Calcaneal lengthening osteotomy for treatment of idiopathic flexible flat foot in children
|
|
|
- Avice Whitehead
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Soudy SE-E. Int J Res Orthop Dec;2(4): Original Research Article DOI: Calcaneal lengthening osteotomy for treatment of idiopathic flexible flat foot in children Sayed El-Etewy Soudy* Department of orthopedic surgery, Faculty of human Medicine, Zagazig University, Egypt Received: 27 September 2016 Accepted: 04 November 2016 *Correspondence: Dr. Sayed El-Etewy Soudy, yousufmmkh@gmail.com Copyright: the author(s), publisher and licensee Medip Academy. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. ABSTRACT Background: The modified Evans osteotomy technique of calcaneal osteotomy was reported to be effective in correction of flexible flat foot in restoring foot alignment. Methods: The modified Evans technique of calcaneal lengthening osteotomy was used in treatment of 18 feet of 12 patients. The mean follow-up period was 24 months (18-42). The etiology was idiopathic flexible flat foot deformity in all patients. Preoperative conservative therapy was tried in all patients. For clinical evaluation a modified point scoring system containing 32 points for patients' assessment with added 4 points for radiological evaluation the total of score became 36 points. Results: According to the modified points scoring system the results were satisfactory in 16 feet (88.9%) and unsatisfactory in two feet (11.1%) at the final follow up All osteotomies were united within a mean time of 11 months (range 9-14 months). All 6 angles were measured at the end of the follow up and assessed as points added to the 32 points score. The score in 14 feet (77.7%) were (4) having the 6 angels within normal values. The values from 4 angles were within normal values and take score 3 in 3 feet (16.5%). In one foot (5.5%), 3 angles felt in normal range with score 2. Conclusions: Calcaneal lengthening osteotomy for symptomatic flexible flat foot is effective in correction of the deformity and pain relief. Keywords: Flexible, Flat foot, Calcaneal, Lengthening, Osteotomy INTRODUCTION The term flat foot defined as a deformity composed of flattening of the medial arch of the foot with heel valgus either in pediatric, adolescent or adults. The deformity may be rigid, which commonly congenital, or flexible which is usually acquired. 1 The pathology of flatfoot may be an isolated pathology or a part from a disorder like neurologic and muscular diseases (as poliomyelitis, cerebral palsy, myelomeningocele), generalized ligamentous laxity, genetic or collagen disorders. 2 The mean complaints of the patients are pain accompanied by skin ulcerations, difficult shoe wear and serious problems in walking. The galls of treatment was utilized to solve this previous problems. 3-5 After failure of conservative methods to solve the problem, surgical methods are indicated. The advantages of surgical procedures are restoring the foot alignment, relieving pain and skin. Surgical procedures in flexible flat foot vary from soft tissue to bony osteotomies, extra- articular arthrodesis of the subtalar joint, and triple arthrodesis. 2,3,6,7 Arthrodesis is largely discouraged in children because of the problems associated with these techniques. 6-9 One of the effective techniques is the calcaneal lengthening osteotomy. Evans in 1975 is the first to describe and modified by Mosca in ,10 In this prospective the clinical and radiological results of eighteen patients with flexible flat foot (FFF) treated International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics October-December 2016 Vol 2 Issue 4 Page 340
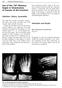
2 using modified Evans calcaneal osteotomy technique were evaluated in a mean follow up of 24 months (range 18-36). METHODS Through the period from June 2010 to June 2013, eighteen feet in 12 patients were presented by FFF. Six patients were operated on for both sides, the right side was operated in 4 patients and left in 2 patients. There were 8 males, and 4 females. Calcaneal lengthening operation was performed using modified Evans osteotomy technique in all feet. The mean age at time of operation was 8.5 years (range years). The mean duration of follow-up was 24 months (range months). The mean age at the end of follow-up was 12.5 years (range years). In bilateral cases the operation was done in two stages with 6 months interval. All cases were idiopatic in etiology. All patients received conservative treatment as orthosis and before the operation. Surgical technique All operations were done under general anesthesia in supine position and under pneumatic tourniquet. Over the sinus tarsi, a lateral longitudinal incision from 3-4 cm. With careful dissection the inferior extensor retinaculum was incised from the superolateral calcaneal border. Special care was carried out to preserve the sural nerve and peroneal nerve superficial branches. Next step was elevation of fleshy fibers of extensor digitorum brevis and the contents of sinus tarsi. The tendons of peroneus longus and brevis were released to be easily retracted. Under image intensifier the calcaneocuboid joint was identified and the site of osteotomy was determined between the medial and anterior facets of the calcaneus was identified. After release of the periosteum over the calcaneus the osteotomy began from about 1.5 cm proximal to the calcaneocuboid joint and directed obliquely from proximal laterally to distal medially. This obliquity was done to correct the valgus and distraction for lengthening of the lateral column. While using a laminar spreader to open the osteotomy site, the size of the graft was measured and the trapezoidal tricortical graft was harvested from the iliac crest through a separate incision. The reduction of the talo-navicular and subtalar joints was evaluated clinically and radiologically before any fixation. The graft is impacted from lateral to medial while distracting to open the osteotomy site. Two K- wires were used, one to fix lateral column through calcaneocuboid, and the other through the talo-navicular to fix the medial column. The K- wires were bended long outside the skin for easy removal after healing. A long leg cast was applied after skin closure for 2 weeks postoperative. After removal of stitches by 2 weeks the cast was changed for another 4 weeks. The K- wires were removed after 6 weeks postoperative in outpatient clinic and a walking cast was applied for 4 weeks. For clinical evaluation a modified point scoring system containing 32 points for patients' assessment. When added 4 points for radiological evaluation the total of score became 36 points as given in Table 1. The patients have points are of excellent results, points for good, for fair, and less than 20 points for poor results. Collectively, the excellent and good results were classified as satisfactory and fair and poor results were classified as unsatisfactory. For radiological evaluation, the postoperative films (anteroposterior and lateral weight- bearing radiographs of the foot) were compared to the preoperative films for each patient measuring the angles used for assessment of the deformity and correction which are: the talohorizontal (TH), talometatarsal (TMT), calcaneal pich (CP) and talocalcaneal (TC) angles in lateral view and TMT and TC angles in anterioposterior view as in Table 2. RESULTS Figure 1: The operative technique A) preoperative photo of the foot clinically; B) intraoperative photo after doing the calcaneal osteotomy; C) intraoperative photo after impacting the graft into the osteotomy site; D) intraoperative photo of the foot after correction and K- wire fixation; E) X-ray 4months postoperative after removal of K- wires and bony union of the osteotomy with incorporation of the graft; F) the foot clinically after correction. Clinically as given in Table 2 the modified points scoring system the results were satisfactory in 16 feet (88.9%) and unsatisfactory in two feet (11.1%) at the final follow up. As regards the pain, 14 feet (77.7%) were asymptomatic and 4 feet (22.3 %) had occasional pain during activity. There was collapse of the medial arch in 2 feet (11.1%). Heel posture was mild varus in 3 feet (16.6%), moderate valgus in one foot (5.5%). Talar head prominence was mild in 3 feet (16.5%). The range of motion of ankle joint was (93%) of normal in 15 feet (83.5%), and 88% of normal in three feet (16.5%). Range of motion of subtalar joints was limited by 30% of International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics October-December 2016 Vol 2 Issue 4 Page 341
