OVERUSE AND SPORTS-RELATED INJURIES. Overuse and sports-related injuries of the ankle and hindfoot: MR imaging findings
|
|
|
- Rudolph Barnett
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 OVERUSE ND SPORTS-RELTED INJURIES CHPTER 10 Overuse and sports-related injuries of the ankle and hindfoot: MR imaging findings Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, d P.G. van Gils 1, Eduard E. de Lange 2 From the departments of Radiology 1 University Hospital Utrecht and Central Military Hospital, Utrecht From the department of Radiology 2 University of Virginia Health Sciences Center, Charlottesville US Submitted for publication 89
2 CHPTER 10 bstract Professional and recreational sporting activities have increased substantially in recent years and have led to a rise in the number of sports-related and overuse injuries. Magnetic Resonance (MR) imaging has become an important tool for evaluating the lower leg, providing the necessary information for patient management and rehabilitation following this injury [1]. The purpose of this essay is to give an overview of the MR findings of common overuse injuries and sports-related injuries to the bones and soft-tissue structures of the hindfoot and ankle. Introduction Professional and recreational sporting activities have increased substantially in recent years and have led to a rise in the number of sports-related injuries. The foot and ankle are often affected, particularly by exercise activities such as running and aerobics. Magnetic Resonance (MR) imaging has become an important tool for evaluating the lower leg providing the necessary information for patient management and rehabilitation following sports-related injury [1]. lthough most studies have focussed on the changes occurring after trauma, the effect of continued, repetitive stress has had less attention. The purpose of this essay is to give an overview of the MR imaging findings of common stress syndromes of the foot and ankle. Osseous injuries one bruises one bruises together with ligamental injuries are common after recurrent ankle sprains. These subchondral contusions, particularly when they are minor, are usually not detected by conventional radiography [2]. The clinical manifestation of these lesions is often nonspecific. Repeated trauma can lead to more severe osteochondral injury which in turn may result in osteochondral fractures with progressive disability [3]. one bruises usually arise when impactional and rotational forces occur during an inversion injury, causing trabecular microfractures, hemorrhage, edema and hyperemia [4,5]. Using MR imaging, the hemorrhage and edema are visualized as ill-defined semi-circular areas of abnormal signal intensity in the subcortical bone especially short tau inversion recovery (STIR) images have been shown to be helpful (Fig.1). With MR imaging the abnormalities are demonstrated with high sensitivity, allowing early detection and treatment of the findings. 90
3 OVERUSE ND SPORTS-RELTED INJURIES Figure 1. Runner, 18-year- old, with a bone contusion after inversion injury. Coronal short tau inversion recovery (STIR) demonstrates a bone contusion in the lateral aspect of the talar dome, with an area of high-signal intensity presenting hemorrhage and edema (white arrow). The overlying cortex is intact (small white arrows). Osteochondritis dissecans Osteochondritis dissecans occurs with (repetitive) inversion injury to the ankle. In particular, the talus is prone to these changes because of its blood supply and the convex surface of the joint. Military recruits are especially prone to this kind of injury. With conventional radiographs the osteochondral fracture is difficult to diagnose or may not be recognized [2,5]. Using MR imaging, the fractured segment can be visualised and the condition of the articular cartilage can be assessed with high accuracy [2,5]. In particular, it can be assessed whether the fragment is still situated in its fracture bed or whether loosening has occurred (Fig. 2). Diagnosis of the severity of osteochondritis dissecans is important as treatment is based on the status of the osteochondral fragment [5]. Stress response and stress fractures The bones are in a constant process of resorption and formation as a response to daily activities. With repetitive stress this remodeling of the bone is distorted, leading to an increase of bone resorption and less bone formation.this in turn is followed by focal trabecular microfractures with associated edema and hemorrhage, (stress response, Fig. 3) which may further progress into a stress fracture (Fig. 4) [5]. Considering the foot and ankle, runners and jumpers are by far the most affected group with changes of stress to the bones. In these individuals, the tibia, fibula and calcaneus are most commonly involved [1]. MR imaging has been demonstrated to be a highly sensitive technique for detecting changes of stress at an early stage. 91
4 CHPTER 10 Figure 2. Male jumper with two years pain in the medial side of the ankle., Coronal T1-weighted SE demonstrates an osteochondral fragment in the medial aspect of the talar dome (white arrow). The talar cortex is fractured (arrowheads)., Sagittal GRE MR image demonstrates an area of high-signal intensity around the osteochondral fragment typical of loosening (arrows). Figure 3. Stress response in the distal tibia in a 42-year-old male runner., nteroposterior radiograph demonstrates no abnormalities., Coronal STIR T2-weighted MR image demonstrates diffuse high signal intensity (arrow) in the intramedullary space of the right tibia, representing bone marrow edema. The cortex shows no abnormalities. 92
5 O VERUSE ND SPORTS - RELTED INJURIES Figure 4. Tri-athlete with stress fractures of both tali., Coronal T1-weighted spin-echo MR image shows moderately decreased signal intensity (black arrows) of the tali with a line (white arrows) representing stress fractures., Coronal CT of both hindfeet showing stress fractures (arrows). C, Coronal STIR T2-weighted MR image obtained at the same level as figure demonstrates edema (white arrows) in the talus and the low signal intensity fracture lines (black arrows) extending to the cortex. C 93
