Congenital generalised bone dysplasias: a clinical, radiological, and epidemiological survey
|
|
|
- Leslie Burns
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Journal of Medical Genetics 1989, 27, Congenital generalised bone dysplasias: a clinical, radiological, and epidemiological survey POUL ERIK ANDERSEN JR AND MOGENS HAUGE From the Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Odense University Hospital; and the Institute of Clinical Genetics, Odense University, Denmark. SUMMARY The point prevalence at birth of generalised bone dysplasias was estimated by a study of all children born between 1 January 1970 and 31 December 1983 in the county of Fyn (Denmark). Additionally the population prevalence on 31 December 1983 of all patients with generalised bone dysplasias in this county was determined. The county is a well defined, representative subregion of Denmark which demographically comprises a cross section of about 9% of the Danish population. In total, bone dysplasias were found to be more frequent than generally assumed. Achondroplasia was, however, less common with a point prevalence at birth of 1-3 per , while osteogenesis imperfecta (21-8), multiple epiphyseal dysplasia tarda (9-0), achondrogenesis (6.4), osteopetrosis (5-1), and thanatophoric dysplasia (3.8) were found more frequently. It is striking how many bone dysplasias are still erroneously classified as achondroplasia. Correct diagnosis is important for a valid prognosis, for treatment, and for genetic counselling. The diagnosis relies almost exclusively on the radiographical findings. Comprehensive epidemiological studies, based on total populations, are difficult to perform for geographical and administrative reasons. The available reports on generalised bone dysplasias are few and incompletel 2 and quite elementary epidemiological data are missing. Many of the conditions are difficult to study satisfactorily because they are hard to diagnose and thus often misclassified, or because they remain undiagnosed, especially in stillborn babies and in children dying shortly after birth. The county of Fyn (Funen) forms a geographically and administratively well defined region, which, with regard to area and population, comprises about 9% of Denmark. Analyses of a number of demographic, economic, social, and health conditions have established that the population constitutes a representative cross section of the Danish population. Thus, this county is very suitable for epidemiological investigations. Materials and methods The investigation consisted of two parts: (1) the determination of the point prevalence at biith, including all newborn children (livebirths and still- Received for publication 1 February Revised version accepted for publication 27 April births, that is, those born dead after the end of the 28th gestational week) with generalised bone dysplasias, delivered between 1 January 1970 and 31 December 1983 to mothers with a permanent address in the county; and (2) the population prevalence of generalised bone dysplasias in all who were alive on 31 December 1983 and had a permanent address in the county. The generalised bone dysplasia (intrinsic bone anomaly) should have been present at birth though it might have escaped observation until later in life. Bone changes secondary to endocrinological disorders, inborn errors of metabolism, malnutrition, organ failure, and chromosome defects have not been included and abortions were disregarded in this study. Ascertainment of patients was performed through a Central computerised inpatient register for the period 1 April 1973 to 31 December All discharge diagnoses from the 10 hospitals in the county have been entered in this register since 1 April Before this date, cases were collected from the files of all surgical, obstetrical, paediatric, and orthopaedic departments of each of the hospitals in the county as far back as diagnostic archives were kept. Furthermore, the diagnostic archive of the x ray department at Odense University Hospital was searched right back to its establishment in
2 38 This archive includes inpatients as well as outpatients. In all cases of bone dysplasia, irrespective of the certainty of the diagnosis, the case records, x ray pictures, necropsy reports, and histological descriptions, as well as any filed genetic records available, were perused. When bone dysplasia was found or suspected, a detailed family history was obtained in all cases by contacting the probands or their closest relatives and, if necessary, by calling them in for supplementary clinical and radiological examinations. Data on all first degree relatives were considered indispensable in all cases. Only when complete accordance between the clinical, radiological, pathological and genetic findings was present was the diagnosis considered definite and the patient entered into the study. Results The results are given in the table. In the period 1 January 1970 to 31 December 1983 a total of children, including stillbirths, was born in the county of Fyn. Fifty-five of these had generalised bone dysplasia which gives a point prevalence at birth of 75*7 per On 31 December 1983 the population of Fyn amounted to , of whom TABLE Generalised bone dysplasias in the county offyn (Funen), Denmark. Poul Erik Andersen Jr and Mogens Hauge FIG 1 Osteogenesis imperfecta type II. The baby died shortly after birth. Multiple fractures and deformity of all long bones, many ribs, and vertebral bodies, and severe osteoporosis. Born Death Alive on Point prevalence Prevalence on at birth (per ) (per ) Osteogenesis imperfecta I 12 0 II III 2 0 IV 1 0 Achondroplasia Hypochondroplasia Thanatophoric dysplasia Micromelic bone dysplasia with cloverleaf skull Achondrogenesis III IV 3 3 Asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (Jeune) Chondrodysplasia punctata (Conradi-Hunermann) Campomelic dysplasia Multiple cartilaginous exostoses Multiple epiphyseal dysplasia tarda Metatropic dysplasia Metaphyseal chondrodysplasia (Schmid) Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia Tarda, brachyarchitic (Lenz) Pseudoachondroplastic (type I, Kozlowski) Pseudoachondroplastic (type III) Osteopetrosis (non-lethal) Unclassifiable lethal micromelic dysplasia Total (95% confidence limits) 59 (44-74) 19 (11-28) 150 ( ) 75.7 ( ) 33-0( ) Newborns : Population :
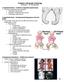
3 Congenital generalised bone dysplasias: a clinical, radiological, and epidemiological survey 150 had generalised bone dysplasia. Thus, the prevalence is 33-0 per The distribution of the dysplasias over the years was even; there was no conspicuous geographical accumulation and no significant sex difference. Osteogenesis imperfecta constitutes by far the largest group with a point prevalence at birth of 21-8 (95% confidence limits 12-7 to 31-0) and a population prevalence of 10-6 (4-2 to 17-0) per Both values are far higher than previously reported.3 Classification in the four types was performed according to Sillence et al.3 Radiographical examples of types II, III, and IV are given in figs 1 to 4. Achondroplasia was found to be much less frequent than generally assumed5 and with a lower prevalence at birth (1-3 (0 to 3-5)) than achondrogenesis (6-4 (1-4 to 11.4)), multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (MED) tarda (9-0 (3-1 to 14.9)), autosomal dominant osteopetrosis (5.1 (0.7 to 9.5)), and thanatophoric dysplasia (3-8 (0 to 7.6)). Only one patient with achondroplasia was born in the period 1 January 1970 to 31 December Of the remain- Osteogenesis imperfecta type IV. Boy oftwo years. FIG 3 Wormian bones. There was generalised osteoporosis, dentinogenesis imperfecta, and normal coloured sclerae. ing 58 patients, 13 had erroneously been classified _ t under the diagnosis of achondroplasia. One of the three patients with thanatophoric dysplasia had cloverleaf skull. Micromelic bone dysplasia with cloverleaf skull has been described earlier.6 This dysplasia has similarities to thanatophoric dysplasia, achondrogenesis type IV, and achondroplasia, but is different from these and should probably be looked upon as a separate entity. Achondrogenesis has been classified into four types according to length/width of the femur.7 Following this, two (identical twins) were classified as type III8 and three as type IV. Two were originally erroneously diagnosed as achondroplasia, both clinically and histologically, and one as thanatophoric dysplasia. Two of the cases of asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia (Jeune) were sibs. The first born was erroneously FIG 2 Osteogenesis imperfecta type III. Woman of69 diagnosed as achondroplasia. As both parents were years. Right crus with severe deformity, osteoporosis and phenotypically normal and unrelated, it was incorthin diaphyses. Progressive deformity ofspine and long rectly concluded (on the basis of the wrong diagnobones with age. sis) that a dominant mutation was likely to be the 39
