Upper Extremity Fractures & Lawn Mower Injury Prevention 7/16/2012. Viewing Time. Faculty Disclosure. Target Audience. Speaker Faculty Disclosure
|
|
|
- Janel Flowers
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Viewing Time This presentation will take approximately one hour to complete. Target Audience This program is designed for primary care physicians. Other health care professionals working with patients and their families may also find this program of interest. Faculty Disclosure It is the policy of Children s Hospitals and Clinics of Minnesota to ensure balance, independence, objectivity, and scientific rigor in all its educational programs. Our faculty have been asked to disclose to our program audience any real or apparent conflicts of interest related to the content of their presentations. They have also been requested to let you know when any products mentioned in their presentations are not labeled for the use under discussion or are still under investigation. 3 Speaker Faculty Disclosure Jennifer C. Laine, MD has disclosed no actual or apparent conflict of interest in relation to this educational activity. During this educational activity Dr. Laine will not be discussing the off-label use of any commercial or investigational product not approved for any purpose by the FDA. Upper Extremity Fractures & Lawn Mower Injury Prevention Pediatric Grand Rounds: July 12, 2012 Jennifer C. Laine, MD Orthopedic Surgeon Gillette Children s Specialty Healthcare Children s Hospitals and Clinics of Minnesota 5 1
2 Upper Extremity Fractures & Lawn Mower Injury Prevention Pediatric Grand Rounds: July 12, 2012 A lecture on the evaluation, treatment and management of pediatric upper extremity fractures. Includes a discussion of lawnmower safety for children. Program Objectives Upon completion of this program, participants should be able to: Overview of unique aspects of the pediatric skeleton with respect to injury, healing and remodeling. Review of the initial assessment of a patient with upper extremity injury history, physical exam, imaging. Review initial management of pediatric upper extremity injuries; when to splint, when to follow-up with orthopaedics and when surgery is indicated. Discuss pitfalls associated with managing the injured child. Disclaimer Children s Hospitals and Clinics of Minnesota accepts no responsibility for the materials presented through these Grand Rounds seminars. Each professional presenter assumes all responsibility for maintaining confidentiality or obtaining authorization, in accordance with all applicable laws. Accreditation Children s Hospitals and Clinics of Minnesota is accredited by the Minnesota Medical Association to provide continuing medical education for physicians. Children s Hospitals and Clinics of Minnesota designates this educational activity for a maximum of 1 AMA Category 1 Credit TM toward the AMA Physician s Recognition Award. Each Physician should only claim credit for the actual time he/she spent in the activity. Retention of CME Records It is the policy of Children s Medical Education program that we cannot offer to retain CME records for physicians attending or viewing the online CME activity. The Minnesota Medical Association designates that physicians are responsible for maintaining their own CME records. Receiving CME Credit To receive CME credit, you must view the entire program. When the program is completed, click the Post Test button on the interface to access the Post Test. You must successfully pass the Post Test to receive CME credit. 2
3 Disclosures Pediatric Upper Extremity Fractures: Diagnosis and Initial Management No Disclosures Jennifer C. Laine, MD Pediatric Grand Rounds at Children s - MN July 12, 2012 Objectives Overview of unique aspects of the pediatric skeleton with respect to injury and healing Review of the initial assessment of a patient with upper extremity injury History, physical exam, imaging Review initial management of pediatric upper extremity injuries When to splint When to follow-up with orthopaedics When surgery is indicated Pitfalls associated with managing the injured child Provide an awareness of lawnmower injuries and prevention Outline Epidemiology Pediatric Injury Overview Specific Injuries Clavicle Shoulder Humerus Elbow Forearm Wrist Cooper, et al. JBMR
4 Pediatric Skeleton Children are not simply small adults Though some adults are simply large children Pediatric Skeleton Less dense and more porous Periosteum is very thick Presence of growth plates (physes) Ends of long bones are nonossified cartilage The Pediatric Skeleton Comminuted fractures are uncommon The Pediatric Skeleton Comminuted fractures are uncommon Large pores in the immature cortex can prevent propagation (greenstick) Large pores in the immature cortex can prevent propagation (greenstick) Fail with tension or compression (buckle fracture Fail with tension or compression (buckle fracture Images: radiologyassistant.com; Images: radiologyassistant.com; Anatomy of the Pediatric Skeleton Anatomic Differences Growth Plates Most obvious difference is the presence of growth plates and thick periosteum Growth plate injuries may lead to significant growth disturbances Missed diagnoses Reduction of the growth plate injury must be precise Image: davidlnelsonmd.com 4
5 Anatomic Differences Periosteum Periosteum has greater bone forming potential Helps to maintain alignment of simple fractures Reduces the amount of displacement of fractures Can aid in the reduction of fractures Remodeling Remodeling may make reduction accuracy somewhat less important than in an adult Intra-articular fractures must be anatomically reduced and will not remodel Image: Remodeling Years of growth remaining Location vs. physis Growth potential of physis Plane of motion Evaluation History: Mechanism, velocity, timing Hand dominance? Exam: Look at whole child Deformity? Spontaneous movement? Remove splints, bandages Squeeze each extremity Range every major joint in all extremities Point of maximal tenderness Capillary refill, pulses Pain with passive stretch Staheli L. Fundamentals of Pediatric Orthopedics, 2008 Point of Maximal Tenderness Clavicle Shoulder Length of humerus Medial and lateral epicondyle Posterior distal humerus Olecranon Radial head Length of radius and ulna Snuffbox tenderness (scaphoid) Evaluation Upper Extremity Thumbs-up Posterior Interosseous Nerve (PIN radial) A-OK Anterior Interosseous Nerve (AIN median) Spread or cross fingers Ulnar Image: mountnittany.org Image: childbehaviorsolution.blogspot.com, danceswithchaos.wordpress.com 5
