B. Sensory Systems and Behaviour
|
|
|
- Joan Robertson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 B. Sensory Systems and Behaviour Animals perceive their environment using a suite of senses: hearing, vision, smell, taste, touch, and, in some cases, possibly through magnetism. Marine mammals are no exception, but because they live part or all of their lives in an aquatic environment, some senses are developed over others. Water has a number of properties that influence the role that different senses may play. Sound travels better through water than air, whereas light penetrates less well through water. It is therefore not surprising to find that those marine mammals most dependent upon water for living have developed sound as the most sophisticated sense for the detection of cues from their environment, and for communication to others both in close proximity and over great distances. This is exemplified by the order Cetacea, which has also been the group where sound production and hearing have been best studied, and, in chapter 4, Jonathan Gordon and Peter Tyack explore the many facets of the use of sound by cetaceans. Marine mammals can hear sounds over a wide range of frequencies, with the smaller odontocete cetacean species being sensitive to sounds at the highest frequencies (ultrasounds up to khz), and the largest mysticete cetaceans apparently to sounds at the lowest frequencies (down to 20 Hz). Although audiograms have been established for several odontocete cetaceans, as well as pinnipeds, there are scarcely any data for mysticete whales, and so we have to infer their hearing sensitivities from the normal frequency range of sounds they produce. Both mysticetes and odontocetes have soft-tissue channels for sound conduction to the ear; sirenians, the other truly aquatic group, have similar hearing structures. Pinnipeds need to be able to hear sounds both in air and underwater. Above water they use their external air-filled canal for sound reception. However, it is not known whether they have specialised mechanisms underwater for maintaining the external canal as the point for sound reception or whether they too use softtissue channels for this function. Phocid seals appear to be better adapted to hearing underwater than otariids (with bigger differences in peak sensitivities underwater compared with in air) and this fits in with their more aquatic lifestyle (Wartzok and Ketten, 1999). Peak hearing sensitivity in pinnipeds is between 10 and 30 khz (with a high frequency limit of 60 khz in phocids, and 40 khz in otariids). Although little data exist for sirenians, manatees appear to have a hearing range of approximately 0.l-40 khz, with peak sensitivities in the West Indian manatee near 16 khz, and 5-10 khz in the Amazonian manatee, although their audiograms are very flat compared with odontocete cetaceans, and more similar to phocid seals (Richardson et at., 1995). 133
2 134 Marine Mammals: Biology and Conservation Sea otters have ears most similar to those of land mammals. There is no information on how well they hear underwater. The same applies to polar bears. Unlike terrestrial mammals, all marine mammals have middle ears that are strongly modified structurally to reduce the impact of rapid and extreme changes in pressure. This may possibly predispose them to some protection from injury by high intensity noise (Wartzok and Ketten, 1999). Of the other senses, vision appears to be the one that remains most important for marine mammals, and is probably used by most species even at depth. Cetaceans apparently have the most acute underwater vision, adapting the lens of their eye to accommodate for the loss of focusing power of the air-cornea interface. Sirenians are less well adapted to underwater vision, and pinnipeds, with their dual need to see in air and water, have poor visual acuity in air except in bright light. The sea otter has good visual acuity in both media, achieved by changing the radius of curvature of the lens with the use of the ciliary and iris muscles, although like others, its visual acuity is poorer in low light. The polar bear, living primarily on land, has a similar eye anatomy to terrestrial mammals. The sense of smell, or olfaction, has been reduced in many marine mammals. It is apparently absent in cetaceans (adult odontocetes do not possess olfactory bulbs or nerves, whilst these are greatly reduced in mysticete whales), and only rudimentary in sirenians. Pinnipeds, on the other hand, use olfaction on land particularly during activities related to breeding, as do sea otters and polar bears. Taste is also not unduly developed amongst marine mammals, although tests have shown that different chemicals can be distinguished. This applied particularly to those with a bitter or sour taste, whereas there was a less well-developed ability to detect salinity and an apparent inability to detect sugar. Most work has been conducted on captive odontocete cetaceans, although limited studies on pinnipeds gave broadly similar results. Sirenians possess more taste buds than cetaceans but they remain less than herbivorous land mammals. Amongst marine mammals, sirenians have the most developed sensory hairs. These cover the entire body, although particularly dense around the muzzle. The manatee is unique in being able to use its bristles or vibrissae in a prehensile manner; the bristles can actually be everted and used to grasp and manipulate objects, as when feeding. The vibrissae ofpinnipeds are also extensively developed, and well supplied with nerve endings. They provide seals particularly with information about form and texture and are often used in a social context (Wartzok and Ketten, 1999). Cetaceans appear to be most sensitive around the blowhole although some baleen whales also have hairs around the mouth.
3 Sensory Systems and Behaviour 135 The presence of magnetite, which has been implicated in magnetic field detection, has been demonstrated in a wide variety of animal taxa including cetaceans. However, magnetite is a very common contaminant from industrial processes and to distinguish this from functional magnetite, researchers have identified those characteristics most likely to indicate its use in magnetic field detection. These include single-domain crystals, magnetite with few oxides (besides iron oxide), and location of magnetite consistently in certain parts of the body, notably associated with the cerebrum and cerebellum. However, increasing magnetite concentrations with age parallels the ossification of these structures, for which it has a known function, providing structural support by increasing the hardness of chitin in teeth. Other evidence that has been used relates to correlations between locations where geomagnetic lows intersected with the coast or islands, with live strandings of cetaceans. This was demonstrated for the UK and eastern United States, but no such correlation was found in New Zealand, possibly because that country lacks the consistent orientation of magnetic contours that the North Atlantic possesses (Klinowska, 1986; Kirschvink et al., 1986; Kirschvink, 1990; Brabyn and Frew, 1994). The difficulty of demonstrating in any experimental way the mechanism by which this potential sense could be used continues to limit our ability to determine its role with confidence. Two excellent reviews of sensory systems in marine mammals are Thomas et al. (1992), and Wartzok and Ketten (1999), whilst Thomas and Kastelein (1990) present evidence from laboratory and field studies specifically upon cetaceans. The ways that animals perceive their environment mould their behaviour within it. Information about the environment is first processed by the nervous system, and, in mammals, especially by the brain. This is termed cognition. We do not have a specific chapter on this subject, but Schusterman et al. (1986) have a book on cognition in dolphins; Tyack (1999) gives a brief review of the role of cognition in marine mammal communication; and it is explored further in Chapter 4 of this book, by Jonathan Gordon and Peter Tyack. Cetaceans in particular are often represented as big-brained, highly intelligent creatures displaying altruistic traits and a sophisticated vocal learning and communication system that invite comparison with humans. Given the very different evolutionary paths taken by these two taxa, and the fact that cetaceans live in an aquatic medium, and humans a terrestrial one, this comparative approach may not be very helpful. True, the sperm whale has the largest brain (7.8kg) of any mammal, though not relative to its body size (and by allometric growth, larger mammals have larger brains). Ifbody weight is taken into account, the bottlenose dolphin (and some other small
