Laboratory Diagnosis. Dr. M Saraei
|
|
|
- Giles Watkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Laboratory Diagnosis of toxoplasmosis Dr. M Saraei Qazvin University of Medical Sciences
3 Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite that infects most species of warm-blooded animals
4 Definitive Host
5 Intermediate Host
6 Intermediate Host
7
8 Fecal-Oral Transmission Oocyst
9 Carnivorism
10 Transplacental Tachyzoite
11
12 Tissue cyst in meat Oocysts Tissue cyst Acute Phase Chronic Phase
13 Acute Phase
14 Chronic Phase
15 Toxoplasmosis Aquired A i dtoxoplasmosis Congenital toxoplasmosis
16 Aquired toxoplasmosis In immunocompetent individuals, acute infection is usually asymptomatic and spontaneous recovery is the rule. Most often, toxoplasmosis manifests as asymptomatic cervical lymphadenopathy, but any or all lymph node groups may be enlarged.
17 Toxoplasmic encephalitis in immunocompromised patients
18 Congenital toxoplasmosis
19 Congenital toxoplasmosis Chorioretinitis is the most common manifestation of congenital toxoplasmosis
20 Lb Laboratory Diagnosis i of toxoplasmosis
21 The laboratory diagnosis of toxoplasmosis may be established by: Serological tests Histological demonstration of the parasite and/or its antigens (i.e. immunoperoxidase stain) Isolation I l of fthe organism. Molecular diagnosis (PCR/ Real Time PCR)
22 Diagnostic method may differ considerably with the clinical entity: Immunocompetent patient Immunodeficient patient Ocular toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy Congenital toxoplasmosis.
23 Main challenge for diagnosis of toxoplasmosis is differentiation of acute and chronic infections
24 Acute infection is diagnosed by: Isolation of T. gondii from blood or body fluids PCR blood or body fluids Demonstration of tachyzoites in histologic sections of tissue or in cytologic preparations of body fluids Demonstration of a characteristic lymph node histologic appearance Serologic test results Demonstration of T. gondii tissue cysts in the placenta,,f fetus, or neonate.
25 Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasmosis Serologic tests for the demonstration of specific antibody to T. gondii is the primary method of diagnosis.
26 Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasmosis IgG, IgM, IgA, and IgE antibodies produce to T. gondii Initial serologic testing can be accomplished by simultaneously requesting IgG and IgM antibody tests.
27 Pattern of IgG& IgM antibodies in acute and chronic infection
28 Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasmosis ELISA, IFA, Chemiluminescent tests use for detection of specific IgG and IgM antibodies to T. gondii
29 Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasmosis Sabin-Feldman Dye Test Immunosorbent Agglutination Assay (ISAGA) Differential agglutination (AC/HS) IgG avidity Test
30 Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasmosis Commercial or nonreference laboratories can easily perform this task.
31 Serodiagnosis of Toxoplasmosis Only positive results in IgM antibody tests need to be sent for confirmatory testing to reference laboratories
32 IgM test is used to help dt determinie ii whether hth a patient t has been infected recently or in the distant past
33 Defect of IgM test for serodiagnosis of toxoplasmosis oplasmosis IM IgM antibodies can persist itfor months to more than one year
34 IgG avidity test have been introduced to help discriminate i i between recently acquired and distant infection.
35 IgG avidity test Studies of the kinetics of the avidity of IgG in pregnant women who have seroconverted tdduring gestation tti have shown that women with high avidity test results were infected with T. gondii at least 3 to 5 months earlier (time to conversion from low to high avidity antibodies varies with the method used).
36 Defect of IgG avidity test low avidity antibodies may persist for many months. Therefore, low avidity antibodies does not necessarily indicate recently acquired infection.
37 What is solution Because of the significant potential of misinterpreting a positive IgM test result, confirmatory testing should be performed
38 Confirmatory test for toxoplasmosis A combination of serological tests is frequently required to establish whether an individual has been more likely infected in the distant past or has been recently infected.
39 The TSP has been clinically helpful in the setting of: Lymphadenitis Myocarditis Polymyositis Chorioretinitis iti During gpregnancy
40 For confirmatory testing, TSL-PAMFRI* offers a panel of tests t Sabin-Feldman Dye Test (DT) Double sandwich IgM ELISA IgA ELISA IgE ELISA AC/HS test IgG Avidity test * Toxoplasma Serology Laboratory of the Palo Alto Medical Foundation Research Institute (TSL-PAMFRI)
41 Sabin-Feldman Dye Test (DT) Available mainly in reference laboratories Requires use of live organisms Considered the gold standard
42 Sabin-Feldman Dye Test (DT) A positive DT establishes that the patient has been exposed to the parasite. A negative DT essentially rules out prior exposure to T. gondii (unless the patient is hypogammaglobulinemic). However, in a small number of patients, IgG antibodies might not tbe detected t d within 2 to 3 weeks after the initial exposure to the parasite.
43 Sabin-Feldman Dye Test (DT) In addition, rare cases of toxoplasmic chorioretinitis and toxoplasmic encephalitis (TE) in immunocompromised patients have been documented in patients negative for T. gondii-specific p IgG antibodies.
44 IFA Easier, safer and more economical than the Sabin Feldman dye test and yields ild parallel lllresults. False positives obtained in patients with ANA.
45 Differential agglutination (AC/HS) The differential agglutination test (also known as the "AC/HS test") uses two antigen preparations that t express antigenic determinants found early following acute infection (AC antigen) or in the later stages of infection (HS).
46 Differential agglutination (AC/HS) This test has proved useful in helping differentiate acute from chronic infections but is best used in combination with a panel of other tests (e.g.: the TSP).
47 IgG Avidity Test The functional affinity of specific IgG antibodies is initially low after primary antigenic challenge and increases during subsequent weeks and months.
48 IgG Avidity Test Protein-denaturing reagents including urea are used to dissociate the antibody-antigen complex. The avidity result is determined using the ratios of antibody titration curves of urea-treated and untreated serum
49 IgG Avidity Test Clinical laboratories involved in the care of pregnant women should be aware that t avidity testing ti is a confirmatory test and not the ultimate test for decision-making.
50 IgM-ELISA Does not differentiate between acute and chronic infection. FDA warns against use as the sole method of determining infection during pregnancy.
51 Double-Sandwich IgM-ELISA This method avoids false positive results due to the presence of RF and ANA
52 IgA- ELISA IgA antibodies may be detected in sera of acutely infected adults and congenitally infected infants using ELISA or ISAGA methods. As is true for IgM antibodies to the parasite, IgA antibodies may persist for many months to more than one year
53 IgA- ELISA The increased sensitivity of IgA assays over IgM assays for diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis represents an advance in diagnosis of the infection in the fetus and newborn
54 IgA-ELISA In a number of newborns with congenital toxoplasmosis and negative IgM antibodies, the serological diagnosis has been established by the presence of IgA and IgG antibodies.
55 IgE-ELISA ELISA IgE antibodies are detectable by ELISA in sera of acutely infected adults, congenitally infected infants, and children with congenital toxoplasmic chorioretinitis iti
56 IgE-ELISA ELISA The duration of IgE seropositivity is less than with IgM or IgA antibodies and hence appears useful as an adjunctive method for identifying recently acquired infections.
57 Panel Toxoplasma Pregnancy Panel (16 weeks gestation or earlier): IgG G(Dye Test), IgM-ELISA, IgG Avidity Toxoplasma Pregnancy Panel (more than 16 weeks gestation): IgG (Dye Test), IgM-ELISA, AC/HS Toxoplasma Infant Panel (less than 6 months of age): IgG (Dye Test), IgM-ISAGA, IgA-ELISA Toxoplasma Panel (6 months of age or older): IgG (Dye Test), IgM-ELISA, IgA-ELISA, IgE-ELISA, AC/HS
58 IgM -ISAGA The test is simple to perform, does not require the use of enzyme conjugate, and is read in the same manner as the agglutination test. Overall, it is more sensitive and specific than the IgM-IFA IFA test. The presence of RF or ANA does not cause false- The presence of RF or ANA does not cause false positive results in the IgM-ISAGA.
59 IgM -ISAGA In adults, it is more sensitive but much less specific than the double-sandwich d IM IgM- ELISA method. In infants, the IgM-ISAGA is the most sensitive method and is used effectively for the diagnosis of congenital infection in infants 6 months of age or younger.
60 IgM -ISAGA A positive IgM-ISAGA test result in the first 10 days of life should be repeated after 10 days to rule out the possibility of maternal contamination ti of fim IgM antibodies. The ISAGA method has also been used to detect IgA and IgE antibodies.
61
62 Molecular diagnosis of toxoplasmosis Serological diagnosis can be difficult in prenatal cases or in patients with immunodeficiency. The use of molecular diagnostic techniques is particularly appropriate for such patients
63 Molecular diagnosis of toxoplasmosis It is generally accepted that fetuses or immunocompromissed patients with toxoplasmosis must be treated as early as possible
64 Molecular diagnosis of toxoplasmosis Appropriate treatment can thus be started earlier and serious complications i in the foetus or immunocompromissed patients can be prevented.
