This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication in Journal of Neonatal Nursing following peer review.
|
|
|
- Diana Briggs
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 This is a pre-copyedited, author-produced PDF of an article accepted for publication in Journal of Neonatal Nursing following peer review. The version of record [Journal of Neonatal Nursing (February 2013) Vol 19 (1): First published online December 6, 2012] is available online at: doi: /j.jnn
2 FACT SHEET Understanding Neonatal Non invasive ventilation: Part 1 Julia Petty Introduction Many of the babies admitted to the neonatal unit require some degree of respiratory support at varying levels for a given time period as dictated by individualised assessment of their overall condition. This Fact Sheet, following on from Oxygen therapy by Fallon (2012), offers an overview of current non-invasive ventilation practice in neonatal care focusing on the terms and modes used. The aim is for the reader to understand the range of strategies used to support the neonate s respiratory system in line with the relevant evidence for delivery of best practice for the neonate and family. Respiratory management in the context of neonatal care Neonates require ventilator support to augment their own respiratory system when this is unable to provide adequate support and gaseous exchange during respiratory compromise or failure. The aim of any neonatal respiratory support strategy is to achieve adequate gaseous exchange without lung injury: in other words, the goal must be a healthy neonate and child with no resultant chronic lung disease (Bellettato et al, 2011), one of the potential and significant long-term effects of prolonged mechanical ventilation in the neonatal period. Ventilation support can be viewed within the framework of dependency levels as described by BAPM (2010) and the DoH (2009): 1- Special care: A neonate in special care may not require any respiratory support and may simply be observed if there is a suspected or actual concern at birth or they may receive a low percentage and / or flow of oxygen due to mild or recovering respiratory compromise or disease. 1
3 2- High Dependency: A neonate in high dependency requires a greater level of support and may receive modes such as continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), Biphasic pressure and / or high flow oxygen therapy, again as dictated by their condition. 3- Intensive care; A neonate in intensive care in many cases will require full ventilation for a given time period either by conventional or non-conventional means. A neonate can be admitted to any of these three levels or they may experience all of them during their neonatal unit stay. As an example, the sickest neonate is generally admitted to intensive care for full ventilator support. The subsequent journey through the neonatal unit then involves them progressing to high dependency when their condition allows and when they are able to be extubated to CPAP or Biphasic pressure. Thereafter the aim is for them to progress to special care where they may still require oxygen therapy. As their need for support for their respiratory and other systems lessens and their condition improves, they will then be able to wean off oxygen to be discharged home at an appropriate time. Overview of non-invasive respiratory support strategies in the neonatal unit Explanations of the strategies will now be given according to the above dependency levels from 1 through to 3. OXYGEN THERAPY: Supplementary oxygen in self ventilating neonates can be delivered by various means depending on the oxygen requirement. If requirements are relatively low, then ambient oxygen can be given into an incubator or via a head box with the use of an oxygen analyzer to measure the percentage administered. For longer term delivery, low flow (less than 1 litre / minute) nasal cannula oxygen is given and weaned down slowly until the neonate is able to ventilate in room air. In addition, high flow (1-8 litres/ minute) nasal cannula oxygen therapy has recently been introduced in the form of the Vapotherm device (Image 1). This is a thermally controlled humidification system (at 95% or greater relative humidity) that flushes nasopharyngeal dead space. It is documented that this therapy can be suitable as an 2
4 alternative to continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), for neonates with nasal injury or for those who are very unsettled from prolonged CPAP (Lawn, 2007). Research in this therapy within the adult field is overall positive and as Lawn reports, the benefits from one unit s experience in neonates is clear. Although work is emerging on this therapy in neonates, further research is required to substantiate benefits (Hochwald and Osiovich; 2010; Wilkinson et al, 2008; Wilkinson et al, 2011). High flow oxygen via this method is one of the non-invasive strategies available, a vitally important concept in neonatal ventilation practice given the potential damaging effects of full respiratory support by endotracheal intubation and long term ventilation. This will be addressed in more detail in a later Fact sheet. Most commonly used in clinical practice in relation to non-invasive intervention is continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP). Image 1: High Flow oxygen Vapotherm device Source: CPAP: A constant positive pressure is applied to the airway of a spontaneously breathing neonate to maintain adequate functional residual capacity within the alveoli and prevent atelectasis. In current practice, binasal CPAP has superseded the single nasal prong and is administered non-invasively by a Flow driver via two short prongs (see images 2 and 3) or nasal mask. DePaoli et al (2008) report on this method being preferable to single prong use when delivered by a flow driver. The device used to deliver the gases to the neonate s nose is designed to support the baby s breathing throughout the respiratory cycle in that there is a 3
5 special flip mechanism. This is best explained in the following Table taken and adapted from the product information provided by Carefusion (2012) as follows: Table 1: Explanation of the flip mechanism in the Flow driver Inspiratory flow; The flow provided by the Infant Flow SiPAP system is accelerated in the twin injector nozzles of the Infant Flow generator. When the baby makes a spontaneous inspiratory effort, the Flow generator converts the kinetic energy of the flow to pressure, thereby reducing the work of breathing and maximizing pressure stability at the baby interface. Expiratory flow; When the baby exhales, the forward velocity of the airflow decreases. This allows the gas flow to flip from the nasal prongs to the expiratory tube and this continuous gas flow provides residual gas pressure enabling stable CPAP pressure delivery throughout the respiratory cycle. When expiratory effort stops, the flow instantly flips back to the inspiratory position. Davis and Henderson Smart (2003) also report how binasal CPAP prevents failure of extubation. Given the relationship between flow and pressure, generally, a flow of 8-10 litres / minute should give a pressure of 4-6 cm / water (see image 2) provided that there is an adequate seal at the nostrils. Altering the flow will affect the pressure given. For some neonates, it is necessary to increase the flow to give a higher pressure of 6-7 cm / water (subject to individual assessment by ward medical / nursing team). Once the baby s lungs improve, the flow and subsequent pressure can then be reduced according to the baby s condition and or the neonate can cycle on and off for agreed periods of time until able to tolerate ventilating without pressure. Jardine et al (2011) found that weaning from CPAP takes less time by reducing the pressure down gradually to an agreed value and then stopping rather than the cycling method. However, in practice decisions are guided by the individual neonate s condition. 4
6 Image 2: Neonate on binasal Flow driver CPAP Source: Image 3: Flow driver CPAP Source; J Petty 5