4 136 Marine Mammals: Biology and Conservation odontocetes like the white-beaked dolphin) has a brain nearly as large (c %) as a human ( %). Pinnipeds show relative brain sizes (termed encephalisation quotients, or EQs) close to the overall pattern for mammals, whilst sperm whales, mysticete whales, and sirenians have relatively small brains (Worthy and Rickie, 1986). Furthermore, relative brain size is not equivalent to intelligence. A more meaningful feature is probably the degree of folding of the cerebral cortex; that part of the brain most concerned with higher level neuronal processing. In this respect, odontocetes do actually exceed humans and other animals, and various theories have been proposed to explain these findings. They include the need to rapidly process complex, high frequency sounds as used in echolocation; historical redundancy of the large brain (which has been large in odontocetes over a long period of evolution); and the associated development in sociality with long term individual associations (Wood and Evans, 1980; Herman, 1980; Ridgway and Brownson, 1984; Ridgway, 1986; Worthy and Rickie, 1986; Marino, 1998). At present, we do not know which of these theories, if any of them, is correct, although there is increasing support for the latter explanation (see, for example, summaries by Evans, 1987: 202, and Tyack, 1999: ). The study of behavioural ecology attempts to answer questions about the functions of behaviour, particularly in the context of an individual's or species' environment (Krebs and Davies, 1997). In Chapter 5, James Boran, Peter Evans and Martin Rosen examine patterns of behaviour as exhibited by cetaceans in terms of two main survival strategies - foraging and mating. They review the roles of locating resources (food and mates) and avoiding predators in the development of sociality, and they show how recent advances in genetics have enabled us to have a better idea of the mating systems of species with various ecologies. Luis Cappozzo continues this theme in Chapter 6, when he reviews new perspectives on the behavioural ecology of pinnipeds, with particular reference to the evolution of pinniped social organisation and mating behaviour. REFERENCES Brabyn, M. and Frew, R.V.C. (1994) New Zealand herd stranding sites do not relate to geomagnetic topography. Marine Mammal Science, 10, Evans, P.G.H. (1987) The Natural History of Whales and Dolphins. Christopher Helm/Academic Press, London, and Facts on File, New York. 343pp. Hennan, L.M. (1980) Cognitive characteristics of dolphins. In: Cetacean Behavior (Ed. by L.M. Hennan), pp Wiley Interscience, New York, NY.
5 Sensory Systems and Behaviour 137 Kirschvink, ll. (1990) Geomagnetic sensitivity in cetaceans: An update with live stranding records in the United States. In: Sensory Abilities of Cetaceans: Laboratory and Field Evidence (Ed. by J.A. Thomas and R.A. Kastelein), pp Plenum, New York, NY. Kirschvink, ll., Dizon, A.E., and Westphal, la. (1986) Evidence from strandings for geomagetic sensitivity in cetaceans. Journal of Experimental Biology, 120, Klinowska, M. (1986) The cetacean magnetic sense - evidence from strandings. In: Research on Dolphins (Ed. by M.M. Bryden and R. Harrison), pp Clarendon Press, Oxford. Krebs, lr. and Davies, N.B. (1997) Behavioural Ecology: An Evolutionary Approach. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford. Marino, L. (1998) A comparison of encephalization between odontocete cetaceans and anthropoid primates. Evolutionary Anthropology, 5, Richardson, W.J., Greene, C.R. Jr., Malme, c.r. and Thomson, D.H. (1995) Marine Mammals and Noise. Academic Press, San Diego. 576pp. Ridgway, S. (1986) Physiological observations of dolphin brains. In: Dolphin Cognition and Behavior: A Comparative Approach (Ed. by R.J. Schusterman, la. Thomas, and F.G. Wood, F.G.), pp. 3 I-59. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale, Nl Ridgway, S.H. and Brownson, R. H. (1984) Relative brain sizes and cortical areas of odontocetes. Acta Zoologica Fennica, 172, Schusterman, R.J., Thomas, la., and Wood, F.G. (Eds.) (1986) Dolphin Cognition and Behavior: A Comparative Approach. Lawrence Erlbaum, Hillsdale, Nl Thomas, la. and Kastelein, R.A. (Eds.) (I990) Sensory Abilities of Cetaceans: Laboratory and Field Evidence. Plenum, New York, NY. Thomas, la., Kastelein, R.A., and Supin, A.Y. (Eds.) (1992) Marine Mammal Sensory Systems. Plenum, New York, NY. Tyack, P. (1999) Communication and Cognition. In: Biology of Marine Mammals (Ed. by J.E. Reynolds III and S.A. Rommel), pp Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington DC. 578pp. Wartzok, D. and Ketten, D.R. (1999) Marine Mammal Sensory Systems. In: Biology of Marine Mammals (Ed. by J.E. Reynolds III and S.A. Rommel), pp Smithsonian Institution Press, Washington DC. 578pp. Wood, F.G. and Evans, W.E. (1980) Adaptiveness and ecology of echolocation in toothed whales. In: Animal Sonar Systems (Ed. by R.-G. Busnel and J. Fish), pp Plenum, New York, NY. Worthy, G.A.J. and Hickie, J.P. (1986) Relative brain size in marine mammals. American Naturalist, 128,
Underwater Acoustics: Webinar Series for the International Regulatory Community
 Underwater Acoustics: Webinar Series for the International Regulatory Community Webinar Outline: Marine Animal Sound Production and Reception Tuesday, April 24, 2018 12:00 pm U.S. (Eastern, Daylight Time);
Underwater Acoustics: Webinar Series for the International Regulatory Community Webinar Outline: Marine Animal Sound Production and Reception Tuesday, April 24, 2018 12:00 pm U.S. (Eastern, Daylight Time);
Chapter 12: Marine Mammals. By: Da Lynne Cousar, Megan Dudenbostel, Kyle Nemeth, Matt Boyle, and Steven Miller
 Chapter 12: Marine Mammals By: Da Lynne Cousar, Megan Dudenbostel, Kyle Nemeth, Matt Boyle, and Steven Miller Four different kinds of Marine Mammals Cetaceans- includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises
Chapter 12: Marine Mammals By: Da Lynne Cousar, Megan Dudenbostel, Kyle Nemeth, Matt Boyle, and Steven Miller Four different kinds of Marine Mammals Cetaceans- includes whales, dolphins, and porpoises
Reproduction: Cetaceans.
 Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy 24 May 2010 Reproduction: Cetaceans. Course website: http://faculty.washington.edu/glennvb/fish475 Text reading reference: Chapter 10 Cetacean reproduction Some general patterns:
Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy 24 May 2010 Reproduction: Cetaceans. Course website: http://faculty.washington.edu/glennvb/fish475 Text reading reference: Chapter 10 Cetacean reproduction Some general patterns:
Course evaluation submission:
 Course evaluation submission: 1. Forms to pick up today: a) one yellow form for overall course comments; b) one form A to evaluate Glenn; c) one form H to evaluate your TA. 2. Return forms to Sophie: At
Course evaluation submission: 1. Forms to pick up today: a) one yellow form for overall course comments; b) one form A to evaluate Glenn; c) one form H to evaluate your TA. 2. Return forms to Sophie: At
Midterm 2: Scantron results. Term Paper Due on Thursday!