4 40 FIG 4 Osteogenesis imperfecta type IV. Same patient as in fig 3, aged two years. Osteoporosis and several fractured vertebral bodies. J Med Genet: first published as /jmg on 1 January Downloaded from Poul Erik Andersen Jr and Mogens Hauge FIG 6 Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia-pseudoachondroplasia type I (Kozlowski). Same patient as in fig 5. Agefive and a halfyears. Irregular epiphyses and metaphyseal flaring. Triangular shaped distalfemoral epiphysis wedged into a wide V shaped intercondylar notch ofthefemoral metaphysis. Genu varum. FIG 5 Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia-pseudoachondroplasia type I (Kozlowski). Age three and a halfyears. Delayed appearance, underdevelopment, and irregular ossification offemoral heads. Acetabular cavities dysplastic. on 22 December 2018 by guest. Protected by
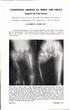
5 Congenital generalised bone dysplasias: a clinical, radiological, and epidemiological survey FIG 7 Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia-pseudoachondroplasia type IlI. Age 56 years. Severe 4_tX < I11 ldeformity ofhips with coxa vara and shortfemora with wide metaphyses. Bow legs, short limbs in relation to trunk, and normal face and head. 141A cause. Consequently, the recurrence risk was not assumed to be increased. However, a diagnosis of asphyxiating thoracic dysplasia, which is an autosomal recessive trait, was made retrospectively when the parents had another child with the same bone dysplasia. Four of the patients with MED tarda were first cousins; two of these and four other cases were for a long time wrongly diagnosed and treated as bilateral Legg-Perthes disease until the correct diagnosis was made. Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda and pseudoachondroplasia were classified according to Bailey9 and Wynne-Davies et al" (figs 5 to 8). The three cases of spondyloephiphyseal dysplasia ' y"! tarda were a mother and her two sons. Autosomal dominant osteopetrosis was also found to be more frequent than previously assumed." The cases of osteopetrosis could be classified radiologically into two types12: type I, characterised by sclerosis, mainly of the calvarium and to a lesser degree of the vertebral arches and other parts of the skeleton. The vertebral bodies were almost normal (figs 9 and 10). Type II showed characteristic sclerosis of the end plates of the vertebral bodies ('sandwich' vertebrae or 'rugger jersey' spine) and to a lesser degree of the cranial base and tubular bones. The calvarium was FIG 8 Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia-pseudoachondroplasia almost normal (figs 11 and 12). All patients could be classified into one of these two types, 18 into type I and nine into type II. There was no significant sex or type III. Same patient as infig 7, aged 57years. Irregular vertebral bodies in lumbar spine with narrow anterior portions. 41
6 42 age difference between the types. Within a given family, only the same type was found. Two cases of neonatal lethal micromelic dysplasia were unclassifiable as x rays were not obtained. FIG 10 Osteopetrosis type I. Same patient as in fig 9, aged 20 years. Slightly diffuse sclerosis of the lumbar spine. Discussion Poul Erik Andersen Jr and Mogens Hauge FIG 9 Osteopetrosis type L. Skull with pronounced sclerosis of the vault. Age 20 years. The ascertainment of patients was based on all available inpatient registers as well as the radiological register at Odense University Hospital, which comprises both inpatients and outpatients. Furthermore, detailed family histories and examinations were performed. One-third of the patients were ascertained from the radiological register and from family examinations. Thus, ascertainment is considered as complete as possible, but complete ascertainment of all bone dysplasias is probably not a _*_, FIG 1 1 Osteopetrosis type II. Almost normal cranial vault but sclerosis of the base. Age 24 years.
7 Congenital generalised bone dysplasias: a clinical, radiological, and epidemiological survey FIG 12 Osteopetrosis type ll. 'Sandwich' or 'ruggerjersey' spine. Age 15 years. possible. In particular, dysplasias with no or very few symptoms are likely to be underrepresented as these will often not be examined. However, the clinical importance of such dysplasias is minor. By a thorough and systematic investigation of a population sample, it has been shown that generalised bone dysplasias are more common than generally assumed and that the distribution of the individual types differs markedly from what is commonly described. Achondroplasia, however, has been found to be less common, while other bone dysplasias, formerly included among the achondroplasias, have been found to have a higher prevalence. A very high prevalence of osteogenesis imperfecta was found. The demographic characteristics which are controllable do not show any differences from the other Danish counties and no indications of a higher coefficient of inbreeding were found in the county. No indications of clusters were observed. Thus, no special genetic or environmental regional conditions are considered to be the cause of the high prevalences. The error in the estimates of the population prevalence is greater the longer back in time we go, as radiographical documentation is missing in a larger number of cases because it was formerly uncommon to obtain x rays of newborn and stillborn infants with suspected bone dysplasia. The point prevalence at birth calculated from the period 1 January 1970 to 31 December 1983 is assumed to be as exact as possible, as knowledge of the bone dysplasias has grown and the patients are more carefully examined, including x ray examinations at birth. A few conditions like multiple cartilaginous exostoses, osteopetrosis (autosomal dominant), osteogenesis imperfecta types I and IV, and tarda types of spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia and MED are often not diagnosed during the first years of life unless discovered incidentally. Therefore, these groups will probably be underrepresented in the last years of the study period. However, all patients from the study period are at present over four years old, and therefore conditions which are not immediately obvious at birth will have been recognised by now in most cases. The characteristic stippling in the epiphyses in chondrodysplasia punctata will often disappear during the first year of life.13 If.the diagnosis is not made until then, these patients will often erroneously be classified as MED tarda or brevitas extremitatis inferioris unilateralis (in cases of the Conradi-Hunermann type) later on. Multiple cartilaginous exostoses is usually only diagnosed when the exostoses are symptomatic and so is probably underrepresented. When osteopetrosis is suspected, x ray examinations of the skull and spine as well as the pelvis and tubular bones should be obtained, as sclerosis is located mainly in the calvarium (type I) or the end plates of the vertebral bodies (type II). The radiological findings in the spine in type II resemble the findings in hyperparathyroidism or in uraemic osteodystrophy ('rugger jersey spine'), but blood analysis in patients with osteopetrosis excludes these conditions. Many cases of MED tarda and spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia tarda are erroneously diagnosed as Legg-Perthes disease and even treated as such. When bilateral Legg-Perthes disease is suspected, supplementary x ray examination of the spine and other joints to exclude generalised epiphyseal disease should be performed before treatment is instituted. 14 The radiological findings in generalised bone dysplasias are often characteristic and an exact diagnosis can be made. Even in cases where the therapeutic possibilities are few or non-existent, a correct diagnosis is important for valid genetic counselling and evaluation of the clinical prognosis. This again can influence therapy.15 It is therefore 43