6 CHPTER 10 Impingement syndromes nterior impingement syndrome Osteophyte formation in the ankle joint is most often seen at the anterior lip of the tibia secondary to athletic injuries [6]. Repetitive bouncing of the anterior aspect of the tibia onto the neck of the talus, resulting in anterior impingement syndrome with joint swelling, limited motion and pain. Entrapment of synovial tissue between the talus and tibia leads to osteophytes which maintain the inflammation and irritation of the synovia [5]. nterolateral impingement syndrome fter (repetitive) ankle sprain, intra-articular hematoma and/or capsular tear of the anterior talofibular ligament and synovitis causes hyperplasia of synovial tissue in the anterolateral gutter. This increases further hyperplasia and subsequent fibrosis of synovial tissue in the anterolateral gutter, causing the anterolateral impingement syndrome [5,6]. Typically with this syndrome, a soft tissue mass can be found with MR imaging, representing hyperplastic synovia and fibrotic tissue (Fig. 5). Posterior impingement syndrome In case of posterior impingement syndrome, the talus and posterior capsule of the ankle joint and attached synovium become entrapped between the posterior aspect of the tibia and posterior facet of the calcaneus during plantar flexion of the foot. This results in bone and/or soft tissue lesions. The synovia hypertrophies due to the repetitive entrapment and becomes inflamed. allet dancers repetitively plantar hyperflex the foot are most commonly affected by this entity [7]. However, posterior impingement can also be the result of repetitive trauma due to impingement, occurring in runners. On occasion, the syndrome may be caused by a prominent os trigonum. With MR imaging, the hypertrophied synovial tissue is identified as a soft tissue mass in the posterior aspect of the joint (Fig. 6 and 7). Figure 5. Female runner (21-year-old) with anterior impingement syndrome of the right ankle resulting from repetitive inversion injuries. xial proton density weighted fast spin-echo MR image demonstrates increased soft tissue mass (arrow) in the right anterolateral gutter representing thickening of the anterior tibiofibular ligament, synovial hyperplasia and fluid. The left ankle is normal. 94
7 OVERUSE ND SPORTS-RELTED INJURIES Tenosynovitis, Tendinosis and tendon rupture chilles tendon chilles tendon injury is very common in running athletes. Typically, the entity occurs when there is a sudden increase in training frequency or intensity [5]. With overuse, the peritendinous structures of the chilles tendon and the bursa between the tendon and calcaneus become inflamed, a condition termed peritendinitis (posterior located called paratenonitis) and bursitis. chilles tendinosis represents intratendinous degeneration of the tendon itself with focal areas of mucoid degeneration and intrasubstance hemorrhage (Fig. 8 and 9). This degeneration leads to weakness of the tendon, thereby increasing the risk of a rupture. When the tendinosis is located near the insertion of the chilles tendon together with a prominent posterior superior tuberosity of the calcaneus and bony impingement on the retrocalcaneal bursa, the entity is called the Haglund syndrome (Fig. 10) [5]. Tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior, and peroneal tendons Tenosynovitis of the tibialis anterior, tibialis posterior and/or peroneal tendon resulting from overuse is frequently seen in runners. Repetitive microtrauma of the tendon in these individuals causes an increase of the synovial fluid which in turn causes distention of the Figure 6. Os trigonum in a 44-year-old ballet dancer., Lateral radiograph of the ankle demonstrates a prominent os trigonum (arrow) at the posterior aspect of the talus., Coronal T1 -weighted spin-echo MR image with edema in the left os trigonum (arrow). Right os trigonum is normal. 95
8 C HPTER 10 Figure 7. Posterior impingement syndrome in 24-year-old runner. Sagittal T2-weighted GRE MR image shows soft tissue mass (arrow) representing hypertrophied synovia caused by repetitive entrapment of the talus and soft tissue between the tibia and calcaneus during hyperflexion of the foot. Figure 8. Peritendinitis in male marathon runner. xial T2-weighted spin-echo MR image at the level of the talus shows fluid (arrows) around the posterior aspect of the chilles tendon. The tendon is also slightly thickened with subtle intratendoninous signal intensity (arrowheads) tendinous sheath (Fig. 11). With further progress chronic tendinitis occurs with thickening of the tendon and eventually, the tendon can rupture. Posterior tibialis tendinitis at the insertion of the tendon is often associated with an accessory navicular bone (Fig. 12). peroneal splits syndrome is present when there are repetitive subluxations of the peroneus brevis tendon over the lateral ridge of the fibula, leading to longitudinal rupture of the tendon (Fig. 13) [8]. Plantar Fasciitis The plantar fascia is a thick aponeurosis in the foot that arises from the medial calcaneal tuberosity and inserts onto the base of each proximal phalanx. Inflammation of the fascia near its attachment is frequently seen in distance runners caused by repetitive trauma. Due to microtears, inflammation and fibrous repair degeneration and focal thickening of the plantar fascia surrounded by edema occurs [9]. In chronic plantar fasciitis the entire fascia is thickened. s the plantar fascia is not attached to the heel spur often found on xray films, the presence of such a spur is not reliable for making the diagnosis of plantar fasciitis (Fig. 14) [9]. 96
9 OVERUSE ND SPORTS-RELTED INJURIES Figure 9. Long distance runner, 29-year-old, with inflammation of the chilles tendon and retrocalcaneal bursitis., Sagittal T2-weighted GRE MR image demonstrates fluid in the distended bursa between the chilles tendon and calcaneus (arrow). There is also moderately increased signal intensity in the distal chilles tendon (arrowhead)., xial T2-weighted GRE MR image showing the enlarged, fluid filled retrocalcaneal bursa (arrow) and increased signal intensity in the chilles tendon (arrowhead). Figure 10. Haglund syndrome in a 23-year-old female runner. Sagittal fast spin-echo inversion recovery MR image shows focal edema in the calcaneus (small arrows), and around the chilles tendon near its insertion. n associated Haglund s deformity with bony prominence of the postero-superior calcaneal tuberosity is seen (white arrow). Intratentendinous high signal intensity (arrowhead). 97
10 C HPTER 10 Figure 11. cute tenosynovitis of the tibialis anterior tendon in a 38year-old sportsman., Sagittal T2-weighted gradient echo MR image demonstrates normal caliber of tibialis anterior tendon surrounded by fluid in the tendon sheath (arrows)., xial T2-weighted fast spin-echo GRE MR image of the ankle shows the fluid (arrow) in the distended tendon sheath. Figure year-old runner with rupture of the posterior tibialis tendon associated with accessory navicular bone., Coronal T1-weighted GRE MR image at the level of the sinus tarsi (black arrow) showing accessory navicular bone on the medial side (white arrow)., xial proton density weighted fast spin-echo MR image at the level of the talus demonstrates rupture of the left posterior tibialis tendon at the insertion of the accessory navicular bone. There is edema (small white arrows) in the adjacent soft tissue. Normal right posterior tibialis tendon (white arrow), flexor hallucis longus tendons (black arrows), and flexor digitorum longus tendons (double black arrows). 98