 Midterm 2: Scantron results Mean = 81% Term Paper Due on Thursday! Follow formatting instructions on website May be slightly different than the example Example citation format: State space models are now
Midterm 2: Scantron results Mean = 81% Term Paper Due on Thursday! Follow formatting instructions on website May be slightly different than the example Example citation format: State space models are now
What Do Whales Feel?
 Reading Practice What Do Whales Feel? An examination of the functioning of the senses in cetaceans, the group of mammals comprising whales, dolphins and porpoises Some of the senses that we and other terrestrial
Reading Practice What Do Whales Feel? An examination of the functioning of the senses in cetaceans, the group of mammals comprising whales, dolphins and porpoises Some of the senses that we and other terrestrial
Chapter 09 Marine Reptiles, Birds, and Mammals
 Chapter 09 Marine Reptiles, Birds, and Mammals Multiple Choice Questions 1. Marine amphibians: A. Do not exist at all B. Are gill-breathers C. Are fish-like D. Include only tropical species E. Are oviparous
Chapter 09 Marine Reptiles, Birds, and Mammals Multiple Choice Questions 1. Marine amphibians: A. Do not exist at all B. Are gill-breathers C. Are fish-like D. Include only tropical species E. Are oviparous
SIO133 Study Guide: Week 6 5/12/ Great Job on the midterm. If you need help please let us know.
 Lecture 15. Anthropogenic noise and marine mammals Lecture 16. Anatomy - Skulls Lecture 17. Locomotion Announcements: 1. Great Job on the midterm. If you need help please let us know. 2. Outlines for term
Lecture 15. Anthropogenic noise and marine mammals Lecture 16. Anatomy - Skulls Lecture 17. Locomotion Announcements: 1. Great Job on the midterm. If you need help please let us know. 2. Outlines for term
SIO133 Study Guide: Week 6 5/12/ Echolocation is particularly sophisticated why put all the effort into evolving a new system?
 Whale Acoustics Practice Questions 1. Why do odontocetes make sounds? 2. Echolocation is particularly sophisticated why put all the effort into evolving a new system? 3. How does sound travel to create
Whale Acoustics Practice Questions 1. Why do odontocetes make sounds? 2. Echolocation is particularly sophisticated why put all the effort into evolving a new system? 3. How does sound travel to create
MARINE SCIENCE. Monday 23 Jan 2017
 MARINE SCIENCE Monday 23 Jan 2017 Entry Task Cyberlab discussion: Based on your field research from Friday, which marine mammals are never observed on land? Why? Agenda Housekeeping Unit 21 (Marine Mammals)
MARINE SCIENCE Monday 23 Jan 2017 Entry Task Cyberlab discussion: Based on your field research from Friday, which marine mammals are never observed on land? Why? Agenda Housekeeping Unit 21 (Marine Mammals)
Distribution Ecology attempts to explain the restricted and generally patchy distribution of species
 Marine Mammal Ecology Ecology : An attempt to describe and explain the patterns of distribution and abundance of organisms. These patterns reflect the history of complex interactions with other organisms
Marine Mammal Ecology Ecology : An attempt to describe and explain the patterns of distribution and abundance of organisms. These patterns reflect the history of complex interactions with other organisms
Unit 2. Lesson 2. Sound Production and Reception
 Unit 2. Lesson 2. Sound Production and Reception Lesson Objectives: After completing this lesson and the activities, students will be able to grasp the basic ideas of how sound is generated and how it
Unit 2. Lesson 2. Sound Production and Reception Lesson Objectives: After completing this lesson and the activities, students will be able to grasp the basic ideas of how sound is generated and how it
Criteria and Thresholds for U.S. Navy Acoustic and Explosive Effects Analysis
 April 2012 Criteria and Thresholds for U.S. Navy Acoustic and Explosive Effects Analysis J. J. Finneran and A. K. Jenkins SSC Pacific Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. SSC Pacific
April 2012 Criteria and Thresholds for U.S. Navy Acoustic and Explosive Effects Analysis J. J. Finneran and A. K. Jenkins SSC Pacific Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. SSC Pacific
Topic 10: Origin of Cetaceans: A Macroevolutionary Case Study
 Topic 10: Origin of Cetaceans: A Macroevolutionary Case Study All content and conclusions, except for photos, CR Hardy 1. Fully aquatic, mostly marine mammals Colloquially called dolphins, porpoises, &
Topic 10: Origin of Cetaceans: A Macroevolutionary Case Study All content and conclusions, except for photos, CR Hardy 1. Fully aquatic, mostly marine mammals Colloquially called dolphins, porpoises, &
BIOLOGY 183 MARINE BIOLOGY PIMA COMMUNITY COLLEGE, DOWNTOWN CAMPUS WORKSHEETS FOR UNIT 7 UNIT 7 LEARNING OBJECTIVES UNIT 7 ACTIVITIES
 BIOLOGY 183 MARINE BIOLOGY PIMA COMMUNITY COLLEGE, DOWNTOWN CAMPUS WORKSHEETS FOR UNIT 7 UNIT 7 LEARNING OBJECTIVES See the Biology 183 Unit 7 website. UNIT 7 ACTIVITIES Step 1: Read Chapter 9 in your
BIOLOGY 183 MARINE BIOLOGY PIMA COMMUNITY COLLEGE, DOWNTOWN CAMPUS WORKSHEETS FOR UNIT 7 UNIT 7 LEARNING OBJECTIVES See the Biology 183 Unit 7 website. UNIT 7 ACTIVITIES Step 1: Read Chapter 9 in your
Lesson 2: Cetaceans What makes a whale a whale?
 Cetaceans 4 th Grade Curriculum Lesson 2: What makes a whale a whale? Page 2-1 Lesson 2: Cetaceans What makes a whale a whale? Objectives: Students will learn about general whale (and dolphin) biology.
Cetaceans 4 th Grade Curriculum Lesson 2: What makes a whale a whale? Page 2-1 Lesson 2: Cetaceans What makes a whale a whale? Objectives: Students will learn about general whale (and dolphin) biology.
