Toxins in Brain! Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging of Toxic Leukoencephalopathy A Pictorial Essay
|
|
|
- Rafe McCoy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Signature: Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: DOI: /PJR REVIEW ARTICLE Received: Accepted: Published: Authors Contribution: A Study Design B Data Collection C Statistical Analysis D Data Interpretation E Manuscript Preparation F Literature Search G Funds Collection Toxins in Brain! Magnetic Resonance (MR) Imaging of Toxic Leukoencephalopathy A Pictorial Essay Yogesh Kumar 1 ABCDEFG, Douglas Drumsta 2 AFG, Manisha Mangla 3 AFG, Nishant Gupta 4 ABCDEF, Kusum Hooda 1 ABF, Jeevak Almast 2 ABCDEFG, Rajiv Mangla 5 ABCDEFG 1 Department of Radiology, Yale New Haven Health System at Bridgeport Hospital, Bridgeport, CT, U.S.A. 2 Department of Imaging Sciences, University of Rochester Medical Centre, Rochester NY, U.S.A. 3 State University of New York (SUNY) Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY, U.S.A. 4 Department of Radiology, St. Vincent s Medical Center, Bridgeport, CT, U.S.A. 5 Department of Radiology, State University of New York (SUNY) Upstate Medical University, Syracuse, NY, U.S.A. Author s address: Nishant Gupta, Department of Radiology, St Vincent s Medical center, 2800 Main Street, Bridgeport, CT 06606, U.S.A., drngupta20@gmail.com Summary Toxic leukoencephalopathy results from damage to the white matter caused by various toxins. It manifests itself as white matter signal abnormalities with or without the presence of restricted diffusion. These changes are often reversible if the insulting agent is removed early, with the exception of posthypoxic leukoencephalopathy that can manifest itself 1 2 weeks after the initial insult. However, many other potential causes of white matter signal abnormalities can mimic the changes of toxic leukoencephalopathy. Thus, familiarity with the causes, clinical presentation and particularly imaging findings of toxic leukoencephalopathy is critical for early treatment and improved prognosis. The purpose of this pictorial essay is to familiarize the reader with the various causes of toxic leukoencephalopathy along with its differential diagnoses and mimics. MeSH Keywords: Brain Diseases, Metabolic Magnetic Resonance Imaging Toxic Actions PDF file: Background Toxic leukoencephalopathies can have similar imaging appearances even when caused by different agents. Moreover, various mimics of toxic leukoencephalopathy can have similar imaging findings, delaying the correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Thus, differentiating these entities from each other is very important. In this pictorial essay, the known causes of toxic leukoencephalopathy will be listed (Table 1) and discussed along with numerous case examples. This article discusses the imaging findings of the various differential diagnoses and mimics of toxic leukoencephalopathy with corresponding case examples (Table 2). Toxic Leukoencephalopathies Chemotherapeutic agents A variety of chemotherapeutic agents are known to cause toxic leukoencephalopathy including melphalan, purine analogs, cisplatin and methotrexate - probably the best known offender (Table 1). Patients often present with acute neurotoxic effects such as transient ischemic attacks, seizures, encephalopathy and ataxia [1]. Spinal cord involvement presents as myelopathy. MRI findings include symmetric, focal to diffuse, increases in T2-FLAIR signal intensity (Figure 1), with transient diffusion restriction involving the periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale [1]. Radiation induced leukoencephalopathy Radiation induced injury to the brain can be classified into three categories - acute, early delayed and late delayed, which are described as different phases of an evolution. Patients are often asymptomatic, however, impaired cognitive function is affected most commonly in clinically apparent patients. The acute injury occurs during therapy and has little prognostic significance. In the early delayed and late delayed phases, diffuse leukoencephalopathy can develop, which is manifested by an increased T2-FLAIR signal 311
2 Review Article Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Table 1. Various causes of toxic leukoencephalopathy. Chemotherapeutic agents Methotrexate Melphalan 1,3-bis(2-chloroethyl)-1-nitrosourea (BCNU) Fludarabine Cytarabine 5-fluorouracil Cisplatin Cranial irradiation Metabolic disorders Uremia Phenylketonuria (PKU) Occupational exposures Organic solvents Hypoxia Environmental toxins Carbon monoxide Arsenic CCl 4 Drugs of abuse Heroin Methamphetamine Ethanol Cocaine Toluene Immunosuppresive agents Amphotericin B Hexachlorophene intensity in the periventricular white matter (Figure 2). Early in the process, there is relative sparing of the subcortical U-fibers. Diffusion restriction varies and is dependent upon the severity of the injury. As time progresses, associated cerebral atrophy becomes more evident. A more focal form of radiation-induced injury can result in necrosis and enhancement of the cortex and white matter [2]. Table 2. Toxic leukoencephalopathy mimics. Demyelinating disease Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) Genetic leukodystrophies AIDS dementia complex Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis (SSPE) Cytomegalovirus (CMV) Rubella Varicella zoster (VZV) Vascular disease Gliomatosis cerebri Postictal Metabolic disorders Uremia is commonly associated with the posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES); however, there are reports of uremia resulting in cytotoxic edema [3]. The MRI findings typically include confluent, increased T2-FLAIR signal intensity (Figure 3A) and diffusion restriction involving the supratentorial white matter (Figure 3B, 3C). Phenylketonuria (PKU) is an inborn error of metabolism resulting in an impaired metabolism of phenylalanine. It manifests on MRI as areas of increased T2 signal intensity (Figure 4A) with a corresponding diffusion restriction (Figure 4B, 4C) in the periventricular parietal and occipital white matter. The signal abnormalities can extend to the frontal subcortical white matter in more severe cases [4]. Delayed posthypoxic leukoencephalopathy Delayed posthypoxic leukoencephalopathy typically occurs 1 2 weeks after the initial insult, whether resulting from cardiorespiratory compromise or other toxic causes [5]. MRI findings are similar to other toxic leukoencephalopathies and include high T2-FLAIR signal intensity in the periventricular Figure 1. A 15-year-old girl treated for acute lymphoblastic leukemia who presented with headache after methotrexate treatment initiation. Axial T2-FLAIR image (A) demonstrates slightly increased signal intensity with restricted diffusion involving periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale (white arrows) as seen on DWI (B) and ADC (C) images. 312
