgeons, provides quick referrals for injections, facilitates accurate and efficient injections as they are grouped together, and maintains both continuity and productivity within the orthopedic clinic. Limitations of the current study include varying levels of experience with ultrasound-guided hip injections among the providers performing the injections. Although the purpose of the study was not to evaluate the number of injections necessary to determine procedural proficiency, provider experience could be considered a limitation. In addition, a single anteroposterior radiograph was obtained without additional views. Orthogonal radiographic views were deferred to limit radiation exposure; however, it is possible that they may have been beneficial for the indeterminate injections. Conclusion Intra-articular hip injections have been shown to have diagnostic and therapeutic value in the work-up and management of many patients presenting with hip pain. Either fluoroscopic or ultrasound guidance is recommended to improve accuracy and avoid neurovascular structures. As a result, many orthopedic surgeons either perform hip injections in the OR using fluoroscopic guidance or refer these patients to radiology for the injection. The findings of the current study demonstrate that ultrasound-guided intra-articular hip injections can be performed accurately and safely in the orthopedic clinic by a surgeon or physician assistant with minimal patient discomfort. References 1. Nho SJ, Kymes SM, Callaghan JJ, Felson DT. The burden of hip osteoarthritis in the United States: epidemiologic and economic considerations. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2013; 21(suppl 1):S1-S6. MARCH/APRIL 2017 Volume 40 Number 2 99
5 2. Bozic KJ, Chan V, Valone FH III, Feeley BT, Vail TP. Trends in hip arthroscopy utilization in the United States. J Arthroplasty. 2013; 28(8)(suppl): Deshmukh AJ, Thakur RR, Goyal A, Klein DA, Ranawat AS, Rodriguez JA. Accuracy of diagnostic injection in differentiating source of atypical hip pain. J Arthroplasty. 2010; 25(6)(suppl): Leopold SS, Battista V, Oliverio JA. Safety and efficacy of intraarticular hip injection using anatomic landmarks. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; 391: Kurup H, Ward P. Do we need radiological guidance for hip joint injections? Acta Orthop Belg. 2010; 76(2): Krych AJ, Griffith TB, Hudgens JL, Kuzma SA, Sierra RJ, Levy BA. Limited therapeutic benefits of intra-articular cortisone injection for patients with femoro-acetabular impingement and labral tear. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014; 22(4): Ziv YB, Kardosh R, Debi R, Backstein D, Safir O, Kosashvili Y. An inexpensive and accurate method for hip injections without the use of imaging. J Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 15(3): Masoud MA, Said HG. Intra-articular hip injection using anatomic surface landmarks. Arthrosc Tech. 2013; 2(2):e147-e Smith J, Hurdle MB, Weingarten TN. Accuracy of sonographically guided intra-articular injections in the native adult hip. J Ultrasound Med. 2009; 28(3): Byrd JW, Potts EA, Allison RK, Jones KS. Ultrasound-guided hip injections: a comparative study with fluoroscopy-guided injections. Arthroscopy. 2014; 30(1): Macario A. What does one minute of operating room time cost? J Clin Anesth. 2010; 22(4): Legrand M. New orthopaedic CPT codes for AAOS Now. 2015; 9(1):
The utility of hip arthroscopy has certainly increased
 Hip Arthroscopy and the Anterolateral Portal: Avoiding Labral Penetration and Femoral Articular Injuries Stephen Kenji Aoki, M.D., James Thomas Beckmann, M.D., and James Derek Wylie, M.D. Abstract: Establishing
Hip Arthroscopy and the Anterolateral Portal: Avoiding Labral Penetration and Femoral Articular Injuries Stephen Kenji Aoki, M.D., James Thomas Beckmann, M.D., and James Derek Wylie, M.D. Abstract: Establishing
Efficacy of a non-image-guided diagnostic hip injection in patients with clinical and radiographic evidence of intra-articular hip pathology
 Journal of Hip Preservation Surgery Vol. 0, No. 0, pp. 1 6 doi: 10.1093/jhps/hny013 Research article Efficacy of a non-image-guided diagnostic hip injection in patients with clinical and radiographic evidence
Journal of Hip Preservation Surgery Vol. 0, No. 0, pp. 1 6 doi: 10.1093/jhps/hny013 Research article Efficacy of a non-image-guided diagnostic hip injection in patients with clinical and radiographic evidence
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
The Relationship Between Hip Physical Examination Findings and Intra-articular Pathology Seen at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy Craig M. Capeci, MD Mohaned Al-Humadi, MD Malachy P. McHugh, PhD Alexis Chiang-Colvin,
Risk Factors for 30-Day Readmission Following Hip Arthroscopy
 Risk Factors for 30-Day Readmission Following Hip Arthroscopy Matthew Hartwell, MD Allison Morgan, BA Daniel Johnson, MD Richard Nicolay, MD Ryan Selley, MD Michael Terry, MD Vehniah Tjong, MD Disclosures
Risk Factors for 30-Day Readmission Following Hip Arthroscopy Matthew Hartwell, MD Allison Morgan, BA Daniel Johnson, MD Richard Nicolay, MD Ryan Selley, MD Michael Terry, MD Vehniah Tjong, MD Disclosures
The Education and Training of Future Hip Preservation Surgeons: The Aggregate Recommendations of High-Volume Surgeons
 The Education and Training of Future Hip Preservation Surgeons: The Aggregate Recommendations of High-Volume Surgeons A Chen 1,2, M Steffes 3, J Laseter 1, D Maldonado 1, V Ortiz-Declet 1,4, I Perets 1,
