Primary Renal Candidiasis
|
|
|
- Trevor Rodgers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Case Series Primary Renal Candidiasis Importance of Imaging and Clinical History in Diagnosis and Management Barry J. Sadegi, MD, Bhargavi K. Patel, MD, Andrew C. Wilbur, MD, Anil Khosla, MD, Ejaz Shamim, MD Objective. Primary renal candidiasis is rare but increasing in incidence. The purpose of this series is to provide imaging and clinical findings for diagnosing candidiasis and to discuss imaging in the management of this disease. Methods. Ten sonographic, 8 retrograde pyelographic, 2 intravenous pyelographic, 2 antegrade pyelographic, and 2 computed tomographic examinations of 5 patients (4 adult male patients and 1 16-year-old female patient) were reviewed. Results. The clinical presentation was variable. Sonography showed renal pelvic wall thickening (n = 5), echogenic debris (n = 4), and fungus balls (n = 2). Papillary necrosis (n = 4), filling defects due to debris (n = 3), and fungus balls (n = 2) were seen on retrograde pyelography. Conclusions. Untreated candidiasis may progress to fungus ball or abscess formation. Sonography is commonly used as the initial imaging procedure. Retrograde and antegrade pyelography are used for biopsy, diagnosis, and treatment. Awareness of this condition and knowledgeable imaging evaluation can help detect and define the site, infection severity, and subsequent therapy. Key words: fungus ball; papillary necrosis; pyelography; renal candidiasis; sonography. Abbreviations CT, computed tomography; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus Received October 17, 2008, from the Department of Radiology, University of Illinois, Chicago, Illinois USA (B.J.S., B.K.P., A.C.W., E.S.); and Veterans Administration Medical Center, John Cochran Division, St Louis, Missouri USA (A.K.). Revision requested December 1, Revised manuscript accepted for publication December 22, Address correspondence and to Bhargavi K. Patel, MD, Department of Radiology, University of Illinois, 1740 W Taylor St, M-C 931, Room 2483, Chicago, IL USA. Primary renal candidiasis is an invasive infection of the upper urinary tract that involves the renal pelvis and medulla. Although rare, it is increasing in incidence. 1,2 The risk for developing primary renal candidiasis (primary Candida pyelonephritis) is increased after urinary tract surgery or when host defenses are compromised because of diabetes, prior antibiotics, malignancy, or immunosuppressive therapy. 1,3,4 Inconsistencies remain in the diagnosis of primary renal candidiasis because patients usually have variable clinical presentations or have no systemic signs and symptoms of infection, unlike patients with renal candidiasis secondary to disseminated infection. 1,3 5 Sonography is commonly performed as the initial imaging modality. Retrograde and antegrade pyelography are useful for biopsy, diagnosis, and therapy during the course of patient treatment. Because untreated disease may gradually progress to fungus ball (mycetoma) or abscess formation, appropriate imaging at the outset may result in 2009 by the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28: /09/$3.50
2 Primary Renal Candidiasis earlier treatment and prevent these complications and the resulting need for surgical or other invasive intervention. In the literature, the few published reports on primary renal candidiasis describe imaging findings in neonates, children, and female patients. This series describes the imaging features on sonography, retrograde pyelography, intravenous pyelography, antegrade pyelography, and computed tomography (CT) in 5 patients, including 4 adult men, with histologically proven primary urinary tract candidiasis. Materials and Methods Ten sonographic, 8 retrograde pyelographic, 2 intravenous pyelographic, 2 antegrade pyelographic, and 2 CT examinations of 5 patients (4 adult male patients and 1 16-year-old female patient) with the diagnosis of primary renal candidiasis during an approximately 5-year period were retrospectively reviewed (Table 1). Imaging findings were correlated with the clinical histories, laboratory values, blood culture results, urinalysis results, and urine culture results. Retrograde and antegrade pyelography were performed to allow urinary drainage, to extract debris and fungus balls for tissue biopsies and treatment, and to locally instill antifungal medications. Longitudinal and transverse sonography and color Doppler sonography were performed with 5- to 2-MHz transducers. Oblique and coronal views and magnification were used to better visualize findings. The diagnosis of primary renal candidiasis was confirmed by histopathologic analysis of specimens obtained from urinary debris or fungus balls within the renal pelvis during ureteroscopy in 4 patients and urinalysis in 1. Results Four adult male patients between 54 and 68 years underwent renal sonography and retrograde pyelography; 2 had intravenous excretory pyelography; 2 had antegrade pyelography and nephrostomy; and 2 had contrast-enhanced CT (Table 2). A 16-year-old female patient had renal sonography. Sonography showed pyelocalyceal uroepithelial wall thickening (n = 5; Figures 1, 2A, 3A, and 4), debris in the calyces and renal pelvis (n = 4; Figures 2B, 3B, and 5A), avascular fungus balls in the renal pelvis (n = 2; Figure 3, B and C), and loss of corticomedullary differentiation and papillitis (n = 4; Figures 2A, 3A, and 5A and Table 2). Color and power Doppler (n = 3) studies showed diffuse increased vascularity in the renal sinus and peripelvic region (n = 2; Figures 1 and 3B). Retrograde pyelography showed papillary necrosis (n = 4; Figure 2C), a filling defect in calyces and the renal pelvis (n = 4; Figure 2C), and a filling defect due to large fungus ball masses (n = 2; Table 2). Antegrade nephrostogaphy showed a molded filling defect due to fungus masses (n = 2; Figure 3D). Excretory pyelography showed papillary necrosis and a filling defect due to debris (n = 2; Figure 5B). Computed tomography showed Table 1. Clinical Features and Imaging Procedures in 5 Patients With Primary Renal Candidiasis Age, Clinical Imaging Procedures Case y/sex Risk Factors Presentations Urinalysis Performed 1 66/M DM, TURP, UTI, antibiotics Fever, flank pain C albicans Sonography, intravenous pyelography, retrograde pyelography 2 68/M DM, postoperative rectal CA, Fever, flank pain, C albicans, Sonography, CT, retrograde pyelography, pelvic abscess, pneumonia, hematuria, polyuria C tropicalis antegrade nephrostomy antibiotic 3 66/M DM, AK amputation, antibiotic Flank pain, hematuria, C albicans Sonography, CT, retrograde pyelography, renal failure antegrade nephrostomy 4 54/M HIV, diabetes mellitus Fever, hematuria, C albicans, Sonography, intravenous pyelography, renal failure C tropicalis retrograde pyelography 5 16/F Cerebral palsy, neurogenic Fever, flank pain C albicans Sonography bladder, frequent bladder catheterization AK indicates above-the-knee; CA, carcinoma; DM diabetes mellitus; F, female; M, male; TURP, transureteral resection of the prostate; and UTI, urinary tract infection. 508 J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
3 Sadegi et al renal medullary enhancement (n = 1) and caliectasis (n = 2; Figure 2, D and E, and Table 2). Clinically, risk factors for immunocompromise included diabetes mellitus (n = 4), antibiotic therapy (n = 3), human immunodeficiency virus (HIV; n = 1), colon carcinoma (n = 1), transurethral prostatectomy (n = 1), and a neurogenic urinary bladder (n = 1; Table 3). The clinical presentations included fever (n = 4), painless hematuria (n = 3), flank pain (n = 4), and acute renal failure (n = 2; Table 1). All patients had candiduria and negative blood culture results for Candida albicans. Specimens obtained from the renal pelvis in the 4 adult male patients (tissue and debris) showed inflammatory and necrotic material with C albicans in all 4 cases (Figure 3E) and Candida tropicalis in 2 cases. Discussion Asymptomatic Candida colonization of the urine is common and increasingly detected in hospitalized patients. Invasive primary urinary tract infection with Candida is rare unless host defenses are weakened. 1,5 In our series, associated medical and immunocompromise risks included diabetes mellitus, recent antibiotic therapy, HIV, colon cancer, and previous prostate surgery (Table 3). Primary renal candidiasis should be suspected in immunocompromised patients with persistent candiduria and abnormal renal imaging findings. The filamentous form of Candida can cause ascending invasive infection with a predilection for urinary drainage structures when the opportunity arises. 4 6 It is characterized by a subacute or chronic clinical course and the absence of fungemia. It is associated with a superficial mat of fungal growth (uroepithelial thrush) on pyelocalyceal mucosa, vasculitis, and the presence of pseudohyphae in the interstitium and results in invasive inflammatory changes. 6 This leads to sloughing of tissue and debris formation. Mycelia form clumps over inflammatory necrotic debris and form fungus balls. 3,4,6 Systemic candidiasis is an acute hematogenous infection, which predominantly involves the cortex and medulla with microabscess formation. 