Kugelman A, Riskin A, Said W, Shoris I, Mor F, Bader D.
|
|
|
- Candice Hubbard
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) vs. Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) for the Primary Treatment of RDS, A Randomized, Controlled, Prospective, Pilot Study Kugelman A, Riskin A, Said W, Shoris I, Mor F, Bader D. Pediatric Pulmonary Unit and Department of Neonatology, Bnai Zion Medical Center The B&R Rappaport Faculty of Medicine, Haifa, Israel Pediatric Pulmonoloy. March 2014
2 Conflict of Interest Disclosure Vapotherm Inc. supplied the equipment for HHHFNC for our study.
3 Introduction Because mechanical ventilation is associated with morbidity, mainly BPD, the trend today is to minimize the use of mechanical ventilation.
4 Introduction - Nasal Respiratory Support Nasal respiratory support (NRS) Nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) * Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) ** NRS was shown to be effective in treating infants in the acute phase of RDS Enables the avoidance of mechanical ventilation in a relatively large number of infants * Ho et al, Cochrane 2000; Morley et al, N Engl J Med 2008; Finer NN et al, N Engl J Med 2010.** Kugelman et al, J Pediatr 2007
5 Introduction - Nasal Respiratory Support While NCPAP is currently the common practice for the initial treatment of RDS, NIPPV is probably more beneficial. * * Total cohort Infants <1500 g Endotracheal Ventilation * Total cohort NCPAP NIPPV Infants <1500 g BPD * * p<0.05 NIPPV is our NICU drug of choice. * Kugelman et al, J Pediatr 2007
6 Introduction - Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) HHHFNC is frequently used to deliver oxygen and as a mode of NRS. Few RCT have recently reported that HHHFNC was as good as NCPAP for the early stages of RDS (Yoder et al, Pediatrics 2013) For later treatment post extubation, after endotracheal ventilation and surfactant administration for RDS (Yoder et al, Pediatrics, 2013; Collins et al, J Peds 2012; Manley et al, NEJM 2013) For apnea of prematurity (Sreenan et al, Pediatrics 2001).
7 Introduction - HHHFNC By definition HHHFNC delivers flow rates that exceed patient inspiratory flow rates at various minute volumes. High flows Result in washout of anatomical and physiological dead space Contribute to improved fractions of alveolar gases with respect to carbon dioxide and oxygen. * HHHFNC creates inadvertent PEEP that may contribute to its beneficial effect.**, *** * Dewan et al, Chest 1994, ** Kubicka et al, Pediatrics 2008; *** Sreenan et al, Pediatrics 2001
8 Non Invasive Ventilatory Approach to Treat RDS Delivery Room or NICU Endotracheal Intubation Caffeine INSURE Approach Surfactant Steroids- Selective use Nutrition Vitamin A? MIST Immediate Extubation Extubation at RDS Resolution Nasal Respiratory Support HHHFNC NCPAP Nasal Ventilation (NIPPV/SNIPPV) 1Permissive Hypercapnia 2Adequate Oxygenation Spontaneous Unsupported Breathing (Kugelman A. Ped Pulmonol 2011)
9 Introduction - HHHFNC No randomized prospective study was published yet that Evaluated HHHFNC in the primary treatment of RDS. Compared HHHFNC with NIPPV for the primary treatment of RDS.
10 Hypothesis We hypothesized that: While the ELBW infants (<1000 g) may need NIPPV as NRS for the treatment of RDS, Larger infants may enjoy the comfort benefits associated with HHHFNC while getting comparable respiratory support to NIPPV.
11 Objective To determine the need for endotracheal ventilation in preterm infants treated with early HHHFNC compared with NIPPV for the primary treatment of RDS.
12 Methods: Procedure This was a prospective, randomized, controlled, single center, clinical, pilot study. The study was approved by the IRB in our center. All the parents signed an informed consent. We performed an intention-to-treat analysis, with a sample size calculation of 37 infants in each arm of the study.
13 Methods: Procedure Early NRS (HHHFNC or NIPPV) was initiated in any spontaneously breathing premature infant showing signs of respiratory distress (tachypnea, grunting, nasal flaring, retractions). * If NRS was indicated, the mode was decided randomly between HHHFNC and NIPPV. Cross over between groups was not encouraged but was allowed. * Gittermann et al, Eur J Pediatr 1997
14 Subjects Infants that were born in Bnai Zion Medical Center, Haifa, Israel, during the study period and met the inclusion criteria participated in the study.
15 Inclusion Criteria 1. Gestational age <35 weeks and weight >1000 g. 2. Infants with RDS who needed NRS as initial therapy. 3. Written informed consent.
16 Exclusion Criteria 1. Significant morbidity apart from RDS including: - Cardiac disease (not including PDA) - Congenital malformation - Cardiovascular or respiratory instability because of sepsis, anemia or severe IVH
17 Respiratory Management Endotracheal intubation was performed in the delivery room if: Heart rate did not increase to >100 beats per minute The infant had insufficient spontaneous respiratory effort Marked and increasing dyspnea * Exogenous surfactant ( mg/kg, 1 to 2 doses as needed, Curosurf, Chiesi Farmaceutici, Parma, Italy) was given only as rescue therapy. *Lindner et al, Pediatrics 1999
18 HHHFNC Respiratory Management HHHFNC was delivered by the Vapotherm device (Precision Flow, Vapotherm Inc., Stevensville, MD), using flows between l/m. Flows were started on 1 l/m and increased at intervals of 1 l/m according to: - Clinical condition - Respiratory [retractions, respiratory rate, grunting] - Hemodynamic [blood pressure and heart rate]) - Ventilation (PaCO 2 ) - Oxygenation
19 HHHFNC Respiratory Management FiO 2 was set to keep SpO 2 between 88-92%. The HHHFNC was given via the Vapotherm nasal prongs (outer diameter: 0.2 cm-0.3 cm). Leak was created/allowed by using the nasal prongs no larger than 1/2 the diameter of the nares and no chin rap was allowed.
20 NIPPV Respiratory Management NIPPV was delivered by the SLE 2000 or 5000 (Specialized Laboratory Equipment Ltd., South Croydon, UK) via nasal prongs (INCA, Ackrad Labs, Berlin, Germany). NIPPV was set at a synchronized mode Rate of breaths per minute (according to PaCO 2 ) Inspiratory time of 0.3 seconds PEEP of 6 cmh 2 O PIP of cmh 2 O according to chest excursion and the infant's weight FiO 2 was set to keep SpO 2 between 88-92%.
