Playing the Goblin Post Office game improves movement control of the core: A case study.
|
|
|
- Elfreda Holmes
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 International Conference on Virtual Rehabilitation 211 Rehab Week Zurich, ETH Zurich Science City, Switzerland, June 27-29, 211 Playing the Goblin Post Office game improves movement control of the core: A case study. Gabor J Barton, Malcolm B Hawken, Richard J Foster Research Institute for Sport and Exercise Sciences Liverpool John Moores University Liverpool, United Kingdom. g.j.barton@ljmu.ac.uk Gill Holmes North West Movement Analysis Centre Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust Liverpool, United Kingdom. Penny B Butler The Movement Centre Oswestry, United Kingdom. Abstract Movement function of the core (trunk and pelvis) can be improved in cerebral palsy, potentially leading to benefits which transfer to activities of daily living. A single child with CP diplegia played our custom made game which runs on the CAREN system. Three playing postures gradually introduced more and more joints in the legs to be controlled. Vicon cameras tracked trunk and pelvic rotations which drove a dragon towards envelope targets. Forward speed of the game was adjusted by an adaptive algorithm leading to a maximum settled speed for the various conditions. Results showed that core control improved after the six week training period. The trunk was better controlled than the pelvis, sideways rotations were better controlled than fore-aft rotations of body segments, and single plane rotations were more efficient than cross-plane rotations of the core. The quantifiable improvements suggest a good potential for our technique to improve core control which is a prerequisite for good movement control of the legs and arms. Keywords cerebral palsy; movement training; core control; virtual rehabilitation I. INTRODUCTION Traditionally the core of the body (pelvis and trunk) has been regarded as a passenger unit carried by the lower extremities which are termed the locomotor unit [1] suggesting a passive role for the pelvis and trunk in gait. There is however evidence supporting a more active role for the pelvis and trunk. Responses triggered by balance perturbations involve trunk, neck and thigh muscles which contract at the same time, or even before the activation of muscles around the ankle joint [2-5]. In prospective studies [6,7] reduced strength and impaired proprioception around the core could be associated with increased risk of injuries, specifically around the knee, suggesting that control over the core is a prerequisite for efficient and effective use of the legs. Cerebral palsy (CP) is a neuro-musculo-skeletal disorder caused by damage to the immature brain around birth. It has an incidence of 1 in live births [8]. The treatment of children with CP focuses mainly on secondary abnormalities (altered bone and muscle growth) and avoids addressing the primary abnormalities characterizing CP which include loss of selective muscle control, muscle imbalance and deficient equilibrium reactions [9]. These abnormalities affecting the pelvis and trunk lead to reduced stability and control of the core, which impairs movement control of distal body segments (arms and legs) leading to inefficient performance of activities of daily living. In spite of the primary damage to the central nervous system in CP, global motor function can be improved by controlled exercises that take advantage of the brain s capacity to reorganize in targeted areas (neuroplasticity). Reactive balance training of children with CP on a movable platform led to improvement of muscle responses, and the quantifiable benefits were carried over for one month after training [1]. Balance training improved stance and gait leading to a more symmetrical walking pattern in a group of children with hemiplegic CP [11]. The clinical application of virtual reality (VR) is expanding dramatically. It is a promising area for the application of new technologies in movement rehabilitation, underpinned by a growing number of published studies supporting the feasibility and benefits of virtual rehabilitation [12]. Research efforts in the area of movement rehabilitation using VR have focused mainly on training the arms and legs [13-17]. The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of a six week training programme using a custom made VR game developed to train movement control of the trunk and pelvis. Results from a single child with CP diplegia are presented here. II. METHODS A. Participant and training/testing protocol One boy with CP diplegia (age: 1 years; height: 1.34 m; mass: 36 kg) trained on a custom-made computer game called the Goblin Post Office (GPO) for a period of six weeks, twice a week, for 3 minutes in each session. The child had no previous history of surgical intervention and received no This project was funded by The WellChild Trust and Alder Hey Children s NHS Foundation Trust /11/$ IEEE
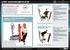
2 conventional physiotherapy or core specific rehabilitation which might influence VR training. He maintained his regular physical activity in PE lessons and swimming with family throughout the study. Prior to and shortly after the six week training period, the child s performance was measured using the GPO to establish whether there were any changes in response to VR training. B. The Goblin Post Office game A Computer Assisted Rehabilitation Environment (CAREN System, Motek Medical, Amsterdam, The Netherlands) was used to create the interactive game. The CAREN system consists of an 8-camera Vicon 612 optoelectronic motion capture system (Oxford Metrics, Oxford, UK), a six degreesof-freedom moving platform and video projection. Components of the system are controlled by the CAREN D-Flow software (Fig. 1). The aim of the Goblin Post Office (GPO) was to use movement of the trunk or pelvis to navigate a dragon through a virtual cave consisting of alternating straight segments and 9 bends. The horn protruding from the dragon s head was used to burst targets that contain virtual letters. Two clusters of three retro-reflective markers, each forming a triangle, were placed on the trunk and on the pelvis to track the segments during game-play. dragon could only move horizontally or vertically in order to navigate towards the virtual targets which appeared unpredictably in a horizontal or vertical row. After familiarization with cross-plane movements driven by simultaneous rotation and tilt, the virtual targets appeared in unpredictable locations requiring navigation in oblique directions. Targets were presented in blocks of 8 in the straight segments of the cave. Movements between targets were always the same length, and in one of eight possible directions. D. Levels of difficulty The theory of Targeted Training [18,19] aims to simplify movement tasks by stabilizing the body below the level of the targeted joint. We used this concept to define three levels of difficulty of core control (Fig 2.). The purpose of the first level, kneel sitting, was to stabilize the leg and pelvis, thereby focusing on movement of the trunk only. At the second level the child assumed a high kneeling position which introduced additional control of the hip and knee joints while stabilizing the shank and foot segments during game-play. The third level was standing which required coordinated movement of all joints and body segments involved in upright standing. At all levels, the child began with single plane movements of the trunk segment, followed by cross-plane movements, eventually controlling the game with their pelvis. The criterion for progressing to the next level was either reaching a settled level of performance or reaching a time limit. Figure 2: The three postures of kneel sitting, high kneeling, and standing which introduced progressively more joints and segments making the control of trunk and pelvis movements more and more difficult. Figure 1: The Goblin Post Office game as played by the participant. Note the infra-red cameras mounted on the walls, tracking positions of the two marker clusters on the trunk and pelvis. C. Control Schemes To steer the dragon right or left in the GPO required rotation of the trunk or pelvis in the transverse plane, whilst anterior and posterior tilt in the sagittal plane steered down and up respectively. Angular displacement of the body segment controlled speed of flight, not displacement, in the appropriate direction. In a familiarization session the child moved the dragon right, left, up and down without any forward progression, by rotating and tilting the trunk and then the pelvis in order to understand the mapping of segmental movements to motion in the game. At first, the participants used rotation or tilt of the trunk or pelvis to play the game. This meant the E. Measure of performance during game-play For the game to remain interesting the level of difficulty needed to match the subject's performance, which varied over time and between subjects. The GPO game incorporates an adaptive algorithm (PEST) [2] which varies game difficulty, but in addition provides a method of measuring performance. The algorithm adjusts the forward speed of the virtual dragon during game-play to vary game difficulty. Speed increases in response to a successful collision with a target, thus increasing difficulty for the subject, speed reduces following a miss. The algorithm also adjusts the size of speed increments automatically over time, and so speed (and hit rate) converge towards a settled value at which increments were minimum, representing stable performance. A custom MATLAB (MathWorks, Natick MA, USA) program was used to determine the maximum settled speed (MSS), defined as the highest mean speed with the smallest speed variance over a straight segment of the virtual cave.
