Noncommunicable diseases progress monitoring. Are we meeting the time-bound United Nations targets?
|
|
|
- Patience Dean
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Noncommunicable diseases progress monitoring Are we meeting the time-bound United Nations targets? Background paper for the WHO European Meeting of National NCD Directors and Programme Managers, Moscow, Russian Federation, 8 9 June 2017
2 Summary In 2013, the World Health Assembly adopted the Global Action Plan and its comprehensive Global Monitoring Framework for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases (NCDs), including nine targets and 25 indicators (1). In 2014, despite several years of action, a United Nations high-level meeting considered that improvements in various areas were unsatisfactory to reach those targets and required a new stimulus for the implementation of best-buy policies addressing them. As a result, the United Nations proposed new time-bound targets and indicators and a progress-monitoring process to report on countries progress in the implementation of the policies (2). This report is a preliminary assessment of progress made by individual countries in implementing their national NCD policies, measures and interventions against the 10 progress-monitoring indicators of the four time-bound commitments. It largely uses the data collected from 53 Member States in the WHO European Region through the web-based WHO Global Country Capacity survey (CCS) (3), 2015 and 2017 versions (see Annex 1 containing detailed technical notes for their specifications). Other data sources are necessary for specific indicators not covered by the CCS; these data have been included where available. In general, each indicator represents a composite indicator (index) made up of different variables (not shown here, but available for review if requested). The results are presented here in graphical form as heat maps to show levels of progress on their achievement. This report was prepared for the WHO European Meeting of National NCD Directors and Programme Managers that takes place in Moscow, Russian Federation, on 8 9 June It is accompanied by a paper on premature mortality from NCDs and a report showing progress against the Global Monitoring Framework targets. These documents will be followed by a more substantial European NCD status report later in Together, they are intended as a contribution to the preparations for the WHO Global Conference on NCDs in October 2017 in Montevideo, Uruguay, and the third United Nations High-level Meeting on NCDs, scheduled to take place in Highlights and heat map results Data on progress-monitoring indicators for 2015 and 2017 (preliminary analysis) are shown for each country in the following heat maps. All 53 Member States in the Region responded to the WHO CCS for the first time in 2017, indicating their commitment to contributing to monitoring progress on NCD policy implementation. At the time of this assessment, data for both 2015 and 2017 (preliminary) were available for 14 of the 18 indicators, enabling changes in implementation to be determined; these are summarized in Table 1. Some progress was observed in 11 of those 14 indicators between 2015 and 2017, and for seven of these (indicators 1 on national policies; 5c and 5d on tobacco use; 7a, 7b and 7c on healthy diets; and 10 on cardiometabolic risk assessment and management) there was over 20% improvement from the 2015 value. In summary, important progress has been achieved in the implementation of NCD time-bound commitments in European countries and a positive trend is generally observed on progress-monitoring indicators. Some noticeable changes have occurred with different indicators in each category in a relatively short period. However, increased and improved implementation will be necessary to achieve the NCD time-bound commitments and modify the prevalence of key risk factors to the levels suggested by the Global Action Plan/Global Monitoring Framework. 1
3 2 Table 1. Summary scorecard for the WHO European Region Indicator 1. Setting national targets and indicators for monitoring and evaluation of progress 2. Strengthening existing mortality and disease registries Preliminary results for 2017 and trends since 2015 for the WHO European Region progress on full achievement of indicators Between 2015 and 2017 the percentage of countries with both a set of national targets and indicators for them doubled from 23% to 51%. The situation in countries in the Region was already quite satisfactory and increased further from 77% in 2015 to 85% in Risk factors surveys The percentage of countries that had conducted risk factor surveys and particularly recent (in the last five years) surveys reached 40% in 2015, a figure that decreased to 32% in Development and implementation of national multisectoral NCD policies and action plans 5. Tobacco demand-reduction measures Between 2015 and 2017, the proportion of countries that reported they had an operational integrated policy, strategy or action plan increased from 43% to 51%. a. Taxation Although taxation increased in most countries, with rates between 50% and 60%, only one country reached the 70% rate required for full achievement. b. Smoke-free environments Progress in the implementation of smoke-free environments that is, all indoor workplaces, public places and public transport increased only slightly from 19% in 2015 to 21% in c. Health warnings A 10-fold increase was reported on the implementation of warnings of the dangers of tobacco and tobacco smoke through effective health warnings and mass media campaigns between 2015 and 2017, reaching 58% of countries. d. Advertising bans Implementation of bans on all forms of tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship had been achieved fully in less than 10% of countries by Harmful use of alcohol reduction measures 2017 data are not available based on data collected through the WHO global survey on alcohol and health, which is due Unhealthy diet reduction measures a. Salt/sodium consumption Almost three quarters (74%) of countries reported adoption of national policies to reduce population salt consumption. b. Saturated fats and trans-fats 58% of countries had policies to limit saturated fatty acids and virtually eliminate industrially produced trans-fats in the food supply in 2017, increasing from 41% in c. Marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages to children d. Marketing restrictions of breast-milk substitutes 8. Promoting awareness on diet and physical activity 9. Availability of evidence-based national guidelines, protocols and standards for the management of NCDs through a primary care approach, and their implementation status 10. Assessment and management of cardiometabolic risk factors Key to colour coding: Red Fully achieved in less than 50% of countries in the Region Amber Fully achieved in at least 50% but less than 75% of countries in the Region Green Fully achieved in at least 75% of countries in the Region 66% of countries had policies to reduce the impact on children of marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages high in saturated fats, trans-fatty acids, free sugars or salt in 2017, increasing from 41% in Data are not yet available. The proportion of countries that had implemented at least one national public awareness programme in the last five years increased from 75% to 85%. Almost half (45%) of countries had government-approved, evidence-based national guidelines, protocols and standards for the management of all four major NCDs through a primary care approach that were fully implemented in 2017 this figure has not changed since The proportion of countries offering all of the eight essential medicines as well as providing cardiovascular risk stratification in more than half of primary health care facilities increased from 30% in 2015 to 53% in 2017.