21 Primary Outcome Measure The percent of infants who failed NRS and needed endotracheal ventilation or were switched to another mode of NRS.
22 Criteria for Failure of Nasal Support * Clinical deterioration [increased respiratory distress] accompanied by at least one of the following or worsening of the following: 1. ph<7.20 and PCO 2 >60 mmhg 2. PaO 2 <50 mmhg or SpO 2 <88% on FiO 2 >50% 3. Recurrent significant apnea requiring repeated stimulation or bag-and-mask ventilation despite the use caffeine or adequate nasal support Switch was allowed in failure of NRS mode or in cases of nasal septal damage. * Kugelman et al, J Pediatr 2007
23 Results
24 Infant Enrollment Delivered infants < 35 weeks 317 Exclusion criteria (<1000 g =22, cardiac anomaly=1, CDH=1) 24 Eligible infants 293 Included in study 76 Did not participate 217 Refusal 2 Technical 3 NIPPV 38 HHHFNC 38 Ventilated in delivery room 15 No respiratory support 197 Ventilated Not Ventilated Ventilated Not Ventilated
25 Demographic Characteristics NIPPV (38) HHHFNC (38) p value Gestational age (weeks) 32.7 ( ) 32.5 ( )* NS** Birth weight (g) NS Infants<1500 g 12 (31%) 13 (34%) NS Male/Female 24/14 26/12 NS Prenatal steroids 19 (50%) 19 (50%) NS Caffeine 14 (36.8%) 15 (39.5%) NS Cardio-Respiratory Status at Study Entry NIPPV (38) NHHHFNC (38) p value FiO ( ) 0.25 ( ) NS SpO 2 (%) 90 (46-100) 92 (70-100) NS PCO 2 (mm Hg) NS ph NS Grunting or retractions (%) 35 (92) 36 (94) NS RR (breaths/min) NS HR (beats/min) NS MBP # (mmhg) NS Start nasal support (hours) NS * Mean+SD or median (range), ** Not significant, # mean blood pressure (No difference between groups for infants <1500 g, 12 on NIPPV, 13 on HHHFNC)
26 Main Findings: Endotracheal Intubation and BPD % * NS Total cohort * 38 Infants <1500 g Endotracheal Ventilation NS 50 NS Total cohort BPD HHHFNC NIPPV NS 16.7 Infants <1500 g * One infant (< 1500 g) met intubation criteria on HHHFNC, was switched to NIPPV and did not need ETT.
27 Clinical Outcomes NIPPV (n=38) HHHFNC (n=38) p value Pneumothorax 0 2 (5.2%) NS Trauma NS # 0 0 NS Mean comfort score 1.36±0.41 (1.25) 1.33±0.50 (1.00) NS MV # Duration (d) * NS NRS # Duration (d) BPD 2 (5.2%) 1 (2.6%) NS IVH 1 (2.6%) 2 (5.3%) NS PDA 4 (10.5%) 9 (23.7%) NS NEC 0 2 (5.3%) NS Sepsis 3 (7.8%) 4 (10.5) NS Time to FF # (d) 11.0 (5-49) 13.0 (96-28) NS (p=0.07) Length of stay (d) 39.5 (9-113) 35.0 (8-91) NS Death 0 0 NS (No difference between groups for infants <1500 g) # NS - nasal septum, MV - mechanical ventilation, NRS nasal respiratory support, IVH - intraventricular hemorrhage, BPD - bronchopulmonary dysplasia, FF - full feeds, * mean+sd or median (range),
28 DISCUSSION
29 Physiology and Practice HHHFNC and NIPPV act physiologically different and need to be set accordingly in a different manner. When using NIPPV we occlude the nares and possibly the mouth to avoid leak and to create a monitored PEEP. In contrast, while on HHHFNC we create purposely a leak, as we can not measure a possible inadvertent PEEP, to avoid air leak.
30 HHHFNC Strategy Because No previous clinical prospective trials were published for the initial treatment of RDS, Concerns for air leak, We chose a safe and a relatively conservative approach in using the HHHFNC. The two strategies for use of HHHFNC, Starting with high flows and then weaning Using a "step-up" approach Were not compared in any study.
31 Study Limitations 1) The mode of support assignment could not be blinded to the medical team. Use of objective failure criteria and management protocols reduce the possibility of a bias that this might have caused. 2) We included for safety issues only infants weighing >1000 g and we had only a small sample size for infants <1500 g. Thus, our results in the VLBW infants should be taken with caution. These infants should be the target population for future studies.
32 Conclusions HHHFNC was found to be as effective as NIPPV in preventing endotracheal ventilation in the initial treatment of RDS in premature infants (<35 weeks GA, with BW >1000 g). The rates of neonatal morbidities were comparable in both modes of NRS.. HHHFNC seems to be safe.
33 Summary Our pilot study provides the basis for further, larger trials of this intervention before it can be concluded that HHHFNC is safe and can serve as primary mode of NRS in premature infants with RDS. Thank you!!!
34 NRS NIPPV (n=38) HHHFNC (n=38) p value Initial flow HHHFNC (l/min) - Maximal flow HHFNC (l/min) - % infants on max. flow - 14/38 (37%) - Time to stop NRS 2.0 ( ) 4.0 ( ) P=0.006 Time to stop O2 3.0 ( ) 5.0 (0-69.0) NS Failed NS 13 (34.2%) 12 (31.6%) NS Intubation 13 (34.2%) 11 (28.9%) NS Duration of MV 4.0 ( ) 3.0 ( ) NS Surfactant 13 (34.2%) 11 (28.9%) NS (No difference between groups for infants <1500 g) # NS - nasal septum, MV - mechanical ventilation, NRS nasal respiratory support, * mean+sd or median (range).
