IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18
|
|
|
- Sabina Golden
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 IMAGING OF HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC INJURY IN A NEONATE FN3 STATE MEETING NEMOURS CHILDREN'S HOSPITAL ORLANDO,FL 08/04/18 Dhanashree Rajderkar,MD Assistant Professor Department of Radiology University of Florida in Gainesville, FL Contact:rajdda@radiology.ufl.edu
2 OBJECTIVES: To discuss the role of Imaging in the neonates suspected top have Hypoxic Ischemic injury To assess imaging patterns in neonates with hypoxic-ischemic injury in term versus premature infants To discuss the technical aspects of obtaining the ideal imaging in the patients with suspected HIE
3
4 HEAD US: INDICATIONS-PREMATURE INFANTS To detect Intracranial hemorrhage Periventricular leukomalacia/ischemia Hydrocephalus Extra-axial fluid collections
5 HEAD US: INDICATIONS-PREMATURE INFANTS To follow Intracranial hemorrhage, hydrocephalus, extra-axial fluid collections Usually at day 7. Day 1-PENUT, Seizures, decreased hematocrit, changes in neurologic status, bradycardia < 32 weeks or < 1500 g
6 HEAD US:TECHNIQUE Transducers MHz for extraaxial fluid, dura, meninges, convexities MHz for posterior fossa, entire brain Anterior fontanelle - large enough up to 6 months(closes 9-15 mths) Posterior fontanelle - posterior fossa Mastoid fontanelle - posterior lateral(open until 2 yrs)
7
8
9 PATIENT IMAGING-MRI Right preparation Imaging parameters Safety- Team, Suction pump,o2 supply,laryngoscope,monitoring devices Examination on the day of the study Swaddling-Feed and wrap technique Scan on side Adult knee coil
10 MRI Neonates vital signs are prone to fluctuate, and several parameters must be closely monitored STABLE- sugar, temperature, artificial breathing, blood pressure, and laboratory test results High-quality coronal diffusion-weighted images also can be obtainedneonates lack pneumatized paranasal sinuses
11
12
13
14 FLAIR-Poor due to high water content Imaging best -1-2 week Diffusion-False negative < 24 hrs Pseudonormalize- 6 day
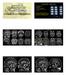
15
16 NORMAL MRS IN A TERM INFANT NORMAL MRS IN AN ADULT
17 Premie MRSpectroscopy Varies Preterm may contain lactate
18 PROGRESSION OF MYELINATION Rostral to caudal; Posterior to anterior; Central to peripheral
19 Myelination 20 weeks-pons,post medulla 29 weeks-sup and Inf cerebellar peduncles 32 weeks-midbrain 33 weeks-inferior colliculi, lateral putamen,ventrolateral thalami 35 weeks-post limb of Internal capsule 35 weeks-2 mths- Optic tracts,medial temporal lobes,perirolandic fissures,calcarine,central white matter,rest of the basal ganglia
20 Courtesy: Dr. Robert McKinstry
21 Sulcation 16 weeks-interhemispheric and sylvian 22 weeks-parietooccipital, Hippocampal,Callosal weeks- Calcarine 24 weeks-cingulate 26 weeks-central 27-Precentral,Superior temporal,marginal 28 weeks-post central 29 weeks-superior frontal,inferior frontal 33 weeks-inferior temporal
22 29 WEEKS
23 33 WEEKS
24 PRE-TERM (26 WKS) T1 T2
25 PRE-TERM (30-WEEK)
26 34-WEEK PRETERM INFANT
27
28 26 WK
29 32 WK
30
31 Sulcation 16 weeks-interhemispheric and sylvian 22 weeks-parietooccipital, Hippocampal,Callosal weeks- Calcarine 24 weeks-cingulate 26 weeks-central 27-Precentral,Superior temporal,marginal 28 weeks-post central 29 weeks-superior frontal,inferior frontal 33 weeks-inferior temporal
32 Sulcation 16 weeks-interhemispheric and sylvian 22 weeks-parietooccipital, Hippocampal,Callosal weeks- Calcarine 24 weeks-cingulate 26 weeks-central 27-Precentral,Superior temporal,marginal 28 weeks-post central 29 weeks-superior frontal,inferior frontal 33 weeks-inferior temporal
33
34
35 26 WK
36 32 WK
37 Germinal matrix 5-14 wk-ventricular zone-ependymal wk Subependymal, deep WM,Gangilionic eminences-20% cortical,bg,amygdala,hippocampus Lateral sparse/dense cellular-glial cells
38 Normal preterm MRI Germinal matrix-low on T2,high on T1 WM-Low TI,high T Weeks-Band of low T2 and high T1-Migrating cells Crossroads by frontal horns-36 weeks
39 GMH/IVH < 3 days Hypo T1,Marked hypo T2 3-7 days-hyper T1,Hypo T2 7 days-months-hypo to CSF T1,hyper to CSF on T2
40
41
42 Report gestational age Age at time of scan Scoring System from A. James Barkovich, MD
43 HIE IN PRETERM 50% of cases of cerebral palsy Premature infants Up to 19% of infants born before 28 weeks of gestation develop cerebral palsy Hypoperfusion Watershed Ischemia-Premyelinating neurons Lack of autoregulation
44
45 PREMATURE INFANTS White Matter Injury (WMI) of Prematurity Focal (cystic/noncystic) Diffuse Encephalopathy of prematurity Cerebellar Injury Hemorrhagic HIE of premature-wm Injury Chronic WM injury-mixed pattern Chronic WM injury
