SY 2017/ nd Final Term Revision. Student s Name: Grade: 11A. Subject: Biology. Teacher Signature
|
|
|
- Prosper McCormick
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SY 2017/ nd Final Term Revision Student s Name: Grade: 11A Subject: Biology Teacher Signature
2 Grade 11 Biology A/B Revision Work Sheet Modified True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. If false, change the identified word or phrase to make the statement true. 1. Why questions address the evolution of behavior. 2. Inherited behaviors are not modified by experience. 3. Over time, traits that provide a survival advantage become less common. 4. Natural selection favors traits that improve the likelihood that an individual will survive and reproduce. 5. In classical conditioning, the animal associates a related response with a stimulus. 6. Defensive behavior is a strategy for locating, obtaining, and consuming food. 7. Monarch butterflies that fly thousands of kilometers to breed are displaying migratory behavior. 8. Each species has a unique set of courtship signals. 9. Sexual selection influences the evolution of species. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
3 1. Which behavior provides an answer to a why question? a. Birds sing by pushing air through the vocal cords. b. Bird sing in treetops. c. Birds sing to attract mates. d. Birds sing in the morning. 2. Which behavior provides an answer to a how question? a. Birds sing to attract mates. c. Birds sing to defend territories. b. Birds sing in treetops. d. Birds sing to protect their young. 3. Natural selection favors traits that benefit the a. species. c. group. b. individual. d. order. 4. Innate animal behaviors are primarily influenced by a. genes. c. reasoning. b. age. d. experience. 5. Trial-and-error learning is also called a. classical conditioning. c. imprinting. b. operant conditioning. d. habituation. 6. Learning that occurs only during a specific period early in an animal s life is called a. operant. c. reasoning. b. classical. d. imprinting. 7. Learned animal behaviors are primarily influenced by a. genes. c. reasoning.
4 b. age. d. experience. 8. In classical conditioning, a. a related response is associated with a stimulus. b. a related stimulus is associated with a response. c. an unrelated response is associated with a stimulus. d. animals learn by trial and error. 9. When Konrad Lorenz raised a group of newly hatched goslings, the goslings showed a. operant conditioning. c. imprinting. b. reasoning. d. classic conditioning. 10. Pavlov : classical conditioning :: a. dog : meat powder c. rat : box b. trial : error d. Lorenz : imprinting 11. Behavior in which animals locate, obtain, and consume food is called a. foraging behavior. c. migratory behavior. b. territorial behavior. d. circadian rhythm. 12. The hognose snake that flips onto its back and pretends to be dead is displaying a. foraging behavior. c. social behavior. b. territorial behavior. d. antipredator behavior. 13. Which of the following is not an example of an animal signal? a. sound c. movement b. posture d. migration
5 14. Animal signals have been shaped by a. photoperiod. c. classical conditioning. b. natural selection. d. reasoning. 15. The purpose of animal signals is to a. stimulate a response in another animal. b. obtain food. c. travel to a more suitable environment. d. learn a new behavior. 16. Which behavior is most likely to have evolved through sexual selection? a. running ability in a cheetah c. flying to Mexico for the winter b. singing ability in a robin d. playing dead when threatened Completion Complete each statement. 1. A(n) is an action performed in response to a stimulus. 2. Investigations into the circumstance that trigger a specific behavior are usually outlined in questions. 3. Evolution by natural selection is a process by which change in response to their environment.
6 4. Behaviors that do not stop once they have begun and have little variation are. 5. Inherited behavior may be called behavior. 6. is the development of behaviors through experience. 7. The ability to analyze a problem and think of a possible solution is called. 8. Behavior that can be learned only during a specific period in an animal s life and that remains fixed once it is learned is called. 9. Dogs that salivate in response to a bell have probably undergone conditioning. 10. behavior is observed in many bird species that have regular seasonal movements. 11. Animals use signals to with other animals. 12. A cat rubbing her face against a fencepost to leave her scent is using to signal her presence. 13. When animals mate based on the presence of desirable traits, they are demonstrating. Short Answer 1. In the following example, identify the stimulus and the response: A rattlesnake strikes at a lizard running across its path. 2. Identify two external factors that influence behavior. 3. What is meant by the term innate behavior?
7 4. What are two types of associative learning? 5. How are classical conditioning and operant conditioning different from each other? 6. Distinguish between specialists and generalists in terms of foraging behavior. 7. How is hibernation adaptive? 8. Compare and contrast nocturnal and diurnal behavior. 9. What are two purposes of courtship behavior? 10. Why would it be advantageous for predators to learn the courtship signals of their prey? Essay 1. Explain how a behavior such as the killing of cubs by male lions can arise through natural selection. 2. Explain how spider-web building is a fixed action pattern. 3. Explain how singing in humans is a behavior that exhibits both genetic and learned components. 4. Imprinting is adaptive because a duckling is fed and protected by the first object it sees usually its mother. How is having a short sensitive period for imprinting adaptive? Consider the consequences if the first object a duckling sees is another species. Explain how imprinting on this other species would be maladaptive.
8 5. Natural selection has shaped animal signals so that they reach the intended receiver effectively. Based on this, explain what kinds of signals would be most effective and least effective in a dense forest with limited visibility. 6. Using examples, describe four kinds of communication signals that animals use to influence behavior.
