Complex fractures of the humeral shaft treated with antegrade locked intramedullary nail: clinical experience and long-term results
|
|
|
- Ira Palmer
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Biomed 2015; Vol. 86, N. 1: Mattioli 1885 Original article Complex fractures of the humeral shaft treated with antegrade locked intramedullary nail: clinical experience and long-term results Gabriele Campochiaro,Paolo Baudi,Roberta Loschi, F. Serafini, Fabio Catani Department of Orthopaedic and Traumatology, Modena Policlinic, University of Modena and Reggio Emilia Summary. Backgound: indications for surgical treatment of complex humeral shaft fractures are still controversial. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the outcomes of treating humeral shaft fractures using antegrade locked intramedullary nail, compared to the treatment with traditional more aggressive techniques such as plate and screws. Methods: between February 2008 and January patients were treated with antegrade locked intramedullary nail for humeral shaft fractures, divided according to the AO classification. 28 patients were clinically followed: disability, pain and functional recovery were evaluated using the Constant score and DASH score and the ROM of the shoulder was checked. Results: Bony union was obtained in 27 patients at a mean time of 2.7 months. One fracture ended in nonunion, healed after replacing the nail with a longer one. Patients achieved satisfactory shoulder function with a mean Constant score of points and with a mean DASH score of 4.69 points. There were no other complications. Conclusion: the antegrade locked intramedullary nail represents a recommended option for the treatment of humeral shaft fractures, obtaining a steady synthesis, a short time of consolidation and a rapid functional recovery. ( Key words: fracture, humeral shaft, intramedullary nail Introduction The humeral shaft extends from the lower edge of the pectoralis major insertion to the supracondylar ridge of the distal humerus. The fracture which occurs in this space is called humeral shaft fracture, which is found in a proportion of about 3% of all the fractures (1). These fractures usually present with two incidence peaks: a peak below 50 years, with a clear predominance of males, and one above 70 years, with a predominance of females (2). The causes in younger patients are commonly represented by high-energy trauma (car accident or sports injury), while in older patients by lower energy trauma (such as an accidental fall), but they often associated with osteoporosis. AO classification is based on simple criterions: it divides the humeral shaft fractures in 3 main groups: type A (simple fractures with two fragments), type B fractures (three fragments), type C (complex fractures with four or more fragments or comminuted) (3). Epidemiologically, type A fractures appear to be prevalent with 63% of cases, while type B and C are found respectively in 26.2% and 10.4% of cases (2-4). From the biomechanical point of view, the morphology of the fracture is related to the intensity of trauma and to the site of the lesion. In the low-energy trauma, there is commonly a modest displacement of fracture fragments, especially in old patient with osteoporosis, while in the high-energy trauma there is a comminution of the fracture. The site of the lesion
2 70 G. Campochiaro,P.Baudi,R. Loschi, F.Serafini, F. Catani determines a different morphology of the fracture according to the different stress exerted by muscles groups, and therefore we can find a the different secondary displacement as Fernandez-Esteve described in the functional classification of humeral shaft fractures (5). There is a debate about the choice of treatment of humeral shaft fractures. It has been shown that an adequate conservative treatment allows a high rate of healing (24). However, the casts are not very tolerated and long periods of immobilization can lead to a stiffness of the shoulder and literature underlines the problems associated with nonoperative treatment, such as an increased frequency of nonunion. (6-7). Compared to the past when nonoperative treatment was considered the gold standard, now there is the belief that surgical treatment can offer superior advantages in terms of final outcomes and patient management, especially in those fractures characterized by a unacceptable orthopedic reduction, by the presence of a exposed or bifocal fracture, by the concomitant radial nerve palsy, or by general conditions, such as polytraumatic patient, which require a synthesis in a short time. Surgical treatment is caracterized by a more efficient and accurate reduction and an immediate stability that helps to reduce pain. The purposes of the surgical treatment are the reduction with restoration of the length and the control of rotations (peri-humeral muscular structures can tolerate an anterior angle of 20, varus of 30 and a shortening of 3 cm without the deterioration of the functionality and the morphology (8), while rotational defects, in particular the internal rotation, are less acceptable). Other purposes are the stabilization and early mobilization of neighboring joints. The literature describes several surgical options of treatment: plates and screws (ORIF), external fixators, the antegrade and retrograde intramedullary nail fixation (CRIF). The use of locked intramedullary nails with advanced technology has allowed us to obtain better results compared to the past and now several publications highlight the good results in the treatment of these fractures with this method ( ). This intervention, using a minimal surgical access, offers the advantages of the preservation of the site of fracture, and it maintains the vascularity and the biologic bone repair; however, it exposes the orthopedic surgeons at a moderate load of radiations. The intramedullary nailing also has disadvantages represented by the juxta-articular fractures, particularly the distal ones, fractures in childhood and puberty, and fracture of the medullary canal with obstruction or concomitant infection (13-14). Objectives The objectives of this study are to examine the advantages and disadvantages of surgical treatment of complex humeral shaft fractures with minimally invasive surgical technique based on the introduction of the antegrade locked intramedullary nail, compared to the treatment with traditional more aggressive techniques such as plates and screws. Materials and methods In the period between February 2008 and January 2011 at the Orthopedic department of Polyclinic of Modena, 38 patients were treated with intramedullary nail Polarus for multifragmentary humeral shaft fracture. In two cases a mini-open access was associated for the stabilization of a fragment with screws. According to the classification AO-ASIF, 34 cases of complex fractures were divided into 12-B type with three fragments (89%) and 4 cases in 12-C comminuted fractures type (11%). It s been possible to control clinically and radiographically 28 patients, 9 males (32%) and 19 females (68%) with an average age of years (Stand. Dev. 18,3), with a follow-up of 19 months (range 6-32 months). 9 patients were not traceable and one patient died other causes. The right side was affected in 15 cases (54%), the left side in 13 cases (46%). The dominant side was involved in 19 cases (68%). The mechanism of injury was a trauma for an accidental fall to the ground in 25 cases (89%), a motorcycle crash in 2 cases (7%) and 1 case of traction injury (4%) (Table 1). The exclusion criteria for our study were pathologic fractures, nonunions, fractures associated with radial nerve injury.
