Evaluation of Spinal Tuberculosis by Plain X-Rays and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Northern India -A Prospective Study
|
|
|
- Dortha Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Section: Radiology ORIGINAL RESEARCH Evaluation of Spinal Tuberculosis by Plain X-Rays and Magnetic Resonance Imaging in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Northern India -A Prospective Study Rumeet Kukreja 1, Mukta Mital 2, Prashant K. Gupta 3 ABSTRACT Introduction: Plain X-ray remains the primary imaging modality to evaluate spinal tuberculosis. MRI additionally detects spinal canal narrowing, cord compression / cord oedema and can also pick up clinically/x-ray occult cases as well as multilevel involvement, without the risk of ionizing radiation. The purpose of the study was to describe the radiological features of spinal tuberculosis on MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and plain X-rays, to co-relate the findings and to evaluate the role of each in spinal tuberculosis. Method and Materials: The study was conducted on sixty five patients suspected of spinal tuberculosis. After taking an informed consent, all patients were subjected to evaluation by plain radiographs and MRI, while post contrast MRI study was done, wherever required. Results: Dorsal vertebrae were most commonly involved with the paradiscal type being the most common radiological type of involvement. Disc involvement, endplate irregularity, abscess, calcification, reduction in vertebral height and spinal cord compromise were important radiological features. MRI was noted to be a better modality for the evaluation of the spinal cord/ canal status. Plain radiography showed a crucial role in picking up calcification within the abscess. Conclusion: MRI is the modality of choice in evaluation of spinal tuberculosis, however, both X-rays and MRI are complimentary to each other. Keywords: Tuberculosis, Spinal, Plain X-rays, MRI. INTRODUCTION Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. 1,2 It is more common in the Eastern hemisphere of the world. In fact it is estimated that India alone has got one-fifth of the total world population of tuberculous patients. 2 Tuberculosis typically affects the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body. 3 Of all the patients suffering from tuberculosis, nearly 1 2% have involvement of the skeletal system 4 with spinal tuberculosis being the most common form of skeletal tuberculosis, constituting about 50% of all cases. 2 Spinal tuberculosis is possibly one of the oldest demonstrated diseases of mankind, having been documented in ancient Egyptian mummies. 5,6 The first modern case of spinal tuberculosis was described by Sir Percival Pott 7,8 was first to describe the spinal tuberculosis in 1779, after whom the disease is commonly referred to as Pott s Spine. Spinal TB occurs most commonly by haematogenous spread from pulmonary tuberculosis but could be from extra pulmonary site as well.,9,10 It usually involves the thoracic and lumbar spine with thoracolumbar junction being the most frequent site of involvement. 11 Other sites like cervical region and sacrum being less common. 2 Four radiological types of vertebral involvement have been described: paradiscal, anterior, central, neural arch or appendiceal. 1,12,13 Out of these paradiscal type is the most common. The diagnosis of spinal TB can be challenging due to the non-specific constitutional symptoms. Imaging plays an important role in the early diagnosis and treatment decisions. 14 Plain film radiography (PFR) is one of the first and the most common imaging technique used to confirm the diagnosis of spine tuberculosis by the radiologists in most clinical settings and has been reported to have a diagnostic efficacy of 91-99%. 15 The best diagnostic modality in the present scenario for the diagnosis of spinal tuberculosis is MRI. It is more sensitive than radiography and more specific than CT in the diagnosis and can also provide the diagnosis of Pott s spine 4-6 months earlier than conventional methods, offering the benefits of earlier detection and treatment. 11,16,17,18,19 The present study was conducted with the aim to describe the radiological features of spinal TB on plain X-Rays and Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), to co-relate the findings and evaluate the role of each modality in spinal TB. MATERIAL AND METHODS This observational study was conducted on sixty five (65) patients suspected of spinal tuberculosis on clinical examination and referred to the Radiology department of a tertiary care hospital for evaluation by Plain X-Rays and MR Imaging, after taking approval from the ethical committee. A detailed clinical history and examination was done for each patient and general observations were made in respect to demographic distribution and detailed signs and symptoms. Each patient selected for the study was explained the entire procedure and an informed consent was taken from 1 Resident, 2 Professor, 3 Director and Professor, Department of Radiology, Subharti Institute of Medical Sciences, Meerut, U. P., India Corresponding author: Dr. Mukta Mital, B-13, Damodar Colony, Garh Road, Meerut, U. P , India How to cite this article: Rumeet Kukreja, Mukta Mital, Prashant K. Gupta. Evaluation of spinal tuberculosis by plain x-rays and magnetic resonance imaging in a tertiary care hospital in Northern India -a prospective study. International Journal of Contemporary Medical Research 2018;5(2):B4-B9. B4 Volume 5 Issue 2 February 2018 ICV: ISSN (Online): X; (Print):
2 Kukreja, et al. each before enrolrment. Old treated cases/ cases already undergoing treatment for Spinal Tuberculosis and patients who did not give consent for the participation in the study were excluded. X-ray was done on 500 milli-amperes (ma) SIEMENS X-ray Kienscope Unit, 800 milli-amperes (ma) ALLENGER HF Unit and Care Stream Health Care Computerized Radiography system 850(CRS) with Dry View Camera 6800(DV) for Computerized Radiography(CR) with small focal spot. X-ray of region of interest of spine was done in two perpendicular planes i.e. Antero-Posterior [AP] and Lateral using collimation and relevant Kvp and ma techniques and the X-Ray findings were recorded in detail. Chest X-Ray was done as a part of routine investigation in all patients, mostly in postero-anterior view, however in some cases antero-posterior view was also done. MRI - After taking an informed consent from the patient, the patient was made to lie down supine on the gantry table with arms resting by the side in a 1.5T imaging system (G.E.Healthcare).8 channel MR coils were placed over the patient. After taking the planar images, the following sequences were taken at baseline Sagittal Fast Spin Echo T2 weighted image, Sagittal Fast Spin Echo T1 weighted image, Coronal STIR image, Axial T2 frfs image, Axial T1 FSE image and Sagittal STIR image. Diffusion weighted images were done, wherever required and contrast studies were done in cases where above sequences lead to inconclusive diagnosis. The MRI findings were recorded in detail. The radiological observations in all cases were made with respect to level of vertebral involvement, intervertebral disc space narrowing or involvement, end plate irregularity, paravertebral / prevertebral / epidural abscess formation, calcification, wedging and compression fracture, vertebral body height reduction, scalloping of anterior vertebral surface, bone density, kyphosis and scoliosis, spinal canal narrowing and cord compression and oedema. The X-Ray and MRI Imaging findings were correlated with clinical history and clinical examination. Clinical response to treatment and/or clinico-pathological findings were considered confirmatory for the diagnosis of spinal TB in all patients. STATISTICAL ANALYSIS All data were compiled in tabulated manner and results were expressed as mean +standard deviation for the statistical analysis using stat Graphics Centurion (Version 6.2). RESULTS Out of the total 65 patients enrolled for the study majority of the patients, that is, 27 patients (41.5%) were between years. The mean age was calculated to be 39.68±18.7 years. 32 patients were male (49.2 percent) and 33 were female (50.8 percent) with M:F ratio of 1:1.03. No specific sex predilection was seen in the study. The mean duration of symptoms was calculated to be 14.25±11.8 months.the most common complaint was backache noted in 53(81.5%) patients, followed by fever noted in 45(69.2%) patients. Other common complaints were weight loss noted in 36 cases (55.4%), malaise in 35 cases (53.8%), local tenderness in 32 cases (49.2%). 31 patients (47.7%) had bladder and bowel involvement and 29 cases (44.6%) had neurological involvement (excluding bladder and bowel involvement). The most common site of involvement was dorsal spine noted in 35(53.8%) cases, followed by the lumbar spine in 31(47.7%) patients. Sacral involvement was noted in 8(12.3%) cases and cervical spine was involved in 4(6.2%) of patients. Non -contiguous multiple level vertebral involvement was noted in 3 cases out of 65, that is 4.6 percent of the total cases studied [Collage 1-Figure 1-6]. The most common type of involvement was Paradiscal type in 51 cases (78.5%) [Collage 2-Figure 7-11], followed by Anterior subligamentous type which was noted in 14 cases (21.5%) [ Collage 3-Figure 12-13]. The Central type of lesion was noted in 9 patients (13.8%) and Posterior element involvement was noted in the least number of cases accounting for 3 patients (7.7%) of the total 65 studied patients. Chest X-ray revealed evidence of healed or active pulmonary lesion in 35.4% (23 cases) in association with the imaging Section: Radiology Radiological Findings Plain Radiography Findings(Frequency) MRI Findings (Frequency) Difference in percentage (MRI-X-Ray) I.V. Disc space/disc Involvement 36(55.4%) 51(78.5%) 23.1 Abscess 21(32.3%) 38(58.5%) 26.2 End Plate Irregularity 24(36.9%) 51(78.5%) 41.6 Thecal Sac Indentation - 37(56.9%) 56.9 SpinalCord Compromise/Canal Stenosis - 12(18.5%) 18.5 Cord Oedema - 5(7.7%) 7.7 Calcification 7(10.8%) Reduced Bone Density 26(40%) Wedge Collapse 16(24.6%) 16(24.6%) 0 Compression Fracture 9(13.8%) 9(13.8%) 0 Vertebral Body Height Reduction 28(43.1%) 28(43.1%) 0 Kyphosis 26(40%) 26(40%) 0 Scoliosis 12(18.5%) 12(18.5%) 0 Table-1: Shows the correlation between the frequency of plain radiography and MRI findings ISSN (Online): X; (Print): ICV: Volume 5 Issue 2 February 2018 B5