9
Study Guide A. Answer Key. Animal Behavior
 Animal Behavior Answer Key SECTION 1. ADAPTIVE VALUE OF BEHAVIOR 1. stimulus; behavior 2. Internal; body 3. External; surroundings 4. b, c, a 5. constant; stimuli 6. increase; particular 7. internal; external
Animal Behavior Answer Key SECTION 1. ADAPTIVE VALUE OF BEHAVIOR 1. stimulus; behavior 2. Internal; body 3. External; surroundings 4. b, c, a 5. constant; stimuli 6. increase; particular 7. internal; external
Chapter 51 Behavioral Biology
 Chapter 51 Behavioral Biology Essential Knowledge 2.C.2 Organisms respond to changes in their external environments 2.E.2 Timing and coordination of physiological events are regulated by multiple mechanisms
Chapter 51 Behavioral Biology Essential Knowledge 2.C.2 Organisms respond to changes in their external environments 2.E.2 Timing and coordination of physiological events are regulated by multiple mechanisms
Animal Behavior. Types of Communication 4/22/2013
 Animal Behavior A behavior is the nervous system s response to a stimulus and is carried out by the muscular or the hormonal system Behavior is subject to natural selection Behaviors have an impact on
Animal Behavior A behavior is the nervous system s response to a stimulus and is carried out by the muscular or the hormonal system Behavior is subject to natural selection Behaviors have an impact on
Animal Behavior. Thur March 24: Animal Behavior: outline. Questions: What, How, and Why. Behavior is shaped partly by inheritance
 Thur March 24: Animal Behavior Animal Behavior: outline Animal Behavior Questions Behavior is partly shaped by Inheritance Behavior is partly shaped by Learning Hormones and Behavior The Genetics of Behavior
Thur March 24: Animal Behavior Animal Behavior: outline Animal Behavior Questions Behavior is partly shaped by Inheritance Behavior is partly shaped by Learning Hormones and Behavior The Genetics of Behavior
Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1
 Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1 1. Suppose you observe that song sparrows sing more at dawn than at other times of the day. Hmm, maybe singing early in the morning communicates to female
Bi412/512 Animal Behavior, Exam 1 Practice Page 1 1. Suppose you observe that song sparrows sing more at dawn than at other times of the day. Hmm, maybe singing early in the morning communicates to female
8. 4 types of communication signals: visual, sound, chemical, electrical
 Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 35 BEHAVIORAL ADAPTATIONS TO THE ENVIRONMENT 1. stimulus vs. response 2. nature vs. nurture 3. fixed action pattern, innate behaviors 4. imprinting vs. learning 5. types of
Honors Biology Unit 5 Chapter 35 BEHAVIORAL ADAPTATIONS TO THE ENVIRONMENT 1. stimulus vs. response 2. nature vs. nurture 3. fixed action pattern, innate behaviors 4. imprinting vs. learning 5. types of
Behavior. What causes behavior? Chapter 35: Behavioral Adaptations. Honors Biology Wide range of activities
 Chapter 35: Behavioral Adaptations Honors Biology 2013 1 Behavior Wide range of activities Both observable actions and chemical communication Response to internal and external environmental stimuli (environmental
Chapter 35: Behavioral Adaptations Honors Biology 2013 1 Behavior Wide range of activities Both observable actions and chemical communication Response to internal and external environmental stimuli (environmental
(A) Drive (B) Innate behavior (C) Learning, based on experience (D) A & B (E) None of the above
 CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 24: Behavior No. 1 of 10 1. Habituation is a type of. (A) Drive (B) Innate behavior (C) Learning, based on experience (D) A & B (E) None of the above Having a certain drive
CLEP Biology - Problem Drill 24: Behavior No. 1 of 10 1. Habituation is a type of. (A) Drive (B) Innate behavior (C) Learning, based on experience (D) A & B (E) None of the above Having a certain drive
Behavioral Animal Adaptations. Survival of organisms
 Behavioral Animal Adaptations Survival of organisms ANIMAL BEHAVIOR BEHAVIOR = anything an animal does in response to a stimulus in its environment What is a stimulus for bears beginning to hibernate?
Behavioral Animal Adaptations Survival of organisms ANIMAL BEHAVIOR BEHAVIOR = anything an animal does in response to a stimulus in its environment What is a stimulus for bears beginning to hibernate?
3/30/17. Animal Behavior. What is behavior? Why study behavior?
 Animal Behavior meerkat s What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned ability
Animal Behavior meerkat s What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned ability
AP Biology. What is behavior & Why study it? Animal Behavior. Ethology. What questions do we ask? Innate behavior. Types of behaviors
 Animal Behavior What is behavior & Why study it? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate = inherited or developmentally fixed learned = develop
Animal Behavior What is behavior & Why study it? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate = inherited or developmentally fixed learned = develop
AP Biology. What is behavior? Behavioral Ecology. Why study behavior? What questions can we ask? Evolutionary perspective.
 Behavioral Ecology What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned ability to learn
Behavioral Ecology What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned ability to learn
Animal Behavior. AP Biology. meerkats
 Animal Behavior meerkats What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned QuickTime
Animal Behavior meerkats What is behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment innate inherited, instinctive automatic & consistent learned QuickTime
What Is Behavior? Behavioral Biology: Ethology. Behavioral Ecology. Behavioral Biology: Experimental
 What Is Behavior? Behavior: change in activity in response to stimuli Is what an animal does and how it does it Includes muscular and non-muscular activity Cognition: the ability of an animal s nervous
What Is Behavior? Behavior: change in activity in response to stimuli Is what an animal does and how it does it Includes muscular and non-muscular activity Cognition: the ability of an animal s nervous
Name Date Class. Innate Behavior. SC.F The student knows that organisms respond to internal and external stimuli.