8 44 important in cases of congenital malformations including skeletal abnormalities and dwarfism to obtain x ray pictures of the whole skeleton as soon as possible in order to make a correct diagnosis. As the bone dysplasias are individually relatively rare, it is difficult for most hospitals to obtain sufficient experience in diagnosing individual cases. There is a need for sufficiently large regional centres collecting cases which will improve knowledge and service in a field which includes many patients with a severe, lifelong, or even lethal handicap. We thank Dr Jens Bollerslev for cooperation on the osteopetrosis patients. The study was supported by a grant from 'Forskningsfonden vedr Medf0dte Sygdomme under Vanf0refonden'. References Wynne-Davies R, Gormley J. The prevalence of skeletal dysplasias. An estimate of their minimum frequency and the number of patients requiring orthopaedic care. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 1985;67: Orioli IM, Castilla EE, Barbosa-Neto JG. The birth prevalence rates for the skeletal dysplasias. J Med Genet 1986;23: Sillence DO, Senn A, Danks DM. Genetic heterogeneity in osteogenesis imperfecta. J Med Genet 1979;16: Sillence D. Osteogenesis imperfecta: An expanding panorama of variants. Clin Orthop 1981;159: Oberklaid F, Danks DM, Jensen F, Stace L, Rosshandler S. J Med Genet: first published as /jmg on 1 January Downloaded from Poul Erik Andersen Jr and Mogens Hauge Achondroplasia and hypochondroplasia. J Med Genet 1979; 16: Kozlowski K, Warren PS, Fisher CC. Cloverleaf skull with generalised bone dysplasia. Report of a case with short review of the literature. Pediatr Radiol 1985;15: Whitley CB, Gorlin RJ. Achondrogenesis: new nosology with evidence of genetic heterogeneity. Radiology 1983;148: Andersen PE Jr. Achondrogenesis type II in twins. Br J Radiol 1981 ;54:61-5. Bailey JA II. Disproportionate short stature. Diagnosis and management. Philadelphia: Saunders, Wynne-Davies R, Hall CM, Apley AG. Atlas of skeletal dysplasias. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, Johnston CC Jr, Lavy N, Lord T, Vellios F, Merrit AD, Deiss WP. Osteopetrosis. A clinical, genetic, metabolic and morphologic study of the dominant inherited, benign form. Medicine (Baltimore) 1968;47: Andersen PE Jr, Bollerslev J. Heterogeneity of autosomal dominant osteopetrosis. Radiology 1987;164: Andersen PE Jr, Justesen P. Chondrodysplasia punctata. Reports of two cases. Skeletal Radiol 1987;16: Crossan JF, Wynne-Davies R, Fulford GE. Bilateral failure of the capital femoral epiphysis: bilateral Perthes disease, multiple epiphyseal dysplasia, pseudoachondroplasia, and spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita and tarda. J Pediatr Orthop 1983;3: Poznanski AK. Bone dysplasias: not so rare, definitely important. AJR 1984;142: Correspondence and requests for reprints to Dr P E Andersen Jr, Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Odense University Hospital, DK-5000 Odense C, Denmark. on 22 December 2018 by guest. Protected by
= Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue
 = Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue Common Orthopedic Problems Dwarfism Short Stature Pathologic Short Stature Normal Variant Short Stature Proportionate Short Stature Midget Endocrine/nutritional
= Developmental disorders of chondro-osseous tissue Common Orthopedic Problems Dwarfism Short Stature Pathologic Short Stature Normal Variant Short Stature Proportionate Short Stature Midget Endocrine/nutritional
The birth prevalence rates for the skeletal dysplasias
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 328-332 The birth prevalence rates for the skeletal dysplasias IlDA M ORIOLI*, EDUARDO E CASTILLAt, AND JOAO G BARBOSA-NETOT From *the Department of Genetics, Institute
Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 328-332 The birth prevalence rates for the skeletal dysplasias IlDA M ORIOLI*, EDUARDO E CASTILLAt, AND JOAO G BARBOSA-NETOT From *the Department of Genetics, Institute
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX
 DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX MSK-1 FOR 2 ND YEAR MEDICAL STUDENTS Dr. Nisreen Abu Shahin CONGENITAL DISEASES WITH ABNORMAL MATRIX OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA (OI): also known as "brittle bone disease" a group
PROTOCOLS. Osteogenesis imperfecta. Principal investigator. Co-investigators. Background
 Osteogenesis imperfecta Principal investigator Leanne M. Ward, MD, FRCPC, paediatric endocrinologist Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Children s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, 401 Smyth Rd., Ottawa
Osteogenesis imperfecta Principal investigator Leanne M. Ward, MD, FRCPC, paediatric endocrinologist Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Children s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, 401 Smyth Rd., Ottawa
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24,
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 597-601 A family with spondyloepimetaphyseal dwarfism: a 'new' dysplasia or Kniest disease with autosomal recessive inheritance? T I FARAG*, S A AL-AWADI*, M C HUNTt,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1987, 24, 597-601 A family with spondyloepimetaphyseal dwarfism: a 'new' dysplasia or Kniest disease with autosomal recessive inheritance? T I FARAG*, S A AL-AWADI*, M C HUNTt,
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases
 Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Pediatric metabolic bone diseases Classification and overview of clinical and radiological findings M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid www.ifpia.com Introduction Metabolic bone
Instability of the upper cervical spine
 Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 283-288 Special report Instability of the upper cervical spine SKELETAL DYSPLASIA GROUP* There are probably about 100 different types of skeletal dysplasia (osteochondrodystrophy),
Archives of Disease in Childhood, 1989, 64, 283-288 Special report Instability of the upper cervical spine SKELETAL DYSPLASIA GROUP* There are probably about 100 different types of skeletal dysplasia (osteochondrodystrophy),
TERMINOLOGY. portion of a bone ossified from a primary center. portion of a bone ossified from a secondary center.
 Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
Embryology APPENDICULAR SKELETON Consists of the pectoral and the pelvic girdles and the bones of the limbs. Beginning at the 4 th \ menstrual week primordial bone patterns evolve into cartilaginous bone
.. -. U. SPONDYLOMETAPHYSEAL DYSPL.ASIA
 Spondylometaphyseal Dysplasia A family is described in which the father, son, and daughter have spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, consistent with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. Radiologic changes
Spondylometaphyseal Dysplasia A family is described in which the father, son, and daughter have spondylometaphyseal dysplasia, consistent with an autosomal dominant pattern of inheritance. Radiologic changes
Spondyloperipheral dysplasia
 JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
JOSEF VANEK Journal of Medical Genetics, 1983, 20, 117-121 From the Clinic of Orthopaedics, Medical Faculty of Charles University, County Hospital, Plzeh, Czechoslovakia. SUMMARY Skeletal dysplasia with
Recent studies of the fibroblast growth factor
 Genotype phenotype correlation in achondroplasia and hypochondroplasia Y. Matsui, N. Yasui, T. Kimura, N. Tsumaki, H. Kawabata, T. Ochi From Osaka University Medical School and Osaka Medical Centre and
Genotype phenotype correlation in achondroplasia and hypochondroplasia Y. Matsui, N. Yasui, T. Kimura, N. Tsumaki, H. Kawabata, T. Ochi From Osaka University Medical School and Osaka Medical Centre and
Prenatal Imaging of Skeletal Dysplasia. Dorothy Bulas MD Professor of Pediatrics and Radiology Children s National Medical Center
 Prenatal Imaging of Skeletal Dysplasia Dorothy Bulas MD Professor of Pediatrics and Radiology Children s National Medical Center OBJECTIVE Identify key features on prenatal imaging that aid in diagnosis
Prenatal Imaging of Skeletal Dysplasia Dorothy Bulas MD Professor of Pediatrics and Radiology Children s National Medical Center OBJECTIVE Identify key features on prenatal imaging that aid in diagnosis
W J R. World Journal of Radiology. Skeletal dysplasias: A radiographic approach and review of common non-lethal skeletal dysplasias.
