Fibrous dysplasia. An analysis of options for treatment
|
|
|
- Maximillian Parks
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Fibrous dysplasia. An analysis of options for treatment RB Stephenson, MD London, FM Hankin and H Kaufer J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1987;69: This information is current as of June 25, 2009 Reprints and Permissions Publisher Information Click here to order reprints or request permission to use material from this article, or locate the article citation on jbjs.org and click on the [Reprints and Permissions] link. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 20 Pickering Street, Needham, MA
2 ((p right 957 k The Journal f B,flt a,:(i JOUSt Surgery. Imorporwed Fibrous Dysplasia AN ANALYSIS OF OPTIoNs FOR TREATMENT*t BY ROBERT B. STEPhENSON, M.D4, MICHAEL D. LONDON, M.D4, FRED M. 1-IANKIN, M.I)4, AND HERBERT KAUFER, M.D4, ANN ARBOR, MICHIGAN bron: the Seetio,i of OrtIou die Surgc rv. Universiv of Michigan Medical ScI,ool. Ann Arbor ABSTRACT: The results of treatment of sixty-five symptomatic lesions in forty-three patients who had fibrous dysplasia were reviewed. For fourteen (93 per cent) of the fifteen times that a lesion in the upper extremity was treated non-operatively, the result was satisfactory. These results were independent ofthe patient s age when first seen. In contrast, in the lower extremity, the results were highly dependent on the age of the patients at the time of the initial presentation of symptoms. In patients who were eighteen years old or older, eight (88 per cent) of the nine times that a lesion involving the lower extremity had closed treatment and both times that a lesion was treated with curettage and bone-grafting, the result was satisfactory. The results of these modalities of treatment in patients who were less than eighteen years old were discouraging. Twenty-eight (88 per cent) of the thirty-two times that closed treatment was used and twenty-five (81 per cent) of the thirty-one times that curettage and bone-grafting was used, the result was unsatisfactory. However, after eighteen (86 per cent) of the twenty-one times that a lesion in the lower extremity was treated by internal fixation in a patient who was less than eighteen years old, there was a satisfactory outcome. We concluded that closed treatment of a symptomatic lesion in the upper extremity generally provides satisfactory results. In patients who are less than eighteen years old, neither closed treatment nor curettage and bone-grafting is adequate treatment for a symptomatic lesion in the lower extremity. Internal fixation should he strongly considered in these young patients. Fibrous dysplasia is a benign pathological condition that affects skeletal development. The lesion and its association with pigmentation of the skin and dysfunction of the endocrine system were described initially by Albright et al. in Lichtenstein and Jaffe classified fibrous dysplasia as a congenital anomaly that is manifested by a malfunction of bone-forming mesenchyme. The histological characteristics of this fibro-osseous tissue, with its poorly oriented * No henelits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject ofthis article. No funds were received in support of this study. t Read in part at the Annual Meeting of The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons. New Orleans. Louisiana. February 20, and at the Mid.America Orthopaedic Association. Orlando. Florida. April :1:2912 Taubman Center. Box Universily of Michigan Hospitals, Ann Arbtr. Michigan Please address requests for reprints to Dr. Hankin. osseous trabeculae and islands of cartilage, have been studied by numerous authors269. As fibrous dysplasia can compromise the structural integrity of affected bones, patients are often initially seen during the first two decades of life with progressive deformities and pathological fractures. Fractures that result from fibrous dysplasia are often managed non-operatively, as it is thought that these fractures usually heal without difficulty4. Harris et al., in a classic study of fibrous dysplasia, recommended surgical treatment under only very limited circumstances: severe or progressive deformity of an extremity, non-union of a fracture, fracture of the femoral shaft in an adult, and persistent pain in a site of fibrous dysplasia that is unresponsive to non-operative treatment. Grabias and Campbell recommended non-operative treatment of fractures that are associated with fibrous dysplasia. They advocated traction for patients who have a fracture ofthe femoral shaft, and they suggested that traction followed by the use of a cast-brace could be used to treat fractures of the upper and lower extremities in children. In most reviews concerning fibrous dysplasia, the authors have paid little attention to the results of different methods of treatment467. In order to assess the effect of treatment on outcome, we retrospectively reviewed our experience with patients who had symptomatic fibrous dysplasia of the extremities. We sought to correlate the method of treatment, the patient s age at the time of the initial symptoms, the location ofthe lesion, and the type of disease (monostotic or polyostotic) with the outcome of treatment. Each symptomatic lesion, rather than each patient, was followed over time in order to document the results of the treatment or treatments that were required for that lesion. Materials and Methods Between 1954 and 1984, fifty-nine patients who had fibrous dysplasia were treated at our affiliated institutions. In sixteen patients the disease involved only the skull or mandible, and they were excluded from additional analysis. Of the remaining patients, forty had a total of sixty-one symptomatic skeletal lesions of an appendage, and three patients had four symptomatic lesions of the spine or pelvis; they formed the basis of this retrospective study. The lesions were categorized according to whether they had a monostotic or polyostotic pattern, to their location in the upper or lower extremity, and to the skeletal maturity or immaturity of the patient at the time of the initial examination. A patient was considered to be skeletally mature if he or she was eighteen years old or older. Twenty-four patients had monostotic and nineteen had polyostotic fibrous 4(X) THE JOURNAL OF BONE ANt) JOINT SURGERY
3 FIBROUS DYSPLASIA 401 MONOSTOT IC POLYOSTOTIC Nunber Pate,its of Aqo ( Y(irs) Age (Years) Fi ;. I The ages of the patienls ai the time that they were inilially seen with symplomalic fibrous dysplasia. dysplasia. Twenty-three patients were male and twenty were female. The average duration of follow-up was 10.4 years (range, two to fifty-five years). The clinical history, radiographs, and histological characteristics of the treated lesions in each patient were reviewed. In all twenty-four patients who had a monostotic lesion, that was confirmed histologically. All ofthe patients who had polyostotic lesions had characteristic radiographic features, and in seventeen of the nineteen the lesions were confirmed histologically. Two patients had Albright syndrome. Fifty-one per cent of the patients had pain alone when they were initially seen, while 49 per cent had pain that was secondary to a pathological fracture. Lesions that involved the spine or pelvis originally caused only pain. The age at which the initial symptoms occurred ranged from one and a half to sixty-eight years. The average age at which the symptoms occurred in the patients who had monostotic disease was fifteen and a half years (range, one and a half to sixty years), and in the patients who had polyostotic disease it was thirteen years (range, two to sixty-eight years) (Fig. I). When a patient was first seen with a symptomatic Icsion, an independent plan for treatment was prescribed by the attending physician. A number of orthopaedic surgeons (including H. K.) at our affiliated hospitals were involved in these decisions. No specific protocol for treatment was used; it was the choice ofthe individual physician. A patient was considered to have completed the course of treatment if he or she returned to the pre-morbid level of activity and an attending physician thought that osseous healing and rehabilitation were complete, or when the method of treatment had failed and a new plan was initiated. Each time the treatment for a symptonlatic lesion was completed, the lesion was retrospectively assigned to One of four groups: ( I ) closed methods (cast, splint. or traction). (2) curettage and autogenous bone-grafting, (3) internal fixation (intramedullary rods or bone-plates). or (4) amputation or excision. Subsequent treatment of a lesion resulted in its reassignment to the appropriate treatment group. Therefcre, a single lesion that was treated several times required multiple entries into the data base. The sixty-five symptomatic TABLE I DIsTRIBuTIoN OF LEsIoNs A(CORI)IN( TO LOCATION ANI) METHoD OF TREATMENT I.ocatiori of t.es,o,i No. of Lesions ( Monostolic/Polyostotic) No. of Times Treatment Employed* ( Monostotic Polyostotic ) Closed CI3G ORIF Amputat. or Excis. Total No. of Times Treatment Employed Upper extremily I 0 24 Humerus 37 2/5 22 l() Radius I 4 0/3 1/ I 0/() 0/0 5 Ulna I 3 03 I /0 0/0 (1:0 4 Hand 02 0/2 0/ I 0/0 0/0 3 Spine or pelvis 2i Ut) 4 Lower extremity Femur - proximal part 10i13 6/22 10 I I 4/12 2 I 68 Femur - mid-part of shaft 2/ i0 0/ and distal part Tibia / Fihula 2 I 0/1 I/O 0/() l() 3 * CBG = curellage and honc-grafling and ORIF = open reduction and inlernal Iixalion. VOL. 69-A, NO. 3. NIAR( H 1987