5,6 It is associated with involvement of other organs, commonly the heart, and fungemia is present. Table 2. Imaging Findings in 5 Patients With Primary Renal Candidiasis Imaging Finding Patients, n Sonography (n = 5) Wall thickening of renal pelvis and calyces 5 Caliectasis and echogenic debris 4 Loss of the corticomedullary differentiation, papillitis 4 Hydronephrosis 2 Fungus ball in renal pelvis 2 Retrograde pyelography (n = 4) Papillary necrosis, irregular calyces 4 Caliectasis 4 Calyceal filling defects 3 Hydronephrosis 2 Large molded filling defect in the renal pelvis 2 Intravenous pyelography (n = 2) Irregular calyces and blunting of the fornices 2 Caliectasis 2 Calyceal filling defects 2 Hydronephrosis 1 Large filling defect in the renal pelvis 1 Antegrade nephrostomy (n = 2) Caliectasis and papillary necrosis 2 Filling defect due to fungus ball 2 Hydronephrosis 2 Contrast-enhanced CT (n = 2) Caliectasis 2 Irregular medullary enhancement 1 Figure 1. Image from a 66-year-old male patient with diabetes mellitus and recent antibiotic therapy for a urinary tract infection after transurethral prostatectomy who had flank pain and fever. Transverse color Doppler sonography of the left kidney shows wall thickening and increased vascularity (long arrow) of the renal pelvis. A thin hyperechoic line at the mucosa (short arrow), a thick hypoechoic layer at the submucosa, and a thick hyperechoic muscularis outer layer (arrowhead) of the renal pelvis are shown. J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
4 Primary Renal Candidiasis A Renal abscess formation is more likely to occur than renal fungus ball formation. The clinical diagnosis of primary renal candidiasis or primary Candida pyelonephritis is usually difficult because of variable clinical presenting features and the presence of associated diseases and because affected patients usually lack systemic signs and symptoms. 7 9 The clinical presentations in our series were variable: 4 patients had fever; 4 flank pain or pain; 3 had painless B C Figure 2. Images from a 68-year-old male patient with diabetes mellitus, rectal carcinoma, and recent antibiotic therapy for urinary tract infection who had flank pain, fever, and acute renal failure. A, Transverse sonography of the right kidney shows layered wall thickening of the renal pelvis. A thin hyperechoic line at the mucosa (short arrow), a hypoechoic layer at the submucosa, and a deeper thick hyperechoic layer (arrowhead) are shown. Loss of corticomedullary differentiation and hypoechoic pyramids (long arrow) are visible. B, Longitudinal sonography of the right kidney shows echogenic debris (long arrow) within the mildly dilated and irregular calyces (short arrows). C, Right retrograde pyelography shows filling defects within the mildly dilated and irregular calyces (arrow) due to debris. Papillary necrosis (arrowheads) is shown. D, Contrast-enhanced CT shows enlargement of the right kidney and irregular medullary enhancement (arrows). E, Delayed phase CT shows bilateral caliactasis (arrows). D E 510 J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
5 Sadegi et al hematuria; and 2 had acute renal failure. C albicans was present in urine but not in blood cultures in all 5 patients. Urine cultures are nonspecific because the number of fungal Figure 3. Images from a 66-year-old male patient with diabetes mellitus, left above-the-knee amputation, and recent antibiotic therapy who had gross hematuria. A, Sonography of the right kidney shows layered wall thickening of a dilated calyx. A thin hyperechoic line at the mucosa (arrow), a hypoechoic layer at the submucosa, and a thick outer hyperechoic layer (arrowhead) are shown. B, Transverse power Doppler sonography at the midrenal area shows an avascular echogenic fungus mass (arrow) in the renal pelvis and extending into the calyx, mild hydronephrosis, and vessels (arrowheads) in the peripelvic area. C, Transverse oblique sonography of the right kidney (short arrows) with magnification and focusing in the renal pelvis at 3 weeks follow-up for persistent symptoms shows a large obstructing echogenic mass (long arrows) of a fungal ball formation, resulting in dilatation of the renal pelvis (curved arrows) and a dilated calyx (arrowhead). D, Antegrade nephropyelography via percutaneous nephrostomy (long thin arrow) confirms the presence of a large, irregular filling defect due to a fungus ball (thick arrows) in the renal pelvis and calyces. E, Histopathologic examination of tissue obtained from a biopsy specimen of a fungus ball in the renal pelvis shows budding septated hyphae of C albicans (arrowheads) and necrotic and inflammatory material (arrows). colonies does not differentiate asymptomatic colonization from infection of the bladder or kidney. 1,8 Clinically, the problem that arises is whether substantial candiduria requiring treatment is present. 8,9 Safdar et al 10 reported candiduria in about 11% of renal transplant patients. 11 In high-risk patients who have candiduria but do not have invasive infection, there is reportedly no increased benefit from treating the candiduria alone Imaging allows assessment of the disease in patients with candiduria, and this assists in patient treatment and poten- C A D B E J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
6 Primary Renal Candidiasis Figure 4. Image from a 16-year-old female patient with cerebral palsy and a neurogenic urinary bladder who had fever and flank pain. Transverse sonography of the right kidney (arrowheads) shows wall thickening (curved arrow) and hyperechoic mucosa (short arrow) of the renal pelvis with echogenic debris (long arrow) within the renal pelvis. tially can favorably change the course and outcome of this disease. 1,3,11 Limitations of our observation include the small size of the series. Biopsy of tissue and urinalysis were performed for identification of Candida pseudohyphae for final diagnosis, although there was a lack of histopathologic or uroepithelial wall changes to directly correlate with our imaging findings. Because patients with primary renal candidiasis frequently have renal dysfunction, sonography is often the first radiologic examination performed. There is very little in the literature about the sonographic features of primary renal candidiasis in adult patients. 1,2,6 All sonographic studies in our series showed renal pelvic and calyceal wall thickening. A pattern of layered wall thickening consisting of an inner echogenic rim representing the damaged mucosa, a middle hypoechoic layer probably caused by submucosal edema and infiltration, and a thick hyper - echoic outer layer of muscularis may be seen. This pattern of layered wall thickening is a nonspecific sonographic finding and can be seen in other forms of pyelitis, although in our experience, it was noted in all cases. This feature of renal candidiasis may be due to invasive inflammation and vasculitis in Candida pyelonephritis. Color Doppler imaging showed increased vascularity in the peripelvic and renal sinus areas. Ureter and renal pelvis wall thickening are Figure 5. Images from a 54-year-old male patient with HIV and diabetes mellitus who had fever, hematuria, and acute renal failure. A, Longitudinal sonography of the right kidney shows mild dilatation of the renal pelvis (arrow) and calyces, papillary necrosis, irregular calyces (arrowhead), and loss of the corticomedullary region. B, Excretory intravenous pyelography shows the renal pelvis (arrow), papillary necrosis, and calyceal filling defects (arrowheads). A B 512 J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
7 Sadegi et al described as sonographic findings of ureteritis cystica, acute tuberculosis, and transitional cell neoplasms and should be clinically differentiated. 6 Loss of the sonographic corticomedullary region and papillitis, although nonspecific, were present in 3 patients. As the infection progresses, sloughed papilla from papillary necrosis serve as a nidus for fungal ball formation. 1,3,4 Echogenic debris within dilated calyces, the renal pelvis, and the ureter may be seen in early fungus ball formation. Once a fungus ball has formed, a mobile, molded echogenic, avascular mass without an acoustic shadow can be seen in the renal pelvis, often obstructing the collecting system and resulting in hydronephrosis. 3,4,12 Mobility of an intraluminal echogenic avascular mass, along with diffuse wall thickening of the renal pelvis, favors an inflammatory process over a neoplasm. Evidence of papillary necrosis, calyceal filling defects due to debris from sloughed papilla, large filling defects in the renal pelvis due to fungal ball formation, and caliectasis and hydropelvis are seen on excretory intravenous pyelography and retrograde and antegrade pyelography. 2,3,6 Papillary necrosis is most often seen with analgesic use, diabetes mellitus, and sickle cell disease. However, associated wall thickening seen on sonography and the presence of candiduria favors candidiasis. If filling defects due to debris from sloughed papilla or large filling defects in the renal pelvis due to fungal ball formation are identified, further evaluation with antegrade nephrostomy or retrograde pyelography is useful to facilitate biopsy for histopathologic diagnosis and to evaluate the extent of involvement. Antegrade nephrostomy and retrograde pyelography are frequently used to guide therapy with local amphotericin B irrigation, extraction of fungal balls, and placement of stents to relieve hydronephrosis. 