 Innate Behavior Before You Read SC.F.1.4.7 The student knows that organisms respond to internal and external stimuli. You may live in an area where you can observe animals migrating. Have you seen flocks
Innate Behavior Before You Read SC.F.1.4.7 The student knows that organisms respond to internal and external stimuli. You may live in an area where you can observe animals migrating. Have you seen flocks
Lecture 6 Behavior ethology Communication
 Lecture 6 Behavior ethology Communication Rich history of behavioral studies of birds Birds display a wide range of innate and learned behavior patterns Overview - Behavior Chapter 8 (Gill) Vocalizations
Lecture 6 Behavior ethology Communication Rich history of behavioral studies of birds Birds display a wide range of innate and learned behavior patterns Overview - Behavior Chapter 8 (Gill) Vocalizations
Animal Behavior. Chapter 51. Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for
 Chapter 51 Animal Behavior PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
Chapter 51 Animal Behavior PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Copyright
We know that humans can learn
 We know that humans can learn Learning in Animals Which animals are able to learn? (Hint: all animals have nervous systems) Reasonable guess: All animals can learn!! (Def.) Learning is a relatively long-lasting
We know that humans can learn Learning in Animals Which animals are able to learn? (Hint: all animals have nervous systems) Reasonable guess: All animals can learn!! (Def.) Learning is a relatively long-lasting
BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O Brien) Chapter 47 Behavior
 BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O Brien) 2005 Chapter 47 Behavior I. Causes of Behavior A. PROXIMAL CAUSATION 1. Describes how actions occur in terms of the neurological, hormonal, and skeletomuscular mechanisms
BLY 122 Lecture Notes (O Brien) 2005 Chapter 47 Behavior I. Causes of Behavior A. PROXIMAL CAUSATION 1. Describes how actions occur in terms of the neurological, hormonal, and skeletomuscular mechanisms
Types of behaviors that are elicited in response to simple stimuli
 Lecture 19: Animal Behavior I. Background A. Animal behavior reflects and arises from biological properties 1. Exhibited behavior defends on the physiological systems and processes unique to a given organism
Lecture 19: Animal Behavior I. Background A. Animal behavior reflects and arises from biological properties 1. Exhibited behavior defends on the physiological systems and processes unique to a given organism
The How and Why of Animal Activity
 The How and Why of Animal Activity Fiddler crabs feed with their small claw and wave their large claw Why do male fiddler crabs engage in claw waving behavior? Claw waving is used to repel other males
The How and Why of Animal Activity Fiddler crabs feed with their small claw and wave their large claw Why do male fiddler crabs engage in claw waving behavior? Claw waving is used to repel other males
Animal Behavior 2/21/2017. What is Behavior? Understanding Behavior. Types of Behavior. Types of Behavior
 What is Behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment Animal Behavior Why Study Behavior? Evolutionary perspective part of phenotype acted upon by
What is Behavior? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment Animal Behavior Why Study Behavior? Evolutionary perspective part of phenotype acted upon by
Launch Lab. How do scientists observe animal behavior in the field? Video. WebQuest. Assessment. Audio. Concepts in Motion. Review.
 CHAPTER 31 Animal Behavior Your one-stop online resource connected.mcgraw-hill.com Video WebQuest Audio Assessment Review Concepts in Motion? Inquiry g Multilingual eglossary Launch Lab How do scientists
CHAPTER 31 Animal Behavior Your one-stop online resource connected.mcgraw-hill.com Video WebQuest Audio Assessment Review Concepts in Motion? Inquiry g Multilingual eglossary Launch Lab How do scientists
Animal Behavior. Hormones and Neurons Organize Behavior
 Animal Behavior Hormones and Neurons Organize Behavior Controlling Neural Responses What controls neurons? Ganglia -clusters of neuron cell bodies. Brain-greatest concentration of cell bodies. Praying
Animal Behavior Hormones and Neurons Organize Behavior Controlling Neural Responses What controls neurons? Ganglia -clusters of neuron cell bodies. Brain-greatest concentration of cell bodies. Praying
FILM SESSIONS. Film session I - Behaviour of Communication (September 30)
 FILM SESSIONS Film session I - Behaviour of Communication (September 30) 1. Talking to Strangers (60 min.) 1 This film surveys some of the general communication signals used by animals from diverse taxa,
FILM SESSIONS Film session I - Behaviour of Communication (September 30) 1. Talking to Strangers (60 min.) 1 This film surveys some of the general communication signals used by animals from diverse taxa,
Assessment Schedule 2013 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of evolutionary processes leading to speciation (91605)
 NCEA Level 3 Biology (91605) 2013 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2013 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of evolutionary processes leading to speciation (91605) Assessment Criteria Evidence Achievement
NCEA Level 3 Biology (91605) 2013 page 1 of 6 Assessment Schedule 2013 Biology: Demonstrate understanding of evolutionary processes leading to speciation (91605) Assessment Criteria Evidence Achievement
PSY 2364 Animal Communication. Tinbergen s four questions. Niko Tinbergen ( ) Niko Tinbergen ( ) Niko Tinbergen ( )
 PSY 2364 Animal Communication The curious naturalist noninvasive field experiments Studies of herring gull behavior, spatial learning in insects Tinbergen s four questions 1) What is the mechanism? 2)
PSY 2364 Animal Communication The curious naturalist noninvasive field experiments Studies of herring gull behavior, spatial learning in insects Tinbergen s four questions 1) What is the mechanism? 2)
11.1 Genetic Variation Within Population. KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool.
 KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. Genetic variation in a population increases the chance that some individuals will survive. Genetic variation leads to phenotypic variation. Phenotypic
KEY CONCEPT A population shares a common gene pool. Genetic variation in a population increases the chance that some individuals will survive. Genetic variation leads to phenotypic variation. Phenotypic
Lecture #4 Ethology, continued Konrad Lorenz jackdaws
 9.20 M.I.T. 2013 Lecture #4 Ethology, continued Konrad Lorenz jackdaws 1 Konrad Lorenz Ethology: The Jackdaws of Altenberg, Austria Reading: King Solomon s Ring (1952), Chapter 11, The Perennial Retainers
9.20 M.I.T. 2013 Lecture #4 Ethology, continued Konrad Lorenz jackdaws 1 Konrad Lorenz Ethology: The Jackdaws of Altenberg, Austria Reading: King Solomon s Ring (1952), Chapter 11, The Perennial Retainers
AP Biology. Behavioral Biology
 AP Biology Behavioral Biology Day 1 Objectives Describe how organisms get innate behaviors Explain how learning occurs Explain how living organisms regulate behavior Analyze how environmental factors can
AP Biology Behavioral Biology Day 1 Objectives Describe how organisms get innate behaviors Explain how learning occurs Explain how living organisms regulate behavior Analyze how environmental factors can
Exercise 13: Behavior of the House Cricket (Acheta domesticus)
 Exercise 13: Behavior of the House Cricket (Acheta domesticus) 1 Animal Behavior Why do praying mantises display a unique mating system, called sexual cannibalism, where a member of a male-female pair
Exercise 13: Behavior of the House Cricket (Acheta domesticus) 1 Animal Behavior Why do praying mantises display a unique mating system, called sexual cannibalism, where a member of a male-female pair
The Gene Propagation Game
 The Gene Propagation Game Social Living has Costs and Benefits Competition, Territoriality and Dominance Altruism in the Animal Kingdom Genetic Relatedness and Inclusive Fitness Mating Behavior Depends
The Gene Propagation Game Social Living has Costs and Benefits Competition, Territoriality and Dominance Altruism in the Animal Kingdom Genetic Relatedness and Inclusive Fitness Mating Behavior Depends
Background. Vigilance in African mammalian carnivores. Antipredator behaviors: 1. Avoid detection. Undergrad: McGill University Dr.