3 normal in 6 feet (33.3%), and in 12 feet the limitation was less than 15% from normal (23%). Radiologically as shown in Table 2 and 3 all osteotomies were united Table 1: The point scoring system. within a mean time of 11 months (range 9-14 months). All 6 angles were measured at the end of the follow up and assessed as points added to the 32 points score. Parameters 4 points 3 points 2 points 1 points Clinical A. Subjectively 1. Pain No pain Occasional pain Pain with strenuous activity Pain 2. Activity Normal Mild reduction Unable to do heavy work Difficulty of walking B. Objectively 1. Medial arch Normal Decreased absent convex 2. Heal posture Normal Mild valgus or Moderate valgus Severe valgus varus or varus or varus 3. Forefoot Normal Moderate Severe Mild abduction or abduction or abduction or adduction adduction adduction 4. Prominence of talar head None Mild Moderate severe 5. Range of motion a. ankle joint b. subtalar and mid tarsal joints 6. Radiological Good range of motion Good range of motion 5 angles or more fell within normal range Slight limitation Limited sutalar and mobil idtarsal joints Only 4 angles fell within normal range Table 2: The clinical point system for all feet. Stiff in neutral position limitation of the subtalar and midtarsal joints 3 angles fell within normal range Deformity in equinus or dorsi-flexion stiffness of the whole tarsus Less than 3 angles fell within normal range Subjective Objective Total Radiolog Foot Prominen Range of motion clinic Total Medial Heel Fore ical no Pain Activity ce talar Ankle al score arch posture foot Subtala score head joint score International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics October-December 2016 Vol 2 Issue 4 Page 342
4 Table 3: The preoperative and postoperative angels of the foot after surgical correction compared to normal range. Angle Normal range Preoperative angles Postoperative angles Range Mean Range Mean Lateral view GVB TMT (-4)-(4) (-5)-(9) 2.4 TH CP (-6)-(15) TC AP view TMT (-15)-(10) (-10)-(10) 0 TC TMT- Tarsometatarsal angle; TH- Talo horizontal angle; CP- Calcaneal pitch angle, TC- Talocalcaneal angle. The score in 14 feet (77.7%) were (4) having the 6 angels within normal values. The values from 4 angles were within normal values and take score 3 in 3 feet (16.5%). In one foot (5.5%), 3 angles felt in normal range with score 2. DISCUSSION Flexible flat foot (FFF) is a deformity represented with supination of forefoot in relation to hind foot, shorter lateral column to the medial column, inappropriate talonavicular joint alignment as seen in Figure 2. Many treatment options are utilized and vary from simple orthosis to triple arthrodesis. 1,3,11 When conservative methods failed to control pain and shoe wear the surgical treatment is indicated. Many options like soft tissue procedures, calcaneal osteotomy, subtalar and triple arthrodesis. These techniques have short term good results. Calcaneal displacement osteotomies are successfully correcting hind foot valgus but insufficient for severe cases. The limited arthrodesis is widely reviewed in the literature and correction without arthrodesis is better in long term results. 12,13 In this study the results of calcaneal lengthening osteotomy in 18 feet of 12 patients with idiopathic FFF deformity are evaluated. The hind and mid-foot were clinically corrected in all cases with reformation of medial longitudinal arc. The recommendation of Evans is that the ideal age group for this technique was between 8 and 12 years old. The mean age of our patients at time of operation was 8.5 years (range years). Evans claimed that full correction cannot achieved with this technique especially in the patients with poliomyelitis. In our study the aetiology in all cases was idiopathic deformity. The amount of correction is related to the size of the graft. In this study, the correction position was obtained and stabilized with K-wire fixation until union. Intraoperative radiology was used to assess the correction before fixation in all cases. Davitt et al evaluated plantar pressure contribution and contact surface after calcaneal lengthening operation in children and adolescents and certifying the clinical correction they showed that contact surface in both hind foot and forefoot and maximum mean pressure decreased in the medial side but increased in the lateral side and also that medial longitudinal arc was formed with all of the plantar pressure parameters that they have used. 14 Figure 2: Clinical and radiological description of the deformity preoperative. Ragab et al in a cadaveric study, they claimed that calcaneal lengthening osteotomy was an effective method for correction of FFF deformity in short term results, but they did not report on long term results. 15 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics October-December 2016 Vol 2 Issue 4 Page 343
5 Phillips in 1983 reviewed the cases that were operated by Phillips. 16 The results were good in 15, fair in 3 and poor in 3 patients, but their evaluation of cases was based on the subjective parameters like clinical appearance, patient satisfaction, and relief of symptoms. The radiological evaluation did not use the angular parameters for correction, but classified as complete correction and acceptable partial correction. They reported that poor results in 3 cases were due to progressive deformities with aetiologies but there was no information about these aetiologies. Yoo et al evaluated 92 feet of 69 cases and classified the clinical results by assessing pain improvement, and callus. 17 They reported the reformation of medial longitudinal arc, correction of the forefoot abduction and hind foot valgus. They evaluated standing lateral radiographies, and the results were poor when the talocalcaneal angle is less than 35 degrees, talus-first metatarsal angle was greater than 25 degrees and calcaneal slope angle was less than 5 degrees. In this work, clinical evaluation was made according to a modified point scoring system containing 32 points for patients' assessment, and added 4 points for radiological evaluation to get a total of score of 36 points as shown in Table 1. For radiological evaluation, we used the talohorizontal (TH), talometatarsal (TMT), calcaneal pich (CP) and talocalcaneal (TC) angles in lateral view and TMT and TC angles in anteroposterior view as in Table 2. The overall results were satisfactory in 16 feet (88.9%) and unsatisfactory in two feet (11.1%) at the final follow up. 14 feet (77.7 %) were asymptomatic and 4 feet (22.3%) had occasional pain during activity. There was collapse of the medial arch in 2 feet (11.1%). mild heel varus in 3 feet (16.6%), moderate valgus in one foot (5.5%). Talar head prominence was mild in 3 feet (16.5%). In this study we used the modifications of Mosca on skin incision, direction of the osteotomy, shape of the graft, application of internal fixation. Mosca [-] also used allografts in 24 of 31 patients and he reported no problems in osteotomy site bone union. In all of our cases a tricortical autograft from iliac crest was used. CONCLUSION Calcaneal lengthening osteotomy in symptomatic FFF is a successful technique and can provide clinical and radiological correction of the deformity in hind foot and forefoot. It is possible to gain complete reduction in the flexible cases. The calcaneal lengthening osteotomy is technically easy to be performed, with low risk of neurovascular injury. The limitation of the study is the short term follow up period as the changes in subtalar joint may take a long time to occur. One of the advantages of this technique is that other procedures can be performed later on unlike arthrodesis which is a terminal operation. Funding: No funding sources Conflict of interest: None declared Ethical approval: The study was approved by the institutional ethics committee REFERENCES 1. Farzin H, eza M, Maryam M, Ladan A. Pediatric Flexi le Flatfoot; linical Aspects and Algorithmic Approach. Iran J Pediatr. 