VEPTR. Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib. Disclosures
|
|
|
- Tobias Mason
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures Standardizing VEPTR Incision Site Documentation I have no relevant disclosures. Roni Lynn Robinson, RN, MSN, CRNP Department of Orthopedic Surgery Learning Objective Gain knowledge about a novel way to assess and reduce surgical wound complications and surgical site infections (SSI) for a specific low volume, high risk surgical procedure. Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib VEPTR Thoracic Insufficiency Syndrome (TIS) Inability of the thorax to support normal respiration or lung growth. Thoracic Insufficiency Syndrome (TIS) What Causes TIS? Underlying Pathologies 1. Deformity of the spine causing distortion of the rib cage with both volume and function loss. 2. Primary thoracic dysplasia which can compromise chest volume and rib cage function. 3. Neuromuscular dysfunction causing secondary spine and chest deformity. CHARGE Syndrome VACTERL Congenital Scoliosis Early Onset Scoliosis Juene Syndrome Jarcho Levine Syndrome Hemihypertrophy Charcot Marie Tooth Syndrome Spina bifida Muscular dystrophy SMA Friedreich s ataxia many more 1
2 1989 Dr. Robert Campbell placed the 1 st titanium rib in a child in Texas 1994 Synthes Spine Company took over production 2004 VEPTR approved by FDA VEPTR Device History VEPTR Device VEPTR expands outward to mimic the width of a typical child s chest Attaches to the ribs and either the ribs, pelvis or the spine With permission, Campbell et.al; Thoracic insufficiency. syndrome.curr Probl Pediatr Health Care 2016 Mar; 46(3): VEPTR Device Scoliosis VEPTR can be used as a jack to straighten the spine & keep it straight as the patient grows. Post VEPTR Insertion Real life VEPTRs Background Varying, nondescript documentation of incision sites in the EHR Difficult to capture which incision is from which surgery when there are wound concerns Potential to incorrectly report Surgical Site Incisions (SSI) Could lead to difficulty with providing optimal therapy, classification, as well as proactive identification of high risk sites Parents not consistently educated on incision site nomenclature when calling or coming to the ED with a wound concern No way of identifying specific incision sites in nursing flowsheets Quality Improvement Project Goals Provide a consistent approach when communicating a VEPTR patient s incision sites across the organization Standardize SSI documentation using the Center for Thoracic Insufficiency Syndrome (CTIS) Incision Site Schematic (ISS) for all skin & wound issues related to a VEPTR procedure Educate at least 80% of the patients/families using the ISS 2
3 Incision Site Schematic Developed within the CTIS Safety Group Ability to track & monitor multiple skin incisions following a VEPTR procedure Ability to discern which specific SSI there are concerns about Allows for a standardized communication of incision sites across the board VEPTR Post Surgery PFE Patient Family Education: VEPTR Care Post Surgery When can I remove my child s dressing? Remove your child s secondary or cover dressing on (Date:) How to Care for the spine dressing When can my child shower or take a bath? How do I care for my child s incision? Signs/symptoms of infection VEPTR Incision Diagram in EHR VEPTR Incision Diagram in EHR Nurses are able to refer to ISS while documenting in flowsheet. Who will utilize the ISS? Ortho attending documents the specific sites in the CTIS physician survey (REDCap) Nursing newly created LDA specific to VEPTR incisions (active in EHR) Will allow for easy identification of which sites have concerns Nursing & Inpatient NP s complete PFE sheet (ISS) & educate families prior to discharge An image of the completed ISS sheet is uploaded into the patient s media tab Outpatient NP s & coordinators utilize the ISS (media tab) to follow up with the families post operatively Parents use the ISS sheet provided when concerned about an incision site PFE:VEPTR Care Post Surgery Quality Improvement Project Results A PFE was created for consistent education at discharge Post discharge follow up showed that 100% of families in March 2017 reported receiving the VEPTR ISS & felt comfortable using it 3
4 Quality Improvement Project Results Qlikview Accessibility Goal: To educate 80% of patients/parents using the ISS As of March, % of families had received the education 4
5 5
6 My Kid Falls ALL the Time: Common Causes of In-toeing Learning Objectives Understand the 3 most common causes of in-toeing Describe treatment for 3 the most common causes of in-toeing Understand when to refer and when to watch In-toeing Very common Most resolves spontaneously Treatment for all 3: Reassurance Reassurance 2 nd opinion for reassurance Evaluation Thorough H&P Family history Pain? Height/Weight LLD? Neuro exam Femoral Anterversion Normal anterversion 15 to 20 Increases until age 4 or 5 Resolved by age W sitting- don t worry about it Surgical treatment-rare Osteotomy if functionally limiting by early teen Physical Exam: Hip motion Increased internal rotation > 70 Decreased external rotation of < 20 Patella internally rotated when ambulating Internal Tibial Torsion Presents at walking age Most often bilateral Resolves by 7 or 8 REASSURANCE Surgical treatment-rare Derotational osteotomy Physical Exam Thigh foot angle > 15
7 Increased foot progression angle Patella faces forward, feet turn in Metatarsus Adductus Packaging problem Torticollis DDH Excessive anterversion Internal tibial torsion Treatment Diaper change stretching 90% resolve by 1-2 years REASSURANCE (no special shoes) Metatarsus Adductus Physical Exam: Normal hindfoot Medially deviated forefoot C shaped lateral border Mild, moderate, severe References The American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America OrthoBullets
