Teacher Resource CD: Learning About Paper
|
|
|
- Steven Willis
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Inquiry Investigations Forensic Science MODULE Grades: 7-10 Frey Scientific 80 Northwest Boulevard Nashua, NH Washington Essential Academic Learning Requirements (EALR) Science Grade 7 EALR WA.1. Systems: The student knows and applies scientific concepts and principles to understand the properties, structures, and changes in physical, earth/space, and living systems. COMPONENT 1.1. Properties: Understand how properties are used to identify, describe, and categorize substances, materials, and objects and how characteristics are used to categorize living things. BENCHMARK / GLE Physical Systems: Properties of Substances: Understand how to use physical and chemical properties to sort and identify substances. W a. Identify, categorize, describe, and sort substances using physical and/or chemical properties (i.e., boiling point, density, freezing point, mass, acidity [ph], solubility, magnetism) d. Describe why substances with the same volume or same mass may have different densities. EALR WA.1. Systems: The student knows and applies scientific concepts and principles to understand the properties, structures, and changes in physical, earth/space, and living systems. COMPONENT 1.1. Properties: Understand how properties are used to identify, describe, and categorize substances, materials, and objects and how characteristics are used to categorize living things. BENCHMARK / GLE Physical Systems: Wave Behavior: Understand sound waves, water waves, and light waves using wave properties, including amplitude, wavelength, and speed. Understand wave behaviors, including reflection, refraction, transmission, and absorption. W c. Describe how the observed properties of light, sound, and water are related to amplitude, frequency, wavelength, and speed of waves (e.g., color and brightness of light, pitch and volume of sound, height of water waves, light waves are faster than sound waves). Teacher Resource CD: Learning About Paper d. Describe the behavior of light waves when light interacts with transparent, translucent, and opaque substances (e.g., blue objects appear blue in color because the object reflects mostly blue light and absorbs the other colors of light, transparent objects transmit most light through them, lenses refract light).
2 Teacher Resource CD: Learning About Paper EALR WA.1. Systems: The student knows and applies scientific concepts and principles to understand the properties, structures, and changes in physical, earth/space, and living systems. COMPONENT 1.1. Properties: Understand how properties are used to identify, describe, and categorize substances, materials, and objects and how characteristics are used to categorize living things. BENCHMARK / GLE Earth and Space Systems: Nature and Properties of Earth Materials: Understand how to classify rocks, soils, air, and water into groups based on their chemical and physical properties. W a. Describe properties of minerals and rocks that give evidence of how they were formed (e.g., crystal size and arrangement, texture, luster, cleavage, hardness, layering, reaction to acid). Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence EALR WA.1. Systems: The student knows and applies scientific concepts and principles to understand the properties, structures, and changes in physical, earth/space, and living systems. COMPONENT 1.2. Structures: Understand how components, structures, organizations, and interconnections describe systems. BENCHMARK / GLE Earth and Space Systems: Components and of Earth Systems: Understand the components and interconnections of Earth's systems. W a. Describe the components of the Earth's systems (i.e., the core, the mantle, oceanic and crustal plates, landforms, the hydrosphere and atmosphere). Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Teacher Resource CD: Analyzing Writing EALR WA.1. Systems: The student knows and applies scientific concepts and principles to understand the properties, structures, and changes in physical, earth/space, and living systems. COMPONENT 1.2. Structures: Understand how components, structures, organizations, and interconnections describe systems. BENCHMARK / GLE Living Systems: Structure and Organization of Living Systems: Understand that specialized cells within multicellular organisms form different kinds of tissues, organs, and organ systems to carry out life functions. W b. Describe basic cell functions (i.e., extracting energy from food, using energy, and getting rid of waste). Teacher Resource CD: Simulating DNA c. Describe the life function of specialized cells or tissues (e.g., red blood cells carry oxygen to body tissues; cells in plant leaves capture light energy). Teacher Resource CD: Simulating DNA d. Describe the life function of organs or organ systems (e.g., the stomach breaks down food and the intestines absorb food in the digestive system).
3 EALR WA.1. Systems: The student knows and applies scientific concepts and principles to understand the properties, structures, and changes in physical, earth/space, and living systems. COMPONENT 1.2. Structures: Understand how components, structures, organizations, and interconnections describe systems. BENCHMARK / GLE Living Systems: Molecular Basis of Heredity: Understand that organisms pass on genetic information in their life cycle and that an organism's characteristics are determined by both genetic and environmental influences. W b. Explain that organisms require a set of instructions for specifying their traits (i.e., heredity is the passage of these instructions from one generation to another). DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Teacher Resource CD: Simulating DNA c. Describe that genes inherited from parents are combined in their offspring to produce a new combination of characteristics. DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Teacher Resource CD: Simulating DNA d. Explain how physical characteristics of living things can be affected by genetic information and/or by interactions with the environment (e.g., nutrition, disease, sanitation).
4 DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Teacher Resource CD: Simulating DNA EALR WA.1. Systems: The student knows and applies scientific concepts and principles to understand the properties, structures, and changes in physical, earth/space, and living systems. COMPONENT 1.2. Structures: Understand how components, structures, organizations, and interconnections describe systems. BENCHMARK / GLE Living Systems: Human Biology: Understand human life functions and the interconnecting organ systems necessary to maintain human life. W a. Describe the components and functions of the organ systems (i.e., circulatory, digestive, reproductive, excretory, nervous-sensory [brain, nerves, spinal cord, hearing, vision], respiratory, and muscular-skeletal systems). DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s c. Compare human body systems to another organism's body system (e.g., human lungs to plant leaves, human skeletal or circulatory systems to plant stems).