2 13;23(3): Evans AM, ome K, Peet L. The foot posture index, ankle lunge test, Beighton scale and the lower lim assessment score in healthy children: a relia ility study. J Foot Ankle es. 2 12;5(1):1. 3. Lin J, Lai KA, Kuan T, et al. orrelating factors and clinical significance of flexible flatfoot in preschool children. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001;21(3): Lee JH, ung I, oo J. linical or radiologic measurements and 3- gait analysis in children with pes planus. Pediatr Int. 2 9;51(2): orer G, agatur AE, ogan A, nlu T. ennyson- Fulford su talar extra- articular arthrodesis in the treatment of paralytic pes planovalgus and its value in the alignment of the foot. Acta Orthop Traumato Turc. 2 3;37: Evans. alcaneo-valgus deformity. J one Joint urg r. 1975;57: Flexible flatfoot (pes planovalgus). In: Herring JA. Tachdjian s pediatric orthopedics. olume 2, 3rd edition. Philadelphia: aunders; 2 2: anderwilde, taheli LT, hew E, Malagon. Measurements on radiographs of the foot in normal infants and children. J one Joint urg Am. 1988;7 : iegas G. econstruction of the pediatric flexi le planovalgus foot y using an Evans calcaneal osteotomy and augmentative medial split ti ialis anterior tendon transfer. J Foot Ankle urg. 2 3;42: Mosca VS. Calcaneal lengthening for valgus deformity of the hindfoot. esults in children who had severe, symptomatic flatfoot and skewfoot. J one Joint urg Am. 1995;77: Andreacchio A, Orellana A, Miller F, owen T. Lateral column lengthening as treatment for planovalgus foot deformity in am ulatory children with spastic cere ral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2 ;2 : Hadley N, ahm M, ain TE. ennyson-fulford su talar arthrodesis. J Pediatr Orthop. 1994;14: Mosca VS. Flexible flatfoot and tarsal coalition. In: ichards, editor. Orthopedic knowledge update: pediatrics. Illinois: American Academy of Orthopedic urgeons; avitt J, Mac- illiams A, Armstrong PF. Plantar pressure and radiographic changes after International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics October-December 2016 Vol 2 Issue 4 Page 344
6 distal calcaneal lengthening in children and adolescents. J Pediatr Orthop. 2001;21: aga AA, tewart L, ooperman. Implications of su talar joint anatomic variation in calcaneal lengthening osteotomy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2 3;23: Phillips GE. A review of elongation of os calcis for flat feet. J one Joint urg r. 1983;65: oo J, hung, hoi IH, ho TJ, Kim H. alcaneal lengthening for the planovalgus foot deformity in children with cere ral palsy. J Pediatr Orthop. 2005;25: Cite this article as: Soudy SE-E. Calcaneal lengthening osteotomy for treatment of idiopathic flexible flat foot in children. Int J Res Orthop 2016;2: International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics October-December 2016 Vol 2 Issue 4 Page 345
FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]
![FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test] FACTS 1. Most need only Gastro aponeurotic release [in positive Silverskiold test]](/thumbs/83/88335212.jpg) FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
FOOT IN CEREBRAL PALSY GAIT IN CEREBRAL PALSY I True Equinus II Jump gait III Apparent Equinus IV Crouch gait Group I True Equinus Extended hip and knee Equinus at ankle II Jump Gait [commonest] Equinus
SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT
 C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
C H A P T E R 1 7 SUBTALAR ARTHROEREISIS IN THE OLDER PATIENT William D. Fishco, DPM, MS INTRODUCTION Arthroereisis is a surgical procedure designed to limit the motion of a joint. Subtalar joint arthroereisis
Case. 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms. Your diagnosis?
 Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
Case 15 Y old boy presented with pain in the foot. No history of injury or any constitutional symptoms Your diagnosis? Diagnosis: Calcaneo-navicular tarsal coalition. C sign Talar beaking Ant eaters nose
The Valgus Foot in Cerebral Palsy Equinovalgus not Plano-Valgus. Alfred D. Grant, M.D. David Feldman, M.D.
 The Valgus Foot in Cerebral Palsy Equinovalgus not Plano-Valgus Alfred D. Grant, M.D. David Feldman, M.D. Norman Otsuka, MD M.D. THE PURPOSE OF THIS PRESENTATION IS TO STATE CLEARLY THAT THE VALGUS FOOT
The Valgus Foot in Cerebral Palsy Equinovalgus not Plano-Valgus Alfred D. Grant, M.D. David Feldman, M.D. Norman Otsuka, MD M.D. THE PURPOSE OF THIS PRESENTATION IS TO STATE CLEARLY THAT THE VALGUS FOOT
SUB-TALAR AND TRIPLE ARTHRODESIS
 SUB-TALAR AND TRIPLE ARTHRODESIS J de Halleux With the members of Education Committee INDICATIONS ARTHRITIS OF THE SUB-TALAR AND/OR MID-TARSAL JOINTS RIGID VARUS OR VALGUS DEFORMITY OF THE HIND-FOOT COALITIONS
SUB-TALAR AND TRIPLE ARTHRODESIS J de Halleux With the members of Education Committee INDICATIONS ARTHRITIS OF THE SUB-TALAR AND/OR MID-TARSAL JOINTS RIGID VARUS OR VALGUS DEFORMITY OF THE HIND-FOOT COALITIONS
Use of Allograft in Skeletally Immature Patients for Calcaneal Neck Lengthening Osteotomy
 Yonsei Med J 49(1):79-83, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.1.79 Use of Allograft in Skeletally Immature Patients for Calcaneal Neck Lengthening Osteotomy Yoon Hae Kwak, 1 Kun Bo Park, 2 Hui Wan Park, 1 and
Yonsei Med J 49(1):79-83, 2008 DOI 10.3349/ymj.2008.49.1.79 Use of Allograft in Skeletally Immature Patients for Calcaneal Neck Lengthening Osteotomy Yoon Hae Kwak, 1 Kun Bo Park, 2 Hui Wan Park, 1 and
Tarsal Coalition On MR
 Tarsal Coalition On MR By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in Tarsal coalition is a congenital anomaly with fusion of the tarsal bones. The fusion may be bony, fibrous or cartilaginous.
Tarsal Coalition On MR By William Renner, M.D. This and other topics will be discussed in Tarsal coalition is a congenital anomaly with fusion of the tarsal bones. The fusion may be bony, fibrous or cartilaginous.
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Results of Calcaneal Osteotomy & Flexor Digitorum Longus transfer in Stage II Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Mr Amit Chauhan Mr Prasad Karpe Ms Maire-claire Killen Mr Rajiv Limaye University Hospital of North
Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module
 1.5 CME AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 ABSTRACT
1.5 CME AJR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LEARNING FOR RADIOLOGY Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Self-Assessment Module Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 ABSTRACT
Double calcaneal osteotomy for severe adolescent flexible flatfoot reconstruction
 Xu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:153 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0655-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Double calcaneal osteotomy for severe adolescent flexible flatfoot reconstruction
Xu et al. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research (2017) 12:153 DOI 10.1186/s13018-017-0655-3 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Double calcaneal osteotomy for severe adolescent flexible flatfoot reconstruction
Copyright 2004, Yoshiyuki Shiratori. All right reserved.
 Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Ankle and Leg Evaluation 1. History Chief Complaint: A. What happened? B. Is it a sharp or dull pain? C. How long have you had the pain? D. Can you pinpoint the pain? E. Do you have any numbness or tingling?
Peggers Super Summaries: Foot Injuries
 Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Lisfranc Injury ANATOMY Roman arch with recessed 2 nd MT base AP medial side of intermediate cuneiform to 2 nd MT base Oblique medial side of lateral cuneiform with 3 rd MT base and 4 th with medial boarder
Index. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 309 314 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abductor digiti minimi muscle, myectomy of, for tailor s bunionette, 243 Achilles tendon, lengthening
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 22 (2005) 309 314 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Abductor digiti minimi muscle, myectomy of, for tailor s bunionette, 243 Achilles tendon, lengthening
Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot. Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s s Hospital, The Catholic University
 Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s s Hospital, The Catholic University Contents Metatarsus Adductus Skewfoot Hallux Valgus Hallux Valgus
Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s s Hospital, The Catholic University Contents Metatarsus Adductus Skewfoot Hallux Valgus Hallux Valgus
Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2004, 70, 586-590 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of percutaneous V osteotomy of the calcaneus with Ilizarov application for correction of complex foot deformities Hani EL-MOWAFI From Mansoura
ISSN (O): ; ISSN (P): Lateral Calcaneal Lengthening Osteotomy In Management Symptomatic Flexible Flat Foot.
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.6.OR6 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Lateral Calcaneal Lengthening Osteotomy In Management Symptomatic Flexible Flat Foot. Yehia Nour Eldin Tarraf 1,
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2017.3.6.OR6 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Lateral Calcaneal Lengthening Osteotomy In Management Symptomatic Flexible Flat Foot. Yehia Nour Eldin Tarraf 1,
Triple Arthrodesis of Foot for Correction of Lower Extremity Deformities
 Triple Arthrodesis of Foot for Correction of Lower Extremity Deformities 振興醫療財團法人振興醫院骨科部 * 熊永萬 A triple arthrodesis consists of surgical fusion of the talocalcaneal (TC), talonavicular (TN), and calcaneocuboid
Triple Arthrodesis of Foot for Correction of Lower Extremity Deformities 振興醫療財團法人振興醫院骨科部 * 熊永萬 A triple arthrodesis consists of surgical fusion of the talocalcaneal (TC), talonavicular (TN), and calcaneocuboid
Conservative management of idiopathic clubfoot: Kite versus Ponseti method
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2009;17(1):67-71 Conservative management of idiopathic clubfoot: Kite versus Ponseti method AV Sanghvi, 1 VK Mittal 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2009;17(1):67-71 Conservative management of idiopathic clubfoot: Kite versus Ponseti method AV Sanghvi, 1 VK Mittal 2 1 Department of Orthopaedics, Government Medical College
Surgical Correction of Lower Extremity Deformities by Triple Arthrodesis
 Surgical Correction of Lower Extremity Deformities by Triple Arthrodesis 足踝畸形矯治 振興醫療財團法人振興醫院 骨科部 熊永萬醫師 Introduction: The primary goals of a triple arthrodesis are to relieve pain from arthritic, deformed,
Surgical Correction of Lower Extremity Deformities by Triple Arthrodesis 足踝畸形矯治 振興醫療財團法人振興醫院 骨科部 熊永萬醫師 Introduction: The primary goals of a triple arthrodesis are to relieve pain from arthritic, deformed,
Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot]
![Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot] Scar Engorged veins. Size of the foot [In clubfoot, small foot]](/thumbs/78/77722241.jpg) 6. FOOT HISTORY Pain: Walking, Running Foot wear problem Swelling; tingly feeling Deformity Stiffness Disability: At work; recreation; night; walk; ADL, Sports Previous Rx Comorbidities Smoke, Sugar, Steroid
6. FOOT HISTORY Pain: Walking, Running Foot wear problem Swelling; tingly feeling Deformity Stiffness Disability: At work; recreation; night; walk; ADL, Sports Previous Rx Comorbidities Smoke, Sugar, Steroid
TRIPLE ARTHRODESIS FOR ADULT ACQUIRED FLATFOOT
 TRIPLE ARTHRODESIS FOR ADULT ACQUIRED FLATFOOT Alan R. Catanzariti, DPM Brian T. Dix, DPM Phillip E. Richardson, DPM Robert W. Mendicino, DPM INTRODUCTION Triple arthrodesis for adult acquired flatfoot
TRIPLE ARTHRODESIS FOR ADULT ACQUIRED FLATFOOT Alan R. Catanzariti, DPM Brian T. Dix, DPM Phillip E. Richardson, DPM Robert W. Mendicino, DPM INTRODUCTION Triple arthrodesis for adult acquired flatfoot
Financial Disclosure. The authors have not received any financial support for the preparation of this work.
