Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients
|
|
|
- Julius Terry
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Med. J. Cairo Univ., Vol. 83, No. 1, June: , Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients FARES AUF, M.D.; AHMED ABO-NAGLH, M.D.; MOUSTAFA ZEDAN, M.D. and MOHAMMAD AL-SOKROMI, M.Sc. The Department of Chest, Faculty of Medicine, Al-Azhar Univerisity Abstract Background: X-ray is widely recognized as a crucial step in the diagnosis of pneumonia. The limitations of chest X- ray in the diagnosis of pneumonia are more evident in some sites of care such as the ICU or emergency department. Aim of the Work: The aim of this work is to study the role of transthoracic ultrasound in diagnosis and follow-up of pneumonia in ICU patients. Subjects and Methods: This study was conducted on 38 RICU patients in Bab El-Sha'eria University Hospital suspected of pneumonia by history and physical examination, after recording a written consent at the period from November 2013 to May All patients undergone: Complete history taking, general and local chest examination, laboratory investigation including. CBC, ESR, renal and hepatic profile, CURB-65 score assessment, plain chest radiography, Computerized tomography (CT) chest scan and transthoracic ultrasound was done for all patients. On clinical suspicion of pneumonia, transthoracic ultrasonography was done, then chest radiography was carried out and CT chest was done for all patients (38 patients) as a gold standard test. Then patients was classified into two groups: Confirmed pneumonia group, patients with positive CT finding for pneumonia (30 patients) and confirmed non pneumonia group, patients with negative CT findings for pneumonia (8 patients with other diagnosis). Results: The sensitivity and specificity of transthoracic ultrasound in diagnosing pneumonia in ICU when compared with CT chest were 93.33% and 75.0% respectively. While the sensitivity and specificity of chest X-ray in diagnosing pneumonia in ICU when compared with CT chest were.0% and 62.5% respectively. Conclusion: Transthoracic ultrasound has a valuable role in the diagnosis and follow-up of pneumonia in ICU patients, as it is a bedside real-time, reliable, rapid and noninvasive technique. Recommendation: Pneumonia in ICU could be diagnosed and followed-up by transthoracic ultrasound. Key Words: Pneumonia ICU patients Transthoracic Ultrasound. Correspondence to: Dr. Fares Auf, The Department of Chest, Faculty of Medicine, Al-Azhar Univerisity Introduction PNEUMONIA in adults is a common disorder, potentially life threatening with a high hospitalization rate. Therefore, a correct and rapid diagnosis is mandatory [1]. X-ray is widely recognized as a crucial step in the diagnosis of pneumonia. The limitations of chest X-ray in the diagnosis of pneumonia are more evident in some sites of care such as the ICU or emergency department [2]. Diagnosis of pneumonia by chest CT has became more common, although CT could be considered the "gold standard" technique in the diagnosis of pneumonia, it cannot be used as a firstline radiological examination in all patients with suspected pneumonia, this is mainly due to the fact that it is often not available and that it involves a high radiation dose and is costly [3]. Aim of the work: The aim of this work is to study the role of transthoracic ultrasound in diagnosis and followup of pneumonia in ICU patients. Subjects and Methods This study was conducted on 38 RICU patients in Bab El-Sha'eria Al-Azhar University Hospital suspected of pneumonia by history and physical examination, after recording a written consent, at the period from November 2013 to May All patients underwent: Complete history taking, thorough general and local chest examination, laboratory investigation including. CBC, ESR, renal and hepatic profile, CURB-65 score assessment, plain chest radiography, computerized tomography (CT) chest scan, and transthoracic ultrasound were done for all patients. 307
2 308 Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients Criteria for pneumonia diagnosis: Suggestive history (fever, cough, sputum production, dyspnea). General and local physical signs suggestive of pneumonia [4]. Criteria for I. C. U admission: CURB-65 score 3. The score is an acronym for each of the risk factors measured. Each risk factor scores one point, for a maximum score of 5 [2]. Confusion of new onset. Urea greater than 7mmol/l (19mg/dL). Respiratory rate of 30 breaths per minute or greater. Blood pressure less than 90mmHg systolic or 60mmHg diastolic. Age 65 or older. Exclusion criteria: Pregnant women was excluded because of the restrictions in the use of CT chest which is required for the study. On clinical suspicion of pneumonia, transthoracic ultrasound was done, then chest radiography was carried out. CT chest was done for all patients (38 patients) as a gold standard test. Then patients was classified into two groups Confirmed pneumonia group, patients with positive CT finding for pneumonia (30 patients), and Confirmed non pneumonia group, patients with negative CT findings for pneumonia (8 patients) with other diagnosis. Transthoracic ultrasound: The process was performed by a single physician who was non blinded to patients clinical condition. The ultrasound examination involved longitudinal and oblique scans of the of the anterior, lateral and posterior chest wall. The probe was set perpendicular, oblique, and parallel to the ribs. For a total of 12 areas bilaterally (6 zones per hemithorax). Sonography was performed with a 3-to 6MHz convex transducer because of its suitability to the intercostal approach named (Sonoescape B5). Diagnostic criteria of pneumonia by transthoracic ultrasound: The main diagnostic sonomorphologic criteria of pneumonia by transthoracic ultrasound are defined as follow: Consolidation which is mainly subpleural lung consolidation (presenting a tissular pattern), air bronchograms (impresses a multiple small air inlets within a consolidation measuring a few millimeters in diameter or as a tree shaped echogenic structure) with or without pleural effusion (demonstrated as an echo-poor/echo-free space between visceral and parietal pleura) [5]. Diagnostic criteria of pneumonia by C-T chest: By presence of consolidation and air bronchogram. Plain chest X-ray, was performed either as a supine or seated anterior-posterior view or an upright posterior-anterior views depending on the patient's condition. Diagnostic criteria of pneumonia by X-ray chest: By presence of consolidation, opacity and airbronchogram with or without pleural effusion. The results of transthoracic ultrasound and chest X-ray were compared with chest CT as, a gold standard for pneumonia diagnosis. 38 patient diagnosed as pneumonia on clinical basis X-ray chest, transthoracic ultrasound, C-T chest According to result of C-T chest 30 patient C-T positive for presence of pneumonia (confirmed pneumonia) Criteria for pneumonia diagnosis: Suggestive history (fever, cough, sputum production, dyspnea). General and local physical signs suggestive of pneumonia. Criteria for I. C. U admission: CURB-65 score 3. 8 patient C-T negative for presence of pneumonia (confirmed non pneumonia) other diseases on C-T chest Fig. (1): Flow chart for protocol of research. Results Table (1): Age distribution among the studied groups. Range Mean ± SD ± Table (2): Sex distribution among the studied groups. Sex Confirmed pneumonia Group A (n=30) Chi-Square N % X2 p-value Male Female Total %
3 Fares Auf, et al Male Female Histogram (1): Sex distribution among the studied groups. Table (3): Co-morbidity distribution among the studied groups. Co-morbidity Group A (n=30) N % X2 Chi-Square p-value Chronic Chest Disease DM IHD Renal disease No Co-morbidity Total Table (5): Sensitivity and specificity of CXR in relation to CT chest in the diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU. CXR +ve (succeded) ve (failed) 20% failed Cases by CT chest Confirmed pneumonia N % Total Chi-Square X2 p-value Accuracy * Sens. Spec. PPV NPV Relation of X-ray chest to C-T chest in diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU % succeded Table (4): Sensitivity and specificity of thoracic ultrasound in relation to CT chest in the diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU. U/S +ve (succeded) ve (failed) 7% failed 93% succeded +Ve Cases by CT chest Confirmed pneumonia N % 28 2 Ve Total Chi-Square Sens. X2 p-value Accuracy Spec. <0.001* PPV NPV Relation of thoracic ultrasound to C-T chest in diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU Histogram (2): Relation of thoracic ultrasound to C-T chest in diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU Succeded Failed Histogram (3): Relation of x-ray chest to C-T chest in diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU. Sensitivity and specifcity of chest X-ray and thoracic ultrasound in dianosis of pneumonia in ICU Sens. Chest X-ray 62.5 Spec. 75 Thoracic ultrasound Histogram (4): Sensitivity and specificityof chest X-ray and thoracic ultrasound in diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU.