35 Secondary Outcome Measure 1. Clinical features during treatment (hourly): blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, SpO 2, and respiratory status prior to mechanical ventilation if needed according to arterial blood gas (PaO 2, PCO 2, ph), and time to stop nasal support (only oxygen or low nasal cannula flow <1 L/min, and allowed when infants on nasal support were on FiO 2 <30%, had normal blood gases, and no respiratory distress or apnea). 2. Incidence of IVH, duration of mechanical ventilation, incidence of BPD (oxygen at 36 weeks post conceptional age to keep SpO 2 >92%), time until full feeds, and length of stay. 3. Safety: nasal trauma due to NRS, rate of air leak (pneumothorax), gastrointestinal perforation, irritability and discomfort assessed by a validated score given by the nurses at the first 4 hours on NRS. * * Kugelman et al, Acta Pediatr 2008
36 Introduction - HHHFNC HHHFNC may decrease the work of breathing. New devices enable high flows Humidified and warmed air (HHHFNC) Were shown to perform better than a standard HFNC immediately following extubation In maintaining a normal appearing nasal mucosa A lower respiratory effort score Averting reintubation. * HHHFNC probably creates inadvertent PEEP that may contribute to its beneficial effect.**, *** * Woodhead et al, J Perinatol 2006, ** Kubicka et al, Pediatrics 2008; *** Sreenan et al, Pediatrics 2001
Name and title of the investigators responsible for conducting the research: Dr Anna Lavizzari, Dr Mariarosa Colnaghi
 Protocol title: Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula vs Nasal CPAP for Respiratory Distress Syndrome of Prematurity. Protocol identifying number: Clinical Trials.gov NCT02570217 Name and title of
Protocol title: Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula vs Nasal CPAP for Respiratory Distress Syndrome of Prematurity. Protocol identifying number: Clinical Trials.gov NCT02570217 Name and title of
Is There a Treatment for BPD?
 Is There a Treatment for BPD? Amir Kugelman, Pediatric Pulmonary Unit and Department of Neonatology Bnai Zion Medical Center, Rappaport Faculty of Medicine Haifa, Israel Conflict of Interest Our study
Is There a Treatment for BPD? Amir Kugelman, Pediatric Pulmonary Unit and Department of Neonatology Bnai Zion Medical Center, Rappaport Faculty of Medicine Haifa, Israel Conflict of Interest Our study
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call
 AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call November 12, 2015 Forward Looking Statement To the extent that statements in this presentation are not strictly historical, including statements
AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call November 12, 2015 Forward Looking Statement To the extent that statements in this presentation are not strictly historical, including statements
Non-Invasive PCO 2 Monitoring in Infants Hospitalized with Viral Bronchiolitis
 Non-Invasive PCO 2 Monitoring in Infants Hospitalized with Viral Bronchiolitis Gal S, Riskin A, Chistyakov I, Shifman N, Srugo I, and Kugelman A Pediatric Department and Pediatric Pulmonary Unit Bnai Zion
Non-Invasive PCO 2 Monitoring in Infants Hospitalized with Viral Bronchiolitis Gal S, Riskin A, Chistyakov I, Shifman N, Srugo I, and Kugelman A Pediatric Department and Pediatric Pulmonary Unit Bnai Zion
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants <34 weeks gestation.
 Page 1 of 5 PURPOSE: Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants
Page 1 of 5 PURPOSE: Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants
5/3/2012. Goals and Objectives HFNC. High-Flow Oxygen Therapy: Real Benefit or Just a Fad?
 High-Flow Oxygen Therapy: Real Benefit or Just a Fad? Timothy R. Myers MBA, RRT-NPS Director, Women s & Children s Respiratory Care & Procedural Services and Pediatric Heart Center Rainbow Babies & Children
High-Flow Oxygen Therapy: Real Benefit or Just a Fad? Timothy R. Myers MBA, RRT-NPS Director, Women s & Children s Respiratory Care & Procedural Services and Pediatric Heart Center Rainbow Babies & Children
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. DD Woodhead, DK Lambert, JM Clark and RD Christensen. Intermountain Healthcare, McKay-Dee Hospital, Ogden, UT, USA
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparing two methods of delivering high-flow gas therapy by nasal cannula following endotracheal extubation: a prospective, randomized, masked, crossover trial DD Woodhead, DK Lambert,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparing two methods of delivering high-flow gas therapy by nasal cannula following endotracheal extubation: a prospective, randomized, masked, crossover trial DD Woodhead, DK Lambert,
Clinical Guideline: Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) Guideline
 EOE Neonatal ODN Clinical Guideline: Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) Guideline Authors: Dr Eliana Panayiotou and Dr Bharat Vakharia For use in: EoE Neonatal Units Guidance specific to
EOE Neonatal ODN Clinical Guideline: Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) Guideline Authors: Dr Eliana Panayiotou and Dr Bharat Vakharia For use in: EoE Neonatal Units Guidance specific to
Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 19: 573-577 Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome B.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 19: 573-577 Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome B.
9/15/2017. Disclosures. Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula: Hot Air or Optimal Noninvasive Support? Objectives. Aerogen Pharma
 Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula: Hot Air or Optimal Noninvasive Support? Rob DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Program Manager Research/QI, Respiratory Therapy Principle Investigator, Seattle Children s Research Institute
Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula: Hot Air or Optimal Noninvasive Support? Rob DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Program Manager Research/QI, Respiratory Therapy Principle Investigator, Seattle Children s Research Institute
Von Reuss and CPAP, Disclosures CPAP. Noninvasive respiratory therapieswhy bother? Noninvasive respiratory therapies- types
 Noninvasive respiratory therapiesby a nose? NEO- The Conference for Neonatology February 21, 2014 Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflicts of interest to release.
Noninvasive respiratory therapiesby a nose? NEO- The Conference for Neonatology February 21, 2014 Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflicts of interest to release.
Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) NICU POCKET GUIDE
 Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) TM NICU POCKET GUIDE Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following symptoms: These
Guidelines and Best Practices for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) TM NICU POCKET GUIDE Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following symptoms: These
Objectives. Apnea Definition and Pitfalls. Pathophysiology of Apnea. Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes 5/18/2015
 Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes Deepak Jain MD Care of Sick Newborn Conference May 2015 Objectives Differentiating between apnea and hypoxemia episodes. Pathophysiology Diagnosis of apnea and
Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes Deepak Jain MD Care of Sick Newborn Conference May 2015 Objectives Differentiating between apnea and hypoxemia episodes. Pathophysiology Diagnosis of apnea and
Hyaline membrane disease. By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg
 Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience
 Original Article Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience Pedro Paz, MD, MPH 1 Rangasamy Ramanathan, MD 1,2 Richard Hernandez, RCP 2 Manoj Biniwale, MD 1 1 Division of Neonatal
Original Article Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience Pedro Paz, MD, MPH 1 Rangasamy Ramanathan, MD 1,2 Richard Hernandez, RCP 2 Manoj Biniwale, MD 1 1 Division of Neonatal
Minimizing Lung Damage During Respiratory Support
 Minimizing Lung Damage During Respiratory Support University of Miami Jackson Memorial Medical Center Care of the Sick Newborn 15 Eduardo Bancalari MD University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Jackson
Minimizing Lung Damage During Respiratory Support University of Miami Jackson Memorial Medical Center Care of the Sick Newborn 15 Eduardo Bancalari MD University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Jackson
Guidelines and Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide
 Guidelines Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following signs or symptoms of respiratory distress:
Guidelines Best Practices for High Flow Nasal Cannula (HFNC) Pediatric Pocket Guide Patient Selection Diagnoses Patient presents with one or more of the following signs or symptoms of respiratory distress:
Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants. Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid
 Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid Summary Noninvasive ventilation begings in the delivery room
Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid Summary Noninvasive ventilation begings in the delivery room
Dr. AM MAALIM KPA 2018
 Dr. AM MAALIM KPA 2018 Journey Towards Lung protection Goals of lung protection Strategies Summary Conclusion Before 1960: Oxygen; impact assessed clinically. The 1960s:President JFK, Ventilators mortality;
Dr. AM MAALIM KPA 2018 Journey Towards Lung protection Goals of lung protection Strategies Summary Conclusion Before 1960: Oxygen; impact assessed clinically. The 1960s:President JFK, Ventilators mortality;
Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study
 D-32084-2011 Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study Robert DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Respiratory Care Manager of Research & Quality
D-32084-2011 Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study Robert DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Respiratory Care Manager of Research & Quality
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY
 PS1006 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR THE Job Title of Reviewer: EFFECTIVE DATE: REVISED DATE: Director, Respiratory Care Services 126.685 (neo) 3/26/15
PS1006 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR THE Job Title of Reviewer: EFFECTIVE DATE: REVISED DATE: Director, Respiratory Care Services 126.685 (neo) 3/26/15
High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC. Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand
 786 High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand Disclaimer I was a scep@c un@l I used it Now I am a firm believer HFNC The Fisher and Paykel
786 High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand Disclaimer I was a scep@c un@l I used it Now I am a firm believer HFNC The Fisher and Paykel
Newborn Life Support. NLS guidance.
 Kelly Harvey, ANNP NWNODN, previously Wythenshawe Hospital has shared this presentation with the understanding that it is for personal use following your attendance at the 8th Annual Senior Neonatal Nursing
Kelly Harvey, ANNP NWNODN, previously Wythenshawe Hospital has shared this presentation with the understanding that it is for personal use following your attendance at the 8th Annual Senior Neonatal Nursing
Surfactant Administration
 Approved by: Surfactant Administration Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual
Approved by: Surfactant Administration Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual
Non-invasive ventilatory strategies, such as
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula versus Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure as Primary Mode of Respiratory Support for Respiratory Distress in Preterm Infants DEEPARAJ
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula versus Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure as Primary Mode of Respiratory Support for Respiratory Distress in Preterm Infants DEEPARAJ
ROLE OF EARLY POSTNATAL DEXAMETHASONE IN RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME
 INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-FEBRUAKY 1998 ROLE OF EARLY POSTNATAL DEXAMETHASONE IN RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Kanya Mukhopadhyay, Praveen Kumar and Anil Narang From the Division of Neonatology, Department
INDIAN PEDIATRICS VOLUME 35-FEBRUAKY 1998 ROLE OF EARLY POSTNATAL DEXAMETHASONE IN RESPIRATORY DISTRESS SYNDROME Kanya Mukhopadhyay, Praveen Kumar and Anil Narang From the Division of Neonatology, Department
NAVA. In Neonates. Howard Stein, M.D. Director Neonatology. Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist. Toledo Children s Hospital Toledo, Ohio
 NAVA Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist In Neonates Howard Stein, M.D. Director Neonatology Toledo Children s Hospital Toledo, Ohio Disclaimers Dr Stein: Is discussing products made by Maquet Has no
NAVA Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist In Neonates Howard Stein, M.D. Director Neonatology Toledo Children s Hospital Toledo, Ohio Disclaimers Dr Stein: Is discussing products made by Maquet Has no
The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation
 The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Departments of Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Some definitions
The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Departments of Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Some definitions
Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery
 Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery Opening Scenario (Links to Section 1) You are an evening-shift respiratory therapist in a large hospital with a level III neonatal unit. You are paged
Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery Opening Scenario (Links to Section 1) You are an evening-shift respiratory therapist in a large hospital with a level III neonatal unit. You are paged
Weaning and extubation in PICU An evidence-based approach
 Weaning and extubation in PICU An evidence-based approach Suchada Sritippayawan, MD. Div. Pulmonology & Crit Care Dept. Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Kanokporn Udomittipong, MD.
Weaning and extubation in PICU An evidence-based approach Suchada Sritippayawan, MD. Div. Pulmonology & Crit Care Dept. Pediatrics Faculty of Medicine Chulalongkorn University Kanokporn Udomittipong, MD.
Learning Objectives. 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence
 Learning Objectives 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence Pre-hospital Non-invasive vventilatory support Marc Gillis, MD Imelda Bonheiden Our goal out there
Learning Objectives 1. Indications versus contra-indications 2. CPAP versus NiVS 3. Clinical evidence Pre-hospital Non-invasive vventilatory support Marc Gillis, MD Imelda Bonheiden Our goal out there
Practical Application of CPAP
 CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
Lung Wit and Wisdom. Understanding Oxygenation and Ventilation in the Neonate. Jennifer Habert, BHS-RT, RRT-NPS, C-NPT Willow Creek Women s Hospital
 Lung Wit and Wisdom Understanding Oxygenation and Ventilation in the Neonate Jennifer Habert, BHS-RT, RRT-NPS, C-NPT Willow Creek Women s Hospital Objectives To review acid base balance and ABG interpretation
Lung Wit and Wisdom Understanding Oxygenation and Ventilation in the Neonate Jennifer Habert, BHS-RT, RRT-NPS, C-NPT Willow Creek Women s Hospital Objectives To review acid base balance and ABG interpretation
Title Neonatal and Paediatric High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy Guideline. Department Paediatrics / Neonates Date Issued
 Document Control Title Author Neonatal and Paediatric High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy Guideline Author s job title Directorate Medical Version Department Paediatrics / Neonates Date Issued Status
Document Control Title Author Neonatal and Paediatric High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy Guideline Author s job title Directorate Medical Version Department Paediatrics / Neonates Date Issued Status
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy
 An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
An Overview of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Chronic Lung Disease in Infancy Housekeeping: I have no financial disclosures Learning objectives: Develop an understanding of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD)
Ge Zheng, 1,2 Xiao-qiu Huang, 2 Hui-hui Zhao, 2 Guo-Xing Jin, 2 and Bin Wang Introduction. 2. Methods
 Hindawi Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2017, Article ID 3782401, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3782401 Clinical Study The Effect of the Treatment with Heated Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula
Hindawi Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2017, Article ID 3782401, 6 pages https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3782401 Clinical Study The Effect of the Treatment with Heated Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula
Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Received: 22 May 2013; Received in revised form: 12 Sep. 2013; Accepted: 17 Sep.