Chapter 18. The Senses SENSORY RECEPTION. Introduction: Superhuman Senses. Introduction: Superhuman Senses
 Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
Introduction: Superhuman Senses Chapter 18 The Senses! Three senses found in some animals but not humans Echolocation locating objects by detecting echoes of emitted sound waves Electroreception ability
Foundation for the course:
 Start thinking about term paper topics Foundation for the course: Taxonomy: who are they? Evolution: how did they get here? 1 Important Points Most important Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia
Start thinking about term paper topics Foundation for the course: Taxonomy: who are they? Evolution: how did they get here? 1 Important Points Most important Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia
Cetaceans whales, dolphins and porpoises
 Cetaceans whales, dolphins and porpoises -Breathe air through a blowhole -90 species of cetacean all are marine except 5 species of freshwater dolphin -divided into two groups; Baleen whales and toothed
Cetaceans whales, dolphins and porpoises -Breathe air through a blowhole -90 species of cetacean all are marine except 5 species of freshwater dolphin -divided into two groups; Baleen whales and toothed
MARINE SCIENCE. Monday 14 May 2018
 MARINE SCIENCE Monday 14 May 2018 Entry Task Grab a ChromeBook from the cart. Be sure to grab the number that corresponds to the number on your desk. Log in & go to the following link @ www.kahoot.it Wait
MARINE SCIENCE Monday 14 May 2018 Entry Task Grab a ChromeBook from the cart. Be sure to grab the number that corresponds to the number on your desk. Log in & go to the following link @ www.kahoot.it Wait
Basic Hearing and Echolocation Mechanisms of Marine Mammals: Measured Auditory Evoked Potential and Behavioral Experiments FY 2008
 Basic Hearing and Echolocation Mechanisms of Marine Mammals: Measured Auditory Evoked Potential and Behavioral Experiments FY 2008 Paul E. Nachtigall Marine Mammal Research Program Hawaii Institute of
Basic Hearing and Echolocation Mechanisms of Marine Mammals: Measured Auditory Evoked Potential and Behavioral Experiments FY 2008 Paul E. Nachtigall Marine Mammal Research Program Hawaii Institute of
Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy
 Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy Welcome! Course website: http://faculty.washington.edu/glennvb/fish475 Course staff Glenn R. VanBlaricom Professor of Marine Mammal Studies Washington Cooperative Fish and Wildlife
Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy Welcome! Course website: http://faculty.washington.edu/glennvb/fish475 Course staff Glenn R. VanBlaricom Professor of Marine Mammal Studies Washington Cooperative Fish and Wildlife
Ecological Constraints on Sound Production in Marine Animals: the Importance of Listening
 Ecological Constraints on Sound Production in Marine Animals: the Importance of Listening Lance Barrett-Lennard Vancouver Aquarium University of British Columbia Overview. passive vs active use of sound
Ecological Constraints on Sound Production in Marine Animals: the Importance of Listening Lance Barrett-Lennard Vancouver Aquarium University of British Columbia Overview. passive vs active use of sound
Marine Turtles, Mammals and Seabirds. Chapter 9
 Marine Turtles, Mammals and Seabirds Chapter 9 Seabirds Seabirds, like mammals, are able to maintain a constant body temperature derived through metabolic means (homeotherms, endotherm) Seabirds The feathers
Marine Turtles, Mammals and Seabirds Chapter 9 Seabirds Seabirds, like mammals, are able to maintain a constant body temperature derived through metabolic means (homeotherms, endotherm) Seabirds The feathers
Underwater hearing in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus): Expansion and interpretation of existing data
 MARINE MAMMAL SCIENCE, **(*): *** *** (*** 2011) C 2011 by the Society for Marine Mammalogy DOI: 10.1111/j.1748-7692.2011.00473.x Underwater hearing in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus): Expansion
MARINE MAMMAL SCIENCE, **(*): *** *** (*** 2011) C 2011 by the Society for Marine Mammalogy DOI: 10.1111/j.1748-7692.2011.00473.x Underwater hearing in California sea lions (Zalophus californianus): Expansion
MARINE SCIENCE. Monday 21 May 2018
 MARINE SCIENCE Monday 21 May 2018 Entry Task What was one of the major types of sea mammals named in the video? Pinnipeds When was the Marine Mammal Protection Act established? 1972 Agenda Housekeeping
MARINE SCIENCE Monday 21 May 2018 Entry Task What was one of the major types of sea mammals named in the video? Pinnipeds When was the Marine Mammal Protection Act established? 1972 Agenda Housekeeping
Marine Mammal Auditory System Noise Impacts: Evidence and Incidence
 Marine Mammal Auditory System Noise Impacts: Evidence and Incidence Darlene R. Ketten 1 Introduction Sound is an inevitable element of every human activity in the oceans. Some, like exploration and military
Marine Mammal Auditory System Noise Impacts: Evidence and Incidence Darlene R. Ketten 1 Introduction Sound is an inevitable element of every human activity in the oceans. Some, like exploration and military
Lecture Nektons Pearson Education, Inc.
 Lecture Nektons Marine Animals Avoid Sinking May increase buoyancy Use of gas containers Rigid gas containers Swim bladders Macroscopic Zooplankton Krill Resemble mini shrimp or large copepods Abundant
Lecture Nektons Marine Animals Avoid Sinking May increase buoyancy Use of gas containers Rigid gas containers Swim bladders Macroscopic Zooplankton Krill Resemble mini shrimp or large copepods Abundant
The rapidly increasing pressure of human activity in coastal and pelagic marine environments has led to
 Sound production and reception in southern sea otters (Enhydra lutris nereis) Asila Ghoul 1, Colleen Reichmuth 2 1 Department of Ocean Sciences, Long Marine Laboratory, University of California Santa Cruz,
Sound production and reception in southern sea otters (Enhydra lutris nereis) Asila Ghoul 1, Colleen Reichmuth 2 1 Department of Ocean Sciences, Long Marine Laboratory, University of California Santa Cruz,
Chapter 38: Sense Organs
 Chapter 38: Sense Organs AP Curriculum Alignment Big Idea 1 technically requests that students be able to choose a eukaryotic structure, such as the brain, to provide evidence that organisms continue to
Chapter 38: Sense Organs AP Curriculum Alignment Big Idea 1 technically requests that students be able to choose a eukaryotic structure, such as the brain, to provide evidence that organisms continue to
INTERPRETING RESEARCH RESULTS: GOVERNMENT REGULATION OF ANTHROPOGENIC NOISE SOURCES
 INTERPRETING RESEARCH RESULTS: GOVERNMENT REGULATION OF ANTHROPOGENIC NOISE SOURCES By Naomi A. Rose, Ph.D. Marine Mammal Scientist The Humane Society of the United States INTRODUCTION The Precautionary
INTERPRETING RESEARCH RESULTS: GOVERNMENT REGULATION OF ANTHROPOGENIC NOISE SOURCES By Naomi A. Rose, Ph.D. Marine Mammal Scientist The Humane Society of the United States INTRODUCTION The Precautionary
Sonar induced temporary hearing loss in dolphins
 Sonar induced temporary hearing loss in dolphins T. Aran Mooney 1*+, Paul E. Nachtigall 1 and Stephanie Vlachos 1 1 Department of Zoology and HIMB, University of Hawaii, Kaneohe, HI, 96734, USA *Author
Sonar induced temporary hearing loss in dolphins T. Aran Mooney 1*+, Paul E. Nachtigall 1 and Stephanie Vlachos 1 1 Department of Zoology and HIMB, University of Hawaii, Kaneohe, HI, 96734, USA *Author
Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy 20 May 2009
 Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy 20 May 2009 Trophic biology II Anthony J. Orr SAFS/UW & NMFS/NOAA Course website: http://faculty.washington.edu/glennvb/fish475 1 Trophic biology of pinnipeds Otariids: Shallow
Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy 20 May 2009 Trophic biology II Anthony J. Orr SAFS/UW & NMFS/NOAA Course website: http://faculty.washington.edu/glennvb/fish475 1 Trophic biology of pinnipeds Otariids: Shallow
Overview of Sensory Receptors
 Sensory Systems Chapter 45 Overview of Sensory Receptors Sensory receptors provide information from our internal and external environments that is crucial for survival and success -Exteroceptors sense
Sensory Systems Chapter 45 Overview of Sensory Receptors Sensory receptors provide information from our internal and external environments that is crucial for survival and success -Exteroceptors sense
Psychophysical Studies of Auditory Masking in Marine Mammals: Key Concepts and New Directions
 Psychophysical Studies of Auditory Masking in Marine Mammals: Key Concepts and New Directions Colleen Reichmuth 1 Introduction In recent years, growing awareness of the potentially harmful effects of human-generated
Psychophysical Studies of Auditory Masking in Marine Mammals: Key Concepts and New Directions Colleen Reichmuth 1 Introduction In recent years, growing awareness of the potentially harmful effects of human-generated
Sensory Physiology. Sensory Range Varies. Introduction to the Special Senses. How do we sense the world around us?