4 310 Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients Accuracy of thoracic ultrasound and chest X-ray in diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU Accuracy of thoracic ultrasound Accuracy chest X-ray Histogram (5): Accuracy of thoracic ultrasound and chest X- ray in diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU Chest X-ray Thoracic ultrasound % % after 1 week after 2 week Histogram (6): Detection of improvement by CXR and Sonar after 1 week and 2 weeks. Table (6): Sonographic findings in cases of pneumonia. Diagnostic signs N % Total Air bronchogram 18* Consolidation 23* 76.6 Pleural effusion 5* 16.6 Normal findings * Some cases presented by more than one finding. Table (7): Detection of improvement by CXR after 1 week and 2 weeks. Fig. (2-A): X-ray chest with left lower lobe pneumonia. Comparison of detection of improvement* After 1 week After 2 week N % N % CXR: Positive cases at start Not improved Improved Negative cases at start Total cases: X p Table (8): Detection of improvement by thoracic ultrasound U/S after 1 week and 2 weeks. Fig. (2-B): C-T chest of the same patient. Comparison of detection of improvement* After 1 week After 2 week N % N % Thoracic U/S: Positive cases at start Not improved Improved Negative cases at start Total: X p * Improvement appeared by follow-up for number and size of infiltrate by reduction in number and size or by disappearance of infiltrate. Fig. (2-C): Thoracic ultrasound.
5 Fares Auf, et al. 311 Fig. (3-A): Female patient 45 with X-ray shows right lower lobe pneumonia. Fig. (3-B): C-T chest. Fig. (3-C): Thoracic ultrasound. Discussion Transthoracic ultrasound has only recently been appreciated by the greater medical community because for a long time respected sources considered ultrasound to be unfit for assessing the pulmonary parenchyma [6]. On the contrary, during the past decade, lung ultrasound has been shown to be a very useful tool in the hands of intensivists and emergency physicians for the diagnosis of pneumothorax, pleural effusions and other thoracic conditions. Its use in the diagnosis of pneumonia has also been investi- gated in consideration of the great limitations of CXR [7]. This is of particular importance when chest X- ray is performed in the ED, where many patients are critically ill and can be examined only in the supine position, often with bedside equipment [8]. Although chest X-ray is widely recognized as a crucial step in the diagnosis of pneumonia, this technique has several limitations and is not 100% sensitive or 100% specific [9]. During the last decade, diagnosis of pneumonia by chest CT has become more common. Although CT could be considered the "gold standard" technique in the diagnosis of pneumonia, it cannot be used as a first-line radiologic examination in all patients with suspected pneumonia [10]. Thus in the present study we evaluate effectiveness of transthoracic ultrasound to confirm clinical suspicion of pneumonia in ICU patients. In the present study most cases were old age ranged from 43 years to 87 years with mean age ± years. This can be explained by pneumonia in old age is mostly severe (Table 1). This is in agreement with Parlamento et al., study who mentioned that the mean age of confirmed patients with pneumonia was 60.9 years (SD, 21.8) [11]. This result also, is in agreement with Nafae et al., who reported that, the age of 76.25% of confirmed cases with pneumonia was 50 years [12]. In the present study we found that there is a male predominance among the studied groups of pneumonia patients (Table 2). This result is in agreement with Cortellaro et al., study. They found that out of 120 patients with pneumonia 77 were males with a percentage of (64%) [13]. This result also, is in agreement with Nafae et al., who reported that, there were male predominance, as there was 45 male patients of overall patients confirmed as a pneumonia patients with percentage of 56% [12]. In the present study we found that co-morbidities are highly present among studied patients especially, chronic chest diseases in 10 cases (33.3%), and diabetes mellitus in 6 cases (20%) (Table 3). These results are in agreement with Reissig and Kroegel, study who mentioned that in 21 (70%)
6 312 Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients of the patients, pneumonia was associated with co morbidity, mostly with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (n= 16) [14]. These results also, are in agreement to Nafae et al., study who stated that co-morbidities are highly presented among studied groups of pneumonia patients especially Chronic chest disease and Cardiac disease with percentage of 37% and 31.25% respectively [12]. In the present study we found that cases confirmed to have pneumonia by CT-chest were 30, and cases proved by thoracic ultrasound were 28 cases (succeded) with percentage of success 93.3% in diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU from 30 cases with p-value < and Sensitivity 93,3% and specificity 75% and accuracy (Table 4). In the present study we found that cases proved pneumonia by X-ray chest in relation 30 cases diagnosed by C-T chest were 24 cases with percentage of success % and Sensitivity % and specificity 62.5 for chest X-ray in relation to CT chest in the diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU. With accuracy with p-value This can be explained by the limitation of X- ray in the diagnosis of pneumonia in ICU and emergency settings due to improper positioning of these critically ill patients. In those patients, plain X-ray films are antero-posterior and patients are usually supine. In the present study there were 2 false negative (6.6%) failed to be diagnosed by thoracic ultrasound, that is due to limitation of the lung ultrasound to detect deep lung lesions (Table 4). This is in agreement with Bourcier et al., 2007 study they found there were 6 false negative results observed by lung ultrasound from 144 patients involved in the study (4. 