3 Speed (m/s) III. RESULTS A. Speed profiles and the maximum settled speed The game starts at 5 m/s forward speed of the dragon (in game-scale metres) and then the speed varies as a result of the speed adjustment algorithm. A typical speed profile recorded during game-play is shown in Fig. 3 illustrating how the game speed settles over time Target number Period of Maximum Settled Speed Figure 3. A typical example of a speed profile while playing the Goblin Post Office game driven by rotation of the trunk. Game speed changes dynamically as a function of target hit ratios. The maximum settled speed was reached in the 6 th straight section after popping the th balloon. B. compared to cross-plane motion of the trunk The maximum settled speeds (MSS) reached using single and dual plane motion at pre- and post-training suggest that greater speeds were achieved in the GPO game when using either trunk rotation or trunk tilt alone, rather than rotating and tilting the trunk simultaneously. This was the case for all levels of the GPO game in kneel sitting, high kneeling and standing (Fig. 4) Combined Figure 4. Comparison of single plane and cross-plane maximum settled speed (MSS) values in kneel sitting, high kneeling, standing, and averaged, before and after training on the Goblin Post Office game. C. compared to trunk tilt Performance peaked when steering the dragon using trunk rotation rather than trunk tilt, at all levels of the game separately (kneel sitting, high kneeling, standing), and with a mean difference of 6.7 m/s during pre-training, and 3. m/s post-training when averaging the values across levels (Fig. 5) Combined Figure 5. Comparison of maximum settled speed (MSS) achieved with rotation compared to tilt of the trunk in kneel sitting, high kneeling, standing, and averaged, before and after training. D. compared to pelvis rotation Higher values of MSS were achieved using trunk rotation to steer the dragon in both high kneeling and standing (Fig. 6). Combining the results of high kneeling and standing, mean MSS of 5.3 m/s (pre-training), and 86.4 m/s (post-training) was found when using trunk rotation, compared to 38.9 m/s (pre-training) and.8 m/s (post-training) when using pelvic rotation. 2 Pelvic rotation 2 Pelvic rotation Figure 6. Comparison of maximum settled speed (MSS) values reached with trunk and pelvis rotation in high kneeling and standing, before and after training. Note that pelvic rotation was not possible in kneel sitting. E. Comparison of performance at three GPO levels pre- and post-training In kneel sitting, there was a significant difference in performance from pre- to post-training (t 2 = , p =.18), evidenced by an increase in mean MSS from 33.8 ± 4. m/s to 69.6 ± 12.3 m/s across all levels (Fig. 7. There was a significant difference between pre- and post-training in high kneeling (t 3 = p =.7), shown by an increase in mean MSS from 42.1 ± 9. m/s to 67.5 ± 11.5 m/s (Fig. 7. In standing there was also a significant difference between preand post-training (t 3 = p =.12), demonstrated by an increase in mean MSS from 37.9 ± 8.7 m/s to 75.2 ± 21.2 m/s (Fig. 7.
4 Trunk Rot. Trunk Rot. Pelvic Rot. Trunk Rot. Pelvic Rot. Δ F. Overall comparison of performance between pre- and post-training MSS increased at all levels of the GPO game, with a mean change in speed of 32.6 ± 11. m/s. The largest increase was demonstrated during standing whilst using the trunk to drive the game (49.3 m/s) (Fig Pelvis rotation Kneel sitting High kneeling Pelvis rotation Figure 7. The changes of maximum settled speed (MSS) between pre- and post-training when playing the game in kneel sitting, high kneeling, and standing. Short horizontal bars indicate the mean MSS pre- and posttraining. Differences of MSS between pre- and post-training for all conditions are shown in where the dotted line shows the mean difference across all conditions. IV. DISCUSSION The boy completed the six weeks training without missing any of the sessions. He received minimal encouragement from the experimenters and parents and so his motivation was maintained mostly by the varying difficulty of the game set by the adaptive speed adjustment algorithm. A systematic analysis of the maximum settled speeds reached while playing the game leads to a number of observations. In addition to confirming the effect of game training, interpretation of these observations reveals several underlying mechanisms which improve our understanding of how the trunk and pelvis are used by a child with CP diplegia in a real-time biofeedback setting. A. movements are better controlled than crossplane movements. The quasi-random positions of balloon targets were such that the child had to navigate by rotating and tilting the body segment (trunk or pelvis) at different ratios resulting in oblique flight paths of the dragon. This combined task of simultaneously controlling segmental movement across principal planes appeared to be more difficult than single plane movements in the transverse or sagittal planes. In addition, the MSS improved pre- to post-training more in single plane movements than in cross-plane movements. Gait involves small range movements of the pelvis but these occur simultaneously combining pelvic tilt, obliquity and rotation and so the inclusion of cross-plane movements of the core in game training might be expected to translate to daily living activities better than single plane movements. B. is controlled better than trunk tilt. Reduced control of segmental tilt in comparison to rotation may occur due to the destabilizing effect of the body s centre of gravity as it translates outside the base of support, whilst rotation is likely to result in less displacement of the whole body s centre of gravity. Another factor may be that retraction of one side is unambiguously mapped to steering in the same direction but anterior tilt may be expected to produce either upward or downward movement, depending on the participant s previous experience of computer games. In addition, the range of motion when rotating a segment in the transverse plane is symmetrical but is asymmetrical for pelvic tilt with greater range of anterior tilt than posterior tilt in the sagittal plane. Gains mapping tilt of the segment to vertical speed of the dragon were set so that the child was able to reach all targets using the more limited posterior tilt range but as a result only a reduced section of the full range of anterior tilt was used. Such anatomically determined asymmetry might have posed an added level of complexity resulting in lower MSS when using tilt. C. is controlled better than pelvic rotation. Higher MSS values were reached when using rotation of the more cephalic trunk segment in comparison to the more caudal pelvic segment. This finding confirms the theories underlying Targeted Training [18,19] with development of trunk control progressing segmentally in a cephalo-caudal direction in typically developing infants [21]. Control has also been shown to improve cephalo-caudally with Targeted Training in children with CP [22,23]. Thus the observation in this study of reduced movement control of the pelvis compared to the trunk is not unexpected. The inability of the child to use pelvic tilt to drive the game sufficiently well (ruling out comparison of trunk tilt and pelvic tilt) further suggests reduced control at pelvic level. D. The ranking order remains unchanged for body segments and planes of movement pre- to post-training. With only one exception, none of the lines in the above figures cross confirming that the constraints determining the level of control of a certain segment in a specific task change in parallel. E. The highest maximum settled speed was reached in high kneeling pre-training but in standing post-training. After training the child performed best in the most complex task of standing where all segments of the body required simultaneous control. Such an improvement is likely to confer greater ability in activities of daily living. F. The maximum settled speed improved as a result of playing the GPO game. Movement control of both the pelvis and trunk segments improved in kneel sitting, high kneeling and standing with either single or dual plane motions of the targeted segment controlling the game. The statistically significant differences confirm that a six week training programme resulted in measurable improvements at all levels.
