5 COMMON UPPER EXTREMITY COMPLAINTS LEARNING OBJECTIVES
|
|
|
- Aron Weaver
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 5 COMMON UPPER EXTREMITY COMPLAINTS ANTHONY J. FERRETTI, D.O., MHSA LECOM HEALTH LEARNING OBJECTIVES Understanding the signs/symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of rotator cuff impingement syndrome Understanding the signs/symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of lateral epicondylitis Understanding the signs/symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of cubital tunnel syndrome Understanding the signs/symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome Understanding the signs/symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment of trigger finger 1
2 5 Common Upper Extremity Complaints Rotator Cuff Impingement Syndrome Lateral Epicondylitis (Tennis Elbow) Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Trigger Finger Rotator Cuff Impingement Syndrome Differentiate from: Glenohumeral instability Cervical radiculitis Calcific tendonitis Adhesive capsulitis DJD Acromioclavicular (AC) osteoarthritis 2
3 History Meyer RCT results from friction on supraspinatus by undersurface of acromion Codman Critical zone: 1 cm medial to insertion on greater tuberosity where most RCT occur History Armstrong Supraspinatus syndrome Acromionectomy Neer Rotator cuff impinged by anterior 1/3 of acromion, CA ligament, and AC joint Impingement zone 3
4 Impingement syndrome Neer Treatment Anterior acromioplasty & bursectomy Ellman Arthroscopic acromioplasty Anatomy Subacromial space Height cm Contents: Supraspinatus Biceps tendon Bursa CA ligament 4
5 Pathoanatomy Intrinsic theory Tension overload with arm overhead Eccentric contraction supraspinatus Throwing, swimming, manual labor Overuse Pathoanatomy Extrinsic theory Acromial morphology Bigliani Type 3 Rockwood Anterior prominence 5
6 Diagnosis History Pain Repetitive overhead use Position of max pain Insidious, can begin with trauma Previous tx > 40 yo < 40 yo differentiate from instability Diagnosis Physical Exam C-spine exam ROM Strength testing Apprehension/relocation 6
7 Diagnosis Physical Exam Neer impingement sign passive forward flexion >90 causes pain Neer impingement test a subacromial injection relieves pain associated with passive forward flexion >90 Hawkins test internal rotation and passive forward flexion to 90 causes pain Jobe test pain with resisted pronation and forward flexion to 90 indicates supraspinatus pathology Imaging Plain films True AP of the shoulder useful in evaluating the acromiohumeral interval normal distance is 7-14 mm 30 caudal tilt view useful in identifying subacromial spurring supraspinatus outlet view useful in defining acromial morphology 7
8 Imaging Plain films Common radiographic findings associated with impingement proximal migration of the humerus as seen in rotator cuff tear arthropathy traction osteophytes calcification of the coracoacromial ligament cystic changes within the greater tuberosity Type III-hooked acromion os acromiale Imaging MRI Diagnostic of rotator cuff pathology Indications Suspicion for pain or weakness attributable to a rotator cuff tear Findings size, shape, and degree of retraction of tear degree of muscle fatty atrophy (best seen on sagittal image) medial biceps tendon subluxation indicative of a subscapularis tear cyst in humeral head on MRI seen in almost all patients with chronic RCT In asymptomatic patients 60 yrs and older, 55% will have a RCT 8
9 Imaging Ultrasound Indications suspicion of rotator cuff pathology need for dynamic examination advantages include allows for dynamic testing & inexpensive readily available at most centers helpful to confirm intraarticular injections disadvantages include highly user dependent limited ability to evaluate other intraarticular pathology sensitivity/specificity similar sensitivity, specificity, and overall accuracy for diagnosis of rotator cuff disease as compared to MRI 23% of asymptomatic patients had a rotator cuff tear on ultrasound in one series Treatment Nonoperative physical therapy, oral anti-inflammatory medication, subacromial injections Indications subacromial impingement syndrome Techniques aggressive rotator cuff strengthening and periscapular stabilizing exercises Rehab program is indicated in the presence of scapular dyskinesia which aims to regain full shoulder range of motion and coordinate the scapula with trunk motion 9
10 Treatment Operative Anterior acromioplasty with CA ligament resection Open vs. arthroscopic Biceps tenodesis if symptomatic Distal Clavicle Resection if indicated Indicated in patients that have failed 4-6 months of nonoperative treatment Outcomes Poor subjective outcomes observed after acromioplasty in patients with workers' compensation Treatment Arthroscopic / open rotator cuff repair Indications Acute full-thickness tears Bursal-sided tears >25%)in depth Partial articular-side tears>50% Partial articular-side tears <50% treated with debridement alone Younger patients with acute, traumatic tears In situ repair leave bursal sided tissue intact Older patients with degenerative tears Tendon release, debridement of degenerative tissue and repair 10
11 11
12 Treatment Post operative (Rotator Cuff Repair) Rate-limiting step for recovery is biologic healing of RTC tendon to greater tuberosity Believed to take 8-12 weeks Peribursal tissue and holes drilled in greater tuberosity are major source of vascularity to repaired rotator cuff Vascularity can increase with exercise Postop with limited passive ROM (no active ROM) Lateral Epicondylitis 12
13 Lateral Epicondylitis Overuse injury involving eccentric overload at origin of common extensor tendon Leads to tendinosis and inflammation at origin of ECRB Incidence most common cause for elbow symptoms in patients with elbow pain Demographics Up to 50% of all tennis players develop Mechanism Occurs in activities with repetitive pronation and supination with elbow in extension Common in tennis players (backhand implicated) Pathoanatomy Usually begins as a microtear of the origin of ECRB Angiofibroblastic hyperplasia and disorganized collagen Lateral Epicondylitis Symptoms Pain with resisted wrist extension and gripping activities Decreased grip strength Physical exam Point tenderness at ECRB insertion into lateral epicondyle Few mm distal to tip of lateral epicondyle May have decreased grip strength Neurological exam helps to differentiate from entrapment syndromes Provocative tests Diagnosis resisted wrist extension with elbow fully extended resisted extension of the long fingers maximal flexion of the wrist Diagnosis is primarily based on symptoms and physical exam 13
14 Lateral Epicondylitis Elbow Radiographs AP/Lateral of elbow MRI Findings usually normal Increased signal intensity at ECRB tendon may be seen Not necessary for diagnosis Lateral Epicondylitis Nonoperative Activity modification, ice, NSAIDS, physical therapy, ultrasound First line of treatment Techniques Tennis modifications (slower playing surface, more flexible racquet, lower string tension, larger grip) Counter-force brace (strap) Steroid injections (up to three) Stretching of extensors Outcomes Up to 95% success rate with nonoperative treatment Operative Open or Arthroscopic release and debridement of ECRB origin Indications If prolonged nonoperative (9-12 months) fails 14
15 Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Cubital Tunnel Syndrome A compressive neuropathy of the ulnar nerve 2nd most common compression neuropathy of the upper extremity Sites of entrapment Between the two heads of FCU Most common site Within arcade of Struthers Hiatus in medial intermuscular septum Between Osborne's ligament and MCL Medial epicondyle nonunions Osteophytes Heterotopic ossification Ganglion cysts 15