7 Bi-phasic positive airway pressure (BIPAP) is where two pressure levels are set, a background continuous measurement and a higher one which is delivered at intervals either triggered by the neonate or set as a mandatory rate. Infant flow SIPAP provides bi-level nasal CPAP for the spontaneously breathing neonate through the delivery of pulses or sighs (brief periods of increased pressure) above a baseline CPAP pressure (See image 4). These may be timed, or triggered by neonates own inspiratory efforts. (Bhandari, 2010). Literature often refers to the setting of these positive pressure sighs as nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV; Sweet, 2008; Owen et al, 2008), not to be confused with intermittent positive pressure ventilation or IPPV via full intubation as will be covered shortly. A study by Khalaf et al (2001) found that NIPPV is more effective that NCPAP in weaning neonates with respiratory distress syndrome. A meta-analysis of three studies comparing NIPPV and CPAP after neonates were extubated found a reduction in re-intubation rates in the former group (Davies et al, 2001)and more recently Lista et al (2010) report, following a randomized controlled trial comparing single and bi-level CPAP, found the latter group was associated with improved respiratory outcomes allowing earlier discharge. However, Meneses et al (2011) found that early NIPPV did not decrease the need for mechanical ventilation compared with NCPAP, overall, in the first 72 hours of life. Owen et al (2011) also found no differences between the two in relation to the variations in pressure concluding that it is probably the increase in overall pressure that is beneficial. 6
8 Image 4: Bi-phasic screen showing 2 levels of support Source: Glossary of modes CPAP CPAP is a mode itself on all ventilators as well as support strategy in it s own right known as ncpap (nasal CPAP). On the Flow driver, it can be given with or without apnoea. If CPAP with apnoea is required, then an abdominal transducer is necessary in order to monitor any apnoeic episode and raise the alarm according to the apnoea time interval which is set by the user. On the older Flow driver module that just delivers one level of CPAP, generally a flow is set to 8 litres / minute to aim for a pressure of 5-6 cm / H20 (again subject to assessment of the individual baby). The humidifier should be set to deliver gases at 37 degrees Celcius to the baby s airway. BIPAP- BIPAP has the following mode options namely: Biphasic timed; The machine delivers a set baseline pressure using the high pressure flow metre (set to 8 L/minute on average). The extra pressure supported sighs are 7
9 delivered according to a set rate and Ti. The user will set the additional pressure with the low pressure flow metre and will set the number per minute and length of each extra sigh. Trigger Biphasic; As above but the extra pressure sighs are not timed. These are now triggered by the neonate initiating a breath. BiPhasic + apnoea - as for biphasic times but there is additional apnoea monitoring and an alarm will sound if the neonate does not breathe within the apnoea interval, as for CPAP and apnoea above. Flow there are 2 flow meters (See Image 4) on the SIPAP model. The left one pictured is known as low pressure where the CPAP pressure is set. The right hand one is high pressure which is set 2 litres / minute above the low pressure dial. This is what delivers the second or additional pressure when bi-phasic mode is required. It is important not to set the high pressure flow too high. When delivering ventilator support to neonates, it is important to be aware of the potential negative effects of ventilation (Claure and Bancalari, 2007); for example: lung injury from barotrauma (pressure) and / or volume leading to chronic lung disease, oxygen toxicity, hypotension, and lung hyperinflation and nosocomial respiratory infection. Bedside assessment and monitoring is the key to ensuring any negative effect is identified as soon as possible e.g. CXR findings, blood pressure. Bedside care must keep the negative effects in mind such as avoiding high oxygen concentrations, supporting the BP and continuous 02 monitoring. Current respiratory support strategies must also have these dangers as a central consideration. Overall protective lung strategies that include the use of non-invasive ventilation modes should be employed as appropriate from the point of birth and beyond. Surfactant and non-invasive modes such as CPAP (Davies et al, 2009)and biphasic ventilation has significantly influenced the 8
10 current ethos behind the support of preterm neonates with respiratory failure (DiBlasi, 2011), Recent European Guidelines for the management of preterm neonates born with RDS recommend very early Surfactant followed by extubation to CPAP as a way of potentially reducing lung damage (Sweet et al, 2007) and this is an area of current interest (SUPPORT Study Group, 2010). The use of early delivery room CPAP is also well documented (Finer et al, 2004; tepas et AL, 2007). The Newborn life Support Guidelines (UK Resuscitation Council, 2010) support the use of positive end pressure in the stabilisation of preterm babies at delivery as required. As, Mulder et al (2012) put forward for discussion, the advent and increasing use of non-invasive ventilation strategies should lead to a significantly reduced incidence of chronic lung disease from prematurity. Conclusion Technological advances have resulted in improvements in ventilation strategies that offer a wider range of non-invasive modalities. Knowledge of the terms used in neonatal clinical respiratory practice is valuable since this practice comprises a significant proportion of care given to sick neonates within the neonatal unit. It is not possible to cover within the scope of this paper, the nursing care given to the neonate receiving the above mentioned strategies; this will be the subject of a future edition. Those caring for such sick and vulnerable neonates owe it to them and their families to have a full understanding of common but often complex practice while at the same time work towards minimising any resultant damage and respiratory morbidity. This is not only so that care is supported by best evidence based rationale but also so that parents can be given information about the strategies their babies receive and outcomes, a vital component of true holistic family centered neonatal care. Note Subsequent Fact Sheets will follow on from the current topic in future editions; namely, the nursing care for neonates on non-invasive respiratory support and an overview of invasive mechanical ventilation in the neonatal unit. 9
11 References Bellettato B, Carlo W, Rosenkrantz T, Carter BS and Windle. ML. Assisted Ventilation of the Newborn (accessed 24th October 2012) Bhandari, V. Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation in the Newborn: Review of Literature and Evidence-based Guidelines J Perinatol 2010 Nature Publishing Group (accessed 28th September 2012) British Association of Perinatal Medicine (BAPM). Standards for hospitals providing Neonatal Intensive and High dependency care (2 nd edition). 2010, BAPM, London Carefusion (2012) Taking Neonatal Non-invasive ventilation to the next level Carefusion; Yorba Linda, CA Claure N and Bancalari, E. New modes of mechanical ventilation in the preterm newborn: evidence of benefit Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2007; 92: F Davis PG, Lemyre B, De Paoli AG. Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation (NIPPV) versus nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) for preterm neonates after extubation. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 3. Art. No.: CD DOI: / CD Davis PG, Morley CJ, Owen LS. Non-invasive respiratory support of preterm neonates with respiratory distress: continuous positive airway pressure and nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation. Semin Fetal Neonatal Med. 2009; 14: (1), Department of Health (DoH). Toolkit for High Quality Neonatal Services The Department of Health, London DiBlasi RM. Neonatal Noninvasive Ventilation Techniques: Do we really need to intubate? Respiratory Care. 2011; 56: (9), Lawn. C. High Flow humidified oxygen therapy for neonates requiring respiratory support Infant 2001; 3: (3), De Paoli AG, Davis PG, Faber B, Morley CJ. Devices and pressure sources for administration of nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) in preterm neonates. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2008, Issue 1. Art. No.: CD DOI: / CD pub2. Davis PG, Henderson-Smart DJ. Nasal continuous positive airway pressure immediately after extubation for preventing morbidity in preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 2. Art. No.: CD DOI: / CD
