Short segment pedicle screw fixation for unstable T11-L2 fractures : with or without fusion? A three-year follow-up study
|
|
|
- Prosper Joseph
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2009, 75, ORIGINAL STUDY Short segment pedicle screw fixation for unstable T11-L2 fractures : with or without fusion? A three-year follow-up study Jin-Ho HWANG, Hitesh N. MODI, Jae-Hyuk YANG, Seong-Jun KIM, Suk-Ha LEE From the Division of Spine Surgery, Department of Orthopedics, Konkuk University Hospital, Seoul, South Korea In unstable thoracolumbar fractures T11-L2, exaggerated kyphosis at the end of treatment may predispose to late back pain and poor functional outcome. Short-segment (SS) (3 vertebrae) pedicle instrumentation has become a popular method of treatment. However the question to add a fusion or not is still under debate. The authors retrospectively evaluated the radiological and functional results in 74 patients who had undergone an SS pedicle screw fixation. They were divided into two groups : group 1 (39 patients) was the non-fusion group ; group 2 (35 patients) was the fusion group. In the non-fusion group the mean preoperative, immediate post - operative and final kyphosis angles at the fracture site were respectively 20.8 ± 6.4, 8.2 ± 4.8, and 15.2 ± 6.0. In the fusion group the corresponding angles were 26.6 ± 4.1, 7.9 ± 2.1, and 8.4 ± 2.4, which demonstrated a distinctly better final result (p < ). In the non-fusion group the preoperative, immediate postoperative and final follow-up visual analog scores (VAS) for back pain were respectively 7.3 ± 0.8, 3.9 ± 0.8, and 3.4 ± 0.9. In the fusion group the corresponding scores were 7.5 ± 1.0, 3.9 ± 1.1, and 1.6 ± 0.7 ; the final result pleaded again in favour of fusion (p < ). Moreover, there were significantly more implant-related complications (screw loosening and breakage) in the non-fusion group (p < ). The authors conclude that fusion is advisable to obtain a better final outcome with respect to kyphosis and pain, and to avoid implant-related complications. However, at least one other study has led to the opposite conclusion : the issue remains controversial. Keywords : unstable thoracolumbar fracture ; T11-L2 ; short-segment fusion ; pedicle screw ; fusion versus nonfusion ; kyphosis ; back pain. INTRODUCTION Thoracolumbar junction (T11-L2) burst fractures involve thoracic as well as lumbar vertebrae. Anatomically, however, the thoracic spine differs from the thoracolumbar junction, which again differs from the mid and lower lumbar spine. Over the course of healing, deformity will progress to some extent under physiologic loading. An exaggerated kyphosis at the end of treatment may predispose to late back pain and a poor functional outcome (7). Pedicle screw devices allow immediate stable fixation, as the screws traverse all the three columns. Jin-Ho Hwang, MD, Orthopaedic Fellow. Hitesh N. Modi, MS, Research Fellow. Jae-Hyuk Yang, MD, Orthopaedic Fellow. Seong-Jun Kim, MD, Orthopaedic Resident. Suk-Ha Lee, MD, PhD, Professor of Orthopaedic Surgery. Division of Spine Surgery, Department of Orthopaedics, Konkuk University Hospital, Seoul, South Korea. Correspondence : Suk-Ha Lee, Division of Spine Surgery, Department of Orthopaedics, Konkuk University Hospital, Seoul, South Korea. osshlee@gmail.com 2009, Acta Orthopædica Belgica. No benefits or funds were received in support of this study
2 FUSION OR NON-FUSION IN THORACOLUMBAR FRACTURES 823 Short-segment (SS) pedicle instrumentation has become a popular method since Dick et al (5) introduced the fixateur interne device. But the question to fuse or not to fuse in posterior short segment instrumentation for unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures is still under debate. Advocates of both techniques base their preference on variables such as maintenance of correction, pain, complications, operative time, blood loss etc... Lindsey and Dick (12) reviewed the clinical results of 80 patients after thoracolumbar spinal fractures treated with a fixateur interne. A fusion was added in only 30% of the cases, but no formal comparison was made between the non-fusion and the fusion group. Somehow, they felt that fusion was to be recommended. Wang et al (22) conducted a prospective randomized study in 58 patients with thoracolumbar and lumbar burst fractures, treated with short segment fixation. The radiographic parameters were significantly better in the nonfusion group ; there was no difference as to pain complaints. Their other arguments in favour of nonfusion were : elimination of donor site complications, preservation of more motion segments, and reduction of blood loss and operative time. METHODS The authors retrospectively evaluated the radiological and functional outcome in 74 patients whit unstable thoracolumbar spine fractures (T11-L2), operated in a single center, by two spine surgeons with similar experience (SHL, HJH). The first surgeon preferred SS pedicle screw fixation without fusion while the second one added a fusion. The non-fusion group (group 1) included 39 patients (28 males and 11 females), the fusion group (group 2) 35 patients (20 males and 15 females). There was no difference between both groups regarding the male/female ratio (p = 0.187, chi-square test). The average ages were 45.8 ± 16.5 and 40.5 ± 12.7 years in group 1 and 2, respectively (p = 0.223). All patients had unstable thoracolumbar fractures from T11 to L2 included. Involvement of T11, T12, L1 and L2 was noted, respectively in 5, 8, 20 and 6 patients in the non-fusion group and 7, 13, 11 and 4 in the fusion group : no significant difference (p = 0.227, chi-square test). In the non-fusion group 16 fractures were due to a motor vehicle accident (MVA) and 23 to a fall from a height (FFH) ; in the fusion group these numbers were 19 and 16 (p = 0.254). The inclusion criteria were : 1. preoperative kyphosis 20 or anterior vertebral height loss 50% ; 2. two or more than two columns involvement ; 3. no or partial neurological deficit ; 4. single level vertebral involvement. Patients with involvement of more than one vertebra or with complete neurological deficit were excluded. Clinical examination, plain radiographs and CT-scan were routine. McAfee s (14) system was used to classify the fractures : all fractures were unstable burst fractures. The Frankel classification of neurological deficits was used, initially and at follow-up. A Frankel grade D and E was noted, respectively in 3 and 36 patients in the nonfusion group, and in 1 and 34 patients in the fusion group ; the post-operative and final scores were compared with the preoperative scores. Surgical technique The patients were positioned prone, in hyperextension, with the abdomen hanging free, thus preventing excessive intra-operative bleeding and achieving a significant initial reduction of the spinal fracture. All patients underwent a single-stage posterior short segment instrumentation (SS = one level above and one level below the fractured vertebra). The pedicle screws were inserted under C-arm guidance, one level above and one level below. Rods were then fixed to the four screws, following which the fracture was reduced. Cross fixation was not used. None of the patients underwent discectomy and/or laminectomy or another decompressive procedure. Posterior fusion was added in the fusion group (group 2), with cancellous bone grafts harvested from the posterior iliac crest. All patients wore a custom-molded thoracolumbo - sacral brace for three months. They were followed clinically and roentgenographically. Kyphosis or lordosis were measured from the superior end-plate of the intact vertebra cephalad, to the inferior end-plate of the vertebra caudad to the fracture. A visual analog score (VAS) was used to evaluate pain before surgery, immediately after surgery, and at final follow-up. RESULTS The average follow-up period was 35.7 ± 4.6 months (range : 29-45) in the non-fusion group (group 1) and 38.8 ± 8.0 months (range : 29-52) in the fusion group (group 2) : the difference was not statistically significant (p = 0.187, Kruskal-Wallis test) (table I). Also the injury-to-surgery time
