Unusual new signs of pneumothorax at lung ultrasound
|
|
|
- Ginger Malone
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unusual new signs of pneumothorax at lung ultrasound Volpicelli et al. Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10
2 Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 SHORT COMMUNICATION Open Access Unusual new signs of pneumothorax at lung ultrasound Giovanni Volpicelli 1*, Enrico Boero 1, Valerio Stefanone 1 and Enrico Storti 2 Abstract Background: The diagnosis of pneumothorax with a bedside lung ultrasound is a powerful methodology. The conventional lung ultrasound examination consists of a step-by-step procedure targeted towards the detection of four classic ultrasound signs, the lung sliding, the B lines, the lung point and the lung pulse. In most cases, a combination of these signs allows a safe diagnosis of pneumothorax. However, the widespread application of sonographic methodology in clinical practice has brought out unusual cases which raise new sonographic signs. The purpose of this article was to introduce some of these new signs that are described after the analysis of unusual and complex cases encountered during the clinical daily practice in an emergency department. Findings: The double lung point consists of the alternating patterns of sliding and non-sliding lung intermittently appearing at the two opposite sides of the scan. The septate pneumothorax allows B lines and lung pulse to be still visible in a condition of pneumothorax with absent sliding. In hydropneumothorax, the air/fluid border is imaged by lung ultrasound as the interposition between an anechoic space and a non-sliding A-pattern, a sign that may be named hydro-point. Conclusions: In bedside lung ultrasound, the operator should be aware and interpret double lung point, septate pneumothorax and hydro-point. The conventional diagnostic protocol of bedside lung ultrasound for pneumothorax should be occasionally adapted to such complex cases. Keywords: Emergency ultrasound; Critical ultrasound; Lung ultrasound; Pneumothorax Findings Introduction Lung ultrasound is nowadays acknowledged as a useful methodology for the diagnosis of pneumothorax at bedside [1]. The diagnostic value of the sonographic signs of pneumothorax is similar to the well-known and largely used radiologic signs of the same condition in chest radiography. Visualization of a gap between the parietal and visceral pleura in a chest film is largely used, and intuitively diagnostic of pneumothorax, even though, to our knowledge there are no published studies specifically designed to evaluate its specificity in comparison with a gold standard. Nevertheless, there is not any doubt about the power and high specificity of this radiologic sign of pneumothorax. Similarly, the sonographic signs of pneumothorax are largely intuitive of the condition and share the same very high specificity with the radiologic signs [2,3]. Absence of * Correspondence: gio.volpicelli@tin.it 1 Emergency Medicine, San Luigi Gonzaga University Hospital, Turin 10043, Italy Full list of author information is available at the end of the article lung sliding or pulse and absence of B lines combined with a lung point during a lung ultrasound examination have the same diagnostic meaning of the visualization of a pleural gap in a chest radiography. However, whereas chest radiography is a conventional method, lung ultrasound needed to break the wall of scientific prejudices before it was acknowledged as a viable method for a neumothorax diagnosis. This is the reason why many years and clinical studies were needed to change clinical guidelines and protocols and finally introduce bedside lung ultrasound in clinical practice. We cannot say anything unless this process has been completed. The need for a widespread use of lung ultrasound is compelling. If it is true, as it has been proven, that thespecificityofachestradiographyisashighasalung ultrasound, it is also true that many studies showed that sensitivity of lung ultrasound is far higher [1,4-6]. The category of radio-occult pneumothorax is part of the daily experience of any physician who faces trauma patients, post-procedural thoracic complications and spontaneous pneumothoraces Volpicelli et al.; licensee Springer. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License ( which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
3 Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 Sonographic diagnosis of pneumothorax The bedside lung ultrasound diagnostic methodology for pneumothorax has been described in literature. A recent consensus process of the main experts in the field has led to the approval of a step-by-step methodology that consists of combining the four main sonographic signs of pneumothorax: the lung sliding, the lung pulse, the B lines and the lung point [1]. While the first three signs are strongly predictive of the absence of the condition, the lung point is the only sign that confirms a pneumothorax. However, the value of this general rule varies if we consider different settings and scenarios. In the stable patient, the conventional methodology consists of scanning the most superior aspect of the chest with respect to gravity, bilaterally. In the supine patient, this area corresponds to the anterior-inferior chest. The probe should be applied on this area, on both sides. Detection of lung sliding and/or B lines is enough to conclude the examination and rule-out pneumothorax. Absence of sliding and B lines need to be confirmed by moving the probe towards the lateral chest to visualize the lung point. If the latter is detected, then the examination is concluded and the pneumothorax is diagnosed with an extremely high specificity. When the lung point cannot be detected, then absence of a lung pulse should also be checked. In this condition, absence of even the slightest pulsation of the subpleural lung image allows the diagnosis of a pneumothorax characterized by a complete pulmonary collapse. Conversely, even in the absence of sliding and B lines, visualization of a lung pulse rules out pneumothorax. In the unstable patient or in a scenario of cardiac arrest, the methodology varies slightly. The most superior area of the chest is scanned for any sliding, pulse and B lines Page 2 of 4 bilaterally. Absence of these three signs is enough to conclude the diagnostic process and move to an immediate lifesaving invasive treatment. Faced with these extreme emergencies, there is no need to waste any more time checking for the presence of a lung point, because visualization of this latter sign would not change our decision to drain. Indeed, if we do not detect a lung point, then a tension pneumothorax is the diagnosis and we should treat it in the immediate; if we visualize a lung point in any part of the chest, the pneumothorax needs to be treated anyway. Instead, visualization of even one among sliding, pulse or B lines allows ruling out pneumothorax as the cause of the clinical storm. The procedure described so far is generally accepted and widely applied. However, there are some exceptions that should be always considered and known by the operators. These conditions represent sonographic challenges and may be indicated in the category of complex pneumothorax. Sonographic signs of complex pneumothorax Double lung point: when for some reason the air of a pneumothorax is not free to float inside the pleural space, a minimal amount of pleural air may remain in the lateral or dorsal chest without migrating in the most superior area in a supine patient, which corresponds to the anterior-inferior chest zone. In this case, the operator may visualize two lung points, i.e. the alternating patterns of sliding and non-sliding lung intermittently appearing at the two opposite sides of the scan (Additional file 1) [7,8]. These two lung points represent the visualization of the two edges of the air trapped in the pleural space (Figure 1). Pneumothorax with air trapping may be caused not only by pleural adherences in chronic pleural and pulmonary diseases but also by acute lung contusions in blunt torso Figure 1 Visualization of the two edges of the air trapped in the pleural space.
