Surgical technique. Large and Medium-Size External Fixators. Modular rod systems.
|
|
|
- Aldous Dawson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
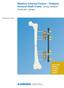
1 Surgical technique Large and Medium-Size External Fixators. Modular rod systems.
2
3 Table of contents System description 4 Indications and contraindications 5 Fixation components for the large external fixator 6 Fixation components for the medium-size external fixator 7 Implants 8 Instruments 9 Surgical approaches 13 Setting the Schanz screws 16 Modular frame with the rod-to-rod technique 22 Additional treatment options using the rod-to-rod technique 25 Unilateral frame with single-rod or double-rod construction 30 Pelvic use supraacetabular assembly 32 Bilateral frame for arthrodesis and osteotomies 38 Bibliography 40 Image intensifier control Warning This description is not sufficient for immediate application of the instrumentation. Instruction by a surgeon experienced in handling this instrumentation is highly recommended. Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique 1
4 2 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
5 Large External Fixator. Allows modularity in all three planes. User-oriented handling Clamps with a clip-on self-holding mechanism Color-coded for easy identification Comprehensible product line Free frame design Frames can be freely assembled; no limi tations from the assembly system Free pin placement Modular technique allows rapid and precise reduction during and after surgery Radiolucent carbon fibre rods ensure excellent fracture visualization Magnetic resonance safe Enables magnetic resonance examinations of patients stabilized with External Fixators 3
6 System description The modular construction of Large and Medium-size External Fixators makes them highly flexible. A variety of proven forms of assembly can be used to externally stabilize long, tubular bones and pelvic ring fractures as well as arthrodesis and osteotomies. The Synthes system is becoming increasingly popular as a minimally-invasive repositioning instrument using the three-rod modular technique. This form of assembly spares soft tissue, is easy to learn and is recommended as a standard by the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation (AO), and makes it much easier to handle and use the External Fixator. Additional benefit is provided by the latest clamps, which are also magnetic resonance safe. Patients with External Fixators can be reliably diagnosed in magnetic resonance tomograms. 4 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
7 Indications and contraindications Indications The Large External Fixator (rod diameter: 11 mm) is particularly suitable for treating the lower extremities. The Medium-size External Fixator (rod diameter: 8 mm) is particularly appropriate for the extremities of adults, and the upper and lower extrem i- ties of children and small adults. The most important indications for Large and Medium-size External Fixators are: Second and third-degree open fractures Infected pseudoarthrosis Rapid, initial immobilization of soft tissue injuries and fractures in severely injured patients Immobilization of closed fractures with severe soft tissue trauma (bruising of the soft tissue mantle, burns, skin diseases) Extensive shaft and periarticular fractures Transient joint-bridging immobilization in severe soft tissue and ligament injuries Certain injuries to the pelvic ring, and selected fractures in children Arthrodeses and osteotomies Contraindications Patients who for social and physical reasons are not suitable for an External Fixator. Patients in whom no screws can be inserted due to a bone or soft tissue disease. 5
8 Fixation components for the Large External Fixator Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Multi Pin Clamp, 6 positions, large, MR-safe Multi Pin Clamp, 4 positions, large, MR-safe Rod-to-Rod Clamp, MR-safe Rod Attachment for large Multi-Pin Clamp Carbon Fibre Rod, 11.0 mm, lengths mm 6 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
9 Fixation components for the Medium-size External Fixator Clamp, medium, clip-on, self holding, MR-safe Combination Clamp, medium, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Clamp 8.0/11.0, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Multi Pin Clamp, 4 positions, medium, MR-safe Multi Pin Clamp, 6 positions, medium, MR-safe Rod Attachment for medium Multi Pin Clamp Clamp for External Fixator for Distal Radius, MR-safe Carbon Fibre Rod, 8.0 mm, lengths mm 7
10 Implants Fits the Large External Fixator Seldrill Schanz Screws Titanium Steel Diameter Length (mm) (mm) Self-Tapping Schanz Screws Titanium Steel Diameter Length (mm) (mm) Fits the medium external fixator Seldrill Schanz Screws Titanium Steel Diameter Length (mm) (mm) / / / Self-Tapping Schanz Screws Titanium Steel Diameter Length (mm) (mm) / / Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
11 Instruments Adapters Adapter for Seldrill Schanz Screw 4.0 mm Adapter for Seldrill Schanz Screw 5.0 mm Adapter for Seldrill Schanz Screw 6.0 mm Protective caps Protective Cap for Schanz Screws and Steinmann Pins 4.0 mm Protective Cap for Schanz Screws and Steinmann Pins 5.0 mm Combination wrenches Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Combination Wrench 8.0 mm 9
12 Handles for drill sleeves Drill Guide Handle, 6 positions Handle for Drill Sleeve Drill sleeves Drill sleeves 6.0 mm (for use with 5.0 mm system) Drill Sleeve 8.0/6.0, short, with thread Drill Sleeve 8.0/6.0, long, with thread Drill sleeves 5.0 mm Drill Sleeve 6.0/5.0, short, with thread Drill Sleeve 5.0/3.5, short Trocar 3.5 mm, short Drill Sleeve 6.0/5.0, long, with thread Drill Sleeve 5.0/3.5, long Trocar 3.5 mm, long 10 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
13 Drill sleeves 4.0 mm Drill Sleeve 4.0, with thread Drill Sleeve 4.0/ Trocar 2.5 mm 11
14 12 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
15 Surgical approaches The Large and Medium-size External Fixators must be affixed within safe zones. The construction may not hinder the approach for a primary wound debridement or for a secondary operation. Skin transplants, sequestrectomies, bone grafting or a later osteo synthesis must be performable without restriction. Approach to the tibia The soft-tissue zone through which Schanz screws can be inserted without damaging important structures (vessels, nerves, muscles and tendons) is anteromedial to the tibia. The angles of this safe zone vary. If the lateral surface of the distal third of the tibia is avoided, damage to the anterior tibial artery can be avoided. If the ventral zone of the distal tibia is avoided, interference with the tendons can also be avoided. In addition, this minimizes the probability of potential pin channel infection. 13
16 Approach to the femur A lateral approach to the femur within a 30 angle is recommended. A medial approach is also possible from a distal direction. Approach to the pelvis There are two recommended options for pin placement of the external fixation assembly in the pelvis. Supraacetabular pin placement Given the pronounced bone structure, the more technically difficult supraacetabular pin placement is preferred over that of the iliac crest. Proceeding from the superior anterior crest, the site of entry is approximately 4 6 cm in a caudal direction, and 3 4 cm in a medial direction. When the patient is in a supine position, the alignment for drilling the screws is angled approximately 20 in a cranial direction and 30 inward. Iliac crest pin placement To keep from damaging the femoral cutaneous nerve, avoid insertion up to 15 mm in a dorsal direction from the superior anterior iliac spine. The orientation of the os ilium can be determined by palpation with a finger or an additional instrument. The screws are then inserted delicately between the two laminae of the os ilium. 14 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