1,4,8,9 Multiple debris extractions and irrigations are frequently needed after Candida has invaded into the interstitium. 1 8 A filling defect in the renal pelvis should be differentiated from a blood clot, nonopaque renal calculus, transitional cell neoplasm, or ureteritis cystica, especially in adult patients. 4,6 In our series, all adult patients had retrograde pyelography and tissue biopsies. Antegrade nephrostomies were used for urinary drainage in 2 cases with fungus balls in the renal pelvis. Table 3. Risk Factors in 5 Patients With Primary Renal Candidiasis Medical Risk Factor Although CT is typically not the first examination, it may be performed when a renal mass or renal calculus is suspected. Thickening of the renal pelvic wall and hydronephrosis may be seen on CT, although these findings were better appreciated on sonography in 2 of our cases. When there is invasion of the renal parenchyma, multiple small hypoattenuated foci representing microabscesses may be shown, as in 1 of our patients. In conclusion, primary renal candidiasis is a rare opportunistic infection with variable clinical presentations and imaging findings. Imaging findings due to renal pelvic wall uroepithelial thickening, urinary debris, papillary inflammation, and hydronephrosis are seen. Sonography is the commonly used initial imaging modality and is also used for follow-up of treatment. Although the sonographic findings are nonspecific, several suggestive findings are often present. Retrograde pyelography and antegrade nephrostomy are secondary imaging modalities used during management for obtaining tissue biopsy specimens for diagnosis, for extracting debris and fungal balls, and for local instillation of drugs and urinary drainage for obstruction in advanced disease. Familiarity with the imaging findings associated with Candida involvement of the renal collecting system plays an important role in the management of primary renal candidiasis and complications in the appropriate clinical setting. References 1. Lundstrom T, Sobel J. Nosocomial candiduria: a review. Clin Infect Dis 2001; 32: Richards MJ, Edwards JR, Culver DH, Gaynes RP. Nosocomial infections in medical intensive care units in the United States. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. Crit Care Med 1999; 27: Patients, n Diabetes mellitus 4 Recent antibiotic therapy 3 HIV 1 Colon carcinoma 1 Transurethral prostatectomy 1 Cerebral palsy, neurogenic urinary bladder 1 J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
8 Primary Renal Candidiasis 3. Gerle RD. Roentgenographic features of primary renal candidiasis: fungus ball of the renal pelvis and ureter. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med 1973; 119: Dembner AG, Pfister AC. Fungal infections of the urinary tract: demonstration by antegrade pyelography and drainage by percutaneous nephrostomy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1977; 129: Fisher JF, Chew WH, Shadomy S, Duma RJ, Mayhall CG, House WC. Urinary tract infections due to Candida albicans. Rev Infect Dis 1982; 4: Pollack HM. Clinical Urography: An Atlas and Textbook of Urological Imaging. Vol I. Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders Co; Ang BS, Telenti A, King B, Steckelberg JM, Wilson WR. Candidemia from a urinary tract source: microbiological aspects and clinical significance. Clin Infect Dis 1993; 17: Kauffman CA, Vazquez JA, Sobel JD, et al. Prospective multicenter surveillance study of funguria in hospitalized patients. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) Mycoses Study Group. Clin Infect Dis 2000; 30: Sobel JD, Kauffman CA, McKinsey D et al. Candiduria: a randomized, double blind study of treatment with fluconazole and placebo. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases (NIAID) Mycoses Study Group. Clin Infect Dis 2000; 30: Safdar N, Slattery WR, Knasinski V, et al. Predictors and outcomes of candiduria in renal transplant recipients. Clin Infect Dis 2005; 40: Matignon M, Botterel F, Audard V, et al. Outcome of renal transplantation in eight patients with Candida sp. contamination of preservation fluid. Am J Transplant 2008; 8: Patel B, Khosla A, Chenoweth J. Bilateral fungal bezoars in the renal pelvis. Br J Urol 1996; 78: J Ultrasound Med 2009; 28:
Candida Bezoars with Urinary Tract Obstruction in Two Women without Immunocompromising Conditions
 Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2011) 11, 1168 1172 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2011.119 Candida Bezoars with Urinary Tract Obstruction in Two Women without Immunocompromising Conditions
Case Study TheScientificWorldJOURNAL (2011) 11, 1168 1172 TSW Urology ISSN 1537-744X; DOI 10.1100/tsw.2011.119 Candida Bezoars with Urinary Tract Obstruction in Two Women without Immunocompromising Conditions
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen. Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university
 US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
US in non-traumatic acute abdomen Lalita, M.D. Radiologist Department of radiology Faculty of Medicine ChiangMai university Sagittal Orientation Transverse (Axial) Orientation Coronal Orientation Intercostal
Sonographic Features of Necrosed Renal Papillae Causing Hydronephrosis
 Case Series Sonographic Features of Necrosed Renal Papillae Causing Hydronephrosis S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD, Sangampalayam Vedhanayagam Kandasamy, MS, MCh, Mylsamy Arul, MS, DNB (Uro), Muniappan
Case Series Sonographic Features of Necrosed Renal Papillae Causing Hydronephrosis S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD, Sangampalayam Vedhanayagam Kandasamy, MS, MCh, Mylsamy Arul, MS, DNB (Uro), Muniappan
Outline. Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system. Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract
 Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning
Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning
Outline. Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system. Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract
 Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Diagnostic Investigations in Urinary System PLAIN KUB EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY RETROGRADE
Outline Introduction to imaging modalities of the urinary system Case base learning of common diseases in urinary tract Diagnostic Investigations in Urinary System PLAIN KUB EXCRETORY UROGRAPHY RETROGRADE
Candiduria in ICU : when and how to treat? Dr. Debashis Dhar Dept of Critical Care and Emergency Medicine Sir Ganga Ram Hospital
 Candiduria in ICU : when and how to treat? Dr. Debashis Dhar Dept of Critical Care and Emergency Medicine Sir Ganga Ram Hospital Introduction Nosocomial bacteriuria or candiduria develops in up to 25%
Candiduria in ICU : when and how to treat? Dr. Debashis Dhar Dept of Critical Care and Emergency Medicine Sir Ganga Ram Hospital Introduction Nosocomial bacteriuria or candiduria develops in up to 25%
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations
 Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Acute flank pain in children: Imaging considerations Carlos J. Sivit MD Rainbow Babies and Children s Hospital Case Western Reserve School of Medicine Flank pain Results from distention of ureter or renal
Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder)
 Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder) Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc.Phd ISRRT Associate Member Lecturer (National university) Reporting Sonographer (PHC) Objective By
Urinary system Ultrasound (Renal & Urinary bladder) Edited & Presented by ; Hussien A.B ALI DINAR. Msc.Phd ISRRT Associate Member Lecturer (National university) Reporting Sonographer (PHC) Objective By
Abdominal ultrasound:
 Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
Abdominal ultrasound: Non-traumatic acute abdomen Wittanee Na-ChiangMai, MD Department of Radiology ChiangMai University 26/04/2017 Contents Technique of examination Normal anatomy Emergency conditions
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION
 CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
CASE REPORT RENAL TUBERCULOSIS CAUSE OF RENAL REPLACEMENT LIPOMATOSIS : A RARE ASSOCIATION DR ANAND AARTI 1, DR CHANDAK PRIYA 2,DR SURESH PARVATHY 3 1. PROF AND HOD, DEPARTMENT OF RADIODIAGNOSIS, GOVERNMENT
Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1
 Contributions Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1 Gregory P. Borkowski, M.D. Craig R. George, M.D. Peter B. O'Donovan, M.D. While excretory urography has been useful in the evaluation
Contributions Nonurographic evaluation of renal calculous disease 1 Gregory P. Borkowski, M.D. Craig R. George, M.D. Peter B. O'Donovan, M.D. While excretory urography has been useful in the evaluation
Introduction. Study of fungi called mycology.
 Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
Fungi Introduction Study of fungi called mycology. Some fungi are beneficial: ex a) Important in production of some foods, ex: cheeses, bread. b) Important in production of some antibiotics, ex: penicillin
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 1/22/2011 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 4 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Michigan Medical School, Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System, Ann Arbor
 SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Candiduria Carol A. Kauffman Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Michigan Medical School, Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System, Ann Arbor Candiduria is a common finding.
SUPPLEMENT ARTICLE Candiduria Carol A. Kauffman Division of Infectious Diseases, University of Michigan Medical School, Veterans Affairs Ann Arbor Healthcare System, Ann Arbor Candiduria is a common finding.
Imaging Ejaculatory Disorders and Hematospermia
 ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology Imaging Ejaculatory Disorders and Hematospermia Parvati Ramchandani, MD Professor, Radiology and Surgery University of Pennsylvania Medical
ATHENS 4-6 October 2018 European Society of Urogenital Radiology Imaging Ejaculatory Disorders and Hematospermia Parvati Ramchandani, MD Professor, Radiology and Surgery University of Pennsylvania Medical
Spectrum of High-Resolution Sonographic Features of Urinary Tuberculosis
 Article Spectrum of High-Resolution Sonographic Features of Urinary Tuberculosis S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD, Sangampalayam V. Kandasamy, MS, MCh, Mylsamy Arul, MS, DNB, Muniappan Prabhakar, MS,
Article Spectrum of High-Resolution Sonographic Features of Urinary Tuberculosis S. Boopathy Vijayaraghavan, MD, DMRD, Sangampalayam V. Kandasamy, MS, MCh, Mylsamy Arul, MS, DNB, Muniappan Prabhakar, MS,
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation
 Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
Urologic Surgical Complications In Renal Transplantation Chris Freise, MD Professor of Surgery UCSF Transplant Division Urologic Complications Review of Bladder Anastomosis Complications and Management
A Case of Calcified Ureteritis Cystica: An Indiscernible Condition from Ureterolithiasis
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 110 (2009) No. 3, p. 245 249 245) A Case of Calcified Ureteritis Cystica: An Indiscernible Condition from Ureterolithiasis Alicioglu B. 1, Kaplan M. 2, Aktoz T. 3, Atakan I.
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 110 (2009) No. 3, p. 245 249 245) A Case of Calcified Ureteritis Cystica: An Indiscernible Condition from Ureterolithiasis Alicioglu B. 1, Kaplan M. 2, Aktoz T. 3, Atakan I.
Separating and Distorted Nephroliths Signs of Renal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
 Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 203-208 203 Separating and Distorted Nephroliths Signs of Renal Squamous Cell Carcinoma TZE-YU LEE SHEUNG-FAT KO CHUNG-CHENG HUANG YU-FENG CHENG Department of Radiology, Chang Gung
Chin J Radiol 2003; 28: 203-208 203 Separating and Distorted Nephroliths Signs of Renal Squamous Cell Carcinoma TZE-YU LEE SHEUNG-FAT KO CHUNG-CHENG HUANG YU-FENG CHENG Department of Radiology, Chang Gung
Find Medical Solutions to Your Problems HYDRONEPHROSIS. (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis)
 HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
HYDRONEPHROSIS (Distension of Renal Calyces & Pelvis) Hydronephrosis is the distension of the renal calyces and pelvis due to accumulation of the urine as a result of the obstruction to the outflow of
Abdominal Ultrasound : Aorta, Kidneys, Bladder
 Abdominal Ultrasound : Aorta, Kidneys, Bladder Nilam J. Soni, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Divisions of Hospital Medicine and Pulmonary/Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine University
Abdominal Ultrasound : Aorta, Kidneys, Bladder Nilam J. Soni, MD, MSc Associate Professor of Medicine Divisions of Hospital Medicine and Pulmonary/Critical Care Medicine Department of Medicine University
URINARY SYSTEM. Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3
 URINARY SYSTEM Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3 Objectives 1- Describe the structure of the urinary bladder, 2- Describe the structure of the ureters, bladder,
URINARY SYSTEM Lecturer Dr.Firdous M.Jaafar Department of anatomy/histology section Lecture 3 Objectives 1- Describe the structure of the urinary bladder, 2- Describe the structure of the ureters, bladder,
Candiduria: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study of Treatment with Fluconazole and Placebo
 19 Candiduria: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study of Treatment with Fluconazole and Placebo J. D. Sobel, 1 C. A. Kauffman, 2 D. McKinsey, 3 M. Zervos, 1 J. A. Vazquez, 1 A. W. Karchmer, 4 J. Lee, 5 C. Thomas,
19 Candiduria: A Randomized, Double-Blind Study of Treatment with Fluconazole and Placebo J. D. Sobel, 1 C. A. Kauffman, 2 D. McKinsey, 3 M. Zervos, 1 J. A. Vazquez, 1 A. W. Karchmer, 4 J. Lee, 5 C. Thomas,
Five Views of Transitional Cell Carcinoma: One Man s Journey
 September 2006 Five Views of Transitional Cell Carcinoma: One Man s Journey Amsalu Dabela, Harvard Medical School III Outline Overview: Renal Anatomy Our Patient s Story Diagnostic Imaging Studies Appearance
September 2006 Five Views of Transitional Cell Carcinoma: One Man s Journey Amsalu Dabela, Harvard Medical School III Outline Overview: Renal Anatomy Our Patient s Story Diagnostic Imaging Studies Appearance
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA LEARNING OBJECTIVES DEFINITION. KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer
 MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
MODULE 5: HEMATURIA KEY WORDS: Hematuria, Cystoscopy, Urine Cytology, UTI, bladder cancer LEARNING OBJECTIVES At the end of this clerkship, the learner will be able to: 1. Define microscopic hematuria.
Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009
 www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers IMAGING
www.ivis.org Proceedings of the 34th World Small Animal Veterinary Congress WSAVA 2009 São Paulo, Brazil - 2009 Next WSAVA Congress : Reprinted in IVIS with the permission of the Congress Organizers IMAGING
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY. THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel
 PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
PROFESSIONAL SKILLS 1 3RD YEAR SEMESTER 6 RADIOGRAPHY THE URINARY SYSTEM Uz. Fatema shmus aldeen Tel. 0925111552 Professional skills-2 THE URINARY SYSTEM The urinary system (review anatomy and physiology)
Radiological Assessment of the Kidney in Patients with Hematuria
 March 2005 Radiological Assessment of the Kidney in Patients with Hematuria Jeremy L. McKay, Harvard Medical School Year III Hematuria Signs and Symptoms Microscopic or gross hematuria Abdominal pain Fever
March 2005 Radiological Assessment of the Kidney in Patients with Hematuria Jeremy L. McKay, Harvard Medical School Year III Hematuria Signs and Symptoms Microscopic or gross hematuria Abdominal pain Fever
Cystitis cystica is a rare chronic reactive inflammatory
 JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 34 38 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0010 Case Report Cystitis Cystica as a Large Solitary Bladder Cyst Stephanie Potts, MBChB and
JOURNAL OF ENDOUROLOGY CASE REPORTS Volume 3.1, 2017 Mary Ann Liebert, Inc. Pp. 34 38 DOI: 10.1089/cren.2017.0010 Case Report Cystitis Cystica as a Large Solitary Bladder Cyst Stephanie Potts, MBChB and
RATIONALE: The organs making up the urinary system consist of the kidneys, bladder, urethra, and ureters.
 Chapter 12 Section Review 12.1 1. A. Kidneys RATIONALE: The renal pelvis receives urine from the kidney, travels through the ureters on the way to the bladder, but urine is formed in the kidney. 2. C.
Chapter 12 Section Review 12.1 1. A. Kidneys RATIONALE: The renal pelvis receives urine from the kidney, travels through the ureters on the way to the bladder, but urine is formed in the kidney. 2. C.
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging
 Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
Excretory urography (EU) or IVP US CT & radionuclide imaging MRI arteriography studies requiring catherization or direct puncture of collecting system EU & to a lesser extent CT provide both functional
XANTHOGRANULOMATOUS PYELONEPHRITIS: radiologic review.
 XANTHOGRANULOMATOUS PYELONEPHRITIS: radiologic review. Poster No.: C-0557 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Barral, J. M. Sánchez Crespo, J. C. Pérez Herrera, J. L. 1 2 3 1 1 1 Ortega
XANTHOGRANULOMATOUS PYELONEPHRITIS: radiologic review. Poster No.: C-0557 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Barral, J. M. Sánchez Crespo, J. C. Pérez Herrera, J. L. 1 2 3 1 1 1 Ortega
Imaging the Urinary Tract
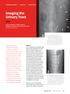 Imaging the Urinary Tract Laura Armbrust, DVM, DACVR Gregory F. Grauer, DVM, MS, DACVIM Kansas State University Radiographic and ultrasound imaging in addition to history, physical examination, and clinicopathologic
Imaging the Urinary Tract Laura Armbrust, DVM, DACVR Gregory F. Grauer, DVM, MS, DACVIM Kansas State University Radiographic and ultrasound imaging in addition to history, physical examination, and clinicopathologic
National Defense Medical Center, Taipei, Taiwan.
 CONGENITAL SEMINAL VESICLE CYST ASSOCIATED WITH IPSILATERAL RENAL AGENESIS MIMICKING BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Chien-Chang Kao, 1 Ching-Jiunn Wu, 2 Guang-Huan
CONGENITAL SEMINAL VESICLE CYST ASSOCIATED WITH IPSILATERAL RENAL AGENESIS MIMICKING BLADDER OUTLET OBSTRUCTION: A CASE REPORT AND REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE Chien-Chang Kao, 1 Ching-Jiunn Wu, 2 Guang-Huan
Clinico-radiological Features and Classification of Emphysematous Pyelonephritis: A prospective study
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinico-radiological Features and Classification of Emphysematous Pyelonephritis: A prospective study Singh A Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Amritsar, Punjab,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Clinico-radiological Features and Classification of Emphysematous Pyelonephritis: A prospective study Singh A Department of Radiodiagnosis, Government Medical College, Amritsar, Punjab,
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract
 My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
My Patient Has Abdominal Pain PoCUS of the Biliary Tract and the Urinary Tract Objectives PoCUS for Biliary Disease PoCUS for Renal Colic PoCUS for Urinary Retention Biliary Disease A patient presents
Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL
 Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL Overview Principles Individual organs Small pieces Partial resections Whole organs Data recording and data sets Principles You are working for the patient
Urology An introduction to cut up DR J R GOEPEL Overview Principles Individual organs Small pieces Partial resections Whole organs Data recording and data sets Principles You are working for the patient
Imaging Features of Acute Pyelonephritis in Contrast Computed Tomography as Predictors of Need for Intervention
 Imaging Features of Acute Pyelonephritis in Contrast Computed Tomography as Predictors of Need for Intervention Poster No.: C-0088 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Y. Lee, C. W.
Imaging Features of Acute Pyelonephritis in Contrast Computed Tomography as Predictors of Need for Intervention Poster No.: C-0088 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Y. Lee, C. W.
Imaging Features of Acute Pyelonephritis in Contrast Computed Tomography as Predictors of Need for Intervention
 Imaging Features of Acute Pyelonephritis in Contrast Computed Tomography as Predictors of Need for Intervention Poster No.: C-0088 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Y. Lee, C. W.
Imaging Features of Acute Pyelonephritis in Contrast Computed Tomography as Predictors of Need for Intervention Poster No.: C-0088 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Y. Lee, C. W.
Role of imaging in RCC. Ultrasonography. Solid lesion. Cystic RCC. Solid RCC 31/08/60. From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective
 Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Role of imaging in RCC From Diagnosis to Treatment: the Radiologist Perspective Diagnosis Staging Follow up Imaging modalities Limitations and pitfalls Duangkamon Prapruttam, MD Department of Therapeutic
Erin Kane, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman BIDMC Radiology Core Clerkship March 2009
 Erin Kane, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman BIDMC Radiology Core Clerkship March 2009 Agenda Patient OH: Initial presentation Kidney transplantation: Menu of tests Routine imaging for kidney donors Selected
Erin Kane, HMS III Dr. Gillian Lieberman BIDMC Radiology Core Clerkship March 2009 Agenda Patient OH: Initial presentation Kidney transplantation: Menu of tests Routine imaging for kidney donors Selected
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound. Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa
 Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Kidney & Urinary Tract Ultrasound Fatina Fadel Hafez Bazaraa Ultrasonography Ultrasound Available Rapid Inexpensive Painless & no sedation needed No adverse effects/ complications Can be repeated Useful
Chan, IHY; Lam, WWM; Wong, KKY; Tam, PKH
 Title Letters to the editor Author(s) Chan, IHY; Lam, WWM; Wong, KKY; Tam, PKH Citation Journal Of Paediatrics And Child Health, 2010, v. 46 n. 6, p. 361-362 Issued Date 2010 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/92175
Title Letters to the editor Author(s) Chan, IHY; Lam, WWM; Wong, KKY; Tam, PKH Citation Journal Of Paediatrics And Child Health, 2010, v. 46 n. 6, p. 361-362 Issued Date 2010 URL http://hdl.handle.net/10722/92175
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY. Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin
 CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
CYSTIC DISEASES of THE KIDNEY Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin 1 Types of cysts 1-Simple Cysts 2-Dialysis-associated acquired cysts 3-Autosomal Dominant (Adult) Polycystic Kidney Disease 4-Autosomal Recessive (Childhood)
Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka. Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia. 1991, 36
 NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Large Periureteral Lipoma Associa Hydronephrosis. Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Imamura, Atushi Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
NAOSITE: Nagasaki University's Ac Title Author(s) A Large Periureteral Lipoma Associa Hydronephrosis. Hayashi, Tomayoshi; Imamura, Atushi Matsunaga, Naofumi; Saito, Yutaka Citation Acta medica Nagasakiensia.