1 %). They reported that ultrasound performance is probably very good at detecting superficial pneumonia, it remains however poor at detecting deep alveolar lesions [15]. These results also, in agreement with Reissig and Copetti, study who reported that there were about 8% of patients diagnosed as pneumonia patients could not be detected by Lung ultrasound, because ultrasound may only detect lesions reaching the pleura [16]. In the present study, echographic findings in cases of pneumonia were consolidation in 23 cases (76.6%), air-bronchogram sign in 18 cases (60.00%), pleural effusion in 5 cases (16.6%), and most of the cases have more than one finding (26 cases with percentage of 86.6%) (Table 6). These results are in contrast with Reissig and Kroegel, study who found that multiple hyperechoic inclusions indicating air inlets within the pneumonic lesions (positive bronchoaerogram) were shown in 32 of 33 (96.9%) pneumonias. Intense bronchoaerograms were visible in 3 of the 32 cases (9.3%), whereas the bronchoaerogram in 6 patients was weak (i.e. only few hyperechoic inclusions were found). No bronchoaerogram could be detected in only 1 patient (3%). They concluded that thoracic ultrasound represents a further imaging technique for identifying pneumonic lesions and thus provides an additional tool for diagnosing pneumonia [14]. Cortellaro et al., study found that: Pattern of consolidation in 73 from cases (91.25%) with dynamic air bronchograms almost always present within the consolidation. An interstitial pattern surrounded the consolidation in 42 cases from cases (52.5%) as an expression of perilesional inflammatory edema [13]. These results agreed with Reissig and Kroegel, 2007 study who found that the sensitivity and specificity of thoracic ultrasound in diagnosing pneumonia were 93.4% and 97.7% [14]. These results, also are in agreement with Cortellaro et al., study that ultrasound showed a sensitivity of 99% and a specificity of 95%, Chest X- ray fared much worse, with a sensitivity of 67% and a specificity of 85% [13]. This study also, agreed with Nafae et al., who found the sensitivity and specificity of lung ultrasound in diagnosing pneumonia when compared with CT chest were 97.5% and 75.0% respectively and for chest X-ray were 77.5% and 60% [12]. Bourcier et al., also agreed with these results as it found a significantly higher sensitivity of lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of acute pneumonia compared to chest X-ray (95% vs 60%, p<0.0 1). Interestingly lung ultrasound appears to be particularly more effective than chest X-ray when pneumonia is evolving for less than 24 hours [15]. In the present study we found that the cases confirmed not to have pneumonia by CT-chest were 8 cases from 38 cases. These cases presented with clinical suspicion of pneumonia and C-T chest show other diagnosis include two cases with mass lesion with distal Collapse, one case with Subpulmonic empyema, one case with deep seated lung abscess, one case with acute exacerbation for bronchectasis, one case with pulmonary embolism and infarction and two cases with acute exacerbation of COPD with heart failure and right side pleural effusion.
7 Fares Auf, et al. 313 These results are in agreement with Bourcier et al., who reported that: 9 patients who were diagnosed with pneumonia from 144 patients after lung ultrasound had another diagnosis: 4 patients with sepsis of other origin, 2 patients with pulmonary embolism, 1 with acute respiratory distress syndrome, 1 with pulmonary fibrosis and one with acute anemia from gastric origin [15]. These results also, agree with Cortellaro et al., 2012 who mentioned that there were two false positive results. One of the two false-positive patients had a subphrenic abscess with atelectasia of the right lung just above the diaphragm and a small pleural effusion, whereas the other had cardiac failure with pleural effusion and atelectasia [13]. In the present study we found that during follow-up of pulmonary infiltrate in the cases for two weeks by X-ray and thoracic ultrasound, the same course for the pulmonary lesions was present and the detection of improvement (appeared by reduction in number, size or by disappearance of infiltrate) in cases of pneumonia by lung ultrasound more than by chest X-ray. After the first week the detection of improvement by chest X-ray and thoracic ultrasound were 13.3% and 40% respectively, while after the second week the ratios were 66.67% and 86.6% respectively without statistically significant difference (Tables 7,8). These results are in agreement with Angelika and Claus, 2007 they reported that during follow-up of pneumonia in 33 pulmonary infiltrate by using thoracic ultrasound and X-ray for comparison the course of pneumonia they found that, lesions decreased in size or disappeared (30/33) or decreased in number (4/9). The bronchoaerogram became less pronounced (13/32), basal pleural effusion either diminished (7/20) [17]. Conclusion: Transthoracic ultrasound has a valuable role in the diagnosis and follow-up of pneumonia in ICU patients, as it is a bedside realtime, reliable, rapid and noninvasive technique. Recommendation: Pneumonia in ICU could be diagnosed and followed-up by transthoracic ultrasound. References 1- ALMIRALL J. and BOLÍBAR I.: Risk factors for community acquired pneumonia in adults: A population-based case-control study. Eur. Respir. J., 13 (2): , LIM W.S., BAUDOUIN S.V. and GEORGE R.C.: BTS guidelines for the management of community acquired pneumonia in adults: Update Thorax, 64 (Suppl. 3): III 1-55, SYRJALA H., BROAS M., SURAMO I., et al.: Highresolution computed tomography for the diagnosis of community acquired pneumonia. Clin. Infect. Dis., 27: , JONTHAN GLEADLE: History and examination at a glance, pneumonia, Blackwell Science, page 166, SPERANDEO M., CARNEVALE V., MUSCARELLA S., et al.: Clinical application of transthoracic ultrasonography in inpatients with pneumonia. Eur. J. Clin. Invest., 41 (1): 1-7, BECKH S., BOLCSKEI P.L. and LESSNAU K.D.: Real time chest ultrasonography. A comprehensive review for the pulmonologist. Chest, 122: 1759e73, WEINBERGER S.E. and DRAZEN J.M.: Diagnostic procedures in respiratory diseases. Harrison's principles of internal medicine. 17 th edn. New York: McGraw-Hill, Chapter 247, ESAYAG Y., NIKITIN I. and BAR-ZIV J.: Diagnostic value of chest radiographs in bedridden patients suspected of having pneumonia. Am. J. Med., 123: 88.e1e5, ALBAUM M.N., HILL L.C. and MURPHY M.: Interobserver reliability of the chest radiograph in communityacquired pneumonia. PORT Investigators. Chest, 110: , GEHMACHER O., MATHIS G., KOPF A. and SCHEIER M.: Ultrasound imaging of pneumonia. Ultrasound Med. Biol., Vol. 21. No. 9. pp. I I IY 1122, PARLAMENTO S., COPETTI R. and DI BARTOLOMEO S.: Evaluation of lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of pneumonia in the ED. Am. J. Emerg. Med., 27 (4): , NAFAE and SHEBL R. EMAN: Adjuvant role of lung ultrasound in the diagnosis of pneumonia in intensive care unit-patients. Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis, 62: 281-5, CORTELLARO F., COLOMBO S., COEN D., et al.: Lung ultrasound is an accurate diagnostic tool for the diagnosis of pneumonia in the emergency department. Emerg. Med. J., 29: 19-23, REISSIG A. and KROEGEL C.: Sonographic diagnosis and follow-up of pneumonia: A prospective study. Respiration, 74 (5): , BOURCIER J.E., BRICCOLI A., GALLETTI S. and SALONE M.: Ultrasonography is superior to computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging in determining superficial resection margins of malignant chest wall tumors. J. Ultrasound. Med., 26: , REISSIG A and COPETTI R.: Lung Ultrasound in the Diagnosis and Follow-up of Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Prospective, Multicenter, Diagnostic Accuracy Study. Chest, Vol. 142, No 4, pp , ANGELIKA REISSIG and L. CLAUS KROEGE: Sonographic diagnosis and follow-up of pneumonia: A prospective study, Respiration, 74: , 2007.