17 Approach to the humerus When dealing with the humerus, primary consideration should be given to the radial and axillary nerves. Distally, a dorsal approach to the humerus is appropriate. Proximally, it is recommendable to introduce the Schanz screws from a ventrolateral direction, caudal to the path of the axillary nerve. 15
18 Setting the Schanz screws using the example of the tibia in the diaphyseal region The following steps will be explained with reference to a 5.0 mm self-drilling, self-tapping (Seldrill ) Schanz screw, and a conventional 5.0 mm Schanz screw inserted in a tibia. Seldrill Schanz screw The Seldrill is a self-drilling, self-tapping Schanz screw. The optimized radial preloading helps minimize the rate of pin infections. Note: When the new adaptors for Schanz screws are used, the Seldrill Schanz screws do not have to be clamped in the drill chuck. The adapters are compatible with the universal chuck and AO/ASIF Quick Coupling. 1 Set the drill sleeves on the bone Handle for Drill Sleeve Drill Sleeve 6.0/5.0 short, with thread Drill Sleeve 5.0/3.5, short Trocar 3.5 mm, short Insert the drill sleeve assembly through a stab incision and set it directly on the bone surface. Then remove the trocar 3.5 mm and the drill sleeve 5.0/ Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
19 2 Insert Seldrill Schanz screws Seldrill Schanz Screws 5.0 mm X Handle for Drill Sleeve Drill Sleeve 6.0/5.0 short, with thread Adapter for Seldrill Schanz Screws 5.0 mm Drill with attachment for AO/ASIF Quick Coupling type-dependent Insert the Seldrill Schanz screw in the 5.0 mm adapter, and use the drill to screw it through the drill sleeve 6.0/5.0 until the drill tip is anchored in the distant cortical bone. If it is difficult to determine whether the screw has entered the opposite side of the cortical bone, it is recommendable to check the screw s penetration depth with the image intensifier. It is not necessary to completely penetrate the distant cortical bone since anchoring the thread in the near cortical bone and sinking the drill tip in the distant cortical bone effectively absorbs bending force. After screwing in the Seldrill Schanz screw, remove the drill sleeve and the drill with the adapter. 17
20 Alternative technique: Seldrill Schanz Screws 5.0 mm X Handle for Drill Sleeve Drill Sleeve 6.0/5.0, short, with thread Drill Sleeve 5.0/3.5, short Trocar 3.5 mm, short Adapter for Seldrill Schanz Screws 5.0 mm Universal Chuck with T-Handle Drill with attachment for AO/ASIF Quick Coupling Type-dependent Insert the Seldrill Schanz screw 5.0 mm in the adapter, and use the drill to screw it through the drill sleeve 6.0/5.0 into the near cortical bone. Remove the drill and replace it with the universal drill chuck with the T-handle ( ). The screw can now be delicately screwed manually into the middle of the distance cortical bone. It is not necessary to completely penetrate the distant cortical bone since anchoring the thread in the near cortical bone and sinking the drill tip in the distant cortical bone effectively absorbs bending force. Remove the drill sleeve and the universal chuck T-handle with. Note: Only when bones are osteoporotic does the Seldrill Schanz screw have to be screwed a bit further into the distant cortical bone, and it may even slightly penetrate through it since this can increase anchoring stability. Use in the metaphyseal region The individual surgical steps are the same as when the screws are used in the shaft area. 18 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
21 Conventional self-tapping Schanz screw Instead of self-drilling Schanz screws (Seldrill ), self-tapping screws can also be used. In contrast to the Seldrill screws, selftapping screws must be predrilled. 1 Set the drill sleeve on the bone Handle for Drill Sleeve Drill Sleeve 6.0/5.0 short, with thread Drill Sleeve 5.0/3.5, short Trocar 3.5 mm, short Insert the drill sleeve assembly through a stab incision and set it directly on the bone surface and remove the trocar 3.5 mm. 2 Predrilling Drill Bit 3.5 mm, length 195/170 mm, 2-flute, for Quick Coupling Drill with attachment for AO/ASIF Quick Coupling Type-dependent Drill through both sides of the cortical bone with the 3.5 mm drill bit, then remove the drill sleeve 5.0/
22 3 Insert the self-tapping Schanz screw Self-Tapping Schanz Screw X Handle for Drill Sleeve Drill Sleeve 6.0/5.0 short, with thread Universal Chuck with T-Handle The Schanz screw can now be screwed in through the drill sleeve 6.0/5.0. The tip must be anchored in the distant cortical bone to effectively absorb bending force. 20 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
23 Alternative technique Alternately, the length of the required Schanz screw can also be precisely checked using the length gauge. Handle for Drill Sleeve Drill Sleeve 6.0/5.0 short, with thread Depth Gauge for Schanz Screws Universal Chuck with T-Handle After predrilling as described in step 2, the length gauge is guided through the drill sleeve 6.0/5.0 and hooked in the distant cortical bone. Then move the retaining disk to the height of the drill sleeve and lock it with the locking screw. Remove the length gauge, and insert the tip of the Schanz screw into the recess of the retaining disk. Slide the universal chuck over the smooth shaft of the Schanz screw to the height of the tip of the length gauge, and tighten the chuck on the Schanz screw. Determining the length in this manner will ensure that the screw will be firmly anchored in the distant cortical bone. The Schanz screw can now be screwed in through the drill sleeve 6.0/5.0 until the drill chuck stops on the drill sleeve. Note: If the Schanz screw is screwed in beyond this point, it will strip the thread due to the resistance of the drill sleeve. 21
24 Modular frame using the rod-to-rod technique You can choose between a unilateral or modular frame construction. If a modular frame is chosen, you can freely choose how to set the Schanz screws. This method is recommended by the AO as a standard technique for fractures that require re duction. Schanz screws, clamps and carbon fibre rods are required to construct the different frames. Instead of radiolucent carbon fibre rods, steel rods can be employed for all constructions with Large External Fixators. 1 Set the Schanz screws Set two Schanz screws per main fragment using the drill sleeve assembly. Freely select their position appropriate for the fracture, soft tissue, and anatomical situation. The greater the distance between the Schanz screws, the greater the stability of the frame. 2 Connect the Schanz screws with carbon fibre rods Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Wrench 11.0 mm The two Schanz screws per main fragment are connected with a rod. Clip-on, self-holding clamps are used. Make sure that the rods project a bit beyond the fracture zone so that sufficient length remains for the combination clamp. Tighten all the clamp nuts. 22 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
25 3 Connect the carbon fibre rods Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm Combination Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Connect the two ends of the rods near the fracture to a third rod using two self-holding combination clamps. Do not yet tighten the nuts for the combination clamps. 4 Reduce the fracture Use the two partial frames as handles to reduce the fracture. After checking the reduction, alternately tighten the nuts of the combination clamps in the image intensifier while manually holding the reduction. Alternative technique: Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm For each fragment, additionally affix one long rod that can be used as a temporary lever for reduction. The leverage can be used for controlled reduction that requires less force (particularly recommended for the femur). In addition, your hands will remain safely outside the X-rays when this technique is applied. 23