4 Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 Page 3 of 4 trauma [9]. Even without abnormal pleural adherences, very small spontaneous pneumothoraces may not have enough pressure to allow complete detachment of the pleural layers and the floating of air towards the most superior chest areas [7]. Being aware of this condition or in case of strong suspicion, the operator should always complete the scan of the lateral chest in the supine patient to confirm lung siding even when this latter is first visualized in the parasternal anterior-inferior chest. In the unstable patient, this extension of the technique is less important. Presence of lung sliding in the anterior-inferior chest may conclude the ultrasound examination, unless the patient is intubated for pressure ventilation or is going to be transported by helicopter [10]. In these two latter cases, the lateral chest should always be scanned to rule out even the smallest pneumothorax that may need to be monitored or warrant prophylactic drainage. Septate pneumothorax: recurrent pneumothoraces after invasive therapeutic procedures are often characterized by abnormal ultrasound findings. In patients with failed pleurodesis, it is quite common to observe the typical ultrasound pattern of septate pneumothorax [11]. In this case, the absence of sliding may be combined with the persistence of B lines and lung pulse in the same scan (Additional file 2). While, in the majority of patients, visualization of B lines and lung pulse rules out pneumothorax, there are rare cases where the negative predictive power of B lines and lung pulse may be misleading. In the context of absent lung sliding, the small areas showing B lines and lung pulse correspond to small lung regions where the parietal and visceral pleura are still touching due to the presence of septa (Figure 2). Demonstration of a lung point in other areas of the chest is a decisive step to conclude the examination and diagnose pneumothorax. A sonographic pattern that combines an absence of lung sliding but presence of B lines and/or lung pulse with presence of a lung point is diagnostic of septate pneumothorax. Hydropneumothorax: iatrogenic pneumothorax following procedures of thoracentesis in pleural effusion is a well known complication. While interposition between the normally aerated lung and pneumothorax (air/air interface) is demonstrated in a lung ultrasound by the lung point sign, air/fluid interface in the pleural space gives a different sonographic pattern. In hydropneumothorax, the pleural effusion is demonstrated by the visualization of space, usually anechoic, between the two pleural layers while pneumothorax gives the well-known A pattern, i.e. the reverberation of the chest wall image below the pleural line with A lines, absence of sliding or pulse and absence of B lines (Additional file 3). Opposition between these two patterns is the hydro-point (Figure 3). This recently described sonographic sign shares the same diagnostic power with the lung point for the diagnosis of pneumothorax [12]. Conclusion Lung ultrasound is rapidly spreading as a safe bedside methodology for the diagnosis of pneumothorax in different settings. Because of its increasing use in the clinical practice, observations of some unusual and complicated cases are also emerging. The conventional step-by-step sonographic technique and the four conventional ultrasound signs of pneumothorax should be slightly modified Figure 2 The small areas showing B lines and lung pulse correspond to small pleural adherences. Figure 3 Opposition between the air/fluid patterns is the hydro-point.
5 Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 Page 4 of 4 to consider the possibility of facing complex cases. Complicated pneumothorax may be encountered in many different settings, such as trauma patients, spontaneous pneumothorax, recurrent pneumothorax after pleurodesis and post-procedural pneumothorax. The operator should be aware and know how to interpret unusual sonographic signs and patterns, such as the double lung point, the septate pneumothorax and the hydro-point. Additional files Additional file 1: The double lung point: video shows the alternating patterns of sliding and non-sliding lung intermittently appearing at the two opposite sides of the scan. This pattern represents the visualization of the two edges of the air trapped in the pleural space. Additional file 2: Septate pneumothorax: video shows presence of B lines and lung pulse in a condition of absence of lung sliding. The areas where B lines and pulse are still visible correspond to small lung regions where the parietal and visceral pleura are still touching due to the presence of septa. Additional file 3: Hydropneumothorax: video shows the interposition between a fluid filled anechoic space and the lung non-sliding A-pattern. This sign is the hydro-point and has the same meaning of the lung point. 8. Volpicelli G, Audino B (2011) The double lung point: an unusual sonographic sign of juvenile spontaneous pneumothorax. Am J Emerg Med 29(3):355. e Soldati G, Sher S, Copetti R (2010) If you see the contusion, there is no pneumothorax. Am J Emerg Med 28(1): Kirkpatrick AW, Rizoli S, Ouellet JF, Roberts DJ, Sirois M, Ball CG, Xiao ZJ, Tiruta C, Meade M, Trottier V, Zhu G, Chagnon F, Tien H, Canadian Trauma Trials Collaborative and the Research Committee of the Trauma Association of Canada (2013) Occult pneumothoraces in critical care: a prospective multicenter randomized controlled trial of pleural drainage for mechanically ventilated trauma patients with occult pneumothoraces. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 74(3): Volpicelli G, Garofalo G, Lamorte A, Frascisco MF (2012) Images in emergency medicine. Young man with left thoracic pain. Recurrent pneumothorax after failed pleurodesis. Ann Emerg Med 60(2):e3 e4 12. Volpicelli G, Lamorte A, Tullio M, Boero E, Stefanone V (2013) Worsening dyspnea and cough following thoracentesis. Chest 144(2):e1 e3 doi: / Cite this article as: Volpicelli et al.: Unusual new signs of pneumothorax at lung ultrasound. Critical Ultrasound Journal :10. Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests. Authors contributions GV observed the cases and collected the videos, conceived and wrote the manuscript. EB, VS and ES contributed to collect the videos and to write the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript. Author details 1 Emergency Medicine, San Luigi Gonzaga University Hospital, Turin 10043, Italy. 2 Intensive Care Unit, Niguarda Ca Granda Hospital, Milan 20162, Italy. Received: 11 June 2013 Accepted: 10 December 2013 Published: 19 December 2013 References 1. Volpicelli G, Elbarbary M, Blaivas M, Lichtenstein DA, Mathis G, Kirkpatrick AW, Melniker L, Gargani L, Noble VE, Via G, Dean A, Tsung JW, Soldati G, Copetti R, Bouhemad B, Reissig A, Agricola E, Rouby JJ, Arbelot C, Liteplo A, Sargsyan A, Silva F, Hoppmann R, Breitkreutz R, Seibel A, Neri L, Storti E, Petrovic T, International Liaison Committee on Lung Ultrasound for International Consensus Conference on Lung Ultrasound (2012) International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med 38(4): Lichtenstein DA (2007) Ultrasound in the management of thoracic disease. Crit Care Med 35(5 Suppl):S250 S Volpicelli G (2011) Sonographic diagnosis of pneumothorax. Intensive Care Med 37(2): Lichtenstein DA, Meziere G, Lascols N, Biderman P, Courret JP, Gepner A, Goldstein I, Tenoudji-Cohen M (2005) Ultrasound diagnosis of occult pneumothorax. Crit Care Med 33(6): Reissig A, Kroegel C (2005) Accuracy of transthoracic sonography in excluding post-interventional pneumothorax and hydropneumothorax. Comparison to chest radiography. Eur J Radiol 53(3): Soldati G, Testa A, Sher S, Pignataro G, La Sala M, Silveri NG (2008) Occult traumatic pneumothorax: diagnostic accuracy of lung ultrasonography in the emergency department. Chest 133(1): Volpicelli G (2011) The double lung point. Am J Emerg Med 29(7): Submit your manuscript to a journal and benefit from: 7 Convenient online submission 7 Rigorous peer review 7 Immediate publication on acceptance 7 Open access: articles freely available online 7 High visibility within the field 7 Retaining the copyright to your article Submit your next manuscript at 7 springeropen.com
Identification of lung sliding: a basic ultrasound technique with a steep learning curve
 SIGNA VITAE 2013; 8(1): 31-35 ORIGINAL Identification of lung sliding: a basic ultrasound technique with a steep learning curve MATEJ STRNAD SABINA ZADEL ZALIKA KLEMENC-KETIS MATEJ STRNAD ( ) SABINA ZADEL
SIGNA VITAE 2013; 8(1): 31-35 ORIGINAL Identification of lung sliding: a basic ultrasound technique with a steep learning curve MATEJ STRNAD SABINA ZADEL ZALIKA KLEMENC-KETIS MATEJ STRNAD ( ) SABINA ZADEL
Usefulness of transthoracic lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of mild pneumothorax
 Original Article J Vet Sci 2018, 19(5), 660-666 ㆍ https://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2018.19.5.660 JVS Usefulness of transthoracic lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of mild pneumothorax Tae Sung Hwang 1, Young
Original Article J Vet Sci 2018, 19(5), 660-666 ㆍ https://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2018.19.5.660 JVS Usefulness of transthoracic lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of mild pneumothorax Tae Sung Hwang 1, Young
The Inspiration of Venue Ultrasound
 The Inspiration of Venue Ultrasound The papers that inspired the designers Venue is a special kind of ultrasound system. It has been designed for many applications. Among its capabilities is a set of tools
The Inspiration of Venue Ultrasound The papers that inspired the designers Venue is a special kind of ultrasound system. It has been designed for many applications. Among its capabilities is a set of tools
Impact of lung ultrasound on clinical decision making in critically ill patients
 Intensive Care Med DOI 10.1007/s00134-013-3133-3 ORIGINAL Nektaria Xirouchaki Eumorfia Kondili George Prinianakis Polychronis Malliotakis Dimitrios Georgopoulos Impact of lung ultrasound on clinical decision
Intensive Care Med DOI 10.1007/s00134-013-3133-3 ORIGINAL Nektaria Xirouchaki Eumorfia Kondili George Prinianakis Polychronis Malliotakis Dimitrios Georgopoulos Impact of lung ultrasound on clinical decision
Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of Pneumothorax in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1 Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1 Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung
Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax.
 Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax. Poster No.: C-0526 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Stefanidis, K. Vintzilaios, D. D. Cokkinos, E. Antypa, S. Dimopoulos, S. Nanas,
Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax. Poster No.: C-0526 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Stefanidis, K. Vintzilaios, D. D. Cokkinos, E. Antypa, S. Dimopoulos, S. Nanas,
Chest Ultrasound: Pneumothorax
 WINFOCUS BASIC ECHO (WBE) Chest Ultrasound: Pneumothorax Mark Hamlin, MD, MS Associate Professor of Anesthesiology and Surgery University of Vermont College of Medicine Co-Director of Surgical Critical
WINFOCUS BASIC ECHO (WBE) Chest Ultrasound: Pneumothorax Mark Hamlin, MD, MS Associate Professor of Anesthesiology and Surgery University of Vermont College of Medicine Co-Director of Surgical Critical
Ultrasound. FAST Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma
 Ultrasound FAST Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Ultrasound FAST Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Thoracic Ultrasound: Pictorial review of pneumothorax, the fastest and easiest method to diagnose.
 Thoracic Ultrasound: Pictorial review of pneumothorax, the fastest and easiest method to diagnose. Poster No.: C-1588 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. A. Guirola, V. Mayoral Campos,
Thoracic Ultrasound: Pictorial review of pneumothorax, the fastest and easiest method to diagnose. Poster No.: C-1588 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. A. Guirola, V. Mayoral Campos,
Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient Pleural Effusions
 Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient Pleural Effusions Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient Pleural Effusions Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Chest Sonography in the Diagnosis of Pneumothorax
 Original Article Chest Sonography in the Diagnosis of Pneumothorax Jitendra Balesa 1, Vinita Rathi 1, Sunil Kumar 2 and Anupama Tandon 1 Departments of Radiology and Imaging 1 and Surgery 2, University
Original Article Chest Sonography in the Diagnosis of Pneumothorax Jitendra Balesa 1, Vinita Rathi 1, Sunil Kumar 2 and Anupama Tandon 1 Departments of Radiology and Imaging 1 and Surgery 2, University
World Journal of Radiology
 W J R World Journal of Radiology Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.230 World J Radiol 2014 June 28; 6(6): 230-237
W J R World Journal of Radiology Submit a Manuscript: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/ Help Desk: http://www.wjgnet.com/esps/helpdesk.aspx DOI: 10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.230 World J Radiol 2014 June 28; 6(6): 230-237
Lung ultrasound: Present and future
 Review Article Lung ultrasound: Present and future Ashish Saraogi Department of Anaesthesiology, National Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India ABSTRACT The scope of ultrasound
Review Article Lung ultrasound: Present and future Ashish Saraogi Department of Anaesthesiology, National Institute of Medical Sciences and Research, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India ABSTRACT The scope of ultrasound
Diagnosis of Pneumothorax by Radiography and Ultrasonography
 CHEST Original Research PULMONARY PROCEDURES Diagnosis of Pneumothorax by Radiography and Ultrasonography A Meta-analysis Wu Ding, MM ; Yuehong Shen, MM ; Jianxin Yang, MM ; Xiaojun He, MM ; and Mao Zhang,
CHEST Original Research PULMONARY PROCEDURES Diagnosis of Pneumothorax by Radiography and Ultrasonography A Meta-analysis Wu Ding, MM ; Yuehong Shen, MM ; Jianxin Yang, MM ; Xiaojun He, MM ; and Mao Zhang,
Point-of-care lung ultrasound
 Ultrasound Point-of-care lung ultrasound Philips tutorial Michael B. Stone, MD, RDMS Director, Division of Emergency Ultrasound Department of Emergency Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston, MA
Ultrasound Point-of-care lung ultrasound Philips tutorial Michael B. Stone, MD, RDMS Director, Division of Emergency Ultrasound Department of Emergency Medicine Brigham and Women s Hospital, Boston, MA
Lung ultrasound in critically ill patients: comparison with bedside chest radiography
 Intensive Care Med (2011) 37:1488 1493 DOI 10.1007/s00134-011-2317-y ORIGINAL Nektaria Xirouchaki Eleftherios Magkanas Katerina Vaporidi Eumorfia Kondili Maria Plataki Alexandros Patrianakos Evaggelia
Intensive Care Med (2011) 37:1488 1493 DOI 10.1007/s00134-011-2317-y ORIGINAL Nektaria Xirouchaki Eleftherios Magkanas Katerina Vaporidi Eumorfia Kondili Maria Plataki Alexandros Patrianakos Evaggelia
Ultrasound-guided Aspiration of the Iatrogenic Pneumothorax Caused by Paravertebral Block
 Case Report Korean J Pain 2012 January; Vol. 25, No. 1: 33-37 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.1.33 Ultrasound-guided Aspiration of the Iatrogenic Pneumothorax Caused
Case Report Korean J Pain 2012 January; Vol. 25, No. 1: 33-37 pissn 2005-9159 eissn 2093-0569 http://dx.doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2012.25.1.33 Ultrasound-guided Aspiration of the Iatrogenic Pneumothorax Caused
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress
 A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors.