8 314 Role of Transthoracic Ultrasound in Detection of Pneumonia in ICU Patients
Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP)
 Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Dr Neetu Talwar Senior Consultant, Pediatric Pulmonology Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram Study To compare
Pediatric Lung Ultrasound (PLUS) In Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia (CAP) Dr Neetu Talwar Senior Consultant, Pediatric Pulmonology Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurugram Study To compare
ASSESSMENT OF LUNG PARENCHYMAL ABNORMALITIES
 2016 by the author Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as
2016 by the author Thank you for viewing this presentation. We would like to remind you that this material is the property of the author. It is provided to you by the ERS for your personal use only, as
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress
 A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
A Practical Approach to Ultrasound Assessment of Respiratory Distress Yanick Beaulieu, MD, FRCPC Director, Bedside Ultrasound Curriculum Division of Cardiology and Critical Care Hôpital du Sacré-Coeur
Role of chest ultrasonography in the prognostic evaluation of patients with community acquired pneumonia: a prospective study
 International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Rennis KD et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Jan;5(1):25-30 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20164510
International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences Rennis KD et al. Int J Res Med Sci. 2017 Jan;5(1):25-30 www.msjonline.org pissn 2320-6071 eissn 2320-6012 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2320-6012.ijrms20164510
Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia.
 Supplementary 1 Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia. Imaging finding Definition Implication CR Consolidation Interstitial
Supplementary 1 Definitions and diagnostic implications of terms used in the chest radiograph and lung ultrasound diagnoses of pneumonia. Imaging finding Definition Implication CR Consolidation Interstitial
Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient Pleural Effusions
 Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient Pleural Effusions Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient Pleural Effusions Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Role of Chest Low-dose Computed Tomography in Elderly Patients with Suspected Acute Pulmonary Infection in the Emergency Room
 Role of Chest Low-dose Computed Tomography in Elderly Patients with Suspected Acute Pulmonary Infection in the Emergency Room Poster No.: C-1461 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Role of Chest Low-dose Computed Tomography in Elderly Patients with Suspected Acute Pulmonary Infection in the Emergency Room Poster No.: C-1461 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax.
 Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax. Poster No.: C-0526 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Stefanidis, K. Vintzilaios, D. D. Cokkinos, E. Antypa, S. Dimopoulos, S. Nanas,
Lung sonography in the diagnosis of pneumothorax. Poster No.: C-0526 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: K. Stefanidis, K. Vintzilaios, D. D. Cokkinos, E. Antypa, S. Dimopoulos, S. Nanas,
and localized ground glass opacities, or bronchiolar focal or multifocal micronodules;
 E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
Accuracy of Lung Ultrasonography in Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia as Compared to Chest X-Ray in Pediatric Age Group
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (8), Page 4977-4983 Accuracy of Lung Ultrasonography in Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia as Compared to Chest X-Ray in Pediatric Age
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2018) Vol. 72 (8), Page 4977-4983 Accuracy of Lung Ultrasonography in Diagnosis of Community Acquired Pneumonia as Compared to Chest X-Ray in Pediatric Age
Chest Ultrasound: Pneumothorax
 WINFOCUS BASIC ECHO (WBE) Chest Ultrasound: Pneumothorax Mark Hamlin, MD, MS Associate Professor of Anesthesiology and Surgery University of Vermont College of Medicine Co-Director of Surgical Critical
WINFOCUS BASIC ECHO (WBE) Chest Ultrasound: Pneumothorax Mark Hamlin, MD, MS Associate Professor of Anesthesiology and Surgery University of Vermont College of Medicine Co-Director of Surgical Critical
This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors.
 This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. - Figure S1: The four quadrant approach lung ultrasound at the bedside. * The anterolateral
This appendix was part of the submitted manuscript and has been peer reviewed. It is posted as supplied by the authors. - Figure S1: The four quadrant approach lung ultrasound at the bedside. * The anterolateral
Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis?
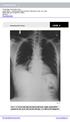 1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
1 Interpreting Chest X-Rays CASE 1 Fig. 1.1 Case 1. A 35-year-old male presented with fever, cough, and purulent sputum for one week. This was his CXR (Fig. 1.1). What is the diagnosis? CASE 1 Interpreting
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus
 Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Interpreting thoracic x-ray of the supine immobile patient: Syllabus Johannes Godt Dep. of Radiology and Nuclear Medicine Oslo University Hospital Ullevål NORDTER 2017, Helsinki Content - Why bedside chest
Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of Pneumothorax in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1 Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Bedside Sonographic Diagnosis of in Pediatric Patients: A Preliminary Report Chia-Wang Tang 1, Kai-Sheng Hsieh 1 1 Division of Pediatric Pulmonology, Department of Pediatrics, Kaohsiung
Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications
 No disclosures But Heavy accent Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications 1973: Goldberg et al in JCUS 30 mediastinal masses in pts. age 1-84 yrs. 1977: Kangarloo et al in
No disclosures But Heavy accent Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications 1973: Goldberg et al in JCUS 30 mediastinal masses in pts. age 1-84 yrs. 1977: Kangarloo et al in
POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions
 POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions Jeremy S. Boyd, MD, FACEP Asst. Professor of Emergency Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Illustrations courtesy of Robinson Ferre, MD, FACEP
POCUS for the Internist: Lungs & Pericardial Effusions Jeremy S. Boyd, MD, FACEP Asst. Professor of Emergency Medicine Vanderbilt University Medical Illustrations courtesy of Robinson Ferre, MD, FACEP