26 5 Tighten nuts Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Finally, recheck all the nuts with the wrench to ensure they are all tight. Retighten all the nuts after 24 hours. 6 Secondary reduction A secondary correction of the reduction can be performed within the first few days after surgery. Only the two combination clamps are released. The correction can then be made using the partial frames that move relative to each other. After the correction, retighten the two combination clamps. 24 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
27 Additional treatment options using the rod-to-rod technique 11.0 mm system Adult femur Insert 2 3 Schanz screws into the proximal and distal main fragment from a lateral direction. With adipose patients, it is recommendable to use 6.0 mm screws. The stability of the rodto-rod assembly can be increased with an additional neutral ization rod. Bridging the ankle Unilateral Insert the screws into the calcaneus and talus from a medial direction. In the tibia, set the screws at an anteromedial to medial angle, and connect them using the rod-to-rod technique. Triangular Insert the first screw from an anteromedial direction into the tibial shaft. Insert the Steinmann pin through the calcaneus, and affix the rods in the form of a tent between the first screw and Steinmann pin. Then reduce the fracture by pulling lengthwise with balanced ligamentotaxis. Then insert two screws into the tibia starting from the medial rod. For prophylaxis of pes equines, insert an additional Schanz screw at an angle from above into the first and fifth metatarsal bone. Bridging the knee joint Insert two Schanz screws into the distal femur from a lateral or ventral direction, and into the proximal tibia from an antero medial direction. Connect them using the rod-to-rod technique. 25
28 8.0 mm system Humerus Insert the Schanz screws in the proximal humerus from a lateral direction and into the distal humerus from a dorsal direction, avoiding injury to the radial nerve. Connect the Schanz screws using the rod-to-rod technique. Bridging the elbow Insert Schanz screws into the distal humerus from a dorsal direction. The screws can be introduced into the forearm from a dorsal direction into the ulna. Connect the Schanz screws using the rod-to-rod technique. It is only recommendable to insert an additional screw in the radius to stabilize the radio-ulnar joint. Child femur Insert 2 3 Schanz screws into the proximal and distal main fragment from a lateral direction. The stability of the rod-to-rod assembly can be increased with an additional neutralization rod. 26 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
29 Using multi pin clamps The advantage of multi pin clamps is that reduction can be carried out using the above-described rod-to-rod technique. The Schanz screws with clamps serve as an external reduction instrument system. Additional reduction levers may be used to lengthen the lever arm (see alternative technique). 1 Set the Schanz screws for multi pin clamps Seldrill TM Schanz Screws X Drill Guide Handle, 6 positions Drill Sleeve 6.0/5.0, short, with thread Drill Sleeve 5.0/3.5, short Trocar 3.5 mm, short Drill Sleeve 6.0/5.0 long, with thread Drill Sleeve 5.0/3.5, long Trocar 3.5 mm, long Adapter for Selldrill TM Schanz Screws 5.0 mm Universal Chuck with T-Handle Drill with attachment for AO/ASIF Quick coupling Type-dependent Insert two Schanz screws into the distal and proximal fragments using a parallel drill sleeve. 2 Assembling the Fixator Multi Pin Clamp, 6 positions, large, MR-safe Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Guide the clamps of the premounted clamp-rod construction over the Schanz screws, and tighten the clamps on the screws with the 11.0 combination wrench. 27
30 3 Reduction Thanks to the clamps that enable the Schanz screws and carbon fibre rod to be independently fixed, the fracture can be optimally reduced using the modular technique with the double Schanz screws as levers. Alternative technique Reduction Handle for Large Multi Pin Clamp Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Wrench, hexagonal 5.0 mm, long, angled In certain cases, it is recommendable to use additional reduction levers. Greater force can be applied from the increased leverage. In addition, the levers enable free image intensifier control. 4a Unilateral single frame with multi pin clamps Combination Wrench 11.0 mm After reduction, tighten all the screws of the clamps. 28 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
31 4b Unilateral double frame construction with multi pin clamps Rod Attachment for large Multi Pin Clamp Combination Wrench 11.0 mm If additional rod connectors are attached to the frame, a doubleframe construction can be created to increase the stability of the frame. 29
32 Unilateral frame with single-rod or double-rod construction 1 Provisionally reduce the fracture, and set the first Schanz screw Provisionally reduce the fracture, and insert the first Schanz screw in a main fragment. From a ventrolateral direction, locate the first screw as distally as possible. 2 Mount the carbon fibre rod and clamp Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Mount the rod with the assistance of a clip-on, self-holding clamp. 3 Definitively reduce the fracture, and set the second Schanz screw After reducing the fracture, set the second Schanz screw as proximally as possible. Secure the reduction by tightening the proximal and distal clamp, yet continue to hold the reduction until the fracture is definitively fixed (see following pages). 30 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
33 4a Unilateral frame with single-rod construction Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Insert the remaining Schanz screws, and place the required clipon, self-holding clamps on the rod to the side of the screws. Tighten all the clamp nuts. 4b Unilateral frame with double-rod construction Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm Combination Wrench 11.0 mm A double-rod construction increases stability of the assembly in the case of bone defects or comminuted fractures. Use the same procedure as for single-rod construction; however, after setting the first two Schanz screws, place the second rod over the first. The double-rod construction should be standard for the femur. 31
34 Pelvic use Particular care is required with external fixation assemblies in the pelvis. Indications for stabilizing the anterior pelvic ring with a large external fixator are: Unstable fractures in the anterior pelvic ring, or symphysis fractures with or without participation of the posterior pelvic ring. This type of stabilization is also possible in emergencies such as polytrauma, open wounds and, where appropriate, as an alternative to internal osteosynthesis. The pelvis can be stabilized with an external fixator both at the iliac crest and the supraacetabular region. Although the point of entry for the Schanz screw is easier to find on the iliac crest, it is frequently difficult or impossible to attain a permanent and secure seat for the Schanz screws in the curved ala of the ilium. For this reason, the treatment of the pelvis will be illustrated first with reference to supraacetabular fixation in the following surgical instructions. 32 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