5 V. CONCLUSIONS Our study confirms the beneficial effects of playing a custom made computer game on movement control of the trunk and pelvis in a child with cerebral palsy. The maximum settled speed algorithm provides a measure of motor performance and enables monitoring of change over time. Changes in the MSS suggest that the trunk is better controlled than the pelvis, rotation is better controlled than tilt, and single plane movements are executed with more control than cross-plane movements. Improvement of motor performance was highest in standing confirming the potential of this technique to improve activities of daily living. REFERENCES [1] J. Perry, Gait Analysis: Normal and Pathological Function. Thorofare, NJ: SLACK- Inc., [2] J. H. Allum, B. R. Bloem, M. G. Carpenter, M. Hulliger, and M. Hadders-Algra, Proprioceptive control of posture: a review of new concepts Gait Posture, vol. 8(3), pp , [3] E. A. Keshner, M. H. Woollacott, and B. Debu, Neck, trunk and limb muscle responses during postural perturbations in humans. Exp. Brain Res., vol. 71(3), pp , [4] J. H. Allum, F. Honegger, and H. Acuña, Differential control of leg and trunk muscle activity by vestibulo-spinal and proprioceptive signals during human balance corrections. Acta Otolaryngol., vol. 115(2), pp , [5] H. Forssberg H, and H. Hirschfeld, Postural adjustments in sitting humans following external perturbations: muscle activity and kinematics. Exp. Brain Res., vol. 97(3), pp , [6] D. T. Leetun, M. L. Ireland, J. D. Willson, B. T. Ballantyne, and I. M. Davis, Core stability measures as risk factors for lower extremity injury in athletes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc., vol. 36(6), pp , 24. [7] B. T. Zazulak, T. E. Hewett, N. P. Reeves, B. Goldberg, and J. Cholewicki, The effects of core proprioception on knee injury: a prospective biomechanical-epidemiological study. Am. J. Sports Med., vol. 35(3), pp , 27. [8] L. A. Koman, B. P. Smith, and J. S. Shilt, Cerebral palsy. Lancet, vol. 363(9421), pp , 24. [9] J. R. Gage, and T. F. Novacheck, An update on the treatment of gait problems in cerebral palsy. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B, vol 1(4), pp , 21. [1] M. H. Woollacott, A. Shumway-Cook, S. Hutchinson, M. Ciol, R. Price, and D. Kartin, Effect of balance training on muscle activity used in recovery of stability in children with cerebral palsy: a pilot study. Dev. Med. Child Neur., vol. 47(7), pp , 25. [11] A. Ledebt, J. Becher, J. Kapper, R. M. Rozendaalr, R. Bakker, and I. C. Leenders, Balance training with visual feedback in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy: effect on stance and gait. Motor Control, vol. 9(4), pp , 25. [12] F. D. Rose, B. M. Brooks, and A. A. Rizzo, Virtual reality in brain damage rehabilitation: review. Cyberpsychol. Behav., vol. 8, pp ; discussion pp , 25. [13] J. E. Deutsch, J. Latonio, G. C. Burdea, and R. Boian, Post-stroke rehabilitation with the Rutgers Ankle system: A case study. Presence- Teleoperators and Virtual Environments, vol. 1(4), pp , 21. [14] A. S. Merians, D. Jack, R. Boiau, M. Tremaine, G. C. Burdea, and S. V. Adamovich, Virtual reality-augmented rehabilitation for patients following stroke. Physical Therapy, vol. 82(9), pp , 22. [15] C. Bryanton, J. Bosse, M. Brien, J. McLean, A. McCormick, and H. Sveistrup, Feasibility, motivation, and selective motor control: Virtual reality compared to conventional home exercise in children with cerebral palsy. Cyberpsychol. Behav., vol 9(2), pp , 26. [16] A. S. Merians, H. Poizner, R. Boian, G. Burdea, and S. Adamovich, Sensorimotor training in a virtual reality environment: Does it improve functional recovery poststroke? Neurorehab. Neur. Rep., vol. 2(2), pp , 26. [17] S. H. You, S. H. Jang, Y. H. Kim, M. Hallett, S. H. Ahn, and Y. H. Kwon, Virtual reality-induced cortical reorganization and associated locomotor recovery in chronic stroke An experimenter-blind randomized study. Stroke, vol. 36(6), pp , 25. [18] P. B. Butler, and R. E. Major, The learning of motor control. Biomechanical considerations. Physiotherapy, vol 78(1), pp. 1-6, [19] R. E. Major, G. R. Johnson, and P. B. Butler, Learning motor control in the upright position: A mechanical engineering approach. Proc. Inst. Of Mech. Eng., vol. 215, pp , 21. [2] M. M. Taylor, and C. D. Creelman, PEST: Efficient estimates on probability functions. J. Acoust. Soc. Am., vol. 41(4A), pp , [21] S. Saavedra, and M. H. Woollacott, Development of trunk control in typically developing children and children with cerebral palsy Proc. of meeting of the Collaborative Project on Developmental Neurology, Groningen, The Netherlands, pp [22] P. B. Butler, A preliminary report on the effectiveness of trunk targeting in achieving independent sitting balance in children with cerebral palsy. Clinical Rehabilitation, vol. 12(4), pp , [23] S. Saavedra, and M. H. Woollacott, Effects of segmental training on trunk control in children with neuromotor disability: a pilot study. Proc. of meeting of the Collaborative Project on Developmental Neurology, Groningen, The Netherlands, pp , 21.
The effects of virtual reality game training on trunk to pelvis coupling in a child with cerebral palsy
 Barton et al. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 2013, 10:15 JOURNAL OF NEUROENGINEERING JNERAND REHABILITATION RESEARCH Open Access The effects of virtual reality game training on trunk to
Barton et al. Journal of NeuroEngineering and Rehabilitation 2013, 10:15 JOURNAL OF NEUROENGINEERING JNERAND REHABILITATION RESEARCH Open Access The effects of virtual reality game training on trunk to
EVALUATION OF THE ANKLE ROLL GUARD S EFFECTIVENESS TO IMPROVE ITS CLINICAL BENEFIT PROGRESS REPORT. Prepared By:
 EVALUATION OF THE ANKLE ROLL GUARD S EFFECTIVENESS TO IMPROVE ITS CLINICAL BENEFIT PROGRESS REPORT Prepared By: Dr. Tyler Brown, Principal Investigator Wyatt Ihmels, Graduate Research Assistant Research
EVALUATION OF THE ANKLE ROLL GUARD S EFFECTIVENESS TO IMPROVE ITS CLINICAL BENEFIT PROGRESS REPORT Prepared By: Dr. Tyler Brown, Principal Investigator Wyatt Ihmels, Graduate Research Assistant Research
BIOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF THE DEADLIFT DURING THE 1999 SPECIAL OLYMPICS WORLD GAMES
 63 Biomechanics Symposia 2001 / University of San Francisco BIOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF THE DEADLIFT DURING THE 1999 SPECIAL OLYMPICS WORLD GAMES Rafael F. Escamilla, Tracy M. Lowry, Daryl C. Osbahr, and
63 Biomechanics Symposia 2001 / University of San Francisco BIOMECHANICAL ANALYSIS OF THE DEADLIFT DURING THE 1999 SPECIAL OLYMPICS WORLD GAMES Rafael F. Escamilla, Tracy M. Lowry, Daryl C. Osbahr, and
PHYSICAL PROFILING FOR GOLF. PAUL DARBY Chartered Physiotherapist And Golf Conditioning Consultant
 PHYSICAL PROFILING FOR GOLF PAUL DARBY Chartered Physiotherapist And Golf Conditioning Consultant Components of the Elite Athlete Physiological Flexibility, Strength & Power Control of Movement Technical
PHYSICAL PROFILING FOR GOLF PAUL DARBY Chartered Physiotherapist And Golf Conditioning Consultant Components of the Elite Athlete Physiological Flexibility, Strength & Power Control of Movement Technical
VIPR and Power plate EXERCISE - 1 EXERCISE Fitness Professionals Ltd 2011 Job No. 2968
 FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
FIT FOR DAILY LIFE To be fit for daily life includes many movement abilities. Dynamic stability, co-ordination, balance, motor control, mobility and efficiency are all vital (including basic strength and
A Pilot Evaluation of the Practicality 1. A Pilot Evaluation of the Practicality of the Surrey Virtual Rehabilitation System: Perspectives from
 A Pilot Evaluation of the Practicality 1 A Pilot Evaluation of the Practicality of the Surrey Virtual Rehabilitation System: Perspectives from End-Users A Pilot Evaluation of the Practicality 2 Abstract
A Pilot Evaluation of the Practicality 1 A Pilot Evaluation of the Practicality of the Surrey Virtual Rehabilitation System: Perspectives from End-Users A Pilot Evaluation of the Practicality 2 Abstract
Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine
 Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine Pavel Kolá!, 1996 Dpt. of Rehabilitation, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic (Czech Journal of Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy)
Importance of Developmental Kinesiology for Manual Medicine Pavel Kolá!, 1996 Dpt. of Rehabilitation, University Hospital Motol, Prague, Czech Republic (Czech Journal of Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy)
Journal of Biomechanics
 Journal of Biomechanics 43 (2010) 2648 2652 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Biomechanics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jbiomech www.jbiomech.com Short communication All
Journal of Biomechanics 43 (2010) 2648 2652 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Biomechanics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jbiomech www.jbiomech.com Short communication All
The influence of forefoot binding force change on vertical jump kinematics variation
 Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(2):554-558 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The influence of forefoot binding force change on
Available online www.jocpr.com Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research, 2014, 6(2):554-558 Research Article ISSN : 0975-7384 CODEN(USA) : JCPRC5 The influence of forefoot binding force change on
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018
 Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Lecture 2. Statics & Dynamics of Rigid Bodies: Human body 30 August 2018 Wannapong Triampo, Ph.D. Static forces of Human Body Equilibrium and Stability Stability of bodies. Equilibrium and Stability Fulcrum
Multi-Segmental Rotation Corrective Exercises
 Multi-Segmental Rotation Corrective Exercises Side Lying Thoracic Rotation keep one knee on a folded pillow or small ball with the hip flexed at least 90 degrees. Place the hand on the stomach/ribs and
Multi-Segmental Rotation Corrective Exercises Side Lying Thoracic Rotation keep one knee on a folded pillow or small ball with the hip flexed at least 90 degrees. Place the hand on the stomach/ribs and
Realtà virtuale: l esperienza dell IRCCS Medea
 Emilia Biffi Realtà virtuale: l esperienza dell IRCCS Medea Emilia Biffi, C. Maghini, E. Beretta, E. Diella, D. Panzeri, F. Brunati, M. Delle Fave, S. Strazzer, A.C. Turconi, G. Reni Scientific Institute
Emilia Biffi Realtà virtuale: l esperienza dell IRCCS Medea Emilia Biffi, C. Maghini, E. Beretta, E. Diella, D. Panzeri, F. Brunati, M. Delle Fave, S. Strazzer, A.C. Turconi, G. Reni Scientific Institute
EFFECT OF POSTURAL SWAY SCALE AS A PROGNOSTIC TOOL IN LOW BACK PAIN MANAGEMENT.