 W J R World Journal of Radiology Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.808 World J Radiol 2014 October 28; 6(10):
W J R World Journal of Radiology Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i10.808 World J Radiol 2014 October 28; 6(10):
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation
 Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Results of Surgical Treatment of Coxa Vara in Children: Valgus Osteotomy with Angle Blade Plate Fixation Chatupon Chotigavanichaya MD*, Duangjai Leeprakobboon MD*, Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamolporn Kaewpornsawan
Cleidocranial Dysplasia
 BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
BRIEF REPORTS Cleidocranial Dysplasia Anita Sharma Rohtash Yadav Kuldip Ahlawat Cleidocranial dysplasia (CCD), is characterized by short stature, typical facial features and variable degree of pan-skeletal
G enetic disorders of the skeleton or skeletal dysplasias
 201 LETTER TO JMG Acrocapitofemoral dysplasia: an autosomal recessive skeletal dysplasia with cone shaped epiphyses in the hands and hips G R Mortier, PPGKramer, A Giedion, F A Beemer... J Med Genet 2003;40:201
201 LETTER TO JMG Acrocapitofemoral dysplasia: an autosomal recessive skeletal dysplasia with cone shaped epiphyses in the hands and hips G R Mortier, PPGKramer, A Giedion, F A Beemer... J Med Genet 2003;40:201
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
The Surgical Management of Rickets & Osteogenesis Imperfecta Dr Greg Firth Chris Hani Baragwanath Academic Hospital Department of Orthopaedics University of the Witwatersrand Rickets Inadequate mineralization
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF DYSPLASIA
 PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
Case A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI.
 Case 12659 A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 F. Vanhoenacker 1, 2 F. Malfait 3 D. Mortier 4 G.
Case 12659 A rare case of polycarpyly in a patient with Ellis - van Creveld syndrome: plain film findings and additional value of MRI. M. Mespreuve 1, 2 F. Vanhoenacker 1, 2 F. Malfait 3 D. Mortier 4 G.
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum
 Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Lower Extremity Alignment: Genu Varum / Valgum Arthur B Meyers, MD Nemours Children s Hospital & Health System Associate Professor of Radiology, University of Central Florida Clinical Associate Professor
Romanian Journal of Oral Rehabilitation Vol. 7, Issue 4, October - December 2015
 ASSOCIATION OF BILATERAL RADIOULNAR SYNOSTOSIS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA TYPE 1 CASE PRESENTATION Valeriu V. Lupu 1, Mirabela Subotnicu 1, Ancuța Ignat 1, Gabriela Păduraru 1 *, Irina Naumcieff 1, Bogdan
ASSOCIATION OF BILATERAL RADIOULNAR SYNOSTOSIS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA TYPE 1 CASE PRESENTATION Valeriu V. Lupu 1, Mirabela Subotnicu 1, Ancuța Ignat 1, Gabriela Păduraru 1 *, Irina Naumcieff 1, Bogdan
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Genetic Counseling I- Introduction II- Motives for genetic counseling requests II-1. Couple before reproduction II-2. Couple at risk III-
Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology Genetic Counseling I- Introduction II- Motives for genetic counseling requests II-1. Couple before reproduction II-2. Couple at risk III-
FISH VERTEBRAE RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE DONALD L. RESNICK
 ~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
~ 1073 RADIOLOGIC VIGNETTE FISH VERTEBRAE DONALD L. RESNICK The term fish verfebru is applied to a vertebral body that has an abnormal shape characterized by biconcavity due to depression of its superior
Content Part I Thorax Abnormal Shape or Size of the Chest Skull Abnormalities of the Shape and/or Size Rib Abnormalities of the Skull
 Content Part I Chapter 1 Skull........................ 3 Abnormalities of the Shape and/or Size of the Skull..................... 5 Microcephaly.................. 5 Macrocephaly.................. 11 Craniosynostosis................
Content Part I Chapter 1 Skull........................ 3 Abnormalities of the Shape and/or Size of the Skull..................... 5 Microcephaly.................. 5 Macrocephaly.................. 11 Craniosynostosis................
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Congenita in a nigerian baby
 Osteogenesis Imperfecta Congenita in a nigerian baby O Akiode ( ), OB Ogunfowora, A. Shonubi, AA Bajomo, AA Musa & SA Sotimehin Olabisi Onabanjo University Teaching Hospital, Sagamu, Nigeria. Correspondence:
Osteogenesis Imperfecta Congenita in a nigerian baby O Akiode ( ), OB Ogunfowora, A. Shonubi, AA Bajomo, AA Musa & SA Sotimehin Olabisi Onabanjo University Teaching Hospital, Sagamu, Nigeria. Correspondence:
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS
 HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
Incidence of Skeletal Dysplasias in North Coastal Andhra Pradesh
 Incidence of Skeletal Dysplasias in North Coastal Andhra Pradesh *B Narasinga Rao, M Pramila Padmini Department of Anatomy, Maharajah s Institute of Medical Sciences, Nellimarla *Author for Correspondence:
Incidence of Skeletal Dysplasias in North Coastal Andhra Pradesh *B Narasinga Rao, M Pramila Padmini Department of Anatomy, Maharajah s Institute of Medical Sciences, Nellimarla *Author for Correspondence:
A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease
 A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease Cyndie Seraphin Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient A 4 year-old boy is complaining of severe L hip pain. The differential diagnosis of acute
A 4 year old with hip pain: Legg-Calvé-Perthes Disease Cyndie Seraphin Harvard Medical School Year III Our Patient A 4 year-old boy is complaining of severe L hip pain. The differential diagnosis of acute
ISSN (Online) ISSN (Print)
 Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2017; 5(9):626-630 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
Scholars Academic Journal of Biosciences (SAJB) Sch. Acad. J. Biosci., 2017; 5(9):626-630 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publisher (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources) www.saspublisher.com
DYSPLASIA EPIPHYSIALIS MULTIPLEX IN THREE SISTERS
 DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
DYSPLASA EPPHYSALS MULTPLEX N THREE SSTERS \\T WAUGH, LONDON, ENGLAND From the Orthopaedic Department, King s College Hospital, London Dysplasia epiphysialis multiplex, first described by Fairbank (1947),
Mlicrospherophakia-metaphyseal dysplasia:
 I Med Genet 1990; 27: 467-471 Mlicrospherophakia-metaphyseal dysplasia: a 'new' dominantly inherited bone dysplasia with severe eye involvement Alain Verloes, Lionel Van Maldergem, Pierre de Marneffe,
I Med Genet 1990; 27: 467-471 Mlicrospherophakia-metaphyseal dysplasia: a 'new' dominantly inherited bone dysplasia with severe eye involvement Alain Verloes, Lionel Van Maldergem, Pierre de Marneffe,