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
ARDS - a must know. Page 1 of 14
 ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
Ultrasound. FAST Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma
 Ultrasound FAST Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Ultrasound FAST Focused Assessment with Sonography in Trauma Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida
Objectives. The Extended FAST Exam. Focused Assessment e With Sonography In. Trauma (FAST)
 Northern California Emergency Ultrasound Course Objectives The Extended FAST Exam Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS UC SF Discuss the components of the EFAST exam Evaluate the utility of the EFAST Review how to
Northern California Emergency Ultrasound Course Objectives The Extended FAST Exam Rimon Bengiamin, MD, RDMS UC SF Discuss the components of the EFAST exam Evaluate the utility of the EFAST Review how to
4/16/2017. Learning Objectives. Interpretation of the Chest Radiograph. Components. Production of the Radiograph. Density & Appearance
 Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Interpretation of the Arthur Jones, EdD, RRT Learning Objectives Identify technical defects in chest radiographs Identify common radiographic abnormalities This Presentation is Approved for 1 CRCE Credit
Predictors of Outcomes of Community Acquired Pneumonia in Egyptian Older Adults
 Original Contribution/Clinical Investigation Predictors of Outcomes of Community Acquired Pneumonia in Egyptian Older Adults Hossameldin M. M. Abdelrahman Amal E. E. Elawam Ain Shams University, Faculty
Original Contribution/Clinical Investigation Predictors of Outcomes of Community Acquired Pneumonia in Egyptian Older Adults Hossameldin M. M. Abdelrahman Amal E. E. Elawam Ain Shams University, Faculty
Lung Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Failure: BLUE Protocol Based Evaluation
 Lung Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Failure: BLUE Protocol Based Evaluation Niyas. K. Naseer 1, Muhammad Shafeek 2*, Rajani. M 3, Manoj. D. K 3 1Junior Resident, 2* Assistant Professor, 3
Lung Ultrasound in Diagnosis of Acute Respiratory Failure: BLUE Protocol Based Evaluation Niyas. K. Naseer 1, Muhammad Shafeek 2*, Rajani. M 3, Manoj. D. K 3 1Junior Resident, 2* Assistant Professor, 3
Ultrasound in the ICU
 Ultrasound in the ICU Kristine E. W. Breyer, MD Assistant Professor Anesthesia & Critical Care Medicine UCSF DISCLOSURES: NONE Definition The Ultrasound Exam Types & Uses Training Clinical Examples Objectives
Ultrasound in the ICU Kristine E. W. Breyer, MD Assistant Professor Anesthesia & Critical Care Medicine UCSF DISCLOSURES: NONE Definition The Ultrasound Exam Types & Uses Training Clinical Examples Objectives
Case N 1. Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds. Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania
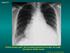 Case N 1 Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania Case N 1 Enlargment of cardiac silhouette. Notice the symetry
Case N 1 Anterior thoracic paint with increasing dyspnea for few days. No cough. Decrease of cardiac sounds Courtesy Dr Van den Homberg-Tanzania Case N 1 Enlargment of cardiac silhouette. Notice the symetry
Objectives. What is a Chest X Ray? CXR Workshop. Definition (diagnostic tool/internal PE) Types. Cost
 Objectives CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson, PA C Georgia Lung Associates Identify the radiographic landmarks on a chest radiograph Recognize identifiers of poor quality on the chest radiograph Outline an approach
Objectives CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson, PA C Georgia Lung Associates Identify the radiographic landmarks on a chest radiograph Recognize identifiers of poor quality on the chest radiograph Outline an approach
OVERVIEW. Need for USG. Weaning assessment. Mechanics of USG. Pneumonia / VAP. Principles of lung USG. Prone position ventilation assessment
 OVERVIEW Need for USG Mechanics of USG Principles of lung USG BLUE protocol Alveolar syndrome Interstitial syndrome Weaning assessment Pneumonia / VAP Prone position ventilation assessment ETT positioning
OVERVIEW Need for USG Mechanics of USG Principles of lung USG BLUE protocol Alveolar syndrome Interstitial syndrome Weaning assessment Pneumonia / VAP Prone position ventilation assessment ETT positioning
Research Article Quantitative Analysis of Lung Ultrasonography for the Detection of Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Pilot Study
 BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 868707, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/868707 Research Article Quantitative Analysis of Lung Ultrasonography for the Detection of Community-Acquired
BioMed Research International Volume 2015, Article ID 868707, 8 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2015/868707 Research Article Quantitative Analysis of Lung Ultrasonography for the Detection of Community-Acquired
CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ QUESTION
 Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 4/7/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 67 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Donald L. Renfrew, MD Radiology Associates of the Fox Valley, 333 N. Commercial Street, Suite 100, Neenah, WI 54956 4/7/2012 Radiology Quiz of the Week # 67 Page 1 CLINICAL PRESENTATION AND RADIOLOGY QUIZ
Lung ultrasound in the diagnosis and follow-up of community-acquired pneumonia. A prospective multicentre diagnostic accuracy study.
 Page 1 of 28 1 Lung ultrasound in the diagnosis and follow-up of community-acquired pneumonia. A prospective multicentre diagnostic accuracy study. (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00808457) Running
Page 1 of 28 1 Lung ultrasound in the diagnosis and follow-up of community-acquired pneumonia. A prospective multicentre diagnostic accuracy study. (ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT00808457) Running
Contents& & & 1.! Ultrasound&basics& 1! 2.! Image&generation& 15!
 A l i n e press é % % % Contents& & & 1. Ultrasound&basics& 1 1.1. What,is,ultrasound?, 1 1.2. Ultrasound,probes,send,and,receive,ultrasound, 3 1.3. How,does,ultrasound,behave,travelling,through,tissue?,
A l i n e press é % % % Contents& & & 1. Ultrasound&basics& 1 1.1. What,is,ultrasound?, 1 1.2. Ultrasound,probes,send,and,receive,ultrasound, 3 1.3. How,does,ultrasound,behave,travelling,through,tissue?,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations
 Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
Chest XRay interpretation INTERPRETATIONS Identifications: Name & Date Technical evaluation Basic Interpretations TECHNICAL EVALUATION 1. Projection: AP/PA view To differentiate between AP & PA films,
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1).
 PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1). 1 Inform Consent Date: / / dd / Mmm / yyyy 2 Patient identifier: Please enter the 6 digit Patient identification number from your site patient log
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1). 1 Inform Consent Date: / / dd / Mmm / yyyy 2 Patient identifier: Please enter the 6 digit Patient identification number from your site patient log
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings
 Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
Imaging of Pleural Effusion: Comparing Ultrasound, X-Ray and CT findings Poster No.: C-2067 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. M. Almeida, N. Antunes, C. Leal, L. Figueiredo ; Lisboa/PT,
Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome
 Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome Imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration (PS)
Lung sequestration and Scimitar syndrome Imaging approaches M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Rotterdam, The Netherlands Pulmonary sequestration Pulmonary sequestration (PS)
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
UERMMMC Department of Radiology. Basic Chest Radiology
 UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
UERMMMC Department of Radiology Basic Chest Radiology PHYSICS DENSITIES BONE SOFT TISSUES WATER FAT AIR TELEROENTGENOGRAM Criteria for an Ideal Chest Radiograph 1. Upright 2. Posteroanterior View 3. Full
Computed Tomography for the Diagnosis and Evaluation of the Severity of Community-acquired Pneumonia in the Elderly
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Computed Tomography for the Diagnosis and Evaluation of the Severity of Community-acquired Pneumonia in the Elderly Takahiro Haga 1,2, Mizuki Fukuoka 1,2, Mizuo Morita 1, Kohei Cho 1 and
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Computed Tomography for the Diagnosis and Evaluation of the Severity of Community-acquired Pneumonia in the Elderly Takahiro Haga 1,2, Mizuki Fukuoka 1,2, Mizuo Morita 1, Kohei Cho 1 and
Lecture Notes. Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia
 Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
Lecture Notes Chapter 16: Bacterial Pneumonia Objectives Explain the epidemiology Identify the common causes Explain the pathological changes in the lung Identify clinical features Explain the treatment
The Intensive Care Unit
 Imaging of the ADRS patient: Risk of transportation and alternative to repetitive radiation exposure Jean-Jacques Rouby Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital The Intensive Care Unit The Intensive Care Unit Multidisciplinary
Imaging of the ADRS patient: Risk of transportation and alternative to repetitive radiation exposure Jean-Jacques Rouby Pitié-Salpêtrière Hospital The Intensive Care Unit The Intensive Care Unit Multidisciplinary
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Lung
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Lung Page 1 of 8 01/17 Lung Syllabus Purpose: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for lung ultrasound in
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Lung Page 1 of 8 01/17 Lung Syllabus Purpose: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for lung ultrasound in
Making the Right Call With. Pneumonia. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a. Community-Acquired. What exactly is CAP?
 Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient BASICS
 Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient BASICS Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida Introduction
Lung ultrasound in the critically ill patient BASICS Rohit Patel, MD University of Florida Health Director, Critical Care Ultrasound Surgical ICU Center for Intensive Care Gainesville, Florida Introduction
Management of Pleural Effusion
 Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
Management of Pleural Effusion Development of Pleural Effusion pulmonary capillary pressure (CHF) capillary permeability (Pneumonia) intrapleural pressure (atelectasis) plasma oncotic pressure (hypoalbuminemia)
The clinical sign of pleurisy is characterized by a
 Contrast-Enhanced Sonography for Differential Diagnosis of Pleurisy and Focal Pleural Lesions of Unknown Cause* Christian Görg, MD; Tillmann Bert, MD; and Konrad Görg, MD Background: Ultrasound enables
Contrast-Enhanced Sonography for Differential Diagnosis of Pleurisy and Focal Pleural Lesions of Unknown Cause* Christian Görg, MD; Tillmann Bert, MD; and Konrad Görg, MD Background: Ultrasound enables
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Bedside ultrasound - Lung ultrasound in the Intensive Care Unit
 Bedside ultrasound - Lung ultrasound in the Intensive Care Unit Kishore K. Pichamuthu, Professor, Department of Critical Care, Christian Medical College, Vellore. Summary In an ICU setting, ultrasonographic
Bedside ultrasound - Lung ultrasound in the Intensive Care Unit Kishore K. Pichamuthu, Professor, Department of Critical Care, Christian Medical College, Vellore. Summary In an ICU setting, ultrasonographic
Chest X rays and Case Studies. No disclosures. Outline 5/31/2018. Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital
 Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
Chest X rays and Case Studies Carlo Manalo, M.D. Department of Radiology Loma Linda University Children s Hospital No disclosures. Outline Importance of history Densities delineated on radiography An approach
8/14/2017. Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features
 What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
What is that lung disease? Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Dr. Russell Tucker, DACVR Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual lung pathologic features Improved
امعة زهر قسم ا مراض الصدریة
 Al- Azhar University Faculty of Medicine Department of Chest diseases امعة زهر كلیة الطب (بنين) قسم ا مراض الصدریة مقرر الصدریة ا مراض الدبلوم لطلبة COURSE of Chest diseases For Diploma Degree 2013-2014
Al- Azhar University Faculty of Medicine Department of Chest diseases امعة زهر كلیة الطب (بنين) قسم ا مراض الصدریة مقرر الصدریة ا مراض الدبلوم لطلبة COURSE of Chest diseases For Diploma Degree 2013-2014
Case Study #2. Case Study #1 cont 9/28/2011. CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C. LH is 78 yowf with PMHx of metz breast CA presents
 Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Case Study #1 CAPA 2011 Christy Wilson PA C 46 yo female presents with community acquired PNA (CAP). Her condition worsened and she was transferred to the ICU and placed on mechanical ventilation. Describe
Introduction to transthoracic ultrasound for the pulmonologist
 Review Introduction to transthoracic ultrasound for the pulmonologist Clementine Bostantzoglou 1, Charalampos Moschos 2 1 7 th Pulmonary Department, Sotiria Hospital for Chest Diseases, Athens, Greece
Review Introduction to transthoracic ultrasound for the pulmonologist Clementine Bostantzoglou 1, Charalampos Moschos 2 1 7 th Pulmonary Department, Sotiria Hospital for Chest Diseases, Athens, Greece
Signs in Chest Radiology
 Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
Signs in Chest Radiology Jonathan H. Chung, MD Disclosures No pertinent disclosures Jonathan H. Chung, MD Assistant Professor Institute t of fadvanced d Biomedical Imaging National Jewish Health Denver,
Pneumonia. Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine
 Pneumonia Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine Definition Pneumonia is an acute respiratory illness caused by an infection of the lung parenchyma, associated with recently developed
Pneumonia Dr. Rami M Adil Al-Hayali Assistant professor in medicine Definition Pneumonia is an acute respiratory illness caused by an infection of the lung parenchyma, associated with recently developed
Unusual new signs of pneumothorax at lung ultrasound
 Unusual new signs of pneumothorax at lung ultrasound Volpicelli et al. Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 SHORT COMMUNICATION
Unusual new signs of pneumothorax at lung ultrasound Volpicelli et al. Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 Volpicelli et al. Critical Ultrasound Journal 2013, 5:10 SHORT COMMUNICATION
Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology
 Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Russell Tucker, DVM, DACVR Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual
Pulmonary Patterns & Correlated Pathology Russell Tucker, DVM, DACVR Washington State University College of Veterinary Medicine Objective: correlate radiographic findings of common lung diseases to actual
Interactive Lecture. Lecture 7 - Interactive. Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease. Editing File. Done By. Color Coding Important Notes Extra
 Lecture 7 - Interactive 436 Teams Interactive Lecture Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Ghaida Alsaeed Maha Alissa Nawwaf AlHarbi
Lecture 7 - Interactive 436 Teams Interactive Lecture Radiology of cardiorespiratory disease Done By Team Leaders: Khalid Alshehri Hanin Bashaikh Team Members: Ghaida Alsaeed Maha Alissa Nawwaf AlHarbi
The Irregular Diaphragmatic Pleural Interface
 CSE SERIES The Irregular Diaphragmatic Pleural Interface Novel Sonographic Sign Facilitating the Diagnosis of Pneumonia Jacob O. vila, MD, RDMS, Vicki E. Noble, MD Videos online at www.jultrasoundmed.org
CSE SERIES The Irregular Diaphragmatic Pleural Interface Novel Sonographic Sign Facilitating the Diagnosis of Pneumonia Jacob O. vila, MD, RDMS, Vicki E. Noble, MD Videos online at www.jultrasoundmed.org
Pulmonary Embolism. Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri
 Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Pulmonary Embolism Thoracic radiologist Helena Lauri 8.5.2017 Statistics 1-2 out of 1000 adults annually are diagnosed with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and/or pulmonary embolism (PE) About half of patients
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis
 Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Chest Radiology Interpretation: Findings of Tuberculosis Get out your laptops, smart phones or other devices pollev.com/chestradiology Case #1 1 Plombage Pneumonia Cancer 2 Reading the TB CXR Be systematic!
