McKeever metallic hemiarthroplasty of the knee in unicompartmental degenerative arthritis. Long-term clinical follow-up and current indications
|
|
|
- Ashlee Cecilia Eaton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. McKeever metallic hemiarthroplasty of the knee in unicompartmental degenerative arthritis. Long-term clinical follow-up and current indications RD Scott, MJ Joyce, FC Ewald and WH Thomas J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1985;67:3-7. This information is current as of February 5, 8 Reprints and Permissions Publisher Information Click here to order reprints or request permission to use material from this article, or locate the article citation on jbjs.org and click on the [Reprints and Permissions] link. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery Pickering Street, Needham, MA
2 Copyright 985 by The Journal of Bone and Joan: Surgen. Incorporated McKeever Metallic Hemiarthroplasty of the Knee in Unicompartmental Degenerative Arthritis LONG-TERM CLINICAL FOLLOW-UP AND CURRENT INDICATIONS BY RICHARD D. SCOTT, M.D.*, MICHAEL J. JOYCE, M.D.t, FREDERICK C. EWALD, M.D.*, AND WILLIAM H. THOMAS, M.D.*, BOSTON, MASSACHUSETTS From the Department of Orthopedic Surgery. Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston ABSTRACT: Forty patients with forty-four unicornpartmental McKeever metallic uncemented herniarthroplasties were followed for five to thirteen years (average, eight years). Thirty-nine knees had a medial and five, a lateral arthroplasty. The age at surgery ranged from thirty-two to eighty-two years (average, sixty-seven years). At the final follow-up, 7 per cent of the knees were rated as good or excellent. Seventy-nine per cent of the knees in patients who were less than sixty-five years old at the time of surgery were in these categories. Six knees (1 per cent) had required revision to either a unicompartmental or a bicompartmental total knee replacement. The average preoperative and postoperative knee flexion did not change, but knees with initially poor motion improved. The average preoperative flexion contracture of 1 degrees improved postoperatively to 5 degrees. Complications were rare and no cases of infection, peroneal palsy, or clinically detectable phlebitis occurred. Obesity did not seem to adversely affect the outcome. This study indicated that the McKeever unicompartmental metallic hemiarthroplasty can provide an attractive alternative in the treatment of unicornpartmental degenerative arthritis when proximal tibial osteotomy is contraindicated or has failed or when the patient is too young, heavy, or active to consider total knee replacement. The surgical options that currently are available for the treatment of advanced unicompartmental osteoarthritis of the knee include tibial osteotomy, metallic hemiarthroplasty, and metal-to-plastic unicompartmental, bicompartmental, or tricompartmental knee replacement. If tibial osteotomy is contraindicated or has failed, most surgeons do not consider metallic hemiarthroplasty but proceed directly to metal-to-plastic knee replacement. In the late 195 s, McKeever introduced a metallic hemiarthroplasty to resurface the tibial plateau. He reported good initial results in thirty-nine of forty knees. Macintosh designed a similar interpositional hemiarthroplasty and reported good initial results in seventy-two of 13 knees with * Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Brigham and Women s Hospital, 75 Francis Street. Boston, Massachusetts t Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland Metropolitan Hospital, University Hospital, 3395 Scranton Road. Cleveland, Ohio 19. a minimum six-month follow-up56. Potter et al. followed nineteen osteoarthritic knees that had either a McKeever or a Macintosh prosthesis for an average of three years (range, one to nine years) and noted good to excellent results in seventeen. Despite these early encouraging reports, metallic hemiarthroplasty never became popular, possibly because of the advent of metal-to-plastic cemented total knee replacement. However, as the rate of loosening of cemented prosthetic components increases with both time and higher stresses across the bone-cement interface, younger, heavier, and more active patients risk a higher failure rate than do older, lighter, and less active patients. Bone stock is cornpromised by the insertion of the total knee components and by the effects of loosening, which makes revision surgery difficult. The revised knee arthroplasty is then in turn subjected to the same risks of failure as the initial knee arthroplasty. Bridges have been burned, and the opportunity to take advantage of subsequent technological advances with the second operation may have been compromised. For this reason, we believe that metallic herniarthroplasty should still be considered in a select group of patients before proceeding to total knee replacement. The purpose of this report is to review our long-term results with McKeever arthroplasty in unicompartmental degenerative arthritis and to suggest which patients may be candidates. Materials and Methods At the Robert Breck Brigham Hospital (now Brigham and Women s Hospital), unicompartmental McKeever amthroplasty was performed on fifty-one patients (fifty-five knees) with degenerative arthritis between January 1968 and January 1976 by one of six staff surgeons. Eleven patients were lost to follow-up before the five-year examination could be performed. Two had died within two years after surgery, one had insufficient data to be included in the study, and eight were lost to follow-up within the first three years. This left forty patients (forty-four knees) who had been followed for five to thirteen years (average, eight years). Thirty-nine knees had had a medial and five, a lateral amthroplasty. Thirty-two of the knees were in thirty women and twelve, in ten men. The age at the time of surgery ranged from thirty-two to eighty-two years (average, sixtyseven years). Prior operative procedures had been performed on the ipsilateral knee in four patients, and consisted of VOL. 67-A, NO., FEBRUARY
3 R. D. SCOTT, M. J. JOYCE, F. C. EWALD, AND W. H. THOMAS impingement with the tibial spine. All peripheral osteophytes that press against the collateral ligaments and capsule on the concave side of the knee deformity should be removed to assist passive correction of the deformity #{176}. The correct thickness of the prosthesis is that which fills the joint space in the arthritic compartment but which is not so tight that it causes subluxation of the tibia on the femur or excessive pressure on the contralateral compartment. As a rule, the correct prosthesis in the medial compartment should allow the medial joint space to be opened approximately one mulimeter when a valgus stress is applied with the knee in full extension. The knee must also be tested in flexion, as ex- TABLE 1* KNEE ARTHROPLASTY EVALUATION Demerit Points Fio. The McKeever metallic prostheses. They are available in thicknesses ranging from two to fifteen millimeters. three medial meniscectomies and one proximal tibial osteotomy. In two knees there had been a prior fracture of the tibial plateau. in nine knees the meniscus in the contralateral compartment was found at surgery to be torn and was memoved. Eleven patients subsequently had had surgery on the contralateral knee. Four of them had had a contralateral unicompartmental McKeever arthroplasty; four, a unicornpartmentai metal-to-plastic knee replacement; two, a bicornpartmental total knee replacement; and one, a proximal tibial osteotomy. I McKeever Vitallium prostheses were used in this series. Their shape roughly simulates that of a tibial plateau, with a slightly concave and a highly polished superior surface (Fig. 1 ). The inferior surface has a T-shaped fin that is inserted into a corresponding T-shaped slot made in the tibial plateau for fixation. The transverse limb of the T is anterior, for ease of insertion. The prostheses are designed as right and left mirror-images. A right prosthesis resurfaces either the right lateral or the left medial tibial plateau and a