4 Table 2. Heat maps to show achievement against the indicators of the time-bound commitments by Member States in the WHO European Region CATEGORY Indicator Indicator 1. Member State has set time-bound targets and indicators based on WHO guidance Indicator 2. Member State has a functioning system for generating reliable cause-specific mortality data on a routine basis GOVERNANCE Indicator 3. Member State has a STEPS survey or a comprehensive health examination survey every five years Indicator 4. Member State has an operational multisectoral national strategy/action plan that integrates the major NCDs and their shared risk factors Country Albania Andorra no data Armenia Austria Azerbaijan Belarus Belgium Bosnia and Herzegovina 1 DK Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark 1 no data Estonia Finland France 1 DK Georgia Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Israel Italy Kazakhstan 2 DK Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg no data no data 2 no data 1 Malta Monaco no data Montenegro Netherlands 1 DK Norway Poland Portugal DK 3 Republic of Moldova Romania Russian Federation San Marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia Turkey Turkmenistan Ukraine United Kingdom Uzbekistan Percent fully achieved (=3) 22.6% 50.9% 77.4% 84.9% 39.6% 32.1% 43.4% 50.9% Relative change % 10% -19% 17% Colour code 1 not achieved DK: Don t know 2 partially achieved 3 fully achieved 3
5 4 CATEGORY Indicator REDUCING RISK FACTORS ON NCDs: TOBACCO USE Indicator 5. Member State has implemented demand-reduction measures of the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (FCTC) at the highest level of achievement to: (a) reduce affordability of tobacco products by increasing tobacco excise taxes (b) create by law completely smoke-free environments in all indoor workplaces, public places and public transport (c) warn people of the dangers of tobacco and tobacco smoke through effective health warnings and mass media campaigns (d) ban all forms of tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship Country Albania Andorra Armenia Austria Azerbaijan Belarus Belgium Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Estonia Finland France Georgia Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Israel Italy Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Monaco no data no data Montenegro Netherlands Norway Poland Portugal Republic of Moldova Romania Russian Federation San Marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia Turkey Turkmenistan Ukraine United Kingdom Uzbekistan Percent fully achieved (=3) 1.9% 1.9% 18.9% 20.8% 5.7% 58.5% 7.5% 9.4% Relative change % 10% 933% 25% Colour code 1 not achieved 2 partially achieved 3 fully achieved
6 CATEGORY Indicator REDUCING RISK FACTORS ON : ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION Indicator 6. Member State has implemented, as appropriate according to national circumstances, measures to reduce the harmful use of alcohol as per the WHO Global Strategy to Reduce the Harmful Use of Alcohol, including: (a) regulations over commercial and public availability of alcohol (b) comprehensive restrictions or bans on alcohol advertising and promotions (c) pricing policies such as excise tax increases on alcoholic beverages Country Albania 2 Not available 1 Not available 2 Not available Andorra 2 Not available 1 Not available 2 Not available Armenia 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Austria 2 Not available 1 Not available 1 Not available Azerbaijan 2 Not available 2 Not available 3 Not available Belarus 2 Not available 2 Not available 3 Not available Belgium 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Bosnia and Herzegovina 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Bulgaria 2 Not available 3 Not available 1 Not available Croatia 2 Not available 2 Not available 1 Not available Cyprus 2 Not available 2 Not available 1 Not available Czech Republic 2 Not available 3 Not available 2 Not available Denmark 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Estonia 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Finland 2 Not available 3 Not available 2 Not available France 2 Not available 3 Not available 3 Not available Georgia 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Germany 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Greece 2 Not available 1 Not available 1 Not available Hungary 2 Not available 3 Not available 1 Not available Iceland 2 Not available 2 Not available 3 Not available Ireland 3 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Israel 2 Not available 3 Not available 3 Not available Italy 2 Not available 3 Not available 1 Not available Kazakhstan 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Kyrgyzstan 2 Not available 3 Not available 1 Not available Latvia 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Lithuania 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Luxembourg 2 Not available 1 Not available 2 Not available Malta 2 Not available 2 Not available 1 Not available Monaco 2 Not available 2 Not available 3 Not available Montenegro 2 Not available 3 Not available 2 Not available Netherlands 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Norway 2 Not available 2 Not available 3 Not available Poland 2 Not available 3 Not available 2 Not available Portugal 2 Not available 3 Not available 1 Not available Republic of Moldova 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Romania 2 Not available 2 Not available 3 Not available Russian Federation 2 Not available 3 Not available 2 Not available San Marino 2 Not available 1 Not available 1 Not available Serbia 2 Not available 2 Not available 3 Not available Slovakia 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Slovenia 2 Not available 3 Not available 2 Not available Spain 2 Not available 2 Not available 1 Not available Sweden 2 Not available 3 Not available 2 Not available Switzerland 2 Not available 2 Not available 1 Not available Tajikistan 2 Not available 1 Not available 3 Not available The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Turkey 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available Turkmenistan 2 Not available 3 Not available 2 Not available Ukraine 2 Not available 2 Not available 2 Not available United Kingdom 2 Not available 2 Not available 3 Not available Uzbekistan 2 Not available 3 Not available no data Not available Percent fully achieved (=3) 1.9% 30.2% 20.8% Relative change Colour code 1 not achieved 2 partially achieved 3 fully achieved 5
7 6 CATEGORY Indicator (a) Adopted national policies to reduce population salt/ sodium consumption REDUCING RISK FACTORS: UNHEALTHY DIET Indicator 7. Member State has implemented the following four measures to reduce unhealthy diets: (b) Adopted national policies that limit saturated fatty acids and virtually eliminate industrially produced trans-fatty acids in the food supply (c) WHO set of recommendations on marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages to children (d) Legislation/ regulations fully implementing the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes Country Albania Not available Andorra Not available Armenia Not available Austria Not available Azerbaijan Not available Belarus Not available Belgium Not available Bosnia and Herzegovina Not available Bulgaria Not available Croatia Not available Cyprus Not available Czech Republic Not available Denmark Not available Estonia Not available Finland Not available France Not available Georgia Not available Germany Not available Greece Not available Hungary Not available Iceland Not available Ireland Not available Israel Not available Italy 1 1 DK DK Not available Kazakhstan Not available Kyrgyzstan Not available Latvia Not available Lithuania Not available Luxembourg no data 0 no data 0 no data 0 no data Not available Malta Not available Monaco no data 0 no data 1 no data 1 no data Not available Montenegro Not available Netherlands Not available Norway Not available Poland DK Not available Portugal Not available Republic of Moldova Not available Romania Not available Russian Federation Not available San Marino Not available Serbia DK Not available Slovakia Not available Slovenia Not available Spain Not available Sweden Not available Switzerland Not available Tajikistan Not available The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia Not available Turkey Not available Turkmenistan Not available Ukraine Not available United Kingdom Not available Uzbekistan Not available Percent fully achieved (=3) 58.5% 73.6% 41.5% 58.5% 41.5% 66.0% 54.7% Relative change % 41% 59% Colour code 0 not achieved DK: Don t know 1 fully achieved
8 CATEGORY Indicator Indicator 8. Member State has implemented at least one recent national public awareness programme on diet and/ or physical activity IMPROVING HEALTH SYSTEMS RESPONSE Indicator 9. Member State has evidence-based national guidelines /protocols/ standards for the management of major NCDs through a primary care approach, recognized/ approved by government or competent authorities Indicator 10. Member State has provision of drug therapy, including glycaemic control, and counselling for eligible persons at high risk to prevent heart attacks and strokes, with emphasis on the primary care level Country Albania Andorra DK DK Armenia Austria DK 3 Azerbaijan 1 1 DK Belarus Belgium DK DK DK Bosnia and Herzegovina DK 3 Bulgaria Croatia DK DK 3 Cyprus DK 3 DK Czech Republic DK 3 Denmark DK 3 Estonia Finland France 1 1 no data DK no data 1 Georgia Germany Greece DK DK Hungary DK 3 3 Iceland DK DK Ireland DK 3 Israel DK 1 Italy DK 1 Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lithuania DK 3 Luxembourg no data 1 no data 1 no data DK Malta Monaco no data 1 no data 3 no data 3 Montenegro DK 1 1 Netherlands Norway DK 3 Poland 1 1 DK DK DK 3 Portugal Republic of Moldova Romania DK Russian Federation San Marino DK DK Serbia DK DK 3 Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland 1 1 DK DK DK 3 Tajikistan The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia Turkey DK 1 Turkmenistan Ukraine United Kingdom DK 3 DK Uzbekistan Percent fully achieved (=3) 75.5% 84.9% (=3) 45.3% 45.3% 30.2% 52.8% Relative change % 0% 75% Colour code Status Color code DK: Don t know 0 not achieved 1 not achieved 1 fully achieved 2 partially achieved 3 fully achieved 7