12 Fallon A (2012) Fact Sheet Oxygen Therapy Journal of Neonatal Nursing Finer NN, Carlo WA, Duara S, et al. Delivery room continuous positive airway pressure/positive end-expiratory pressure in extremely low birth weight infants: a feasibility trial. Pediatrics. 2004; 114: (3), Greenough A, Donn SM. Matching ventilatory support strategies to respiratory pathophysiology. Clin Perinatol. 2007;34: (1), 35-53, v-vi. Hochwald O and Osiovich H., The use of high flow nasal cannulae in neonatal intensive care units: Is clinical practice consistent with the evidence? Journal of Neonatal-Perinatal Medicine (3), Jardine LA, Inglis GDT, Davies MW. Strategies for the withdrawal of nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) in preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 2. Art. No.: CD DOI: / CD pub2. Khalaf MN, Brodsky N, Hurley J, Bhandari V. A prospective randomized, controlled trial comparing synchronized nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation versus nasal continuous positive airway pressure as modes of extubation. Pediatrics. 2001;108: (1):13-7. Lista G, Castoldi F, Fontana P, et al. Nasal continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) versus bilevel nasal CPAP in preterm babies with respiratory distress syndrome: a randomised control trial. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. Mar 2010; 95:(2):F85-9. Mulder. EEM, Lopriore. E, Rijken. M Walther. FJ and te Pas. AB. Changes in Respiratory Support of Preterm Infants in the Last Decade: Are We Improving? Neonatology 2012; 101: (DOI: / ) Owen LS, Morley CJ, Davis PG. Neonatal nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation: a survey of practice in England. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2008; 93: F148-F150. Resuscitation Council UK (2010) Newborn Life Support SUPPORT Study Group of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver NICHD Neonatal Research Network. Early CPAP versus Surfactant in Extremely Preterm Infants New England Journal of Medicine 2010; 362: Sweet D., Bevilaqua G., Carnielli V. et al. European Consensus Guidelines on the management of neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. J Perinatal Med 2007; 35: Sweet, D. Synchronised Nasal ventilation Where are we now? Infant 2008; 4: (2), 40 te Pas AB, Walther FJ. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Delivery-Room Respiratory Management in Very Preterm Infants. Pediatr. 2007; 120:
13 Wilkinson DJ, Andersen CC, Smith K, Holberton J. Pharyngeal pressure with high-flow nasal cannulae in premature infants. J Perinatol 2008;28 (1), Wilkinson D, Andersen C,O Donnell CPF,De Paoli AG. High flow nasal cannula for respiratory support in preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2011, Issue 5. Art. No.: CD DOI: / CD pub2. 12
Introducing Infant Flow Advance SIPAP. By Joanne Cookson March 2008
 Introducing Infant Flow Advance SIPAP By Joanne Cookson March 2008 Aim To introduce clinical practioners to the new SiPAP machine Objectives To define what is SiPAP To look at different modes able to be
Introducing Infant Flow Advance SIPAP By Joanne Cookson March 2008 Aim To introduce clinical practioners to the new SiPAP machine Objectives To define what is SiPAP To look at different modes able to be
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
 Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
Table 1. NIV: Mechanisms Of Action Decreases work of breathing Increases functional residual capacity Recruits collapsed alveoli Improves respiratory gas exchange Reverses hypoventilation Maintains upper
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION
 CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
CONTINUOUS POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (CPAP) DEFINITION Method of maintaining low pressure distension of lungs during inspiration and expiration when infant breathing spontaneously Benefits Improves oxygenation
Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience
 Original Article Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience Pedro Paz, MD, MPH 1 Rangasamy Ramanathan, MD 1,2 Richard Hernandez, RCP 2 Manoj Biniwale, MD 1 1 Division of Neonatal
Original Article Neonatal Resuscitation Using a Nasal Cannula: A Single-Center Experience Pedro Paz, MD, MPH 1 Rangasamy Ramanathan, MD 1,2 Richard Hernandez, RCP 2 Manoj Biniwale, MD 1 1 Division of Neonatal
Evaluation of a Nasal Cannula in Noninvasive Ventilation Using a Lung Simulator
 Evaluation of a Nasal in Noninvasive Ventilation Using a Lung Simulator Narayan P Iyer MD and Robert Chatburn MHHS RRT-NPS FAARC BACKGROUND: Nasal noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a common form of noninvasive
Evaluation of a Nasal in Noninvasive Ventilation Using a Lung Simulator Narayan P Iyer MD and Robert Chatburn MHHS RRT-NPS FAARC BACKGROUND: Nasal noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a common form of noninvasive
Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants. Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid
 Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid Summary Noninvasive ventilation begings in the delivery room
Non Invasive Ventilation In Preterm Infants Manuel Sanchez Luna Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón Complutense University Madrid Summary Noninvasive ventilation begings in the delivery room
Surfactant Administration
 Approved by: Surfactant Administration Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual
Approved by: Surfactant Administration Gail Cameron Senior Director Operations, Maternal, Neonatal & Child Health Programs Dr. Paul Byrne Medical Director, Neonatology Neonatal Policy & Procedures Manual
A multipurpose ventilator. Flow-SNIPPV - a new challenge in neonatal respiratory care
 Neonatal Ventilator A multipurpose ventilator Giulia Ventilator is a next-generation ventilator designed to give the best respiratory support at every step of the clinical treatment of the respiratory
Neonatal Ventilator A multipurpose ventilator Giulia Ventilator is a next-generation ventilator designed to give the best respiratory support at every step of the clinical treatment of the respiratory
Von Reuss and CPAP, Disclosures CPAP. Noninvasive respiratory therapieswhy bother? Noninvasive respiratory therapies- types
 Noninvasive respiratory therapiesby a nose? NEO- The Conference for Neonatology February 21, 2014 Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflicts of interest to release.
Noninvasive respiratory therapiesby a nose? NEO- The Conference for Neonatology February 21, 2014 Disclosures I have no relevant financial relationships to disclose or conflicts of interest to release.
Minimizing Lung Damage During Respiratory Support
 Minimizing Lung Damage During Respiratory Support University of Miami Jackson Memorial Medical Center Care of the Sick Newborn 15 Eduardo Bancalari MD University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Jackson
Minimizing Lung Damage During Respiratory Support University of Miami Jackson Memorial Medical Center Care of the Sick Newborn 15 Eduardo Bancalari MD University of Miami Miller School of Medicine Jackson
SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY
 PS1006 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR THE Job Title of Reviewer: EFFECTIVE DATE: REVISED DATE: Director, Respiratory Care Services 126.685 (neo) 3/26/15
PS1006 SARASOTA MEMORIAL HOSPITAL DEPARTMENT POLICY TITLE: NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION FOR THE Job Title of Reviewer: EFFECTIVE DATE: REVISED DATE: Director, Respiratory Care Services 126.685 (neo) 3/26/15
GE Healthcare. Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator. Relief, Relax, Recovery
 GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
GE Healthcare Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) For the Engström Ventilator Relief, Relax, Recovery COPD is currently the fourth leading cause of death in the world, and further increases in the prevalence
Clinical Guideline: Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) Guideline
 EOE Neonatal ODN Clinical Guideline: Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) Guideline Authors: Dr Eliana Panayiotou and Dr Bharat Vakharia For use in: EoE Neonatal Units Guidance specific to
EOE Neonatal ODN Clinical Guideline: Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) Guideline Authors: Dr Eliana Panayiotou and Dr Bharat Vakharia For use in: EoE Neonatal Units Guidance specific to
Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome
 European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 19: 573-577 Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome B.
European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences 2015; 19: 573-577 Usefulness of DuoPAP in the treatment of very low birth weight preterm infants with neonatal respiratory distress syndrome B.
Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor
 Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
Mechanical Ventilation Prepared by : Bayan Kaddourah RN,MHM. GICU Clinical Instructor 1 Definition Is a supportive therapy to facilitate gas exchange. Most ventilatory support requires an artificial airway.