The Education and Training of Future Hip Preservation Surgeons: The Aggregate Recommendations of High-Volume Surgeons A Chen 1,2, M Steffes 3, J Laseter 1, D Maldonado 1, V Ortiz-Declet 1,4, I Perets 1,
Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy
 Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy ISHA Annual Scientific Meeting 2012 Boston, MA Crispin Ong MD, Michael Hall MD, Thomas Youm MD Disclosures Consultancy: Arthrex, Depuy Lectures/speakers
Treatment Of Heterotopic Ossification After Hip Arthroscopy ISHA Annual Scientific Meeting 2012 Boston, MA Crispin Ong MD, Michael Hall MD, Thomas Youm MD Disclosures Consultancy: Arthrex, Depuy Lectures/speakers
Comparison of ultrasound-guided versus blind glenohumeral injections: a cadaveric study
 J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2012) 21, 1664-1668 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse BASIC SCIENCE Comparison of ultrasound-guided versus blind glenohumeral injections: a cadaveric study Deepan N. Patel, MD*, Samir
J Shoulder Elbow Surg (2012) 21, 1664-1668 www.elsevier.com/locate/ymse BASIC SCIENCE Comparison of ultrasound-guided versus blind glenohumeral injections: a cadaveric study Deepan N. Patel, MD*, Samir
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology
 Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology URMC Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation Raymond J. Kenney, MD Kelly L. Adler, MEd, ATC P. Christopher Cook, MD Brian D.
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology URMC Sports Medicine and Hip Preservation Raymond J. Kenney, MD Kelly L. Adler, MEd, ATC P. Christopher Cook, MD Brian D.
Introduction to Ultrasound Guided Shoulder Injections. Alison Hall Consultant Sonographer Keele University Cannock Chase Hospital
 Introduction to Ultrasound Guided Shoulder Injections Alison Hall Consultant Sonographer Keele University Cannock Chase Hospital Safe Robust Aim: to provide a service that is Cost effective To enable patients
Introduction to Ultrasound Guided Shoulder Injections Alison Hall Consultant Sonographer Keele University Cannock Chase Hospital Safe Robust Aim: to provide a service that is Cost effective To enable patients
A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1
 A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1 Joo Yeon Ji, M.D. Purpose: To assess the feasibility of ultrasound-guided shoulder
A Comparison between the Anterior and Posterior Approach to US-guided Shoulder Articular Injections for MR Arthrography 1 Joo Yeon Ji, M.D. Purpose: To assess the feasibility of ultrasound-guided shoulder
Incidence and Complications of Open Hip Preservation Surgery: An American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Database Review
 Incidence and Complications of Open Hip Preservation Surgery: An American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Database Review Jon P Hedgecock MD, 1 P Christopher Cook MD FRCS(C), 1 John Harrast PhD,2 Judith F
Incidence and Complications of Open Hip Preservation Surgery: An American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Database Review Jon P Hedgecock MD, 1 P Christopher Cook MD FRCS(C), 1 John Harrast PhD,2 Judith F
Viviane Khoury, MD. Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania
 U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
U Penn Diagnostic Imaging: On the Cape Chatham, MA July 11-15, 2016 Viviane Khoury, MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Pennsylvania Hip imaging has changed in recent years: new
Disclosure. FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software. Acceptance of Hip Arthroscopy & FAI. Public. Payors. Orthopaedic Community
 2015 Chicago Sports Medicine Symposium Chicago, Illinois USA FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software Allston J. Stubbs, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director Hip Arthroscopy & Associate Professor
2015 Chicago Sports Medicine Symposium Chicago, Illinois USA FAI: Imaging Modalities and Dynamic Imaging Software Allston J. Stubbs, M.D., M.B.A. Medical Director Hip Arthroscopy & Associate Professor
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
 October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
October 1999, Supplement 1 Volume 15 Number 7
STAIRS. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care. I have no relevant disclosures. Top 5 (or 6) Pathologies. Big 3- Questions to Ask
 I have no relevant disclosures. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery December, 2015
I have no relevant disclosures. What s Hip: Top 5 Hip Problems in Primary Care Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery December, 2015
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip 15195 Heathcote Blvd Suite 334 Haymarket, VA 20169 Phone: 703-369-9070 Fax: 703-369-9240 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from a variety
Evaluation and Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Prior to Arthroscopic Surgery
 Evaluation and Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Prior to Arthroscopic Surgery International Society for Hip Arthroscopy Annual Scientific Meeting Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Benjamin D. Streufert,
Evaluation and Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement Prior to Arthroscopic Surgery International Society for Hip Arthroscopy Annual Scientific Meeting Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Benjamin D. Streufert,
Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail?
 Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail? Andrew J. Bryan 1, MD K. Poehling-Monaghan 1, MD Rohith Mohan 1, BA Nick R Johnson 1, BS Aaron J. Krych 1, MD Bruce A. Levy
Hip Arthroscopy in Patients with Mild to Moderate Dysplasia: When do they Fail? Andrew J. Bryan 1, MD K. Poehling-Monaghan 1, MD Rohith Mohan 1, BA Nick R Johnson 1, BS Aaron J. Krych 1, MD Bruce A. Levy
Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan, BA a James Capon, BS, MS a Hayden Smith, BA a Alexandra Napoli, BS a Patrick Gaspar, MD b
 Pre-operative Lumbar Plexus Block Provides Superior Post-operative Analgesia when compared with Fascia Iliaca Block or General Anesthesia alone in Hip Arthroscopy Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan,
Pre-operative Lumbar Plexus Block Provides Superior Post-operative Analgesia when compared with Fascia Iliaca Block or General Anesthesia alone in Hip Arthroscopy Andrew B. Wolff, MD a Geoffrey Hogan,
Who Doesn t Need a Hip Scope?
 AOSSM 2013 Annual Meeting Chicago, Illinois July 14, 2013 I. Hip arthroscopy only helps if it is a hip joint problem A. Not always evident - Among athletes, 60% of intraarticular disorders treated for
AOSSM 2013 Annual Meeting Chicago, Illinois July 14, 2013 I. Hip arthroscopy only helps if it is a hip joint problem A. Not always evident - Among athletes, 60% of intraarticular disorders treated for
Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review
 Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review Poster No.: P-0127 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Karsandas, J. Tuckett, R. Sinha,
Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Injections in the Treatment of Shoulder Pain: A Multimedia Review Poster No.: P-0127 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: A. Karsandas, J. Tuckett, R. Sinha,
Investigation performed at the University of Rochester, Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation, Rochester, NY USA
 Intra-articular cocktail offers clinical advantages over femoral nerve block for postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing arthroscopic hip surgery Sean Childs, MD; Sonia Pyne, MD; Kiritpaul Nandra,
Intra-articular cocktail offers clinical advantages over femoral nerve block for postoperative analgesia in patients undergoing arthroscopic hip surgery Sean Childs, MD; Sonia Pyne, MD; Kiritpaul Nandra,
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery. Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery
 Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Non-Arthroplasty Hip Surgery Javad Parvizi MD FRCS Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery Subcapital reduction osteotomy Relative lengthening of femoral neck (Perthes) AVN surgery Femoral osteotomy Trap door
Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2015, Article ID 210827, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/210827 Case Report Unusual Bilateral Rim Fracture in Femoroacetabular Impingement Claudio Rafols, Juan
ULTRASOUND- GUIDED INJECTIONS A TECHNICAL REVIEW
 PRACTICAL ADVICE ULTRASOUND- GUIDED INJECTIONS A TECHNICAL REVIEW Written by Akira M. Murakami, USA Ultrasound is a powerful modality for guiding the intra-articular injection of both therapeutic medication
PRACTICAL ADVICE ULTRASOUND- GUIDED INJECTIONS A TECHNICAL REVIEW Written by Akira M. Murakami, USA Ultrasound is a powerful modality for guiding the intra-articular injection of both therapeutic medication
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES
 ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement Gary J. Farkas, BS 1, Marc Haro, MD 1, Simon Lee, MPH 1, Philip Malloy 2, Alejandro A.
Hip Center Edge Angle and Alpha Angle Morphological Assessment Using Gait Analysis in Femoroacetabular Impingement Gary J. Farkas, BS 1, Marc Haro, MD 1, Simon Lee, MPH 1, Philip Malloy 2, Alejandro A.
Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine
 Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine Poster No.: C-1352 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. García Yavar, J. Cabezudo, S.
Hip pain rating after preforming MRI with gadolinium arthrography and intra-articular lidocaine Poster No.: C-1352 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: J. García Yavar, J. Cabezudo, S.
CLINICAL PAPER / ORTHOPEDIC
 HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
HIP LEG LENGTH AND OFFSET Kelley T.C. and Swank M.L. (2009) Using CAS leads to more accurate positioning within the safe zone (inclination between 30 and 50, anteversion between 5 and 25 ) CAS improves
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults
 What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
What s Hip: Common Hip Problems and Kids and Adults Alan Zhang MD Assistant Professor Sports Medicine and Hip Arthroscopy UCSF Department of Orthopaedic Surgery I have no relevant disclosures. 2 1 Most
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems?