 Persistent Clubfoot Deformity Following Treatment by the Ponseti Method W.B. Lehman, M.D. Alice Chu, M.D. New York Ponseti Clubfoot Center Department of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Financial Disclosure
Persistent Clubfoot Deformity Following Treatment by the Ponseti Method W.B. Lehman, M.D. Alice Chu, M.D. New York Ponseti Clubfoot Center Department of Pediatric Orthopaedic Surgery Financial Disclosure
Management of Chronic Lateral Ligament Instability
 Management of Chronic Lateral Ligament Instability Bony Anatomy Curved trochlear surface of talus produces a cone-shaped articulation whose apex is directed medially; thus the fan-shaped deltoid is all
Management of Chronic Lateral Ligament Instability Bony Anatomy Curved trochlear surface of talus produces a cone-shaped articulation whose apex is directed medially; thus the fan-shaped deltoid is all
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Adult-Acquired Flatfoot Deformity Glendale Adventist Medical Center 1509 Wilson Terrace Glendale, CA 91206 Phone: (818) 409-8000 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle AOFAS Resident Review Course September 28, 2013
 Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Cavus Foot: Subtle and Not-So-Subtle Course September 28, 2013 Matthew M. Roberts, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Orthopaedic Surgery Co-Chief, Foot and Ankle Service Hospital for Special Surgery Disclosure
Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction & Repair
 1 Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction & Repair Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: The posterior tibialis muscle arises from the interosseous membrane and the adjacent
1 Posterior Tibialis Tendon Dysfunction & Repair Surgical Indications and Considerations Anatomical Considerations: The posterior tibialis muscle arises from the interosseous membrane and the adjacent
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle
 Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Anatomy of Foot and Ankle Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Surface anatomy of the ankle & foot Medial orientation point medial malleous sustentaculum tali tuberosity of navicular TA muscle TP muscle
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries
 Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
Managing Tibialis Posterior Tendon Injuries by Thomas C. Michaud, DC Published April 1, 2015 by Dynamic Chiropractic Magazine Tibialis posterior is the deepest, strongest, and most central muscle of the
Physical Examination of the Foot & Ankle
 Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
Inspection Standing, feet straight forward facing toward examiner Swelling Deformity Flatfoot (pes planus and hindfoot valgus) High arch (pes cavus and hindfoot varus) Peek-a-boo heel Varus Too many toes
Metatarsus adductus, Skew foot, Club foot 성균관대학교삼성창원병원 장현정
 Metatarsus adductus, Skew foot, Club foot 성균관대학교삼성창원병원 장현정 Metatarsus adductus Epidemiology and Etiology 0.1-12% with higher number for multiple birth Deformation and compression from intrauterine crowding
Metatarsus adductus, Skew foot, Club foot 성균관대학교삼성창원병원 장현정 Metatarsus adductus Epidemiology and Etiology 0.1-12% with higher number for multiple birth Deformation and compression from intrauterine crowding
Results of Using Reversed Ponseti Technique in Treatment of Congenital Vertical Talus
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 4, June: 1447-1453, 217 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Results of Using Reversed Ponseti Technique in Treatment of Congenital Vertical Talus MOHAMED F. EL-KHOSOUSY,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 85, No. 4, June: 1447-1453, 217 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Results of Using Reversed Ponseti Technique in Treatment of Congenital Vertical Talus MOHAMED F. EL-KHOSOUSY,
What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne
 What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne We don t know!! Population Studies 2300 children aged 4-13 years Shoe wearers Flat foot 8.6% Non-shoe wearers
What Happens to the Paediatric Flat Foot? Peter J Briggs Freeman Hospital Newcastle upon Tyne We don t know!! Population Studies 2300 children aged 4-13 years Shoe wearers Flat foot 8.6% Non-shoe wearers
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement
 Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Extraarticular Lateral Ankle Impingement Poster No.: C-1282 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C. Cevikol; Keywords: Trauma, Diagnostic procedure, MR, CT, Musculoskeletal system, Musculoskeletal
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision
 Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
Calcaneal Fractures: Lateral Extensile Incision AS Flemister JR, MD University of Rochester Disclosures I have no financial disclosures 1/27/2016 2 Mechanism Axial Loading Fall From Height MVA BAD SOFT
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium
 MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
MIDFOOT INJURIES-ARE WE UNDERTREATING IT? Mr Rajiv Limaye Mr Prasad Karpe University Hospital of North Tees 3 rd Foot and Ankle Symposium Introduction Increasing sports injuries RTA and traumatic injuries
Changes in Dynamic Pedobarography after Extensive Plantarmedial Release for Paralytic Pes Cavovarus
 Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.766 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 55(3):766-772, 2014 Changes in Dynamic Pedobarography after Extensive Plantarmedial Release
Original Article http://dx.doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2014.55.3.766 pissn: 0513-5796, eissn: 1976-2437 Yonsei Med J 55(3):766-772, 2014 Changes in Dynamic Pedobarography after Extensive Plantarmedial Release
Original Article. Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine INTRODUCTION
 Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):369-375 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.369 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Effects of Custom-Made Rigid Foot Orthosis
Original Article Ann Rehabil Med 2014;38(3):369-375 pissn: 2234-0645 eissn: 2234-0653 http://dx.doi.org/10.5535/arm.2014.38.3.369 Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine Effects of Custom-Made Rigid Foot Orthosis
Marut Arunakul, M.D. Phinit Phisitkul, M.D. Jessica Goetz, PhD. John Femino, M.D. Annunziato Amendola, M.D. University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics
 Marut Arunakul, M.D. Phinit Phisitkul, M.D. Jessica Goetz, PhD. John Femino, M.D. Annunziato Amendola, M.D. University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Tripod Index Part 1: New radiographic parameter assessing
Marut Arunakul, M.D. Phinit Phisitkul, M.D. Jessica Goetz, PhD. John Femino, M.D. Annunziato Amendola, M.D. University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Tripod Index Part 1: New radiographic parameter assessing
Radiographic Assessment of Pediatric Foot Alignment: Review
 JR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LERNING FOR RDIOLOGY Radiographic ssessment of Pediatric Foot lignment: Review Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 Objective The purpose of this article
JR Integrative Imaging LIFELONG LERNING FOR RDIOLOGY Radiographic ssessment of Pediatric Foot lignment: Review Mahesh M. Thapa 1,2, Sumit Pruthi 1,2, Felix S. Chew 2 Objective The purpose of this article
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children
 A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
A Patient s Guide to Flatfoot Deformity (Pes Planus) in Children 2350 Royal Boulevard Suite 200 Elgin, IL 60123 Phone: 847.931.5300 Fax: 847.931.9072 DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet is compiled
Dorsal surface-the upper area or top of the foot. Terminology
 It is important to learn the terminology as it relates to feet to properly communicate with referring physicians when necessary and to identify the relationship between the anatomical structure of the
It is important to learn the terminology as it relates to feet to properly communicate with referring physicians when necessary and to identify the relationship between the anatomical structure of the
V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2008;16(2):215-9 V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet E Segev, E Ezra, M Yaniv, S Wientroub, Y Hemo Department of Pediatric Orthopaedics,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2008;16(2):215-9 V osteotomy and Ilizarov technique for residual idiopathic or neurogenic clubfeet E Segev, E Ezra, M Yaniv, S Wientroub, Y Hemo Department of Pediatric Orthopaedics,
Foot & Ankle Disorders
 Foot & Ankle Disorders Hillingdon PGMC 6-7-2013 Htwe Zaw FRCS (Tr&Orth) Consultant Foot & Ankle and Trauma Surgeon Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Overview Anatomy: hindfoot-midfoot coupling
Foot & Ankle Disorders Hillingdon PGMC 6-7-2013 Htwe Zaw FRCS (Tr&Orth) Consultant Foot & Ankle and Trauma Surgeon Hillingdon Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust Overview Anatomy: hindfoot-midfoot coupling
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY
 BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY B.Resseque, D.P.M. ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing a ruler from the heel to the first metatarsal head Compare arch
ATYPICAL MIDFOOT- DRIVEN ADULT FLATFOOT
 ATYPICAL MIDFOOT- DRIVEN ADULT FLATFOOT MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA DISCLOSURES 3B: BESPA, INC. (CONSULTANT) EXTREMITY MEDICAL, INC. ACKNOWLEDGMENT AK WALLING III,
ATYPICAL MIDFOOT- DRIVEN ADULT FLATFOOT MICHAEL P. CLARE, MD FLORIDA ORTHOPAEDIC INSTITUTE TAMPA, FL USA DISCLOSURES 3B: BESPA, INC. (CONSULTANT) EXTREMITY MEDICAL, INC. ACKNOWLEDGMENT AK WALLING III,
Single Stage Surgery for Treatment of Congenital Vertical Talus in Children 1 4 Years old
 SURGERY THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE FOR VERTICAL MEDICAL TALUS IN JOURNAL CHILDREN Single Stage Surgery for Treatment of Congenital Vertical Talus in Children 1 4 Years old Issam H. Ali*, Mohammed H. Salal**,
SURGERY THE IRAQI POSTGRADUATE FOR VERTICAL MEDICAL TALUS IN JOURNAL CHILDREN Single Stage Surgery for Treatment of Congenital Vertical Talus in Children 1 4 Years old Issam H. Ali*, Mohammed H. Salal**,
There are few conditions in foot and ankle surgery that elicit
 SPECIAL FOCUS The Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity: A Treatment Algorithm Troy Watson, MD Abstract: The presentation of an adult with acquired flatfoot deformity is highly variable with a wide range of
SPECIAL FOCUS The Adult Acquired Flatfoot Deformity: A Treatment Algorithm Troy Watson, MD Abstract: The presentation of an adult with acquired flatfoot deformity is highly variable with a wide range of
Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot
 Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot Han-Yong Lee, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s Hospital, The Catholic University Contents Introduction Foot Deformities Metatarsus
Other Congenital and Developmental Diseases of the Foot Han-Yong Lee, M.D. Department of Orthopedic Surgery St. Vincent s Hospital, The Catholic University Contents Introduction Foot Deformities Metatarsus
Horizon Subtalar. Surgical Technique
 Horizon Subtalar Surgical Technique Contents Product The BioPro Horizon Subtalar Implant is used for the treatment of flatfoot and posterior tibial tendon dysfunction in both children and adults. Implanted
Horizon Subtalar Surgical Technique Contents Product The BioPro Horizon Subtalar Implant is used for the treatment of flatfoot and posterior tibial tendon dysfunction in both children and adults. Implanted
Toe walking gives rise to parental concern. Therefore, toe-walkers are often referred at the 3 years of age.
