Diagnostic Value of MRI CSF Flowmetry for the Diagnosis of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
|
|
|
- Belinda Fisher
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Original Article Diagnostic Value of MRI CSF Flowmetry for the Diagnosis of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus Omar M. El Falaky 1, Lamiaa I.A. Metwally 2, Ahmed M. Abdelalim 3 Departments of Neurosurgery 1, Radiology 2, Neurology 3, Cairo University; Egypt ABSTRACT Background: Normal pressure hydrocephalus is a rare disease, with unpredictable surgical outcome after shunt placement. To date, no single diagnostic tool or combination of tools has proved capable of reliably predicting whether the condition of a patient with suspected NPH will improve or not after a shunting procedure. Objective: To evaluate the value of MRI CSF Flowmetry as a non-invasive method to help establish the diagnosis of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus. Method: Between June 2009 and December 2011, 8 patients in whom NPH had been diagnosed (on the basis of clinical findings and imaging) underwent CSF Flowmetry, and diagnostic lumbar tap for confirmation of diagnosis followed by a programmable shunt insertion. A review and analysis of the surgical outcome of the 8 cases was done. Result: Variable degrees of improvement were noted in all patients. 75% of cases had gait and cognitive improvement. 50 % of cases had improved bladder control. It was noted that the degree of improvement was better in patients with higher preoperative stroke volume. Conclusion: MRI CSF Flowmetry proved to be a reliable, safe and non invasive investigation to be used for the diagnosis of normal pressure hydrocephalus- To start reconsidering the need for the diagnostic lumbar tap; further studies are needed, with more patients and longer follow up periods. [Egypt J Neurol Psychiat Neurosurg. 2012; 49(3): ] Key Words: Normal pressure hydrocephalus, Shunt placement, Cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics, Programmable shunt INTRODUCTION In 1965, Hakim and Adams proposed for the first time a form of communicating hydrocephalus that could result in a treatable dementia. The CSF pressure in those patients is generally normal 1. The diagnosis and management of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus (INPH) remains unclear. Many supplementary tests have been used to predict which patients would benefit from placement of a shunt, the value of those tests have not been established 2. To distinguish which older patients with ventriculomegaly and suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) should undergo surgical shunting remains difficult as the differential diagnosis of the disease includes all types of dementia, and traumatic and vascular brain atrophy 3. MRI is very sensitive to fluid motion. This normal movement of CSF results in a loss of signal (flow void) within the cerebral aqueduct. In NPH, CSF flow is hyperdynamic, with an increase in the amount and velocity of CSF passing rostrally, then caudally, through the cerebral aqueduct with each cardiac cycle 4. This was characterized by enlargement of the CSF flow void within the cerebral aqueduct and the fourth ventricle on Correspondence to Omar M. El Falaky, Neurosurgery Department, Cairo University, Egypt. Tel.: omarfalaky@hotmail.com axial T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans 5. This new MRI technique allows quantification of CSF flow. Measurements are performed in the cerebral aqueduct, the narrowest portion of the ventricular system and therefore the location of highest CSF flow velocity 6. Since CSF motion is pulsatile, the average of the volume of CSF moving caudally during systole and rostrally during diastole is calculated. This is defined as the CSF stroke volume. It was found in the initial study with this technique that CSF stroke volumes above 42 microliter were associated with a favorable response to shunting 7. This is a promising tool for screening patients with clinical symptoms of NPH and thus identifying a treatable dementia without risking postsurgical complications in patients who will not benefit 8. PATIENTS AND METHODS Between June 2009 and December 2011, 12 patients presented with clinical syndrome suggestive of NPH (Dementia, gait disturbance). They were subjected to the following: Evaluation: I. Clinical assessment: Full Medical History and Clinical examination, establishing the diagnosis, Cognitive functions are assessed with the MiniMental State Examination (MMSE) 9. Egypt J Neurol Psychiat Neurosurg. July 2012 Vol 49 Issue 3 277
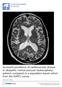
2 II. Radiological Assessment: CT and MRI Brain done demonstrating Ventriculomegaly and any associated pathology.mri Flowmetry is done in positive cases after clinical improvement following diagnostic lumbar tap, according to the following protocol: CSF Flowmetry Technique: Patients underwent the CSF flowmetry examination on MR machine a 1.5-T Super conducting system. The demonstrated technique was applied to all the patients included in this the study; figures below are those of one of the patients included in the study. CSF flow properties were analyzed at the level of the aqueduct of Sylvius in all patients. A circular polarized head-array coil and ultra gradients and the same parameters of examination were chosen. Conventional MRI of the brain was performed in axial T1WI, axial and sagittal T2WI were obtained (Figure 1). For phase-contrast MR imaging, the axial technique: CSF flow dynamics were quantitatively studied by using a cardiac gated (ECG being used for cardiac synchronization) high resolution axial phase contrast protocol with an imaging plane perpendicular to the proximal 1/3 of the cerebral aqueduct. The direction of flow encoding was caudo-cranial. The images were displayed on a gray scale, so as low signal intensity indicated caudal flow while bright signal intensity represented cranial flow. CSF flow quantification was performed on those phase images using the region-of-interest (ROI) measurements and a CSF flow wave form was generated (Figure 2). The generated CSF flow wave form analysis: Plotting time of the cardiac cycle on the x axis and the velocity on the y axis. During CSF diastole, CSF moves in caudo-cranial direction (positive velocity), and during CSF systole, CSF flows in the craniocaudal direction (negative velocity). A corresponding table that shows the CSF velocity and flow values for each time frame is obtained (Figure 3). Post processing calculations: Following the acquisition of the CSF flow velocity curves analysis: The end diastolic peak velocity (in cm/sec), the peak systolic velocity (in cm/sec), mean systolic velocity and flow (in ml/sec). The mean flow was calculated from the following equation: mean flow (in cm³/sec) = mean velocity (in cm/sec) area of ROI (in cm²), (the mean velocity was automatically determined from the mean value of the obtained velocities of each cardiac phase and the area of ROI detected by the MR unit). Then detection of onset of CSF systole (in msec), time of CSF peak systole (in msec), and duration of CSF systole (in msec). Calculation of the systolic stroke volume as follows: systolic stroke volume (in microliters) = mean systolic flow duration of CSF systole. III. Lumbar Tap: Lumbar tap was done in left lateral position and CSF manometry and release of cm. of CSF was performed and clinical improvement was observed within 72 hours. Surgical intervention In Patients with clinical improvement following the lumbar tap (n=8) the following was performed: a. Operative Intervention: Surgical placement of a programmable ventriculo-peritoneal shunt b. Post Operative Assessment: of the clinical outcome, and complications. Patient who did not improve in cerebrospinal lumbar tap were excluded from this study (n=4). Figure 1. Pre operative Sagittal T2WI MRI of the brain of one of the patients in the studied group showing the dilatation of the lateral ventricle. 278 Egypt J Neurol Psychiat Neurosurg. July 2012 Vol 49 Issue 3