5 DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: The Case of the Telling Blood Group Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing EALR WA.1. Systems: The student knows and applies scientific concepts and principles to understand the properties, structures, and changes in physical, earth/space, and living systems. COMPONENT 1.3. Changes: Understand how interactions within and among systems cause changes in matter and energy. BENCHMARK / GLE Physical Systems: Nature of Force: Understand factors that affect the strength and direction of forces. W a. Observe and describe factors that affect the strength of forces (e.g., an object with a greater mass has a greater gravitational force [weight]; certain types of magnets have greater magnetic forces; a larger muscle can pull with a greater force). DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing
6 Teacher Resource CD: The Case of the Telling Blood Group Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing b. Describe how forces acting on an object may balance each other (e.g., the downward force of gravity on an object sitting on a table is balanced by an upward force from the table). DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: The Case of the Telling Blood Group Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing EALR WA.1. Systems: The student knows and applies scientific concepts and principles to understand the properties, structures, and changes in physical, earth/space, and living systems. COMPONENT 1.3. Changes: Understand how interactions within and among systems cause changes in matter and energy. BENCHMARK / GLE Physical Systems: Conservation of Matter and Energy: Understand that matter is conserved during physical and chemical changes. W b. Observe and describe that substances undergoing physical changes produce matter with the same chemical properties as the original substance and the same total mass (e.g., tearing paper, freezing water, breaking wood, sugar dissolving in water). DNA s
7 Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: The Case of the Telling Blood Group Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing c. Observe and describe that substances may react chemically to form new substances with different chemical properties and the same total mass (e.g., baking soda and vinegar; light stick mass before, during, and after reaction). Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Learning About Paper Teacher Resource CD: The Case of the Silent Sentinel EALR WA.2. Inquiry: The student knows and applies the skills, processes, and nature of scientific inquiry. COMPONENT 2.1. Investigating Systems: Develop the knowledge and skills necessary to do scientific inquiry. BENCHMARK / GLE Investigating Systems: Questioning: Understand how to generate a question that can be answered through scientific investigation. W c. Generate a new question that can be investigated with the same materials and/or data as a given investigation. Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s
8 DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing EALR WA.2. Inquiry: The student knows and applies the skills, processes, and nature of scientific inquiry. COMPONENT 2.1. Investigating Systems: Develop the knowledge and skills necessary to do scientific inquiry. BENCHMARK / GLE Investigating Systems: Planning and Conducting Safe Investigations: Understand how to plan and conduct scientific investigations. W a. Make predictions (hypothesize) and give reasons. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details
9 Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T
10 Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing b. Generate a logical plan for, and conduct, a scientific controlled investigation with the following attributes: prediction (hypothesis); appropriate materials, tools, and available computer technology; controlled variables (kept the same); one manipulated (changed) variable; responding (dependent) variable; gather, record, and organize data using appropriate units, charts, and/or graphs; multiple trials. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA
11 using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood
12 Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing c. Generate a logical plan for a simple field investigation with the following attributes: identify multiple variables; select observable or measurable variables related to the investigative question. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s
13 Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing d. Identify and explain safety requirements that would be needed in the investigation. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s
14 Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T
15 Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing EALR WA.2. Inquiry: The student knows and applies the skills, processes, and nature of scientific inquiry. COMPONENT 2.1. Investigating Systems: Develop the knowledge and skills necessary to do scientific inquiry. BENCHMARK / GLE Investigating Systems: Explaining: Apply understanding of how to construct a scientific explanation using evidence and inferential logic. W a. Generate a scientific conclusion including supporting data from an investigation using inferential logic (e.g., chewing gum loses more mass than bubble gum after being chewed for 5 minutes; chewing gum lost 2.00 grams while bubble gum only lost 1.47 grams). DNA
16 Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing b. Describe a reason for a given conclusion using evidence from an investigation. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s c. Generate a scientific explanation of an observed phenomenon using given data. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing
17 Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating
18 Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing d. Predict what logically might occur if an investigation lasted longer or changed. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA
19 using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing
20 Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing e. Describe the difference between evidence (data) and conclusions. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s
21 Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: Analyzing Writing Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Learning About Paper Teacher Resource CD: Simulating DNA Teacher Resource CD: The Case of the Silent Sentinel Teacher Resource CD: The Case of the Telling Blood Group Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing EALR WA.2. Inquiry: The student knows and applies the skills, processes, and nature of scientific inquiry. COMPONENT 2.1. Investigating Systems: Develop the knowledge and skills necessary to do scientific inquiry. BENCHMARK / GLE Investigating Systems: Modeling: Analyze how models are used to investigate objects, events, systems, and processes. W a. Compare models or computer simulations of phenomena to the actual phenomena. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing
22 Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating
23 Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing b. Explain how models or computer simulations are used to investigate and predict the behavior of objects, events, systems, or processes. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s
24 DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood
25 Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing c. Create a model or computer simulation to investigate and predict the behavior of objects, events, systems, or processes (e.g., phases of the Moon using a solar system model). Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence d. Explain the advantages and limitations of investigating with a model. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s EALR WA.2. Inquiry: The student knows and applies the skills, processes, and nature of scientific inquiry. COMPONENT 2.1. Investigating Systems: Develop the knowledge and skills necessary to do scientific inquiry. BENCHMARK / GLE Investigating Systems: Communicating: Apply understanding of how to report investigations and explanations of objects, events, systems, and processes. W
26 2.1.5.a. Report observations of scientific investigations without making inferences. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s
27 Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing b. Summarize an investigation by describing: reasons for selecting the investigative plan; materials used in the investigation; observations, data, results; explanations and conclusions in written, mathematical, oral, and information technology presentation formats; ramifications of investigations; safety procedures used. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s
28 Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence c. Describe the difference between an objective summary of data and an inference made from data. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s
29 Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing EALR WA.2. Inquiry: The student knows and applies the skills, processes, and nature of scientific inquiry. COMPONENT 2.2. Nature of Science: Understand the nature of scientific inquiry. BENCHMARK / GLE Nature of Science: Intellectual Honesty: Apply curiosity, honesty, skepticism, and openness when considering explanations and conducting investigations. W a. Explain why an honest response to questionable results, conclusions, or explanations is important to the scientific enterprise. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s
30 2.2.1.b. Describe a flaw in a claim or a conclusion (i.e., limited data, flawed procedure, or overgeneralization) c. Describe how scientists accurately and honestly record, report, and share observations and measurements without bias. Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence d. Explain why honest acknowledgement of the contributions of others and information sources are necessary. using DNA Frequency Calculations EALR WA.2. Inquiry: The student knows and applies the skills, processes, and nature of scientific inquiry. COMPONENT 2.2. Nature of Science: Understand the nature of scientific inquiry. BENCHMARK / GLE Nature of Science: Limitations of Science and Technology: Understand that scientific theories explain facts using inferential logic. W a. Describe how a principle or theory logically explains a given set of facts. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details
31 Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T
32 Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing EALR WA.2. Inquiry: The student knows and applies the skills, processes, and nature of scientific inquiry. COMPONENT 2.2. Nature of Science: Understand the nature of scientific inquiry. BENCHMARK / GLE Nature of Science: Evaluating Inconsistent Results: Analyze inconsistent results from scientific investigations to determine how the results can be explained. W a. Compare two or more similar investigations and explain why different results were produced (e.g., insufficient data could be interpreted as inconsistent results). Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence b. Explain whether sufficient information has been obtained to make a conclusion. Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence c. Explain why the results from a single investigation or demonstration are not sufficient to describe a phenomenon. Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence EALR WA.2. Inquiry: The student knows and applies the skills, processes, and nature of scientific inquiry. COMPONENT 2.2. Nature of Science: Understand the nature of scientific inquiry. BENCHMARK / GLE Nature of Science: Evaluating Methods of Investigation: Understand how to make the results of scientific investigations reliable and how to make the methods of investigation valid. W a. Describe how the method of an investigation ensures reliable results (e.g., multiple trials ensure more reliable results).
