Surgical Approaches of Parotidectomy: Overview
|
|
|
- Brian Henderson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Surgical Approaches of Parotidectomy: Overview 1 Dr. Raed Rasheed Z Almutairi, 2 Dr. Rakan Mansour H Aldhahri, 3 Dr. Dheifullah Mastour D ALzaidy, 4 Dr. Ahmad Faisal Albishry, 5 Dr. Ibrahim Saleh Almalki, 6 Dr. Najdi Ibrahem Najdi, 7 Dr. Hassan Ali Alzahrani Abstract: We aimed by this review paper to focus on discussing different aspects concerning parotidectomy, intended to review evidence about the surgical techniques of this surgical intervention, and then discuss the complications and outcomes following this type of surgery. We searched Medline, PubMed, Cochrane, and CINHAL databases for studies reporting and concerning with parotidectomy that was published in English language and in the period of establishment of these databases up to 2016, December. We used parotidectomy and the following free Mesh terms; surgical techniques, surgical procedures, indications, outcomes, and complications,. And we restricted our search to the English-language literature on human subjects. Reference lists were screened manually to find more relevant studies. Surgical methods for salivary gland surgical procedure will continuously develop as new modern technologies develop. A detailed understanding of the disease processes as well as anatomy will certainly remain of extremely important value in the effective medical administration of salivary gland disease. Although a number of records in the literature have actually documented the medical technique, as well as the oncological result attained with parotidectomy, just a few articles have actually explained the problems of parotid gland surgical treatment and also their monitoring. Numerous problems have been reported in parotid surgical treatment. Keywords: Surgical Approaches of Parotidectomy, Cochrane, and CINHAL databases. 1. INTRODUCTION The parotid gland is a largely serous salivary gland that is located high in the neck in the preauricular location expanding towards the cheek. The extratemporal facial nerve as well as its branches go through the parotid gland as well as supply motor innervation to the muscles of face, as well as to the postauricular muscle mass, the posterior tummy of the digastric muscular tissue, as well as the stylohyoid muscle mass (1). Parotid tumors represent 2-- 3% of tumors influencing the head and neck, as well as % of those taking place in the salivary glands (2). The majority of sores are benign as well as influence the superficial parotid lobe. Currently, surgical excision is the most efficient treatment for parotid tumors, yet debate continues to be with respect to making use of superficial parotidectomy (SP) (3) or partial superficial parotidectomy (PSP) (4). The primary distinction between both procedures is that the branching pattern and place of the facial nerve, as opposed to the size and degree of the tumor, figures out the size of dissection and also the quantity of parotid cells that is gotten rid of in SP (5). Regardless of the picked method, potential morbidities adhering to parotidectomy, consisting of pain, facial nerve paralysis, salivary fistulae, Frey's syndrome and also a loss of feeling, may influence lifestyle (QoL) (6,7). However, effective surgical procedure should achieve excellent practical results. A number of previous research studies have contrasted the two sorts of parotid surgical treatment by keeping in mind the occurrence of post-operative problems (8,9). We aimed by this review paper to focus on discussing different aspects concerning parotidectomy, intended to review evidence about the surgical techniques of this surgical intervention, and then discuss the complications and outcomes following this type of surgery. Page 1993
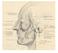
2 2. METHODOLOGY We searched Medline, PubMed, Cochrane, and CINHAL databases for studies reporting and concerning with parotidectomy that was published in English language and in the period of establishment of these databases up to 2016, December. We used parotidectomy and the following free Mesh terms; surgical techniques, surgical procedures, indications, outcomes, and complications,. And we restricted our search to the English-language literature on human subjects. Reference lists were screened manually to find more relevant studies. 3. RESULTS The parotid gland is the largest salivary gland and lies in the parotid compartment, a triangular room anterior and inferior to the auricle. Included in this room are the facial nerve (cranial nerve VII) (Figure 1), (4) numerous sensory and also free nerves, the external carotid artery as well as its branches, the retromandibular capillary, as well as parotid lymphatics. The parotid is an irregular wedgeshaped gland that twists around the posterior side of the ramus of the mandible and also expands posteriorly to the outside acoustic canal and also mastoid pointer. Around 80% of the gland overlaps the masseter muscular tissue anteriorly. There is no structural attribute that officially divides the parotid gland right into surface and also deep wattles, yet the aircraft of the facial nerve (see the image below) typically offers for separation of the shallow and deep portions of the gland (Figure 1) (4,6,7). o Surgical technique of parotidectomy: Figure 1: The surgical anatomy and landmarks of the facial nerve. Surface Parotidectomy Superficial parotidectomy is indicated for a lot of benign and malignant tumors in the surface wattle, for chronic sialadenitis, and as part of a lymphadenectomy for skin cancer of the scalp. Parotid masses ought to not be enucleated due to risk of tumor reappearance and also the raised risk to the facial nerve throughout alteration surgery. Tumors that expand into the deep lobe may call for total parotidectomy including both the deep as well as superficial wattles (10). The customized Blair incision for shallow parotidectomy begins in a natural crease just anterior to the helix, extends beneath the earlobe and also superiorly over the mastoid, then curves inferiorly over the anterior border of the sternocleidomastoid muscular tissue. The cut proceeds below the angle of the mandible at a distance safe from the marginal mandibular nerve (2 finger breadths). Placing the cut back instead of anterior to the tragus might improve the aesthetic outcome. Breakdown is carried greatly to the depth of the parotid fascia in the preauricular region and with the platysma muscle in the cervical area. Anterior and posterior flaps are elevated along this airplane, exposing the gland Page 1994
3 anteriorly as well as the former border of the sternocleidomastoid muscle posteriorly (11). Care needs to be taken to not" button-hole" the skin flap by raising an excessively thin flap. The flaps are then sutured in position or pulled back far from the medical field. Using sharp breakdown, the tail of the parotid gland is after that divided from the sternocleidomastoid muscular tissue, the cartilaginous exterior acoustic canal, and also the posterior digastric as well as stylohyoid muscle mass. The greater auricular nerve is encountered throughout mobilization of the lateral wattle. Its former department must typically be given up to mobilize the gland sufficiently. When possible, the posterior division of the better auricular nerve should be protected to preserve experience to the earlobe (12). The tragal guideline as well as tympanomastoid stitch line are also revealed throughout this dissection. Attention is after that focused on the essential job of localizing the facial nerve. Numerous medical spots help in the identification of the 7th nerve. o Outcomes and complications follow Parotidectomy: Research studies by Erkan et al (12) and Nitzan et al (13) reported that, complying with a parotidectomy, the general health condition of the majority of patients excelled. These studies wrapped up that parotidectomy did not show up to severely influence the general QoL, they did not evaluate whether there was a difference in the QoL following different resection types. In today research, it was also observed that most of patients within the total example remained in excellent general health and wellness, which PSP conferred a comparable general wellness outcome compared with SP. Foghsgaard et al (14) examined instant