 Sensory Physiology How do we sense the world around us? We do not see things as they are; we see things as we are. --Anais Nin Anais Nin, French author 1903-1977 Sensory Range Varies Introduction to the
Sensory Physiology How do we sense the world around us? We do not see things as they are; we see things as we are. --Anais Nin Anais Nin, French author 1903-1977 Sensory Range Varies Introduction to the
Whales Dolphins And Seals A Field Guide To The Marine Mammals Of The World
 Whales Dolphins And Seals A Field Guide To The Marine Mammals Of The World We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing
Whales Dolphins And Seals A Field Guide To The Marine Mammals Of The World We have made it easy for you to find a PDF Ebooks without any digging. And by having access to our ebooks online or by storing
Chapter 29 The Senses
 Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
Chapter 29 The Senses PowerPoint Lectures for Biology: Concepts & Connections, Sixth Edition Campbell, Reece, Taylor, Simon, and Dickey Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc. Lecture by Edward J. Zalisko
The Perceptual Experience
 Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Pages: 35 TEXT: Lefton, Lester A. and Brannon, Linda (2003). PSYCHOLOGY. (Eighth Edition.) Needham
Dikran J. Martin Introduction to Psychology Name: Date: Lecture Series: Chapter 5 Sensation and Perception Pages: 35 TEXT: Lefton, Lester A. and Brannon, Linda (2003). PSYCHOLOGY. (Eighth Edition.) Needham
Charismatic Megafauna (Marine Mammals) Marine Mammals
 Charismatic Megafauna (Marine Mammals) Marine Mammals - Who s Who Among Marine Mammals - Adaptations - Whales and Whaling Review for Final Exam Reading: 6.24-6.25 15.35-15.38 17.22 Graphic: Humback whale
Charismatic Megafauna (Marine Mammals) Marine Mammals - Who s Who Among Marine Mammals - Adaptations - Whales and Whaling Review for Final Exam Reading: 6.24-6.25 15.35-15.38 17.22 Graphic: Humback whale
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception
 Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
Unit 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation a process by which our sensory receptors and nervous system receive and represent stimulus (or physical) energy and encode it as neural signals. Perception a
All about Marine Mammals
 All about Marine Mammals Read the passage below. As we already know, mammals are animals that have lungs and breathe air. They also are warm-blooded which means that they can keep warm even when it is
All about Marine Mammals Read the passage below. As we already know, mammals are animals that have lungs and breathe air. They also are warm-blooded which means that they can keep warm even when it is
Cetacean Brains Cogs 143 * UCSD
 Cetacean Brains Cogs 143 * UCSD EQ -- Encephalization Quotient EQ = Actual brain mass / Expected brain mass Where expected = 0.12 x (Body mass) 2/3 EQ -- Encephalization Quotient Chimp Human Dolphin Globular
Cetacean Brains Cogs 143 * UCSD EQ -- Encephalization Quotient EQ = Actual brain mass / Expected brain mass Where expected = 0.12 x (Body mass) 2/3 EQ -- Encephalization Quotient Chimp Human Dolphin Globular
SIO 133 Marine Mammal Popula4on Dynamics. John Hildebrand, Scripps Inst. Oceanography, UCSD
 SIO 133 Marine Mammal Popula4on Dynamics John Hildebrand, Scripps Inst. Oceanography, UCSD Popula4on Dynamics Study fundamental life history characteris4cs such as birth and death rates Age Distribu4on
SIO 133 Marine Mammal Popula4on Dynamics John Hildebrand, Scripps Inst. Oceanography, UCSD Popula4on Dynamics Study fundamental life history characteris4cs such as birth and death rates Age Distribu4on
Key Concepts Characteristics of Marine Mammals Sea Otters
 Key Concepts Mammals have a body covering of hair, maintain a constant warm body temperature, and nourish their young with milk produced by the mammary glands of the mother. Sea otters have thick coats
Key Concepts Mammals have a body covering of hair, maintain a constant warm body temperature, and nourish their young with milk produced by the mammary glands of the mother. Sea otters have thick coats
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration. Draft Guidance for Assessing the Effects of Anthropogenic Sound on Marine Mammals
 National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 Draft Guidance for Assessing the Effects of Anthropogenic Sound on Marine Mammals Acoustic Threshold Levels for Onset of Permanent and
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 1 Draft Guidance for Assessing the Effects of Anthropogenic Sound on Marine Mammals Acoustic Threshold Levels for Onset of Permanent and
Term Paper. Midterm Exam
 Term Paper Outline due on Thursday (paper copy) See website for details and example 1 outline paragraph, title, 2 references Goals Read and cite scientific papers Learn about a specific topic of marine
Term Paper Outline due on Thursday (paper copy) See website for details and example 1 outline paragraph, title, 2 references Goals Read and cite scientific papers Learn about a specific topic of marine
Sensing and Perceiving Our World
 PSYCHOLOGY: Perspectives & Connections 2 nd Edition GREGORY J. FEIST ERIKA L. ROSENBERG Sensing and Perceiving Our World Chapter Four Chapter Preview The Long Strange Trip From Sensation to Perception
PSYCHOLOGY: Perspectives & Connections 2 nd Edition GREGORY J. FEIST ERIKA L. ROSENBERG Sensing and Perceiving Our World Chapter Four Chapter Preview The Long Strange Trip From Sensation to Perception
Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System
 Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System Looking for answers? Visit http://msjadah.weebly.com 1. The Nervous System a) What is the function of nervous system? The nervous system receives,
Review on Nervous System, Senses and Musculoskeletal System Looking for answers? Visit http://msjadah.weebly.com 1. The Nervous System a) What is the function of nervous system? The nervous system receives,
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
 Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception Sensation and Perception Sensation The process by which our sense organs receive information from the environment Perception The sorting out, interpretation, analysis,
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY
 NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
NERVOUS SYSTEM & SENSES TEACHER COPY FUNCTIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM What are the three functions of the Nervous System? 1. Receives information about what is happening inside and outside of your body
Sperm Whale. The Kid s Times: Volume II, Issue 8. NOAA s National Marine Fisheries Service, Office of Protected Resources
 NOAA s National Marine Fisheries Service, Office of Protected Resources The Kid s Times: Volume II, Issue 8 Sperm Whale Females, young of both sexes, and calves live in groups. Older males are solitary.