33 Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence b. Describe how to increase the reliability of the results of an investigation (e.g., repeating an investigation exactly the same way increases the reliability of the results). Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence c. Describe how the method of an investigation is valid (i.e., validity means that the investigation answered the investigative question with confidence; the manipulated variable caused the change in the responding or dependent variable). Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s
34 Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing d. Describe the purpose of the steps and materials of an investigation's procedure in terms of the validity of the investigation. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing
35 Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating
36 Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing e. Modify an investigation to improve the validity of the investigation and explain how the modifications improved the validity (e.g., more controlled variables, more accurate measuring techniques, greater sample size). Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s
37 DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic
38 Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing EALR WA.2. Inquiry: The student knows and applies the skills, processes, and nature of scientific inquiry. COMPONENT 2.2. Nature of Science: Understand the nature of scientific inquiry. BENCHMARK / GLE Nature of Science: Evolution of Scientific Ideas: Understand that increased comprehension of systems leads to new inquiry. W a. Describe how scientific inquiry results in new facts, evidence, unexpected findings, ideas, and explanations. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s
39 Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing b. Describe how results of scientific inquiry may change our understanding of the systems of the natural and constructed world. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing
40 Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating
41 Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing c. Describe how increased understanding of systems leads to new questions to be investigated. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s
42 DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document
43 Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing d. Describe how new ideas need repeated inquiries before acceptance. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s
44 Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing e. Describe how new investigative questions arise at the completion of scientific inquiry. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s
45 Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T
46 Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing EALR WA.3. Application: The student knows and applies science concepts and skills to develop solutions to human problems in societal contexts. COMPONENT 3.1. Designing Solutions: Apply knowledge and skills of science and technology to design solutions to human problems or meet challenges. BENCHMARK / GLE Designing Solutions: Identifying Problems: Analyze common problems or challenges in which scientific design can be or has been used to design solutions. W a. Describe how science and technology could be used to solve all or part of a human problem and vice versa (e.g., understanding erosion can be used to solve some flooding problems). Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA
47 using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing
48 Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing b. Describe the scientific concept, principle, or process used in a solution to a human problem (e.g., understanding of the relationship between electricity and magnetism has been used to make electric motors and generators). Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s
49 Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing c. Explain how to scientifically gather information to develop a solution (e.g., collect data by measuring all the factors and establish which are the most important to solve the problem). Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s
50 Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T
51 Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing d. Describe an appropriate question that could lead to a possible solution to a problem. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s
52 Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing EALR WA.3. Application: The student knows and applies science concepts and skills to develop solutions to human problems in societal contexts. COMPONENT 3.1. Designing Solutions: Apply knowledge and skills of science and technology to design solutions to human problems or meet challenges. BENCHMARK / Designing Solutions: Designing and Testing Solutions: Apply the scientific design process to develop and implement solutions to problems or challenges. W
53 GLE a. Propose, implement, and document the scientific design process used to solve a problem or challenge: define the problem; scientifically gather information and collect measurable data; explore ideas; make a plan; list steps to do the plan; scientifically test solutions; document the scientific design process. Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 2: The Forged Forensic Science: Unit 1 Case Activity 4: The Confusing Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 4 Case Activity 5: The Fraudulent Thread Forensic Science: Unit 4 Skill Learning Activity 3: Demonstrating Fabrics and Weave Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 1: The Curious Line Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 2: The Peculiar Letter T
54 Forensic Science: Unit 5 Case Activity 5: Case of the Hudson Doggerel Skills Forensic Science: Unit 5 Skill Learning Activity 2: Practicing Handwriting Skills Document Skills Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 1: Toxicological Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 2: Chromatographic Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 3: Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 4: Document Forensic Science: Unit 6 Activity 5: Blood Teacher Resource CD: ing Teacher Resource CD: Trace Evidence Virtual Laboratory: ABO-Rh Blood Typing b. Explain possible solutions to the problem (e.g., use pulleys instead of levers to lift a heavy object). Ridge Details Identification Skills Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 4: Latent s Forensic Science: Unit 1 Skill Learning Activity 5: Latent s DNA using DNA Frequency Calculations DNA s
Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP!
 Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP! Program description: Discover how whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students
Indiana Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP! Program description: Discover how whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students
Ohio Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP
 Ohio Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP Program description: Discover whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students will use
Ohio Academic Standards Addressed By Zoo Program WINGED WONDERS: SEED DROP Program description: Discover whether all seeds fall at the same rate. Do small or big seeds fall more slowly? Students will use
Science skills progression KS2
 The principal focus of science teaching in lower key stage 2 is to enable pupils to broaden their scientific view of the world around them. They should do this through exploring, talking about, testing
The principal focus of science teaching in lower key stage 2 is to enable pupils to broaden their scientific view of the world around them. They should do this through exploring, talking about, testing
overview Living Systems Grade 5 content goals
 Grade 5 overview Living Systems content goals The Living Systems Module consists of three sequential investigations, each designed to introduce students to transport systems in multicellular organisms.
Grade 5 overview Living Systems content goals The Living Systems Module consists of three sequential investigations, each designed to introduce students to transport systems in multicellular organisms.