 IDIOPATHIC TOE WALKING Toe walking is a common feature in immature gait and is considered normal up to 3 years of age. As walking ability improves, initial contact is made with the heel. Toe walking gives
IDIOPATHIC TOE WALKING Toe walking is a common feature in immature gait and is considered normal up to 3 years of age. As walking ability improves, initial contact is made with the heel. Toe walking gives
Outcomes after Lengthening Calcaneal Osteotomy for Flexible Flatfoot Deformity Evans- versus Hintermann-Osteotomy
 Outcomes after Lengthening Calcaneal Osteotomy for Flexible Flatfoot Deformity Evans- versus Hintermann-Osteotomy Ettinger, S. 1, Mattinger, T. 1, Yao, D. 1, Claassen, L. 1, Daniilidis, K. 2, Stukenborg-Colsman,
Outcomes after Lengthening Calcaneal Osteotomy for Flexible Flatfoot Deformity Evans- versus Hintermann-Osteotomy Ettinger, S. 1, Mattinger, T. 1, Yao, D. 1, Claassen, L. 1, Daniilidis, K. 2, Stukenborg-Colsman,
«Foot & Ankle Surgery» 04. Sept THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT. Norman Espinosa, MD
 THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT Norman Espinosa, MD Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich Balgrist Switzerland www.balgrist.ch WHAT TO DO? INTRINSIC > EXTRINSIC ETIOLOGIES Repetitive microtrauma combined
THE PAINFUL FLATFOOT Norman Espinosa, MD Department of Orthopaedics University of Zurich Balgrist Switzerland www.balgrist.ch WHAT TO DO? INTRINSIC > EXTRINSIC ETIOLOGIES Repetitive microtrauma combined
TENDON TRANSFER IN CAVUS FOOT
 TENDON TRANSFER IN CAVUS FOOT Cavovarus deformity is defined by fixed equinus of the forefoot on the hindfoot, resulting in a pathologic elevation of the longitudinal arch, with either a fixed or flexible
TENDON TRANSFER IN CAVUS FOOT Cavovarus deformity is defined by fixed equinus of the forefoot on the hindfoot, resulting in a pathologic elevation of the longitudinal arch, with either a fixed or flexible
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program
 Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Therapeutic Foot Care Certificate Program Part I: Online Home Study Program 1 Anatomy And Terminology Of The Lower Extremity Joan E. Edelstein, MA, PT, FISPO Associate Professor of Clinical Physical Therapy
Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month a
 Case presentations Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month after Progressive limited elbow flexion
Case presentations Case 1 7 yo male Right elbow injury 3 months ago Medial elbow pain and tenderness over medial epicondyle Long arm cast given but off himself 1 month after Progressive limited elbow flexion
Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
 Injury Extra (2008) 39, 291 295 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
Injury Extra (2008) 39, 291 295 available at www.sciencedirect.com journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/inext CASE REPORT Unusual fracture combination with Charcot arthropathy and juvenile-onset diabetes
How to approach the pediatric flatfoot
 Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i1.1 World J Orthop 2016 January 18; 7(1): 1-7 ISSN 2218-5836 (online) 2016 Baishideng
Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.5312/wjo.v7.i1.1 World J Orthop 2016 January 18; 7(1): 1-7 ISSN 2218-5836 (online) 2016 Baishideng
AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING. Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion
 AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
AOFAS 2012 ANNUAL SUMMER MEETING Subtalar Distraction Two Bone-Block Arthrodesis for Calcaneal Malunion My disclosure is in the Final AOFAS Program Book. I have no potential conflicts with this presentation.
2017 AOFAS Specialty Day. Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction: Stage III Getting the Most Out of Your Triple Arthrodesis
 2017 AOFAS Specialty Day Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction: Stage III Getting the Most Out of Your Triple Arthrodesis Jeffrey E. Johnson, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Chief, Foot and
2017 AOFAS Specialty Day Posterior Tibial Tendon Dysfunction: Stage III Getting the Most Out of Your Triple Arthrodesis Jeffrey E. Johnson, M.D. Professor, Dept. of Orthopaedic Surgery Chief, Foot and
Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture
 Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 3264172, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3264172 Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture Takaaki Ohmori, 1,2 Shinichi
Case Reports in Orthopedics Volume 2016, Article ID 3264172, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/3264172 Case Report A Case Report of Isolated Cuboid Nutcracker Fracture Takaaki Ohmori, 1,2 Shinichi
Assessment of the Medial Longitudinal Arch in children with Flexible Pes Planus by Plantar Pressure Mapping
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2016, 82, 737-744 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of the Medial Longitudinal Arch in children with Flexible Pes Planus by Plantar Pressure Mapping Elhussein M. Elmoatasem, Mohamed A. Eid
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2016, 82, 737-744 ORIGINAL STUDY Assessment of the Medial Longitudinal Arch in children with Flexible Pes Planus by Plantar Pressure Mapping Elhussein M. Elmoatasem, Mohamed A. Eid
Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain
 May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
May 2006 Evaluation of Pediatric Foot Pain John Flibotte, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient AP is a 10 year old boy with chronic R foot pain 2 Anatomy of the Foot Manusov EG, et al. (1996), Part
Introduction. The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking.
 The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
The ankle 1 Introduction The primary function of the ankle and foot is to absorb shock and impart thrust to the body during walking. OSTEOLOGRY The term ankle refers primarily to the talocrural joint,
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY 3. TALRSALS = (FOOT BONES) Fibula. Frances Daly MSc 1 CALCANEUS 2. TALUS 3. NAVICULAR 4. CUBOID 5.
 ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
ANKLE JOINT ANATOMY The ankle joint is a synovial joint of the hinge type. The joint is formed by the distal end of the tibia and medial malleolus, the fibula and lateral malleolus and talus bone. It is
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy
 Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
Ankle Valgus in Cerebral Palsy Freeman Miller Contents Introduction... 2 Natural History... 2 Treatment... 3 Diagnostic Evaluations... 3 Indications for Intervention... 3 Outcome of Treatment... 5 Complications
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine FOOT. Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan
 The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine FOOT Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Due to compression of Tibial nerve as it travels through the
The University Of Jordan Faculty Of Medicine FOOT Dr.Ahmed Salman Assistant Prof. of Anatomy. The University Of Jordan Tarsal Tunnel Syndrome Due to compression of Tibial nerve as it travels through the
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم
 بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Laboratory RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Department of Physical Therapy King Saud University Talocrural and Subtalar Joint
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Laboratory RHS 221 Manual Muscle Testing Theory 1 hour practical 2 hours Dr. Ali Aldali, MS, PT Department of Physical Therapy King Saud University Talocrural and Subtalar Joint
Clarification of Terms
 Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Clarification of Terms The plantar aspect of the foot refers to the role or its bottom The dorsal aspect refers to the top or its superior portion The ankle and foot perform three main functions: 1. shock
Change of Alignment by Calcaneocuboid Distraction Arthrodesis for Acquired Flatfoot
 Change of Alignment by Calcaneocuboid Distraction Arthrodesis for Acquired Flatfoot Akira Taniguchi, Yasuhito Tanaka, Kunihiko Kadono, Kiyonori Tomiwa, So Kameda, Hiroaki Kurokawa, Takenori Matsuda, Tsukasa
Change of Alignment by Calcaneocuboid Distraction Arthrodesis for Acquired Flatfoot Akira Taniguchi, Yasuhito Tanaka, Kunihiko Kadono, Kiyonori Tomiwa, So Kameda, Hiroaki Kurokawa, Takenori Matsuda, Tsukasa
Management of congenital vertical talus: comparison between mini invasive reduction and extensive surgical technique in early age
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Chauhan P et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):197-201 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170031
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics Chauhan P et al. Int J Res Orthop. 2017 Mar;3(2):197-201 http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20170031
CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS
 CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS ABC s of Comprehensive Musculoskeletal Care December 1 st, 2007 Stephen Pinney MD Chief, UCSF Foot and Ankle Service Chronic problems typically occur gradually
CHRONIC FOOT PROBLEMS FOOT and ANKLE BASICS ABC s of Comprehensive Musculoskeletal Care December 1 st, 2007 Stephen Pinney MD Chief, UCSF Foot and Ankle Service Chronic problems typically occur gradually
STS. Subtalar Spacer System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE
 STS Subtalar Spacer System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 4 Introduction 4 Device Description Chapter 2 5 Intended Use 5 Indications Chapter 3 6 Surgical Technique 9 Postoperative Protocol 9 Explant
STS Subtalar Spacer System SURGICAL TECHNIQUE Contents Chapter 1 4 Introduction 4 Device Description Chapter 2 5 Intended Use 5 Indications Chapter 3 6 Surgical Technique 9 Postoperative Protocol 9 Explant
Surgical Technique Horizon Subtalar Implant
 Surgical Technique Horizon Subtalar Implant Table of contents Introduction... 1 Features and Benefits... 1 Ordering Information...2-3 Indications... 4 Contraindications... 4 Surgical Technique... 5-6 Post
Surgical Technique Horizon Subtalar Implant Table of contents Introduction... 1 Features and Benefits... 1 Ordering Information...2-3 Indications... 4 Contraindications... 4 Surgical Technique... 5-6 Post
The effect on radiographic parameters of Dwyer s osteotomy and 1 st metatarsal osteotomy for pes cavo-varus correction
 The effect on radiographic parameters of Dwyer s osteotomy and 1 st metatarsal osteotomy for pes cavo-varus correction Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, South Korea
The effect on radiographic parameters of Dwyer s osteotomy and 1 st metatarsal osteotomy for pes cavo-varus correction Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Inje University, Ilsan Paik Hospital, South Korea
Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES
 Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Resident will at all times demonstrate behavior that is beyond reproach. Residents must be
Updated 2/8/10 Columbia/NYOH FOOT and ANKLE ROTATION-SPECIFIC OBJECTIVES INTERPERSONAL AND COMMUNICATION SKILLS Resident will at all times demonstrate behavior that is beyond reproach. Residents must be
Evaluating midcalcaneal length after Evans calcaneal osteotomy: a comparison of the locking plate and tricortical allograft wedge
 IFFAS AOFAS Chicago, 2014 Evaluating midcalcaneal length after Evans calcaneal osteotomy: a comparison of the locking plate and tricortical allograft wedge Garrett M. Wobst, DPM, AACFAS, Nicole M. Protzman,
IFFAS AOFAS Chicago, 2014 Evaluating midcalcaneal length after Evans calcaneal osteotomy: a comparison of the locking plate and tricortical allograft wedge Garrett M. Wobst, DPM, AACFAS, Nicole M. Protzman,
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique. Description of Plate
 Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
Merete PlantarMAX Lapidus Plate Surgical Technique Description of Plate Merete Medical has designed the PlantarMax; a special Plantar/Medial Locking Lapidus plate which places the plate in the most biomechanically
radiologymasterclass.co.uk
 http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
http://radiologymasterclass.co.uk Hip X-ray anatomy - Normal AP (anterior-posterior) Shenton's line is formed by the medial edge of the femoral neck and the inferior edge of the superior pubic ramus Loss
Classifications in Brief: Johnson and Strom Classification of Adult-acquired Flatfoot Deformity
 Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4581-6 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons IN BRIEF Classifications in Brief: Johnson and
Clin Orthop Relat Res DOI 10.1007/s11999-015-4581-6 Clinical Orthopaedics and Related Research A Publication of The Association of Bone and Joint Surgeons IN BRIEF Classifications in Brief: Johnson and
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY 2017
 BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY 2017 B. RESSEQUE, D.P.M., D.A.B.P.O. Professor, N.Y. College of Podiatric Medicine ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing
BIOMECHANICAL EXAMINATION OF THE PEDIATRIC LOWER EXTREMITY 2017 B. RESSEQUE, D.P.M., D.A.B.P.O. Professor, N.Y. College of Podiatric Medicine ARCH HEIGHT OFF WEIGHTBEARING Evaluate arch height by placing
Peritalar Dislocation After Tibio-Talar Arthrodesis: Fact or Fiction?