O) or to bi-level NCPAP (group B; n=20, lower CPAP level=4.5 cm H 2
 1 NICU, Children s Hospital, Via Castelvetro, Milan, Italy 2 Laboratory, V.Buzzi Children s Hospital ICP, Milan, Italy 3 Department of Statistics, Catholic University, Milan, Italy Correspondence to Gianluca
1 NICU, Children s Hospital, Via Castelvetro, Milan, Italy 2 Laboratory, V.Buzzi Children s Hospital ICP, Milan, Italy 3 Department of Statistics, Catholic University, Milan, Italy Correspondence to Gianluca
Newborn Life Support. NLS guidance.
 Kelly Harvey, ANNP NWNODN, previously Wythenshawe Hospital has shared this presentation with the understanding that it is for personal use following your attendance at the 8th Annual Senior Neonatal Nursing
Kelly Harvey, ANNP NWNODN, previously Wythenshawe Hospital has shared this presentation with the understanding that it is for personal use following your attendance at the 8th Annual Senior Neonatal Nursing
Kugelman A, Riskin A, Said W, Shoris I, Mor F, Bader D.
 Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) vs. Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) for the Primary Treatment of RDS, A Randomized, Controlled, Prospective, Pilot Study Kugelman
Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula (HHHFNC) vs. Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation (NIPPV) for the Primary Treatment of RDS, A Randomized, Controlled, Prospective, Pilot Study Kugelman
WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator. Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients.
 EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
Title Neonatal and Paediatric High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy Guideline. Department Paediatrics / Neonates Date Issued
 Document Control Title Author Neonatal and Paediatric High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy Guideline Author s job title Directorate Medical Version Department Paediatrics / Neonates Date Issued Status
Document Control Title Author Neonatal and Paediatric High-Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy Guideline Author s job title Directorate Medical Version Department Paediatrics / Neonates Date Issued Status
What is the next best step?
 Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
Noninvasive Ventilation William Janssen, M.D. Assistant Professor of Medicine National Jewish Health University of Colorado Denver Health Sciences Center What is the next best step? 65 year old female
WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator. Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients.
 EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
EN WILAflow Elite Neonatal Ventilator Non-invasive treatment for the most delicate patients. 0197 Infant Ventilation redefined A new generation in Infant Ventilation WILAflow Elite is a microprocessor
Objectives. Apnea Definition and Pitfalls. Pathophysiology of Apnea. Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes 5/18/2015
 Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes Deepak Jain MD Care of Sick Newborn Conference May 2015 Objectives Differentiating between apnea and hypoxemia episodes. Pathophysiology Diagnosis of apnea and
Apnea of Prematurity and hypoxemia episodes Deepak Jain MD Care of Sick Newborn Conference May 2015 Objectives Differentiating between apnea and hypoxemia episodes. Pathophysiology Diagnosis of apnea and
Early nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation(nippv) versus early nasal continuous positive airway pressure(ncpap) for preterm
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Early nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation(nippv) versus early nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) for preterm infants(review) LemyreB,LaughonM,BoseC,DavisPG
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Early nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation(nippv) versus early nasal continuous positive airway pressure (NCPAP) for preterm infants(review) LemyreB,LaughonM,BoseC,DavisPG
Advantages and disadvantages of different nasal CPAP systems in newborns
 Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:926 930 DOI 10.1007/s00134-004-2267-8 N E O N A T A L A N D P A E D I A T R I C I N T E N S I V E C A R E V. Buettiker M. I. Hug O. Baenziger C. Meyer B. Frey Advantages and
Intensive Care Med (2004) 30:926 930 DOI 10.1007/s00134-004-2267-8 N E O N A T A L A N D P A E D I A T R I C I N T E N S I V E C A R E V. Buettiker M. I. Hug O. Baenziger C. Meyer B. Frey Advantages and
** SURFACTANT THERAPY**
 ** SURFACTANT THERAPY** Full Title of Guideline: Surfactant Therapy Author (include email and role): Stephen Wardle (V4) Reviewed by Dushyant Batra Consultant Neonatologist Division & Speciality: Division:
** SURFACTANT THERAPY** Full Title of Guideline: Surfactant Therapy Author (include email and role): Stephen Wardle (V4) Reviewed by Dushyant Batra Consultant Neonatologist Division & Speciality: Division:
NEONATAL NEWS Here s Some More Good Poop
 NEONATALNEWS Here ssomemoregoodpoop WINTEREDITION2010 THISNEWSLETTERISPUBLISHEDPERIODICALLYBYTHENEONATOLOGISTSOF ASSOCIATESINNEWBORNMEDICINETOCONVEYNEWANDUPDATEDPOLICIES ANDGUIDELINESANDPROVIDEGENERALEDUCATIONTONICUCARETAKERSAT
NEONATALNEWS Here ssomemoregoodpoop WINTEREDITION2010 THISNEWSLETTERISPUBLISHEDPERIODICALLYBYTHENEONATOLOGISTSOF ASSOCIATESINNEWBORNMEDICINETOCONVEYNEWANDUPDATEDPOLICIES ANDGUIDELINESANDPROVIDEGENERALEDUCATIONTONICUCARETAKERSAT
Scope This guideline is aimed at all healthcare professionals involved in the care of infants within the neonatal service.
 UHL Neonatal Guideline: CPAP Nursing Care University Hospitals of Leicester NHS NHS Trust Nov 2018 Nov 2021 Scope This guideline is aimed at all healthcare professionals involved in the care of infants
UHL Neonatal Guideline: CPAP Nursing Care University Hospitals of Leicester NHS NHS Trust Nov 2018 Nov 2021 Scope This guideline is aimed at all healthcare professionals involved in the care of infants
Clinical Guideline: Management of a baby on CPAP
 Clinical Guideline: Management of a baby on CPAP Authors: EOE Neonatal Benchmarking Group For use in: EoE Neonatal Units Guidance specific to the care of neonatal patients. Used by: For use in neonatal
Clinical Guideline: Management of a baby on CPAP Authors: EOE Neonatal Benchmarking Group For use in: EoE Neonatal Units Guidance specific to the care of neonatal patients. Used by: For use in neonatal
5/3/2012. Goals and Objectives HFNC. High-Flow Oxygen Therapy: Real Benefit or Just a Fad?