3 824 J.-H. HWANG, H. N. MODI, J.-H. YANG, S.-J. KIM, S.-H. LEE Table I. Demographics, average preoperative, immediate postoperative and final kyphosis angles and pain score, mean operation time, estimated blood loss (EBL) and hospital stay Group 1 Group 2 p value Non-fusion Fusion Number (male/female) 39 (28/11) 35 (20/15) Average age ± SD 45.8 ± ± Average follow-up (months) ± SD 35.7 ± ± Injury-surgery interval (days) ± SD 4.8 ± ± Canal compromise % ± SD 39.2% ± % ± Injury (vehicle/fall from height) 39 (16/23) 35 (19/16) Preoperative kyphosis ± SD 20.8 ± ± 4.1 < * Immediate postop. kyphosis ± SD 8.2 ± ± 2.1 < * Final kyphosis ± SD 15.2 ± ± 2.4 < * Preoperative VAS pain ± SD 7.3 ± ± Immediate postop.vas pain ± SD 3.9 ± ± Final VAS pain ± SD 3.4 ± ± 0.7 < * Operative time (min) ± SD 117 ± ± 28 < * Estimated blood loss (ml) ± SD 315 ± ± 78 < * Hospital stay (days) ± SD 11.6 ± ± * Indicates significant difference between non-fusion and fusion group. interval (ISI) was similar in both groups (p = 0.965, Kruskal-Wallis test). The average percentage of canal compromise was 39.2% ± 19.3 in the nonfusion group, and 47.0% ± 13.5 in the fusion group (p = 0.052, Kruskal-Wallis test). The mechanism of injury (motor vehicle accident or fall from a height) was comparable in both groups (p = 0.254). Table I further shows the average thoracolumbar kyphosis angle and pain scores before and immediately after surgery and at final follow-up : in the non-fusion group (group 1) they were respectively 20.8 ± 6.4, 8.2 ± 4.8, and 15.2 ± 6.0. These results demonstrated that an important initial correction was only partially maintained : it decreased from 12.6 to 5.6, which means a loss of 7 or 55% (p < ) (fig 1). In the fusion group (group 2) the corresponding kyphosis values were respectively 26.6 ± 4.1, 7.9 ± 2.1, and 8.4 ± 2.4, which suggested that a significant correction was maintained at final follow-up (p = 0.887) (fig 2). In other words, the correction decreased from 18.7 to 18.2, which means a loss of only 0.5 or 3%. In the non-fusion group the preoperative, immediate postoperative and final follow-up visual analogue scores (VAS) for back pain were 7.3 ± 0.8, 3.9 ± 0.8, and 3.4 ± 0.9. In group 2, the fusion group, the corresponding values were 7.5 ± 1.0, 3.9 ± 1.1, and 1.6 ± 0.7. In other words, after an important initial improvement in the non-fusion group there was only little further improvement at final follow-up. In the fusion group the initial improvement was comparable with the non-fusion group (p = 0.957), but improvement continued up to the final follow-up, so that the difference between groups became very significant (p < ). The mean operative time was 117 ± 33 minutes in the non-fusion group, and 152 ± 28 minutes in the fusion group (p < ). The mean estimated blood loss (EBL) during the operation was 315 ± 57 ml in the non-fusion group, and 455 ± 78 ml in the fusion-group (p < ). There was no significant difference in the hospital stay (p = 0.524) between both groups (11.6 ± 3.8 days in the non-fusion and 12.1 ± 4.1 days in the fusion group). As to neurological improvement, all patients in both groups reached Frankel grade E at final follow-up. Complications : there were 11 (11/39 = 28.2%) patients with implant-related problems in the nonfusion group versus 2 (2/35 = 5.7%) in the fusion group : the difference is significant (p = 0.011, chi-square test). Screw loosening was noted in 7 patients in the non-fusion group versus one in the fusion group ; screw breakage occurred in
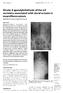
4 FUSION OR NON-FUSION IN THORACOLUMBAR FRACTURES 825 Fig 1. Preoperative, immediate postoperative, and final follow-up AP and lateral radiograms of L1 fracture treated with short segment pedicle screw fixation without fusion (group 1). Although good correction was achieved immediately after the operation, it was not maintained at final follow-up (37 months). Fig 2. Preoperative, immediate postoperative and final follow-up AP and lateral radiograms of L1 fracture treated with short segment pedicle screw fixation with fusion (group 2). Good correction was achieved immediately after the operation and was maintained at final follow-up (42 months). 4 patients in the non-fusion group versus one in the fusion group. All these problems probably increased back pain in the affected patients. Screw breakage necessitated a revision operation ; screw loosening was left untouched, because the patients denied further surgery. DISCUSSION The thoracolumbar junction is the most common level of spinal injury. Injury to both the anterior and middle columns results in a burst fracture with retropulsion of bone into the spinal canal. The surgical approach to burst fractures with significant canal compromise has always been controversial (21). Stability of the anterior column plays a pivotal role in the success or failure of the procedure. Transpedicular screw fixation offers superior three-column control and obviates the need for intracanal placement of hardware (24). Shortsegment posterior fixation (SSPF) is the most common and simple treatment, offering the advantage of incorporating fewer motion segments in the fusion (1,10,17).
5 826 J.-H. HWANG, H. N. MODI, J.-H. YANG, S.-J. KIM, S.-H. LEE With or without fusion? Only a few authors have concentrated on the success or failure of short segment posterior fixation, completed with fusion (13) or not (18). Even rarer are those who compared non-fusion and fusion in a prospective randomized study : as stated above, Wang et al (22) found that the radiographic parameters were significantly better in the non-fusion group, while the low back pain outcome was practically similar in both groups. In sharp contrast with these statements were the results of the current study, where the fusion group did better as to kyphosis and back pain. Loss of correction and subsequent pain In the non-fusion group, the loss of correction may be mainly attributed to collapse of the injured disc, according to Sanderson et al (18), who treated 28 thoracolumbar burst fractures with short-segment fixation without fusion. They reported that the segmental motion did not reach the criteria of instability (more than 10 of angular change of one motion segment in the dynamic flexion-extension lateral views) (24). Mumford et al (16) preferred a non-operative management and noted that the body collapse progressed significantlyby +/- 8%. They also found that the residual deformity did not correlate with the pain complaints at follow-up. This was not confirmed by the current study, where the pain complaints at final follow-up were significantly more important in the non-fusion group with its progressing kyphosis, although the pain score was similar immediately after surgery in the non-fusion and in the fusion group. McLain et al (15) also noted that patients who had progressive kyphosis of more than 10 had substantially more pain than those who had little or no progression. Short segment or long segment instrumentation? Tezeren and Kuru (20) reported that in a posterior-only approach for thoracolumbar burst fractures, radiographic parameters were better after long-segment instrumentation, while the clinical outcome was the same. On the other hand, short segment fusion offers the advantage of incorporating fewer motion segments in the fusion (1,10,17). Prevention of implant failure Implant failure is one of the criteria determining the success of the treatment. The current study clearly shows that in the non-fusion group 28.2% of the patients had implant-related complications versus only 5.2% in the fusion group (p = 0.011), which correlated with more severe back pain in the non-fusion group. A review of the literature shows that short segment (SS) posterior fixation without fusion led to a 9-54% incidence of implant failure and re-kyphosis in the long-term follow-up, while 50% of the patients with implant failure had moderate to severe pain (2,4,10,19). McLain et al (15) also reported that the high rate of hardware failure associated with a short segment (SS) fixation without fusion suggests that posterior screw fixation alone is not effective. In order to avoid hardware failure, several techniques have been developed to augment the anterior column in burst fractures : transpedicular bone grafting (2,4), placement of body augmenter (11), polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) injection (3), anterior instrumentation and strut grafting (9). However, their effect should be studied separately in non-fusion and fusion groups. CONCLUSION The authors conclude that, although shortsegment pedicle screw fixation without fusion yields satisfactory results in unstable thoracolumbar fractures T11-L2, fusion is advisable to maintain the postoperative kyphosis correction and to reduce the incidence of implant-related complications and back pain, despite diverging findings by Wang et al (22). The advantages of non-fusion are the elimination of donor site complications, the saving of motion segments, and the reduction of blood loss and operative time at initial treatment, which is crucial for polytraumatized or critical patients (6,22). But a little more operative time and blood loss, due to a fusion, would grant less low back pain and implant related complications. A weakness of this study is the fact that it was not a randomized study.