left prosthesis resurfaces either the left lateral or the right medial plateau. Varying thicknesses of the prostheses are available, ranging from two to fifteen millimeters. Three and four-millimeter prostheses were used in twenty-seven (61 per cent) of the knees in this series. Operative Technique We prefer a slightly median vertical parapatellar incision to expose the joint, such as is used for unicompartmental total joint replacement #{176}. The details of the surgical approach and the technique for insertion of the prosthesis have been previously described8. An oscillating saw or burr is used to remove any irregularity on the opposing femoral condyle and to shape the tibial plateau so as to achieve maximum surface contact with the tibial prosthesis. It is not necessary to remove all remnants of articular cartilage, but only what is needed to properly shape the tibial plateau. Intercondylar osteophytes should be removed to relieve any Pain None; no limitation of activity Occasionally with prolonged walking; no limitation of usual activity After walking short distances; some limitation of usual activity Sufficient to require narcotics for relief: marked limitation of activity At rest: patient incapacitated Knee motion 8 degrees or more 6 to 8 degrees 3 to 6 degrees Less than 3 degrees Flexion contracture None to 5 degrees 5 to 15 degrees 15 to 3 degrees 3 to 5 degrees More than 5 degrees Varus or valgus deformity Less than 1 degrees 1 to degrees to 3 degrees More than 3 degrees Medial-lateral instability Less than 1 degrees 1 to degrees More than degrees Quadriceps power Normal to good Good minus to fair plus Fair Poor No motion 6 Support None Occasionally uses cane Uses cane all the time Uses crutches Final rating Excellent Good , 6 3 to 3 to 6 Fair 7 to 1 Poor 11+ * Reproduced from Potter, T. A. ; Weinfeld, M. S. ; and Thomas, W. H. : Arthroplasty of the Knee in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis. A Follow-up Study after Implantation of the McKeever and MacIntosh Prostheses. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 5-A: 1, Jan THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
4 McKEEVER METALLIC HEMIARTHROPLASTY OF THE KNEE 5 cessive tightness will cause the prosthesis to lift up anteriorly as the femoral condyle rolls posteriorly on the prosthesis during flexion. Ifthis does occur, it can usually be prevented by resecting a little more of the posterior femoral condyle or by contouring the bone of the tibial plateau so that it slopes downward posteriorly 1 or 15 degrees rather than sloping upward. Postoperative Regimen Postoperatively, the knee is immobilized in full extension with a knee-immobilizer. Quadriceps-setting exercises are initiated on the first postoperative day and active flexion in the side-lying position is begun on the second day. Active knee flexion over the side of the bed is begun after the patient has achieved 5 degrees of active side-lying flexion. Walking is begun on the third or fourth postoperative day using the knee-immobilizer and two crutches. Thirty to 5 per cent weight-bearing is allowed. The splint is discontinued after the patient is able to actively raise the leg with the knee fully extended. When sufficient active flexion has been gained, a stationary bicycle is used for fifteen minutes twice a day. If the patient fails to regain the flexion that was achieved at the end of the operative procedure within two weeks after surgery, manipulation under general anesthesia is performed. Seven (16 per cent) of the forty-four knees in this series required manipulation. Two crutches are used for a minimum of six weeks. At that time, external support is decreased, as tolerated, to the use of one cane outdoors and no support indoors. By twelve weeks postoperatively, the continued use of any support depends on the patient s progress. Recovery after a McKeever arthroplasty can be expected to be longer than that after a cemented total knee arthroplasty. Some soreness in the resurfaced compartment usually persists for six to nine months, but gradually improves with time. This is often accompanied by an effusion. Support with a cane or crutch is continued as long as either pain or swelling is present. Results We examined all but three of the patients (four knees) who had retained the McKeever prosthesis at the time of the latest follow-up. Fir these three patients the last examination had been done within eighteen months by the operating surgeon, but they had moved away, and data on pain and functional status were obtained from these patients by telephone. Preoperative data and intermediate results were obtained from their records and confirmed by the patient. The over-all results were classified as excellent, good, fair, or poor according to the demerit system used by Potter et al. (Table I). In essence, an excellent knee had no pain and normal function. A good knee had mild, trivial pain related to activities and little or no functional limitation. A fair knee had satisfactory pain relief but moderate functional limitation, and a poor knee had an unsatisfactory level of function. The results at one year, three years, five years, and the latest follow-up (five to thirteen years) are shown in Table II. At one year, thirty-eight (86 per cent) of the forty-four knees were in the good or excellent category, but this had gradually diminished to thirty-one (7 per cent) at the final follow-up evaluation. Three knees (7 per cent) had a poor result at the one-year evaluation, and this number gradually increased to seven knees ( 16 per cent) at the time of the final follow-up. TABLE EVOLUTION OF RESULTS (IN PER CENT) AFTER MCKEEVER ARTHROPLASTY IN FORTY-FOUR KNEES Result At I Yr. At 3 Yrs. At 5 Yrs. At >5 to 13 Yrs.* Excellent Good Fair Poor 7 7 Il 16 Revised * Average, eight years. Six knees ( 1 per cent) required revision because of inadequate relief of pain. Three knees were revised to a unicompartmental total knee replacement and three, to a bicompartmental total knee replacement. All of them were graded as good or excellent when last seen. The revision was accomplished without difficulty, as the McKeever prosthesis did not compromise the bone stock of the tibial plateau. Two revisions were done within the first postoperative year and one each was done at four and a half, five, seven, and ten years. Pain relief: All of the patients had had significant pain on weight-bearing before surgery. In patients who had had preoperative pain at night, this was relieved by the end of the first postoperative year and did not recur except in the patients who required revision. The three knees that had been rated as excellent and had had no pain at the one-year follow-up continued to be pain-free at the final follow-up. Eight of the thirty-five knees that were rated as good at one year had no pain regardless of activity. The remaining twenty-seven knees had some mild discomfort after strenuous activity, but no limitation of function. Range of motion: Preoperative flexion of the knee averaged 11 degrees (range, 7 to 135 degrees). The flexion at final follow-up also averaged I 1 degrees (range, 85 to 135 degrees). The average preoperative flexion contracture was 1 degrees (range, zero to degrees), while the average flexion contracture at final follow-up was reduced to 5 degrees (range, zero to degrees). Results in younger patients: As we thought that the McKeever arthroplasty might have particular advantages in younger patients, we singled out, for special study, thirteen patients (fourteen knees) who were less than sixty-five years old at the time of surgery. The average age of these patients was fifty-four years (range, thirty-two to sixty-four years). Five years after surgery, thirteen of the fourteen knees were rated good or excellent. At five to twelve years of follow- II VOL. 67-A, NO.. FEBRUARY 1985