35 Supraacetabular pin placement 1 Setting the first two Schanz screws Anatomical landmarks for the supraacetabular placement of the Schanz screws are the superior anterior iliac crest and inferior anterior iliac crest. Set a self-drilling/self-tapping Schanz screw (Seldrill ) on the right and left between the inferior anterior iliac spine, and the ventral labrum of the acetabulum. Proceeding from the superior anterior iliac crest, this site of entry is 4 to 6 cm in a caudal direction, and 3 to 4 cm in a medial direction. When inserting the screw, make sure that the lateral femoral cutaneous nerve is not damaged. To prevent the screws from penetrating the acetabulum, make sure that the screw is aligned medially and cranially. When the screws are mechanically inserted, concentrate on feeling if the screw is properly screwing into the bone substance. Monitor the site of entry and the advance of the selfdrilling screws with the image intensifier. The final turns and fine adjustment of the Schanz screw should be done manually with the universal handle. 33
36 2 Setting the second two Schanz screws The second Schanz screws to be set on both sides are introduced somewhat cranially to the first set of screws. The two tips can slightly converge. 3 Ventral connection Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Initially, the two caudal screws of the bilaterally set Schanz screws are connected with two carbon fibre rods and a self-holding combination clamp. It is important for the assembly to be large enough to allow a sufficient degree of freedom to accommodate swelling of the abdomen. The rods are held with a combination clamp but are not tightened. 34 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
37 4 Reduction Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Manually reduce the pelvic ring by pressure, stretching, or using the Schanz screws as levers. In certain cases, distraction by pulling on a leg can be advantageous. After reduction, tighten the combination clamp. 5 Connect the second pair of screws Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Wrench 11.0 mm If the reduction of the pelvis has been correctly carried out, the two top Schanz screws can be connected with each other. Note: Instead of the rods and combination clamps, a curved carbon fibre rod can be used for both the first and second pair of screws. 6 Connecting the partial frames Connecting Rod 5.0 mm, Stainless Steel Self-Tapping Schanz Screw X Protective Cap, for Schanz Screws and Steinmann Pins 5.0 mm To substantially increase the stability of the construction, the two partial frames are connected with additional 4.0 mm crossbraces (such as 4.0 mm carbon fibre rods or Schanz screws with a protective cap). The clip-on, self-holding clamps are particularly suitable for mounting an additional cross-brace. 35
38 Placing pins in the Iliac crest 1 Setting the first two Schanz screws The iliac crests serve as landmarks for introducing the Schanz screws. Marking the inner and outer surfaces of the ala of the ilium with Kirschner wires can help establish the alignment for placing the first Schanz screw. Note: It is advantageous to place at least one screw in the margin of the os ilium on both sides. 2 Setting the second two Schanz screws The second screw is set slightly posterior (approximately 2 cm) to the first Schanz screw. 36 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
39 3 Reduction and definitive assembly Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm Clamp, clip-on, self holding, MR-safe Combination Clamp, clip-on, self holding, MR-safe Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Self-Tapping Schanz Screw X Protective Cap, for Schanz Screws and Steinmann Pins 5.0 mm The additional steps for fixing the pelvis are analogous to points 3 6 on the previous page. Note: In individual cases, the supraacetabular assembly and crest assembly can be combined. 37
40 Bilateral frame for arthrodesis and osteotomies Arthrodesis and osteotomies generally require symmetrical compression that is best generated using a bilateral frame construction. Bilateral frames for arthrodesis Steinmann Pin 5 mm with trocar tip X X Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Protective Cap, for Schanz Screws and Steinmann Pins 5.0 mm Compressor, open Drill Bit 3.5 mm, length 195/170 mm, 2-flute, for Quick Coupling The large external fixator enables effective compression by pretensioning the Steinmann pins in relation to each other. Maximum stability is attained by first untightening the relevant clamp nuts, then generating the desired compression using the open compressor, and then retightening the nuts. Knee arthrodesis Ankle arthrodesis 38 Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
41 Bilateral frames for Osteotomies Steinmann Pin 5 mm with trocar tip X X Carbon Fibre Rod 11.0 mm Clamp, clip-on, self-holding, MR-safe Combination Wrench 11.0 mm Protective Cap, for Schanz Screws and Steinmann Pins 5.0 mm Compressor, open Drill Bit 3.5 mm, length 195/170 mm, 2-flute, for Quick Coupling In the case of osteotomies of the proximal and distal tibia, inner fixation is generally preferred if there are no associated softtissue problems. Compression osteotomies with a bilateral frame construction are supportive of the metaphysis of rapid bone healing. Proximal tibia osteotomy Distal tibia osteotomy 39
42 Bibliography Bennek J (2000) The use of upper limb external fixation in paediatric trauma. Injury, Int J Care Injured 31, Gausepohl T, Koebke J, Pennig D, Hobrecker S, Mader K (2000) The anatomical base of unilateral external fixation in the upper limb. Injury, Int J Care Injured 31, Miner T, Carroll KL (2000) Outcomes of External Fixation of Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures. Journal of Pediatric Ortho - paedics, 20: Rüedi TP, Murphy WM (2000) AO Principles of Fracture Management. Thieme, Stuttgart, New York. Regazzoni P (1989) Das Ilizarov-Konzept mit einem modularen Rohrfixateursystem. Operative Orthopädie und Traumatologie, No 21, Rüter A, Brutscher R (1988) Die Behandlung ausgedehnter Knochen defekte am Unterschenkel durch die Verschiebungs osteotomie nach Ilizarov. Der Chirurg, 59, Alonso JE, Horowitz M (1987) Use of the AO/ASIF External Fixator in Children. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics, 7: Ruland WO (2000) Is there a place for external fixation in humeral shaft fractures? Injury. Int. J. Care Injured 31, Kapukaya A, Subasi M, Necmioglu S, Arslan H, Kesemenli lc, Yildirim K (1998) Treatment of closed femoral diaphyseal fractures with external fixators in children. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg, 117: Hull JB, Bell MJ (1997) Modern Trends for External Fixation of Fractures in Children: A critical Review. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics, 6: Gregory P, Pevny T, Teague D (1996) Early Complications with External Fixation of Pediatric Femoral Shaft Fractures. Journal of Orthopaedic Trauma, Vol 10, No 3, Buckley SL (1995) Technique of External Fixation of grossly unstable or open tibial shaft fractures in children. Operative Techniques in Orthopaedics, Vol 5, No 2 (April): Davis TJ, Topping RE, Blanco JS (1995) External Fixation of Pediatric Femoral Fractures. Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research, No 318, Aronson J, Tursky EA (1992) External Fixation of Femur Fractures in Children. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics, 12: Gregory RJH, Cubison TCS, Pinder IM, Smith SR (1992) External Fixation of lower limb fractures in children. The Journal of Trauma, Vol 33, No 5, pp Heim D, Regazzoni P, Perren S (1992) Der Fixateur externe bei offenen Frakturen: Gegenwärtiger Stand seiner Anwendung. Injury, No 23, suppl Synthes Large and Medium-Size External Fixators Surgical technique
43
44 Presented by: Ö öAA-ä SE_ AA Synthes 2005 Printed in Switzerland LAG Subject to modifications.
Large and Medium-Size External Fixators. Modular rod systems.
 Large and Medium-Size External Fixators. Modular rod systems. Surgical technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table
Large and Medium-Size External Fixators. Modular rod systems. Surgical technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation Table
Elbow Hinge Fixator. Guided Flexion/Extension for Unstable Elbow Fractures.