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of INSURE Method with Conventional Mechanical Ventilation after Surfactant Administration in Preterm Infants with Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Therapeutic Challenge Fatemeh
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparison of INSURE Method with Conventional Mechanical Ventilation after Surfactant Administration in Preterm Infants with Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Therapeutic Challenge Fatemeh
Noah Hillman M.D. IPOKRaTES Conference Guadalajaira, Mexico August 23, 2018
 Postnatal Steroids Use for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in 2018 + = Noah Hillman M.D. IPOKRaTES Conference Guadalajaira, Mexico August 23, 2018 AAP Policy Statement - 2002 This statement is intended for
Postnatal Steroids Use for Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in 2018 + = Noah Hillman M.D. IPOKRaTES Conference Guadalajaira, Mexico August 23, 2018 AAP Policy Statement - 2002 This statement is intended for
Disclosure. Learning Objectives. Bernadette Zelaya, RRT. Area Clinical Manager
 High Velocity Nasal Insufflation An Important Therapeutic Approach for Use in the Emergency Department Presented by Vapotherm Accredited for 1 CEU by the American Association for Respiratory Care Provider
High Velocity Nasal Insufflation An Important Therapeutic Approach for Use in the Emergency Department Presented by Vapotherm Accredited for 1 CEU by the American Association for Respiratory Care Provider
Quality Improvement Approaches to BPD. Jay P. Goldsmith, M.D. Tulane University New Orleans, Louisiana
 Quality Improvement Approaches to BPD Jay P. Goldsmith, M.D. Tulane University New Orleans, Louisiana goldsmith.jay@gmail.com No conflicts of interest to declare There is nothing more dangerous to the
Quality Improvement Approaches to BPD Jay P. Goldsmith, M.D. Tulane University New Orleans, Louisiana goldsmith.jay@gmail.com No conflicts of interest to declare There is nothing more dangerous to the
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2014; 56:
 The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2014; 56: 232-237 Original INSURE method (INtubation-SURfactant-Extubation) in early and late premature neonates with respiratory distress: factors affecting the outcome
The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics 2014; 56: 232-237 Original INSURE method (INtubation-SURfactant-Extubation) in early and late premature neonates with respiratory distress: factors affecting the outcome
Bubble CPAP for Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Preterm Infants
 R E S E A R C H P A P E R Bubble CPAP for Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Preterm Infants JAGDISH KOTI*, SRINIVAS MURKI, PRAMOD GADDAM, ANUPAMA REDDY AND M DASARADHA RAMI REDDY From Fernandez Hospital
R E S E A R C H P A P E R Bubble CPAP for Respiratory Distress Syndrome in Preterm Infants JAGDISH KOTI*, SRINIVAS MURKI, PRAMOD GADDAM, ANUPAMA REDDY AND M DASARADHA RAMI REDDY From Fernandez Hospital
** SURFACTANT THERAPY**
 ** SURFACTANT THERAPY** Full Title of Guideline: Surfactant Therapy Author (include email and role): Stephen Wardle (V4) Reviewed by Dushyant Batra Consultant Neonatologist Division & Speciality: Division:
** SURFACTANT THERAPY** Full Title of Guideline: Surfactant Therapy Author (include email and role): Stephen Wardle (V4) Reviewed by Dushyant Batra Consultant Neonatologist Division & Speciality: Division:
Advantages and disadvantages of different nasal CPAP systems in newborns
 Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:926 930 DOI 10.1007/s00134-004-2267-8 N E O N A T A L A N D P A E D I A T R I C I N T E N S I V E C A R E V. Buettiker M. I. Hug O. Baenziger C. Meyer B. Frey Advantages and
Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:926 930 DOI 10.1007/s00134-004-2267-8 N E O N A T A L A N D P A E D I A T R I C I N T E N S I V E C A R E V. Buettiker M. I. Hug O. Baenziger C. Meyer B. Frey Advantages and
NEONATAL NEWS Here s Some More Good Poop
 NEONATALNEWS Here ssomemoregoodpoop WINTEREDITION2010 THISNEWSLETTERISPUBLISHEDPERIODICALLYBYTHENEONATOLOGISTSOF ASSOCIATESINNEWBORNMEDICINETOCONVEYNEWANDUPDATEDPOLICIES ANDGUIDELINESANDPROVIDEGENERALEDUCATIONTONICUCARETAKERSAT
NEONATALNEWS Here ssomemoregoodpoop WINTEREDITION2010 THISNEWSLETTERISPUBLISHEDPERIODICALLYBYTHENEONATOLOGISTSOF ASSOCIATESINNEWBORNMEDICINETOCONVEYNEWANDUPDATEDPOLICIES ANDGUIDELINESANDPROVIDEGENERALEDUCATIONTONICUCARETAKERSAT
Work of breathing using high-flow nasal cannula in preterm infants
 (), 7 8 r Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 73-83/ $3 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Work of breathing using high-flow nasal cannula in preterm infants JG Saslow 1,, ZH Aghai 1,, TA Nakhla
(), 7 8 r Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 73-83/ $3 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Work of breathing using high-flow nasal cannula in preterm infants JG Saslow 1,, ZH Aghai 1,, TA Nakhla
USE OF INHALED NITRIC OXIDE IN THE NICU East Bay Newborn Specialists Guideline Prepared by P Joe, G Dudell, A D Harlingue Revised 7/9/2014
 USE OF INHALED NITRIC OXIDE IN THE NICU East Bay Newborn Specialists Guideline Prepared by P Joe, G Dudell, A D Harlingue Revised 7/9/2014 ino for Late Preterm and Term Infants with Severe PPHN Background:
USE OF INHALED NITRIC OXIDE IN THE NICU East Bay Newborn Specialists Guideline Prepared by P Joe, G Dudell, A D Harlingue Revised 7/9/2014 ino for Late Preterm and Term Infants with Severe PPHN Background:
Nasal respiratory Support: The best Option for Resource Restricted (and Rich) Countries?
 Nasal respiratory Support: The best Option for Resource Restricted (and Rich) Countries? Rangasamy Ramanathan, MD. Professor of Pediatrics Division Chief, Division of Neonatology Program Director, NPM
Nasal respiratory Support: The best Option for Resource Restricted (and Rich) Countries? Rangasamy Ramanathan, MD. Professor of Pediatrics Division Chief, Division of Neonatology Program Director, NPM
Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor
 Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Patent Ductus Arteriosus: Philosophy or Pathology?