16 Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Symptoms Paresthesias of small finger, ulnar half of ring finger, and ulnar dorsal hand Exacerbating activities include Cell phone use (excessive flexion) Occupational or athletic activities requiring repetitive elbow flexion and valgus stress Night symptoms Caused by sleeping with arm in flexion Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Physical exam Interosseous & first web space atrophy Ring & small finger clawing Unar nerve subluxation over the medial epicondyle as the elbow moves through a flexion-extension arc Sensory Motor Tinel sign positive over cubital tunnel Decreased sensation in ulnar 1-1/2 digits Weakened grasp Weak pinch From loss of thumb adduction (70% of pinch strength) Froment sign Compensatory thumb IP flexion by FPL (AIN) during key pinch Compensates for the loss of MCP flexion by adductor pollicis (ulna n.) 16
17 Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Association with Medial Epicondylitis Overuse syndrome of flexor-pronator mass (Golfers, Pitchers) Dominant Extremity in 75% of cases Micro-trauma to Pronator Teres > Flexor Carpi Radialis Physical exam Tenderness 5-10mm distal and anterior to medial epicondyle Soft tissue swelling Pain with resisted forearm pronation and wrist flexion Treatment Rest, ice, activity modification (stop throwing x 6-12wks), PT (passive stretching), bracing, NSAIDS First line of treatment Technique Counter-force bracing / kinesiology taping Ultrasound shown to be beneficial Multiple corticosteroid injections should be avoided Cubital Tunnel Syndrome EMG / NCV Helpful in establishing diagnosis and prognosis Threshold for diagnosis Conduction velocity <50 m/sec across elbow Low amplitudes of sensory nerve action potentials and compound muscle action potentials 17
18 Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Nonoperative NSAIDs, activity modification, and nighttime elbow extension splinting First line of treatment with mild symptoms Technique Night bracing in 45 extension with forearm in neutral rotation Outcomes Management is effective in 50% of cases Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Operative In situ ulnar nerve decompression without transposition Indications When nonoperative management fails Before motor denervation occurs Technique Medial approach open release of cubital tunnel retinaculum Endoscopically-assisted cubital tunnel release Outcomes Meta-analyses have shown similar clinical results with significantly fewer complications compared to decompression with transposition 80-90% good results when symptoms are intermittent and denervation has not yet occurred Poor prognosis correlates most with intrinsic muscle atrophy 18
19 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Most common compressive neuropathy Pathologic (inflamed) synovium most common cause of idiopathic CTS Risk factors Female sex Obesity Pregnancy Hypothyroidism Rheumatoid arthritis Advanced age Chronic renal failure Smoking or alcoholism Diabetes Mellitus Repetitive motion activities 19
20 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Branches of median nerve Palmar cutaneous branch Lies between PL and FCR at level of the wrist flexion crease Recurrent motor branch 50% are extraligamentous with recurrent innervation 30% are subligamentous with recurrent innervation 20% are transligamentous with recurrent innervation Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Symptoms numbness and tingling in radial 3-1/2 digits clumsiness pain and paresthesias that awaken patient at night self administered hand diagram the most specific test (76%) for carpal tunnel syndrome 20
21 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Physical exam Inspection may show thenar atrophy Carpal tunnel compression test (Durkan's test) Most sensitive test Phalen test Wist volar flexion for ~60 sec produces symptoms Less sensitive than Durkin compression test Tinel's test Tapping the median nerve over the volar carpal tunnel Carpal Tunnel Syndrome EMG and NCV Not needed to establish diagnosis (diagnosis is clinical) but recommended if surgical management is being considered NCV increase latencies (slowing) of NCV distal sensory latency of > 3.2 ms motor latencies > 4.3 ms decreased conduction velocities less specific than latencies EMG velocity of < 52 m/sec is abnormal test the electrical activity of individual muscle fibers and motor units potential pathologic findings sharp waves, fibrillations, fasciculations 21
22 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Nerve histology characterized by: Edema Fibrosis Vascular sclerosis Scattered lymphocytes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Nonoperative NSAIDS, night splints, activity modifications First line of treatment Steroid injections Indications Adjunctive conservative treatment Outcomes 80% have transient improvement of symptoms 22% remain symptom free at 1 year Failure to improve after injection is poor prognostic factor Surgery is less effective in these patients 22
23 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Operative Carpal tunnel release Indications Failure of nonoperative treatment (including steroid injections) Temporary improvement with steroid injections Good prognostic factor that the patient will have a good result with surgery Acute CTS following ORIF of a distal radius fx Outcomes Pinch strength return in 6 week Grip strength is expected to return to 100% preop by 12 wks postop Rate of continued symptoms at 1+ year is 2% in moderate and 20% in severe CTS Trigger Finger 23
24 Trigger Finger Stenosing tenosynovitis caused by inflammation of the flexor tendon sheath Epidemiology more common in diabetics ring finger most commonly involved Mechanism caused by entrapment of the flexor tendons at the level of the A1 pulley fibrocartilaginous metaplasia of tendon and pulley found in pathology Trigger Finger Green Classification Grade I Palm pain and tenderness at A-1 pulley Grade II Catching of digit Grade III Locking of digit, passively correctable Grade IV Fixed, locked digit 24
25 Trigger Finger Symptoms finger clicking pain at distal palm near A1 pulley finger becoming "locked in flexed position Physical exam tenderness to palpation over A1 pulley a palpable bump may be present near the same location Trigger Finger Nonoperative night splinting, activity modification, NSAIDS first line of treatment Steroid injections Indications Best initial treatment for fingers (not for thumb) Technique Give 1 to 3 injections in flexor tendon sheath Diabetics do not respond as well as non-diabetics 25
26 Trigger Finger Operative Surgical debridement and release of the A-1 pulley Indications Cases that fail nonoperative treatment Release of A1 pulley and 1 slip of FDS (ulnar slip) Indications Pediatric trigger finger Presents with Notta's nodule (proximal to A1 pulley), flexion contracture, and triggering May need to release remaining FDS slip and A3 pulley Question 1 A 45-year-old man sustained the injury seen in Figure 130a 6 weeks ago. He denies any prior injury to his shoulder. After treatment of the injury in the emergency department, he was noted to have significant weakness with empty can testing and external rotation at the side. He has full passive range of motion with forward flexion, abduction, and internal and external rotation, but has difficulty initiating abduction with his arm at his side. He has negative apprehension and relocation signs. A detailed neurologic examination shows no deficits. A coronal image from a follow-up MRI scan is seen in Figure 130b. Follow-up radiographs reveal no fractures. What is the most appropriate next step in his treatment? 1. Coracoid transfer 2. Rotator cuff repair 3. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty 4. Arthroscopic anteroinferior labral repair 5. Physical therapy for range of motion and strength improvements 26