65 Molecular diagnosis of toxoplasmosis It was proven that prenatal treatment within 4 weeks of seroconversion reduced dthe risk of intracranial lesions compared with no treatment
66 Brain biopsy pyin toxoplasmic encephalitis Although brain biopsy can establish a definitive diagnosis of TE, it is an invasive i and risky procedure associated with significant morbidity and mortality, while only half of the TE cases are confirmed
67 Prenatal diagnosis of toxoplasmosis PCR performed on amniotic fluid has revolutionized the diagnosis of fetal T. gondii infection
68 Prenatal diagnosis of toxoplasmosis A negative result from PCR performed on amniotic fluid cannot rule out congenital if infection. i
69 Prenatal diagnosis of toxoplasmosis The rate of false negatives is variable according to the centres
70 Sequence targets & Protocoles in molecular l diagnosis i of toxoplasmosis Various sequence targets and PCR protocols have been developed for molecular diagnosis of toxoplasmosis
71 B1 gene For detection of T. gondii, the sequence used most frequently is the B1 gene, which there are 35 copies in the genome Its high specificity is now well- established
72 529-bp sequence The sequence is specific for T. gondii, which has over 300 copies in the genome
73 Real-time PCR Real-time PCR is very sensitive and is a promising technique that is capable of providing a quantitative result.
74 Comparision REP-529 and B1 gene Real-time PCR using the REP-529 Taqman probes was more efficient than B1 gene amplification for the diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis
75 Comparison REP-529 and B1 gene In a study REP-529 sequence was detected in all 20 samples from patients with congenital toxoplasmosis, whereas B1 gene sequence was detected in only 16 of the 20 specimens
76 Comparison REP-529 and B1 gene A comparison of methods using the B1 and 529-bp sequences with realtime PCR revealed a ten-fold improvement in sensitivity when the 529-bp sequence was used
77 Comparison REP-529 and B1 gene Under specific conditions, the detection limit for T. gondii genomic DNA was 200 fg for the B1 gene, compared to 20 fg for the 529-bp sequence
78 Interlaboratory Evaluation In an attempt to establish standardised methodology, the EU BioMed 2 Programme performed an anonymous test of protocols used in 15 European laboratories. The participating laboratories were required to p p g q detect T. gondii in 12 'artificial samples' of amniotic fluid (four negative, eight positive)
79 Interlaboratory Evaluation Two laboratories identified all samples correctly Three laboratories failed to detect the sample containing T. gondii at the lowest concentration (one tachyzoite/ml), without any false-positive results. There were also laboratories that failed to detect T. gondii in any of the samples Four laboratories reported at least one negative control as positive.
80 Real-Time PCR: short-term quantitative result fewer handling steps. Perspective Application of this technique is limited at present because of the relatively l high hcosts of the necessary equipment.
81
82 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNOCOMPETENT PATIENT IgG and IgM antibodies should be used for initial evaluation of immunocompetent patients. Testing of serial specimens obtained 3 weeks apart (in parallel) provides the best discriminatory power if the results in the initial specimen are equivocal
83 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNOCOMPETENT PATIENT Histologic diagnosis can be useful in some cases of suspected toxoplasmosis Endomyocardial biopsy and biopsy of skeletal muscle have been successfully used to establish T. gondii as the etiologic agent of myocarditis and polymyositis in the rare cases Isolation studies and PCR have rarely proved useful Isolation studies and PCR have rarely proved useful in immunocompetent patients.
84 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNODEFICIENT PATIENT In patients with AIDS and toxoplasmosis, the IgG titer may be relatively low, and tests for IgM, IgA, and IgE antibodies may be negative. A definitive iti diagnosis i of toxoplasmosis in the immunodeficient patient relies on: Histologic demonstration of the parasite Detection of T.gondii DNA Isolation of fthe parasite
85 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNODEFICIENT PATIENT The presence of tachyzoites is diagnostic of active infection. The epese presence ceof asolitary tay T. gondii tissue cyst may only reflect chronic infection unless it is associated with an area of inflammation Visualization of several tissue cysts virtually Visualization of several tissue cysts virtually always means that active infection is present.
86 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNODEFICIENT PATIENT Brain biopsy should be considered in immunodeficient patients with presumed TE if: A single lesion is seen on MRI An IgG antibody test result is negative An inadequate clinical response
87 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNODEFICIENT PATIENT An impression smear of the brain biopsy specimen can be made and immediately examined for the presence of tachyzoites using the conventional staining
88 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNODEFICIENT PATIENT In addition to H&E staining, T. gondiispecific immunoperoxidase staining should be performed.
89 Toxoplasma gondii, purulent meningitis Oil immersion observation discloses that bananashaped or crescentic tachyzoites (a proliferative form) possess a single nucleus (HE). Image Source Page:
90 Toxoplasma gondii, purulent meningitis Indirect immunoperoxidase staining using a 1:500 diluted human serum with high Toxoplasma antibody titer demonstrates positive membrane signals on the disseminated tachyzoites Image Source Page:
91 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNODEFICIENT PATIENT Because the amount of brain tissue obtained at aspiration or biopsy is usually small, sufficient tissue for mouse inoculation may not be available; however, this should be performed whenever feasible
92 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNODEFICIENT PATIENT PCR has been used successfully in brain tissue to diagnose TE, but a positive result should be interpreted t with caution because it may not distinguish a patient with TE from one with latent infection (asymptomatic carrier of brain tissue cysts) who has CNS pathology due to a process other than toxoplasmosis.
93 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNODEFICIENT PATIENT In the appropriate clinical setting, it is important to include toxoplasmosis in the differential diagnosis of pulmonary symptoms, particularly in those individuals with interstitial infiltrates. Wright-Giemsa stain and PCR of BAL specimens are useful for the diagnosis of pulmonary toxoplasmosis
94 TOXOPLASMOSIS IN THE IMMUNODEFICIENT PATIENT In patients with visual symptoms in whom toxoplasmic chorioretinitis is a possibility, PCR examination of vitreous or aqueous fluid can be considered and is particularly helpful in patients with atypical clinical features of toxoplasmic chorioretinitis.'
95 OCULAR TOXOPLASMOSIS Low titers of IgG antibody are usual in patients with active chorioretinitis due to reactivation of congenital gondii infection; IgM antibodies are not usually detected. When sera from such patients are examined in the dye test, they should be titered beginning with undiluted serum because, in some cases, the conventional initial dilution of 1: 16 may be negative.
96 OCULAR TOXOPLASMOSIS In most cases, toxoplasmic chorioretinitis is diagnosed by ophthalmologic examination, and empirical ii therapy directed dagainst the organism is often instituted based on clinical findings and serologic test results.
97 OCULAR TOXOPLASMOSIS In a number of patients, the morphology of the retinal lesion or lesions may be nondiagnostic or, the response to treatment t t may be suboptimal or both. In such cases, the detection ti of an abnormal T. gondiiantibody response in ocular fluids or PCR has been used successfully to establish the diagnosis or demonstration of the parasite by isolation, histopathology.
98 CONGENITAL INFECTION IN THE FETUS AND NEWBORN Prenatal diagnosis of congenital toxoplasmosis is currently based on ultrasonography and amniocentesis. PCR on amniotic fluid for the detection of T. gondii-specific DNA performed at 18 weeks of gestation or later is more sensitive, more rapid, and safer than conventional diagnostic procedures involving fetal blood sampling.
99 CONGENITAL INFECTION IN THE FETUS AND NEWBORN Amniotic fluid should be tested by PCR in all cases with serologic test results diagnostic of or highly suggestive of acute acquired infection during pregnancy and also if there is evidence of fetal damage on ultrasound examination (e.g., hydrocephalus and/or calcifications). PCR on amniotic f1uid had a sensitivity of 64%, specificity of 100%,,positive predictive value of 100%, and negative predictive value of 88%.
100 CONGENITAL INFECTION IN THE FETUS AND NEWBORN Maternal IgG antibodies present in the newborn may reflect either past or recent infection in the mother. For this reason, tests t for the detection ti of figa and IgM antibodies are commonly used for the diagnosis of infection in the newborn. The demonstration of IgA antibodies seems to be more sensitive than the detection of IgM antibodies for establishing infection in the newborn.