8 39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care Pediatric Fractures: A Tough Break for All March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures I have nothing to disclose. Kimberly R. Joo, DNP, APRN, CPNP PC, CNE Learning Objectives Define key terms Describing a fracture Review Bone Anatomy State the indications for an x ray Identify the different types of pediatric fractures Cases that require immediate referral Indicate cases that require follow up testing Splinting fractures Key Terms for Fractures Salter Harris: classification of growth plate and epiphyseal fractures Greenstick: incomplete fracture with angular deformity Buckle: compression fracture that causes the bone to bend or buckle on the damaged side Reduce: procedure to restore a fracture to original alignment Displaced: a fracture where the 2 ends of a bone are not lined up straight Angulated: a fracture with loss of alignment, the degree of rotation or change in bone length Transverse: fracture is perpendicular to the shaft Key Terms for Fractures Avulsion: a fragment of bone has torn away from the main mass of bone Effusion: abnormal accumulation of fluid in a joint Open: a broken bone that penetrates the skin Comminuted: more than 2 fracture fragments Oblique: an angulated fracture line Segmental: comminuted fracture where a completely separate segment of bone is bordered by fracture lines Torus: an incomplete buckle fracture of one cortex Key Terms for Fractures Spiral: multiplanar and complex fracture line Intra articular: the fracture line crosses the articular cartilage and enters the joint Impaction: a fracture that occurs when one bone hits an adjacent bone Compression: type of impaction fracture that occurs in the vertebrae, resulting in depression of the end plates Depression: a type of impaction fracture that occurs in the knee when the femoral condyle strikes the softer tibial plateau 1
9 Bone Anatomy Growth Plate Anatomy Indications for Imaging Injury Pain Point tenderness Deformity Decreased range of motion Edema Bruising Pain with ambulation Inability to bear weight (Slideplayer.com, 2016) What X Ray Should I Order? Describing a Fracture Anatomic Region Wrist Plain Radiograph Fracture Views All patients: AP, lateral Oblique: if fracture suspected, but AP and lateral are negative: Elbow Shoulder Knee Foot Tibia, femur, humerus, & forearm Ankle Scaphoid: if scaphoid fracture is suspected AP, lateral, and oblique AP, scapular Y AP, lateral, oblique (internal or externally rotated) Sunrise (axial, tangential): patellar injury AP, lateral Oblique: if fracture seen AP, lateral AP, lateral, and mortise (UpToDate, 2018) 2
10 Type of Fracture: Buckle (torus) Compression fracture Often at the junction between the porous metaphysis and the denser metaphysis Locations: distal radius, distal tibia, fibula and femur Stable Splint Ortho follow up Buckle (Torus) Fracture Image Type of Fracture: Plastic Deformation Bowing fracture Longitudinal force exceeds the bone s ability to recoilto it s normal position Microscopic fractures Locations: ulna, radius, and occasionally the fibula Self correcting if < 20 degrees and/or < 4 years of age Closed reduction or surgical intervention Plastic Deformation Fracture Image Type of Fracture: Greenstick Bone that is bent with a fracture line that does not extend completely through the width of the bone Risk for repeat fracture % of forearm refractures Location: forearm Greenstick Fracture Image 3
11 Type of Fracture: Physeal (Growth Plate) Growth plates are susceptible to fracture Weak point in pediatric bones Tensile strength of pediatric bone is less than that of ligaments 21 30% of pediatric long bone fractures Locations: distal radius and distal ulna Girls: 9 12 years Boys: years 30% cause bone growth disturbance Once the physis closes, fractures follow adult patterns Type of Fracture: Physeal Salter Harris Classification Type I: Disrupts the physis Type II: Break from the growth plate into the metaphysis Type III: Intraarticular through the epiphysis and extend across the physis Type IV: Cross the epiphysis, physis, and metaphysis Type V: Compression to the physis Types of Fractures: Physeal Salter Harris Classification Salter Harris Ankle Fracture Images Green = growth plate Red = fracture (UpToDate, 2018) (Epomedicine, 2016) Salter Harris Humor Type of Fracture: Apophyseal Avulsion Fibrocartilage physes instead of columnar cartilage Prone to overuse traction avulsions Osgood Schlatter disease: tibial tuberosity Sinding Larsen Johnsson syndrome: inferior pole of the patella Self limited Do not interfere with growth Adolescent athletes (Wordpress, 2014) 4
12 Apophyseal Avulsion Fracture Image Special Circumstance Fracture: Stress Fracture Overuse injuries Accumulated microtrauma from repetitive strain Small but progressive cracks in the periosteum Adolescents Female > males Locations: tibia, fibula, pars interarticularis (spondylolysis) and femur Radiographic findings don t present until 1 2 weeks of symptoms MRI is more sensitive (Science Direct, 2012) (KoreamedSynapse, 2009) Stress Fracture Sports and Sites Stress Fracture Images Sport Baseball Basketball Gymnastics Ice Skating Running Soccer Swimming Volleyball Fracture Site Tibia Anterior cortex of tibia, tarsal navicular Tibia, fibula Distal fibula Proximal tibial metaphysis, distal tibial metaphysis, fibula, tarsal navicular, midshaft of femur, distal femur, femoral neck Patella Proximal tibia Tibia (UpToDate, 2018) Special Circumstance Fracture: Child Abuse Fracture in a child < 1 year Lower extremity fracture in a non ambulatory child Posterior rib fractures Metaphyseal lesions (bucket handle or corner fractures) Bilateral long bone fractures Complex skull fractures Spinous process fractures Repeat fracture in an unusual location Stage of healing that is inconsistent with injury description Multiple fractures in various stages of healing Mandatory reporter Child Abuse Fracture Image 5
13 Special Circumstance Fracture: Pathologic Fracture Fracture in a bone that is weakened by an underlying abnormality Bone tumors Rickets McCune Albright syndrome Juvenile osteoporosis Chronic renal insufficiency Osteogenesis imperfecta Osteopetrosis Location: proximal femur and humerus Pathologic Fracture Image (Radiopaedia, 2018) Special Circumstance Fracture: Repeat Fractures 1 in 1, % of forearm fractures Risk: Incomplete bony union Residual angulation Early cast removal Radial or ulnar diaphyseal fracture Greenstick fracture Immediate Referral Open fractures Deformed/angulated fractures Rotated fractures Displaced fractures Fractures with dislocations Joint/articular surface involvement Any fracture with neurovascular compromise Consult orthopedics whenever you have a question Immobilization Guidelines 1. Document vascular, sensory, and motor function before and after immobilization. Immobilize above and below the site of injury, generally in a position of function. 2. Immediate consultation with orthopedics for all findings on previous slide. 3. Consult orthopedics whenever you have a question. If you consult an attending physician, follow up with that physician. 4. With any fracture (except torus), the fracture could progress (even in a cast). 5. True buckle/torus fractures should not demonstrate completion of fracture through volar cortex and should not have angulation. Immobilization Guidelines 6. Elbows: for children < 6 years, consider obtaining comparative lateral film of contralateral elbow; for condyle fractures, consider obtaining oblique view to more clearly delineate amount of displacement. 7. Any displacement at a growth plate should prompt a consult to ortho. 8. Ensure good after care instructions, pain control, and specify follow up (ortho or PCP and timing). 9. These guidelines are very generalized. Care must be taken to alter treatment according to individualized patient situation. 6