NOAA s National Marine Fisheries Service, Office of Protected Resources The Kid s Times: Volume II, Issue 8 Sperm Whale Females, young of both sexes, and calves live in groups. Older males are solitary.
M-weighting. high-frequency cetaceans, M. hf mid-frequency cetaceans, M mf. low-frequency cetaceans, M lf. Frequency (Hz) M-weighting
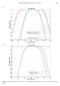 Marine Mammal Noise Exposure Criteria 435 (A) M-weighting Weighting (db) high-frequency cetaceans, M hf mid-frequency cetaceans, M mf low-frequency cetaceans, M lf Frequency (Hz) (B) M-weighting Weighting
Marine Mammal Noise Exposure Criteria 435 (A) M-weighting Weighting (db) high-frequency cetaceans, M hf mid-frequency cetaceans, M mf low-frequency cetaceans, M lf Frequency (Hz) (B) M-weighting Weighting
Cetacean Social & Reproductive Systems
 Cetacean Social & Reproductive Systems Group Living Benefits Reduced predation risk Enhanced detection/ capture of prey Improved reproduction Reduced harassment Larger prey Costs Share food Increased competition
Cetacean Social & Reproductive Systems Group Living Benefits Reduced predation risk Enhanced detection/ capture of prey Improved reproduction Reduced harassment Larger prey Costs Share food Increased competition
Cetacea. Modern Cetacean Traits, Whales are highly specialized. 2. Whales are artiodactyls. 3. Whales and hippos are sister taxa (DNA evidence)
 Cetacea 1. Whales are highly specialized. 2. Whales are artiodactyls. 3. Whales and hippos are sister taxa (DNA evidence) Walking with whales Nature 413, 259-260 (20 September 2001) The evolutionary route
Cetacea 1. Whales are highly specialized. 2. Whales are artiodactyls. 3. Whales and hippos are sister taxa (DNA evidence) Walking with whales Nature 413, 259-260 (20 September 2001) The evolutionary route
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Marine Mammals and Sound
 Marine Mammals and Sound Acoustics Why sound? Light attenuates rapidly Sound travels farther & faster (higher density of fluid) Over large spatial scales in water, visual communication is not practical
Marine Mammals and Sound Acoustics Why sound? Light attenuates rapidly Sound travels farther & faster (higher density of fluid) Over large spatial scales in water, visual communication is not practical
Some characteristics of hearing of the Brazilian manatee, Trichechus inunguis
 Aqualic Mammals 1990, 16.3,139-144 Some characteristics of hearing of the Brazilian manatee, Trichechus inunguis V. O. Klishin*, R. Pezo Diazt, V. V. Popov* and A. Ya. Supin* Severlsov InslilUie ofevolu/ionary
Aqualic Mammals 1990, 16.3,139-144 Some characteristics of hearing of the Brazilian manatee, Trichechus inunguis V. O. Klishin*, R. Pezo Diazt, V. V. Popov* and A. Ya. Supin* Severlsov InslilUie ofevolu/ionary
Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities
 Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities Module B.6. Polar Bears The full CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental
Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities Module B.6. Polar Bears The full CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental
Measurements of the low frequency components of active and passive sounds produced by dolphins
 Aquatic Mammals 2000, 26.3, 167 174 Measurements of the low frequency components of active and passive sounds produced by dolphins Paul E. Nachtigall 1, Whitlow W. L. Au 1,Jeffrey L. Pawloski 1, Kimberly
Aquatic Mammals 2000, 26.3, 167 174 Measurements of the low frequency components of active and passive sounds produced by dolphins Paul E. Nachtigall 1, Whitlow W. L. Au 1,Jeffrey L. Pawloski 1, Kimberly
Psychology Chapter 4. Sensation and Perception. Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed!
 Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Psychology Chapter 4 Sensation and Perception Most amazing introduction ever!! Turn to page 77 and prepare to be amazed! Chapter 4 Section 1 EQ: Distinguish between sensation and perception, and explain
Constructing a retinal map. blind spot. cone density
 Hearing Transduction in hair cells Lateral-line system Electroreception Vestibular and acoustic systems Characteristics of sound Inner, middle, and outer ears Sound for communication and navigation Constructing
Hearing Transduction in hair cells Lateral-line system Electroreception Vestibular and acoustic systems Characteristics of sound Inner, middle, and outer ears Sound for communication and navigation Constructing
The reaction of Southern resident orca to sensitive frequencies produced by nearby vessels
 The reaction of Southern resident orca to sensitive frequencies produced by nearby vessels Literature Review Luritta E. Whiting Beam Reach Marine Science and Sustainability School Friday Harbor Labs, University
The reaction of Southern resident orca to sensitive frequencies produced by nearby vessels Literature Review Luritta E. Whiting Beam Reach Marine Science and Sustainability School Friday Harbor Labs, University
SIO Marine Mammal Behavior, and Social Systems: Ma;ng. John Hildebrand, Scripps Inst. Oceanography, UCSD
 SIO 133 - Marine Mammal Behavior, and Social Systems: Ma;ng John Hildebrand, Scripps Inst. Oceanography, UCSD Ma;ng Strategies Individuals behave to maximize reproduc;ve success Male and female reproduc;ve
SIO 133 - Marine Mammal Behavior, and Social Systems: Ma;ng John Hildebrand, Scripps Inst. Oceanography, UCSD Ma;ng Strategies Individuals behave to maximize reproduc;ve success Male and female reproduc;ve
Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy
 Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy Taxonomy III 5 April 2010 Course website: http://faculty.washington.edu/glennvb/fish475 Text reading reference: Section 1.2.4 Pinnipeds: General characteristics I: 1. Rear limbs
Fish 475: Marine Mammalogy Taxonomy III 5 April 2010 Course website: http://faculty.washington.edu/glennvb/fish475 Text reading reference: Section 1.2.4 Pinnipeds: General characteristics I: 1. Rear limbs
Marine Protected Species Permi:ng: In-water construc8on and noise impact assessment
 July 20, 2016 Florida Permi,ng Summer School Marine Protected Species Permi:ng: In-water construc8on and noise impact assessment Florida Marine Mammals and Turtles Shelf 2 whale species (North Atlan8c
July 20, 2016 Florida Permi,ng Summer School Marine Protected Species Permi:ng: In-water construc8on and noise impact assessment Florida Marine Mammals and Turtles Shelf 2 whale species (North Atlan8c
NATURAL SCIENCES 3 UNIT 3 OUR SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION INTERACTION REPRODUCTION. ü Excretory system
 NATURAL SCIENCES 3 UNIT 3 OUR SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION INTERACTION REPRODUCTION ü Digestive system ü Circulatory system ü The senses ü Nervous system ü Reproductive system
NATURAL SCIENCES 3 UNIT 3 OUR SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES AND SYSTEMS LIFE PROCESSES NUTRITION INTERACTION REPRODUCTION ü Digestive system ü Circulatory system ü The senses ü Nervous system ü Reproductive system
Animal Social Complexity
 Animal Social Complexity Intelligence, Culture, and Individualized Societies EDITED BY Frans B. M. de Waal and Peter L. Tyack HARVARD UNIVERSITY PRESS Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England 2003 CASE