101 IgG/lgM Ideally, requested at first prenatal visit or preconception IgG-/lgM- IgG+/lgM- IgG-/lgM+ IgG+/lgM+ Woman has not been infected with T. gondii; risk for CT only if primary infection is acquired during gestation. IgG/lgM should be tested throughout pregnancy in order to detect seroconversion. In some countries (e.g., France) IgG (-) women are tested every month <18 weeks Infection acquired prior to pregnancy; risk for C.T. is essentially non-existent unless patient is immunocompromised No further action required >18 weeks It is difficult to distinguish between infection acquired during pregnancy vs acquired in the distant past (e.g., patient may have been infected early in pregnancy and become IgM negative) Consultation with a reference laboratory is recommended Repeat IgG/lgM in 2 to 3 weeks or send to a reference laboratory IgG-/lgM+ Serum should be sent to reference laboratory Confirmatory serologic tests are performed at reference lab. Results are consistent with an acute infection acquired during gestation Risk for CT. Treatment should be initiated Amniotic fluid PCR and monthly U/S should be performed. IgM positive result has no clinical an infection acquired prior to gestation relevance. No risk for CT unless Manage as patient is immunocompromised IgG (-)/lgm equivocal interpretation: (-) patient usually requires follow-up serum and consultation with medical experts in toxoplasmosis
102 Detection of cases depends on the clinician i i and the laboratory Be vigilant! iil
103 موفق باشيد و چون گل خوشرو و شادی بخش
104 Laboratory diagnosis of amebiasis Dr Mehrzad Saraei Qazvin University of Medical Sciences
105 Entamoeba histolytica Entamoeba histolytica is well recognized as a pathogenic ameba, associated with intestinal and extraintestinal infections. The other species are important because they may be confused with E. histolytica in diagnostic investigations
106
107 Trophozoites are typically y Cysts are typically y found found in diarrheal stool in formed stool.
108 Clinical Features Asymptomatic infection Intestinal amebiasis (dysentery, colitis, appendicitis, toxic megacolon, amebomas) Extraintestinal amebiasis (liver abscess, peritonitis, pleuropulmonary abscess, cutaneous and genital amebic lesions).
109 Flask-shaped ulcer of invasive intestinal amebiasis
110 dysentery showing diffuse ulceration of mucosa moebiasis/clinicalpresentations.html
111 moebiasis/clinicalpresentations.html Gross Pathology of amoebic liver abscess
112 Abscesses on the skin
113 This amebiasis patient presented with tissue destruction, and granulation of the anoperineal region due to an Entamoeba histolytica infection.
114 Patient with amoebiasis liver absess, with perforation of abscess through abdominal skin moebiasis/clinicalpresentations.html
115 Laboratory ato Diagnosis of amoebiasis Microscopy Immunodiagnosis Molecular Methods
116 Microscopy Inadequacies of the stool examination have been appreciated since at least 1978 Surprisingly, 30 years later, the stool examination remained the most common test ordered by United States physicians when intestinal amebiasis was suspected.
117 Stool Examination Fresh stool or Concentrates from fresh stool: wet mounts, with or without iodine stain permanently p ystained preparations p (e.g., trichrome). Concentration procedures are not useful for demonstrating trophozoites
118 Microscopy Entamoeba histolytica must be differentiated from other intestinal protozoa including: E. coli E. hartmanni Endolimax nana Iodamoeba buetschlii Dientamoeba fragilis Entamoeba polecki.
119 15 to 20 µm (range 10 to 60 µm) Entamoeba histolytica. Trophozoite in fecal smear (saline wet mount, high power). Numerous ingested erythrocytes are present in the cytoplasm, but the nucleus is not visible.
120 Direct Wet mount stained with iodine Trophozoites of E. histolytica/e. dispar in a direct wet mount stained with iodine
121 Direct Wet mount stained with iodine T h it fe hi t l ti /E di Trophozoites of E. histolytica/e. dispar in a direct wet mount stained with iodine
122 Trophozoites of E. histolytica/e. dispar stained with trichrome
123 Permanent smear stained with Tih Trichrome Trophozoite of E. histolytica/e. dispar, Trophozoite of E. histolytica/e. dispar, measuring approximately 16.7 µm, stained with trichrome
124 Permanent smear stained with Trichrome Erythrophagocytosis is the only characteristic that can be used to differentiate morphologically E. histolytica from the nonpathogenic E. dispar
125 Trophozoites of E. histolytica with ingested erythrocytes stained with tih trichrome
126 Cyst of E. histolytica/e. dispar in an unstained concentrated wet mount of stool Notice the chromatoid body with blunt, rounded ends (arrow). Mature E. histolytica/ E. dispar cysts : 1-4 nuclei have centrally located karyosomes and fine, uniformly distributed peripheral chromatin. usually measure 12 to 15 µm.
127 E. histolytica/e. dispar cyst with three visible nuclei
128 Cyst of E. histolytica/e. dispar in a Cys o. istolytica/. dispa concentrated wet mount stained with iodine
129 E. histolytica/e. dispar cyst in iodine with one visible nucleus and a glycogen vacuole E. histolytica/e. dispar cyst
130 Cyst of E. histolytica/e. dispar in a concentrated wet mount stained with iodine Cyst of E. histolytica/e. dispar
131 Cyst of E. histolytica/e. dispar stained with Trichrome Th l i i ibl i th f l l (bl k Three nuclei are visible in the focal plane (black arrows), and the cyst contains a chromatoid body with typically blunted ends (red arrow).
132 Cyst of E. histolytica/e. dispar stained with Trichrome Notice the chromatoid body with blunt, rounded ends (arrow).
133
134 Other intestinal amebae that may be mistaken for E. histolytica/e.dispar
135
136
137 Cyst of E. nana in a direct wet mount stained with iodine
138 Cysts of E. nana stained with trichrome
139 Trophozoites of E. nana stained with trichrome
140 Trophozoites of E. nana stained with trichrome
141 Cyst of E. coli in a concentrated wet mount stained with iodine. Five nuclei are visible in this focal plane
142 Cyst of E. coli in a concentrated wet mount stained with iodine. Seven nuclei are visible in this focal plane p
143 Mature cyst of E. coli, stained with trichrome a trophozoite of Endolimax nana can be se
144 Mature cyst of E. coli, stained with trichrome
145 Immature cyst of E. coli, stained with trichrome Notice the presence of only two nuclei, and a large glycogen vacuole
146 Mature cyst of E. coli, stained with trichrome five nuclei are visible in the shown focal plane
147 Trophozoites of E. coli stained with trichrome
148 Trophozoites of E. coli stained with trichrome
149 Cyst of an E. hartmanni in a wet mount, stained with iodine
150 Cyst of E. hartmanni stained with trichrome Notice the bluntly-ended chromatoid bodies
151 Trophozoite of E. hartmanni stained with trichrome
152 Trophozoite of E. hartmanni stained with trichrome. In the upper-right of the image is a cyst-like body of Blastocystis hominis
153 Amoebae Entamoeba histolytica/dispar Entamoeba hartmanni Entamoeba coli Entamoeba polecki Endolimax nana Iodamoeba beutschlii 10 µm
154 What is main problem? The main problem for microscopy detection is defferentiation of E. histolytica from E. dispar and E. moshkovskii.
155 Why? Because it is not possible with a stool examination to distinguish morphologically the three closely related and common amebae: pathogenic E. histolytica and commensal E. dispar and E. moshkovskii. kii
156 Microscopy The presence of ingested erythrocytes was the sole morphologic characteristic that was of some use in identifying E. histolytica
157 Microscopy In one study, erythrocytes were present in only 68% of cases of E. histolytica but also present in 16% of cases of E. dispar.
158 Microscopy The problems with stool examination were magnified by the fact that only 5% (3) of the 65 positive results for E. histolytica/e.dispar complex were in fact E. histolytica
159 In most industrialized countries, E. dispar is 10 times more common than E. histolytica and even in a developing country, E. histolytica and E. dispar can be equally prevalent.
160 In a study of preschool children from an urban slum in Bangladesh: E. moshkovskii: 21 % E. histolytica: 16% E. dispar: 36%
161 Microscopy In a study from Tanzania of approximately 100 HIV-infected individuals with diarrhea: E. moshkovskii: 13% E. histolytica: i 4% E. dispar: 5%
162 Microscopy In Sydney, Australia, 50% of Entamoeba organisms identified d by stool O&P examination were E. moshkovskii
163 Microscopy Conclusion stool O&P examination suffers from insensitivity and the inability to distinguish E. histolytica from E. dispar and E. moshkovskii
164 Culture of E. histolytica Is available in only a few research laboratories woridwide Sensitivity: stool exam< Culture<antigen detection or PCR Not specific for E. histolytica Thus an E. histolytica-specific antigen detection or PCR test must be used on the cultured material.
165 Colonoscopy & Biopsy helpful in the diagnosis of intestinal amebiasis. Amebas can be difficult to visualize in the biopsy samples PAS or, ideally, immunoperoxidase with anti- E. histolytica antibodies, can help to identify the parasites. A limitation of colonoscopy is that it is an invasive procedure and not widely available in developing nations.
166 Trophozoites of E. histolytica in a colon biopsy specimen, stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E).
167 Trophozoites of E. histolytica in a perianal biopsy specimens, stained with H&E.
168 Immunodiagnosis Antibody Detection Antibody detection is most useful in patients with extraintestinal amoebiasis (i.e., amebic liver abscess) when organisms are not generally found on stool examination.
169 Antibody Detection ELISA test detects antibody specific for E. histolytica in approximately : 95% of patients with extraintestinal amebiasis 70% of patients with active intestinal infection 10% of asymptomatic persons who are passing cysts of E. histolytica.
170 Antibody Detection If antibodies are not detectable in patients with an acute presentation of suspected amebic liver abscess, a second specimen should be drawn 7-10 days later.
171 Antibody Detection If the second specimen does not show seroconversion, other agents should be considered.
172 Limitation of Antibody Detection Detectable E. histolytica-specific antibodies may persist for years after successful treatment, so the presence of antibodies does not necessarily indicate acute or current infection.