11 OVERUSE ND SPORTS-RELTED INJURIES Figure 13. Male runner, 41-year-old, with peroneal splits syndrome., xial T1-weighted spin-echo MR image of the left ankle at the level of the posterior subtalar joint. There is enlarge-ment of the peroneal tendon sheath due to fluid with two peroneal brevis tendons (white arrows and one peroneus longus tendon (black arrow)., xial T2-weighted GRE MR image, at the same level better demonstrates the fluid in the enlarged tendon sheath. lso noted is splitting of the peroneal brevis tendon seen anteriorly in the tendon sheath: the tendon is seen as two separate structures (white arrows). The peroneus longus tendon seen posteriorly is normal (black arrow). Sinus tarsi syndrome The tarsal sinus is an anatomic space between the inferior aspect of the talus and the superior aspect of the calcaneus, just anterior to the posterior subtalar joint [10]. It consists of ligaments, vessels and nerves, surrounded by connective and fatty tissue. Inversion injury either as a result of single or repetitive trauma of the ankle can lead to stretching and tearing of the ligamentous structures of the sinus tarsi, causing inflammation of the structures and subtalar instability [11]. Routine radiographs are negative as are stress views [1]. The edema and fibrosis of inflamed tarsal sinus fat are readily visualized with MR imaging (Fig. 15) [1,10,11]. Tarsal tunnel syndrome (jogger s foot) Tarsal tunnel syndrome occurs when the posterior tibial nerve becomes entrapped as it passes through the tarsal tunnel. tumor, ganglion-cyst or large accessory soleus muscle can compress the entrance or the tarsal tunnel itself (Fig. 16). lood supply of the soleus muscle is marginal and therefore exercise may induce ischemia and edema in this muscle. Typically, after sports training when the medial neurovascular bundle is compressed, the patient notices a burning pain in the heel and a reduced sensation in the sole of the foot [12]. 99
12 C HPTER 10 Figure 14. Plantar fasciitis in a 18-year-old jumper., Sagittal T1-weighted spin-echo image of the left foot shows marked thickening and signal heterogeneity (arrows) of the plantar fascia near its attachment to the medial calcaneal tuberosity., Coronal T2-weighted fast inversion recovery MR image demonstrates thickened fascia (black arrow) surrounded by edema (white arrows). The right ankle is normal. Figure 15. Sinus tarsi syndrome in a 22-year-old female runner after recurrent inversion injuries., T1-weighted coronal spin-echo MR image shows diffuse infiltration (arrow) of the left tarsal sinus obliterating the fat and interosseous talo-calcaneal ligament. The right side is normal., Coronal STIR T2-weighted MR image at the level of the sinus tarsi demonstrates increased signal intensity (arrow) on the left, representing chronic synovitis and inflammation. 100
13 OVERUSE ND SPORTS-RELTED INJURIES Figure 16. Tarsal tunnel syndrome in a 36-year-old runner with symptoms caused by hypertrophy of an accessory soleus muscle., xial T1-weighted spin-echo MR image at the level of the talus demonstrates accessory soleus muscle (between white arrows). The right ankle is normal., xial T1-weighted spin-echo MR image at a higher level shows accessory soleus muscle causing compression of the medial neurovascular bundle after exercise (between white arrows). References 1. Clanton TO. thletic injuries to the soft tissue of the foot and ankle. In: Coughlin MJ, Mann R, eds. Surgery of the foot and ankle St Louis: Mosby, 1999: Deutsch L. Osteochondral injuries of the talar dome. In: Deutsch L, Mink JH, Kerr R, eds. MRI of the foot and ankle. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven,1992: Schweitzer ME. Magnetic resonance imaging of the foot and ankle. Magn Reson Q 1993;9: Kaplan P, Craig WW, Kilcoyne RF, rown DE, Tusek D, Dussault RG. Occult fracture patterns of the knee associated with anterior cruciate ligament tears: assessment with MR imaging. Radiology 1992;183: encardino J, Rosenberg ZS, Delfaut E. MR imaging in sports injuries of the foot and ankle. MRI Clin North m 1999;7: Farooki S, Yao L, Seeger LL. nterolateral impingement of the ankle: effectiveness of MR imaging. Radiology 1998;207: Khan K, rown J, Way S, et al. Overuse injuries in classical ballet. Sports Med 1995;19: Schweitzer ME, Eid ME, Deely D et al. Using MR imaging to differentiate peroneal splits from other peroneal disorders. JR 1997;168: Kier R. Magnetic resonance imaging of plantar fasciitis and other causes of heel pain. MRI Clin North m 1994;2: eltran J. Sinus tarsi syndrome. MRI Clin North m 1994;2: Klein M, Spreitzer M. MR imaging of the tarsal sinus and canal: normal anatomy, pathologic findings, and features of the sinus tarsi syndrome. Radiology 1993;186: Kerr R. Spectrum of disorders. In: Deutsch L, Mink JH, Kerr R, eds. MRI of the foot and ankle. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven,1992:
14 CHPTER
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle Tendons in Athletes. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Ankle Tendons in Athletes Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Outline Protocols Normal Anatomy Tendinopathy, partial and complete tears Posterior tibial, Flexor Hallucis Longus, Achilles, Peroneal and Anterior Tibial
Ankle Tendons in Athletes Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Outline Protocols Normal Anatomy Tendinopathy, partial and complete tears Posterior tibial, Flexor Hallucis Longus, Achilles, Peroneal and Anterior Tibial
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review.
 Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Ankle impingement syndromes - pictorial review. Poster No.: P-0148 Congress: ESSR 2015 Type: Educational Poster Authors: R. D. T. Mesquita, J. Pinto, J. L. Rosas, A. Vieira ; Porto/PT, 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 Matosinhos/PT,
Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions
 KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
KISSING CONTUSIONS CHAPTER 7 Posttraumatic subchondral bone contusions and fractures of the talotibial joint: Occurrence of kissing lesions Elizabeth S. Sijbrandij 1, Ad P.G. van Gils 1, Jan Willem K.