Nerves and Digestion. Chapter 6, Lesson 3
 Nerves and Digestion Chapter 6, Lesson 3 Do Now. In your own words (without the book), answer the following questions. 1. What is the nervous system? 2. What are the cells called that make up the nervous
Nerves and Digestion Chapter 6, Lesson 3 Do Now. In your own words (without the book), answer the following questions. 1. What is the nervous system? 2. What are the cells called that make up the nervous
Information for Parents/Carers SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST
 SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST Working scientifically (Y1 and Y2) I can ask simple scientific questions. I can use simple equipment to make observations. I can carry out simple tests. I can identify
SCIENCE TARGETS - A YEAR 1 SCIENTIST Working scientifically (Y1 and Y2) I can ask simple scientific questions. I can use simple equipment to make observations. I can carry out simple tests. I can identify
Section 1.1: What is Science? Section 1.2: Science in Context Section 1.3: Studying Life
 Section 1.1: What is Science? Section 1.2: Science in Context Section 1.3: Studying Life 1.1 What science is and is not Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural
Section 1.1: What is Science? Section 1.2: Science in Context Section 1.3: Studying Life 1.1 What science is and is not Science is an organized way of gathering and analyzing evidence about the natural
Class 3. Year A. Autumn Term Spring Term Summer term Invaders and Settlers (Saxons, Vikings and Romans) Science Year 3 Magnets and friction
 Class 3 Year A Autumn Term Spring Term Summer term Invaders and Settlers (Saxons, Vikings and Romans) Tomb Raiders (Egyptians) Fantastic Fenland Year 3 Magnets and friction Year 4 Sound Year 3 Plants compare
Class 3 Year A Autumn Term Spring Term Summer term Invaders and Settlers (Saxons, Vikings and Romans) Tomb Raiders (Egyptians) Fantastic Fenland Year 3 Magnets and friction Year 4 Sound Year 3 Plants compare
IB 133 Life Science Standards for California Public Schools (1998 present) Kindergarten
 Kindergarten Different types of plants and animals inhabit the earth. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to observe and describe similarities and differences in the appearance
Kindergarten Different types of plants and animals inhabit the earth. As a basis for understanding this concept: a. Students know how to observe and describe similarities and differences in the appearance
SRS Achievement Statements. Science
 SRS Achievement Statements Science Scales SRS Achievement Statements for Science 2018/19 2 Year 1 Achievement Statements Working Scientifically talk about what I see, hear, smell, taste or touch ask you
SRS Achievement Statements Science Scales SRS Achievement Statements for Science 2018/19 2 Year 1 Achievement Statements Working Scientifically talk about what I see, hear, smell, taste or touch ask you
Page 1. Name:
 Name: 5021-1 - Page 1 1) A student measures his pulse rate while he is watching television and records it. Next, he walks to a friend's house nearby and when he arrives, measures and records his pulse
Name: 5021-1 - Page 1 1) A student measures his pulse rate while he is watching television and records it. Next, he walks to a friend's house nearby and when he arrives, measures and records his pulse
Digestive and Excretory Systems
 Digestive and Excretory Systems Homeostasis Q: How are the materials that enter and leave your body related to the processes that maintain homeostasis? 30.1 How is the human body organized and regulated?
Digestive and Excretory Systems Homeostasis Q: How are the materials that enter and leave your body related to the processes that maintain homeostasis? 30.1 How is the human body organized and regulated?
Chapter 1.1. The Process of Science. Essential Questions
 Chapter 1.1 The Process of Science Essential Questions 1. How does scientific inquiry answer questions about the living world? 2. How do observations lead to scientific inferences? 3. How do scientific
Chapter 1.1 The Process of Science Essential Questions 1. How does scientific inquiry answer questions about the living world? 2. How do observations lead to scientific inferences? 3. How do scientific
Levels of Organization
 Levels of Organization What do you think the 5 Levels of Organization are in the body?? Brainstorm with your group and write down what you think are the 5 Levels Pick a recorder. Levels of Organization:
Levels of Organization What do you think the 5 Levels of Organization are in the body?? Brainstorm with your group and write down what you think are the 5 Levels Pick a recorder. Levels of Organization:
Prepared using Wordle.net for fiendishlyclever.com by R Butler
 Prepared using Wordle.net for fiendishlyclever.com by R Butler Scientific enquiry Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Pupils describe or respond appropriately to simple features of objects, living things and events
Prepared using Wordle.net for fiendishlyclever.com by R Butler Scientific enquiry Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 Pupils describe or respond appropriately to simple features of objects, living things and events
2014 National Curriculum Science Band 1
 2014 National Curriculum Science Band 1 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways (Year 1 variety of common animals including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and
2014 National Curriculum Science Band 1 ask simple questions and recognise that they can be answered in different ways (Year 1 variety of common animals including fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds and
KeslerScience.com. Digestive System. Integumentary System. Circulatory System. Function: Function: Function: Main Organs: Main Organs: Main Organs:
 KeslerScience.com Integumentary System Circulatory System Digestive System Muscular System Nervous System Skeletal System Endocrine System (Female) Endocrine System (Male) Excretory System Reproductive
KeslerScience.com Integumentary System Circulatory System Digestive System Muscular System Nervous System Skeletal System Endocrine System (Female) Endocrine System (Male) Excretory System Reproductive
One Stop Shop For Educator
 One Stop Shop For Educator The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved
One Stop Shop For Educator The following instructional plan is part of a GaDOE collection of Unit Frameworks, Performance Tasks, examples of Student Work, and Teacher Commentary. Many more GaDOE approved
Big Book Science Set 1 Content and Process Skills
 Big Book Science Set 1 Content and Process Skills I Learn with My Senses The Mystery Seeds Living Things Are Everywhere! The Life of a Butterfly Our Earth What Is Weather? Tell Me All About It Watch What
Big Book Science Set 1 Content and Process Skills I Learn with My Senses The Mystery Seeds Living Things Are Everywhere! The Life of a Butterfly Our Earth What Is Weather? Tell Me All About It Watch What
Levels of Organization Notes
 Name period date assigned date due date returned 1. Levels of organization Levels of Organization Notes 1. basic of structure and function for things. 2. groups of cells that perform a specific function.
Name period date assigned date due date returned 1. Levels of organization Levels of Organization Notes 1. basic of structure and function for things. 2. groups of cells that perform a specific function.
Tumwater School District FOSS Science Third Grade: Earth Materials
 FOSS Investigation All Investigations All Investigations Standard FOSS Science Third Grade: Earth Materials EALR 2 INQA Question Scientific investigations are designed to gain knowledge about the natural
FOSS Investigation All Investigations All Investigations Standard FOSS Science Third Grade: Earth Materials EALR 2 INQA Question Scientific investigations are designed to gain knowledge about the natural
Science curriculum: Reception. Working Scientifically - Skills. Plants and Animals
 Science curriculum: Working Scientifically - Skills Reception Plants and Animals Identify and name common plants (green plants, wild plants and trees, deciduous and evergreen) Label parts of a plant Identify
Science curriculum: Working Scientifically - Skills Reception Plants and Animals Identify and name common plants (green plants, wild plants and trees, deciduous and evergreen) Label parts of a plant Identify
Unscramble THE HUMAN BODY. aehtr. taryre. vreil. hmsotac. crathea. Riddle: Why didn t the teddy bear tell the doll the bad news? Answer: He didn t.
 Unscramble Name Date Directions: To answer the riddle, unscramble each word and write it in the squares. Then write the circled letters in order on the numbered spaces below. 1 3 taryre 5 9 11 a blood
Unscramble Name Date Directions: To answer the riddle, unscramble each word and write it in the squares. Then write the circled letters in order on the numbered spaces below. 1 3 taryre 5 9 11 a blood
amygdala (ah MIG da la) a region of the brain involved in emotional memory, such as fear (SRB)
 FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
FOSS Human Systems Interactions, Next Generation Edition Glossary abnormal different from what is usual (SRB) aerobic cellular respiration the process by which a cell releases energy using chemical reactions
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
Human Body Systems Structure, Movement, and Control What do you think? Read the two statements below and decide whether you agree or disagree with them. Place an A in the Before column if you agree with
The diagram below represents the root growth of various plants. Use the diagram to answer question 2.