 This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. - Figure S1: The four quadrant approach lung ultrasound at the bedside. * The anterolateral
This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. - Figure S1: The four quadrant approach lung ultrasound at the bedside. * The anterolateral
The role of chest ultrasonography in the management of respiratory diseases: document I
 Zanforlin et al. Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine 2013, 8:54 REVIEW Open Access The role of chest ultrasonography in the management of respiratory diseases: document I Alessandro Zanforlin 1, Rosangela
Zanforlin et al. Multidisciplinary Respiratory Medicine 2013, 8:54 REVIEW Open Access The role of chest ultrasonography in the management of respiratory diseases: document I Alessandro Zanforlin 1, Rosangela
Objectives. The Extended FAST Exam. Focused Assessment e With Sonography In. Trauma (FAST)
 Northern California Emergency Ultrasound Course Objectives The Extended FAST Exam Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS UC SF Discuss the components of the EFAST exam Evaluate the utility of the EFAST Review how to
Northern California Emergency Ultrasound Course Objectives The Extended FAST Exam Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS UC SF Discuss the components of the EFAST exam Evaluate the utility of the EFAST Review how to
Ultrasound for Lung Monitoring of Ventilated Patients
 Clinical Concepts and Commentary Jerrold H. Levy, M.D., F.A.H.A., F.C.C.M., Editor Ultrasound for Lung Monitoring of Ventilated Patients Belaïd Bouhemad, M.D., Ph.D., Silvia Mongodi, M.D., Gabriele Via,
Clinical Concepts and Commentary Jerrold H. Levy, M.D., F.A.H.A., F.C.C.M., Editor Ultrasound for Lung Monitoring of Ventilated Patients Belaïd Bouhemad, M.D., Ph.D., Silvia Mongodi, M.D., Gabriele Via,
Clinical Study Lung Ultrasound Diagnostic Accuracy in Neonatal Pneumothorax
 Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2016, Article ID 6515069, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6515069 Clinical Study Lung Ultrasound Diagnostic Accuracy in Neonatal Pneumothorax Luigi Cattarossi,
Canadian Respiratory Journal Volume 2016, Article ID 6515069, 5 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2016/6515069 Clinical Study Lung Ultrasound Diagnostic Accuracy in Neonatal Pneumothorax Luigi Cattarossi,
Extended FAST Exam. Goal of Trauma Care. Golden Hour of Trauma
 Extended FAST Exam Goal of Trauma Care Golden Hour of Trauma Best INITIAL screening modality in trauma efast 2014 LLSA Article (ACEP Policy Statement) Level B Recommendation: In hemodynamically unstable
Extended FAST Exam Goal of Trauma Care Golden Hour of Trauma Best INITIAL screening modality in trauma efast 2014 LLSA Article (ACEP Policy Statement) Level B Recommendation: In hemodynamically unstable
Introduction to transthoracic ultrasound for the pulmonologist
 Review Introduction to transthoracic ultrasound for the pulmonologist Clementine Bostantzoglou 1, Charalampos Moschos 2 1 7 th Pulmonary Department, Sotiria Hospital for Chest Diseases, Athens, Greece
Review Introduction to transthoracic ultrasound for the pulmonologist Clementine Bostantzoglou 1, Charalampos Moschos 2 1 7 th Pulmonary Department, Sotiria Hospital for Chest Diseases, Athens, Greece
POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions
 POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions Jeremy S. Boyd, MD, FACEP Asst. Professor of Emergency Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Illustrations courtesy of Robinson Ferre, MD, FACEP
POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions Jeremy S. Boyd, MD, FACEP Asst. Professor of Emergency Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Illustrations courtesy of Robinson Ferre, MD, FACEP
Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
 Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Dr Neetu Talwar Senior Consultant, Pediatric Pulmonology Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram Study To compare
Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Dr Neetu Talwar Senior Consultant, Pediatric Pulmonology Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram Study To compare
Lung Ultrasound Predicts Well Extravascular Lung Water but Is of Limited Usefulness in the Prediction of Wedge Pressure
 CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Lung Ultrasound Predicts Well Extravascular Lung Water but Is of Limited Usefulness in the Prediction of Wedge Pressure Giovanni Volpicelli, M.D.,
CRITICAL CARE MEDICINE Lung Ultrasound Predicts Well Extravascular Lung Water but Is of Limited Usefulness in the Prediction of Wedge Pressure Giovanni Volpicelli, M.D.,
Could the use of bedside lung ultrasound reduce the number of chest x-rays in the intensive care unit?
 Brogi et al. Cardiovascular Ultrasound (2017) 15:23 DOI 10.1186/s12947-017-0113-8 RESEARCH Open Access Could the use of bedside lung ultrasound reduce the number of chest x-rays in the intensive care unit?
Brogi et al. Cardiovascular Ultrasound (2017) 15:23 DOI 10.1186/s12947-017-0113-8 RESEARCH Open Access Could the use of bedside lung ultrasound reduce the number of chest x-rays in the intensive care unit?
ASSESSMENT OF LUNG PARENCHYMAL ABNORMALITIES
 2016 by the author Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as
2016 by the author Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as
Lung Ultrasound for Critical Care Physiotherapists: A Narrative Review
 INVITED REVIEW Lung Ultrasound for Critical Care Physiotherapists: A Narrative Review Maja Leech 1 *, Bernie Bissett 1,2, Marta Kot 3 & George Ntoumenopoulos 4 1 Physiotherapy Department, Canberra Hospital,
INVITED REVIEW Lung Ultrasound for Critical Care Physiotherapists: A Narrative Review Maja Leech 1 *, Bernie Bissett 1,2, Marta Kot 3 & George Ntoumenopoulos 4 1 Physiotherapy Department, Canberra Hospital,
Pulmonary Ultrasound in Emergency Medicine and Critical Care
 Pulmonary Ultrasound in Emergency Medicine and Critical Care www.rmgultrasound.com Author: Virginia M Stewart, MD RDMS RDCS RDMSK Dr Stewart is a practicing Emergency Physician in Eastern Virginia, USA.
Pulmonary Ultrasound in Emergency Medicine and Critical Care www.rmgultrasound.com Author: Virginia M Stewart, MD RDMS RDCS RDMSK Dr Stewart is a practicing Emergency Physician in Eastern Virginia, USA.
Contents& & & 1.! Ultrasound&basics& 1! 2.! Image&generation& 15!