 What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide Toacetabular Component Anteversion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 65-69 www.iosrjournals.org Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 65-69 www.iosrjournals.org Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide
CHAPTER 5 Femoral Nerve Block. Arun Nagdev, MD Mike Mallin, MD, RDCS, RDMS
 CHAPTER 5 Femoral Nerve Block Arun Nagdev, MD Mike Mallin, MD, RDCS, RDMS SECTION 1 Introduction An ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block (USFNB) can be a rapid and definitive tool for pain control for
CHAPTER 5 Femoral Nerve Block Arun Nagdev, MD Mike Mallin, MD, RDCS, RDMS SECTION 1 Introduction An ultrasound-guided femoral nerve block (USFNB) can be a rapid and definitive tool for pain control for
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics)
 Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Mr Simon Jennings BSc, MB BS, FRCS, Dip Sports Med FRCS (Trauma & Orthopaedics) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Northwick Park Hospital 107 Harley Street RSM 16 th September 2010 Orthopaedic Surgeon Knee
Labral Penetration Rate in a Consecutive Series of 300 Hip Arthroscopies
 AJSM PreView, published on February 28, 2012 as doi:10.1177/0363546512437152 Labral Penetration Rate in a Consecutive Series of 300 Hip Arthroscopies Benjamin Domb,* yz MD, Bryan Hanypsiak, MD, and Itamar
AJSM PreView, published on February 28, 2012 as doi:10.1177/0363546512437152 Labral Penetration Rate in a Consecutive Series of 300 Hip Arthroscopies Benjamin Domb,* yz MD, Bryan Hanypsiak, MD, and Itamar
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip Sports-related injuries require specialized care to promote optimum healing. Whether you are a weekend jogger or tennis player, a professional soccer player
A Patient s Guide to Labral Tears of the Hip Sports-related injuries require specialized care to promote optimum healing. Whether you are a weekend jogger or tennis player, a professional soccer player
A Novel Biomechanical Model for Hip Microinstability
 A Novel Biomechanical Model for Hip Microinstability Leandro Ejnisman, MD 1,2 Adam Johannsen, MD 1 Anthony Behn, MS 1 Kotaro Shibata, MD 1,3,4 Timothy Tio, MS 1 Marc R. Safran, MD 1 1. Stanford University,
A Novel Biomechanical Model for Hip Microinstability Leandro Ejnisman, MD 1,2 Adam Johannsen, MD 1 Anthony Behn, MS 1 Kotaro Shibata, MD 1,3,4 Timothy Tio, MS 1 Marc R. Safran, MD 1 1. Stanford University,
Femoroacetabular impingement has recently been
 Improved Arthroscopic Visualization of Peripheral Compartment Adam G. Suslak, M.D., Richard C. Mather III, M.D., Bryan T. Kelly, M.D., and Shane J. Nho, M.D., M.S. Abstract: Femoroacetabular impingement
Improved Arthroscopic Visualization of Peripheral Compartment Adam G. Suslak, M.D., Richard C. Mather III, M.D., Bryan T. Kelly, M.D., and Shane J. Nho, M.D., M.S. Abstract: Femoroacetabular impingement
The Pie-Crusting Technique for Capsular. Management during Hip Arthroscopy
 1 2 The Pie-Crusting Technique for Capsular Management during Hip Arthroscopy 3 4 5 Jorge Chahla, MD, PhD 1 Benjamin Sherman, DO 2, Frank Wydra, MD 1 and Michael B. Gerhardt, MD 1 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
1 2 The Pie-Crusting Technique for Capsular Management during Hip Arthroscopy 3 4 5 Jorge Chahla, MD, PhD 1 Benjamin Sherman, DO 2, Frank Wydra, MD 1 and Michael B. Gerhardt, MD 1 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
Complex Fractures and Hip Dislocations
 IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
IMAGING OF HIP PAIN Patients may present with acute (< 2 weeks) or chronic hip pain. Acute pain may be related or not related to an acute traumatic event such as fall or trauma from a motor vehicle accident.
The Young Adult Hip: FAI. Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California
 The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
The Young Adult Hip: FAI Jason Snibbe, M.D. Snibbe Orthopedics Team Physician, University of Southern California Introduction Femoroacetabular Impingment(FAI) Presentation and Exam Imaging Surgical Management
ORTHOPEDIC PRIMARY CARE Joint Injections in Primary Care. Jackson Orthopaedic Foundation
 ORTHOPEDIC PRIMARY CARE Joint Injections in Primary Care Jackson Orthopaedic Foundation Joint Injections in Primary Care Kathleen A. Geier, DNP, NP, ONC A.J. Benham, DNP, NP, ONC kgeier@jacksonortho.org
ORTHOPEDIC PRIMARY CARE Joint Injections in Primary Care Jackson Orthopaedic Foundation Joint Injections in Primary Care Kathleen A. Geier, DNP, NP, ONC A.J. Benham, DNP, NP, ONC kgeier@jacksonortho.org
Contribution of the Pubofemoral Ligament to Hip Stability: A Biomechanical Study
 Contribution of the Pubofemoral Ligament to Hip Stability: A Biomechanical Study E-Poster Abstract # 1808 Anthony Khoury M.Sc. 1,2 ; Ricardo G. Schröder, PT 2 ; Eric Johnson B.S. 2,3; Salvador Campos,
Contribution of the Pubofemoral Ligament to Hip Stability: A Biomechanical Study E-Poster Abstract # 1808 Anthony Khoury M.Sc. 1,2 ; Ricardo G. Schröder, PT 2 ; Eric Johnson B.S. 2,3; Salvador Campos,
Pragmatic use of US in intraarticular and periarticular procedures
 Pragmatic use of US in intraarticular and periarticular procedures Plovdiv, 13. January 2018 Dr. med. Giorgio Tamborrini-Schütz www.irheuma.com member of the EULAR Network of Imaging Training Centres Ulrasound
Pragmatic use of US in intraarticular and periarticular procedures Plovdiv, 13. January 2018 Dr. med. Giorgio Tamborrini-Schütz www.irheuma.com member of the EULAR Network of Imaging Training Centres Ulrasound
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures
 Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Ultrasound of the Hip: Anatomy, Pathology, and Procedures Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Outline Hip Joint Native hip
Hip Arthroscopy After Traumatic Hip Dislocation
 Hip Arthroscopy After Traumatic Hip Dislocation Victor M. Ilizaliturri Jr., MD, Bernal Gonzalez-Gutierrez, MD, Humberto Gonzalez-Ugalde, MD, Javier Camacho-Galindo, MD Adult Joint Reconstruction Service
Hip Arthroscopy After Traumatic Hip Dislocation Victor M. Ilizaliturri Jr., MD, Bernal Gonzalez-Gutierrez, MD, Humberto Gonzalez-Ugalde, MD, Javier Camacho-Galindo, MD Adult Joint Reconstruction Service
Does hydrodilatation help avoid the need for surgical intervention in adhesive capsulitis?