6 Evaluation Upper Extremity Sensory Exam: Axillary Radial Median Ulnar Imaging Plain Radiographs Orthogonal views; obliques Image joint above/below Contralateral imaging MRI: rare Image: healthhype.com Incidence Upper extremity fractures account for up to 75% of all childhood fractures Clavicle Fracture Obstetrical injury: 0.5% ~90% of obstetrical fractures 8-15% of all pediatric fractures Fall onto shoulder Usually midshaft (80%) Image: shoulderdistociainfo.com, shoulderdoc.co.uk Clavicle Fractures Skin tenting? Neurologically intact? AP clavicle Cephalad-directed view Medial Clavicle/SC Joint: serendipity view Lateral Clavicle: axillary lateral Clavicle Fractures Treatment Supportive; sling No reduction attempt No sports 6-8 weeks Bump will remodel Image: Tachdjian s Pediatric Orthopaedics 2008 panoramapeds.com 6
7 Clavicle Fracture Operative Indications? Uncommon Skin tenting Neurologic compromise Multiple injuries (floating shoulder) Older Adolescent? Grey zone Earlier follow-up Proximal Humerus Fractures <5% of all pediatric fractures Enormous healing and remodeling potential Birth injury: Physeal injury/separation Child (5-12): metaphyseal Adolescent (13-16): physeal Cary, et al. JPO 2011 Image: Tachdjian s Pediatric Orthopaedics 2008; jbjs.org Proximal Humerus Fractures Mechanism Direct: blow to shoulder Indirect: fall on outstretched arm Sports, MVA Presentation Pain, swelling, ecchymosis Internally rotated Associated: dislocation, brachial plexus injury, PTX, rib fxs Image: concordortho.com; autoaccidentlawyeroregon.com Proximal Humerus Fractures AP Axillary Lateral (Scapulary Y) (CT) Image: orthobullets.com Proximal Humerus Fractures <11yo no reduction needed Good results regardless of displacement >11yo grossly displaced fractures need reduction Traction, abduction, flexion, ER Goal: <50% displacement, 20 degrees angulation High rate re-displacement Barriers Rockwood and Wilkins 2006 Image: courtesy of M. Diab, MD Proximal Humerus Fractures Immobilization Sling and swathe Shoulder immobilizer Hanging arm cast Shoulder spica Rockwood and Wilkins 2006 Image: creativecastingconcepts.com, allegromedical.com 7
8 Humeral Shaft Fractures <10% of pediatric humerus fractures 2-5% pediatric fractures <3yo >12yo 10yoM Fall from tree 10 days after cast One month after injury Rockwood and Wilkins 2006 Image: wheelessonline.com Humeral Shaft Fracture <3yo: Spiral twisting injury Transverse direct blow Abuse 61% of all new fxs in child abuse Accidental > abuse Humeral Shaft Fracture >12yo: Transverse fractures Direct blow Fall PVA GSW Pathologic fracture through cyst Sports Direct blow Throwing stress injury Humeral Shaft Fracture Young child: pseudoparalysis Older child: pain, swelling, refusal to move extremity Supported with contra hand, held to body Neurologic exam Radial Nerve Vascular exam Imaging: orthogonal views humerus Shoulder/elbow Image: e-radiography.net Humeral Shaft Fracture: Alignment Not Weightbearing Shoulder compensation Beatty: <5yo: 70 degrees, complete displacement 5-12: degrees >12yo: 40 degrees and 50% apposition Clinical appearance >> XR alignment Beatty AAOS Instr Course Lecture 1992 Rockwood and Wilkins
9 Treatment Infant: ACE wrap swathe Coaptation splint Hanging arm cast Functional bracing 6mo M 2 weeks after fall 30 degrees varus 12mo M Image: steinergraphics.com; creativecastingconcepts.com, swissorthoma.ch Incidence 8-9% of all pediatric fractures occur about the elbow THE ELBOW Image: Tachdjian s Pediatric Orthopaedics 2008;jbjs.org Distal humerus 86.4% 69% supracondylar 17% lateral condyle 14% medial epicondyle 1% T-condylar Challenges in Diagnosis Difficult physical exam Pediatric elbow ossification centers Different fracture types than in adult Work-up Mechanism Careful assessment of: Soft tissues Neurologic status Vascular status pulses, capillary refill, warmth Don t forget radial neck, wrist! Image ENTIRE extremity Multiple fractures common Images: orange44.blogspot.com, wheelessonline.com, jbjs.org 9
10 Radiographic Anatomy Ossification Centers Radiographic Anatomy Ossification Centers 5moM 3+8M 6+7M 10+7M Skaggs, D. JAAOS 1997 Radiographic Anatomy Radiographic Anatomy Image: emedicine.medscape.com Radiographic Anatomy Radius should point at capitellum in every view! Radius should point at capitellum in every view! Image: Tachdjian s Pediatric Orthopaedics Skaggs, D. JAAOS
11 Transphyseal Fracture Difficult to recognize <4yo; esp. <18mos Shear force muffled crepitus Non-accidental trauma! Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Most common elbow fracture - 60% Age 1-7 years; peak 5-7 Thin supracondylar region - 1mm thick Extension type 96% Flexion type 4% Image: Rockwood and Wilkins 2006 Mechanism Fall on outstretched hand, elbow extended Most have hyperextensible elbows Directs force to anatomically weak olecranan fossa Associated Injuries Nerve % Radial 45% Median 32% - AIN Ulnar 23% - usually flexion type Image: Rockwood and Wilkins 2006 Image: Tachdjian s Pedaitric Orthopaedics; jbjs.org Associated Injuries Vascular 1% Brachialis muscle protects brachial artery Tethering, spasm, tear, entrapment Classification Gartland Classification Type I Nondisplaced Type II Angulated, one cortex intact Type III Displaced Image: courtesy M. Diab, MD; Rowell PJW. Injury
12 TYPE I Type I X-ray findings may be minimal Fracture line may not be visible Tenderness on exam, posterior fat pad Immobilization Posterior long-arm splint in 90degrees Follow-up with ortho in few days Ensure alignment Type II Type II Most can be reduced simply by flexing elbow Controversial Most are now treated surgically Closed reduction and percutaneous pinning Long arm splint 5yoM Fall from monkey bars Call ortho or have ortho follow-up in 1-2 days Type III Type III More commonly associated with neurovascular injury, compartment syndrome Most treated with closed reduction, pinning Open reduction rarely required 6yoM Fall from Monkey Bars Splint elbow as it lies degrees flexion Do not wrap tightly Check neurovascular exam before and after! Ortho Consult 12