 Patent Ductus Arteriosus: Philosophy or Pathology? Disclosure Ray Sato, MD is a speaker for Prolacta Biosciences, Inc. This presentation will discuss off-label uses of acetaminophen and ibuprofen. RAY
Patent Ductus Arteriosus: Philosophy or Pathology? Disclosure Ray Sato, MD is a speaker for Prolacta Biosciences, Inc. This presentation will discuss off-label uses of acetaminophen and ibuprofen. RAY
Nasal CPAP in Neonatology: We Can Do Better
 Nasal CPAP in Neonatology: We Can Do Better COI Disclosure I do not have any conflict of interest, nor will I be discussing any off-label product use. This class has no commercial support or sponsorship,
Nasal CPAP in Neonatology: We Can Do Better COI Disclosure I do not have any conflict of interest, nor will I be discussing any off-label product use. This class has no commercial support or sponsorship,
BPD. Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care. Disease. Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Baby Jane
 1 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Disease 2 Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia 3 is a 33-day-old prematurely born girl who weighs 1420 g. At birth, her estimated gestational age was 28 weeks. Her initial
1 Neonatal/Pediatric Cardiopulmonary Care Disease 2 Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia 3 is a 33-day-old prematurely born girl who weighs 1420 g. At birth, her estimated gestational age was 28 weeks. Her initial
With wider acceptance of the early use of
 Weaning of nasal CPAP in preterm infants: who, when and how? a systematic review of literature Shaili Amatya, Deepa Rastogi, Alok Bhutada, Shantanu Rastogi New York, USA Background: There is increased
Weaning of nasal CPAP in preterm infants: who, when and how? a systematic review of literature Shaili Amatya, Deepa Rastogi, Alok Bhutada, Shantanu Rastogi New York, USA Background: There is increased
CPAP failure in preterm infants: incidence, predictors and consequences
 CPAP failure in preterm infants: incidence, predictors and consequences SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT METHODS Study setting The Royal Hobart Hospital has an 11-bed combined Neonatal and Paediatric Intensive Care Unit
CPAP failure in preterm infants: incidence, predictors and consequences SUPPLEMENTAL TEXT METHODS Study setting The Royal Hobart Hospital has an 11-bed combined Neonatal and Paediatric Intensive Care Unit
Received: Jun 15, 2013; Accepted: Nov 08, 2013; First Online Available: Jan 24, 2014
 Original Article Iran J Pediatr Feb 2014; Vol 24 (No 1), Pp: 57-63 Management of Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome Employing ACoRN Respiratory Sequence Protocol versus Early Nasal Continuous Positive
Original Article Iran J Pediatr Feb 2014; Vol 24 (No 1), Pp: 57-63 Management of Neonatal Respiratory Distress Syndrome Employing ACoRN Respiratory Sequence Protocol versus Early Nasal Continuous Positive
Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification
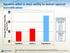 Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
O) or to bi-level NCPAP (group B; n=20, lower CPAP level=4.5 cm H 2
 1 NICU, Children s Hospital, Via Castelvetro, Milan, Italy 2 Laboratory, V.Buzzi Children s Hospital ICP, Milan, Italy 3 Department of Statistics, Catholic University, Milan, Italy Correspondence to Gianluca
1 NICU, Children s Hospital, Via Castelvetro, Milan, Italy 2 Laboratory, V.Buzzi Children s Hospital ICP, Milan, Italy 3 Department of Statistics, Catholic University, Milan, Italy Correspondence to Gianluca
Early nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation(nippv) versus early nasal continuous positive airway pressure(ncpap) for preterm
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Early nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation(nippv) versus early nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) for preterm infants(review) LemyreB,LaughonM,BoseC,DavisPG
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Early nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation(nippv) versus early nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) for preterm infants(review) LemyreB,LaughonM,BoseC,DavisPG
Prophylactic nasal continuous positive airway pressure for preventing morbidity and mortality in very preterm infants(review)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Prophylactic nasal continuous positive airway pressure for preventing morbidity and mortality in very preterm infants (Review) SubramaniamP,HoJJ,DavisPG Subramaniam
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Prophylactic nasal continuous positive airway pressure for preventing morbidity and mortality in very preterm infants (Review) SubramaniamP,HoJJ,DavisPG Subramaniam
Nottingham Children s Hospital
 High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Guide line for the use of HFNCT (High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy) Contact Name
High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy Title of Guideline (must include the word Guideline (not protocol, policy, procedure etc) Guide line for the use of HFNCT (High Flow Nasal Cannula Therapy) Contact Name
Randomized study of nasal continuous positive airway pressure in the preterm infant with respiratory distress syndrome
 Acta Pñdiatr 92: 1±6. 2003 Randomized study of nasal continuous positive airway pressure in the preterm infant with respiratory distress syndrome J Tooley and M Dyke Department of Paediatrics, Norfolk
Acta Pñdiatr 92: 1±6. 2003 Randomized study of nasal continuous positive airway pressure in the preterm infant with respiratory distress syndrome J Tooley and M Dyke Department of Paediatrics, Norfolk
Simulation 08: Cyanotic Preterm Infant in Respiratory Distress
 Flow Chart Simulation 08: Cyanotic Preterm Infant in Respiratory Distress Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: DM As staff therapist assigned to a Level 2 NICU in a 250 bed rural medical center you are called
Flow Chart Simulation 08: Cyanotic Preterm Infant in Respiratory Distress Opening Scenario Section 1 Type: DM As staff therapist assigned to a Level 2 NICU in a 250 bed rural medical center you are called
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither?
 Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
Keeping Patients Off the Vent: Bilevel, HFNC, Neither? Robert Kempainen, MD Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Hennepin County Medical Center University of Minnesota School of Medicine Objectives Summarize
infants. This review provides some perspectives on this increasingly complex debate surrounding CPAP and its further development.