post-operative pain complying with SP, and recognized no significant distinction in the pain rating between patients with a transected or preserved posterior branch of the terrific auricular nerve (GAN). It is most likely that the reported pains were an outcome of surgical injury, as well as consequently, whether or not the various surgical strategies had an adverse effect upon pain would certainly require additional examining subsequent to a longer follow-up duration. Wormald et al (15) analyzed pain following parotidectomy using an aesthetic analogue scale and also identified that pain appeared to have little effect after the patients. Nevertheless, the study did report one patient who presented with serious and consistent pain. A possible explanation for this may have been neuroma development following damages to the GAN. In the here and now research, efforts were made to maintain the GAN posterior branch in each patient. As there were no records of neuroma formation during the follow-up, patients from each of the groups showed high pain ratings. The distinction in these ratings was not recognized to be significant between the teams. In a study by Nitzan et al (13), 70% of patients reported a change in appearance; 60% because of scarring and 58% as a result of regional depression. Therefore, it is feasible that the domains of look, scarring and also facial contours are connected, and also must for that reason be evaluated together. A research study by Koch et al (16) determined that the majority of patients were not totally satisfied with the aesthetic result following surgical procedure. Nevertheless, the mean score was relatively high as well as the writers did not show a substantial connection in between cosmetic look and also the extent of surgical procedure (PSP vs. SP). In the present research, it was revealed that most of patients who were satisfied with the cosmetic result, and those that's mean rating was dramatically different to that of the SP group, were those that had undergone PSP. It was for that reason hypothesized that a bigger amount of gland tissue removal resulted in enhanced cosmetic morbidity. The searchings for of Ciuman et al (18) and also Roh et al (19) also support this result. The majority of the parotidectomies in today research were carried out making use of modified Blair lacerations. Previous researches (20) have actually suggested that this laceration would cause a famous scar, nonetheless, the majority of patients in the here and now research reported that the scar was hardly obvious. This might be the result of the sutures being executed by an experienced surgeon, or the post-operative application of a mark formation inhibitor. Loss of experience is a difficulty reported following GAN sacrifice. In a research study by Koch et alia (16), the mean score for loss of sensation was 4.3, without any substantial distinction determined in between PSP as well as SP. This searching for was consistent with that of today research. By contrast, Ciuman et al (18) demonstrated statistically substantial distinctions in between sensory impairment and also the degree of surgery. The duration of sensory disability was substantially longer complying with SP compared to PSP. This searching for may be the outcome of varied follow-up times and the opportunity that sensory deficits could lower with time (16). Adhering to a parotidectomy, Frey's syndrome has been shown to impact between 1.5 and also 27.7% of patients (21,22). The pathogenesis is believed to be the aberrant healing of understanding as well as parasympathetic nerves. In a research by Emodi et alia (21), Frey's syndrome happened in 27.7% of the patients: Four situations treated with SP and 9 instances treated with PSP. Likewise, Papadogeorgakis et alia (20) reported that Frey's syndrome influenced 18% of patients who had actually undertaken SP, and 5% who had undertaken PSP. However, these research studies did not reveal a considerable distinction in the occurrence of Frey's syndrome in patients dealt with by PSP or SP, which may have been the outcome of Page 1995
4 tiny example sizes.). This could be due to that less parotid tissue was eliminated by SP, and also as the parotid fascia was closed straight (20). In the QoL evaluation, a higher percentage of patients dealt with by SP reported this difficulty. PSP might not only lower the occurrence of Frey's syndrome, however likewise attain excellent QoL results (18). Intra-operative complications of parotid gland surgical procedure comprise transection of the facial nerve or one of its branches, rupture of the capsulae of a parotid tumor or insufficient surgical resection thereof. The specialist has to instantly acknowledge an intra-operative complication as well as monitoring thereof have to be performed right away. In case of nerve injury, immediate nerve fixing is necessary. Once the segments have been completely activated and combined without stress, both ends need to be sutured with each other. The nerves are delicately understood with some Bishop forceps. With an 8-0 nylon stitch and also a GS-8 needle, the epineurium is understood at one end and then sutured to the various other, preventing deep cuts in the perineurium. 3 stitches are typically ample to keep the anastomosis. As an alternative to sutures, the doctor may use fibrin cells adhesive. If the nerve size is inadequate, a nerve graft of the higher auricular nerve, can be used (23,24). Intra-operative opening of the pseudocapsule of pleomorphic adenomas is commonly held to raise the risk of recurrence (23,25). However, Laskawi et al. examining individual experience on parotidectomy for pleomorphic adenoma located no evidence of reoccurrence in any one of the 18 from 475 patients in whom the tumor capsule had to be opened intraoperatively on account of tough problems (26). The main factor for pleomorphic adenoma reappearance is incomplete surgical resection. In these situations, it is suggested to do post-operative radiotherapy (25,27). Table 1: complications of parotid gland surgery (intra and post-operative) Intra-operative complications Post-operative complications Early Late Transection of facial nerve Facial nerve paralysis Facial sinkinesis after facial palsy Rupture of capsulae of parotid Haemorrhage or Hypoesthesia of greater auricular tumour haematoma nerve Incomplete surgical resection of Infection Recurrent tumour parotid tumour Skin flap necrosis Soft tissue deficit Cosmetic deformity Hypertrophic scar or keloid Trismus Frey s syndrome Parotid fistula Facial palsy follows parotidectomy: Post-operative facial nerve dysfunction involving some or all the branches of the nerve is one of the most regular early problem of parotid gland surgery. Momentary facial nerve paresis, including all or just one or two branches of the facial nerve, as well as long-term total paralysis have happened, specifically, in 9.3% to 64.6% and in 0% to 8% of parotidectomies, reported in the literary works. The cases of transient facial nerve paresis typically resolved within 6 months, with 90% within 1 month (28,29,30). Short-term paresis normally resolves, inning accordance with Laccourreye, within the 18th post-operative month (28). The occurrence of facial nerve paralysis is greater with total, compared to with surface parotidectomy, which could be connected to stretch injury or as outcome of surgical interference with the vasa nervorum. Modification parotidectomy or parotidectomies for parotid fistula are usually associated with a greater incidence of face weakness. The branch of the facial nerve most in danger for injury during parotidectomy is the marginal mandibular branch. Older patients seem extra susceptible to facial nerve injury. Short-lived facial nerve weakness is a cosmetic problem, as well as patients ought to be informed their appearance will go back to normal. Nonetheless, eye defense must be ensured. If facial paresis triggers incomplete closure of the eye, the patient should be recommended to utilize ophthalmic wetness drops regularly during the day and also a sensory ointment and eye defense during the night. Routine follow-up with an ophthalmologist is obligatory (30). 4. CONCLUSION Surgical methods for salivary gland surgical procedure will continuously develop as new modern technologies develop. A detailed understanding of the disease processes as well as anatomy will certainly remain of extremely important value in the effective medical administration of salivary gland disease. Although a number of records in the literature have actually documented the medical technique, as well as the oncological result attained with parotidectomy, just a few articles have actually explained the problems of parotid gland surgical treatment and also their monitoring. Numerous problems have been reported in parotid surgical treatment. Page 1996