3 (A) (B) Figure 2. (A) MRI of one of the patients in the studied group showing the displayed images on a grey scale and the low signal intensity indicated caudal flow while bright signal intensity represented cranial flow. (B) The generated CSF flow wave form. Figure 3. CSF velocity and flow values for each time frame is obtained on MRI scanner. RESULTS This study included a total of 8 patients with ventriculomegaly on CT and or conventional MRI with provisional clinical diagnosis of normal pressure hydrocephalus. The diagnosis was confirmed in patients improving clinically after lumbar cerebrospinal tap and with a positive MRI CSF flowmetry and they were operated upon by insertion of a programmable VP shunt. The other 4 patients who did not show clinical improvement after Lumbar tap were excluded from the study. Age of the patients ranged between 64 and 76 years (mean 68 Years).63% of patients were males (5/8 cases) and 37% Females (3/5 cases).all the patients included suffered the clinical triad of NPH with variable degree of intensity. CSF flowmetry stroke volume recording showed all 8 patients had a systolic stroke volume above 42 microliters. Range microliters. Mean systolic stroke volume 60 microliters. Clinical outcome: All patients included in this study had clinical improvement in at least one of their symptoms. Gait improvement was found in 75% of cases. Cognitive function also improved in 75% of cases. Bladder control improved in 50% of cases. It was noted that the degree of improvement was better in patients with higher preoperative stroke volume. Complications: Two cases suffered postoperative subdural hygroma and one case had a thin film of subdural hematoma, the post-operative collections were mild enough not to cause any symptoms, yet they were closely observed. This was managed by elevating the opening pressure of the programmable shunt 2 cm (from 14cm used in all patients to 16 cm) and the collections disappeared on follow up scans and the patients improved. Follow up period: of patients ranged between 6-24 months.mean follow up period was 12 months Egypt J Neurol Psychiat Neurosurg. July 2012 Vol 49 Issue 3 279
4
5 Table 1. NPH patient population and postoperative clinical outcome. Patient Age/Sex 64/F 68/M 73/M 61/F 76/M 73/M 64/M 66/M Stroke Volume* Cognitive Improvement Gait Improvement Bladder Improvement Operative Complication - _ Thin Subdural Hygroma - - Thin Subdural blood Thin Subdural Hygroma Follow Up / months *CSF Flowmetry Systolic Stroke Volume (Microliters) DISCUSSION Normal pressure hydrocephalus (NPH) is one of the few causes of dementia that is potentially reversible.the Presentation of NPH can occur in various forms and degrees of each element of the classic triad of: dementia, gait disturbance and urine incontinence. Generally, gait disturbance plus one additional feature is required to consider the diagnosis 10. Two, forms of NPH exist, idiopathic and secondary. Cases where earlier trauma, hemorrhage, infection, mass lesions, or aqueductal stenosis contribute to hydrocephalus are considered symptomatic or secondary forms of NPH 11. In our study, both idiopathic and secondary forms of NPH were included; one case had a history of tumor resection. Two cases had history of cerebrovascular strokes, yet the diagnosis was still established according to criteria mentioned in our study, and clinical improvement was noted in those cases, compared to the other patients in the study who presented with idiopathic type. Surgical complications in our study was found in 3 patients of post-operative subdural Hygroma and blood collections (38%) of cases, comparable with complication rate of Eide et al., who had a 30% postoperative shunt complication rate in a much larger population of patients 12. Our complications however were transient and disappeared on follow up, due to raising the opening pressure of the programmable shunts inserted. Many earlier studies focused on the value of basic tests such as the continuous lumbar drain for diagnosis of NPH, however, Marmarou et al. 2 claimed a positive predictive value of 90.5% in NPH patients who had a clinical improvement after inserting the external lumbar drain, but in his series of 151 patients, 22.3% of patients whose condition was not improved after external lumbar drain had a good outcome after a CSF shunting procedure. Also, such a maneuver is invasive with recorded complications such as wound infection and meningitis and root irritation 13. Other investigations that were assessed included CSF cisternography and CSF outflow resistance (RO), and lumbar infusion tests, but such invasive tests inspite of their usefulness, showed complications such as headache and signs of meningism 2 thus the interest in their use was fading away. In the literature, the predictive Value of Aqueductal CSF Flow Velocity was controversial, partially because of the few number of cases and the few number of studies. Bradley et al. After studying 18 patients with suspected NPH, found no statistical significance between aqueductal flow void score and responsiveness to shunting. He noticed on the other hand that a relationship between CSF stroke volume greater than 42 and response to shunting were statistically significant. He also noted no complications related to MRI have been reported 7. Marmarou et al. found that, neither MRI CSF flow void sign nor quantitative CSF flow velocity seems to have significant diagnostic value. On the other hand, they also agreed that CSF stroke volume may potentially have greater prognostic value than aqueductal flow void 2. In our study there was an evident correlation between the systolic stroke volume and degree of clinical improvement: all symptoms (dementia, gait and bladder disturbance improved in the patients with systolic stroke volumes above 60 microliters. Kahlon Egypt J Neurol Psychiat Neurosurg. July 2012 Vol 49 Issue 3 277
6 et al. 14 and Tarnaris et al. 15 share our belief that systolic stroke volume is a promising tool in selecting patients with normal pressure hydrocephalus symptoms to shunt surgery. Conclusion - MRI CSF Flowmetry proved to be a reliable, safe and non invasive tool of investigation to be used for the diagnosis of normal pressure hydrocephalus. - To start reconsidering the need for the lumbar tap, further studies are needed, with more patients and longer follow up periods. - Programmable shunt, though relatively expensive yet it provided a solution that spared the patients with post-operative subdural collections, the need for another surgery. [Disclosure: Authors report no conflict of interest] REFERENCES 1. Hakim S, Adams RD. The special clinical problem of symptomatic hydrocephalus with normal cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Observations on cerebrospinal fluid hydrodynamics. J Neurol Sci. 1965; 2(4): Marmarou A, Bergsneider M, Klinge P, Relkin N, Black PM. The value of supplemental prognostic tests for the preoperative assessment of idiopathic normalpressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 2005; 57(3 Suppl): S17-28; discussion ii-v. 3. Luetmer PH, Huston J, Friedman JA, Dixon GR, Petersen RC, Jack CR, et al. Measurement of cerebrospinal fluid flow at the cerebral aqueduct by use of phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging: technique validation and utility in diagnosing idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgery. 2002; 50(3): ; discussion Bradley WG, Kortman KE, Burgoyne B. Flowing cerebrospinal fluid in normal and hydrocephalic states: appearance on MR images. Radiology. 1986; 159(3): Bradley WG, Whittemore AR, Kortman KE, Watanabe AS, Homyak M, Teresi LM, et al. Marked cerebrospinal fluid void: indicator of successful shunt in patients with suspected normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Radiology. 1991; 178(2): Schroeder HW, Schweim C, Schweim KH, Gaab MR. Analysis of aqueductal cerebrospinal fluid flow after endoscopic aqueductoplasty by using cine phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg. 2000; 93(2): Bradley WG, Scalzo D, Queralt J, Nitz WN, Atkinson DJ, Wong P. Normal-pressure hydrocephalus: evaluation with cerebrospinal fluid flow measurements at MR imaging. Radiology. 1996; 198(2): Hurley RA, Bradley WG, Latifi HT, Taber KH. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: significance of MRI in a potentially treatable dementia. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci. 1999; 11(3): Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR. "Minimental state". A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. J Psychiatr Res. 1975; 12(3): Conn HO. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: new complications and concepts. Pract Neurol. 2007; 7(4): Shprecher D, Schwalb J, Kurlan R. Normal pressure hydrocephalus: diagnosis and treatment. Curr Neurol Neurosci Rep. 2008; 8(5): Eide PK, Sorteberg W. Diagnostic intracranial pressure monitoring and surgical management in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: a 6-year review of 214 patients. Neurosurgery. 2010; 66(1): Anile C, De Bonis P, Albanese A, Di Chirico A, Mangiola A, Petrella G, et al. Selection of patients with idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus for shunt placement: a singleinstitution experience. J Neurosurg. 2010; 113(1): Kahlon B, Annertz M, Ståhlberg F, Rehncrona S. Is aqueductal stroke volume, measured with cine phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging scans useful in predicting outcome of shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus? Neurosurgery. 2007; 60(1): 124-9; discussion Tarnaris A, Kitchen ND, Watkins LD. Noninvasive biomarkers in normal pressure hydrocephalus: evidence for the role of neuroimaging. J Neurosurg. 2009; 110(5): Egypt J Neurol Psychiat Neurosurg. July 2012 Vol 49 Issue 3 281