 A l i n e press é % % % Contents& & & 1. Ultrasound&basics& 1 1.1. What,is,ultrasound?, 1 1.2. Ultrasound,probes,send,and,receive,ultrasound, 3 1.3. How,does,ultrasound,behave,travelling,through,tissue?,
A l i n e press é % % % Contents& & & 1. Ultrasound&basics& 1 1.1. What,is,ultrasound?, 1 1.2. Ultrasound,probes,send,and,receive,ultrasound, 3 1.3. How,does,ultrasound,behave,travelling,through,tissue?,
Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems
 Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems Pneumothorax Definition Air accumulation in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse Sources Visceral pleura Ruptured esophagus Chest wall defect Gas-forming
Pneumothorax and Chest Tube Problems Pneumothorax Definition Air accumulation in the pleural space with secondary lung collapse Sources Visceral pleura Ruptured esophagus Chest wall defect Gas-forming
Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography in the Acute Assessment of Common Thoracic Lesions After Trauma
 CHEST Original Research CRITICAL CARE Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography in the Acute Assessment of Common Thoracic Lesions After Trauma Anne-Claire Hyacinthe, MD ; Christophe Broux, MD ; Gilles Francony,
CHEST Original Research CRITICAL CARE Diagnostic Accuracy of Ultrasonography in the Acute Assessment of Common Thoracic Lesions After Trauma Anne-Claire Hyacinthe, MD ; Christophe Broux, MD ; Gilles Francony,
Imaging of small amounts of pleural fluid. Part two - physiologic pleural fluid
 review Imaging of small amounts of pleural fluid. Part two - physiologic pleural fluid Igor Kocijančič Department of Radiology, Institute of Oncology, Ljubljana, Slovenia Background. There are only a few
review Imaging of small amounts of pleural fluid. Part two - physiologic pleural fluid Igor Kocijančič Department of Radiology, Institute of Oncology, Ljubljana, Slovenia Background. There are only a few
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists. International authors and editors
 We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
We are IntechOpen, the world s leading publisher of Open Access books Built by scientists, for scientists 3,800 116,000 120M Open access books available International authors and editors Downloads Our
CHEST Recent Advances in Chest Medicine
 CHEST Recent Advances in Chest Medicine Thoracic Ultrasonography for the Pulmonary Specialist Seth J. Koenig, MD; Mangala Narasimhan, DO, FCCP; and Paul H. Mayo, MD, FCCP Thoracic ultrasonography is a
CHEST Recent Advances in Chest Medicine Thoracic Ultrasonography for the Pulmonary Specialist Seth J. Koenig, MD; Mangala Narasimhan, DO, FCCP; and Paul H. Mayo, MD, FCCP Thoracic ultrasonography is a
Pneumothorax. Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms
 Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
Pneumothorax Defined as air in the pleural space which can occur through a number of mechanisms Traumatic pneumothorax Penetrating chest trauma Common secondary to bullet or knife penetration Chest tube
Using Ultrasound Lung Comets in the Diagnosis of High Altitude Pulmonary Edema: Fact or Fiction?
 WILDERNESS & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE, 24, 159 164 (2013) REVIEW ARTICLE Using Ultrasound Lung Comets in the Diagnosis of High Altitude Pulmonary Edema: Fact or Fiction? Yashvi Wimalasena, BM, FCEM, DiMM;
WILDERNESS & ENVIRONMENTAL MEDICINE, 24, 159 164 (2013) REVIEW ARTICLE Using Ultrasound Lung Comets in the Diagnosis of High Altitude Pulmonary Edema: Fact or Fiction? Yashvi Wimalasena, BM, FCEM, DiMM;
ECBSE Chest 29/01/2014 / 1:52 1. EFSUMB European Course Book Student Edition Editors: Jan Tuma, Radu Badea, Christoph F. Dietrich.
 ECBSE Chest 29/01/2014 / 1:52 1 EFSUMB European Course Book Student Edition Editors: Jan Tuma, Radu Badea, Christoph F. Dietrich Chest Gebhard Mathis Internistische Praxis, Rankweil, Austria Corresponding
ECBSE Chest 29/01/2014 / 1:52 1 EFSUMB European Course Book Student Edition Editors: Jan Tuma, Radu Badea, Christoph F. Dietrich Chest Gebhard Mathis Internistische Praxis, Rankweil, Austria Corresponding
The efficacy of bedside chest ultrasound: from accuracy to outcomes
 EUROPEAN RESPIRATORY UPDATE EFFICACY OF BEDSIDE CHEST ULTRASOUND The efficacy of bedside chest ultrasound: from accuracy to outcomes Mark Hew 1,2 and Tunn Ren Tay 1,3 Affiliations: 1 Allergy, Immunology
EUROPEAN RESPIRATORY UPDATE EFFICACY OF BEDSIDE CHEST ULTRASOUND The efficacy of bedside chest ultrasound: from accuracy to outcomes Mark Hew 1,2 and Tunn Ren Tay 1,3 Affiliations: 1 Allergy, Immunology
BLUE-Protocol and FALLS-Protocol Two Applications of Lung Ultrasound in the Critically Ill
 [ Recent Advances in Chest Medicine ] BLUE-Protocol and FALLS-Protocol Two Applications of Lung Ultrasound in the Critically Ill Daniel A. Lichtenstein, MD, FCCP This review article describes two protocols
[ Recent Advances in Chest Medicine ] BLUE-Protocol and FALLS-Protocol Two Applications of Lung Ultrasound in the Critically Ill Daniel A. Lichtenstein, MD, FCCP This review article describes two protocols
Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients
 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, June: 307-314, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients FARES AUF, M.D.; AHMED ABO-NAGLH,
Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, June: 307-314, 2015 www.medicaljournalofcairouniversity.net Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients FARES AUF, M.D.; AHMED ABO-NAGLH,
Non Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the ED
 Is haemodinamic monitoring useful in the ED? Non Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the ED Roberta PETRINO Director Emergency Medicine Unit S. Andrea Hospital, Vercelli - Italy EuSEM Vice-president Helps
Is haemodinamic monitoring useful in the ED? Non Invasive Hemodynamic Monitoring in the ED Roberta PETRINO Director Emergency Medicine Unit S. Andrea Hospital, Vercelli - Italy EuSEM Vice-president Helps
Lung ultrasound for severe acute dyspnea evaluation in critical care patients
 Page 950 VOJNOSANITETSKI PREGLED Vojnosanit Pregl 2016; 73(10): 950 955. PRACTICAL ADVICE FOR PHYSICIANS UDC: 616-08-039.74::616.14-073.432.19 DOI: 10.2298/VSP150609085R Lung ultrasound for severe acute
Page 950 VOJNOSANITETSKI PREGLED Vojnosanit Pregl 2016; 73(10): 950 955. PRACTICAL ADVICE FOR PHYSICIANS UDC: 616-08-039.74::616.14-073.432.19 DOI: 10.2298/VSP150609085R Lung ultrasound for severe acute
Lung Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Failure: BLUE Protocol Based Evaluation
 Lung Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Failure: BLUE Protocol Based Evaluation Niyas. K. Naseer 1, Muhammad Shafeek 2*, Rajani. M 3, Manoj. D. K 3 1Junior Resident, 2* Assistant Professor, 3
Lung Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Failure: BLUE Protocol Based Evaluation Niyas. K. Naseer 1, Muhammad Shafeek 2*, Rajani. M 3, Manoj. D. K 3 1Junior Resident, 2* Assistant Professor, 3
Is thoracic ultrasound a viable alternative to conventional imaging in the critical care setting?