3 Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Kumar Y. et al. MRI of toxic leukoencephalopathy T2-FLAIR signal intensity (Figure 6A) along with corresponding diffusion restriction in the acute phase. The caudate, putamen, thalami, cerebellum and brainstem may also be affected, but much less commonly than the globus pallidus. Carbon monoxide poisoning can also result in diffuse hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy or focal cortical necrosis with diffuse or focal cortical diffusion restriction, respectively [6]. Cerebral white matter demyelination occurs after the acute stage and is manifested by increased T2-FLAIR signal intensity with diffusion restriction in the periventricular white matter, centrum semiovale, and in severe cases in the subcortical white matter, corpus callosum and internal capsule (Figure 6B 6D). Drugs of abuse Figure 2. A 60-year-old man with whole-brain radiation therapy for brain metastasis from lung cancer. Axial T2-FLAIR image demonstrates increased signal in the periventricular white matter (white arrow) with relative sparing of the subcortical U-fibers. white matter and centrum semiovale (Figure 5A) with associated diffusion restriction (Figure 5B, 5C). Carbon monoxide The most common site affected by CO poisoning is the globus pallidus, which presents on MRI as increased T2 and Drugs of abuse, including heroin, toluene, cocaine, methamphetamine among others, are a well-known cause of toxic leukoencephalopathy. Chasing the Dragon refers to a method of heroin administration where the heroin is heated to a liquid form and the vapors are inhaled. MRI findings are characteristic and involve symmetrically increased T2 and T2-FLAIR signal intensity in the cerebellar white matter (Figure 7A, 7B) and the posterior limb of the internal capsule. There is also symmetrically increased T2 and T2-FLAIR signal intensity involving the supratentorial white matter as seen with other leukoencephalopathies [7]. Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Mimics Demyelinating disease Demyelinating diseases include a wide array of diseases. Multiple sclerosis is the most common of the demyelinating diseases that affect the supra- and infratentorial white matter. A careful inspection of these lesions will help differentiate it from toxic leukoencephalopathies. Classically, the high-signal T2-FLAIR lesions of MS have a predilection for the periventricular white matter. The lesions follow the Figure 3. A 48-year-old woman with chronic renal failure and uremia presented with altered mental status. Coronal T2-FLAIR (A) MR image shows confluent increased T2-FLAIR signal (white arrow) with a corresponding diffusion restriction involving bilateral supratentorial white matter on DWI (B) and ADC map (C). 313
4 Review Article Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Figure 4. A 24-year-old man with phenylketonuria. Axial T2-FLAIR (A), DWI (B) images and ADC map (C) showing increased T2-FLAIR signal with a corresponding diffusion restriction in the periventricular parietal, and occipital white matter (white arrows). Figure 5. A 40-year-old woman imaged 2 weeks following hypoxic-anoxic injury. Axial T2-FLAIR (A), DWI (B) and ADC map (C) show high T2-FLAIR signal in the periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale with associated diffusion restriction (white arrows). D Figure 6. A 35-year-old man with carbon monoxide poisoning. Axial T2-FLAIR image (A) on the day of poisoning shows increased T2-FLAIR signal in the globus pallidus (white arrow) along with a corresponding diffusion restriction (not shown). One month after carbon monoxide exposure, axial T2-FLAIR (B), DWI (C) and ADC map (D) show increased T2-FLAIR signal with diffusion restriction in the periventricular white matter and centrum semiovale (white arrows). 314
5 Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Kumar Y. et al. MRI of toxic leukoencephalopathy A B Figure 7. A 48-year-old woman with a history of heroin abuse. Axial T2-FLAIR images through the cerebellum (A) and temporal lobes (B) show increased signal involving the cerebellar and bilateral temporal white matter (white arrows). Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome (PRES) The MRI features of PRES classically demonstrate symmetric T2-FLAIR hyperintensities involving the cortical and subcortical white matter of the parietal and occipital lobes, and less commonly the frontal lobes, temporal lobes, cerebellum and brainstem (Figure 9). FLAIR signal abnormalities become more confluent as the disease progresses, however, they resolve when the offending agent is removed. Diffusion restriction is uncommon [9]. AIDS dementia complex The imaging findings of the AIDS Dementia Complex include diffuse cerebral atrophy that is out of proportion to the patient s age, and symmetrically increased T2 signal intensity in the periventricular and deep white matter (Figure 10). Diffusion restriction is never found, in contrast to the acute phase of toxic leukoencephalopathies [10]. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) Figure 8. A 52-year-old woman with a long-standing history of multiple sclerosis. Axial T2-FLAIR image shows areas of increased T2-FLAIR signal in the bilateral periventricular white matter (white arrows) oriented perpendicular to the ventricular surfaces. medullary veins and are oriented perpendicular to the ventricular surface (Figure 8). Further inspection may reveal high T2-FLAIR signal lesions affecting the corpus callosum, subcortical white matter, brainstem, cerebellum, optic nerves and spinal cord. In the acute phase, MS plaques exhibit contrast enhancement [8]. PML demonstrates multifocal areas of increased T2 signal intensity involving the periventricular and subcortical white matter along with the subcortical U-fibers (Figure 11). These areas of abnormal T2 signal are typically asymmetric which can distinguish them from toxic leukoencephalopathies. Usually, there is no mass effect or enhancement [10,11]. Genetic leukodystrophies It is beyond the scope of this pictorial essay to describe in detail the genetic leukodystrophies; however, it is imperative that the interpreting radiologist is aware of these entities in the differential diagnosis of toxic leukoencephalopathy. Many of the leukodystrophies begin early in life making the patient s history vital, although late-onset 315
6 Review Article Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Figure 9. A 31-year-old woman with SLE and hypertension presented with headache and change in vision progressing to a generalized seizure. Axial T2-FLAIR images (A C) show symmetric T2-FLAIR hyperintensities involving the cortical and subcortical white matter of the parietal and occipital lobes, and to a lesser extent also the frontal lobes, temporal lobes, cerebellum and brainstem (white arrows), consistent with PRES. Figure 10. A 40-year-old man with a history of AIDS. Axial T2-FLAIR image shows diffuse cerebral atrophy that is out of proportion to the patient s age, and symmetrically increased T2 signal in the periventricular and deep white matter (white arrows) sparing the subcortical U-fibers. leukodystrophies are not uncommon. The X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy, one of the more common varieties, typically manifests itself as increased T2 signal intensity in the peritrigonal regions and extends across the splenium of the corpus callosum [12]. As the disease progresses, the abnormal white matter signal becomes more confluent and spreads outward and cephalad until most of the cerebral white matter is affected (Figure 12). Figure 11. A 45-year-old man with Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML). Axial T2-FLAIR image shows a large area of increased T2 signal involving the periventricular and subcortical white matter including the subcortical U-fibers (white arrows). Vascular disease Chronic small-vessel disease can lead to changes on MRI that may mimic a toxic leukoencephalopathy. The findings usually include patchy areas of increased T2-FLAIR signal intensity in the periventricular, deep and subcortical white matter, without a corresponding diffusion restriction, unless seen in the acute phase. In severe cases, the areas of abnormal T2-FLAIR signal can often become more confluent, possibly resulting in a diagnostic dilemma. 316