Treatment of choice for end stage renal disease Imaging to establish baseline and diagnosis of potential complications Review common surgical
 Treatment of choice for end stage renal disease Imaging to establish baseline and diagnosis of potential complications Review common surgical techniques Review normal appearance Discuss US diagnosis of
Treatment of choice for end stage renal disease Imaging to establish baseline and diagnosis of potential complications Review common surgical techniques Review normal appearance Discuss US diagnosis of
Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA
 Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA Outline I. Introduction highlighting normal renal enhancement physiology including normal
Kristina M. Nowitzki, M.D., Ph.D. and Hao S. Lo, M.D. University of Massachusetts Medical School, Worcester, MA Outline I. Introduction highlighting normal renal enhancement physiology including normal
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93
 Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Chapter 6: Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems 93 Chapter 6 Genitourinary and Gastrointestinal Systems Embryology Three sets of excretory organs or kidneys develop in human embryos: Pronephros:
Ultrasonographic diagnosis and typing of renal tuberculosis
 International Journal of Urology (2008) 15, 135 139 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2007.01962.x, Original Article: Clinical Investigation Ultrasonographic diagnosis and typing of renal tuberculosis Xuefang Rui,
International Journal of Urology (2008) 15, 135 139 doi: 10.1111/j.1442-2042.2007.01962.x, Original Article: Clinical Investigation Ultrasonographic diagnosis and typing of renal tuberculosis Xuefang Rui,
Hydronephrosis. What is hydronephrosis?
 What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
What is hydronephrosis? Hydronephrosis Hydronephrosis describes the situation where the urine collecting system of the kidney is dilated. This may be a normal variant or it may be due to an underlying
Symptoms, Diagnosis and Classification
 Patient Information English 2 Symptoms, Diagnosis and Classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour
Patient Information English 2 Symptoms, Diagnosis and Classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour
Imaging findings in renal infections
 Imaging findings in renal infections Poster No.: C-0221 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. lópez blasco, D. Soriano Mena, R. Pastor Toledo, S. Paz Maya, A. M. Julve Parreño, J. Palmero
Imaging findings in renal infections Poster No.: C-0221 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. lópez blasco, D. Soriano Mena, R. Pastor Toledo, S. Paz Maya, A. M. Julve Parreño, J. Palmero
Contents. Review anatomy of the urinary tract Imaging modalities
 Contents Review anatomy of the urinary tract Imaging modalities The Urinary Tract Kidneys ตาแหน งไต (position) อย ใน retroperitoneum ระด บ T12-L3 โดยไต ขวาจะม ระด บตากว าไตซ ายเล กน อย ร ปร าง (shape)
Contents Review anatomy of the urinary tract Imaging modalities The Urinary Tract Kidneys ตาแหน งไต (position) อย ใน retroperitoneum ระด บ T12-L3 โดยไต ขวาจะม ระด บตากว าไตซ ายเล กน อย ร ปร าง (shape)
DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM
 DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM Acute tubular injury (ATI) Pyelonephritis Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) Myeloma cast NP Renal stones Urinary outflow obstruction: hydronephrosis
DISEASES AFFECTING TUBULES AND INTERSTITIUM Acute tubular injury (ATI) Pyelonephritis Drug-induced tubulointerstitial nephritis (TIN) Myeloma cast NP Renal stones Urinary outflow obstruction: hydronephrosis
Diagnosis and classification
 Patient Information English 2 Diagnosis and classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour is present.
Patient Information English 2 Diagnosis and classification The underlined terms are listed in the glossary. Signs and symptoms Blood in the urine is the most common symptom when a bladder tumour is present.
Sonographic Detection of Cervical Carcinoma With Metastases
 634026JDMXXX10.1177/8756479316634026Journal of Diagnostic Medical SonographyChappell and Fisher research-article2016 Case Study Sonographic Detection of Cervical Carcinoma With Metastases Journal of Diagnostic
634026JDMXXX10.1177/8756479316634026Journal of Diagnostic Medical SonographyChappell and Fisher research-article2016 Case Study Sonographic Detection of Cervical Carcinoma With Metastases Journal of Diagnostic
Bladder Case 1 SURGICAL PATHOLOGY REPORT. Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT)
 Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Bladder Case 1 February 17, 2007 Specimen (s) received: Bladder Tumor Pre-operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Post operative Diagnosis: Bladder Cancer Procedure: Cystoscopy, transurethral resection of
Functions of the kidney:
 Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
Diseases of renal system : Normal anatomy of renal system : Each human adult kidney weighs about 150 gm, the ureter enters the kidney at the hilum, it dilates into a funnel-shaped cavity, the pelvis, from
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys II. Nephron Unit and Urine Formation
 URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
URINARY SYSTEM I. Kidneys A. Location and Structure 1. Retroperitoneal 2. Between T12 and L3 3. Rt. kidney slightly lower 4. Two bean shaped organs 5. Adrenal gland 6. Internal construction a. Renal cortex
Obstructive Uropathy. PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO. Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta
 Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
Obstructive Uropathy PATHOPHYSIOLOGIC CHANGES UUO vs BUO Arry Rodjani Urology Department Ciptomangunkusumo Hospital Jakarta INTRODUCTION Obstructive uropathy refers to the functional or anatomic obstruction
FHS Appendicitis US Protocol
 FHS Appendicitis US Protocol Reviewed By: Shireen Khan, MD; Sarah Farley, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: May 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible
FHS Appendicitis US Protocol Reviewed By: Shireen Khan, MD; Sarah Farley, MD; Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: May 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible
Ultrasonography of acute flank pain: a focus on renal stones and acute pyelonephritis
 Ultrasonography of acute flank pain: a focus on renal stones and acute pyelonephritis Ki Choon Sim Department of Radiology, Korea University nam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Ultrasonography of acute flank pain: a focus on renal stones and acute pyelonephritis Ki Choon Sim Department of Radiology, Korea University nam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
Radiological changes of renal papillary necrosis
 Kidney International, Vol. 13 (1978), pp. 93-1 06 Radiological changes of renal papillary necrosis NILs LINDVALL Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Karolinska Sjukhuset, Stockholm, Sweden Necrosis of
Kidney International, Vol. 13 (1978), pp. 93-1 06 Radiological changes of renal papillary necrosis NILs LINDVALL Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Karolinska Sjukhuset, Stockholm, Sweden Necrosis of
Common Fungi. Catherine Diamond MD MPH
 Common Fungi Catherine Diamond MD MPH Birth Month and Day & Last Four Digits of Your Cell Phone # BEFORE: http://tinyurl.com/kvfy3ts AFTER: http://tinyurl.com/lc4dzwr Clinically Common Fungi Yeast Mold
Common Fungi Catherine Diamond MD MPH Birth Month and Day & Last Four Digits of Your Cell Phone # BEFORE: http://tinyurl.com/kvfy3ts AFTER: http://tinyurl.com/lc4dzwr Clinically Common Fungi Yeast Mold
URINARY TRACT IMAGING - BASIC PRINCIPLES