 TEKS 10B describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of transport, reproduction, and response in plants 10C analyze the levels of organization in biological systems and
TEKS 10B describe the interactions that occur among systems that perform the functions of transport, reproduction, and response in plants 10C analyze the levels of organization in biological systems and
ARE YOU READY FOR THE JUNE 2016 SECONDARY 3 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EXAM?
 ARE YOU READY FOR THE JUNE 2016 SECONDARY 3 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EXAM? So what s this document for? This document is designed to help you get prepared for the Secondary 3 Science & Technology exam. Often
ARE YOU READY FOR THE JUNE 2016 SECONDARY 3 SCIENCE & TECHNOLOGY EXAM? So what s this document for? This document is designed to help you get prepared for the Secondary 3 Science & Technology exam. Often
Introduction to Body Systems
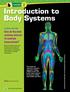 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems ESSENTIAL QUESTION How do the body systems interact to maintain homeostasis? By the end of this lesson, you should be able to describe the functions of the human body
Forensic Science Final Exam Review
 Forensic Science Final Exam Review Human Identity (Fingerprints, Forensic Anthropology, DNA) 1.Who developed the system known as anthropometry? 2.Who postulated the exchange of evidence principle? 3.In
Forensic Science Final Exam Review Human Identity (Fingerprints, Forensic Anthropology, DNA) 1.Who developed the system known as anthropometry? 2.Who postulated the exchange of evidence principle? 3.In
Body Systems. Before You Read. What parts make up each system of the human body? What is tissue? What is an organ?
 BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 20 Body Systems Textbook pages 52 63 Before You Read In this section, you will find out about the s of the human body. A is made of two or more parts that work together
BC Science 8 CH02 11/5/06 11:39 AM Page 20 Body Systems Textbook pages 52 63 Before You Read In this section, you will find out about the s of the human body. A is made of two or more parts that work together
Barlows Primary School Science Curriculum Content Key Stage 1 and
 Science Curriculum Content Key Stage 1 and 2 2017-2018 Curriculum Content Year 1 Curriculum. The content for Year 1 is detailed below: During year 1, pupils should be taught to use the following practical
Science Curriculum Content Key Stage 1 and 2 2017-2018 Curriculum Content Year 1 Curriculum. The content for Year 1 is detailed below: During year 1, pupils should be taught to use the following practical
The Human Body. Mrs. Green
 The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
The Human Body Mrs. Green Bell Work Which of the following helps the body to cool down? a) Shivering b) Sweating c) Running a fever d) Taking a deep breath Which of the following is a function of the digestive
Day 1 Essential Questions:
 Day 1 Essential Questions: ~What are the different body systems? ~What are the parts of the systems? ~How is this system connected to other body systems? ~How do you keep this system working properly?
Day 1 Essential Questions: ~What are the different body systems? ~What are the parts of the systems? ~How is this system connected to other body systems? ~How do you keep this system working properly?
Bodies and Systems. What is your body made of?
 What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
What is your body made of? You might say that you are made of organs like skin and a heart. You might say that you are made of tissue, cells, or even atoms. All these answers are correct. Multicellular
Life Science Unit I. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells
 Name: ate: 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells. are much smaller. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. ell iagram. have permeable membranes.. have
Name: ate: 1. Eukaryotic cells are differentiated from prokaryotic cells because eukaryotic cells. are much smaller. 4. Use the diagram to answer the question. ell iagram. have permeable membranes.. have
Amarillo ISD Science Curriculum
 Amarillo ISD _Anatomy & Physiology Stards Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum documents resources are aligned to the TEKS. The
Amarillo ISD _Anatomy & Physiology Stards Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum documents resources are aligned to the TEKS. The
Structure, Movement, and Control
 Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Lesson 2 Structure, Movement, and Control Scan Lesson 2. Read the lesson titles and bold words. Look at the pictures. Identify three facts you discovered about the structure, movement, and control of the
Amarillo ISD Science Curriculum
 Amarillo ISD _Anatomy & Physiology Stards Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum documents resources are aligned to the TEKS. The
Amarillo ISD _Anatomy & Physiology Stards Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum documents resources are aligned to the TEKS. The
Lesson 1 Understanding Science
 Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Content Vocabulary 6 Lesson Outline 7 Content Practice A 9 Content Practice B 10 School to Home 11 Key Concept Builders 12 Enrichment 16 Challenge 17 Scientific
Lesson 1 Student Labs and Activities Page Content Vocabulary 6 Lesson Outline 7 Content Practice A 9 Content Practice B 10 School to Home 11 Key Concept Builders 12 Enrichment 16 Challenge 17 Scientific
UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2
 Science Science UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2 Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Engage Eat a Cracker 1. Your teacher will give you two unsalted crackers. 2. Chew
Science Science UNIT 5: Structure and Function of Organisms, Part 2 Lesson 1: Physical and Chemical Changes in Digestion Engage Eat a Cracker 1. Your teacher will give you two unsalted crackers. 2. Chew
TEACHER RESOURCES IV UNIT SPECIFIC RESOURCES. Body Systems ISSUES AND LIFE SCIENCE REVISED FOR NGSS BODY SYSTEMS UNIT SPECIFIC RESOURCES 265
 ISSUES AND LIFE SCIENCE Body Systems T H I R D E D I T I O N REVISED FOR NGSS BODY SYSTEMS UNIT SPECIFIC RESOURCES 265 UNIT OVERVIEW BODY SYSTEMS Listed below is a summary of the activities in this unit.
ISSUES AND LIFE SCIENCE Body Systems T H I R D E D I T I O N REVISED FOR NGSS BODY SYSTEMS UNIT SPECIFIC RESOURCES 265 UNIT OVERVIEW BODY SYSTEMS Listed below is a summary of the activities in this unit.
Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs
 Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs and organ systems). A multicellular living thing will
Multicellular living things are able to divide up the labor required to perform life functions between the different levels of organization ( organs and organ systems). A multicellular living thing will
Diagnostic Assessment for The Inside Story
 Diagnostic Assessment for The Inside Story Cells, Organs, and Systems of the Human Body Table of Contents Item Page Number Diagnostic Assessment, The Inside Story, Instructions page 2 Diagnostic Assessment,
Diagnostic Assessment for The Inside Story Cells, Organs, and Systems of the Human Body Table of Contents Item Page Number Diagnostic Assessment, The Inside Story, Instructions page 2 Diagnostic Assessment,
The Nervous System. Two Systems Within a System. 526 Chapter 17
 1 The Nervous System Key Concept Your nervous system is an organ system that gathers, interprets, and responds to sensory information. What You Will Learn The central nervous system processes and responds
1 The Nervous System Key Concept Your nervous system is an organ system that gathers, interprets, and responds to sensory information. What You Will Learn The central nervous system processes and responds
Food Science TEKS/LINKS Student Objectives One Credit
 First Six Weeks Professional Skills & Scientific FS 1(A) The student will apply interpersonal communication skills in business and industry settings. FS 1(B) The student will explain and recognize the
First Six Weeks Professional Skills & Scientific FS 1(A) The student will apply interpersonal communication skills in business and industry settings. FS 1(B) The student will explain and recognize the
Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities
 Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities Vocabulary List and Student Definitions (elementary level): Cell: basic unit of life, too small to see with the naked eye Tissue: group
Body Science: Cell Theory (3 rd -5 th Grades) Pre-Visit Activities Vocabulary List and Student Definitions (elementary level): Cell: basic unit of life, too small to see with the naked eye Tissue: group
Life Science. From Molecules to Organisms: Structures and Processes
 Essential Questions: Life Science 1. How do the structures of organisms contribute to life s functions? 2. How does matter and energy move through individual organisms and ecosystems? 3. How does genetic
Essential Questions: Life Science 1. How do the structures of organisms contribute to life s functions? 2. How does matter and energy move through individual organisms and ecosystems? 3. How does genetic
Pennsylvania Assessment Anchors for Biological Science, Grade 11. High School Biology 1
 Pennsylvania Assessment Anchors for Biological Science, Grade 11 High School Biology 1 Science and Global Issues: Biology (SGI Biology) is written by the SEPUP group, at the Lawrence Hall of Science, University
Pennsylvania Assessment Anchors for Biological Science, Grade 11 High School Biology 1 Science and Global Issues: Biology (SGI Biology) is written by the SEPUP group, at the Lawrence Hall of Science, University
Test Review Unit 0_1 Scientific knowlege
 Test Review Unit 0_1 Scientific knowlege THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD The scientific method is a process used by scientists to study the world around them and to obtain objective knowledge about it. WHAT ARE
Test Review Unit 0_1 Scientific knowlege THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD The scientific method is a process used by scientists to study the world around them and to obtain objective knowledge about it. WHAT ARE
Below are the 2018 end of year targets for Year 1-6 students to achieve a satisfactory grade (C Grade) for Science.
 End of Year Targets for Science 2018 Dear Parents and Carers, Below are the 2018 end of year targets for Year 1-6 students to achieve a satisfactory grade (C Grade) for Science. End of Year Targets for
End of Year Targets for Science 2018 Dear Parents and Carers, Below are the 2018 end of year targets for Year 1-6 students to achieve a satisfactory grade (C Grade) for Science. End of Year Targets for
Nervous System. Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body
 Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
Human Body Systems Nervous System Functions Controls all body s functions Senses and recognizes information from inside and outside of the body Nervous System Main Parts Brain Nerves Spinal cord What it
What is the Scientific Process? It s a logical, problem solving technique. Experimental Design is an excellent example of scientific process.
 Scientific Process What is the Scientific Process? It s a logical, problem solving technique. Experimental Design is an excellent example of scientific process. What leads to an experimental design? Having
Scientific Process What is the Scientific Process? It s a logical, problem solving technique. Experimental Design is an excellent example of scientific process. What leads to an experimental design? Having
Name Teacher Hour
 http://www.citizenofthemonth.com/wp-content/images/frink.gif Name Teacher Hour www.mononagrove.org/faculty/ips/index.cfm Scientific Models What is a scientific model? The scientific process making observations,
http://www.citizenofthemonth.com/wp-content/images/frink.gif Name Teacher Hour www.mononagrove.org/faculty/ips/index.cfm Scientific Models What is a scientific model? The scientific process making observations,
Designing an experiment 7 TH /8 TH GRADE SCIENCE
 Designing an experiment 7 TH /8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Scientific inquiry 1. Make an observation 2. Ask a question 3. Create a hypothesis 4. Design an experiment 5. Gather and analyze data 6. Draw conclusions
Designing an experiment 7 TH /8 TH GRADE SCIENCE Scientific inquiry 1. Make an observation 2. Ask a question 3. Create a hypothesis 4. Design an experiment 5. Gather and analyze data 6. Draw conclusions
First Grade Science Report Card Rubric Fourth Nine Weeks
 Matter How Energy Changes Matter I can classify solid objects by properties. accurately sort the sample 1.5A objects by any of the following properties: shape, color, texture, relative size, or relative
Matter How Energy Changes Matter I can classify solid objects by properties. accurately sort the sample 1.5A objects by any of the following properties: shape, color, texture, relative size, or relative
Chapter 7: Human body system
 Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Grade: 8 END OF SEMESTER EXAMINATION FIRST SEMESTER REVISION BOOKLET AY 2018-2019 Subject: Science Teacher: Mr. Hafiz Muhammad Ahsan Ali Chapter 7: Human body system 1. Directions: On the line before each
Science 8. Unit 2. Body Systems
 Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Science 8 Unit 2 Body Systems Name: Class: TOPIC 2 Parts of a Compound Light BLM 2-2 Microscope Goal Practise calculating different magnifications of a microscope. Think About It A magnifying lens that
Breakdown ACTIVITY OVERVIEW SUMMARY KEY CONCEPTS AND PROCESS SKILLS. Teacher s Guide B-37 L A B O R ATO R Y
 Breakdown 14 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY Students use antacid tablets and vinegar to model the processes of chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. After
Breakdown 14 40- to 2 50-minute sessions ACTIVITY OVERVIEW L A B O R ATO R Y SUMMARY Students use antacid tablets and vinegar to model the processes of chemical and mechanical breakdown of food. After
What is the function of the urinary system? How do the kidneys filter the blood? What are common problems with the urinary system?
 CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
CHAPTER 24 2 The Urinary System SECTION The Digestive and Urinary Systems BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What is the function of the urinary
Utah Core Standards for Agricultural Science I
 A Correlation of To the for Agricultural Science I Resource Title:, 6e Publisher: Pearson ISBN (10 or 13 digit unique identifier is required): Student Edition 978-1-269-54296-8 Media (text, software, internet,
A Correlation of To the for Agricultural Science I Resource Title:, 6e Publisher: Pearson ISBN (10 or 13 digit unique identifier is required): Student Edition 978-1-269-54296-8 Media (text, software, internet,
LAB-AIDS Correlations to New Mexico 9-12 Science Standards 1 HIGH SCHOOL BIOLOGY
 LAB-AIDS Correlations to New Mexico 9-12 Science Standards 1 HIGH SCHOOL BIOLOGY Science and Global Issues: Biology (SGI Biology) is written by the SEPUP group, at the Lawrence Hall of Science, University
LAB-AIDS Correlations to New Mexico 9-12 Science Standards 1 HIGH SCHOOL BIOLOGY Science and Global Issues: Biology (SGI Biology) is written by the SEPUP group, at the Lawrence Hall of Science, University
After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions:
 CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
CHAPTER 17 1 The Nervous System SECTION Communication and Control 7.5.a, 7.5.b California Science Standards BEFORE YOU READ After you read this section, you should be able to answer these questions: What
Human Body. The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related.
 Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Human Body The student knows that the human body is made of systems with structure and functions that are related. Cells Cells are the smallest living structures. All living things are made up of one or
Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
Name: Period: Due Date: Unit 6.1 Test Review - Teacher THE NERVOUS, INTEGUMENTARY, CIRCULATORY, AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS The Nervous System: 1. What are the 3 parts of a neuron and what do they do? Dendrites:
The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge and skills that it brings.
 WOODLEA W Science Y6 Essential Characteristics The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge and skills that it brings. Confidence and competence
WOODLEA W Science Y6 Essential Characteristics The ability to think independently and raise questions about working scientifically and the knowledge and skills that it brings. Confidence and competence
CARTERVILLE SCHOOL DISTRICT SCIENCE CURRICULUM
 FIRST NINE WEEKS CARTERVILLE SCHOOL DISTRICT SCIENCE CURRICULUM GRADE 2 Revised 2009 Identify words and construct meanings from text, illustrations, graphics, and charts. Acknowledge that people use scientific
FIRST NINE WEEKS CARTERVILLE SCHOOL DISTRICT SCIENCE CURRICULUM GRADE 2 Revised 2009 Identify words and construct meanings from text, illustrations, graphics, and charts. Acknowledge that people use scientific
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems
 3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
3.0 Healthy human function depends on a variety of interacting and reacting systems Vocabulary: Mechanical digestion: physical break down of food into very small pieces. Chemical digestion: breakdown of
Ok, here s the deal. My name is Mel, but my close friends call me Messy Mel. I think it s their way of showing respect.
 The next few pages feature detailed review sheets for your students to study key topics. Messy Mel will serve as the narrator and walk students through a wide variety of terms and concepts (with his special
The next few pages feature detailed review sheets for your students to study key topics. Messy Mel will serve as the narrator and walk students through a wide variety of terms and concepts (with his special
The Nature of Science
 The Nature of Science To be scientifically literate, science students should have deeper understandings of science that studying the Nature of Science (NOS) provides. Write an account of what you think
The Nature of Science To be scientifically literate, science students should have deeper understandings of science that studying the Nature of Science (NOS) provides. Write an account of what you think
BENCHMARK REVIEW (THIS WILL BE GRADED)
 BENCHMARK REVIEW (THIS WILL BE GRADED) NAME D E F C B J A I H G QL QN QN QL QL 4 5 1 2 3 USE THE WORDBANK AND WRITE THE WORD THAT BEST FITS THE DEFINITION TESTABLE VARIABLE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE Sample
BENCHMARK REVIEW (THIS WILL BE GRADED) NAME D E F C B J A I H G QL QN QN QL QL 4 5 1 2 3 USE THE WORDBANK AND WRITE THE WORD THAT BEST FITS THE DEFINITION TESTABLE VARIABLE INDEPENDENT VARIABLE Sample
Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015 Sources of Information: Use your notes, ppts and review material on teacher s website, and online resources. Cells 1. What are the 3 components
Name: Class Period: Due Date: Spring Final Exam Review 2015 Sources of Information: Use your notes, ppts and review material on teacher s website, and online resources. Cells 1. What are the 3 components
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0982216887* TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE 0608/03 Paper 3 May/June 2013 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *0982216887* TWENTY FIRST CENTURY SCIENCE 0608/03 Paper 3 May/June 2013 1 hour 30 minutes Candidates
SE: , 323. TECH: Student CD-Rom, Instructor s CD-Rom, A002: Interpret motto, emblem, and dress code for members SE:
 DUTY A: Career and Technical Student Organizations Task: A001: Discuss basic knowledge of national student organizations SE: 318-321, 323 TE: 376-381 TR: 218-220; Transparency 14-9 14-11 A002: Interpret
DUTY A: Career and Technical Student Organizations Task: A001: Discuss basic knowledge of national student organizations SE: 318-321, 323 TE: 376-381 TR: 218-220; Transparency 14-9 14-11 A002: Interpret
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
The Scientific Process
 The Scientific Process Before we begin. What does science mean to you? How would you define life to a young child? Do you believe there is life elsewhere in the universe? Why or why not? List the steps
The Scientific Process Before we begin. What does science mean to you? How would you define life to a young child? Do you believe there is life elsewhere in the universe? Why or why not? List the steps
30.1 Organization of the Human Body
 30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
30.1 Organization of the Human Body Lesson Objectives Describe how the human body is organized. Explain homeostasis. Lesson Summary Organization of the Body The levels of organization in a multicellular
Chapter 1. The Science of Biology. h+p://www.bozemanscience.com/biology
 Chapter 1 The Science of Biology h+p://www.bozemanscience.com/biology Section 1: What is Science? The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural
Chapter 1 The Science of Biology h+p://www.bozemanscience.com/biology Section 1: What is Science? The goal of science is to investigate and understand the natural world, to explain events in the natural
Organs of the Nervous System: brain, spinal cord, and nerves
 Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 2: Cellular Chemistry
 Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 2: Cellular Chemistry NC Essential Standard: 1.2.1 Explain how cells use buffers to regulate cell ph 4.1.1 Compare the structure and functions
Unit 2: Cellular Chemistry, Structure, and Physiology Module 2: Cellular Chemistry NC Essential Standard: 1.2.1 Explain how cells use buffers to regulate cell ph 4.1.1 Compare the structure and functions
Specialized cells are cells that have a specific. Similar specialized cells working together create.
 Body Systems Review Specialized cells are cells that have a specific. Similar specialized cells working together create. Similar specialized tissues working together create. Organs working together create.
Body Systems Review Specialized cells are cells that have a specific. Similar specialized cells working together create. Similar specialized tissues working together create. Organs working together create.
Science is a way of learning about the natural world by observing things, asking questions, proposing answers, and testing those answers.
 Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 The Nature of Science and Scientific Inquiry Online resources: www.science.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe9/centre.html Remember to ask your teacher whether your classroom
Science 9 Unit 1 Worksheet Chapter 1 The Nature of Science and Scientific Inquiry Online resources: www.science.nelson.com/bcscienceprobe9/centre.html Remember to ask your teacher whether your classroom
Science & Technology Exam?
 ARE YOU READY FOR THE SECONDARY 3 2015 Science & Technology Exam? So what s this document for? This document is designed to help you get prepared for the Secondary 3 Science & Technology exam. Often parents
ARE YOU READY FOR THE SECONDARY 3 2015 Science & Technology Exam? So what s this document for? This document is designed to help you get prepared for the Secondary 3 Science & Technology exam. Often parents
Pre- Assessment. Prompt. Advance. 1. Duplicate assessment for each student
 Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
Pre- Assessment Concepts Assessed Living things are organized structurally from microscopic cells to tissues, organs, and organ systems; within each of these levels, living things demonstrate a structure
SCIENCE POLICY. Date: March Signed: Review: March 2019
 SCIENCE POLICY Date: March 2018 Signed: Review: March 2019 T:\1 Policies 2017_2018 new or under review\curriculum final\science Policy T:\1 Policies 2017_2018 new or under review\curriculum final\science
SCIENCE POLICY Date: March 2018 Signed: Review: March 2019 T:\1 Policies 2017_2018 new or under review\curriculum final\science Policy T:\1 Policies 2017_2018 new or under review\curriculum final\science
How the Nervous System Works (pp )
 How the Nervous System Works (pp. 600 604) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, identify the
How the Nervous System Works (pp. 600 604) This section describes what the nervous system does in the body. It also tells how nerve impulses travel. Use Target Reading Skills As you read, identify the
Human Body Systems. Long narrow tube mixes enzymes with food Small nutrient molecules diffuse into blood
 Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
Human Body Systems Living Environment AIS Mr. DuRoss Digestive System : Break down large food molecules into smaller parts that the body can use Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine
BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS STANDARD REVIEW
 4.B.9.B BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS (B.9) Science concepts. The student knows the significance of various molecules involved in metabolic processes and energy conversions that occur in living organisms.
4.B.9.B BIOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS (B.9) Science concepts. The student knows the significance of various molecules involved in metabolic processes and energy conversions that occur in living organisms.
Name: Class: Date: Question #1. Question #2. What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels.
 9/30/2017 ody Systems Test Name: lass: ate: Question #1 What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels. It transports oxygen to all body cells. It helps the
9/30/2017 ody Systems Test Name: lass: ate: Question #1 What is the role of the heart in the circulatory system? It forms a network of blood vessels. It transports oxygen to all body cells. It helps the
What is the major site of digestion? If you answered stomach, you missed it! The correct answer is small intestine.
 DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
DIGESTION SIMULATION LAB PAP CLASS SET BACKGROUND INFORMATION What is digestion and where does it begin? Digestion is the breaking down of food into forms that our bodies can use. Your digestive system
Objective 1.e. Justify whether an argument defending a conclusion is logical. Case 21 1 st Benchmark Study Guide
 Case 21 1 st Benchmark Study Guide Objective 1: Inquiry 1. What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data? 2. Why is skepticism an important part of science? 3. What is an inference?
Case 21 1 st Benchmark Study Guide Objective 1: Inquiry 1. What is the difference between qualitative and quantitative data? 2. Why is skepticism an important part of science? 3. What is an inference?
PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND SPORT 2Ä ESO UNIT I THE HUMAN BODY AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY
 IES LAS MARINAS SECCIÓN BILINGÜE PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND SPORT 2Ä ESO UNIT I THE HUMAN BODY AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY MICHAEL PHELPS The human body The human body is the most wonderful, complex machine in the
IES LAS MARINAS SECCIÓN BILINGÜE PHYSICAL EDUCATION AND SPORT 2Ä ESO UNIT I THE HUMAN BODY AND PHYSICAL ACTIVITY MICHAEL PHELPS The human body The human body is the most wonderful, complex machine in the
Pose a question means come up with a question that can be answered by gathering scientific evidence (using measurements/ observations).
 The Scientific Method The 5 steps of the scientific method are: 1. Pose a question 2. Develop a 3. Design an experiment 4. Interpret Data (Results) 5. Draw a conclusion Pose a question means come up with
The Scientific Method The 5 steps of the scientific method are: 1. Pose a question 2. Develop a 3. Design an experiment 4. Interpret Data (Results) 5. Draw a conclusion Pose a question means come up with
Reporting Category 4: Biological Processes and Systems (11questions)
 Reporting Category 4: Biological Processes and Systems (11questions) Major topics include: 1) Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration (energy and matter) 2) Role of enzymes 3) Animal systems* 4) Plant
Reporting Category 4: Biological Processes and Systems (11questions) Major topics include: 1) Photosynthesis and Cellular respiration (energy and matter) 2) Role of enzymes 3) Animal systems* 4) Plant
Honors Biology Chapter 2. The Science of Biology
 Honors Biology Chapter 2 The Science of Biology Concept 2.1: Discovery Science Emphasizes Inquiry and Observation I. Science as Inquiry A. Science = to know, to answer? s about the natural world 1. 2 main
Honors Biology Chapter 2 The Science of Biology Concept 2.1: Discovery Science Emphasizes Inquiry and Observation I. Science as Inquiry A. Science = to know, to answer? s about the natural world 1. 2 main
S7L Which part of the body receives messages transmitted by nerve cells located throughout the body?
 S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
S7L2-3 1. Which of the following is the heart's function? A. pumping blood B. breaking down food C. removing wastes from the blood D. taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide 2. The body takes in
Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers
 Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers 1. What are the five levels of structural organization in order from largest to smallest? Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems - Organism 2. What are the phases of
Human Body Systems Study Guide Answers 1. What are the five levels of structural organization in order from largest to smallest? Cells Tissues Organs Organ Systems - Organism 2. What are the phases of
Name Class Date. KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate.
 Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Section 1: How Organ Systems Communicate KEY CONCEPT The nervous system and the endocrine system provide the means by which organ systems communicate. VOCABULARY nervous system central nervous system (CNS)
Unit 3 - Homeostasis in the Human Body
 Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 6. Which diagram best represents a blood cell from
Living Environment Practice Exam- Parts A and B-1 1. Base your answer to the following question on the diagram below and on your knowledge of biology. 6. Which diagram best represents a blood cell from
Forensic Science TEKS/LINKS Student Objectives One Credit
 First Six Weeks Professional Standards/Employability Skills FS 1(A) The student will demonstrate professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected
First Six Weeks Professional Standards/Employability Skills FS 1(A) The student will demonstrate professional standards/employability skills as required by business and industry. The student is expected