Animal Social Complexity Intelligence, Culture, and Individualized Societies EDITED BY Frans B. M. de Waal and Peter L. Tyack HARVARD UNIVERSITY PRESS Cambridge, Massachusetts London, England 2003 CASE
Marine Mammals Chapter 10
 Marine Mammals Chapter 10 Mammals: 1. Have a four-chambered heart 2. Females have mammary glands 3. Have hair Order: Cetaceans There are about 80 different species Include whales, dolphins, and porpoises
Marine Mammals Chapter 10 Mammals: 1. Have a four-chambered heart 2. Females have mammary glands 3. Have hair Order: Cetaceans There are about 80 different species Include whales, dolphins, and porpoises
Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Outline Nervous System Sensory Systems I. II. III. IV. V. VI. Biol 105 Lecture 11 Chapter 9 Senses Sensory receptors Touch Vision Hearing and balance Smell Senses Sensory receptor cells Sensory receptors
Beaked whales. 1) Zoophysiology, Dept. of Bioscience, Aarhus University, Denmark. 2) BIOECOMAC, La Laguna University, Tenerife, Spain
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Beaked whales Madsen P.T. 1*, Aguilar de Soto N. 2, Tyack P.L. 3, and Johnson M. 3 10 11 12 13 14 15 1) Zoophysiology, Dept. of Bioscience, Aarhus University, Denmark 2) BIOECOMAC, La
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Beaked whales Madsen P.T. 1*, Aguilar de Soto N. 2, Tyack P.L. 3, and Johnson M. 3 10 11 12 13 14 15 1) Zoophysiology, Dept. of Bioscience, Aarhus University, Denmark 2) BIOECOMAC, La
MBA Education. For non profit use only.
 Underwater noise and marine mammals - Teacher Notes AIM: To introduce the effects on marine species of noise associated with building and operating wind farms, with specific reference to marine mammals
Underwater noise and marine mammals - Teacher Notes AIM: To introduce the effects on marine species of noise associated with building and operating wind farms, with specific reference to marine mammals
Behavioural response studies of marine mammals in relation to noise
 Behavioural response studies of marine mammals in relation to noise CREEM (MOCHA project): Catriona Harris, Len Thomas, Lindesay Scott Hayward, Louise Burt, Tiago Marques, Monique MacKenzie, Roland Langrock,
Behavioural response studies of marine mammals in relation to noise CREEM (MOCHA project): Catriona Harris, Len Thomas, Lindesay Scott Hayward, Louise Burt, Tiago Marques, Monique MacKenzie, Roland Langrock,
Sensation and Perception
 Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Sensation and Perception Sensation & Perception The interplay between the external world, physiological systems, and psychological experience How the external world makes impressions on our nervous system
Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 3: Senation and Perception. Module 7: Sensation; Module 8: Perception
 Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 3: Senation and Perception Module 7: Sensation; Module 8: Perception SENSORY PROCESSES: How Do We Perceive The World? ThEcOwgAvecOla..rat eht saw tac eht The quick
Unit Two: Biopsychology Domain Chapter 3: Senation and Perception Module 7: Sensation; Module 8: Perception SENSORY PROCESSES: How Do We Perceive The World? ThEcOwgAvecOla..rat eht saw tac eht The quick
High Frequency Acoustic Recording Package Annual Data Summary Report March 14, 2009 March 26, 2010 SOCAL Site N
 High Frequency Acoustic Recording Package Annual Data Summary Report March 14, 2009 March 26, 2010 SOCAL Site N John Hildebrand, Hannah Bassett, Simone Baumann, Greg Campbell, Amanda Cummins, Sara Kerosky,
High Frequency Acoustic Recording Package Annual Data Summary Report March 14, 2009 March 26, 2010 SOCAL Site N John Hildebrand, Hannah Bassett, Simone Baumann, Greg Campbell, Amanda Cummins, Sara Kerosky,
Whale Week Activity Booklet!
 1 Whale Week Activity Booklet! This half term we are learning all about whales, dolphins and porpoises! Why not have a go at completing our fun activities so you can find out all about these beautiful
1 Whale Week Activity Booklet! This half term we are learning all about whales, dolphins and porpoises! Why not have a go at completing our fun activities so you can find out all about these beautiful
Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY
 Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY Contents UNIT SCIENCE SYLLABUS TOPICS STARTER 4 1 Our senses 6 2 Our body 14 3 Living things 22 People, culture and society Health and personal development Health and personal
Essential Science Plus 3 PRIMARY Contents UNIT SCIENCE SYLLABUS TOPICS STARTER 4 1 Our senses 6 2 Our body 14 3 Living things 22 People, culture and society Health and personal development Health and personal
3. Sensory and Perception
 3. Sensory and Perception Now we will discuss the topics of sensation and perception. This section will cover the different perceptual processes as well as its development. It will also cover the components
3. Sensory and Perception Now we will discuss the topics of sensation and perception. This section will cover the different perceptual processes as well as its development. It will also cover the components
Seismic testing and the impacts of high intensity sound on whales. Lindy Weilgart Department of Biology Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia
 Seismic testing and the impacts of high intensity sound on whales Lindy Weilgart Department of Biology Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia Marine Seismic Surveys Main technique for finding and monitoring
Seismic testing and the impacts of high intensity sound on whales Lindy Weilgart Department of Biology Dalhousie University Halifax, Nova Scotia Marine Seismic Surveys Main technique for finding and monitoring
Nervous System. Made of two parts. Central Peripheral
 Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Nervous System Made of two parts Central Peripheral The Central Nervous System is made of the brain and the spinal cord. The Central Nervous System controls everything in the body. A system that controls
Organs of the Nervous System: brain, spinal cord, and nerves
 Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Nervous System The Nervous System functions as a control center and coordinates all actions and reactions, sending immediate and specific information as electrical impulses. Organs of the Nervous System:
Ganglion Cells Blind Spot Cornea Pupil Visual Area of the Bipolar Cells Thalamus Rods and Cones Lens Visual cortex of the occipital lobe
 How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
How We See How We See Cornea Ganglion Cells whose axons form the optic nerve Blind Spot the exit point at the back of the retina Pupil which is controlled by the iris Bipolar Cells Visual Area of the Thalamus
Sequential structure analysis in the vocal repertoire of the Southern Resident Killer Whales orcinus orca
 Sequential structure analysis in the vocal repertoire of the Southern Resident Killer Whales orcinus orca Ashleigh Kemp October 27, 2007 Beam Reach Marine Science and Sustainability School http://beamreach.org/071
Sequential structure analysis in the vocal repertoire of the Southern Resident Killer Whales orcinus orca Ashleigh Kemp October 27, 2007 Beam Reach Marine Science and Sustainability School http://beamreach.org/071