5 REFERENCES [1] Emerick KS, Fabian RL, Deschler DG. Clinical presentation, management, and outcome of high-grade mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the parotid gland. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg May. 136(5): [2] Upton DC, McNamar JP, Connor NP, Harari PM, Harting GK. Parotidectomy: ten-year review of 237 cases at a single institution. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2007;136: doi: /j.otohns [3] Pia F, Policarpo M, Dosdegani R, Olina M, Brovelli F, Aluffi P. Centripetal approach to the facial nerve in parotid surgery: personal experience. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2003;23: [4] Bhattacharyya N, Richardson ME, Gugino LD. An objective assessment of the advantages of retrograde parotidectomy. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2004;131: doi: /j.otohns [5] Emodi O, El-Naaj IA, Gordin A, Akrish S, Peled M. Superficial parotidectomy versus retrograde partial superficial parotidectomy in treating benign salivary gland tumor (pleomorphic adenoma) J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68: doi: /j.joms [6] Erkan AN, Yavuz H, Ozer C, Ozer F, Ozluoglu L. Quality of life after surgery for benign disease of the parotid gland. J Laryngol Otol. 2008;122: doi: /S [7] Nitzan D, Kronenberg J, Horowitz Z, et al. Quality of life following parotidectomy for malignant and benign disease. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;114: doi: /01.PRS C1. [8] Koch M, Zenk J, Iro H. Long-term results of morbidity after parotid gland surgery in benign disease. Laryngoscope. 2010;120: doi: /lary [9] Zhang SS, Ma DQ, Guo CB, Huang MX, Peng X, Yu GY. Conservation of salivary secretion and facial nerve function in partial superficial parotidectomy. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;42: doi: /j.ijom [10] Futran ND, Parvathaneni U, Martins RG, et al. Malignant salivary gland tumors. Part A: general principles and management. In: Harrison LB, Sessions RB, Hong WK, editors. Head and neck cancer: a multidisciplinary approach. 3rd edition. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; p [11] Elluru RG, Kumar M, et al. Physiology of the salivary glands. In: Cummings CW, Haughey BH, Thomas JR, et al, editors. Cummings otolaryngology: head and neck surgery, 4th edition 2. Philadelphia: Mosby Inc.; p [12] Lore J, Medina J. The parotid salivary gland and management of malignant salivary gland neoplasia. In: Lore J, Medina J, editors. An atlas of head and neck surgery. 4th edition. Philadelphia: WB Saunders; p [13] Erkan AN, Yavuz H, Ozer C, Ozer F, Ozluoglu L. Quality of life after surgery for benign disease of the parotid gland. J Laryngol Otol. 2008;122: [14] Nitzan D, Kronenberg J, Horowitz Z, et al. Quality of life following parotidectomy for malignant and benign disease. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004;114: [15] Foghsgaard S, Foghsgaard J, Homøe P. Early post-operative morbidity after superficial parotidectomy: a prospective study concerning pain and resumption of normal activity. Clin Otolaryngol. 2007;32: [16] Wormald R, Donnelly M, Timon C. Minor morbidity after parotid surgery via the modified Blair incision. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2009;62: [17] Koch M, Zenk J, Iro H. Long-term results of morbidity after parotid gland surgery in benign disease. Laryngoscope. 2010;120: [18] Ciuman RR, Oels W, Jaussi R, Dost P. Outcome, general, and symptom-specific quality of life after various types of parotid resection. Laryngoscope. 2012;122: [19] Roh JL, Kim HS, Park CI. Randomized clinical trial comparing partial parotidectomy versus superficial or total parotidectomy. Br J Surg. 2007;94: doi: /bjs Page 1997
6 [20] Papadogeorgakis N. Partial superficial parotidectomy as the method of choice for treating pleomorphic adenomas of the parotid gland. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2011;49: [21] Emodi O, El-Naaj IA, Gordin A, Akrish S, Peled M. Superficial parotidectomy versus retrograde partial superficial parotidectomy in treating benign salivary gland tumor (pleomorphic adenoma) J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68: [22] Ali NS, Nawaz A, Rajput S, Ikram M. Parotidectomy: a review of 112 patients treated at a teaching hospital in Pakistan. Asian Pacific J Cancer Prev. 2010;11: [23] Bailey BJ. Head and Neck Surgery-Otolaryngology. 3rd Edn. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; [24] Dulguerov P, Marchal F, Lehmann W. Postparotidectomy facial nerve paralysis: possible etiologic factors and results with routine facial nerve monitoring. Laryngoscope 1999;109: [25] Natvig K, Soberg R. Relationship of intraoperative rupture of pleomorphic adenomas to recurrence: an year follow-up study. Head Neck 1994;16: [26] Laskawi R, Schott T, Mirzaie-Petri M, Schroeder M. Surgical management of pleomorphic adenomas of the parotid gland: a follow-up study of three methods. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1996;54: [27] Piekarski J, Nejc D, Szymczak W, Wronski K, Jeziorski A. Results of extracapsular dissection of pleomorphic adenoma of parotid gland. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2004;62: [28] Laccourreye H, Laccourreye O, Cauchois R, Jouffre V, Menard M, Brasnu D. Total conservative parotidectomy for primary benign pleomorphic adenoma of the parotid gland: a 25-year experience with 229 patients. Laryngoscope 1994;104: [29] Laskawi R, Schott T, Mirzaie-Petri M, Schroeder M. Surgical management of pleomorphic adenomas of the parotid gland: a follow-up study of three methods. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1996;54: [30] Olsen KD. Superficial parotidectomy. Oper Techn Gen Surg 2004;6: Page 1998
Partial Parotidectomy Versus Superficial or Total Parotidectomy
 Middle East Journal of Applied Sciences, 3(4): 259-264, 2013 ISSN: 2077-4613 259 Partial Parotidectomy Versus Superficial or Total Parotidectomy 1 Ibrahim Abde-Albare and 2 Mohamed A. Foda 1 Health Director
Middle East Journal of Applied Sciences, 3(4): 259-264, 2013 ISSN: 2077-4613 259 Partial Parotidectomy Versus Superficial or Total Parotidectomy 1 Ibrahim Abde-Albare and 2 Mohamed A. Foda 1 Health Director
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP STEP 3 SEPARATE PAROTID GLAND FROM SCM STEP 2 IDENTIFICATON OF GREAT AURICULAR NERVE
 STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
STEP 1 INCISION AND ELEVATION OF SKIN FLAP Create a modified Blair Figure 1 or facelift incision. Figure 2 Raise a superficial cervico-fascial flap between the Superficial Musculo Aponeurotic System (SMAS)
Small access postaural parotidectomy: an analysis of techniques, feasibility and safety
 Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2016) 273:1879 1883 DOI 10.1007/s00405-015-3691-9 HEAD AND NECK Small access postaural parotidectomy: an analysis of techniques, feasibility and safety Anthony Po-Wing Yuen 1
Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol (2016) 273:1879 1883 DOI 10.1007/s00405-015-3691-9 HEAD AND NECK Small access postaural parotidectomy: an analysis of techniques, feasibility and safety Anthony Po-Wing Yuen 1
A survey of facial nerve dissection techniques in benign parotid surgery among maxillofacial and ear, nose, and throat surgeons in Nigeria
 Original Article A survey of facial nerve dissection techniques in benign parotid surgery among maxillofacial and ear, nose, and throat surgeons in Nigeria WL Adeyemo, OA Taiwo, OA Somefun 1, HO Olasoji
Original Article A survey of facial nerve dissection techniques in benign parotid surgery among maxillofacial and ear, nose, and throat surgeons in Nigeria WL Adeyemo, OA Taiwo, OA Somefun 1, HO Olasoji
Lya Crichlow, MD Lutheran Medical Center November 21, 2008
 Lya Crichlow, MD Lutheran Medical Center November 21, 2008 Case Presentation 64 year old male presented with a painless mass posterior to the right angle of the mandible for 3 months PMHx HTN COPD BPH