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology
 Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology Levon N. Nazarian, M.D. Professor of Radiology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Educational Objective Following
Ultrasound of Mid and Hindfoot Pathology Levon N. Nazarian, M.D. Professor of Radiology Thomas Jefferson University Hospital Disclosures None relevant to this presentation Educational Objective Following
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) Index
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) 335 344 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Accessory soleus muscle, magnetic resonance imaging of, 300 Achilles tendon injury of, magnetic
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) 335 344 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Accessory soleus muscle, magnetic resonance imaging of, 300 Achilles tendon injury of, magnetic
Anterior Impingement
 Anterior Impingement Ziali Sivardeen BMedSci, (MRCS), AFRCS, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgeon (Shoulder, Knee and Sports Injuries) Aims Causes of Anterior Ankle Pain Ankle Impingement
Anterior Impingement Ziali Sivardeen BMedSci, (MRCS), AFRCS, FRCS (Tr & Orth) Consultant Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgeon (Shoulder, Knee and Sports Injuries) Aims Causes of Anterior Ankle Pain Ankle Impingement
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain
 Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Imaging of Ankle and Foot pain Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University 1 Outlines Plain film: anatomy Common causes of ankle and foot pain Exclude:
Impingement Syndromes of the Ankle. Noaman W Siddiqi MD 5/4/2006
 Impingement Syndromes of the Ankle Noaman W Siddiqi MD 5/4/2006 Ankle Impingement Overview Clinical DX Increasingly recognized cause of chronic ankle pain Etiology can be soft tissue or osseous Professional
Impingement Syndromes of the Ankle Noaman W Siddiqi MD 5/4/2006 Ankle Impingement Overview Clinical DX Increasingly recognized cause of chronic ankle pain Etiology can be soft tissue or osseous Professional
Index. Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) 169 173 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles enthesopathy, calcaneal spur with, 133 clinical presentation of, 135 136 definition of, 131
Clin Sports Med 23 (2004) 169 173 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Achilles enthesopathy, calcaneal spur with, 133 clinical presentation of, 135 136 definition of, 131
THE JOURNAL OF NUCLEAR MEDICINE Vol. 56 No. 3 March 2015 Rauscher et al.
 Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
Supplemental Figure 1 Correlation analysis of tracer between and subsequent as assessed by SUV max in focal lesions (A). x-axis displays quantitative values as obtained by, and y-axis displays corresponding
17/10/2017. Foot and Ankle
 17/10/2017 Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Foot and Ankle Plantar Fasciitis Hallux Valgus Deformity Achilles Tendinosis Posterior Tibialis Tendon tendinopathy Stress Fracture Ligamentous tearing Turf
17/10/2017 Alicia M. Yochum RN, DC, DACBR, RMSK Foot and Ankle Plantar Fasciitis Hallux Valgus Deformity Achilles Tendinosis Posterior Tibialis Tendon tendinopathy Stress Fracture Ligamentous tearing Turf
Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology. Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018 Overview: Pathology of the Posteromedial Ankle Flexor Tendon Pathology Accessory Navicular Bone Pathology Tarsal
Ultrasound Evaluation of Posteromedial Ankle Pathology Andrew C Cordle, M.D., Ph.D. 9/21/2018 Overview: Pathology of the Posteromedial Ankle Flexor Tendon Pathology Accessory Navicular Bone Pathology Tarsal
Why? Ultrasound of the Foot. Ultrasound of the Foot. General Rules. Plantar Fascia. Plantar Fasciitis 18/09/2018
 Ultrasound of the Foot Why? Ultrasound of the Foot Plantar fasciitis Plantar fascia fibromatosis Morton s neuroma Intermetatarsal bursitis Adventitial bursitis Plantar plate tears MTP joint synovitis Ganglia
Ultrasound of the Foot Why? Ultrasound of the Foot Plantar fasciitis Plantar fascia fibromatosis Morton s neuroma Intermetatarsal bursitis Adventitial bursitis Plantar plate tears MTP joint synovitis Ganglia
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation. Disclosures. Outline. Joint Effusion. Suprapatellar recess
 Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
Knee, Ankle, and Foot: Normal and Abnormal Features with MRI and Ultrasound Correlation Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan
Persistent ankle pain after inversion lesions: what the radiologist must look for
 Persistent ankle pain after inversion lesions: what the radiologist must look for Poster No.: P-0118 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Poster R. Leao, L. C. Zattar-Ramos, E.
Persistent ankle pain after inversion lesions: what the radiologist must look for Poster No.: P-0118 Congress: ESSR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Poster R. Leao, L. C. Zattar-Ramos, E.
Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle. Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle
 Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Objectives Review relevant anatomy of the foot and ankle Learn the approach to examining the foot and ankle Learn the basics of diagnosis and treatment of ankle sprains Overview of other common causes
Imaging of posterior ankle pain : Main etiologies and differential diagnosis
 Imaging of posterior ankle pain : Main etiologies and differential diagnosis Poster No.: C-2399 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Frikha, M. MECHRI, S. boukriba, H. RIAHI, M. CHELLI
Imaging of posterior ankle pain : Main etiologies and differential diagnosis Poster No.: C-2399 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: W. Frikha, M. MECHRI, S. boukriba, H. RIAHI, M. CHELLI
Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month a
 Case presentations Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month after Progressive limited elbow flexion
Case presentations Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month after Progressive limited elbow flexion
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries. Anatomy. Anatomy. Tibia: the second longest bone in the body
 Prevention and Treatment of Injuries The Ankle and Lower Leg Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy Tibia: the second longest bone in the body Serves as the principle weight-bearing bone of the leg.
Prevention and Treatment of Injuries The Ankle and Lower Leg Westfield High School Houston, Texas Anatomy Tibia: the second longest bone in the body Serves as the principle weight-bearing bone of the leg.
Outline. Ankle/Foot Anatomy Ankle Sprains Ottawa Ankle Rules DDx: The Sprain That Wasn t
 Ankle Injuries Outline Ankle/Foot Anatomy Ankle Sprains Ottawa Ankle Rules DDx: The Sprain That Wasn t Anatomy: Ankle Mortise Bony Anatomy Lateral Ligament Complex Medial Ligament Complex Ankle Sprains
Ankle Injuries Outline Ankle/Foot Anatomy Ankle Sprains Ottawa Ankle Rules DDx: The Sprain That Wasn t Anatomy: Ankle Mortise Bony Anatomy Lateral Ligament Complex Medial Ligament Complex Ankle Sprains
Tarsal Coalition On MR
 Tarsal Coalition On MR By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in Tarsal coalition is a congenital anomaly with fusion of the tarsal bones. The fusion may be bony, fibrous or cartilaginous.
Tarsal Coalition On MR By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in Tarsal coalition is a congenital anomaly with fusion of the tarsal bones. The fusion may be bony, fibrous or cartilaginous.