13 Lateral Condylar Fracture 17% elbow fractures Ages 5-10 Varus stress to extended elbow Spectrum from nondisplaced fractures without articular surface disruption to displaced intraarticular fractures 3yoM Fall from bike Lateral Condylar Fracture Nondisplaced - rare. Beware! May be treated with immobilization Displaced - open reduction Complications Nonunion Permanent loss of motion Cubitus valgus Tardy ulnar nerve palsy Internal Oblique View 3yoM Fall from playground Consult ortho Follow-up 1-2 days Image: Rockwood and Wilkins 2006 Treatment: Open reduction, pinning Monteggia Fractures Proximal 1/3 ulnar fracture, dislocated radial head 0.4% all pediatric forearm fractures Peak incidence age 4-10 years 11-20% nerve palsies - PIN most common 13
14 Diagnosis Anterior 70% AP/Lat x-rays including wrist and elbow Line through radial head must pass through center of capitellum Plastic deformation of ulna Lateral 24% Radial N injury Image: emedicine.medscape.com Forearm Fractures 45% of all childhood fractures 62% upper limb fractures 81% occur in those > 5 yea 75-84% distal third 15-18% middle third THE FOREARM Forearm Fractures Most treated closed Goal of treatment is to align extremity longitudinally and rotationally Requires understanding of: Mechanism of injury Anatomy Deforming forces Remodeling ability Forearm Shaft Fractures 3.4% all childhood, 18% forearm fractures Peak - latter part first decade More complex than distal fractures Require a more aggressive approach Angulation results in loss of rotation 14
15 Forearm Shaft Fractures Angulation post reduction frequent X-ray weekly for at least 3 weeks Remanipulation is possible up to 4 weeks Forearm Shaft Fractures Angulation post reduction frequent X-ray weekly for at least 3 weeks Remanipulation is possible up to 4 weeks Careful cast molding essential 3 point, interosseous mold, straight ulnar border Consider extension casting in small children Proximal fractures 3 point mold Immobilization 8-10 weeks common Forearm Fractures Rotation is lost most often 60% lose > 20 degrees Rarely does this result in functional deficit 85% treated with closed reduction have satisfactory results Role of Open Reduction Irreducible or unstable reduction Age 10 or older Segmental or open fractures Associated elbow, humeral,vascular injury Refracture Plate vs. Intramedullary fixation Image: Tachdjian s Pediatric Orthopaedics; jbjs.org 11yoF Fall from monkey bars 15
16 Distal Radius/Ulna Fractures 21% all pediatric fractures Occur ages 2-14, peak 9-10 girls, 3-14 boys Low energy injury Spectrum of injury from buckle to displaced physeal or metaphyseal fractures Remodeling Potential Age Degree of angulation Is angulation in plane of motion? Metaphyseal fractures have a greater capacity to remodel Most correction occurs in the distal physis Larsen - up to 28 degrees of correction can occur at the distal physis in those < 11 Bayonet apposition acceptable in < age 8-10 Management If uncomfortable with reductions ortho consult If comfortable closed reduction Sugartong splint to immobilize wrist and elbow If not too swollen, can use LAC Ortho follow-up within the week to ensure reduction has been maintained Distal Radius Physeal Fx Most common physeal fracture: 28-46% 75% occur between years Salter-Harris Type 2: 58-75% Hyperextension injury - dorsal displacement Image: radiologytutorial.com 16
17 Distal Radial Physeal Fracture Reduce displaced fractures promptly Some SH 2 are difficult to reduce - accept 50% apposition if angulation corrected Remanipulation difficult after 10 days Single reduction - physeal arrest rare Premature physeal arrest occurs in 27% undergoing 2 or more reduction attempts Distal Radial Physeal Fracture Heal rapidly - 3 to 4 weeks Long arm cast Three-point moulding, not excessive flexion Open reduction rarely necessary Image: accessem.com Buckle Fractures (= Torus) Compression fx at metaphyseal-diaphyseal junction Torus fracture = Buckle fracture Torus = Ring at column base If uncertain: re-xray 1 week Brief casting 2-3 weeks needed Small children require a long arm cast simply to keep the cast on Torus fracture = Buckle fracture Torus = Ring at column base Management Well-molded splint or long arm cast Heal well 17
18 Summary Pediatric skeletal anatomy leads to unique injuries Injuries can be easily missed without the proper work-up Most injuries do well with non-operative management Any fracture that might need surgery: consult ortho or at least follow-up in first few days Any fracture that has been reduced or might displace follow-up within one week Please do not hesitate to call us with questions or consults! Lawnmower Related Injuries 100% Preventable Jennifer C. Laine, MD Gillette Children s Specialty Healthcare Image: pediatricsnow.com Thebrownwall.blogspot.com The Stats The Stats US Consumer Product Safety Commission (2003): 60 million lawnmowers in use in 2003; 9.5 million riding mowers US Consumer Product Safety Commission (2007): 210,000 people treated in doctors offices, emergency departments and clinics for lawnmower injuries 16,000 children Lau ST. Pediatric Surg Int 2006 AAOS 2012 (US CPSC) 18
19 The Stats The Stats ~75 deaths per year due to lawnmowers 1 in 5 is a young child From , the number of lawn mower related injuries per year increased by 18% Lau ST. Pediatric Surg Int 2006 Lau ST. Pediatric Surg Int 2006 The Stats The Stats ~3/4 boys Average age: ~7-11 years old bimodal Loder RT. Journal Pediatric Orthopaedics 1997 Lau ST. Pediatric Surg Int 2006 Vollman D and Smith G. Pediatrics 2006 Vollman D and Smith GA. Pediatrics 2006 The Setting The Season 89% in own yard 72% walking up to mower 50% injured while mower in reverse 78% injured by the usual operator of the mower Farley FA, et al. Journal Pediatric Orthopaedics 1996 Volman D and Smith GA. Pediatrics
20 The Injuries Projectiles Image: cartoonstock.com Volman D and Smith GA. Pediatrics 2006 Projectiles Most common mechanism for injury 80% of foreign body injuries are to eyeball/face or lower extremities Kinetic energy is three times the power of a magnum Amputations Momentum at the tip of a blade could launch a 1.2lb object at a speed of 232mph Costilla V and Bishai DM. Annals of Emergency Medicine 2006 Loder RT, et al.. Journal Pediatric Orthopaedics 1997 Ourfreedomproducts.com Image: offthemark.com Amputations Lawnmower was #1 cause of traumatic amputation (21.6%) 83% of foot and ankle amputations Average age: 4.6y 69% were <5yo Riding Mowers Mean length of stay: 12.5 days Mean total procedures per extremity: 4.8 Mean charge: $21,777 (1996) Image: cartoonstock.com 20