Development of genu varum in achondroplasia
 Development of genu varum in achondroplasia RELATION TO FIBULAR OVERGROWTH S. T. Lee, H. R. Song, R. Mahajan, V. Makwana, S. W. Suh, S. H. Lee From Korea University, Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea Genu varum
Development of genu varum in achondroplasia RELATION TO FIBULAR OVERGROWTH S. T. Lee, H. R. Song, R. Mahajan, V. Makwana, S. W. Suh, S. H. Lee From Korea University, Guro Hospital, Seoul, Korea Genu varum
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier
 Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Proposal form for the evaluation of a genetic test for NHS Service Gene Dossier Test Disease Population Triad Disease name and description (please provide any alternative names Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Stickler syndrome. Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium
 Stickler syndrome Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Third European Course in Clinical Dysmorphology Rome, November 20-21, 2009 Stickler syndrome
Stickler syndrome Geert Mortier, MD, PhD Center for Medical Genetics Ghent University Hospital Ghent, Belgium Third European Course in Clinical Dysmorphology Rome, November 20-21, 2009 Stickler syndrome
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2004; 46:
 Toplam: 98 Sayfa + 2 adet kapak sayfasý. The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2004; 46: 197-203 Original A new concept of skeletal dysplasias Beyhan Tüysüz Division of Genetics, Department of Pediatrics,
Toplam: 98 Sayfa + 2 adet kapak sayfasý. The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2004; 46: 197-203 Original A new concept of skeletal dysplasias Beyhan Tüysüz Division of Genetics, Department of Pediatrics,
VPM Systemic Pathology II
 CASE 1 - LAB PATHOLOGY OF BONES W-2012 VPM 222 - Systemic Pathology II PATHOLOGY OF BONES LABORATORY* January 11, 2012 Dr. Carlos Lopez * Many images used in this section were obtained from the Noah s
CASE 1 - LAB PATHOLOGY OF BONES W-2012 VPM 222 - Systemic Pathology II PATHOLOGY OF BONES LABORATORY* January 11, 2012 Dr. Carlos Lopez * Many images used in this section were obtained from the Noah s
Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports
 Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports Sch J Med Case Rep 2016; 4(4):265-269 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers) (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports Sch J Med Case Rep 2016; 4(4):265-269 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers) (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Diagnostic accuracy of paediatric skull radiograph versus whole skeletal survey in skeletal dysplasias and dysostoses in high risk groups
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 5 Ver. X (May. 2017), PP 31-38 www.iosrjournals.org Diagnostic accuracy of paediatric skull
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 16, Issue 5 Ver. X (May. 2017), PP 31-38 www.iosrjournals.org Diagnostic accuracy of paediatric skull
Achondroplasia and Hypochondroplasia Genes
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 11. Observations Suggesting Allelism of the Achondroplasia and Hypochondroplasia Genes VICTOR A. McKUSICK, THADDEUS E. KELLY, and JOHN P. DORST From the Division
Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 11. Observations Suggesting Allelism of the Achondroplasia and Hypochondroplasia Genes VICTOR A. McKUSICK, THADDEUS E. KELLY, and JOHN P. DORST From the Division
Friday Teaching. Bones
 Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Two brothers with heart defects and limb shortening:
 746 7 Med Genet 199; 27: 746-751 Two brothers with heart defects and limb shortening: case reports and review W Reardon, J Hurst, T I Farag, C Hall, M Baraitser Abstract Two male Arab sibs are reported
746 7 Med Genet 199; 27: 746-751 Two brothers with heart defects and limb shortening: case reports and review W Reardon, J Hurst, T I Farag, C Hall, M Baraitser Abstract Two male Arab sibs are reported
Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
Journal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 253. Hereditary Brachydactyly Associated with Hypertension N. BILGINTURAN, S. ZILELI, S. KARACADAG, and T. PIRNAR Departments of Paediatrics, Internal Medicine,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, the result of mutations in the structural gene
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, 521-527 Structural and segregation analysis of the type II collagen gene (COL2A1) in some heritable chondrodysplasias PAUL WORDSWORTH*, DONALD OGILVIE*, LINDA PRIESTLEY*,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1988, 25, 521-527 Structural and segregation analysis of the type II collagen gene (COL2A1) in some heritable chondrodysplasias PAUL WORDSWORTH*, DONALD OGILVIE*, LINDA PRIESTLEY*,
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh
 Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Pediatric Orthopedic Pathology Pathology 2 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Congenital Defects - Clubfoot (congenital equinovarus) Forefoot is adducted and supinated o Positional equinovarus o Idiopathic congenital equinovarus
Know all the bones of the skull, lateral view and frontal view. From the worksheets, one of the earlier ones in this unit.
 Study Guide for Skeleton unit. Here are many of the questions minus the answers and minus the matching. Matching will be vocab on bone fractures and vocab on bones of the axial skeleton and their common
Study Guide for Skeleton unit. Here are many of the questions minus the answers and minus the matching. Matching will be vocab on bone fractures and vocab on bones of the axial skeleton and their common
Bone Development. V. Gilsanz and O. Ratib, Hand Bone Age, DOI / _2, Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2012
 Bone Development 2 Skeletal maturity is a measure of development incorporating the size, shape and degree of mineralization of bone to define its proximity to full maturity. The assessment of skeletal
Bone Development 2 Skeletal maturity is a measure of development incorporating the size, shape and degree of mineralization of bone to define its proximity to full maturity. The assessment of skeletal
ISCHIOPUBIC HYPOPLASIA : A RARE CONSTITUENT OF CONGENITAL SYNDROMES
 ISCHIOPUBIC HYPOPLASIA : A RARE CONSTITUENT OF CONGENITAL SYNDROMES N. K. SFEROPOULOS, I. TSITOURIDIS Hypoplasia of the ischiopubic region is described in four patients. An adolescent was referred for
ISCHIOPUBIC HYPOPLASIA : A RARE CONSTITUENT OF CONGENITAL SYNDROMES N. K. SFEROPOULOS, I. TSITOURIDIS Hypoplasia of the ischiopubic region is described in four patients. An adolescent was referred for
The data were analysed using Fisher s exact test and the chi-squared test.