 AOFAS Annual Meeting, July 17-20th 2013 Hollywood, Florida Peritalar Dislocation After Tibio-Talar Arthrodesis: Fact or Fiction? Fabrice Colin, MD; Lukas Zwicky, MSc; Alexej Barg, MD; Beat Hintermann,
AOFAS Annual Meeting, July 17-20th 2013 Hollywood, Florida Peritalar Dislocation After Tibio-Talar Arthrodesis: Fact or Fiction? Fabrice Colin, MD; Lukas Zwicky, MSc; Alexej Barg, MD; Beat Hintermann,
RESIDUAL ADDUCTION OF THE FOREFOOT IN TREATED CONGENITAL
 RESIDUAL ADDUCTION OF THE FOREFOOT IN TREATED CONGENITAL CLUB FOOT L. W. LOWE and M. A. HANNON, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Hospitalfor Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London Adduction of the forefoot
RESIDUAL ADDUCTION OF THE FOREFOOT IN TREATED CONGENITAL CLUB FOOT L. W. LOWE and M. A. HANNON, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Hospitalfor Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London Adduction of the forefoot
)402( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY
 )402( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of Clinical and Radiological Results of Calcaneal Lengthening Osteotomy in Pediatric Idiopathic Flexible Flatfoot
)402( COPYRIGHT 2018 BY THE ARCHIVES OF BONE AND JOINT SURGERY RESEARCH ARTICLE Evaluation of Clinical and Radiological Results of Calcaneal Lengthening Osteotomy in Pediatric Idiopathic Flexible Flatfoot
Technique Guide. 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt. For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot.
 Technique Guide 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt. For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot. Table of Contents Introduction 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Technique Guide 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt. For intramedullary fixation of the medial column of the foot. Table of Contents Introduction 6.5 mm Midfoot Fusion Bolt 2 AO Principles 4 Indications 5 Surgical
Ankle Pain After a Sprain.
 Ankle Pain After a Sprain www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anterior Drawer Stress Test Talar Tilt Talar Tilt (CFL) Difficult to isolate from subtalar ROM Slight plantar flexion (dorsi = relative subtalar isolation)
Ankle Pain After a Sprain www.fisiokinesiterapia.biz Anterior Drawer Stress Test Talar Tilt Talar Tilt (CFL) Difficult to isolate from subtalar ROM Slight plantar flexion (dorsi = relative subtalar isolation)
Foot Injuries. Dr R B Kalia
 Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
Foot Injuries Dr R B Kalia Overview Dramatic impact on the overall health, activity, and emotional status More attention and aggressive management Difficult appendage to study and diagnose. Aim- a stable
POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY
 1 POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY The following instructions are general guidelines, but surgeon post-op instructions will dictate the individual patient's post-op management
1 POSTOP FOLLOW-UP & REHABILITATION FOLLOWING FOOT & ANKLE SURGERY The following instructions are general guidelines, but surgeon post-op instructions will dictate the individual patient's post-op management
ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION
 ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION Evaluation and Measurements By Isabelle Devreux 1 Ankle Plantar Flexion: Gastrocnemius and Soleus ROM: 0 to 40-45 A. Soleus: Origin: Posterior of head of fibula and proximal1/3 of
ANKLE PLANTAR FLEXION Evaluation and Measurements By Isabelle Devreux 1 Ankle Plantar Flexion: Gastrocnemius and Soleus ROM: 0 to 40-45 A. Soleus: Origin: Posterior of head of fibula and proximal1/3 of
International Journal of Biological & Medical Research
 Int J Biol Med Res. 2013; 4(1): 2986-2990 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 1, Jan 2012 www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect Publications Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International
Int J Biol Med Res. 2013; 4(1): 2986-2990 Int J Biol Med Res Volume 3, Issue 1, Jan 2012 www.biomedscidirect.com BioMedSciDirect Publications Contents lists available at BioMedSciDirect Publications International
Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot
 Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot Dane K. Wukich M.D. Chief, Division of Foot and Ankle Surgery Medical Director, UPMC Foot and Ankle Center University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosure
Amputations of the digit, ray and midfoot Dane K. Wukich M.D. Chief, Division of Foot and Ankle Surgery Medical Director, UPMC Foot and Ankle Center University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Disclosure
PTTD Reconstruction-Turning Failure into Your Guide to Success Michael D. Dujela DPM, FACFAS
 PTTD Reconstruction-Turning Failure into Your Guide to Success Michael D. Dujela DPM, FACFAS Visiting Fellowship Alumnus, Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Center A.O. Fellowship Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Alumnus
PTTD Reconstruction-Turning Failure into Your Guide to Success Michael D. Dujela DPM, FACFAS Visiting Fellowship Alumnus, Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Center A.O. Fellowship Orthopaedic Foot and Ankle Alumnus
V E R I TAS MGH 1811 MGH 1811 V E R I TAS. *Gerber JP. Persistent disability with ankle sprains. Foot Ankle Int 19: , 1998.
 MGH 1811 Management of Ankle Instability Richard J. de Asla, M.D. V E R I TAS MGH 1811 I have no potential conflicts with this presentation. V E R I TAS It s just a sprain Lateral Ankle Sprains Most common
MGH 1811 Management of Ankle Instability Richard J. de Asla, M.D. V E R I TAS MGH 1811 I have no potential conflicts with this presentation. V E R I TAS It s just a sprain Lateral Ankle Sprains Most common
Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot
 168 Forefoot Reconstruction Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot Definition, History, Generalities This staple first provides a permanent compression both in the prongs
168 Forefoot Reconstruction Use of the 20 Memory Staple in Osteotomies of Fusions of the Forefoot Definition, History, Generalities This staple first provides a permanent compression both in the prongs
Revision Surgery for Recurrent Pain after Excision of the Accessory Navicular and Relocation of the Tibialis Posterior Tendon
 Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:232-238 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.2.232 Revision Surgery for Recurrent Pain after Excision of the Accessory Navicular and Relocation of the
Original Article Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2017;9:232-238 https://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2017.9.2.232 Revision Surgery for Recurrent Pain after Excision of the Accessory Navicular and Relocation of the
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) Index
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) 335 344 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Accessory soleus muscle, magnetic resonance imaging of, 300 Achilles tendon injury of, magnetic
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 19 (2002) 335 344 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in bold face type. A Accessory soleus muscle, magnetic resonance imaging of, 300 Achilles tendon injury of, magnetic
Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy
 Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy Hank Chambers, MD San Diego Children s Hospital San Diego, California Indications Fixed contracture Joint dislocations Shoe wear problems Pain Perineal
Lower Extremity Orthopedic Surgery in Cerebral Palsy Hank Chambers, MD San Diego Children s Hospital San Diego, California Indications Fixed contracture Joint dislocations Shoe wear problems Pain Perineal
Fractures of the Calcaneus
 Fractures of the Calcaneus Diagnosis and Treatment CARL E. HORN, M.D., Sacramento Good lateral, Anthonsen oblique, anterior-posterior, and axial roentgenograms are necessary to define the extent of fractures
Fractures of the Calcaneus Diagnosis and Treatment CARL E. HORN, M.D., Sacramento Good lateral, Anthonsen oblique, anterior-posterior, and axial roentgenograms are necessary to define the extent of fractures
Index. Clin Podiatr Med Surg 23 (2006) Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Clin Podiatr Med Surg 23 (2006) 233 239 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acclimatization, in sports preconditioning program, 197 Achilles tendon lengthening of, for equinus
Clin Podiatr Med Surg 23 (2006) 233 239 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acclimatization, in sports preconditioning program, 197 Achilles tendon lengthening of, for equinus