3 Complex fractures of the humeral shaft treated with antegrade locked intramedullary nail 71 Notes for the surgical technique All patients were treated with intramedullary nail Polarus Plus Acumed with antegrade insertion (Fig. 1). The antegrade nailing requires particular attention in the surgical access. The patient is positioned in a beach chair by performing an access of 3 cm in line with the anterolateral fibers of the deltoid muscle. After the split of the deltoid, the surgeon has to lance the supraspinatus tendon, on the outside of the insertional area of the tendon and along the course of its fibers in order to Table 1. Age Gender Mechanism of Injury Classification Side 1 20 M MC 12-C2.2 LD 2 80 M AF 12-B1.1 L 3 75 M AF 12-B1.2 RD 4 82 F AF 12-B1.1 RD 5 62 F AF 12-B1.1 LD 6 84 F AF 12-B1.2 RD 7 48 M MC 12-B1.2 L 8 76 M AF 12-C1.1 L 9 42 M TI 12-B1.1 RD F AF 12-B1.2 RD F AF 12-B2.2 RD F AF 12-B1.1 LD F AF 12-B1.1 RD F AF 12-B1.1 RD F AF 12-B1.2 RD F AF 12-B3.1 L F AF 12-B1.1 L M AF 12-B2.2 RD F AF 12-B1.1 RD F AF 12-B1.2 L F AF 12-B2.2 L M AF 12-B2.2 RD M AF 12-B2.2 RD F AF 12-B2.2 RD F AF 12-C1.1 L F AF 12-B1.2 L F AF 12-B1.2 RD F AF 12-B1.2 RD avarage 67,75 M = 32% AF= 89% 12B = 89% R = 54% F = 68% MC= 7% 12C = 11% L = 46% TI= 4% D = 68% Stand. Dev. 18,30 Mechanism of Injury: AF: Accidental Fall; MC: Motorcycle Crash; TI: Traction Injury Side: L= Left; R= Right; D= Dominant
4 72 G. Campochiaro,P.Baudi,R. Loschi, F.Serafini, F. Catani reduce functional complications (17). The entry point is medial to the great tubercle. It s important to insert the antegrade nail at least at 4 mm below the articular surface to avoid the subacromial impingment, determined by the protrusion of the nail within the subacromial space. The nail, occuping a reduced intramedullary space, doesn t require the enlargement of the medullary canal, with the exception of the proximal part, that is performed with suitable introducers. A series of interchangeable masks allows an easy stabilization, and it is led both proximally at the level of the humeral head with 4 screws (two 5 mm screws and two 3.5 mm screws) and distally with a 3.5 mm screw, avoiding the use of freehand stabilization techniques, which ask a long time of execution. These characteristics allow good control of the rotations, which is essential in the treatment of fractures with several fragments. Rati ng All patients were clinically reviewed with the use of the Constant score (0-100) and the Dash score (Disability Assessment for the Shoulder and Hand) and radiographically controlled with assessment at 1 month, 3 months and 6 months after surgery (Fig. 2). Clinically, we have checked the ROM of patients evaluating the degrees of abduction, flexion, external rotation and internal rotation of the shoulder. Figure 1. Polarus Plus Acumed intramedullary nail Figure 2. Male, 20 years old, motorcycle crash, plurifragmentary fracture with a fragment in humeral shaft (12-C2.2), treated with Polarus Plus Acumed nail and radiographical controlled at months after surgery. The upper limb disability was measured with the DASH questionnaire, which investigates both on the physical and social function, both on symptoms of upper limb, and it consists of a questionnaire of 30 questions, which allows to obtain a score between 0 and 100, where a high DASH score indicates severe disability. (18). The Constant score is a scoring system that provides to evaluate all the clinical aspects related to the functional recovery. The evaluation scheme is divided into 4 parts, and it consider respectively: pain (15 points), the common daily activities (20 points), the excursions of motion (40 points) and strength (25 points), for a total maximum of 100 points for a normal shoulder. The score decreases if there are any functional impairments. A normal shoulder has a Constant score of 100 points (19).
5 Complex fractures of the humeral shaft treated with antegrade locked intramedullary nail 73 Results At follow-up of 24 months (range months) 28 patients were reviewed, and they were followed until complete healing. The fracture healing was obtained in 27 patients (96.4%) with a mean time of radiographic union of 2.7 months (min 1, max 5.2) after surgery. Only one case (3,6%) has evolved into nonunion, which required the replacement of the nail with a new longer nail and autologous bone graft with subsequent healing. Apart from this case, no other failures of fixation occurred and there were no cases of infection or peripheral-nerve-damage. Clinically, we found a Constant score of points (stand. Dev. 12,09) and a DASH score of 4.69 (stand. Dev. 9,95). Assessing the ROM of the operated shoulder, we got a mean abduction of (stand. Dev. 31,21), an average flexion of (stand. Dev. 29,93), an average external rotation of (stand. Dev. 17,50) and an internal rotation in 18 patients up to D7 (Table 2). In 93% of cases the patient reported a good or excellent subjective satisfaction. The full resumption of daily activities occurred after a mean of 2.8 months after surgery, professional and sports activities after 4.1 months. Some patients reported moderate pain at rest, and two of these cases were completely resolved with the removal of the intramedullary nail. Conclusions Currently there is no universally accepted surgical technique for the treatment of diaphyseal fractures of the humerus, and in the literature different methods of fixation show variable results. Our study has produced comparable results to those reported by similar studies in terms of average time of healing and complication rate. In particular, Biggi et al. examined 50 humeral shaft fractures treated with antegrade intramedullary nailing in 76% and with retrograde nailing in 24%, and they have achieved complete consolidation in 96% of cases in an average time of 3 months and a sore consolidation with nonunion in 4%. (16). In the case of a fracture of the humeral diaphysis with a surgical indication, it isn t still recognized if it is better to proceed with an intramedullary nail or a compression plate. In our study, we evaluated the results of surgical treatment of minor impact for the resolution of this type of fracture, highlighting the advantages of a less invasive but equally effective for the healing of so complex fractures. Antegrade intramedullary nailing has many advantages: it is simple to perform, it doesn t expose the site of fracture, it respects the biology of osteosinthesis, allowing an immediate primary stability and early functional recovery. The Polarus Plus nail well responds to these purposes for its features; the dedicated instruments make easier the distal stabilization, allowing good control of the rotations, the reduced intramedullary space also allows the possible use of metal screws for the synthesis of free fragments. This type of technique has resulted in complete healing in 97.4% of cases at 2 months postoperatively, the humeral axis was always correctly restored and there were no migration of free fragments. This technique is indicated in all humeral fractures regardless of their morphology and extension, while it isn t indicated for distal juxta-articular fractures, for joints fractures, for fractures in childhood, and those severely displaced associated with radial nerve palsy, in which however it is advisable the direct nerve exploration and the plate osteosynthesis. The literature ( ) indicates a valid option for the treatment of these lesions also open osteosynthesis with plate and screws with the aim of restoring the proper bone contact and control of free fragments. The plaque technique makes it possible the anatomical synthesis of fragments, it prevents the onset of the outbreak and hypertrophic ossification, and it allows the revision of the radial nerve, which is often affected in humeral shaft fractures. (22). However, this technique exposes patients to increased risk of nonunion, infection and iatrogenic nerve injury. In our study, we have virtually wiped out the potential complications that are observed in the use of more aggressive surgical procedures, such as infection, dehiscence of the wound, soft tissue damage, iatrogenic nerve injury of radial nerve. We recorded one case of pseudoarthrosis, equal to 3.6% of all treated cases, which represents a lower value than the data reported in the literature, of 6-8%, with the use of the plate (20) and