21 Riding Mowers Riding Mowers US Consumer Product Safety Commission Survey: 2.6 injuries per year per 1000 ride-on mowers 3x injury rate versus walk-behind power mowers 55% of households with riding mowers and children under 10 allow their children to ride on mowers 9% of injured operators are 14 or younger Rate of injury for 5-14yo more than twice that for 15-65yo 8% of deaths related to ride-on mowers involve passengers (6yo) and bystanders (4yo) Lau ST. Pediatric Surg Int 2006 Smith G. Pediatrics 2001 Psychologic Effects Unique psychosocial circumstances Parent is usually the operator! Survey: Half of children altered goals and plans for future Majority reported moderate regular pain 56% of parent survey profiles showed defensive response denial or underreporting psych symptoms Prevention Farley FA, et al. Journal Pediatric Orthopaedics 1996 Prevention 16yo riding AAP Recommendations Children indoors 12yo walking Pick up the yard before mowing No passengers Sturdy shoes Education No mowing in reverse 21
22 So this year we finally broke that stronghold of fear and invited our children to ride on our mower. The smiles on their faces tell the story of growing up enjoying all things in life. The joy of independence. Of trying new things and growing in confidence. Aswewalk.wordpress.com How can we best educate our patients and families regarding these preventable injuries?? Thank You Special Thanks to Stephen Sundberg, MD Mark Dahl, MD Richard Andersen, MD Mickey Starr John Crampton Lee Kanten Question We ve been told that Ibuprofen hinders the bone remodeling process, but it helps control swelling and pain. What do you think about the use of Ibuprofen on kids with fractures? Thank you for viewing this presentation! To receive CME credit, please click the Post Test button on the interface, and complete the post test 22
Upper Extremity Fractures
 Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
Upper Extremity Injury Management. Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP
 Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Other Upper Extremity Trauma. Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin
 Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
Other Upper Extremity Trauma Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital Yong-Woon Shin Forearm Fractures Forearm fractures - the most common orthopaedic injuries in children - 30-50% of all pediatric fractures
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus. H. Sithebe 2012
 Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Fractures of the shoulder girdle, elbow and fractures of the humerus H. Sithebe 2012 Fractures of the Clavicle (mid-shaft). Fractures of the clavicle Fractures of the clavicle Treatment- conservative.
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD
 Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018
 PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018 DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose. 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the diagnosis,
PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018 DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose. 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the diagnosis,
Pediatric Elbow Radiology. Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar
 Pediatric Elbow Radiology Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or
Pediatric Elbow Radiology Seema Awatramani, MD Friday, April 5, 2018 ACOEP Spring Seminar Disclosure I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer(s) of any commercial product(s) and/or
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
Goals. Initial management skeletal trauma. Physical Exam ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT 12/4/2010
 ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Brian Feeley, MD UCSF Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Goals Discuss common fractures and initial management, treatment guidelines Let your patients
ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Brian Feeley, MD UCSF Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Goals Discuss common fractures and initial management, treatment guidelines Let your patients
11/5/14. I will try to make this painless. Great, a Fracture, Now What? Objectives. Basics for Fracture Workup. Basics for Fracture Workup
 Great, a Fracture, Now What? I will try to make this painless Mary Greve MS, PA-C Department of Orthopedic Surgery Trauma Team University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Mary-Greve@uiowa.edu Pager 2121 Objectives
Great, a Fracture, Now What? I will try to make this painless Mary Greve MS, PA-C Department of Orthopedic Surgery Trauma Team University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Mary-Greve@uiowa.edu Pager 2121 Objectives
St Mary Orthopaedic Conference. Steven A. Caruso, MD Trenton Orthopaedic Group Trauma and Complex Fracture Surgeon October 25, 2014
 St Mary Orthopaedic Conference Steven A. Caruso, MD Trenton Orthopaedic Group Trauma and Complex Fracture Surgeon October 25, 2014 Nothing to disclose Goals To discuss common orthopaedic pathologies and
St Mary Orthopaedic Conference Steven A. Caruso, MD Trenton Orthopaedic Group Trauma and Complex Fracture Surgeon October 25, 2014 Nothing to disclose Goals To discuss common orthopaedic pathologies and
---Start of Pediatric and Adolescent Upper Extremity Fractures---
 Presented by: Mary Lloyd Ireland Professor Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sports Medicine University of Kentucky Lexington KY www.marylloydireland.com ---Start of Pediatric and Adolescent Upper Extremity
Presented by: Mary Lloyd Ireland Professor Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery and Sports Medicine University of Kentucky Lexington KY www.marylloydireland.com ---Start of Pediatric and Adolescent Upper Extremity
Pediatric Injuries/Fractures. Rena Heathcote
 Pediatric Injuries/Fractures Rena Heathcote INTRODUCTION Incidence Anatomy of the Growing Bone Injury Patterns What can we X-ray PEDIATRIC FRACTURES INCIDENCE What makes children susceptible to fractures?