Lya Crichlow, MD Lutheran Medical Center November 21, 2008 Case Presentation 64 year old male presented with a painless mass posterior to the right angle of the mandible for 3 months PMHx HTN COPD BPH
2. Materials and Methods
 e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 564053, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/564053 Research Article Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid: Extracapsular Dissection Compared with Superficial Parotidectomy
e Scientific World Journal, Article ID 564053, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/564053 Research Article Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid: Extracapsular Dissection Compared with Superficial Parotidectomy
THE GREAT auricular nerve
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Randomized Prospective Study of the Validity of the Great Auricular Nerve Preservation in Parotidectomy Mauro ecker Martins Vieira, MD; Amélio Ferreira Maia, MD; Jaime Carlos Ribeiro,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Randomized Prospective Study of the Validity of the Great Auricular Nerve Preservation in Parotidectomy Mauro ecker Martins Vieira, MD; Amélio Ferreira Maia, MD; Jaime Carlos Ribeiro,
Thank You Joe Curry, MD David Cognetti, MD Ryan Heffelfinger, MD
 Thank You Joe Curry, MD David Cognetti, MD Ryan Heffelfinger, MD Anatomy Epidemiology Pathology Treatment Controversies Current Research Largest Salivary Gland 80% is superficial lobe Encased in Superficial
Thank You Joe Curry, MD David Cognetti, MD Ryan Heffelfinger, MD Anatomy Epidemiology Pathology Treatment Controversies Current Research Largest Salivary Gland 80% is superficial lobe Encased in Superficial
Parotid Disease Case Discussions. Valerie Jefford November 28, 2002
 Parotid Disease Case Discussions Valerie Jefford November 28, 2002 Case 1 44 y.o. man referred with lump anterior to R ear. Q1 What do you want to know? no pain 2 years but bigger now Smoker Q2 What to
Parotid Disease Case Discussions Valerie Jefford November 28, 2002 Case 1 44 y.o. man referred with lump anterior to R ear. Q1 What do you want to know? no pain 2 years but bigger now Smoker Q2 What to
Outcome, General, and Symptom-Specific Quality of Life After Various Types of Parotid Resection
 The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Outcome, General, and Symptom-Specific Quality of Life After Various Types of Parotid Resection Raphael Richard
The Laryngoscope VC 2012 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc. Outcome, General, and Symptom-Specific Quality of Life After Various Types of Parotid Resection Raphael Richard
Partial Superficial Parotidectomy for Pleomorphic Adenoma. Khalid B Alghamdi, MD*
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 35, No. 4, December 2013 Partial Superficial Parotidectomy for Pleomorphic Adenoma Khalid B Alghamdi, MD* Objective: This study aimed to determine the indications of partial
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 35, No. 4, December 2013 Partial Superficial Parotidectomy for Pleomorphic Adenoma Khalid B Alghamdi, MD* Objective: This study aimed to determine the indications of partial
THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL
 British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981) 19, 116-120 0 The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00170116$02.00 THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL OF SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE STRUCTURE HAITHEM A.
British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981) 19, 116-120 0 The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00170116$02.00 THE ANGULAR TRACT: AN ANATOMICAL OF SURGICAL SIGNIFICANCE STRUCTURE HAITHEM A.
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV
 DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
DISORDERS OF THE SALIVARY GLANDS Neoplasms Dr.M.Baskaran Selvapathy S IV NEOPLASMS A) Epithelial I. Benign Pleomorphic adenoma( Mixed tumour) Adenolymphoma (Warthin s tumour) Oxyphil adenoma (Oncocytoma)
Alexander C Vlantis. Selective Neck Dissection 33
 05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
05 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II Alexander C Vlantis Selective Neck Dissection 33 Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II INCISION Various incisions can be used for a neck dissection. The incision
Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :
![Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Tikrit University collage of dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. Lec [5] / Temporal fossa :](/thumbs/88/115294566.jpg) Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
Lec [5] / Temporal fossa : Borders of the Temporal Fossa: Superior: Superior temporal line. Inferior: gap between zygomatic arch and infratemporal crest of sphenoid bone. Anterior: Frontal process of the
be very thin and variable. Facial nerve branches that exit the parotid gland are deep to the SMAS.
 The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
The Superficial musculoaponeurotic system (SMAS) fascia is a fanlike fascia that envelops the face and provides a suspensory sheet which distributes forces of facial expression.. The SMAS is continuous
Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y. جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102
 جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
جامعة تكريت كلية طب االسنان التشريح مادة املرحلة الثانية أ.م.د. بان امساعيل صديق 6102/6102 Parotid region The part of the face in front of the ear and below the zygomatic arch is the parotid region. The
A study of complications of superficial parotidectomy
 A study of complications of superficial parotidectomy *Dr. Probal Chatterji ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
A study of complications of superficial parotidectomy *Dr. Probal Chatterji ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Contemporary treatment of salivary gland tumors. A review of the literature
 DOI: 10.18044/Medinform.201742.682 Contemporary treatment of salivary gland tumors. A review of the literature Ioanna Polichroniadou 1, Panagiotis Karakostas 2, Svetoslav Slavkov 3, Assya Krasteva 4 1.
DOI: 10.18044/Medinform.201742.682 Contemporary treatment of salivary gland tumors. A review of the literature Ioanna Polichroniadou 1, Panagiotis Karakostas 2, Svetoslav Slavkov 3, Assya Krasteva 4 1.
Original Article ABSTRACT
 Kasr El-Aini J. Clin. Oncol. Nucl. Med. Vol.4, No.3-4, July-Oct. 28:51-57 NEMROCK Original Article GREAT AURICULAR NERVE PRESERVATION IMPROVES OUTCOME OF SUPERFICIAL PAROTIDECTOMY Hamed Rashad, Emad Abdel
Kasr El-Aini J. Clin. Oncol. Nucl. Med. Vol.4, No.3-4, July-Oct. 28:51-57 NEMROCK Original Article GREAT AURICULAR NERVE PRESERVATION IMPROVES OUTCOME OF SUPERFICIAL PAROTIDECTOMY Hamed Rashad, Emad Abdel
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY
 OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
OPEN ACCESS ATLAS OF OTOLARYNGOLOGY, HEAD & NECK OPERATIVE SURGERY BUCCINATOR MYOMUCOSAL FLAP The Buccinator Myomucosal Flap is an axial flap, based on the facial and/or buccal arteries. It is a flexible
Original Article. Section: Surgery INTRODUCTION
 DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.3.SG5 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Retrograde Facial Nerve Dissection Using Zygomatic Branch as Landmark in Parotid Gland Surgery for Pleomorphic Adenoma:
DOI: 10.21276/aimdr.2018.4.3.SG5 Original Article ISSN (O):2395-2822; ISSN (P):2395-2814 Retrograde Facial Nerve Dissection Using Zygomatic Branch as Landmark in Parotid Gland Surgery for Pleomorphic Adenoma:
B I O L I F E R E S E A R C H A R T I C L E
 AN INTERNATIONAL QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCES 5(2):170-177 B I O L I F E R E S E A R C H A R T I C L E Partial superficial parotidectomy versus conventional superficial parotidectomy for
AN INTERNATIONAL QUARTERLY JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY & LIFE SCIENCES 5(2):170-177 B I O L I F E R E S E A R C H A R T I C L E Partial superficial parotidectomy versus conventional superficial parotidectomy for
This is the largest of the three major glands. It lies partly in the front of the lower half of the ear and partly below the earlobe.