 High-Flow Oxygen Therapy: Real Benefit or Just a Fad? Timothy R. Myers MBA, RRT-NPS Director, Women s & Children s Respiratory Care & Procedural Services and Pediatric Heart Center Rainbow Babies & Children
High-Flow Oxygen Therapy: Real Benefit or Just a Fad? Timothy R. Myers MBA, RRT-NPS Director, Women s & Children s Respiratory Care & Procedural Services and Pediatric Heart Center Rainbow Babies & Children
Airway Clearance Devices
 Print Page 1 of 11 Wisconsin.gov home state agencies subject directory department of health services Search Welcome» August 2, 2018 5:18 PM Program Name: BadgerCare Plus and Medicaid Handbook Area: Durable
Print Page 1 of 11 Wisconsin.gov home state agencies subject directory department of health services Search Welcome» August 2, 2018 5:18 PM Program Name: BadgerCare Plus and Medicaid Handbook Area: Durable
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE
 Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Emergency Medicine High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI) VAPOTHERM POCKET GUIDE Indications for Vapotherm High Velocity Nasal Insufflation (Hi-VNI ) administration, the patient should be: Spontaneously
Dr. AM MAALIM KPA 2018
 Dr. AM MAALIM KPA 2018 Journey Towards Lung protection Goals of lung protection Strategies Summary Conclusion Before 1960: Oxygen; impact assessed clinically. The 1960s:President JFK, Ventilators mortality;
Dr. AM MAALIM KPA 2018 Journey Towards Lung protection Goals of lung protection Strategies Summary Conclusion Before 1960: Oxygen; impact assessed clinically. The 1960s:President JFK, Ventilators mortality;
CURRENT TRENDS IN NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION. Disclosures. Why not invasive ventilation? Objectives. Currently available modes
 CURRENT TRENDS IN NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION ----------------------------------------------------------- Karen Drinkard, RRT-NPS Neonatal Respiratory Clinical Specialist University of Washington Medical
CURRENT TRENDS IN NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION ----------------------------------------------------------- Karen Drinkard, RRT-NPS Neonatal Respiratory Clinical Specialist University of Washington Medical
Name and title of the investigators responsible for conducting the research: Dr Anna Lavizzari, Dr Mariarosa Colnaghi
 Protocol title: Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula vs Nasal CPAP for Respiratory Distress Syndrome of Prematurity. Protocol identifying number: Clinical Trials.gov NCT02570217 Name and title of
Protocol title: Heated, Humidified High-Flow Nasal Cannula vs Nasal CPAP for Respiratory Distress Syndrome of Prematurity. Protocol identifying number: Clinical Trials.gov NCT02570217 Name and title of
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices
 Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Mechanical Ventilation Principles and Practices Dr LAU Chun Wing Arthur Department of Intensive Care Pamela Youde Nethersole Eastern Hospital 6 October 2009 In this lecture, you will learn Major concepts
Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study
 D-32084-2011 Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study Robert DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Respiratory Care Manager of Research & Quality
D-32084-2011 Volume Guarantee Initiation and ongoing clinical management of an infant supported by Volume Guarantee A Case Study Robert DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Respiratory Care Manager of Research & Quality
ROLE OF PRESSURE IN HIGH FLOW THERAPY
 ROLE OF PRESSURE IN HIGH FLOW THERAPY Thomas L. Miller, PhD, MEd Director, Clinical Research and Education Vapotherm, Inc. Research Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Jefferson Medical College This information
ROLE OF PRESSURE IN HIGH FLOW THERAPY Thomas L. Miller, PhD, MEd Director, Clinical Research and Education Vapotherm, Inc. Research Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Jefferson Medical College This information
COMPARISON OF THE EFFICIENCY OF CAFFEINE VERSUS AMINOPHYLLINE FOR THE TREATMENT OF APNOEA OF PREMATURITY
 CASE STUDIES COMPARISON OF THE EFFICIENCY OF CAFFEINE VERSUS AMINOPHYLLINE FOR THE TREATMENT OF APNOEA OF PREMATURITY Gabriela Ildiko Zonda 1, Andreea Avasiloaiei 1, Mihaela Moscalu 2, Maria Stamatin 1
CASE STUDIES COMPARISON OF THE EFFICIENCY OF CAFFEINE VERSUS AMINOPHYLLINE FOR THE TREATMENT OF APNOEA OF PREMATURITY Gabriela Ildiko Zonda 1, Andreea Avasiloaiei 1, Mihaela Moscalu 2, Maria Stamatin 1
9/15/2017. Disclosures. Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula: Hot Air or Optimal Noninvasive Support? Objectives. Aerogen Pharma
 Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula: Hot Air or Optimal Noninvasive Support? Rob DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Program Manager Research/QI, Respiratory Therapy Principle Investigator, Seattle Children s Research Institute
Heated High Flow Nasal Cannula: Hot Air or Optimal Noninvasive Support? Rob DiBlasi RRT-NPS, FAARC Program Manager Research/QI, Respiratory Therapy Principle Investigator, Seattle Children s Research Institute
Lung Wit and Wisdom. Understanding Oxygenation and Ventilation in the Neonate. Jennifer Habert, BHS-RT, RRT-NPS, C-NPT Willow Creek Women s Hospital
 Lung Wit and Wisdom Understanding Oxygenation and Ventilation in the Neonate Jennifer Habert, BHS-RT, RRT-NPS, C-NPT Willow Creek Women s Hospital Objectives To review acid base balance and ABG interpretation
Lung Wit and Wisdom Understanding Oxygenation and Ventilation in the Neonate Jennifer Habert, BHS-RT, RRT-NPS, C-NPT Willow Creek Women s Hospital Objectives To review acid base balance and ABG interpretation
Work of breathing using high-flow nasal cannula in preterm infants
 (), 7 8 r Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 73-83/ $3 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Work of breathing using high-flow nasal cannula in preterm infants JG Saslow 1,, ZH Aghai 1,, TA Nakhla
(), 7 8 r Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved. 73-83/ $3 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Work of breathing using high-flow nasal cannula in preterm infants JG Saslow 1,, ZH Aghai 1,, TA Nakhla
Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation in the newborn: review of literature and evidence-based guidelines
 STATE-OF-THE-ART Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation in the newborn: review of literature and evidence-based guidelines (2010) 30, 505 512 r 2010 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved.
STATE-OF-THE-ART Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation in the newborn: review of literature and evidence-based guidelines (2010) 30, 505 512 r 2010 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved.
NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION. Lijun Ding 23 Jan 2018
 NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION Lijun Ding 23 Jan 2018 Learning objectives What is NIV The difference between CPAP and BiPAP The indication of the use of NIV Complication of NIV application Patient monitoring
NON-INVASIVE VENTILATION Lijun Ding 23 Jan 2018 Learning objectives What is NIV The difference between CPAP and BiPAP The indication of the use of NIV Complication of NIV application Patient monitoring
Practical Application of CPAP
 CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
CHAPTER 3 Practical Application of CPAP Dr. Srinivas Murki Neonatologist Fernadez Hospital, Hyderabad. A.P. Practical Application of CPAP Continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) applied to premature
Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC)
 Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC) 1. Introduction and Who Guideline applies to Heated humidified high flow nasal cannula treatment (HHHFNC), otherwise called as High flow oxygen
Heated Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula Treatment (HHHFNC) 1. Introduction and Who Guideline applies to Heated humidified high flow nasal cannula treatment (HHHFNC), otherwise called as High flow oxygen
1. Can you convince me that one should use CPAP and avoid mechanical ventilation?
 CHAPTER 12 FAQ's Dr Rhishikesh Thakre Neonatologist Aurangabad, Mahrashtra Following are bedside tips one learns with experience. So as to guide the newcomer who should not repeat the same mistakes, the
CHAPTER 12 FAQ's Dr Rhishikesh Thakre Neonatologist Aurangabad, Mahrashtra Following are bedside tips one learns with experience. So as to guide the newcomer who should not repeat the same mistakes, the
AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call
 AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call November 12, 2015 Forward Looking Statement To the extent that statements in this presentation are not strictly historical, including statements
AEROSURF Phase 2 Program Update Investor Conference Call November 12, 2015 Forward Looking Statement To the extent that statements in this presentation are not strictly historical, including statements
Effectiveness of Synchronized Noninvasive Ventilation to Prevent Intubation in Preterm Infants
 e264 Case Report THIEME Effectiveness of Synchronized Noninvasive Ventilation to Prevent Intubation in Preterm Infants Cristina Ramos-Navarro, MD 1 Manuel Sanchez-Luna, MD, PhD 1 Ester Sanz-López, MD 1
e264 Case Report THIEME Effectiveness of Synchronized Noninvasive Ventilation to Prevent Intubation in Preterm Infants Cristina Ramos-Navarro, MD 1 Manuel Sanchez-Luna, MD, PhD 1 Ester Sanz-López, MD 1
Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants <34 weeks gestation.