 Vigilance in African mammalian carnivores Background Undergrad: McGill University Dr. Kramer s lab Ph.D.: MSU Dr. Holekamp s lab Wiline Trouilloud Photo: Jaime Tanner Antipredator behaviors: 1. Avoid detection
Vigilance in African mammalian carnivores Background Undergrad: McGill University Dr. Kramer s lab Ph.D.: MSU Dr. Holekamp s lab Wiline Trouilloud Photo: Jaime Tanner Antipredator behaviors: 1. Avoid detection
Vibration volleys. Standard repeating unit. crossed with. Chrysoperla johnsoni parent: Volley period RESULTS
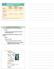 Table 51 1 Regulatory Genes and Behavior A master regulatory gene can control many behaviors Example a single gene controls many behaviors of the male fruit fly courtship ritual Mul:ple independent genes
Table 51 1 Regulatory Genes and Behavior A master regulatory gene can control many behaviors Example a single gene controls many behaviors of the male fruit fly courtship ritual Mul:ple independent genes
BIOLOGY. Animal Behavior CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 51 Animal Behavior Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The How and Why of Animal Activity Fiddler
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 51 Animal Behavior Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick The How and Why of Animal Activity Fiddler
Erick Sepulveda. Genetic basis. Life experiences. Nature vs. Nuture (it s a tie!)
 http://light.simanonok.com/euglenaphototaxis.jpg Erick Sepulveda A set of activities that orient an animal to its environment Most notable are observable reactions Internal responses also occur Taxes Simple
http://light.simanonok.com/euglenaphototaxis.jpg Erick Sepulveda A set of activities that orient an animal to its environment Most notable are observable reactions Internal responses also occur Taxes Simple
How to Escape a Predator Featured scientists: Amy Worthington and John Swallow from Washington State University and University of Colorado, Denver
 How to Escape a Predator Featured scientists: Amy Worthington and John Swallow from Washington State University and University of Colorado, Denver Research Background: Stalk-eyed flies are insects that
How to Escape a Predator Featured scientists: Amy Worthington and John Swallow from Washington State University and University of Colorado, Denver Research Background: Stalk-eyed flies are insects that
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS
 LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 51 Animal Behavior Lectures by
LECTURE PRESENTATIONS For CAMPBELL BIOLOGY, NINTH EDITION Jane B. Reece, Lisa A. Urry, Michael L. Cain, Steven A. Wasserman, Peter V. Minorsky, Robert B. Jackson Chapter 51 Animal Behavior Lectures by
Name Date Class. As you read Chapter 13, which begins on page 302 of your textbook, answer the following questions.
 CHAPTER 13 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Animals and Behavior As you read Chapter 13, which begins on page 302 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 302) 1a. What did
CHAPTER 13 DIRECTED READING WORKSHEET Animals and Behavior As you read Chapter 13, which begins on page 302 of your textbook, answer the following questions. This Really Happened... (p. 302) 1a. What did
The function or adaptive value of signals has been broken down into the following classes:
 Communication notes.doc 1 Communication and signals an action on the part of one animal that alters the behavior of another (Wilson 1975). The essence of communication is the relationship between signaler
Communication notes.doc 1 Communication and signals an action on the part of one animal that alters the behavior of another (Wilson 1975). The essence of communication is the relationship between signaler
Biology 352, Spring 2018 Exam Number KEY Second midterm exam Part 1 (short answer worth 21 % of grade)
 Part 1 (short answer worth 21 % of grade) 1-1) Match the following terms used in behavioral ecology with the appropriate topics of behavioral study listed to the right (you may apply more than one topic
Part 1 (short answer worth 21 % of grade) 1-1) Match the following terms used in behavioral ecology with the appropriate topics of behavioral study listed to the right (you may apply more than one topic
Animal Science. Study of animal behaviour Involves observations of animals actions and reactions to different stimuli
 Animal Science Contents: 1. Behaviour 2. Reproductive systems 3. Growth and maturity 4. Lactation system 5. Sensory system 6. Integumentary system 7. Endocrine system 8. Nervous system 9. Immune system
Animal Science Contents: 1. Behaviour 2. Reproductive systems 3. Growth and maturity 4. Lactation system 5. Sensory system 6. Integumentary system 7. Endocrine system 8. Nervous system 9. Immune system
Introduction to Neuroscience: Behavioral Neuroscience Lecture 1: Introduction to Animal Behavior
 Introduction to Neuroscience: Behavioral Neuroscience Lecture 1: Introduction to Animal Behavior Tali Kimchi Department of Neurobiology Tali.kimchi@weizmann.ac.il Jakob von Uexküll (1864-1944) Umwelt
Introduction to Neuroscience: Behavioral Neuroscience Lecture 1: Introduction to Animal Behavior Tali Kimchi Department of Neurobiology Tali.kimchi@weizmann.ac.il Jakob von Uexküll (1864-1944) Umwelt
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 14: Animals
 Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 14: Animals NC Essential Standard: 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish life functions 2.1.3 Explain various ways organisms interact with each other Did you
Unit 5: The Kingdoms of Life Module 14: Animals NC Essential Standard: 2.1.2 Analyze how various organisms accomplish life functions 2.1.3 Explain various ways organisms interact with each other Did you
Sexual selection and the evolution of sex differences
 Sexual selection and the evolution of sex differences Males and females have the same genes. Why do the sexes often look and act so differently? Why is the male often insanely ornamented? (Or simply insane?)