9 8 Annex 1. Technical notes Given the nature of the survey questionnaire, data reported by countries are sometimes based on incomplete information, on estimates or on expert opinion rather than on established monitoring systems; thus, challenges with validation and accuracy of some questions may arise. Issues concerning understanding or interpreting questions, including some subtle changes of their wording over time, are also possible, making overall judgement more difficult. To minimize these potential issues, WHO has established intense contact with national focal points for completion and clarification of questionnaires and requesting supporting evidence when required. As far as possible, an attempt was made to validate the results, based on different mechanisms including review of specific health policy documentation and other sources and consultations with WHO programme managers and other experts about their knowledge of the implementation of NCD commitments. Consistency of observations across different indicators and countries and the systematic positive trends over time also provide strength for interpretation of results. 10 Progress-monitoring indicators: definitions and achievement criteria (4) Indicator 1: setting national targets and indicators for monitoring and evaluation of progress Definition. Country has set national targets and indicators. The NCD-related targets and indicators should be time-bound and based on the nine voluntary global targets and 25 indicators from the WHO Global Monitoring Framework. Achievement criteria. This indicator is considered fully achieved if a country responded Yes to the questions Is there a set of national NCD indicators? and to the subquestion Is there a set of time-bound national targets for these indicators? Targets must be time-bound, based on the nine global targets, and need to address NCD mortality, as well as key risk factors in the country and/or health systems. This indicator is considered partially achieved if the country responded Yes to the questions Is there a set of national NCD indicators? and to the subquestion Is there a set of time-bound national targets for these indicators?, but the targets do not cover two of the three areas addressed in the nine global targets (including mortality) or they are not timebound. Indicator 2: strengthening existing mortality and disease registries Definition. Country has a vital registration system that captures deaths and the causes of death routinely. The International Form of Medical Certificate of the Cause of Death is completed by certifiers. The International Classification of Diseases (ICD) is used to code the causes of death. The data compiled are made available to policy-makers and researchers. Achievement criteria. WHO collects mortality data, including cause of death, from civil registration systems in the WHO mortality database through a routine annual call for data. Data are considered to generate reliable cause-specific mortality data on a routine basis if: 1) data from the five most recent reporting years are, on average, at least 70% usable usability is calculated as (completeness (%))*(1 proportion garbage); 2) at least five years of cause-of-death data have been reported to WHO; and 3) the most recent year of data reported to WHO is no more than five years old. This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country meets all of the above criteria. Indicator 3: risk factors surveys Definition. Country has completed a WHO STEPwise approach to surveillance (STEPS) survey or another risk factor survey which includes physical measurements and biochemical assessments covering the key behavioural and metabolic risk factors for NCDs. Country must indicate that survey frequency is at least every five years. Achievement criteria. This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country responded Yes to each of the following for adults: Have surveys of risk factors (may be a single risk factor or multiple) been conducted in your country for all of the
10 following: harmful alcohol use (optional for Member States according to national circumstances), physical inactivity, tobacco use, raised blood glucose/diabetes, raised blood pressure/hypertension, overweight and obesity, and salt /sodium intake. Additionally, for each risk factor, the country must indicate that the last survey was conducted in the past five years (i.e or later for the 2015 NCD CCS responses) and must respond Every 1 2 years or Every 3 5 years to the subquestion How often is the survey conducted? This indicator is considered partially achieved if the country responded that at least three, but not all, of the above risk factors are covered, or that the surveys were conducted more than five years ago but less than 10 years ago. Indicator 4: development and implementation of national multisectoral NCD policies and action plans Definition. Country has a multisectoral, national integrated NCD and risk factor policy/strategy/action plan that addresses the four main NCDs (cardiovascular disease and/or diabetes, and/or cancer and/or respiratory disease) and their main risk factors (tobacco use, unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, harmful use of alcohol). Multisectoral refers to engagement with one or more government sectors outside of health. Operational refers to a policy, strategy or action plan which is being used and implemented in the country, and has resources and funding available to implement it. Achievement criteria. This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country responded Yes to the questions Does your country have a national NCD policy, strategy or action plan which integrates several NCDs and their risk factors? and to the subquestion Is it multisectoral?. Countries also had to respond operational to the subquestion Indicate its stage and Yes to all of the subquestions pertaining to the four main risk factors and four main NCDs: Does it address one or more of the following major risk factors: harmful use of alcohol (optional for Member States according to national circumstances), unhealthy diet, physical inactivity, tobacco (all four must have Yes ) and Does it combine early detection, treatment and care for: cancer, cardiovascular diseases, chronic respiratory diseases and diabetes (all four must have Yes ). This indicator is considered partially achieved if the country responded Yes to the questions Does your country have a national NCD policy, strategy or action plan which integrates several NCDs and their risk factors? and to the subquestion Is it multisectoral?. Countries also had to respond operational to the subquestion Indicate its stage and Yes to at least two of the four main risk factors and at least two of the four main NCDs. Indicator 5: tobacco demand-reduction measures Indicator 5a. Implemented measures to reduce affordability of tobacco products by increasing tobacco excise taxes Definition. Country has tobacco excise tax set at a level that accounts for at least 70% of the retail prices of tobacco products. Achievement criteria. Excise tax is calculated as a proportion of the price of the tobacco product. Currently, this is only collected in relation to the most sold brand of cigarettes. This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country has set an excise tax at least 70% of the retail price. This indicator is considered partially achieved if the country has set an excise tax at least 50% but less than 70% of the retail price. Indicator 5b. Implemented measures to create by law completely smoke-free environments Definition. Country has all public places completely smoke-free (or at least 90% of the population covered by complete subnational smoke-free legislation). Completely means that smoking is not permitted, with no exemptions allowed, except in residences and indoor places that serve as equivalents to long-term residential facilities, such as prisons and long-term health and social care facilities 9
11 10 such as psychiatric units and nursing homes. Ventilation and any form of designated smoking rooms and/or areas do not protect from the harms of second-hand tobacco smoke, and the only laws that provide protection are those that result in the complete absence of smoking in all public places. Achievement criteria. Legislation is assessed to determine whether smoke-free laws provided for a complete indoor smokefree environment at all times, in all the facilities of each of the following eight places: health care facilities; educational facilities other than universities; universities; government facilities; indoor offices and workplaces not considered in any other category; restaurants or facilities that serve mostly food; cafés, pubs and bars or facilities that serve mostly beverages; public transport. This indicator is considered fully achieved if all public places in the country are completely smoke-free (or at least 90% of the population covered by complete subnational smoke-free legislation). This indicator is considered partially achieved if three to seven public places are completely smoke-free, or the law allows designated smoking rooms with strict technical requirements in five or more places. Indicator 5c. Implemented measures to warn people of the dangers of tobacco and tobacco smoke through effective health warnings and mass media campaigns Definition. Country has large warnings which are defined as covering on average at least 50% of the front and back of the package with all appropriate characteristics. Appropriate characteristics include: 1) specific health warnings mandated; 2) appearing on individual packages as well as on any outside packaging and labelling used in retail sale; 3) describing specific harmful effects of tobacco use on health; 4) are large, clear, visible and legible (e.g. specific colours and font style and sizes are mandated); 5) whether the warnings rotate; 6) include pictures or pictograms; and 7) written in (all) the principal language(s) of the country. Achievement criteria. Health warnings: legislation is assessed to determine the size of the warnings (the front and back of the cigarette pack are averaged to calculate the percentage of the total pack surface area covered by warnings) and warning characteristics. This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country has large health warnings with all appropriate characteristics as detailed above. This indicator is considered partially achieved if there are medium-size warnings with some or all appropriate characteristics, or if large warnings are missing some appropriate characteristics. Indicator 5d. Implemented measures to ban all forms of tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship Definition. Country has a ban on all forms of direct and indirect advertising. Direct advertising bans include: national television and radio; local magazines and newspapers; billboards and outdoor advertising; point of sale. Indirect advertising bans include: free distribution of tobacco products in the mail or through other means; promotional discounts; non-tobacco goods and services identified with tobacco brand names (brand extension); brand names of non-tobacco products used for tobacco products (brand sharing); appearance of tobacco brands (product placement) or tobacco products in television and/or films; and sponsorship, including corporate social responsibility programmes. Achievement criteria. Legislation is assessed to determine whether the law completely bans all forms of direct and indirect tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship. This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country has a ban on all forms of direct and indirect advertising. This indicator is considered partially achieved if the country has a ban on national TV, radio and print media, but not on all other forms of direct and/or indirect advertising.).