6 FUSION OR NON-FUSION IN THORACOLUMBAR FRACTURES 827 REFERENCES 1. Akbarnia BA, Crandall DG, Burkus K, Matthews T. Use of long rods and a short arthrodesis for burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. A long-term follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg 1994 ; 76-A : Alanay A, Acaroglu E, Yazici M, Oznur A, Surat A. Short-segment pedicle instrumentation of thoracolumbar burst fractures : does transpedicular intracorporeal grafting prevent early failure? Spine 2001 ; 26 : Cho DY, Lee WY, Sheu PC. Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures with polymethylmethacrylate vertebroplasty and short-segment pedicle screw fixation. Neurosurgery 2003 ; 53 : ; discussion de Peretti F, Hovorka I, Cambas PM, Nasr JM, Argenson C. Short device fixation and early mobilization for burst fractures of the thoracolumbar junction. Eur Spine J 1996 ; 5 : Dick W, Kluger P, Magerl F, Woersdörfer O, Zäch G. A new device for internal fixation of thoracolumbar and lumbar spine fractures : the fixateur interne. Paraplegia 1985 ; 23 : Frymoyer JW, Howe J, Kuhlmann D. The long-term effects of spinal fusion on the sacroiliac joints and ilium. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1978 ; 134 : Gertzbein SD. Scoliosis Research Society. Multicenter spine fracture study. Spine 1992 ; 17 : Gurr KR, McAfee PC. Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation in adults. A preliminary report. Spine 1988 ; 13 : Kaneda K, Taneichi H, Abumi K et al. Anterior decompression and stabilization with the Kaneda device for thoracolumbar burst fractures associated with neurological deficits. J Bone Joint Surg 1997 ; 79-A : Knop C, Bastian L, Lange U et al. Complications in surgical treatment of thoracolumbar injuries. Eur Spine J 2002 ; 11 : Li KC, Hsieh CH, Lee CY, Chen TH. Transpedicle body augmenter : a further step in treating burst fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2005 ; 436 : Lindsey RW, Dick W. The fixateur interne in the reduction and stabilization of thoracolumbar spine fractures in patients with neurologic deficit. Spine 1991 ; 16 : S140-S Liu CL, Wang ST, Lin HJ et al. AO fixateur interne in treating burst fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi (Taipei) 1999 ; 62 : McAfee PC, Yuan HA, Fredrickson BE, Lubicky JP. The value of computed tomography in thoracolumbar fractures. An analysis of one hundred consecutive cases and a new classification. J Bone Joint Surg 1983 ; 65-A : McLain RF, Sparling E, Benson DR. Early failure of short-segment pedicle instrumentation for thoracolumbar fractures. A preliminary report. J Bone Joint Surg 1993 ; 75-A : Mumford J, Weinstein JN, Spratt KF, Goel VK. Thoracolumbar burst fractures. The clinical efficacy and outcome of nonoperative management. Spine 1993 ; 18 : Parker JW, Lane JR, Karaikovic EE, Gaines RW. Successful short-segment instrumentation and fusion for thoracolumbar spine fractures : a consecutive 41/2-year series. Spine 2000 ; 25 : Sanderson PL, Fraser RD, Hall DJ et al. Short segment fixation of thoracolumbar burst fractures without fusion. Eur Spine J 1999 ; 8 : Shen WJ, Liu TJ, Shen YS. Nonoperative treatment versus posterior fixation for thoracolumbar junction burst fractures without neurologic deficit. Spine 2001 ; 26 : Tezeren G, Kuru I. Posterior fixation of thoracolumbar burst fracture : short-segment pedicle fixation versus longsegment instrumentation. J Spinal Disord Tech 2005 ; 18 : Verlaan JJ, Diekerhof CH, Buskens E et al. Surgical treatment of traumatic fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine : a systematic review of the literature on techniques, complications, and outcome. Spine 2004 ; 29 : Wang ST, Ma HL, Liu CL et al. Is fusion necessary for surgically treated burst fractures of the thoracolumbar and lumbar spine? : a prospective, randomized study. Spine 2006 ; 31 : ; discussion White AA, Panjabi MM. The problem of clinical insta - bility in the human spine : a systematic approach. In : White AA, Panjabi MM (eds). Clinical Biomechanics of the Spine. 2nd ed, Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, 1990, pp Yue JJ, Sossan A, Selgrath C et al. The treatment of unstable thoracic spine fractures with transpedicular screw instrumentation : a 3-year consecutive series. Spine 2002 ; 27 :
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2016;8:71-77 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2016.8.1.71 More than 5-Year Follow-up Results of Two- Level and Three-Level Posterior Fixations of Thoracolumbar
Results of Two Above- One Below Approach with Intermediate Screws at the Fracture Site in the Surgical Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures
 Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 56 No2, pp. E67-E78 2010 Results of Two Above- One Below Approach with Intermediate Screws at the Fracture Site in the Surgical Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures ONAT UZUMCUGIL
Kobe J. Med. Sci., Vol. 56 No2, pp. E67-E78 2010 Results of Two Above- One Below Approach with Intermediate Screws at the Fracture Site in the Surgical Treatment of Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures ONAT UZUMCUGIL
Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip.
 Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip. MIS SURGERY. WHY NOT? Murcia. October 5, 2012. Dr. Pedro Cortés García. Spinal Unit. Orthopaedic department. Canary Islands University Hospital
Thoracolumbar fractures. Treatment options. A long trip. MIS SURGERY. WHY NOT? Murcia. October 5, 2012. Dr. Pedro Cortés García. Spinal Unit. Orthopaedic department. Canary Islands University Hospital
Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture: Severe Canal Compromise but Neurologically Intact Cases
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2013;9:101-105 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2013.9.2.101 Short Segment Screw Fixation without Fusion for Low Lumbar Burst Fracture:
Posterior Instrumentation of Thoracolumbar Fracture
 Posterior Instrumentation of Thoracolumbar Fracture Jin-Young Lee, MD, and Gab-Lae Kim, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Abstract The thoracolumbar
Posterior Instrumentation of Thoracolumbar Fracture Jin-Young Lee, MD, and Gab-Lae Kim, MD Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea Abstract The thoracolumbar
Original Article Journal of Bone and Joint Diseases Jul - Sep ;(2):37-42
 Original Article Journal of Bone and Joint Diseases Jul - Sep 2017 32;(2):37-42 Short Segment Posterior Pedicle Instrumentation for Traumatic Thoracic and Lumbar Fractures: Is Bone Grafting Really Needed?
Original Article Journal of Bone and Joint Diseases Jul - Sep 2017 32;(2):37-42 Short Segment Posterior Pedicle Instrumentation for Traumatic Thoracic and Lumbar Fractures: Is Bone Grafting Really Needed?
INTRODUCTION.
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/1.334/jkns.212.51.4.23 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 51 : 23-27, 212 Print ISSN 25-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 212 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical Article
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/1.334/jkns.212.51.4.23 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 51 : 23-27, 212 Print ISSN 25-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 212 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical Article
Open Access. George Sapkas 1, Konstantinos Kateros 2, Stamatios A. Papadakis *,3, Emmanouel Brilakis 2, George Macheras 3 and Pavlos Katonis 4
 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2010, 4, 7-13 7 Open Access Treatment of Unstable Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures by Indirect Reduction and Posterior Stabilization: Short-Segment Versus Long- Segment Stabilization
The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2010, 4, 7-13 7 Open Access Treatment of Unstable Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures by Indirect Reduction and Posterior Stabilization: Short-Segment Versus Long- Segment Stabilization
 www.chirurgieorthopedique.com www.chirurgieorthopedique.com www.chirurgieorthopedique.com Vertebral body cage use in thoracolumbar fractures: Outcomes in a prospective series of 23 cases at 2 years follow-up
www.chirurgieorthopedique.com www.chirurgieorthopedique.com www.chirurgieorthopedique.com Vertebral body cage use in thoracolumbar fractures: Outcomes in a prospective series of 23 cases at 2 years follow-up
CLINICAL ARTICLE. Page 68 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Winter 2009
 Page 68 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Winter 2009 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Short-segment posterior instrumentation of thoracolumbar fractures as standalone treatment J Davis, Registrar, Department of Orthopaedics,
Page 68 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Winter 2009 C L I N I C A L A RT I C L E Short-segment posterior instrumentation of thoracolumbar fractures as standalone treatment J Davis, Registrar, Department of Orthopaedics,
Departement of Neurosurgery A.O.R.N A. Cardarelli- Naples.
 Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Bone Cement-Augmented Short Segment Fixation with Percutaneous Screws for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures Accompanied by Severe Osteoporosis
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.52.4.353 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 52 : 353-358, 2012 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2012 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2012.52.4.353 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 52 : 353-358, 2012 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2012 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
Spinal Cord (2011) 49, & 2011 International Spinal Cord Society All rights reserved /11 $
 (2011) 49, 573 579 & 2011 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/11 $32.00 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior/anterior combined surgery for thoracolumbar burst fracturesfposterior
(2011) 49, 573 579 & 2011 International Society All rights reserved 1362-4393/11 $32.00 www.nature.com/sc ORIGINAL ARTICLE Posterior/anterior combined surgery for thoracolumbar burst fracturesfposterior
Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral shortening
 Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
Eur Spine J (2002) 11 :8 12 DOI 10.1007/s005860000214 TECHNICAL INNOVATION Alejandro Reyes-Sanchez Luis M. Rosales Victor P. Miramontes Dario E. Garin Treatment of thoracolumbar burst fractures by vertebral
SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS
 STUDY SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS *Hashem, N.; **A Subai, N. *Faculty of Medicine, Ains Shams University, Egypt ^Department of Orthopedics,
STUDY SHORT SEGMENT FIXATION THORACOLUMBAR UNSTABLE BURST FRACTURES USING DC PLATES & PEDICLE SCREWS *Hashem, N.; **A Subai, N. *Faculty of Medicine, Ains Shams University, Egypt ^Department of Orthopedics,
Although unstable thoracolumbar injuries are a common
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior-Only Stabilization of Three-Column Thoracolumbar Injuries Rick C. Sasso, MD, Natalie M. Best, BS, Thomas M. Reilly, MD, and Robert A. McGuire, Jr., MD Objective: The optimal treatment
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Anterior-Only Stabilization of Three-Column Thoracolumbar Injuries Rick C. Sasso, MD, Natalie M. Best, BS, Thomas M. Reilly, MD, and Robert A. McGuire, Jr., MD Objective: The optimal treatment
Posterior Short-segmental Fixation Combined With Intermediate Screws vs Conventional Intersegmental Fixation for Monosegmental Thoracolumbar Fractures
 Posterior Short-segmental Fixation Combined With Intermediate Screws vs Conventional Intersegmental Fixation for Monosegmental Thoracolumbar Fractures JI-WEI TIAN, MD; LEI WANG, MD; TIAN XIA, MD; CHENG-YI
Posterior Short-segmental Fixation Combined With Intermediate Screws vs Conventional Intersegmental Fixation for Monosegmental Thoracolumbar Fractures JI-WEI TIAN, MD; LEI WANG, MD; TIAN XIA, MD; CHENG-YI
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life
 Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
Original Study Delayed surgery in neurologically intact patients affected by thoraco-lumbar junction burst fractures: to reduce pain and improve quality of life Lorenzo Nigro 1, Roberto Tarantino 1, Pasquale
There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid Construct in the Correction of Lenke Type-1 Curves
 DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.20522-17.1 Received: 11.04.2017 / Accepted: 12.07.2017 Published Online: 21.09.2017 Original Investigation There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid
DOI: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.20522-17.1 Received: 11.04.2017 / Accepted: 12.07.2017 Published Online: 21.09.2017 Original Investigation There is No Remarkable Difference Between Pedicle Screw and Hybrid
Advantages of MISS. Disclosures. Thoracolumbar Trauma: Minimally Invasive Techniques. Minimal Invasive Spine Surgery 11/8/2013.
 3 rd Annual UCSF Techniques in Complex Spine Surgery Program Thoracolumbar Trauma: Minimally Invasive Techniques Research Support: Stryker Disclosures Murat Pekmezci, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF/SFGH
3 rd Annual UCSF Techniques in Complex Spine Surgery Program Thoracolumbar Trauma: Minimally Invasive Techniques Research Support: Stryker Disclosures Murat Pekmezci, MD Assistant Clinical Professor UCSF/SFGH
Postero-lateral approach with open view vertebroplasty - eggshell technique
 Romanian Neurosurgery (2013) XX 4: 357-368 357 Postero-lateral approach with open view vertebroplasty - eggshell technique E.Fl. Exergian 1, I.Fl. Luca-Husti 2, D. Şerban 1 1 Spine Surgery Department,
Romanian Neurosurgery (2013) XX 4: 357-368 357 Postero-lateral approach with open view vertebroplasty - eggshell technique E.Fl. Exergian 1, I.Fl. Luca-Husti 2, D. Şerban 1 1 Spine Surgery Department,
Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia: A Case Series
 C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
C a s e R e p o r t J. of Advanced Spine Surgery Volume 2, Number 2, pp 60~65 Journal of Advanced Spine Surgery JASS Stage Operation for Unstable Lumbar Spine Fracture- Dislocation with Incomplete Paraplegia:
Classification of Thoracolumbar Spine Injuries
 Classification of Thoracolumbar Spine Injuries Guillem Saló Bru 1 IMAS. Hospitals del Mar i de l Esperança. ICATME. Institut Universitari Dexeus USP. UNIVERSITAT AUTÒNOMA DE BARCELONA Objectives of classification
Classification of Thoracolumbar Spine Injuries Guillem Saló Bru 1 IMAS. Hospitals del Mar i de l Esperança. ICATME. Institut Universitari Dexeus USP. UNIVERSITAT AUTÒNOMA DE BARCELONA Objectives of classification
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
Ch ng Hwei Choo, Mun Keong Kwan, Yin Wei Chris Chan. Case presentation. Introduction
 Case Report Page 1 of 5 Surgical reduction technique (transpedicle) for unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures with retropulsion resulting in severe spinal canal stenosis: a preliminary case report Ch
Case Report Page 1 of 5 Surgical reduction technique (transpedicle) for unstable thoracolumbar burst fractures with retropulsion resulting in severe spinal canal stenosis: a preliminary case report Ch
Classification? Classification system should be: Comprehensive Usable Accurate Predictable Able to guide intervention
 Moderator: Dr. P.S. Chandra Dr. Dr Deepak Gupta Classification? Classification system should be: Comprehensive Usable Accurate Predictable Able to guide intervention A precise, comprehensive, ideal
Moderator: Dr. P.S. Chandra Dr. Dr Deepak Gupta Classification? Classification system should be: Comprehensive Usable Accurate Predictable Able to guide intervention A precise, comprehensive, ideal
Treatment Options for Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures
 & Treatment Options for Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures Eldin E. Karaiković¹*, Hector O. Pacheco² 1. Assistant Professor, Northwestern University, and Director of the Spine Center and Lead Physician, Orthopaedic
& Treatment Options for Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures Eldin E. Karaiković¹*, Hector O. Pacheco² 1. Assistant Professor, Northwestern University, and Director of the Spine Center and Lead Physician, Orthopaedic
Short segment pedicle screw fixation of thoracolumbar fracture: a case series of 33 patients
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Hussain N et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Jul;3(4):681-687 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20172550
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Hussain N et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Jul;3(4):681-687 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20172550
Results of surgical treatment for kyphotic deformity of the spine secondary to trauma or Scheuermann s disease
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 344-348 Results of surgical treatment for kyphotic deformity of the spine secondary to trauma or Scheuermann s disease Teoman ATICI, Ufuk AYDINLI, Burak AKESEN, Rasim ŠERIFOĞLU
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 344-348 Results of surgical treatment for kyphotic deformity of the spine secondary to trauma or Scheuermann s disease Teoman ATICI, Ufuk AYDINLI, Burak AKESEN, Rasim ŠERIFOĞLU
Juliete M. Diniz, MD, and Ricardo V. Botelho, PhD. Department of Neurosurgery, Hospital do Servidor Público Estadual IAMSPE, São Paulo, Brazil
 LITERATURE REVIEW J Neurosurg Spine 27:584 592, 2017 Is fusion necessary for thoracolumbar burst fracture treated with spinal fixation? A systematic review and meta-analysis Juliete M. Diniz, MD, and Ricardo
LITERATURE REVIEW J Neurosurg Spine 27:584 592, 2017 Is fusion necessary for thoracolumbar burst fracture treated with spinal fixation? A systematic review and meta-analysis Juliete M. Diniz, MD, and Ricardo
Combined Anterior-Posterior Surgery Versus Posterior Surgery for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Systematic Review of the Literature
 The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2010, 4, 93-100 93 Open Access Combined Anterior-Posterior Surgery Versus Posterior Surgery for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Systematic Review of the Literature Pim P.