Sexual selection and the evolution of sex differences Males and females have the same genes. Why do the sexes often look and act so differently? Why is the male often insanely ornamented? (Or simply insane?)
EnSt/Bio 295 Exam II This test is worth 100 points; you have approximately 50 minutes. Allocate your time accordingly.
 Name: 1 NAME: EnSt/Bio 295 Exam II This test is worth 100 points; you have approximately 50 minutes. Allocate your time accordingly. 1) Describe the following concepts in a few sentences (2 points each)
Name: 1 NAME: EnSt/Bio 295 Exam II This test is worth 100 points; you have approximately 50 minutes. Allocate your time accordingly. 1) Describe the following concepts in a few sentences (2 points each)
10/6/14. Writing Assignment 1. Writing Assignment 1. How to test hypotheses in behavioral ecology. Niko Tinbergen s Four Questions
 Writing Assignment 1 Writing Assignment #1 Due Wednesday October 15th at the beginning of lecture To read: A Tephritid Fly Mimics the Territorial Displays of its Jumping Spider Predators Erick Greene;
Writing Assignment 1 Writing Assignment #1 Due Wednesday October 15th at the beginning of lecture To read: A Tephritid Fly Mimics the Territorial Displays of its Jumping Spider Predators Erick Greene;
Animal Behavior. Chapter 51. PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 51 Animal Behavior PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
Chapter 51 Animal Behavior PowerPoint Lecture Presentations for Biology Eighth Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Lectures by Chris Romero, updated by Erin Barley with contributions from Joan Sharp Overview:
survival value causation development evolutionary history
 The focus of ethology is observing animal behavior under natural conditions; animal behavior is how an animal responds to the environment that surrounds it and to conditions within its body. Considering
The focus of ethology is observing animal behavior under natural conditions; animal behavior is how an animal responds to the environment that surrounds it and to conditions within its body. Considering
Evolutionary Forces. What changes populations?
 Evolutionary Forces What changes populations? 2007-2008 Forces of evolutionary change Natural selection traits that improve survival or reproduction will accumulate in the population adaptive change Genetic
Evolutionary Forces What changes populations? 2007-2008 Forces of evolutionary change Natural selection traits that improve survival or reproduction will accumulate in the population adaptive change Genetic
Writing Assignment 1
 Writing Assignment 1 Writing Assignment #1 Due Wednesday October 15th at the beginning of lecture To read: A Tephritid Fly Mimics the Territorial Displays of its Jumping Spider Predators Erick Greene;
Writing Assignment 1 Writing Assignment #1 Due Wednesday October 15th at the beginning of lecture To read: A Tephritid Fly Mimics the Territorial Displays of its Jumping Spider Predators Erick Greene;
Evolutionary Forces. What changes populations?
 Evolutionary Forces What changes populations? Forces of evolutionary change Natural selection traits that improve survival or reproduction accumulate in the population ADAPTIVE change Genetic drift frequency
Evolutionary Forces What changes populations? Forces of evolutionary change Natural selection traits that improve survival or reproduction accumulate in the population ADAPTIVE change Genetic drift frequency
Chapter 51: Animal Behavior
 Chapter 51: Animal Behavior AP Biology Lindemulder 2013 1 Behavior Behavior - the nervous system s response to a stimulus and is carried out by the muscular system or the hormonal system Behavior is subject
Chapter 51: Animal Behavior AP Biology Lindemulder 2013 1 Behavior Behavior - the nervous system s response to a stimulus and is carried out by the muscular system or the hormonal system Behavior is subject
Lecture K3- Behavioral Ecology Dr. Kopeny
 4/17 Included on Test #4! Lecture K3- Behavioral Ecology Dr. Kopeny Mates, Families and Societies Male Prairie Chickens on Lek (Booming Ground) displaying male Prairie Chicken two male Prairie Chickens
4/17 Included on Test #4! Lecture K3- Behavioral Ecology Dr. Kopeny Mates, Families and Societies Male Prairie Chickens on Lek (Booming Ground) displaying male Prairie Chicken two male Prairie Chickens
(adaptations) Today s Vocabulary: Behavior- Migration- Hibernation- Instinct- Stimuli- WARM UP. 1. What is an adaptation?
 (adaptations) 1. What is an adaptation? WARM UP 2. How do you think adaptations are related to variations and environments? Behavior- Migration- Today s Vocabulary: Hibernation- Instinct- Stimuli- 1 Part
(adaptations) 1. What is an adaptation? WARM UP 2. How do you think adaptations are related to variations and environments? Behavior- Migration- Today s Vocabulary: Hibernation- Instinct- Stimuli- 1 Part
Microevolution: The Forces of Evolutionary Change Part 2. Lecture 23
 Microevolution: The Forces of Evolutionary Change Part 2 Lecture 23 Outline Conditions that cause evolutionary change Natural vs artificial selection Nonrandom mating and sexual selection The role of chance
Microevolution: The Forces of Evolutionary Change Part 2 Lecture 23 Outline Conditions that cause evolutionary change Natural vs artificial selection Nonrandom mating and sexual selection The role of chance
Chapter 51. Behavioral Ecology. PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition. Neil Campbell and Jane Reece
 Chapter 51 Behavioral Ecology PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Overview: Studying Behavior Humans have probably studied animal behavior for as long as we have
Chapter 51 Behavioral Ecology PowerPoint Lectures for Biology, Seventh Edition Neil Campbell and Jane Reece Overview: Studying Behavior Humans have probably studied animal behavior for as long as we have
1. Distinguish between releaser and modifier hormones. 2. Give and example of a reflex, a fixed action pattern and a stimulus response chain.
 1 Study Guide 1. Distinguish between releaser and modifier hormones. 2. Give and example of a reflex, a fixed action pattern and a stimulus response chain. 3. Explain how the results presented in the Figure
1 Study Guide 1. Distinguish between releaser and modifier hormones. 2. Give and example of a reflex, a fixed action pattern and a stimulus response chain. 3. Explain how the results presented in the Figure
So what is a species?