12 Indicator 6: harmful use of alcohol reduction measures Indicator 6a. Implemented, as appropriate according to national circumstances, regulations over commercial and public availability of alcohol Definition. Country has a licensing system or monopoly on retail sales of beer, wine, spirits. Country has restrictions for on-/ off-premise sales of beer, wine, spirits regarding hours, days and locations of sales. Country has legal age limits for being sold and served alcoholic beverages. Achievement criteria. Data are collected through the WHO Global Survey on Alcohol and Health. This indicator is considered fully achieved if: 1) a licensing system or monopoly exists on retail sales of beer, wine and spirits; 2) restrictions exist for on- and off-premise sales of beer, wine and spirits regarding hours and locations of sales and restrictions exist for off-premise sales of beer, wine and spirits regarding days of sales; and 3) legal age limits for being sold and served alcoholic beverages are 18 years or above for beer, wine and spirits. This indicator is considered partially achieved if there are any, but not all, positive responses to the three indicators above. Indicator 6b. Implemented, as appropriate according to national circumstances, regulations over commercial and public availability of alcohol Definition. Country has regulatory or co-regulatory frameworks for alcohol advertising through different channels (public service/national TV, commercial/private TV, national radio, local radio, print media, billboards, points of sale, cinema, internet, social media). Country has a detection system for infringements on marketing restrictions. Achievement criteria. Data are collected through the WHO Global Survey on Alcohol and Health. This indicator is considered fully achieved if: 1) restrictions exist on alcohol advertising for beer, wine and spirits through all channels; and 2) a detection system exists for infringements on marketing restrictions. This indicator is considered partially achieved if there are restrictions on at least public service/national TV, national radio and billboards but no detection system exists for infringements. Indicator 6c. Implemented, as appropriate according to national circumstances, pricing policies such as excise tax on alcoholic beverages Definition. Country has excise tax on beer, wine, spirits. Country adjusts level of taxation for inflation for alcoholic beverages. Achievement criteria. Data are collected through the WHO Global Survey on Alcohol and Health. This indicator is considered fully achieved if: 1) excise tax on all alcoholic beverages (beer, wine and spirits) is implemented; and 2) adjustment of level of taxation for inflation for beer, wine and spirits is implemented. This indicator is considered partially achieved if there is excise tax on all alcoholic beverages as specified above and adjustment of the level of taxation for inflation is implemented on at least one of the alcoholic beverages (beer, wine, spirits). 11
13 12 Indicator 7: unhealthy diet reduction measures Indicator 7a. Adopted national policies to reduce population salt/sodium consumption Definition. Country has implemented a policy or policies to reduce population salt/sodium consumption such as product reformulation by industry, regulation of salt content of food, or public awareness programmes. Achievement criteria. The WHO NCD CCS is completed by a team at the country level to ensure a comprehensive response is compiled. This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country responds Yes to the question Is your country implementing any policies to reduce population salt consumption? Indicator 7b. Adopted national policies that limit saturated fatty acids and virtually eliminate industrially produced trans-fatty acids in the food supply Definition. Country has implemented a policy(ies) to limit saturated fatty acids and virtually eliminate industrially produced trans-fats in the food supply. Achievement criteria. The WHO NCD CCS is completed by a team at the country level to ensure a comprehensive response is compiled. This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country responds Yes to the question Is your country implementing any national policies that limit saturated fatty acids and virtually eliminate industrially produced trans-fats (i.e. partially hydrogenated vegetable oils) in the food supply? Indicator 7c. Implemented the WHO set of recommendations on marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages to children Definition. Country has implemented a policy or policies to reduce the impact on children of marketing of foods and nonalcoholic beverages high in saturated fats, trans-fatty acids, free sugars or salt. Achievement criteria. The WHO NCD CCS is completed by a team at the country level to ensure a comprehensive response is compiled. This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country responds Yes to the question Is your country implementing any policies to reduce the impact on children of marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages high in saturated fats, transfatty acids, free sugars or salt? Indicator 7d. Legislation/regulations fully implementing the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes Definition. Country has implemented legislation/regulations that fully implement the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes. Achievement criteria. The WHO NCD CCS is completed by a team at the country level to ensure a comprehensive response is compiled. This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country responds Yes to the question Is your country implementing the International Code of Marketing of Breast-milk Substitutes through adoption of national laws? Indicator 8: promoting awareness on diet and physical activity Definition. Country has implemented at least one recent national public awareness programme on diet, physical activity or both. Achievement criteria. The WHO NCD CCS is completed by a team at the country level to ensure a comprehensive response is compiled.
14 This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country responds Yes to at least one of the following questions: 1) Has your country implemented any national public awareness programme on diet within the past five years? ; and 2) Has your country implemented any national public awareness programme on physical activity within the past five years? Indicator 9: availability of evidence-based national guidelines, protocols and standards for the management of NCDs through a primary care approach, and their implementation status Definition. Government-approved evidence-based national guidelines/protocols/standards for the management (diagnosis and treatment) of the four main NCDs cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer and chronic respiratory diseases. Achievement criteria. The WHO NCD CCS is completed by a team at the country level to ensure a comprehensive response is compiled. This indicator is based on the number of countries who have indicated that national guidelines/protocols/standards exist for all four NCDs (cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer and chronic respiratory diseases), and that these are being partially or fully implemented. This indicator is considered fully achieved if national guidelines/protocols/standards exist for all four NCDs (cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer and chronic respiratory diseases) which are being partially or fully implemented. This indicator is considered partially achieved if the country has guidelines/protocols/standards for at least two of the four NCDs (cardiovascular disease, diabetes, cancer and chronic respiratory diseases), but not for all four, and that these are being partially or fully implemented. Indicator 10: assessment and management of cardiometabolic risk factors Definition. Country has provision of drug therapy including glycaemic control, and counselling for eligible persons at high risk to prevent heart attacks and strokes, with emphasis on the primary care level. Achievement criteria. The WHO NCD CCS is completed by a team at the country level to ensure a comprehensive response is compiled. This indicator is based on the number of countries who respond more than 50% to the question What proportion of primary health care facilities are offering cardiovascular risk stratification for the management of patients at high risk for heart attack and stroke?. Additionally, countries must have said all the following drugs were generally available in the primary care facilities of the public health sector: insulin, aspirin (100 mg), metformin, Thiazide diuretics, ACE inhibitors, CC blockers, statins and sulphonylurea(s). This indicator is considered fully achieved if the country reports that more than 50% of primary health care facilities are offering cardiovascular risk stratification for the management of patients at high risk for heart attack and stroke and that all drugs listed above were generally available in the primary care facilities of the public health sector. This indicator is considered partially achieved if the country reports that between 25% and 50% of primary health care facilities are offering cardiovascular risk stratification for the management of patients at high risk for heart attack and stroke and that all of the drugs listed above were generally available in the primary care facilities of the public health sector. 13
15 14 References 1. Noncommunicable Diseases Global Monitoring Framework. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013 ( who.int/nmh/global_monitoring_framework/en/, accessed 24 May 2017). 2. Outcome document of the high-level meeting of the General Assembly on the comprehensive review and assessment of the progress achieved in the prevention and control of non-communicable diseases. New York: United Nations; 2014 (A/RES/68/300; accessed 24 May 2017). 3. Assessing national capacity for the prevention and control of NCDs [website]. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017 ( accessed 24 May 2017). 4. Assessing national capacity for the prevention and control of noncommunicable diseases: report of the 2015 global survey. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2016 ( accessed 24 May 2017).