 British Journal of Anaesthesia 111 (2): 152 60 (2013) Advance Access publication 12 April 2013. doi:10.1093/bja/aet076 REVIEW ARTICLES Is thoracic ultrasound a viable alternative to conventional imaging
British Journal of Anaesthesia 111 (2): 152 60 (2013) Advance Access publication 12 April 2013. doi:10.1093/bja/aet076 REVIEW ARTICLES Is thoracic ultrasound a viable alternative to conventional imaging
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings
 Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
ORIGINAL ARTICLE. Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings
 Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 66 August 2018 13 Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings Tanvi Vaidya 1*, Pradeep D costa 2, Satish Pande 3 ORIGINAL
Journal of The Association of Physicians of India Vol. 66 August 2018 13 Role of Ultrasound in Evaluation of Undifferentiated Shock in ICU Settings Tanvi Vaidya 1*, Pradeep D costa 2, Satish Pande 3 ORIGINAL
Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications
 No disclosures But Heavy accent Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications 1973: Goldberg et al in JCUS 30 mediastinal masses in pts. age 1-84 yrs. 1977: Kangarloo et al in
No disclosures But Heavy accent Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications 1973: Goldberg et al in JCUS 30 mediastinal masses in pts. age 1-84 yrs. 1977: Kangarloo et al in
Usefulness of Cardiothoracic Chest Ultrasound in the Management of Acute Respiratory Failure in Critical Care Practice
 CHEST Original Research CRITICAL CARE Usefulness of Cardiothoracic Chest Ultrasound in the Management of Acute Respiratory Failure in Critical Care Practice Stein Silva, MD, PhD ; Caroline Biendel, MD
CHEST Original Research CRITICAL CARE Usefulness of Cardiothoracic Chest Ultrasound in the Management of Acute Respiratory Failure in Critical Care Practice Stein Silva, MD, PhD ; Caroline Biendel, MD
Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient BASICS
 Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient BASICS Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida Introduction
Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient BASICS Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida Introduction
The Intensive Care Unit
 Imaging of the ADRS patient: Risk of transportation and alternative to repetitive radiation exposure Jean-Jacques Rouby Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital The Intensive Care Unit The Intensive Care Unit Multidisciplinary
Imaging of the ADRS patient: Risk of transportation and alternative to repetitive radiation exposure Jean-Jacques Rouby Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital The Intensive Care Unit The Intensive Care Unit Multidisciplinary
Bedside ultrasound - Lung ultrasound in the Intensive Care Unit
 Bedside ultrasound - Lung ultrasound in the Intensive Care Unit Kishore K. Pichamuthu, Professor, Department of Critical Care, Christian Medical College, Vellore. Summary In an ICU setting, ultrasonographic
Bedside ultrasound - Lung ultrasound in the Intensive Care Unit Kishore K. Pichamuthu, Professor, Department of Critical Care, Christian Medical College, Vellore. Summary In an ICU setting, ultrasonographic
Assesment of hemodynamics by basic ultrasound
 SIGNA VITAE 2017; 13(SUPPL 1): 27-31 Assesment of hemodynamics by basic ultrasound RADOVAN RADONIC, MD, PHD Address of correspondence Prof. dr. RADOVAN RADONIC (Corresponding author) Department of Internal
SIGNA VITAE 2017; 13(SUPPL 1): 27-31 Assesment of hemodynamics by basic ultrasound RADOVAN RADONIC, MD, PHD Address of correspondence Prof. dr. RADOVAN RADONIC (Corresponding author) Department of Internal
Chest Ultrasonography in Lung Contusion*
 CHEST Chest Ultrasonography in Lung Contusion* Gino Soldati, MD; Americo Testa, MD; Fernando R. Silva, MD; Luigi Carbone, MD, PhD; Grazia Portale, MD; and Nicolò G. Silveri, MD Original Research CHEST
CHEST Chest Ultrasonography in Lung Contusion* Gino Soldati, MD; Americo Testa, MD; Fernando R. Silva, MD; Luigi Carbone, MD, PhD; Grazia Portale, MD; and Nicolò G. Silveri, MD Original Research CHEST
Putting it all together: 1. The arrested patient 2. The shocked patient 3. The breathless patient
 Putting it all together: 1. The arrested patient 2. The shocked patient 3. The breathless patient 1 The Arrested Patient Adapted from Lichtenstein's SESAME protocol, with permission 2 Summary 1. (Ongoing
Putting it all together: 1. The arrested patient 2. The shocked patient 3. The breathless patient 1 The Arrested Patient Adapted from Lichtenstein's SESAME protocol, with permission 2 Summary 1. (Ongoing
BELLWORK page 343. Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary Remember the structures of the respiratory system 1
 BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
BELLWORK page 343 Apnea Dyspnea Hypoxia pneumo pulmonary respiratory system 1 STANDARDS 42) Review case studies that involve persons with respiratory disorders, diseases, or syndromes. Citing information
Performance of lung ultrasonography in children with community-acquired pneumonia
 Esposito et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics 2014, 40:37 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF PEDIATRICS RESEARCH Open Access Performance of lung ultrasonography in children with community-acquired pneumonia Susanna Esposito
Esposito et al. Italian Journal of Pediatrics 2014, 40:37 ITALIAN JOURNAL OF PEDIATRICS RESEARCH Open Access Performance of lung ultrasonography in children with community-acquired pneumonia Susanna Esposito
Lung ultrasound in follow-up of low birth weight with respiratory distress syndrome: clinical application and reduction of x-rays examinations
 Lung ultrasound in follow-up of low birth weight with respiratory distress syndrome: clinical application and reduction of x-rays examinations Poster No.: C-1724 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper
Lung ultrasound in follow-up of low birth weight with respiratory distress syndrome: clinical application and reduction of x-rays examinations Poster No.: C-1724 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper
The clinical sign of pleurisy is characterized by a
 Contrast-Enhanced Sonography for Differential Diagnosis of Pleurisy and Focal Pleural Lesions of Unknown Cause* Christian Görg, MD; Tillmann Bert, MD; and Konrad Görg, MD Background: Ultrasound enables
Contrast-Enhanced Sonography for Differential Diagnosis of Pleurisy and Focal Pleural Lesions of Unknown Cause* Christian Görg, MD; Tillmann Bert, MD; and Konrad Görg, MD Background: Ultrasound enables
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Lung
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Lung Page 1 of 8 01/17 Lung Syllabus Purpose: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for lung ultrasound in
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Lung Page 1 of 8 01/17 Lung Syllabus Purpose: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for lung ultrasound in
B. Chinardet, H. Brisson, C. Arbelot, O. Langeron, J.-J. Rouby and Q. Lu
 (Acta Anaesth. Belg., 2016, 67, 29-35) Ultrasound assessment of lung consolidation and reaeration after pleural effusion drainage in patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome : a pilot study B.
(Acta Anaesth. Belg., 2016, 67, 29-35) Ultrasound assessment of lung consolidation and reaeration after pleural effusion drainage in patients with Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome : a pilot study B.