 Original Research Article Allied Science International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 EFFECT OF POSTURAL SWAY SCALE AS A PROGNOSTIC TOOL IN LOW BACK PAIN MANAGEMENT. 1 MANJULADEVI.NB.P.T,
Original Research Article Allied Science International Journal of Pharma and Bio Sciences ISSN 0975-6299 EFFECT OF POSTURAL SWAY SCALE AS A PROGNOSTIC TOOL IN LOW BACK PAIN MANAGEMENT. 1 MANJULADEVI.NB.P.T,
Accuracy and validity of Kinetisense joint measures for cardinal movements, compared to current experimental and clinical gold standards.
 Accuracy and validity of Kinetisense joint measures for cardinal movements, compared to current experimental and clinical gold standards. Prepared by Engineering and Human Performance Lab Department of
Accuracy and validity of Kinetisense joint measures for cardinal movements, compared to current experimental and clinical gold standards. Prepared by Engineering and Human Performance Lab Department of
FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist. Concept ENGSTRÖM
 FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist Starting with a few questions! How are your clients sitting? What kind of problems do you see? How long time are your clients
FUNDAMENTAL SEATING PRINCIPLES Power Point PDF Bengt Engström Physiotherapist Starting with a few questions! How are your clients sitting? What kind of problems do you see? How long time are your clients
Discrepancies in Knee Joint Moments Using Common Anatomical Frames Defined by Different Palpable Landmarks
 Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2008, 24, 185-190 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. Discrepancies in Knee Joint Moments Using Common Anatomical Frames Defined by Different Palpable Landmarks Dominic Thewlis,
Journal of Applied Biomechanics, 2008, 24, 185-190 2008 Human Kinetics, Inc. Discrepancies in Knee Joint Moments Using Common Anatomical Frames Defined by Different Palpable Landmarks Dominic Thewlis,
Effect of backward walking training on dynamic balance in children with spastic. hemiplegic cerebral palsy.
 Effect of backward walking training on dynamic balance in children with spastic hemiplegic cerebral palsy Yu-Jin Kim 1, Hyun-Ik Jang 2, Kum-Hee Ko 3, Woo-Nam Chang 4, Sun-Kyu Lim 5 1,2,3,4,5 Department
Effect of backward walking training on dynamic balance in children with spastic hemiplegic cerebral palsy Yu-Jin Kim 1, Hyun-Ik Jang 2, Kum-Hee Ko 3, Woo-Nam Chang 4, Sun-Kyu Lim 5 1,2,3,4,5 Department
In Vitro Analysis of! Foot and Ankle Kinematics:! Robotic Gait Simulation. William R. Ledoux
 In Vitro Analysis of! Foot and Ankle Kinematics:! Robotic Gait Simulation William R. Ledoux RR&D Center of Excellence for Limb Loss Prevention and Prosthetic Engineering, VA Puget Sound Departments of
In Vitro Analysis of! Foot and Ankle Kinematics:! Robotic Gait Simulation William R. Ledoux RR&D Center of Excellence for Limb Loss Prevention and Prosthetic Engineering, VA Puget Sound Departments of
Dave Juehring DC, DACRB Director Rehabilitation and Sport Injury Department and Rehabilitation Residency Palmer Chiropractic Clinics Davenport IA
 Dave Juehring DC, DACRB Director Rehabilitation and Sport Injury Department and Rehabilitation Residency Palmer Chiropractic Clinics Davenport IA Dynamic Neuromuscular Stability the Czech Approach to Stability
Dave Juehring DC, DACRB Director Rehabilitation and Sport Injury Department and Rehabilitation Residency Palmer Chiropractic Clinics Davenport IA Dynamic Neuromuscular Stability the Czech Approach to Stability
Evaluating Fundamental
 12 Locomotor Lab 12.1 Evaluating Fundamental Skills Purpose Practice in learning to observe and evaluate locomotor skills from video performance. Procedures Listed below are several websites showing children
12 Locomotor Lab 12.1 Evaluating Fundamental Skills Purpose Practice in learning to observe and evaluate locomotor skills from video performance. Procedures Listed below are several websites showing children
ORTOVOX NAKED SHEEP EXERCISES TRAINING SESSION 1
 TRAINING SESSION OPEN DOORS DESCRIPTION PICTURE PICTURE PICTURE COUCH STRETCH Bring your knee as close as possible to the wall and straighten upper body backward; you need to be able to activate your glutes
TRAINING SESSION OPEN DOORS DESCRIPTION PICTURE PICTURE PICTURE COUCH STRETCH Bring your knee as close as possible to the wall and straighten upper body backward; you need to be able to activate your glutes
ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL
 ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL page 1 INTRODUCTION The STOTT PILATES Athletic Conditioning stream serves as a bridge between STOTT PILATES standard repertoire and the CORE Athletic Conditioning
ATHLETIC CONDITIONING ON THE ARC BARREL page 1 INTRODUCTION The STOTT PILATES Athletic Conditioning stream serves as a bridge between STOTT PILATES standard repertoire and the CORE Athletic Conditioning
Issues in Cerebral Palsy Part 1: Physical Handling Assessment by Christine A. Nelson, Ph.D., OTR with contribution by W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR
 The following article is granted 1 Contact Hour/ equivalent to.15 CEU/equivalent to 1.25 PDUs. To receive CEU credit you must complete the CEU Exam after reading the article. Close the PDF file after reading
The following article is granted 1 Contact Hour/ equivalent to.15 CEU/equivalent to 1.25 PDUs. To receive CEU credit you must complete the CEU Exam after reading the article. Close the PDF file after reading
Normal development & reflex
 Normal development & reflex Definition of Development : acquisition & refinement of skills 1 대근육운동발달 2 소근육운동발달 3 대인관계및사회성발달 4 적응능력혹은비언어성발달 5 의사소통및언어발달 6 학습, 청각, 시각의발달 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,
Normal development & reflex Definition of Development : acquisition & refinement of skills 1 대근육운동발달 2 소근육운동발달 3 대인관계및사회성발달 4 적응능력혹은비언어성발달 5 의사소통및언어발달 6 학습, 청각, 시각의발달 Department of Rehabilitation Medicine,
The Female Athlete: Train Like a Girl. Sarah DoBroka Wilson, PT, SCS Ron Weathers, PT, DPT, ATC, LAT
 The Female Athlete: Train Like a Girl Sarah DoBroka Wilson, PT, SCS Ron Weathers, PT, DPT, ATC, LAT Page 1 of 6 The Female Athlete: Train Like a Girl Sarah DoBroka Wilson PT, SCS Ron Weathers PT, DPT,
The Female Athlete: Train Like a Girl Sarah DoBroka Wilson, PT, SCS Ron Weathers, PT, DPT, ATC, LAT Page 1 of 6 The Female Athlete: Train Like a Girl Sarah DoBroka Wilson PT, SCS Ron Weathers PT, DPT,
ebavir, easy Balance Virtual Rehabilitation system: a study with patients
 ebavir, easy Balance Virtual Rehabilitation system: a study with patients M. González-Fernández 1, José-Antonio Gil-Gómez 1, M. Alcañiz 1, E. Noé 2, C. Colomer 2 1 Instituto Interuniversitario de Investigación
ebavir, easy Balance Virtual Rehabilitation system: a study with patients M. González-Fernández 1, José-Antonio Gil-Gómez 1, M. Alcañiz 1, E. Noé 2, C. Colomer 2 1 Instituto Interuniversitario de Investigación
3 Moves To Improve Your Lifts
 1 Each lift has three exercises outlined to help you perform at your best. Muscle strength, endurance and stability are taken into account and serves as a guide to help coordinate all of your systems.