27 Question 1 A 45-year-old man sustained the injury seen in Figure 130a 6 weeks ago. He denies any prior injury to his shoulder. After treatment of the injury in the emergency department, he was noted to have significant weakness with empty can testing and external rotation at the side. He has full passive range of motion with forward flexion, abduction, and internal and external rotation, but has difficulty initiating abduction with his arm at his side. He has negative apprehension and relocation signs. A detailed neurologic examination shows no deficits. A coronal image from a follow-up MRI scan is seen in Figure 130b. Follow-up radiographs reveal no fractures. What is the most appropriate next step in his treatment? 1. Coracoid transfer 2. Rotator cuff repair 3. Reverse total shoulder arthroplasty 4. Arthroscopic anteroinferior labral repair 5. Physical therapy for range of motion and strength improvements 27
28 Question 2 All of the following are predictive findings for correctly diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome EXCEPT: 1. Abnormal hand diagram 2. Abnormal Semmes-Weinstein testing in wrist-neutral position 3. Positive median nerve compression test (Durkan's sign) 4. Presence of night pain 5. Loss of small digit adduction (Wartenberg sign) Question 2 All of the following are predictive findings for correctly diagnosing carpal tunnel syndrome EXCEPT: 1. Abnormal hand diagram 2. Abnormal Semmes-Weinstein testing in wrist-neutral position 3. Positive median nerve compression test (Durkan's sign) 4. Presence of night pain 5. Loss of small digit adduction (Wartenberg sign) 28
29 Question 3 A 50-year-old man complains of numbness and tingling along his right small finger. Physical exam is notable for the finding demonstrated in Figure A. Elbow flexion reproduces the numbness and tingling. Physical therapy and splinting have failed to relieve the symptoms. Which of the following is the most appropriate surgical intervention to alleviate the symptoms while minimizing complications? 1. Simple ulnar nerve decompression at the cubital tunnel 2. Ulnar nerve decompression at the cubital tunnel with anterior submuscular transposition 3. Ulnar nerve decompression at the cubital tunnel with anterior subcutaneous transposition 4. Open carpal tunnel release 5. Endoscopic carpal tunnel release 29
30 Question 3 A 50-year-old man complains of numbness and tingling along his right small finger. Physical exam is notable for the finding demonstrated in Figure A. Elbow flexion reproduces the numbness and tingling. Physical therapy and splinting have failed to relieve the symptoms. Which of the following is the most appropriate surgical intervention to alleviate the symptoms while minimizing complications? 1. Simple ulnar nerve decompression at the cubital tunnel 2. Ulnar nerve decompression at the cubital tunnel with anterior submuscular transposition 3. Ulnar nerve decompression at the cubital tunnel with anterior subcutaneous transposition 4. Open carpal tunnel release 5. Endoscopic carpal tunnel release Question 4 A 50-year-old carpenter has chronic pain over the lateral aspect of the elbow. He notes pain when using a hammer. On exam, he has pain with resisted wrist extension while the elbow is fully extended. Which muscle attachment is likely to be involved? 1. Distal biceps brachii 2. Brachioradialis 3. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 4. Extensor carpi radialis longus 5. Supinator 30
31 Question 4 A 50-year-old carpenter has chronic pain over the lateral aspect of the elbow. He notes pain when using a hammer. On exam, he has pain with resisted wrist extension while the elbow is fully extended. Which muscle attachment is likely to be involved? 1. Distal biceps brachii 2. Brachioradialis 3. Extensor carpi radialis brevis 4. Extensor carpi radialis longus 5. Supinator Question 5 A 64-year-old diabetic female presents with sudden catching and locking of her ring finger when trying to extend it. Attempts at finger extension are painful, and she notes tenderness in her distal palm. A clinical photo is shown in Figure A. Which of the following structures are implicated in the pathogenesis of this condition? 1. Extensor digitorum tendon 2. Grayson's ligament 3. Oblique retinacular ligament 4. A1 pulley 5. Transverse carpal ligament 31
32 Question 5 A 64-year-old diabetic female presents with sudden catching and locking of her ring finger when trying to extend it. Attempts at finger extension are painful, and she notes tenderness in her distal palm. A clinical photo is shown in Figure A. Which of the following structures are implicated in the pathogenesis of this condition? 1. Extensor digitorum tendon 2. Grayson's ligament 3. Oblique retinacular ligament 4. A1 pulley 5. Transverse carpal ligament 32
33 THE END References Miller, M., Thompson, S., Hart, J. (2012). Sports Medicine. Review of Orthopaedics. Philadelphia, PA: Saunders Elsevier. Moore, D. Orthobullets: Hand. Linage Medical May, 21 Moore, D. Orthobullets: Sports. Linage Medical May,
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT
 ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
ROTATOR CUFF DISORDERS/IMPINGEMENT Dr.KN Subramanian M.Ch Orth., FRCS (Tr & Orth), CCT Orth(UK) Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Special interest: Orthopaedic Sports Injury, Shoulder and Knee Surgery, SPARSH
Disclaimer. Evaluation & Treatment of Shoulder and Elbow Pain in the Adult Patient. Objectives. Anatomy
 Evaluation & Treatment of Shoulder and Elbow Pain in the Adult Patient William T. Crowe, RN-C, FNP, MSN, MBA Disclaimer! I, William T Crowe, have relevant financial relationships to be discussed, directly
Evaluation & Treatment of Shoulder and Elbow Pain in the Adult Patient William T. Crowe, RN-C, FNP, MSN, MBA Disclaimer! I, William T Crowe, have relevant financial relationships to be discussed, directly
OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES OF THE ELBOW
 PLEASE STAND BY WEBINAR WILL BEGIN AT 12:00 PM PST FOR AUDIO: CALL 866-740-1260 / ACCESS CODE: 764-4915# JAMES VAN DEN BOGAERDE, MD OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES OF THE ELBOW Conflict of Interest Disclosure I,
PLEASE STAND BY WEBINAR WILL BEGIN AT 12:00 PM PST FOR AUDIO: CALL 866-740-1260 / ACCESS CODE: 764-4915# JAMES VAN DEN BOGAERDE, MD OCCUPATIONAL INJURIES OF THE ELBOW Conflict of Interest Disclosure I,
Sick Call Screener Course
 Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Common Elbow Problems
 Common Elbow Problems Duncan Ferguson FRACS Knee and Shoulder Specialist Elbow Instability Common 10-25% of elbow injuries Median age 30 yrs Most simple dislocations are stable after reduction recurrence
Common Elbow Problems Duncan Ferguson FRACS Knee and Shoulder Specialist Elbow Instability Common 10-25% of elbow injuries Median age 30 yrs Most simple dislocations are stable after reduction recurrence
Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity. Mark Tait MD
 Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity Mark Tait MD Tendonitis History Pain and swelling (any tendon, any location) Overuse Physical examination findings Localized swelling Pain with resistance
Common Tendon Disorders of the Upper Extremity Mark Tait MD Tendonitis History Pain and swelling (any tendon, any location) Overuse Physical examination findings Localized swelling Pain with resistance
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome/ Cubital Tunnel Syndrome. Nerve anatomy. Pathophysiology 6/14/2014. Most common compression neuropathies of the upper extremity
 Carpal Tunnel Syndrome/ Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Justin Arnold MD Family Medicine Update 2014 Most common compression neuropathies of the upper extremity Increasing prevalence CTS 50/1000 subjects Up to
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome/ Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Justin Arnold MD Family Medicine Update 2014 Most common compression neuropathies of the upper extremity Increasing prevalence CTS 50/1000 subjects Up to
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of
 Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Review shoulder anatomy Review the physical exam of the shoulder Discuss some common causes of acute shoulder pain Discuss some common causes of chronic shoulder pain Review with some case questions Bones:
Elbow Pain. Lateral Elbow Pain. Lateral Elbow Pain. tennis elbow lateral epicondylitis extensor tendinopathy
 Elbow Pain Peter Brukner OAM, FACSP Associate Professor in Sports Medicine Centre for Health, Exercise and Sports Medicine University of Melbourne Lateral Elbow Pain tennis elbow lateral epicondylitis
Elbow Pain Peter Brukner OAM, FACSP Associate Professor in Sports Medicine Centre for Health, Exercise and Sports Medicine University of Melbourne Lateral Elbow Pain tennis elbow lateral epicondylitis
Diagnostic and Management Approach to the Painful Shoulder
 Diagnostic and Management Approach to the Painful Shoulder Introduction What conditions causing shoulder pain commonly present in General Practice? Subacromial impingement Rotator cuff tears AC joint pathology
Diagnostic and Management Approach to the Painful Shoulder Introduction What conditions causing shoulder pain commonly present in General Practice? Subacromial impingement Rotator cuff tears AC joint pathology
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel!
 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders
79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! 79a Orthopedic Massage: Introduction! Rotator Cuff and Carpal Tunnel! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders
Elbow. Chapter 2 LISTEN. Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Pain
 Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group
 Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group Disclosures There has been no commercial support or sponsorship for this program. The planners and presenters
Evaluating shoulder injuries in primary care Bethany Reed, MSn, AGPCNP-BC One Medical Group Disclosures There has been no commercial support or sponsorship for this program. The planners and presenters
ARM Brachium Musculature
 ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
ARM Brachium Musculature Coracobrachialis coracoid process of the scapula medial shaft of the humerus at about its middle 1. flexes the humerus 2. assists to adduct the humerus Blood: muscular branches
The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand. Jennifer R Marks, MD
 The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Elbow A 44 yo M presents to clinic complaining of a sore elbow What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential
The Painful Elbow, Wrist, and Hand Jennifer R Marks, MD The Painful Elbow A 44 yo M presents to clinic complaining of a sore elbow What further questions do you have for this patient? What is on your differential
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader. Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS
 Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
Anatomy Workshop Upper Extremity David Ebaugh, PT, PhD Workshop Leader Lab Leaders: STATION I BRACHIAL PLEXUS A. Posterior cervical triangle and axilla B. Formation of plexus 1. Ventral rami C5-T1 2. Trunks
UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES. Recognizing common injuries to the upper extremity
 UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES Recognizing common injuries to the upper extremity ANATOMY BONES Clavicle Scapula Spine of the scapula Acromion process Glenoid fossa/cavity Humerus Epicondyles ANATOMY BONES Ulna
UPPER EXTREMITY INJURIES Recognizing common injuries to the upper extremity ANATOMY BONES Clavicle Scapula Spine of the scapula Acromion process Glenoid fossa/cavity Humerus Epicondyles ANATOMY BONES Ulna
Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow
 Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow I. Bones a. b. c. II. What movements does the elbow perform? a. Flexion b. c. Pronation d. III. Muscles in motion a. FLEXION (supinated) i Brachialis (pronated) ii (neutral)
Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow I. Bones a. b. c. II. What movements does the elbow perform? a. Flexion b. c. Pronation d. III. Muscles in motion a. FLEXION (supinated) i Brachialis (pronated) ii (neutral)
Acromioplasty. Surgical Indications and Considerations
 1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
1 Acromioplasty Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: Any abnormality that disrupts the intricate relationship within the subacromial space may lead to impingement. Both intrinsic
Nerves of Upper limb. Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh
 Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Nerves of Upper limb Dr. Brijendra Singh Professor & Head Department of Anatomy AIIMS Rishikesh 1 Objectives Origin, course & relation of median & ulnar nerves. Motor & sensory distribution Carpal tunnel
Upper Extremity Injuries in Youth Baseball: Causes and Prevention
 Upper Extremity Injuries in Youth Baseball: Causes and Prevention Biomechanics Throwing a baseball is an unnatural movement Excessively high forces are generated at the elbow and shoulder Throwing requires
Upper Extremity Injuries in Youth Baseball: Causes and Prevention Biomechanics Throwing a baseball is an unnatural movement Excessively high forces are generated at the elbow and shoulder Throwing requires
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
 Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy The true shoulder joint is called the glenohumeral joint and consists humeral head and the glenoid. It is a ball and socket joint. Anatomy of the Shoulder
The Muscular System. Chapter 10 Part C. PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College
 Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Chapter 10 Part C The Muscular System Annie Leibovitz/Contact Press Images PowerPoint Lecture Slides prepared by Karen Dunbar Kareiva Ivy Tech Community College Table 10.9: Muscles Crossing the Shoulder
Shoulder and Elbow ORTHOPAEDIC SYPMPOSIUM APRIL 8, 2017 DANIEL DOTY MD
 Shoulder and Elbow ORTHOPAEDIC SYPMPOSIUM APRIL 8, 2017 DANIEL DOTY MD Shoulder Articulations Glenohumeral Joint 2/3 total arc of motion Shallow Ball and Socket Joint Allows for excellent ROM Requires
Shoulder and Elbow ORTHOPAEDIC SYPMPOSIUM APRIL 8, 2017 DANIEL DOTY MD Shoulder Articulations Glenohumeral Joint 2/3 total arc of motion Shallow Ball and Socket Joint Allows for excellent ROM Requires
Elbow Injuries in the Adult Athlete. Tamara A. Scerpella, MD Professor, Orthopedic Surgery University of Wisconsin
 Elbow Injuries in the Adult Athlete Tamara A. Scerpella, MD Professor, Orthopedic Surgery University of Wisconsin Acute Elbow Dislocation Fracture Distal humerus Olecranon Radial head Distal Biceps Rupture
Elbow Injuries in the Adult Athlete Tamara A. Scerpella, MD Professor, Orthopedic Surgery University of Wisconsin Acute Elbow Dislocation Fracture Distal humerus Olecranon Radial head Distal Biceps Rupture
Anatomical Considerations/ Pathophysiology The shoulder is the most mobile joint in the body. : Three bones:
 Introduction Musculoskeletal training is generally underrepresented in medical training and residency curriculums. There is a general deficit in musculoskeletal knowledge amongst current medical students,
Introduction Musculoskeletal training is generally underrepresented in medical training and residency curriculums. There is a general deficit in musculoskeletal knowledge amongst current medical students,
Soft Tissue Rheumatism. Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group
 Soft Tissue Rheumatism Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating most causes of joint pain are not! Common areas of
Soft Tissue Rheumatism Elinor Mody, MD Chief, Division of Rheumatology Reliant Medical Group Some problems are difficult, but diagnosing and treating most causes of joint pain are not! Common areas of
 Nerve Compression Syndromes Median Nerve Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pronator Syndrome Ulnar Nerve Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome TOS www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition
Nerve Compression Syndromes Median Nerve Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Pronator Syndrome Ulnar Nerve Cubital Tunnel Syndrome Ulnar Tunnel Syndrome TOS www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) Definition
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2
 Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Clinical Orthopaedic Rehabilitation Volume 1 and 2 COURSE DESCRIPTION This program is a practical, clinical guide that provides guidance on the evaluation, differential diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation
Common Upper Extremity Neuropathies (Not Carpal Tunnel Syndrome)
 Common Upper Extremity Neuropathies (Not Carpal Tunnel Syndrome) Nerve Compressions Common in adults, rare in children Frequently cause missed days of work and sleepless nights CDC 2001 26,794 cases of
Common Upper Extremity Neuropathies (Not Carpal Tunnel Syndrome) Nerve Compressions Common in adults, rare in children Frequently cause missed days of work and sleepless nights CDC 2001 26,794 cases of
Other Elbow Concerns in Overhead Athletes
 Other Elbow Concerns in Overhead Athletes John A. Steubs, M.D. Team Physician, Minnesota Twins TRIA Orthopaedic Center Disclosures None relevant to this presentation. Other Elbow Problems Valgus extension
Other Elbow Concerns in Overhead Athletes John A. Steubs, M.D. Team Physician, Minnesota Twins TRIA Orthopaedic Center Disclosures None relevant to this presentation. Other Elbow Problems Valgus extension
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow
 Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
Functional Anatomy of the Elbow Orthopedic Institute Daryl C. Osbahr, M.D. Chief of Sports Medicine, Orlando Health Chief Medical Officer, Orlando City Soccer Club Orthopedic Consultant, Washington Nationals
Rotator Cuff Strain and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 Rotator Cuff Strain and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: SG, Arms, and Hands Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn
Rotator Cuff Strain and Carpal Tunnel Syndrome 5 minutes: Attendance and Breath of Arrival 50 minutes: Problem-Solving: SG, Arms, and Hands Punctuality- everybody's time is precious: o o Be ready to learn
Physical Examination of the Shoulder
 General setup Patient will be examined in both the seated and supine position so exam table needed 360 degree access to patient Expose neck and both shoulders (for comparison); female in gown or sports
General setup Patient will be examined in both the seated and supine position so exam table needed 360 degree access to patient Expose neck and both shoulders (for comparison); female in gown or sports
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. The Thrower s Elbow: When to Operate. Medial Elbow Pain in the Athlete. Goal of This Talk
 Slide 1 The Thrower s Elbow: When to Operate Luke S. Oh, MD Massachusetts General Hospital Team Physician, Boston Red Sox Team Physician, New England Revolution Consultant, Harvard University Athletics
Slide 1 The Thrower s Elbow: When to Operate Luke S. Oh, MD Massachusetts General Hospital Team Physician, Boston Red Sox Team Physician, New England Revolution Consultant, Harvard University Athletics
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME
 ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
ROTATOR CUFF INJURIES / IMPINGEMENT SYNDROME Shoulder injuries are common in patients across all ages, from young, athletic people to the aging population. Two of the most common problems occur in the
Gross Anatomy Questions That Should be Answerable After October 27, 2017
 Gross Anatomy Questions That Should be Answerable After October 27, 2017 1. The inferior angle of the scapula of a woman who was recently in an automobile accident seems to protrude making a ridge beneath
Gross Anatomy Questions That Should be Answerable After October 27, 2017 1. The inferior angle of the scapula of a woman who was recently in an automobile accident seems to protrude making a ridge beneath
12/3/2011. Trigger Finger Dequervain s tenosynovitis Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medial and Lateral Epicondylitis
 Mohana Amirtharajah Assistant Professor Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Trigger Finger Dequervain s tenosynovitis Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medial and Catching or locking
Mohana Amirtharajah Assistant Professor Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Trigger Finger Dequervain s tenosynovitis Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medial and Catching or locking
SHOULDER PAIN. A Real Pain in the Neck. Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017
 SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
SHOULDER PAIN A Real Pain in the Neck Michael Wolk, MD Northeastern Rehabilitation Associates October 31, 2017 THE SHOULDER JOINT (S) 1. glenohumeral 2. suprahumeral 3. acromioclavicular 4. scapulocostal
Shoulder examination. P Sripathi Rao Arthroscopy & Sports Injuries Unit Dean, Kasturba Medical College
 Shoulder examination P Sripathi Rao Arthroscopy & Sports Injuries Unit Dean, Kasturba Medical College Manipal University, Manipal Common symptoms Tingling Numbness Pain Loss of movements Weakness Approach
Shoulder examination P Sripathi Rao Arthroscopy & Sports Injuries Unit Dean, Kasturba Medical College Manipal University, Manipal Common symptoms Tingling Numbness Pain Loss of movements Weakness Approach
Evaluation of the Knee and Shoulder
 Evaluation of the Knee and Shoulder Karen J. Boselli, MD Northeast Regional Nurse Practitioner Conference May 2018 Knee Overview History Examination Top 5 diagnoses When to image When to refer Pain most
Evaluation of the Knee and Shoulder Karen J. Boselli, MD Northeast Regional Nurse Practitioner Conference May 2018 Knee Overview History Examination Top 5 diagnoses When to image When to refer Pain most
The use of Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Treatment of the Musculoskeletal System
 The use of Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Treatment of the Musculoskeletal System St. Joseph s Refresher Course March 2019 Kenneth Iles, DC John Finkenstadt, MD THIS WORKSHOP WILL FOCUS ON 2 MAIN TOPICS:
The use of Ultrasound for the Diagnosis and Treatment of the Musculoskeletal System St. Joseph s Refresher Course March 2019 Kenneth Iles, DC John Finkenstadt, MD THIS WORKSHOP WILL FOCUS ON 2 MAIN TOPICS:
12/3/2010. Trigger Finger Dequervain s tenosynovitis Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medial and Lateral Epicondylitis
 Mohana Amirtharajah Assistant Professor Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Trigger Finger Dequervain s tenosynovitis Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medial and Catching or locking
Mohana Amirtharajah Assistant Professor Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Trigger Finger Dequervain s tenosynovitis Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Medial and Catching or locking
Golf Injuries in the Upper Extremity
 Golf Injuries in the Upper Extremity David S. Zelouf, MD Philadelphia Hand to Shoulder Center March Meeting 2019 I have nothing to disclose Except that I m an avid, competitive golfer and I ve had golfer
Golf Injuries in the Upper Extremity David S. Zelouf, MD Philadelphia Hand to Shoulder Center March Meeting 2019 I have nothing to disclose Except that I m an avid, competitive golfer and I ve had golfer
Stefan C Muzin, MD PM&R Attending Physician, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Onsite Physiatrist, GE Aviation, Lynn, MA
 Stefan C Muzin, MD PM&R Attending Physician, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Onsite Physiatrist, GE Aviation, Lynn, MA Consultant, OEHN (Occupational and Environmental Network)
Stefan C Muzin, MD PM&R Attending Physician, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School Onsite Physiatrist, GE Aviation, Lynn, MA Consultant, OEHN (Occupational and Environmental Network)
Nerve Injury. 1) Upper Lesions of the Brachial Plexus called Erb- Duchene Palsy or syndrome.
 Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Nerve Injury - Every nerve goes to muscle or skin so if the nerve is injured this will cause paralysis in the muscle supplied from that nerve (paralysis means loss of function) then other muscles and other
Practical 2 Worksheet
 Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Practical 2 Worksheet Upper Extremity BONES 1. Which end of the clavicle is on the lateral side (acromial or sternal)? 2. Describe the difference in the appearance of the acromial and sternal ends of the
Management of Chronic Elbow Pain
 Mr. Nashat Siddiqui Consultant Upper Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Management of Chronic Elbow Pain Patients presenting with elbow pain can pose a diagnostic challenge, especially if there is no obvious recent
Mr. Nashat Siddiqui Consultant Upper Limb Orthopaedic Surgeon Management of Chronic Elbow Pain Patients presenting with elbow pain can pose a diagnostic challenge, especially if there is no obvious recent
Shoulder Joint Examination. Shoulder Joint Examination. Inspection. Inspection Palpation Movement. Look Feel Move
 Shoulder Joint Examination History Cuff Examination Instability Examination AC Joint Examination Biceps Tendon Examination Superior Labrum Examination Shoulder Joint Examination Inspection Palpation Movement
Shoulder Joint Examination History Cuff Examination Instability Examination AC Joint Examination Biceps Tendon Examination Superior Labrum Examination Shoulder Joint Examination Inspection Palpation Movement
TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM
 TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM OBJECTIVES Understand how we interact with technology new and old Understand how injury occurs Texting
TECHNOLOGY AND HOW WE USE IT TO DAMAGE OURSELVES WILLIAM A. DELP, DO ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF OMM GA PCOM OBJECTIVES Understand how we interact with technology new and old Understand how injury occurs Texting
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES
 ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
ORTHOPAEDIC INJECTION AND ASPIRATION TECHNIQUES OAAPN October 20, 2016 David H. Sohn, JD MD Chief, Shoulder and Sports Medicine University of Toledo Medical Center When to aspirate? To rule out infection
Office Orthopedics. No conflict of interest No financial disclosures 1/31/2018
 Office Orthopedics Amin Afsari DO Orthopedic Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery Orthopedic Institute of Wisconsin Midwest Orthopedic Specialty Hospital 1 No conflict of interest No financial disclosures
Office Orthopedics Amin Afsari DO Orthopedic Hand and Upper Extremity Surgery Orthopedic Institute of Wisconsin Midwest Orthopedic Specialty Hospital 1 No conflict of interest No financial disclosures
C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
 Evaluation and Treatment of the Painful Shoulder in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center A 65-year-old
Evaluation and Treatment of the Painful Shoulder in the Primary Care Setting C. Christopher Smith, M.D. Associate Professor of Medicine Harvard Medical School Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center A 65-year-old
Anatomy Your shoulder is made up of three bones: your upper arm bone (humerus), your shoulder blade (scapula), and your collarbone (clavicle).
 Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Shoulder Impingement/Rotator Cuff Tendinitis One of the most common physical complaints is shoulder pain. Your shoulder is made up of several joints combined with tendons and muscles that allow a great
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand
 Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Clinical examination of the wrist, thumb and hand 20 CHAPTER CONTENTS Referred pain 319 History 319 Inspection 320 Functional examination 320 The distal radioulnar joint.............. 320 The wrist.......................
Cubital Tunnel Syndrome
 Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Disclaimer This movie is an educational resource only and should not be used to manage Orthopaedic Health. All decisions about must be made in conjunction with your Physician or a licensed healthcare provider.
Overuse Injuries & special skeletal injuries Dr M.Taghavi Director of sport medicine center of olympic academy
 Overuse Injuries & special skeletal injuries Dr M.Taghavi Director of sport medicine center of olympic academy Prevalence of Overuse Injuries 30 to 50% of all sport injuries are from overuse In some sports
Overuse Injuries & special skeletal injuries Dr M.Taghavi Director of sport medicine center of olympic academy Prevalence of Overuse Injuries 30 to 50% of all sport injuries are from overuse In some sports
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology. Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University
 The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
The Elbow and Radioulnar Joints Kinesiology Dr Cüneyt Mirzanli Istanbul Gelisim University 1 The Elbow & Radioulnar Joints Most upper extremity movements involve the elbow & radioulnar joints. Usually
Pain Assessment Patient Interview (location/nature of symptoms), Body Diagram. Observation and Examination: Tests and Measures
 Examination of Upper Quarter Neurogenic Pain Jane Fedorczyk, PT, PhD, CHT Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA Center of Excellence for Hand and Upper Limb Rehabilitation I. History Mechanism
Examination of Upper Quarter Neurogenic Pain Jane Fedorczyk, PT, PhD, CHT Thomas Jefferson University, Philadelphia, PA Center of Excellence for Hand and Upper Limb Rehabilitation I. History Mechanism
1-Apley scratch test.