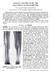
4 402 R. B. STEPHENSON ET AL. lesions in the forty-three patients required 1 30 separate evaluations. The clinical result of each treatment was classified as satisfactory or unsatisfactory. A satisfactory result was defined as: normal use of the affected extremity, no symptoms or only occasional pain that could be relieved by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medication, and a limb-length discrepancy of less than two centimeters. An unsatisfactory result was defined by the presence of one or more of the following characteristics : recurrent pathological fracture, chronic pain necessitating additional intervention, limblength discrepancy of two centimeters or more, progressive skeletal deformity, symptomatic non-union, or postoperative infection. The locations and methods of treatment of the symptomatic lesions are listed in Table I. Both the monostotic and the polyostotic lesions predominantly involved the long bones, with the femur being the most common site. The proximal part of the femur was symptomatic much more often than the remainder of the femur. Closed treatment and curettage with bone-grafting were the most frequently employed methods. Upper Extremit ) Results Twenty-one symptomatic lesions were treated a total of twenty-four times (Table II). Closed treatment was used fifteen times; curettage and bone-grafting, eight; and internal fixation, once. No excisions or amputations were performed. Twenty-one (88 per cent) of the twenty-four times Figs. 2-A, 2-B. and 2-C: A sixteen-year-old boy who had polyostotic disease and a pathological fracture of the humerus. Fig. 2-A: Initial radiograph. Fig. 2-B: The limb was ininiobilized in a cast. THE JOURNAL OF HONE AN!) JOINT SURGERY
5 FIBROUS DYSPLASIA 403 TABLE II RESUlTS OF TREATMENT OF MONOSTOTIC AND POLYOSTO TIC LESIONS OF THE ER EXTREMITY AC CORDING TO AGE-GRoup Type Treatment of Satisfactory Result Unsatisfactory Total Age-Group in Total Series in <18 yrs. old Closed 7 1* 8 Curettage and bone-grafling Open reduction and internal fixation 0 l8 yrs. old Closed Curettage and I I * 2 8 bone-grafting Open reduction and internal fixation I I * Pathological fracture. that a lesion of the upper extremity was treated, there was recurrent pathological fracture. These failures occurred in a satisfactory clinical result (Figs. 2-A, 2-B, and 2-C). There two patients; one of them was skeletally immature and had were only three unsatisfactory results, and each was due to polyostotic disease, and the other patient was skeletally FI;. 2-C FI;. 3 Fig. 2-C: The healing fracture fur months later. Fig. 3: An eleven-year-old girl who had a monostotic lesion of the middle of the femoral shaft underwent curettage and bone-grafting for persistent pain of two years duration. A satisfactory outcome followed this procedure.
6 404 R. B. STEPHENSON ET AL. TABLE Ill-A RESULTS OF TREATMENT OF P0LY0sT0TIC LESIONS IN THE LOWER EXTREMITY ACCORDING TO AGE-GROUP Unsatisfactory Method of Satisfactory Path. Progress. Symptomat. Limb-Length Treatment Results Fract. Infect. Pain Deform. Non-Union Discrep. <18 yrs. old Closed I Curettage and I I bone-grafting Open reduction and I I 0 internal fixation Excision or 2 I amputation l8 yrs. old Closed Curettage and bone-grafting Open reduction and I internal fixation Excision or amputation Results mature and had monostotic disease. closed a total of forty-one times. The skeletally immature patients who had polyostotic disease were treated closed a Spine and Pelvis total of twenty-seven times; in twenty-three (85 per cent) There were four lesions in the spine or pelvis in three instances the result was unsatisfactory. Nineteen of these patients. They were treated non-operatively with bed rest unsatisfactory results were due to recurrent pathological and non-specific measures for the symptoms. A satisfactory fracture. All five times that a skeletally immature patient result was achieved after the treatment of each lesion. who had monostotic disease was given closed treatment,. the result was unsatisfactory, because of a recurrent path- Lmver Extremity ological fracture in four instances. Eight of the nine skel- The data on the lesions of the lower extremity were etally mature patients who were managed by closed analyzed relative to the pattern of the disease (monostotic treatment had a satisfactory result, regardless of whether or polyostotic) and the skeletal maturity of the patient the disease was monostotic or polyostotic. The one failure (younger than eighteen years or eighteen years or older) at was a recurrent pathological fracture in the femur of a patient the time of the initial examination (Tables Ill-A and Ill-B). who had polyostotic disease. Forty symptomatic lesions were treated a total of 102 times. Curettage and bone-grafting: Curettage and bone- Closed treatment: Thirty-four lesions were treated grafting was performed thirty-three times for eighteen le- TABLE Ill-B RESUlTS OF TREATMENT OF M0NOsTOTIC LESIONS IN THE LOWER EXTREMITY ACCORDING TO AGE-GROUP Unsatisfactory Method of Satisfactory Path. Progress. Symptomat. Limb-Length Treatment Results Fract. Infect. Pain Deform. Non-Union Discrep. <18 yrs. old Closed Curettage and bone-grafting Open reduction and internal fixation Excision or amputation I8 yrs. old Closed Curettage and bone-grafting Open reduction and internal fixation Excision or amputation Results THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
7 FIBROUS DYSPLASIA 405 sions in the femur, tibia, and fibula (Fig. 3). There were twenty-five (74 per cent) unsatisfactory and eight (26 per cent) satisfactory results. Thirteen (93 per cent) of the fourteen times that such treatment was performed in a skeletally immature patient who had polyostotic disease, there was an unsatisfactory result. All of the unsatisfactory results were due to recurrent pathological fracture. In addition, twelve (7 1 per cent) of the seventeen times that curettage and bonegrafting was done in a skeletally immature patient who had a monostotic lesion, there was an unsatisfactory result. The results in the two skeletally mature patients were satisfactory. Open reduction (111(1 internal fi.vation: Open reduction and internal fixation was performed twenty-two times for nineteen symptomatic lesions of the lower extremity. There were nineteen (86 per cent) satisfactory results (Figs. 4-A and 4-B). The devices for fixation included fifteen intramedullary rods of various types, three sliding hip-screws. and four compression plates. There were no recurrent fractures after internal fixation. The treatment was performed six times in skeletally immature patients who had monostotic disease, and there were five satisfactory results. The only unsatisfactory result was in a seven-year-old child in whom a non-union developed after intramedullary fixation of the tibia with a Rush rod. Internal fixation was performed fifteen times in skeletally immature patients who had polyostotic disease. There were thirteen (87 per cent) satisfactory and two (13 per cent) unsatisfactory results. One failure was due to infection after the use of a Badgley hip-nail for a proximal fracture of the femur and the other was due to a tibial non-union after the insertion of a Lottes nail. E.wision or amputation: Excision or amputation was Fig. 4-A: A fourteen-year-old boy who had polyostotic disease and a pathological fracture of the femur. Fig. 4-13: The healing fracture six months after insertion of an intramedullary rod. VOL. 69-A, NO. 3. MARCII 1957