Pediatric Injuries/Fractures Rena Heathcote INTRODUCTION Incidence Anatomy of the Growing Bone Injury Patterns What can we X-ray PEDIATRIC FRACTURES INCIDENCE What makes children susceptible to fractures?
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children
 Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
1/19/2018. Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust)
 Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Chapter XIX.1. Fractures May 2002
 Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and Residents Department of Pediatrics, University of Hawaii John A. Burns School of Medicine Chapter XIX.1. Fractures May 2002 Annemarie Uliasz The skeletal
Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and Residents Department of Pediatrics, University of Hawaii John A. Burns School of Medicine Chapter XIX.1. Fractures May 2002 Annemarie Uliasz The skeletal
OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries. Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Disclosure. Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies. I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program or presentation.
 Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Robin Pearce MSN, RN-BC Trauma Performance Improvement Manager Henrico Doctors Hospital, Forest Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation
Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Robin Pearce MSN, RN-BC Trauma Performance Improvement Manager Henrico Doctors Hospital, Forest Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation
Practice Changes I Hope You Make
 Is that Bad? What PCPs (& Parents) Need to Know about Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein, MD Pediatric Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Assistant Professor, Orthopaedics Baylor College
Is that Bad? What PCPs (& Parents) Need to Know about Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein, MD Pediatric Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Assistant Professor, Orthopaedics Baylor College
Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review
 Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-750 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors: A. M. Veitch, J. Harington, K. Franklin ; Plymouth/UK,
Traumatic injuries of the paediatric elbow: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-750 Congress: ECR 2009 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Pediatric Authors: A. M. Veitch, J. Harington, K. Franklin ; Plymouth/UK,
Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department. October 2012
 Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department October 2012 Victorian Paediatric Orthopaedic Network What this presentation covers Paediatric bone anatomy Buckle injury of distal radius Supracondylar
Paediatric fractures in the Emergency Department October 2012 Victorian Paediatric Orthopaedic Network What this presentation covers Paediatric bone anatomy Buckle injury of distal radius Supracondylar
Ouch, That s Gotta Hurt! Pediatric Fractures & Injuries
 Ouch, That s Gotta Hurt! Pediatric Fractures & Injuries Greg Canty, MD Medical Director, Sports Medicine Center Attending Physician, Emergency Medicine Children s Mercy Kansas City 2011 Children s Mercy
Ouch, That s Gotta Hurt! Pediatric Fractures & Injuries Greg Canty, MD Medical Director, Sports Medicine Center Attending Physician, Emergency Medicine Children s Mercy Kansas City 2011 Children s Mercy
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES. Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly.
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the shaft of the humerus are common, especially in the elderly. The majority can be treated conservatively but patient coping issues may be significant.
EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA. Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009
 EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009 MORAL OF THE STORY Fracture distal radius and intact ulna W/O radius fracture will most likely
EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009 MORAL OF THE STORY Fracture distal radius and intact ulna W/O radius fracture will most likely
PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES.
 PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz INCIDENCE SECOND MOST COMMON PEDIATRIC INJURY OSSIFICATION 1. CAPITELLUM (6 mo. - 2 yrs.) 2. MED. EPICONDYLE (5-9 yrs.) 3. TROCHLEA (7-13 yrs.) 4. LAT.
PEDIATRIC ELBOW FRACTURES www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz INCIDENCE SECOND MOST COMMON PEDIATRIC INJURY OSSIFICATION 1. CAPITELLUM (6 mo. - 2 yrs.) 2. MED. EPICONDYLE (5-9 yrs.) 3. TROCHLEA (7-13 yrs.) 4. LAT.