The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2010, 4, 93-100 93 Open Access Combined Anterior-Posterior Surgery Versus Posterior Surgery for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures: A Systematic Review of the Literature Pim P.
KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients
 Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan Hong Hui Hospital,
Xi an Hong Hui Hospital Xi an, Shaanxi, China KumaFix fixation for thoracolumbar burst fractures: a prospective study on selective consecutive patients Dingjun Hao, Baorong He, Liang Yan Hong Hui Hospital,
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE?
 FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE? Original Article Orthopaedics R S Bajoria 1, Mahendra Panwar 2, Anand Rao 3, Sameer Gupta 4 1 - Associate
FUNCTIONAL OUTCOMES OF TRAUMATIC PARAPLEGIA PATIENTS: DOES SURGERY IMPROVE THE QUALITY OF LIFE? Original Article Orthopaedics R S Bajoria 1, Mahendra Panwar 2, Anand Rao 3, Sameer Gupta 4 1 - Associate
R A (2005)
 4, 2005 2, 3 1 J Sp inal Surg, February 2005, Vol 3, No 1,,,,,, 1999 3 2004 568 45, 23,14 61,36. 7 : T 11 1 T 12 20 L 1 33 L 2 12, L 1, 2 1L 2, 3 1 : 10, 58 : Z2PLATE43, PROF ILE19, ALPS6 : 45 23 Frankel
4, 2005 2, 3 1 J Sp inal Surg, February 2005, Vol 3, No 1,,,,,, 1999 3 2004 568 45, 23,14 61,36. 7 : T 11 1 T 12 20 L 1 33 L 2 12, L 1, 2 1L 2, 3 1 : 10, 58 : Z2PLATE43, PROF ILE19, ALPS6 : 45 23 Frankel
Successful Short-Segment Instrumentation and Fusion for Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures
 Successful Short-Segment Instrumentation and Fusion for Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures A Consecutive 4 1 2-Year Series Jeffrey W. Parker, MD, Joel R. Lane, MD, Eldin E. Karaikovic, MD, PhD, and Robert W.
Successful Short-Segment Instrumentation and Fusion for Thoracolumbar Spine Fractures A Consecutive 4 1 2-Year Series Jeffrey W. Parker, MD, Joel R. Lane, MD, Eldin E. Karaikovic, MD, PhD, and Robert W.
Functional Outcome of Transpedicular Screw Fixation in patients with unstable Thoracolumbar Spine Injury
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Functional Outcome of Transpedicular Screw Fixation in patients with unstable Thoracolumbar Spine Injury MIRZA SAMAR AHMAD, IJAZ AHMAD, AIQ UZ ZAMAN, RIZWAN AKRAM, AMER AZIZ ABSTRACT Background:
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Functional Outcome of Transpedicular Screw Fixation in patients with unstable Thoracolumbar Spine Injury MIRZA SAMAR AHMAD, IJAZ AHMAD, AIQ UZ ZAMAN, RIZWAN AKRAM, AMER AZIZ ABSTRACT Background:
Efficiency of Ligamentotaxis Using PLL for Thoracic and Lumbar Burst Fractures in the Load-sharing Classification
 Efficiency of Ligamentotaxis Using PLL for Thoracic and Lumbar Burst Fractures in the Load-sharing Classification Won-Ju Jeong, MD; Joon-Woo Kim, MD; Dong-Kyo Seo, MD; Hyun-Joo Lee, MD; Jun-Young Kim,
Efficiency of Ligamentotaxis Using PLL for Thoracic and Lumbar Burst Fractures in the Load-sharing Classification Won-Ju Jeong, MD; Joon-Woo Kim, MD; Dong-Kyo Seo, MD; Hyun-Joo Lee, MD; Jun-Young Kim,
Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2003: 11(2): 202 206 Degenerative spondylolisthesis at the L4 L5 in a 32-year-old female with previous fusion for idiopathic scoliosis: A case report RB Winter Clinical Professor,
Fixation of Thoracolumbar Fractures by Fixator Internae
 Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.I. Vol: 26(1): pp. 41-46, 2012. Fixation of Thoracolumbar Fractures by Fixator Internae Shafique Ahmed Shafaq, Abbas Bajwa and Zaigham Ali Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed
Proceeding S.Z.P.G.M.I. Vol: 26(1): pp. 41-46, 2012. Fixation of Thoracolumbar Fractures by Fixator Internae Shafique Ahmed Shafaq, Abbas Bajwa and Zaigham Ali Department of Orthopaedics, Shaikh Zayed
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis
 Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
Adolescent Idiopathic Scoliosis Surgical Treatment Comparisons By: Dr. Alex Rabinovich and Dr. Devin Peterson Options 1. Pedicle Screws versus Hooks 2. Posterior versus Anterior Instrumentation 3. Open
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft. Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD
 Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Induction and Maintenance of Lordosis in MultiLevel ACDF Using Allograft Saad Khairi, MD Jennifer Murphy Robert S. Pashman, MD Purpose Is lordosis induced by multilevel cortical allograft ACDF placed on
Surgical Outcome in Thoracolumbar Fractures Managed by Short-segment Pedicle Instrumentation
 24 Original Article Surgical Outcome in Thoracolumbar Fractures Managed by Short-segment Pedicle Instrumentation Min Yang, 1 MD, PhD, Guo Zheng Ding, 1 MD, Zhu Jun Xu, 1 MD Abstract Introduction: This
24 Original Article Surgical Outcome in Thoracolumbar Fractures Managed by Short-segment Pedicle Instrumentation Min Yang, 1 MD, PhD, Guo Zheng Ding, 1 MD, Zhu Jun Xu, 1 MD Abstract Introduction: This
Comparison of clinical, radiological and functional outcome of short segment V/S long segment posterior fixation of tuberculosis of spine
 2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
The Neurologic Outcome Of Posterior Fixation Of Thoraco- Lumbar Spine Fractures In A Rural Tertiary Care Centre Without Help Of Image Intensifier
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 4, Issue 6 (Jan.- Feb. 2013), PP 36-40 The Neurologic Outcome Of Posterior Fixation Of Thoraco- Lumbar
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861. Volume 4, Issue 6 (Jan.- Feb. 2013), PP 36-40 The Neurologic Outcome Of Posterior Fixation Of Thoraco- Lumbar
Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit
 Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit Shih-Tien Wang MD, Chien-Lin Liu MD 王世典劉建麟 School of Medicine,
Long Posterior Fixation with Short Fusion for the Treatment of TB Spondylitis of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine with or without Neurologic Deficit Shih-Tien Wang MD, Chien-Lin Liu MD 王世典劉建麟 School of Medicine,
Percutaneous Posterior Fixation: A Unique Entity to minimize Further Damage to Patient with Traumatic Spine
 Kaushal R Patel et al RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1129 Percutaneous Posterior Fixation: A Unique Entity to minimize Further Damage to Patient with Traumatic Spine 1 Kaushal R Patel, 2 Jayprakash
Kaushal R Patel et al RESEARCH ARTICLE 10.5005/jp-journals-10039-1129 Percutaneous Posterior Fixation: A Unique Entity to minimize Further Damage to Patient with Traumatic Spine 1 Kaushal R Patel, 2 Jayprakash
Thoracic Fracture-Dislocations Without Spinal Cord Injury - Two Cases Reports -
 Thoracic Fracture-Dislocations Without Spinal Cord Injury - Two Cases Reports - Dong Eun Shin, MD, Seung Yong Rhee, MD, Hak Sun Kim, MD # Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Bundang CHA Hospital, College
Thoracic Fracture-Dislocations Without Spinal Cord Injury - Two Cases Reports - Dong Eun Shin, MD, Seung Yong Rhee, MD, Hak Sun Kim, MD # Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Bundang CHA Hospital, College
Early Failure of Short-Segment Pedicle Instrumentation for Thoracolumbar Fractures
 ( irpyright 993 by ii:, Journal of hone and Joint Surge rv, Incorporated Early Failure of Short-Segment Pedicle Instrumentation for Thoracolumbar Fractures A PRELIMINARY REPORT* BY ROBERT F. M1.AIN. M.D.t.