Ultrasonography in trauma: a nation wide cross sectional investigation
 DOI 10.118/s13089-017-0071- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Ultrasonography in trauma: a nation wide cross sectional investigation Jesper Weile 1,*, Klaus Nielsen 3, Stine C. Primdahl, Christian A. Frederiksen
DOI 10.118/s13089-017-0071- ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Ultrasonography in trauma: a nation wide cross sectional investigation Jesper Weile 1,*, Klaus Nielsen 3, Stine C. Primdahl, Christian A. Frederiksen
The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax
 Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
A Porcine Pneumothorax Model for Teaching Ultrasound Diagnostics
 EDUCATIONAL ADVANCE A Porcine Pneumothorax Model for Teaching Ultrasound Diagnostics Nils Petter Oveland, MD, Erik Sloth, MD, PhD, DMsc, Gratien Andersen, MD, and Hans Morten Lossius, MD, PhD Abstract
EDUCATIONAL ADVANCE A Porcine Pneumothorax Model for Teaching Ultrasound Diagnostics Nils Petter Oveland, MD, Erik Sloth, MD, PhD, DMsc, Gratien Andersen, MD, and Hans Morten Lossius, MD, PhD Abstract
Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Pleural effusions Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases A pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production or decreased
Pleural effusions Dr. A.Torossian, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases A pleural effusion is an abnormal collection of fluid in the pleural space resulting from excess fluid production or decreased
Top Tips for Pleural Disease in 2012
 Top Tips for Pleural Disease in 2012 The unilateral pleural effusion on the Post Take Ward Round Pleural Effusion on CXR Bedside ultrasound + Pleural aspirate Empyema Nil evidence infection Admit IV antibiotics
Top Tips for Pleural Disease in 2012 The unilateral pleural effusion on the Post Take Ward Round Pleural Effusion on CXR Bedside ultrasound + Pleural aspirate Empyema Nil evidence infection Admit IV antibiotics
Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore Catheter in the Patients with Iatrogenic Pneumothorax
 Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 20;44:48-422 ISSN: 2233-60X (Print) ISSN: 2093-656 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/0.5090/kjtcs.20.44.6.48 Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore
Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 20;44:48-422 ISSN: 2233-60X (Print) ISSN: 2093-656 (Online) Clinical Research http://dx.doi.org/0.5090/kjtcs.20.44.6.48 Comparative Study for the Efficacy of Small Bore
NON INVASIVE LIFE SAVERS. Ultrasound in PICU
 VOL 1 NO.1 Jan March 2014 54 Table 1. Selected Applications of Point-of-Care Ultrasonography, According to Medical Specialty. Specialty Ultrasound Applications Anesthesia Cardiology Guidance for vascular
VOL 1 NO.1 Jan March 2014 54 Table 1. Selected Applications of Point-of-Care Ultrasonography, According to Medical Specialty. Specialty Ultrasound Applications Anesthesia Cardiology Guidance for vascular
Echocardiography Volume assessment. Justin Mandeville 2014
 Echocardiography Volume assessment Justin Mandeville 2014 Volume assessment and the intensivist Hypovolaemic shock Fluid tolerance Optimising cardiac output Avoiding overloading Guided fluid removal Add
Echocardiography Volume assessment Justin Mandeville 2014 Volume assessment and the intensivist Hypovolaemic shock Fluid tolerance Optimising cardiac output Avoiding overloading Guided fluid removal Add
Physical Signs in the Chest Part II
 Res Medica, Spring 1964, Volume 4, Number 2 Page 1 of 5 Physical Signs in the Chest Part II Professor John Crofton Abstract In this section some of the causes of the common physical signs are listed. Mediastinal
Res Medica, Spring 1964, Volume 4, Number 2 Page 1 of 5 Physical Signs in the Chest Part II Professor John Crofton Abstract In this section some of the causes of the common physical signs are listed. Mediastinal
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Thoraxdrainage SGP Jahresversammlung 2016, Lausanne
 Thoraxdrainage SGP Jahresversammlung 2016, Lausanne Dr. med. Lukas Kern a bit of history (incomplete.) a bit of physiology (basic ) indication data guidelines a bit of history (incomplete.) a bit of physiology
Thoraxdrainage SGP Jahresversammlung 2016, Lausanne Dr. med. Lukas Kern a bit of history (incomplete.) a bit of physiology (basic ) indication data guidelines a bit of history (incomplete.) a bit of physiology
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3
 Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Pneumothorax lecture no. 3 Is accumulation of air in a pleural space or accumulation of extra pulmonary air within the chest, Is uncommon during childhood, may result from external trauma, iatrogenic,
Using Thoracic Ultrasonography to Accurately Assess Pneumothorax Progression During Positive Pressure Ventilation
 CHEST Using Thoracic Ultrasonography to Accurately Assess Pneumothorax Progression During Positive Pressure Ventilation A Comparison With CT Scanning Original Research INTERVENTIONAL PULMONOLOGY Nils Petter
CHEST Using Thoracic Ultrasonography to Accurately Assess Pneumothorax Progression During Positive Pressure Ventilation A Comparison With CT Scanning Original Research INTERVENTIONAL PULMONOLOGY Nils Petter
Immediate versus delayed integrated point-ofcare-ultrasonography
 Pirozzi et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2014, 6:5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Immediate versus delayed integrated point-ofcare-ultrasonography to manage acute dyspnea in the emergency department Concetta
Pirozzi et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2014, 6:5 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Open Access Immediate versus delayed integrated point-ofcare-ultrasonography to manage acute dyspnea in the emergency department Concetta
Advanced Interventions
 Advanced Interventions Dr. Coenraad Frederik Nicolaas Koegelenberg Stellenbosch University 7602 Cape Town SOUTH AFRICA coeniefn@sun.ac.za AIMS Optimisation of patient positioning prior to and safety during
Advanced Interventions Dr. Coenraad Frederik Nicolaas Koegelenberg Stellenbosch University 7602 Cape Town SOUTH AFRICA coeniefn@sun.ac.za AIMS Optimisation of patient positioning prior to and safety during
Systematic review and meta analysis for the use of ultrasound versus radiology in diagnosing of pneumonia
 DOI 10.1186/s13089-017-0059-y REVIEW Open Access Systematic review and meta analysis for the use of ultrasound versus radiology in diagnosing of pneumonia Saeed Ali Alzahrani 1, Majid Abdulatief Al Salamah
DOI 10.1186/s13089-017-0059-y REVIEW Open Access Systematic review and meta analysis for the use of ultrasound versus radiology in diagnosing of pneumonia Saeed Ali Alzahrani 1, Majid Abdulatief Al Salamah
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion
 Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Diagnostic Approach to Pleural Effusion Objectives Define the leading causes of pleural effusion Classify the type of effusion Identify procedures and tests associated with diagnosis 2 Agenda Basic anatomy
Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT
 Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT Tracheobronchial rupture as a result of blunt thoracic trauma is extremely
Pediatric Isolated Trachea Rupture Treated with a Conservative Approach İ Akdulum 1, M Öztürk 2, N Dağ 1, A Sığırcı 1 ABSTRACT Tracheobronchial rupture as a result of blunt thoracic trauma is extremely
The Irregular Diaphragmatic Pleural Interface
 CSE SERIES The Irregular Diaphragmatic Pleural Interface Novel Sonographic Sign Facilitating the Diagnosis of Pneumonia Jacob O. vila, MD, RDMS, Vicki E. Noble, MD Videos online at www.jultrasoundmed.org
CSE SERIES The Irregular Diaphragmatic Pleural Interface Novel Sonographic Sign Facilitating the Diagnosis of Pneumonia Jacob O. vila, MD, RDMS, Vicki E. Noble, MD Videos online at www.jultrasoundmed.org
ACUTE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA Tina Gaarder, MD, PhD
 ACUTE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA Tina Gaarder, MD, PhD Trauma represents a leading cause of disability and preventable death and is mainly affecting people between 15 and 40 years of age, accounting
ACUTE CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF TRAUMA Tina Gaarder, MD, PhD Trauma represents a leading cause of disability and preventable death and is mainly affecting people between 15 and 40 years of age, accounting
Current Opinion in Anesthesiology Basic concepts in the use of thoracic and lung ultrasound
 Manuscript Number: Current Opinion in Anesthesiology Basic concepts in the use of thoracic and lung ultrasound --Manuscript Draft-- Full Title: Article Type: Corresponding Author: Basic concepts in the
Manuscript Number: Current Opinion in Anesthesiology Basic concepts in the use of thoracic and lung ultrasound --Manuscript Draft-- Full Title: Article Type: Corresponding Author: Basic concepts in the
CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION
 CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION Introduction Pulmonary contusion refers to blunt traumatic lung parenchymal injury which results in oedema and haemorrhaging into alveolar spaces. It may also result in
CHEST INJURY PULMONARY CONTUSION Introduction Pulmonary contusion refers to blunt traumatic lung parenchymal injury which results in oedema and haemorrhaging into alveolar spaces. It may also result in
Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis?