7 الملخص العربي القيمة التشخيصية لفحص الرنين المغناطيسي لقياس تدفق السائل النخاعي بالمخ في تشخيص حاالت االستسقاء الدماغي ذو الضغظ الطبيعي مقدمة: يعتبر االستسقاء الدماغي ذو الضغط الطبيعي مرضا ناد ار. تحسن هذه الحاالت بعد الج ارحة لتركيب الصمما النخمايي غيمر مضممون وذلم لعد وجود أدوات تشخيصية دامغة حتى اآلن تتنبأ بمدى التحسن الج ارحي لهذه الحاالت. الهدد : تقيمي دور فحم المرنين المغناطيسمي لقيما تمدف السما النخمايي كأحمد الوسما الحديثمة فمي تشمخي همذا الممرض. أسديل البحد : تم أد ارج 8 حماالت تعماني ممن االستسمقاء المدماغي ذو الضمغط الطبيعممي فممي الفتممرة ممما بممين تمم تشممخي هممذه الحمماالت إكمينيكيمما ثمم تمم إجمم ارء فحمم الممرنين المغناطيسممي لقيمما تممدف السمما النخمايي لهمذه الحماالت. بعمد ذلم تم إجم ارء بمذ نخمايي قطنمي تشخيصمي. و يفم الحماالت التمي أظهمرت تحسمنا إكمينيكيما بعمد البمذ تم تركيمب صمما نخمايي مبمرم الضمغط. ثم تم تحميمم النتما الج ارحيمة. نتدي البحدد : أظهمرت النتما حمدوث نسمب تحسممن متفاوتمة فمي كم الحماالت. %57 نسممبة التحسممن فممي اإلد ار والمشممي. و %70 نسممبة التحسممن فممي الممتحك فممي البممو. تمم رصممد يالقممة بممين مقممدار التحسممن اإلكمينيكممي وقيمما كميممة السمما النخمايي بالضممربة االنقباضممية. االسددتنتي : أثبممت فحم الممرنين المغناطيسممي لقيمما تمدف السمما النخممايي أنممة وسميمة تشخيصممية فايمممة وآمنممة يمكممن االيتماد يميها بصورة أكبر بدال من البذ النخايي التشخيصي في المستقب. ويوصى بعم د ارسات تكميمية. 282 Egypt J Neurol Psychiat Neurosurg. July 2012 Vol 49 Issue 3
Utility of radiologic imaging in the diagnosis and follow up of normal pressure hydrocephalus
 Utility of radiologic imaging in the diagnosis and follow up of normal pressure hydrocephalus Poster No.: C-0312 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Rodríguez, D. Marquina, A. Mir Torres,
Utility of radiologic imaging in the diagnosis and follow up of normal pressure hydrocephalus Poster No.: C-0312 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Rodríguez, D. Marquina, A. Mir Torres,
Normal and Abnormal Cerebrospinal Fluid Dynamics Evaluated by Optimized Cine Phase-contrast MR Imaging
 Chin J Radiol 2000; 25: 191-195 191 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Normal and Abnormal Cerebrospinal Fluid Dynamics Evaluated by Optimized Cine Phase-contrast MR Imaging LUNG-HUI GIIANG 1,3 CHENG-YU CHEN 1 MING-YEN
Chin J Radiol 2000; 25: 191-195 191 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Normal and Abnormal Cerebrospinal Fluid Dynamics Evaluated by Optimized Cine Phase-contrast MR Imaging LUNG-HUI GIIANG 1,3 CHENG-YU CHEN 1 MING-YEN
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1291-1296 Role of MRI CSF Flowmetry in Evaluation of Hydrocephalus in Pediatric Patients Abeer Maghawry Abdelhameed, Eman Ahmed Fouad
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1291-1296 Role of MRI CSF Flowmetry in Evaluation of Hydrocephalus in Pediatric Patients Abeer Maghawry Abdelhameed, Eman Ahmed Fouad
Natural history of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus
 DOI 10.1007/s10143-011-0316-7 REVIEW Natural history of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Ahmed K. Toma & Simon Stapleton & Marios C. Papadopoulos & Neil D. Kitchen & Laurence D. Watkins Received:
DOI 10.1007/s10143-011-0316-7 REVIEW Natural history of idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Ahmed K. Toma & Simon Stapleton & Marios C. Papadopoulos & Neil D. Kitchen & Laurence D. Watkins Received:
Alternate Methods: Pros and Cons (With a Focus on NPH)
 Alternate Methods: Pros and Cons (With a Focus on NPH) William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor and Chair Department of Radiology University of California, San Diego Alternate Imaging Methods for
Alternate Methods: Pros and Cons (With a Focus on NPH) William G. Bradley, Jr, MD, PhD, FACR Professor and Chair Department of Radiology University of California, San Diego Alternate Imaging Methods for
CSF flowmetry: an innovative technique in diagnosing normal pressure hydrocephalus
 International Journal of Advances in Medicine Senger KPS et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Jun;4(3):682-687 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20171996
International Journal of Advances in Medicine Senger KPS et al. Int J Adv Med. 2017 Jun;4(3):682-687 http://www.ijmedicine.com pissn 2349-3925 eissn 2349-3933 Original Research Article DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3933.ijam20171996
Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections in Patients with Hydrocephalus
 The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
The Scientific World Journal Volume 2013, Article ID 461896, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/461896 Clinical Study The Value of Programmable Shunt Valves for the Management of Subdural Collections
John H. Woo, MD Associate Professor, Department of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center October 28, 2016
 John H. Woo, MD Associate Professor, Department of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center October 28, 2016 Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Bulk model (traditional) Production:
John H. Woo, MD Associate Professor, Department of Radiology Perelman School of Medicine, University of Pennsylvania Medical Center October 28, 2016 Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Bulk model (traditional) Production:
CSF Flow Quantification of the Cerebral Aqueduct in Normal Volunteers Using Phase Contrast Cine MR Imaging
 CSF Flow Quantification of the Cerebral Aqueduct in Normal Volunteers Using Phase Contrast Cine MR Imaging Jeong Hyun Lee, MD 1 Ho Kyu Lee, MD 1 Jae Kyun Kim, MD 1 Hyun Jeong Kim, MD 1 Ji Kang Park, MD
CSF Flow Quantification of the Cerebral Aqueduct in Normal Volunteers Using Phase Contrast Cine MR Imaging Jeong Hyun Lee, MD 1 Ho Kyu Lee, MD 1 Jae Kyun Kim, MD 1 Hyun Jeong Kim, MD 1 Ji Kang Park, MD
The Challenges of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
 CE/CME The Challenges of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus A Case-Based Review Freddi Segal-Gidan, PA, PhD Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph) is one of the few reversible causes of dementia. Unfortunately,
CE/CME The Challenges of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus A Case-Based Review Freddi Segal-Gidan, PA, PhD Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph) is one of the few reversible causes of dementia. Unfortunately,
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph) is characterized
 Published May 14, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4340 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Aqueductal Stroke Volume: Comparisons with Intracranial Pressure Scores in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus X G. Ringstad,
Published May 14, 2015 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4340 ORIGINAL RESEARCH ADULT BRAIN Aqueductal Stroke Volume: Comparisons with Intracranial Pressure Scores in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus X G. Ringstad,
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) depicts cerebral tissue without
 Diagn Interv Radiol 2009; 15:227 231 Turkish Society of Radiology 2009 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cine phase-contrast MRI evaluation of normal aqueductal cerebrospinal fluid flow according to sex
Diagn Interv Radiol 2009; 15:227 231 Turkish Society of Radiology 2009 NEURORADIOLOGY ORIGINAL ARTICLE Cine phase-contrast MRI evaluation of normal aqueductal cerebrospinal fluid flow according to sex
The influence of breathing on cerebrospinal fluid movement in the brain
 The influence of breathing on cerebrospinal fluid movement in the brain A computational study based on in vivo pressure measurements Vegard Vinje Simula Research Laboratory GA Ringstad ME Rognes PK Eide
The influence of breathing on cerebrospinal fluid movement in the brain A computational study based on in vivo pressure measurements Vegard Vinje Simula Research Laboratory GA Ringstad ME Rognes PK Eide
Aqueductal CSF stroke volume (ACSV) measured by
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Scollato P. Gallina B. Gautam G. Pellicanò C. Cavallini R. Tenenbaum N. Di Lorenzo Changes in Aqueductal CSF Stroke Volume in Shunted Patients with Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus
ORIGINAL RESEARCH A. Scollato P. Gallina B. Gautam G. Pellicanò C. Cavallini R. Tenenbaum N. Di Lorenzo Changes in Aqueductal CSF Stroke Volume in Shunted Patients with Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus
Cover Page. The handle holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation.
 Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35771 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Palm, Walter Miguel Title: Ventricular dilatation in aging and dementia Issue
Cover Page The handle http://hdl.handle.net/1887/35771 holds various files of this Leiden University dissertation. Author: Palm, Walter Miguel Title: Ventricular dilatation in aging and dementia Issue
Original Research JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 30: (2009)
 JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 30:708 715 (2009) Original Research Value of Quantitative MRI Biomarkers (Evans Index, Aqueductal Flow Rate, and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient) in Idiopathic Normal
JOURNAL OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING 30:708 715 (2009) Original Research Value of Quantitative MRI Biomarkers (Evans Index, Aqueductal Flow Rate, and Apparent Diffusion Coefficient) in Idiopathic Normal
Intracranial CSF Flow in Pediatric Hydrocephalus: Evaluation with Cine-MR Imaging
 Intracranial CSF Flow in Pediatric Hydrocephalus: Evaluation with Cine-MR Imaging Robert M. Quencer 1 Purpose: 1) To describe the pattern of normal intracranial CSF flow in children and 2) to demonstrate
Intracranial CSF Flow in Pediatric Hydrocephalus: Evaluation with Cine-MR Imaging Robert M. Quencer 1 Purpose: 1) To describe the pattern of normal intracranial CSF flow in children and 2) to demonstrate
The classic teaching is that cerebrospinal fluid is formed primarily. CSF Flow in the Brain in the Context of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
 REVIEW ARTICLE CSF Flow in the Brain in the Context of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus W.G. Bradley Jr ABSTRACT SUMMARY: CSF normally flows back and forth through the aqueduct during the cardiac cycle. During
REVIEW ARTICLE CSF Flow in the Brain in the Context of Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus W.G. Bradley Jr ABSTRACT SUMMARY: CSF normally flows back and forth through the aqueduct during the cardiac cycle. During
Intraventricular CSF Pulsation Artifact on Fast Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR Images: Analysis of 100 Consecutive Normal Studies
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:503 508, March 2000 Intraventricular CSF Pulsation Artifact on Fast Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR Images: Analysis of 100 Consecutive Normal Studies Rohit Bakshi, Shelton
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:503 508, March 2000 Intraventricular CSF Pulsation Artifact on Fast Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR Images: Analysis of 100 Consecutive Normal Studies Rohit Bakshi, Shelton
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph) is an
 J Neurosurg 120:178 184, 2014 AANS, 2014 The callosal angle measured on MRI as a predictor of outcome in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Clinical article Johan Virhammar, M.D., 1 Katarina Laurell,
J Neurosurg 120:178 184, 2014 AANS, 2014 The callosal angle measured on MRI as a predictor of outcome in idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Clinical article Johan Virhammar, M.D., 1 Katarina Laurell,
Neuroradlology. Evaluation with Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow Measurements at MR Imaging
 Neuroradlology William C. Bradley, Jr. MD, PhD #{149}David Scalzo, MD2 #{149}John Queralt, MD Wolfgang N. Nitz, MS #{149}Dennis J. Atkinson, MS #{149}Priscilla Wong, MD Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus: Evaluation
Neuroradlology William C. Bradley, Jr. MD, PhD #{149}David Scalzo, MD2 #{149}John Queralt, MD Wolfgang N. Nitz, MS #{149}Dennis J. Atkinson, MS #{149}Priscilla Wong, MD Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus: Evaluation
First identified in 1965,5 idiopathic normal pressure. focus Neurosurg Focus 41 (3):E2, 2016
 neurosurgical focus Neurosurg Focus 41 (3):E2, 2016 Timing of surgical treatment for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: association between treatment delay and reduced short-term benefit Sharif
neurosurgical focus Neurosurg Focus 41 (3):E2, 2016 Timing of surgical treatment for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus: association between treatment delay and reduced short-term benefit Sharif
Lumbar infusion test in normal pressure hydrocephalus
 Acta Neurol Scand 2005: 111: 379 384 DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2005.00417.x Copyright Ó Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Lumbar infusion test in normal pressure hydrocephalus Kahlon
Acta Neurol Scand 2005: 111: 379 384 DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.2005.00417.x Copyright Ó Blackwell Munksgaard 2005 ACTA NEUROLOGICA SCANDINAVICA Lumbar infusion test in normal pressure hydrocephalus Kahlon
Hydrocephalus 1/16/2015. Hydrocephalus. Functions of Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Flow of CSF
 Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Ruth Arms, MSN, CNS-BC, SCRN Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The excess fluid increases the size of the ventricles
Hydrocephalus Hydrocephalus Ruth Arms, MSN, CNS-BC, SCRN Hydrocephalus is the buildup of fluid in the cavities (ventricles) deep within the brain. The excess fluid increases the size of the ventricles
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts
 Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts Exceptional healthcare, personally delivered Ventriculo-Peritoneal/ Lumbo-Peritoneal Shunts What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is the build up of an excess
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
subdural hematoma : SDH
 Dementia Japan 26 : 343-348, 2012 343 85 NPH NPH Masaya Oda 1, Masanori Hiji 1, Hijiri Ito 1, Yuishin Izumi 1,2 1 728-0001 605-20 Department of Neurology, Mifukai Vihara Hananosato Hospital 605-20 Yamaga
Dementia Japan 26 : 343-348, 2012 343 85 NPH NPH Masaya Oda 1, Masanori Hiji 1, Hijiri Ito 1, Yuishin Izumi 1,2 1 728-0001 605-20 Department of Neurology, Mifukai Vihara Hananosato Hospital 605-20 Yamaga
Falling and Forgetting
 Falling and Forgetting Dr TC Chan Dr LW Chu Inter-hosipital Geriatric Meeting 29-5-2009 Case 1 Mr A 86/M ADL-I Walk unaided Live with family Non smoker non drinker Good past health Attend A&E 10/2008 due
Falling and Forgetting Dr TC Chan Dr LW Chu Inter-hosipital Geriatric Meeting 29-5-2009 Case 1 Mr A 86/M ADL-I Walk unaided Live with family Non smoker non drinker Good past health Attend A&E 10/2008 due
Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus. Neurosurgical Service, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts
 J Neurosurg 52:371-377, 1980 Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Results of shunting in 62 patients PETER McL. BLACK, M.D., PH.D. Neurosurgical Service, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts
J Neurosurg 52:371-377, 1980 Idiopathic normal-pressure hydrocephalus Results of shunting in 62 patients PETER McL. BLACK, M.D., PH.D. Neurosurgical Service, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, Massachusetts