 Elbow Hinge Fixator. Guided Flexion/Extension for Unstable Elbow Fractures. Surgical Technique MR Safe Radiolucent Table of Contents System Description 3 Indications and Contraindications 4 Fixation Components
Elbow Hinge Fixator. Guided Flexion/Extension for Unstable Elbow Fractures. Surgical Technique MR Safe Radiolucent Table of Contents System Description 3 Indications and Contraindications 4 Fixation Components
Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics
 MEFiSTO Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF MEFiSTO Table
MEFiSTO Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF MEFiSTO Table
MEFiSTO. Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics.
 MEFiSTO. Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
MEFiSTO. Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
For Small-Statured Adults and Pediatric Patients. Medium External Fixator Basic Modular Frame
 For Small-Statured Adults and Pediatric Patients Medium External Fixator Basic Modular Frame Surgical Technique MRI Information DePuy Synthes Medium External Fixation devices are labeled MR Conditional
For Small-Statured Adults and Pediatric Patients Medium External Fixator Basic Modular Frame Surgical Technique MRI Information DePuy Synthes Medium External Fixation devices are labeled MR Conditional
MEFiSTO. Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics.
 MEFiSTO. Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
MEFiSTO. Monolateral External Fixation System for Trauma and Orthopaedics. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
Medium External Fixator Humeral Shaft Frame. Modular frame for upper extremity use.
 Medium External Fixator Humeral Shaft Frame. Modular frame for upper extremity use. Technique Guide Part of the Medium External Fixation System MRI Information Synthes Medium External Fixation devices
Medium External Fixator Humeral Shaft Frame. Modular frame for upper extremity use. Technique Guide Part of the Medium External Fixation System MRI Information Synthes Medium External Fixation devices
Mandible External Fixator II. Provides treatment for fractures of the maxillofacial area.
 Mandible External Fixator II. Provides treatment for fractures of the maxillofacial area. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Mandible External Fixator II. Provides treatment for fractures of the maxillofacial area. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Mini External Fixator.
 Mini External Fixator. Assembly and Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier control Warning
Mini External Fixator. Assembly and Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Image intensifier control Warning
Technique Guide. The Distraction Osteogenesis Ring System. Nonarticular tibia frame.
 Technique Guide The Distraction Osteogenesis Ring System. Nonarticular tibia frame. Table of Contents Introduction The Distraction Osteogenesis Ring System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide The Distraction Osteogenesis Ring System. Nonarticular tibia frame. Table of Contents Introduction The Distraction Osteogenesis Ring System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system.
 LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment Locking Compression Plate (LCP) system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
LCP Distal Humerus Plates
 The anatomic fixation system for the distal humerus with angular stability Surgical technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 5 Preparation
The anatomic fixation system for the distal humerus with angular stability Surgical technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Contents Indications and contraindications 2 Implants 3 Instruments 5 Preparation
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE. The PreFix Fixator (92000 Series) ALWAYS INNOVATING
 21 The PreFix Fixator (92000 Series) ALWAYS INNOVATING INTRODUCTION The PreFix fixator is designed to provide temporary external fixation. This may be needed when local facilities or the condition of the
21 The PreFix Fixator (92000 Series) ALWAYS INNOVATING INTRODUCTION The PreFix fixator is designed to provide temporary external fixation. This may be needed when local facilities or the condition of the
External Distal Radius Fixator. Supplement to the 8 mm rod fixator system
 External Distal Radius Fixator. Supplement to the 8 mm rod fixator system Surgical technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
External Distal Radius Fixator. Supplement to the 8 mm rod fixator system Surgical technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation
Small External Fixator
 Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of Contents Description of System 2 Indications/ Contraindications 3 Bridging Surgical
Surgical Technique Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of Contents Description of System 2 Indications/ Contraindications 3 Bridging Surgical
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. Using pin clamps with outrigger posts.
 Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. Using pin clamps with outrigger posts. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. Using pin clamps with outrigger posts. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
Technique Guide. Locking Attachment Plate. For treatment of periprosthetic fractures.
 Technique Guide Locking Attachment Plate. For treatment of periprosthetic fractures. Table of Contents Introduction Locking Attachment Plate 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Patient Positioning 5 Preparation
Technique Guide Locking Attachment Plate. For treatment of periprosthetic fractures. Table of Contents Introduction Locking Attachment Plate 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Patient Positioning 5 Preparation
LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle.
 Technique Guide LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Superior Clavicle
Technique Guide LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Superior Clavicle
Surgical Technique. Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90
 Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
Surgical Technique Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Cannulated Angled Blade Plate 3.5 and 4.5, 90 Table of contents Indications/Contraindications 2 Implants 3 Surgical technique 5 Implant
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. For staged fixation of the distal tibia.
 Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. For staged fixation of the distal tibia. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge. For staged fixation of the distal tibia. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Technique
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique
 TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique For TransFx External Fixation
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique For TransFx External Fixation
Surgical Technique. Distal Radius and Foot
 Surgical Technique Distal Radius and Foot JET-X BAR Unilateral Fixator Distal Radius and Foot Surgical Technique Contents Design Features...2 Distal Radius Surgical Technique Indications...10 Surgical
Surgical Technique Distal Radius and Foot JET-X BAR Unilateral Fixator Distal Radius and Foot Surgical Technique Contents Design Features...2 Distal Radius Surgical Technique Indications...10 Surgical
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique
 TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique Choice, Simplicity, Transition TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique
TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique Choice, Simplicity, Transition TransFx External Fixation System Large and Intermediate Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique
Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments for LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Arm Instrument System (large).
 Technique Guide Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments for LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Arm Instrument System (large). Image intensifier control Warning This description
Technique Guide Periarticular Aiming Arm Instruments for LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Aiming Arm Instrument System (large). Image intensifier control Warning This description
Surgical Technique. Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates
 Surgical Technique Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates PERI-LOC Periarticular Locked Plating System Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates Surgical Technique Contents Product
Surgical Technique Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates PERI-LOC Periarticular Locked Plating System Anterolateral and Medial Distal Tibia Locking Plates Surgical Technique Contents Product
LCP Distal Tibia Plate
 Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
Surgical Technique LCP Locking Compression Plate Original Instruments and Implants of the Association for the Study of Internal Fixation AO/ASIF Table of contents Indications 3 Implants/Instruments 5 Surgical
Large External Fixator Modular Knee Bridge
 Using Multi-pin Clamps Large External Fixator Modular Knee Bridge Surgical Technique Large External Fixator Modular Knee Bridge DePuy Synthes Large External Fixation devices are labeled MR Conditional
Using Multi-pin Clamps Large External Fixator Modular Knee Bridge Surgical Technique Large External Fixator Modular Knee Bridge DePuy Synthes Large External Fixation devices are labeled MR Conditional
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes LCP periarticular plating system.
 LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes LCP periarticular plating system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
LCP Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the Synthes LCP periarticular plating system. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Technique Guide. LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Femoral Hook Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Table of Contents Introduction Features and Benefits 2 AO ASIF Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Medium External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge
 For Small-Statured Adults Medium External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Surgical Technique MRI Information DePuy Synthes Medium External Fixation devices are labeled MR Conditional according to the
For Small-Statured Adults Medium External Fixator Delta Frame Ankle Bridge Surgical Technique MRI Information DePuy Synthes Medium External Fixation devices are labeled MR Conditional according to the
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System. 3.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates 2 AO
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates 2 AO
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments. Part of the 3.5 mm LCP Percutaneous Instrument System. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal
VA-LCP Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle.
 Technique Guide VA-LCP Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Table of Contents Introduction VA-LCP Anterior
Technique Guide VA-LCP Anterior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Table of Contents Introduction VA-LCP Anterior
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM
 3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
3.5 MM VA-LCP PROXIMAL TIBIA PLATE SYSTEM Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Periarticular Plating System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm VA-LCP Proximal Tibial Plate 2 AO
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation.
 LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Medial Distal Tibia Plate, without Tab. The Low Profile Anatomic Fixation System with Angular Stability and Optimal Screw Orientation. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius.
 Technique Guide LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Proximal
Technique Guide LCP Proximal Radius Plates 2.4. Plates for radial head rim and for radial head neck address individual fracture patterns of the proximal radius. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Proximal
3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Extra-articular Distal Humerus
3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate
 For Treatment of Periprosthetic Fractures 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Preparation
For Treatment of Periprosthetic Fractures 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm Locking Attachment Plate 2 Indications 4 Surgical Technique Preparation
Knee spanning solutions
 Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
Knee spanning solutions System features Indications Intended to be used on adults or pediatric patients as required for fracture fixation (open or closed); post-traumatic joint contracture which has resulted
3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments
 Part of the 3.5 mm LCP 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate 2 Aiming Instruments
Part of the 3.5 mm LCP 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate Aiming Instruments Surgical Technique TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION 3.5 mm LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plate 2 Aiming Instruments
Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate
 Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer MIS
Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular 3.5mm Proximal Tibial Locking Plate Surgical Technique 1 Zimmer MIS
Surgical Technique. Targeter Systems Overview
 Surgical Technique Targeter Systems Overview PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Targeter Systems Overview Table of contents Product overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Indications... 2 Design features and benefits...
Surgical Technique Targeter Systems Overview PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Targeter Systems Overview Table of contents Product overview... 2 Introduction... 2 Indications... 2 Design features and benefits...
Humerus Block. Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) Surgical Technique. This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA.
 Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
Humerus Block Surgical Technique Discontinued December 2016 DSEM/TRM/0115/0296(1) This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation. Contents
3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications
FLT105 12/02.
 FLT105 12/02 www.biometmerck.co.uk Disclaimer Biomet Merck Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend this or any other surgical technique for use on a
FLT105 12/02 www.biometmerck.co.uk Disclaimer Biomet Merck Ltd, as the manufacturer of this device, does not practice medicine and does not recommend this or any other surgical technique for use on a
Surgical Technique. 3.5mm and 4.5mm Lateral Proximal Tibia Locking Plates
 Surgical Technique 3.5mm and 4.5mm Lateral Proximal Tibia Locking Plates PERI-LOC Periarticular Locked Plating System 3.5mm and 4.5mm Lateral Proximal Tibia Locking Plate Surgical Technique Contents Product
Surgical Technique 3.5mm and 4.5mm Lateral Proximal Tibia Locking Plates PERI-LOC Periarticular Locked Plating System 3.5mm and 4.5mm Lateral Proximal Tibia Locking Plate Surgical Technique Contents Product
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System. Table of Contents AO ASIF Principles of Internal Fixation 4 Indications/Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Tibia Plate. Part of the Synthes Small Fragment LCP System. Table of Contents AO ASIF Principles of Internal Fixation 4 Indications/Contraindications 5 Surgical Technique
Medium External Fixator Pediatric Femoral Shaft Frame. Using medium multi-pin clamps.
 Medium External Fixator Pediatric Femoral Shaft Frame. Using medium multi-pin clamps. Technique Guide Part of the Medium External Fixation System MRI Information Synthes Medium External Fixation devices
Medium External Fixator Pediatric Femoral Shaft Frame. Using medium multi-pin clamps. Technique Guide Part of the Medium External Fixation System MRI Information Synthes Medium External Fixation devices
Technique Guide. PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus.
 Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide PHILOS and PHILOS Long. The anatomic fixation system for the proximal humerus. Table of Contents Introduction PHILOS and PHILOS Long 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures.
 LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the
LCP Low Bend Medial Distal Tibia Plates 3.5 mm. Anatomic plates with low profile head for intra- and extraarticular fractures. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the
Choice, Simplicity, Transition. TransFx External Fixation System Small and Mini Surgical Technique
 Choice, Simplicity, Transition TransFx External Fixation System Small and Mini Surgical Technique TransFx External Fixation System Small and Mini Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique For TransFx External
Choice, Simplicity, Transition TransFx External Fixation System Small and Mini Surgical Technique TransFx External Fixation System Small and Mini Surgical Technique 1 Surgical Technique For TransFx External
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Olecranon Plates 2 AO Principles 3 Indications 3 Clinical
2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology.
 Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4
Technique Guide 2.4 mm Variable Angle LCP Volar Extra-Articular Distal Radius System. For fragment-specific fracture fixation with variable angle locking technology. Table of Contents Introduction 2.4
Zimmer MIS Periarticular Distal Femoral Locking Plate
 For Clinical Evaluations Zimmer MIS Periarticular Distal Femoral Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular Distal Femoral Locking Plate Surgical Technique
For Clinical Evaluations Zimmer MIS Periarticular Distal Femoral Locking Plate Surgical Technique The Science of the Landscape Zimmer MIS Periarticular Distal Femoral Locking Plate Surgical Technique
Olecranon Osteotomy Nail. For simple fractures and osteotomies of the olecranon.
 Olecranon Osteotomy Nail. For simple fractures and osteotomies of the olecranon. Technique Guide Discontinued June 2016; AVAILABLE FOR IMPLANT REMOVAL PURPOSES ONLY DSEM/TRM/0517/0843 Table of Contents
Olecranon Osteotomy Nail. For simple fractures and osteotomies of the olecranon. Technique Guide Discontinued June 2016; AVAILABLE FOR IMPLANT REMOVAL PURPOSES ONLY DSEM/TRM/0517/0843 Table of Contents
4.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes LCP Periarticular Plating System 4.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 4.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates 2 AO Principles
Part of the DePuy Synthes LCP Periarticular Plating System 4.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 4.5 mm LCP Medial Proximal Tibia Plates 2 AO Principles
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System. Surgical Technique
 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System 1 Zimmer Small Fragment Universal Locking System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction
The Hybrid Ring Fixator Surgical Technique
 The Hybrid Ring Fixator Surgical Technique Table of contents Page Indications 4 Preoperative planning 6 Tibial plateau fracture 7 Restore articular surface and stabilize... 7 Determine wire position...