 Page 1 of 5 PURPOSE: Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants
Page 1 of 5 PURPOSE: Provide guidelines for the management of mechanical ventilation in infants
AFCH NEUROMUSCULAR DISORDERS (NMD) PROTOCOL
 AFCH NEUROMUSCULAR DISORDERS (NMD) PROTOCOL A. Definition of Therapy: 1. Cough machine: 4 sets of 5 breaths with a goal of I:E pressures approximately the same of 30-40. Inhale time = 1 second, exhale
AFCH NEUROMUSCULAR DISORDERS (NMD) PROTOCOL A. Definition of Therapy: 1. Cough machine: 4 sets of 5 breaths with a goal of I:E pressures approximately the same of 30-40. Inhale time = 1 second, exhale
NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP)
 Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
Introduction NIV - BI-LEVEL POSITIVE AIRWAY PRESSURE (BIPAP) Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) is a method of delivering oxygen by positive pressure mask that allows for the prevention or postponement of invasive
LRI Children s Hospital
 LRI Children s Hospital Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHFNC) Oxygen Therapy Staff relevant to: Medical and Nursing staff Team approval date: 5.01.18 Version: 1 Revision due: January 2020 Written
LRI Children s Hospital Humidified High Flow Nasal Cannula (HHFNC) Oxygen Therapy Staff relevant to: Medical and Nursing staff Team approval date: 5.01.18 Version: 1 Revision due: January 2020 Written
Mechanical Ventilation ศ.พ.ญ.ส ณ ร ตน คงเสร พงศ ภาคว ชาว ส ญญ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล
 Mechanical Ventilation ศ.พ.ญ.ส ณ ร ตน คงเสร พงศ ภาคว ชาว ส ญญ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Goal of Mechanical Ventilation Mechanical ventilation is any means in which physical device or machines are
Mechanical Ventilation ศ.พ.ญ.ส ณ ร ตน คงเสร พงศ ภาคว ชาว ส ญญ ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร ศ ร ราชพยาบาล Goal of Mechanical Ventilation Mechanical ventilation is any means in which physical device or machines are
Transnasal Humidified Rapid Insufflation Ventilatory Exchange (THRIVE): An Optimal Method of Preoxygenation for General Anaesthesia in Obstetrics
 Transnasal Humidified Rapid Insufflation Ventilatory Exchange (THRIVE): An Optimal Method of Preoxygenation for General Anaesthesia in Obstetrics Dr E McMaster, Dr E Gent, Dr T Mahendrayogam, Dr A Surendran
Transnasal Humidified Rapid Insufflation Ventilatory Exchange (THRIVE): An Optimal Method of Preoxygenation for General Anaesthesia in Obstetrics Dr E McMaster, Dr E Gent, Dr T Mahendrayogam, Dr A Surendran
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device
 I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
I. Subject: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by Continuous Flow Device II. Policy: Continuous Positive Airway Pressure CPAP by the Down's system will be instituted by Respiratory Therapy personnel
Worksheet No. NRP-002A.doc Page 1 of 10
 Worksheet No. NRP-002A.doc Page 1 of 10 WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Emergency Cardiac Care Worksheet author(s) Colm P.F O Donnell Date Submitted for review: 3 rd February 2010 Clinical
Worksheet No. NRP-002A.doc Page 1 of 10 WORKSHEET for Evidence-Based Review of Science for Emergency Cardiac Care Worksheet author(s) Colm P.F O Donnell Date Submitted for review: 3 rd February 2010 Clinical
Continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress in preterm infants(review)
 Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress in preterm infants(review) HoJJ,SubramaniamP,DavisPG Ho JJ, Subramaniam P, Davis PG.. Cochrane Database of
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress in preterm infants(review) HoJJ,SubramaniamP,DavisPG Ho JJ, Subramaniam P, Davis PG.. Cochrane Database of
INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2
 2 Effects of CPAP INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2 ). The effect on CO 2 is only secondary to the primary process of improvement in lung volume and
2 Effects of CPAP INTRODUCTION The effect of CPAP works on lung mechanics to improve oxygenation (PaO 2 ). The effect on CO 2 is only secondary to the primary process of improvement in lung volume and
A Trial Comparing Noninvasive Ventilation Strategies in Preterm Infants
 T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e original article A Trial Comparing Noninvasive Ventilation Strategies in Preterm Infants Haresh Kirpalani, B.M., M.Sc., David Millar, M.B., Brigitte
T h e n e w e ngl a nd j o u r na l o f m e dic i n e original article A Trial Comparing Noninvasive Ventilation Strategies in Preterm Infants Haresh Kirpalani, B.M., M.Sc., David Millar, M.B., Brigitte
How to write bipap settings
 How to write bipap settings 6-6-2013 Living On O2 for Life If you use a bipap machine, like I do, this post is for you. I've been using a bipap machine since 1993 which is a pretty long time. BiPAP 's
How to write bipap settings 6-6-2013 Living On O2 for Life If you use a bipap machine, like I do, this post is for you. I've been using a bipap machine since 1993 which is a pretty long time. BiPAP 's
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. DD Woodhead, DK Lambert, JM Clark and RD Christensen. Intermountain Healthcare, McKay-Dee Hospital, Ogden, UT, USA
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparing two methods of delivering high-flow gas therapy by nasal cannula following endotracheal extubation: a prospective, randomized, masked, crossover trial DD Woodhead, DK Lambert,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Comparing two methods of delivering high-flow gas therapy by nasal cannula following endotracheal extubation: a prospective, randomized, masked, crossover trial DD Woodhead, DK Lambert,
Yorkshire & Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline
 Yorkshire & Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline Title: Ventilation Author: Dr Cath Smith updated September 2017, written by Dr Elizabeth Pilling May 2011 Date written: May 2011 Review date:
Yorkshire & Humber Neonatal ODN (South) Clinical Guideline Title: Ventilation Author: Dr Cath Smith updated September 2017, written by Dr Elizabeth Pilling May 2011 Date written: May 2011 Review date:
The use of noninvasive ventilatory
 Gas exchange and lung inflammation using nasal intermittent positive-pressure ventilation versus synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation in piglets with saline lavage-induced lung injury: An observational
Gas exchange and lung inflammation using nasal intermittent positive-pressure ventilation versus synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation in piglets with saline lavage-induced lung injury: An observational
Acute Paediatric Respiratory Pathway
 Guideline for the use of high Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy (Optiflow or Airvo) in Children with Bronchiolitis or an acute respiratory illness Introduction: High flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen enables
Guideline for the use of high Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen Therapy (Optiflow or Airvo) in Children with Bronchiolitis or an acute respiratory illness Introduction: High flow nasal cannula (HFNC) oxygen enables
Randomised controlled trial of weaning strategies for preterm infants on nasal continuous positive airway pressure
 Tang et al. BMC Pediatrics (2015) 15:147 DOI 10.1186/s12887-015-0462-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Randomised controlled trial of weaning strategies for preterm infants on nasal continuous positive airway
Tang et al. BMC Pediatrics (2015) 15:147 DOI 10.1186/s12887-015-0462-0 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Randomised controlled trial of weaning strategies for preterm infants on nasal continuous positive airway
High-Flow Nasal Cannulae in Very Preterm Infants after Extubation