Ventriculo peritoneal Shunt Malfunction with Anti-siphon Device in Normal pressure Hydrocephalus Report of -Three Cases-
 Ventriculo peritoneal Shunt Malfunction with Anti-siphon Device in Normal pressure Hydrocephalus Report of -Three Cases- Mitsuru SEIDA, Umeo ITO, Shuichi TOMIDA, Shingo YAMAZAKI and Yutaka INABA* Department
Ventriculo peritoneal Shunt Malfunction with Anti-siphon Device in Normal pressure Hydrocephalus Report of -Three Cases- Mitsuru SEIDA, Umeo ITO, Shuichi TOMIDA, Shingo YAMAZAKI and Yutaka INABA* Department
Comparison of 3 and 7 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Obstructive Hydrocephalus Caused by Tectal Glioma
 CASE REPORT Brain Tumor Res Treat 2016;4(2):150-154 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 http://dx.doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2016.4.2.150 Comparison of 3 and 7 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Obstructive
CASE REPORT Brain Tumor Res Treat 2016;4(2):150-154 / pissn 2288-2405 / eissn 2288-2413 http://dx.doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2016.4.2.150 Comparison of 3 and 7 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Obstructive
A quantitative analysis of cerebrospinal fluid flow in post-traumatic syringomyelia
 Paraplegia (1995) 33, 203-207 1995 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 0031-1758/95 $9.00 A quantitative analysis of cerebrospinal fluid flow in post-traumatic syringomyelia
Paraplegia (1995) 33, 203-207 1995 International Medical Society of Paraplegia All rights reserved 0031-1758/95 $9.00 A quantitative analysis of cerebrospinal fluid flow in post-traumatic syringomyelia
UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS
 UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Offering solutions for patients. 1 UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Dear Reader: Your doctor has either recommended the CODMAN HAKIM Precision Fixed Pressure Valve, the CODMAN HAKIM
UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Offering solutions for patients. 1 UNDERSTANDING HYDROCEPHALUS Dear Reader: Your doctor has either recommended the CODMAN HAKIM Precision Fixed Pressure Valve, the CODMAN HAKIM
CASE REPORT. Jackson Hayes, Marie Roguski and Ron I Riesenburger *
 Hayes et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:393 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Rapid resolution of an acute subdural hematoma by increasing the shunt valve pressure in
Hayes et al. Journal of Medical Case Reports 2012, 6:393 JOURNAL OF MEDICAL CASE REPORTS CASE REPORT Open Access Rapid resolution of an acute subdural hematoma by increasing the shunt valve pressure in
Ventricle wall movements and cerebrospinal fluid flow in hydrocephalus. Richard D. Penn, M.D., 1 Sukhraaj Basati, B.S., 1 Brian Sweetman, M.S.
 J Neurosurg 115:159 164, 2011 Ventricle wall movements and cerebrospinal fluid flow in hydrocephalus Clinical article Richard D. Penn, M.D., 1 Sukhraaj Basati, B.S., 1 Brian Sweetman, M.S., 1 Xiaodong
J Neurosurg 115:159 164, 2011 Ventricle wall movements and cerebrospinal fluid flow in hydrocephalus Clinical article Richard D. Penn, M.D., 1 Sukhraaj Basati, B.S., 1 Brian Sweetman, M.S., 1 Xiaodong
Don t lose your life to NPH.
 Don t lose your life to NPH. NPH The little-known neurological disorder that affects more than one in every two hundred adults over 55. Never heard of NPH? Well, you re not alone. NPH, or Normal Pressure
Don t lose your life to NPH. NPH The little-known neurological disorder that affects more than one in every two hundred adults over 55. Never heard of NPH? Well, you re not alone. NPH, or Normal Pressure
TECHNICAL NOTE. Introduction
 Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; XX; XXX XXX doi:10.2463/mrms.tn.2017-0032 Published Online: August 24, 2017 TECHNICAL NOTE Time-spatial Labeling Inversion Pulse (Time-SLIP) with Pencil Beam Pulse: A Selective
Magn Reson Med Sci 2017; XX; XXX XXX doi:10.2463/mrms.tn.2017-0032 Published Online: August 24, 2017 TECHNICAL NOTE Time-spatial Labeling Inversion Pulse (Time-SLIP) with Pencil Beam Pulse: A Selective
MRI MEASUREMENTS OF CRANIOSPINAL AND INTRACRANIAL VOLUME CHANGE IN HEALTHY AND HEAD TRAUMA CASES
 1of 4 MRI MEASUREMENTS OF CRANIOSPINAL AND INTRACRANIAL VOLUME CHANGE IN HEALTHY AND HEAD TRAUMA CASES N. Alperin, Y. Kadkhodayan, B. Varadarajalu, C. Fisher, B. Roitberg Department of Radiology and Neurosurgery,
1of 4 MRI MEASUREMENTS OF CRANIOSPINAL AND INTRACRANIAL VOLUME CHANGE IN HEALTHY AND HEAD TRAUMA CASES N. Alperin, Y. Kadkhodayan, B. Varadarajalu, C. Fisher, B. Roitberg Department of Radiology and Neurosurgery,
Infusion studies in clinical practice. Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London
 Infusion studies in clinical practice Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London 10 th September 2018 infusion study + hydrocephalus 216 publications Clinical
Infusion studies in clinical practice Kristian Aquilina Consultant paediatric neurosurgeon Great Ormond Street Hospital London 10 th September 2018 infusion study + hydrocephalus 216 publications Clinical
Eide and Pripp FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS
 FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS Increased prevalence of cardiovascular disease in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus patients compared to a population-based cohort from the HUNT3 survey Eide and Pripp
FLUIDS AND BARRIERS OF THE CNS Increased prevalence of cardiovascular disease in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus patients compared to a population-based cohort from the HUNT3 survey Eide and Pripp
Citation for the original published paper (version of record):
 http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper published in Fluids and Barriers of the CNS. Citation for the original published paper (version of record): Johansson, E., Ambarki, K.,
http://www.diva-portal.org This is the published version of a paper published in Fluids and Barriers of the CNS. Citation for the original published paper (version of record): Johansson, E., Ambarki, K.,
Time-Spatial Labeling Inversion
 White Paper Time-Spatial Labeling Inversion Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow Evaluation Erin Kelly, PhD Clinical Marketing Scientist, MR Canon Medical Systems INTRODUCTION Impairment to the natural flow of cerebrospinal
White Paper Time-Spatial Labeling Inversion Cerebrospinal Fluid Flow Evaluation Erin Kelly, PhD Clinical Marketing Scientist, MR Canon Medical Systems INTRODUCTION Impairment to the natural flow of cerebrospinal
Thesis. Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus in neurological practice. - A study of epidemiology and methods for selection of patients for surgery
 Thesis Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus in neurological practice - A study of epidemiology and methods for selection of patients for surgery Are Brean The faculty of Medicine University of Oslo
Thesis Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus in neurological practice - A study of epidemiology and methods for selection of patients for surgery Are Brean The faculty of Medicine University of Oslo
Postprint.