5 6 R. D. SCOTT, M. J. JOYCE, F. C. EWALD, AND W. H. THOMAS FIG. -A FIG. -B Fig. -A: Preoperative radiograph of a knee with osteoarthritis involving the lateral compartment. The patient was fifty-eight years old and worked daily in the winter as a downhill-skiing instructor. Fig. -B: Radiograph made three years after arthroplasty. Eburnated bone on the lateral condyle of the krnur was drilled at the time of surgery. Minimum bone stock was sacrificed. The knee had a full range of motion, good stability. no effusion, and no pain. The patient returned to downhill skiing with no difficulty. up (average, eight years) eleven knees (79 per cent) were still in the good or excellent category, one knee was rated fair, and two knees had been revised. Complications: There were few perioperative complications and no infections. In one patient the surgical drain was retained, and repeat surgery was necessary to remove it. One patient had a large intra-articular hematoma that gradually resolved and did not compromise the result, and one patient had a superficial wound hematoma that drained spontaneously, with no effect on wound-healing. Theme were no clinically manifested cases of thrombophlebitis. Discussion We are strong advocates of proximal tibial osteotomy as the procedure of choice in the younger, heavy, or active patient with medial unicompartmental degenerative arthritis. The McKeever interpositional arthroplasty, however, can provide an attractive surgical alternative in a knee with unicompartmental degenerative arthritis when proximal tibial osteotomy is contraindicated or has failed and the patient is too young, too heavy, or too active to consider total knee replacement. In our opinion, the relative contraindications to osteotomy include active flexion of the knee of less than 9 degrees, a flexion contracture of more than 15 degrees, intercondylar osteophyte impingement as shown on a tunnel radiograph, the presence of pain at rest, a history of phlebothrombosis or venous stasis disease in that extremity, or signs of internal derangement (especially episodes of locking). Early degenerative changes in the contralateral joint compartment shown on a standing plain radiograph (peripheral osteophytes, subchondral sclerosis, mild joint-space narrowing, or chondmocalcinosis) or a bone scan showing increased uptake in the opposite compartment are also contraindications. It is more difficult to define what we mean by too young, too heavy, or too active to consider total knee replacement, as so many factors must be considered for each individual patient. For example, we would not consider a twelve-year-old bedridden patient with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis who weighs forty kilograms to be too young for total knee replacement9, but we might think that a fifty-fiveyear-old laborer weighing 1 kilograms is too heavy and too active for the procedure. The McKeever arthmoplasty has some distinct advantages over tibial osteotomy, as a torn meniscal fragment and bone impingement can be removed at the time of surgery. After such d#{33}bridement and the release of intma-articular adhesions, it is possible to gain both flexion and extension in patients who have significant preoperative limitation of motion. As we have not found postoperative immobilization to be necessary after a McKeever arthroplasty, the chance of venous thrombosis is diminished. Also, both knees can be operated on during the same hospitalization, significantly diminishing recovery time in a patient with bilateral involvement. The potential problem of delayed union or nonunion of an osteotomy is avoided, and the incidence of peroneal palsy is less. In patients who already have early degenerative changes in the contralateral joint compartment of the same knee, the McKeever arthroplasty has an additional advantage over osteotomy. Slight overcorrection of the preoper- THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
6 MCKEEVER METALLIC HEMIARTHROPLASTY OF THE KNEE 7 ative yams or valgus deformity, which is the goal of osteotomy, transfers extra weight-bearing forces to the contralateral compartment with early involvement. In the knee with preoperative yams alignment that has advanced medialcompartment disease but only early lateral-compartment disease, the correctly chosen width of McKeever prosthesis can adjust the postoperative alignment to neutral or only a few degrees of valgus angulation. This permits the resurfaced medial compartment to share substantial weight-bearing forces while protecting the opposite compartment from overload. It is permissible to allow the patient to engage in vigorous physical activity as tolerated. Finally, at an average of eight years of follow-up, the results in our patients were equal to or better than those that have been reported for t1 A McKeever arthroplasty cannot be expected to produce an initial result that is comparable with that after cemented unicompartmental or bicompartmental total knee replacement. All of the patients in this series who had a cemented total knee replacement in the opposite knee or who eventually had a conversion to a total knee replacement preferred the total knee arthroplasty. However, the Mc- Keever arthroplasty has several advantages over unicompartmental or bicompartmental total knee replacement in selected patients. As bone cement is not required, the potential adverse effects on bone of late cement failure are eliminated. The minimum resection of bone stock results in little or no compromise of any later salvage procedure. The patients can resume vigorous physical activity as tolerated, allowing their potential return to a strenuous occupation or avocation (Figs. -A and -B). Two categories of patients benefit from these advantages: the obese and the young. The obese patient is at greater risk of component loosening - the heavier the patient, the higher are the stresses that are generated across the bone-cement interface. However, obesity did not appear to adversely affect the outcome of the McKeever arthroplasty in our series and is, perhaps, a relative indication for the procedure. We have obtained good results with three years of follow-up in patients who were as heavy as 17 kilograms. Youth is a relative contraindication to any prosthetic joint replacement. The McKeever arthroplasty, however, can be used to maintain a good functional knee during the years prior to a probably inevitable total knee replacement. Bone stock is preserved, and the delay will enable the patient to have the advantage of the latest joint-replacement technology. NotE: The authors would like to thank Dr. C. B. Sledge, Dr. M. S. Weinfeld. and Dr. R. Poss for their contribution to this study. References I. COVENTRY, M. B. : Upper Tibial Osteotomy for Gonarthrosis. The Evolution of the Operation in the Last 18 Years and Long Term Results. Orthop. Clin. North America, 1: 191-1, DEVAS. M. B.: High Tibial Osteotomy for Arthritis of the Knee. A Method Specially Suitable for the Elderly. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 51-B(l): 95-99, INSALL, JOHN: SHJI, HIROMU; and MAYER, VICTOR: High Tibial Osteotomy. A Five-Year Evaluation. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 56-A: , Oct JACKSON, J. P.; WAUGH, W.; and GREEN, J. P.: Tibial Osteotomy for Osteoarthritis of the Knee. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 51-B(1): 88-9, MACINTOSH, D. L. : Hemiarthroplasy of the Knee using a Space Occupying Prosthesis for Painful Varus and Valgus Deformities. In Proceedings of the Joint Meeting of the Orthopaedic Associations of the English-Speaking World. J. Bone and Joint Surg.. -A: 131, Dec MACINTOSH, D. L. : Arthroplasty of the Knee in Rheumatoid Arthritis using the Hemiarthroplasty Prosthesis. In Synovectomy and Arthroplasty in Rheumatoid Arthritis; Second International Symposium, pp Edited by George Chapchal. Stuttgart, Thieme, MCKEEVER, D. C. : Tibial Plateau Prosthesis. Clin. Orthop., 18: 86-95, POTTER, T. A. ; WEINFELD, M. S.: and THOMAS, W. H.: Arthroplasty of the Knee in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Osteoarthritis. A Follow-up Study after Implantation of the McKeever and MacIntosh Prostheses. J. Bone and Joint Surg.. 5-A: 1-, Jan SAROKHAN, A. J. ; SCOTT, R. D.: THOMAS, W. H.; SLEDGE, C. B.; EWALD, F. C.; and CLOOS, D. W.: Total Knee Arthroplasty in Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 65-A: , Oct SCOTT, R. D., and SANTORE, R. F. : Unicondylar and Unicompartmental Replacement for Osteoarthritis of the Knee. J. Bone and Joint Surg., 63-A: 536-5, April TORGERSON, W. R., JR.; KETTELKAMP, D. B.; IGU, R. A., JR.: and LEACH, R. E.: Tibial Osteotomy for the Treatment of Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee. Clin. Orthop., 11: 6-5. June 197. VOL. 67-A, NO., FEBRUARY 1985