16 The WHO Regional Office for Europe The World Health Organization (WHO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations created in 1948 with the primary responsibility for international health matters and public health. The WHO Regional Office for Europe is one of six regional offices throughout the world, each with its own programme geared to the particular health conditions of the countries it serves. Member States Albania Andorra Armenia Austria Azerbaijan Belarus Belgium Bosnia and Herzegovina Bulgaria Croatia Cyprus Czechia Denmark Estonia Finland France Georgia Germany Greece Hungary Iceland Ireland Israel Italy Kazakhstan Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lithuania Luxembourg Malta Monaco Montenegro Netherlands Norway Poland Portugal Republic of Moldova Romania Russian Federation San Marino Serbia Slovakia Slovenia Spain Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan The former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia Turkey Turkmenistan Ukraine United Kingdom Uzbekistan World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe UN City, Marmorvej 51, DK-2100 Copenhagen Ø, Denmark Tel.: Fax: contact@euro.who.int
European status report on alcohol and health Leadership, awareness and commitment
 European status report on alcohol and health 2014 Leadership, awareness and commitment Leadership, awareness and commitment Background Strong leadership from national and local governments is essential
European status report on alcohol and health 2014 Leadership, awareness and commitment Leadership, awareness and commitment Background Strong leadership from national and local governments is essential
Alcohol-related harm in Europe and the WHO policy response
 Alcohol-related harm in Europe and the WHO policy response Lars Moller Programme Manager World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Date of presentation NCD global monitoring framework: alcohol-related
Alcohol-related harm in Europe and the WHO policy response Lars Moller Programme Manager World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Date of presentation NCD global monitoring framework: alcohol-related
Monitoring noncommunicable disease commitments in Europe Theme in focus: progress monitor indicators
 Monitoring noncommunicable disease commitments in Europe Theme in focus: progress monitor indicators Monitoring noncommunicable disease commitments in Europe Theme in focus: progress monitor indicators
Monitoring noncommunicable disease commitments in Europe Theme in focus: progress monitor indicators Monitoring noncommunicable disease commitments in Europe Theme in focus: progress monitor indicators
European Status report on Alcohol and Health
 European Status report on Alcohol and Health Dr Lars Moller Regional Advisor a.i. WHO Regional Office for Europe Main killers in the WHO European Region Source: Preventing chronic diseases. A vital investment.
European Status report on Alcohol and Health Dr Lars Moller Regional Advisor a.i. WHO Regional Office for Europe Main killers in the WHO European Region Source: Preventing chronic diseases. A vital investment.
WHO REGIONAL OFFICE FOR EUROPE RECOMMENDATIONS ON INFLUENZA
 WHO REGIONAL OFFICE FOR EUROPE RECOMMENDATIONS ON INFLUENZA September 2017 Address requests about publications of the WHO Regional Office for Europe to: Publications WHO Regional Office for Europe Marmorvej
WHO REGIONAL OFFICE FOR EUROPE RECOMMENDATIONS ON INFLUENZA September 2017 Address requests about publications of the WHO Regional Office for Europe to: Publications WHO Regional Office for Europe Marmorvej
RECOMMENDATIONS ON INFLUENZA VACCINATION DURING THE WINTER SEASON
 RECOMMENDATIONS ON INFLUENZA VACCINATION DURING THE 2018 2019 WINTER SEASON October 2018 Address requests about publications of the WHO Regional Office for Europe to: Publications WHO Regional Office for
RECOMMENDATIONS ON INFLUENZA VACCINATION DURING THE 2018 2019 WINTER SEASON October 2018 Address requests about publications of the WHO Regional Office for Europe to: Publications WHO Regional Office for
A report on the epidemiology of selected vaccine-preventable diseases in the European Region 30% 20% 10%
 % of reported measles cases WHO EpiBrief A report on the epidemiology of selected vaccine-preventable diseases in the European Region No. /17 This issue of WHO EpiBrief provides an overview of selected
% of reported measles cases WHO EpiBrief A report on the epidemiology of selected vaccine-preventable diseases in the European Region No. /17 This issue of WHO EpiBrief provides an overview of selected
The cancer burden in the European Union and the European Region: the current situation and a way forward
 The cancer burden in the European Union and the European Region: the current situation and a way forward Presented by Zsuzsanna Jakab WHO Regional Director for Europe Informal Meeting of Health Ministers
The cancer burden in the European Union and the European Region: the current situation and a way forward Presented by Zsuzsanna Jakab WHO Regional Director for Europe Informal Meeting of Health Ministers
Media Release. Inaugural study reveals that more than one in four women in European and Central Asian prisons locked up for drug offences
 Media Release Embargoed 00.01 CET Monday 12 th March 2012 Inaugural study reveals that more than one in four women in European and Central Asian prisons locked up for drug offences Up to 70 percent of
Media Release Embargoed 00.01 CET Monday 12 th March 2012 Inaugural study reveals that more than one in four women in European and Central Asian prisons locked up for drug offences Up to 70 percent of
Budapest, Hungary, September 2017 xx July xxx. Progress reports
 Regional Committee for Europe 67th session EUR/RC67/xx Budapest, Hungary, 11 14 September 2017 xx July 2017 170xxx Provisional agenda item 5(h) ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Progress reports This document contains
Regional Committee for Europe 67th session EUR/RC67/xx Budapest, Hungary, 11 14 September 2017 xx July 2017 170xxx Provisional agenda item 5(h) ORIGINAL: ENGLISH Progress reports This document contains
Highlighting in the WHO European Region: Summary. No. 21(February 2012)
 No. 21(February 2012) Issue 15, April 2011 A monthly publication on vaccine preventable diseases and immunization data and analysis Highlighting in the WHO European Region: Update on measles in the European
No. 21(February 2012) Issue 15, April 2011 A monthly publication on vaccine preventable diseases and immunization data and analysis Highlighting in the WHO European Region: Update on measles in the European
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SWEDEN
 WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SWEDEN SWEDEN NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 11,043 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 17,906 Total number of
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SWEDEN SWEDEN NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 11,043 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 17,906 Total number of
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 HUNGARY
 WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 HUNGARY HUNGARY NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 727 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 4,000 Total number of practising
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 HUNGARY HUNGARY NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 727 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 4,000 Total number of practising
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SERBIA
 WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SERBIA SERBIA NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 622 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 3,323 Total number of practising
WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2017 SERBIA SERBIA NUMBERS WCPT Members Practising physical therapists 622 Total number of physical therapist members in your member organisation 3,323 Total number of practising
Inequalities in health: challenges and opportunities in Europe Dr Zsuzsanna Jakab WHO Regional Director for Europe
 Inequalities in health: challenges and opportunities in Europe Dr Zsuzsanna Jakab WHO Regional Director for Europe 21st Congress of the European Association of Dental Public Health 1 October 2016 Budapest
Inequalities in health: challenges and opportunities in Europe Dr Zsuzsanna Jakab WHO Regional Director for Europe 21st Congress of the European Association of Dental Public Health 1 October 2016 Budapest
EURO POLIO PAGE Data as of 04 October 2005 (Week 38)
 World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe EURO POLIO PAGE Data as of 04 October 2005 (Week 38) Vaccine-preventable Diseases and Immunization programme, Division of Technical Support website:
World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe EURO POLIO PAGE Data as of 04 October 2005 (Week 38) Vaccine-preventable Diseases and Immunization programme, Division of Technical Support website:
Q1 What age are you?
 Q1 What age are you? Answered: 504 Skipped: 0 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 4.56% 23 3.77% 19 4.56% 23 6.15% 31 3.97% 20 6.55% 33 5.95% 30 6.75% 34 6.35% 32 4.37% 22 6.75% 34 5.56%
Q1 What age are you? Answered: 504 Skipped: 0 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 4.56% 23 3.77% 19 4.56% 23 6.15% 31 3.97% 20 6.55% 33 5.95% 30 6.75% 34 6.35% 32 4.37% 22 6.75% 34 5.56%
Smokefree Policies in Europe: Are we there yet?