 Does hydrodilatation help avoid the need for surgical intervention in adhesive capsulitis? Poster No.: P-0122 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Rajesparan, S. Molathoti, T. Sikdar,
Does hydrodilatation help avoid the need for surgical intervention in adhesive capsulitis? Poster No.: P-0122 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Rajesparan, S. Molathoti, T. Sikdar,
Sonography of the Acetabular Labrum
 Case Series Visualization of Labral Injuries During Intra-Articular Injections Carolyn M. Sofka, MD, Ronald S. Adler, PhD, MD, Martha A. Danon, MD Objective. The purpose of this series was to describe
Case Series Visualization of Labral Injuries During Intra-Articular Injections Carolyn M. Sofka, MD, Ronald S. Adler, PhD, MD, Martha A. Danon, MD Objective. The purpose of this series was to describe
Goals and Objectives for the Orthopaedic Surgery Resident McGill Orthopaedic Sports Medicine and Minimally Invasive (MGH & Shriners) Junior Residents
 Goals and Objectives for the Orthopaedic Surgery Resident McGill Orthopaedic Sports Medicine and Minimally Invasive (MGH & Shriners) Junior Residents The following document is intended to guide you in
Goals and Objectives for the Orthopaedic Surgery Resident McGill Orthopaedic Sports Medicine and Minimally Invasive (MGH & Shriners) Junior Residents The following document is intended to guide you in
b. Non-arthritic hip (non-capsular patterns)
 Evaluation of Hip Disorders and Ruling Out the Lumbosacral Spine Richard Erhard, PT,DC University of Pittsburgh erhardre@upmc.edu Differential Diagnosis Lumbar/Pelvis/Hip 1. Subjective examination a. History
Evaluation of Hip Disorders and Ruling Out the Lumbosacral Spine Richard Erhard, PT,DC University of Pittsburgh erhardre@upmc.edu Differential Diagnosis Lumbar/Pelvis/Hip 1. Subjective examination a. History
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6
 Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Total Hip Arthroplasty Performed Using Conventional and Computer-Assisted, Tissue- Preserving Techniques 6 Stephen B. Murphy, MD, Timo M. Ecker, MD and Moritz Tannast, MD Introduction Less invasive techniques
Surgical Trends in Arthroscopic Hip Surgery using a Large National Database
 Surgical Trends in Arthroscopic Hip Surgery using a Large National Database Nicholas A. Bonazza, M.D. 1, Guodong Liu, Ph.D. 2, Douglas Leslie, Ph.D. 2, Aman Dhawan, M.D. 1 1 Department of Orthopaedics
Surgical Trends in Arthroscopic Hip Surgery using a Large National Database Nicholas A. Bonazza, M.D. 1, Guodong Liu, Ph.D. 2, Douglas Leslie, Ph.D. 2, Aman Dhawan, M.D. 1 1 Department of Orthopaedics
Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain
 Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain Anthony J. Ferretti, D.O., MHSA Hip Pain in the Adult Various etiologies: Traumatic Infectious Neurovascular Degenerative Congenital Pathologic 1 Hip Pain Complex interaction
Evaluation of Posterior Hip Pain Anthony J. Ferretti, D.O., MHSA Hip Pain in the Adult Various etiologies: Traumatic Infectious Neurovascular Degenerative Congenital Pathologic 1 Hip Pain Complex interaction
Hip arthroscopy using the Smith & Nephew Hip Access System
 Hip Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew HIP ACCESS SYSTEM Hip Arthroscopy System Hip arthroscopy using the Smith & Nephew Hip Access System Victor M. Ilizaliturri, Jr., M.D. Hip arthroscopy using the
Hip Series Technique Guide *smith&nephew HIP ACCESS SYSTEM Hip Arthroscopy System Hip arthroscopy using the Smith & Nephew Hip Access System Victor M. Ilizaliturri, Jr., M.D. Hip arthroscopy using the
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder
 Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
Common Applications for Sonography and Guided Intervention: Shoulder Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant:
RSNA 2009 Essentials of Arthrography ES32: Essentials of Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ES32: Essentials of Musculoskeletal Imaging Focus on Arthrography Tuesday 12/1/09 10:30-12:00 Ken Schreibman, PhD/MD University of Wisconsin, Madison David Rubin, MD Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology,
ES32: Essentials of Musculoskeletal Imaging Focus on Arthrography Tuesday 12/1/09 10:30-12:00 Ken Schreibman, PhD/MD University of Wisconsin, Madison David Rubin, MD Mallinckrodt Institute of Radiology,
Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
1/25/2017. ABC s in the OR: Patient Set up, Positioning, Central and Peripheral Compartment Access and Portal Placement.