6 74 G. Campochiaro,P.Baudi,R. Loschi, F.Serafini, F. Catani Table 2. Follow Up Dash Score Constant Score ROM Abduction Flexion Extrarotation Intrarotation , D , D , D , D , D , L , L , D , L , D , D , D , L , D , D , D , D , D , D , D , D , D , D , D , D , D , D , D7 Standard 7,77 9,95 12,09 31,21 29,93 17,50 deviation Media 19,25 4,69 90,57 161,07 164,24 77,14 D7=64% D12=21% L3=4% L5=11% Min max 32 37,
7 Complex fractures of the humeral shaft treated with antegrade locked intramedullary nail 75 Figure 3. Male, 76 years old, accidental fall, 3 fragments fracture of the left proximal humeral shaft (12-C1.1) treated with Polarus Plus Acumed nail and e 7 interfragmentary screws. Clinical controlled at 12 after surgery with Constant score = 92 and Dash score = 1. Radiographical control before and after surgery. even lower than those reported in the literature, with the use of the intramedullary nail. (5%) (20) In relation to criticism (20) to the use of antegrade intramedullary nails for the possible deleterious effects on the rotator cuff, in our series we recorded very satisfactory average values of the Constant score (90.57). This value can be compared with the results published by Jiang et al (23): with the use of a compression plate for complex humeral shaft fractures they have achieved a Constant score of 83.1 points (range ) and averaged values of abduction 142 (range ) and averaged flexion 164 (range ), lower than the values that we collect. We have had some cases of pain at rest, two of them were completely resolved with the removal of the nail, 4 more cases improved with the physiotherapy treatment. In one case (fig. 3), it was necessary to open the focus of fracture because, during the surgery, we couldn t reduce the diaphyseal fragments and we had to stabilize them with 7 screws to made synthesis with the nail. Probably, this case was border line for indication of treatment with intramedullary nail and the best choice for this fracture was the reduction and synthesis with plate and screws. In conclusion, the plurifragmentary humeral shaft fractures can be treated in different ways. In our opinion antegrade locked intramedullary nailing represents a surgical alternative to open techniques to keep in consideration in the treatment of diaphyseal fractures with multiple fragments. In particular the use of locked intramedullary nail has allowed us to obtain stable synthesis, optimization of time of healing, recovery of the humeral axis, enabling even the combination of fixation with interfragmentary screws. The good results and the low number of complications justify our interest in this type of method. References 1. Fernandez F et al. Five Years Clinical experience with unreamend humeral nail in the treatment of humeral shaft fractures. Injury 2004 mar;35(3): EkHolm R, Adami J, Tidermark J et al (2006) Fractures of the shaft of the humerus. An epidemiological study of 401 fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88: Murphy W M, Ruedi TP(2001) Principi AO per il trattmento delle fratture Edizioni CIC, Roma 4. Tytherleigh-Strong G, Walls N, Mc Queen MM (1998) The epidemiology of humeral shaft fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 80: Diaria A, Bottai M, Marchetti N, Spinelli M, Fernandez- Esteve F et al (1979) I gessi funzionali: prinicipi generali, indicazioni, tecnica e risultati. Edizioni Scientifiche della Clinica Ortopedica dell Università di Pisa 6. Ring D, Chin K, Taghinia AH, Jupiter JB (2007) Nonunion after functional brace treatment of diaphyseal humerus fractures. J Trauma 62: Rosenberg N, Soudry M (2006) Shoulder impairment following treatment of diaphyseal fractures of humerus by functional brace. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 126: Klenerman L(1969) Experimenatl fractures of the adult humerus. Med Biol Eng 7: Petsatodes G et al. Antegrade interlocking nailing of humeral shaft fractures. JOS 2004, 9: Interlocking nailing of humeral shaft fractures a retrospective study of 114 patients. Indian J Med Sci. 2005,Oct 59(10): Mallick E. The fixion nailing system for stabilising diaphyseal fractures of the humerus: a two-year clinical experience. Acta Orthop Belg 2008, Jun 74(3): Muckley T et al. Results of the T2 humeral nailing system with special focus on compression interlocking. Injury 2008 mar; 39(3):
8 76 G. Campochiaro,P.Baudi,R. Loschi, F.Serafini, F. Catani 13. Watanabe RS (1993) Intramedullary fixation of complicated fractures of the humeral shaft. Clin Orthop 292: Lin J, Hou SM (2003) Locked nailing of severely comminuted or segmental humeral fractures. Clin Orthop 406: Schoots IG, Simons MP, Nork SE et al (2007) Antegrade locked nailing of open humeral shaft fractures. Orthopedics 30: Biggi F, Di Fabio S, D Antimo C et al (2008) Inchiodamento endomidollare anterogrado e retrogrado nelle fratture diafisarie dell omero. GIOT 34: Berizzi A, Aldeghieri R (2008) I chiodi bloccati anterogradi nelle fratture omerali. Studio retrospettivo. Aggiorn Club Ital Osteosint 14(suppl.): Hudak PL,Amadio PC Bombardier C(1996) Development of an upper extremity outcome measure: the DASH Disabilities of the Arm, Shoulder, and Hand. The Upper Extremity Collaborative Group (UECG) Am L Ind Med 29: Constant CR, Murley AHG : A clinical method of functional assesment of the shoulder. Clin Orthop. 1987;214: Singisetti K, Ambedkar M. Nailing vs plating in humerus shaft fractures: a prospective comparative study. International Orthopaedics Dic Chao tc et al. Humeral shaft fractures treated by dynamic compression plate, Ender nails and interlocking nails. Int Orth, 2005 apr;29(2): Bell M, Beauchamp C, Mcmurty R. The results of plating humeral shaft fractures in patients with multiple injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Br 1985; 67: Jiang R. et. Al. Minimally invasive plating for complex humeral shaft fractures. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, : Fontanesi G. Libri R, Masetti G, et al. Trattamento cruento delle fratture diafisarie di omero. Chir Org Mov : Received: 5 January 2014 Accepetd: 17 March 2014 Correspondance: Dr. Gabriele Campochiaro Via del Pozzo, Modena campochiaro.g@libero.it
The study of distal ¼ diaphyseal extra articular fractures of humerus treated with antegrade intramedullary interlocking nailing
 2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
2018; 4(4): 46-50 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(4): 46-50 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-08-2018 Accepted: 03-09-2018 Dr. Ankur Parikh Orthopaedics, Jehangir Hospital, Sassoon road, Pune, Dr.