 1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
1-Apley scratch test. The patient attempts to touch the opposite scapula to test range of motion of the shoulder. 1-Testing abduction and external rotation( +ve sign touch the opposite scapula, -ve sign
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity
 Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
Current Developments in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion Injuries of the Upper Extremity D. Mowry 1 Mowry, D. 1995. Current Development in the Prevention and Treatment of Repetitive Motion
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS. Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran
 TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
TENDINOSIS: TRIGGER FINGER DE QUERVAIN S TENOSYNOVITIS Renita Sirisena Mark Puhaindran Tendinosis vs Tendinitis Tendinosis: Degeneration of the tendon s collagen Related to chronic use Tendinitis Tendon
Overuse Injuries of the Upper Extremity. Overuse Injuries 7/23/2018. Peadiatric Overuse Sports Injuries. Al Hess, MD
 Overuse Injuries of the Upper Extremity Al Hess, MD 7/21/2018 1 Overuse Injuries Everything? Not Trauma, infection, tumor, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis Onset of pain associated with repetitive
Overuse Injuries of the Upper Extremity Al Hess, MD 7/21/2018 1 Overuse Injuries Everything? Not Trauma, infection, tumor, rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis Onset of pain associated with repetitive
Mr. Duy Thai Orthopaedic Surgeon, Melbourne VIC
 Mr. Duy Thai Orthopaedic Surgeon, Melbourne VIC International Convention of the Vietnamese Physicians, Dentists and Pharmacists of the Free World Melbourne 8 10 August 2014 Conflict of Interest None Subacromial
Mr. Duy Thai Orthopaedic Surgeon, Melbourne VIC International Convention of the Vietnamese Physicians, Dentists and Pharmacists of the Free World Melbourne 8 10 August 2014 Conflict of Interest None Subacromial
Inspection. Physical Examination of the Elbow. Anterior Elbow 2/14/2017. Inspection. Carrying angle. Lateral dimple. Physical Exam of the Elbow
 of the Elbow Anthony A. Romeo, MD Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Rush University President-Elect, American Shoulder Elbow Surgeons Team Physician, Chicago
of the Elbow Anthony A. Romeo, MD Professor, Department of Orthopedics Head, Section of Shoulder and Elbow Surgery Rush University President-Elect, American Shoulder Elbow Surgeons Team Physician, Chicago
Elbow. Chapter 2 LISTEN. Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Pain
 Preface The first decade of the twenty-first century has witnessed the continuation of an explosion in our knowledge and understanding of all aspects of disease. Accompanying this has been the increasing
Preface The first decade of the twenty-first century has witnessed the continuation of an explosion in our knowledge and understanding of all aspects of disease. Accompanying this has been the increasing
Wrist and Hand Complaints
 Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Wrist and Hand Complaints Charles S. Day, M.D., M.B.A. Chief, Hand & Upper Extremity Surgery St. Elizabeth s Medical Center Tufts University School of Medicine Primary Care Internal Medicine 2018 Outline
Main Menu. Wrist and Hand Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
1 The Wrist and Hand Joints click here Main Menu K.5 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k5/k5entry.htm[3/23/18, 1:40:40 PM] Bones 29 bones, including radius and ulna 8 carpal bones in 2 rows of
PG Session: Power Ortho: Hand & Wrist/ Kyle Bickel, MD, FACS
 WOHC 2012 Hand & Wrist Kyle D. Bickel, M.D., FACS The Hand Center of San Francisco Disclosure Information Western Occupational Health Conference 2012 Kyle D. Bickel, MD, FACS I have no pertinent financial
WOHC 2012 Hand & Wrist Kyle D. Bickel, M.D., FACS The Hand Center of San Francisco Disclosure Information Western Occupational Health Conference 2012 Kyle D. Bickel, MD, FACS I have no pertinent financial
Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods )
 Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods ) M.N. Naderi Fellowship in shoulder and arthroscopic surgery Neer : Definition Impingement on the tendinous portion of the rotator cuff by the coracoacromial
Subacromial Impingement (diagnostic methods ) M.N. Naderi Fellowship in shoulder and arthroscopic surgery Neer : Definition Impingement on the tendinous portion of the rotator cuff by the coracoacromial
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand
 Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Physical therapy of the wrist and hand Functional anatomy wrist and hand The wrist includes distal radius, scaphoid, lunate, triquetrum, pisiform, trapezium, trapezoid, capitate, and hamate. The hand includes
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery
 Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Hand / wrist Injections. MATS. June 2018. Condition Symptoms Conservative Treatments Location of injection CBA for surgery Carpal Tunnel Tingling / numbness in median nerve distribution (lateral 3 fingers)
Upper limb injuries II. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 Upper limb injuries II Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Capsulitis = inflammatory lesion of the glenohumeral joint capsule leading to: thickening and loss of joint volume painful stiffness of the
Upper limb injuries II Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Capsulitis = inflammatory lesion of the glenohumeral joint capsule leading to: thickening and loss of joint volume painful stiffness of the
RN(EC) ENC(C) GNC(C) MN ACNP *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT ***
 HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (i.e. Full rotator cuff tears are more common over the age of 45, traumatic injuries
HISTORY *** MECHANISM OF INJURY.. MOST IMPORTANT *** Age - Certain conditions are more prevalent in particular age groups (i.e. Full rotator cuff tears are more common over the age of 45, traumatic injuries
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition
 Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Netter's Anatomy Flash Cards Section 6 List 4 th Edition https://www.memrise.com/course/1577581/ Section 6 Upper Limb (66 cards) Plate 6-1 Humerus and Scapula: Anterior View 1.1 Acromion 1.2 Greater tubercle
Official Definition. Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist.
 Mod 2 MMT Course Official Definition Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. epidemiology Affects an estimated 3
Mod 2 MMT Course Official Definition Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common focal peripheral neuropathy, results from compression of the median nerve at the wrist. epidemiology Affects an estimated 3
Shoulder Arthroscopy. Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij. NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018
 Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
Shoulder Arthroscopy Dr. J.J.A.M. van Raaij NOV Jaarvergadering Den Bosch 25 jan 2018 No disclosures Disclosure Shoulder Instability Traumatic anterior Traumatic posterior Acquired atraumatic Multidirectional
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5. September 30, 2011
 STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
STRUCTURAL BASIS OF MEDICAL PRACTICE EXAMINATION 5 September 30, 2011 PART l. Answer in the space provided. (12 pts) 1. Identify the structures. (2 pts) EXAM NUMBER A. Suprascapular nerve B. Axillary nerve
Lab Activity 11: Group II
 Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Lab Activity 11: Group II Muscles Martini Chapter 11 Portland Community College BI 231 Origin and Insertion Origin: The place where the fixed end attaches to a bone, cartilage, or connective tissue. Insertion:
Dr. Stefan C. Muzin, MD PM&R Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Consultant, GE Aviation, OEHN.