 Congenital malformations are a major cause of perinatal and neonatal death [1], both in developed and developing countries [2]. These malformations have multifactorial etiologies and 40% of cases are idiopathic
Congenital malformations are a major cause of perinatal and neonatal death [1], both in developed and developing countries [2]. These malformations have multifactorial etiologies and 40% of cases are idiopathic
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates December 2014 2 Abu Asbeh J, Bystricka A, Qadir M, Nikolay M, Khan J, Neonatal Intensive
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY Raine syndrome: clinical and radiological features of a case from the United Arab Emirates December 2014 2 Abu Asbeh J, Bystricka A, Qadir M, Nikolay M, Khan J, Neonatal Intensive
The Accuracy of Current Methods in Deciding the Timing of Epiphysiodesis
 The Accuracy of Current Methods in Deciding the Timing of Epiphysiodesis Soon Chul Lee MD 1, Sung Wook Seo MD 2, Kyung Sup Lim MD 2, Jong Sup Shim MD 2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, 1 Bundang CHA
The Accuracy of Current Methods in Deciding the Timing of Epiphysiodesis Soon Chul Lee MD 1, Sung Wook Seo MD 2, Kyung Sup Lim MD 2, Jong Sup Shim MD 2 Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, 1 Bundang CHA
Skeletal Dysplasias. Let me Count the Whys. Normal Skeletal Development. Fetal Musculoskeletal System & Skeletal Dysplasias 3/6/2017
 Fetal Musculoskeletal System & Skeletal Dysplasias Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager
Fetal Musculoskeletal System & Skeletal Dysplasias Director of Ultrasound Education & Quality Assurance Baylor College of Medicine Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine Maternal Fetal Center Imaging Manager
Original Article Analysis of the vacuum phenomenon in plain hip radiographs in children
 Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):3325-3331 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0005361 Original Article Analysis of the vacuum phenomenon in plain hip radiographs in children Zhenjiang Liu, Wei Yan, Lijun Zhang
Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8(3):3325-3331 www.ijcem.com /ISSN:1940-5901/IJCEM0005361 Original Article Analysis of the vacuum phenomenon in plain hip radiographs in children Zhenjiang Liu, Wei Yan, Lijun Zhang
Department Of Paediatrics, Deccan College of Medical Sciences, Princess Esra Hospital, Hyderabad , Andhra Pradesh, India.
 Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports Sch J Med Case Rep 2015; 3(8A):748-753 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers) (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Scholars Journal of Medical Case Reports Sch J Med Case Rep 2015; 3(8A):748-753 Scholars Academic and Scientific Publishers (SAS Publishers) (An International Publisher for Academic and Scientific Resources)
Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia with joint
 Syndrome of the month MRC Research Unit for Medical Genetics, Department of Human Genetics, Medical School, University of Cape Town, Observatory 7925, South Africa P Beighton Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia
Syndrome of the month MRC Research Unit for Medical Genetics, Department of Human Genetics, Medical School, University of Cape Town, Observatory 7925, South Africa P Beighton Spondyloepimetaphyseal dysplasia
Autosomal Dominant Type I Osteopetrosis Is Related with Iatrogenic Fractures in Arthroplasty
 Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:484-488 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.484 Autosomal Dominant Type I Osteopetrosis Is Related with Iatrogenic Fractures in Arthroplasty Ruud P.
Case Report Clinics in Orthopedic Surgery 2014;6:484-488 http://dx.doi.org/10.4055/cios.2014.6.4.484 Autosomal Dominant Type I Osteopetrosis Is Related with Iatrogenic Fractures in Arthroplasty Ruud P.
Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia related osteoporosis in a young male patient
 CASE REPORT Aytekin et al. 1 PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia related osteoporosis in a young male patient Ebru Aytekin, Nil Sayiner Caglar, Ertan Yüce, Yasemin Pekin Dogan, Didemİnceboy
CASE REPORT Aytekin et al. 1 PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia related osteoporosis in a young male patient Ebru Aytekin, Nil Sayiner Caglar, Ertan Yüce, Yasemin Pekin Dogan, Didemİnceboy
Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient
 September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
September 2005 Evaluation of a Pediatric Patient Percy Ballard, Harvard Medical School Year III Our Little Man: 6mo old male transferred to Children s from hospital in the Philippines 3mo history of meningitis,
CONGENITAL ABSENCE OF FEMUR AND FIBULA Report of Two Cases
 CONGENITAL ABSENCE OF FEMUR AND FIBULA Report of Two Cases Reprinted by permission of the author and publisher from Clinical Orthopaedics, Philadelphia, J.B. Lippincott Co., 1959, 15, 203-207. By ROBERT
CONGENITAL ABSENCE OF FEMUR AND FIBULA Report of Two Cases Reprinted by permission of the author and publisher from Clinical Orthopaedics, Philadelphia, J.B. Lippincott Co., 1959, 15, 203-207. By ROBERT
Method We performed a general and orthopaedic examination as well as a radiologic skeletal survey of the above four family members.
 Page 34 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Winter 2011 Vol 10 No 2 C A S E R E P O RT A N D R E V I E W O F T H E L I T E R AT U R E Cleidocranial dysplasia presenting as familial coxa vara in a South African family
Page 34 / SA ORTHOPAEDIC JOURNAL Winter 2011 Vol 10 No 2 C A S E R E P O RT A N D R E V I E W O F T H E L I T E R AT U R E Cleidocranial dysplasia presenting as familial coxa vara in a South African family
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY. A severe case of osteogenesis imperfecta
 SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY A severe case of osteogenesis imperfecta October 2016 Pohl C, Kämpfen S, Filges I, Wellmann S, Division of Neonatology (PC, KS, WS), University of Basel Children s Hospital,
SWISS SOCIETY OF NEONATOLOGY A severe case of osteogenesis imperfecta October 2016 Pohl C, Kämpfen S, Filges I, Wellmann S, Division of Neonatology (PC, KS, WS), University of Basel Children s Hospital,
Physiological Genu Varum
 Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Physiological Genu Varum Lars Ingvar Hansson & Mohammed Zayer To cite this article:
Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Physiological Genu Varum Lars Ingvar Hansson & Mohammed Zayer To cite this article:
Thanatophoric Dwarfism