Disclosure. Learning ObjecAves. A Quick Review. Pediatric Fractures. The Developing Bone
 How to Bend but not Break Managing Pediatric Orthopedic Injuries in the Emergency Department Disclosure Nothing to disclosure No conflict of interest related to this topic Adam Cheng, MD, FRCPC Division
How to Bend but not Break Managing Pediatric Orthopedic Injuries in the Emergency Department Disclosure Nothing to disclosure No conflict of interest related to this topic Adam Cheng, MD, FRCPC Division
Disclosures. Fracture vs. Break: Is There a Difference? Jennifer Weiner, MS, RN, CPNP AC/PC March 21, Fracture vs. Break. Learning Objectives
 39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care Fracture vs. Break: Is There a Difference? Jennifer Weiner, MS, RN, CPNP AC/PC March 21, 2018 March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures I have no conflicts
39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care Fracture vs. Break: Is There a Difference? Jennifer Weiner, MS, RN, CPNP AC/PC March 21, 2018 March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures I have no conflicts
Trauma-related Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies. Javier Gonzalez del Rey, M.D. Professor Pediatrics Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center
 Trauma-related Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Javier Gonzalez del Rey, M.D. Professor Pediatrics Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Room # 10 7 month old sick since birth Room # 11 5 y/o Fell
Trauma-related Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Javier Gonzalez del Rey, M.D. Professor Pediatrics Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Room # 10 7 month old sick since birth Room # 11 5 y/o Fell
Childhood Fractures. Incomplete fractures more common. Ligaments stronger than bone. Tendons stronger than bone. Fractures may be pathologic
 Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Trauma Films for Upper Body. LCDR. Naruebade Rungrattanawilai RTN M.D., LL.B. FRCOST, DMOC
 Trauma Films for Upper Body LCDR. Naruebade Rungrattanawilai RTN M.D., LL.B. FRCOST, DMOC Objective A 42 year-old housekeeper with history of motorcycle accident. There was no external wound but she have
Trauma Films for Upper Body LCDR. Naruebade Rungrattanawilai RTN M.D., LL.B. FRCOST, DMOC Objective A 42 year-old housekeeper with history of motorcycle accident. There was no external wound but she have
Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries. J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics
 Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics 10. Proximal Humerus Fractures Treatment Simple sling ICE, pain meds Button-down shirts Recliner to sleep in It will be up to the surgeon
Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics 10. Proximal Humerus Fractures Treatment Simple sling ICE, pain meds Button-down shirts Recliner to sleep in It will be up to the surgeon
Upper limb injuries in children. Key points, # & dislocations 7/23/2009 (MIMIC)
 Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles. Striated Skeletal. Smooth
 1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Fracture Guideline
 Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Guideline Disclaimers This document is designed to assist physicians working in our emergency department in caring for
Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Guideline Disclaimers This document is designed to assist physicians working in our emergency department in caring for
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES
 MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
MEDIAL EPICONDYLE FRACTURES Demographic 20% of elbow fractures 60% of which are associated with elbow dislocation. 75% in boys between 6-12 years 20% of elbow dislocation with ME fracture, the ME is incarcerated
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Orthopedics in Motion Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016
 Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Orthopedics in Motion 2016 Tristan Hartzell, MD January 27, 2016 Humerus fractures Proximal Shaft Distal Objectives 1) Understand the anatomy 2) Epidemiology and mechanisms of injury 3) Types of fractures
Lower Extremity Fracture Management. Fractures of the Hip. Lower Extremity Fractures. Vascular Anatomy. Lower Extremity Fractures in Children
 Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow
 Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow I. Bones a. b. c. II. What movements does the elbow perform? a. Flexion b. c. Pronation d. III. Muscles in motion a. FLEXION (supinated) i Brachialis (pronated) ii (neutral)
Sports Medicine Unit 16 Elbow I. Bones a. b. c. II. What movements does the elbow perform? a. Flexion b. c. Pronation d. III. Muscles in motion a. FLEXION (supinated) i Brachialis (pronated) ii (neutral)
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty
 Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
Rehabilitation after Total Elbow Arthroplasty Total Elbow Atrthroplasty Total elbow arthroplasty (TEA) Replacement of the ulnohumeral articulation with a prosthetic device. Goal of TEA is to provide pain
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest
 Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
CASE ONE CASE ONE. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Mason Classification. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Mechanism of Injury. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Imaging
 CASE ONE An eighteen year old female falls during a basketball game, striking her elbow on the court. She presents to your office that day with a painful, swollen elbow that she is unable to flex or extend
CASE ONE An eighteen year old female falls during a basketball game, striking her elbow on the court. She presents to your office that day with a painful, swollen elbow that she is unable to flex or extend
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Introduction to Fractures. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 3
 Introduction to Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 3 Definitions A fracture is an interruption in the continuity of bone Fracture = Break Fracture: mechanical damage produced in a
Introduction to Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 3 Definitions A fracture is an interruption in the continuity of bone Fracture = Break Fracture: mechanical damage produced in a
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES. Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures
 REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
REHABILITATION FOR SHOULDER FRACTURES & SURGERIES Clavicle fractures Proximal head of humerus fractures By Dr. Mohamed Behiry Lecturer Department of physical therapy for Orthopaedic and its surgery. Delta
Upper Extremity Trauma.
 Upper Extremity Trauma www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Topics Clavicle Shoulder Dislocation Humerus Elbow Forearm Distal Radius Clavicle Fractures Clavicle Fractures Mechanism Fall onto shoulder (87%) Direct
Upper Extremity Trauma www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Topics Clavicle Shoulder Dislocation Humerus Elbow Forearm Distal Radius Clavicle Fractures Clavicle Fractures Mechanism Fall onto shoulder (87%) Direct
COURSE TITLE: Skeletal Anatomy and Fractures of the Lower Arm, Wrist, and Hand
 COURSE DESCRIPTION Few parts of the human body are required to pivot, rotate, abduct, and adduct like the wrist and hand. The intricate and complicated movements of the arm, wrist, and hand exist partly
COURSE DESCRIPTION Few parts of the human body are required to pivot, rotate, abduct, and adduct like the wrist and hand. The intricate and complicated movements of the arm, wrist, and hand exist partly
Elbow. Chapter 2 LISTEN. Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Pain
 Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
Chapter 2 Elbow LISTEN Mechanism of Injury (If Applicable) Patient usually remembers their position at the time of injury Certain mechanisms of injury result in characteristic patterns Fall on outstretched
1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint
 1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
1 Executive Editor: Chris Colton Authors: Mariusz Bonczar, Daniel Rikli, David Ring 1 Humeral fractures 1.13 l Distal humeral fractures Treatment with a splint Indication All 13-A type fractures, excluding
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017
 PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
Pediatric Orthopedics
 Pediatric Orthopedics Alexander Rogers, MD Associate Professor Emergency Medicine and Pediatrics Michigan Medicine/University of Michigan Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose I will
Pediatric Orthopedics Alexander Rogers, MD Associate Professor Emergency Medicine and Pediatrics Michigan Medicine/University of Michigan Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest to disclose I will
How to Triage Orthopaedic Care. David W. Gray, M.D.