 Parotid Gland Lumps The lining of the mouth contains many small saliva glands. In addition there are three major glands on each side of the face, the parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands. The Parotid
Parotid Gland Lumps The lining of the mouth contains many small saliva glands. In addition there are three major glands on each side of the face, the parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands. The Parotid
Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine
 MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2014; 9(1): 39-43 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Study of Preoperative Predictive Signs in Management of Facial Nerve in Parotid Tumors Magdalena
MAEDICA a Journal of Clinical Medicine 2014; 9(1): 39-43 Mædica - a Journal of Clinical Medicine ORIGINAL PAPERS Study of Preoperative Predictive Signs in Management of Facial Nerve in Parotid Tumors Magdalena
ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 )
 2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
2 Neck Anatomy ANTERIOR CERVICAL TRIANGLE (Fig. 2.1 ) The boundaries are: Lateral: sternocleidomastoid muscle Superior: inferior border of the mandible Medial: anterior midline of the neck This large triangle
Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa
 M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
M1 - Anatomy Parotid Gland, Temporomandibular Joint and Infratemporal Fossa Jeff Dupree Sanger 9-057 jldupree@vcu.edu Parotid gland: wraps around the mandible positioned between the mandible and the sphenoid
Since Gutierrez in 1903,
 Facelift Approach With a Hybrid SMAS Rotation Advancement Flap in Parotidectomy for Prevention of Scars and Contour Deficiency Affecting the Neck and Sweat Secretion of the Cheek Johannes Franz Hönig,
Facelift Approach With a Hybrid SMAS Rotation Advancement Flap in Parotidectomy for Prevention of Scars and Contour Deficiency Affecting the Neck and Sweat Secretion of the Cheek Johannes Franz Hönig,
THIEME. Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region
 CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
CHAPTER 2 Scalp and Superficial Temporal Region Scalp Learning Objectives At the end of the dissection of the scalp, you should be able to identify, understand and correlate the clinical aspects: Layers
Anatomical Landmarks to Avoid Injury to the Great Auricular Nerve During Rhytidectomy
 Facial Surgery Anatomical Landmarks to Avoid Injury to the Great Auricular Nerve During Rhytidectomy Todd Lefkowitz, MD; Ron Hazani, MD; Saeed Chowdhry, MD; Josh Elston, BS; Michael J. Yaremchuk, MD; and
Facial Surgery Anatomical Landmarks to Avoid Injury to the Great Auricular Nerve During Rhytidectomy Todd Lefkowitz, MD; Ron Hazani, MD; Saeed Chowdhry, MD; Josh Elston, BS; Michael J. Yaremchuk, MD; and
Microsurgical dissection of facial nerve in parotidectomy: a discussion of techniques and long-term results
 Original Article Microsurgical dissection of facial nerve in parotidectomy: a discussion of techniques and long-term results Fabio Nicoli 1,2,3, Christopher D Ambrosia 1,4, Davide Lazzeri 2,3, Georgios
Original Article Microsurgical dissection of facial nerve in parotidectomy: a discussion of techniques and long-term results Fabio Nicoli 1,2,3, Christopher D Ambrosia 1,4, Davide Lazzeri 2,3, Georgios
ISPUB.COM. Cutting Burr Otoplasty. D Wynne, N Balaji INTRODUCTION ANATOMY CUTTING BURR TECHNIQUE
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 1 D Wynne, N Balaji Citation D Wynne, N Balaji.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 7 Number 1. Abstract Prominent
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology Volume 7 Number 1 D Wynne, N Balaji Citation D Wynne, N Balaji.. The Internet Journal of Otorhinolaryngology. 2006 Volume 7 Number 1. Abstract Prominent
Facelift incision and superficial musculoaponeurotic system advancement in parotidectomy: case reports
 Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2015) 37:40 DOI 10.1186/s40902-015-0040-2 CASE REPORT Facelift incision and superficial musculoaponeurotic system advancement in parotidectomy:
Kim et al. Maxillofacial Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery (2015) 37:40 DOI 10.1186/s40902-015-0040-2 CASE REPORT Facelift incision and superficial musculoaponeurotic system advancement in parotidectomy:
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Review Article A Review of Our Experience of Surgery for Parotid Gland Neoplasms Nanjundappa 1*, Vasu Reddy Challa 2,
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Review Article A Review of Our Experience of Surgery for Parotid Gland Neoplasms Nanjundappa 1*, Vasu Reddy Challa 2,
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies. No Disclosures or Conflicts of Interest. Anatomy 10/4/2013
 Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
Management of Salivary Gland Malignancies Daniel G. Deschler, MD Director: Division of Head and Neck Surgery Massachusetts Eye & Ear Infirmary Massachusetts General Hospital Professor Harvard Medical School
Recurrent Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid Gland: Treatment Outcomes and Risks of Ulterior Recurrence
 Recurrent Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid Gland: Treatment Outcomes and Risks of Ulterior Recurrence Mahendra Maharjan 1, Pranay R. Sakya 2, Zhang Fuyin 3 1,2 Assistant professor, 3 Professor & Head
Recurrent Pleomorphic Adenoma of the Parotid Gland: Treatment Outcomes and Risks of Ulterior Recurrence Mahendra Maharjan 1, Pranay R. Sakya 2, Zhang Fuyin 3 1,2 Assistant professor, 3 Professor & Head
Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery
 Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery Topic Joo Heon Lee 1, Tae Suk Oh 2, Sung Wan Park 3, Jae Hoon Kim 3, Tanvaa Tansatit 4 1 Area88 Plastic Surgery Clinic, Seoul; 2 Department
Temple and Postauricular Dissection in Face and Neck Lift Surgery Topic Joo Heon Lee 1, Tae Suk Oh 2, Sung Wan Park 3, Jae Hoon Kim 3, Tanvaa Tansatit 4 1 Area88 Plastic Surgery Clinic, Seoul; 2 Department
Continuing Education Independent Study Series
 Continuing Education Independent Study Series Association of Surgical Technologists Publication made possible by an educational grant provided by Kimberly-Clark Corporation OF SURGICAL ECHNOLOGISTS AEGER
Continuing Education Independent Study Series Association of Surgical Technologists Publication made possible by an educational grant provided by Kimberly-Clark Corporation OF SURGICAL ECHNOLOGISTS AEGER
이하선에발생한와르틴종양 : 증례보고. Warthin Tumor of the Parotid Gland: A Case Report. Jungwoo Cho, Seung Hwan Jung, Jin Su Kim, Je Uk Park, Chang Hyen Kim *
 Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology 2017;41(4):175-179 ISSN:1225-1577(Print); 2384-0900(Online) Available online at http://journal.kaomp.org https://doi.org/10.17779/kaomp.2017.41.4.004
Korean Journal of Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology 2017;41(4):175-179 ISSN:1225-1577(Print); 2384-0900(Online) Available online at http://journal.kaomp.org https://doi.org/10.17779/kaomp.2017.41.4.004
Parotid Swellings: Report of 110 Consecutive Cases
 Parotid Swellings: Report of 110 Consecutive Cases A R Arshad, FRCS, Department of Plastic Surgery, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Jalan Pahang, 50586 Kuala Lumpur Parotid swellings are uncommon. They usually
Parotid Swellings: Report of 110 Consecutive Cases A R Arshad, FRCS, Department of Plastic Surgery, Hospital Kuala Lumpur, Jalan Pahang, 50586 Kuala Lumpur Parotid swellings are uncommon. They usually
The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies. Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology
 The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology www.ifhnos.net The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies
The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies Current Concepts in Head and Neck Surgery and Oncology www.ifhnos.net The International Federation of Head and Neck Oncologic Societies
Complications after surgery for benign parotid gland neoplasms: A prospective cohort study