3 Section: Radiology Kukreja, et al. Figures 1-6: X-Ray lumbar spine AP/LAT reveals reduced height and endplate irregularity of D12 vertebrae and partial destruction of L5 AND S1 vertebrae. MR Sag T2 and Cor STIR Images showing altered signals and reduced height of D12 body and reduced disc height at D11-12 Level with bilateral paravertebral collection. Associated destruction of L5,S1 and S2 vertebral bodies, with i/v disc involvement and subligamentous collection. Additionally irregularity of endplates of D9 and D10 vertebra seen (not picked on X- Ray).MR Axial T2 images reveal epidural collection at D12 and subligamentous collection at L5-S1 Level. findings in the spine Plain X- Ray findings of patients revealed I.V. Disc space/ disc involvement in 36 patients (55.4%), abscess in 21 patients (32.3%), calcification in 7 patients (10.8%), end plate irregularity in 24 patients (36.9%), reduced bone density in 26 patients (40.0%), wedging in 16 patients (24.6%), compression fracture in 9 patients (13.8%), vertebral body height reduction in 28 patients (43.1%), kyphosis in 26 patients (40.0%) and scoliosis in 12 patients (18.5%) out of total 65 studied patients. MRI findings of patients revealed I.V. Disc space/ disc involvement in 51 patients (78.5%), abscess in 38 patients (58.5%), end plate irregularity in 41 patients (63.1%), thecal sac indentation in 37 patients (56.9%), spinal cord compromise/ canal stenosis in 12 patients (18.5 percent), cord oedema in 5 Figures 7-11: X-Ray DORSOLUMBAR Spine AP/LAT Views reveal reduced heights of D11 and D12 vertebral bodies with end plate irregularity and reduced intervening i/v disc height. MR Sag T2, Coronal STIR and AXIAL T2 images reveal reduced heights and altered signal in D11-12 vertebrae with end plate irregularity and reduced intervening i/v disc height. Associated pre and bilateral paravertebral collections with epidural collection causing spinal canal stenosis. patients (7.7 percent), wedge collapse in 16 patients (24.6%), compression fracture in 9 patients (13.8%), vertebral body height reduction in patients 28(43.1%), kyphosis in 26 patients (40.0%) and scoliosis in 12 patients (18.5%). Diffusion weighted imaging was done in 45 patients, in which 34 patients showed evidence of restriction in the abscess. Post contrast studies were done in 19 patients out of the total 65 patients. 11patients showed post contrast enhancement. The X-Ray and MRI findings were co-related [Table 1]. The plain radiograph described changes consistent with TB spine were seen in 98.4% (64 out of 65) of cases. In the remaining 1 case, MRI picked up the findings suggesting spinal tuberculosis. DISCUSSION Out of the total 65 patients enrolled for the study, the most B6 Volume 5 Issue 2 February 2018 ICV: ISSN (Online): X; (Print):
4 Kukreja, et al. Figures 12-13: MR Sag T2 and Axial T2 images reveal anterior subligamentous type of involvement at sacral level common age group affected was between years with 27 patients (41.5%), followed by years age group with 18 patients (27.7%). The mean age group affected was calculated to be 39.68±18.7 years. This is in corroboration to the findings of Mirsaeidi et al., 20 who found a mean age of years. Similar finding was also stated by Sinan et al., 21 who found 43% cases in their study belonged to the age group of years. Osborn 22 also stated that in the developing countries like India, spinal tuberculosis was prevalent in the younger age group, while in the western world, it was found in the middle age (mean years). No specific sex predilection was noted in our study, which is in corroboration with Osborn 22, however, tuberculosis of the spine was found to be more common in males than in females in few of the previously published series 20,21 Chest X-ray revealed evidence of healed or active pulmonary lesion in 35.4% (23 cases) in association with the imaging findings in the spinal tuberculosis. Several authors. 23,24 in the past have also stated that 33-50% of patients with spinal TB have an associated primary lung focus or have a reported history of pulmonary TB. The lower thoracic and upper lumbar levels have been reported to be the most common site of involvement in several previous studies 21,25,26 which is in corroboration with our study, in which also the most common site of involvement was dorsal spine noted in 53.8% cases (35 patients), followed by lumbar spine in 47% cases (31 patients). In this study, the most common type of involvement was Paradiscal type in 51 cases (78.5%), followed by Anterior subligamentous type which was noted in 14 cases (21.5%). The Central type of lesion was noted in 9 patients (13.8%) and Posterior element involvement was noted in the least number of cases accounting for 3 patients (7.7%) of the total 65 studied patients. Ansari S et al 1 also quoted that paradiscal type was the most common in their study, noted in 83.3% of the total cases, followed by central, anterior subligamentous and neural arch type in descending order. Tuli et al 4 also stated that paradiscal lesions are the most common type in vertebral tuberculosis. Diagnosis of spinal tuberculosis depends on the presence of characteristic clinical and neuroimaging findings. Plain radiographs give a good overview and often provide enough information for the diagnosis and treatment of spinal TB especially in a resource poor country like India. MRI is useful in determining the spread of the disease to the soft tissues and to determine the extent of spinal cord involvement. The radiological findings included were intervertebral disc involvement, abscess formation, endplate irregularity, the cal sac indentation, spinal cord compression /canal stenosis, cord oedema, calcification, reduced bone density, wedging, compression fracture, vertebral body height reduction, kyphosis and scoliosis. In fact the presence calcification within the abscess is considered virtually diagnostic of spinal tuberculosis. 27 In our study intervertebral disc space involvement was noted in 36 cases (55.4%) on plain X- rays and in 51 cases (78.5%) on MRI. This is in corroboration with the studies of Rivas- Garcia A et al 28, Sinan et al., 21 who found the involvement of the intervertebral disc in majority of their cases. Bajwa GR 29 found intervertebral disc space involvement in 95 percent of cases. Ansari S et al 1 in addition also noted that MRI was better than X-Rays to visualize intervertrbral disc involvement. Osborn 22 stated that a paraspinal abscess was present in 55-95% of the cases, which is in corroborance to our study in which X-Ray showed presence of abscess in 21 cases (32.3% of cases) while on MRI it was noted in38 cases (58.5%). Other authors 1,28 have also reported better detection rates of abscesses on MRI. In our study post contrast study showed rim enhancement of abscess in 13 of 19 patients. Sharif HS 30 reported that thick rim enhancement in these abscesses is strongly suggestive of spinal TB and is not seen in nongranulomatous spondylitis. The presence of calcification within the abscess is virtually diagnostic of spinal tuberculosis. Such calcifications are formed because of the lack of proteolytic enzymes in M. tuberculosis. 27 In our study Plain X-Ray was superior to MRI for evaluation of calcification. On X_Ray, it was noted in Section: Radiology ISSN (Online): X; (Print): ICV: Volume 5 Issue 2 February 2018 B7