 CHAPTER 2 1 2 3 Dr. Neeraj Gupta, Dr. S. Giridhar & Dr. Praveen Kumar 1 2 3 AIIMS, Jodhpur, CHRI, Kelambakkam, Chennai & PGIMER, Chandigarh Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) is the most common
CHAPTER 2 1 2 3 Dr. Neeraj Gupta, Dr. S. Giridhar & Dr. Praveen Kumar 1 2 3 AIIMS, Jodhpur, CHRI, Kelambakkam, Chennai & PGIMER, Chandigarh Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP) is the most common
Potential Conflicts of Interest
 Potential Conflicts of Interest Patient Ventilator Synchrony, PAV and NAVA! Bob Kacmarek PhD, RRT Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 4-27-09 WSRC Received research
Potential Conflicts of Interest Patient Ventilator Synchrony, PAV and NAVA! Bob Kacmarek PhD, RRT Massachusetts General Hospital, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts 4-27-09 WSRC Received research
Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC)
 Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC) 1. Introduction and Who Guideline applies to Heated humidified high flow nasal cannula treatment (HHHFNC), otherwise called as High flow oxygen
Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC) 1. Introduction and Who Guideline applies to Heated humidified high flow nasal cannula treatment (HHHFNC), otherwise called as High flow oxygen
Mirhadi Mussavi, 1 Keyvan Mirnia, 1 and Khairollah Asadollahi 2,* Iran J Pediatr October; 26(5):e5743. doi: /ijp.5743.
 Iran J Pediatr. 2016 October; 26(5):e5743. Published online 2016 July 25. doi: 10.5812/ijp.5743. Research Article Comparison of the Efficacy of Three Natural Surfactants (Curosurf, Survanta, and Alveofact)
Iran J Pediatr. 2016 October; 26(5):e5743. Published online 2016 July 25. doi: 10.5812/ijp.5743. Research Article Comparison of the Efficacy of Three Natural Surfactants (Curosurf, Survanta, and Alveofact)
Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet
 Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1. Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure 2. Purpose of Procedure/ Guidelines/ Protocol Guideline for
Children & Young People s Directorate Paediatric-Neonatal Guidelines Checklist & Version Control Sheet 1. Name of Guideline / Policy/ Procedure 2. Purpose of Procedure/ Guidelines/ Protocol Guideline for
Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat
 Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 18\7\2010 Transient Tachpnea of the Definition:- newborn (TTN) TTN is a benign disease of near term or term infant who display respiratory distress shortly after delivery.
Presented By : Kamlah Olaimat 18\7\2010 Transient Tachpnea of the Definition:- newborn (TTN) TTN is a benign disease of near term or term infant who display respiratory distress shortly after delivery.
ROLE OF PRESSURE IN HIGH FLOW THERAPY
 ROLE OF PRESSURE IN HIGH FLOW THERAPY Thomas L. Miller, PhD, MEd Director, Clinical Research and Education Vapotherm, Inc. Research Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Jefferson Medical College This information
ROLE OF PRESSURE IN HIGH FLOW THERAPY Thomas L. Miller, PhD, MEd Director, Clinical Research and Education Vapotherm, Inc. Research Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Jefferson Medical College This information
PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE. Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre
 PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre Outline of lecture Bronchiolitis Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Asthma ARDS Bronchiolitis
PAEDIATRIC RESPIRATORY FAILURE Tang Swee Fong Department of Paediatrics University Kebangsaan Malaysia Medical Centre Outline of lecture Bronchiolitis Bronchopulmonary dysplasia Asthma ARDS Bronchiolitis
The use of noninvasive ventilatory
 Gas exchange and lung inflammation using nasal intermittent positive-pressure ventilation versus synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation in piglets with saline lavage-induced lung injury: An observational
Gas exchange and lung inflammation using nasal intermittent positive-pressure ventilation versus synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation in piglets with saline lavage-induced lung injury: An observational
GE Healthcare. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator. Relief, Relax, Recovery
 GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices
 Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Sustainable use of continuous positive airway pressure in extremely preterm infants during the first week after delivery
 F398 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sustainable use of continuous positive airway pressure in extremely preterm infants during the first week after delivery C Booth, M H Premkumar, A Yannoulis, M Thomson, M Harrison,
F398 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sustainable use of continuous positive airway pressure in extremely preterm infants during the first week after delivery C Booth, M H Premkumar, A Yannoulis, M Thomson, M Harrison,
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation. Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim
 Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim Content Definition Classification Weaning criteria Weaning methods Criteria for extubation Introduction Weaning comprises 40% of the duration
Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Dr Azmin Huda Abdul Rahim Content Definition Classification Weaning criteria Weaning methods Criteria for extubation Introduction Weaning comprises 40% of the duration
B13. Baby s Breath: Ventilation Strategies and Blood Gas Interpretation. Session Summary. Session Objectives. Test Questions.
 B13 Baby s Breath: Ventilation Strategies and Blood Gas Interpretation Karen Wright, PhD, NNP-BC DNP NNP Program Director Rush University, Chicago, IL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated
B13 Baby s Breath: Ventilation Strategies and Blood Gas Interpretation Karen Wright, PhD, NNP-BC DNP NNP Program Director Rush University, Chicago, IL The speaker has signed a disclosure form and indicated
Concerns and Controversial Issues in NPPV. Concerns and Controversial Issues in Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation
 : Common Therapy in Daily Practice Concerns and Controversial Issues in Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Rongchang Chen Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Disease as the first choice of mechanical
: Common Therapy in Daily Practice Concerns and Controversial Issues in Noninvasive Positive Pressure Ventilation Rongchang Chen Guangzhou Institute of Respiratory Disease as the first choice of mechanical
Aim: Reduction in the rate of CLD in ELBW infants (<1000 grams) by 30% from its baseline of 72 % by January 2016.
 LIVE (Less Invasive Ventilation of ELBW infants) HEALTHY WVU Children s Hospital, Morgantown, WV, USA Rebecca Tilley, RN; Jamie Karr, RT; Tiffany Blosser, RN; Christy Dixon, RT; Melinda Connolly, ANP;
LIVE (Less Invasive Ventilation of ELBW infants) HEALTHY WVU Children s Hospital, Morgantown, WV, USA Rebecca Tilley, RN; Jamie Karr, RT; Tiffany Blosser, RN; Christy Dixon, RT; Melinda Connolly, ANP;
Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo
 Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
OmniOx (HFT 500) Jan Prepared by MEKICS. OmniOx-HFT500 Jan ver1.1 1
 OmniOx (HFT 500) Jan. 2013. Prepared by MEKICS OmniOx-HFT500 Jan. 2013 ver1.1 1 0. Index 1. Introduce of OmniOx (HTF500) 2. Specification (HFT, CPAP+) 3. The World Best Features 2 OmniOx-HFT500 Jan. 2013
OmniOx (HFT 500) Jan. 2013. Prepared by MEKICS OmniOx-HFT500 Jan. 2013 ver1.1 1 0. Index 1. Introduce of OmniOx (HTF500) 2. Specification (HFT, CPAP+) 3. The World Best Features 2 OmniOx-HFT500 Jan. 2013
This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication in Journal of Neonatal Nursing following peer review.