The Hybrid Ring Fixator Surgical Technique Table of contents Page Indications 4 Preoperative planning 6 Tibial plateau fracture 7 Restore articular surface and stabilize... 7 Determine wire position...
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery. Zimmer NCB Plating System
 A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
A locking plate system that expands a surgeon s options in trauma surgery Zimmer NCB Plating System The Power of Choice The power of having true intraoperative options is at your fingertips. Using standard
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures.
 Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures. Technique Guide Part of the Small External Fixation System Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame When to use The
Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures. Technique Guide Part of the Small External Fixation System Small External Fixator Wrist Spanning Frame When to use The
Knee Surgical Technique
 Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
Knee Surgical Technique COMPASS Universal Hinge by Jimmy Tucker, M.D. Orthopaedic Surgeon Director, Arkansas Sports Medicine, P.A. Little Rock, Arkansas Table of contents Design features 3 Indications
3.0/3.5/4.0/4.5/6.5/7.0/7.3. Cannulated Screws. Surgical Technique
 3.0/3.5/4.0/4.5/6.5/7.0/7.3 Cannulated Screws Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes products. Instruction
3.0/3.5/4.0/4.5/6.5/7.0/7.3 Cannulated Screws Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use of DePuy Synthes products. Instruction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability.
 LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
LCP Anterolateral Distal Tibia Plate 3.5. The low profile anatomic fixation system with optimal plate placement and angular stability. Technique Guide LCP Small Fragment System Table of Contents Introduction
NCB Distal Femur System. Surgical Technique
 NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique 3 Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Table of Contents Introduction 4 Indications 8 Preoperative Planning
NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Surgical Technique 3 Surgical Technique NCB Distal Femur System Table of Contents Introduction 4 Indications 8 Preoperative Planning
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL
 LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
LOCKING TEP LOCKING TITANIUM ELASTIC PIN INTRAMEDULLARY NAIL ... Index -3 3-8 8 9 9 0 7 Introduction Features Indicatiıons Surgical Technique Femoral Surgical Technique Tibial Surgical Technique Ulna Radius
Hoffmann II External Fixation System
 Hoffmann II External Fixation System Modular System for Long Bones Pelvis Introduction In 1938, Raoul Hoffmann, a surgeon from Geneva, Switzerland, designed a revolutionary External Fixation System. The
Hoffmann II External Fixation System Modular System for Long Bones Pelvis Introduction In 1938, Raoul Hoffmann, a surgeon from Geneva, Switzerland, designed a revolutionary External Fixation System. The
Technique Guide. LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
Technique Guide LCP Distal Fibula Plates. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Distal Fibula Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical Technique
2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP. Ankle Trauma System
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate (VA LCP ) System 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm
Part of the DePuy Synthes Variable Angle Locking Compression Plate (VA LCP ) System 2.7 mm/3.5 mm Variable Angle LCP Ankle Trauma System Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 2.7 mm/3.5 mm
Surgical Technique. Distal Humerus Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Distal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Distal Humerus Locking Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Surgical Technique Distal Humerus Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Distal Humerus Locking Plate Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Technique Guide. TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee.
 Technique Guide TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee. Table of Contents Introduction TomoFix Osteotomy System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Technique Guide TomoFix Osteotomy System. A comprehensive plating system for stable fixation of osteotomies around the knee. Table of Contents Introduction TomoFix Osteotomy System 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Small External Fixator Nonspanning Wrist Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures.
 Small External Fixator Nonspanning Wrist Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures. Technique Guide Part of the Small External Fixation System Small External Fixator Nonspanning Wrist Frame When to use
Small External Fixator Nonspanning Wrist Frame. For the treatment of wrist fractures. Technique Guide Part of the Small External Fixation System Small External Fixator Nonspanning Wrist Frame When to use
The Titanium Tibial Nail System
 The Titanium Tibial Nail System Solid Tibial Nails (UTN) and Cannulated Tibial Nails (CTN) Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
The Titanium Tibial Nail System Solid Tibial Nails (UTN) and Cannulated Tibial Nails (CTN) Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved
Hoffmann II Micro External Fixation System
 Trauma Hoffmann II Micro External Fixation System Indications for the Hand Components 9 3 4 5 1 2 7 8 6 1 Hoffmann II Micro Multi-Pin Clamp 2 Hoffmann II Micro 90 Multi-Pin Clamp 3 Hoffmann II Micro Rod
Trauma Hoffmann II Micro External Fixation System Indications for the Hand Components 9 3 4 5 1 2 7 8 6 1 Hoffmann II Micro Multi-Pin Clamp 2 Hoffmann II Micro 90 Multi-Pin Clamp 3 Hoffmann II Micro Rod
Surgical Technique. Olecranon Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Olecranon Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Olecranon Locking Plate Surgical Techniquealog Infor Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Surgical Technique Olecranon Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Olecranon Locking Plate Surgical Techniquealog Infor Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Large Distractor Femur
 Fracture Reduction and Provisional Stabilization Large Distractor Femur Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Standard Femoral Distraction 2 Large Distractor System 4 Surgical Technique Prepare
Fracture Reduction and Provisional Stabilization Large Distractor Femur Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction Standard Femoral Distraction 2 Large Distractor System 4 Surgical Technique Prepare
OPERATING MANUAL AND TECHNIQUE GUIDE FOR TITANIUM FEMORAL AND TIBIAL NAILING SYSTEMS
 OPERATING MANUAL AND TECHNIQUE GUIDE FOR TITANIUM FEMORAL AND TIBIAL NAILING SYSTEMS ORTHO-MEDICAL GMBH TITANIUM FEMORAL NAIL OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE Introduction: Why a new type of femoral nail? The latest
OPERATING MANUAL AND TECHNIQUE GUIDE FOR TITANIUM FEMORAL AND TIBIAL NAILING SYSTEMS ORTHO-MEDICAL GMBH TITANIUM FEMORAL NAIL OPERATIVE TECHNIQUE Introduction: Why a new type of femoral nail? The latest
Technique Guide. 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system.
 Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide 3.5 mm LCP Periarticular Proximal Humerus Plate. Part of the Synthes locking compression plate (LCP) system. Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Proximal Humerus Plate 2 AO Principles
Double Engine Orthopedic Bone Nail System Universal Humeral Nail
 Double Engine Orthopedic Bone Nail System ----------- Universal Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic
Double Engine Orthopedic Bone Nail System ----------- Universal Humeral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic
Pelvic Implants and Instruments. A dedicated system for reconstructive pelvic and acetabular surgery.