173 Antibody Detection The IHA and EIA tests are more suitable for laboratories that have frequent requests for amebiasis serology.
174 Antibody Detection Microtiter ELISA,ImmunoTab and IHA were compared in one study of amebic liver abscess patients from Kuwait. All three tests had equal sensitivities of 98% to 99%. The ImmunoTab and Microtiter ELISA specificities were 95%, less than the 99.8% calculated specificity of the IHA.
175 Antibody Detection In a study in Egypt, IgG antibodies to the Gal/GalNAc lectin were found in the sera of: 89% of patients with amebic colitis 86%( (six) of seven patients t with intestinal amebiasis Gal/GalNAc lectin is a novel multifunctional virulence factor of the human parasite Entamoeba histolytica galactose (Gal) and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (GalNAc) inhibitable lectin
176 Antibody Detection Although detection of IgM antibodies specific for E. histolytica has been reported, sensitivity is only about 64% in patients with current invasive disease.
177 Antibody Detection Although the immunodiffusion test is as specific, it is slightly less sensitive than the IHA and EIA and requires a minimum i of 24 hours to obtain a result, in contrast to 2 hours required for the IHA or EIA tests. However, the simplicity i of the procedure makes it ideal for the laboratory that has only an occasional specimen to test.
178 Antibody Detection Conclusion Antibody detection is an important part of the diagnosis i of intestinal i and extra intestinal amebiasis.
179 Antibody Detection Conclusion Antibody detection can be particularly hlfl helpful when E. Ehistolytica-specific ti ifi stool diagnostic techniques (antigen detection or PCR) are not available
180 Antigen detection Antigen detection may be useful as an adjunct to microscopic diagnosis in detecting parasites and can distinguish between pathogenic and nonpathogenic infections.
181 Antigen Detection Recent studies indicate improved sensitivity and specificity of fecal antigen assays with the use of monoclonal antibodies which can distinguish between E. histolytica and E. dispar infections.
182 Antigen Detection The only fecal antigen test that distinguishes ishes E. histolytica ti from E. dispar and E. moshkovskii is the TechLab E. histolytica II enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). This microwell ELISA,which detects the Gal/GalNAc adherence lectin of E. histolytica, is more sensitive than stool O&P examination or culture, and it is rapid (<2 hours).
183 Antigen Detection In one study, the TechLab E. histolytica II assay detected Gal/GalNAc lectin in the sera of 96% (22) of 23 patients with amebic liver abscess before they underwent treatment with the antiamebic drug metronidazole.
184 Antigen Detection For liver abscess pus, it was 41% to 74% sensitive for detection of the parasite. Furthermore, for stool specimens collected at the time of diagnosis i of amebic liver abscess (and before metronidazole treatment), it detected the parasite in 43% %(3 of 7).
185 Molecular diagnosis Real-time PCR is superior in sensitivity to stool antigen detection but unfortunately is still a technically complex means for the diagnosis of amebiasis. Real-time PCR is more sensitive than conventional PCR.
186 Molecular diagnosis Real-time PCR is also a sensitive test for detection of E. histolytica in liver abscess pus. In one study, Real-Time PCR yielded positive results in 20 of 23 liver abscess pus specimens; e s; the 3 specimens e s with negative findings had been collected from patients who had already received antiamebic therapy (8 days for one patient and 30 days for two patients).
187 Molecular diagnosis In reference diagnosis laboratories, molecular analysis by PCR-based assays is the method of choice for discriminating between the pathogenic species (E. histolytica) and the nonpathogenic species (E. dispar).
188 Conclusion TechLab E. histolytica II ELISAantigen detection test has sensitivity and specificity it superior to those of stool O&P examination, and its sensitivity inferior but its specificity comparable with those of PCR, but it is technically simpler to perform.
189
190
Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases. (Amoebiasis)
 Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases (Amoebiasis) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University This document contains materials modified or
Laboratory diagnosis of parasitic diseases (Amoebiasis) Sarah Alharbi Clinical Laboratory department Collage of Applied Medical Sciences King Saud University This document contains materials modified or
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 15 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A biopsy was performed on a 27-year-old man with no known travel history, presenting with a perianal ulcer. The specimen was preserved in formalin
Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016
 TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
TOXOPLASMOSIS Lecture-7- Hazem Al-Khafaji 2016 TOXOPLASMOSIS It is a disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii which is a protozoan parasite that is infects a variety of mammals and birds throughout the world.
Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans:
 The parasite protozoa Phylum: Sarcomastigophora Sarcodina االميبات Amoebae Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans: 1. Entamoeba hartmanii, contain trophozoite and cyst 2. Entamoeba coli, cyst and trophozoite
The parasite protozoa Phylum: Sarcomastigophora Sarcodina االميبات Amoebae Non_ pathogenic Amoeba of humans: 1. Entamoeba hartmanii, contain trophozoite and cyst 2. Entamoeba coli, cyst and trophozoite
American Association of Bioanalysts 5615 Kirby Drive, Suite 870 Houston, TX
 Q3 2018 Parasitology American Association of Bioanalysts 5615 Kirby Drive, Suite 870 Houston, TX 77005 800-234-5315 281-436-5357 Specimen 1 Referees Extent 1 Extent 2 Total Few to 534 Giardia lamblia Many
Q3 2018 Parasitology American Association of Bioanalysts 5615 Kirby Drive, Suite 870 Houston, TX 77005 800-234-5315 281-436-5357 Specimen 1 Referees Extent 1 Extent 2 Total Few to 534 Giardia lamblia Many
Parasitology. Lab. Amoeba
 Parasitology. Lab. Kingdom : Protista Subkingdom : Protozoa Phylum : Sacromastigophora Subphylum : Sarcodina Superclass : Rhizopoda Class : Lobosea Order : Amoebida Amoeba Protozoa Amoebae geneus Entamoeba
Parasitology. Lab. Kingdom : Protista Subkingdom : Protozoa Phylum : Sacromastigophora Subphylum : Sarcodina Superclass : Rhizopoda Class : Lobosea Order : Amoebida Amoeba Protozoa Amoebae geneus Entamoeba
Entamoeba histolytica/e. dispar. A. Haghighi,
 Entamoeba histolytica/e. dispar A. Haghighi, Wednesday, February 14, 2018 Classification of Protozoa? The protozoa are generally unicellular and may be divided for convenience, into four distinct groups
Entamoeba histolytica/e. dispar A. Haghighi, Wednesday, February 14, 2018 Classification of Protozoa? The protozoa are generally unicellular and may be divided for convenience, into four distinct groups
Classification - Protozoa. Parasitology Intestinal Amoeba. Stools for O&P Examination. Stool Specimen. What to look for.