 CLINICAL REVIEW David W. Eisele, MD, Section Editor Complications after surgery for benign parotid gland neoplasms: A prospective cohort study Johanna Ruohoalho, MD, 1 * Antti A. M akitie, MD, PhD, 1,2
CLINICAL REVIEW David W. Eisele, MD, Section Editor Complications after surgery for benign parotid gland neoplasms: A prospective cohort study Johanna Ruohoalho, MD, 1 * Antti A. M akitie, MD, PhD, 1,2
The Neck the lower margin of the mandible above the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle
 The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
The Neck is the region of the body that lies between the lower margin of the mandible above and the suprasternal notch and the upper border of the clavicle below Nerves of the neck Cervical Plexus Is formed
Temporal region. temporal & infratemporal fossae. Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy
 Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
Temporal region temporal & infratemporal fossae Zhou Hong Ying Dept. of Anatomy Temporal region is divided by zygomatic arch into temporal & infratemporal fossae. Temporal Fossa Infratemporal fossa Temporal
cally, a distinct superior crease of the forehead marks this spot. The hairline and
 4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
4 Forehead The anatomical boundaries of the forehead unit are the natural hairline (in patients without alopecia), the zygomatic arch, the lower border of the eyebrows, and the nasal root (Fig. 4.1). The
Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2004) 57, 238 244 Aesthetic reconstruction of the nasal tip using a folded composite graft from the ear Yong Oock Kim*, Beyoung Yun Park, Won Jae Lee Institute
Follow-up of parotid pleomorphic adenomas treated by extracapsular dissection
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Follow-up of parotid pleomorphic adenomas treated by extracapsular dissection Heinrich Iro, MD, PhD*, Johannes Zenk, MD, PhD, Michael Koch, MD, PhD, Nils Klintworth, MD Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Follow-up of parotid pleomorphic adenomas treated by extracapsular dissection Heinrich Iro, MD, PhD*, Johannes Zenk, MD, PhD, Michael Koch, MD, PhD, Nils Klintworth, MD Department of Otorhinolaryngology,
doi: /j.anl
 doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2006.07.001 Synchronous unilateral parotid gland neoplasms of three different histological types Shuho Tanaka 1, Keiji Tabuchi 1, Keiko Oikawa 1, Rika Kohanawa 1, Hideki Okubo 1, Dai
doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2006.07.001 Synchronous unilateral parotid gland neoplasms of three different histological types Shuho Tanaka 1, Keiji Tabuchi 1, Keiko Oikawa 1, Rika Kohanawa 1, Hideki Okubo 1, Dai
Clinical evaluation. Imaging Surgical treatment
 Parapharyngeal Space Khalid adhussain AL-Qahtani a MD,MSc,FRCS(c) Assistant Professor Consultant of Otolaryngology Advance Head & Neck Oncology, Thyroid & Parathyroid,Microvascular Reconstruction, ti and
Parapharyngeal Space Khalid adhussain AL-Qahtani a MD,MSc,FRCS(c) Assistant Professor Consultant of Otolaryngology Advance Head & Neck Oncology, Thyroid & Parathyroid,Microvascular Reconstruction, ti and
Neck-2. Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology
 Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Neck-2 ` Dr. Heba Kalbouneh Associate Professor of Anatomy and Histology Triangles of the neck Side of the neck Midline Lower border of mandible Line between angle of mandible and mastoid Superior nuchal
Tympanic Bulla Temporal Bone. Digastric Muscle. Masseter Muscle
 Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
Superior view Hyoid Bone The hyoid bone does not articulate with any other bones. It is held in place by ligaments to the styloid process of the temporal bone and the thyroid cartilage of the larynx. It
A study on structural variations of the parotid glands
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Jayamma C et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3790-3794 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151444
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Jayamma C et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2015 Dec;3(12):3790-3794 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20151444
Extracapsular dissection versus superficial parotidectomy in benign parotid gland tumors: The Vienna Medical School experience
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extracapsular dissection versus superficial parotidectomy in benign parotid gland tumors: The Vienna Medical School experience Lorenz Kadletz, MD, 1 Stefan Grasl, MD, 1 Matth aus C. Grasl,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Extracapsular dissection versus superficial parotidectomy in benign parotid gland tumors: The Vienna Medical School experience Lorenz Kadletz, MD, 1 Stefan Grasl, MD, 1 Matth aus C. Grasl,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve. The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions
 Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Cranial Nerve VII - Facial Nerve The facial nerve has 3 main components with distinct functions Somatic motor efferent Supplies the muscles of facial expression; posterior belly of digastric muscle; stylohyoid,
Use of Modified Retro-mandibular subparotid approach for treatment of Condylar fracture: a Technical note
 Original article: Use of Modified Retro-mandibular subparotid approach for treatment of Condylar fracture: a Technical note 1 DR.Sonal Anchlia, 2 DR.BIPIN.S.SADHWANI, 3 DR.ROHIT KUMAR, 4 Dr.Vipul 1Assistant
Original article: Use of Modified Retro-mandibular subparotid approach for treatment of Condylar fracture: a Technical note 1 DR.Sonal Anchlia, 2 DR.BIPIN.S.SADHWANI, 3 DR.ROHIT KUMAR, 4 Dr.Vipul 1Assistant
PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY
 PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
PATIENT CENTERED MEDICINE - 1 GOALS & OUTCOMES: PCM1 Physical Exam Skills Session: Head and Neck FACILITATOR & STUDENT COPY 1. To introduce the applied anatomy relevant for the examination of the head
Face. Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face
 Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Face Definition: The area between the two ears and from the chin to the eye brows. The muscles of the face The muscle of facial expression (include the muscle of the face and the scalp). All are derived
Complications after superficial parotidectomy for pleomorphic adenoma
 Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.22386 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.22386 for pleomorphic adenoma Pedro Infante-Cossio 1, Eduardo Gonzalez-Cardero
Journal section: Oral Surgery Publication Types: Research doi:10.4317/medoral.22386 http://dx.doi.org/doi:10.4317/medoral.22386 for pleomorphic adenoma Pedro Infante-Cossio 1, Eduardo Gonzalez-Cardero
The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects
 The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 593 598 The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects Mohammed G. Ellabban*, Maamoun I. Maamoun, Moustafa Elsharkawi
The British Association of Plastic Surgeons (2003) 56, 593 598 The bi-pedicle post-auricular tube flap for reconstruction of partial ear defects Mohammed G. Ellabban*, Maamoun I. Maamoun, Moustafa Elsharkawi
Head and Face Anatomy
 Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
Head and Face Anatomy Epicranial region The Scalp The soft tissue that covers the vault of skull. Extends from supraorbital margin to superior nuchal line. Layers of the scalp S C A L P = skin = connective
3-Deep fascia: is absent (except over the parotid gland & buccopharngeal fascia covering the buccinator muscle)
 The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
The Face 1-Skin of the Face The skin of the face is: Elastic Vascular (bleed profusely however heal rapidly) Rich in sweat and sebaceous glands (can cause acne in adults) It is connected to the underlying
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide
 Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
Head and neck cancer - patient information guide The development of reconstructive surgical techniques in the last 20 years has led to major advances in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer.