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do?
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Complex fractures of the humeral shaft. Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden
 Complex fractures of the humeral shaft Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Kopenhagen 2018 Complex fracture Changes in the AO/OTA classification system Complex Multifragmentary
Complex fractures of the humeral shaft Janos Solyom Sahlgrenska University Hospital Gothenburg, Sweden Kopenhagen 2018 Complex fracture Changes in the AO/OTA classification system Complex Multifragmentary
Humeral shaft fractures: retrospective results of non-operative and operative. treatment of 186 patients
 1 2 3 4 Humeral shaft fractures: retrospective results of non-operative and operative treatment of 186 patients Kiran C. Mahabier, MD 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels, MD 1, Bas J. Punt, MD 2, Gert R. Roukema, MD
1 2 3 4 Humeral shaft fractures: retrospective results of non-operative and operative treatment of 186 patients Kiran C. Mahabier, MD 1, Lucas M.M. Vogels, MD 1, Bas J. Punt, MD 2, Gert R. Roukema, MD
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures. OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD
 Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 299-303 ORIGINAL STUDY Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results Anani ABALO, Ekoué D. DOSSEh, Komlan ADABRA, Atsi WALLA,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2011, 77, 299-303 ORIGINAL STUDY Open reduction and internal fixation of humeral non-unions : Radiological and functional results Anani ABALO, Ekoué D. DOSSEh, Komlan ADABRA, Atsi WALLA,
Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective clinical and radiographic assesment
 ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
ARS Medica Tomitana - 2013; 4(75): 197-201 DOI: 10.2478/arsm-2013-0035 Șerban Al., Botnaru V., Turcu R., Obadă B., Anderlik St. Fractures of the tibia shaft treated with locked intramedullary nail Retrospective
Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2006, 72, 395-399 ORIGINAL STUDY Posteromedial approach to the distal humerus for fracture fixation Cédric LAPORTE, Maurice THIONGO, Dominique JEGOU From the General Hospital of Meaux,
Modified extra rotator-cuff entry point in antegrade humeral nailing
 Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2005) 125: 27 32 DOI 10.1007/s00402-004-0757-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Panayiotis Dimakopoulos Æ Andreas X. Papadopoulos Michalis Papas Æ Andreas Panagopoulos Æ Elias Lambiris Modified
Arch Orthop Trauma Surg (2005) 125: 27 32 DOI 10.1007/s00402-004-0757-3 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Panayiotis Dimakopoulos Æ Andreas X. Papadopoulos Michalis Papas Æ Andreas Panagopoulos Æ Elias Lambiris Modified
A clinical study of minimal invasive anterior bridge plating for humerus shaft fractures
 2018; 4(2): 01-05 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 01-05 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2018 Accepted: 02-03-2018 Mohammed Ibrahim Dr. Vijay H Rathod A clinical study of minimal invasive
2018; 4(2): 01-05 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(2): 01-05 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 01-02-2018 Accepted: 02-03-2018 Mohammed Ibrahim Dr. Vijay H Rathod A clinical study of minimal invasive
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE
 EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
EVIDENCE BASED MEDICINE VOICE Orthofix approach to Evidence Based Medicine: For years, clinical decision-making was based primarily on physician knowledge and expert opinion. Now, the medical community
INTERNAL FIXATION OF THE METACARPALS AND PHALANGES P. BURGE
 Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 INTERNL FIXTION OF THE METCRPLS ND PHLNGES P. URGE Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford, UK SUMMRY Techniques and instrumentation for open reduction and internal fixation
Riv Chir Mano - Vol. 43 (3) 2006 INTERNL FIXTION OF THE METCRPLS ND PHLNGES P. URGE Nuffield Orthopaedic Centre, Oxford, UK SUMMRY Techniques and instrumentation for open reduction and internal fixation
陳書佑 / 吳基銓副部長
 陳書佑 / 吳基銓副部長 2012-12-25 1 30 y/o male, TA no radial nerve injury 2 s/p splint arrange functional brace 3 1 month 4 2 months 5 3 months 6 4 months 7 One year 8 Conservative Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures
陳書佑 / 吳基銓副部長 2012-12-25 1 30 y/o male, TA no radial nerve injury 2 s/p splint arrange functional brace 3 1 month 4 2 months 5 3 months 6 4 months 7 One year 8 Conservative Treatment of Humeral Shaft Fractures
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty
 Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
Elbow Fractures ORIF VS Arthroplasty Oke Anakwenze, M.D. Olympus Orthopedics No disclosures Disclosures Distal humerus fractures 0.5-0.7% of all fractures 30% of all elbow fractures Bimodal etiology Young
P.R.C.T II FIXATION PLATE FOR ARTICULAR FRACTURE OF THE PROXIMAL HUMERUS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 P.R.C.T II FIXATION PLATE FOR ARTICULAR FRACTURE OF THE PROXIMAL HUMERUS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INDICATIONS - Surgical technique...page 0 - Mini invasive approach...page 04 - Diaphyseal plates...page 05 -
P.R.C.T II FIXATION PLATE FOR ARTICULAR FRACTURE OF THE PROXIMAL HUMERUS SURGICAL TECHNIQUE INDICATIONS - Surgical technique...page 0 - Mini invasive approach...page 04 - Diaphyseal plates...page 05 -
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
UPPER LIMB TRACTION DEVICE FOR ANTEROGRADE INTRAMEDULLARY LOCKED NAIL OF HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES
 PRELIMINARY NOTE UPPER LIMB TRACTION DEVICE FOR ANTEROGRADE INTRAMEDULLARY LOCKED NAIL OF HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Mário Chaves Corrêa 1, Felipe Antônio Gomes 2, Daniel Campos Linhares 2, Lucas Braga Jacques
PRELIMINARY NOTE UPPER LIMB TRACTION DEVICE FOR ANTEROGRADE INTRAMEDULLARY LOCKED NAIL OF HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Mário Chaves Corrêa 1, Felipe Antônio Gomes 2, Daniel Campos Linhares 2, Lucas Braga Jacques
Surgical Technique. Intramedullary locked Nailing With Screws for Humerus Fractures Solid/Cannulated. Humeral Interlocking Nail.
 Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
Screws for Humerus Fractures Surgical Technique Humeral Interlocking Nail Approved by Humerus Nail Kit Code 08050001 Contents Introduction Implant design Indications Pre-operative planning Patient positioning
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails
 Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Angular Malalignment in Subtrochanteric and Proximal Shaft Femur Fractures after Intramedullary Nailing using SIGN Nails Rolando Junior L. Torres, MD Jeremiah R. Morales, MD, FPOA Subtrochanteric Femur
Index. B Backslap technique depth assessment, 82, 83 diaphysis distal trocar, 82 83
 Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Index A Acromial impingement, 75, 76 Aequalis intramedullary locking avascular necrosis, 95 central humeral head, 78, 80 clinical and functional outcomes, 95, 96 design, 77, 79 perioperative complications,
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Złamania trzonu kości ramiennej kiedy nie operować?
 Złamania trzonu kości ramiennej kiedy nie operować? Jakub Kamiński, Damian Kusz. Humeral shaft fractures when not to operate? Jakub Kamiński, Damian Kusz. Humeral shaft fx general considerations Incidence
Złamania trzonu kości ramiennej kiedy nie operować? Jakub Kamiński, Damian Kusz. Humeral shaft fractures when not to operate? Jakub Kamiński, Damian Kusz. Humeral shaft fx general considerations Incidence
Dr. Raja Rathnam Korani
 2018; 2(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(1): 06-10 Received: 12-11-2017 Accepted: 15-12-2017 Civil Surgeon Specialist, District
2018; 2(1): 06-10 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(1): 06-10 Received: 12-11-2017 Accepted: 15-12-2017 Civil Surgeon Specialist, District
Mark VanDer Kaag 1, Ajmal Ikram 2. Hand Unit, Tygerberg Hospital University of Stellenbosch
 A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
A Prospective, Randomized Controlled Study To Determine The Radiological And Functional Outcomes Of IMN Fixation Of Distal Radius Fractures Using A Novel Device The Sonoma Wrx Distal Radius Nail Compared
Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments.
 CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
CAPITELLAR FRACTURE Vasu Pai Nearly all of these fractures are displaced, given the paucity of soft tissue attachments. Nonsurgical management is fraught with complications including chronic pain, mechanical
Techique. Results. Discussion. Materials & Methods. Vol. 2 - Year 1 - December 2005
 to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
to each other. The most distal interlocking hole is 3 mm proximal to distal end of nail, is in anteroposterior direction & proximal distal interlocking hole is in medial to lateral direction i.e. at right
DISTAL HUMERUS FRACTURES WHAT I HAVE LEARNED DISTAL HUMERUS FRACTURES WHAT I HAVE LEARNED 63 YO WOMAN CT FIXABLE OSTEOTOMY NOT NEEDED
 AMERICAN SHOULDER AND ELBOW SURGEONS ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA ASSOCIATION SPECIALTY DAY SAN DIEGO, MARCH 2017 Graham JW King MD, MSc, FRCSC 63 YO WOMAN CT FIXABLE OSTEOTOMY NOT NEEDED 64 YO WOMAN FALL OF LADDER
AMERICAN SHOULDER AND ELBOW SURGEONS ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA ASSOCIATION SPECIALTY DAY SAN DIEGO, MARCH 2017 Graham JW King MD, MSc, FRCSC 63 YO WOMAN CT FIXABLE OSTEOTOMY NOT NEEDED 64 YO WOMAN FALL OF LADDER
Case Presentation: Comminuted Fractures of the Proximal Ulna 11/28/2017. Disclosures. Surgical Strategy. Implant Choice. Melvin P.
 Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
Current Solutions in Orthopaedic Trauma Case Presentation: Comminuted Fracture of the Proximal Ulna Melvin P. Rosenwasser, MD Robert E. Carroll Professor of Surgery of the Hand Chief, Orthopaedic Hand
Management of Fractures. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5
 Management of Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5 Common methods of fracture immobilization Plaster of Paris (POP): A high quality gypsum The standard method of external splinting
Management of Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 5 Common methods of fracture immobilization Plaster of Paris (POP): A high quality gypsum The standard method of external splinting
International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURE FIXATION WITH ANTEGRADE INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL: A STUDY ABSTRACT
 Research Article Orthopedics International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURE FIXATION WITH ANTEGRADE INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL: A STUDY 1 DR.RAJU KULKARNI
Research Article Orthopedics International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURE FIXATION WITH ANTEGRADE INTRAMEDULLARY INTERLOCKING NAIL: A STUDY 1 DR.RAJU KULKARNI
Functional outcome of antegrade interlocking intramedullary nailing for humeral shaft fractures
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Rajagopal HP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Nov;3(6):1127-1131 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20174147
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Rajagopal HP et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Nov;3(6):1127-1131 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20174147
E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus
 Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Shoulder & Elbow. ISSN 1758-5732 E ORIGINAL ARTICLE Low extra-articular (transcondylar) fractures of the distal humerus Alexander A. Weening, Kim M. Brouwer, Margaritha Adams & David Ring Orthopaedic Hand
Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 1 Closed reduction and internal fixation of fractures of the shaft of the femur by the Titanium Elastic Nailing System in children.
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons.
 Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
Locked plating constructs are creating a challenge for surgeons. Three recent studies examining supracondylar femur fractures show concern for the high degree of stiffness of locked plating constructs
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES
 BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
BRIDGE PLATING OF COMMINUTED SHAFT OF FEMUR FRACTURES Mohammad Abul kalam, Pradeep Kumar, Mohammad Afzal Hussain and Iqbal Ahmad Abstract A prospective study of forty comminuted femoral shaft fractures,
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow.
 Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Preliminary Report Choosing Wisely Identifying Musculoskeletal Interventions with Limited Levels of Efficacy in the Shoulder & Elbow. Prepared for The Canadian Orthopaedic Association Contents Executive
Humerus shaft - Reduction & Fixation - Compression plate - AO Surgery Reference. Compression plating
 Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Humerus shaft 12-A3 ORIF 1. Principles Compression plating Authors Compression plate Compression plating provides fixation with absolute stability for two-part fracture patterns, where the bone fragments
Forearm Fracture Solutions. Product Overview
 Forearm Fracture Solutions Product Overview Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions includes plating and rodding systems with a range of diaphyseal radius and ulna fracture
Forearm Fracture Solutions Product Overview Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions Acumed Forearm Fracture Solutions includes plating and rodding systems with a range of diaphyseal radius and ulna fracture
Results Of Antegrade Humeral Interlocking Nailing In Adults A Prospective Study. S Rawa, M Farooq, S Singh, M Wani, M Bhat, A Hussain, M Mussa
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 24 Number 2 Results Of Antegrade Humeral Interlocking Nailing In Adults A Prospective Study S Rawa, M Farooq, S Singh, M Wani, M Bhat, A Hussain, M Mussa
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Surgery Volume 24 Number 2 Results Of Antegrade Humeral Interlocking Nailing In Adults A Prospective Study S Rawa, M Farooq, S Singh, M Wani, M Bhat, A Hussain, M Mussa
Minimally Invasive Plating Osteosynthesis for Mid-distal Third Humeral Shaft Fractures
 Minimally Invasive Plating Osteosynthesis for Mid-distal Third Humeral Shaft Fractures Kejian Lian, MD; Lei Wang, MD; Dasheng Lin, MD; Zhiwen Chen, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics.
Minimally Invasive Plating Osteosynthesis for Mid-distal Third Humeral Shaft Fractures Kejian Lian, MD; Lei Wang, MD; Dasheng Lin, MD; Zhiwen Chen, MD abstract Full article available online at Healio.com/Orthopedics.
CASE REPORT. Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 79. 551 ~ 557, 2017 doi:10.18999/nagjms.79.4.551 CASE REPORT Distal radius nonunion after volar locking plate fixation of a distal radius fracture: a case report Takaaki Shinohara 1
AcUMEDr. Locking Proximal Humeral Plate. PoLARUSr PHPt
 AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
AcUMEDr Locking Proximal Humeral Plate PoLARUSr PHPt PoLARUSr PHPt LOCKING PROXIMAL HUMERAL PLATE Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons,
Treatment of fracture of shaft of humerus in adults by intramedullary interlocking nail fixation
 Original Article Chaudhary et.al. of shaft of humerus in adults by intramedullary interlocking nail fixation P Chaudhary, NK Karn, BP Shrestha, GP Khanal, RPS Kalawar Department of Othopaedics B.P. Koirala
Original Article Chaudhary et.al. of shaft of humerus in adults by intramedullary interlocking nail fixation P Chaudhary, NK Karn, BP Shrestha, GP Khanal, RPS Kalawar Department of Othopaedics B.P. Koirala
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
JMSCR Volume 03 Issue 02 Page February 2015
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Comparative Study of Functional Outcome of Compression Plating and Interlocking Nailing For Fracture Shaft Humerus in Adults Authors Dr.
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 3.79 ISSN (e)-2347-176x Comparative Study of Functional Outcome of Compression Plating and Interlocking Nailing For Fracture Shaft Humerus in Adults Authors Dr.
Antigrade Humerus Interlocking Nailing for Diaphyseal Fractures of Humerus: A Study of Clinical Outcomes
 Original Article Antigrade Humerus Interlocking Nailing for Diaphyseal Fractures of Humerus: A Study of Clinical Outcomes Prasanth Ganji *, PR Naidu Pothula, Nandam Ramarao, Raj Kumar Vijay, Bharath chandra
Original Article Antigrade Humerus Interlocking Nailing for Diaphyseal Fractures of Humerus: A Study of Clinical Outcomes Prasanth Ganji *, PR Naidu Pothula, Nandam Ramarao, Raj Kumar Vijay, Bharath chandra
Proximal Humerus Fractures
 Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Proximal Humerus Fractures Trafford General Hospital, June 2010 Nehmat Singh, Jawad Sultan Anatomy of the Proximal Humerus Consists of four parts: humeral head, surgical neck and greater and lesser tubercles
Upper limb fractures. Mithun Nambiar Orthopaedic Resident Royal Melbourne Hospital
 Upper limb fractures Mithun Nambiar Orthopaedic Resident Royal Melbourne Hospital http://janeaustensworld.files.wordpress.com/2010/10/17_skeleton.jpg Principles of fracture management Restoration of anatomy
Upper limb fractures Mithun Nambiar Orthopaedic Resident Royal Melbourne Hospital http://janeaustensworld.files.wordpress.com/2010/10/17_skeleton.jpg Principles of fracture management Restoration of anatomy
Segmental tibial fractures treated with unreamed interlocking nail A prospective study
 2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
2017; 3(2): 714-719 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2017; 3(2): 714-719 2017 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 13-02-2017 Accepted: 14-03-2017 Ashok Singhvi Hemant Jain Siddharth Jauhar Kishore Raichandani Segmental
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
THE HUMERUS 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW
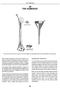 20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
20 THE HUMERUS* CROSS SECTION CROSS SECTION SUPERIOR VIEW The marrow canal of the humerus is funnel-shaped. Its successful pinning is influenced by many factors. With a few exceptions, the entire humerus
Injuries of the upper extremity
 Injuries of the upper extremity Dep. of Traumatology M.Szebeny Egon Schiele Sternoclavicular dislocation Direction: towards the outside or inside (what is behind the dislocation!) Reduction? Retention?
Injuries of the upper extremity Dep. of Traumatology M.Szebeny Egon Schiele Sternoclavicular dislocation Direction: towards the outside or inside (what is behind the dislocation!) Reduction? Retention?