 Smokefree Policies in Europe: Are we there yet? 14 April 2015, 9:00 10:30am Rue de l Industrie 24, 1040 Brussels Permanent Partners: Temporary Partners: The research for the SFP Smokefree Map was partially
Smokefree Policies in Europe: Are we there yet? 14 April 2015, 9:00 10:30am Rue de l Industrie 24, 1040 Brussels Permanent Partners: Temporary Partners: The research for the SFP Smokefree Map was partially
Highlighting in the WHO European Region: measles outbreaks rubella surveillance acute flaccid paralysis surveillance
 No. 17 (September 2011) A monthly publication on vaccine preventable diseases and immunization data and analysis Issue 15, April 2011 Highlighting in the WHO European Region: measles outbreaks rubella
No. 17 (September 2011) A monthly publication on vaccine preventable diseases and immunization data and analysis Issue 15, April 2011 Highlighting in the WHO European Region: measles outbreaks rubella
Highlighting in the WHO European Region:
 No. 23(April 2012) Issue 15, April 2011 A monthly publication on vaccine preventable diseases and immunization data and analysis Highlighting in the WHO European Region: Update on measles in the European
No. 23(April 2012) Issue 15, April 2011 A monthly publication on vaccine preventable diseases and immunization data and analysis Highlighting in the WHO European Region: Update on measles in the European
The main indicators of the WHO Global Monitoring Framework (GMF) on Noncommunicable Diseases
 The main indicators of the WHO Global Monitoring Framework (GMF) on Noncommunicable Diseases 2016 In the spotlight diabetes, target indicators Preface Noncommunicable diseases (NCD) are major public health
The main indicators of the WHO Global Monitoring Framework (GMF) on Noncommunicable Diseases 2016 In the spotlight diabetes, target indicators Preface Noncommunicable diseases (NCD) are major public health
Better Health for All in Latvia
 Better Health for All in Latvia The health strategy for the European Region (Health 2020) and the Latvian Public Health Strategy 2011 2017 Zsuzsanna Jakab WHO Regional Director for Europe 18 April 2011,
Better Health for All in Latvia The health strategy for the European Region (Health 2020) and the Latvian Public Health Strategy 2011 2017 Zsuzsanna Jakab WHO Regional Director for Europe 18 April 2011,
Summary. Primary care data. Week 49/2014. Season
 Summary Week 49/2014 In week 49/2014, influenza activity remained low across the WHO European Region. Twenty countries reported sporadic influenza activity and nine reported increasing trends in consultations
Summary Week 49/2014 In week 49/2014, influenza activity remained low across the WHO European Region. Twenty countries reported sporadic influenza activity and nine reported increasing trends in consultations
Nutrition, diet and health in the WHO European Region Progress and opportunities for further action to achieve SDGs by 2030
 Nutrition, diet and health in the WHO European Region Progress and opportunities for further action to achieve SDGs by 2030 João Breda Head, WHO European Office for Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable
Nutrition, diet and health in the WHO European Region Progress and opportunities for further action to achieve SDGs by 2030 João Breda Head, WHO European Office for Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable
Prevention of Oral Cancer Special Interest Working Group
 Prevention of Oral Cancer Special Interest Working Group Dr Colwyn Jones, Consultant in Dental Public Health, NHS Health Scotland, 1 South Gyle Crescent, Edinburgh EH12 9EB, Scotland. colwyn.jones@nhs.net
Prevention of Oral Cancer Special Interest Working Group Dr Colwyn Jones, Consultant in Dental Public Health, NHS Health Scotland, 1 South Gyle Crescent, Edinburgh EH12 9EB, Scotland. colwyn.jones@nhs.net
European Association of Dental Public Health Prevention of Oral Cancer
 European Association of Dental Public Health Prevention of Oral Cancer Special Interest Working Group Thursday 14th November 2013 PD Dr. Katrin Hertrampf, MPH Dr. Colwyn Jones, Associate Editor Malta 2013
European Association of Dental Public Health Prevention of Oral Cancer Special Interest Working Group Thursday 14th November 2013 PD Dr. Katrin Hertrampf, MPH Dr. Colwyn Jones, Associate Editor Malta 2013
Engagement in language assessment / Regions of Europe
 Summary table: Engagement in language / Regions of This table lists the statistically significant differences in the engagement in activities by the respondents from different s of : If the word or appears
Summary table: Engagement in language / Regions of This table lists the statistically significant differences in the engagement in activities by the respondents from different s of : If the word or appears
The challenge of obesity in the WHO European Region
 Fact sheet EURO/13/05 Copenhagen, Bucharest, 12 September 2005 The challenge of obesity in the WHO European Region Obesity poses one of the greatest public health challenges for the 21st century, with
Fact sheet EURO/13/05 Copenhagen, Bucharest, 12 September 2005 The challenge of obesity in the WHO European Region Obesity poses one of the greatest public health challenges for the 21st century, with
World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Surveillance of measles and rubella Data as of 15 March 2006
 World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Surveillance of measles and rubella Data as of 15 March 2006 WHO Regional Office for Europe Vaccine-preventable Diseases and Immunization programme,
World Health Organization Regional Office for Europe Surveillance of measles and rubella Data as of 15 March 2006 WHO Regional Office for Europe Vaccine-preventable Diseases and Immunization programme,
Situation update in the European Region: overview of influenza surveillance data week 40/2009 to week 07/2010.
 Situation update in the European Region: overview of influenza surveillance data week 40/2009 to week 07/2010. WHO/Europe publishes a weekly electronic bulletin on influenza activity in the Region 1 and
Situation update in the European Region: overview of influenza surveillance data week 40/2009 to week 07/2010. WHO/Europe publishes a weekly electronic bulletin on influenza activity in the Region 1 and
A new scale to measure tobacco control activity in a country: data tables and questionnaire
 A new scale to measure tobacco control activity in a country: data tables and questionnaire 1 Appendix 1: Smoke free public places - score on 1 July 2005 in 30 European countries Country Bars and restaurants
A new scale to measure tobacco control activity in a country: data tables and questionnaire 1 Appendix 1: Smoke free public places - score on 1 July 2005 in 30 European countries Country Bars and restaurants
Burden and cost of alcohol, tobacco and illegal drugs globally and in Europe
 Burden and cost of alcohol, tobacco and illegal drugs globally and in Europe Jürgen Rehm 1-4 Kevin D. Shield 1,2,3 1) Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, Canada 2) University of Toronto, Canada
Burden and cost of alcohol, tobacco and illegal drugs globally and in Europe Jürgen Rehm 1-4 Kevin D. Shield 1,2,3 1) Centre for Addiction and Mental Health, Toronto, Canada 2) University of Toronto, Canada
Country profile. Angola
 Country profile Angola WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 29 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 20 September 2007 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Angola WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 29 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 20 September 2007 Socioeconomic context Population
Analysis of 3-dose oral/inactivated poliovirus vaccine (OPV3/IPV3) immunization coverage
 A MONTHLY NEWSLETTER OF THE COMMUNICABLE DISEASE UNIT, WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION REGIONAL OFFICE FOR EUROPE, COPENHAGEN, DENMARK Issue 5, March 2009 Analysis of 3-dose oral/inactivated poliovirus vaccine
A MONTHLY NEWSLETTER OF THE COMMUNICABLE DISEASE UNIT, WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION REGIONAL OFFICE FOR EUROPE, COPENHAGEN, DENMARK Issue 5, March 2009 Analysis of 3-dose oral/inactivated poliovirus vaccine
Where we stand in EFORT
 Where we stand in EFORT Engaging with the new EU regulatory landscape for medical devices. Challenges & opportunities Brussel, Belgium April 6, 2018 Per Kjaersgaard-Andersen Associate Professor Section
Where we stand in EFORT Engaging with the new EU regulatory landscape for medical devices. Challenges & opportunities Brussel, Belgium April 6, 2018 Per Kjaersgaard-Andersen Associate Professor Section
Country profile. Senegal
 Country profile Senegal WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 19 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 27 January 2005 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Senegal WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 19 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 27 January 2005 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Russian Federation. WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status
 Country profile Russian Federation WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature t signed Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 3 June 2008 Socioeconomic context
Country profile Russian Federation WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature t signed Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 3 June 2008 Socioeconomic context
Manuel Cardoso RARHA Executive Coordinator Public Health MD Senior Advisor Deputy General-Director of SICAD - Portugal
 Manuel Cardoso RARHA Executive Coordinator Public Health MD Senior Advisor Deputy General-Director of SICAD - Portugal Public Health Public health is the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging
Manuel Cardoso RARHA Executive Coordinator Public Health MD Senior Advisor Deputy General-Director of SICAD - Portugal Public Health Public health is the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging
Country profile. Austria
 Country profile Austria WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 28 August 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 15 September 2005 Socioeconomic context
Country profile Austria WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 28 August 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 15 September 2005 Socioeconomic context
Bosnia and Herzegovina
 Country profile Bosnia and Herzegovina WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature t signed Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 10 July 2009 Socioeconomic context
Country profile Bosnia and Herzegovina WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature t signed Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 10 July 2009 Socioeconomic context
Country profile. Cuba
 Country profile Cuba WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 29 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) t ratified Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Cuba WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 29 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) t ratified Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Republic of Moldova
 Country profile Republic of Moldova WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 29 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 3 February 2009 Socioeconomic
Country profile Republic of Moldova WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 29 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 3 February 2009 Socioeconomic
Lao People's Democratic Republic
 Country profile Lao People's Democratic Republic WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 29 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 6 September 2006
Country profile Lao People's Democratic Republic WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 29 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 6 September 2006
2008 EUROBAROMETER SURVEY ON TOBACCO
 8 EUROBAROMETER SURVEY ON TOBACCO KEY MSAG Support for smoke-free places: The survey confirms the overwhelming support that smoke-free policies have in the EU. A majority of EU citizens support smoke-free