46 FOCAL NON CYSTIC EX 30 WEEK EGA MRI at term Follow up MRI
47 WHITE MATTER INJURY (WMI) OF PREMATURITY FOCAL, NONCYSTIC Common % Difficult to detect with US Microscopic focal necroses-glial scar Foci of increased T1, decreased T2 Foci disappear on follow-up MR scans Decreased ADC in acute stages * Need to look at ADC map as trace DWI images can look normal
48 2 PATIENTS WITH CYSTIC TYPE INJURY
49 WHITE MATTER INJURY (WMI) OF PREMATURITY FOCAL, CYSTIC Declining incidence, <5% of WMI in VLBW Large cysts can be detected with US or MRI Cysts shrink - volume loss seen at follow-up MRI Risk Factor: NEC Periventricular leukomalacia is most commonly seen adjacent to the trigones of the lateral ventricles and to the Monro foramen, areas that correspond to the watershed zones in periventricular white matter in the premature brain Kidokoro et al Peds 2014
50 WHITE MATTER INJURY (WMI) OF PREMATURITY FOCAL, CYSTIC The condition probably represents toxic injury -cerebral ischemia, reperfusion, or both End-stage periventricular leukomalacia manifests as a reduction in volume of the periventricular white matter and the centrum semiovale, with passive dilatation and irregularity of the ventricular wall
51 CEREBELLAR GM HEMORRHAGE
52 HEMORRHAGIC HIE OF PREMATURE- CEREBELLAR INJURY Increasingly recognized form of preterm injury (10-40%) Common, esp in VLBW (<1500g) Germinal matrix hemorrhages in external granule cell layer- cerebellar germinal zone 28-40wks Large hemorrhages can be seen with US, MRI Small hemorrhages best seen with MRI Best seen on T2, SWI Increase detection with 3T Can lead to cerebellar hypoplasia
53 HEMORRHAGIC HIE OF PREMATURE-WM INJURY
54 MORE EXAMPLES
55 CHRONIC WM INJURY-MIXED PATTERN
56 CHRONIC WM INJURY Thinning of the corpus callosum, particularly in the posterior body and splenium, is a characteristic late feature of periventricular leukomalacia
57 PREMATURE- SEVERE INJURY Severe-deep gray nuclei/brainstem Thalami Dorsal brainstem Anterior vermis Lentiform nuclei Perirolandic gyri Cerebral cortex spared WM/GMH
58 31 WEEK EGA ABRUPTION
59 Diffusion in the cortex is more restricted because of the higher ratio of cells to extracellular space
60 NEURODEVELOPMENTAL DEFICITS IN WM DISEASE OF THE PREMATURE Outcomes: Cognitive and motor delay-spastic diplegia/quadriplegia Neurosensory Impairment Visual Predictors/Term equivalent Moderate to severe WM abnormalities Grey matter less strongly associated US-III/IV;Cystic PVL Postnatal steroids
61 DIFFUSE EXCESSIVE HIGH SIGNAL INTENSITY IN WM(DEHSI) Controversial WM Increase diffusion Poor neurologic outcome Transient normal process No difference; No difference ADC values with controls
62 ENCEPHALOPATHY OF PREMATURITY Selective vulnerability of pre-oligodendrocytes and immature oligodendrocytes AND subplate neurons to H-I and inflammtion Impaired pre oligodendrocyte maturation-decreased myelin Subplate neurons-role in thalamocortical and associative/commisural cortico-cortico connections Likely combination of 1 destructive process and 2 maturation/trophic disturbance
63 FULL TERM INFANTS Severe, basal ganglia pattern Severe, total hypoxia Mixed pattern
64 NORMAL 2 day old 36 week EGA boy Hypointense T1 signal in post. Limb of internal capsule. This is normal for age in 36 wk EGA Range of variation in signal intensity that can be seen in normal brain basal ganglia show moderately hyperintense signal, although less than that typically seen in hypoxia
65 DAY 4 DAY 47 Injury to the basal ganglia and thalamus BASAL GANGLIA PATTERN High T1 signal in basal ganglia and thalamus from intracellular calcium shift and necrosis DWI ADC
66 MRI FINDINGS IN THE NEONATE WITH SEVERE, TOTAL HYPOXIA
67 Abnormal high signal throughout the WM on T2 Blurring of GW differentiation more evident on B=0 than conventional T2- weighted images ABNORMAL NORMAL
68 DAY 3
69 DAY 49
70 Reduction in glutamate release Decrease in intracellular acidosis and lactic acid accumulation Prevention of blood-brain barrier disruption and brain edema Preservation of endogenous antioxidants Reduction of leukotriene production Inhibition of apoptosis Reduction in cerebral metabolism
71 38 WEEK EGA GIRL INFANT BORN AFTER INDUCTION FOR MATERNAL PRE-ECLAMPSIA Hypoxic ischemic injury s/p cooling. Infant is now 5 days old and is being re-warmed
72 Inc T1 signal in corticospinal tracts, lentiform nuclei and thalami (subtle), and decreased T1 signal in posterior limbs of internal capsule
73 Subtle decreased signal on ADC map in corticospinal tracts, lentiform nuclei and posterior limbs of internal capsules. No DWI changes because they ve already normalized.