Original Report. Sonography of Ankle Tendon Impingement with Surgical Correlation
 Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 162.158.89.91 on 08/23/18 from IP address 162.158.89.91. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Monisha Shetty 1 David P. Fessell 1 John E. Femino
Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 162.158.89.91 on 08/23/18 from IP address 162.158.89.91. Copyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved Monisha Shetty 1 David P. Fessell 1 John E. Femino
~, /' ~::'~ EXTENSOR HALLUCIS LONGUS. Leg-anterolateral :.:~ / ~\,
 TIBIALIS ANTERIOR Lateral condyle of tibia, upper half of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Medial side and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone, and base of first metatarsal bone Dorsiflexes
TIBIALIS ANTERIOR Lateral condyle of tibia, upper half of lateral surface of tibia, interosseous membrane Medial side and plantar surface of medial cuneiform bone, and base of first metatarsal bone Dorsiflexes
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines. VI. Ankle
 European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines VI. Ankle Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
European Society of MusculoSkeletal Radiology Musculoskeletal Ultrasound Technical Guidelines VI. Ankle Ian Beggs, UK Stefano Bianchi, Switzerland Angel Bueno, Spain Michel Cohen, France Michel Court-Payen,
SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY
 Página 1 de 9 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "47 - ANKLE FRACTURES"
Página 1 de 9 Copyright 2001 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Bucholz, Robert W., Heckman, James D. Rockwood & Green's Fractures in Adults, 5th Edition SURGICAL AND APPLIED ANATOMY Part of "47 - ANKLE FRACTURES"
Copyright 2012 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill/Irwin
 CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
CHAPTER 8: THE LOWER EXTREMITY: KNEE, ANKLE, AND FOOT KINESIOLOGY Scientific Basis of Human Motion, 12 th edition Hamilton, Weimar & Luttgens Presentation Created by TK Koesterer, Ph.D., ATC Humboldt State
Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2016, Article ID 8739362, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/8739362 Case Report Painful Os Peroneum Syndrome: Underdiagnosed Condition in the Lateral Midfoot Pain
Leg. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
Leg Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Skin of the Leg Cutaneous Nerves Medially: The saphenous nerve, a branch of the femoral nerve supplies the skin on the medial surface
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY 3. TALRSALS = (FOOT BONES) Fibula. Frances Daly MSc 1 CALCANEUS 2. TALUS 3. NAVICULAR 4. CUBOID 5.
 ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
emoryhealthcare.org/ortho
 COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
COMMON SOCCER INJURIES Oluseun A. Olufade, MD Assistant Professor, Department of Orthopedics and PM&R 1/7/18 GOALS Discuss top soccer injuries and treatment strategies Simplify hip and groin injuries in
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and
 Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
Section Three: The Leg, Ankle, and Foot Lecture: Review of Clinical Anatomy, Patterns of Dysfunction and Injury, and Treatment Implications for the Leg, Ankle, and Foot Levels I and II Demonstration and
ii ANKLE INJURIES SPECIFIC TRAINING AFTER INJURY TO THE FOOT OR ANKLE
 40 Ankle injuries are among the most common injuries in sport. Ankle sprain (which is a mechanism rather than a diagnosis) is the most common injury in virtually all epidemiological studies. Being the
40 Ankle injuries are among the most common injuries in sport. Ankle sprain (which is a mechanism rather than a diagnosis) is the most common injury in virtually all epidemiological studies. Being the
Physical Examination of the Foot & Ankle
 Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
The Lower Limb VII: The Ankle & Foot Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 7 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Ankle joint Synovial, hinge joint Allow movement of the foot in the sagittal plane only (1 degree of freedom): dorsiflexion:
IMAGING TECHNIQUES CHAPTER 4. Imaging techniques
 IMAGING TECHNIQUES Imaging techniques 23 4.1. Conventional radiographic findings Conventional radiography, tomography, arthrography and stress views have traditionally been used for imaging the ankle and
IMAGING TECHNIQUES Imaging techniques 23 4.1. Conventional radiographic findings Conventional radiography, tomography, arthrography and stress views have traditionally been used for imaging the ankle and
ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION
 ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION Evaluation and Measurements By Isabelle Devreux 1 Ankle Plantar Flexion: Gastrocnemius and Soleus ROM: 0 to 40-45 A. Soleus: Origin: Posterior of head of fibula and proximal1/3 of
ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION Evaluation and Measurements By Isabelle Devreux 1 Ankle Plantar Flexion: Gastrocnemius and Soleus ROM: 0 to 40-45 A. Soleus: Origin: Posterior of head of fibula and proximal1/3 of
11/2/17. Lateral Collateral Complex Medial Collateral Complex Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Spring Ligament
 Andrew J Grainger Leeds, UK Lateral Collateral Complex ial Collateral Complex Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Spring Ligament Brief anatomy review Scan tips and tricks Pathological appearances andrewgrainger@nhs.net
Andrew J Grainger Leeds, UK Lateral Collateral Complex ial Collateral Complex Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmosis Spring Ligament Brief anatomy review Scan tips and tricks Pathological appearances andrewgrainger@nhs.net
The Leg. Prof. Oluwadiya KS
 The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
The Leg Prof. Oluwadiya KS www.oluwadiya.sitesled.com Compartments of the leg 4 Four Compartments: 1. Anterior compartment Deep fibular nerve Dorsiflexes the foot and toes 2. Lateral Compartment Superficial
Sports Injuries of the Ankle and Ankle Arthritis. Mr Amit Amin Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Parkside Hospital
 Sports Injuries of the Ankle and Ankle Arthritis Mr Amit Amin Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Parkside Hospital Impingement Painful mechanical limitation of full ankle movement secondary to osseous
Sports Injuries of the Ankle and Ankle Arthritis Mr Amit Amin Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Parkside Hospital Impingement Painful mechanical limitation of full ankle movement secondary to osseous
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle
 Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor, Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic 2012 MFMER slide MFMER slide-3
 Ultrasound Foot and Ankle Pathology Disclosures None relevant Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor, Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic Florida @ShaneShapiroMD 2012 MFMER slide-2 Foot and Ankle Fundamentals
Ultrasound Foot and Ankle Pathology Disclosures None relevant Shane A. Shapiro, M.D. Assistant Professor, Orthopedic Surgery Mayo Clinic Florida @ShaneShapiroMD 2012 MFMER slide-2 Foot and Ankle Fundamentals
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity
 Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Recognizing common injuries to the lower extremity Bones Femur Patella Tibia Tibial Tuberosity Medial Malleolus Fibula Lateral Malleolus Bones Tarsals Talus Calcaneus Metatarsals Phalanges Joints - Knee
Arthroscopy Of the Ankle.