Revolution. Unicompartmental Knee System
 Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Revolution Unicompartmental Knee System While Total Knee Arthroplasty (TKA) is one of the most predictable procedures in orthopedic surgery, many patients undergoing TKA are in fact excellent candidates
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements:
 Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
Early Results of Total Knee Replacements: "A Clinical and Radiological Evaluation" K.S. Dhillon, FRCS* Jamal, MS* S. Bhupinderjeet, MBBS** * Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery University of Malaya, Kuala Lumpur
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR
 CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
CLINICAL AND OPERATIVE APPROACH FOR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT DR.VINMAIE ORTHOPAEDICS PG 2 ND YEAR Evolution of TKR In 1860, Verneuil proposed interposition arthroplasty, involving the insertion of soft tissue
Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 9 Number 2 Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella R Gupta, S Canty, W Ryan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 9 Number 2 Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella R Gupta, S Canty, W Ryan Citation
Life. Uncompromised. The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout
 Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
Life Uncompromised The KineSpring Knee Implant System Surgeon Handout 2 Patient Selection Criteria Patient Selection Criteria Medial compartment degeneration must be confirmed radiographically or arthroscopically
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON. Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD
 CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
CONTRIBUTING SURGEON Barry Waldman, MD Director, Center for Joint Preservation and Replacement Sinai Hospital of Baltimore Baltimore, MD System Overview The EPIK Uni is designed to ease the use of the
Osteotomy of the Upper Portion of the Tibia for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee
 Osteotomy of the Upper Portion of the Tibia for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee BY MARK B. COVENTRY, M.D.", ROCHESTER, MINNESOTA From the Section of Orthopedic Surgery, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation,
Osteotomy of the Upper Portion of the Tibia for Degenerative Arthritis of the Knee BY MARK B. COVENTRY, M.D.", ROCHESTER, MINNESOTA From the Section of Orthopedic Surgery, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation,
Investigation performed at the Department of Orthopedics, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota
 1090 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Total Knee Arthroplasty in Young Patients with Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis BY JAVAD PARVIZI, MD, FRCS, CLAUDETTE M. LAJAM, MD,
1090 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Total Knee Arthroplasty in Young Patients with Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis BY JAVAD PARVIZI, MD, FRCS, CLAUDETTE M. LAJAM, MD,
Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY
 1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
1470 COPYRIGHT 2005 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Range of Motion of Standard and High-Flexion Posterior Stabilized Total Knee Prostheses A PROSPECTIVE, RANDOMIZED STUDY BY YOUNG-HOO
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
SEVERE VARUS AND VALGUS DEFORMITIES TREATED BY TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Th. KARACHALIOS, P. P. SARANGI, J. H. NEWMAN From Winford Orthopaedic Hospital, Bristol, England We report a prospective case-controlled
Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique
 Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Surgical Procedure Total Knee Original System Primary Surgical Technique Where as a total hip replacement is primarily a bony operation, a total knee replacement is primarily a soft tissue operation. Excellent
Custom Patellofemoral Arthroplasty of the Knee. Surgical Technique
 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Custom Patellofemoral Arthroplasty of the Knee. Surgical Technique Domenick
This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Custom Patellofemoral Arthroplasty of the Knee. Surgical Technique Domenick
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
PARTIAL KNEE REPLACEMENT A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete
 Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Unicondylar Knee Vs Total Knee Replacement: Is Less Better In the Middle Aged Athlete Chair: Maurilio Marcacci, MD Alois Franz "Basic principles and considerations of the Unis" Joao M. Barretto "Sport
Partial Knee Replacement
 Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
Partial Knee Replacement A partial knee replacement removes damaged cartilage from the knee and replaces it with prosthetic implants. Unlike a total knee replacement, which removes all of the cartilage,
A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients
 Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Original Research Article A study of functional outcome after Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty in elderly patients Ragesh Chandran 1*, Sanath K Shetty 2, Ashwin Shetty 3, Bijith Balan 1, Lawrence J Mathias
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC. Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
Stephen R Smith Northeast Nebraska Orthopaedics PC Ligament Preserving Techniques in Total Knee Arthroplasty 10-15% have Fair to poor Results? Why? The complication rate is 2.567% If It happens To You
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing
 A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
A Patient s Guide to Partial Knee Resurfacing Surgical Outcomes System (SOS ) www.orthoillustrated.com OrthoIllustrated is a leading Internet-based resource for patient education. Please visit this website
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT
 YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. M.S. Barrow Barrow Physiotherapy MBBch (Wits), FCS (SA) Orth. Waterfall City Hospital Orthopaedic Surgeon Tel: 011 304 7829 Suite 5, East Wing, Sunninghill Hospital www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za
YOUR TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENT Dr. M.S. Barrow Barrow Physiotherapy MBBch (Wits), FCS (SA) Orth. Waterfall City Hospital Orthopaedic Surgeon Tel: 011 304 7829 Suite 5, East Wing, Sunninghill Hospital www.barrowphysiotherapy.co.za
Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with an Ankylosing Knee after Previous Patellectomy
 Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2014;26(3):182-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2014.26.3.182 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with
Case Report Knee Surg Relat Res 2014;26(3):182-186 http://dx.doi.org/10.5792/ksrr.2014.26.3.182 pissn 2234-0726 eissn 2234-2451 Knee Surgery & Related Research Total Knee Arthroplasty in a Patient with
Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty
 Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
Clin Orthop Relat Res (2008) 466:579 583 DOI 10.1007/s11999-007-0104-4 SYMPOSIUM: NEW APPROACHES TO SHOULDER SURGERY Augmented Glenoid Component for Bone Deficiency in Shoulder Arthroplasty Robert S. Rice
The Unispacer TM unicompartmental knee implant: Its outcomes in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 410 417 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Unispacer TM unicompartmental knee implant: Its outcomes in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis C. Catier, M.