5 Section: Radiology Kukreja, et al. 7 cases (10.8%). Calcification was noted in 46 percent of cases in a study by Rivas-Garcia A et al 28 while Bajwa GR et al 29 found calcification in 40 percent of the cases which is in contrast to our study. End plate irregularity was also better picked on MRI as compared to plain X-Rays. Wedging, compression fractures and vertebral body height reduction were equally detected on both modalities. This is in corroboration with other studies. 1,29 Reduction in bone density could only be picked up on X-Ray, that too in 40% cases. Approximately one third of the calcium must be lost from a particular area for osteolysis to be appreciated radiographically. Similar incidence has been reported by Ansari S et al. 1 Thecal sac indentation, spinal cord compromise/ canal stenosis and cord oedema which are important findings for deciding patient management and future prognosis were picked up only on MRI. In our study the plain radiographic described changes consistent with spinal TB were picked up in 98.4%(64 out of 65) of cases. Imaging evaluation of patients with spinal TB showed that disc involvement, abscess and end plate irregularity were statistically better visualized on MRI as compared to X ray. Bone density and calcification were only noted on X-Ray, while spinal canal narrowing, cord compression and compressive myelopathy could only be commented upon on MRI. CONCLUSION Both Plain X-Rays and MRI are important imaging modalities for diagnosis of spinal tuberculosis and are also useful to monitor the response of the patients to the treatment. Plain X-ray remains the primary and the first imaging modality to evaluate the disease. It is a considerably less expensive investigation and is easily and widely available within the reach of most patients. One of the key roles of X-rays is ability to detect calcification and reduced bone density, which are important diagnostic features of the disease. However, plain radiography has few shortcomings in that radiographs generally remain normal in the early stages of the disease, hence by the time the disease is evident on plain X-Ray, the patient has already reached an advanced stage. Spinal canal narrowing, cord compression and cord oedema which are particularly important for further patient management cannot be commented upon on plain X-Rays. X-rays are also less perceptive than MRI to evaluate intervertebral disc involvement, soft tissue involvement, abscesses and end plate irregularity. MRI has the advantages of improved contrast resolution for bone and soft tissues along with possibility of multiplanar imaging. It carries no risk of radiation which is particularly important in children and pregnant women. It can even pick up clinically/xray occult multilevel involvement. However, MRI has the disadvantage of being a relatively expensive imaging modality which is particularly important in our country where quite a few patients belong to the low socio economic staus. It is also not readily available in all the hospitals and is also contraindicated in patients with pacemakers, cardiac defibrillators, etc. It is also unable to identify the soft tissue calcification, which is an important imaging feature of the tubercular infection of the spine and has little role in guided percutaneous diagnostic abscess aspiration or soft tissue biopsy. Therefore, we would like to conclude that MRI is a better and more informative imaging modality in evaluation of patients of Pott s spine, however, both X-rays and MRI have their own diagnostic importance, advantages and disadvantages and both are complementary to each other for evaluation of tuberculosis of spine. REFERENCES 1. Ansari S, Amanullah MF, Ahmad K, Rauniyar RK. Pott s Spine: Diagnostic Imaging Modalities and Technology Advancements. N Am J Med Sci. 2013; 5: Agrawal V, Patgaonkar PR, Nagariya SP. Tuberculosis of spine. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2010;1: Konstantinos A. Testing for tuberculosis. Australian Prescriber 2010; 33: Tuli SM. 3rd ed. New Delhi: Jaypee Brothers; Textbook- Tuberculosis of the skeletal system (Bones, Joints, Spine and Bursal sheaths) 5. Taylor GM, Murphy E, Hopkins R, Rutland P, Chistov Y. First report of Mycobacterium bovis DNA in human remains from the Iron Age. Microbiology. 2007: 153: Bynum H. Spitting blood. The history of tuberculosis. Oxford: Oxford University Press; Sai Kiran NA, Vaishya S, Kale SS, Sharma BS, Mahapatra AK. Surgical results in patients with tuberculosis of the spine and severe lower-extremity motor deficits: a retrospective study of 48 patients. J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6: Pott P. The chirurgical works of Percivall Pott, F.R.S., surgeon to St. Bartholomew's Hospital, a new edition, with his last corrections Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2002; 398: Boachie-Adjei O, Squillante RG. Tuberculosis of the spine. Orthop Clin North Am. 1996;27: Schirmer P, Renault CA, Holodniy M. Is spinal tuberculosis contagious? Int J Infect Dis. 2010;14:e Moorthy S, Prabhu NK. Spectrum of MR imaging findings in spinal tuberculosis. AJR Am J Roentgenol.2002;179: Gautam MP, Karki P, Rijal S, Singh R. Pott's spine and paraplegia. J Nepal Med Assoc.2005;44: Gard RK, Somvanshi DS. Spinal tuberculosis: A review. J Spinal Cord Med. 2011;34: Jain AK, Dhammi IK. Tuberculosis of the spine: A review. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2007;460: Bello AI, Ofori EK, Alabi OJ, Adjei DN. Assessment of the level of agreement in the interpretation of plain radiographs of lumbar spondylosis among clinical physiotherapists in Ghana. BMC Medical Imaging. 2014;14: Turunc T, DemirogluYZ, Uncu H, Colakoglu S, Arslan H. A comparative analysis of tuberculous, brucellar and B8 Volume 5 Issue 2 February 2018 ICV: ISSN (Online): X; (Print):
6 Kukreja, et al. pyogenic spontaneous spondylodiscitis patients. J Infect 2007; 55: Omari B, Robertson JM, Nelson RJ, Chiu LC. Pott's disease. A resurgent challenge to the thoracic surgeon. Chest. 1989;95: Shanley DJ. Tuberculosis of the spine: Imaging features. Am J Roentgenol 1995;164: Griffith JF, Kumta SM, Leung PC, Cheng JC, Chow LT, Metreweli C. Imaging of musculoskeletal tuberculosis: a new look at an old disease. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2002;398: Mirsaeidi SM, Tabarsi P, Amiri MV, Mansoori SD, Bakhshayesh-Karam M, Masjedi MR, et al. Clinical and Radiological Presentation of Adult Tuberculous Spondylitis. Tanaffos 2003;2: Sinan T, Al-Khawari H, Ismail M, Ben-Nakhi A, Sheikh M. Spinal tuberculosis: CT and MRI features. Ann Saudi Med 2004;24: Osborn AG. Non neoplastic disorders of the spine and spinal cord. 1e ed. Elsevier; Diagnostic Neuroradiology; pp Chapter Kaya A, Topu Z, Fitoz S, Numanoglu N. Pulmonary tuberculosis with multifocal skeletal involvement. Monaldi Arch Chest Dis 2004: 61: Daniel TM, Debanne SM. The serodiagnosis of tuberculosis and other mycobacterial diseases by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Am Rev Respir Dis 1987;135: Owolabi LF, Nagoda MM, Samaila AA, Aliyu I. Spinal tuberculosis in adults: A study of 87 cases in Northwestern Nigeria. Neurology Asia 2010;15: Burrill J, Williams CJ, Bain G, Conder G, Hine AL, Misra RR. Tuberculosis: A radiologic review. Radiographics 2007; 27: Das B, Pu TA and Watanakunakom C. Tuberculosis of the spine (Pott s spine) presenting as compression fractures. Journal Spinal cord 2002;40: Rivas-Garcia A, Sarria-Estrada S, Torrents-Odin C, Casas-Gomila L, Franquet E. Imaging findings of Pott s disease. European Spine Journal. 2013;22: G.R. Bajwa. Evaluation of the role of MRI in spinal tuberculosis: A study of 60 cases. Pak J Med Sci, 2009; 25: Sharif HS. Granulomatous spinal infections: MR imaging. Radiology 1990;177: Section: Radiology Source of Support: Nil; Conflict of Interest: None Submitted: ; Accepted: ; Published: ISSN (Online): X; (Print): ICV: Volume 5 Issue 2 February 2018 B9
MRI is the gold standard investigation for early detection, extent of involvement and management of patient in Pott s spine
 Original Research Article MRI is the gold standard investigation for early detection, extent of involvement and management of patient in Pott s spine Anil Rathva 1, Siddharth Zala 2* 1 Assistant Professor,
Original Research Article MRI is the gold standard investigation for early detection, extent of involvement and management of patient in Pott s spine Anil Rathva 1, Siddharth Zala 2* 1 Assistant Professor,
MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis
 CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
CASE ORIGINAL REPORT ARTICLE MRI findings in proven Mycobacterium tuberculosis (TB) spondylitis D J Kotzé, MB ChB L J Erasmus, MB ChB Department of Diagnostic Radiology, University of the Free State, Bloemfontein
Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging
 Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging Poster No.: C-1422 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Beretis, K. Giannaki, M. Fasoula, D. Kypriotis, T. Dagla, T.-P. Mantzouranis;
Pott disease (spinal tuberculosis): MR and CT imaging Poster No.: C-1422 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. Beretis, K. Giannaki, M. Fasoula, D. Kypriotis, T. Dagla, T.-P. Mantzouranis;
Imaging of tuberculosis of the spine
 P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(9) : 439 CME Article Imaging of tuberculosis of the spine E L H J Teo, W C G Peh ABSTRACT Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of death worldwide
P i c t o r i a l E s s a y Singapore Med J 2004 Vol 45(9) : 439 CME Article Imaging of tuberculosis of the spine E L H J Teo, W C G Peh ABSTRACT Tuberculosis (TB) is the leading cause of death worldwide
Spinal infection. Outline ANATOMY 6/2/2017. Anatomy Pathogen
 Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
Outline Spinal infection Pramot Tanutit, M.D. Department of Radiology, Songklanagarind Hospital Faculty of Medicine, Prince of Songkla University Anatomy Pathogen Pyogenic spondylodiscitis Tuberculous
ISPUB.COM. Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay. P Chudgar INTRODUCTION SPINE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 8 Number 2 Spectrum Of MRI Findings In Musculoskeletal Tuberculosis: Pictoral Essay P Chudgar Citation P Chudgar.. The Internet Journal of Radiology.