 Dr. Stefan C. Muzin, MD PM&R Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Consultant, GE Aviation, OEHN Work Related Workshop WorkInjuries Related Injuries Workshop Think of the Big Picture
Dr. Stefan C. Muzin, MD PM&R Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center Harvard Medical School Consultant, GE Aviation, OEHN Work Related Workshop WorkInjuries Related Injuries Workshop Think of the Big Picture
SHOULDER Highly mobile, so less stable. Abnormalities cloaked within extensive musculature, dx can be difficult Bony abnormalities less common than li
 SPORTS MEDICINE CASES A quick tour of some local joints Featuring gco common o and unusual problems SHOULDER Highly mobile, so less stable. Abnormalities cloaked within extensive musculature, dx can be
SPORTS MEDICINE CASES A quick tour of some local joints Featuring gco common o and unusual problems SHOULDER Highly mobile, so less stable. Abnormalities cloaked within extensive musculature, dx can be
Grundkurs SGSM-SSMS Sion Sports Elbow. Dr Stéphane Kämpfen
 Grundkurs SGSM-SSMS Sion 2015 Sports Elbow Dr Stéphane Kämpfen Type of pathologies! Acute:! Fractures - dislocation! Sprain! Chronic:! Overload syndrome Fractures - Radial head: Mason classification Mason
Grundkurs SGSM-SSMS Sion 2015 Sports Elbow Dr Stéphane Kämpfen Type of pathologies! Acute:! Fractures - dislocation! Sprain! Chronic:! Overload syndrome Fractures - Radial head: Mason classification Mason
The Shoulder. Jill Inouye Primary Care Sports Medicine Family Medicine Resident School February 26, 2014
 The Shoulder Jill Inouye Primary Care Sports Medicine Family Medicine Resident School February 26, 2014 Objectives Review shoulder anatomy Explain and demonstrate shoulder physical exam Diagnosis and management
The Shoulder Jill Inouye Primary Care Sports Medicine Family Medicine Resident School February 26, 2014 Objectives Review shoulder anatomy Explain and demonstrate shoulder physical exam Diagnosis and management
10/1/2009. October 15, 2009 Christina Kuo MD. Anatomy and pathophysiology of Epicondylitis Diagnosis
 October 15, 2009 Christina Kuo MD Anatomy and pathophysiology of Epicondylitis Diagnosis Treatment options Lawn tennis elbow Morris 1882 - described as an injury occurring from the backhand stroke Age
October 15, 2009 Christina Kuo MD Anatomy and pathophysiology of Epicondylitis Diagnosis Treatment options Lawn tennis elbow Morris 1882 - described as an injury occurring from the backhand stroke Age
Clinical Anatomy of the Upper Limb. Kara Mudd, MSPAS, PA-C
 Clinical Anatomy of the Upper Limb Kara Mudd, MSPAS, PA-C Contents Bones and Joints Clinical Anatomy of Upper Limb Joints Clinical Anatomy of Upper Limb Muscles Clinical Anatomy of Nerve affect Upper Limb
Clinical Anatomy of the Upper Limb Kara Mudd, MSPAS, PA-C Contents Bones and Joints Clinical Anatomy of Upper Limb Joints Clinical Anatomy of Upper Limb Muscles Clinical Anatomy of Nerve affect Upper Limb
THE WRIST. At a glance. 1. Introduction
 THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
THE WRIST At a glance The wrist is possibly the most important of all joints in everyday and professional life. It is under strain not only in many blue collar trades, but also in sports and is therefore
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY
 8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
8 Recovering From HAND FRACTURE SURGERY Hand fractures are caused by trauma and result in breaking (fracturing) the phalanges or metacarpals. Surgery involves achieving acceptable alignment and providing
The Shoulder. Jennifer R Marks, MD
 The Shoulder Jennifer R Marks, MD Shoulder Anatomy Skeletal & ligamentous components: The joint is comprised of a confluence of Scapula Clavicle Humerus https://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article/ http/ www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article/117777
The Shoulder Jennifer R Marks, MD Shoulder Anatomy Skeletal & ligamentous components: The joint is comprised of a confluence of Scapula Clavicle Humerus https://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article/ http/ www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article/117777
Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy
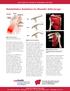 UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Acromion Supraspinatus Back View Supraspinatus Long head of bicep Type I Infraspinatus Short head of bicep
UW HEALTH SPORTS REHABILITATION Rehabilitation Guidelines for Shoulder Arthroscopy Front View Acromion Supraspinatus Back View Supraspinatus Long head of bicep Type I Infraspinatus Short head of bicep
Biceps Brachii. Muscles of the Arm and Hand 4/4/2017 MR. S. KELLY
 Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
Muscles of the Arm and Hand PSK 4U MR. S. KELLY NORTH GRENVILLE DHS Biceps Brachii Origin: scapula Insertion: radius, fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) Action: supination and elbow flexion Innervation:
UCL Sprain/Tear MEDIAL ELBOW PAIN. Moving Valgus Stress Test. Valgus Instability/Ulnar Collateral Ligament Sprain. Property of VOMPTI, LLC
 UCL Sprain/Tear MEDIAL ELBOW PAIN Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Valgus Instability/Ulnar Collateral Ligament Sprain History Acute
UCL Sprain/Tear MEDIAL ELBOW PAIN Kristin Kelley, DPT, OCS, FAAOMPT Orthopaedic Manual Physical Therapy Series Charlottesville 2017-2018 Valgus Instability/Ulnar Collateral Ligament Sprain History Acute
The examination of the painful knee. Maja K Artandi, MD, FACP Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University
 The examination of the painful knee Maja K Artandi, MD, FACP Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University Objectives of the talk By the end of this talk you will know The important anatomy
The examination of the painful knee Maja K Artandi, MD, FACP Clinical Associate Professor of Medicine Stanford University Objectives of the talk By the end of this talk you will know The important anatomy
Elbow Elbow Anatomy. Flexion extension. Pronation Supination. Anatomy. Anatomy. Romina Astifidis, MS., PT., CHT
 Elbow Elbow Anatomy Romina Astifidis, MS., PT., CHT Curtis National Hand Center Baltimore, MD October 6-8, 2017 Link between the arm and forearm to position the hand in space Not just a hinge Elbow = 70%
Elbow Elbow Anatomy Romina Astifidis, MS., PT., CHT Curtis National Hand Center Baltimore, MD October 6-8, 2017 Link between the arm and forearm to position the hand in space Not just a hinge Elbow = 70%
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
 A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Concord Orthopaedics 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this
A Patient s Guide to Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Concord Orthopaedics 264 Pleasant Street Concord, NH 03301 Phone: 6032243368 Fax: 6032287268 marketing.copa@concordortho.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this
Elbow Muscle Power Deficits
 1 Elbow Muscle Power Deficits ICD-9-CM code: 726.32 Lateral epicondylitis ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4300 Lifting, d4452 Reaching, d4401 Grasping Body Structure code: s73012 Muscles
1 Elbow Muscle Power Deficits ICD-9-CM code: 726.32 Lateral epicondylitis ICF codes: Activities and Participation code: d4300 Lifting, d4452 Reaching, d4401 Grasping Body Structure code: s73012 Muscles
Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned
 Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned Jessica Leschied, MD Sections of Pediatric and Musculoskeletal Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan Ann
Pediatric Musculoskeletal Ultrasound: Cases reviewed and lessons learned Jessica Leschied, MD Sections of Pediatric and Musculoskeletal Radiology C.S. Mott Children s Hospital University of Michigan Ann