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2011) 97, 410 417 ORIGINAL ARTICLE The Unispacer TM unicompartmental knee implant: Its outcomes in medial compartment knee osteoarthritis C. Catier, M.
Intramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Intramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Intramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 IM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Intramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Intramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 IM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Biomechanics of. Knee Replacement. Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm
 Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
Biomechanics of Knee Replacement Mujda Hakime, Paul Malcolm 1 Table of contents Knee Anatomy Movements of the Knee Knee conditions leading to knee replacement Materials Alignment and Joint Loading Knee
Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis*
 Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis* ROBY C. THOMPSON, JR., M. D. Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville One of the most important
Surgical Care of the Lower Extremity in Rheumatoid Arthritis* ROBY C. THOMPSON, JR., M. D. Professor of Orthopedic Surgery, University of Virginia School of Medicine, Charlottesville One of the most important
Uniglide. Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique
 Uniglide Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique Uniglide Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative assessment 6 Preparation 7 Incision 7 Approach 7 Medial procedure 8 Tibial preparation
Uniglide Unicompartmental Knee Replacement Mk III surgical technique Uniglide Contents Operative summary 4 Pre-operative assessment 6 Preparation 7 Incision 7 Approach 7 Medial procedure 8 Tibial preparation
Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 14 Number 1 Comparison of high-flex and conventional implants for bilateral total knee arthroplasty C Martin-Hernandez, M Guillen-Soriano, A
THE USE OF THE HEMIARTHROPLASTY PROSTHESIS FOR ADVANCED OSTEOARTHRITIS AND RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE
 THE USE OF THE HEMIARTHROPLASTY PROSTHESIS FOR ADVANCED OSTEOARTHRITIS AND RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE D. L. MACINTOSH and G. A. HUNTER, TORONTO, ONTARIO, CANADA From the Orthopaedic Service of the
THE USE OF THE HEMIARTHROPLASTY PROSTHESIS FOR ADVANCED OSTEOARTHRITIS AND RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE D. L. MACINTOSH and G. A. HUNTER, TORONTO, ONTARIO, CANADA From the Orthopaedic Service of the
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository)
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Combined intra-articular and varus opening wedge osteotomy for lateral depression and valgus malunion of the proximal part of the tibia. Surgical technique Kerkhoffs,
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) Combined intra-articular and varus opening wedge osteotomy for lateral depression and valgus malunion of the proximal part of the tibia. Surgical technique Kerkhoffs,
Massive Varus- Overview. Massive Varus- Classification. Massive Varus- Definition 07/02/14. Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR
 07/02/14 Massive Varus- Overview Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR Myles Coolican Val d Isere 2014 Massive Varus- Classification Classification Intra articular Massive Varus- Classification Classification
07/02/14 Massive Varus- Overview Correction of Massive Varus Deformity in TKR Myles Coolican Val d Isere 2014 Massive Varus- Classification Classification Intra articular Massive Varus- Classification Classification
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY
 EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
EARLY CLINICAL RESULTS OF PRIMARY CEMENTLESS TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Benkovich V. Perry T., Bunin A., Bilenko V., Unit for Joint Arthroplasty, Soroka Medical Center Ben Gurion University of Negev Beer
The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis
 DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
DOI 10.1007/s00264-009-0908-9 ORIGINAL PAPER The UniSpacer : correcting varus malalignment in medial gonarthrosis Michael Clarius & Justus F. Becker & Holger Schmitt & Joern B. Seeger Received: 20 October
FOLLOW-UP OF THE MACINTOSH ARTHROPLASTY OF THE KNEE JOINT*
 Rheum, phys. Med., 1972,11, 217 ORIGINAL PAPER FOLLOW-UP OF THE MACINTOSH ARTHROPLASTY OF THE KNEE JOINT* BY J. D. JESSOPt AND C. J. MOOREt SUMMARY The results of arthroplasty of the knee joint in 2 patients
Rheum, phys. Med., 1972,11, 217 ORIGINAL PAPER FOLLOW-UP OF THE MACINTOSH ARTHROPLASTY OF THE KNEE JOINT* BY J. D. JESSOPt AND C. J. MOOREt SUMMARY The results of arthroplasty of the knee joint in 2 patients
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty
![Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty](/thumbs/90/102636395.jpg) Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Vasu Pai D orth, MS, National Board [orth],mch, FRACS, FICMR Total Hip Arthroplasty Introduction Hip arthritis is a common problem, most often due to osteoarthritis. In hip arthritis affects a patient,
Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty
 Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Progress in Clinical Medicine Complications of Total Knee Arthroplasty JMAJ 44(5): 235 240, 2001 Shinichi YOSHIYA*, Masahiro KUROSAKA** and Ryosuke KURODA*** *Director, Department of Orthopaedic Surgery,
Extramedullary Tibial Preparation
 Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
Surgical Technique Extramedullary Tibial Preparation Primary Total Knee Arthroplasty LEGION Total Knee System Extramedullary tibial preparation Contents Introduction...2 EM tibial highlights...3 Preoperative
arthritis of the knee.