( irpyright 993 by ii:, Journal of hone and Joint Surge rv, Incorporated Early Failure of Short-Segment Pedicle Instrumentation for Thoracolumbar Fractures A PRELIMINARY REPORT* BY ROBERT F. M1.AIN. M.D.t.
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...)
 Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Systematic review Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine: a systematic review (...) 59 59 66 Cervical artificial disc replacement versus fusion in the cervical spine:
Asymmetric T5 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy (PSO) for complex posttraumatic deformity
 Eur Spine J (2013) 22:2130 2135 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-2942-y OPEN OPERATING THEATRE (OOT) Asymmetric T5 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy (PSO) for complex posttraumatic deformity Ibrahim Obeid Fethi Laouissat
Eur Spine J (2013) 22:2130 2135 DOI 10.1007/s00586-013-2942-y OPEN OPERATING THEATRE (OOT) Asymmetric T5 Pedicle Subtraction Osteotomy (PSO) for complex posttraumatic deformity Ibrahim Obeid Fethi Laouissat
Short term radiological outcome of inserting screw at fracture level in posterior short segment fixation in thoracolumbar burst fractures
 Journal of Kathmandu Medical College, Vol. 4, No. 3, Issue 13, Jul.-Sep., 2015 Original Article Short term radiological outcome of inserting screw at fracture level in posterior short segment fixation
Journal of Kathmandu Medical College, Vol. 4, No. 3, Issue 13, Jul.-Sep., 2015 Original Article Short term radiological outcome of inserting screw at fracture level in posterior short segment fixation
Saudi Journal of Medicine (SJM)
 Saudi Journal of Medicine (SJM) Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-3389 (Print) ISSN 2518-3397 (Online) A Comparative Study of Thoracolumbar
Saudi Journal of Medicine (SJM) Scholars Middle East Publishers Dubai, United Arab Emirates Website: http://scholarsmepub.com/ ISSN 2518-3389 (Print) ISSN 2518-3397 (Online) A Comparative Study of Thoracolumbar
University of Groningen
 University of Groningen Nonoperative Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures Stadhouder, Agnita; Buskens, Erik; Vergroesen, Diederik A.; Fidler, Malcolm W.; de Nies, Frank; Oner, F. C. Published
University of Groningen Nonoperative Treatment of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures Stadhouder, Agnita; Buskens, Erik; Vergroesen, Diederik A.; Fidler, Malcolm W.; de Nies, Frank; Oner, F. C. Published
REFERENCE DOCTOR Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options. Hyeun Sung Kim, MD, PhD,
 Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean Neurosurgical Society / Korean
Thoracolumbar Trauma MIS Options Medical College of Chosun University, Gwangju, South Korea (1994) / Board of Neurosurgery (1999) MEMBERSHIPS & PROFESSIONAL SOCIETIES Korean Neurosurgical Society / Korean
A review of the management of thoracolumbar burst fractures
 Surgical Neurology 67 (2007) 221 231 Spine A review of the management of thoracolumbar burst fractures Li-Yang Dai, MD, PhD4, Sheng-Dan Jiang, MD, MSci, Xiang-Yang Wang, MD, PhD, Lei-Sheng Jiang, MD, MSci
Surgical Neurology 67 (2007) 221 231 Spine A review of the management of thoracolumbar burst fractures Li-Yang Dai, MD, PhD4, Sheng-Dan Jiang, MD, MSci, Xiang-Yang Wang, MD, PhD, Lei-Sheng Jiang, MD, MSci
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2): /ISSN: /IJCEM Yi Yang, Hao Liu, Yueming Song, Tao Li
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Int J Clin Exp Med 2018;11(2):1278-1284 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0063093 Case Report Dislocation and screws pull-out after application of an Isobar TTL dynamic stabilisation system at L2/3 in
Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Akita Kumiai General Hospital, Akita, Japan 2
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 2, pp 123~130, 2012 Surgery for lumbar burst fracture / 123 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.2.123 Anterior Decompression and Shortening Reconstruction with a Titanium
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 6, No. 2, pp 123~130, 2012 Surgery for lumbar burst fracture / 123 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2012.6.2.123 Anterior Decompression and Shortening Reconstruction with a Titanium
Thoracolumbar Spine Trauma: II. Principles of Management
 Thoracolumbar Spine Trauma: II. Principles of Management Jeffrey M. Spivak, MD, Alexander R. Vaccaro, MD, and Jerome M. Cotler, MD Abstract The care of patients with thoracolumbar spine trauma with or
Thoracolumbar Spine Trauma: II. Principles of Management Jeffrey M. Spivak, MD, Alexander R. Vaccaro, MD, and Jerome M. Cotler, MD Abstract The care of patients with thoracolumbar spine trauma with or
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
The Relationship between Superior Disc-Endplate Complex Injury and Correction Loss in Young Adult Patients with Thoracolumbar Stable Burst Fracture
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:465-471 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.465 The Relationship between Superior Disc-Endplate Complex Injury and Correction Loss in Young Adult
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:465-471 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.465 The Relationship between Superior Disc-Endplate Complex Injury and Correction Loss in Young Adult
Comparison of anterolateral and posterior approaches in the management of thoracolumbar burst fractures
 J Neurosurg Spine 5:117 125, 2006 Comparison of anterolateral and posterior approaches in the management of thoracolumbar burst fractures PATRICK W. HITCHON, M.D., JAMES TORNER, PH.D., KURT M. EICHHOLZ,
J Neurosurg Spine 5:117 125, 2006 Comparison of anterolateral and posterior approaches in the management of thoracolumbar burst fractures PATRICK W. HITCHON, M.D., JAMES TORNER, PH.D., KURT M. EICHHOLZ,
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures
 MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
MISS in Thoracolumbar Fractures Guillem Saló Bru, MD, Phd Spine Unit. Orthopaedic Department. Hospital del Mar. Barcelona. Associated Professor. Universitat Autónoma de Barcelona. Introduction. The application
Metal Failure of Pedicle Screw System
 Metal Failure of Pedicle Screw System Kyu Yeol Lee, MD, Chul Hong Kim, MD, Chang Geun Song, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea Abstract Study design
Metal Failure of Pedicle Screw System Kyu Yeol Lee, MD, Chul Hong Kim, MD, Chang Geun Song, MD Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, College of Medicine, Dong-A University, Busan, Korea Abstract Study design
vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in
 e287 Case Report Grade 4 spondylolisthesis of the L5 vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in neurofibromatosis Modi H N, Srinivasalu S, Suh S W, Yang J H ABSTRACT Spondylolisthesis associated with neurofibromatosis
e287 Case Report Grade 4 spondylolisthesis of the L5 vertebra associated with dura) ectasia in neurofibromatosis Modi H N, Srinivasalu S, Suh S W, Yang J H ABSTRACT Spondylolisthesis associated with neurofibromatosis
Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery: Advanced Techniques and Case Management journal homepage:
 Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery: Advanced Techniques and Case Management 4 (2016) 1 5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery: Advanced Techniques and Case Management journal
Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery: Advanced Techniques and Case Management 4 (2016) 1 5 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Interdisciplinary Neurosurgery: Advanced Techniques and Case Management journal
Association between bicortical screw fixation at upper instrumented vertebra and risk for upper instrumented vertebra fracture