8 406 R. B. STEPHENSON ET AL. performed six times for five symptomatic lesions. Amputation was done in two patients who had polyostotic disease: a Syme amputation in an eleven-year-old boy who had severe deformity of the ipsilateral femur and tibia that resulted in a ten-centimeter limb-length discrepancy, and a belowthe-knee amputation as the definitive treatment in a twentyyear-old man whose tibia remained deformed despite multiple previous corrective osteotomies (Figs. 5-A and 5-B). Fi;. 5-A FIG. 5-B A twenty-year-old man who had polyostotic disease. Despite multiple interventions, progressive deformity of the leg culminated in a below-theknee amputation. Excision of a lesion was performed four times. The involved segment of bone was removed for the treatment of one fibular lesion, and the outcome was satisfactory. Excisional arthroplasty of the hip was performed three times and two satisfactory results were obtained, both following a Girdlestone arthroplasty. The unsatisfactory result involved refracture distal to the site of resection in a Colonna trochanteric arthroplasty. Discussion In 1942, Lichtenstein and Jaffe first recognized and differentiated the monostotic and polyostotic patterns of fibrous dysplasia. Early efforts were directed at describing the pathological and radiographic appearance of the disease, and it was demonstrated that monostotic and polyostotic fibrous dysplasias are histologically indistinguishable6. The radiographic appearance of a lesion can range from purely lytic, to a classic ground-glass appearance. to sclerotic and densely calcified (Figs. 6-A, 6-B, and 6-C). Therefore, it may be very difficult to diagnose monostotic fibrous dysplasia solely by radiographic criteria, and a biopsy is usually necessary for confirmation269. In contrast, polyostotic fibrous dysplasia can frequently be diagnosed radiographically due to the presence of multiple lesions that may also lead to characteristic deformities (Fig. 7). In the majority of patients, the lesions of fibrous dysplasia become clinically manifest in the first two decades of life. The appearance of the disease this early is consistent with a congenital origin, followed by a functional deficit as the patient grows and his or her level of activity increases. Whether the lesions of fibrous dysplasia resolve or become inactive with the onset of puberty or skeletal maturation is unclear. Reed noted no change in biopsy specimens that were obtained over periods as long as ten years. Similarly, Harris et al. reported that the examination of serial biopsy specimens demonstrated only subtle histological differences over time. They observed decreased cellularity and a slightly decreased quantity of bone relative to fibrous tissue, but no conversion of fiber-bone trabeculae to lamellar bone. Malignant sarcomatous transformation has been reported in fewer than 1 per cent of patients552. and it was not seen in our patients. In contrast to the relatively stable histological appearance of fibrous dysplasia, radiographic progression of the disease has been documented. In the study by Harris et al., twenty-six patients had a complete radiographic skeletal survey, and thirteen (50 per cent) were noted to have extension of the osseous lesions over time. This was observed both before and after puberty. Henry documented radiographic progression of the disease with pregnancy. Although patients usually seek medical attention because of pain, with or without a pathological fracture, there have been few reports on treatment and functional outcome. Harris et al. reviewed the cases of fifty patients who had fibrous dysplasia, thirteen of whom had monostotic and thirty-seven, polyostotic disease. They did not evaluate the results of treatment, but they noted that fractures were seldom displaced and healing was usually not delayed. Consequently, closed treatment of these pathological fractures, even in areas of polyostotic involvement. was advocated. Henry, in a study of the cases of fifty-six patients who had monostotic disease, noted a rate of success of 61 per cent after treatment with curettage and cancellous bone-grafting. These results improved with extraperiosteal excision. However, Henry s data are difficult to interpret because he included the radiographic appearance as an integral part of a THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
9 FIBROUS DYSPLASIA 407 FIG. 6-A FI;. 6-B Figs. 6-A, 6-B. and 6-C: Spectrum of the radiographic presentation of fibrous dysplasia. Fig. 6-A: Lytic lesion. Fig. 6-B : Classic ground-glass appearance. successful outcome. Stewart et al. reported the results of treatment in twenty patients. Thirteen ofthe sixteen patients who had monostotic disease had involvement of a lower extremity. Seven good, three poor. and three uncertain resuits were recorded after curettage and bone-grafting. They recommended early curettage and bone-grafting for weight- Fig. 6-C: Sclerotic lesion. Fig. 7: An eighteen-year-old man who had polyostotic disease and a characteristic shepherds crook deformity of the proximal part of the right femur. VOL. 69-A, NO. 3. MARCH 1987
10 408 R. B. STEPHENSON ET AL. bearing bones but asserted that good results were unusual in skeletally inimature patients. Internal fixation was used in three patients. hut no conclusions were drawn due to inadequate follow-up. Strasshurger et al. reported on the cases of nine patients. of whom live had curettage and bonegrafting. By our criteria, only two of the five had a satisfactory result. They concluded that only small, solitary lesions responded well to curettage and bone-grafting. Fibrous dysplasia of the hip and proximal part of the femur has been the subject of relatively recent reports3. The loss of structural integrity in the proximal part of the femur. coupled with the stresses of weight-bearing. can result in pathological fractures that are difficult to treat. Nakashima et al. reviewed the cases of eight patients who had monostotic disease that involved the femoral neck. Curettage and bone-grafting was considered curative in six patients, but the authors failed to elaborate on the functional outcome. Funk and Wells contended that monostotic disease of the hip is more predictable and easier to control than polyostotic disease. The two patients in their series who had monostotic disease were treated with curettage and bonegrafting. followed by a period of non-weight-bearing. Nevertheless, each patient subsequently sustained two fractures each, and ultimately required osteotomy with internal fixation to correct a deformity of the proximal part of the femur. Four of their patients who had polyostotic disease (in seven hips) required nineteen operations. Funk and Wells stated that repeated bone-grafting and osteotomy may not control the defcrmities that are associated with severe polyostotic disease. lo. S Fi;. 9 Fig. 8: A twenty-two-year.old man who hid plyst&tic disease engaged in normal activities with the dominant upper extremity and had only occasional pain that could he relieved by aspirirr. Fig. 9: A twenty-one-year-old ssoman ss ho had nionostotic fibrous dysplasia with deformity of the proximal pail of the femur and pain. After osteotoifly and internal Ii xatiorr. she hecanre as mptomatic. THE JOURNAL 01 ItONEi AND JOINT SURGERY