 1351 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Current Concepts Review Unicompartmental Arthritis of the Knee BY RICHARD IORIO, MD, AND WILLIAM L. HEALY, MD Investigation performed
1351 COPYRIGHT 2003 BY THE JOURNAL OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY, INCORPORATED Current Concepts Review Unicompartmental Arthritis of the Knee BY RICHARD IORIO, MD, AND WILLIAM L. HEALY, MD Investigation performed
BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS IN TOTAL KNEE REPLACEMENTS
 Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology Vol. 5, No. 3 (2005) 469 475 c World Scientific Publishing Company BIOMECHANICAL MECHANISMS FOR DAMAGE: RETRIEVAL ANALYSIS AND COMPUTATIONAL WEAR PREDICTIONS
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: Revised Date: 07/26/17 Page 1 of 9
 Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
Page 1 of 9 Disclaimer Description Coverage Determination/ Clinical Indications Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 7/28/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 83 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2001, 9(1): 45 50 Bilateral total knee arthroplasty: One mobile-bearing and one fixed-bearing KY Chiu, TP Ng, WM Tang and P Lam Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, The University
Osteoarthritis. Dr Anthony Feher. With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides
 Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
Osteoarthritis Dr Anthony Feher With special thanks to Dr. Tim Williams and Dr. Bhatia for allowing me to use some of their slides No Financial Disclosures Number one chronic disability in the United States
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle
 A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle Introduction Surgery to replace the ankle joint with an artificial joint (called ankle arthroplasty) is becoming more common. This surgery
A Patient s Guide to Artificial Joint Replacement of the Ankle Introduction Surgery to replace the ankle joint with an artificial joint (called ankle arthroplasty) is becoming more common. This surgery
Unicompartmental Knee Resurfacing
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage knee pain. All decisions about the management of knee pain must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed
Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee
 Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Sports-Related Injuries and Disorders Medical Practice for Sports Injuries and Disorders of the Knee JMAJ 48(1): 20 24, 2005 Hirotsugu MURATSU*, Masahiro KUROSAKA**, Tetsuji YAMAMOTO***, and Shinichi YOSHIDA****
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury
 Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Mr Aslam Mohammed FRCS, FRCS (Orth) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon Specialising in Lower Limb Arthroplasty and Sports Injury I qualified from the Welsh National School of Medicine in Cardiff in 1984. I
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with:
 Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
Arthrex Open Wedge Osteotomy Technique Designed in conjunction with: Dr. Giancarlo Puddu, M.D. Dr. Peter Fowler, M.D. Dr. Ned Amendola, M.D. To treat pain and instability associated with lower extremity
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA)
 TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY (TKA) 1 Anatomy, Biomechanics, and Design 2 Femur Medial and lateral condyles Convex, asymmetric Medial larger than lateral 3 Tibia Tibial plateau Medial tibial condyle: concave
15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 18 No. 8 2003 15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jun Ito, MD, PhD, Tomihisa Koshino, MD, PhD, Renzo Okamoto, MD, PhD,
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 18 No. 8 2003 15-Year Follow-up Study of Total Knee Arthroplasty in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis Jun Ito, MD, PhD, Tomihisa Koshino, MD, PhD, Renzo Okamoto, MD, PhD,
1 Introduction. 2 Data and method
 Open Med. 2015; 10: 457 461 Research Article Open Access Si Yulou, Xue Yanqin, Xing Yongjun* Method and effect of total knee arthroplasty osteotomy and soft tissue release for serious knee joint space
Open Med. 2015; 10: 457 461 Research Article Open Access Si Yulou, Xue Yanqin, Xing Yongjun* Method and effect of total knee arthroplasty osteotomy and soft tissue release for serious knee joint space
Abramsohn Retractor 1
 Abramsohn Retractor 1 Calibrated Femoral Tibial Spreaders Small Medium Large Designed to remain in position, with the femur and tibia separated, without the need of an assistant, and to minimize crushing
Abramsohn Retractor 1 Calibrated Femoral Tibial Spreaders Small Medium Large Designed to remain in position, with the femur and tibia separated, without the need of an assistant, and to minimize crushing
Periarticular knee osteotomy
 Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
Periarticular knee osteotomy Turnberg Building Orthopaedics 0161 206 4803 All Rights Reserved 2018. Document for issue as handout. Knee joint The knee consists of two joints which allow flexion (bending)
JOINT RULER. Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement
 JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
JR JOINT RULER Surgical Technique For Knee Joint JRReplacement INTRODUCTION The Joint Ruler * is designed to help reduce the incidence of flexion, extension, and patellofemoral joint problems by allowing
There have been conflicting results reported in the
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 1 & 2 2002-2003 5 Total Knee Replacement Following High Tibial Osteotomy Sanjeev Madan, M.Ch.Orth., F.R.C.S. (Orth), M.Sc.(Orth), M.B.A., R. K. Ranjith,
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 61, Numbers 1 & 2 2002-2003 5 Total Knee Replacement Following High Tibial Osteotomy Sanjeev Madan, M.Ch.Orth., F.R.C.S. (Orth), M.Sc.(Orth), M.B.A., R. K. Ranjith,
iunig2 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE Patient-specific UNICOMPARTMENTALknee resurfacing system
 iunig2 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE Patient-specific UNICOMPARTMENTALknee resurfacing system iunig2 UNICOMPARTMENTAL Table of Contents Introduction...page 3 Pre-Operative Image Review...page 6 Step 1: Site
iunig2 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE Patient-specific UNICOMPARTMENTALknee resurfacing system iunig2 UNICOMPARTMENTAL Table of Contents Introduction...page 3 Pre-Operative Image Review...page 6 Step 1: Site
The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the
 The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
The Arthritic Knee The causes of OA of the knee are multiple and include aging (wear and tear), obesity, and previous knee trauma or surgery. OA affects usually the medial compartment of the knee, and
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Bicruciate-Retaining or Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis Pritchett 225 Fig. 3. The MP total knee prosthesis. Fig. 1. An anteroposterior radiograph o
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 26 No. 2 2011 Patients Prefer A Bicruciate-Retaining or the Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis James W. Pritchett, MD, FACS Abstract: Four-hundred forty patients underwent
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 26 No. 2 2011 Patients Prefer A Bicruciate-Retaining or the Medial Pivot Total Knee Prosthesis James W. Pritchett, MD, FACS Abstract: Four-hundred forty patients underwent
Total Knee Replacement
 Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
Total Knee Replacement A total knee replacement, also known as total knee arthroplasty, involves removing damaged portions of the knee, and capping the bony surfaces with man-made prosthetic implants.