Repeated Pneumonia Severity Index Measurement After Admission Increases its Predictive Value for Mortality in Severe Community-acquired Pneumonia
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Repeated Pneumonia Severity Index Measurement After Admission Increases its Predictive Value for Mortality in Severe Community-acquired Pneumonia Chiung-Zuei Chen, 1 Po-Sheng Fan, 2 Chien-Chung
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Repeated Pneumonia Severity Index Measurement After Admission Increases its Predictive Value for Mortality in Severe Community-acquired Pneumonia Chiung-Zuei Chen, 1 Po-Sheng Fan, 2 Chien-Chung
Different Sonographic Pictures of Traumatic Hepatic Herniation and Reasons for Their Differences
 C S E R E P O R T Different Sonographic Pictures of Traumatic Hepatic Herniation and Reasons for Their Differences Chih-Shun Wu*, Wei-Jen Yao 1, Yen-Hua Huang 2 Sonographic features used in the diagnosis
C S E R E P O R T Different Sonographic Pictures of Traumatic Hepatic Herniation and Reasons for Their Differences Chih-Shun Wu*, Wei-Jen Yao 1, Yen-Hua Huang 2 Sonographic features used in the diagnosis
Chest X-ray Interpretation
 Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Chest X-ray Interpretation Introduction Routinely obtained Pulmonary specialist consultation Inherent physical exam limitations Chest x-ray limitations Physical exam and chest x-ray provide compliment
Extended FAST Exam. Goal of Trauma Care. Golden Hour of Trauma
 Extended FAST Exam Goal of Trauma Care Golden Hour of Trauma Best INITIAL screening modality in trauma efast 2014 LLSA Article (ACEP Policy Statement) Level B Recommendation: In hemodynamically unstable
Extended FAST Exam Goal of Trauma Care Golden Hour of Trauma Best INITIAL screening modality in trauma efast 2014 LLSA Article (ACEP Policy Statement) Level B Recommendation: In hemodynamically unstable
Bronchial syndrome. Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis
 Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
Bronchial syndrome Atelectasis Draining bronchus Bronchiectasis Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Atelectasis Consequence
A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough
 Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA
 KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Methodology: Expert opinion Issue Date: 8-97 Champion: Pulmonary Medicine Most Recent Update: 6-08, 7-10, 7-12 Key Stakeholders: Pulmonary Medicine,
KAISER PERMANENTE OHIO COMMUNITY ACQUIRED PNEUMONIA Methodology: Expert opinion Issue Date: 8-97 Champion: Pulmonary Medicine Most Recent Update: 6-08, 7-10, 7-12 Key Stakeholders: Pulmonary Medicine,
Causes of pleural effusion and its imaging approach in pediatrics. M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid
 Causes of pleural effusion and its imaging approach in pediatrics M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Pleural fluid A tiny amount of fluid in the pleural cavity is physiological.
Causes of pleural effusion and its imaging approach in pediatrics M. Mearadji International Foundation for Pediatric Imaging Aid Pleural fluid A tiny amount of fluid in the pleural cavity is physiological.
Imaging of small amounts of pleural fluid. Part two - physiologic pleural fluid
 review Imaging of small amounts of pleural fluid. Part two - physiologic pleural fluid Igor Kocijančič Department of Radiology, Institute of Oncology, Ljubljana, Slovenia Background. There are only a few
review Imaging of small amounts of pleural fluid. Part two - physiologic pleural fluid Igor Kocijančič Department of Radiology, Institute of Oncology, Ljubljana, Slovenia Background. There are only a few
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1135-1140 Role of High Resolution Computed Tomography in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases in Patients with Collagen Diseases
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1135-1140 Role of High Resolution Computed Tomography in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases in Patients with Collagen Diseases
Radiology of the respiratory disease
 Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
Radiology of the respiratory disease [ Color index: Important Notes Extra ] [ Editing file Feedback Share your notes Shared notes ] Resources: - 435 Slides - 434 Team - 435 Notes Done by: - Mai Alageel
Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications
 Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications 1973: Goldberg et al in JCUS 30 mediastinal masses in pts. age 1-84 yrs. 1977: Kangarloo et al in Radiology Juxtadiaphragmatic lesions
Initially for cardiac echo Subsequent studies non-cardiac applications 1973: Goldberg et al in JCUS 30 mediastinal masses in pts. age 1-84 yrs. 1977: Kangarloo et al in Radiology Juxtadiaphragmatic lesions
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Identification of lung sliding: a basic ultrasound technique with a steep learning curve
 SIGNA VITAE 2013; 8(1): 31-35 ORIGINAL Identification of lung sliding: a basic ultrasound technique with a steep learning curve MATEJ STRNAD SABINA ZADEL ZALIKA KLEMENC-KETIS MATEJ STRNAD ( ) SABINA ZADEL
SIGNA VITAE 2013; 8(1): 31-35 ORIGINAL Identification of lung sliding: a basic ultrasound technique with a steep learning curve MATEJ STRNAD SABINA ZADEL ZALIKA KLEMENC-KETIS MATEJ STRNAD ( ) SABINA ZADEL
Man, 65 years old, heavy smoker, cough, dyspnea and weight loss. AFB negative in sputum. Is TB possible?
 Chapter 10 Man, 65 years old, heavy smoker, cough, dyspnea and weight loss. AFB negative in sputum. Is TB possible? The opacity of the left upper lobe is not cavited and looks like a tissular mass, not
Chapter 10 Man, 65 years old, heavy smoker, cough, dyspnea and weight loss. AFB negative in sputum. Is TB possible? The opacity of the left upper lobe is not cavited and looks like a tissular mass, not
The efficacy of bedside chest ultrasound: from accuracy to outcomes
 EUROPEAN RESPIRATORY UPDATE EFFICACY OF BEDSIDE CHEST ULTRASOUND The efficacy of bedside chest ultrasound: from accuracy to outcomes Mark Hew 1,2 and Tunn Ren Tay 1,3 Affiliations: 1 Allergy, Immunology
EUROPEAN RESPIRATORY UPDATE EFFICACY OF BEDSIDE CHEST ULTRASOUND The efficacy of bedside chest ultrasound: from accuracy to outcomes Mark Hew 1,2 and Tunn Ren Tay 1,3 Affiliations: 1 Allergy, Immunology
Accuracy of lung ultrasonography in diagnosis of community acquired pneumonia in hospitalized children as compared to chest x-ray
 International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Tirdia PR et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2016 Aug;3(3):1026-1031 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3291.ijcp20162385
International Journal of Contemporary Pediatrics Tirdia PR et al. Int J Contemp Pediatr. 2016 Aug;3(3):1026-1031 http://www.ijpediatrics.com pissn 2349-3283 eissn 2349-3291 Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3291.ijcp20162385
The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax
 Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Respiratory 131 The diagnosis and management of pneumothorax Pneumothorax is a relatively common presentation in patients under the age of 40 years (approximately, 85% of patients are younger than 40 years).