11 FIBROUS DYSPLASIA 409 Our retrospective review of the cases of patients who had fibrous dysplasia dealt specifically with the results of four different methods of treatment. Each symptomatic lesion, rather than each patient, was followed to document the clinical outcome fully. In this way, we thought that the true morbidity of the disease could be assessed. All patients in whom a symptomatic lesion of the spine or pelvis was treated by closed means had a satisfactory result. Although the number of symptomatic lesions of the spine and pelvis in our series was small, our data suggest that non-operative management may be sufficient. Eight patients had twenty-one symptomatic lesions of the upper extremity. Twenty-one (88 per cent) ofthe twentyfour times that such a lesion was treated, the result was satisfactory. There was no correlation between the clinical outcome and the size or location of the lesion (Fig. 8). Closed treatment was usually sufficient, and the long-term functional morbidity that was caused by these lesions was minimum. Open reduction and internal fixation was available as a final option, but our data suggested that it is rarely, if ever, indicated as the primary treatment. While minimum functional morbidity was associated with symptomatic fibrous dysplasia of the upper extremity in our patients, regardless of age, this was not the case for the lesions of the lower extremity. In the lower extremity, the results were highly dependent on the patient s age at time of the initial presentation of symptoms. In patients who were eighteen years old or more, eight (88 per cent) of the nine times that a lesion involving the lower extremity had closed treatment, and both times that a lesion was treated with curettage and bone-grafting, the result was satisfactory. In contrast, patients who were less than eighteen years old usually had an unsatisfactory outcome. Eighty-eight per cent of the lesions that were treated closed and 8 1 per cent of those that were treated by curettage and bone-grafting had an unsatisfactory result. The failure of these lesions to heal after curettage and bone-grafting has been ascribed to resorption of the graft and subsequent recurrence of the disease. The technical difficulty of totally eradicating the disease by intralesional curettage is apparent. Wide local excision, radical resection, and amputation are the only definitive means of total ablation of the lesion. In contrast to the results after closed treatment or curettage and bone-grafting, 86 per cent of the lesions in the lower extremity that were treated by internal fixation had a satisfactory result, independent of the patient s skeletal maturity or whether the disease was monostotic or polyostotic. Internal fixation does not alter the basic disease process, but it provides mechanical support of the structurally compromised bone (Fig. 9). Although the use of internal fixation for this purpose has received little attention in the literature, we could find no reported case of failure after internal fixation if the procedure had been technically correct. less than eighteen years old and who had a lesion ofthe lower extremity had significant morbidity. They had an unsatisfactory clinical outcome with closed treatment or curettage and bone-grafting. They sustained additional fractures, progressive deformities developed, and they required additional treatment. In contrast, effective internal fixation consistently avoided these problems and provided satisfactory clinical results in this group. Conversely, patients who were more than eighteen years old and who had a lesion of the lower extremity generally had a satisfactory outcome with closed treatment. In this particular group of patients, non-operative management may be sufficient. Conclusions Our review of symptomatic lesions of fibrous dysplasia revealed that significant long-term morbidity is associated with this disease. Closed treatment of symptomatic lesions in the upper extremity provided a satisfactory functional outcome regardless of the pattern of the disease or the age of the patient, and neither closed treatment nor curettage and bone-grafting were adequate for symptomatic lesions ofthe lowerextremity in skeletally immature patients. These lesions frequently require internal fixation in order to achieve a satisfactory result. Noi i-: The authors thank Ms. Micheic Decker for her usioancc. References I. ALBRIGHT. FULLER; BUTLER. A. M.: HAMPTON. A. 0.; and SMITH. PATRICIA: Syndrome Characterized by Osteitis Fibrosa Disseminata. Areas of Pigmentation and Endocrine Dysfunction. with Precocious Puberty in Females. Report of Five Cases. New England J. Med.. 216: COHEN, JONATHAN: Fibrous Dysplasia. Histological Study of Two Unusual Cases. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 38-A: , April FUNK, F. J., and WELLS, R. E.: Hip Problems in Fibrous Dysplasia. Clin. Orthop., 90: 77-82, GRABIAS, S. L., and CAMPBELL, C. J.: Fibrous Dysplasia. Orthop. Clin. North America, 8: , HALAWA, MAHER, and Aziz, A. A. : Chondrosarcoma in Fibrous Dysplasia of the Pelvis. A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Bone and Joint Surg.. 66-B(S): HARRIS, W. H. DUDLEY, H. R., JR.: and BARRY, R. J.: The Natural History of Fibrous Dysplasia. An Orthopaedic, Pathological, and Roentgenographic Study. J. Bone and Joint Surg.. 44-A: , March HENRY, ADRIAN: Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia. J. Bone and Joint Surg.. S1-B(2): , HUVOS, A. G. HIGINBOTHAM, N. L.; and MILLER, T. R.: Bone Sarcomas Arising in Fibrous Dysplasia. J. Bone and Joint Surg.. 54-A: , July LICHTENSTEIN, LOUIS, and JAFFE, H. L.: Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone. A Condition Affecting One, Several or Many Bones, The Graver Cases of Which May Present Abnormal Pigmentation of Skin. Premature Sexual Development. Hyperthyroidism or Still Other Extraskeletal Abnormalities. Arch. Pathol., 33: , NAKASHIMA. Y. KOTOURA, Y. NAGASHIMA. T. ; YAMAMURO, T. : and HAMASHIMA. Y.: Monostotic Fibrous Dysplasia in the Femoral Neck. A Clinicopathologic Study. Clin. Orthop.. 191: REED, R. J. : Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone. A Review of 25 Cases. Arch. Pathol.. 75: , RIDDELL, D. M.: Malignant Changes in Fibrous Dysplasia. Report of a Case. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 46-B(2): , STEWART, M. J.: GILMER, W. S.; and EDMONSON, A. S.: Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 44-B(2): , STRASSBURGER. PAUL: GARBER, C. Z.: and HAI.FORD. HALLOCK: Fibrous Dysplasia of Bone. J. Bone and Joint Surg.. 33-A: , April VOL. 69-A, NO. 3. MARCH 1987
A Case of Fibrous Dysplasia with Bilateral Shepherd Crook Deformity Treated with Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation
 Case Report Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2018 May-June : 8(3):Page 33-37 A Case of Fibrous Dysplasia with Bilateral Shepherd Crook Deformity Treated with Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation J K Giriraj Harshavardhan¹,
Case Report Journal of Orthopaedic Case Reports 2018 May-June : 8(3):Page 33-37 A Case of Fibrous Dysplasia with Bilateral Shepherd Crook Deformity Treated with Dynamic Hip Screw Fixation J K Giriraj Harshavardhan¹,
Bone and Joint Surgery
 The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American Volume VOLUME 59-A, No. 4 JUNE 1977 Fracture of the Neck and Intertrochanteric Region of the Femur in Children* BY S. TERRY CANALE, M.D.t, AND WILLIAM L.
The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery American Volume VOLUME 59-A, No. 4 JUNE 1977 Fracture of the Neck and Intertrochanteric Region of the Femur in Children* BY S. TERRY CANALE, M.D.t, AND WILLIAM L.
Fibrous Dysplasia in Children. Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK
 Fibrous Dysplasia in Children Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Overview What is Fibrous Dysplasia? Clinical Presentations Endocrine Problems Skeletal Problems Treatment Options Fibrous
Fibrous Dysplasia in Children Professor Nick Shaw Birmingham Children s Hospital, UK Overview What is Fibrous Dysplasia? Clinical Presentations Endocrine Problems Skeletal Problems Treatment Options Fibrous
Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2, Patrick Smith, M.D. 2, and Larry S. Matthews, M.D. 2
 Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Skeletal Radiol (1986) 15:27-31 Skeletal Radiology Computed tomography and plain radiography in experimental fracture healing Ethan M. Braunstein, M.D. 1, Steven A. Goldstein, Ph.D. 2, Janet Ku, M.S. 2,
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation
 Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Femoral Fractures in Adolescents: A Comparison of Four Methods of Fixation By Leonhard E. Ramseier, MD, Joseph A. Janicki, MD, Shannon Weir, BSc, and Unni G. Narayanan, MBBS, MSc, FRCSC Investigation performed
Intramedullary Rodding and Bisphosphonate Treatment of Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia Associated With the. rodding McCune-Albright syndrome.
 Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 22:255 260 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Intramedullary Rodding and Bisphosphonate Treatment of Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia Associated With
Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics 22:255 260 2002 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Inc., Philadelphia Intramedullary Rodding and Bisphosphonate Treatment of Polyostotic Fibrous Dysplasia Associated With
ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Volume 17, Number 2, June 1995 Original ILIZAROV TECHNIQUE IN CORRECTING LIMBS DEFORMITIES: PRELIMINARY RESULTS Saleh W. Al-Harby, FRCS(Glasg)* This is a prospective study of
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures
 Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest
 Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
The disease process may be localized to: A single bone (monostotic fibrous dysplasia) Multiple bones (polyostotic fibrous dysplasia) [4]
![The disease process may be localized to: A single bone (monostotic fibrous dysplasia) Multiple bones (polyostotic fibrous dysplasia) [4] The disease process may be localized to: A single bone (monostotic fibrous dysplasia) Multiple bones (polyostotic fibrous dysplasia) [4]](/thumbs/95/124167277.jpg) Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2017; 5(11E):4651-4655 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Applied Medical Sciences (SJAMS) Sch. J. App. Med. Sci., 2017; 5(11E):4651-4655 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, 842-846 CASE REPORT Isolated congenital anterolateral bowing of the fibula : A case report with 24 years follow-up Karolien LELIEFELD, Hans VAN DER SLUIJS, Ibo VAN DER HAVEN
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR. Physician-in-Chief, AIRP. Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging
 ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE MARK D. MURPHEY MD, FACR Physician-in-Chief, AIRP Chief, Musculoskeletal Imaging ALPHABET SOUP AND CYSTIC LESIONS OF THE BONE Giant cell tumor (GCT) Unicameral
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BONE TRANSPLANTATION IN LIMB SAVING SURGERIES: THE PHILIPPINE EXPERIENCE
 BONE TRANSPLANTATION IN LIMB SAVING SURGERIES: THE PHILIPPINE EXPERIENCE EDWARD HM WANG, MD UP-Musculoskeletal Tumor Unit and Tissue & Bone Bank Dept. of Orthopedics University of the Philippines-Philippine
BONE TRANSPLANTATION IN LIMB SAVING SURGERIES: THE PHILIPPINE EXPERIENCE EDWARD HM WANG, MD UP-Musculoskeletal Tumor Unit and Tissue & Bone Bank Dept. of Orthopedics University of the Philippines-Philippine
COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED
 84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
84 COPYRIGHT 2004 BY THE JOURNAL BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Radiographic Evaluation of Pathological Bone Lesions: Current Spectrum of Disease and Approach to Diagnosis BY BENJAMIN G. DOMB, MD,
Major Lower Limb Amputations
 Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 3 No. 3 September 19 Major Lower Limb Amputations Abdul Hamid Abdul Kadir, MBBS, FRCSEd, MChOrth, AM Myint Han, MBBS, Dip Phy Med Department oforthopaedics and Traumatology Faculty
Med. J. Malaysia Vol. 3 No. 3 September 19 Major Lower Limb Amputations Abdul Hamid Abdul Kadir, MBBS, FRCSEd, MChOrth, AM Myint Han, MBBS, Dip Phy Med Department oforthopaedics and Traumatology Faculty
Multifocal fibrous Dysplasia with enchondroma-like areas: Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 7 Number 2 Multifocal fibrous Dysplasia with enchondroma-like areas: Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia V Monappa, R Kudva Citation V Monappa, R Kudva. Multifocal
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Pathology Volume 7 Number 2 Multifocal fibrous Dysplasia with enchondroma-like areas: Fibrocartilaginous Dysplasia V Monappa, R Kudva Citation V Monappa, R Kudva. Multifocal
Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Spine
 Copynghi 1985 8) The Journal o[ Bone and Joint.5urger IPIOrp()ratetI Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Spine BY R. CAPANNA, M.D.*, U. ALBISINNI, M.D.*, P. PICCI, M.D.*, P. CALDERONI, M.D.*, M. CAMPANACCI, M.D.*,
Copynghi 1985 8) The Journal o[ Bone and Joint.5urger IPIOrp()ratetI Aneurysmal Bone Cyst of the Spine BY R. CAPANNA, M.D.*, U. ALBISINNI, M.D.*, P. PICCI, M.D.*, P. CALDERONI, M.D.*, M. CAMPANACCI, M.D.*,
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS MULTIPLEX IN THREE SISTERS
 DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur
 CASE REPORT Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur WI Faisham, M.Med{Ortho)*, W Zulmi, M.S{Ortho)*, B M Biswal, MBBS** 'Department of Orthopaedic, "Department of Oncology and Radiotherapy, School of
CASE REPORT Metastatic Disease of the Proximal Femur WI Faisham, M.Med{Ortho)*, W Zulmi, M.S{Ortho)*, B M Biswal, MBBS** 'Department of Orthopaedic, "Department of Oncology and Radiotherapy, School of
Patient Guide. Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening
 Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Patient Guide Intramedullary Skeletal Kinetic Distractor For Tibial and Femoral Lengthening Introduction You have decided to have a limb lengthening operation. The surgery you have chosen uses a device
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation
 Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia
 Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia 5 th Annual SLAOTI Meeting Sao Paolo, Brazil October 12-14, 2017 Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research Children s Mercy
Congenital Pseudarthrosis of the Tibia 5 th Annual SLAOTI Meeting Sao Paolo, Brazil October 12-14, 2017 Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research Children s Mercy
Designing a Novel Fixation Device for Pediatric Orthopaedic Tibia Fractures
 Designing a Novel Fixation Device for Pediatric Orthopaedic Tibia Fractures Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Paul Thompson, PhD Biomedical
Designing a Novel Fixation Device for Pediatric Orthopaedic Tibia Fractures Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Paul Thompson, PhD Biomedical
Lower Extremity Fracture Management. Fractures of the Hip. Lower Extremity Fractures. Vascular Anatomy. Lower Extremity Fractures in Children
 Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
MANAGEMENT OF OSTEOFIBROUS DYSPLASIA OF THE ULNAAFTER RESECTION WITH ELASTIC INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL AND NON VASCULAR FIBULAR GRAFT: A CASE REPORT
 MANAGEMENT OF OSTEOFIBROUS DYSPLASIA OF THE ULNAAFTER RESECTION WITH ELASTIC INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL AND NON VASCULAR FIBULAR GRAFT: A CASE REPORT *Ujwal Ramteke and Hitesh Mangukiya Department of Orthopaedics,
MANAGEMENT OF OSTEOFIBROUS DYSPLASIA OF THE ULNAAFTER RESECTION WITH ELASTIC INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL AND NON VASCULAR FIBULAR GRAFT: A CASE REPORT *Ujwal Ramteke and Hitesh Mangukiya Department of Orthopaedics,
EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA. Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009
 EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009 MORAL OF THE STORY Fracture distal radius and intact ulna W/O radius fracture will most likely
EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009 MORAL OF THE STORY Fracture distal radius and intact ulna W/O radius fracture will most likely
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT
 EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
EXPERT TIBIAL NAIL PROTECT Enhance your first line of defense This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. CLINICAL EVIDENCE CONTENT AUTHOR TITLE OF CHAPTER PAGE ETN PROtect clinical evidence
Conservative surgical management of simple monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the proximal femur in a 19-year-old basketballer: a case report
 Yung et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2018) 12:240 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-018-1763-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Conservative surgical management of simple monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the
Yung et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports (2018) 12:240 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13256-018-1763-3 CASE REPORT Open Access Conservative surgical management of simple monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the
Feiyan Chen, Yibing Wei, Jun Xia, Jianguo Wu, Siqun Wang, Gangyong Huang, Jie Chen, Jingsheng Shi
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):14188-14195 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010686 Case Report Double-level osteotomy and one-stage reconstruction with long intramedullary femoral nail to correct a severe
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(8):14188-14195 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0010686 Case Report Double-level osteotomy and one-stage reconstruction with long intramedullary femoral nail to correct a severe
Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2007, 73, 630-634 ORIGINAL STUDY Treatment of delayed union or non-union of the tibial shaft with partial fibulectomy and an Ilizarov frame Jo DUJARDYN, Johan LAMMENS From the University
A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
A Patient s Guide to Adult Forearm Fractures Orthopedic and Sports Medicine 825 South 8th Street, #550 Minneapolis, MN 55404 Phone: 612-333-5000 Fax: 612-333-6922 1 DISCLAIMER: The information in this
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS
 HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
Equalization of Limb Length Discrepancy using Growth Arrest vs Intramedullary Lengthening
 Equalization of Limb Length Discrepancy using Growth Arrest vs Intramedullary Lengthening Ahmed Hammouda, MD Vivian Szymczuk, MD Martin G. Gesheff, BS Shawn Standard, MD John E. Herzenberg, MD International
Equalization of Limb Length Discrepancy using Growth Arrest vs Intramedullary Lengthening Ahmed Hammouda, MD Vivian Szymczuk, MD Martin G. Gesheff, BS Shawn Standard, MD John E. Herzenberg, MD International
Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 50-54 Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis Shrestha BK 1, Rajbhandary T 2, Bijukachhe B 2, Banskota AK 3 1 Associate Professor,
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 50-54 Surgical interventions in chronic osteomyelitis Shrestha BK 1, Rajbhandary T 2, Bijukachhe B 2, Banskota AK 3 1 Associate Professor,
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
Treatment of Pathological Fracture of Femur in Mc-Cune Albright Syndrome Using A Custom Made Intramedullary Nail - A Case Report
 International Journal Dental and Medical Sciences Research (IJDMSR) ISSN: 2393-073X Volume 3, Issue 1 (Jan- 2019), PP 52-57 Treatment of Pathological Fracture of Femur in Mc-Cune Albright Syndrome Using
International Journal Dental and Medical Sciences Research (IJDMSR) ISSN: 2393-073X Volume 3, Issue 1 (Jan- 2019), PP 52-57 Treatment of Pathological Fracture of Femur in Mc-Cune Albright Syndrome Using
Page Proof 1 of 5. Fig. E1-A The INTERTAN nail was short or long.