 Classification - Protozoa Parasitology Intestinal Amoeba Phylum Phylum Sarcomastigophora Sarcomastigophora Subkingdom Subkingdom Protozoa Protozoa Phylum Phylum Ciliophora Ciliophora Phylum Phylum Apicomplexa
Classification - Protozoa Parasitology Intestinal Amoeba Phylum Phylum Sarcomastigophora Sarcomastigophora Subkingdom Subkingdom Protozoa Protozoa Phylum Phylum Ciliophora Ciliophora Phylum Phylum Apicomplexa
TYPES OF ORGANISM RELATIONSHIPS
 TYPES OF ORGANISM RELATIONSHIPS Normal Flora. Normal flora consists of microorganisms that are normally and consistently found in or on the body in the absence of disease. Symbiosis. This is the close
TYPES OF ORGANISM RELATIONSHIPS Normal Flora. Normal flora consists of microorganisms that are normally and consistently found in or on the body in the absence of disease. Symbiosis. This is the close
CHAPTER FOUR. Intestinal Amebae
 PART II Protozoa CHAPTER FOUR Intestinal Amebae OUTLINE INTESTINAL AMEBAE Entamoeba histolytica/entamoeba dispar (EN-ta-MEE-buh HIS-toe-LIT-I-ka/EN-ta-MEEbuh DIS-par) Entamoeba hartmanni (EN-ta-MEE-buh
PART II Protozoa CHAPTER FOUR Intestinal Amebae OUTLINE INTESTINAL AMEBAE Entamoeba histolytica/entamoeba dispar (EN-ta-MEE-buh HIS-toe-LIT-I-ka/EN-ta-MEEbuh DIS-par) Entamoeba hartmanni (EN-ta-MEE-buh
Entamoeba histolytica
 Entamoeba histolytica cosmopolitan distribution no animal reservoirs facultative pathogen most clear the infection spontaneous in 6-12 months with mild or no symptoms can cause a serious invasive disease
Entamoeba histolytica cosmopolitan distribution no animal reservoirs facultative pathogen most clear the infection spontaneous in 6-12 months with mild or no symptoms can cause a serious invasive disease
VIDAS Test for Avidity of Toxoplasma-Specific Immunoglobulin G for Confirmatory Testing of Pregnant Women
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 2002, p. 2504 2508 Vol. 40, No. 7 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.7.2504 2508.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, July 2002, p. 2504 2508 Vol. 40, No. 7 0095-1137/02/$04.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.40.7.2504 2508.2002 Copyright 2002, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
1 Trophozoite stage : The typical characteristics of this stage are :
 Lecturer : Nerran K.F.AL- Rubaey Practical parasites Lab - 2 - Genus : Entamoeba coli It is considered to be a nonpathogenic with world wide distribution. That frequently exists as a commensal parasite
Lecturer : Nerran K.F.AL- Rubaey Practical parasites Lab - 2 - Genus : Entamoeba coli It is considered to be a nonpathogenic with world wide distribution. That frequently exists as a commensal parasite
Toxoplasma gondii. Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK
 Toxoplasma gondii Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK Toxoplasma gondii Apicomplexa, Koccidia Obligate intracellular parasite Distribution: cosmopolite Transmission: alimentary transplacentary (transfusions,
Toxoplasma gondii Jarmila Kliescikova, MD 1. LF UK Toxoplasma gondii Apicomplexa, Koccidia Obligate intracellular parasite Distribution: cosmopolite Transmission: alimentary transplacentary (transfusions,
Coccidia. Eucoccidioside
 Coccidia Kingdom Sub-Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Protista Protozoa Apicomplexa Sporozoasida Eucoccidioside Sarcocystidae Toxoplasma gondii 1 Toxoplasma gondii (life cycle) Sexual cycle
Coccidia Kingdom Sub-Kingdom Phylum Class Order Family Genus Species Protista Protozoa Apicomplexa Sporozoasida Eucoccidioside Sarcocystidae Toxoplasma gondii 1 Toxoplasma gondii (life cycle) Sexual cycle
Short Video. shows/monsters-inside- me/videos/toxoplasma-parasite/
 The word Toxoplasma Originated from the Greek word toxon, which meant "bow." The Latin word toxicum, which meant "poison." The original Greek meaning is the one used for the word Toxoplasma, meaning "bow
The word Toxoplasma Originated from the Greek word toxon, which meant "bow." The Latin word toxicum, which meant "poison." The original Greek meaning is the one used for the word Toxoplasma, meaning "bow
Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections
 Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections Laboratory diagnosis of HSV Direct staining Tzanck test Immunostaining HSV isolation Serology PCR Tzanck test Cell scrape from base of the lesion smear on
Laboratory diagnosis of congenital infections Laboratory diagnosis of HSV Direct staining Tzanck test Immunostaining HSV isolation Serology PCR Tzanck test Cell scrape from base of the lesion smear on
Toxoplasmosis Objective :
 Toxoplasmosis Objective : Describe the Life cycle Mention the Infective stages Define Congenital Toxoplasmosis List the Lab.Diagnosis Illustrate the Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Show the relationship between
Toxoplasmosis Objective : Describe the Life cycle Mention the Infective stages Define Congenital Toxoplasmosis List the Lab.Diagnosis Illustrate the Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Show the relationship between
Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy. Medical Parasitology
 Dr. Abdullah A. Hama Microbiology/ parasitology and virology ( Chapter 1) Text book: 7-695-57059-1-978 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Medical Parasitology Lec. 2 part 1 Protozoa/ class: Sarcodina
Dr. Abdullah A. Hama Microbiology/ parasitology and virology ( Chapter 1) Text book: 7-695-57059-1-978 Sulaimani University College of Pharmacy Medical Parasitology Lec. 2 part 1 Protozoa/ class: Sarcodina
African Trypanosomes
 African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
African Trypanosomes Giemsa-stained blood smear of African trypanosomes viewed under the 100X objective lens. The block arrows denote trypomastigote forms of the African trypanosomes found within the blood
ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease
 ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
ccess safe drinking wa r is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
Effect of Testing for IgG Avidity in the Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pregnant Women: Experience in a US Reference Laboratory
 1248 Effect of Testing for IgG Avidity in the Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pregnant Women: Experience in a US Reference Laboratory Oliver Liesenfeld, 1,2,3 Jose G. Montoya, 1,2 Sandra Kinney,
1248 Effect of Testing for IgG Avidity in the Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii Infection in Pregnant Women: Experience in a US Reference Laboratory Oliver Liesenfeld, 1,2,3 Jose G. Montoya, 1,2 Sandra Kinney,
Comparison of the efficiency of two commercial kits ELFA and Western blot in estimating the phase of Toxoplasma gondii infection in pregnant women
 Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine 2016, Vol 23, No 4, 570 575 www.aaem.pl ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the efficiency of two commercial kits ELFA and Western blot in estimating the phase
Annals of Agricultural and Environmental Medicine 2016, Vol 23, No 4, 570 575 www.aaem.pl ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of the efficiency of two commercial kits ELFA and Western blot in estimating the phase
Evaluation of the Immunoglobulin G Avidity Test for Diagnosis of Toxoplasmic Lymphadenopathy
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 2004, p. 4627 4631 Vol. 42, No. 10 0095-1137/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.10.4627 4631.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 2004, p. 4627 4631 Vol. 42, No. 10 0095-1137/04/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/JCM.42.10.4627 4631.2004 Copyright 2004, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
News and Notes. Parasitology Comprehensive 2 October Sample Preparation and Quality Control. 12 K (All Parasites)
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Recent reports in the literature have indicated a high rate of Cryptosporidium sp. false positive associated with Rapid Cartridge
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Recent reports in the literature have indicated a high rate of Cryptosporidium sp. false positive associated with Rapid Cartridge
Ocular Toxoplasmosis - A Laboratory View. Chatterton JMW* Evans R. Ho-Yen DO
 Ocular Toxoplasmosis - A Laboratory View Chatterton JMW* Evans R Ho-Yen DO Scottish Toxoplasma Reference Laboratory Microbiology Department Raigmore Hospital Inverness IV UJ * corresponding author Introduction
Ocular Toxoplasmosis - A Laboratory View Chatterton JMW* Evans R Ho-Yen DO Scottish Toxoplasma Reference Laboratory Microbiology Department Raigmore Hospital Inverness IV UJ * corresponding author Introduction
Toxoplasmosis. Life cycle Infective stages Congenital Toxoplasmosis Lab.Diagnosis Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis & Pregnancy
 Toxoplasmosis Life cycle Infective stages Congenital Toxoplasmosis Lab.Diagnosis Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis & Pregnancy Human Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease Caused by Coccidian
Toxoplasmosis Life cycle Infective stages Congenital Toxoplasmosis Lab.Diagnosis Immunity to Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis & Pregnancy Human Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is a zoonotic disease Caused by Coccidian
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Amoebiasis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August 2011 August 2011 October
August 2011 Amoebiasis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) Case Definition August 2011 August 2011 October
Received 8 April 1996/Returned for modification 19 June 1996/Accepted 15 July 1996
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1996, p. 2526 2530 Vol. 34, No. 10 0095-1137/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Study of Abbott Toxo IMx System for Detection of Immunoglobulin
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Oct. 1996, p. 2526 2530 Vol. 34, No. 10 0095-1137/96/$04.00 0 Copyright 1996, American Society for Microbiology Study of Abbott Toxo IMx System for Detection of Immunoglobulin
Toxoplasma gondii. Definitive Host adult forms sexual reproduction. Intermediate Host immature forms asexual reproduction
 Toxoplasma gondii cosmopolitan distribution seropositive prevalence rates vary generally 20-75% generally causes very benign disease in immunocompetent adults tissue cyst forming coccidia predator-prey
Toxoplasma gondii cosmopolitan distribution seropositive prevalence rates vary generally 20-75% generally causes very benign disease in immunocompetent adults tissue cyst forming coccidia predator-prey
Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate. Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University
 Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University Objectives After the lecture, students must know 1. General morphology of pathogenic