14 Immobilization/Splinting: Upper Extremity Site of Injury Immobilization Follow Up Timing Clavicle 1. Clavicle strap with sling or cuff & collar 7 15 days ortho or PCP 2. Sling & swath *ortho if athlete/teen Humerus proximal Sling & swath 5 7 days Humerus shaft Sugar tong splint with sling & swath 5 7 days Elbow lateral condyle <2mm displacement Elbow medial condyle <2mm displacement Supracondylar Type 1 Non angulated Type 2 Supracondylar Angulated Type 2 All Type 3 1. Long Arm posterior splint (elbow 90) with cuff & collar (simple sling for older kids) 2. Long Arm cast (elbow 90) with C&C or SS only with mild edema Long Arm posterior splint with C&C 3 7 days Immediate consult with ortho Immobilization/Splinting: Upper Extremity Site of Injury Immobilization Follow Up Timing Scaphoid (other carpal) Radial Head/Neck Thumb Spica 1. Long Arm posterior splint with C&C or SS 2. Long Arm cast with C&C or SS if mild edema Radius and Ulna Shaft Long Arm cast with C&C 7 10 days Radius and Ulna Distal Long Arm cast with C&C (if mild edema) Long Arm posterior splint or Reserve Sugar Tong with C&C 7 10 days Radius and Ulna Buckle or Torus Long Arm cast Short Arm cast for simple buckle 3 5 days (actual fracture) 7 10 days (suspected) 5 7 days Immediate consult with ortho if displaced days Olecranon 1. Long Arm posterior splint with C&C or SS 3 7 days 2. Long Arm cast with C&C or SS if mild edema (partial elbow Immediate consult if complete extension ) fracture Immobilization/Splinting: Upper Extremity Immobilization/Splinting: Lower Extremity Site of Injury Immobilization Follow Up Timing 1 st Metacarpal Thumb Spica splint 5 7 days 2 nd Metacarpal Radial Gutter splint 5 7 days 3 rd Metacarpal Volar splint 5 7 days 4 th & 5 th Metacarpals Ulnar Gutter splint 5 7 days Fingers Splint and/or buddy tape PCP for minor fractures Ortho if: 1. Intra articular 2. Displaced 3. Angulated 4. Rotational deformity Site of Injury Immobilization Follow Up Timing Femur Position of comfort Immediate consult Knee x ray negative Knee immobilizer (KI) Long Leg Sugar Tong splint (LLST) 3 7 days with ortho or sports med Long Leg Posterior splint (LLPS) Tibial Spine/Plateau LLST Immediate consult Proximal Fibula KI or Schantz wrap with crutches Consult ortho Tibia/Fibula: Toddler s fracture Long Leg Cast (LLC) 7 10 days Distal Fibula fracture LLC, LLPS, Short Leg Sugar Tong (SLST), Short Leg Posterior Splint (SLPS) 3 7 days if splinted 7 10 days if casted Distal Tibia fracture LLPS / SLST, LLC if minimal displacement 3 7 days if splinted 7 10 days if casted Immobilization/Splinting: Lower Extremity References Site of Injury Immobilization Follow Up Timing Ankle: Tri planar fracture LLPS Immediate consult Ankle: Tibia fracture LLPS Immediate consult Ankle: Tillaux < 2mm displacement LLPS or LLC (if mild edema) 5 7 days Ankle: Tillaux >/= 2mm displacement LLPS Immediate consult Salter Harris I Fibula fracture SLPS, SLST or air cast 7 10 days Foot: Tarsal fracture SLPS 5 7 days Single Schantz Reese shoe Foot: Metatarsal fracture Reese shoe or SLPS 7 10 days Toe (angulated may require reduction Reese shoe and/or buddy tape days with PCP or ortho if angulated Great toe open or with nail bed disturbance Reese shoe and/or buddy tape Antibiotics for 10 days 5 7 days with ortho Mathison, D.J., & Aggrawal, D. (2017). General principles of fracture management: Fracture patterns and description in children. In R.G. Bachur (Ed.), UpToDate. Watham, Mass.: UpToDate. Retrieved from Burns, C.E., Dunn, A.M., Brady, M.A., Starr, N.B., Blosser, C.G. & Garzon, D. L.(2017). Pediatric primary care: A handbook for nurse practitioners (6 th Ed). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders Company. 7
Pediatric Fractures. Objectives. Epiphyseal Complex. Anatomy and Physiology. Ligaments. Bony matrix
 1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
1 Pediatric Fractures Nicholas White, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Eastern Virginia Medical School Attending, Pediatric Emergency Department Children s Hospital of The King s Daughters Objectives
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES
 PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
PEM GUIDE CHILDHOOD FRACTURES INTRODUCTION Skeletal injuries account for 10-15% of all injuries in children; 20% of those are fractures, 3 out of 4 fractures affect the physis or growth plate. Always consider
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
Childhood Fractures. Incomplete fractures more common. Ligaments stronger than bone. Tendons stronger than bone. Fractures may be pathologic
 Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
Childhood Fractures Incomplete fractures more common Plastic bowing Torus / Buckle Greenstick Ligaments stronger than bone Fracture patterns different Physeal injury, not dislocation Tendons stronger than
4/28/2010. Fractures. Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms. Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis
 Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Fractures Normal Bone and Normal Ossification Bone Terms Epiphysis Epiphyseal Plate (physis) Metaphysis Diaphysis 1 Fracture Classifications A. Longitudinal B. Transverse C. Oblique D. Spiral E. Incomplete
Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Fracture Guideline
 Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Guideline Disclaimers This document is designed to assist physicians working in our emergency department in caring for
Montreal Children s Hospital McGill University Health Center Emergency Department Guideline Disclaimers This document is designed to assist physicians working in our emergency department in caring for
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time!
 FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
FOOSH It sounded like a fun thing at the time! Evaluating acute hand and wrist injuries Larry Collins, MPAS, PA-C, ATC, DFAAPA Assistant Professor, Physician Assistant Program Assistant Professor, Department
OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries. Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
 1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
1 2 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency
Disclosures. Fracture vs. Break: Is There a Difference? Jennifer Weiner, MS, RN, CPNP AC/PC March 21, Fracture vs. Break. Learning Objectives
 39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care Fracture vs. Break: Is There a Difference? Jennifer Weiner, MS, RN, CPNP AC/PC March 21, 2018 March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures I have no conflicts
39 th National Conference on Pediatric Health Care Fracture vs. Break: Is There a Difference? Jennifer Weiner, MS, RN, CPNP AC/PC March 21, 2018 March 19-22, 2018 CHICAGO Disclosures I have no conflicts
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD
 Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Basic Care of Common Fractures Utku Kandemir, MD Assistant Clinical Professor Trauma & Sports Medicine Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery UCSF / SFGH History Physical Exam Radiology Treatment History Acute trauma
Surgical Care at the District Hospital. EMERGENCY & ESSENTIAL SURGICAL CARE
 Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Surgical Care at the District Hospital 1 18 Orthopedic Trauma Key Points 2 18.1 Upper Extremity Injuries Clavicle Fractures Diagnose fractures from the history and by physical examination Treat with a
Upper Extremity Fractures
 Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
Upper Extremity Fractures Ranie Whatley, RN,FNP-C David W. Gray, MD Skeletal Trauma 10 to 15 % of all Childhood Injuries Physeal (Growth Plate) Injuries are ~ 15% of all Skeletal Injuries Orthopaedic Assessment
11/5/14. I will try to make this painless. Great, a Fracture, Now What? Objectives. Basics for Fracture Workup. Basics for Fracture Workup
 Great, a Fracture, Now What? I will try to make this painless Mary Greve MS, PA-C Department of Orthopedic Surgery Trauma Team University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Mary-Greve@uiowa.edu Pager 2121 Objectives
Great, a Fracture, Now What? I will try to make this painless Mary Greve MS, PA-C Department of Orthopedic Surgery Trauma Team University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Mary-Greve@uiowa.edu Pager 2121 Objectives
AMERICAN RED CROSS FIRST AID RESPONDING TO EMERGENCIES FOURTH EDITION Copyright 2006 by The American National Red Cross All rights reserved.
 Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Musculoskeletal injuries are most commonly caused by Mechanical forms of energy. Chemicals. Electrical energy. Heat Mechanical energy produces direct, indirect, twisting and contracting forces. Can be
Chapter XIX.1. Fractures May 2002
 Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and Residents Department of Pediatrics, University of Hawaii John A. Burns School of Medicine Chapter XIX.1. Fractures May 2002 Annemarie Uliasz The skeletal
Case Based Pediatrics For Medical Students and Residents Department of Pediatrics, University of Hawaii John A. Burns School of Medicine Chapter XIX.1. Fractures May 2002 Annemarie Uliasz The skeletal
Upper Extremity Injury Management. Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP
 Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Upper Extremity Injury Management Jonathan Pirie MD, Med, FRCPC, FAAP Learning Objectives At the end of this session, you will be able to manage common fractures of the: 1. Humerus 2. Elbow 3. Forearm
Disclosure. Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies. I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this program or presentation.
 Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Robin Pearce MSN, RN-BC Trauma Performance Improvement Manager Henrico Doctors Hospital, Forest Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation
Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Robin Pearce MSN, RN-BC Trauma Performance Improvement Manager Henrico Doctors Hospital, Forest Disclosure I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation
Trauma-related Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies. Javier Gonzalez del Rey, M.D. Professor Pediatrics Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center
 Trauma-related Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Javier Gonzalez del Rey, M.D. Professor Pediatrics Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Room # 10 7 month old sick since birth Room # 11 5 y/o Fell
Trauma-related Pediatric Orthopedic Emergencies Javier Gonzalez del Rey, M.D. Professor Pediatrics Cincinnati Children s Hospital Medical Center Room # 10 7 month old sick since birth Room # 11 5 y/o Fell
Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System Skeletal System Skeletal System Functions
Practice Changes I Hope You Make
 Is that Bad? What PCPs (& Parents) Need to Know about Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein, MD Pediatric Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Assistant Professor, Orthopaedics Baylor College
Is that Bad? What PCPs (& Parents) Need to Know about Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein, MD Pediatric Orthopaedics & Sports Medicine Texas Children s Hospital Assistant Professor, Orthopaedics Baylor College
PRESENTED BY: JOHN STIMLER, DO, CPC, CHC, FACEP BSA HEALTHCARE AND BSA HEALTHCARE ADVISORY GROUP
 PRESENTED BY: JOHN STIMLER, DO, CPC, CHC, FACEP BSA HEALTHCARE AND BSA HEALTHCARE ADVISORY GROUP TOPICS (1) Fracture types ICD-10-CM diagnostic coding CPT procedure coding Fracture care treatments: Manipulated
PRESENTED BY: JOHN STIMLER, DO, CPC, CHC, FACEP BSA HEALTHCARE AND BSA HEALTHCARE ADVISORY GROUP TOPICS (1) Fracture types ICD-10-CM diagnostic coding CPT procedure coding Fracture care treatments: Manipulated
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles. Striated Skeletal. Smooth
 1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
1 Chapter 29 Orthopaedic Injuries Principles of Splinting 2 Types of Muscles Striated Skeletal Smooth 3 Anatomy and Physiology of the Musculoskeletal System 4 Skeletal System 5 Skeletal System Functions
Pediatric Injuries/Fractures. Rena Heathcote
 Pediatric Injuries/Fractures Rena Heathcote INTRODUCTION Incidence Anatomy of the Growing Bone Injury Patterns What can we X-ray PEDIATRIC FRACTURES INCIDENCE What makes children susceptible to fractures?
Pediatric Injuries/Fractures Rena Heathcote INTRODUCTION Incidence Anatomy of the Growing Bone Injury Patterns What can we X-ray PEDIATRIC FRACTURES INCIDENCE What makes children susceptible to fractures?