 This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication in Journal of Neonatal Nursing following peer review. The version of record [Journal of Neonatal Nursing (February 2013)
This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication in Journal of Neonatal Nursing following peer review. The version of record [Journal of Neonatal Nursing (February 2013)
Randomised controlled trial of weaning strategies for preterm infants on nasal continuous positive airway pressure
 Tang et al. BMC Pediatrics (2015) 15:147 DOI 10.1186/s12887-015-0462-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Randomised controlled trial of weaning strategies for preterm infants on nasal continuous positive airway
Tang et al. BMC Pediatrics (2015) 15:147 DOI 10.1186/s12887-015-0462-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Randomised controlled trial of weaning strategies for preterm infants on nasal continuous positive airway
INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2
 2 Effects of CPAP INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2 ). The effect on CO 2 is only secondary to the primary process of improvement in lung volume and
2 Effects of CPAP INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2 ). The effect on CO 2 is only secondary to the primary process of improvement in lung volume and
You are caring for a patient who is intubated and. pressure control ventilation. The ventilator. up to see these scalars
 Test yourself Test yourself #1 You are caring for a patient who is intubated and ventilated on pressure control ventilation. The ventilator alarms and you look up to see these scalars What is the most
Test yourself Test yourself #1 You are caring for a patient who is intubated and ventilated on pressure control ventilation. The ventilator alarms and you look up to see these scalars What is the most
Innovations in Neonatal Ventilation
 Innovations in Neonatal Ventilation NAVA Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist Howard Stein, M.D. Director Neonatology, Promedica Toledo Children s Hospital Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University
Innovations in Neonatal Ventilation NAVA Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist Howard Stein, M.D. Director Neonatology, Promedica Toledo Children s Hospital Clinical Professor of Pediatrics, University
Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation in the newborn: review of literature and evidence-based guidelines
 STATE-OF-THE-ART Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation in the newborn: review of literature and evidence-based guidelines (2010) 30, 505 512 r 2010 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved.
STATE-OF-THE-ART Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation in the newborn: review of literature and evidence-based guidelines (2010) 30, 505 512 r 2010 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved.
Neonatal Resuscitation in What is new? How did we get here? Steven Ringer MD PhD Harvard Medical School May 25, 2011
 Neonatal Resuscitation in 2011- What is new? How did we get here? Steven Ringer MD PhD Harvard Medical School May 25, 2011 Conflicts I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this
Neonatal Resuscitation in 2011- What is new? How did we get here? Steven Ringer MD PhD Harvard Medical School May 25, 2011 Conflicts I have no actual or potential conflict of interest in relation to this
Respiratory Management and Outcome of Preterm Infants
 Respiratory Management and Outcome of Preterm Infants 6 th Annual Care Of The Sick Newborn Conference Shu Wu, MD. Department of Pediatrics Division of Neonatology University of Miami School of Medicine
Respiratory Management and Outcome of Preterm Infants 6 th Annual Care Of The Sick Newborn Conference Shu Wu, MD. Department of Pediatrics Division of Neonatology University of Miami School of Medicine
LRI Children s Hospital
 LRI Children s Hospital Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHFNC) Oxygen Therapy Staff relevant to: Medical and Nursing staff Team approval date: 5.01.18 Version: 1 Revision due: January 2020 Written
LRI Children s Hospital Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHFNC) Oxygen Therapy Staff relevant to: Medical and Nursing staff Team approval date: 5.01.18 Version: 1 Revision due: January 2020 Written
Disclosures. Learning Objectives. Mechanical Ventilation of Infants with Severe BPD: An Interdisciplinary Approach 3/10/2017
 Mechanical Ventilation of Infants with Severe BPD: An Interdisciplinary Approach Steven H. Abman, MD Professor, Department of Pediatrics Director, Pediatric Heart Lung Center University of Colorado School
Mechanical Ventilation of Infants with Severe BPD: An Interdisciplinary Approach Steven H. Abman, MD Professor, Department of Pediatrics Director, Pediatric Heart Lung Center University of Colorado School
COMPARISON OF THE EFFICIENCY OF CAFFEINE VERSUS AMINOPHYLLINE FOR THE TREATMENT OF APNOEA OF PREMATURITY
 CASE STUDIES COMPARISON OF THE EFFICIENCY OF CAFFEINE VERSUS AMINOPHYLLINE FOR THE TREATMENT OF APNOEA OF PREMATURITY Gabriela Ildiko Zonda 1, Andreea Avasiloaiei 1, Mihaela Moscalu 2, Maria Stamatin 1
CASE STUDIES COMPARISON OF THE EFFICIENCY OF CAFFEINE VERSUS AMINOPHYLLINE FOR THE TREATMENT OF APNOEA OF PREMATURITY Gabriela Ildiko Zonda 1, Andreea Avasiloaiei 1, Mihaela Moscalu 2, Maria Stamatin 1
CURRENT TRENDS IN NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION. Disclosures. Why not invasive ventilation? Objectives. Currently available modes
 CURRENT TRENDS IN NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION ----------------------------------------------------------- Karen Drinkard, RRT-NPS Neonatal Respiratory Clinical Specialist University of Washington Medical
CURRENT TRENDS IN NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION ----------------------------------------------------------- Karen Drinkard, RRT-NPS Neonatal Respiratory Clinical Specialist University of Washington Medical
Acute Paediatric Respiratory Pathway
 Guideline for the use of high Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy (Optiflow or Airvo) in Children with Bronchiolitis or an acute respiratory illness Introduction: High flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen enables
Guideline for the use of high Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy (Optiflow or Airvo) in Children with Bronchiolitis or an acute respiratory illness Introduction: High flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen enables
1. Which of the following arterial blood gas results indicate metabolic acidosis?
 B10 Baby s Breath: Ventilation Strategies and Blood Gas Interpretation Mary Beth Bodin, DNP, CRNP, NNP-BC Assistant Professor School of Nursing, University of Alabama at Birmingham Neonatal Nurse Practitioner
B10 Baby s Breath: Ventilation Strategies and Blood Gas Interpretation Mary Beth Bodin, DNP, CRNP, NNP-BC Assistant Professor School of Nursing, University of Alabama at Birmingham Neonatal Nurse Practitioner
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems
 Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
Review of Neonatal Respiratory Problems Respiratory Distress Occurs in about 7% of infants Clinical presentation includes: Apnea Cyanosis Grunting Inspiratory stridor Nasal flaring Poor feeding Tachypnea