 J7ournal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 243. Thanatophoric Dwarfism K. SHAH, R. ASTLEY, and A. H. CAMERON The Children's Hospital, Birmingham B16 8ET Summary. A review of the radiographs of children previously
J7ournal of Medical Genetics (1973). 10, 243. Thanatophoric Dwarfism K. SHAH, R. ASTLEY, and A. H. CAMERON The Children's Hospital, Birmingham B16 8ET Summary. A review of the radiographs of children previously
Spinal dysraphism: genetic relation to
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 343-350. Spinal dysraphism: genetic relation to neural tube malformations C. 0. CARTER, K. A. EVANS, and K. TILL* From MRC Clinical Genetics Unit, Institute of Child
Journal of Medical Genetics (1976). 13, 343-350. Spinal dysraphism: genetic relation to neural tube malformations C. 0. CARTER, K. A. EVANS, and K. TILL* From MRC Clinical Genetics Unit, Institute of Child
BY Dr Farooq Khan Aman Ullah khan
 Lecture 01 General Anatomy & Classification of Bone BY Dr Farooq Khan Aman Ullah khan Dated: 22.012.2017 Skeleton The hard, supporting framework of the body is called the skeleton. Skeleton includes bones
Lecture 01 General Anatomy & Classification of Bone BY Dr Farooq Khan Aman Ullah khan Dated: 22.012.2017 Skeleton The hard, supporting framework of the body is called the skeleton. Skeleton includes bones
a Genetics Unit, Department of Paediatrics, Faculty of Medicine, University of Received 29 June 2004 Accepted 3 November 2004
 Original article 1 Further delineation of Al-Gazali syndrome (multiple skeletal abnormalities with anterior segment anomalies of the eye and early lethality) in a Malaysian family Meow-Keong Thong a, Lee-Gaik
Original article 1 Further delineation of Al-Gazali syndrome (multiple skeletal abnormalities with anterior segment anomalies of the eye and early lethality) in a Malaysian family Meow-Keong Thong a, Lee-Gaik
The surgical treatment of Perthes disease by
 Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in Perthes disease A REVIEW AT THE END OF GROWTH K. Daly, C. Bruce, A. Catterall From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore, England The surgical treatment of
Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in Perthes disease A REVIEW AT THE END OF GROWTH K. Daly, C. Bruce, A. Catterall From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore, England The surgical treatment of
autosomal dominant mode of inheritance
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1982, 19, 104-109 A new variant of spondylometaphyseal dysplasia with autosomal dominant mode of inheritance J M GARCIA-CASTRO, C M ISALES-FORSYTHE, AND P DIAZ DE GARAU From
Journal of Medical Genetics 1982, 19, 104-109 A new variant of spondylometaphyseal dysplasia with autosomal dominant mode of inheritance J M GARCIA-CASTRO, C M ISALES-FORSYTHE, AND P DIAZ DE GARAU From
Case Report: Perinatal Lethal Form of Hypophosphatasia
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, December: 273-277, 201 5 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Case Report: Perinatal Lethal Form of Hypophosphatasia NAHLA BARAKAT, M.D.*; WALEED SHABAAN, M.R.C.P.*
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 2, December: 273-277, 201 5 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Case Report: Perinatal Lethal Form of Hypophosphatasia NAHLA BARAKAT, M.D.*; WALEED SHABAAN, M.R.C.P.*
Hip Joint Trevor Disease: Literature Review and a Case Report
 http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Case Report (Pages: 6809-6814) Hip Joint Trevor Disease: Literature Review and a Case Report Mohammad Hallaj Moghadam 1, *Ali Parsa 2,3, Mohammad Hassani 4, Maryam Mirzaie 5, Reza
http:// ijp.mums.ac.ir Case Report (Pages: 6809-6814) Hip Joint Trevor Disease: Literature Review and a Case Report Mohammad Hallaj Moghadam 1, *Ali Parsa 2,3, Mohammad Hassani 4, Maryam Mirzaie 5, Reza
28/04/2016. I have nothing to declare and no financial. interest or relationship to disclose
 I have nothing to declare and no financial interest or relationship to disclose Skeletal Anomalies are diverse range of complexities which is NOT Easy to diagnose. It is NOT Difficult to detect-just be
I have nothing to declare and no financial interest or relationship to disclose Skeletal Anomalies are diverse range of complexities which is NOT Easy to diagnose. It is NOT Difficult to detect-just be
THE RISK OF ITERATIVE FRACTURES IN PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - CASE REPORT
 Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 1 SURGERY CASE REPORTS THE RISK OF ITERATIVE FRACTURES IN PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - CASE REPORT D. Popescu 1*, B. Puha 1, B. Veliceasa
Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat., Iaşi 2017 vol. 121, no. 1 SURGERY CASE REPORTS THE RISK OF ITERATIVE FRACTURES IN PATIENTS WITH OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA - CASE REPORT D. Popescu 1*, B. Puha 1, B. Veliceasa
Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases
 Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 350-354 Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases M D BAIN*, R M WINTERt, AND J BURNt From *the Section of Perinatal and Child Health,
Journal of Medical Genetics 1986, 23, 350-354 Robinow syndrome without mesomelic 'brachymelia': a report of five cases M D BAIN*, R M WINTERt, AND J BURNt From *the Section of Perinatal and Child Health,
Abdullah Alaraj. Mohammad Alfarra. Mousa al abbadi. Modified by : Saif Yamin. 1 P a g e
 #2 Abdullah Alaraj Mohammad Alfarra Mousa al abbadi Modified by : Saif Yamin 1 P a g e introduction to what we will cover: -dysostosis is caused by genetic abnormalities in homeobox genes, cytokines and
#2 Abdullah Alaraj Mohammad Alfarra Mousa al abbadi Modified by : Saif Yamin 1 P a g e introduction to what we will cover: -dysostosis is caused by genetic abnormalities in homeobox genes, cytokines and
SPR 2015 POSTGRADUATE COURSE
 SPR 2015 POSTGRADUATE COURSE Musculoskeletal Imaging On this knee MRI from a 16 year old male, which component of the posterolateral corner is indicated by the arrow? A. Popliteus tendon B. Arcuate ligament
SPR 2015 POSTGRADUATE COURSE Musculoskeletal Imaging On this knee MRI from a 16 year old male, which component of the posterolateral corner is indicated by the arrow? A. Popliteus tendon B. Arcuate ligament
Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test
 Name: Date: 1/2/18 Section Broughton High School 1 Section 1: - True or False Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test 1. The number of bones in the body increases from the time of birth to adulthood.
Name: Date: 1/2/18 Section Broughton High School 1 Section 1: - True or False Forensic Anthropology Open Notes Practice Test 1. The number of bones in the body increases from the time of birth to adulthood.