 http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper published in Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final
http://www.diva-portal.org Postprint This is the accepted version of a paper published in Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry. This paper has been peer-reviewed but does not include the final
Neglected case of hydrocephalus in a five-year-old child
 www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Neglected case of hydrocephalus in a five-year-old child Moataz Hesham Abdelreheem, Marwa Mohammed Basyouni ABSTRACT Introduction: Hydrocephalus
www.edoriumjournals.com CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Neglected case of hydrocephalus in a five-year-old child Moataz Hesham Abdelreheem, Marwa Mohammed Basyouni ABSTRACT Introduction: Hydrocephalus
N ormal pressure hydrocephalus was first described by
 PAPER Comparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus B Kahlon, G Sundbärg, S Rehncrona... See end of article
PAPER Comparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus B Kahlon, G Sundbärg, S Rehncrona... See end of article
Posttraumatic Hydrocephalus: Risk Factors, Treatment Modalities, and Prognosis
 198 Original Article THIEME Posttraumatic Hydrocephalus: Risk Factors, Treatment Modalities, and Prognosis Vamsi Krishna Yerramneni 1 Vamsi Krishna Kotha 1 1 Department of Neurosurgery, Nizam s Institute
198 Original Article THIEME Posttraumatic Hydrocephalus: Risk Factors, Treatment Modalities, and Prognosis Vamsi Krishna Yerramneni 1 Vamsi Krishna Kotha 1 1 Department of Neurosurgery, Nizam s Institute
Adult hydrocephalus and shunts. Information for patients
 Adult hydrocephalus and shunts Information for patients Contents What is hydrocephalus? 3 Causes 4 Symptoms 4 What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds
Adult hydrocephalus and shunts Information for patients Contents What is hydrocephalus? 3 Causes 4 Symptoms 4 What is hydrocephalus? Hydrocephalus is a condition in which cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) builds
The resistance to CSF outflow in hydrocephalus what it is and what it isn t.
 The resistance to CSF outflow in hydrocephalus what it is and what it isn t. Davson et al 1970, The mechanism of drainage of CSF. Brain 93:665-8 1989, Copenhagen, Alfred Benzon Foundation CSf outflow is
The resistance to CSF outflow in hydrocephalus what it is and what it isn t. Davson et al 1970, The mechanism of drainage of CSF. Brain 93:665-8 1989, Copenhagen, Alfred Benzon Foundation CSf outflow is
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure. Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point
 Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
Body position and eerebrospinal fluid pressure Part 2' Clinical studies on orthostatic pressure and the hydrostatic indifferent point BJORN MAGNAES, M.D. Department of Neurosurgery, Rikshospitalet, Oslo
Copyright 2017 Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. All rights reserved.
 DNA ILLUSTRATIONS / SCIENCE SOURCE 26 l Nursing2017 l Volume 47, Number 9 www.nursing2017.com 1.0 ANCC CONTACT HOUR Recognizing normal pressure hydrocephalus in older adults By Carolyn E. Smith, MS, RN,
DNA ILLUSTRATIONS / SCIENCE SOURCE 26 l Nursing2017 l Volume 47, Number 9 www.nursing2017.com 1.0 ANCC CONTACT HOUR Recognizing normal pressure hydrocephalus in older adults By Carolyn E. Smith, MS, RN,
A Case of Stent Placement for Intracranial Hypertension Associated with Venous Sinus Stenosis
 DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0080 A Case of Stent Placement for Intracranial Hypertension Associated with Venous Sinus Stenosis Rei Yamaguchi, Koji Sato, Hiroya Fujimaki, and Ken Asakura Objective: We encountered
DOI: 10.5797/jnet.cr.2016-0080 A Case of Stent Placement for Intracranial Hypertension Associated with Venous Sinus Stenosis Rei Yamaguchi, Koji Sato, Hiroya Fujimaki, and Ken Asakura Objective: We encountered
Transient obstructive hydrocephalus due to intraventricular hemorrhage: A case report and review of literature
 Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2013 Transient obstructive hydrocephalus due to intraventricular hemorrhage: A case report and review of literature Eriks A. Lusis Ananth K. Vellimana Wilson
Digital Commons@Becker Open Access Publications 2013 Transient obstructive hydrocephalus due to intraventricular hemorrhage: A case report and review of literature Eriks A. Lusis Ananth K. Vellimana Wilson
A case of normal pressure hydrocephalus with peripheral vestibular disorder-like findings.
 A case of normal pressure hydrocephalus with peripheral vestibular disorder-like findings. Yuzuru Sainoo 1)2), Hidetaka Kumagami 3), Haruo Takahashi 1) 1) Goto Chuoh Hospital, Otorhinolaryngology 2) Department
A case of normal pressure hydrocephalus with peripheral vestibular disorder-like findings. Yuzuru Sainoo 1)2), Hidetaka Kumagami 3), Haruo Takahashi 1) 1) Goto Chuoh Hospital, Otorhinolaryngology 2) Department
Imaging appearances of programmable ventricular shunt systems : What the radiologist needs to know
 Imaging appearances of programmable ventricular shunt systems : What the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-2030 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gontsarova, S. C. Thust, J.
Imaging appearances of programmable ventricular shunt systems : What the radiologist needs to know Poster No.: C-2030 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Gontsarova, S. C. Thust, J.
Fast Multiphase MR Imaging of Aqueductal CSF Flow: 2. Study 1n
 597 Fast Multiphase MR Imaging of Aqueductal CSF Flow: 2. Study 1n Patients with Hydrocephalus Mario Mascalchi 1 Lilina Ciraolo 1 Marta Bucciolini 1 Domenico lnzitari 2 Graziano Arnetoli 2 Giancarlo Dal
597 Fast Multiphase MR Imaging of Aqueductal CSF Flow: 2. Study 1n Patients with Hydrocephalus Mario Mascalchi 1 Lilina Ciraolo 1 Marta Bucciolini 1 Domenico lnzitari 2 Graziano Arnetoli 2 Giancarlo Dal
MR Advance Techniques. Vascular Imaging. Class II
 MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
MR Advance Techniques Vascular Imaging Class II 1 Vascular Imaging There are several methods that can be used to evaluate the cardiovascular systems with the use of MRI. MRI will aloud to evaluate morphology
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
ViosWorks: A Paradigm Shift in Cardiac MR Imaging
 Figure 1. ViosWorks image of a patient with shunted pulmonary venous return. Image courtesy of Dr. Shreyas Vasanawala, Stanford University. ViosWorks: A Paradigm Shift in Cardiac MR Imaging The value of
Figure 1. ViosWorks image of a patient with shunted pulmonary venous return. Image courtesy of Dr. Shreyas Vasanawala, Stanford University. ViosWorks: A Paradigm Shift in Cardiac MR Imaging The value of
Multiple Gated Acquisition (MUGA) Scanning
 Multiple Gated Acquisition (MUGA) Scanning Dmitry Beyder MPA, CNMT Nuclear Medicine, Radiology Barnes-Jewish Hospital / Washington University St. Louis, MO Disclaimers/Relationships Standard of care research
Multiple Gated Acquisition (MUGA) Scanning Dmitry Beyder MPA, CNMT Nuclear Medicine, Radiology Barnes-Jewish Hospital / Washington University St. Louis, MO Disclaimers/Relationships Standard of care research
Published July 10, 2014 as /ajnr.A4046
 Published July 10, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4046 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Preoperative Prognostic Value of MRI Findings in 108 Patients with Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus J. Virhammar, K. Laurell,
Published July 10, 2014 as 10.3174/ajnr.A4046 ORIGINAL RESEARCH BRAIN Preoperative Prognostic Value of MRI Findings in 108 Patients with Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus J. Virhammar, K. Laurell,
MATERIAL AND METHODS:
 Nuclear Medicine Review 2015, 18, 2: 84 88 DOI: 10.5603/NMR.2015.0020 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Early brain perfusion improvement after ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery in patients with
Nuclear Medicine Review 2015, 18, 2: 84 88 DOI: 10.5603/NMR.2015.0020 Copyright 2015 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Early brain perfusion improvement after ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery in patients with