 Arthroscopy Of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Arthroscopy Anatomy Patient setup Portal placement Procedures Complications Anatomy Portals Anterior Anteromedial Anterolateral Anterocentral Posterior
Arthroscopy Of the Ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Arthroscopy Anatomy Patient setup Portal placement Procedures Complications Anatomy Portals Anterior Anteromedial Anterolateral Anterocentral Posterior
Ankle Injuries. Resident Guidebook. Achilles tendon sprain/tear. Peroneal tendinopathy Peroneal subluxation. Extensor Hallucis Longus Tenosynovitis
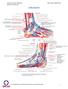 Ankle Injuries Achilles tendon sprain/tear Peroneal tendinopathy Peroneal subluxation Extensor Hallucis Longus Tenosynovitis Weber Fracture Stress fracture Calcaneal bursitis Calcaneal fracture Base of
Ankle Injuries Achilles tendon sprain/tear Peroneal tendinopathy Peroneal subluxation Extensor Hallucis Longus Tenosynovitis Weber Fracture Stress fracture Calcaneal bursitis Calcaneal fracture Base of
Bone Marrow Edema Patterns in the Ankle and Hindfoot: Distinguishing MRI Features
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Rios et al. MRI of the Ankle and Hindfoot Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Adriana Martins Rios 1 Zehava Sadka Rosenberg 2 Jenny Teresa Bencardino 2 Silvia
Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Rios et al. MRI of the Ankle and Hindfoot Musculoskeletal Imaging Pictorial Essay Adriana Martins Rios 1 Zehava Sadka Rosenberg 2 Jenny Teresa Bencardino 2 Silvia
mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading
 Tendinopathy.. How does it happen? mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading Impingement of the tendon between adjacent structures (bones, ligaments) and impaired blood supply Presentation
Tendinopathy.. How does it happen? mechanical stresses on the tendon with repetitive loading Impingement of the tendon between adjacent structures (bones, ligaments) and impaired blood supply Presentation
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses
 Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Ultrasound Evaluation of Masses Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Advisory Panel: GE,
Foot and ankle update
 Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
Foot and ankle update Mr Ian Garnham Consultant Foot and Ankle Surgeon Whipps Cross University Hospital Hallux Rigidus Symptoms first ray and 1st MTP pain and swelling worse with push off or forced dorsiflexion
Anatomy and evaluation of the ankle.
 Anatomy and evaluation of the ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Anatomical Structures Tibia Fibular Talus Tibia This is the strongest largest bone of the lower leg. It bears weight and the bone creates
Anatomy and evaluation of the ankle www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Ankle Anatomical Structures Tibia Fibular Talus Tibia This is the strongest largest bone of the lower leg. It bears weight and the bone creates
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Evaluation of Musculoskeletal Diseases of Ankle and Foot
 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Evaluation of Musculoskeletal Diseases of Ankle and Foot Sharma UK, 1 Dhungel K, 1 Pokhrel Dinesh, 1 Tamang S, 1 Parajuli NP 2 ABSTRACT Background 1 Department of Radiology 2
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Evaluation of Musculoskeletal Diseases of Ankle and Foot Sharma UK, 1 Dhungel K, 1 Pokhrel Dinesh, 1 Tamang S, 1 Parajuli NP 2 ABSTRACT Background 1 Department of Radiology 2
Ankle Injuries. Ankle Sprain. Range of Motion. The most likely diagnosis is lateral ligament sprain. Dorsiflexion Plantarflexion Inversion
 Ankle Injuries Dr Peter Brukner, OAM Sports Physician Associate Professor Centre for Sports Medicine Research & Education The University of Melbourne Adjunct Professor School of Human Movement Studies
Ankle Injuries Dr Peter Brukner, OAM Sports Physician Associate Professor Centre for Sports Medicine Research & Education The University of Melbourne Adjunct Professor School of Human Movement Studies
Anterior impingement syndrome in dancers
 Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med (2008) 1:12 16 DOI 10.1007/s12178-007-9001-4 Anterior impingement syndrome in dancers John William O Kane Æ Nancy Kadel Published online: 6 November 2007 Ó Humana Press 2007
Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med (2008) 1:12 16 DOI 10.1007/s12178-007-9001-4 Anterior impingement syndrome in dancers John William O Kane Æ Nancy Kadel Published online: 6 November 2007 Ó Humana Press 2007
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology KNEE & ANKLE MUSCLES
 BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology KNEE & ANKLE MUSCLES MSAK201-I Session 3 1) REVIEW a) THIGH, LEG, ANKLE & FOOT i) Tibia Medial Malleolus
BLUE SKY SCHOOL OF PROFESSIONAL MASSAGE AND THERAPEUTIC BODYWORK Musculoskeletal Anatomy & Kinesiology KNEE & ANKLE MUSCLES MSAK201-I Session 3 1) REVIEW a) THIGH, LEG, ANKLE & FOOT i) Tibia Medial Malleolus
Ultrasound of the Knee
 Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Ultrasound of the Knee Jon A. Jacobson, M.D. Professor of Radiology Director, Division of Musculoskeletal Radiology University of Michigan Disclosures: Consultant: Bioclinica Book Royalties: Elsevier Advisory
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG
 Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Understanding Leg Anatomy and Function THE UPPER LEG The long thigh bone is the femur. It connects to the pelvis to form the hip joint and then extends down to meet the tibia (shin bone) at the knee joint.
Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain
 May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
Main Menu. Ankle and Foot Joints click here. The Power is in Your Hands
 1 The Ankle and Foot Joints click here Main Menu Copyright HandsOn Therapy Schools 2009 K.8 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k8/k8entry.htm[3/27/18, 1:40:03 PM] Ankle and Foot Joint 26 bones
1 The Ankle and Foot Joints click here Main Menu Copyright HandsOn Therapy Schools 2009 K.8 http://www.handsonlineeducation.com/classes/k8/k8entry.htm[3/27/18, 1:40:03 PM] Ankle and Foot Joint 26 bones
The Foot. Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob:
 The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The Foot Dr. Wegdan Moh.Mustafa Medicine Faculty Assistant Professor Mob: 0127155717 The skeleton of the foot Cutaneous innervations Sole of foot layers of muscles First layer -Abductor hallucis -Flexor
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine FOOT. Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine FOOT Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Due to compression of Tibial nerve as it travels through the
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine FOOT Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Due to compression of Tibial nerve as it travels through the
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg. Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa
 The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
The Lower Limb VI: The Leg Anatomy RHS 241 Lecture 6 Dr. Einas Al-Eisa Muscles of the leg Posterior compartment (superficial & deep): primary plantar flexors of the foot flexors of the toes Anterior compartment:
Peggers Super Summaries: Foot Injuries
 Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Anatomy MCQs Week 13
 Anatomy MCQs Week 13 1. Posterior to the medial malleolus of the ankle: The neurovascular bundle lies between Tibialis Posterior and Flexor Digitorum Longus The tendon of Tibialis Posterior inserts into
Anatomy MCQs Week 13 1. Posterior to the medial malleolus of the ankle: The neurovascular bundle lies between Tibialis Posterior and Flexor Digitorum Longus The tendon of Tibialis Posterior inserts into
MR Imaging of normal ankle anatomy: What the radiologists need to know
 MR Imaging of normal ankle anatomy: What the radiologists need to know Poster No.: P-0110 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. M. Simonet Redondo, I. Santos Gomez, A. Marin Canete,
MR Imaging of normal ankle anatomy: What the radiologists need to know Poster No.: P-0110 Congress: ESSR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: M. M. Simonet Redondo, I. Santos Gomez, A. Marin Canete,
Ankle Arthroscopy.
 Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Ankle Arthroscopy Key words: Ankle pain, ankle arthroscopy, ankle sprain, ankle stiffness, day case surgery, articular cartilage, chondral injury, chondral defect, anti-inflammatory medication Our understanding
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries. Laura W. Bancroft, M.D.
 Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Knee Contusions and Stress Injuries Laura W. Bancroft, M.D. Objectives Review 5 types of contusion patterns Pivot shift Dashboard Hyperextension Clip Lateral patellar dislocation Demonstrate various stress
Foot. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
Foot Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Dorsum of the Foot Sole of the Foot Plantar aponeurosis It is a triangular thickening of deep fascia in the sole of the foot Attachments:
First & second layers of muscles of the sole
 The FOOT First & second layers of muscles of the sole introduction The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic muscles arise from
The FOOT First & second layers of muscles of the sole introduction The muscles acting on the foot can be divided into two distinct groups; extrinsic and intrinsic muscles. The extrinsic muscles arise from
2013/10/18 GANGLION CYSTS ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY ARTHROSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OPEN GANGLIONECTOMY COMPARED TO FOOT AND ANKLE
 GANGLION CYSTS gelatinous fluid filled, encapsulated soft tissue masses adjacent to a joint or tendon ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Dr TH Lui North District Hospital HKSAR Pain, mass
GANGLION CYSTS gelatinous fluid filled, encapsulated soft tissue masses adjacent to a joint or tendon ENDOSCOPIC GANGLIONECTOMY OF THE FOOT AND ANKLE Dr TH Lui North District Hospital HKSAR Pain, mass
EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle]
![EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle] EDL EHL. Extensor Hallucis Longus L5 Extensor Digitorum longus L5,1 Peroneus Tertius L5 1 Extensor Digitorum Brevis S1,2 [like intrinsic muscle]](/thumbs/78/77875930.jpg) ANATOMY OF ANKLE AND FOOT Lateral aspect: [Dorsal medial to lateral= dorsal under extensor retinaculum] Tibialis Anterior EHL Artery [Dorsal pedal A] and Anterior tibial N EDL Peroneus Tertius Behind the
ANATOMY OF ANKLE AND FOOT Lateral aspect: [Dorsal medial to lateral= dorsal under extensor retinaculum] Tibialis Anterior EHL Artery [Dorsal pedal A] and Anterior tibial N EDL Peroneus Tertius Behind the
MR Imaging of Ankle Anatomy and Review of Common Ankle Pathologies
 MR Imaging of Ankle Anatomy and Review of Common Ankle Pathologies Poster No.: C-0284 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Flaherty, D. Stedman, M. Chen, G. Bean, R. Loredo; San Antonio,
MR Imaging of Ankle Anatomy and Review of Common Ankle Pathologies Poster No.: C-0284 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Flaherty, D. Stedman, M. Chen, G. Bean, R. Loredo; San Antonio,
MRI of the Ankle and Foot
 Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XX, nº 79, pág. 55-63, Jul.-Set., 2008 MRI of the Ankle and Foot Mark Anderson University of Virginia Health Sciences Center, Charlottesville, Virginia discuss the basic
Acta Radiológica Portuguesa, Vol.XX, nº 79, pág. 55-63, Jul.-Set., 2008 MRI of the Ankle and Foot Mark Anderson University of Virginia Health Sciences Center, Charlottesville, Virginia discuss the basic
Chapter 3 Ankle and Foot Injuries
 Chapter 3 Ankle and Foot Injuries Ne Siang Chew, Justin Lee, Mark Davies, and Jeremiah Healy Introduction The ankle and foot is a common site of injury amongst sportsmen [1]. According to the International
Chapter 3 Ankle and Foot Injuries Ne Siang Chew, Justin Lee, Mark Davies, and Jeremiah Healy Introduction The ankle and foot is a common site of injury amongst sportsmen [1]. According to the International
 P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
P R E S E N T S Dr. Mufa T. Ghadiali is skilled in all aspects of General Surgery. His General Surgery Services include: General Surgery Advanced Laparoscopic Surgery Surgical Oncology Gastrointestinal
ANKLE MRI. TENDONS: (dark on all sequences except distal PTT and Achilles)
 TENDONS: (dark on all sequences except distal PTT and Achilles) ANKLE MRI -ANTERIOR EXTENSOR ( Tom Hates Dick ) -Tibialis anterior (medial and largest; abnormal in grumpy old men with DM or Gout; may appear
TENDONS: (dark on all sequences except distal PTT and Achilles) ANKLE MRI -ANTERIOR EXTENSOR ( Tom Hates Dick ) -Tibialis anterior (medial and largest; abnormal in grumpy old men with DM or Gout; may appear
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle. Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018
 Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
Sports Injuries of the Foot and Ankle Mark McEleney, MD University of Iowa College of Medicine Refresher Course for the Family Physician 4/4/2018 I. Objectives A. By the end of the lecture attendees will
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer
 musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
musculoskeletal system anatomy muscles of foot sheet done by: dina sawadha & mohammad abukabeer Extensor retinaculum : A- superior extensor retinaculum (SER) : originates from the distal ends of the tibia
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D
 Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Dr Nabil khouri MD. MSc. Ph.D Foot Anatomy The foot consists of 26 bones: 14 phalangeal, 5 metatarsal, and 7 tarsal. Toes are used to balance the body. Metatarsal Bones gives elasticity to the foot in
Foot and Ankle Complaints.