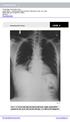 1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
Pleural ultrasonography. Pictorial essay.
 Pictorial essay Med Ultrason 2014, Vol. 16, no. 4, 364-371 DOI: 10.11152/mu.201.3.2066.164.racc Pleural ultrasonography. Pictorial essay. Romeo Chira 1, Alexandra Chira 2, Roberta Mânzat Săplăcan 1, Georgiana
Pictorial essay Med Ultrason 2014, Vol. 16, no. 4, 364-371 DOI: 10.11152/mu.201.3.2066.164.racc Pleural ultrasonography. Pictorial essay. Romeo Chira 1, Alexandra Chira 2, Roberta Mânzat Săplăcan 1, Georgiana
Removal of Chest Tube to Diagnose Pneumothorax Pak Armed Forces Med J 2017; 67 (4):
 Open Access Original Article Removal of Chest Tube to Diagnose Pneumothorax Pak Armed Forces Med J 2017; 67 (4): 641-45 CLINICAL ASSESSMENT COMPARED WITH CHEST-X-RAY AFTER REMOVAL OF CHEST TUBE TO DIAGNOSE
Open Access Original Article Removal of Chest Tube to Diagnose Pneumothorax Pak Armed Forces Med J 2017; 67 (4): 641-45 CLINICAL ASSESSMENT COMPARED WITH CHEST-X-RAY AFTER REMOVAL OF CHEST TUBE TO DIAGNOSE
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS. Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP
 APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
APPROACH TO PLEURAL EFFUSIONS Raed Alalawi, MD, FCCP CASE 65-year-old woman with H/O breast cancer presented with a 1 week H/O progressively worsening exersional dyspnea. Physical exam: Diminished breath
Lung ultrasound: a useful tool in diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis
 Basile et al. BMC Pediatrics (2015) 15:63 DOI 10.1186/s12887-015-0380-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lung ultrasound: a useful tool in diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis Vincenzo Basile 1, Antonio
Basile et al. BMC Pediatrics (2015) 15:63 DOI 10.1186/s12887-015-0380-1 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Lung ultrasound: a useful tool in diagnosis and management of bronchiolitis Vincenzo Basile 1, Antonio
RSV infection and lung ultrasound
 RSV infection and lung ultrasound Neonatology Clinic, University Hospital, Krakow Joanna Hurkała Joanna Pietras Agnieszka Ochoda-Mazur Poznań, 28.09.2018 1 Disclosure In relations to this presentation,
RSV infection and lung ultrasound Neonatology Clinic, University Hospital, Krakow Joanna Hurkała Joanna Pietras Agnieszka Ochoda-Mazur Poznań, 28.09.2018 1 Disclosure In relations to this presentation,
Methods ORIGINAL ARTICLES ABSTRACT
 Bedside lung ultrasound, mobile radiography and physical examination: a comparative analysis of diagnostic tools in the critically ill Andrew J Inglis, Marek Nalos, Kwan-Hing Sue, Jan Hruby, Daniel M Campbell,
Bedside lung ultrasound, mobile radiography and physical examination: a comparative analysis of diagnostic tools in the critically ill Andrew J Inglis, Marek Nalos, Kwan-Hing Sue, Jan Hruby, Daniel M Campbell,
Ultrasound (US) evaluation of peritoneal thickness in children and young patients on peritoneal dialysis (PD): A single centre experience
 Ultrasound (US) evaluation of peritoneal thickness in children and young patients on peritoneal dialysis (PD): A single centre experience Poster No.: C-2812 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Ultrasound (US) evaluation of peritoneal thickness in children and young patients on peritoneal dialysis (PD): A single centre experience Poster No.: C-2812 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Causes of pleural effusion and its imaging approach in pediatrics. M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid
 Causes of pleural effusion and its imaging approach in pediatrics M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Pleural fluid A tiny amount of fluid in the pleural cavity is physiological.
Causes of pleural effusion and its imaging approach in pediatrics M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Pleural fluid A tiny amount of fluid in the pleural cavity is physiological.
Simplified lung ultrasound protocol shows excellent prediction of extravascular lung water in ventilated intensive care patients
 Enghard et al. Critical Care (2015) 19:36 DOI 10.1186/s13054-015-0756-5 RESEARCH Open Access Simplified lung ultrasound protocol shows excellent prediction of extravascular lung water in ventilated intensive
Enghard et al. Critical Care (2015) 19:36 DOI 10.1186/s13054-015-0756-5 RESEARCH Open Access Simplified lung ultrasound protocol shows excellent prediction of extravascular lung water in ventilated intensive
Ultrasound in the ICU
 Ultrasound in the ICU Kristine E. W. Breyer, MD Assistant Professor Anesthesia & Critical Care Medicine UCSF DISCLOSURES: NONE Definition The Ultrasound Exam Types & Uses Training Clinical Examples Objectives
Ultrasound in the ICU Kristine E. W. Breyer, MD Assistant Professor Anesthesia & Critical Care Medicine UCSF DISCLOSURES: NONE Definition The Ultrasound Exam Types & Uses Training Clinical Examples Objectives
In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma but penetrating injuries also treated here (usually as single injuries, like stab wound)
 Chest Trauma Dr Csaba Dioszeghy MD PhD FRCEM FFICM FERC East Surrey Hospital Emergency Department Scope Thoracic injuries are common and can be life threatening In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma
Chest Trauma Dr Csaba Dioszeghy MD PhD FRCEM FFICM FERC East Surrey Hospital Emergency Department Scope Thoracic injuries are common and can be life threatening In ESH we usually see blunt chest trauma
Purpose This Operating Procedure provides guidance on the management of blunt thoracic traumatic injury
 Blunt Thoracic Trauma HELI.CLI.09 Purpose This Operating Procedure provides guidance on the management of blunt thoracic traumatic injury Procedure Management of Blunt Thoracic Traumatic Injury For Review
Blunt Thoracic Trauma HELI.CLI.09 Purpose This Operating Procedure provides guidance on the management of blunt thoracic traumatic injury Procedure Management of Blunt Thoracic Traumatic Injury For Review
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