 Page 1 of 5 Fig. E1-A The INTERTAN nail was short or long. Fig. E1-B The sliding hip screw comes in different lengths, and is used with or without a trochanteric stabilizing plate. Page Proof 1 of 5 Page
Page 1 of 5 Fig. E1-A The INTERTAN nail was short or long. Fig. E1-B The sliding hip screw comes in different lengths, and is used with or without a trochanteric stabilizing plate. Page Proof 1 of 5 Page
Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures
 대한정형외과학회지 : 제 43 권제 1 호 2008 J Korean Orthop Assoc 2008; 43: 30-35 Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures Do-Young Kim, M.D., Sung-Ryong
대한정형외과학회지 : 제 43 권제 1 호 2008 J Korean Orthop Assoc 2008; 43: 30-35 Comparison of Flexible Intramedullary Nailing with External Fixation in Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures Do-Young Kim, M.D., Sung-Ryong
Resection Angulation Osteotomy in Treatment of Postseptic Ankylosis of the Hip
 Resection Angulation Osteotomy in Treatment of Postseptic Ankylosis of the Hip DG Nabi, MS, TS Rashid, MS, KK Ahmed, MS Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College, Srinagar, India ABSTRACT
Resection Angulation Osteotomy in Treatment of Postseptic Ankylosis of the Hip DG Nabi, MS, TS Rashid, MS, KK Ahmed, MS Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College, Srinagar, India ABSTRACT
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Dynamic Splinting of the
 Dynamic Splinting of the Rheumatoid Hand BY F. RICHARD CONVERY, M.D.,* J. PIERCE CONATY, M.D.** AND VERNON L. NICKEL, M.D.** Rancho Los Amigos Hospital, Downey, California (University of Southern California
Dynamic Splinting of the Rheumatoid Hand BY F. RICHARD CONVERY, M.D.,* J. PIERCE CONATY, M.D.** AND VERNON L. NICKEL, M.D.** Rancho Los Amigos Hospital, Downey, California (University of Southern California
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Index. orthopedic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures pediatric, 494 498 classification of, 494 diagnostic imaging of, 494, 496 497 epidemiology of, 494 treatment of, 494 498
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures pediatric, 494 498 classification of, 494 diagnostic imaging of, 494, 496 497 epidemiology of, 494 treatment of, 494 498
Title: An intramedullary free vascularized fibular graft combined with pasteurized
 Title: An intramedullary free vascularized fibular graft combined with pasteurized autologous bone graft in leg reconstruction for patients with osteosarcoma Names of authors Masataka Noguchi, Hiroo Mizobuchi,
Title: An intramedullary free vascularized fibular graft combined with pasteurized autologous bone graft in leg reconstruction for patients with osteosarcoma Names of authors Masataka Noguchi, Hiroo Mizobuchi,
Cluster - 26 ORTHOPEDICS. X Ray of Affected Limb, MIR of Shoulder
 Sr.No Package no 1708 26.1 Orthopeidc 1709 26.2 Orthopeidc Sub speciality Procedure name Pre-Operative Investigation AC joint reconstruction/ Stabilization/ Acromionplasty (Nonoperative management is recommended
Sr.No Package no 1708 26.1 Orthopeidc 1709 26.2 Orthopeidc Sub speciality Procedure name Pre-Operative Investigation AC joint reconstruction/ Stabilization/ Acromionplasty (Nonoperative management is recommended
Case McCune Albright Syndrome (MAS) - polyostotic fibrous dysplasia
 Case 14477 McCune Albright Syndrome (MAS) - polyostotic fibrous dysplasia Lukasz Augsburg 1, Filip M. Vanhoenacker 1, 2, 3, Jan Gielen1 1. University Hospital Antwerp, Department of Radiology, University
Case 14477 McCune Albright Syndrome (MAS) - polyostotic fibrous dysplasia Lukasz Augsburg 1, Filip M. Vanhoenacker 1, 2, 3, Jan Gielen1 1. University Hospital Antwerp, Department of Radiology, University
New Implantable Lengthening Nail: Preliminary Results. Matthew Harris MD, MBA Dror Paley MD, FRCS(C) Daniel Prince MD, MPH
 New Implantable Lengthening Nail: Preliminary Results Matthew Harris MD, MBA Dror Paley MD, FRCS(C) Daniel Prince MD, MPH LLRS New York, NY July 19, 2013 Disclosures Dror Paley MD, FRCS(C) Paid Consultant
New Implantable Lengthening Nail: Preliminary Results Matthew Harris MD, MBA Dror Paley MD, FRCS(C) Daniel Prince MD, MPH LLRS New York, NY July 19, 2013 Disclosures Dror Paley MD, FRCS(C) Paid Consultant
A Patient s Guide to Rotational Deformities in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Rotational Deformities in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
A Patient s Guide to Rotational Deformities in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled from
The Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) Technique with a Locking Compression Plate for Femoral Lengthening
 2008 62 5 333 339 The Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) Technique with a Locking Compression Plate for Femoral Lengthening a* b a a a a a a b 334 62 5 5 1 16 9 0 100 11 31 131 14 2 16 9 0
2008 62 5 333 339 The Minimally Invasive Plate Osteosynthesis (MIPO) Technique with a Locking Compression Plate for Femoral Lengthening a* b a a a a a a b 334 62 5 5 1 16 9 0 100 11 31 131 14 2 16 9 0
Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis
 Acta Orthop Scand 1988;59(4):425-429 Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis 03 17878 1 luli lrl Herman H. de Boer', Abraham J. Verbout', Hans K. L. Nielsen2 and
Acta Orthop Scand 1988;59(4):425-429 Free vascularized fibular graft for tibial pseudarthrosis in neurofibromatosis 03 17878 1 luli lrl Herman H. de Boer', Abraham J. Verbout', Hans K. L. Nielsen2 and
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients
 Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Original article Comparison of two modality of fixation in unstable trochantric fractures in elderly patients 1Dr. Vipin Garg, 2 Dr. Anjul Agarwal 1MS Orhtopaedics, Assistant professor, Department of orthopaedics,
Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 555-559 ORIGINAL STUDY Outcome of Girdlestone s resection arthroplasty following complications of proximal femoral fractures Himanshu SHARMA, Rahul KAKAR From the Royal Alexandra
Outcome of Treatment of Nonunion Tibial Shaft Fracture by Intramedullary Interlocking Nail augmentated with Autogenous Cancellous Bone Graft.
 Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2014; 16(1): 58-62 Outcome of Treatment of Nonunion Tibial Shaft Fracture by Intramedullary Interlocking Nail augmentated with Autogenous Cancellous Bone Graft. Shah SB,
Original Article Nepal Med Coll J 2014; 16(1): 58-62 Outcome of Treatment of Nonunion Tibial Shaft Fracture by Intramedullary Interlocking Nail augmentated with Autogenous Cancellous Bone Graft. Shah SB,
Chondroblastoma of bone
 Chronology Chondroblastoma of bone LONG-TERM RESULTS AND FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER INTRALESIONAL CURETTAGE R. Suneja, R. J. Grimer, M. Belthur, L. Jeys, S. R. Carter, R. M. Tillman, A. M. Davies From The
Chronology Chondroblastoma of bone LONG-TERM RESULTS AND FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME AFTER INTRALESIONAL CURETTAGE R. Suneja, R. J. Grimer, M. Belthur, L. Jeys, S. R. Carter, R. M. Tillman, A. M. Davies From The
Fracture fixation. Types. Mechanical considerations. Biomechanics of fracture fixation. External fixation. Internal fixation
 Fracture fixation Biomechanics of fracture fixation Types External fixation Mechanical considerations Internal fixation Mechanical considerations in treatment of 1. In the external fixation: fracture When
Fracture fixation Biomechanics of fracture fixation Types External fixation Mechanical considerations Internal fixation Mechanical considerations in treatment of 1. In the external fixation: fracture When
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Study of Ender s Nailing in Paediatric Tibial Shaft Fractures Dr. Himanshu G. Ladani 1* 1 Ex. Assistant Professor of Orthopaedics, M.P.Shah Medical College, Jamnagar, Gujarat. ABSTRACT Background: Closed
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Age of the patients-the average age of our patients
 TWO-LEVEL FRACTURES OF THE TIBIA Results in Thirty-six Cases Treated by Blind Nailing J. ZUCMAN and P. MAURER, PARIS, FRANCE From the Cliizique de Chirurgie Orthop#{232}dique et R#{233}paratrice, H#{243}pital
TWO-LEVEL FRACTURES OF THE TIBIA Results in Thirty-six Cases Treated by Blind Nailing J. ZUCMAN and P. MAURER, PARIS, FRANCE From the Cliizique de Chirurgie Orthop#{232}dique et R#{233}paratrice, H#{243}pital
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid Carcinoma: A Case Report
 CASE REPORT Hip Pelvis 28(3): 173-177, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.3.173 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid
CASE REPORT Hip Pelvis 28(3): 173-177, 2016 http://dx.doi.org/10.5371/hp.2016.28.3.173 Print ISSN 2287-3260 Online ISSN 2287-3279 Pathologic Fracture of the Femur in Brown Tumor Induced in Parathyroid
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Fractures Healing & Management. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4
 Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
Fractures Healing & Management Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 4 Fractures Despite their strength, bones are susceptible to fractures. In young people, most fractures result from trauma
A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral
 Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
Kanda et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2015, 9:17 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access A 42-year-old patient presenting with femoral head migration after hemiarthroplasty performed
The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 322-326 The long term fate of the fibula when used as an intraosseous graft Onkar N. NAGI, Mandeep S. DHILLON, Sameer AGGARWAL From the Post Graduate Institute of Medical
Fibula bone grafting in infected gap non union: A prospective case series
 2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
2019; 3(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2019; 3(1): 06-10 Received: 03-11-2018 Accepted: 06-12-2018 Dr. Mohammed Nazim M.S (Ortho),
5/31/2018. Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction. Ipsilateral Neck-Shaft Fractures Introduction
 Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Ipsilateral Femoral Neck And Shaft Fractures Exchange Nailing For Non- Union Donald Wiss MD Cedars-Sinai Medical Center Los Angeles, California Introduction Uncommon Injury Invariably High Energy Trauma
Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do?
 Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do? Gerald E. Wozasek Thomas M. Tiefenboeck 5 October 2016, Washington Medical University of Vienna, Department of Trauma Surgery ordination @wozasek.at
Failed Subtrochanteric Fracture How I Decide What to Do? Gerald E. Wozasek Thomas M. Tiefenboeck 5 October 2016, Washington Medical University of Vienna, Department of Trauma Surgery ordination @wozasek.at
DifficultTibialNailRemovalusingtheExtendedTrochantericOsteotomyTechniquePriortoTotalKneeArthroplasty
 : H Orthopedic and Musculoskeletal System Volume 14 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
: H Orthopedic and Musculoskeletal System Volume 14 Issue 3 Version 1.0 Year 2014 Type: Double Blind Peer Reviewed International Research Journal Publisher: Global Journals Inc. (USA) Online ISSN: 2249-4618
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell
 Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Primary bone tumors > metastases from other sites Primary bone tumors widely range -from benign to malignant. Classified according to the normal cell counterpart and line of differentiation. Among the
Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula
 Royal Liverpool & Broadgreen University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula Michael Smith MBChB, Zuned
Royal Liverpool & Broadgreen University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula Michael Smith MBChB, Zuned
Intercalary Femur and Tibia Segmental Allografts Provide an Acceptable Alternative in Reconstructing Tumor Resections
 CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 426, pp. 97 102 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Intercalary Femur and Tibia Segmental Allografts Provide an Acceptable Alternative in Reconstructing
CLINICAL ORTHOPAEDICS AND RELATED RESEARCH Number 426, pp. 97 102 2004 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Intercalary Femur and Tibia Segmental Allografts Provide an Acceptable Alternative in Reconstructing
Review Article. Fibrous dysplasia: A rare bone disorder
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(1):628-633 Review Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Fibrous dysplasia: A rare bone disorder Ashish Gawai*,
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2015, 7(1):628-633 Review Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 Fibrous dysplasia: A rare bone disorder Ashish Gawai*,
Management for Postoperative Infection of Fractures
 The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12, No2, April, 1999 = Abstract = Management for Postoperative Infection of Fractures Eui-Hwan Ahn, MD, In-Whan Chung, MD, Jeong-Hwan Oh, MD, Seong-Tae
The Journal of the Korean Society of Fractures Vol12, No2, April, 1999 = Abstract = Management for Postoperative Infection of Fractures Eui-Hwan Ahn, MD, In-Whan Chung, MD, Jeong-Hwan Oh, MD, Seong-Tae
Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
Evaluation of surgical treatment results in parosteal osteosarcoma
 Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 24, No. 1, May, 2010. pp. 11-16. Downloaded from mjiri.iums.ac.ir at 1:31 IRDT on Wednesday September 19th 2018 Evaluation of surgical
Original Research Medical Journal of the Islamic Republic of Iran.Vol. 24, No. 1, May, 2010. pp. 11-16. Downloaded from mjiri.iums.ac.ir at 1:31 IRDT on Wednesday September 19th 2018 Evaluation of surgical
Unicameral bone cysts are benign, fluid-filled cavities