7 Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Kumar Y. et al. MRI of toxic leukoencephalopathy Also included in the vascular mimics of toxic leukoencephalopathy is cerebral amyloid angiopathy (CAA)-related inflammation. MRI findings of CAA-related inflammation reveal confluent zones of increased T2 signal with localized mass effect that is usually confined to the subcortical white matter; however, cortical involvement has been described. The key to making this diagnosis is the presence of multiple punctate hypointense foci on GRE and SWIweighted sequences (Figure 13) that are characteristic of cerebral amyloid angiopathy [13]. Cerebral autosomal dominant arteriopathy with subcortical infarcts and leukoencephalopathy (CADASIL) is also a vascular etiology that can mimic toxic leukoencephalopathy. MRI findings include focal and confluent areas of high T2-FLAIR signal affecting the subcortical white matter and centrum semiovale with a particular predilection for the frontal, parietal and anterior temporal regions along with the external capsule (Figure 14). Corresponding Figure 12. A 14-year-old boy with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Axial T2-FLAIR image shows increased T2 signal in the peritrigonal regions extending across the splenium of the corpus callosum (white arrow) as well as the involvement of the frontal lobe white matter bilaterally (black asterisks). A B C D E F Figure 13. A 70-year-old man with amyloid angiopathy. Axial T2W (A), T2-FLAIR (B), contrast-enhanced T1W (C), DWI mages (D) and ADC map (E) show confluent zones of increased T2 signal (white arrow) without restricted diffusion, with the presence of multiple punctate hypointense foci on SWI (F), characteristic of cerebral amyloid angiopathy (white arrow). 317
8 Review Article Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: A B Figure 14. A 40-year-old woman with CADASIL. Axial T2-FLAIR images show focal and confluent areas of high T2-FLAIR signal affecting the subcortical white matter and centrum semiovale with particular predilection for the frontal (A), parietal and anterior temporal regions (B). D Figure 15. A 50-year-old man with Gliomatosis cerebri. Axial T2W (A), post-gadolinium T1W (B), DWI (C) and ADC map (D) and mages show increased T2-FLAIR signal affecting the cerebral white matter with mass effect, mild contrast enhancement and mildly restricted diffusion (white arrows). diffusion restriction is present in the acute phase of the infarcts [14]. Gliomatosis cerebri Gliomatosis cerebri is a diffuse infiltrating neoplasm that by definition involves at least three lobes. MRI findings reveal increased T2-FLAIR signal affecting the cerebral white matter and less commonly the cortex (Figure 15A). There is typically no to minimal enhancement (Figure 15B), and diffusion restriction is uncommon, although the case that we present does have corresponding diffusion restriction (Figure 15C, 15D). One of the key features that distinguish gliomatosis cerebri from toxic leukoencephalopathy is the associated mass effect [15]. Postictal In the immediate postictal period, imaging findings usually include abnormal cortical and subcortical signal abnormalities associated with restricted diffusion. However, in the late postictal phase after one week, increased T2 signal intensity (Figure 16A) with a corresponding diffusion restriction (Figure 16B, 16C) in the centrum semiovale bilaterally, similar to the findings in toxic leukoencephalopathy, can also be seen [16]. Summary/Conclusions In addition to the known toxic causes of leukoencephalopathy, there are several diseases that can present with a 318
9 Pol J Radiol, 2017; 82: Kumar Y. et al. MRI of toxic leukoencephalopathy Figure 16. A 12-year-old boy 2 weeks following status epilepticus. Axial T2W (A), DWI (B) and ADC map (C) images show increased signal in the centrum semiovale bilaterally with restricted diffusion (white arrows). similar constellation of signs and symptoms. As a result, the imaging findings of toxic leukoencephalopathy are often nonspecific and there are many other disease entities that can mimic the findings, resulting in a diagnostic dilemma for the interpreting radiologist. It is imperative that a detailed clinical history is kept in mind and that the interpreting radiologist be aware of the differential diagnoses as there are many potential mimics. Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest. References: 1. Vázquez E, Delgado I, Sánchez-Montañez A et al: Side effects of oncologic therapies in the pediatric central nervous system: Update on neuroimaging findings. Radiographics, 2011; 31: Valk PE, Dillon WPL Radiation injury of the brain. Am J Neuroradiol, 1991; 12(1): Kang E, Jeon SJ, Choi S: Uremic encephalopathy with atypical magnetic resonance features on diffusion-weighted images. Korean J Radiol, 2012; 13(6): Moritani T, Smoker WRK, Sato Y et al: Diffusion-weighted imaging of acute excitotoxic brain injury. Am J Neuroradiol, 2005; 26(2): Molloy S, Soh C, Williams TL: Reversible delayed posthypoxic leukoencephalopathy. Am J Neuroradiol, 2005; 27(8): Lo CP, Chen SY, Lee KW et al: Brain injury after acute carbon monoxide poisoning: Early and late complications. Am J Roentgenol, 2007; 189(4): W Tamrazi B, Almast J: Your brain on drugs: Imaging of drug-related changes in the central nervous system. Radiographics, 2012; 32(3): Ge Y: Multiple sclerosis: The role of MR imaging. Am J Neuroradiol, 2006; 27(6): Bartynski WS: Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome, part 1: Fundamental imaging and clinical features. Am J Neuroradiol, 2008; 29(6): Smith AB, Smirniotopoulos JG, Rushing EJ: Central nervous system infections associated with human immunodeficiency virus infection: Radiologic-pathologic correlation. Radiographics, 2008; 28(7): Gourineni VC, Juvet T, Kumar Y et al: Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a 62-year-old immunocompetent woman. Case Rep Neurol Med, 2014; 2014: Cheon J, Kim I, Hwang YS et al: Leukodystrophy in children: A pictorial review of MR imaging features. Radiographics, 2002; 22(3): Auer DP, Pütz B, Gössl C et al: Differential lesion patterns in CADASIL and sporadic subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy: MR imaging study with statistical parametric group comparison. Radiology, 2001; 218(2): Savoiardo M, Erbetta A, Storchi G, Girotti F: Case 159: Cerebral amyloid angiopathy related inflammation. Radiology, 2010; 256(1): Shin YM, Chang KH, Han MH et al: Gliomatosis cerebri: Comparison of MR and CT features. Am J Roentgenol, 1993; 161(4): Mendes A, Sampaio L: Brain magnetic resonance in status epilepticus: A focused review. Seizure, 2016; 38:
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics. Disclosures. Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor 4/14/2017
 Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
Interactive Cases: Demyelinating Diseases and Mimics Disclosures None Brad Wright, MD 27 March 2017 Case 1 25 yo F with nystagmus; look for tumor What do you suspect? A. Demyelinating disease B. Malignancy
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI
 Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
Helpful Information for evaluation of new neurological symptoms in patients receiving TYSABRI This information is provided as an educational resource for healthcare providers and should be considered current
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Clinical. Toxic Encephalopathies. Toxic encephalopathy. Imaging. Exogenous Toxins
 Clinical Toxic Encephalopathies Sumeet Kumar National Neuroscience Institute, Duke-NUS Medical School Singapore Decreased consciousness, confusion Excitability, convulsions Motor/sensory disturbances Extrapyramidal
Clinical Toxic Encephalopathies Sumeet Kumar National Neuroscience Institute, Duke-NUS Medical School Singapore Decreased consciousness, confusion Excitability, convulsions Motor/sensory disturbances Extrapyramidal
Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain
 Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain John R. Hesselink, M.D. T1-Weighted Images Normal White Matter Contents Axons with envelope of myelin Neuroglia
Department of Radiology University of California San Diego Demyelinating Diseases of the Brain John R. Hesselink, M.D. T1-Weighted Images Normal White Matter Contents Axons with envelope of myelin Neuroglia
Patient with vertigo, dizziness and depression
 Clinical Case - Test Yourself Neuro/Head and Neck Radiology Patient with vertigo, dizziness and depression Michael Mantatzis, Paraskevi Argyropoulou, Panos Prassopoulos Radiology Department, Democritus