74 KEY POINTS HIE usually manifests within the first few hours after birth A few days after birth - without an obvious reason, metabolic and infectious causes must be considered Normal Neonate MR Findings->37 weeks EGA T1 & T2 signal in posterior half of posterior limb of internal capsule At a minimum, 1/3 of the length should be T1 hyperintense Usually seen during first 24 hours of life If <36 weeks EGA: no T1 in this region = normal finding
75 Severe hypoxic-ischemic insults to the premature brain typically affects: Thalamus PRETERM Anterior part of the vermis Dorsal brainstem Injury to the basal ganglia is usually less severe and common TERM Severe hypoxic-ischemic injury in term baby involves: Ventral and lateral aspects of the thalamus Posterior aspect of the putamen Perirolandic regions Corticospinal tracts
76 PRETERM Mild to moderate hypoxic-ischemic injury may result in a germinal matrix hemorrhage, periventricular leukomalacia, or both Hypoperfusion causes periventricular border zone of white matter injury TERM Mild to moderate hypoxic-ischemic injury in term baby causes lesions in Watershed areas Parasagittal cortex Subcortical white matter Spares the brainstem, cerebellum, and deep gray matter structures
77 METABOLIC DISORDERS PRESENTING WITH ENCEPHALOPATHY IN NEONATAL PERIOD Amino/organic acidopathies: Nonketotic hyperglycinemia Glutaric aciduria I and II Sulfite oxidase deficiency Maple syrup urine disease Proprionic Acidemia Urea Cycle disorders Mitochondrial/respiratory chain abnormalities Peroxisomal biogenesis disorders
78
79 IMPORTANT CLINICALCORRELATES Long-term studies of the outcome of very prematurely born infants - significant motor, cognitive, and behavioral deficits More prone to develop encephalopathies In comparison to the term-born infants, the premature infants at term demonstrated prominent reductions in cerebral cortical and deep GM volume The major predictors of altered cerebral volumes were gestational age at birth and the presence of cerebral WM injury
80 IMPORTANT CLINICALCORRELATES Infants with significantly reduced cortical GM and deep nuclear GM volumes and increased CSF volume volumes exhibited moderate to severe neurodevelopmental disability at 1 year of age The nature of the cerebral abnormalities that underlie these common and serious developmental disabilities is not entirely understood Postulated-WM injury and delayed WM and GM gyral development
81 CONCLUSIONS: Hypoxic ischemic injury manifests differently in a full term than in a premature on MRI USG of head serves as a baseline examination to enroll a patient in the PENUT trial AND a routine baseline scan on day 7 of a premature baby Imaging of the patients who have undergone cooling demonstrate lesser extent of brain injury
82
83
Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes
 Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Ira Adams-Chapman, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Developmental Progress Clinic Emory University School of Medicine
Insults to the Developing Brain & Effect on Neurodevelopmental Outcomes Ira Adams-Chapman, MD Assistant Professor of Pediatrics Director, Developmental Progress Clinic Emory University School of Medicine
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings
 Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Hypoxic ischemic brain injury in neonates - early MR imaging findings Poster No.: C-1208 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit E.-M. Heursen, R. Reina Cubero, T. Guijo Hernandez,
Insults to the Term Brain
 Insults to the Term Brain Monica Epelman, MD mepelman@nemours.org Literature comparing US and MR has deficiencies Retrospective studies Long time interval between US and MR exams in the same patient
Insults to the Term Brain Monica Epelman, MD mepelman@nemours.org Literature comparing US and MR has deficiencies Retrospective studies Long time interval between US and MR exams in the same patient
Neurosonography: State of the art
 Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Neurosonography: State of the art Lisa H Lowe, MD, FAAP Professor and Academic Chair, University MO-Kansas City Pediatric Radiologist, Children s Mercy Hospitals and Clinics Learning objectives After this
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain
 Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Ultrasound examination of the neonatal brain Guideline for the performance and reporting of neonatal and preterm brain ultrasound examination, by the Finnish Perinatology Society and the Paediatric Radiology
Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review
 Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review Poster No.: C-2615 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Vazquez, R. E. Ochoa Albíztegui
Transfontanelar Ultrasound Technique, Normal Anatomy, Anatomic Variants and Classification Review Poster No.: C-2615 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: S. E. Vazquez, R. E. Ochoa Albíztegui
NEURO IMAGING 2. Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity
 NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
NEURO IMAGING 2 Dr. Said Huwaijah Chairman of radiology Dep, Damascus Univercity I. EPIDURAL HEMATOMA (EDH) LOCATION Seventy to seventy-five percent occur in temporoparietal region. CAUSE Most likely caused
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD
 Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Enhancement of Cranial US: Utility of Supplementary Acoustic Windows and Doppler Harriet J. Paltiel, MD Boston Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School None Disclosures Conventional US Anterior fontanelle
Neuroradiological Imaging Techniques in Pediatric Neurology
 Neuroradiological Imaging Techniques in Pediatric Neurology Rajan Patel, MD Director, Pediatric Neuroimaging Assistant Professor, Division of Neuroradiology DISCLOSURE No financial disclosure. LEARNING
Neuroradiological Imaging Techniques in Pediatric Neurology Rajan Patel, MD Director, Pediatric Neuroimaging Assistant Professor, Division of Neuroradiology DISCLOSURE No financial disclosure. LEARNING
SWI including phase and magnitude images
 On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
On-line Table: MRI imaging recommendation and summary of key features Sequence Pathologies Visible Key Features T1 volumetric high-resolution whole-brain reformatted in axial, coronal, and sagittal planes
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure
 Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Introduction to the Central Nervous System: Internal Structure Objective To understand, in general terms, the internal organization of the brain and spinal cord. To understand the 3-dimensional organization
Characteristic features of CNS pathology. By: Shifaa AlQa qa
 Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Characteristic features of CNS pathology By: Shifaa AlQa qa Normal brain: - The neocortex (gray matter): six layers: outer plexiform, outer granular, outer pyramidal, inner granular, inner pyramidal, polymorphous
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review
 Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alexopoulou 1, A. Mazioti 1, D. K. Filippiadis 2, C. Chrona
Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic brain injury imaging: A pictorial review Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: E. Alexopoulou 1, A. Mazioti 1, D. K. Filippiadis 2, C. Chrona
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury
 Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury Stéphane Sizonenko, MD-PhD Division of Development and Growth Department of Child and Adolescent Medicine Geneva University
Advanced magnetic resonance imaging for monitoring brain development and injury Stéphane Sizonenko, MD-PhD Division of Development and Growth Department of Child and Adolescent Medicine Geneva University
Perinatal cerebral white matter injuries influence early communication and language development
 Perinatal cerebral white matter injuries influence early communication and language development Blazenka Brozovic University of Zagreb Department of Speech and Language Pathology Developmental Neurolinguistic
Perinatal cerebral white matter injuries influence early communication and language development Blazenka Brozovic University of Zagreb Department of Speech and Language Pathology Developmental Neurolinguistic
Essentials of Clinical MR, 2 nd edition. 14. Ischemia and Infarction II
 14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
14. Ischemia and Infarction II Lacunar infarcts are small deep parenchymal lesions involving the basal ganglia, internal capsule, thalamus, and brainstem. The vascular supply of these areas includes the
In utero and perinatal hypoxic brain damage
 In utero and perinatal hypoxic brain damage G Dekker, MB ChB, MFam Med H B Louw, S Andronikou, MB BCh, FC Rad (SA) M Pienaar, BSc, MB ChB S Hlongwane, MB ChB A Brandt, MB ChB D van der Merwe, MB ChB Department
In utero and perinatal hypoxic brain damage G Dekker, MB ChB, MFam Med H B Louw, S Andronikou, MB BCh, FC Rad (SA) M Pienaar, BSc, MB ChB S Hlongwane, MB ChB A Brandt, MB ChB D van der Merwe, MB ChB Department
Slide 1. Slide 2. Slide 3. Tomography vs Topography. Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain. Learning Objective
 Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Slide 1 Computed Tomography (CT): A simplified Topographical review of the Brain Jon Wheiler, ACNP-BC Slide 2 Tomography vs Topography Tomography: A technique for displaying a representation of a cross
Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology
 General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
General Pediatric MS MRI Study Methodology SCAN PREPARATION axial T2-weighted scans and/or axial FLAIR scans were obtained for all subjects when available, both T2 and FLAIR scans were scored. In order
Newborn Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury. Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCh FRCR Lucile Packard Children s Hospital at Stanford
 Newborn Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCh FRCR Lucile Packard Children s Hospital at Stanford NO DISCLOSURES INTRODUCTION Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a major cause
Newborn Hypoxic Ischemic Brain Injury Hisham Dahmoush, MBBCh FRCR Lucile Packard Children s Hospital at Stanford NO DISCLOSURES INTRODUCTION Neonatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) is a major cause
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE
 TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
TOXIC AND NUTRITIONAL DISORDER MODULE Objectives: For each of the following entities the student should be able to: 1. Describe the etiology/pathogenesis and/or pathophysiology, gross and microscopic morphology
Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound
 Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound Priyanka Upadhyay *, Ketki U Patil 1, Rajesh Kuber 2, Vilas Kulkarni 3, Amarjit Singh 4 * Chief
Original article: Evaluation of hypoxic-ischaemic events in preterm neonates using trans cranial ultrasound Priyanka Upadhyay *, Ketki U Patil 1, Rajesh Kuber 2, Vilas Kulkarni 3, Amarjit Singh 4 * Chief
Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR
 Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History Term infant with perinatal distress and attempted forceps delivery. Diagnosis Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Discussion Encephalopathy
Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Joseph Junewick, MD FACR 08/11/2010 History Term infant with perinatal distress and attempted forceps delivery. Diagnosis Term Hypoxic Ischemic Injury Discussion Encephalopathy
Neonatal Hypoxic ischemic Encephalopathy: A Radiological Review
 Review Article Neonatal Hypoxic ischemic Encephalopathy: A Radiological Review Shahina Bano, Vikas Chaudhary 1, Umesh Chandra Garga Department of Radiodiagnosis, PGIMER, Dr. RML Hospital, 1 Department
Review Article Neonatal Hypoxic ischemic Encephalopathy: A Radiological Review Shahina Bano, Vikas Chaudhary 1, Umesh Chandra Garga Department of Radiodiagnosis, PGIMER, Dr. RML Hospital, 1 Department
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound
 SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
SOP: Cerebral Ultrasound Version Author(s) Date Changes Approved by 1.0 Cornelia Hagmann Manon Benders 29.5.2012 Initial Version Gorm Greisen 1.1 Cornelia Hagmann 18.6.2012 Minor changes Gorm Greisen 1.2
Normal myelination: a practical pictorial review
 Normal myelination: a practical pictorial review Poster No.: C-1486 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Gaha, N. Mama, N. Arifa, H. Jemni, K. Tlili Graiess; Sousse/TN
Normal myelination: a practical pictorial review Poster No.: C-1486 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Gaha, N. Mama, N. Arifa, H. Jemni, K. Tlili Graiess; Sousse/TN
Study of correlation severity of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy on MRI brain with clinical findings
 Radiology and Imaging Special Issue December 2017: Vol-7, Issue- 1, P 34-41 Original article: Study of correlation severity of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy on MRI brain with clinical findings *Dr Ramaa
Radiology and Imaging Special Issue December 2017: Vol-7, Issue- 1, P 34-41 Original article: Study of correlation severity of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy on MRI brain with clinical findings *Dr Ramaa
Chronology of normal brain myelination in newborns with MR imaging
 Chronology of normal brain myelination in newborns with MR imaging Poster No.: C-0577 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit F. Fernandez Usagre; Sevilla/ES Neuroradiology
Chronology of normal brain myelination in newborns with MR imaging Poster No.: C-0577 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific Exhibit F. Fernandez Usagre; Sevilla/ES Neuroradiology
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD
 Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Joana Ramalho, MD C. Ryan Miller, MD, PhD Case 1 3 month old baby girl Presented with new onset of seizures Newborn. Questionable blurring of the gray-white junction within the right occipital lobe. Findings
Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI
 Chapter 4 Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI Lishya Liauw Jeroen van der Grond Valerie Slooff Francisca Wiggers-de Bruïne Laura Laan Saskia
Chapter 4 Differentiation between peritrigonal terminal zones and hypoxic-ischemic white matter injury on MRI Lishya Liauw Jeroen van der Grond Valerie Slooff Francisca Wiggers-de Bruïne Laura Laan Saskia
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas. Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template
 Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn
 Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
Quick practical guide to Cranial Ultrasound in the newborn Introduction A standard set of views is taken to assist with consistent visualisation of structures and in the interpretation of possible abnormalities.