 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency Determine
How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency Determine
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX)
 SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Yes, well perfused Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Yes, well perfused Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult
A Patient s Guide to Nursemaid's Elbow in Children. PHYSIO.coza
 A Patient s Guide to Nursemaid's Elbow in Children SANDTON MEDICLINIC 011 706 7495 FAIRWAYS LIFE HOSPITAL 011 875 1827 ST STITHIANS 082 378 9642 JEPPE BOYS HIGH SCHOOL 084 816 5457 JOHANNESBURG, SANDTON@PHYSIO.CO.ZA
A Patient s Guide to Nursemaid's Elbow in Children SANDTON MEDICLINIC 011 706 7495 FAIRWAYS LIFE HOSPITAL 011 875 1827 ST STITHIANS 082 378 9642 JEPPE BOYS HIGH SCHOOL 084 816 5457 JOHANNESBURG, SANDTON@PHYSIO.CO.ZA
Femur Shaft Fractures Under 10 years old
 1 Femur Shaft Fractures Under 10 years old Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City MO, USA rmschwend@cmh.edu 5 th Annual SLAOTI
1 Femur Shaft Fractures Under 10 years old Richard M Schwend MD Professor Orthopaedics and Pediatrics Director of Research Children s Mercy Hospital Kansas City MO, USA rmschwend@cmh.edu 5 th Annual SLAOTI
Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children Noor Rahman, Wasim Anwar, Malik Javed Iqbal, Israr Ahmad, Mohammad
ORIGINAL ARTICLE ABSTRACT Comparison of Below The Elbow Cast with Above The Elbow Cast in Treating Distal Third Forearm Fractures in Children Noor Rahman, Wasim Anwar, Malik Javed Iqbal, Israr Ahmad, Mohammad
Case. 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds
 Case 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds Exam I: Swelling over entire tibia extending to foot P: Tenderness
Case 5 year old with 2 weeks leg pain and now refusing to walk + Fevers, lower leg swelling, warmth Denies and history of trauma or wounds Exam I: Swelling over entire tibia extending to foot P: Tenderness
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do?
 HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
HUMERAL SHAFT FRACTURES: ORIF, IMN, NONOP What to do? TRAUMA 101 2018 FRACTURE CARE FOR THE COMMUNITY ORTHOPEDIST William W. Cross III, MD Assistant Professor Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Chair, Division
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ELBOW & HUMERUS
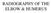 RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ELBOW & HUMERUS Patient Position: ELBOW AP Projection in same plane Part Position: Hand in ; patient Centered to Humeral epicondyles Central Ray: Structures Shown: AP Elbow Criteria
RADIOGRAPHY OF THE ELBOW & HUMERUS Patient Position: ELBOW AP Projection in same plane Part Position: Hand in ; patient Centered to Humeral epicondyles Central Ray: Structures Shown: AP Elbow Criteria
Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
 Comparative study between close reductions versus close reduction with K-Wire fixation in completely dorsally displaced distal radial metaphyseal fracture, in children and adolescent. Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
Comparative study between close reductions versus close reduction with K-Wire fixation in completely dorsally displaced distal radial metaphyseal fracture, in children and adolescent. Abd Ali Muhsin FICMS.
Elbow Problems.
 Elbow Problems www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Hinged joint formed by humerus and ulna produces flexion and extension Rotation producing pronation and supination from radial head and humerus Assessment
Elbow Problems www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anatomy Hinged joint formed by humerus and ulna produces flexion and extension Rotation producing pronation and supination from radial head and humerus Assessment
Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!!
 Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!! Kaye E Wilkins D.V.M,M.D. President's Council/Dielmann Chair in Pediatric Orthopedics Professor
Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!! Kaye E Wilkins D.V.M,M.D. President's Council/Dielmann Chair in Pediatric Orthopedics Professor
Elbow, forearm injuries. K. Fekete
 Elbow, forearm injuries K. Fekete 1. Outline: Fractures of the elbow Dislocation of the elbow Fractures of the forearm Special injuries 2. ANATOMY 3. Lennard Funk Anatomical reminder Three joints: Humero-ulnar
Elbow, forearm injuries K. Fekete 1. Outline: Fractures of the elbow Dislocation of the elbow Fractures of the forearm Special injuries 2. ANATOMY 3. Lennard Funk Anatomical reminder Three joints: Humero-ulnar
Introduction to Fractures and Dislocations. CAPA 2016 Winnipeg, MB
 Introduction to Fractures and Dislocations CAPA 2016 Winnipeg, MB CAPA 2016 Dr. Chris Graham Orthopedic surgeon Practice primarily trauma related Assist. Prof. U of M Health Sciences Centre No conflicts
Introduction to Fractures and Dislocations CAPA 2016 Winnipeg, MB CAPA 2016 Dr. Chris Graham Orthopedic surgeon Practice primarily trauma related Assist. Prof. U of M Health Sciences Centre No conflicts
Hand and wrist emergencies
 Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
RADIAL HEAD FRACTURES. It is far more common in adults than in children, (who more commonly fracture their neck of radius).
 RADIAL HEAD FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the head of the radius are relatively common. The injury can be subtle unless specifically looked for. It is far more common in adults than in children,
RADIAL HEAD FRACTURES Introduction Fractures of the head of the radius are relatively common. The injury can be subtle unless specifically looked for. It is far more common in adults than in children,
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II
 Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
J of Evolution of Med and Dent Sci/ eissn , pissn / Vol. 4/ Issue 50/ June 22, 2015 Page 8632
 MANAGEMENT OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS PINNING P. L. Srinivas 1, K. Jagadish 2, B. Mahesh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. L. Srinivas,
MANAGEMENT OF DISPLACED SUPRACONDYLAR FRACTURES OF THE HUMERUS IN CHILDREN BY CLOSED REDUCTION AND PERCUTANEOUS PINNING P. L. Srinivas 1, K. Jagadish 2, B. Mahesh 3 HOW TO CITE THIS ARTICLE: P. L. Srinivas,
BCCH Emergency Department UPPER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: RENA HEATHCOTE RN
 - 1 - BCCH Emergency Department UPPER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: RENA HEATHCOTE RN - 2 - FRACTURES The shoulder Dislocation +/_ fracture of humeral head A dislocated shoulder generally follows
- 1 - BCCH Emergency Department UPPER LIMB INJURIES Resource pack Developed by: RENA HEATHCOTE RN - 2 - FRACTURES The shoulder Dislocation +/_ fracture of humeral head A dislocated shoulder generally follows
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX)
 SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult Orthopedics
SUPRACONDYLAR HUMERUS FRACTURE (SCH FX) ALGORITHM. Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Page 1 of 12 Algorithm: Vascular Injury 5 Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Pulseless (undopplerable) Consult Orthopedics
Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure?
 Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Doi:http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/MOJ.1307.006 Is Closed Manipulative Reduction and Percutaneous Kirschner Wiring of Supracondylar Humeral Fracture in Children as Day-Care Surgery a Safe Procedure? Ashok R
Elbow Anatomy, Growth and Physical Exam. Donna M. Pacicca, MD Section of Sports Medicine Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Children s Mercy Hospital
 Elbow Anatomy, Growth and Physical Exam Donna M. Pacicca, MD Section of Sports Medicine Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Children s Mercy Hospital Contributing Factors to Elbow Injury The elbow is affected
Elbow Anatomy, Growth and Physical Exam Donna M. Pacicca, MD Section of Sports Medicine Division of Orthopaedic Surgery Children s Mercy Hospital Contributing Factors to Elbow Injury The elbow is affected
GALEAZZI FRACTURE. Galeazzi fracture-dislocations can be difficult to recognize and are often not initially appreciated.
 GALEAZZI FRACTURE Introduction In the Galeazzi fracture-dislocation there is a fracture of the distal third of the shaft of the radius in association with a subluxation or dislocation of the distal radio-ulna
GALEAZZI FRACTURE Introduction In the Galeazzi fracture-dislocation there is a fracture of the distal third of the shaft of the radius in association with a subluxation or dislocation of the distal radio-ulna
Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus Fractures. No disclosures for this presentation 10/29/18. Agenda
 Doernbecher Children s Hospital Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus PRESENTED BY: Scott Yang MD, Assistant Professor, Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Doernbecher Children s Hospital, OHSU No
Doernbecher Children s Hospital Controversies in Pediatric Supracondylar Humerus PRESENTED BY: Scott Yang MD, Assistant Professor, Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Doernbecher Children s Hospital, OHSU No
Sick Call Screener Course
 Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Elbow fractures account for approximately 5% to
 Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures Erin S. Hart Allison Turner Maurice Albright Brian E. Grottkau Fractures of the elbow are a very common injury in children. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall
Common Pediatric Elbow Fractures Erin S. Hart Allison Turner Maurice Albright Brian E. Grottkau Fractures of the elbow are a very common injury in children. The most common mechanism of injury is a fall
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures. OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD
 Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Diaphyseal Humerus Fractures OTA Course Dallas, TX 1/20/17 Ellen Fitzpatrick MD OBJECTIVES TREATMENT OPTIONS SURGICAL INDICATIONS CONTROVERSIES IN MANAGEMENT Humerus Fractures Treatment Goals: Functional
Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4)
 AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
AO Manual of ESIN in children s fractures Chapter 4: Forearm 4.3 Forearm shaft fractures, transverse (12-D/4) Title AO Manual of ESIN in children Subtitle Elastic stable intramedullary nailing (ESIN) Author
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures
 A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
A Patient s Guide to Adult Distal Radius (Wrist) Fractures Suite 11-13/14/15 Mount Elizabeth Medical Center 3 Mount Elizabeth Singapore, 228510 Phone: (65) 6738 2628 Fax: (65) 6738 2629 1 DISCLAIMER: The
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/13/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 94 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 10/13/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 94 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY
Conflict of Interest. Learner Outcome. Management of Pediatric Upper and Lower Extremity Fractures. Pediatric Fractures: Unique Challenges 7/12/2016
 Conflict of Interest Management of Pediatric Upper and Lower Extremity Fractures I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect of my current personal or professional situation might reasonably
Conflict of Interest Management of Pediatric Upper and Lower Extremity Fractures I hereby certify that, to the best of my knowledge, no aspect of my current personal or professional situation might reasonably
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT. By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg
 MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
MANAGEMENT OF INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES OF ELBOW JOINT By Dr B. Anudeep M. S. orthopaedics Final yr pg INTRAARTICULAR FRACTURES Intercondyar fracture Elbow dislocation Capitellum # Trochlea # Radial head
Patient Education. Supracondylar Humerus Fractures
 Patient Education Supracondylar Humerus Fractures This is the most common fracture requiring surgery in children age 3-10. It can happen in younger and older kids as well. *Remember! Fracture, crack, break
Patient Education Supracondylar Humerus Fractures This is the most common fracture requiring surgery in children age 3-10. It can happen in younger and older kids as well. *Remember! Fracture, crack, break
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
Chapter 30 - Musculoskeletal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient
 Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science
Fractures of the Radial and Ulnar Shafts In the Pediatric Patient Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas Health Science
Basic Principles in the Assessment and Treatment of Fractures in Skeletally Immature Patients. Joshua Klatt, MD
 Basic Principles in the Assessment and Treatment of Fractures in Skeletally Immature Patients Joshua Klatt, MD Original Author: Steven Frick, MD; March 2004 1st Revision: Steven Frick, MD; August 2006
Basic Principles in the Assessment and Treatment of Fractures in Skeletally Immature Patients Joshua Klatt, MD Original Author: Steven Frick, MD; March 2004 1st Revision: Steven Frick, MD; August 2006