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
CiSE. PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal Fractures of the Distal Humerus through an Anterolateral Approach. Introduction ORIGINAL ARTICLE
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.3.128 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 3, September, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.3.128 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow PHILOS Plate Osteosynthesis in Metaphyseal
3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 8. DISTAL GUIDED LOCKING FOR PROXIMAL NAIL PROXIMAL LOCKING FOR LONG NAIL 13
 Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL NAIL INSERTION 6-7 7. PROXIMAL LOCKING
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Medial approach to treat humeral mid-shaft fractures: a retrospective study
 Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:32 DOI 10.1186/s13018-016-0366-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Medial approach to treat humeral mid-shaft fractures: a retrospective study
Lu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2016) 11:32 DOI 10.1186/s13018-016-0366-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Medial approach to treat humeral mid-shaft fractures: a retrospective study
Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture
 Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture HT Ling, MBBS (UM), WM Ng, MS Ortho (UM), MK Kwan, MS Ortho (UM), LK Fathi Aizuddeen, MBBS (UM), PCM Tay, MBBS
Use of Unlocked Intramedullary Nailing in Winquist Type I and II Femoral Isthmus Fracture HT Ling, MBBS (UM), WM Ng, MS Ortho (UM), MK Kwan, MS Ortho (UM), LK Fathi Aizuddeen, MBBS (UM), PCM Tay, MBBS
THE NANCY NAIL. The End Caps ADVANTAGES OF NANCY NAIL
 NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
NANCY NAIL THE NANCY NAIL Nancy nails are manufactured from a specific titanyum alloy with proprietary surface treatment, which provides increased fatigue resistance. Six nail diameters (1.5 mm 2.0 mm
Recurrent subluxation or dislocation after surgical
 )263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
)263( COPYRIGHT 2017 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY CASE REPORT Persistent Medial Subluxation of the Ulna with Radiotrochlear Articulation Amir R. Kachooei, MD; David Ring, MD, PhD Research
Nonunion of the Femur Treated with Conventional Osteosynthesis Combined with Autogenous and Strut Allogeneic Bone Grafts
 Original Article 268 Nonunion of the Femur Treated with Conventional Osteosynthesis Combined with Autogenous and Strut Allogeneic Bone Grafts Lin-Hsiu Weng, MD; Jun-Wen Wang, MD Background: In this study,
Original Article 268 Nonunion of the Femur Treated with Conventional Osteosynthesis Combined with Autogenous and Strut Allogeneic Bone Grafts Lin-Hsiu Weng, MD; Jun-Wen Wang, MD Background: In this study,
Open reduction; plate fixation 1 Principles
 Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Executive Editor: Peter Trafton Authors: Martin Jaeger, Frankie Leung, Wilson Li Proximal humerus 11-A2 Open reduction, plate fixation Search search... Shortcuts All Preparations All Approaches All Reductions
Operative treatment of clavicle midshaft fractures using a locking compression plate: Comparison between mini-invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPPO)
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 666 671 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of clavicle midshaft fractures using a locking compression
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (2012) 98, 666 671 Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ORIGINAL ARTICLE Operative treatment of clavicle midshaft fractures using a locking compression
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of The Tibia
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 17 Number 2 A Clinical Study For Evaluation Of Results Of Closed Interlocking Nailing Of Fractures Of The Shaft Of R Gupta, T Motten, N Kalsotra,
Radial Nerve Palsy Following Fractures of the Humerus
 Radial Nerve Palsy Following Fractures of the Humerus Mike Starecki, MD Atlanta Trauma Symposium April 21 st, 2018 No Disclosures Humeral Shaft and Radial Nerve 237,000 humeral shaft fractures in the US
Radial Nerve Palsy Following Fractures of the Humerus Mike Starecki, MD Atlanta Trauma Symposium April 21 st, 2018 No Disclosures Humeral Shaft and Radial Nerve 237,000 humeral shaft fractures in the US
Surgical treatment of acute and chronic acromioclavicular dislocation Tossy type III and V using the Hook Plate
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 4, 441-44 ORIGINAL STUDY Surgical treatment of acute and chronic acromioclavicular dislocation Tossy type and using the Hook Plate Samir EJAM, Thomas LIND, Boe FALKENBERG From
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2008, 4, 441-44 ORIGINAL STUDY Surgical treatment of acute and chronic acromioclavicular dislocation Tossy type and using the Hook Plate Samir EJAM, Thomas LIND, Boe FALKENBERG From
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES
 COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF FUNCTIONAL OUTCOME OF EXTERNAL AND INTERNAL FIXATION IN TREATMENT OF COMMINUTED DISTAL RADIUS FRACTURES R. Sahaya Jose 1 1Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, Sree Mookambika
Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
Tibial Shaft Fractures Mr Krishna Vemulapalli Consultant Orthopaedics Surgeon Queens & King George Hospitals Queens Hospital 14/03/2018 Google Maps Map data 2018 Google 10 km Orthopaedics Department Covers
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT. By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg
 MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series
 Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Article ID: WMC005027 ISSN 2046-1690 Crossed Steinmann Pin Fixation In Supracondylar Femur Fractures In Adults A Case Series Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohit K Jindal, Senior Resident,
Percutaneous elastic fixation of proximal humeral fractures: operative indications, techniques, results and complications
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2002) 2:157 164 Springer-Verlag 2002 ORIGINAL M.A. Rosa G. Maccauro T. Nizegorodcew G. Falcone F. Di Segni Percutaneous elastic fixation of proximal humeral fractures: operative
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2002) 2:157 164 Springer-Verlag 2002 ORIGINAL M.A. Rosa G. Maccauro T. Nizegorodcew G. Falcone F. Di Segni Percutaneous elastic fixation of proximal humeral fractures: operative
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES
 MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR. Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR. Introduction
 Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Xavier A. Duralde, MD Peachtree Orthopaedic Clinic Atlanta, GA Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Consultant: Smith+Nephew Board of Directors: CORR Introduction Incidence
Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Xavier A. Duralde, MD Peachtree Orthopaedic Clinic Atlanta, GA Proximal Humeral Fractures RSA v HHR Consultant: Smith+Nephew Board of Directors: CORR Introduction Incidence
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Minimally Invasive Helical Plating for Shaft of Humerus Fractures: Technique and Outcome
 184 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 184-188 Open Access Minimally Invasive Helical Plating for Shaft of Humerus Fractures: Technique and Outcome James Chung Hui Tan *,1,2, Fareed Husain Yusuf Kagda
184 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2012, 6, 184-188 Open Access Minimally Invasive Helical Plating for Shaft of Humerus Fractures: Technique and Outcome James Chung Hui Tan *,1,2, Fareed Husain Yusuf Kagda
Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4)
 AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus Plate
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 2, March: 643-650, 2017 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Open Reduction and Internal Fixation of Proximal Humeral Fractures with Use of the Locking Proximal Humerus
OF SURGICALLY TREATED FRACTURE FOREARM BONES WITH PLATING IN BOTH BONE VERSUS PLATING IN RADIUS AND NAILING IN ULNA
 www.ijmse.com International Journal Medical Science and Education An ficial Publication Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) Original Research Article pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208
www.ijmse.com International Journal Medical Science and Education An ficial Publication Association for Scientific and Medical Education (ASME) Original Research Article pissn- 2348 4438 eissn-2349-3208
1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint
 1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
Olecranon fracture. Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital
 Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Olecranon fracture Lonnie Froberg, MD, Ph.D Rigshospitalet, Copenhagen University Hospital 20% of forearm fracture 12 per 100.000 persons per year Low-energy fall Increased risk >50 years 90% AO 21.B1.1
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures
 Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Treatment Alternatives for Pediatric Femoral Fractures Gregory A. Schmale, MD Seattle Children's Hospital, USA, gregory.schmale@seattlechildrens.org version 2 I have no conflicts of interest to report
Distal Humerus Fractures: How should they be fixed?