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Spine 26:638 644, 2017 Association between bicortical screw fixation at upper instrumented vertebra and risk for upper instrumented vertebra fracture Young-Seop Park, MD, 1
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Neurosurg Spine 26:638 644, 2017 Association between bicortical screw fixation at upper instrumented vertebra and risk for upper instrumented vertebra fracture Young-Seop Park, MD, 1
Anterior Decompression and Stabilization with the Kaneda Device for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures Associated with Neurological Deficits* 1
 Copyright 1997 by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Incorporated Anterior Decompression and Stabilization with the Kaneda Device for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures Associated with Neurological Deficits*
Copyright 1997 by The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery, Incorporated Anterior Decompression and Stabilization with the Kaneda Device for Thoracolumbar Burst Fractures Associated with Neurological Deficits*
Osteoporotic Compression Fracture of Spine Treated With Posterior Instrumentation and Transpedicular Bone Grafting
 http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1211.003 Osteoporotic Compression Fracture of Spine Treated With Posterior Instrumentation and Transpedicular Bone Grafting Foead AI, MS Orth, Thanapipatsiri S*, MD, Pichaisak
http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1211.003 Osteoporotic Compression Fracture of Spine Treated With Posterior Instrumentation and Transpedicular Bone Grafting Foead AI, MS Orth, Thanapipatsiri S*, MD, Pichaisak
Neurologic Deficit: A Case Report
 Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Spine Research DOI: 10.21767/2471-8173.100006 Unusual 2-Stages Posterior Approach Surgical Treatment for Complete Fracture Dislocation of the Upper Thoracic
Case Report imedpub Journals http://www.imedpub.com Spine Research DOI: 10.21767/2471-8173.100006 Unusual 2-Stages Posterior Approach Surgical Treatment for Complete Fracture Dislocation of the Upper Thoracic
Interbody fusion cage for the transforaminal approach. Travios. Surgical Technique
 Interbody fusion cage for the transforaminal approach Travios Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes
Interbody fusion cage for the transforaminal approach Travios Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes
Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
Thoracolumbar burst fracture with complete paraplegia: rationale for second-stage anterior decompression and fusion regarding functional outcome
 J Orthopaed Traumatol (2009) 10:83 90 DOI 10.1007/s10195-009-0052-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thoracolumbar burst fracture with complete paraplegia: rationale for second-stage anterior decompression and fusion
J Orthopaed Traumatol (2009) 10:83 90 DOI 10.1007/s10195-009-0052-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Thoracolumbar burst fracture with complete paraplegia: rationale for second-stage anterior decompression and fusion
U.S. MARKET FOR MINIMALLY INVASIVE SPINAL IMPLANTS
 U.S. MARKET FOR MINIMALLY INVASIVE SPINAL IMPLANTS idata_usmis15_rpt Published in December 2014 By idata Research Inc., 2014 idata Research Inc. Suite 308 4211 Kingsway Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada,
U.S. MARKET FOR MINIMALLY INVASIVE SPINAL IMPLANTS idata_usmis15_rpt Published in December 2014 By idata Research Inc., 2014 idata Research Inc. Suite 308 4211 Kingsway Burnaby, British Columbia, Canada,
Bone Cement-Augmented Percutaneous Short Segment Fixation : An Effective Treatment for Kummell s Disease?
 www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.54 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (1) : 54-59, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
www.jkns.or.kr http://dx.doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2015.58.1.54 J Korean Neurosurg Soc 58 (1) : 54-59, 2015 Print ISSN 2005-3711 On-line ISSN 1598-7876 Copyright 2015 The Korean Neurosurgical Society Clinical
Early Functional and Radiological Outcomes Between Plaster Cast and Fiberglass Cast in Stable Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture
 Early Functional and Radiological Outcomes Between Plaster Cast and Fiberglass Cast in Stable Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture Zamzuri Z 1, Ariff Ms 1, Mohd Fairuz Ad 1, Mohd Shukrimi A 1, Nazri My 1 1 Dept.
Early Functional and Radiological Outcomes Between Plaster Cast and Fiberglass Cast in Stable Thoracolumbar Burst Fracture Zamzuri Z 1, Ariff Ms 1, Mohd Fairuz Ad 1, Mohd Shukrimi A 1, Nazri My 1 1 Dept.
Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate (TSLP) System. A low-profile plating system for anterior stabilization of the thoracic and lumbar spine.
 Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate (TSLP) System. A low-profile plating system for anterior stabilization of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate (TSLP) System. A low-profile plating system for anterior stabilization of the thoracic and lumbar spine. Technique Guide Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Thoracic or lumbar spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson s disease -A two-center experience of 32 cases-
 Thoracic or lumbar spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson s disease -A two-center experience of 32 cases- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto university Hiroaki Kimura,
Thoracic or lumbar spinal surgery in patients with Parkinson s disease -A two-center experience of 32 cases- Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Graduate School of Medicine, Kyoto university Hiroaki Kimura,
Zhouming Deng, 1 Hui Zou, 2 Lin Cai, 1 Ansong Ping, 1 Yongzhi Wang, 3 and Qiyong Ai Introduction
 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 457634, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/457634 Clinical Study The Retrospective Analysis of Posterior Short-Segment Pedicle Instrumentation without Fusion
e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 457634, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/457634 Clinical Study The Retrospective Analysis of Posterior Short-Segment Pedicle Instrumentation without Fusion
Traumatic thoracic spinal fracture dislocation with minimal or no cord injury
 J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 96:333 337, 2002 Traumatic thoracic spinal fracture dislocation with minimal or no cord injury Report of four cases and review of the literature SCOTT SHAPIRO M.D., TODD ABEL, M.D.,
J Neurosurg (Spine 3) 96:333 337, 2002 Traumatic thoracic spinal fracture dislocation with minimal or no cord injury Report of four cases and review of the literature SCOTT SHAPIRO M.D., TODD ABEL, M.D.,
Harrington rod stabilization for pathological fractures of the spine NARAYAN SUNDARESAN, M.D., JOSEPH H. GALICICH, M.D., AND JOSEPH M. LANE, M.D.
 J Neurosurg 60:282-286, 1984 Harrington rod stabilization for pathological fractures of the spine NARAYAN SUNDARESAN, M.D., JOSEPH H. GALICICH, M.D., AND JOSEPH M. LANE, M.D. Neurosurgery and Orthopedic
J Neurosurg 60:282-286, 1984 Harrington rod stabilization for pathological fractures of the spine NARAYAN SUNDARESAN, M.D., JOSEPH H. GALICICH, M.D., AND JOSEPH M. LANE, M.D. Neurosurgery and Orthopedic
ASJ. Surgical Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Stabilization for Spinal Fractures in Patients with Ankylosing Spinal Disorders
 Asian Spine Journal Clinical Study Asian Spine J 2018;12(3):434-441 https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2018.12.3.434 Surgical Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Stabilization for Spinal Fractures in Patients with
Asian Spine Journal Clinical Study Asian Spine J 2018;12(3):434-441 https://doi.org/10.4184/asj.2018.12.3.434 Surgical Outcomes of Minimally Invasive Stabilization for Spinal Fractures in Patients with
ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc disease: Is there a difference at 12 months?