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
Tissue-sparing surgery with the bi-unicompartmental knee prosthesis: retrospective study with minimum follow-up of 36 months
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2006) 7:108 112 DOI 10.1007/s10195-005- - TSS SECTION N. Confalonieri A. Manzotti Tissue-sparing surgery with the bi-unicompartmental knee prosthesis: retrospective study with minimum
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2006) 7:108 112 DOI 10.1007/s10195-005- - TSS SECTION N. Confalonieri A. Manzotti Tissue-sparing surgery with the bi-unicompartmental knee prosthesis: retrospective study with minimum
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY
 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT INJURY WHAT IS THE ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT? The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of four major ligaments that stabilizes the knee joint. A ligament is a tough band
Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Maquet: Maquet: Biomechanics. Maquet: /21/10. Philippe Landreau, MD
 Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Philippe Landreau, MD Paris, France And if the patient is young?! Anterior displacement of the tibial tuberosity design to reduce the joint reactive force
Which treatment? How I do a Maquet Osteotomy? Philippe Landreau, MD Paris, France And if the patient is young?! Anterior displacement of the tibial tuberosity design to reduce the joint reactive force
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up
 Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Functional Outcome of Uni-Knee Arthroplasty in Asians with six-year Follow-up Ching-Jen Wang, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery Kaohsiung Chang Gung Memorial Hospital Chang Gung University College
Total Joints and Arthritis. Marc A. Roux, M.D. Chief of Surgery, Baylor Medical Center at Waxahachie August 25, 2012
 Total Joints and Arthritis Marc A. Roux, M.D. Chief of Surgery, Baylor Medical Center at Waxahachie August 25, 2012 Joint Replacement Will focus on Knee and Hip OA amd joint replacement Over 500,000
Total Joints and Arthritis Marc A. Roux, M.D. Chief of Surgery, Baylor Medical Center at Waxahachie August 25, 2012 Joint Replacement Will focus on Knee and Hip OA amd joint replacement Over 500,000
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS KNEE SYSTEM
 CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS KNEE SYSTEM IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR WITH THE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE.
CONSENSUS ORTHOPEDICS INC. CONSENSUS KNEE SYSTEM IMPORTANT INFORMATION FOR SURGEON: PLEASE READ PRIOR TO IMPLANTING THIS DEVICE IN A CLINICAL SETTING. THE SURGEON SHOULD BE FAMILIAR WITH THE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE.
Computer aided analysis of total knee replacement
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1983, 42, 415-420 Computer aided analysis of total knee replacement in rheumatoid arthritis G. P. ARDEN From the Windsor Group of Hospitals SUMMARY A computer-aided analysis
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1983, 42, 415-420 Computer aided analysis of total knee replacement in rheumatoid arthritis G. P. ARDEN From the Windsor Group of Hospitals SUMMARY A computer-aided analysis
TRK REVISION KNEE Surgical Technique
 1 TRK REVISION KNEE Surgical Technique 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. INTERCONDYLAR RESECTION...... page FEMORAL STEM...... page NON CEMENTED FEMORAL STEM...... page TRIAL FEMORAL COMPONENTS...... page
1 TRK REVISION KNEE Surgical Technique 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. INTERCONDYLAR RESECTION...... page FEMORAL STEM...... page NON CEMENTED FEMORAL STEM...... page TRIAL FEMORAL COMPONENTS...... page
Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis
 This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis RH Cofield J Bone Joint
This is an enhanced PDF from The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery The PDF of the article you requested follows this cover page. Total shoulder arthroplasty with the Neer prosthesis RH Cofield J Bone Joint
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 12/01/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 101 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:386-392 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.386 Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up Kyung Tae
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:386-392 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.4.386 Clinical Results of Lateral Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty: Minimum 2-Year Follow-up Kyung Tae
H.P. Teng, Y.J. Chou, L.C. Lin, and C.Y. Wong Under general or spinal anesthesia, the knee was flexed gently. In the cases of limited ROM, gentle and
 THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
THE BENEFIT OF ARTHROSCOPY FOR SYMPTOMATIC TOTAL KNEE ARTHROPLASTY Hsiu-Peng Teng, Yi-Jiun Chou, Li-Chun Lin, and Chi-Yin Wong Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung,
Knee Surgical Technique
 Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers
 CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
CEC ARTICLE: Special Medical Conditions Part 3: Hip and Knee Replacement C. Eggers Joint replacement surgery removes a damaged joint and replaces it with a prosthesis or artificial joint. The purpose of
Shoulder Joint Replacement
 Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
Shoulder Joint Replacement Although shoulder joint replacement is less common than knee or hip replacement, it is just as successful in relieving joint pain. Shoulder replacement surgery was first performed
YOU MAY NEED A KNEE REPLACEMENT
 Knee pain? YOU MAY NEED A KNEE REPLACEMENT Introduction If you re reading this brochure, you or a loved one is likely suffering from a severe knee problem. Serious knee joint conditions can cause pain,
Knee pain? YOU MAY NEED A KNEE REPLACEMENT Introduction If you re reading this brochure, you or a loved one is likely suffering from a severe knee problem. Serious knee joint conditions can cause pain,
The Result of PFC (press-fit condylar) Total Knee Replacement Arthroplasty*
 The Seoul Journal of Medicine Vol. 32, No. 1: 27-34, March 1991 The Result of PFC (press-fit condylar) Total Knee Replacement Arthroplasty* Sang Cheol Seong and Gun II Im Depanment of Orthopedic Surgery,
The Seoul Journal of Medicine Vol. 32, No. 1: 27-34, March 1991 The Result of PFC (press-fit condylar) Total Knee Replacement Arthroplasty* Sang Cheol Seong and Gun II Im Depanment of Orthopedic Surgery,
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments
 TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Resection Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA
TRUMATCH PERSONALIZED SOLUTIONS with the SIGMA High Performance Instruments Resection Guide System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE RESECTION GUIDE SURGICAL TECHNIQUE The following steps are an addendum to the SIGMA
Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System
 Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Showa Univ J Med Sci 29 3, 289 296, September 2017 Original Kinematics Analysis of Different Types of Prosthesis in Total Knee Arthroplasty with a Navigation System Hiroshi TAKAGI 1 2, Soshi ASAI 1, Atsushi
Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee
 ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 934-938 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee Sandesh
ISSN: 2319-7706 Volume 4 Number 4 (2015) pp. 934-938 http://www.ijcmas.com Original Research Article Functional and radiological outcome of total knee replacement in varus deformity of the knee Sandesh
Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit. Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care
 Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care OA-HxPE-716.indd 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS HISTORY TAKING... 3 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED
Non Surgical Management Of Hip And Knee Osteoarthritis Toolkit Evaluation and Diagnosis of Osteoarthritis in Primary Care OA-HxPE-716.indd 1 TABLE OF CONTENTS HISTORY TAKING... 3 EVALUATION OF SUSPECTED
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION
 Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Integra Cadence Total Ankle System PATIENT INFORMATION Fibula Articular Surface Lateral Malleolus Tibia Medial Malleolus Talus Anterior view of the right ankle region Talo-fibular Ligament Calcaneal Fibular
Osteotomy of the Knee
 Osteotomy of the Knee Osteotomy literally means "cutting of the bone." In a knee osteotomy, either the tibia (shinbone) or femur (thighbone) is cut and then reshaped to relieve pressure on the knee joint.