 Foot and Ankle Complaints www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals
Foot and Ankle Complaints www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz INTRODUCTION Anatomy and Function Foot Ankle Common complaints Common diagnoses FOOT AND ANKLE ANATOMY 26 bones and 2 sesamoids Forefoot Metatarsals
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot. Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada.
 Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Avascular Necrosis of the Foot Dr. Hema Choudur MD, FRCPC Associate Professor. Dept. of Radiology. McMaster University, Hamilton, Canada. Avascular Necrosis: Pathophysiology Ischemia to the bone from oxygen
Ankle Arthroscopy PAULO ROCKETT, M.D. Porto Alegre Brazil
 Ankle Arthroscopy PAULO ROCKETT, M.D. Porto Alegre Brazil Ankle sprains are among the most common injuries in sports and at work. Between 20 and 40% of patients treated with conservative therapy may have
Ankle Arthroscopy PAULO ROCKETT, M.D. Porto Alegre Brazil Ankle sprains are among the most common injuries in sports and at work. Between 20 and 40% of patients treated with conservative therapy may have
Please differentiate an internal derangement from an external knee injury.
 Knee Orthopaedic Tests Sports and Knee Injuries James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Knee Injury Strain, Sprain, Internal Derangement Anatomy of the Knee Please
Knee Orthopaedic Tests Sports and Knee Injuries James J. Lehman, DC, MBA, DABCO University of Bridgeport College of Chiropractic Knee Injury Strain, Sprain, Internal Derangement Anatomy of the Knee Please
Anatomy of the lower limb
 Anatomy of the lower limb Arches & sole of the foot Dr. Hayder ARCHES OF THE FOOT The foot as a mechanical unit performs two major functions: - It acts as a pliable platform to support the body weigh during
Anatomy of the lower limb Arches & sole of the foot Dr. Hayder ARCHES OF THE FOOT The foot as a mechanical unit performs two major functions: - It acts as a pliable platform to support the body weigh during
Urgent Cases and Foreign Bodies
 Urgent Cases and Foreign Bodies Catherine J. Brandon, MD, MS University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI, USA Introduction: Patients added on to the schedule from the emergency department or as urgent add-on
Urgent Cases and Foreign Bodies Catherine J. Brandon, MD, MS University of Michigan Ann Arbor, MI, USA Introduction: Patients added on to the schedule from the emergency department or as urgent add-on
Index. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type.
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 137 141 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Achilles tendinopathy, 19 43. See also Achilles classification of, 20 differential diagnosis
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 137 141 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Achilles tendinopathy, 19 43. See also Achilles classification of, 20 differential diagnosis
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101
 Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Servers Disease (Calcaneal Apophysitis ) 101 Servers Disease Causes a disturbance to the growing area at the back of the heel bone (calcaneus) where the strong Achilles tendon attaches to it. It is most
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Pediatric sports injuries in foot and ankle
 Pediatric sports injuries in foot and ankle Poster No.: P-0013 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Kobashi 1, T. Mogami 1, S. Yamazoe 1, A. Baba 2, S. Ogiwara 1 ; 1 2 Chiba/JP, Tokyo/JP
Pediatric sports injuries in foot and ankle Poster No.: P-0013 Congress: ESSR 2014 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Kobashi 1, T. Mogami 1, S. Yamazoe 1, A. Baba 2, S. Ogiwara 1 ; 1 2 Chiba/JP, Tokyo/JP
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh:
 5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
5.1 Identify, describe the attachments of and deduce the actions of the muscles of the thigh: Anterior group Proximal attachment Distal attachment Sartorius ASIS» Upper part of shaft tibia (middle surface)»
Feet First. Michael K. Cooper, DO FACOFP Family Practice/OMM St John Clinic - Claremore OOA 2018 Annual Convention
 Feet First Michael K. Cooper, DO FACOFP Family Practice/OMM St John Clinic - Claremore OOA 2018 Annual Convention Disclaimer I have no conflict of interest. I am not on any pharmaceutical company payroll
Feet First Michael K. Cooper, DO FACOFP Family Practice/OMM St John Clinic - Claremore OOA 2018 Annual Convention Disclaimer I have no conflict of interest. I am not on any pharmaceutical company payroll
Posterior Ankle Impingement: Don t Get Pinched
 Posterior Ankle Impingement: Don t Get Pinched 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Continuing Education Conference Gregory P Witkowski, MD Orthopaedic Trauma and Foot/Ankle Surgery Disclosures I have nothing
Posterior Ankle Impingement: Don t Get Pinched 11 th Annual Sports Medicine Continuing Education Conference Gregory P Witkowski, MD Orthopaedic Trauma and Foot/Ankle Surgery Disclosures I have nothing
Ankle and hindfoot Note medial malleolus, lateral malleolus, inferior tibiofibular joint, talocrural joint and subtalar joint form the 3 joint complex
 Session 4 Look at the ankle (talocrural joint) and the subtalar joint (hind foot) Anatomy of the joints Muscles and how the joints move (biomechanics) Structure of tendons and Achilles tendinitis Some
Session 4 Look at the ankle (talocrural joint) and the subtalar joint (hind foot) Anatomy of the joints Muscles and how the joints move (biomechanics) Structure of tendons and Achilles tendinitis Some
MRI Features of Chronic Injuries of the Superior Peroneal Retinaculum
 Zehava Sadka Rosenberg 1 Jenny Bencardino 2 Donna Astion 3 Mark E. Schweitzer 1 Andrew Rokito 3 Steven Sheskier 3 Received July 31, 2002; accepted after revision June 26, 2003. Presented at the annual
Zehava Sadka Rosenberg 1 Jenny Bencardino 2 Donna Astion 3 Mark E. Schweitzer 1 Andrew Rokito 3 Steven Sheskier 3 Received July 31, 2002; accepted after revision June 26, 2003. Presented at the annual
Case. 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms. Your diagnosis?
 Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D.
 Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Ankle (talocrural) joint type: hinge Talocrural joint - medial collateral ligament Medial collateral = deltoid ligament
Joints and muscles of the foot. Architecture of the foot. Sándor Katz M.D.,Ph.D. Ankle (talocrural) joint type: hinge Talocrural joint - medial collateral ligament Medial collateral = deltoid ligament