 Original research ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc ( ) 51 51 56 ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc
Original research ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc ( ) 51 51 56 ProDisc-C versus fusion with Cervios chronos prosthesis in cervical degenerative disc
Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion
 Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.653 Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion Seth S. Molloy 1, Faiz U. Ahmad 2, Griffin R.
Open Access Case Report DOI: 10.7759/cureus.653 Focal Correction of Severe Fixed Kyphosis with Single Level Posterior Ponte Osteotomy and Interbody Fusion Seth S. Molloy 1, Faiz U. Ahmad 2, Griffin R.
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx. White Paper
 3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
3D titanium interbody fusion cages sharx (SLM selective laser melted) Goal of the study: Does the sharx intervertebral cage due to innovative material, new design, and lordotic shape solve some problems
AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES
 AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES T H E A O / A S I F ( A R B E I T S G E M E I N S C H A F T F Ü R O S T E O S Y N T H E S E F R A G E N / A S S O C I A T I O N F O R T H E S T U D Y O
AO CLASSIFICATIONS THORACO-LUMBAR SPINAL INJURIES T H E A O / A S I F ( A R B E I T S G E M E I N S C H A F T F Ü R O S T E O S Y N T H E S E F R A G E N / A S S O C I A T I O N F O R T H E S T U D Y O
Screws versus hooks: implant cost and deformity correction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis
 J Child Orthop (2012) 6:137 143 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0400-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Screws versus hooks: implant cost and deformity correction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis Bradley P. Jaquith
J Child Orthop (2012) 6:137 143 DOI 10.1007/s11832-012-0400-8 ORIGINAL CLINICAL ARTICLE Screws versus hooks: implant cost and deformity correction in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis Bradley P. Jaquith
Fractures of the Thoracic and Lumbar Spine
 A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
A spinal fracture is a serious injury. Nader M. Hebela, MD Fellow of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons http://orthodoc.aaos.org/hebela Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Cleveland Clinic Abu Dhabi Neurological
Clinical Study Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Fixation of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures
 Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 141032, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/141032 Clinical Study Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Fixation of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures Federico De Iure,
Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2012, Article ID 141032, 6 pages doi:10.1155/2012/141032 Clinical Study Minimal Invasive Percutaneous Fixation of Thoracic and Lumbar Spine Fractures Federico De Iure,
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012
 Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Interspinous Fusion Devices. Midterm results. ROME SPINE 2012, 7th International Meeting Rome, 6-7 December 2012 Posterior distraction and decompression Secure Fixation and Stabilization Integrated Bone
Spine and Fusion. Adjacent Segment Disease. 36Ihsan SOLAROGLU M.D., M. Ozerk OKUTAN M.D., Gurdal NUSRAN M.D.
 Lumbar Posterior Hybrid Dynamic Stabilisation and Fusion Systems 36Ihsan SOLAROGLU M.D., M. Ozerk OKUTAN M.D., Gurdal NUSRAN M.D. Spine and Fusion It has been more than a century since 1911 when Albee
Lumbar Posterior Hybrid Dynamic Stabilisation and Fusion Systems 36Ihsan SOLAROGLU M.D., M. Ozerk OKUTAN M.D., Gurdal NUSRAN M.D. Spine and Fusion It has been more than a century since 1911 when Albee
Key Words: Burst fracture, Canal remodeling, Postural reduction, Percutaneous, Pedicle screw
 Journal of Minimally Invasive Spine JMISST Surgery and Technique 2(1):20-26, 2017 Clinical Article eissn 2508-2043 https://doi.org/10.21182/jmisst.2017.00213 www.jmisst.org Spontaneous Spinal Canal Remodeling
Journal of Minimally Invasive Spine JMISST Surgery and Technique 2(1):20-26, 2017 Clinical Article eissn 2508-2043 https://doi.org/10.21182/jmisst.2017.00213 www.jmisst.org Spontaneous Spinal Canal Remodeling
Thoracoscopic transdiaphragmatic approach for anterior body reconstruction of L2 burst fracture
 Thoracoscopic transdiaphragmatic approach for anterior body reconstruction of L2 burst fracture Jongtae Park MD Department of neurosurgery, School of medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea Technical
Thoracoscopic transdiaphragmatic approach for anterior body reconstruction of L2 burst fracture Jongtae Park MD Department of neurosurgery, School of medicine, Wonkwang University, Iksan, Korea Technical
Fracture and complete dislocation of the spine with a normal motor neurology
 Injury Extra (2006) 37, 479 483 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Fracture and complete dislocation of the spine with a normal motor neurology Ashish S. Phadnis *, Chuan Jin Tan, A.S. Raman, R.J.
Injury Extra (2006) 37, 479 483 www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Fracture and complete dislocation of the spine with a normal motor neurology Ashish S. Phadnis *, Chuan Jin Tan, A.S. Raman, R.J.
Traumatic spondylolisthesis of the axis has been
 Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 60, Number 2 2001-2002 61 Traumatic Spondylolisthesis of the Axis 42 Cases Myung-Sang Moon MD Jeong-Lim Moon MD Young-Wan Moon MD Doo-Hoon Sun MD PhD and Won-Tai
Bulletin Hospital for Joint Diseases Volume 60, Number 2 2001-2002 61 Traumatic Spondylolisthesis of the Axis 42 Cases Myung-Sang Moon MD Jeong-Lim Moon MD Young-Wan Moon MD Doo-Hoon Sun MD PhD and Won-Tai
Late Infection of Spinal Instrumentation
 Abstract Late Infection of Spinal Instrumentation Jae-Ik Shim, M.D., Taik-Seon Kim, M.D., Sung-Jong Lee, M.D., Suk-Ha Lee, M.D., Dong-Ki Lee, M.D., Yoen-Sik Yu, M.D., Yun-Yeup Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic
Abstract Late Infection of Spinal Instrumentation Jae-Ik Shim, M.D., Taik-Seon Kim, M.D., Sung-Jong Lee, M.D., Suk-Ha Lee, M.D., Dong-Ki Lee, M.D., Yoen-Sik Yu, M.D., Yun-Yeup Kim, M.D. Department of Orthopaedic
Posterior wedge osteotomy and debridement for Andersson lesion with severe kyphosis in ankylosing spondylitis
 Liang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:54 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0556-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Posterior wedge osteotomy and debridement for Andersson lesion with severe
Liang et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:54 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0556-5 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Posterior wedge osteotomy and debridement for Andersson lesion with severe
A Measure to Avoid Pleura Injuries in XLIF at Upper Lumbar Levels
 A Measure to Avoid Pleura Injuries in XLIF at Upper Lumbar Levels Takao Nakajima 1, Yong Kim 2, Masabumi Miyamoto 3 Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Nippon Medical School, Chiba Hokusoh Hospital 1 Dept. of Orthop.
A Measure to Avoid Pleura Injuries in XLIF at Upper Lumbar Levels Takao Nakajima 1, Yong Kim 2, Masabumi Miyamoto 3 Dept. of Orthop. Surg., Nippon Medical School, Chiba Hokusoh Hospital 1 Dept. of Orthop.
Vertebral body cage use in thoracolumbar fractures: Outcomes in a prospective series of 23 cases at 2 years follow-up
 Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (211) 97, 62 67 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vertebral body cage use in thoracolumbar fractures: Outcomes in a prospective series of 23 cases at 2 years follow-up N.
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research (211) 97, 62 67 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Vertebral body cage use in thoracolumbar fractures: Outcomes in a prospective series of 23 cases at 2 years follow-up N.