 Endoscopic Surgery for Symptomatic Unicameral Bone Cyst of the Proximal Femur Wataru Miyamoto, M.D., Masato Takao, M.D., Youichi Yasui, M.D., Shinya Miki, M.D., and Takashi Matsushita, M.D. Abstract: Recently,
Endoscopic Surgery for Symptomatic Unicameral Bone Cyst of the Proximal Femur Wataru Miyamoto, M.D., Masato Takao, M.D., Youichi Yasui, M.D., Shinya Miki, M.D., and Takashi Matsushita, M.D. Abstract: Recently,
DELAYED OPERATION IN THE OPEN REDUCTION OF FRACTURES OF LONG BONES
 DELAYED OPERATION IN THE OPEN REDUCTION OF FRACTURES OF LONG BONES JOHN CHARNLEY, MANCHESTER, ENGLAND, and ADLY GUINDY, CAIRO, EGYPT From Park Hospital, Davyhulme, Manchester Murray (1941) reviewed evidence
DELAYED OPERATION IN THE OPEN REDUCTION OF FRACTURES OF LONG BONES JOHN CHARNLEY, MANCHESTER, ENGLAND, and ADLY GUINDY, CAIRO, EGYPT From Park Hospital, Davyhulme, Manchester Murray (1941) reviewed evidence
Improving Fixation of a Previously Designed Pediatric Tibial Stent
 Improving Fixation of a Previously Designed Pediatric Tibial Stent Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski, Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker, Lida Acuña-Huete Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Wan-Ju Li, PhD Biomedical
Improving Fixation of a Previously Designed Pediatric Tibial Stent Evan Lange, Karl Kabarowski, Tyler Max, Sarah Dicker, Lida Acuña-Huete Client: Dr. Matthew Halanski, MD Advisor: Dr. Wan-Ju Li, PhD Biomedical
A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2015, 81, 123-130 ORIGINAL STUDY A comparative study of less invasive stabilization system and titanium elastic nailing for subtrochanteric femur fractures in older children Liao-Jun
Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Malunion in floating knee injuries An analysis in 30 patients presenting to a tertiary care facility and are surgically treated
 2017; 3(1): 700-705 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 700-705 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 11-11-2016 Accepted: 12-12-2016 Dr. R Ezhilmaran Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Chengalpattu
2017; 3(1): 700-705 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(1): 700-705 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 11-11-2016 Accepted: 12-12-2016 Dr. R Ezhilmaran Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Chengalpattu
Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER. undisplaced, but as a consequence of the delay in diagnosis displacement occurred SUMMARY
 Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 23-27 Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER Peterborough District Hospital, SUMMARY Thorpe Road, Peterborough From a series of 825 consecutive admissions with a hip
Archives of Emergency Medicine, 1992, 9, 23-27 Missed hip fractures M. J. PARKER Peterborough District Hospital, SUMMARY Thorpe Road, Peterborough From a series of 825 consecutive admissions with a hip
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children
 Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Intramedullary Nailing: History & Rationale
 Intramedullary Nailing: History & Rationale Overview 1. What is IM Nailing? 2. History 3. Design Rationale & Evolution 4. Modern IM Nails 5. The Future What is IM Nailing? Method of internal fixation in
Intramedullary Nailing: History & Rationale Overview 1. What is IM Nailing? 2. History 3. Design Rationale & Evolution 4. Modern IM Nails 5. The Future What is IM Nailing? Method of internal fixation in
THE TRANSARTICULAR GRAFT FOR INFANTILE PSEUDARTHROSIS OF THE TIBIA
 THE TRANSARTICULAR GRAFT FOR INFANTILE PSEUDARTHROSIS OF THE TIBIA A NEW TECHNIQUE SAN BAW, MANDALAY, BURMA From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, General Hospital, Mandalay Fourteen cases of pseudarthrosis
THE TRANSARTICULAR GRAFT FOR INFANTILE PSEUDARTHROSIS OF THE TIBIA A NEW TECHNIQUE SAN BAW, MANDALAY, BURMA From the Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, General Hospital, Mandalay Fourteen cases of pseudarthrosis
Fractures of the Proximal Tibia (Shinbone)
 Fractures of the Proximal Tibia (Shinbone) A fracture, or break, in the shinbone just below the knee is called a proximal tibia fracture. The proximal tibia is the upper portion of the bone where it widens
Fractures of the Proximal Tibia (Shinbone) A fracture, or break, in the shinbone just below the knee is called a proximal tibia fracture. The proximal tibia is the upper portion of the bone where it widens
Surgical treatment of aseptic nonunion in long bones: review of 193 cases
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:11 15 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0155-z ORIGINAL A. Megaro S. Marchesi U.E. Pazzaglia Surgical treatment of aseptic nonunion in long bones: review of 193 cases Received: 5 September
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2007) 8:11 15 DOI 10.1007/s10195-007-0155-z ORIGINAL A. Megaro S. Marchesi U.E. Pazzaglia Surgical treatment of aseptic nonunion in long bones: review of 193 cases Received: 5 September
Mark VanDer Kaag 1, Ajmal Ikram 2. Hand Unit, Tygerberg Hospital University of Stellenbosch
 A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 550 555 Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts K. Muramatsu*, K. Ihara, M. Shigetomi, S. Kawai Department
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 550 555 Femoral reconstruction by single, folded or double free vascularised fibular grafts K. Muramatsu*, K. Ihara, M. Shigetomi, S. Kawai Department
CASE REPORT. Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur
 PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
PRODUCTS CASE REPORT Bone transport utilizing the PRECICE Intramedullary Nail for an infected nonunion in the distal femur Robert D. Fitch, M.D. Duke University Health System 1 1 CONDITION Infected nonunion
McKeever metallic hemiarthroplasty of the knee in unicompartmental degenerative arthritis. Long-term clinical follow-up and current indications
 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. McKeever metallic hemiarthroplasty of the knee in unicompartmental degenerative
This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. McKeever metallic hemiarthroplasty of the knee in unicompartmental degenerative
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
FIRST DESCRIBED RETROGRADE TECHNIQUE USING MEDIAL EPICONDYLE 6/5/2018. RETROGRADE vs. ANTEGRADE FEMORAL NAILING
 What do I do? ISSUES ANTEGRADE vs. RETROGRADE PIRIFORMIS vs. TROCHANTER FLAT vs. FRACTURE TABLE SWIONTKOWSKI, 1984 FIRST DESCRIBED RETROGRADE TECHNIQUE USING MEDIAL EPICONDYLE 1 RETROGRADE NAILING SANDERS
What do I do? ISSUES ANTEGRADE vs. RETROGRADE PIRIFORMIS vs. TROCHANTER FLAT vs. FRACTURE TABLE SWIONTKOWSKI, 1984 FIRST DESCRIBED RETROGRADE TECHNIQUE USING MEDIAL EPICONDYLE 1 RETROGRADE NAILING SANDERS
Effective local and systemic therapy is necessary for the cure of Ewing tumor Most chemotherapy regimens are a combination of cyclophosphamide,
 Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
Ewing Tumor Perez Ewing tumor is the second most common primary tumor of bone in childhood, and also occurs in soft tissues Ewing tumor is uncommon before 8 years of age and after 25 years of age In the
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures. Mohamed E. Habib, Yasser S. Hannout, and Ahmed F. Shams
 Treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures Mohamed E. Habib, Yasser S. Hannout, and Ahmed F. Shams Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of El Minoufiya, Egypt
Treatment of ipsilateral femoral neck and shaft fractures Mohamed E. Habib, Yasser S. Hannout, and Ahmed F. Shams Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Faculty of Medicine, University of El Minoufiya, Egypt