8 EUROBAROMETER SURVEY ON TOBACCO KEY MSAG Support for smoke-free places: The survey confirms the overwhelming support that smoke-free policies have in the EU. A majority of EU citizens support smoke-free
Country profile. Turkmenistan. WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status. Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 13 May 2011
 Country profile Turkmenistan WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature t signed Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 13 May 2011 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Turkmenistan WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature t signed Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 13 May 2011 Socioeconomic context Population
Nutrient profiles for foods bearing claims
 Nutrient profiles for foods bearing claims Fields marked with * are mandatory. Background Regulation (EC) 1924/2006 (Nutrition and Health Claims NHC Regulation) establishes EU rules on nutrition and health
Nutrient profiles for foods bearing claims Fields marked with * are mandatory. Background Regulation (EC) 1924/2006 (Nutrition and Health Claims NHC Regulation) establishes EU rules on nutrition and health
Country profile. Gambia
 Country profile Gambia WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 18 September 2007 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Gambia WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 18 September 2007 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Hungary
 Country profile Hungary WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 7 April 2004 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Hungary WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 7 April 2004 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Trinidad and Tobago
 Country profile Trinidad and Tobago WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 27 August 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 19 August 2004 Socioeconomic
Country profile Trinidad and Tobago WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 27 August 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 19 August 2004 Socioeconomic
Country profile. Egypt
 Country profile Egypt WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 17 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 25 February 2005 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Egypt WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 17 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 25 February 2005 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Italy
 Country profile Italy WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 2 July 2008 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Italy WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 2 July 2008 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Sweden
 Country profile Sweden WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 7 July 2005 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Sweden WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 7 July 2005 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Poland
 Country profile Poland WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 14 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 15 September 2006 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Poland WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 14 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 15 September 2006 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Bahrain. WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status. Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 20 March 2007
 Country profile Bahrain WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature t signed Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 20 March 2007 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Bahrain WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature t signed Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 20 March 2007 Socioeconomic context Population
Animal health situation of OIE Member Countries in Europe 1 st semester 2012 (and previous)
 Animal health situation of OIE Member Countries in Europe 1 st semester 2012 (and previous) 25 th Conference of the OIE Regional Commission for Europe 17 th to 21 st September 2012, Fleesensee Germany
Animal health situation of OIE Member Countries in Europe 1 st semester 2012 (and previous) 25 th Conference of the OIE Regional Commission for Europe 17 th to 21 st September 2012, Fleesensee Germany
Table 6.1 Summary information for colorectal cancer in Ireland,
 6 Colorectal cancer 6.1 Summary Colorectal cancer is the second most common cancer in Ireland (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer). It accounts for 12% of all malignant neoplasia in females and 15% in
6 Colorectal cancer 6.1 Summary Colorectal cancer is the second most common cancer in Ireland (excluding non-melanoma skin cancer). It accounts for 12% of all malignant neoplasia in females and 15% in
Country profile. Norway
 Country profile rway WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 16 June 2003 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile rway WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 16 June 2003 Socioeconomic context Population
United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland
 Country profile United Kingdom of Great Britain and rthern Ireland WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
Country profile United Kingdom of Great Britain and rthern Ireland WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
Iran (Islamic Republic of)
 Country profile Iran (Islamic Republic of) WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 6 November 2005 Socioeconomic
Country profile Iran (Islamic Republic of) WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 6 November 2005 Socioeconomic
Country profile. New Zealand
 Country profile New Zealand WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 27 January 2004 Socioeconomic context
Country profile New Zealand WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 27 January 2004 Socioeconomic context
WHO Meeting on Strengthening measles and rubella laboratory network in the Russian Federation and Newly Independent States
 WHO Meeting on Strengthening measles and rubella laboratory network in the Russian Federation and Newly Independent States 8 10 September 2014 Hammamet, Tunisia MEETING REPORT WHO MEETING ON STRENGTHENING
WHO Meeting on Strengthening measles and rubella laboratory network in the Russian Federation and Newly Independent States 8 10 September 2014 Hammamet, Tunisia MEETING REPORT WHO MEETING ON STRENGTHENING
Country profile. Ukraine
 Country profile Ukraine WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 25 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 6 June 2006 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Ukraine WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 25 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 6 June 2006 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Chad
 Country profile Chad WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 22 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 30 January 2006 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Chad WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 22 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 30 January 2006 Socioeconomic context Population
Development of Palliative Care services in different countries
 Development of Palliative Care services in different countries Nicoleta Mitrea EONS leadership summit, 2017 Disclosure speaker Do you have any interest to declare? No, I don t have any interest to declare.
Development of Palliative Care services in different countries Nicoleta Mitrea EONS leadership summit, 2017 Disclosure speaker Do you have any interest to declare? No, I don t have any interest to declare.
APPENDIX V: COUNTRY PROFILES
 WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX V: COUNTRY PROFILES Argentina Bangladesh Brazil China Egypt France Germany India Indonesia Iran (Islamic Republic of) Italy Japan Mexico Myanmar
WHO REPORT ON THE GLOBAL TOBACCO EPIDEMIC, 2011 APPENDIX V: COUNTRY PROFILES Argentina Bangladesh Brazil China Egypt France Germany India Indonesia Iran (Islamic Republic of) Italy Japan Mexico Myanmar
Country profile. Timor-Leste
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013 Country profile Timor-Leste WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 25 May 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013 Country profile Timor-Leste WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 25 May 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
Table 9.1 Summary information for stomach cancer in Ireland,
 9 Stomach cancer 9.1 Summary Stomach cancer ranks seventh in terms of the most common cancers in Ireland, accounting for 4.1% of all malignant neoplasia in men and 2.8% in women, when non-melanoma skin
9 Stomach cancer 9.1 Summary Stomach cancer ranks seventh in terms of the most common cancers in Ireland, accounting for 4.1% of all malignant neoplasia in men and 2.8% in women, when non-melanoma skin
Country profile. Switzerland
 Country profile Switzerland WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 25 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) t ratified Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Switzerland WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 25 June 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) t ratified Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Myanmar
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013 Country profile Myanmar WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 23 October 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013 Country profile Myanmar WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 23 October 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
Table 7.1 Summary information for lung cancer in Ireland,
 7 Lung cancer 7.1 Summary Lung cancer is the third most common cancer in Ireland, accounting for 15% of cancers in men and 9% in women, if non-melanoma skin cancer is excluded (table 7.1). Each year, approximately
7 Lung cancer 7.1 Summary Lung cancer is the third most common cancer in Ireland, accounting for 15% of cancers in men and 9% in women, if non-melanoma skin cancer is excluded (table 7.1). Each year, approximately
Country profile. Yemen
 Country profile Yemen WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 20 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 22 February 2007 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Yemen WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 20 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 22 February 2007 Socioeconomic context Population
Reflecting on ten years of progress in the fight against AIDS, TB and malaria
 Reflecting on ten years of progress in the fight against AIDS, TB and malaria Michel Kazatchkine UN Secretary General s Special Envoy on HIV/AIDS in Eastern Europe and central Asia Ten years of progress:
Reflecting on ten years of progress in the fight against AIDS, TB and malaria Michel Kazatchkine UN Secretary General s Special Envoy on HIV/AIDS in Eastern Europe and central Asia Ten years of progress:
ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION IN EUROPE; TRADITIONS, GENERATIONS, CULTURE AND POLICY
 ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION IN EUROPE; TRADITIONS, GENERATIONS, CULTURE AND POLICY JACEK MOSKALEWICZ INSTITUTE OF PSCHIATRY AND NEUROLOGY WARSAW, POLAND THIRD EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON ALCOHOL AND LAW ENFORCEMENT,
ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION IN EUROPE; TRADITIONS, GENERATIONS, CULTURE AND POLICY JACEK MOSKALEWICZ INSTITUTE OF PSCHIATRY AND NEUROLOGY WARSAW, POLAND THIRD EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON ALCOHOL AND LAW ENFORCEMENT,
The Current Status of Cardiac Electrophysiology in ESC Member Countries J. Brugada, P. Vardas, C. Wolpert
 Albania. Algeria. Armenia. Austria. Belarus. Belgium. Bosnia & Herzegovina. Bulgaria. Croatia. Cyprus. Czech Republic Denmark. Egypt. Estonia. Finland. Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia. France. Georgia.