EVALUATION OF THE ROLE OF MRI IN SPINAL TUBERCULOSIS
 EVALUATION OF THE ROLE OF MRI IN SPINAL TUBERCULOSIS Anil Kumar Yadav * and Prof. She Yunju Jingzhou central Hospital,Hubei,China ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the role of MRI in assessing the extent
EVALUATION OF THE ROLE OF MRI IN SPINAL TUBERCULOSIS Anil Kumar Yadav * and Prof. She Yunju Jingzhou central Hospital,Hubei,China ABSTRACT Objective: To evaluate the role of MRI in assessing the extent
Pott's Spine: Retrospective Analysis of MRI in 40 Cases.
 Pott's Spine: Retrospective Analysis of MRI in 40 Cases. Poster No.: C-1110 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Avantsa, P. Kala, D. V. Bhargavi; Bangalore/IN Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Pott's Spine: Retrospective Analysis of MRI in 40 Cases. Poster No.: C-1110 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. Avantsa, P. Kala, D. V. Bhargavi; Bangalore/IN Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Conservative treatment of spinal tuberculosis and its outcome: an observational study
 International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20184720 Conservative treatment of spinal tuberculosis
International Journal of Research in Orthopaedics http://www.ijoro.org Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/issn.2455-4510.intjresorthop20184720 Conservative treatment of spinal tuberculosis
A Retrospective Analysis of Management of Tuberculosis of Spine in a Tertiary Care Hospital
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Retrospective Analysis of Management of Tuberculosis of Spine in a Tertiary Care Hospital Prashant N Gedam 1, Prathamesh Kane 2 1. Additional Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, B.Y.L
ORIGINAL ARTICLE A Retrospective Analysis of Management of Tuberculosis of Spine in a Tertiary Care Hospital Prashant N Gedam 1, Prathamesh Kane 2 1. Additional Professor, Department of Orthopaedics, B.Y.L
Clinical Significance of MRI Findings During Medical Treatment for Tuberculous Spondylitis
 Clinical Significance of MRI Findings During Medical Treatment for Tuberculous Spondylitis Dae Jung Kim 1, Tae-Sub Chung 1, Sang Hyun Suh 1, Keun Su Kim 2, Yong Eun Cho 2, Youngsul Yoon 2, Sam Soo Kim
Clinical Significance of MRI Findings During Medical Treatment for Tuberculous Spondylitis Dae Jung Kim 1, Tae-Sub Chung 1, Sang Hyun Suh 1, Keun Su Kim 2, Yong Eun Cho 2, Youngsul Yoon 2, Sam Soo Kim
102 Results RESULTS. Age Mean=S.D Range 42= years -84 years Number % <30 years years >50 years
 102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
102 Results RESULTS A total of 50 cases were studied 39 males and 11females.Their age ranged between 16 years and 84 years (mean 42years). T1 and T2WI were acquired for all cases in sagittal and axial
CORRELATION BETWEEN CLINICAL, RADIOLOGICAL AND OPERATIVE FINDINGS IN MANAGEMENT OF TUBERCULOUS AND PYOGENIC SPONDYLITIS.
 A Yehya et al. Alexandria Bulletin 177 CORRELATION BETWEEN CLINICAL, RADIOLOGICAL AND OPERATIVE FINDINGS IN MANAGEMENT OF TUBERCULOUS AND PYOGENIC SPONDYLITIS. Receive: 12 / 4 /2010 - Accepted: 1 / 6 /
A Yehya et al. Alexandria Bulletin 177 CORRELATION BETWEEN CLINICAL, RADIOLOGICAL AND OPERATIVE FINDINGS IN MANAGEMENT OF TUBERCULOUS AND PYOGENIC SPONDYLITIS. Receive: 12 / 4 /2010 - Accepted: 1 / 6 /
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Abstract. Aim. Materials and methods. Introduction. Results
 Is anatomical distribution helpful for differentiating TB spondylitis from neoplastic causes of extradural spinal cord compression in children? A pilot study Reena George, MD, MMed Rad, FRCR (UK) Savvas
Is anatomical distribution helpful for differentiating TB spondylitis from neoplastic causes of extradural spinal cord compression in children? A pilot study Reena George, MD, MMed Rad, FRCR (UK) Savvas
Contiguous Spinal Metastasis Mimicking Infectious Spondylodiscitis 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.6.408 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례 Chul-Min Lee, MD 1, Seunghun Lee, MD 1 *, Jiyoon Bae, MD 2 1 Department of Radiology,
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2015.73.6.408 감염성척추염과유사하게보였던연속적척추전이의증례 Chul-Min Lee, MD 1, Seunghun Lee, MD 1 *, Jiyoon Bae, MD 2 1 Department of Radiology,
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
JMSCR Vol 04 Issue 05 Page May 2016
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i5.42 Pott s Spine: Diagnosis and Management
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.244 Index Copernicus Value: 5.88 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v4i5.42 Pott s Spine: Diagnosis and Management
SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION
 CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
CLINICAL VIGNETTE 2017; 3:2 SPINAL MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING INTERPRETATION Editor-in-Chief: Idowu, Olufemi E. Neurological surgery Division, Department of Surgery, LASUCOM/LASUTH, Ikeja, Lagos, Nigeria.
factor for identifying unstable thoracolumbar fractures. There are clinical and radiological criteria
 NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
NMJ-Vol :2/ Issue:1/ Jan June 2013 Case Report Medical Sciences Progressive subluxation of thoracic wedge compression fracture with unidentified PLC injury Dr.Thalluri.Gopala krishnaiah* Dr.Voleti.Surya
MRI characteristics of brucellar spondylodiscitis in cervical or thoracic segments.
 Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7820-7825 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info MRI characteristics of brucellar spondylodiscitis in cervical or thoracic segments. Yu-zhen Bai 1, Peng-fei Qiao 2, Yang Gao
Biomedical Research 2017; 28 (18): 7820-7825 ISSN 0970-938X www.biomedres.info MRI characteristics of brucellar spondylodiscitis in cervical or thoracic segments. Yu-zhen Bai 1, Peng-fei Qiao 2, Yang Gao
ASJ. Asian Spine Journal. Somit Mittal 1, Mohd Khalid 1, Aamir Bin Sabir 2, Saifullah Khalid 1
 Asian Spine Journal 734 Somit Mittal Clinical et al. Study Asian Spine J 2016;10(4):734-743 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2016.10.4.734 Asian Spine J 2016;10(4):734-743 Comparison of Magnetic Resonance
Asian Spine Journal 734 Somit Mittal Clinical et al. Study Asian Spine J 2016;10(4):734-743 http://dx.doi.org/10.4184/asj.2016.10.4.734 Asian Spine J 2016;10(4):734-743 Comparison of Magnetic Resonance
Section: Orthopaedics. Original Article INTRODUCTION MATERIALS AND METHODS
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.5.OR10 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Clinical and Radiological Evaluation of Healing In Tuberculosis of Spine-A Retrospective and Prospective Study.
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2016.2.5.OR10 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Clinical and Radiological Evaluation of Healing In Tuberculosis of Spine-A Retrospective and Prospective Study.
Spine MRI in Trauma Patients
 Spine MRI in Trauma Patients 4th Musculoskeletal MRI meeting 2017: Spine MRI 6th May, 2017 Gustav Andreisek, MD, MBA Ospedale Regionale di Lugano, Civico, Aula Magna Professor of Radiology, University
Spine MRI in Trauma Patients 4th Musculoskeletal MRI meeting 2017: Spine MRI 6th May, 2017 Gustav Andreisek, MD, MBA Ospedale Regionale di Lugano, Civico, Aula Magna Professor of Radiology, University
HIGH LEVEL - Science
 Learning Outcomes HIGH LEVEL - Science Describe the structure and function of the back and spine (8a) Outline the functional anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord and peripheral nerves (8a) Describe
Learning Outcomes HIGH LEVEL - Science Describe the structure and function of the back and spine (8a) Outline the functional anatomy and physiology of the spinal cord and peripheral nerves (8a) Describe
Spine. Neuroradiology. Spine. Spine Pathology. Distribution of fractures. Radiological algorithm. Role of radiology 18/11/2015
 Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Spine Neuroradiology Spine Prof.Dr.Nail Bulakbaşı X Ray: AP/L/Oblique Vertebra & disc spaces CT & CTA Vertebra, discs, vessels MRI & MRA Vertebra, disc, vessels, meninges Spinal cord & nerves Myelography
Comparison of clinical, radiological and functional outcome of short segment V/S long segment posterior fixation of tuberculosis of spine
 2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
2018; 2(4): 104-108 ISSN (P): 2521-3466 ISSN (E): 2521-3474 Clinical Orthopaedics www.orthoresearchjournal.com 2018; 2(4): 104-108 Received: 20-08-2018 Accepted: 21-09-2018 Dr. Mitul Mistry Assistant Professor,
Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain
 Original article: Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain Dr Sanjeev Sharma (1), Dr Monika Sharma (2), DR Bhardwaj (3), MD; Dr Asha Negi, (4) Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article: Spectrum of magnetic resonance imaging findings in chronic low back pain Dr Sanjeev Sharma (1), Dr Monika Sharma (2), DR Bhardwaj (3), MD; Dr Asha Negi, (4) Department of Radiodiagnosis,
J Korean Soc Spine Surg 2016 Sep;23(3): Originally published online September 30, 2016;
 Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Multifocal Extensive Spinal Tuberculosis Accompanying Isolated Involvement of Posterior Elements - A Case Report - Dong-Eun Shin, M.D., Sang-June Lee, M.D., Young
Journal of Korean Society of Spine Surgery Multifocal Extensive Spinal Tuberculosis Accompanying Isolated Involvement of Posterior Elements - A Case Report - Dong-Eun Shin, M.D., Sang-June Lee, M.D., Young
Magnetic Resonance Image findings of Spinal Tuberclosis at first presentation
 Alvi et al. International Archives of Medicine 2014, 7:12 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Magnetic Resonance Image findings of Spinal Tuberclosis at first presentation Arsalan Ahmad Alvi 1, Aisha Raees 1,
Alvi et al. International Archives of Medicine 2014, 7:12 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Magnetic Resonance Image findings of Spinal Tuberclosis at first presentation Arsalan Ahmad Alvi 1, Aisha Raees 1,
Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury
 Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Isaac, P. A. Tyler; Stanmore/UK Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Imaging and Management of the Charcot Spine Following Spinal Injury Poster No.: P-0023 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: A. Isaac, P. A. Tyler; Stanmore/UK Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Spectrum of Magnetic Resonance Imaging findings in infective intra spinal complications of dermal sinus and associated inclusion cysts
 Spectrum of Magnetic Resonance Imaging findings in infective intra spinal complications of dermal sinus and associated inclusion cysts Poster No.: C-1443 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Spectrum of Magnetic Resonance Imaging findings in infective intra spinal complications of dermal sinus and associated inclusion cysts Poster No.: C-1443 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors:
Imaging and differential diagnosis of pediatric spinal tuberculosis
 HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Radiology of Infectious Diseases 1 (2015) 78e82 Research article Imaging and differential diagnosis of pediatric spinal tuberculosis Xiao-ying
HOSTED BY Available online at www.sciencedirect.com ScienceDirect Radiology of Infectious Diseases 1 (2015) 78e82 Research article Imaging and differential diagnosis of pediatric spinal tuberculosis Xiao-ying
EVALUATION OF X-RAY FINDINGS ALONG WITH MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI) IN THE CONCEPT OF POTT S SPINE PATIENTS
 wjpmr, 2018,4(1), 104-111 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.103 Research Article WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN 2455-3301 www.wjpmr.com WJPMR EVALUATION OF X-RAY FINDINGS ALONG WITH MAGNETIC
wjpmr, 2018,4(1), 104-111 SJIF Impact Factor: 4.103 Research Article WORLD JOURNAL OF PHARMACEUTICAL AND MEDICAL RESEARCH ISSN 2455-3301 www.wjpmr.com WJPMR EVALUATION OF X-RAY FINDINGS ALONG WITH MAGNETIC
Ligamentous Integrity in Spinal Cord Injury without Radiographic Abnormality. Dr Anria Horn Dr Stewart Dix-Peek
 Ligamentous Integrity in Spinal Cord Injury without Radiographic Abnormality Dr Anria Horn Dr Stewart Dix-Peek Introduction Spinal Cord Injury Without Radiographic Abnormality SCIWORA Pang, Wilberger 1982
Ligamentous Integrity in Spinal Cord Injury without Radiographic Abnormality Dr Anria Horn Dr Stewart Dix-Peek Introduction Spinal Cord Injury Without Radiographic Abnormality SCIWORA Pang, Wilberger 1982
SPINAL PSEUDOARTHROSIS
 485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
485 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE NO. 3 SPINL PSEUDORTHROSIS COMPLICTION OF NKYLOSING SPONDYLITIS WILLIM MRTEL Fracture of the cervical spine is a recognized complication of advanced ankylosing spondylitis ( 1 ).
Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
 THE VALUE OF CORONAL IMAGE IN DETECTING EXTRA SPINAL LESION IN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF THE SPINE Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
THE VALUE OF CORONAL IMAGE IN DETECTING EXTRA SPINAL LESION IN MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING OF THE SPINE Ibtisam Nasir Ahmed. MBChB. DMRD. Specialist Radiological Diagnosis. Al-sadr Teaching Hospital. Basrah-Iraq.