EPIPHYSEAL PLATE IN FEMUR
 Reviewing: Epiphyseal Plates (younger skeletons) eventually will disappear. Bones grow lengthwise up and down from each plate, and in a circular collar like fashion around the diaphysis. These plates will
Reviewing: Epiphyseal Plates (younger skeletons) eventually will disappear. Bones grow lengthwise up and down from each plate, and in a circular collar like fashion around the diaphysis. These plates will
THE Salter-Harris classification is a radiologic
 Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 10 19 Copyright c 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Radiology R O U N D S Column Editor: Jonathan Lee Salter-Harris Fractures
Advanced Emergency Nursing Journal Vol. 29, No. 1, pp. 10 19 Copyright c 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Radiology R O U N D S Column Editor: Jonathan Lee Salter-Harris Fractures
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children
 Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Common Orthopaedic Injuries in Children Rakesh P. Mashru, M.D. Division of Orthopaedic Trauma Cooper University Hospital Cooper Medical School of Rowan University December 1, 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Ouch, That s Gotta Hurt! Pediatric Fractures & Injuries
 Ouch, That s Gotta Hurt! Pediatric Fractures & Injuries Greg Canty, MD Medical Director, Sports Medicine Center Attending Physician, Emergency Medicine Children s Mercy Kansas City 2011 Children s Mercy
Ouch, That s Gotta Hurt! Pediatric Fractures & Injuries Greg Canty, MD Medical Director, Sports Medicine Center Attending Physician, Emergency Medicine Children s Mercy Kansas City 2011 Children s Mercy
Will She Still Make the WNBA? Sports Injuries & Fractures
 Will She Still Make the WNBA? Sports Injuries & Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein MD Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Pediatric Sports Medicine Sports Injuries Chronic (overuse) Acute Who can be treated in PCP
Will She Still Make the WNBA? Sports Injuries & Fractures Aharon Z. Gladstein MD Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Pediatric Sports Medicine Sports Injuries Chronic (overuse) Acute Who can be treated in PCP
Apply this knowledge into proper management strategies and referrals
 1 2 3 Lower Extremity Injuries Jason Kennedy, M.D. Disclosures I have no financial/ industry disclosures. Objectives Identify common lower extremity injury patterns in the child and adolescent Apply this
1 2 3 Lower Extremity Injuries Jason Kennedy, M.D. Disclosures I have no financial/ industry disclosures. Objectives Identify common lower extremity injury patterns in the child and adolescent Apply this
Goals. Initial management skeletal trauma. Physical Exam ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT 12/4/2010
 ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Brian Feeley, MD UCSF Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Goals Discuss common fractures and initial management, treatment guidelines Let your patients
ABC OF PRIMARY CARE MEDICINE FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Brian Feeley, MD UCSF Sports Medicine and Shoulder Surgery Goals Discuss common fractures and initial management, treatment guidelines Let your patients
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017
 PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
PEDIATRIC CASTING AND SPLINTING HEATHER KONG, M.D. SHRINERS HOSPITAL FOR CHILDREN PORTLAND OCTOBER 7, 2017 DISCLOSURES I have no financial relationship with any company or product discussed in this presentation.
How to Triage Orthopaedic Care. David W. Gray, M.D.
 How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency Determine
How to Triage Orthopaedic Care David W. Gray, M.D. OBJECTIVES: Define basic assessments skills needed to identify orthopedic injuries Differentiate when an orthopedic injury is a medical emergency Determine
PEDIATRIC OVERUSE INJURIES. Nick Monson, DO Assistant Professor University of Utah Orthopedic Center U of U Sports Medicine Symposium
 PEDIATRIC OVERUSE INJURIES Nick Monson, DO Assistant Professor University of Utah Orthopedic Center U of U Sports Medicine Symposium MINI-ME Little adults Different injury patterns Ligaments > bones Changing
PEDIATRIC OVERUSE INJURIES Nick Monson, DO Assistant Professor University of Utah Orthopedic Center U of U Sports Medicine Symposium MINI-ME Little adults Different injury patterns Ligaments > bones Changing
Pediatric Orthopedics in Your Office. Laurel Saliman, MD Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon Swedish Pediatric Specialty Care
 Pediatric Orthopedics in Your Office Laurel Saliman, MD Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon Swedish Pediatric Specialty Care Overview for 20 minute whirlwind Clavicle Distal radius fractures Finger fractures
Pediatric Orthopedics in Your Office Laurel Saliman, MD Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon Swedish Pediatric Specialty Care Overview for 20 minute whirlwind Clavicle Distal radius fractures Finger fractures
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II
 Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
Basic Radiographic Principles Part II Kristopher Avant, D.O. October 19 th, 2016 I have no disclosures relevant to the material presented in this discussion. Good Stuff!!! 1 Really? Really! Musculoskeletal
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms.
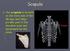 The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
The scapula is located on the back side of the ribcage and helps provide part of the shoulder joint and movement for the arms. Scapula Humerus (Upper Arm Bone) Radius and Ulna Radius on Top Ulna on Bottom
General Concepts. Growth Around the Knee. Topics. Evaluation
 General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
General Concepts Knee Injuries in Skeletally Immature Athletes Zachary Stinson, M.D. Increased rate and ability of healing Higher strength of ligaments compared to growth plates Continued growth Children
Introduction to Fractures. Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 3
 Introduction to Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 3 Definitions A fracture is an interruption in the continuity of bone Fracture = Break Fracture: mechanical damage produced in a
Introduction to Fractures Traumatology RHS 231 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Lecture 3 Definitions A fracture is an interruption in the continuity of bone Fracture = Break Fracture: mechanical damage produced in a
EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA. Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009
 EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009 MORAL OF THE STORY Fracture distal radius and intact ulna W/O radius fracture will most likely
EMERGENCY PITFALLS IN ORTHOPAEDIC TRAUMA Thierry E. Benaroch, MD, FRCS MCH Trauma Rounds February 9, 2009 MORAL OF THE STORY Fracture distal radius and intact ulna W/O radius fracture will most likely
Disclosures Head to Toe: Common Sports Injuries in Kids
 Disclosures Head to Toe: Common Sports Injuries in Kids None R. Jay Lee MD Director Pediatric Orthopaedic Fellowship Assistant Professor Pediatric Orthopaedics Johns Hopkins / Bloomberg Children s Objectives
Disclosures Head to Toe: Common Sports Injuries in Kids None R. Jay Lee MD Director Pediatric Orthopaedic Fellowship Assistant Professor Pediatric Orthopaedics Johns Hopkins / Bloomberg Children s Objectives
Country Health SA Medical Imaging
 Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Country Health SA Medical Imaging REMOTE OPERATORS POSITIONING GUIDE Contents Image Evaluation Page 4 Positioning Guides Section 1 - THORAX 1.1 Chest Page 5 1.2 Bedside Chest Page 7 1.3 Ribs Page 8 Section
Imaging the musculoskeletal system. An Introduction
 Imaging the musculoskeletal system An Introduction Objectives Discuss: commonly used imaging modalities in the musculoskeletal system normal imaging anatomy in the extremities fracture description Imaging
Imaging the musculoskeletal system An Introduction Objectives Discuss: commonly used imaging modalities in the musculoskeletal system normal imaging anatomy in the extremities fracture description Imaging
Orthopedic Emergencies. Peter Gutierrez, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Healthcare of Atlanta
 Orthopedic Emergencies Peter Gutierrez, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Healthcare of Atlanta Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose I do not intend to discuss unapproved
Orthopedic Emergencies Peter Gutierrez, MD Pediatric Emergency Medicine Children s Healthcare of Atlanta Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose I do not intend to discuss unapproved
Chapter 30 - Musculoskeletal_Trauma
 Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Introduction to Emergency Medical Care 1 OBJECTIVES 30.1 Define key terms introduced in this chapter. Slides 11 12, 19 20, 22 23, 37 30.2 Describe the anatomy of elements of the musculoskeletal system.
Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult
 Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Lec: 3 Fractures and dislocations around elbow in adult These include fractures of distal humerus, fracture of the capitulum, fracture of the radial head, fracture of the olecranon & dislocation of the
Basic Principles of Fractures & Easily Missed Fractures. Mr Irfan Merchant Trauma & Orthopaedic Registrar Bedford Hospital, East of England
 Basic Principles of Fractures & Easily Missed Fractures Mr Irfan Merchant Trauma & Orthopaedic Registrar Bedford Hospital, East of England Objectives Types Fracture Patterns Fracture Healing Assessing
Basic Principles of Fractures & Easily Missed Fractures Mr Irfan Merchant Trauma & Orthopaedic Registrar Bedford Hospital, East of England Objectives Types Fracture Patterns Fracture Healing Assessing
CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS. CMS Clinical Concepts
 CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS CMS Clinical Concepts ICD 10 LESSONS FROM OFFICE DOCUMENTATION Presented by Dr. Frankeny OUR CHALLENGE: CHANGING OUR DOCUMENTATION ICD 10 Learn the nomenclature Documenting
CLINICAL CONCEPTS FOR ORTHOPEDICS CMS Clinical Concepts ICD 10 LESSONS FROM OFFICE DOCUMENTATION Presented by Dr. Frankeny OUR CHALLENGE: CHANGING OUR DOCUMENTATION ICD 10 Learn the nomenclature Documenting
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Musculoskeletal System CPT CPT copyright 2011 American Medical Association. All rights reserved. Fee schedules, relative value units, conversion factors and/or related components are not assigned by the
Surgery-Ortho. Fractures of the tibia and fibula. Management. Treatment of low energy fractures. Fifth stage. Lec-6 د.
 Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
Fifth stage Lec-6 د. مثنى Surgery-Ortho 28/4/2016 Indirect force: (low energy) Fractures of the tibia and fibula Twisting: spiral fractures of both bones Angulatory: oblique fractures with butterfly segment.
ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE
 ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE Table of Contents SHOULDER A/P of Shoulder... 4 Tangential (Y-View) of Shoulder... 5 Lateral of Proximal Humerus... 6 ELBOW A/P of Elbow... 7 Extended Elbow... 8 Lateral
ORTHOSCAN MOBILE DI POSITIONING GUIDE Table of Contents SHOULDER A/P of Shoulder... 4 Tangential (Y-View) of Shoulder... 5 Lateral of Proximal Humerus... 6 ELBOW A/P of Elbow... 7 Extended Elbow... 8 Lateral
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents
 Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
Running Injuries in Children and Adolescents Cook Children s SPORTS Symposium July 2, 2014 Running Injuries Overuse injuries Acute injuries Anatomic conditions 1 Overuse Injuries Pain that cannot be tied
7/23/2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE. Pattern Open vs closed Location BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT. Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018.
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF FRACTURE MANAGEMENT Anjan R. Shah MD July 21, 2018 DESCRIBING THE FRACTURE Pattern Open vs closed Location POLL OPEN HOW WOULD YOU DESCRIBE THIS FRACTURE PATTERN? 1 Spiral 2 Transverse
Commonly Missed Injuries of the Extremities
 Commonly Missed Injuries of the Extremities Dr. Tudor H. Hughes M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California 1. Base of skull 2. Odontoid process
Commonly Missed Injuries of the Extremities Dr. Tudor H. Hughes M.D., FRCR Department of Radiology University of California School of Medicine San Diego, California 1. Base of skull 2. Odontoid process
Introduction to Fractures and Dislocations. CAPA 2016 Winnipeg, MB
 Introduction to Fractures and Dislocations CAPA 2016 Winnipeg, MB CAPA 2016 Dr. Chris Graham Orthopedic surgeon Practice primarily trauma related Assist. Prof. U of M Health Sciences Centre No conflicts
Introduction to Fractures and Dislocations CAPA 2016 Winnipeg, MB CAPA 2016 Dr. Chris Graham Orthopedic surgeon Practice primarily trauma related Assist. Prof. U of M Health Sciences Centre No conflicts
.org. Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures. Anatomy. Types of Tibial Shaft Fractures
 Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
Tibia (Shinbone) Shaft Fractures Page ( 1 ) The tibia, or shinbone, is the most common fractured long bone in your body. The long bones include the femur, humerus, tibia, and fibula. A tibial shaft fracture
16 th Annual Primary Care & Sports Medicine Symposium January 29th, 2016
 To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint has blocked automatic download of this picture. 16 th Annual Primary Care & Sports Medicine Symposium January 29th, 2016 Excellence in Orthopaedics Through Education
To help protect your privacy, PowerPoint has blocked automatic download of this picture. 16 th Annual Primary Care & Sports Medicine Symposium January 29th, 2016 Excellence in Orthopaedics Through Education
PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018
 PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018 DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose. 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the diagnosis,
PEDIATRIC UPPER EXTREMITY FRACTURE MANAGEMENT JULIA RAWLINGS, MD SPORTS MEDICINE SYMPOSIUM: THE PEDIATRIC ATHLETE 2 MARCH 2018 DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose. 2 OBJECTIVES Discuss the diagnosis,
42 nd Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine. Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete. Disclosure
 42 nd Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio January 23, 2015 Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure
42 nd Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio January 23, 2015 Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest
 Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Physeal Fractures and Growth Arrest Raymond W. Liu, M.D. Victor M. Goldberg Master Clinician-Scientist in Orthopaedics Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve University Outline General
Hand and wrist emergencies
 Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Chapter1 Hand and wrist emergencies Carl A. Germann Distal radius and ulnar injuries PEARL: Fractures of the distal radius and ulna are the most common type of fractures in patients younger than 75 years.
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions
 Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Caring for Muscle and Bone Injuries From Brady s First Responder (8 th Edition) 54 Questions 1. What is caused by overexerting or tearing of a muscle? p. 375 A.) Dislocation B.) Sprain C.) Fracture *D.)
Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222)
 Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Lower Extremity Radiographic Positioning Summary (Basic Projections RAD 222) AP Pelvis AP Hip (Unilateral) (L or R) AP Femur Mid and distal AP Knee Lateral Knee Pt lies supine on table Align MSP to Center
Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!!
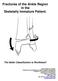 Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!! Kaye E Wilkins D.V.M,M.D. President's Council/Dielmann Chair in Pediatric Orthopedics Professor
Fractures of the Ankle Region in the Skeletally Immature Patient. The Salter Classification is Worthless!! Kaye E Wilkins D.V.M,M.D. President's Council/Dielmann Chair in Pediatric Orthopedics Professor
AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM
 AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME
AAP Boot Camp KNEE AND ANKLE EXAM Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturers of any commercial products and or providers of commercial services discussed in this CME
Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
Chapter 8 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum
10/12/2010. Upper Extremity. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle. Clavicle (collarbone) Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton
 Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton Pectoral girdle Pelvic girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs 8-1 Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle Consists of scapula and clavicle Clavicle articulates with sternum (Sternoclavicular
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne
 Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Vasu Pai FRACS, MCh, MS, Nat Board Ortho Surgeon Gisborne FRACTURE MANAGEMENT I Simple closed fracture : Complete or Incomplete Stable or unstable II Open fracture III Multiple fracture IV Polytrauma Fractures
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery. By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4
 Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Nursing Management: Musculoskeletal Trauma and Orthopedic Surgery By: Aun Lauriz E. Macuja SAC_SN4 The most common cause of musculoskeletal injuries is a traumatic event resulting in fracture, dislocation,
Dr.Israa H. Mohsen. Lecture 5. The vertebral column
 Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Anatomy Lecture 5 Dr.Israa H. Mohsen The vertebral column The vertebral column a flexible structure consisting of 33 vertebrae holds the head and torso upright, serves as an attachment point for the legs,
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls??
 Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
Fractures of the Hand in Children Which are simple? And Which have pitfalls?? Kaye E Wilkins DVM, MD Professor of Orthopedics and Pediatrics Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics University of Texas
7/1/2012. Repetitive valgus stresses cause microfractures in the apophyseal cartilage (weak link) Common in year olds
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 When growing pains are not growing pains David W. Gray,M.D. Medical Director Orthopedics Differential Diagnosis Fracture Ligament Injury Disloclation Cartilage Injury Apophysitis Inflammation
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 When growing pains are not growing pains David W. Gray,M.D. Medical Director Orthopedics Differential Diagnosis Fracture Ligament Injury Disloclation Cartilage Injury Apophysitis Inflammation
Chapter 8B. The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton. The Appendicular Skeleton. Clavicle. Pectoral (Shoulder) Girdle
 The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
The Appendicular Skeleton Chapter 8B The Skeletal System: Appendicular Skeleton 126 bones Pectoral (shoulder) girdle Pelvic (hip) girdle Upper limbs Lower limbs Functions primarily to facilitate movement
Musculoskeletal System
 Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Musculoskeletal System The musculoskeletal system gives the body strength, structure, and capability of movement. Bones are the framework. Ligaments and tendons are the nails Muscles are the way we move
Injuries to the Extremities
 Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
Injuries to the Extremities KNOWLEDGE OBJECTIVES 1. List seven signs and symptoms that suggest a serious extremity injury. 2. Describe how to care for injuries to the shoulder, upper arm, and elbow. 3.
40 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine. Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete. Disclosure
 40 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure Dr. Travis Murray
40 th Annual Symposium on Sports Medicine Travis Murray, MD Assistant Professor University of Texas Health Science Center San Antonio Knee Injuries In The Pediatric Athlete Disclosure Dr. Travis Murray
St Mary Orthopaedic Conference. Steven A. Caruso, MD Trenton Orthopaedic Group Trauma and Complex Fracture Surgeon October 25, 2014
 St Mary Orthopaedic Conference Steven A. Caruso, MD Trenton Orthopaedic Group Trauma and Complex Fracture Surgeon October 25, 2014 Nothing to disclose Goals To discuss common orthopaedic pathologies and
St Mary Orthopaedic Conference Steven A. Caruso, MD Trenton Orthopaedic Group Trauma and Complex Fracture Surgeon October 25, 2014 Nothing to disclose Goals To discuss common orthopaedic pathologies and
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, epidural, 822 824 Achilles tendon rupture, 894 895, 981 982 Acromioclavicular separations, shoulder pain in, 751 753 Adhesive capsulitis,
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abscess, epidural, 822 824 Achilles tendon rupture, 894 895, 981 982 Acromioclavicular separations, shoulder pain in, 751 753 Adhesive capsulitis,
On the Field Management of Pediatric Trauma
 On the Field Management of Pediatric Trauma Kyle Nagle, MD MPH University of Colorado Department of Orthopedics Children s Hospital Colorado Orthopedics Institute Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest
On the Field Management of Pediatric Trauma Kyle Nagle, MD MPH University of Colorado Department of Orthopedics Children s Hospital Colorado Orthopedics Institute Disclosures I have no conflicts of interest
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints. Emergency Medical Response
 Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints Lesson 33: Injuries to Muscles, Bones and Joints You Are the Emergency Medical Responder You are patrolling the state park where you are the emergency medical responder
CASE ONE CASE ONE. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Mason Classification. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Mechanism of Injury. RADIAL HEAD FRACTURE Imaging
 CASE ONE An eighteen year old female falls during a basketball game, striking her elbow on the court. She presents to your office that day with a painful, swollen elbow that she is unable to flex or extend
CASE ONE An eighteen year old female falls during a basketball game, striking her elbow on the court. She presents to your office that day with a painful, swollen elbow that she is unable to flex or extend
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
 Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology 14 th Edition CHAPTER 8 The Skeletal System: The Appendicular Skeleton The Appendicular Skeleton The 126 bones of the appendicular skeleton are primarily concerned
Lecture (10) Bone Fractures. Resources: - Lecture by dr.alboukai - Diagnostic imaging book
 Lecture (10) Bone Fractures Hanan Alsalman Hanan Alrabiah Reem Aljurayyad Ayshah Almahboob Ghadeer Alwuhyad Khawlah AlOthman Dalal Alqadi Suliman Alshammari Maha AlKubaidan Rawabi Alghamdi Resources: -
Lecture (10) Bone Fractures Hanan Alsalman Hanan Alrabiah Reem Aljurayyad Ayshah Almahboob Ghadeer Alwuhyad Khawlah AlOthman Dalal Alqadi Suliman Alshammari Maha AlKubaidan Rawabi Alghamdi Resources: -
Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries. J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics
 Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics 10. Proximal Humerus Fractures Treatment Simple sling ICE, pain meds Button-down shirts Recliner to sleep in It will be up to the surgeon
Top 10 Ortho Urgent Care Injuries J.C. Clark, M.D. ORA Orthopedics 10. Proximal Humerus Fractures Treatment Simple sling ICE, pain meds Button-down shirts Recliner to sleep in It will be up to the surgeon
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC
 BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
BASIC PRINCIPLES OF HAND TRAUMA: ARE CHILDREN DIFFERENT? SUSAN THOMPSON, MD, FRCSC EPIDEMIOLOGY HAND FRACTURES MAKE UP 2.3% OF ER VISITS INCIDENCE VARIES WITH AGE LOW IN TODDLERS INCREASES WITH AGE (20
Y: Orthopedic Specialty
 Y: Orthopedic Specialty Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 253 Major Competency Area: Y Priority: One Competency: Y-1 HPA Authorization and Standards Date: September 1, 2005 Y-1-1 Demonstrate
Y: Orthopedic Specialty Alberta Licensed Practical Nurses Competency Profile 253 Major Competency Area: Y Priority: One Competency: Y-1 HPA Authorization and Standards Date: September 1, 2005 Y-1-1 Demonstrate
The Appendicular Skeleton
 8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
8 The Appendicular Skeleton PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Jason LaPres Lone Star College North Harris 8-1 The Pectoral Girdle The Pectoral Girdle Also called shoulder girdle Connects the
Topics and Cases in Pediatric Orthopaedics (Tuesday 6:30am 4 th Floor Orthopaedic Conference Room at Hamot)
 2015-2016 Topics and Cases in Pediatric Orthopaedics (Tuesday 6:30am 4 th Floor Orthopaedic Conference Room at Hamot) 1. Considerations in the Management of Pediatric Patients Kerry Armet 7 July 2015 Fluid
2015-2016 Topics and Cases in Pediatric Orthopaedics (Tuesday 6:30am 4 th Floor Orthopaedic Conference Room at Hamot) 1. Considerations in the Management of Pediatric Patients Kerry Armet 7 July 2015 Fluid
Upper limb injuries in children. Key points, # & dislocations 7/23/2009 (MIMIC)
 Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
Upper limb injuries in children (MIMIC) Key points, # & dislocations Before the age of 16 around 50% of boys & 25% of girls will sustain a # Dislocations are very uncommon Children s bones are less brittle
A. Incorrect! The appendicular skeleton includes bones of the shoulder, arm, hand, pelvis, leg and foot.
 Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Anatomy and Physiology - Problem Drill 08: The Skeletal System III No. 1 of 10 1. Which of the following statements about the appendicular skeleton is correct? A. The appendicular skeleton includes bones
Lower Extremity Fracture Management. Fractures of the Hip. Lower Extremity Fractures. Vascular Anatomy. Lower Extremity Fractures in Children
 Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Lower Extremity Fracture Management Brian Brighton, MD, MPH Levine Children s s Hospital Carolinas Medical Center Charlotte, NC Oscar Miller Day October 16, 2009 Lower Extremity Fractures in Children Anatomic
Sports Medicine in your office: What not to miss!
 Sports Medicine in your office: What not to miss! 2018 Primary Care Approach to Treating the Injured Athlete May 4, 2018 John H. Wilckens, MD Associate Professor, Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Disclosures
Sports Medicine in your office: What not to miss! 2018 Primary Care Approach to Treating the Injured Athlete May 4, 2018 John H. Wilckens, MD Associate Professor, Dept of Orthopaedic Surgery Disclosures
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures, 462 464 Achilles tendon rupture, 389 Acromioclavicular dislocations, 302 Acromion fractures, 301 Ankle, anatomy of, 376
Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acetabular fractures, 462 464 Achilles tendon rupture, 389 Acromioclavicular dislocations, 302 Acromion fractures, 301 Ankle, anatomy of, 376
Sick Call Screener Course
 Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Sick Call Screener Course Musculoskeletal System Upper Extremities (2.7) 2.7-2-1 Enabling Objectives 1.46 Utilize the knowledge of musculoskeletal system anatomy while assessing a patient with a musculoskeletal
Pediatric Athletic Overuse Injuries. Susan Haralabatos, MD OPSC Annual Meeting 2018
 Pediatric Athletic Overuse Injuries Susan Haralabatos, MD OPSC Annual Meeting 2018 Text I have no disclosures Overview Etiology, Physiology &Anatomy Common Physeal Overuse Injuries Stress Fractures Concussion
Pediatric Athletic Overuse Injuries Susan Haralabatos, MD OPSC Annual Meeting 2018 Text I have no disclosures Overview Etiology, Physiology &Anatomy Common Physeal Overuse Injuries Stress Fractures Concussion
Ankle Sprains and Their Imitators
 Ankle Sprains and Their Imitators Mark Halstead, MD Dr. Mark Halstead is the Associate Professor of the Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics at Washington University School of Medicine; Director of
Ankle Sprains and Their Imitators Mark Halstead, MD Dr. Mark Halstead is the Associate Professor of the Departments of Orthopedics and Pediatrics at Washington University School of Medicine; Director of
Musculoskeletal System
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries
 CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
CHAPTER 28 Musculoskeletal Injuries Musculoskeletal System Anatomy & Physiology Bones provide framework. Joints allow for bending. Muscles allow for movement. Cartilage provides flexibility. Tendons connect
Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents
 A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Jumper s Knee in Children and Adolescents 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
1/19/2018. Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow. Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS Trust)
 Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Winter injuries to the shoulder and elbow Omar Haddo Consultant Orthopaedic Surgeon, Shoulder, Elbow, Hand & Wrist Specialist MBBS, BmedSci, FRCS(Orth) Highgate Private Hospital (Whittington Health NHS
Common Apophyseal Problems in the Athlete
 Disclosure Common Apophyseal Problems in the Athlete Mark Halstead, MD November 19, 2009 Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer
Disclosure Common Apophyseal Problems in the Athlete Mark Halstead, MD November 19, 2009 Faculty Disclosure Information In the past 12 months, I have no relevant financial relationships with the manufacturer