Clinical Case - Test Yourself Neuro/Head and Neck Radiology Patient with vertigo, dizziness and depression Michael Mantatzis, Paraskevi Argyropoulou, Panos Prassopoulos Radiology Department, Democritus
Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) allows for tissue
 MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING / IMAGERIE PAR RÉSONANCE MAGNÉTIQUE Nonischemic causes of hyperintense signals on diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance images: a pictorial essay Jeffrey M. Hinman, MD; James
MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS
 Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies
 Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Neuroradiological, clinical and genetic characterization of new forms of hereditary leukoencephalopathies Principal Investigator: Dr. Donatella Tampieri, MD, FRCPC, Department of Neuroradiology, Montreal
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum
 Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Cerebral malaria: MR imaging spectrum Poster No.: C-2705 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: P. S. Naphade, M. D. Agrawal, S. S. Sankhe, K. M. Siva, B. K. Jain; Mumbai/IN
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University
 Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
Laura Tormoehlen, M.D. Neurology and EM-Toxicology Indiana University Disclosures! No conflicts of interest to disclose Neuroimaging 101! Plain films! Computed tomography " Angiography " Perfusion! Magnetic
MRI OF THE THALAMUS. Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI
 1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome
 A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome Poster No.: C-2780 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: E. Tavernaraki,
A pictorial review of neurological complications of systemic lupus erythematosus and antiphospholipid syndrome Poster No.: C-2780 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro Authors: E. Tavernaraki,
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
Case of the Month September 2015: Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Chasing the Dragon. Andrew Plum, Chasing the Dragon 2012
 Case of the Month September 2015: Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Chasing the Dragon Andrew Plum, Chasing the Dragon 2012 Kate Hames PGY2 September 2015 Case Report 28 y/o M with a known history of drug abuse
Case of the Month September 2015: Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Chasing the Dragon Andrew Plum, Chasing the Dragon 2012 Kate Hames PGY2 September 2015 Case Report 28 y/o M with a known history of drug abuse
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases
 White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
White matter diseases affecting the corpus callosum; demyelinating and metabolic diseases Poster No.: C-0199 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. H. Yoo; Seoul/KR Keywords: Neuroradiology
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution
 CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
CT and MR findings of systemic lupus erythematosus involving the brain: Differential diagnosis based on lesion distribution Poster No.: C-2723 Congress: ECR 2010 Type: Educational Exhibit Topic: Neuro
Atypical Unilateral Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome Mimicking a Middle Cerebral Artery Infarction
 Case Report Neuroimaging and Head & Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.5.1104 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(5):1104-1108 Atypical Unilateral Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy
Case Report Neuroimaging and Head & Neck http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2015.16.5.1104 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2015;16(5):1104-1108 Atypical Unilateral Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy
Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1592 1597, September 2003 Delayed Encephalopathy of Acute Carbon Monoxide Intoxication: Diffusivity of Cerebral White Matter Lesions Ji-hoon Kim, Kee-Hyun Chang, In Chan Song,
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings
 Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
 Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Original Research Article Role of MRI in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis Shashvat Modiya 1*, Jayesh Shah 2, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 1 st year resident, 2 Associate Professor, 3 HOD and Professor Department
Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance imaging: a case report
 Chuang et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-019-0310-z CASE REPORT Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance
Chuang et al. BMC Medical Imaging (2019) 19:11 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12880-019-0310-z CASE REPORT Hypoglycemic encephalopathy mimicking acute ischemic stroke in clinical presentation and magnetic resonance
Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis in a patient with rectal adenocarcinoma: A rare entity
 Hooda et al. 6 CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis in a patient with rectal adenocarcinoma: A rare entity Kusum Hooda, Nishant Gupta, Charu Chanana, Pranav Sharma,
Hooda et al. 6 CASE REPORT PEER REVIEWED OPEN ACCESS Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis in a patient with rectal adenocarcinoma: A rare entity Kusum Hooda, Nishant Gupta, Charu Chanana, Pranav Sharma,
MRI diagnosis of infantile Alexander disease in a 14 month old African boy
 MRI diagnosis of infantile Alexander disease in a 14 month old African boy Nondumiso Dlamini 1*, Vicci du Plessis 2 1. Department of Radiology, Greys' Hospital, Pietermaritzburg Metropolitan Complex, South
MRI diagnosis of infantile Alexander disease in a 14 month old African boy Nondumiso Dlamini 1*, Vicci du Plessis 2 1. Department of Radiology, Greys' Hospital, Pietermaritzburg Metropolitan Complex, South
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari
 Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY
 HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome Cause Renal disease Pheochromocytoma Disseminated vasculitis Eclampsia Acute toxemia Medications & illicit drugs (cocaine)
HYPERTENSIVE ENCEPHALOPATHY Reversible posterior leukoencephalopathy syndrome Cause Renal disease Pheochromocytoma Disseminated vasculitis Eclampsia Acute toxemia Medications & illicit drugs (cocaine)
COPYRIGHT 2012 THE TRANSVERSE MYELITIS ASSOCIATION. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
 The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
The Transverse Myelitis Association...advocating for those with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis, neuromyelitis optica, optic neuritis and transverse myelitis ACUTE DISSEMINATED ENCEPHALOMYELITIS (ADEM)
Brain Injury After Acute Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Early and Late Complications
 T and MRI of arbon Monoxide Poisoning Neuroradiology Pictorial Essay ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.199.82 on 02/28/18 from IP address 46.3.199.82. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights
T and MRI of arbon Monoxide Poisoning Neuroradiology Pictorial Essay ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 46.3.199.82 on 02/28/18 from IP address 46.3.199.82. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights
Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy
 Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy Schepers S, Barthels C Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2011, Nov. 3 Patient: 67 year(s), male Authors' Institution Department of Radiology, Jessa ziekenhuis campus
Case 9511 Hypertensive microangiopathy Schepers S, Barthels C Section: Neuroradiology Published: 2011, Nov. 3 Patient: 67 year(s), male Authors' Institution Department of Radiology, Jessa ziekenhuis campus
Imaging PRES syndrome: typical, atypical and follow up findings.