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN
 PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN DR.JANANI SANKAR SENIOR CONSULTANT - PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS & PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDICS KANCHI KAMAKOTI CHILDS TRUST HOSPITAL CHENNAI,
PITFALLS IN THE DIAGNOSIS OF SKELETAL TUBERCULOSIS IN CHILDREN DR.JANANI SANKAR SENIOR CONSULTANT - PEDIATRICS DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS & PEDIATRIC ORTHOPEDICS KANCHI KAMAKOTI CHILDS TRUST HOSPITAL CHENNAI,
Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients
 Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Original Article J Nepal Health Res Counc 2015 Sep - Dec;13(31):196-200 Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings in Degenerative Disc Disease of Cervical Spine in Symptomatic Patients Karki DB, 1 Gurung G,
Osteo-articular TB in Children
 Osteo-articular TB in Children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, Cape Town, South Africa Questions Spinal TB is the most common
Osteo-articular TB in Children H Simon Schaaf Desmond Tutu TB Centre, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, Stellenbosch University, Cape Town, South Africa Questions Spinal TB is the most common
Properties of Purdue. Anatomy. Positioning AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS 11/30/2018
 AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
AXIAL SKELETAL RADIOLOGY FOR PRIVATE PRACTITIONERS Anatomy Complex Text book is needed Species Contrast Positioning Painful/ non cooperative Sedation General anesthesia Species Contrast 1 Slightly oblique
MRI assessment of vertebral fractures identified by conventional radiography in osteoporotic patients: a preliminary study
 MRI assessment of vertebral fractures identified by conventional radiography in osteoporotic patients: a preliminary study Poster No.: C-1405 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Argirò,
MRI assessment of vertebral fractures identified by conventional radiography in osteoporotic patients: a preliminary study Poster No.: C-1405 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: R. Argirò,
Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment
 Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. G. Trigo,
Tuberculosis afeccting the central nervous sistem and spine: CT and MR imaging implications for diagnosis and treatment Poster No.: C-1854 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. G. Trigo,
Pott s kyphosis. University Affiliated Sixth People s Hospital, 600 Yishan Road, Shanghai , P.
 QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
QJM Advance Access published November 17, 2014 Pott s kyphosis Author Names: Yi Zhang, Yong-Sheng Yu, Zheng-Hao Tang and Guo-Qing Zang Author Affiliations: Department of Infectious Diseases, Shanghai Jiao
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES
 APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Neck Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Updated June, 2017 Contents
APPROPRIATE USE GUIDELINES Appropriateness of Advanced Imaging Procedures (MRI, CT, Bone Scan/PET) in Patients with Neck Pain CDI QUALITY INSTITUTE: PROVIDER LED ENTITY (PLE) Updated June, 2017 Contents
FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY NATIONAL COVERAGE DETERMINATION (NCD) FOR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING:
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines BONE MARROW MRI Original Date: July 2008 Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 77084 Last Review Date: September 2014 NCD 220.2 MRI Last Effective Date: July 2011
Spinal tuberculosis in adults: A study of 87 cases in Northwestern Nigeria
 Neurology Asia 2010; 15(3) : 239 244 Spinal tuberculosis in adults: A study of 87 cases in Northwestern Nigeria LF Owolabi, **MM Nagoda, AA Samaila, I Aliyu Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital (AKTH), Kano; *Murtala
Neurology Asia 2010; 15(3) : 239 244 Spinal tuberculosis in adults: A study of 87 cases in Northwestern Nigeria LF Owolabi, **MM Nagoda, AA Samaila, I Aliyu Aminu Kano Teaching Hospital (AKTH), Kano; *Murtala
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam
 Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
Upper Cervical Spine - Occult Injury and Trigger for CT Exam Main Menu Introduction Clinical clearance of C-SpineC Radiographic evaluation Norms for C-spineC Triggers for CT exam: Odontoid Lateral view
JMSCR Vol 05 Issue 06 Page June 2017
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor 5.84 Index Copernicus Value: 83.27 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v5i6.29 MRI in Clinically Suspected Uterine and
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT
 SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
SUBAXIAL CERVICAL SPINE TRAUMA- DIAGNOSIS AND MANAGEMENT 1 Anatomy 3 columns- Anterior, middle and Posterior Anterior- ALL, Anterior 2/3 rd body & disc. Middle- Posterior 1/3 rd of body & disc, PLL Posterior-
Fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine and thoracolumbar transition
 Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
Most spinal column injuries occur in the thoracolumbar transition, the area between the lower thoracic spine and the upper lumbar spine; over half of all vertebral fractures involve the 12 th thoracic
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: September 1997 THORACIC SPINE CT Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 72128, 72129, 72130 Last Review Date: May 2013 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_043
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: September 1997 THORACIC SPINE CT Page 1 of 5 CPT Codes: 72128, 72129, 72130 Last Review Date: May 2013 Guideline Number: NIA_CG_043
Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity. Department of Spine, General Hospital of Lanzhou Command, Gansu, China
 Int Surg 2017;102:171 177 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-15-00051.1 Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity Xu Lan, Jian-Zhong Xu, Xue-Mei Liu, Bao-Feng Ge Department of Spine,
Int Surg 2017;102:171 177 DOI: 10.9738/INTSURG-D-15-00051.1 Surgical Treatment of Lower Cervical Tuberculosis With Kyphosis Deformity Xu Lan, Jian-Zhong Xu, Xue-Mei Liu, Bao-Feng Ge Department of Spine,
Imaging in neurofibromatosis type 1: An original research article with focus on spinal lesions
 Original Research Article Imaging in neurofibromatosis type 1: An original research article with focus on spinal lesions Kalpesh Patel 1*, Siddharth Zala 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 1
Original Research Article Imaging in neurofibromatosis type 1: An original research article with focus on spinal lesions Kalpesh Patel 1*, Siddharth Zala 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Assistant Professor, 2 1
Departement of Neurosurgery A.O.R.N A. Cardarelli- Naples.
 Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Percutaneous posterior pedicle screw fixation in the treatment of thoracic, lumbar and thoraco-lumbar junction (T12-L1) traumatic and pathological spine fractures. Report of 45 cases. G. Vitale, A. Punzo,
Ross JS, Brant-Zawadzki M, et al. Diagnostic Imaging: Spine 2004; V-1-5. Greenspan A. Orthopedic Radiology: A Practical Approach 1997; V-19-3
 MR Imaging of Spinal Infections 台大醫院 台大醫學院 影像醫學部 放射線科 許昭禹醫師 / 施庭芳主任 2009/02/14 Risk factors of spinal infections Advanced age > 50 Intravenous drug abuse Immunosuppression or immune deficiency Long-term
MR Imaging of Spinal Infections 台大醫院 台大醫學院 影像醫學部 放射線科 許昭禹醫師 / 施庭芳主任 2009/02/14 Risk factors of spinal infections Advanced age > 50 Intravenous drug abuse Immunosuppression or immune deficiency Long-term
SpineFAQs. Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment
 SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
SpineFAQs Neck Pain Diagnosis and Treatment Neck pain is a common reason people visit their doctor. Neck pain typically doesn't start from a single injury. Instead, the problem usually develops over time
Revised Dec Spine MR Protocols
 Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
Spine MR Protocols Sp 1: Cervical spine MRI without contrast Sp 2: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI Sp 3: Pre- and post-contrast cervical spine MRI (multiple sclerosis protocol) Sp 4: Thoracic
University of Groningen. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria
 University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
University of Groningen Thoracolumbar spinal fractures Leferink, Vincentius Johannes Maria IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist. Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation
 Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
Hidayatullah Hamidi. MD Consultant Radiologist Lumbar Spine MR Imaging Interpretation 13/12/2018 Presenter Hidayatullah Hamidi Consultant Radiologist, Radiology PGME program director, FMIC, Kabul, Afghanistan
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
Gillian Wooldridge, DO Houston Methodist Willowbrook Hospital Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellowship May 3, 2018
 Gillian Wooldridge, DO Houston Methodist Willowbrook Hospital Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellowship May 3, 2018 Disclosures Neither I nor any family members have financial disclosures Special thanks
Gillian Wooldridge, DO Houston Methodist Willowbrook Hospital Primary Care Sports Medicine Fellowship May 3, 2018 Disclosures Neither I nor any family members have financial disclosures Special thanks
Epidemiology of Low back pain
 Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Low Back Pain Definition Pain felt in your lower back may come from the spine, muscles, nerves, or other structures in that region. It may also radiate from other areas like the mid or upper back, a inguinal
Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR
 National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
National Imaging Associates, Inc. Clinical guidelines Original Date: October 2015 LUMBAR SPINAL FUSION FOR Page 1 of 9 INSTABILITY AND DEGENERATIVE DISC CONDITIONS FOR CMS (MEDICARE) MEMBERS ONLY CPT4
BJMHR British Journal of Medical and Health Research Journal home page:
 RESEARCH ARTICLE Br J Med Health Res. 2016;3(12) ISSN: 2394-2967 BJMHR British Journal of Medical and Health Research Journal home page: www.bjmhr.com Spinal Stabilization for early mobilization in Pott's
RESEARCH ARTICLE Br J Med Health Res. 2016;3(12) ISSN: 2394-2967 BJMHR British Journal of Medical and Health Research Journal home page: www.bjmhr.com Spinal Stabilization for early mobilization in Pott's
CALCULATION OF CANAL/BODY RATIO FOR LUMBAR SPINAL CANAL IN DRIED VERTEBRAE IN GUJARAT.