For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER
 GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION May 15, 2000 For the following questions, indicate the letter that corresponds to the SINGLE MOST APPROPRIATE ANSWER 1. Pain associated with an infection limited to the middle
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. and histological data. An additional confounding factor is infection, which oftendivertsthephysician sattention.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE First Branchial Cleft Anomalies A Study of 39 Cases and a Review of the Literature Jean-Michel Triglia, MD; Richard Nicollas, MD; Vincent Ducroz, MD; Peter J. Koltai, MD; Erea-Noël Garabedian,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE First Branchial Cleft Anomalies A Study of 39 Cases and a Review of the Literature Jean-Michel Triglia, MD; Richard Nicollas, MD; Vincent Ducroz, MD; Peter J. Koltai, MD; Erea-Noël Garabedian,
Treatment of intractable parotid sialocele occurred after open reduction-fixation of mandibular subcondylar fracture
 2018 June 22 [Epub ahead of print] https://doi.org/10.7181/acfs.2018.01802 Treatment of intractable parotid sialocele occurred after open reduction-fixation of mandibular subcondylar fracture Jungil Hwang,
2018 June 22 [Epub ahead of print] https://doi.org/10.7181/acfs.2018.01802 Treatment of intractable parotid sialocele occurred after open reduction-fixation of mandibular subcondylar fracture Jungil Hwang,
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman
 Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Breast conservation surgery and sentinal node biopsy: Dr R Botha Moderator: Dr E Osman Breast anatomy: Breast conserving surgery: The aim of wide local excision is to remove all invasive and in situ
Salivary Glands tumors
 Salivary Glands tumors Sal.Gl. 1 Salivary Glands tumors Work-up procedure TNM staging Primary treatment Follow-up Treatment of recurrent and/or metastatic disease References Sal.Gl. 2 Standard clinical
Salivary Glands tumors Sal.Gl. 1 Salivary Glands tumors Work-up procedure TNM staging Primary treatment Follow-up Treatment of recurrent and/or metastatic disease References Sal.Gl. 2 Standard clinical
Anatomical localisation of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial nerve
 O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 66, No. 4, pp. 307 313 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Anatomical localisation of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial
O R I G I N A L A R T I C L E Folia Morphol. Vol. 66, No. 4, pp. 307 313 Copyright 2007 Via Medica ISSN 0015 5659 www.fm.viamedica.pl Anatomical localisation of the marginal mandibular branch of the facial
Anterior triangle of neck
 Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
Anterior triangle of neck Dept. of Anatomy Zhou Hong Ying Outline boundary and subdivisions of ant. triangle contents of the triangle Muscles: suprahyoid muscles, infrahyoid muscles Nerves: CNⅩ, CNⅪ, CNⅫ,
A Novel Approach to Submandibular Gland Ptosis: Creation of a Platysma Muscle and Hyoid Bone Cradle
 A Novel Approach to Submandibular Gland Ptosis: Creation of a Platysma Muscle and Hyoid Bone Cradle Robert Lukavsky 1, Gary Linkov 2, Christopher Fundakowski 2,3 1 Department of General Surgery, Temple
A Novel Approach to Submandibular Gland Ptosis: Creation of a Platysma Muscle and Hyoid Bone Cradle Robert Lukavsky 1, Gary Linkov 2, Christopher Fundakowski 2,3 1 Department of General Surgery, Temple
Tikrit University College of Dentistry Dr.Ban I.S. head & neck anatomy 2 nd y.
 Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
Lec [3]/The scalp The scalp extends from the supraorbital margins anteriorly to the nuchal lines at the back of the skull and down to the temporal lines at the sides. The forehead, from eyebrows to hairline,
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions. 4 May 2012
 SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
SCHOOL OF ANATOMICAL SCIENCES Mock Run Questions 4 May 2012 1. With regard to the muscles of the neck: a. the platysma muscle is supplied by the accessory nerve. b. the stylohyoid muscle is supplied by
Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor
 Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 421245, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/421245 Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor Akira Sugamata, 1 Naoki Yoshizawa,
Plastic Surgery International Volume 2011, Article ID 421245, 5 pages doi:10.1155/2011/421245 Clinical Study Open Reduction of Subcondylar Fractures Using a New Retractor Akira Sugamata, 1 Naoki Yoshizawa,
3. The Jaw and Related Structures
 Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Overview and objectives of this dissection 3. The Jaw and Related Structures The goal of this dissection is to observe the muscles of jaw raising. You will also have the opportunity to observe several
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck. M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick. Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974.
 Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Surgical Anatomy of the Neck M. J. Jurkiewicz, John Bostwick Surgical Clinics of North America, Vol 54, No 6, December 1974. The radical neck dissection is a safe, effective therapeutic procedure for eradication
Salivary ultrasound. Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK
 Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Salivary ultrasound Dr T J Beale Royal National Throat Nose & Ear and UCLH Hospitals London UK Two main groups of patients with presenting symptoms of: Obstructive or chronic inflammatory symptoms (salivary
Branchial Cleft and Pouch Anomalies
 Branchial Cleft and Pouch Anomalies Prof.Mohamed Hesham Alexandria Faculty of Medicine Alexandria, Egypt Emberyological Basis Branchial Clefts 1st 2nd Pinna EAC 3rd 4th 4th 6th Cervical sinus Branchial
Branchial Cleft and Pouch Anomalies Prof.Mohamed Hesham Alexandria Faculty of Medicine Alexandria, Egypt Emberyological Basis Branchial Clefts 1st 2nd Pinna EAC 3rd 4th 4th 6th Cervical sinus Branchial
Tumours of Parapharyngeal space
 Tumours of Parapharyngeal space The parapharyngeal spaces (PPS), as the name implies, lie laterally on either side of the pharynx. They are potential spaces, filled with fat and areolar tissue containing
Tumours of Parapharyngeal space The parapharyngeal spaces (PPS), as the name implies, lie laterally on either side of the pharynx. They are potential spaces, filled with fat and areolar tissue containing
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi
 By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
By : Prof Saeed Abuel Makarem & Dr.Sanaa Alshaarawi OBJECTIVES By the end of the lecture, students shouldbe able to: List the nuclei of the deep origin of the trigeminal and facial nerves in the brain
Pleomorphic adenoma of submandibular gland: not so common occurrence
 International Surgery Journal Gajbhiye AS et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Feb;5(2):657-661 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20180371
International Surgery Journal Gajbhiye AS et al. Int Surg J. 2018 Feb;5(2):657-661 http://www.ijsurgery.com pissn 2349-3305 eissn 2349-2902 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-2902.isj20180371
Merkel Cell Carcinoma Case # 2
 DISCHARGE SUMMARY Admitted: 10/11/2010 Discharged: 10/13/2010 Merkel Cell Carcinoma Case # 2 Chief Compliant: A 79 year old lady status post tumor on the scalp excision and left neck likely dissection
DISCHARGE SUMMARY Admitted: 10/11/2010 Discharged: 10/13/2010 Merkel Cell Carcinoma Case # 2 Chief Compliant: A 79 year old lady status post tumor on the scalp excision and left neck likely dissection
Veins of the Face and the Neck
 Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Veins of the Face and the Neck Facial Vein The facial vein is formed at the medial angle of the eye by the union of the supraorbital and supratrochlear veins. connected through the ophthalmic veins with
Alexander C Vlantis. Total Laryngectomy 57
 07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
07 Total Laryngectomy Alexander C Vlantis Total Laryngectomy 57 Total Laryngectomy STEP 1 INCISION AND POSITION OF STOMA A superiorly based apron flap incision is marked with the horizontal limb placed
Comprehensive Management of Head and Neck Tumors. Stanley E Thawley, William R Panje, John G Batsakis, Robert D Lindberg
 Comprehensive Management of Head and Neck Tumors Stanley E Thawley, William R Panje, John G Batsakis, Robert D Lindberg Chapter 46: Controversies Regarding Therapy of Tumors of the Salivary Glands John
Comprehensive Management of Head and Neck Tumors Stanley E Thawley, William R Panje, John G Batsakis, Robert D Lindberg Chapter 46: Controversies Regarding Therapy of Tumors of the Salivary Glands John
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:
![Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve:](/thumbs/94/121295776.jpg) Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Lec [8]: Mandibular nerve: The mandibular branch from the trigeminal ganglion lies in the middle cranial fossa lateral to the cavernous sinus. With the motor root of the trigeminal nerve [motor roots lies
Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery
 Chapter 2 Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Ruchi Singhal 1 ; Virendra Singh 2 ; Amrish Bhagol* 1 Jaipur Dental College, Jaipur, India 2 Senior Professor, PGIDS, Rohtak, India Amrish Bhagol Condylar Fractures
Chapter 2 Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery Ruchi Singhal 1 ; Virendra Singh 2 ; Amrish Bhagol* 1 Jaipur Dental College, Jaipur, India 2 Senior Professor, PGIDS, Rohtak, India Amrish Bhagol Condylar Fractures
Risk of Facial Paralysis Following Parotidectomy. Ayad A Hasan FICMS, Ammar Y Khudhir FICMS
 raqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine SSN 1681-6579 Email: raqi_jms_alnahrain@yahoo.com http://www. colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Risk of Facial Paralysis Following Parotidectomy Ayad A Hasan FCMS,
raqi JMS Published by Al-Nahrain College of Medicine SSN 1681-6579 Email: raqi_jms_alnahrain@yahoo.com http://www. colmed-nahrain.edu.iq/ Risk of Facial Paralysis Following Parotidectomy Ayad A Hasan FCMS,
SOFT TISSUE SUPPORT IS AN
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstructive Application of the Endotine Suspension Devices James H. Boehmler IV, MD; Benjamin L. Judson, MD; Steven P. Davison, MD, DDS Objective: To illustrate the potential reconstructive
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Reconstructive Application of the Endotine Suspension Devices James H. Boehmler IV, MD; Benjamin L. Judson, MD; Steven P. Davison, MD, DDS Objective: To illustrate the potential reconstructive
Medicine. PRISMA Extracapsular Dissection Versus Superficial Parotidectomy in Treatment of Benign Parotid Tumors. Evidence From 3194 Patients
 Medicine SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS PRISMA Extracapsular Dissection Versus Superficial Parotidectomy in Treatment of Benign Parotid Tumors Evidence From 3194 Patients Shang Xie, MD, PhD, Kan Wang,
Medicine SYSTEMATIC REVIEW AND META-ANALYSIS PRISMA Extracapsular Dissection Versus Superficial Parotidectomy in Treatment of Benign Parotid Tumors Evidence From 3194 Patients Shang Xie, MD, PhD, Kan Wang,
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli.
 Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Anatomy: head and Neck (6 questions) 1. Prevertebral Flexor Musculature (lying in front of the vertebrae) include all, EXCEPT: Longus Colli. Rectus Capitis Anterior. Rectus Capitis Lateralis. Rectus Capitis
Thyroidectomy. Siu Kwan Ng. Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47
 06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
06 Thyroidectomy Siu Kwan Ng Modified Radical Neck Dissection Type II 47 Thyroidectomy STEP 1. EXPOSING THE THYROID GLAND The collar incision Figure 1 (curvilinear skin crease incision) is made at 1.5-2
AMSER Rad Path Case of the Month:
 AMSER Rad Path Case of the Month: 62 year old male presents with right-sided facial mass Daniel Morgan, OMS III Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine Dr. Matthew Hartman, M.D. Medical Student Coordinator;
AMSER Rad Path Case of the Month: 62 year old male presents with right-sided facial mass Daniel Morgan, OMS III Lake Erie College of Osteopathic Medicine Dr. Matthew Hartman, M.D. Medical Student Coordinator;
Total versus superficial parotidectomy for stage III melanoma
 DOI: 10.1002/hed.24810 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Total versus superficial parotidectomy for stage III melanoma Aileen P. Wertz, MD 1 Alison B. Durham, MD 2 Kelly M. Malloy, MD 1 Timothy M. Johnson, MD 2 Carol R.
DOI: 10.1002/hed.24810 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Total versus superficial parotidectomy for stage III melanoma Aileen P. Wertz, MD 1 Alison B. Durham, MD 2 Kelly M. Malloy, MD 1 Timothy M. Johnson, MD 2 Carol R.
Functional components
 Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
Facial Nerve VII cranial nerve Emerges from Pons Two roots Functional components: 1. GSA (general somatic afferent) 2. SA (Somatic afferent) 3. GVE (general visceral efferent) 4. BE (Special visceral/branchial
THE SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE CERVICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE FACIAL NERVE. Biology and Anatomy, University of Shefield
 British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981), 19, 171-179 @ The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00260171$02.00 THE SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE CERVICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE FACIAL NERVE HAITHEM
British Journal of Oral Surgery (1981), 19, 171-179 @ The British Association of Oral Surgeons 0007-117X/81/00260171$02.00 THE SURGICAL ANATOMY OF THE CERVICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE FACIAL NERVE HAITHEM
The Subzygomatic Triangle: Rapid, minimally invasive identification of the masseteric nerve for facial ACCEPTED
 Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Advance Online Article DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318290f6dc The Subzygomatic Triangle: Rapid, minimally invasive identification of the masseteric nerve for facial reanimation
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery Advance Online Article DOI: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e318290f6dc The Subzygomatic Triangle: Rapid, minimally invasive identification of the masseteric nerve for facial reanimation
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi. E. mail:
 The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
The Skull and Temporomandibular joint II Prof. Abdulameer Al-Nuaimi E-mail: a.al-nuaimi@sheffield.ac.uk E. mail: abdulameerh@yahoo.com Temporal fossa The temporal fossa is a depression on the temporal