1 Each lift has three exercises outlined to help you perform at your best. Muscle strength, endurance and stability are taken into account and serves as a guide to help coordinate all of your systems.
Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization
 Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization A Criteria-Based Reference Format for Observing & Analyzing Motor Behavior in Children with Learning Disabilities By W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR 3 R D E D I T
Evaluating Movement Posture Disorganization A Criteria-Based Reference Format for Observing & Analyzing Motor Behavior in Children with Learning Disabilities By W. Michael Magrun, MS, OTR 3 R D E D I T
Forskning inden for truncus postural kontrol. CPOP DAG 22. maj What difference does trunk postural control make to function?
 Forskning inden for truncus postural kontrol CPOP DAG 22. maj 2014 Derek Curtis PT MSc Phd stud. Hvidovre Hospital Københavns Universitet What difference does trunk postural control make to function? Clinical
Forskning inden for truncus postural kontrol CPOP DAG 22. maj 2014 Derek Curtis PT MSc Phd stud. Hvidovre Hospital Københavns Universitet What difference does trunk postural control make to function? Clinical
ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation Protocol
 ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation Protocol 1. Pre-OP Visit: a. Patient Education b. Exercises c. Gait Outline rehabilitation timeline. Discuss: Swelling/effusion control (PRICE). Quadriceps inhibition
ACL Reconstruction Rehabilitation Protocol 1. Pre-OP Visit: a. Patient Education b. Exercises c. Gait Outline rehabilitation timeline. Discuss: Swelling/effusion control (PRICE). Quadriceps inhibition
2017 COS ANNUAL MEETING AND EXHIBITION HOME EXERCISES
 UPPER BODY Push Up From a push up position. Lower whole body down to floor. Press up to return to start position. Maintain abdominal hollow and neutral spinal alignment throughout movement. Note: Perform
UPPER BODY Push Up From a push up position. Lower whole body down to floor. Press up to return to start position. Maintain abdominal hollow and neutral spinal alignment throughout movement. Note: Perform
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK
 ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
ACE s Essentials of Exercise Science for Fitness Professionals TRUNK Posture and Balance Posture refers to the biomechanical alignment of the individual body parts and the orientation of the body to the
Design and Implementation study of Remote Home Rehabilitation Training Operating System based on Internet
 IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Design and Implementation study of Remote Home Rehabilitation Training Operating System based on Internet To cite this article:
IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering PAPER OPEN ACCESS Design and Implementation study of Remote Home Rehabilitation Training Operating System based on Internet To cite this article:
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001)
 Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
Functional Movement Screen (Cook, 2001) TEST 1 DEEP SQUAT Purpose - The Deep Squat is used to assess bilateral, symmetrical, mobility of the hips, knees, and ankles. The dowel held overhead assesses bilateral,
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics. ECE 370 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering. Principles of Biomechanics
 University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics ECE 370 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Principles of Biomechanics Introduction What is Biomechanics? The study of internal and external
University of Cyprus Biomedical Imaging and Applied Optics ECE 370 Introduction to Biomedical Engineering Principles of Biomechanics Introduction What is Biomechanics? The study of internal and external
POSTERIOR 1. situated behind: situated at or toward the hind part of the body :
 ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
ANATOMICAL LOCATION Anatomy is a difficult subject with a large component of memorization. There is just no way around that, but we have made every effort to make this course diverse and fun. The first
A marker set for measuring the kinematics of the lumbar spine and thoracic spine during running : a technical note
 A marker set for measuring the kinematics of the lumbar spine and thoracic spine during running : a technical note Preece, SJ, Bramah, C and Mason, D 10.14198/jhse.2016.113.07 Title Authors Type URL A
A marker set for measuring the kinematics of the lumbar spine and thoracic spine during running : a technical note Preece, SJ, Bramah, C and Mason, D 10.14198/jhse.2016.113.07 Title Authors Type URL A
Do the same as above, but turn your head TOWARDS the side that you re holding on to the chair.
 Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Stretch 4-6 times per day and hold each stretch for a minimum of 30 seconds. Perform the stretch gently without bouncing. Discuss any problems with your Chiropractor. Sit upright with your head and shoulder
Gait Assessment & Implications in Geriatric Rehabilitation
 Gait Assessment & Implications in Geriatric Rehabilitation Therapy Network Seminars, Inc. Nicole Dawson, PT, PhD, GCS Learning Objectives Following completion of this webinar, participants will be able
Gait Assessment & Implications in Geriatric Rehabilitation Therapy Network Seminars, Inc. Nicole Dawson, PT, PhD, GCS Learning Objectives Following completion of this webinar, participants will be able
Somatic Adaptation in Cerebral Palsy LINKING ASSESSMENT WITH TREATMENT: AN NDT PERSPECTIVE. By W. Michael Magrun, M.S., OTR/L
 Somatic Adaptation in Cerebral Palsy LINKING ASSESSMENT WITH TREATMENT: AN NDT PERSPECTIVE By W. Michael Magrun, M.S., OTR/L INTRODUCTION Somatic adaptation is one of the primary functions of the central
Somatic Adaptation in Cerebral Palsy LINKING ASSESSMENT WITH TREATMENT: AN NDT PERSPECTIVE By W. Michael Magrun, M.S., OTR/L INTRODUCTION Somatic adaptation is one of the primary functions of the central
What is Kinesiology? Basic Biomechanics. Mechanics
 What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
What is Kinesiology? The study of movement, but this definition is too broad Brings together anatomy, physiology, physics, geometry and relates them to human movement Lippert pg 3 Basic Biomechanics the
REHABILITATION IN VIRTUAL REALITY VAST.REHAB IS DESIGNED FOR PHYSICAL, OCCUPATIONAL AND COGNITIVE THERAPY
 VAST.REHAB IS DESIGNED FOR PHYSICAL, OCCUPATIONAL AND COGNITIVE THERAPY We create a fully-featured virtual reality exercise and diagnostic system with the flexibility to work for everyone from small physiotherapy
VAST.REHAB IS DESIGNED FOR PHYSICAL, OCCUPATIONAL AND COGNITIVE THERAPY We create a fully-featured virtual reality exercise and diagnostic system with the flexibility to work for everyone from small physiotherapy
What is Hippotherapy
 HIPPOTHERAPY Mission Statement Angel Paths mission is to improve the body, mind and spirits of individuals with physical and mental disabilities through high-quality therapeutic programs, specializing
HIPPOTHERAPY Mission Statement Angel Paths mission is to improve the body, mind and spirits of individuals with physical and mental disabilities through high-quality therapeutic programs, specializing
GLOSSARY. Active assisted movement: movement where the actions are assisted by an outside force.
 GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
GLOSSARY The technical words used in this guide are listed here in alphabetic order. The first time one of these words is used in the guide, it is written in italics. Sometimes there is reference to a
INCLUDES EXERCISES! EXERCISE MANUAL
 INCLUDES 20 EXERCISES! EXERCISE MANUAL INTRODUCTION We proudly present the unique designed software to benefit patient satisfaction and motivation, functional improvement of disabilities and impairments.
INCLUDES 20 EXERCISES! EXERCISE MANUAL INTRODUCTION We proudly present the unique designed software to benefit patient satisfaction and motivation, functional improvement of disabilities and impairments.