 CALCULATION OF CANAL/BODY RATIO FOR LUMBAR SPINAL CANAL IN DRIED VERTEBRAE IN GUJARAT. Author(s): Kanani SD, Nirvan AB, Patel JP, Shah RK, Dave RV Kanani SD, Nirvan AB*, Patel JP**, Shah RK***, Dave RV
CALCULATION OF CANAL/BODY RATIO FOR LUMBAR SPINAL CANAL IN DRIED VERTEBRAE IN GUJARAT. Author(s): Kanani SD, Nirvan AB, Patel JP, Shah RK, Dave RV Kanani SD, Nirvan AB*, Patel JP**, Shah RK***, Dave RV
Magnetic resonance imaging in acute spinal trauma: Pictorial essay
 Magnetic resonance imaging in acute spinal trauma: Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1463 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Khurana 1, S. Manchanda 1, N. Rajpal 1, S. Agrawal 1, S. Gupta
Magnetic resonance imaging in acute spinal trauma: Pictorial essay Poster No.: C-1463 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Khurana 1, S. Manchanda 1, N. Rajpal 1, S. Agrawal 1, S. Gupta
MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE
 MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE Vertebrae are your friends Matthew Harper MS-IV LECTURE OBJECTIVES INTRODUCE THE MOST COMMON MODALITIES OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND BASIC TECHNIQUES FOR READING THESE IMAGES
MEDICAL IMAGING OF THE VERTEBRAE Vertebrae are your friends Matthew Harper MS-IV LECTURE OBJECTIVES INTRODUCE THE MOST COMMON MODALITIES OF MEDICAL IMAGING AND BASIC TECHNIQUES FOR READING THESE IMAGES
Utility of Dual-Energy CT to Evaluate Patients with Hip and Pelvis Pain in the ER Setting
 Utility of Dual-Energy CT to Evaluate Patients with Hip and Pelvis Pain in the ER Setting Johnson, T., Moran, E., Glazebrook, K., Leng, S., Fletcher, J., and McCollough, C. An educational review ER011
Utility of Dual-Energy CT to Evaluate Patients with Hip and Pelvis Pain in the ER Setting Johnson, T., Moran, E., Glazebrook, K., Leng, S., Fletcher, J., and McCollough, C. An educational review ER011
Metastatic Spinal Disease
 Metastatic Spinal Disease Mr Neil Chiverton Consultant Spinal Surgeon, Sheffield Objectives The scale and nature of the problem NICE recommendations Surgical decision making Case illustrations Incidence
Metastatic Spinal Disease Mr Neil Chiverton Consultant Spinal Surgeon, Sheffield Objectives The scale and nature of the problem NICE recommendations Surgical decision making Case illustrations Incidence
Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache
 Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache Narayan Bikram Thapa 1, Suraj Bajracharya 2 1 Department of Radiology, KIST Medial College Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur,
Original Article Magnetic resonance imaging findings in patients with low backache Narayan Bikram Thapa 1, Suraj Bajracharya 2 1 Department of Radiology, KIST Medial College Teaching Hospital, Lalitpur,
Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS AND PAIN
 Cox Technic Case Report #100 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent October 2011 on 10/11/11 ) 1 Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS
Cox Technic Case Report #100 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent October 2011 on 10/11/11 ) 1 Case Report: CASE REPORT OF FACET ARTHROPATHY INDUCED NERVE ROOT COMPRESSION RESULTING IN MOTOR WEAKNESS
Role of MRI in the Evaluation of Compressive Myelopathy
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 21-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of MRI in the Evaluation of Compressive
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 15, Issue 4 Ver. XIII (Apr. 2016), PP 21-26 www.iosrjournals.org Role of MRI in the Evaluation of Compressive
Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications
 Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications Poster No.: C-1536 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Veselova, V. Mazaev, M. Molodtsov; Moscow/RU Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Diagnostics of Spondylodiscitis and its most frequent complications Poster No.: C-1536 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Veselova, V. Mazaev, M. Molodtsov; Moscow/RU Keywords: Musculoskeletal
Candida Spondylitis: Comparison of MRI Findings With Bacterial and Tuberculous Causes
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI of Candida Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Sheen-Woo Lee 1 Sang Hoon Lee 2 Hye Won Chung 2 Min Jee Kim 3 Min Jeong Seo 4 Myung
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Lee et al. MRI of Candida Spondylitis Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Sheen-Woo Lee 1 Sang Hoon Lee 2 Hye Won Chung 2 Min Jee Kim 3 Min Jeong Seo 4 Myung
Sue Greenhalgh Consultant Physiotherapist March 18th
 Sue Greenhalgh Consultant Physiotherapist March 18th Caused by the Myobacterium Tuberculosis well known to Hippocrates Sir Percival Pott gave a very good description of the disease in 1779 Consumption
Sue Greenhalgh Consultant Physiotherapist March 18th Caused by the Myobacterium Tuberculosis well known to Hippocrates Sir Percival Pott gave a very good description of the disease in 1779 Consumption
Tubercular spinal epidural abscess involving the dorsal-lumbar-sacral region without osseous involvement
 Case Report Tubercular spinal epidural abscess involving the dorsal-lumbar-sacral region without osseous involvement Sumit Arora 1 and Ramesh Kumar 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Maulana Azad Medical
Case Report Tubercular spinal epidural abscess involving the dorsal-lumbar-sacral region without osseous involvement Sumit Arora 1 and Ramesh Kumar 2 1 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Maulana Azad Medical
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics. Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003
 Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Spinal Cord Injuries: The Basics Kadre Sneddon POS Rounds October 1, 2003 Anatomy Dorsal columntouch, vibration Corticospinal tract- UMN Anterior horn-lmn Spinothalamic tractpain, temperature (contralateral)
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberclous Spondylitis and Pyogenic Spondylitis in Atypical Cases
 Asian Spine Journal Vol. 1, No. 2, pp 75~79, 2007 Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberclous Spondylitis and Pyogenic Spondylitis in Atypical Cases Jae Sung Ahn, June Kyu Lee Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
Asian Spine Journal Vol. 1, No. 2, pp 75~79, 2007 Diagnosis and Treatment of Tuberclous Spondylitis and Pyogenic Spondylitis in Atypical Cases Jae Sung Ahn, June Kyu Lee Department of Orthopedic Surgery,
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 1, 2017,
 International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 1, 2017, 191 198 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) EVALUATION OF RADIOLOGICAL FINDINGS OF DOGS WITH THORACOLUMBAR DISORDERS Thanigaivel
International Journal of Science, Environment and Technology, Vol. 6, No 1, 2017, 191 198 ISSN 2278-3687 (O) 2277-663X (P) EVALUATION OF RADIOLOGICAL FINDINGS OF DOGS WITH THORACOLUMBAR DISORDERS Thanigaivel
Spinal Trauma: Imaging, Diagnosis, And Management READ ONLINE
 Spinal Trauma: Imaging, Diagnosis, And Management READ ONLINE Jul 22, 2013 Thoracic Spinal Trauma Imaging. who have sustained thoracic spinal trauma is to for the diagnosis of a thoracic spinal fracture
Spinal Trauma: Imaging, Diagnosis, And Management READ ONLINE Jul 22, 2013 Thoracic Spinal Trauma Imaging. who have sustained thoracic spinal trauma is to for the diagnosis of a thoracic spinal fracture
Chance Fracture Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Chance Fracture Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/02/2010 History Restrained teenager involved in motor vehicle accident. Diagnosis Chance Fracture (Hyperflexion-Distraction Injury) Discussion Chance-type spinal
Chance Fracture Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/02/2010 History Restrained teenager involved in motor vehicle accident. Diagnosis Chance Fracture (Hyperflexion-Distraction Injury) Discussion Chance-type spinal
Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Differentatial Diagnosis of Pyogenic Spondylodiscitis and Tuberculous Spondylodiscitis