Pathogenic amoebae and ciliate Dr. Narissara Jariyapan Department of Parasitology Faculty of Medicine Chiang Mai University Objectives After the lecture, students must know 1. General morphology of pathogenic
Laboratory Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Toxoplasmosis
 S73 Laboratory Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Toxoplasmosis Jose G. Montoya Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Research Institute, Palo Alto Medical Foundation, Palo Alto,
S73 Laboratory Diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii Infection and Toxoplasmosis Jose G. Montoya Department of Immunology and Infectious Diseases, Research Institute, Palo Alto Medical Foundation, Palo Alto,
TELEFAX. Toxoplasma Serology Laboratory (TSL) DATE: TO: FAX: FROM:
 TELEFAX DATE: TO: FAX: FROM: Toxoplasma Serology Laboratory RE: SPECIMEN REQUIREMENTS AND TESTING INFORMATION (effective 1/15/16) THIS TRANSMISSION CONSISTS OF 16 PAGES INCLUDING THIS COVER PAGE. IF THERE
TELEFAX DATE: TO: FAX: FROM: Toxoplasma Serology Laboratory RE: SPECIMEN REQUIREMENTS AND TESTING INFORMATION (effective 1/15/16) THIS TRANSMISSION CONSISTS OF 16 PAGES INCLUDING THIS COVER PAGE. IF THERE
Learning Objectives. 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic Morphology 5. Name of diesease 6. Prevention and Control
 Learning Objectives At the end of the class student will able to state 1. Life cycle Environment, Human, Animals 2. Name of parasite: (Genus), (Species) 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic
Learning Objectives At the end of the class student will able to state 1. Life cycle Environment, Human, Animals 2. Name of parasite: (Genus), (Species) 3. Epidemiology distribution; endemic; 4. Basic
Laboratory Diagnostic Techniques for Entamoeba Species
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, July 2007, p. 511 532 Vol. 20, No. 3 0893-8512/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00004-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Laboratory Diagnostic
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, July 2007, p. 511 532 Vol. 20, No. 3 0893-8512/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00004-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Laboratory Diagnostic
Laboratory Diagnostic Techniques for Entamoeba Species
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, July 2007, p. 511 532 Vol. 20, No. 3 0893-8512/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00004-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Laboratory Diagnostic
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, July 2007, p. 511 532 Vol. 20, No. 3 0893-8512/07/$08.00 0 doi:10.1128/cmr.00004-07 Copyright 2007, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Laboratory Diagnostic
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program. Parasitology (General) 02 February Sample Preparation and Quality Control
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Parasitology (General) 02 February 2010 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology (General) is
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program Parasitology (General) 02 February 2010 The purpose of the New York State Proficiency Testing Program in the category of Parasitology (General) is
3-Mutualism: It is a relationship between two. organisms; one called. or harmless. 2-Commensalism: It is a relationship in which one
 Host-Parasite relationships Symbiosis: It is the permanent relationship between two dissimilar organisms which depending each others. They are three types 1- Parasitism : It is a relationship between two
Host-Parasite relationships Symbiosis: It is the permanent relationship between two dissimilar organisms which depending each others. They are three types 1- Parasitism : It is a relationship between two
Innovation in Diagnostics. ToRCH. A complete line of kits for an accurate diagnosis INFECTIOUS ID DISEASES
 Innovation in Diagnostics ToRCH A complete line of kits for an accurate diagnosis INFECTIOUS ID DISEASES EN TOXOPLASMOSIS Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by with the obligate intracellular
Innovation in Diagnostics ToRCH A complete line of kits for an accurate diagnosis INFECTIOUS ID DISEASES EN TOXOPLASMOSIS Toxoplasmosis is a parasitic disease caused by with the obligate intracellular
Significance of a positive Toxoplasma Immunoglobulin M test result. in the United States
 JCM Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 9 September 2015 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01663-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Significance of a positive
JCM Accepted Manuscript Posted Online 9 September 2015 J. Clin. Microbiol. doi:10.1128/jcm.01663-15 Copyright 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. 1 2 Significance of a positive
News and Notes. Parasitology Comprehensive 5 November 2013
 NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Beginning with the May 2013 event a separate set of 3 samples were supplied for laboratories performing antigen detection. For the
NEW YORK STATE Parasitology Proficiency Testing Program News and Notes Beginning with the May 2013 event a separate set of 3 samples were supplied for laboratories performing antigen detection. For the
Reliable screening for early diagnosis
 Elecsys TORCH panel Reliable screening for early diagnosis Toxoplasmosis Rubella HSV CMV Toxoplasmosis The safe and sure approach to Toxo screening Ultrasensitive Toxo IgM optimized to detect all potential
Elecsys TORCH panel Reliable screening for early diagnosis Toxoplasmosis Rubella HSV CMV Toxoplasmosis The safe and sure approach to Toxo screening Ultrasensitive Toxo IgM optimized to detect all potential
Schistosome life cycle.
 Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Schistosomiasis infects approximately 200 million persons and kills approximately 280,000 annually. Most of the mortality comes from hepatic granulomas and fibrosis Schistosoma japonicum and Schistosoma
Extra-intestinal coccidians
 Extra-intestinal coccidians Apicomplexa Coccidia Gregarinea Piroplasmida Eimeriida Haemosporida -Theileriidae - Babesiidae - Eimeriidae - Cryptosporidiidae - Sarcocystidae (Sarcocystis) (Toxoplasma) -Haemosporiidae
Extra-intestinal coccidians Apicomplexa Coccidia Gregarinea Piroplasmida Eimeriida Haemosporida -Theileriidae - Babesiidae - Eimeriidae - Cryptosporidiidae - Sarcocystidae (Sarcocystis) (Toxoplasma) -Haemosporiidae
INTESTINAL PROTOZOAN INFECTIONS
 INTESTINAL PROTOZOAN INFECTIONS The protozoa that parasitise the human intestine belong to four groups: amoebae, flagellates, ciliates and coccidia. In general, the intestinal amoebae, flagellates and
INTESTINAL PROTOZOAN INFECTIONS The protozoa that parasitise the human intestine belong to four groups: amoebae, flagellates, ciliates and coccidia. In general, the intestinal amoebae, flagellates and
Toxoplasmosis: Summary of evidences, a Research line
 Toxoplasmosis: Summary of evidences, a Research line José G. Montoya, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Associate Chief for Clinical Affairs Division of Infectious Diseases Stanford University School
Toxoplasmosis: Summary of evidences, a Research line José G. Montoya, MD Associate Professor of Medicine Associate Chief for Clinical Affairs Division of Infectious Diseases Stanford University School
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
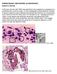 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Ameba has two stages of development: cyst and trophozoite
 Amebiasis A parasitic disease of worldwide public health importance Second to malaria in mortality due to protozoan parasites Invasive amebiasis results in up to 100,000 deaths / year Amebiasis is infection
Amebiasis A parasitic disease of worldwide public health importance Second to malaria in mortality due to protozoan parasites Invasive amebiasis results in up to 100,000 deaths / year Amebiasis is infection
Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System *
 OpenStax-CNX module: m64867 1 Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System * Geo Lin-Cereghino Based on Parasitic Infections of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems by OpenStax This work is produced
OpenStax-CNX module: m64867 1 Protozoan Infections of the Circulatory System * Geo Lin-Cereghino Based on Parasitic Infections of the Circulatory and Lymphatic Systems by OpenStax This work is produced
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients. Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP
 Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP Introduction Toxoplasmosis: Caused by the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Immunocompetent persons with primary infection
Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in HIV-Infected Patients Ahmed Saad,MD,FACP Introduction Toxoplasmosis: Caused by the intracellular protozoan, Toxoplasma gondii. Immunocompetent persons with primary infection
Diagnosis of Amebic Liver Abscess and Intestinal Infection with the TechLab Entamoeba histolytica II Antigen Detection and Antibody Tests
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 2000, p. 3235 3239 Vol. 38, No. 9 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Diagnosis of Amebic Liver Abscess
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 2000, p. 3235 3239 Vol. 38, No. 9 0095-1137/00/$04.00 0 Copyright 2000, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Diagnosis of Amebic Liver Abscess
E. Histolytica IgG (Amebiasis)
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and 116, Woodland hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
Examples of microorganisms causing it : Shigella. Spp : causing bacillary dysentery. Entamoeba.histolyca : causing amoebic dysentery.
 This lecture is about the protozoa which infect the GIS. It is important before we start to mention the two types of diarrhea because diarrhea as you know is the most prominent symptom related to these
This lecture is about the protozoa which infect the GIS. It is important before we start to mention the two types of diarrhea because diarrhea as you know is the most prominent symptom related to these
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN
 PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
PARASITE MRS. OHOUD S.ALHUMAIDAN OUTLINE Intruduction Important terms classification of hosts Mode of parasitic infections General Classification of parasites Specific Classification of parasites Protozoa
Outline EP1201. NEHA 2012 AEC June 2012
 Food and Water Borne Enteric Protozoa: Environmental Health Perspectives Stephanie M. Fletcher, PhD (c) NEHA AEC & Exhibition San Diego June 30, 2012 Outline Introduction Overview of the Epidemiology of
Food and Water Borne Enteric Protozoa: Environmental Health Perspectives Stephanie M. Fletcher, PhD (c) NEHA AEC & Exhibition San Diego June 30, 2012 Outline Introduction Overview of the Epidemiology of
Toxoplasmosis. Seminar. For personal use. Only reproduce with permission from The Lancet Publishing Group.