 original article High-Flow Nasal Cannulae in Very Preterm Infants after Extubation Brett J. Manley, M.B., B.S., Louise S. Owen, M.D., Lex W. Doyle, M.D., Chad C. Andersen, M.B., B.S., David W. Cartwright,
original article High-Flow Nasal Cannulae in Very Preterm Infants after Extubation Brett J. Manley, M.B., B.S., Louise S. Owen, M.D., Lex W. Doyle, M.D., Chad C. Andersen, M.B., B.S., David W. Cartwright,
Nasal intermittent positive pressure ventilation
 S Y S T E M A T I C R E V I E W Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation versus Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in Neonates: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis SHIFANG TANG, JINNING
S Y S T E M A T I C R E V I E W Nasal Intermittent Positive Pressure Ventilation versus Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure in Neonates: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis SHIFANG TANG, JINNING
Hyaline membrane disease. By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg
 Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
Hyaline membrane disease By : Dr. Ch Sarishma Peadiatric Pg Also called Respiratory distress syndrome. It occurs primarily in premature infants; its incidence is inversely related to gestational age and
TO THE OPERATOR AND PERSON IN CHARGE OF MAINTENANCE AND CARE OF THE UNIT:
 fabian HFO Quick guide TO THE OPERATOR AND PERSON IN CHARGE OF MAINTENANCE AND CARE OF THE UNIT: This Quick Guide is not a substitute for the Operation Manual. Read the Operation Manual carefully before
fabian HFO Quick guide TO THE OPERATOR AND PERSON IN CHARGE OF MAINTENANCE AND CARE OF THE UNIT: This Quick Guide is not a substitute for the Operation Manual. Read the Operation Manual carefully before
Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification
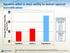 Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
Average Absolute Humidity (mg H 2 O/L) Systems differ in their ability to deliver optimal humidification 45 Flows Tested 40 35 30 Optiflow Airvo 2 Vapotherm Vapotherm 5 L/min 10L/min 20L/min 30L/min 40L/min
NAVA. In Neonates. Howard Stein, M.D. Director Neonatology. Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist. Toledo Children s Hospital Toledo, Ohio
 NAVA Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist In Neonates Howard Stein, M.D. Director Neonatology Toledo Children s Hospital Toledo, Ohio Disclaimers Dr Stein: Is discussing products made by Maquet Has no
NAVA Neurally Adjusted Ventilatory Assist In Neonates Howard Stein, M.D. Director Neonatology Toledo Children s Hospital Toledo, Ohio Disclaimers Dr Stein: Is discussing products made by Maquet Has no
Sustainable use of continuous positive airway pressure in extremely preterm infants during the first week after delivery
 F398 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sustainable use of continuous positive airway pressure in extremely preterm infants during the first week after delivery C Booth, M H Premkumar, A Yannoulis, M Thomson, M Harrison,
F398 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Sustainable use of continuous positive airway pressure in extremely preterm infants during the first week after delivery C Booth, M H Premkumar, A Yannoulis, M Thomson, M Harrison,
King s Research Portal
 King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1007/s00431-015-2595-4 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Shetty, S., Bhat,
King s Research Portal DOI: 10.1007/s00431-015-2595-4 Document Version Peer reviewed version Link to publication record in King's Research Portal Citation for published version (APA): Shetty, S., Bhat,
Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo
 Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Instant dowload and all chapters Test Bank Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6th Edition Cairo https://testbanklab.com/download/test-bank-pilbeams-mechanical-ventilation-physiologicalclinical-applications-6th-edition-cairo/
Essential Practices A clinical decision-making resource for the respiratory care professional
 Essential Practices A clinical decision-making resource for the respiratory care professional Free Continuing Education for Respiratory Therapists (CRCE) and Nurses (CE) See Page 12 Advisory Board Janet
Essential Practices A clinical decision-making resource for the respiratory care professional Free Continuing Education for Respiratory Therapists (CRCE) and Nurses (CE) See Page 12 Advisory Board Janet
I. Subject: Medication Delivery by Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI)
 I. Subject: Medication Delivery by Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI) II. Policy: Aerosol medication administration by metered dose inhaler will be performed upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel.
I. Subject: Medication Delivery by Metered Dose Inhaler (MDI) II. Policy: Aerosol medication administration by metered dose inhaler will be performed upon a physician's order by Respiratory Therapy personnel.
Nasal CPAP in Neonatology: We Can Do Better
 Nasal CPAP in Neonatology: We Can Do Better COI Disclosure I do not have any conflict of interest, nor will I be discussing any off-label product use. This class has no commercial support or sponsorship,
Nasal CPAP in Neonatology: We Can Do Better COI Disclosure I do not have any conflict of interest, nor will I be discussing any off-label product use. This class has no commercial support or sponsorship,
5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide. 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia. Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year
 1 5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) American
1 5 Million neonatal deaths each year worldwide 20% caused by neonatal asphyxia Improvement of the outcome of 1 million newborns every year International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) American
Mechanical Ventilation 1. Shari McKeown, RRT Respiratory Services - VGH
 Mechanical Ventilation 1 Shari McKeown, RRT Respiratory Services - VGH Objectives Describe indications for mcvent Describe types of breaths and modes of ventilation Describe compliance and resistance and
Mechanical Ventilation 1 Shari McKeown, RRT Respiratory Services - VGH Objectives Describe indications for mcvent Describe types of breaths and modes of ventilation Describe compliance and resistance and
Noninvasive Respiratory Support James J. Cummings, MD, FAAP, Richard A. Polin, MD, FAAP, the COMMITTEE ON FETUS AND NEWBORN
 CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care Noninvasive Respiratory Support James J. Cummings, MD, FAAP, Richard A. Polin, MD, FAAP, the COMMITTEE ON FETUS AND NEWBORN Mechanical
CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care Noninvasive Respiratory Support James J. Cummings, MD, FAAP, Richard A. Polin, MD, FAAP, the COMMITTEE ON FETUS AND NEWBORN Mechanical
Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context
 Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context A subcommittee of the Canadian Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) Steering Committee
Addendum to the NRP Provider Textbook 6 th Edition Recommendations for specific modifications in the Canadian context A subcommittee of the Canadian Neonatal Resuscitation Program (NRP) Steering Committee
Noninvasive Respiratory Support James J. Cummings, MD, FAAP, Richard A. Polin, MD, FAAP, the COMMITTEE ON FETUS AND NEWBORN
 CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care Noninvasive Respiratory Support James J. Cummings, MD, FAAP, Richard A. Polin, MD, FAAP, the COMMITTEE ON FETUS AND NEWBORN Mechanical