 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 71-87 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.899606 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.05.17 Accepted: 2016.05.25 Published: 2017.02.10 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: 71-87 DOI: 10.12659/PJR.899606 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Received: 2016.05.17 Accepted: 2016.05.25 Published: 2017.02.10 Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection
Case SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra
 Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Case 15428 SCIWORA in patient with congenital block vertebra Lucas Walgrave 1, Charlotte Vanhoenacker 1-2, Thomas Golinvaux 3, Filip Vanhoenacker3-5 1: Leuven University Hospital, Department of Radiology,
Clinico-Mri Correlation of Compressive Myelopathy (Retrospective Study)
 2015; 1(7): 60-64 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2015; 1(7): 60-64 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 18-04-2015 Accepted: 16-05-2015 Sreeramulu Diguvinti Associate
2015; 1(7): 60-64 ISSN Print: 2394-7500 ISSN Online: 2394-5869 Impact Factor: 5.2 IJAR 2015; 1(7): 60-64 www.allresearchjournal.com Received: 18-04-2015 Accepted: 16-05-2015 Sreeramulu Diguvinti Associate
PhD THESIS -SUMMARY-
 The University of Medicine and Pharmacy from Craiova The Doctoral School PhD THESIS The contribution of imaging in spine injuries -SUMMARY- Scientific, Professor Andrei Bondari PhD, Manea Rosana-Mihaela
The University of Medicine and Pharmacy from Craiova The Doctoral School PhD THESIS The contribution of imaging in spine injuries -SUMMARY- Scientific, Professor Andrei Bondari PhD, Manea Rosana-Mihaela
Symptomatic Multiple Level Lateral Meningoceles with Intraspinal Meningocele: A Case Study and Its Surgical Management
 THIEME Original Article 15 Symptomatic Multiple Level Lateral Meningoceles with Intraspinal Meningocele: A Case Study and Its Surgical Management Vernon Velho 1 Sachin Guthe 1 Pravin Survashe 1 Poonam
THIEME Original Article 15 Symptomatic Multiple Level Lateral Meningoceles with Intraspinal Meningocele: A Case Study and Its Surgical Management Vernon Velho 1 Sachin Guthe 1 Pravin Survashe 1 Poonam
Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 1:948 953, May Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Offers No Advantage over Routine Noncontrast MR Imaging in the Detection of Vertebral Metastases Mauricio Castillo, Andres Arbelaez, J.
Index. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adolescent athlete, anatomy and biomechanics of spine of, 424 425 back pain in. See Back pain, in pediatric and adolescent athlete. injury
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Adolescent athlete, anatomy and biomechanics of spine of, 424 425 back pain in. See Back pain, in pediatric and adolescent athlete. injury
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect!
 MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
MR imaging the post operative spine - What to expect! Poster No.: C-2334 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Jain, M. Paravasthu, M. Bhojak, K. Das ; Warrington/UK, 1 1 1 2 1 2 Liverpool/UK
Objectives. Comprehension of the common spine disorder
 Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Objectives Comprehension of the common spine disorder Disc degeneration/hernia Spinal stenosis Common spinal deformity (Spondylolisthesis, Scoliosis) Osteoporotic fracture Destructive spinal lesions Anatomy
Case Conference: SBRT for spinal metastases D A N I E L S I M P S O N M D 3 / 2 7 / 1 2
 Case Conference: SBRT for spinal metastases D A N I E L S I M P S O N M D 3 / 2 7 / 1 2 Case 79 yo M with hx of T3N0 colon cancer diagnosed in 2008 metastatic liver disease s/p liver segmentectomy 2009
Case Conference: SBRT for spinal metastases D A N I E L S I M P S O N M D 3 / 2 7 / 1 2 Case 79 yo M with hx of T3N0 colon cancer diagnosed in 2008 metastatic liver disease s/p liver segmentectomy 2009
Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at (sent 5/9/17) 1
 Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 5/9/17) 1 Management of Lumbar Radiculopathy Associated with an Extruded L4 L5 disc and concurrent L5 S1 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
Cox Technic Case Report #169 published at www.coxtechnic.com (sent 5/9/17) 1 Management of Lumbar Radiculopathy Associated with an Extruded L4 L5 disc and concurrent L5 S1 Spondylolytic Spondylolisthesis
Case Report Multicentric Spinal Tuberculosis with Sternoclavicular Joint Involvement: A Rare Presentation
 Case Reports in Pulmonology, Article ID 685406, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/685406 Case Report Multicentric Spinal Tuberculosis with Sternoclavicular Joint Involvement: A Rare Presentation Balaji
Case Reports in Pulmonology, Article ID 685406, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/685406 Case Report Multicentric Spinal Tuberculosis with Sternoclavicular Joint Involvement: A Rare Presentation Balaji
JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS
 JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING INTRODUCTION: In accordance with the Victorian Radiation Act 2005 Wodonga Medical Imaging,
JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING ALBURY WODONGA HEALTH WODONGA CAMPUS JUSTIFICATION PROTOCOLS FOR CT SCANNING INTRODUCTION: In accordance with the Victorian Radiation Act 2005 Wodonga Medical Imaging,
Original article: Multidetector computed tomographic evaluation of cervical spine trauma
 Original article: Multidetector computed tomographic evaluation of cervical spine trauma 1Sajid Ansari *, 2 R.K. Rauniyar, 3 Kaleem Ahmad, 4 Mukesh Kumar Gupta 1Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article: Multidetector computed tomographic evaluation of cervical spine trauma 1Sajid Ansari *, 2 R.K. Rauniyar, 3 Kaleem Ahmad, 4 Mukesh Kumar Gupta 1Assistant Professor, Department of Radiodiagnosis,
Introduction to Neuroimaging spine. John J. McCormick MD
 Introduction to Neuroimaging spine John J. McCormick MD Neuroanatomy Netter drawings Radiographic Anatomy Cervical Spine Cervical Spine Oblique View Cervical Spine Dens View Thoracic Spine Lumbar Spine
Introduction to Neuroimaging spine John J. McCormick MD Neuroanatomy Netter drawings Radiographic Anatomy Cervical Spine Cervical Spine Oblique View Cervical Spine Dens View Thoracic Spine Lumbar Spine
Neck Pain: Help! Eric M. Massicotte, MD, MSc, MBA, FRCSC Associate Professor University of Toronto
 Neck Pain: Help! Eric M. Massicotte, MD, MSc, MBA, FRCSC Associate Professor University of Toronto Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied,
Neck Pain: Help! Eric M. Massicotte, MD, MSc, MBA, FRCSC Associate Professor University of Toronto Copyright 2017 by Sea Courses Inc. All rights reserved. No part of this document may be reproduced, copied,
Spinal injury is very common in Ireland: 19 per 100,000 (1). It poses a significant disease burden.
 MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury: a single national spinal centre experience and study of imaging features with clinical correlation with ASIA score and outcome Poster No.: C-1235 Congress: ECR 2011
MRI in traumatic spinal cord injury: a single national spinal centre experience and study of imaging features with clinical correlation with ASIA score and outcome Poster No.: C-1235 Congress: ECR 2011
Common Disease with Uncommon Presentation: Multifocal Tuberculosis
 JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2016;6(4):503-507 Common Disease with Uncommon Presentation: Multifocal Tuberculosis Tarun Bali 1, Malhar N Kumar 2, Santosh Saklecha 3 Department of Orthopaedics, East Point Medical
JOURNAL OF CASE REPORTS 2016;6(4):503-507 Common Disease with Uncommon Presentation: Multifocal Tuberculosis Tarun Bali 1, Malhar N Kumar 2, Santosh Saklecha 3 Department of Orthopaedics, East Point Medical
Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis
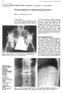 206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
206 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1994; 53: 206-210 CASE STUDIES IN DIAGNOSTIC IMAGING Series Editor: V C Cassar-Pullicino* Pseudoarthrosis in ankylosing spondylitis Wilfred C G Peh, Keith D K Luk Clinical