Biology. Slide 1 of 49. End Show. Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
 Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Biology 1 of 49 2 of 49 Sensory Receptors Neurons that react directly to stimuli from the environment are called sensory receptors. Sensory receptors react to stimuli by sending impulses to other neurons
Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities
 Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities Module B.7. Sirenians The full CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental
Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities Module B.7. Sirenians The full CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental
Criteria and Thresholds for U.S. Navy Acoustic and Explosive Effects Analysis (Phase III)
 TECHNICAL REPORT June 2017 Criteria and Thresholds for U.S. Navy Acoustic and Explosive Effects Analysis (Phase III) SSC Pacific Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...1 2 AUDITORY WEIGHTING FUNCTIONS AND
TECHNICAL REPORT June 2017 Criteria and Thresholds for U.S. Navy Acoustic and Explosive Effects Analysis (Phase III) SSC Pacific Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION...1 2 AUDITORY WEIGHTING FUNCTIONS AND
SIO Marine Mammal Behavior, and Social Systems: Ma;ng. John Hildebrand, Scripps Inst. Oceanography, UCSD
 SIO 133 - Marine Mammal Behavior, and Social Systems: Ma;ng John Hildebrand, Scripps Inst. Oceanography, UCSD Ma;ng Strategies Individuals behave to maximize reproduc;ve success Male and female reproduc;ve
SIO 133 - Marine Mammal Behavior, and Social Systems: Ma;ng John Hildebrand, Scripps Inst. Oceanography, UCSD Ma;ng Strategies Individuals behave to maximize reproduc;ve success Male and female reproduc;ve
Taste buds Gustatory cells extend taste hairs through a narrow taste pore
 The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
The Special Senses Objectives Describe the sensory organs of smell, and olfaction. Identify the accessory and internal structures of the eye, and explain their function. Explain how light stimulates the
Bigger Brains for a Better Future? Imagine a world much different than ours, one that is bitter, frigid and cold. The seas are
 Stuck 1 Shannon Stuck M. Alancraig English 2H April 19, 2010 Bigger Brains for a Better Future? Imagine a world much different than ours, one that is bitter, frigid and cold. The seas are in constant fluctuation
Stuck 1 Shannon Stuck M. Alancraig English 2H April 19, 2010 Bigger Brains for a Better Future? Imagine a world much different than ours, one that is bitter, frigid and cold. The seas are in constant fluctuation
April 28 ii. Outline/References. May 19 iii. Draft (Submission OPTIONAL) May 18 iv. Final Paper Due. June 2
 1. Cetacean Systematics & Evolution 2. Pinniped and Sirenian Taxonomy and Classification 3. Pinniped Systematics and Evolution -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1. Cetacean Systematics & Evolution 2. Pinniped and Sirenian Taxonomy and Classification 3. Pinniped Systematics and Evolution -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
GRAY WHALE. Text source: The Marine Mammal Center
 GRAY WHALE Gray whales are found only in the Pacific Ocean, and they have one of the longest migrations of any mammal. During the summer, they live in the Arctic. In the fall, they travel to Baja California,
GRAY WHALE Gray whales are found only in the Pacific Ocean, and they have one of the longest migrations of any mammal. During the summer, they live in the Arctic. In the fall, they travel to Baja California,
Exploration Guide to the Exhibit Hall
 Exploration Guide to the Exhibit Hall Welcome to The Whale Museum. We hope you enjoy your visit today. As you explore the Museum, please look for the numbered icons upstairs and the lettered icons downstairs.
Exploration Guide to the Exhibit Hall Welcome to The Whale Museum. We hope you enjoy your visit today. As you explore the Museum, please look for the numbered icons upstairs and the lettered icons downstairs.
Auditory Weighting Functions and Frequency-Dependent Effects of Sound in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus)
 DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Auditory Weighting Functions and Frequency-Dependent Effects of Sound in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) James
DISTRIBUTION STATEMENT A: Approved for public release; distribution is unlimited. Auditory Weighting Functions and Frequency-Dependent Effects of Sound in Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) James
A Bandpass filter-bank model of auditory sensitivity in the humpback whale
 Aquatic Mammals 2001, 27.2, 82 91 A Bandpass filter-bank model of auditory sensitivity in the humpback whale Dorian S. Houser 1, David A. Helweg 2 * and Patrick W. B. Moore 3 1 National Research Council
Aquatic Mammals 2001, 27.2, 82 91 A Bandpass filter-bank model of auditory sensitivity in the humpback whale Dorian S. Houser 1, David A. Helweg 2 * and Patrick W. B. Moore 3 1 National Research Council
DOLPHIN RESEARCH CENTER Acoustics
 DOLPHIN RESEARCH CENTER Acoustics Grade Level: 6 th -8 th Objectives: Students will be able to explain how dolphins use sound to communicate and navigate through their underwater environment. Florida Sunshine
DOLPHIN RESEARCH CENTER Acoustics Grade Level: 6 th -8 th Objectives: Students will be able to explain how dolphins use sound to communicate and navigate through their underwater environment. Florida Sunshine
Animal Senses 9/2/16
 Animal Senses 9/2/16 Animal Senses 9/4/15 Fly Hair Cells Animal hearing Elephants can hear lower frequencies than humans 10 Hz (humans 20 Hz) But not as high 12,000 Hz (humans 20,000 Hz) Elephant Ears
Animal Senses 9/2/16 Animal Senses 9/4/15 Fly Hair Cells Animal hearing Elephants can hear lower frequencies than humans 10 Hz (humans 20 Hz) But not as high 12,000 Hz (humans 20,000 Hz) Elephant Ears
Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds. Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor
 Chapter 8 Sensation and Perception Sec 1: Sensation Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor Perception
Chapter 8 Sensation and Perception Sec 1: Sensation Stimulus any aspect of or change in the environment to which an organism responds Sensation what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor Perception
Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities
 Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities Module B.5. Pinnipeds The full CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental
Technical Support Information to the CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental Impact Assessments for Marine Noise-generating Activities Module B.5. Pinnipeds The full CMS Family Guidelines on Environmental
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2B
 INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2B Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 11 SENSING THE ENVIRONMENT Part A Sectional Exercise 11.1 Concept checking p.63 1. False 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. True Questions
INTERACTIVE SCIENCE 2B Workbook Solutions (Enrichment Edition) Chapter 11 SENSING THE ENVIRONMENT Part A Sectional Exercise 11.1 Concept checking p.63 1. False 2. True 3. True 4. False 5. True Questions