SURVEY OF DUCHENNE TYPE AND CONGENITAL TYPE OF MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY IN SHIMANE, JAPAN 1
 Jap. J. Human Genet. 22, 43--47, 1977 SURVEY OF DUCHENNE TYPE AND CONGENITAL TYPE OF MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY IN SHIMANE, JAPAN 1 Kenzo TAKESHITA,* Kunio YOSHINO,* Tadashi KITAHARA,* Toshio NAKASHIMA,** and
Jap. J. Human Genet. 22, 43--47, 1977 SURVEY OF DUCHENNE TYPE AND CONGENITAL TYPE OF MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY IN SHIMANE, JAPAN 1 Kenzo TAKESHITA,* Kunio YOSHINO,* Tadashi KITAHARA,* Toshio NAKASHIMA,** and
Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures
 July 2006 Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures Denise De Las Nueces, Harvard Medical School Year IV General Overview Introduction
July 2006 Radiologic Assessment of Child Abuse in Infants: A Focus on Plain Film Analysis of Highly Specific Fractures Denise De Las Nueces, Harvard Medical School Year IV General Overview Introduction
The Use of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing Fracture Occurrence in Children with Osteogenesis Imperfecta
 Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-8-2014 The Use of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing
Pacific University CommonKnowledge School of Physician Assistant Studies Theses, Dissertations and Capstone Projects Summer 8-8-2014 The Use of Bisphosphonates in Increasing Bone Mineral Density and Decreasing
Clinical Application of Computed Radiography in Orthopedic Surgery
 Clinical Application of Computed Radiography in Orthopedic Surgery Satoru Fujita, Masamichi Tanaka, Sigeaki Hirota, and Takeshi Fuji Since 1988, Fuji Computed Radiography (FCR) system (Fuji Medical Systems,
Clinical Application of Computed Radiography in Orthopedic Surgery Satoru Fujita, Masamichi Tanaka, Sigeaki Hirota, and Takeshi Fuji Since 1988, Fuji Computed Radiography (FCR) system (Fuji Medical Systems,
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Childhood hip conditions. Belen Carsi Paediatric Orthopaedic Consultant
 Childhood hip conditions Belen Carsi Paediatric Orthopaedic Consultant Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Legg-Calve-Perthes disease Slipped Capital femoral epiphysis Limp Arthritis Developmental Dysplasia
Childhood hip conditions Belen Carsi Paediatric Orthopaedic Consultant Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Legg-Calve-Perthes disease Slipped Capital femoral epiphysis Limp Arthritis Developmental Dysplasia
Case Report: Achondroplasia
 Case Report: Achondroplasia Author(s): R.S. Sethi, Lalit Kumar, Om Shankar Chaurasiya, Rohit Gorakh Vol. 15, No. 2 (2011-07 - 2011-12) R.S. Sethi, Lalit Kumar, Om Shankar Chaurasiya, Rohit Gorakh Department
Case Report: Achondroplasia Author(s): R.S. Sethi, Lalit Kumar, Om Shankar Chaurasiya, Rohit Gorakh Vol. 15, No. 2 (2011-07 - 2011-12) R.S. Sethi, Lalit Kumar, Om Shankar Chaurasiya, Rohit Gorakh Department
Treatment of Varus Deformities of the Lower Limbs in Patients with Achondroplasia and Hypochondroplasia
 Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.net The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2013, 7, 33-39 33 Open Access Treatment of Varus Deformities of the Lower Limbs in Patients with Achondroplasia and
Send Orders of Reprints at reprints@benthamscience.net The Open Orthopaedics Journal, 2013, 7, 33-39 33 Open Access Treatment of Varus Deformities of the Lower Limbs in Patients with Achondroplasia and
CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE. Dr. Bahar Naghavi
 2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
2 CURRENT GENETIC TESTING TOOLS IN NEONATAL MEDICINE Dr. Bahar Naghavi Assistant professor of Basic Science Department, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran,Iran 3 Introduction Over 4000
Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics
 Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics Vitamin D physiology Introduction Etiology Clinical feature Radiology Diagnosis Lab Treatment Source: -Fish, liver and oil, - Human milk (30-40 IU/L) - Exposure to sun light
Sachin Soni DNB Pediatrics Vitamin D physiology Introduction Etiology Clinical feature Radiology Diagnosis Lab Treatment Source: -Fish, liver and oil, - Human milk (30-40 IU/L) - Exposure to sun light
Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
Abdullah Alaraj. Mousa al abbadi. Mohammad Alfarra. 1 Page
 f #2 Abdullah Alaraj Mohammad Alfarra Mousa al abbadi 1 Page introduction to what we will cover: -dysostosis is caused by genetic abnormalities in homeobox genes, cytokines and its receptors. However,
f #2 Abdullah Alaraj Mohammad Alfarra Mousa al abbadi 1 Page introduction to what we will cover: -dysostosis is caused by genetic abnormalities in homeobox genes, cytokines and its receptors. However,
Bio 103 Skeletal System 45
 45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
45 Lecture Outline: SKELETAL SYSTEM [Chapters 7, 8] Introduction A. Components B. Functions 1. 2. 3. 4. Classification and Parts A. Bone Shapes 1. Long: 2. Short: 3. Flat: 4. Irregular: 5. Sesamoid: B.
Non-inflammatory joint pain
 Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Non-inflammatory joint pain Lawrence Owino Okong o, Mmed (UoN); Mphil. (UCT). Lecturer, Department of Paediatrics and Child Health, University of Nairobi. Paediatrician/ Rheumatologist. INTRODUCTION Musculoskeletal
Visual Vignette EP VISUAL VIGNETTE
 ENDOCRINE PRACTICE Rapid Electronic Article in Press Rapid Electronic Articles in Press are preprinted manuscripts that have been reviewed and accepted for publication, but have yet to be edited, typeset
ENDOCRINE PRACTICE Rapid Electronic Article in Press Rapid Electronic Articles in Press are preprinted manuscripts that have been reviewed and accepted for publication, but have yet to be edited, typeset
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN
 ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
ESSENTIALS OF PLAIN FILM INTERPRETATION: SPINE DR ASIF SAIFUDDIN Consultant Musculoskeletal Radiologist Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital Stanmore,UK. INTRODUCTION 2 INTRODUCTION 3 INTRODUCTION Spinal
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions. Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions
 Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Single Gene (Monogenic) Disorders Mendelian Inheritance: Definitions A genetic locus is a specific position or location on a chromosome. Frequently, locus is used to refer to a specific gene. Alleles are
Typical Cleft Hand. Windblown Hand. Congenital, Developmental Arrest. Congenital, Failure of Differentiation. Longitudinal (vs.
 Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Typical Cleft Hand Congenital, Developmental Arrest Longitudinal (vs. Transverse) Central Deficiency (vs. Preaxial, Postaxial, Phocomelia) Windblown Hand Congenital, Failure of Differentiation Contracture
Case Report Radiographic and MR Imaging Findings of the Spine after Bisphosphonate Treatment, in a Child with Idiopathic Juvenile Osteoporosis
 Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2015, Article ID 727510, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/727510 Case Report Radiographic and MR Imaging Findings of the Spine after Bisphosphonate Treatment, in
Case Reports in Radiology Volume 2015, Article ID 727510, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/727510 Case Report Radiographic and MR Imaging Findings of the Spine after Bisphosphonate Treatment, in
Cleidocranial Dysplasia - A case report
 Cleidocranial Dysplasia - A case report Author(s): Suhail Rizvi, Hamid Raihan, Tasneem Rizvi Vol. 17, No. 2 (2006-05 - 2006-08) Biomedical Research 2006; 17 (2): 129-132 Suhail Rizvi, Hamid Raihan, Tasneem
Cleidocranial Dysplasia - A case report Author(s): Suhail Rizvi, Hamid Raihan, Tasneem Rizvi Vol. 17, No. 2 (2006-05 - 2006-08) Biomedical Research 2006; 17 (2): 129-132 Suhail Rizvi, Hamid Raihan, Tasneem
Synostosis of First and Second Ribs: A Case Report
 Synostosis of First and Second Ribs: A Case Report VIDYA K. SHIVAKUMAR 1 & PRIYA RANGANATH 2 Department of Anatomy, Bangalore Medical College & Research Institute, Bangalore 560002, Karnataka E-mail: priya_ranganath@rediffmail.com
Synostosis of First and Second Ribs: A Case Report VIDYA K. SHIVAKUMAR 1 & PRIYA RANGANATH 2 Department of Anatomy, Bangalore Medical College & Research Institute, Bangalore 560002, Karnataka E-mail: priya_ranganath@rediffmail.com
NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES
 NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES Fact Sheet FY 2007 What is the Mission of the Bone Coalition? The National Coalition for Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases is dedicated
NATIONAL COALITION FOR OSTEOPOROSIS AND RELATED BONE DISEASES Fact Sheet FY 2007 What is the Mission of the Bone Coalition? The National Coalition for Osteoporosis and Related Bone Diseases is dedicated