For Emergency Doctors. Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011
 For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
For Emergency Doctors Dr Suzanne Smallbane November 2011 A: Orbit B: Sphenoid Sinus C: Temporal Lobe D: EAC E: Mastoid air cells F: Cerebellar hemisphere A: Frontal lobe B: Frontal bone C: Dorsum sellae
MRI OF THE THALAMUS. Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI
 1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
1 MRI OF THE THALAMUS Mohammed J. Zafar, MD, FAAN Kalamazoo, MI Objectives: The thalamic nuclei can be involved in a wide variety of conditions. A systematic imaging approach would be useful for narrowing
Fig.1: A, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a
 Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
Fig.1 E Fig.1:, Sagittal 110x110 mm subimage close to the midline, passing through the cingulum. Note that the fibers of the corpus callosum run at a slight angle are through the plane (blue dots with
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know
 brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
brain MRI for neuropsychiatrists: what do you need to know Christoforos Stoupis, MD, PhD Department of Radiology, Spital Maennedorf, Zurich & Inselspital, University of Bern, Switzerland c.stoupis@spitalmaennedorf.ch
HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY AND THE OBSTETRICIAN
 HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY AND THE OBSTETRICIAN DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose and have no real or potential conflicts with this presentation and its content. Michael P. Nageotte, M.D. CASE:
HYPOXIC ISCHEMIC ENCEPHALOPATHY AND THE OBSTETRICIAN DISCLOSURE I have nothing to disclose and have no real or potential conflicts with this presentation and its content. Michael P. Nageotte, M.D. CASE:
PRETERM BIRTH RESULTS IN ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL CONNECTIVITY AT AGE 16 YEARS
 Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library School of Medicine 8-17-2010 PRETERM BIRTH RESULTS IN ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL CONNECTIVITY
Yale University EliScholar A Digital Platform for Scholarly Publishing at Yale Yale Medicine Thesis Digital Library School of Medicine 8-17-2010 PRETERM BIRTH RESULTS IN ALTERATIONS IN NEURAL CONNECTIVITY
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia.
 Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Neuropathology Specialty Conference
 Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Neuropathology Specialty Conference March 22, 2010 Case 2 Rebecca Folkerth, MD Brigham and Women s Hospital Children s Hospital Harvard Medical School Clinical History 18-gestational-week fetus found on
Cerebro-vascular stroke
 Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Cerebro-vascular stroke CT Terminology Hypodense lesion = lesion of lower density than the normal brain tissue Hyperdense lesion = lesion of higher density than normal brain tissue Isodense lesion = lesion
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods
 Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Analysis between clinical and MRI findings of childhood and teenages with epilepsy after hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy in neonates periods Poster No.: C-0401 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Scientific Exhibit
Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports
 Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports "This work has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health,
Automated Identification of Neoplasia in Diagnostic Imaging text reports "This work has been funded in whole or in part with Federal funds from the National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health,
CNS pathology Third year medical students. Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure
 CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
CNS pathology Third year medical students Dr Heyam Awad 2018 Lecture 5: disturbed fluid balance and increased intracranial pressure ILOs Understand causes and symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Neuroimaging updates on neonatal hypoxic ischemic injury and hypothermia
 Neuroimaging updates on neonatal hypoxic ischemic injury and hypothermia Fabio Triulzi Neuroradiology Dept. Cà Granda Foundation Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Università degli Studi, Milan ITALY Term Neonate
Neuroimaging updates on neonatal hypoxic ischemic injury and hypothermia Fabio Triulzi Neuroradiology Dept. Cà Granda Foundation Ospedale Maggiore Policlinico Università degli Studi, Milan ITALY Term Neonate
When? Incidence of neonatal seizures in a NICU population The incidence of seizures is higher in the neonatal period than in any other age group.
 Incidence of neonatal seizures in a NICU population The incidence of seizures is higher in the neonatal period than in any other age group. Standard EEG 2,3% 8.6% Standard EEG + aeeg Scher MS et al; Pediatrics
Incidence of neonatal seizures in a NICU population The incidence of seizures is higher in the neonatal period than in any other age group. Standard EEG 2,3% 8.6% Standard EEG + aeeg Scher MS et al; Pediatrics
Chapter 3. Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance
 Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
Chapter 3 Neonatal cranial ultrasonography: how to optimize its performance Sylke J. Steggerda Lara M. Leijser Frans J. Walther Gerda van Wezel-Meijler Early Human Development 2009; 85(2): 93-99 Chapter
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia.
 Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Imaging findings in neonates with hypoxic-ischaemic encephalopathy and terapeutic hypothermia. Poster No.: C-1577 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. Manso Garcia, M. J. Velasco Marcos,
Attenuation value in HU From -500 To HU From -10 To HU From 60 To 90 HU. From 200 HU and above
 Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
Brain Imaging Common CT attenuation values Structure Air Fat Water Brain tissue Recent hematoma Calcifications Bone Brain edema and infarction Normal liver parenchyma Attenuation value in HU From -500
White Matter Injury in the Premature Infant: A Comparison between Serial Cranial Sonographic and MR Findings at Term
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:805 809, May 2003 White Matter Injury in the Premature Infant: A Comparison between Serial Cranial Sonographic and MR Findings at Term Terrie E. Inder, Nigel J. Anderson, Carole
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:805 809, May 2003 White Matter Injury in the Premature Infant: A Comparison between Serial Cranial Sonographic and MR Findings at Term Terrie E. Inder, Nigel J. Anderson, Carole
Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy
 Original article: Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy *Dr Harshad Bhagat, ** Dr Ravindra Kawade, ***Dr Y.P.Sachdev *Junior Resident, Department Of Radiodiagnosis,
Original article: Study of role of MRI brain in evaluation of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy *Dr Harshad Bhagat, ** Dr Ravindra Kawade, ***Dr Y.P.Sachdev *Junior Resident, Department Of Radiodiagnosis,
Predicting Outcomes in HIE. Naaz Merchant Consultant Neonatologist Beds & Herts Meeting 17/03/2016
 Predicting Outcomes in HIE Naaz Merchant Consultant Neonatologist Beds & Herts Meeting 17/03/2016 Interactive please! Case 1 Term, 3.5 kg Antenatal: Breech Labour/Delivery: Em CS failure to progress, mec
Predicting Outcomes in HIE Naaz Merchant Consultant Neonatologist Beds & Herts Meeting 17/03/2016 Interactive please! Case 1 Term, 3.5 kg Antenatal: Breech Labour/Delivery: Em CS failure to progress, mec
Outline of the next three lectures
 Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
Outline of the next three lectures Lecture 35 Anatomy of the human cerebral cortex gross and microscopic cell types connections Vascular supply of the cerebral cortex Disorders involving the cerebral cortex
NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE
 1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
1 1 NEURO IMAGING OF ACUTE STROKE ALICIA RICHARDSON, MSN, RN, ACCNS-AG, ANVP-BC WENDY SMITH, MA, RN, MBA, SCRN, FAHA LYNN HUNDLEY, APRN, CNRN, CCNS, ANVP-BC 2 2 1 DISCLOSURES Alicia Richardson: Stryker
Prevalence of "Compressed" and Asymmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic
 Prevalence of "Compressed" and symmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic Study 149 Patricia Winchester 1 Paula W. rill1 Rebecca Cooper2 lfred N. Krauss 2 Hart dec Peterson
Prevalence of "Compressed" and symmetric Lateral Ventricles in Healthy Full Term Neonates: Sonographic Study 149 Patricia Winchester 1 Paula W. rill1 Rebecca Cooper2 lfred N. Krauss 2 Hart dec Peterson
SHORT ANSWER. Write the word or phrase that best completes each statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Exam Name 1) A change in the conditions in the synaptic terminal can influence the soma as a result of axoplasmic transport. 2) The nervous system is composed of the brain and spinal cord. A) efferent
Central nervous system (CNS): brain and spinal cord Collections of cell body and dendrites (grey matter) are called nuclei/nucleus Nucleus can also
 Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
Chapter 3 Part 1 Orientation Directions in the nervous system are described relatively to the neuraxis An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the bottom
PROPERTY OF ELSEVIER SAMPLE CONTENT - NOT FINAL. Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System
 3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
3 Gross Anatomy and General Organization of the Central Nervous System C h a p t e r O u t l i n e The Long Axis of the CNS Bends at the Cephalic Flexure Hemisecting a Brain Reveals Parts of the Diencephalon,
Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1269 1273, August 2004 Diffusion-Weighted and Conventional MR Imaging Findings of Neuroaxonal Dystrophy R. Nuri Sener BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Neuroaxonal dystrophy is a rare progressive
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists.
 Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
Anoxic brain injury CT and MRI patterns - quick pictoral quide for junior radiologists. Poster No.: C-1844 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: A. Kecler - Pietrzyk, W. Torreggiani ; Dublin/IE,
ECMUS The Safety Committee of EFSUMB : Tutorial
 Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Neonatal cranial ultrasound Safety Aspects (2013) Prepared for ECMUS by B.J. van der Knoop, M.D. 1, J.I.P. de Vries, M.D., PhD 1, I.A. Zonnenberg, M.D. 2, J.I.M.L. Verbeke, M.D. 3 R.J. Vermeulen, M.D.,
Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
ORIGINAL RESEARCH K. Johkura Y. Nakae Y. Kudo T.N. Yoshida Y. Kuroiwa Early Diffusion MR Imaging Findings and Short-Term Outcome in Comatose Patients with Hypoglycemia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The relationship
Anatomy Lab (1) Theoretical Part. Page (2 A) Page (2B)
 Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
Anatomy Lab (1) This sheet only includes the extra notes for the lab handout regarding the theoretical part, as for the practical part it includes everything the doctor mentioned. Theoretical Part Page
EEG IN FOCAL ENCEPHALOPATHIES: CEREBROVASCULAR DISEASE, NEOPLASMS, AND INFECTIONS
 246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
246 Figure 8.7: FIRDA. The patient has a history of nonspecific cognitive decline and multiple small WM changes on imaging. oligodendrocytic tumors of the cerebral hemispheres (11,12). Electroencephalogram
Acute stroke. Ischaemic stroke. Characteristics. Temporal classification. Clinical features. Interpretation of Emergency Head CT
 Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Ischaemic stroke Characteristics Stroke is the third most common cause of death in the UK, and the leading cause of disability. 80% of strokes are ischaemic Large vessel occlusive atheromatous disease
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann
 Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. Meninges 2. Cerebral cortex-cytoarchitecture 3. Diencephalon (thalamus/hypothalamus) (this replaces
Psyc 311A, fall 2008 Conference week 3 TA: Jürgen Germann e-mail: jurgen.germann@mcgill.ca Overview: 1. Meninges 2. Cerebral cortex-cytoarchitecture 3. Diencephalon (thalamus/hypothalamus) (this replaces
3T MRI imaging approach to pediatric epileptic seizures:
 3T MRI imaging approach to pediatric epileptic seizures: Poster No.: C-1886 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. S. Alaín, E. M. DE LUCAS, J. C. Quintero Rivera, C. Pérez 1 2 3 3 3
3T MRI imaging approach to pediatric epileptic seizures: Poster No.: C-1886 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: J. S. Alaín, E. M. DE LUCAS, J. C. Quintero Rivera, C. Pérez 1 2 3 3 3
Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of brain maturation in preterm neonates with punctate white matter lesions
 Neuroradiology (2007) 49:161 167 DOI 10.1007/s00234-006-0176-y PAEDIATRIC NEURORADIOLOGY Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of brain maturation in preterm neonates with punctate white matter lesions
Neuroradiology (2007) 49:161 167 DOI 10.1007/s00234-006-0176-y PAEDIATRIC NEURORADIOLOGY Magnetic resonance imaging assessment of brain maturation in preterm neonates with punctate white matter lesions
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16
 Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Anatomy and Physiology (Bio 220) The Brain Chapter 14 and select portions of Chapter 16 I. Introduction A. Appearance 1. physical 2. weight 3. relative weight B. Major parts of the brain 1. cerebrum 2.