A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method for
 Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 1(1), 59-64 (1999) INVITED PAPER Use of MRI in ASD Asessment A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method for Evaluating Atrial Septa1 Defects Godtfred Holmvang Cardiac
Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance, 1(1), 59-64 (1999) INVITED PAPER Use of MRI in ASD Asessment A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Method for Evaluating Atrial Septa1 Defects Godtfred Holmvang Cardiac
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT. G. Tamburrini, Rome
 INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
INTRACRANIAL ARACHNOID CYSTS: CLASSIFICATION AND MANAGEMENT G. Tamburrini, Rome Incidence 2% of occasional neuroradiological findings From clinical studies (1960 s): 0.4-1% of intracranial space occupying
Original Article. Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction. Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH
 Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Original Article Emergency Department Evaluation of Ventricular Shunt Malfunction Is the Shunt Series Really Necessary? Raymond Pitetti, MD, MPH Objective: The malfunction of a ventricular shunt is one
Aging effects on cerebral blood and cerebrospinal fluid flows
 & 2007 ISCBFM All rights reserved 0271-678X/07 $30.00 www.jcbfm.com Aging effects on cerebral blood and cerebrospinal fluid flows Souraya Stoquart-ElSankari 1, Olivier Balédent 2, Catherine Gondry-Jouet
& 2007 ISCBFM All rights reserved 0271-678X/07 $30.00 www.jcbfm.com Aging effects on cerebral blood and cerebrospinal fluid flows Souraya Stoquart-ElSankari 1, Olivier Balédent 2, Catherine Gondry-Jouet
CSF Spaces in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Morphology and Volumetry
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1277 1284, August 1998 CSF Spaces in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Morphology and Volumetry Hajime Kitagaki, Etsuro Mori, Kazunari Ishii, Shigeru Yamaji, Nobutsugu
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1277 1284, August 1998 CSF Spaces in Idiopathic Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus: Morphology and Volumetry Hajime Kitagaki, Etsuro Mori, Kazunari Ishii, Shigeru Yamaji, Nobutsugu
Endosaccular aneurysm occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils for obstructive hydrocephalus caused by a large basilar tip aneurysm Case report
 Neurosurg Focus 7 (4):Article 5, 1999 Endosaccular aneurysm occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils for obstructive hydrocephalus caused by a large basilar tip aneurysm Case report Akira Watanabe, M.D.,
Neurosurg Focus 7 (4):Article 5, 1999 Endosaccular aneurysm occlusion with Guglielmi detachable coils for obstructive hydrocephalus caused by a large basilar tip aneurysm Case report Akira Watanabe, M.D.,
Shunt malfunction and Slight edema surrounding the ventricles: Ten case series
 ISSN: 47-5 Volume Number 8 (August-04) pp. 4-45 www.ijcrar.com Shunt malfunction and Slight edema surrounding the ventricles: Ten case series Firooz Salehpoor, Arastoo Pezeshki, Amirhossein Haghir *, Aidin
ISSN: 47-5 Volume Number 8 (August-04) pp. 4-45 www.ijcrar.com Shunt malfunction and Slight edema surrounding the ventricles: Ten case series Firooz Salehpoor, Arastoo Pezeshki, Amirhossein Haghir *, Aidin
JMSCR Vol 06 Issue 08 Page August 2018
 www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i8.18 Research Article Assessment of
www.jmscr.igmpublication.org Impact Factor (SJIF): 6.379 Index Copernicus Value: 79.54 ISSN (e)-2347-176x ISSN (p) 2455-0450 DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.18535/jmscr/v6i8.18 Research Article Assessment of
Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip
 197 Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip Ching-Yi Lee 1, Chieh-Tsai Wu 1, Kuang-Lin Lin 2, Hsun-Hui Hsu 3 Abstract-
197 Occult Cerebrospinal Fluid Fistula between Ventricle and Extra-Ventricular Position of the Ventriculoperitoneal Shunt Tip Ching-Yi Lee 1, Chieh-Tsai Wu 1, Kuang-Lin Lin 2, Hsun-Hui Hsu 3 Abstract-
Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children
 Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 584567, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/584567 Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children Eva Brichtova, 1
Minimally Invasive Surgery Volume 2013, Article ID 584567, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/584567 Clinical Study Endoscopic Third Ventriculostomy in Previously Shunted Children Eva Brichtova, 1
Complex Hydrocephalus
 2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
2012 Hydrocephalus Association Conference Washington, DC - June 27-July1, 2012 Complex Hydrocephalus Marion L. Walker, MD Professor of Neurosurgery & Pediatrics Primary Children s Medical Center University
Idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph) is
 clinical article J Neurosurg 124:359 367, 2016 A double-blind randomized trial on the clinical effect of different shunt valve settings in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus Dan Farahmand, MD, 1
clinical article J Neurosurg 124:359 367, 2016 A double-blind randomized trial on the clinical effect of different shunt valve settings in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus Dan Farahmand, MD, 1
Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari Malformation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 6 Number 2 Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari M Turgut Citation M Turgut. Parkinsonism after
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Neurosurgery Volume 6 Number 2 Parkinsonism after Shunting for Hydrocephalus Secondary to Aqueductal Stenosis with Chiari M Turgut Citation M Turgut. Parkinsonism after
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion
 Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Case 7391 Intraventricular Lesion Bastos Lima P1, Marques C1, Cabrita F2, Barbosa M2, Rebelo O3, Rio F1. 1Neuroradiology, 2Neurosurgery, 3Neuropathology, Coimbra University Hospitals, Portugal. University
Comparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus.
 Comparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus. Kahlon, Babar; Sundbärg, Göran; Rehncrona, Stig Published in:
Comparison between the lumbar infusion and CSF tap tests to predict outcome after shunt surgery in suspected normal pressure hydrocephalus. Kahlon, Babar; Sundbärg, Göran; Rehncrona, Stig Published in:
Corpus Callosal Signal Changes in Patients with Obstructive Hydrocephalus after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:158 162, January 2001 Corpus Callosal Signal Changes in Patients with Hydrocephalus after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting John I. Lane, Patrick H. Luetmer, and John L. Atkinson BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:158 162, January 2001 Corpus Callosal Signal Changes in Patients with Hydrocephalus after Ventriculoperitoneal Shunting John I. Lane, Patrick H. Luetmer, and John L. Atkinson BACKGROUND
S ome hydrocephalic patients with extracranial shunts
 PAPER Quantitative analysis of continuous intracranial pressure recordings in symptomatic patients with extracranial shunts P K Eide... Competing interests: none declared... Correspondence to: Dr Per Kristian
PAPER Quantitative analysis of continuous intracranial pressure recordings in symptomatic patients with extracranial shunts P K Eide... Competing interests: none declared... Correspondence to: Dr Per Kristian
Estimation of CSF Flow Resistance in the Upper Cervical Spine
 NRJ Digital - The Neuroradiology Journal 3: 49-53, 2013 www.centauro.it Estimation of CSF Flow Resistance in the Upper Cervical Spine K-A. MARDAL 1, G. RUTKOWSKA 1, S. LINGE 1.2, V. HAUGHTON 3 1 Center
NRJ Digital - The Neuroradiology Journal 3: 49-53, 2013 www.centauro.it Estimation of CSF Flow Resistance in the Upper Cervical Spine K-A. MARDAL 1, G. RUTKOWSKA 1, S. LINGE 1.2, V. HAUGHTON 3 1 Center
Increased Intracranial Volume: A Clue to the Etiology of Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus?