 So what is a species? Evolutionary Forces New Groups Biological species concept defined by Ernst Mayr population whose members can interbreed & produce viable, fertile offspring reproductively compatible
So what is a species? Evolutionary Forces New Groups Biological species concept defined by Ernst Mayr population whose members can interbreed & produce viable, fertile offspring reproductively compatible
thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 4.3 Animal behaviour Notes & Questions
 thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 4.3 Animal behaviour Notes & Questions Andy Todd 1 Explain the advantages to organisms of innate behaviour. Behaviour o
thebiotutor.com A2 Biology OCR Unit F215: Control, genomes and environment Module 4.3 Animal behaviour Notes & Questions Andy Todd 1 Explain the advantages to organisms of innate behaviour. Behaviour o
Behavioural Ecology. This subdiscipline studies the behaviour of individuals in an ecological context.
 Behavioural Ecology This subdiscipline studies the behaviour of individuals in an ecological context. In general, the behaviours studies are directed toward food, habitat, and mates. In all three, genetics
Behavioural Ecology This subdiscipline studies the behaviour of individuals in an ecological context. In general, the behaviours studies are directed toward food, habitat, and mates. In all three, genetics
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 15 Primate sociality: Predators and living in groups Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Most haplorrine, and
 Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 15 Primate sociality: Predators and living in groups Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Most haplorrine, and many strepsirrhine, primates are social: they live in
Introduction to Biological Anthropology: Notes 15 Primate sociality: Predators and living in groups Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Most haplorrine, and many strepsirrhine, primates are social: they live in
Animal Behavior. How can we explain behavior? Behavior. Innate or instinctive behavior. Instinctive behavior. Instinctive behavior 11/26/2017
 Animal Behavior Chapter 51 How can we explain behavior? How it works physiologically Proximate answer The adaptive value of the behavior Ultimate answer So, behavioral scientists study what behavior an
Animal Behavior Chapter 51 How can we explain behavior? How it works physiologically Proximate answer The adaptive value of the behavior Ultimate answer So, behavioral scientists study what behavior an
Finding Mr. Right Featured scientist: Carrie Branch from University of Nevada Reno
 Finding Mr. Right Featured scientist: Carrie Branch from University of Nevada Reno Research Background: Depending on where they live, animals can face a variety of challenges from the environment. For
Finding Mr. Right Featured scientist: Carrie Branch from University of Nevada Reno Research Background: Depending on where they live, animals can face a variety of challenges from the environment. For
Operant Condi-oning. Cogni-on and Problem Solving. Cogni-on and Problem Solving. Cogni-on. a process of knowing
 Operant condi-oning a type of associa,ve learning in which an animal learns to associate one of its behaviors with a reward or punishment It is also called trial- and- error learning Example a rat that
Operant condi-oning a type of associa,ve learning in which an animal learns to associate one of its behaviors with a reward or punishment It is also called trial- and- error learning Example a rat that
Evidence for evolution in Darwin s time came from several sources: 1. Fossils 2. Geography 3. Embryology 4. Anatomy
 Evidence for evolution in Darwin s time came from several sources: 1. Fossils 2. Geography 3. Embryology 4. Anatomy 1 Fossils in different layers of rock (sedimentary rock strata) have shown: Evidence
Evidence for evolution in Darwin s time came from several sources: 1. Fossils 2. Geography 3. Embryology 4. Anatomy 1 Fossils in different layers of rock (sedimentary rock strata) have shown: Evidence
Evolution of Mating Systems. Chapter 8
 Evolution of Mating Systems Chapter 8 Mating Systems-Chapter 8 1 Monogamy 2 Polyandry 3 Polygyny And the many combinations within! Why should a male be monogamous? 1 extension of guarding, little chance
Evolution of Mating Systems Chapter 8 Mating Systems-Chapter 8 1 Monogamy 2 Polyandry 3 Polygyny And the many combinations within! Why should a male be monogamous? 1 extension of guarding, little chance
Chapter 2 THEORIES OF CHILD DEVELOPMENT
 Chapter 2 THEORIES OF CHILD DEVELOPMENT THEORETICAL PERSPECTIVES INTERACTION. OFFER INSIGHT INTO WHY WE BEHAVE THE WAY WE DO AND HOW WE LEARN TO ACT IN NEW WAYS. A THEORY PROVIDES A FRAMEWORK OF GENERAL
Chapter 2 THEORIES OF CHILD DEVELOPMENT THEORETICAL PERSPECTIVES INTERACTION. OFFER INSIGHT INTO WHY WE BEHAVE THE WAY WE DO AND HOW WE LEARN TO ACT IN NEW WAYS. A THEORY PROVIDES A FRAMEWORK OF GENERAL
Black Bear Basics:
 How Many Black Bears Will Reproduce? Grade Level: 3 5 Standards: Minnesota Academic Standards in Science Codes 1.4.2.1.1, 1.4.2.1.2 Natural systems have many components that interact to maintain the living
How Many Black Bears Will Reproduce? Grade Level: 3 5 Standards: Minnesota Academic Standards in Science Codes 1.4.2.1.1, 1.4.2.1.2 Natural systems have many components that interact to maintain the living
marijuana and the teen brain MARY ET BOYLE, PH. D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD
 marijuana and the teen brain MARY ET BOYLE, PH. D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD in this talk what is marijuana? the brain on marijuana is the teen brain special? current research what is marijuana?
marijuana and the teen brain MARY ET BOYLE, PH. D. DEPARTMENT OF COGNITIVE SCIENCE UCSD in this talk what is marijuana? the brain on marijuana is the teen brain special? current research what is marijuana?