Balance Rehabilitation Through Virtual Environments
 State of the Science Symposia Series Virtual Reality Applications for Advancing Rehabilitation April 14, 2017 Balance Rehabilitation Through Virtual Environments Dr. Emily A. Keshner Professor and Chair,
State of the Science Symposia Series Virtual Reality Applications for Advancing Rehabilitation April 14, 2017 Balance Rehabilitation Through Virtual Environments Dr. Emily A. Keshner Professor and Chair,
Chia-Wei Lin, Fong-Chin Su Institute of Biomedical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University Cheng-Feng Lin Department of Physical Therapy,
 Chia-Wei Lin, Fong-Chin Su Institute of Biomedical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University Cheng-Feng Lin Department of Physical Therapy, National Cheng Kung University Turning movements are common
Chia-Wei Lin, Fong-Chin Su Institute of Biomedical Engineering, National Cheng Kung University Cheng-Feng Lin Department of Physical Therapy, National Cheng Kung University Turning movements are common
Summary Chart 1 2 months
 NEWBORN Physiological flexion provides stability for posture & random movements Neck righting Labyrinthine righting beginning in prone & supine Primary standing reaction Movements limited by available
NEWBORN Physiological flexion provides stability for posture & random movements Neck righting Labyrinthine righting beginning in prone & supine Primary standing reaction Movements limited by available
6.4 The Ankle. Body Divided into Planes. Health Services: Unit 6 Arms and Legs. Body Movement Vocabulary
 6.4 The Ankle Body Movement Vocabulary When fitness professionals refer to movement of the body, the pattern of movement is described from the anatomical position This position can best be described as
6.4 The Ankle Body Movement Vocabulary When fitness professionals refer to movement of the body, the pattern of movement is described from the anatomical position This position can best be described as
Investigation of Human Whole Body Motion Using a Three-Dimensional Neuromusculoskeletal Model
 Investigation of Human Whole Body Motion Using a Three-Dimensional Neuromusculoskeletal Model 1 Akinori Nagano, 2 Senshi Fukashiro, 1 Ryutaro Himeno a-nagano@riken.jp, fukashiro@idaten.c.u-tokyo.ac.jp,
Investigation of Human Whole Body Motion Using a Three-Dimensional Neuromusculoskeletal Model 1 Akinori Nagano, 2 Senshi Fukashiro, 1 Ryutaro Himeno a-nagano@riken.jp, fukashiro@idaten.c.u-tokyo.ac.jp,
General appearance examination
 Childhood athletic participation has dramatically increased over the past twenty years. Children are being introduced to organised sports at increasingly immature stages of physical development. It is
Childhood athletic participation has dramatically increased over the past twenty years. Children are being introduced to organised sports at increasingly immature stages of physical development. It is
Ways to make sure you achieve your handstand
 Ways to make sure you achieve your handstand What no one tells you about Lay Yong Copyright BodyTree GST Copyright 2015 2015 BodyTree GST Pte LtdPte Ltd Introduction The handstand is a challenging and
Ways to make sure you achieve your handstand What no one tells you about Lay Yong Copyright BodyTree GST Copyright 2015 2015 BodyTree GST Pte LtdPte Ltd Introduction The handstand is a challenging and
S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R
 S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R P O S T O P E R A T I V E H I P M A I N T E N A N C E P R O G R A M -This program provides an ongoing rehab program that
S p o r t s & O r t h o p a e d i c S p e c i a l i s t s D R. R Y A N F A D E R P O S T O P E R A T I V E H I P M A I N T E N A N C E P R O G R A M -This program provides an ongoing rehab program that
Movement System Diagnoses. Movement System Impairment Syndromes of the Lumbar Spine. MSI Syndrome - Assumptions. Return From Forward Bending
 Movement System Diagnoses Kinesiopathologic Pathokinesiologic Movement System Impairment Syndromes of the Lumbar Spine Shirley Sahrmann, PT, PhD, FAPTA Washington University St. Louis School of Medicine
Movement System Diagnoses Kinesiopathologic Pathokinesiologic Movement System Impairment Syndromes of the Lumbar Spine Shirley Sahrmann, PT, PhD, FAPTA Washington University St. Louis School of Medicine
Andrew J Murphy
 FISA World Rowing Coaches Conference 2-23 January 211 Setting the scene Key Performance Indicators for Rowing, PhD Biomechanics Kinematics External forces Anthony MJ Bull Alison H McGregor Imperial College
FISA World Rowing Coaches Conference 2-23 January 211 Setting the scene Key Performance Indicators for Rowing, PhD Biomechanics Kinematics External forces Anthony MJ Bull Alison H McGregor Imperial College
Dynamic Trunk Control Influence on Run-to-Cut Maneuver: A Risk Factor for ACL Rupture
 Dynamic Trunk Control Influence on Run-to-Cut Maneuver: A Risk Factor for ACL Rupture By: Steve Jamison 1 INTRODUCTION Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture is one of the most common knee injuries for
Dynamic Trunk Control Influence on Run-to-Cut Maneuver: A Risk Factor for ACL Rupture By: Steve Jamison 1 INTRODUCTION Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) rupture is one of the most common knee injuries for
Lower Your Handicap Pilates for Golfers
 Lower Your Handicap Pilates for Golfers Cindy Sankhagowit July 20, 2014 CTTC 2014 Portland, OR Abstract To improve one s golf game means shooting a lower score, thereby lowering your handicap. A golf swing
Lower Your Handicap Pilates for Golfers Cindy Sankhagowit July 20, 2014 CTTC 2014 Portland, OR Abstract To improve one s golf game means shooting a lower score, thereby lowering your handicap. A golf swing
 1 of 8 9/21/2006 1:02 PM Smith College Dept. of Athletics Program for The Average Division III Female Athlete Trainer : Timothy Bacon Introduction Core, functional and complementary exercises. Warm Up
1 of 8 9/21/2006 1:02 PM Smith College Dept. of Athletics Program for The Average Division III Female Athlete Trainer : Timothy Bacon Introduction Core, functional and complementary exercises. Warm Up
NZQA Expiring unit standard 7026 version 4 Page 1 of 7. Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics
 Page 1 of 7 Title Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics Level 5 Credits 5 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: apply knowledge of human anatomy relevant to exercise
Page 1 of 7 Title Apply knowledge of functional anatomy and biomechanics Level 5 Credits 5 Purpose People credited with this unit standard are able to: apply knowledge of human anatomy relevant to exercise
Wheelchair Seating: Are We Speaking the Same Language?
 Universal Language Wheelchair Seating: Are We Speaking the Same Language? Andrée Gauthier, OT Reg. (Ont.) Seating Clinic, Lyndhurst Centre Toronto Rehab Institute University Health Network andree.gauthier@uhn.ca
Universal Language Wheelchair Seating: Are We Speaking the Same Language? Andrée Gauthier, OT Reg. (Ont.) Seating Clinic, Lyndhurst Centre Toronto Rehab Institute University Health Network andree.gauthier@uhn.ca
Optic flow in a virtual environment can impact on locomotor steering post stroke
 International Conference on Virtual Rehabilitation 2011 Rehab Week Zurich, ETH Zurich Science City, Switzerland, June 27-29, 2011 Optic flow in a virtual environment can impact on locomotor steering post
International Conference on Virtual Rehabilitation 2011 Rehab Week Zurich, ETH Zurich Science City, Switzerland, June 27-29, 2011 Optic flow in a virtual environment can impact on locomotor steering post
Active-Assisted Stretches
 1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
1 Active-Assisted Stretches Adequate flexibility is fundamental to a functional musculoskeletal system which represents the foundation of movement efficiency. Therefore a commitment toward appropriate
REMEMBER GOOD POSTURE DURING ALL YOUR EXERCISES, AVOID SLOUCHING AS YOUR CURRENT PROGRAM BECOMES EASY SLOWLY INCREASE:
 REMEMBER GOOD POSTURE DURING ALL YOUR EXERCISES, AVOID SLOUCHING Apr 06, 2017 AS YOUR CURRENT PROGRAM BECOMES EASY SLOWLY INCREASE: # OF LAPS YOU ARE WALKING # OF REPITITIONS # OF SECONDS YOU HOLD A STRETCH
REMEMBER GOOD POSTURE DURING ALL YOUR EXERCISES, AVOID SLOUCHING Apr 06, 2017 AS YOUR CURRENT PROGRAM BECOMES EASY SLOWLY INCREASE: # OF LAPS YOU ARE WALKING # OF REPITITIONS # OF SECONDS YOU HOLD A STRETCH
Your Autopilot: Is it efficient?