 URINARY TRACT IMAGING - BASIC PRINCIPLES Clinical Radiology Every physician needs a basic understanding of diagnostic imaging to understand how to order the appropriate studies and to understand the resulting
URINARY TRACT IMAGING - BASIC PRINCIPLES Clinical Radiology Every physician needs a basic understanding of diagnostic imaging to understand how to order the appropriate studies and to understand the resulting
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System
 Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Urinary System Part of the Excretory System Bellwork **only write the term and underlined definition INCONTINENCE involuntary urination, often seem in older persons, or due to illness and disease ENURESIS
Audit of split-bolus CT urography for the investigation of haematuria over a 12 month period at two district general hospitals
 Audit of split-bolus CT urography for the investigation of haematuria over a 12 month period at two district general hospitals Poster No.: C-1349 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary
Audit of split-bolus CT urography for the investigation of haematuria over a 12 month period at two district general hospitals Poster No.: C-1349 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Genitourinary
What s Your Diagnosis??? Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012
 Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012 What s Your Diagnosis??? Signalment Emma, a 9 year old, Female, Spayed, Domestic Short Haired Feline Presenting Complaint Weight loss, vomited the morning of her visit,
Renée Fahrenholz, Class of 2012 What s Your Diagnosis??? Signalment Emma, a 9 year old, Female, Spayed, Domestic Short Haired Feline Presenting Complaint Weight loss, vomited the morning of her visit,
Title with transitional cell carcinoma: a. Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1992), 38(6):
 Title Primary localized amyloidosis of th with transitional cell carcinoma: a Author(s) Shiramizu, Miki; Nakamura, Kaoru; B Yoji; Kinoshita, Hidechika Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1992), 38(6): 699-702 Issue Date
Title Primary localized amyloidosis of th with transitional cell carcinoma: a Author(s) Shiramizu, Miki; Nakamura, Kaoru; B Yoji; Kinoshita, Hidechika Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1992), 38(6): 699-702 Issue Date
Opportunistic Mycoses
 CANDIDIASIS SOFYAN LUBIS DEPARTEMEN MIKROBIOLOGI FAK.KEDOKTERAN USU MEDAN 2009 Opportunistic Mycoses Opportunistic mycoses are fungal infections that do not normally cause disease in healthy people, but
CANDIDIASIS SOFYAN LUBIS DEPARTEMEN MIKROBIOLOGI FAK.KEDOKTERAN USU MEDAN 2009 Opportunistic Mycoses Opportunistic mycoses are fungal infections that do not normally cause disease in healthy people, but
Fungi GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 53: Author Moi Lin Ling, MBBS, FRCPA, CPHQ, MBA
 GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 53: Fungi Author Moi Lin Ling, MBBS, FRCPA, CPHQ, MBA Chapter Editor Ziad A. Memish, MD, FRCPC, FACP Cover heading - Topic Outline Topic outline
GUIDE TO INFECTION CONTROL IN THE HOSPITAL CHAPTER NUMBER 53: Fungi Author Moi Lin Ling, MBBS, FRCPA, CPHQ, MBA Chapter Editor Ziad A. Memish, MD, FRCPC, FACP Cover heading - Topic Outline Topic outline
In Canada, there was a 25% reduction in incidence of genitourinary TB in the period compared with An interesting speculation
 Renal T B EPIDEMIOLOGY Young to middle age usually affected, rare in children Male : female ratio = 2:1 True prevalence and incidence not known as patients are usually asymptomatic With HIV pandemic, there
Renal T B EPIDEMIOLOGY Young to middle age usually affected, rare in children Male : female ratio = 2:1 True prevalence and incidence not known as patients are usually asymptomatic With HIV pandemic, there
Virtual Cystoscopy Using Volume Ultrasound
 GE Healthcare Ultrasound Virtual Cystoscopy Using Volume Ultrasound By Nirvikar Dahiya, MD imagination at work Introduction The urinary bladder has been imaged by multiple modalities over the years. It
GE Healthcare Ultrasound Virtual Cystoscopy Using Volume Ultrasound By Nirvikar Dahiya, MD imagination at work Introduction The urinary bladder has been imaged by multiple modalities over the years. It
P RIMARY carcinoma of the ureter, once considered rare, makes up about I per
 JANUARY, 1973 TUMORS OF THE URETER PROBLEMS IN DIAGNOSIS By J. J. CANCELMO, JR., M.D., R. C. UHLMAN, M.D., J. L. ESHLEMAN, M.D., andn. F. V1EK, M.D. WAYNE, P RIMARY carcinoma of the ureter, once considered
JANUARY, 1973 TUMORS OF THE URETER PROBLEMS IN DIAGNOSIS By J. J. CANCELMO, JR., M.D., R. C. UHLMAN, M.D., J. L. ESHLEMAN, M.D., andn. F. V1EK, M.D. WAYNE, P RIMARY carcinoma of the ureter, once considered
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22
 Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22 Chief complaint Unknown fever for one month Hand tremor and left huge renal tumor was noted Present illness Suffered from fever for one month, hand
Sex: 女 Age: 51 Occupation: 無 Admission date:92/07/22 Chief complaint Unknown fever for one month Hand tremor and left huge renal tumor was noted Present illness Suffered from fever for one month, hand
Upper Tract Tcc. Mohan Arianayagam FRACS (Urology)
 Upper Tract Tcc Mohan Arianayagam FRACS (Urology) Epidemiology Peak incidence 75 to 79 years 2x more common in men 7% of all renal tumours 5% of all urothelial tumours Synchronous bilateral is rare ~ 1.6%
Upper Tract Tcc Mohan Arianayagam FRACS (Urology) Epidemiology Peak incidence 75 to 79 years 2x more common in men 7% of all renal tumours 5% of all urothelial tumours Synchronous bilateral is rare ~ 1.6%
Aspergillus Terreus-related Ureteral Obstruction in a Diabetic Patient
 Kidney Diseases Aspergillus Terreus-related Ureteral Obstruction in a Diabetic Patient Narges Najafi, 1 Tahereh Shokohi, 2 Abbas Basiri, 3 Mahmoud Parvin, 4 Davood Yadegarinia, 5 Faramarz Taghavi, 6 Mohammad
Kidney Diseases Aspergillus Terreus-related Ureteral Obstruction in a Diabetic Patient Narges Najafi, 1 Tahereh Shokohi, 2 Abbas Basiri, 3 Mahmoud Parvin, 4 Davood Yadegarinia, 5 Faramarz Taghavi, 6 Mohammad
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents
 Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
Genitourinary Radiology In-Training Test Questions for Diagnostic Radiology Residents March, 2013 Sponsored by: Commission on Education Committee on Residency Training in Diagnostic Radiology 2013 by American
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER
 MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
MUSCLE-INVASIVE AND METASTATIC BLADDER CANCER (Text update March 2008) A. Stenzl (chairman), N.C. Cowan, M. De Santis, G. Jakse, M. Kuczyk, A.S. Merseburger, M.J. Ribal, A. Sherif, J.A. Witjes Introduction
Renal Transplantation Patient in ER
 10th National Congress of EM & 1st Intercontinental EM Congress 1 Renal Transplantation Patient in ER Mehmet ERGİN; MD, EP, Assist. Prof. Near East University Medicine School Emerg Dep / Lefkoşa Turkish
10th National Congress of EM & 1st Intercontinental EM Congress 1 Renal Transplantation Patient in ER Mehmet ERGİN; MD, EP, Assist. Prof. Near East University Medicine School Emerg Dep / Lefkoşa Turkish
Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts
 Title Page Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts Sabrina H Rossi 1, Brendan Koo 2, Antony Riddick 1, Nimish Shah 1, Grant D Stewart 1 1 Urology Department, Addenbrooke's
Title Page Different successful management strategies for obstructing renal parapelvic cysts Sabrina H Rossi 1, Brendan Koo 2, Antony Riddick 1, Nimish Shah 1, Grant D Stewart 1 1 Urology Department, Addenbrooke's
Index. urologic.theclinics.com. Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type.
 Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acinetobacter baumannii, carbapenem-resistant, 497 498 Adolescents, urinary tract infections in, 520 521 Aminoglycosides, for UTIs and
Index Note: Page numbers of article titles are in boldface type. A Acinetobacter baumannii, carbapenem-resistant, 497 498 Adolescents, urinary tract infections in, 520 521 Aminoglycosides, for UTIs and
 Title Metastatic renal tumor from involvement: a case report the lun Ishihara, Satoshi; Kobayashi, Sator Author(s) Takeuchi, Toshimi; Kuriyama, Manabu Kawada, Yukimichi; Takahashi, Yoshi Isogai, Kazutoshi
Title Metastatic renal tumor from involvement: a case report the lun Ishihara, Satoshi; Kobayashi, Sator Author(s) Takeuchi, Toshimi; Kuriyama, Manabu Kawada, Yukimichi; Takahashi, Yoshi Isogai, Kazutoshi
Author(s) Miyoshi, Nobuyuki; Noda, Shinshi; E. Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1981), 27(6):
 Title INTERESTING UROGRAPHIC CHANGE OF TH IN UPPER URINARY TRACT TUBERCULOSIS Author(s) Miyoshi, Nobuyuki; Noda, Shinshi; E Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1981), 27(6): 703-707 Issue Date 1981-06 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/122902
Title INTERESTING UROGRAPHIC CHANGE OF TH IN UPPER URINARY TRACT TUBERCULOSIS Author(s) Miyoshi, Nobuyuki; Noda, Shinshi; E Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1981), 27(6): 703-707 Issue Date 1981-06 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/122902
Imaging of Hematuria
 Residents Section Structured Review rticle O onnor et al. Hematuria Residents Section Structured Review rticle Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.204.234 on 01/19/18 from IP address 37.44.204.234.
Residents Section Structured Review rticle O onnor et al. Hematuria Residents Section Structured Review rticle Downloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.204.234 on 01/19/18 from IP address 37.44.204.234.
Title: Author: Speciality / Division: Directorate:
 Antifungal guidelines for CANDIDIASIS INFECTIONS (Adults) Proven infection: Targeted antifungal therapy should be prescribed for: o Positive cultures from a sterile site with clinical or radiological abnormality
Antifungal guidelines for CANDIDIASIS INFECTIONS (Adults) Proven infection: Targeted antifungal therapy should be prescribed for: o Positive cultures from a sterile site with clinical or radiological abnormality
Acute Pyelonephritis
 Acute Pyelonephritis Variant 1: Acute pyelonephritis. Uncomplicated patient (eg, no history of diabetes or immune compromise or history of stones or obstruction or prior renal surgery or lack of response
Acute Pyelonephritis Variant 1: Acute pyelonephritis. Uncomplicated patient (eg, no history of diabetes or immune compromise or history of stones or obstruction or prior renal surgery or lack of response
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology. A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement
 Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2014 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
Coding Companion for Urology/Nephrology A comprehensive illustrated guide to coding and reimbursement 2014 Contents Getting Started with Coding Companion...i Integumentary...1 Arteries and Veins...15 Lymph
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017
 Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
Fungal ball.. Clinical and radiological features DR. AHMED ALTUWAIJRI 1/5/2017 Fungal Rhinosinusitis (FRS) Rhinosinusitis, is a common disorder affecting approximately 20% of the population at some time
MEDitorial March Bladder Cancer
 MEDitorial March 2010 Bladder Cancer Last month, my article addressed the issue of blood in the urine ( hematuria ). A concerning cause of hematuria is bladder cancer, a variably malignant tumor starting
MEDitorial March 2010 Bladder Cancer Last month, my article addressed the issue of blood in the urine ( hematuria ). A concerning cause of hematuria is bladder cancer, a variably malignant tumor starting
Acute scrotum. Acute Epididymo-orchitis. Phyllis Yan, APDR (QEH)
 Acute scrotum Acute Epididymo-orchitis Phyllis Yan, APDR (QEH) Conditions leading to acute pain Torsion Acute Epididymitis / Epididymoorchitis Scrotal trauma Inguinal hernias Testicular tumors Epididymitis/epididymo
Acute scrotum Acute Epididymo-orchitis Phyllis Yan, APDR (QEH) Conditions leading to acute pain Torsion Acute Epididymitis / Epididymoorchitis Scrotal trauma Inguinal hernias Testicular tumors Epididymitis/epididymo
Nephrographic and Pyelographic Analysis of CT Urography: Principles, Patterns, and Pathophysiology
 Genitourinary Imaging Review Wolin et al. CT Urography Principles, Patterns, and Genitourinary Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Ely A. Wolin 1 David S. Hartman J. Ryan Olson Wolin EA, Hartman DS, Olson JR Keywords:
Genitourinary Imaging Review Wolin et al. CT Urography Principles, Patterns, and Genitourinary Imaging Review FOCUS ON: Ely A. Wolin 1 David S. Hartman J. Ryan Olson Wolin EA, Hartman DS, Olson JR Keywords:
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols
 Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Abdomen and Retroperitoneum Ultrasound Protocols Reviewed By: Anna Ellermeier, MD Last Reviewed: March 2018 Contact: (866) 761-4200, Option 1 **NOTE for all examinations: 1. If documenting possible flow
Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 6
 Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 6 Learning Objectives for this File: 1. Understand how clinical presentation drives the diagnostic workup 2. Recognize how patient education is
Advanced Pathophysiology Unit 7: Renal-Urologic Page 1 of 6 Learning Objectives for this File: 1. Understand how clinical presentation drives the diagnostic workup 2. Recognize how patient education is
SHABNAM TEHRANI M.D., MPH ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF INFECTIOUS DISEASESE &TROPICAL MEDICINE RESEARCH CENTER, SHAHID BEHESHTI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL
 URINARY TRACT INFECTION SHABNAM TEHRANI M.D., MPH ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF INFECTIOUS DISEASESE &TROPICAL MEDICINE RESEARCH CENTER, SHAHID BEHESHTI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Definition inflammatory
URINARY TRACT INFECTION SHABNAM TEHRANI M.D., MPH ASSISTANT PROFESSOR OF INFECTIOUS DISEASESE &TROPICAL MEDICINE RESEARCH CENTER, SHAHID BEHESHTI UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES Definition inflammatory
Kidneys and Urinary Tract Content Outline. Anatomy Coverings. Location. (Effective February 2007) (16%-24%)
 Kidneys and Urinary Tract Content Outline (Effective February 2007) (16%-24%) Anatomy Coverings true capsule perirenal fat surrounds capsule Gerota s fascia separates perirenal from extraperitoneal fat
Kidneys and Urinary Tract Content Outline (Effective February 2007) (16%-24%) Anatomy Coverings true capsule perirenal fat surrounds capsule Gerota s fascia separates perirenal from extraperitoneal fat
Gas-producing renal infection presenting as pneumaturia: a case report
 Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2013 Gas-producing renal infection presenting as pneumaturia: a case report Youssef S. Tanagho Jonathan M. Mobley
Washington University School of Medicine Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2013 Gas-producing renal infection presenting as pneumaturia: a case report Youssef S. Tanagho Jonathan M. Mobley
CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS
 CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Hamid Emadi M.D Associate professor of Infectious diseases Department Tehran university of medical science The most common nosocomial infection The urinary
CATHETER-ASSOCIATED URINARY TRACT INFECTIONS Hamid Emadi M.D Associate professor of Infectious diseases Department Tehran university of medical science The most common nosocomial infection The urinary