CLINICAL REPORT Guidance for the Clinician in Rendering Pediatric Care Noninvasive Respiratory Support James J. Cummings, MD, FAAP, Richard A. Polin, MD, FAAP, the COMMITTEE ON FETUS AND NEWBORN Mechanical
Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery
 Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery Opening Scenario (Links to Section 1) You are an evening-shift respiratory therapist in a large hospital with a level III neonatal unit. You are paged
Simulation 3: Post-term Baby in Labor and Delivery Opening Scenario (Links to Section 1) You are an evening-shift respiratory therapist in a large hospital with a level III neonatal unit. You are paged
NIV use in ED. Dr. Khalfan AL Amrani Emergency Resuscitation Symposium 2 nd May 2016 SQUH
 NIV use in ED Dr. Khalfan AL Amrani Emergency Resuscitation Symposium 2 nd May 2016 SQUH Outline History & Introduction Overview of NIV application Review of proven uses of NIV History of Ventilation 1940
NIV use in ED Dr. Khalfan AL Amrani Emergency Resuscitation Symposium 2 nd May 2016 SQUH Outline History & Introduction Overview of NIV application Review of proven uses of NIV History of Ventilation 1940
Bubble and ventilator-derived nasal continuous positive airway pressure in premature infants: work of breathing and gas exchange
 (011) 1, 44 50 r 011 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. 04-846/11 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bubble and ventilator-derived nasal continuous positive airway pressure in premature infants:
(011) 1, 44 50 r 011 Nature America, Inc. All rights reserved. 04-846/11 www.nature.com/jp ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bubble and ventilator-derived nasal continuous positive airway pressure in premature infants:
Despite advances in technology, chronic lung
 CONTINUING EDUCATION J Perinat Neonat Nurs Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 349 358 Copyright c 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Noninvasive Ventilation in the Neonate Debbie Fraser Askin, MN,
CONTINUING EDUCATION J Perinat Neonat Nurs Vol. 21, No. 4, pp. 349 358 Copyright c 2007 Wolters Kluwer Health Lippincott Williams & Wilkins Noninvasive Ventilation in the Neonate Debbie Fraser Askin, MN,
Evaluating the Effect of Flow and Interface Type on Pressures Delivered With Bubble CPAP in a Simulated Model
 Evaluating the Effect of Flow and Interface Type on Pressures Delivered With Bubble CPAP in a Simulated Model Stephanie A Bailes RRT-NPS NREMT-B, Kimberly S Firestone MSc RRT, Diane K Dunn RRT-NPS, Neil
Evaluating the Effect of Flow and Interface Type on Pressures Delivered With Bubble CPAP in a Simulated Model Stephanie A Bailes RRT-NPS NREMT-B, Kimberly S Firestone MSc RRT, Diane K Dunn RRT-NPS, Neil
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/46692 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Zanten, Henriëtte van Title: Oxygen titration and compliance with targeting oxygen
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/46692 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation Author: Zanten, Henriëtte van Title: Oxygen titration and compliance with targeting oxygen
Novel Strategies in NICU and PICU for the Child Who is Really Difficult to Ventilate
 Novel Strategies in NICU and PICU for the Child Who is Really Difficult to Ventilate Larry C. Lands, MD, PhD Professor of Pediatrics, McGill University Director, Pediatric Respiratory Medicine Montreal
Novel Strategies in NICU and PICU for the Child Who is Really Difficult to Ventilate Larry C. Lands, MD, PhD Professor of Pediatrics, McGill University Director, Pediatric Respiratory Medicine Montreal
Recent Advances in Respiratory Medicine
 Recent Advances in Respiratory Medicine Dr. R KUMAR Pulmonologist Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) NIV Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) refers to the administration of ventilatory support without using an invasive
Recent Advances in Respiratory Medicine Dr. R KUMAR Pulmonologist Non Invasive Ventilation (NIV) NIV Noninvasive ventilation (NIV) refers to the administration of ventilatory support without using an invasive
South Central Neonatal Network Quality Care Group Working to provide a unified approach to excellence
 South Central Neonatal Network Quality Care Group Working to provide a unified approach to excellence Guideline framework for CPAP Approved by & date Date of publication Neonatal Network Board December
South Central Neonatal Network Quality Care Group Working to provide a unified approach to excellence Guideline framework for CPAP Approved by & date Date of publication Neonatal Network Board December
CHEST PHYSIOTHERAPY IN NICU PURPOSE POLICY STATEMENTS SITE APPLICABILITY PRACTICE LEVEL/COMPETENCIES. The role of chest physiotherapy in the NICU
 PURPOSE The role of chest physiotherapy in the NICU POLICY STATEMENTS In principle chest physiotherapy should be limited to those infants considered most likely to benefit with significant respiratory
PURPOSE The role of chest physiotherapy in the NICU POLICY STATEMENTS In principle chest physiotherapy should be limited to those infants considered most likely to benefit with significant respiratory
7 Initial Ventilator Settings, ~05
 Abbreviations (inside front cover and back cover) PART 1 Basic Concepts and Core Knowledge in Mechanical -- -- -- -- 1 Oxygenation and Acid-Base Evaluation, 1 Review 01Arterial Blood Gases, 2 Evaluating
Abbreviations (inside front cover and back cover) PART 1 Basic Concepts and Core Knowledge in Mechanical -- -- -- -- 1 Oxygenation and Acid-Base Evaluation, 1 Review 01Arterial Blood Gases, 2 Evaluating
The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation
 The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Departments of Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Some definitions
The Art and Science of Weaning from Mechanical Ventilation Shekhar T. Venkataraman M.D. Professor Departments of Critical Care Medicine and Pediatrics University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine Some definitions
Neonatal Respiratory Physiotherapy. Nicky Hawkes Advanced Respiratory Physiotherapist Oct 2011
 Neonatal Respiratory Physiotherapy Nicky Hawkes Advanced Respiratory Physiotherapist Oct 2011 Respiratory Physiotherapy?..Not just percussion! Assessment of baby s respiratory status and deciding what
Neonatal Respiratory Physiotherapy Nicky Hawkes Advanced Respiratory Physiotherapist Oct 2011 Respiratory Physiotherapy?..Not just percussion! Assessment of baby s respiratory status and deciding what
High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC. Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand
 786 High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand Disclaimer I was a scep@c un@l I used it Now I am a firm believer HFNC The Fisher and Paykel
786 High Flow Nasal Cannula Oxygen HFNC Dr I S Kalla Department of Pulmonology University of the Witwatersrand Disclaimer I was a scep@c un@l I used it Now I am a firm believer HFNC The Fisher and Paykel
SESSION 3 OXYGEN THERAPY
 SESSION 3 OXYGEN THERAPY Harith Eranga Yapa Department of Nursing Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka 1 Outline Methods of delivery Complications of oxygen therapy Artificial airways
SESSION 3 OXYGEN THERAPY Harith Eranga Yapa Department of Nursing Faculty of Health Sciences The Open University of Sri Lanka 1 Outline Methods of delivery Complications of oxygen therapy Artificial airways
Dyspnea: Should we use BIPAP?
 Dyspnea: Should we use BIPAP? Thomas R. Gildea MD, MS FCCP Head Section of Bronchoscopy Respiratory Institute Transplant Center Disclosure SuperDimension Inc. PI for single center study Others: Aeris,
Dyspnea: Should we use BIPAP? Thomas R. Gildea MD, MS FCCP Head Section of Bronchoscopy Respiratory Institute Transplant Center Disclosure SuperDimension Inc. PI for single center study Others: Aeris,