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1479 1484, October 2004 Increased Intracranial Volume: A Clue to the Etiology of Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus? William G. Bradley, Francis G. Safar, Claudia Hurtado,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1479 1484, October 2004 Increased Intracranial Volume: A Clue to the Etiology of Idiopathic Normal-Pressure Hydrocephalus? William G. Bradley, Francis G. Safar, Claudia Hurtado,
(Hi-dro-SEF-ah-lus) Hydrocephalus is a build-up of Cerebrospinal Fluid, or CSF within the spaces inside the brain, called ventricles.
 Hydrocephalus in adults What is hydrocephalus? (Hi-dro-SEF-ah-lus) Hydrocephalus is a build-up of Cerebrospinal Fluid, or CSF within the spaces inside the brain, called ventricles. There are 4 ventricles
Hydrocephalus in adults What is hydrocephalus? (Hi-dro-SEF-ah-lus) Hydrocephalus is a build-up of Cerebrospinal Fluid, or CSF within the spaces inside the brain, called ventricles. There are 4 ventricles
Original Article Neuroimaging and Head & Neck
 Original Article Neuroimaging and Head & Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.827 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):827-835 Evaluation of Aqueductal Patency in Patients
Original Article Neuroimaging and Head & Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.6.827 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2014;15(6):827-835 Evaluation of Aqueductal Patency in Patients
Imaging of Moya Moya Disease
 Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
Abstract Imaging of Moya Moya Disease Pages with reference to book, From 181 To 185 Rashid Ahmed, Hurnera Ahsan ( Liaquat National Hospital, Karachi. ) Moya Moya disease is a rare disease causing occlusion
CISTERNOGRAPHY (CEREBRO SPINAL FLUID IMAGING): A VERSATILE DIAGNOSTIC PROCE DURE
 VOL. 115, No. i E D I T 0 R I A L CISTERNOGRAPHY (CEREBRO SPINAL FLUID IMAGING): A VERSATILE DIAGNOSTIC PROCE DURE C ISTERNOGRAPHY (CSF imaging) is a diagnostic study based on the premise that certain
VOL. 115, No. i E D I T 0 R I A L CISTERNOGRAPHY (CEREBRO SPINAL FLUID IMAGING): A VERSATILE DIAGNOSTIC PROCE DURE C ISTERNOGRAPHY (CSF imaging) is a diagnostic study based on the premise that certain
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord
 The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
The Low Sensitivity of Fluid-Attenuated Inversion-Recovery MR in the Detection of Multiple Sclerosis of the Spinal Cord Mark D. Keiper, Robert I. Grossman, John C. Brunson, and Mitchell D. Schnall PURPOSE:
Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma
 Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Neurology Asia 2013; 18(1) : 117 121 Multicompartmental congenital intracranial immature teratoma 1 Dharmendra Ganesan MS FRCS(SN), 1 Sheau Fung Sia MS MRCS, 1 Vairavan Narayanan MS, 2 Gnana Kumar FRCR,
Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury
 Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Chin J Radiol 2005; 30: 173-177 173 Concomitant Traumatic Spinal Subdural Hematoma and Hemorrhage from Intracranial Arachnoid Cyst Following Minor Injury HUI-YI CHEN 1 YING-SHYUAN LI 1 CHUNG-HO CHEN 1
Results of Isotope Cisternography in 175 Patients with a Suspected Hydrocephalus
 CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2015;11(1):11-17 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2015.11.1.11 Results of Isotope Cisternography in 175 Patients with a Suspected
CLINICAL ARTICLE Korean J Neurotrauma 2015;11(1):11-17 pissn 2234-8999 / eissn 2288-2243 http://dx.doi.org/10.13004/kjnt.2015.11.1.11 Results of Isotope Cisternography in 175 Patients with a Suspected
Ventricular size after shunting for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus
 Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 833-837 Ventricular size after shunting for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus HENRY A. SHENKIN', JACK 0. GREENBERG, AND CHARLES B. GROSSMAN
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry, 1975, 38, 833-837 Ventricular size after shunting for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus HENRY A. SHENKIN', JACK 0. GREENBERG, AND CHARLES B. GROSSMAN
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Kor Neurotraumatol Soc 2(2): , 2006
 CLINICAL ARTICLE J Kor Neurotraumatol Soc 2(2):-6, 26 Hydrocephalus in Persistent Vegetative State Jong Yeon Kim, M.D., Chul Hu, M.D., Kum Whang, M.D., Soon Ki Hong, M.D., Jhin Soo Pyen, M.D., and Yong
CLINICAL ARTICLE J Kor Neurotraumatol Soc 2(2):-6, 26 Hydrocephalus in Persistent Vegetative State Jong Yeon Kim, M.D., Chul Hu, M.D., Kum Whang, M.D., Soon Ki Hong, M.D., Jhin Soo Pyen, M.D., and Yong
TCD IN THE NICU, PICU AND OTHER APPLICATIONS. Dorothy Bulas M.D. Professor of Pediatrics & Radiology Children s National Washington D.C.
 TCD IN THE NICU, PICU AND OTHER APPLICATIONS Dorothy Bulas M.D. Professor of Pediatrics & Radiology Children s National Washington D.C. Objectives Recognize normal and abnormal cranial blood flow patterns
TCD IN THE NICU, PICU AND OTHER APPLICATIONS Dorothy Bulas M.D. Professor of Pediatrics & Radiology Children s National Washington D.C. Objectives Recognize normal and abnormal cranial blood flow patterns
Spontaneous Ventriculostomy: Report of Three Cases Revealed by Flow-Sensitive Phase-Contrast Cine MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1647 1652, October 1999 Case Report Spontaneous Ventriculostomy: Report of Three Cases Revealed by Flow-Sensitive Phase-Contrast Cine MR Imaging Alex Rovira, Jaume Capellades,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1647 1652, October 1999 Case Report Spontaneous Ventriculostomy: Report of Three Cases Revealed by Flow-Sensitive Phase-Contrast Cine MR Imaging Alex Rovira, Jaume Capellades,
Signal Intensity Of Cerebrospinal Fluid On MR Images Indicates The Severity Of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 1 Number 2 Signal Intensity Of Cerebrospinal Fluid On MR Images Indicates The Severity Of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis T Sakamaki, H
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Spine Surgery Volume 1 Number 2 Signal Intensity Of Cerebrospinal Fluid On MR Images Indicates The Severity Of Degenerative Lumbar Spinal Canal Stenosis T Sakamaki, H
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore.
 This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph)( Main article
This document is downloaded from DR-NTU, Nanyang Technological University Library, Singapore. Title Endoscopic third ventriculostomy (ETV) for idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (inph)( Main article
MRI and CT of the CNS
 MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
MRI and CT of the CNS Dr.Maha ELBeltagy Assistant Professor of Anatomy Faculty of Medicine The University of Jordan 2018 Computed Tomography CT is used for the detection of intracranial lesions. CT relies
From Cerebrospinal Fluid Pulsation to Noninvasive Intracranial Compliance and Pressure Measured by MRI Flow Studies
 This investigation is directed to using the advances in MRI data to focus on movement of blood through the arteries and veins of the brain and on the movement of CSF through certain passageways in such
This investigation is directed to using the advances in MRI data to focus on movement of blood through the arteries and veins of the brain and on the movement of CSF through certain passageways in such
NANOS Patient Brochure
 NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
NANOS Patient Brochure Pseudotumor Cerebri Copyright 2016. North American Neuro-Ophthalmology Society. All rights reserved. These brochures are produced and made available as is without warranty and for
Policy #: 222 Latest Review Date: March 2009
 Name of Policy: MRI Phase-Contrast Flow Measurement Policy #: 222 Latest Review Date: March 2009 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and
Name of Policy: MRI Phase-Contrast Flow Measurement Policy #: 222 Latest Review Date: March 2009 Category: Radiology Policy Grade: Active Policy but no longer scheduled for regular literature reviews and