Posterior fossa malformations
 ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
ANDREA ROSSI, MD Head, Department of Pediatric Neuroradiology G. Gaslini Children s Research Hospital Genoa Italy andrearossi@ospedale-gaslini.ge.it Posterior fossa malformations Cerebellar ataxia Hypotonia
Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture. caudal = toward the spinal cord)
 Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Insight: Some cranial nerve disorders Brain and Cranial Nerves (Ch. 15) Human Anatomy lecture I. Overview (Directional terms: rostral = toward the forehead caudal = toward the spinal cord) A. 3 Major parts
Cerebellar Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1008 1015, June/July 2004 Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Michael A. Sargent, Kenneth J. Poskitt, Elke H. Roland, Alan Hill, and Glenda Hendson BACKGROUND
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1008 1015, June/July 2004 Vermian Atrophy after Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Michael A. Sargent, Kenneth J. Poskitt, Elke H. Roland, Alan Hill, and Glenda Hendson BACKGROUND
10/3/2016. T1 Anatomical structures are clearly identified, white matter (which has a high fat content) appears bright.
 H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
H2O -2 atoms of Hydrogen, 1 of Oxygen Hydrogen just has one single proton and orbited by one single electron Proton has a magnetic moment similar to the earths magnetic pole Also similar to earth in that
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING
 ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
ISCHEMIC STROKE IMAGING ผศ.พญ พญ.จ ร ร ตน ธรรมโรจน ภาคว ชาร งส ว ทยา คณะแพทยศาสตร มหาว ทยาล ยขอนแก น A case of acute hemiplegia Which side is the abnormality, right or left? Early Right MCA infarction
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum
 Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Development of Brain Stem, Cerebellum and Cerebrum The neural tube cranial to the 4th pair of somites develop into the brain. 3 dilatations and 2 flexures form at the cephalic end of the neural tube during
Periventricular white matter injury, that is, periventricular
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Yoshida K. Hayakawa A. Yamamoto T. Kanda Y. Yamori Pontine Hypoplasia in Children with Periventricular Leukomalacia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The brain stem in patients with periventricular
ORIGINAL RESEARCH S. Yoshida K. Hayakawa A. Yamamoto T. Kanda Y. Yamori Pontine Hypoplasia in Children with Periventricular Leukomalacia BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The brain stem in patients with periventricular
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, Dr. Peter Ostrow
 Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Malformations of the Nervous System November 10, 2016 Dr. Peter Ostrow Malformations of the Nervous System 1. Abnormal closure of the neural tube 1. Disorders of forebrain formation 1. Cortical anomalies
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD
 Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Head CT Scan Interpretation: A Five-Step Approach to Seeing Inside the Head Lawrence B. Stack, MD Five Step Approach 1. Adequate study 2. Bone windows 3. Ventricles 4. Quadrigeminal cistern 5. Parenchyma
Perlman J, Clinics Perinatol 2006; 33: Underlying causal pathways. Antenatal Intrapartum Postpartum. Acute near total asphyxia
 Perlman J, Clinics Perinatol 2006; 33:335-353 Underlying causal pathways Antenatal Intrapartum Postpartum Acute injury Subacute injury Associated problem Reduced fetal movements Placental insufficiency
Perlman J, Clinics Perinatol 2006; 33:335-353 Underlying causal pathways Antenatal Intrapartum Postpartum Acute injury Subacute injury Associated problem Reduced fetal movements Placental insufficiency
Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter. Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
 Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter Bhagwan Moorjani American Society of Neuroimaging 37 th Annual Meeting Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
Metabolic Disorders primarily affecting white matter Bhagwan Moorjani American Society of Neuroimaging 37 th Annual Meeting Disclosure Nothing to disclose Images were obtained form the following sources
MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS
 Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Andrea Falini Italy MRI and differential diagnosis in patients suspected of having MS IMPROVING THE PATIENT S LIFE THROUGH MEDICAL EDUCATION www.excemed.org Outline of presentation - Diagnostic criteria
Diffusion-weighted MR imaging is increasingly being used
 ORIGINAL RESEARCH J. Dudink D.J. Larkman O. Kapellou J.P. Boardman J.M. Allsop F.M. Cowan J.V. Hajnal A.D. Edwards M.A. Rutherford S.J. Counsell High b-value Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Neonatal Brain
ORIGINAL RESEARCH J. Dudink D.J. Larkman O. Kapellou J.P. Boardman J.M. Allsop F.M. Cowan J.V. Hajnal A.D. Edwards M.A. Rutherford S.J. Counsell High b-value Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Neonatal Brain
Brain Damage from Perinatal Asphyxia: Correlation of MR Findings
 1087 Brain Damage from Perinatal Asphyxia: Correlation of MR Findings with Gestational Age A. James Barkovich 1 Charles L. Truwit MR scans of 25 patients who suffered asphyxia at known gestational ages
1087 Brain Damage from Perinatal Asphyxia: Correlation of MR Findings with Gestational Age A. James Barkovich 1 Charles L. Truwit MR scans of 25 patients who suffered asphyxia at known gestational ages
Brainstem. By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan
 Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Brainstem By Dr. Bhushan R. Kavimandan Development Ventricles in brainstem Mesencephalon cerebral aqueduct Metencephalon 4 th ventricle Mylencephalon 4 th ventricle Corpus callosum Posterior commissure
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari
 Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Patologie infiammatorie encefaliche e midollari Maria Laura Stromillo Department of Medicine, Surgery and Neuroscience Inflammatory disorders of the CNS NMOSD ADEM Multiple Sclerosis Neuro-Myelitis Optica
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters
 Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Nervous System, Neuroanatomy, Neurotransmitters Neurons Structure of neurons Soma Dendrites Spines Axon Myelin Nodes of Ranvier Neurons Structure of neurons Axon collaterals 1 Neurons Structure of neurons
Neonatal Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy: Detection with Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :9 96, September Neonatal Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy: Detection with Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Kirsten P. N. Forbes, James G. Pipe, and Roger Bird BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol :9 96, September Neonatal Hypoxic-ischemic Encephalopathy: Detection with Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging Kirsten P. N. Forbes, James G. Pipe, and Roger Bird BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE:
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PERINATAL EVENTS AND BRAIN DAMAGE IN SURVIVING CHILDREN BASED ON PAPERS PRESENTED AT AN INTERNATIONA PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : PERINATAL EVENTS AND BRAIN DAMAGE IN SURVIVING CHILDREN BASED ON PAPERS PRESENTED AT AN INTERNATIONA PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 perinatal events and brain damage in surviving
DOWNLOAD OR READ : PERINATAL EVENTS AND BRAIN DAMAGE IN SURVIVING CHILDREN BASED ON PAPERS PRESENTED AT AN INTERNATIONA PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 perinatal events and brain damage in surviving
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images
 1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
1 MS Lesions in T2-Weighted Images M.A. Sahraian, E.-W. Radue 1.1 Introduction Multiple hyperintense lesions on T2- and PDweighted sequences are the characteristic magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) appearance
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Verse 1: Neocortex, frontal lobe, Brain stem, brain stem, Hippocampus, neural node, Right hemisphere, Pons and cortex visual, Brain stem, brain stem, Sylvian fissure,
Prognosis in. Encephalopathy. Hypoxic-Ischemic. Özge Aydemİr MD
 Prognosis in Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Özge Aydemİr MD Major problems we have to face while caring infants with HIE are; Øto provide families with reliable information about outcome. Øto decide how
Prognosis in Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy Özge Aydemİr MD Major problems we have to face while caring infants with HIE are; Øto provide families with reliable information about outcome. Øto decide how
Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge
 Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge Stein Magnus Aukland Haukeland University Hospital University of Bergen NORWAY No disclosure Imaging modalities O Skull X-ray O Computer Tomography O Cerebral
Imaging the Premature Brain- New Knowledge Stein Magnus Aukland Haukeland University Hospital University of Bergen NORWAY No disclosure Imaging modalities O Skull X-ray O Computer Tomography O Cerebral
Chapter 3. Structure and Function of the Nervous System. Copyright (c) Allyn and Bacon 2004
 Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Chapter 3 Structure and Function of the Nervous System 1 Basic Features of the Nervous System Neuraxis: An imaginary line drawn through the center of the length of the central nervous system, from the
Original Article INTRODUCTION. Abstract
 Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/19 Patterns of Restricted Diffusion within Corpus Callosum in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy and its Significance
Original Article Print ISSN: 2321-6379 Online ISSN: 2321-595X DOI: 10.17354/ijss/2018/19 Patterns of Restricted Diffusion within Corpus Callosum in Neonatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Encephalopathy and its Significance
PEDIATRIC NEWBORN MEDICINE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES
 PEDIATRIC NEWBORN MEDICINE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Term Equivalent Brain MRIs For Very Preterm Infants Clinical Practice Guideline: Term Equivalent Brain MRIs For Very Preterm Infants Points of emphasis/primary
PEDIATRIC NEWBORN MEDICINE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES Term Equivalent Brain MRIs For Very Preterm Infants Clinical Practice Guideline: Term Equivalent Brain MRIs For Very Preterm Infants Points of emphasis/primary
Lecturer. Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014
 Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lecturer Prof. Dr. Ali K. Al-Shalchy MBChB/ FIBMS/ MRCS/ FRCS 2014 Dorsal root: The dorsal root carries both myelinated and unmyelinated afferent fibers to the spinal cord. Posterior gray column: Long
Lab 2. we will look into several angled horizontal sections ( orbitomeatal plane ) i.e passing from the orbit into the ear
 we will look into several angled horizontal sections ( orbitomeatal plane ) i.e passing from the orbit into the ear Figure I page 76 : looking at the key on the left side this section passed through the
we will look into several angled horizontal sections ( orbitomeatal plane ) i.e passing from the orbit into the ear Figure I page 76 : looking at the key on the left side this section passed through the
The Central Nervous System I. Chapter 12
 The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
The Central Nervous System I Chapter 12 The Central Nervous System The Brain and Spinal Cord Contained within the Axial Skeleton Brain Regions and Organization Medical Scheme (4 regions) 1. Cerebral Hemispheres
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT
 Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
Pearls and Pitfalls in Neuroradiology of Cerebrovascular Disease The Essentials with MR and CT Val M. Runge, MD Wendy R. K. Smoker, MD Anton Valavanis, MD Control # 823 Purpose The focus of this educational