 Pelvic Implants and Instruments. A dedicated system for reconstructive pelvic and acetabular surgery. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants
Pelvic Implants and Instruments. A dedicated system for reconstructive pelvic and acetabular surgery. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants
Hybrid Fixator Proximal Tibia Frame. Using rings with clamps.
 Hybrid Fixator Proximal Tibia Frame. Using rings with clamps. Technique Guide Part of the External Fixation System Hybrid Fixator Proximal Tibia Frame Technique Overview 1 Insert wires 2 Attach wires to
Hybrid Fixator Proximal Tibia Frame. Using rings with clamps. Technique Guide Part of the External Fixation System Hybrid Fixator Proximal Tibia Frame Technique Overview 1 Insert wires 2 Attach wires to
Technique Guide. SureLock Distal Targeting Device. C-arm guided targeting for trochanteric fixation nail.
 Technique Guide SureLock Distal Targeting Device. C-arm guided targeting for trochanteric fixation nail. Table of Contents Introduction SureLock Distal Targeting Device 2 Surgical Technique Preoperative
Technique Guide SureLock Distal Targeting Device. C-arm guided targeting for trochanteric fixation nail. Table of Contents Introduction SureLock Distal Targeting Device 2 Surgical Technique Preoperative
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS
 TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
TIPMED EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS ANATOMICAL LOCATIONS FOR EXTERNAL FIXATION SYSTEMS Humeral Dynamic Axial Fixator Elbow Fixator Pelvic Dynamic Axial Fixator Pennig Wrist Fixator Hand Fixator Finger Fixator
3.5 mm LCP Distal Humerus Plates
 Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Distal Humerus Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Distal Humerus Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
Part of the DePuy Synthes Locking Compression Plate (LCP ) System 3.5 mm LCP Distal Humerus Plates Surgical Technique Table of Contents Introduction 3.5 mm LCP Distal Humerus Plates 2 AO Principles 4 Indications
2.4 mm LCP Radial Head Plates. Part of the Synthes LCP Distal Radius Plate System.
 2.4 mm LCP Radial Head Plates. Part of the Synthes LCP Distal Radius Plate System. Technique Guide Instruments and Implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm LCP Radial
2.4 mm LCP Radial Head Plates. Part of the Synthes LCP Distal Radius Plate System. Technique Guide Instruments and Implants approved by the AO Foundation Table of Contents Introduction 2.4 mm LCP Radial
LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle.
 LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution
LCP Superior Clavicle Plate. The anatomically precontoured fixation system with angular stability for clavicle shaft and lateral clavicle. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution
Large External Fixator Modular Knee Bridge. Using multi-pin clamps.
 Large External Fixator Modular Knee Bridge. Using multi-pin clamps. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Modular Knee Bridge Technique Overview Insert Schanz
Large External Fixator Modular Knee Bridge. Using multi-pin clamps. Technique Guide Part of the Large External Fixation System Large External Fixator Modular Knee Bridge Technique Overview Insert Schanz
Large External Fixator Traveling Traction
 Used to Correct Angular Deformity Large External Fixator Traveling Traction Surgical Technique Large External Fixator Traveling Traction DePuy Synthes Large External Fixation devices are labeled MR Conditional
Used to Correct Angular Deformity Large External Fixator Traveling Traction Surgical Technique Large External Fixator Traveling Traction DePuy Synthes Large External Fixation devices are labeled MR Conditional
Technique Guide. VA-Locking Intercarpal Fusion System. Variable angle locking technology for mediocarpal partial arthrodesis.
 Technique Guide VA-Locking Intercarpal Fusion System. Variable angle locking technology for mediocarpal partial arthrodesis. Table of Contents Introduction VA-Locking Intercarpal Fusion System 2 Indications
Technique Guide VA-Locking Intercarpal Fusion System. Variable angle locking technology for mediocarpal partial arthrodesis. Table of Contents Introduction VA-Locking Intercarpal Fusion System 2 Indications
Pre-Operative Planning. Positioning of the Patient
 Surgical Technique Pre-Operative Planning Decide upon the size and angle of the barrel plate to be used from measuring the x-rays. To maximise the sliding action when using shorter lag screws, the Short
Surgical Technique Pre-Operative Planning Decide upon the size and angle of the barrel plate to be used from measuring the x-rays. To maximise the sliding action when using shorter lag screws, the Short
Pelvic Implants and Instruments. A dedicated system for reconstructive pelvic and acetabular surgery.
 Pelvic Implants and Instruments. A dedicated system for reconstructive pelvic and acetabular surgery. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants
Pelvic Implants and Instruments. A dedicated system for reconstructive pelvic and acetabular surgery. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants
Technique Guide. LCP Posterior Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment LCP system.
 Technique Guide LCP Posterior Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment LCP system. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Posterior Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5 2 AO Principles
Technique Guide LCP Posterior Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5. Part of the Synthes small fragment LCP system. Table of Contents Introduction LCP Posterior Medial Proximal Tibial Plate 3.5 2 AO Principles
TSLP Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate
 Anterior thoracolumbar spine locking plate TSLP Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use
Anterior thoracolumbar spine locking plate TSLP Thoracolumbar Spine Locking Plate Surgical Technique Image intensifier control This description alone does not provide sufficient background for direct use
Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual
 Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic surgeons, and this surgical
Orthopedic Bone Nail System - Distal Femoral Nail Surgical Technique Manual Note: The surgical procedures should be performed under the guidance of qualified skilled orthopedic surgeons, and this surgical
Surgical Technique. Calcaneal Locking Plate
 Surgical Technique Calcaneal Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Calcaneal Locking Plate Surgical TechniqueCatalog Infor Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Surgical Technique Calcaneal Locking Plate PERI-LOC Locked Plating System Calcaneal Locking Plate Surgical TechniqueCatalog Infor Table of Contents Introduction...2 Indications...3 Plate Features...3 Patient
Biomet Large Cannulated Screw System
 Biomet Large Cannulated Screw System s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e A Complete System for Simplified Fracture Fixation 6.5mm & 7.3mm The Titanium, Self-drilling, Self-tapping Large Cannulated Screw
Biomet Large Cannulated Screw System s u r g i c a l t e c h n i q u e A Complete System for Simplified Fracture Fixation 6.5mm & 7.3mm The Titanium, Self-drilling, Self-tapping Large Cannulated Screw
LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System.
 LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
LCP Condylar Plate 4.5/5.0. Part of the LCP Periarticular Plating System. Surgical Technique This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments and implants approved by the AO Foundation.
Cannulated Pediatric Osteotomy System (CAPOS). A single system of osteotomy blade plates and cannulated instrumentation.
 Cannulated Pediatric Osteotomy System (CAPOS). A single system of osteotomy blade plates and cannulated instrumentation. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
Cannulated Pediatric Osteotomy System (CAPOS). A single system of osteotomy blade plates and cannulated instrumentation. Technique Guide This publication is not intended for distribution in the USA. Instruments