 Imaging PRES syndrome: typical, atypical and follow up findings. Poster No.: C-2361 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Borrego Jimenez, A. Villalba Gutiérrez, M. Á. López Pino, P.
Imaging PRES syndrome: typical, atypical and follow up findings. Poster No.: C-2361 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: P. Borrego Jimenez, A. Villalba Gutiérrez, M. Á. López Pino, P.
MR neuroimaging of HIV infected patients : A pictorial review
 MR neuroimaging of HIV infected patients : A pictorial review Poster No.: R-0198 Congress: 2014 CSM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: P. F. Kwan, R. Thomas, A. Dixon; SOUTH YARRA/AU Keywords: Neuroradiology
MR neuroimaging of HIV infected patients : A pictorial review Poster No.: R-0198 Congress: 2014 CSM Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: P. F. Kwan, R. Thomas, A. Dixon; SOUTH YARRA/AU Keywords: Neuroradiology
Neuroradiology of AIDS
 Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Neuroradiology of AIDS Frank Minja,, HMS IV Gillian Lieberman MD September 2002 AIDS 90% of HIV patients have CNS involvement 1 10% of AIDS patients present first with neurological symptoms 2 73-80% of
Dean Shibata, M.D. Department of Radiology, University of Washington. White Matter, Metabolic, and Degenerative Disease.
 White Matter, Metabolic, and Degenerative Disease UW Radiology Review 2015 Dean Shibata, M.D Neuroradiology Department of Radiology, University of Washington MS (Multiple Sclerosis) ADEM (Acute Disseminated
White Matter, Metabolic, and Degenerative Disease UW Radiology Review 2015 Dean Shibata, M.D Neuroradiology Department of Radiology, University of Washington MS (Multiple Sclerosis) ADEM (Acute Disseminated
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE
 TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology
 General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review.
 Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review. Poster No.: C-0817 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. I. MICHELIN,
Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder (NMOSD): Brain MRI findings in patients at our institution and literature review. Poster No.: C-0817 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: G. I. MICHELIN,
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Magnetic Resonance Study of White Matter Lesions: A Cross-sectional Study
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/559 Magnetic Resonance Study of White Matter Lesions: A Cross-sectional Study Mallikarjun M Devareddy 1, Shilpa Devakar
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2016/559 Magnetic Resonance Study of White Matter Lesions: A Cross-sectional Study Mallikarjun M Devareddy 1, Shilpa Devakar
Marchiafava Bignami Disease (MBD) and Diffusion Tensor Image (DTI) Tractography. Priscilla Chukwueke, MD, MPH
 Marchiafava Bignami Disease (MBD) and Diffusion Tensor Image (DTI) Tractography Priscilla Chukwueke, MD, MPH INTRODUCTION Definition: A rare CNS disease characterized by demyelination of the Corpus Callosum.
Marchiafava Bignami Disease (MBD) and Diffusion Tensor Image (DTI) Tractography Priscilla Chukwueke, MD, MPH INTRODUCTION Definition: A rare CNS disease characterized by demyelination of the Corpus Callosum.
Common and uncommon differential diagnosis of cerebral microhemorrhages
 Common and uncommon differential diagnosis of cerebral microhemorrhages Poster No.: C-0261 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. C. Rodrigues 1, S. B. Bergamaschi 1, C. F. R. B. Milito
Common and uncommon differential diagnosis of cerebral microhemorrhages Poster No.: C-0261 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: T. C. Rodrigues 1, S. B. Bergamaschi 1, C. F. R. B. Milito
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists.
 Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
1 Maiser. 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy. Samuel Maiser, MD. Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota
 1 Maiser 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Samuel Maiser, MD Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota Case This is a 57-year-old right-handed male with a history of
1 Maiser 5-Fluorouracil (5-FU) Induced Acute Toxic Leukoencephalopathy Samuel Maiser, MD Department of Neurology, University of Minnesota Case This is a 57-year-old right-handed male with a history of
Discovering the hippocampus with cranial-ct.