Albania. Algeria. Armenia. Austria. Belarus. Belgium. Bosnia & Herzegovina. Bulgaria. Croatia. Cyprus. Czech Republic Denmark. Egypt. Estonia. Finland. Former Yugoslav Republic of Macedonia. France. Georgia.
LEBANON. WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018
 LEBANON WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 LEBANON NUMBERS 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 1,480 1,480 Total PTs in country 800000 700000 600000 500000
LEBANON WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 LEBANON NUMBERS 1600 1400 1200 1000 800 600 400 200 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 1,480 1,480 Total PTs in country 800000 700000 600000 500000
Overview of the Global NCD Action Plan
 Regional Consultation to Develop the Strategic Action Plan and Targets for Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases in the SEAR 25-27 February 2013 Overview of the Global NCD Action Plan 2013-2020
Regional Consultation to Develop the Strategic Action Plan and Targets for Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases in the SEAR 25-27 February 2013 Overview of the Global NCD Action Plan 2013-2020
Country profile. Brazil
 Country profile Brazil WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 3 vember 2005 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Brazil WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 June 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 3 vember 2005 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Lebanon
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013 Country profile Lebanon WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 4 March 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013 Country profile Lebanon WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 4 March 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
DENMARK. WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018
 DENMARK WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 DENMARK NUMBERS 14000 12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 11,720 12,975 Total PTs in country 800000 700000 600000
DENMARK WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 DENMARK NUMBERS 14000 12000 10000 8000 6000 4000 2000 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 11,720 12,975 Total PTs in country 800000 700000 600000
Country profile. Nepal
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013 Country profile Nepal WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 3 December 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2013 Country profile Nepal WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 3 December 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
Global NCD Prevention WHO Strategies and Implementation Plan. Dr Ruitai Shao Chronic Disease and Health Promotion
 Global NCD Prevention WHO Strategies and Implementation Plan Dr Ruitai Shao Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Outline Main NCDs and Major risk factors Global Action Plan for implementing the strategy
Global NCD Prevention WHO Strategies and Implementation Plan Dr Ruitai Shao Chronic Disease and Health Promotion Outline Main NCDs and Major risk factors Global Action Plan for implementing the strategy
Report on the alcohol laws in EU countries. Prepared by: Daša Kokole, Rok Primožič and Lukas Galkus, APYN
 Report on the alcohol laws in EU countries Prepared by: Daša Kokole, Rok Primožič and Lukas Galkus, APYN The European Commission support for the production of this publication does not constitute endorsement
Report on the alcohol laws in EU countries Prepared by: Daša Kokole, Rok Primožič and Lukas Galkus, APYN The European Commission support for the production of this publication does not constitute endorsement
EUDY JUNIOR CAMP 2018 FIRST ANNOUNCEMENT
 EUDY JUNIOR CP 2018 FIRST ANNOUNCEMENT 21. 29. July 2018 Tesáre, SLOVAKIA IDENTITY OF THE DEAF EUROPEAN UNION OF THE DEAF YOUTH (EUDY) The European Union of the Deaf Youth is a European non-profit organisation
EUDY JUNIOR CP 2018 FIRST ANNOUNCEMENT 21. 29. July 2018 Tesáre, SLOVAKIA IDENTITY OF THE DEAF EUROPEAN UNION OF THE DEAF YOUTH (EUDY) The European Union of the Deaf Youth is a European non-profit organisation
Country profile. Colombia. WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status. Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 10 April 2008
 Country profile Colombia WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature t signed Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 10 April 2008 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Colombia WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature t signed Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 10 April 2008 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Canada
 Country profile Canada WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 15 July 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 26 vember 2004 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Canada WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 15 July 2003 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 26 vember 2004 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Gambia. Note: Where no data were available, " " shows in the table. Where data were not required, " " shows in the table.
 WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2011 Country profile Gambia te: Where no data were available, " " shows in the table. Where data were not required, " " shows in the table. WHO Framework Convention
WHO Report on the Global Tobacco Epidemic, 2011 Country profile Gambia te: Where no data were available, " " shows in the table. Where data were not required, " " shows in the table. WHO Framework Convention
South Africa. Report card on the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control. 18 July Contents. Introduction
 Report card on the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control South Africa Introduction Tobacco use is the single most preventable cause of death in the world today, and is estimated to kill more than
Report card on the WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control South Africa Introduction Tobacco use is the single most preventable cause of death in the world today, and is estimated to kill more than
Inequality in injury risks
 Inequality in injury risks Rationale Injuries a are a neglected but preventable epidemic and in the 53 countries in the WHO European Region account for nearly 800 000 lives lost annually (equivalent to
Inequality in injury risks Rationale Injuries a are a neglected but preventable epidemic and in the 53 countries in the WHO European Region account for nearly 800 000 lives lost annually (equivalent to
GERMANY. WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018
 GERMANY WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 GERMANY NUMBERS 160000 140000 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 21,502 136,000 Total PTs in country 800000
GERMANY WCPT COUNTRY PROFILE December 2018 GERMANY NUMBERS 160000 140000 120000 100000 80000 60000 40000 20000 0 Physical therapists in the country Members in MO 21,502 136,000 Total PTs in country 800000
Tobacco control achievements and priority areas in the WHO Europe Region: A review
 Tobacco control achievements and priority areas in the WHO Europe Region: A review Andrea Glahn 1, Christina N. Kyriakos 1, Cornel Radu Loghin 1, Dominick Nguyen 1, Polina Starchenko 1, Carlos Jimenez-
Tobacco control achievements and priority areas in the WHO Europe Region: A review Andrea Glahn 1, Christina N. Kyriakos 1, Cornel Radu Loghin 1, Dominick Nguyen 1, Polina Starchenko 1, Carlos Jimenez-
Country profile. Guinea
 Country profile Guinea WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 1 April 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 7 vember 2007 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Guinea WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 1 April 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) 7 vember 2007 Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Morocco
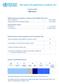 Country profile Morocco WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 April 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) t ratified Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Morocco WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature 16 April 2004 Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) t ratified Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile. Indonesia. WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status. Date of ratification (or legal equivalent)
 Country profile Indonesia WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) t signed t ratified Socioeconomic context Population
Country profile Indonesia WHO Framework Convention on Tobacco Control (WHO FCTC) status Date of signature Date of ratification (or legal equivalent) t signed t ratified Socioeconomic context Population