 374: MELT : Reintegration and Repatterning Series Time Block I - Saturday, 10:30am-12:20pm Presented by: Sue Hitzmann, MS, CST, NMT, Creator of MELT Session Format: Workshop Learn new tools to address
374: MELT : Reintegration and Repatterning Series Time Block I - Saturday, 10:30am-12:20pm Presented by: Sue Hitzmann, MS, CST, NMT, Creator of MELT Session Format: Workshop Learn new tools to address
One hundred and ten individuals participated in this study
 Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare gait characteristics in an asymptomatic population of younger and older adults to older OA patients of different severities Hypothesis(es) The following
Purpose The purpose of this study was to compare gait characteristics in an asymptomatic population of younger and older adults to older OA patients of different severities Hypothesis(es) The following
Low Back Pain Home Exercises
 Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Low Back Pain Home Exercises General Instructions The low back exercise program is a series of stretching exercises and strengthening exercises prescribed by your physician for your medical condition.
Functional Movement Test. Deep Squat
 Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Functional Movement Test Put simply, the FMS is a ranking and grading system that documents movement patterns that are key to normal function. By screening these patterns, the FMS readily identifies functional
Study protocol. Resistance versus Balance Training to improve postural control in Parkinson s disease
 Study protocol (English translation of the german study protocol; for the complete study protocol see german version) Resistance versus Balance Training to improve postural control in Parkinson s disease
Study protocol (English translation of the german study protocol; for the complete study protocol see german version) Resistance versus Balance Training to improve postural control in Parkinson s disease
FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT
 THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
THE WHITE HOUSE PHYSIOTHERAPY CLINIC PRESENT FIT IN LINE EXAMPLE REPORT (15/03/11) A 12 part assessment tool to screen your athletic performance in 4 key components: Flexibility, Balance, Strength & Core
Flexibility. STRETCH: Kneeling gastrocnemius. STRETCH: Standing gastrocnemius. STRETCH: Standing soleus. Adopt a press up position
 STRETCH: Kneeling gastrocnemius Adopt a press up position Rest one knee on mat with the opposite leg straight Maintain a neutral spine position Push through arms to lever ankle into increased dorsiflexion
STRETCH: Kneeling gastrocnemius Adopt a press up position Rest one knee on mat with the opposite leg straight Maintain a neutral spine position Push through arms to lever ankle into increased dorsiflexion
THE APPLICATION OF MOTION PATTERN RECOGNITION IN THE BEHAVIOMETRICS OF HUMAN KINEMATICS
 THE APPLICATION OF MOTION PATTERN RECOGNITION IN THE BEHAVIOMETRICS OF HUMAN KINEMATICS Andar Bagus Sriwarno Research Group of Human and Industrial Product, Industrial Design Section Faculty of Art and
THE APPLICATION OF MOTION PATTERN RECOGNITION IN THE BEHAVIOMETRICS OF HUMAN KINEMATICS Andar Bagus Sriwarno Research Group of Human and Industrial Product, Industrial Design Section Faculty of Art and
ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents
 ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents Susan Sigward PhD, PT, ATC Human Performance Laboratory University of Southern California 1 ACL Injury Season ending/ Career ending 82%
ACL Injury Prevention: Considerations for Children and Adolescents Susan Sigward PhD, PT, ATC Human Performance Laboratory University of Southern California 1 ACL Injury Season ending/ Career ending 82%
Shoulder Exercises. Wall Press Up with Gym Ball
 Shoulder Exercises The exercises listed below are part of a treatment regime for patients attending The Police Rehabilitation Centre. They are reproduced here as an aide memoire for those patients. The
Shoulder Exercises The exercises listed below are part of a treatment regime for patients attending The Police Rehabilitation Centre. They are reproduced here as an aide memoire for those patients. The
Erigo User Script 1. Erigo Background Information. 2. Intended use and indications
 Erigo User Script 1. Erigo Background Information The Erigo was developed in collaboration with the Spinal Cord Injury Center at the Balgrist University Hospital in Zurich, Switzerland and the Orthopaedic
Erigo User Script 1. Erigo Background Information The Erigo was developed in collaboration with the Spinal Cord Injury Center at the Balgrist University Hospital in Zurich, Switzerland and the Orthopaedic
Fitball and Pilates Unite Filex 2017
 Fitball and Pilates Unite Filex 2017 Lisa Westlake www.physicalbest.com Pilates, fitball and physiotherapy blend perfectly to fine tune movement and postural awareness and provide a focus on technique,
Fitball and Pilates Unite Filex 2017 Lisa Westlake www.physicalbest.com Pilates, fitball and physiotherapy blend perfectly to fine tune movement and postural awareness and provide a focus on technique,
What we ll cover... Two types of hamstring injury! What type of athletes tear hamstrings!
 What s'new'in'hamstring'strain' injury'prevention'&'rehabilitation? Craig Ranson PhD Programme Director MSc Sports & Exercise Medicine Cardiff Metropolitan University Wales Rugby Team Physiotherapist @craigarxl
What s'new'in'hamstring'strain' injury'prevention'&'rehabilitation? Craig Ranson PhD Programme Director MSc Sports & Exercise Medicine Cardiff Metropolitan University Wales Rugby Team Physiotherapist @craigarxl
Overview Functional Training
 Overview Functional Training Exercises with Therapist 1. Sitting 2. Standing up vs. Sitting down 3. Standing 4. Stance phase ( Static and dynamic ) 5. Swing phase 6. Gait Evaluation 7. Walking level ground
Overview Functional Training Exercises with Therapist 1. Sitting 2. Standing up vs. Sitting down 3. Standing 4. Stance phase ( Static and dynamic ) 5. Swing phase 6. Gait Evaluation 7. Walking level ground
Inside or Outside you can get it done
 Inside or Outside you can get it done April 21, 2008 An understanding of Strength The definition of strength usually pertains to an amount of force that can be produced maximally by muscles in a single
Inside or Outside you can get it done April 21, 2008 An understanding of Strength The definition of strength usually pertains to an amount of force that can be produced maximally by muscles in a single
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention. Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS
 ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
ACL and Knee Injury Prevention Presented by: Zach Kirkpatrick, PT, MPT, SCS ACL Anatomy ACL Mechanism of Injury Contact ACL Tear Noncontact ACL Tear ACL MOI and Pathology Common in young individual who
PILATES CONDITIONING FOR SURFERS
 PILATES CONDITIONING FOR SURFERS Michelle Hopper January 11, 2018 Body Arts and Science International Comprehensive Teacher Training Program 2013 Jen Pearlstein Oceanside CA ABSTRACT Modern surfing is
PILATES CONDITIONING FOR SURFERS Michelle Hopper January 11, 2018 Body Arts and Science International Comprehensive Teacher Training Program 2013 Jen Pearlstein Oceanside CA ABSTRACT Modern surfing is
Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint
 Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint Kellie McGeoy April 11 th, 2014 Aptos, CA 2013 1 Abstract: Endurance running is defined as any distance over 5 kilometers (3.1 miles)
Pilates for the Endurance Runner With Special Focus on the Hip Joint Kellie McGeoy April 11 th, 2014 Aptos, CA 2013 1 Abstract: Endurance running is defined as any distance over 5 kilometers (3.1 miles)
Jennifer L. Cook, MD
 Jennifer L. Cook, MD Florida Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Center 5243 Hanff Lane New Port Richey, FL 34652 Phone: (727)848-4249 Fax: (727) 841-8934 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE
Jennifer L. Cook, MD Florida Joint Replacement and Sports Medicine Center 5243 Hanff Lane New Port Richey, FL 34652 Phone: (727)848-4249 Fax: (727) 841-8934 ANTERIOR CRUCIATE LIGAMENT RECONSTRUCTION POST-OPERATIVE
Vibramoov NEUROREHABILITATION OF THE LOCOMOTOR SYSTEM THROUGH FUNCTIONAL PROPRIOCEPTIVE STIMULATION
 Vibramoov NEUROREHABILITATION OF THE LOCOMOTOR SYSTEM THROUGH FUNCTIONAL PROPRIOCEPTIVE STIMULATION Principe of action BRAIN ACTIVATION VIBRAMOOV REVOLUTIONIZES FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT THERAPY One of the main