 Discovering the hippocampus with cranial-ct. Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Pozo Piñon, A. B. Barba Arce, E. herrera romero, V. 1 2 3 1 3 3 Fernández Lobo,
Discovering the hippocampus with cranial-ct. Poster No.: C-0378 Congress: ECR 2018 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: F. Pozo Piñon, A. B. Barba Arce, E. herrera romero, V. 1 2 3 1 3 3 Fernández Lobo,
NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE
 THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL SEPTEMBER 2013 NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE Claudia da Costa Leite, MD, PhD Thomas Bouldin, MD CASE 1 6 y-o female with headaches and vomiting
THE UNIVERSITY OF NORTH CAROLINA at CHAPEL HILL SEPTEMBER 2013 NEURORADIOLOGY-NEUROPATHOLOGY CONFERENCE Claudia da Costa Leite, MD, PhD Thomas Bouldin, MD CASE 1 6 y-o female with headaches and vomiting
Marchiafava-Bignami Disease
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 36, No. 4, December 2014 Marchiafava-Bignami Disease Fahd Al-Khamis, MBBS, UODFN* Fozaih Al-Shamrani, MBBS, UODFN** Ibrahim Al- Ghanimi, MBBS, UODFN*** Sarah Abdulhafiz,
HEMORRHAGE IN THE NORMOTENSIVE ELDERLY: THE FACES OF AMYLOID ANGIOPATHY
 HEMORRHAGE IN THE NORMOTENSIVE ELDERLY: THE FACES OF AMYLOID ANGIOPATHY Poster No.: C-2446 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit I. Saralegui; Galdakao (Vizcaya)/ES Neuroradiology
HEMORRHAGE IN THE NORMOTENSIVE ELDERLY: THE FACES OF AMYLOID ANGIOPATHY Poster No.: C-2446 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit I. Saralegui; Galdakao (Vizcaya)/ES Neuroradiology
Masses of the Corpus Callosum
 Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Masses of the Corpus Callosum Kesav Raghavan, HMS Year III Dr. Agenda Corpus Callosum Development and Anatomy Our Patient: Clinical Presentation Differential Diagnosis of Masses in the Corpus Callosum
Stroke mimics. Case 1. Acute cases. History. 43 year old healthy male Shortly after awakening developed:
 Stroke mimics Acute cases Gothenburg 21. may 2007 History Case 1 43 year old healthy male Shortly after awakening developed: Left-sided lower facial weakness Left-sided arm paralysis and weakness in leg
Stroke mimics Acute cases Gothenburg 21. may 2007 History Case 1 43 year old healthy male Shortly after awakening developed: Left-sided lower facial weakness Left-sided arm paralysis and weakness in leg
POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome POSTERIOR REVERSIBLE ENCEPHALOPATHY SYNDROME: MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING AND DIFFUSION-WEIGHTED IMAGING IN 12 CASES Mei-Chun Chou, Ping-Hong Lai, Lee-Ren Yeh,
Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results of Cerebral Perfusion MR Imaging
 pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
pissn 2384-1095 eissn 2384-1109 imri 2018;22:56-60 https://doi.org/10.13104/imri.2018.22.1.56 Complete Recovery of Perfusion Abnormalities in a Cardiac Arrest Patient Treated with Hypothermia: Results
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Abstract
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/19 Patterns of Restricted Diffusion within Corpus Callosum in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy and its Significance
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/19 Patterns of Restricted Diffusion within Corpus Callosum in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy and its Significance
Outline. Neuroradiology. Diffusion Imaging in. Clinical Applications of. Basics of Diffusion Imaging. Basics of Diffusion Imaging
 Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
Clinical Applications of Diffusion Imaging in Neuroradiology No disclosures Stephen F. Kralik Assistant Professor of Radiology Indiana University School of Medicine Department of Radiology and Imaging
An Approach. to Brain. Infection. 37F found down. Disclosures. Approach to CNS Infection. Objectives. Parenchymal. None.
 An Approach Disclosures to Brain None. Infection Jason Shewchuk, MD Clinical Associate Professor Head of Neuroradiology UBC European Course in Neuroradiology 2018 Objectives Following this session the
An Approach Disclosures to Brain None. Infection Jason Shewchuk, MD Clinical Associate Professor Head of Neuroradiology UBC European Course in Neuroradiology 2018 Objectives Following this session the
Index. aneurysm, 92 carotid occlusion, 94 ICA stenosis, 95 intracranial, 92 MCA, 94
 A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
A ADC. See Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) Aneurysm cerebral artery aneurysm, 93 CT scan, 93 gadolinium, 93 Angiography, 13 Anoxic brain injury, 25 Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC), 7 Arachnoid
Disclosure. + Outline. Case-based approach to neurological emergencies that might present to the ED
 Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Kathleen R. Fink, MD University of Washington 5 th Nordic Emergency Radiology Course May 21, 2015 Disclosure My spouse receives research salary support from: Bracco BayerHealthcare Guerbet Outline Case-based
Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports
 Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports "This work has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health,
Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports "This work has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health,
Imaging spectrum of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in adults
 Imaging spectrum of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in adults Poster No.: C-0935 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Benítez Rivero, E. Alventosa Fernández, M. Fernandez del Castillo
Imaging spectrum of hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in adults Poster No.: C-0935 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Benítez Rivero, E. Alventosa Fernández, M. Fernandez del Castillo
Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation
 American Society of Neuroimaging Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation January 21, 2017 Los Angeles, California Joshua P. Klein, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN, FASN Chief, Division of Hospital
American Society of Neuroimaging Imaging in a confused patient: Infections and Inflammation January 21, 2017 Los Angeles, California Joshua P. Klein, MD, PhD, FANA, FAAN, FASN Chief, Division of Hospital
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
CNS Imaging. Dr Amir Monir, MD. Lecturer of radiodiagnosis.
 CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CNS Imaging Dr Amir Monir, MD Lecturer of radiodiagnosis www.dramir.net Types of radiological examinations you know Plain X ray X ray with contrast GIT : barium (swallow, meal, follow through, enema) ERCP
CASE OF THE WEEK PROFESSOR YASSER METWALLY
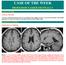 CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE A 40 Years old female patient, known to be suffering from multiple sclerosis, was presented clinically with painful diminution of vision in the right aye and mild weakness
CLINICAL PICTURE CLINICAL PICTURE A 40 Years old female patient, known to be suffering from multiple sclerosis, was presented clinically with painful diminution of vision in the right aye and mild weakness
multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging
 Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
Index terms: Computed tomography Magnetic resonance sequence optimization Multiple sclerosis The evaluation of multiple sclerosis by magnetic resonance imaging Val M. Runge, M.D.*1 4, Ann C. Price, M.D.*
MRI of Pathological Aging Brain
 MRI of Pathological Aging Brain Yukio Miki Department of Radiology, Osaka City University A variety of pathological changes occur in the brain with aging, and many of these changes can be identified by
MRI of Pathological Aging Brain Yukio Miki Department of Radiology, Osaka City University A variety of pathological changes occur in the brain with aging, and many of these changes can be identified by
Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175)
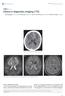 Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
Singapore Med J 2017; 58(3): 121-125 doi: 10.11622/smedj.2017017 CMEArticle Clinics in diagnostic imaging (175) Vijay Krishnan 1, MD, FRCR, Tze Chwan Lim 1, MBBS, FRCR, Francis Cho Hao Ho 2, MBBS, FRANZCR,
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016)
 International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
International Conference on Biological Sciences and Technology (BST 2016) A Better Characterization of Brain Damage in Carbon Monoxide Intoxication Assessed in Vivo Using Diffusion Kurtosis Imaging Wen-Yao
Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History Term infant with perinatal distress and attempted forceps delivery. Diagnosis Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Discussion Encephalopathy
Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History Term infant with perinatal distress and attempted forceps delivery. Diagnosis Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Discussion Encephalopathy
An Unusual Fatal Case of Severe Irreversible Non Steroid Responsive Early Delayed Post-Radiation Leukoencephalopathy
 C A S E R E P O R T JIACM 2007; 8(4): 344-8 An Unusual Fatal Case of Severe Irreversible Non Steroid Responsive Early Delayed Post-Radiation Leukoencephalopathy GA Khwaja*, A Saxena***, N Chaudhry**, S
C A S E R E P O R T JIACM 2007; 8(4): 344-8 An Unusual Fatal Case of Severe Irreversible Non Steroid Responsive Early Delayed Post-Radiation Leukoencephalopathy GA Khwaja*, A Saxena***, N Chaudhry**, S
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter. Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
 Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter Bhagwan Moorjani American Society of Neuroimaging 37 th Annual Meeting Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter Bhagwan Moorjani American Society of Neuroimaging 37 th Annual Meeting Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
Gliomatosis Cerebri: Imaging Findings on Traditional and Advanced Techniques
 Gliomatosis Cerebri: Imaging Findings on Traditional and Advanced Techniques Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Cruz Hernandez, I. Herrera, A. L. Reyes Ortiz,
Gliomatosis Cerebri: Imaging Findings on Traditional and Advanced Techniques Poster No.: C-1464 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: L. M. Cruz Hernandez, I. Herrera, A. L. Reyes Ortiz,
Encephalitis. HSV Encephalitis. Encephalitis. Viral CNS Infection. WNV Encephalitis GRAY MATTER. Zoran Rumboldt
 Encephalitis Viral CNS Infection Hematogenous dissemination ( along peripheral nerves ) Zoran Rumboldt University of Rijeka Medical University of South Carolina Telemedicine Clinic MarinMed Clinic Many
Encephalitis Viral CNS Infection Hematogenous dissemination ( along peripheral nerves ) Zoran Rumboldt University of Rijeka Medical University of South Carolina Telemedicine Clinic MarinMed Clinic Many
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page
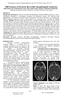 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1229-1235 Abdul-Qader Isam Abdul-Hameed, Salwa Taha Ahmed Isma'il, Shaimaa Abdelsattar Mohammad Radiology Department, Faculty of Medicine,
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1229-1235 Abdul-Qader Isam Abdul-Hameed, Salwa Taha Ahmed Isma'il, Shaimaa Abdelsattar Mohammad Radiology Department, Faculty of Medicine,
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas
 Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
Structural and functional imaging for the characterization of CNS lymphomas Cristina Besada Introduction A few decades ago, Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL) was considered as an extremely
ENCEPHALOPATHY RECOGNIZING METABOLIC AND ANOXIC CHANGES
 ENCEPHALOPATHY RECOGNIZING METABOLIC AND ANOXIC CHANGES ENCEPHALOPATHY Encephalopathy is a general term that means brain disease, damage, or malfunction. The major symptom of encephalopathy is an altered
ENCEPHALOPATHY RECOGNIZING METABOLIC AND ANOXIC CHANGES ENCEPHALOPATHY Encephalopathy is a general term that means brain disease, damage, or malfunction. The major symptom of encephalopathy is an altered
The MRI Appearance of Tumefactive Demyelinating Lesions
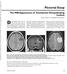 ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.148 on 12/05/17 from IP address 37.44.198.148. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved The MRI ppearance of Tumefactive emyelinating Lesions
ownloaded from www.ajronline.org by 37.44.198.148 on 12/05/17 from IP address 37.44.198.148. opyright RRS. For personal use only; all rights reserved The MRI ppearance of Tumefactive emyelinating Lesions
The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis
 September 2006 The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis David Cochran, Harvard Medical School Year IV Meet our patient WM 49yoF presents to Multiple Sclerosis Clinic for follow-up regarding worsening symptoms
September 2006 The Role of MRI in Multiple Sclerosis David Cochran, Harvard Medical School Year IV Meet our patient WM 49yoF presents to Multiple Sclerosis Clinic for follow-up regarding worsening symptoms
Scope. EEG patterns in Encephalopathy. Diffuse encephalopathy. EEG in adult patients with. EEG in diffuse encephalopathy
 Scope EEG patterns in Encephalopathy Dr.Pasiri Sithinamsuwan Division of Neurology Department of Medicine Phramongkutklao Hospital Diffuse encephalopathy EEG in specific encephalopathies Encephalitides
Scope EEG patterns in Encephalopathy Dr.Pasiri Sithinamsuwan Division of Neurology Department of Medicine Phramongkutklao Hospital Diffuse encephalopathy EEG in specific encephalopathies Encephalitides
with susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine
 Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
Emerg Radiol (2012) 19:565 569 DOI 10.1007/s10140-012-1051-2 CASE REPORT Susceptibility-weighted imaging and computed tomography perfusion abnormalities in diagnosis of classic migraine Christopher Miller
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain
 An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
An Approach to Cystic White Matter Diseases of the Paediatric Brain Poster No.: C-0239 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. Culleton, J. P. Donnellan, E. Laffan, I. Robinson, E. L.
CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype S E V E N
 CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype S E V E N CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype R. van den Boom S.A.J. Lesnik Oberstein A.A. van den
CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype S E V E N CADASIL: structural MR imaging changes and apolipoprotein E genotype R. van den Boom S.A.J. Lesnik Oberstein A.A. van den
EEG IN FOCAL ENCEPHALOPATHIES: CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASE, NEOPLASMS, AND INFECTIONS
 246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
A report of nontraumatic cortical subarachnoid hemorrhage and subsequent management
 For reprint orders, please contact: reprints@futuremedicine.com A report of nontraumatic cortical subarachnoid hemorrhage and subsequent management David Qiyuan Mao*,1, Daniel Addess 1 & Helen Valsamis
For reprint orders, please contact: reprints@futuremedicine.com A report of nontraumatic cortical subarachnoid hemorrhage and subsequent management David Qiyuan Mao*,1, Daniel Addess 1 & Helen Valsamis
Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement
 The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
The Open Medical Imaging Journal, 2012, 6, 103-107 103 Open Access Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma with Lateral Ventricle Involvement Yumi Oie 1,*, Kazuhiro Murayama 1, Shinya Nagahisa 2, Masato
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and MRI: About 6 pediatric cases
 Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and MRI: About 6 pediatric cases Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Hruba, C. ROZEL, C. Treguier, B. CARSIN-NICOL,
Posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome and MRI: About 6 pediatric cases Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2011 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: M. Hruba, C. ROZEL, C. Treguier, B. CARSIN-NICOL,
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis. Anne G. Osborn, M.D.
 RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
RINGS N THINGS: Imaging Patterns in Differential Diagnosis Anne G. Osborn, M.D. ExpDDxs: Intra-axial (Parenchymal) Lesions Ring-enhancing lesions, solitary 1 Ring-enhancing lesion crossing corpus callosum
Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome Case Report POPOVA RD, KALCHEV EB, VALCHEV GN, KALOYANOVA DV, TENEVA TG, BALEV BD
 Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome Case Report POPOVA RD, KALCHEV EB, VALCHEV GN, KALOYANOVA DV, TENEVA TG, BALEV BD Once upon a time on a Saturday shift u An emergency head CT scan was ordered from the ICU
Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome Case Report POPOVA RD, KALCHEV EB, VALCHEV GN, KALOYANOVA DV, TENEVA TG, BALEV BD Once upon a time on a Saturday shift u An emergency head CT scan was ordered from the ICU
Zhenyu Jia, MD,* Wasif Mohammed, MD,* Yiru Qiu, MD, Xunning Hong, MD,* and Haibin Shi, MD, PhD*
 Hypertension Increases the Risk of Cerebral Microbleed in the Territory of Posterior Cerebral Artery: A Study of the Association of Microbleeds Categorized on a Basis of Vascular Territories and Cardiovascular
Hypertension Increases the Risk of Cerebral Microbleed in the Territory of Posterior Cerebral Artery: A Study of the Association of Microbleeds Categorized on a Basis of Vascular Territories and Cardiovascular
myelin in the CNS Multiple axons are oligodendrocyte
 Pathologic classification of white matter disorders d Demyelinating - loss of normal myelin autoimmune/inflammatory component Dysmyelinating - loss of chemically abnormal myelin Hypomyelinating - paucity
Pathologic classification of white matter disorders d Demyelinating - loss of normal myelin autoimmune/inflammatory component Dysmyelinating - loss of chemically abnormal myelin Hypomyelinating - paucity
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18
 IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida
Applicable Neuroradiology
 For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
For the Clinical Neurology Clerkship LSU Medical School New Orleans Amy W Voigt, MD Clerkship Director Introduction The field of Radiology first developed following the discovery of X-Rays by Wilhelm Roentgen
Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease
 Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease Giuseppe Fariello, Carlo Dionisi-Vici, Cinzia Orazi, Saverio Malena, Andrea Bartuli, Paolo Schingo, Enza Carnevale, Isora Saponara, and Gaetano Sabetta
Cranial Ultrasonography in Maple Syrup Urine Disease Giuseppe Fariello, Carlo Dionisi-Vici, Cinzia Orazi, Saverio Malena, Andrea Bartuli, Paolo Schingo, Enza Carnevale, Isora Saponara, and Gaetano Sabetta
Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature.
 Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature. Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Chaves, M. S. TORONCHIK, P. M.
Susac Syndrome: Brain MRI findings in 3 patients at our institution and review of literature. Poster No.: C-0395 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: H. Chaves, M. S. TORONCHIK, P. M.
Magnetic Resonance Neuroimaging Abnormalities in Heat Stroke
 Magnetic Resonance Neuroimaging Abnormalities in Heat Stroke Poster No.: R-0029 Congress: Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: 2016 ASM Educational Exhibit E. Arnfield, Y.-T. T. Huang, F. Cominos, P. Cleland;
Magnetic Resonance Neuroimaging Abnormalities in Heat Stroke Poster No.: R-0029 Congress: Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: 2016 ASM Educational Exhibit E. Arnfield, Y.-T. T. Huang, F. Cominos, P. Cleland;
On-line Table 1: Dementia diagnoses and related ICD codes for the diagnostic groups a
 On-line Table 1: diagnoses and related ICD codes for the diagnostic groups a Diagnosis (N = 1504) ICD Code Patients Scanned with 3T; SWI (%) Subjective cognitive impairment (n 385) Z03.2A, Z03.3, and R41.8A
On-line Table 1: diagnoses and related ICD codes for the diagnostic groups a Diagnosis (N = 1504) ICD Code Patients Scanned with 3T; SWI (%) Subjective cognitive impairment (n 385) Z03.2A, Z03.3, and R41.8A
Marisa Kastoff Blitstein 1 Glenn A. Tung
 litstein and Tung MRI of Cerebral Microhemorrhages Neuroradiology Pictorial Essay 09_07_2249_litstein.fm 7/27/07 Marisa Kastoff litstein 1 Glenn. Tung litstein MK, Tung G Keywords: cerebral microhemorrhages,
litstein and Tung MRI of Cerebral Microhemorrhages Neuroradiology Pictorial Essay 09_07_2249_litstein.fm 7/27/07 Marisa Kastoff litstein 1 Glenn. Tung litstein MK, Tung G Keywords: cerebral microhemorrhages,
FILE / PERIVENTRICULAR MICROVASCULAR ISCHEMIC CHANGES EBOOK
 07 June, 2018 FILE / PERIVENTRICULAR MICROVASCULAR ISCHEMIC CHANGES EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 365.11 KB 0 FILE / PERIVENTRICULAR MICROVASCULAR ISCHEMIC CHANGES EBOOK I recently had a MRI last week with
07 June, 2018 FILE / PERIVENTRICULAR MICROVASCULAR ISCHEMIC CHANGES EBOOK Document Filetype: PDF 365.11 KB 0 FILE / PERIVENTRICULAR MICROVASCULAR ISCHEMIC CHANGES EBOOK I recently had a MRI last week with