Appendix to Gibson et al. Application of a decision rule and a D-dimer assay in the
 Appendix to Gibson et al. Application of a decision rule and a D-dimer assay in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism (Thromb Haemost 2010; 103.4) Case 1 You are paged by an emergency room physician, who
Appendix to Gibson et al. Application of a decision rule and a D-dimer assay in the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism (Thromb Haemost 2010; 103.4) Case 1 You are paged by an emergency room physician, who
Approach to CXR. Terminology. 1.Identification. Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow. Correct patient Correct date and time Correct examination
 Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Approach to CXR Greg Blecher SCH Respir Fellow From Rob Posteraro http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_interpret.txt.html ; http://home.earthlink.net/~rhpos/cxr_main.txt.html) Approach to viewing Chest
Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema
 Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema Poster No.: P-0025 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Lee, C.-K. Park; Guri/KR Keywords: Neoplasia, Biopsy, PET-CT, CT, Thorax, Lung DOI:
Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema Poster No.: P-0025 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Lee, C.-K. Park; Guri/KR Keywords: Neoplasia, Biopsy, PET-CT, CT, Thorax, Lung DOI:
Introduction to Chest Radiography
 Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Introduction to Chest Radiography RSTH 366: DIAGNOSTIC TECHNIQUES Alan Alipoon BS, RCP, RRT Instructor Department of Cardiopulmonary Sciences 1 Introduction Discovered in 1895 by Wilhelm Roentgen Terminology
Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining
 Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining of PBMCs. Forward scatter area (FSC-A) versus side scatter area (SSC-A) was used to select lymphocytes followed
Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining of PBMCs. Forward scatter area (FSC-A) versus side scatter area (SSC-A) was used to select lymphocytes followed
Radiology. Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions
 Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Radiology Undergraduate Radiology Sample Questions April 2012 The following examples are offered of questions that might be used to assess undergraduate radiology. There are 3 different styles: An OSCE
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus. Lung
 Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Lung Page 1 of 8 12/15 Lung Syllabus Purpose: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for lung ultrasound in
Certificate in Clinician Performed Ultrasound (CCPU) Syllabus Lung Page 1 of 8 12/15 Lung Syllabus Purpose: This unit is designed to cover the theoretical and practical curriculum for lung ultrasound in
Pulmonary TB aspects
 Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Pulmonary TB aspects Nodule & infiltrate Cavern Pneumonia Etienne Leroy Terquem Pierre L Her SPI / ISP Soutien Pneumologique International / International Support for Pulmonology Nodules and infiltrates
Pitfalls in Shortness of Breath
 Pitfalls in Shortness of Breath Stuart Swadron, MD FRCPC FACEP Vice-Chair of Education and Program Director Department of Emergency Medicine Los Angeles County-University of Southern California Medical
Pitfalls in Shortness of Breath Stuart Swadron, MD FRCPC FACEP Vice-Chair of Education and Program Director Department of Emergency Medicine Los Angeles County-University of Southern California Medical
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
Community-Acquired Pneumonia OBSOLETE 2
 Community-Acquired Pneumonia OBSOLETE 2 Clinical practice guidelines serve as an educational reference, and do not supersede the clinical judgment of the treating physician with respect to appropriate
Community-Acquired Pneumonia OBSOLETE 2 Clinical practice guidelines serve as an educational reference, and do not supersede the clinical judgment of the treating physician with respect to appropriate
Lung ultrasound in follow-up of low birth weight with respiratory distress syndrome: clinical application and reduction of x-rays examinations
 Lung ultrasound in follow-up of low birth weight with respiratory distress syndrome: clinical application and reduction of x-rays examinations Poster No.: C-1724 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper
Lung ultrasound in follow-up of low birth weight with respiratory distress syndrome: clinical application and reduction of x-rays examinations Poster No.: C-1724 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Scientific Paper
DIASTOLOGY DON T BE SUCH A STIFF
 DIASTOLOGY DON T BE SUCH A STIFF Michael Mallin, MD University of Utah Director Emergency Ultrasound www.ultrasoundpodcast.com Warning: The education found within this presentation is not approved by anyone
DIASTOLOGY DON T BE SUCH A STIFF Michael Mallin, MD University of Utah Director Emergency Ultrasound www.ultrasoundpodcast.com Warning: The education found within this presentation is not approved by anyone
Imaging: ultrasound in lung disease. Educational aims. Summary
 Key points Transthoracic US is an inexpensive, lightweight and portable technique to evaluate the lungs and the pleural space. US-guided punctures are safe procedures in the case of pathological findings
Key points Transthoracic US is an inexpensive, lightweight and portable technique to evaluate the lungs and the pleural space. US-guided punctures are safe procedures in the case of pathological findings
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order. Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital
 Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Veterinary Association Sydney, Australia 2007
 Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress THE LAST GASP II: LUNGS AND THORAX David Holt, BVSc, Diplomate ACVS University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary
Proceedings of the World Small Animal Sydney, Australia 2007 Hosted by: Next WSAVA Congress THE LAST GASP II: LUNGS AND THORAX David Holt, BVSc, Diplomate ACVS University of Pennsylvania School of Veterinary
X-rays. Dr Will Dooley
 X-rays Dr Will Dooley Plan Chest X-Rays Abdominal X-Rays Exam approach Presentation skills EMQ EMQ- answers Chest X-Ray - Systematic Approach D R Details RIP Image Quality +/- OBVIOUS ABNORMALITY A B C
X-rays Dr Will Dooley Plan Chest X-Rays Abdominal X-Rays Exam approach Presentation skills EMQ EMQ- answers Chest X-Ray - Systematic Approach D R Details RIP Image Quality +/- OBVIOUS ABNORMALITY A B C
Supplementary Appendix
 Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Jain S, Kamimoto L, Bramley AM, et al. Hospitalized patients
Supplementary Appendix This appendix has been provided by the authors to give readers additional information about their work. Supplement to: Jain S, Kamimoto L, Bramley AM, et al. Hospitalized patients