YOUR CHAT MODERATOR. Leslie Sinn, DVM,CPDT-KA Behavior Resident in Private Practice Training
 YOUR CHAT MODERATOR Leslie Sinn, DVM,CPDT-KA Behavior Resident in Private Practice Training lsinndvm@gmail.com Managing Behavior Issues in Pet Birds Valarie V. Tynes, DVM, DACVB Premier Veterinary Behavior
YOUR CHAT MODERATOR Leslie Sinn, DVM,CPDT-KA Behavior Resident in Private Practice Training lsinndvm@gmail.com Managing Behavior Issues in Pet Birds Valarie V. Tynes, DVM, DACVB Premier Veterinary Behavior
Evolutionary Processes
 Evolutionary Processes MICROEVOLUTION Population -- all the members of a single species Population genetics studies variations in gene pools *Basically, microevolution studies small changes in alleles
Evolutionary Processes MICROEVOLUTION Population -- all the members of a single species Population genetics studies variations in gene pools *Basically, microevolution studies small changes in alleles
Chapter 09 Marine Reptiles, Birds, and Mammals
 Chapter 09 Marine Reptiles, Birds, and Mammals Multiple Choice Questions 1. Marine amphibians: A. Do not exist at all B. Are gill-breathers C. Are fish-like D. Include only tropical species E. Are oviparous
Chapter 09 Marine Reptiles, Birds, and Mammals Multiple Choice Questions 1. Marine amphibians: A. Do not exist at all B. Are gill-breathers C. Are fish-like D. Include only tropical species E. Are oviparous
Unit 4 Structure, Function and Information Processing
 Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful
Use argument based on empirical evidence and scientific reasoning to support an explanation for how characteristic animal behaviors and specialized plant structures affect the probability of successful
Evolutionary Forces. What changes populations?
 Evolutionary Forces What changes populations? 2007-2008 Forces of evolutionary change Natural selection traits that improve survival or reproduction will accumulate in the population adaptive change Genetic
Evolutionary Forces What changes populations? 2007-2008 Forces of evolutionary change Natural selection traits that improve survival or reproduction will accumulate in the population adaptive change Genetic
Chapter 21.2 Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change
 Beak depth of Beak depth Colonie High AP Biology Chapter 21.2 Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change Populations Evolve! Natural selection acts on individuals differential survival survival of the fittest differential
Beak depth of Beak depth Colonie High AP Biology Chapter 21.2 Mechanisms of Evolutionary Change Populations Evolve! Natural selection acts on individuals differential survival survival of the fittest differential
9.20 M.I.T Lecture #8
 9.20 M.I.T. 2013 Lecture #8 More about innate behavior & motivation Key concepts from Lorenz on fundamentals of ethology: The fixed action pattern 1 Why do animals sleep? A question with multiple levels
9.20 M.I.T. 2013 Lecture #8 More about innate behavior & motivation Key concepts from Lorenz on fundamentals of ethology: The fixed action pattern 1 Why do animals sleep? A question with multiple levels
Name: Block. Reviewing what we have learned:
 Weeks 5 & 6 6.L.4B.2 Defense, Movement, Obtain Resources 6.L.4B.3 Environmental Stimuli & Behavioral Responses 6.L.4B.4 Learned vs. Inherited Behavior Name: Block Reviewing what we have learned: 1 Reviewing
Weeks 5 & 6 6.L.4B.2 Defense, Movement, Obtain Resources 6.L.4B.3 Environmental Stimuli & Behavioral Responses 6.L.4B.4 Learned vs. Inherited Behavior Name: Block Reviewing what we have learned: 1 Reviewing
EVOLUTION MICROEVOLUTION CAUSES OF MICROEVOLUTION. Evolution Activity 2.3 page 1
 AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION ACTIVITY 2.3 NAME DATE HOUR MICROEVOLUTION MICROEVOLUTION CAUSES OF MICROEVOLUTION Evolution Activity 2.3 page 1 QUESTIONS: 1. Use the key provided to identify the microevolution cause
AP BIOLOGY EVOLUTION ACTIVITY 2.3 NAME DATE HOUR MICROEVOLUTION MICROEVOLUTION CAUSES OF MICROEVOLUTION Evolution Activity 2.3 page 1 QUESTIONS: 1. Use the key provided to identify the microevolution cause
From so simple a beginning, endless forms so beautiful and wonderful have been and are being evolved
 VariaTiOn: The KEY to Evolu4on SWBAT describe how natural selec4on acts on genes. From so simple a beginning, endless forms so beautiful and wonderful have been and are being evolved 1 Charles Darwin (the
VariaTiOn: The KEY to Evolu4on SWBAT describe how natural selec4on acts on genes. From so simple a beginning, endless forms so beautiful and wonderful have been and are being evolved 1 Charles Darwin (the
Innate behavior & Learning
 & & has a fixed, genetic component. Despite differing environments, the behavior develops in all individuals. Learned behavior is acquired and modified over development. s can be triggered or enhanced
& & has a fixed, genetic component. Despite differing environments, the behavior develops in all individuals. Learned behavior is acquired and modified over development. s can be triggered or enhanced
Wednesday, September 12, 12. Whiptail Lizard
 Whiptail Lizard Sexual Selection Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace Noticed that males of many species have highly elaborated traits that seem maladaptive (secondary sexual characters) Antlers
Whiptail Lizard Sexual Selection Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace Noticed that males of many species have highly elaborated traits that seem maladaptive (secondary sexual characters) Antlers
Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which one learns to link two stimuli and anticipate events.
 Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which one learns to link two stimuli and anticipate events. behaviorism - the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science
Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning - a type of learning in which one learns to link two stimuli and anticipate events. behaviorism - the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science
April 12: Reproduction III: Female choice. Female choice
 April 12: Reproduction III: Female choice Female choice In general, females are expected to be choosier than males because they have more to lose by making bad mating decisions Costs and Benefits: Possible
April 12: Reproduction III: Female choice Female choice In general, females are expected to be choosier than males because they have more to lose by making bad mating decisions Costs and Benefits: Possible
Mechanisms of Evolution
 Mechanisms of Evolution TEKS 7(F) analyze and evaluate the effects of other evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination Evolution is. For Darwin (1859): Evolution
Mechanisms of Evolution TEKS 7(F) analyze and evaluate the effects of other evolutionary mechanisms, including genetic drift, gene flow, mutation, and recombination Evolution is. For Darwin (1859): Evolution
Name: Date: Period: Unit 1 Test: Microevolution (Original Test) Ms. OK, AP Biology,
 Name: Date: Period: Unit 1 Test: Microevolution (Original Test) Ms. OK, AP Biology, 2014-2015 General Directions: Use your time effectively, working as quickly as you can without losing accuracy. Do not
Name: Date: Period: Unit 1 Test: Microevolution (Original Test) Ms. OK, AP Biology, 2014-2015 General Directions: Use your time effectively, working as quickly as you can without losing accuracy. Do not
9.20 Midterm review notes, questions, topics
 9.20 Midterm review notes, questions, topics TOPICS FOR REVIEW Class 1: Introduction 1. What is the blank slate? In what fields did this idea flourish? 2. Contrast the attitudes about this idea in America
9.20 Midterm review notes, questions, topics TOPICS FOR REVIEW Class 1: Introduction 1. What is the blank slate? In what fields did this idea flourish? 2. Contrast the attitudes about this idea in America
1. (6 pts) a. Can all characteristics of organisms be explained by natural selection? Explain your answer in a sentence (3 pts)
 Zoology 357 - Evolutionary Ecology - First Exam 1. (6 pts) a. Can all characteristics of organisms be explained by natural selection? Explain your answer in a sentence (3 pts) b. Name two non-selectionist
Zoology 357 - Evolutionary Ecology - First Exam 1. (6 pts) a. Can all characteristics of organisms be explained by natural selection? Explain your answer in a sentence (3 pts) b. Name two non-selectionist
Animal Behavior. meerkats
 Animal Behavior meerkats AP Biology 2006-2007 What is behavior & Why study it? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment Why study behavior? part of phenotype
Animal Behavior meerkats AP Biology 2006-2007 What is behavior & Why study it? Behavior everything an animal does & how it does it response to stimuli in its environment Why study behavior? part of phenotype
Natural Selection. species: a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce viable, fertile offspring
 Imagine that you and your classmates are taking a nature hike through a nearby desert ecosystem. The hot sun is beating down on you, and you begin to wonder how anything could live in this harsh climate.
Imagine that you and your classmates are taking a nature hike through a nearby desert ecosystem. The hot sun is beating down on you, and you begin to wonder how anything could live in this harsh climate.
How Organisms Evolve Chapters The Theory of Evolution. The Theory of Evolution. Evolution can be traced through the fossil record.
 How Organisms Evolve Chapters 14-15 The Theory of Evolution Evolution is the process of change in the inherited traits of a population of organisms from one generation to the next. The inherited traits
How Organisms Evolve Chapters 14-15 The Theory of Evolution Evolution is the process of change in the inherited traits of a population of organisms from one generation to the next. The inherited traits
AP PSYCH Unit 6.1 Learning & Classical Conditioning. Before ever opening this book, what did you think learning meant?
 AP PSYCH Unit 6.1 Learning & Classical Conditioning Before ever opening this book, what did you think learning meant? Learning We are not born with a genetic plan that gets us through our entire life Much
AP PSYCH Unit 6.1 Learning & Classical Conditioning Before ever opening this book, what did you think learning meant? Learning We are not born with a genetic plan that gets us through our entire life Much
- These unique traits and behaviours are only seen in one sex
 Coyne chapter 6 how sex drives evolution for lec 6 and 7 - Peacock with its blue tail violates every aspect of Darwin because the traits that make him beautiful is making him maladaptive for survival because
Coyne chapter 6 how sex drives evolution for lec 6 and 7 - Peacock with its blue tail violates every aspect of Darwin because the traits that make him beautiful is making him maladaptive for survival because
Count how many butterflies you can spot on the wall. Count how many butterflies you can spot on the floor
 Count how many butterflies you can spot on the wall Count how many butterflies you can spot on the floor What is an acquired trait? A trait that an organism acquires or gains over its lifetime. It cannot
Count how many butterflies you can spot on the wall Count how many butterflies you can spot on the floor What is an acquired trait? A trait that an organism acquires or gains over its lifetime. It cannot
Biology 441/541 - Animal Behavior page 1 Chapter 3: The development of behavior -- the role of genes
 Biology 441/541 - Animal Behavior page 1 In this chapter, we ll look at some of the techniques by which the role of genes in the development of behavior can be investigated. By doing so, we ll also see
Biology 441/541 - Animal Behavior page 1 In this chapter, we ll look at some of the techniques by which the role of genes in the development of behavior can be investigated. By doing so, we ll also see
Biology 352, Spring 2017 Exam Number KEY Second midterm exam
 Biology 352, Spring 2017 Exam Number KEY Exam Instructions: 1) Write your NAME here: 2) Write your exam number (given above, right) at the top of the other pages. 3) Look over the exam to verify that you
Biology 352, Spring 2017 Exam Number KEY Exam Instructions: 1) Write your NAME here: 2) Write your exam number (given above, right) at the top of the other pages. 3) Look over the exam to verify that you
I. Ethology of Insects II. Patterns of Behavior III. Modifications IV. Operation V. Genetic Basis VI. Life History
 Insect Behavior I. Ethology of Insects II. Patterns of Behavior III. Modifications IV. Operation V. Genetic Basis VI. Life History I. Ethology of Insects Ethology is the comparative study of behavior We
Insect Behavior I. Ethology of Insects II. Patterns of Behavior III. Modifications IV. Operation V. Genetic Basis VI. Life History I. Ethology of Insects Ethology is the comparative study of behavior We
November 4, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 17 The evolution of mating systems. The evolution of sex ratio
 November 4, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 17 The evolution of mating systems The evolution of sex ratio - let us define sex ratio as the proportion of males to females. - in discussing the evolution
November 4, 2009 Bioe 109 Fall 2009 Lecture 17 The evolution of mating systems The evolution of sex ratio - let us define sex ratio as the proportion of males to females. - in discussing the evolution
Learning. Innate: Advantage of speed, no mistakes. Less need for parental care.
 Learning Innate vs learned behaviors Innate: Advantage of speed, no mistakes. Less need for parental care. Learned: Adaptability, Flexibility If learning is advantageous, will selection inevitably lead
Learning Innate vs learned behaviors Innate: Advantage of speed, no mistakes. Less need for parental care. Learned: Adaptability, Flexibility If learning is advantageous, will selection inevitably lead