Osteotomy of the Knee Osteotomy literally means "cutting of the bone." In a knee osteotomy, either the tibia (shinbone) or femur (thighbone) is cut and then reshaped to relieve pressure on the knee joint.
Pre-operative clinical and radiological
 Pre-operative clinical and radiological assessment of the patellofemoral joint in unicompartmental knee replacement and its influence on outcome D. J. Beard, H. Pandit, S. Ostlere, C. Jenkins, C. A. F.
Pre-operative clinical and radiological assessment of the patellofemoral joint in unicompartmental knee replacement and its influence on outcome D. J. Beard, H. Pandit, S. Ostlere, C. Jenkins, C. A. F.
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF THE INTERCONDYLAR FRACTURE OF THE FEMUR
 OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF THE INTERCONDYLAR FRACTURE OF THE FEMUR S G Chee, K S Lam, B K Tay, N Balachandran SYNOPSIS Operative treatment of 28 intercondylar fractures of femur were done from 98 to 985. The
OPERATIVE TREATMENT OF THE INTERCONDYLAR FRACTURE OF THE FEMUR S G Chee, K S Lam, B K Tay, N Balachandran SYNOPSIS Operative treatment of 28 intercondylar fractures of femur were done from 98 to 985. The
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT
 ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
ACL AND PCL INJURIES OF THE KNEE JOINT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery,
Surgical Technique. VISIONAIRE Disposable Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System
 Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE Disposable Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE and LEGION Disposable instrument technique* Note: All disposable instruments are interchangeable with the
Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE Disposable Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE and LEGION Disposable instrument technique* Note: All disposable instruments are interchangeable with the
Surgical Technique. VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System
 Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE FastPak for LEGION Instrument Technique* Nota Bene The technique description herein is made available to the
Surgical Technique VISIONAIRE FastPak Instruments for the LEGION Total Knee System VISIONAIRE FastPak for LEGION Instrument Technique* Nota Bene The technique description herein is made available to the
Dr Doron Sher MBBS MBiomedE FRACS(Orth)
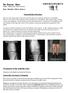 Dr Doron Sher MBBS MBiomedE FRACS(Orth) Knee, Shoulder, Elbow Surgery Osteoarthritis of the Knee The knee is the largest joint in the body and is the joint most commonly affected by osteoarthritis. There
Dr Doron Sher MBBS MBiomedE FRACS(Orth) Knee, Shoulder, Elbow Surgery Osteoarthritis of the Knee The knee is the largest joint in the body and is the joint most commonly affected by osteoarthritis. There
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Management of Periprosthetic Fracture in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Patients: A Case Series
 Management of Periprosthetic Fracture in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Patients: A Case Series Yew Lok Woo, MBBS, Pak Lin Chin, MBBS, FRCS, Ngai Nung Lo, MBBS, FRCS, Shi-Lu Chia, PhD, Darren Keng
Management of Periprosthetic Fracture in Unicompartmental Knee Arthroplasty Patients: A Case Series Yew Lok Woo, MBBS, Pak Lin Chin, MBBS, FRCS, Ngai Nung Lo, MBBS, FRCS, Shi-Lu Chia, PhD, Darren Keng
Dynamic Splinting of the
 Dynamic Splinting of the Rheumatoid Hand BY F. RICHARD CONVERY, M.D.,* J. PIERCE CONATY, M.D.** AND VERNON L. NICKEL, M.D.** Rancho Los Amigos Hospital, Downey, California (University of Southern California
Dynamic Splinting of the Rheumatoid Hand BY F. RICHARD CONVERY, M.D.,* J. PIERCE CONATY, M.D.** AND VERNON L. NICKEL, M.D.** Rancho Los Amigos Hospital, Downey, California (University of Southern California
Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow (Outerbridge-Kashiwagi procedure)
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 306-310 ORIGINAL STUDIES Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow (Outerbridge-Kashiwagi procedure) Bart VINGERHOEDS, Ilse DEGREEF, Luc DE SMET From the University
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 306-310 ORIGINAL STUDIES Debridement arthroplasty for osteoarthritis of the elbow (Outerbridge-Kashiwagi procedure) Bart VINGERHOEDS, Ilse DEGREEF, Luc DE SMET From the University
Mako Partial Knee Medial bicompartmental
 Mako Partial Knee Medial bicompartmental Surgical reference guide Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery Table of contents Implant compatibility.... 3 Pre-operative planning.... 4 Intra-operative planning....
Mako Partial Knee Medial bicompartmental Surgical reference guide Mako Robotic-Arm Assisted Surgery Table of contents Implant compatibility.... 3 Pre-operative planning.... 4 Intra-operative planning....
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research
 New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
New Directions in Osteoarthritis Research Kananaskis October 22, 2015 Nick Mohtadi MD MSc FRCSC No conflicts of interest related to this presentation 1 Osteoarthritis: Disease? Fact of Life? Strong family
Case Study: Christopher
 Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
Case Study: Christopher Conditions Treated Anterior Knee Pain, Severe Crouch Gait, & Hip Flexion Contracture Age Range During Treatment 23 Years to 24 Years David S. Feldman, MD Chief of Pediatric Orthopedic
iuni G2 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE FEMUR FIRST Patient-specific UNICOMPARTMENTALknee resurfacing system
 iuni G2 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE Patient-specific UNICOMPARTMENTALknee resurfacing system FEMUR FIRST iuni G2 UNICOMPARTMENTAL Table of Contents Introduction... page 3 Preoperative Image Review... page
iuni G2 SURGICAL TECHNIQUE GUIDE Patient-specific UNICOMPARTMENTALknee resurfacing system FEMUR FIRST iuni G2 UNICOMPARTMENTAL Table of Contents Introduction... page 3 Preoperative Image Review... page
Original Date: December 2015 Page 1 of 8 FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines TOTAL JOINT ARTHROPLASTY -Total Hip Arthroplasty -Total Knee Arthroplasty -Replacement/Revision Hip or Knee Arthroplasty CPT4 Codes: Please refer to
Arthritis. What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available?
 Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
Arthritis What is arthritis? Who is affected? What treatment options are available? What is Arthritis? arth - joint itis inflammation Arthritis inflammation of the joint(s). What is Inflammation? Inflammation