 Hip Arthroscopy Learning Curve ABC s in the OR: Patient Set up, Positioning, Central and Peripheral Compartment Access and Portal Placement. Michael Banffy, MD Kerlan Jobe Orthopaedic Clinic Hip Capsule
Hip Arthroscopy Learning Curve ABC s in the OR: Patient Set up, Positioning, Central and Peripheral Compartment Access and Portal Placement. Michael Banffy, MD Kerlan Jobe Orthopaedic Clinic Hip Capsule
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Cam- and pincer-type femoroacetabular impingement
 Case Report With Video Illustration Making a Case for Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine/Subspine Hip Impingement: Three Representative Case Reports and Proposed Concept Christopher M. Larson, M.D., Bryan T.
Case Report With Video Illustration Making a Case for Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine/Subspine Hip Impingement: Three Representative Case Reports and Proposed Concept Christopher M. Larson, M.D., Bryan T.
DK7215-Levine-ch12_R2_211106
 12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
12 Arthroscopic Rotator Interval Closure Andreas H. Gomoll Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, U.S.A. Brian J. Cole Departments
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow.
 Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Ultrasound-Guided Calcific Tendinitis Lavage: Application, Technique, and Outcome
 Ultrasound-Guided Calcific Tendinitis Lavage: Application, Technique, and Outcome Andrew Schapiro MD, Humberto Rosas MD, Kenneth Lee MD University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics aschapiro@uwhealth.org
Ultrasound-Guided Calcific Tendinitis Lavage: Application, Technique, and Outcome Andrew Schapiro MD, Humberto Rosas MD, Kenneth Lee MD University of Wisconsin Hospital and Clinics aschapiro@uwhealth.org
EXAMPLE OF STRONG APPLICATION Includes Entries from COTA Awarded Programs
 EXAMPLE OF STRONG APPLICATION Includes Entries from COTA Awarded Programs (NOTE only blinded submissions will be accepted and distributed for COTA review) Orthopaedic Trauma Fellowship Program Goals and
EXAMPLE OF STRONG APPLICATION Includes Entries from COTA Awarded Programs (NOTE only blinded submissions will be accepted and distributed for COTA review) Orthopaedic Trauma Fellowship Program Goals and
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Total hip arthroplasty via the direct anterior approach off the table
 Technical Note Page 1 of 5 Total hip arthroplasty via the direct anterior approach off the table Peter Boyle, Zachary Post, Fabio Orozco, Alvin Ong Rothman Institute, Egg Harbor Township, NJ, USA Correspondence
Technical Note Page 1 of 5 Total hip arthroplasty via the direct anterior approach off the table Peter Boyle, Zachary Post, Fabio Orozco, Alvin Ong Rothman Institute, Egg Harbor Township, NJ, USA Correspondence
Use of Air Arthrograms to Aid in Joint Distraction During Hip Arthroscopic Surgery Decreases Postoperative Pain and Opioid Requirements
 Original Research Use of Air Arthrograms to Aid in Joint Distraction During Hip Arthroscopic Surgery Decreases Postoperative Pain and Opioid Requirements Jonathan D. Hodax,* MD, MS, Sergio E. Flores,*
Original Research Use of Air Arthrograms to Aid in Joint Distraction During Hip Arthroscopic Surgery Decreases Postoperative Pain and Opioid Requirements Jonathan D. Hodax,* MD, MS, Sergio E. Flores,*
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013
 Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
Message of the Month for GPs June 2013 Dr Winn : Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist, Manchester Royal Infirmary Imaging of the musculoskeletal system Musculoskeletal pain is a common problem in the
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP?
 CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
CAN SOFT TISSUES STRUCTURES DIFFERENTIATE BETWEEN DYSPLASIA AND CAM-FAI OF THE HIP? A Le Bouthillier, KS Rakhra 1, PE Beaulé 2, RCB Foster 1 1 Department of Medical Imaging 2 Division of Orthopaedic Surgery
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
WHAT DO YOU THINK? 1. How many people in the United States undergo hip replacement surgery each year? a) 80,000. b) 330,000.
 1 WHAT DO YOU THINK? 1. How many people in the United States undergo hip replacement surgery each year? a) 80,000 b) 330,000 c) 650,000 2. What disease is the leading cause of disability in the U.S.? a)
1 WHAT DO YOU THINK? 1. How many people in the United States undergo hip replacement surgery each year? a) 80,000 b) 330,000 c) 650,000 2. What disease is the leading cause of disability in the U.S.? a)
Sensitivity of MR Arthrography in the Evaluation of Acetabular Labral Tears
 MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
MR Arthrography of Acetabular Labral Tears Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research A C D E M N E U T R Y L I A M C A I G O F I N G Glen A. Toomayan 1 W. Russell Holman 1 Nancy M. Major 1 Shannon M. Kozlowicz
Figure 3 Figure 4 Figure 5
 Figure 1 Figure 2 Begin the operation with examination under anesthesia to confirm whether there are any ligamentous instabilities in addition to the posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. In particular
Figure 1 Figure 2 Begin the operation with examination under anesthesia to confirm whether there are any ligamentous instabilities in addition to the posterior cruciate ligament insufficiency. In particular
Anterolateral Portal Is Less Painful than Superolateral Portal in Knee Intra-Articular Injection
 Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2015;27(4):228-232 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.4.228 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Anterolateral Portal Is Less Painful
Original Article Knee Surg Relat Res 2015;27(4):228-232 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2015.27.4.228 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Anterolateral Portal Is Less Painful
3/20/2017. Disclosures. Ultrasound Fundamentals. Ultrasound Fundamentals. Bone Anatomy. Tissue Characteristics
 Disclosures Images of ultrasound equipment in this presentation are not an endorsement Fundamentals of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Physics and Knobology Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopedic
Disclosures Images of ultrasound equipment in this presentation are not an endorsement Fundamentals of Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Physics and Knobology Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor Orthopedic
Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks
 Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks CONTENTS: 1. Femoral Nerve Block 2. Popliteal Nerve Block Updated December 2017 1 1. Femoral Nerve Block Indications Surgery involving the knee, anterior thigh,
Ultrasound Guided Lower Extremity Blocks CONTENTS: 1. Femoral Nerve Block 2. Popliteal Nerve Block Updated December 2017 1 1. Femoral Nerve Block Indications Surgery involving the knee, anterior thigh,
RadRx Your Prescription for Accurate Coding & Reimbursement Copyright All Rights Reserved.
 Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of October 22, 2018 Paracentesis & Transjugular Liver Biopsy
Interventional Radiology Coding Case Studies Prepared by Stacie L. Buck, RHIA, CCS-P, RCC, CIRCC, AAPC Fellow President & Senior Consultant Week of October 22, 2018 Paracentesis & Transjugular Liver Biopsy
CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE
 Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Clin Sports Med 25 (2006) 365 369 CLINICS IN SPORTS MEDICINE A Acetabular labrum, tears of, hip arthroscopy in, 264 Acetabular rim, trimming of, and labral repair, new method for, 293 297 Acetabulum, femoral
Lateral Mortise Approach for Therapeutic Ankle Injection: An Alternative to the Anteromedial Approach
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Fox et al. Therapeutic Ankle Injection Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Michael G. Fox 1 Philip R. Wright 2 Bennett Alford 1 James T. Patrie 3 Mark W.
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Fox et al. Therapeutic Ankle Injection Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Michael G. Fox 1 Philip R. Wright 2 Bennett Alford 1 James T. Patrie 3 Mark W.
Ultrasound Guided Injections
 Ultrasound Guided Injection Technique More accurate injections Better Results! 1 Benefits: Increased Level of Certainty ie : really know how accurate PRP/Prolotherapy Avoid damage to articular cartilage
Ultrasound Guided Injection Technique More accurate injections Better Results! 1 Benefits: Increased Level of Certainty ie : really know how accurate PRP/Prolotherapy Avoid damage to articular cartilage
Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve block vs procedural sedation for the treatment of upper extremity emergencies
 American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2008) 26, 706 710 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Brief Report Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve vs procedural for the treatment of upper extremity
American Journal of Emergency Medicine (2008) 26, 706 710 www.elsevier.com/locate/ajem Brief Report Ultrasound-guided supraclavicular brachial plexus nerve vs procedural for the treatment of upper extremity
Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy
 Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy John M. Redmond, MD Jon E. Hammarstedt, BS Asheesh Gupta, MD MPH Christine E. Stake, DHA Kevin F. Dunne,
Radiographic and Clinical Risk Factors for the Extent of Labral Injury at the Time of Hip Arthroscopy John M. Redmond, MD Jon E. Hammarstedt, BS Asheesh Gupta, MD MPH Christine E. Stake, DHA Kevin F. Dunne,
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COMPUTER ASSISTED NAVIGATION FOR KNEE AND HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
MEDICAL POLICY PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If the member's subscriber contract excludes coverage for a specific service it is not covered under that contract. In such cases, medical policy criteria are not applied.
Live On Screen: Knee Injections ABCs of Musculoskeletal Care. Knee aspiration. Objectives. I have no disclosures.