 Distal Humerus Fractures: How should they be fixed? Dr. Emil Schemitsch, MD, FRCS(C) Richard Ivey Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery, Western University Chief of Surgery London Health Sciences
Distal Humerus Fractures: How should they be fixed? Dr. Emil Schemitsch, MD, FRCS(C) Richard Ivey Professor and Chairman, Department of Surgery, Western University Chief of Surgery London Health Sciences
A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures
 Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2016) 26:831 836 DOI 10.1007/s00590-016-1817-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SHOULDER - FRACTURES A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures F. R. Hashmi 1 Edgar
Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol (2016) 26:831 836 DOI 10.1007/s00590-016-1817-4 ORIGINAL ARTICLE SHOULDER - FRACTURES A new nail with a locking blade for complex proximal humeral fractures F. R. Hashmi 1 Edgar
AcUMEDr. LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM
 AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
AcUMEDr LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM LoCKING CLAVICLE PLATE SYSTEM Since 1988 Acumed has been designing solutions to the demanding situations facing orthopedic surgeons, hospitals and their patients.
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture.
 Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
Results of tibia nailing with Angular Stable Locking Screws (ASLS); A retrospective study of 107 patients with distal tibia fracture. stud. med. David Andreas Lunde Hatfield stud. med. Mohammed Sherif
System. Humeral Nail. Surgical Technique
 System Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL
System Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Contents IMPLANT FEATURES 2 1. INDICATIONS 3 2. PRE-OPERATIVE PLANNING 3 3. PATIENT POSITIONING & FRACTURE REDUCTION 3 4. INCISION 4 5. ENTRY POINT 4-6 6. PROXIMAL
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points. Christopher Iobst, MD
 Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
Pediatric Tibia Fractures Key Points Christopher Iobst, MD Goals Bone to heal Return to full weight bearing Acceptable alignment rule of 10s 10 degrees of varus 8 degrees of valgus 12 degrees of procurvatum
CiSE. Case Report CASE REPORT. Min Soo Shon, Tae Jung Bang, Jae Chul Yoo 1
 CASE REPORT Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 1, March, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.1.47 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Longitudinal Supraspinatus Tear Associated with Antegrade
CASE REPORT Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Vol. 18, No. 1, March, 2015 http://dx.doi.org/10.5397/cise.2015.18.1.47 CiSE Clinics in Shoulder and Elbow Longitudinal Supraspinatus Tear Associated with Antegrade
Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee): A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee):
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 4 Number 1 Retrograde Locked Intramedullary Nailing For The Stabilisation Of Femoral Fractures With Ipsilateral Tibial Fractures (Floating Knee):
Principles of intramedullary nailing. Management for ORP
 Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Principles of intramedullary nailing Eakachit Sikarinklul,MD Basic Principles of Fracture Management for ORP Bangkok Medical Center Bangkok, 22-24 July 2016 Learning outcomes At the end of this lecture
Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula
 Royal Liverpool & Broadgreen University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula Michael Smith MBChB, Zuned
Royal Liverpool & Broadgreen University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Intramedullary fibular fixation in the operative management of fractures of the distal tibia and fibula Michael Smith MBChB, Zuned
ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES
 CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
CHAPTER 31 ROTATIONAL PILON FRACTURES George S. Gumann, DPM The opinions and commentary of the author should not be construed as refl ecting offi cial U.S. Army Medical Department policy. Pilon injuries
THE RING BUTTERFLY FRAGMENT
 THE RING BUTTERFLY FRAGMENT Pages with reference to book, From 80 To 82 Philip D`Sousa, Masood Umer, Riaz Hussain Lakdawala ( Department of Surgery (Orthopaedics), The Aga Khan University, Karachi. ) In
THE RING BUTTERFLY FRAGMENT Pages with reference to book, From 80 To 82 Philip D`Sousa, Masood Umer, Riaz Hussain Lakdawala ( Department of Surgery (Orthopaedics), The Aga Khan University, Karachi. ) In
Olecranon Fractures. Olecranon Fx Anatomy. Olecranon Fx Considerations 4/26/2018
 Olecranon Fractures Allan Peljovich, MD, MPH The Hand & Upper Extremity Ctr of GA; Shepherd Center; Atlanta Medical Center Orthopedic Residency Program Olecranon Fx Anatomy Olecranon Fx Considerations
Olecranon Fractures Allan Peljovich, MD, MPH The Hand & Upper Extremity Ctr of GA; Shepherd Center; Atlanta Medical Center Orthopedic Residency Program Olecranon Fx Anatomy Olecranon Fx Considerations
1/19/2018. Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust)
 Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 11 Number 2 Type III Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus in Children Straight-Arm Treatment J Gandhi, G Horne Citation J Gandhi, G Horne..