Vibramoov NEUROREHABILITATION OF THE LOCOMOTOR SYSTEM THROUGH FUNCTIONAL PROPRIOCEPTIVE STIMULATION Principe of action BRAIN ACTIVATION VIBRAMOOV REVOLUTIONIZES FUNCTIONAL MOVEMENT THERAPY One of the main
REHABILITATION ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTER TECHNOLOGIES FOR CHILDREN WITH ORTHOPAEDIC DISABILITIES
 REHABILITATION ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTER ON TECHNOLOGIES FOR CHILDREN WITH ORTHOPAEDIC DISABILITIES Program Director: Gerald F. Harris, Ph.D., P.E Co-Director: Li-Qun Zhang, Ph.D. Rehabilitation Engineering
REHABILITATION ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTER ON TECHNOLOGIES FOR CHILDREN WITH ORTHOPAEDIC DISABILITIES Program Director: Gerald F. Harris, Ph.D., P.E Co-Director: Li-Qun Zhang, Ph.D. Rehabilitation Engineering
CHAPTER 11 UNIVERSITY OF DENVER
 CHAPTER 11 UNIVERSITY OF DENVER School of Engineering and Computer Science Department of Engineering 2390 S. York Street Denver, CO 80208 Principal Investigator: Kimberly E. Newman (303)871-3436 kinewman@du.edu
CHAPTER 11 UNIVERSITY OF DENVER School of Engineering and Computer Science Department of Engineering 2390 S. York Street Denver, CO 80208 Principal Investigator: Kimberly E. Newman (303)871-3436 kinewman@du.edu
DVRT Certification: Level 1 Written Exam
 DVRT Certification: Level 1 Written Exam 1. What is NOT a concept or training principle of the DVRT System? A. Addressing specific needs of the client. B. Mixing simplicity with complexity. C. Progressive
DVRT Certification: Level 1 Written Exam 1. What is NOT a concept or training principle of the DVRT System? A. Addressing specific needs of the client. B. Mixing simplicity with complexity. C. Progressive
This Manual is copyright under the Berne Convention. In terms of the Copyright Act 98 of 1978 no part of this leaflet may be reproduced or
 Basic Ball Exercise Manual Train your Core This Manual is copyright under the Berne Convention. In terms of the Copyright Act 98 of 1978 no part of this leaflet may be reproduced or transmitted in any
Basic Ball Exercise Manual Train your Core This Manual is copyright under the Berne Convention. In terms of the Copyright Act 98 of 1978 no part of this leaflet may be reproduced or transmitted in any
EXERCISES FOR AMPUTEES. Joanna Wojcik & Niki Marjerrison
 EXERCISES FOR AMPUTEES Joanna Wojcik & Niki Marjerrison Amputation A condition of disability resulting from the loss of one or more limbs 1.7 million people living with limb loss in the US (1 out of every
EXERCISES FOR AMPUTEES Joanna Wojcik & Niki Marjerrison Amputation A condition of disability resulting from the loss of one or more limbs 1.7 million people living with limb loss in the US (1 out of every
Older Adult Advanced
 Older Adult Advanced Older Adult - Advanced Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women above the age of 55, who have experience in exercise and are relatively fit. The workout includes
Older Adult Advanced Older Adult - Advanced Introduction This exercise routine is created for men and women above the age of 55, who have experience in exercise and are relatively fit. The workout includes
The core of the MIHP Think Tank message is based around Five (5) Key Facts About Your Body s Design:
 Lesson 1 THE FIVE KEY FACTS ABOUT YOUR BODY S DESIGN The design of the human body is so complete, so complex in its interrelationships, so prepared for its world of motion that it allows for its function
Lesson 1 THE FIVE KEY FACTS ABOUT YOUR BODY S DESIGN The design of the human body is so complete, so complex in its interrelationships, so prepared for its world of motion that it allows for its function
AQUATIC PHYSIOTHERAPY IN PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHIES: A REHABILITATIVE PROTOCOL
 AQUATIC PHYSIOTHERAPY IN PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHIES: A REHABILITATIVE PROTOCOL Ilaria Zivi, MD Department of Brain Injury and Parkinson Disease Rehabilitation Moriggia-Pelascini Hospital, Gravedona ed Uniti
AQUATIC PHYSIOTHERAPY IN PERIPHERAL NEUROPATHIES: A REHABILITATIVE PROTOCOL Ilaria Zivi, MD Department of Brain Injury and Parkinson Disease Rehabilitation Moriggia-Pelascini Hospital, Gravedona ed Uniti
Objectives_ Series II
 Interaction Between the Development of Posture Control and Executive Function of Attention (Reilly et. al 2008) Journal of Motor Behavior, Vol. 40, No. 2, 90 102 Objectives_ Series II Gain an understanding
Interaction Between the Development of Posture Control and Executive Function of Attention (Reilly et. al 2008) Journal of Motor Behavior, Vol. 40, No. 2, 90 102 Objectives_ Series II Gain an understanding
2002 Functional Design Systems
 1. Retro rehabilitation and training may have its greatest influence and power with consideration of the proprioceptive reaction. 2. We can transform our Retro/posterior analysis information into what
1. Retro rehabilitation and training may have its greatest influence and power with consideration of the proprioceptive reaction. 2. We can transform our Retro/posterior analysis information into what
Most Dangerous Man! FACTS ON STREGNTH. Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
 FACTS ON STREGNTH We lose strength as we age. Over a 5 year study, Men experienced a 16.1% loss of muscle torque (isometric strength) and women saw a 13.4% loss. (1) Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
FACTS ON STREGNTH We lose strength as we age. Over a 5 year study, Men experienced a 16.1% loss of muscle torque (isometric strength) and women saw a 13.4% loss. (1) Session #627 Functionally Fit Seniors
The High Jump. Terry VanLaningham Sacramento State. USTFCCCA National Convention
 The High Jump Terry VanLaningham Sacramento State USTFCCCA National Convention - 2014 Thank You! Boo for his friendship, mentorship and asking me to speak. Cliff Rovelto for his friendship, mentorship
The High Jump Terry VanLaningham Sacramento State USTFCCCA National Convention - 2014 Thank You! Boo for his friendship, mentorship and asking me to speak. Cliff Rovelto for his friendship, mentorship
Raymond Wiegand, D.C. Spine Rehabilitation Institute of Missouri
 2D Pattern matching of frontal plane radiograph to 3D model identifies structural and functional deficiencies of the spinal pelvic system in consideration of mechanical spine pain (AKA Spine distortion
2D Pattern matching of frontal plane radiograph to 3D model identifies structural and functional deficiencies of the spinal pelvic system in consideration of mechanical spine pain (AKA Spine distortion
Relationship between Body Core Stabilization and Athletic Function in. Football, Basketball and Swimming Athletes
 Relationship between Body Core Stabilization and Athletic Function in Football, Basketball and Swimming Athletes Fatemeh Pouya (Msc) 1, Farahnaz Ghaffarinejad (Msc) 2 1. Department of Anatomy, Kerman University
Relationship between Body Core Stabilization and Athletic Function in Football, Basketball and Swimming Athletes Fatemeh Pouya (Msc) 1, Farahnaz Ghaffarinejad (Msc) 2 1. Department of Anatomy, Kerman University
The Chailey Levels of Ability Assessment Charts
 The Chailey Levels of Ability Assessment Charts Assessment details NAME D.O.B. DIAGNOSIS DATE OF ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT CENTRE NAME OF ASSESSOR Notes CHAILEY HERITAGE CLINICAL SERVICES Beggars Wood Road
The Chailey Levels of Ability Assessment Charts Assessment details NAME D.O.B. DIAGNOSIS DATE OF ASSESSMENT ASSESSMENT CENTRE NAME OF ASSESSOR Notes CHAILEY HERITAGE CLINICAL SERVICES Beggars Wood Road
Managing the runner with knee OA
 Managing the runner with knee OA Dr Christian Barton PhD, Bphysio (Hon), MAPA, MCSP Sport and Exercise Medicine Research Centre, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Australia Clinical Director and Physiotherapist,
Managing the runner with knee OA Dr Christian Barton PhD, Bphysio (Hon), MAPA, MCSP Sport and Exercise Medicine Research Centre, La Trobe University, Melbourne, Australia Clinical Director and Physiotherapist,
BIOMECHANICS. Biomechanics - the application of mechanical laws to living structures, specifically to the locomotor system of the human body.
 1 BIOMECHANICS Biomechanics - the application of mechanical laws to living structures, specifically to the locomotor system of the human body. I. Uses of Biomechanical Analyses Improvement of sports skill
1 BIOMECHANICS Biomechanics - the application of mechanical laws to living structures, specifically to the locomotor system of the human body. I. Uses of Biomechanical Analyses Improvement of sports skill