 I have no disclosures. Live On Screen: Knee Injections ABCs of Musculoskeletal Care Carlin Senter, MD Primary Care Sports Medicine Departments of Medicine and Orthopaedics December 11, 2015 Objectives
I have no disclosures. Live On Screen: Knee Injections ABCs of Musculoskeletal Care Carlin Senter, MD Primary Care Sports Medicine Departments of Medicine and Orthopaedics December 11, 2015 Objectives
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/6/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 93 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/6/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 93 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Factors Associated with the Risk of Articular Surface Perforation during Anchor Placement for Arthroscopic Acetabular Labral Repair
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:405-412 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.405 Factors Associated with the Risk of Articular Surface Perforation during Anchor Placement for Arthroscopic
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:405-412 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.405 Factors Associated with the Risk of Articular Surface Perforation during Anchor Placement for Arthroscopic
Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Patients over 60 Years Old: Preliminary Report of a Pilot Study
 Original Article Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Patients over 60 Years Old: Preliminary Report of a Pilot Study Cartilage 1(3) 188 193 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission:
Original Article Arthroscopic Treatment of Femoroacetabular Impingement in Patients over 60 Years Old: Preliminary Report of a Pilot Study Cartilage 1(3) 188 193 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission:
Hip Arthroscopy Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
 NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Hip Arthroscopy Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives 1. INTRODUCTION AND SCOPE NHS DORSET CLINICAL COMMISSIONING GROUP
NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Hip Arthroscopy Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives 1. INTRODUCTION AND SCOPE NHS DORSET CLINICAL COMMISSIONING GROUP
Disclosure. Pre-Procedural Considerations. Transducer Selection. Sterile Procedure. Sterile Procedure. Ultrasound Guided Foot and Ankle Injections
 Ultrasound Guided Foot and Ankle Injections Disclosure No relevant financial relationships exist Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor, Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic Florida @ShaneShapiroMD 2012
Ultrasound Guided Foot and Ankle Injections Disclosure No relevant financial relationships exist Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor, Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic Florida @ShaneShapiroMD 2012
ARROW EZ-IO Intraosseous Vascular Access System Procedure Template
 ARROW EZ-IO Intraosseous Vascular Access System Procedure Template PURPOSE To provide procedural guidance for establishment of intraosseous vascular access using the ARROW EZ-IO Intraosseous Vascular Access
ARROW EZ-IO Intraosseous Vascular Access System Procedure Template PURPOSE To provide procedural guidance for establishment of intraosseous vascular access using the ARROW EZ-IO Intraosseous Vascular Access
ABOS/CORD Surgical Skills Assessment Program
 American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Establishing Education & Performance Standards for Orthopaedic Surgeons ABOS/CORD Surgical Skills Assessment Program ABOS Essential Knowledge, Skills, and Behaviors
American Board of Orthopaedic Surgery Establishing Education & Performance Standards for Orthopaedic Surgeons ABOS/CORD Surgical Skills Assessment Program ABOS Essential Knowledge, Skills, and Behaviors
Disclosures. Steven B. Cohen, MD I am a paid employee of Zimmer Biomet and receive royalties from Slack, INC.
 Arthroscopic Iliopsoas Tendon Release in Patients with Iliopsoas Tendinopathy Following Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Multicenter Arthroscopic Study of the Hip (MASH) Group Study Steven B. Cohen, MD; Nirav
Arthroscopic Iliopsoas Tendon Release in Patients with Iliopsoas Tendinopathy Following Total Hip Arthroplasty: A Multicenter Arthroscopic Study of the Hip (MASH) Group Study Steven B. Cohen, MD; Nirav
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COMPUTER ASSISTED NAVIGATION FOR KNEE AND HIP ARTHROPLASTY
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COMPUTER ASSISTED PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including an
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: COMPUTER ASSISTED PAGE: 1 OF: 5 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product, including an
Total knee arthroplasty fibrosis following arthroscopic intervention
 Original Article Page 1 of 6 Total knee arthroplasty fibrosis following arthroscopic intervention Jessica L. Churchill 1, Nipun Sodhi 1, Anton Khlopas 1, Nicolas S. Piuzzi 1, Sarah E. Dalton 1, Morad Chughtai
Original Article Page 1 of 6 Total knee arthroplasty fibrosis following arthroscopic intervention Jessica L. Churchill 1, Nipun Sodhi 1, Anton Khlopas 1, Nicolas S. Piuzzi 1, Sarah E. Dalton 1, Morad Chughtai
Sacral, ilioinguinal, and vasal nerve stimulation for treatment of pelvic, sacral, inguinal and testicular Pain.
 Chapter 14 Sacral, ilioinguinal, and vasal nerve stimulation for treatment of pelvic, sacral, inguinal and testicular Pain. Introduction Sacral nerve root stimulation has been recognized as a treatment
Chapter 14 Sacral, ilioinguinal, and vasal nerve stimulation for treatment of pelvic, sacral, inguinal and testicular Pain. Introduction Sacral nerve root stimulation has been recognized as a treatment
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not!
 Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND. CPT Stacey Good, DO Emergency Medicine Ultrasound Fellow Madigan Army Medical Center
 LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND CPT Stacey Good, DO Emergency Medicine Ultrasound Fellow Madigan Army Medical Center Learning Objectives Setup and patient positioning for optimizing success
LOWER EXTREMITY VENOUS COMPRESSION ULTRASOUND CPT Stacey Good, DO Emergency Medicine Ultrasound Fellow Madigan Army Medical Center Learning Objectives Setup and patient positioning for optimizing success
Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Versus Palpation-Guided Acromioclavicular Joint Injections: A Cadaveric Study
 Original Research Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Versus Palpation-Guided Acromioclavicular Joint Injections: A Cadaveric Study Evan Peck, MD, Jim K. Lai, BS, Wojciech Pawlina, MD, Jay Smith, MD Objective:
Original Research Accuracy of Ultrasound-Guided Versus Palpation-Guided Acromioclavicular Joint Injections: A Cadaveric Study Evan Peck, MD, Jim K. Lai, BS, Wojciech Pawlina, MD, Jay Smith, MD Objective:
Ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block for orthopaedic patients with. persistent shoulder pain and stiffness. StR Trauma and Orthopaedics
 Ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block for orthopaedic patients with persistent shoulder pain and stiffness Authors: Jawad Sultan MRCS(Ed), MSc [corresponding author] StR Trauma and Orthopaedics j.sultan@nhs.net
Ultrasound-guided suprascapular nerve block for orthopaedic patients with persistent shoulder pain and stiffness Authors: Jawad Sultan MRCS(Ed), MSc [corresponding author] StR Trauma and Orthopaedics j.sultan@nhs.net