 Seminar Toxoplasmosis J G Montoya, O Liesenfeld Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite that infects up to a third of the world s population. Infection is mainly acquired by ingestion of food or water
Seminar Toxoplasmosis J G Montoya, O Liesenfeld Toxoplasma gondii is a protozoan parasite that infects up to a third of the world s population. Infection is mainly acquired by ingestion of food or water
SLIDE SEMINAR NON NEOPLASTIC LYMPH NODE DISORDERS DR SHEILA NAIR CMC, VELLORE
 SLIDE SEMINAR NON NEOPLASTIC LYMPH NODE DISORDERS DR SHEILA NAIR CMC, VELLORE Case 1 34 year old male, mass right cervical region, for 4 years. No other significant findings. Grossly, the mass was well
SLIDE SEMINAR NON NEOPLASTIC LYMPH NODE DISORDERS DR SHEILA NAIR CMC, VELLORE Case 1 34 year old male, mass right cervical region, for 4 years. No other significant findings. Grossly, the mass was well
Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture GIARDIASIS(lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate)
 Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture Two GIARDIASIS(lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate) Epidemiology: It has worldwide distribution and is not uncommon in South Carolina. It is the most frequent protozoan
Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture Two GIARDIASIS(lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate) Epidemiology: It has worldwide distribution and is not uncommon in South Carolina. It is the most frequent protozoan
Laboratory Diagnosis of Amebiasis
 CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 2003, p. 713 729 Vol. 16, No. 4 0893-8512/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CMR.16.4.713 729.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Laboratory
CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY REVIEWS, Oct. 2003, p. 713 729 Vol. 16, No. 4 0893-8512/03/$08.00 0 DOI: 10.1128/CMR.16.4.713 729.2003 Copyright 2003, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Laboratory
IgG Antibodies To Toxoplasma Gondii ELISA Kit Protocol
 IgG Antibodies To Toxoplasma Gondii ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat. No.:EK-310-85) 330 Beach Road, Burlingame CA Tel: 650-558-8898 Fax: 650-558-1686 E-Mail: info@phoenixpeptide.com www.phoenixpeptide.com INTENDED
IgG Antibodies To Toxoplasma Gondii ELISA Kit Protocol (Cat. No.:EK-310-85) 330 Beach Road, Burlingame CA Tel: 650-558-8898 Fax: 650-558-1686 E-Mail: info@phoenixpeptide.com www.phoenixpeptide.com INTENDED
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit
 Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 02 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Access to safe drinking water is everyone s right. Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease
 Access to safe drinking water is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
Access to safe drinking water is everyone s right Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica 3. Cryptosporidium parvum 4. Cyclospora cayetanensis 1 Giardia
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates
 Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
Flagellates I Genito-urinary & Intestinal flagellates Dr. Anuluck Junkum PARA 317221 Objective Can describe the morphology, life cycle, pathology, diagnosis and prevention of pathogenic flagellate Classification
patient's serum is separated from other serum components by selective absorption of the IgM
 JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1981, p. 486-491 0095-1137/81/1 10486-06$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 5 Immunoglobulin M-Immunosorbent Agglutination Assay for Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases: Diagnosis
JOURNAL OF CLINICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Nov. 1981, p. 486-491 0095-1137/81/1 10486-06$02.00/0 Vol. 14, No. 5 Immunoglobulin M-Immunosorbent Agglutination Assay for Diagnosis of Infectious Diseases: Diagnosis
Anton van Leeuwenhoek. Protozoa: This is what he saw in his own stool sample. Morphology 10/14/2009. Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease
 Access to safe drinking water is everyone s right Anton van Leeuwenhoek Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease This is what he saw in his own stool sample 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica
Access to safe drinking water is everyone s right Anton van Leeuwenhoek Protozoa: Protozoans that cause diarrheal disease This is what he saw in his own stool sample 1. Giardia lamblia 2. Entameba histolytica
Toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised population of Constanta, Romania
 3rd International Conference on Clinical Microbiology & Microbial Genomics September 24-26, 2014 Valencia, Spain Toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised population of Constanta, Romania
3rd International Conference on Clinical Microbiology & Microbial Genomics September 24-26, 2014 Valencia, Spain Toxoplasmosis in immunocompetent and immunocompromised population of Constanta, Romania
Amebiasis rev Jan 2018
 rev Jan 2018 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Entamoeba histolytica, a protozoan parasite. The trophozoite is the active form of the parasite which causes symptoms. Cysts are the infectious form which
rev Jan 2018 BASIC EPIDEMIOLOGY Infectious Agent Entamoeba histolytica, a protozoan parasite. The trophozoite is the active form of the parasite which causes symptoms. Cysts are the infectious form which
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals. Taniawati Supali. Department of Parasitology
 Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Entamoeba histolytica
 Entamoeba histolytica Occurence: -cosmopolitan amoeba lives in the form of trophozoite and cyst in the human colon, but in multifocal invasions may locate various organs including the lungs, -common in
Entamoeba histolytica Occurence: -cosmopolitan amoeba lives in the form of trophozoite and cyst in the human colon, but in multifocal invasions may locate various organs including the lungs, -common in
Parasitology. Helminthology (Helminths)
 Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
Parasitology Protozoology (Protozoa) Helminthology (Helminths) Entomology (Arthropodes) Platyhelminthes (flat worms) Nematheminthes (round worms) Trematodes Nematodes Cestodes Collection of the specimens
Amoebiasis. (Amoebic dysentery)
 Amoebiasis (Amoebic dysentery) Causative agent: Entamoeba histolytica Amoebiasis Harbouring of protozoa E. histolytica inside the body with or without disease only 10% of infected develop disease two types
Amoebiasis (Amoebic dysentery) Causative agent: Entamoeba histolytica Amoebiasis Harbouring of protozoa E. histolytica inside the body with or without disease only 10% of infected develop disease two types
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection. Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA
 Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Clinical Aspect and Application of Laboratory Test in Herpes Virus Infection Masoud Mardani M.D,FIDSA Shahidhid Bh BeheshtiMdi Medical lui Universityit Cytomegalovirus (CMV), Epstein Barr Virus(EBV), Herpes
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit
 Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
Toxoplasma gondii IgM ELISA Kit Catalog Number KA0226 96 assays Version: 01 Intended for research use only www.abnova.com Table of Contents Introduction... 3 Intended Use... 3 Background... 3 Principle
FACT OR ARTIFACT LEARN THE KEYS TO DIFFERENTIATE PARASITES FROM ARTIFACTS
 FACT OR ARTIFACT LEARN THE KEYS TO DIFFERENTIATE PARASITES FROM ARTIFACTS ACMLT CONFERENCE OCTOBER 1, 2005 PRESENTED BY PAULINE TOMLIN Public Health Microbiology 2 FACT OR ARTIFACT Many body sites and
FACT OR ARTIFACT LEARN THE KEYS TO DIFFERENTIATE PARASITES FROM ARTIFACTS ACMLT CONFERENCE OCTOBER 1, 2005 PRESENTED BY PAULINE TOMLIN Public Health Microbiology 2 FACT OR ARTIFACT Many body sites and
Toxoplasmosis in the fetus and newborn: an update on prevalence, diagnosis and treatment
 For reprint orders, please contact reprints@expert-reviews.com Toxoplasmosis in the fetus and newborn: an update on prevalence, diagnosis and treatment Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 10(7), 815 828 (2012)
For reprint orders, please contact reprints@expert-reviews.com Toxoplasmosis in the fetus and newborn: an update on prevalence, diagnosis and treatment Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 10(7), 815 828 (2012)
Toxoplasma gondii IgM (Toxo IgM)
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 21250 Califa Street, Suite 102 and116, Woodland Hills, CA 91367 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com
Area Laboratory Service
 THIS IS A CONTROLLED DOCUMENT. DO NOT COPY Organisational Unit: Title: Ref No: Version No: Date Issued: Author: Authorised by: Review date: Area Laboratory Service Microbiology Scottish Toxoplasma Reference
THIS IS A CONTROLLED DOCUMENT. DO NOT COPY Organisational Unit: Title: Ref No: Version No: Date Issued: Author: Authorised by: Review date: Area Laboratory Service Microbiology Scottish Toxoplasma Reference
DIAGNOSTIC MICROBIOLOGY
 DIAGNOSTIC MICROBIOLOGY Libuše Kolářová Václava Adámková Institute for Immunology and Microbiology, 1st. Fac.Med.,Charles Univ. in Prague Czech Republic Which factors should precipitate testing? CLINICAL
DIAGNOSTIC MICROBIOLOGY Libuše Kolářová Václava Adámková Institute for Immunology and Microbiology, 1st. Fac.Med.,Charles Univ. in Prague Czech Republic Which factors should precipitate testing? CLINICAL
A New Multiplex Real-time PCR Assay For Detection Of Intestinal Parasites
 A New Multiplex Real-time PCR Assay For Detection Of Intestinal Parasites Dr. Andreas Simons Worldwide provider of diagnostic assay solutions Offers a variety of test kit methodologies R-Biopharm Headquarters
A New Multiplex Real-time PCR Assay For Detection Of Intestinal Parasites Dr. Andreas Simons Worldwide provider of diagnostic assay solutions Offers a variety of test kit methodologies R-Biopharm Headquarters
Use of Treponemal Immunoassays for Screening and Diagnosis of Syphilis
 Use of Treponemal Immunoassays for Screening and Diagnosis of Syphilis Guidance for Medical Providers and Laboratories in California These guidelines were developed by the California Department of Public
Use of Treponemal Immunoassays for Screening and Diagnosis of Syphilis Guidance for Medical Providers and Laboratories in California These guidelines were developed by the California Department of Public
Seroprevalence of Toxoplasmosis in High School Girls in Fasa District, Iran
 Seroprevalence of Toxoplasmosis in High School Girls in Fasa District, Iran Gholamreza Hatam 1*, Azra Shamseddin 2, Farhoud Nikouee 3 1 Department of Parasitology and Mycology, School of Medicine, Shiraz
Seroprevalence of Toxoplasmosis in High School Girls in Fasa District, Iran Gholamreza Hatam 1*, Azra Shamseddin 2, Farhoud Nikouee 3 1 Department of Parasitology and Mycology, School of Medicine, Shiraz
Cytomegalovirus IgG, IgM, IgG Avidity II Total automation for accurate staging of infection during pregnancy
 Infectious Disease Cytomegalovirus IgG, IgM, IgG Avidity II Total automation for accurate staging of infection during pregnancy FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY Confidence in Your Results LIAISON Cytomegalovirus
Infectious Disease Cytomegalovirus IgG, IgM, IgG Avidity II Total automation for accurate staging of infection during pregnancy FOR OUTSIDE THE US AND CANADA ONLY Confidence in Your Results LIAISON Cytomegalovirus
January Dear Physician:
 Richard F. Daines, M.D. Commissioner Wendy E. Saunders Executive Deputy Commissioner January 2009 Dear Physician: The purpose of this letter is to bring your attention to the significant increase in reported
Richard F. Daines, M.D. Commissioner Wendy E. Saunders Executive Deputy Commissioner January 2009 Dear Physician: The purpose of this letter is to bring your attention to the significant increase in reported
Human toxoplasmosis in Europe. Parasitology, Paris Descartes University, Cochin Hospital, Paris, France
 Human toxoplasmosis in Europe Prof Jean Dupouy-Camet Parasitology, Paris Descartes University, Cochin Hospital, Paris, France Toxoplasma gondii, discovered in 1908, by Nicolle at Institut Pasteur de Tunis,
Human toxoplasmosis in Europe Prof Jean Dupouy-Camet Parasitology, Paris Descartes University, Cochin Hospital, Paris, France Toxoplasma gondii, discovered in 1908, by Nicolle at Institut Pasteur de Tunis,
Recent Diagnostic Methods for Intestinal Parasitic Infections
 Recent Diagnostic Methods for Intestinal Parasitic Infections By Dr. Doaa Abdel Badie Salem Lecturer of Medical Parasitology, Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Agenda Intestinal parasites. Traditional Diagnostic
Recent Diagnostic Methods for Intestinal Parasitic Infections By Dr. Doaa Abdel Badie Salem Lecturer of Medical Parasitology, Mansoura Faculty of Medicine Agenda Intestinal parasites. Traditional Diagnostic
Gastroenteritis and viral infections
 Gastroenteritis and viral infections A Large number of viruses are found in the human gut; these include some that are associated with gastroenteritis Rotaviruses Adenoviruses 40/41 Caliciviruses Norwalk-like
Gastroenteritis and viral infections A Large number of viruses are found in the human gut; these include some that are associated with gastroenteritis Rotaviruses Adenoviruses 40/41 Caliciviruses Norwalk-like
Opportunistic infections
 Opportunistic infections Opportunistic infections Decrease in number of CD4 lymphocytes is condition for development of opportunistic infections Risk is started, when number of CD4 lymphocytes drops to
Opportunistic infections Opportunistic infections Decrease in number of CD4 lymphocytes is condition for development of opportunistic infections Risk is started, when number of CD4 lymphocytes drops to
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL CEUTICAL RESEARCH AND
 Research Article CODEN: IJPRNK B. V. Ramana, IJPRBS, 2013; Volume 2(4): 253-258 ISSN: 2277-8713 IJPRBS INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMAC CEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE SEROPREVALENCE OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS
Research Article CODEN: IJPRNK B. V. Ramana, IJPRBS, 2013; Volume 2(4): 253-258 ISSN: 2277-8713 IJPRBS INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PHARMAC CEUTICAL RESEARCH AND BIO-SCIENCE SEROPREVALENCE OF ACUTE TOXOPLASMOSIS
cytoplasm contains two 2 nuclei and two parabasal bodies (Figure 7).
 Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture one GIARDIASIS (lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate) Epidemiology: It has worldwide distribution and is not uncommon in South Carolina. It is the most frequent protozoan
Dr. Jabar Etaby Lecture one GIARDIASIS (lambliasis) Etiology: Giardia lamblia (flagellate) Epidemiology: It has worldwide distribution and is not uncommon in South Carolina. It is the most frequent protozoan
Wales Neonatal Network Guideline
 Congenital infection: Diagnosis and management Overview: Infections transmitted and acquired in utero. Most as a result of primary infection of mother during pregnancy, some organisms such as Cytomegalovirus
Congenital infection: Diagnosis and management Overview: Infections transmitted and acquired in utero. Most as a result of primary infection of mother during pregnancy, some organisms such as Cytomegalovirus
Evidence-based diagnosis of toxoplasma infection Evans R, Ho-Yen D O
 Evidence-based diagnosis of toxoplasma infection Evans R, Ho-Yen D O Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion on NHS EED. Each abstract
Evidence-based diagnosis of toxoplasma infection Evans R, Ho-Yen D O Record Status This is a critical abstract of an economic evaluation that meets the criteria for inclusion on NHS EED. Each abstract
J07 Titer dynamics, complement fixation test and neutralization tests
 avllm0421c (spring 2017) J07 Titer dynamics, complement fixation test and neutralization tests Outline titer, antibody titer dynamics complement, complement fixation reaction neutralization tests 2/35
avllm0421c (spring 2017) J07 Titer dynamics, complement fixation test and neutralization tests Outline titer, antibody titer dynamics complement, complement fixation reaction neutralization tests 2/35
Amebiasis Ab E. histolytica IgG
 Code: HP003 96 Test distribuito da: Amebiasis Ab E. histolytica IgG Amebiasis E. histolytica lgg test is an enzyme immunoassay for the detection of specific lgg antibodies against Anti - Entamoeba histolytica
Code: HP003 96 Test distribuito da: Amebiasis Ab E. histolytica IgG Amebiasis E. histolytica lgg test is an enzyme immunoassay for the detection of specific lgg antibodies against Anti - Entamoeba histolytica
The problem with TORCH screening
 : Beyond TORCHeS TORCH or STORCH-a helpful mnemonic? Toxoplasma Other Rubella CMV HSV (HIV) Syphilis 3 The problem with TORCH screening TORCH-first proposed by Nahmias et.al. (Pediatr Res 1971) Toxo, Rubella,
: Beyond TORCHeS TORCH or STORCH-a helpful mnemonic? Toxoplasma Other Rubella CMV HSV (HIV) Syphilis 3 The problem with TORCH screening TORCH-first proposed by Nahmias et.al. (Pediatr Res 1971) Toxo, Rubella,
Protozoa from tissues. Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp.
 Protozoa from tissues Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp. Leishmaniasis Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, in macrophages of man. Female sandflies:
Protozoa from tissues Leishmania spp. Naegleria fowleri Toxoplasma gondii Trichomonas vaginalis Trypanosoma spp. Leishmaniasis Leishmania infantum, Leishmania donovani, in macrophages of man. Female sandflies:
Congenital CMV infection. Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara
 Congenital CMV infection Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Congenital CMV infection Approximately 0.15 2% of live births
Congenital CMV infection Infectious and Tropical Pediatric Division Department of Child Health Medical Faculty, University of Sumatera Utara Congenital CMV infection Approximately 0.15 2% of live births
Neonatal infections. Joanna Seliga-Siwecka
 Neonatal infections Joanna Seliga-Siwecka Neonatal infections Early onset sepsis Late onset sepsis TORCH Early onset sepsis (EOS) Blood or cerebral fluid culture-proven infection at fewer than 7 days
Neonatal infections Joanna Seliga-Siwecka Neonatal infections Early onset sepsis Late onset sepsis TORCH Early onset sepsis (EOS) Blood or cerebral fluid culture-proven infection at fewer than 7 days
An HIV-infected Patient with Confirmed Overlapping Complications of Severe Amebic Colitis and CMV Enteritis
 doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0112-17 Intern Med 57: 1855-1860, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT An HIV-infected Patient with Confirmed Overlapping Complications of Severe Amebic Colitis and CMV Enteritis
doi: 10.2169/internalmedicine.0112-17 Intern Med 57: 1855-1860, 2018 http://internmed.jp CASE REPORT An HIV-infected Patient with Confirmed Overlapping Complications of Severe Amebic Colitis and CMV Enteritis
Immunoglobulin M Toxoplasma Antibodies
 CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, JUlY 1994, p. 401-405 Vol. 1, No. 4 1071-412X/94/$04.00+0 Copyright C) 1994, American Society for Microbiology The Vitek Immunodiagnostic Assay for Detection
CLINICAL AND DIAGNOSTIC LABORATORY IMMUNOLOGY, JUlY 1994, p. 401-405 Vol. 1, No. 4 1071-412X/94/$04.00+0 Copyright C) 1994, American Society for Microbiology The Vitek Immunodiagnostic Assay for Detection
Positive Analysis of Screening for TORCH Infection in Eugenic and Eugenic Children
 2018 4th International Symposium on Biomedical Science, Biotechnology and Healthcare (ISBSBH 2018) Positive Analysis of Screening for TORCH Infection in Eugenic and Eugenic Children Xu Qian1, Yang Genling*,
2018 4th International Symposium on Biomedical Science, Biotechnology and Healthcare (ISBSBH 2018) Positive Analysis of Screening for TORCH Infection in Eugenic and Eugenic Children Xu Qian1, Yang Genling*,
