Role of Physical Therapists in the Treatment of Lymphedema
|
|
|
- Dominic Cameron
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 October 19, 2009 Medical Evidence Development and Coverage Advisory Committee (MEDCAC) Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) Office of Clinical Standards and Quality, Coverage & Analysis Group C , 7500 Security Boulevard Baltimore, MD Dear Sir or Madam: On behalf of the members of the American Physical Therapy Association (APTA), I would like to thank the MEDCAC for the opportunity to comment on the treatment of secondary lymphedema. APTA is a professional association representing 72,000 physical therapists, physical therapist assistants, and students of physical therapy. Physical therapists treat Medicare beneficiaries in a variety of practice settings including private practices, hospitals, skilled nursing facilities, home health agencies, rehabilitation agencies and comprehensive outpatient rehabilitation facilities. It has been noted that the diverse etiology of lymphedema means that patients at risk of developing the disease can be encountered in a wide variety of primary and secondary care settings. 1 As a result, a national coverage decision governing the coverage of lymphedema treatment would impact our members greatly. We look forward to an opportunity to work with the MEDCAC to ensure any policy regarding the coverage of lymphedema reflects best practices and is in the best interest of Medicare beneficiaries. Role of Physical Therapists in the Treatment of Lymphedema Lymphedema is a debilitating progressive condition for which there is no known cure. It requires that the patient, in collaboration with his or her health care providers, manage the condition to prevent disabling side effects and potentially lethal complications such as infection. Lymphedema affects people regardless of age, gender, economic status, and co-morbid conditions. While primary lymphedema is a result of a hereditary or congenital condition, secondary lymphedema is typically related to cancer treatment. It is caused by lymphatic system dysfunction which results in an abnormal protein rich swelling of the tissue. Patients with lymphedema experience pain associated with 1 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus.
2 swelling of the affected limb(s) as well as with additional pressure placed on the joints. These patients also suffer from the psychological impact of having a large or abnormal limb. The occurrence of secondary lymphedema varies based on the type of cancer and treatment provided. For instance, as many as 49% of patients develop breast cancerrelated lymphedema after mastectomy. Approximately 4-17% of patients developed secondary lymphedema after sentinel lymph node biopsy with radiation 2. The incidence of lower limb lymphedema related to gynecological or urogenital cancer ranges from 50-80% 3. The American Cancer Society projected 1.5 million new cancer cases in 2008 alone with an estimated annual cost of $206.3 billion 4. Approximately 10.5 million Americans have a past history of cancer and all cancer survivors who have surgery to remove lymph nodes and/or have radiation therapy are at risk of developing lymphedema 5. In fact, some estimates place the incidence of lymphedema at 30% among cancer survivors. As a result, secondary lymphedema has the potential to have significant personal, societal, and economic impacts. Of primary importance to the treatment of this chronic condition is early diagnosis and intervention. Physical therapists play a crucial role in the early detection, treatment, and long-term management of lymphedema. Physical therapists play an important role in detecting the onset of limb swelling at the earliest onset, when the condition can be reversed and even prevented from progressing to a manifest condition. Additionally, interventions provided by physical therapists can diminish limb swelling for patients who have clinically apparent lymphedema. In both early and late stage lymphedema treatment, physical therapy interventions aimed at treating and managing lymphedema potentiate functional gains Patients with a cancer diagnosis typically receive primary care services including surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. The medical providers focus on ridding the patient s body of the cancer, however, there is particularly limited attention to the frequent co-morbidities associated with these therapies. As a result, patients who develop secondary lymphedema often are not diagnosed until the disease 2 Carlson J, Kauderer J, Walker J, Gold M, O Malley D, et al. Phase III trial of Tisseel to reduce lymphedema after inguinal lymph node dissection: a gynecologic oncology study group. Proceedings of the 38 th annual meeting on women s cancer (abstract 228). San Diego, CA; Werngren-Elgstrom, M Lidman, D. Lymphedema of the lower extremities after surgery and radiotherapy for c,cancer of the cervix. Scandinavian J Plast Reconstruction Surg and Hand Surg. 1994; 28: American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2008: 3. 5 American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures Atlanta: American Cancer Society; 2008: 3. 6 Mondry TE. Riffenburgh RH, Johnstone PA. Prospective trial of complete decongestive therapy and manual lymphatic drainage on treatment-related lymphedema in breast cancer therapy. Cancer J. 2004; 10 (1): Koul R, Dufan T, Russell C, Guenther W, Nugent Z, Sun X, et al. Efficacy of complete decongestive therapy and manual lymphatic drainage on treatment-related lymphedema in breast cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Bio Phys. 2007; 67 (3): Ko DS, Lerner R, Klose G, Cosimi AB. Effective treatment of lymphedema of the extremities. Arch Surg. 1998; 133 (4): Hinrichs CS, Gibbs, JF, Driscoll D, Kepner JL, Wilinson NW, Edge SB. Et al. The effectiveness of complete decongestive therapies for the treatment of lymphedema following groin dissection for melanoma. J. Surg. Oncol. 2004; 85 (4):
3 has advanced to the point where the condition is visibly apparent or the degree of impairment is such that the patient cannot carry out activities of daily living. Physical therapists, as a result of their education and training, are prepared to serve as the provider of choice for the surveillance, early detection, and management of lymphedema at any stage. Early detection is vital to preventing the progression of the disease. Pre-operative assessments conducted by physical therapists provide a baseline from which to monitor the development of lymphedema. Ongoing interval prospective surveillance by a physical therapist enables diagnosis of lymphedema at the earliest presentation, and with conservative compression interventions, may prevent the condition from becoming manifest in the limb and therefore preventing a lifetime of intensive management of a chronic condition. 10 Further, randomized controlled trials have demonstrated that with proper patient education for activity and exercise, along with ongoing monitoring by a physical therapist, lymphedema may be prevented from occurring If lymphedema is not diagnosed early and the limb reaches an intermediate stage of swelling, physical therapists have a variety of tools available to them to treat and alleviate the condition. For example, physical therapists provide complete decongestive therapy for patients with lymphedema. Complete decongestive therapy, also known as complex physical therapy, is considered the gold standard of care for patients with lymphedema. 13 This includes manual lymphatic drainage, compression bandaging, exercise, education regarding skin and nail care and hygiene, and custom compression garments in an effort to restore nearnormal limb girth. Patients undergoing complete decongestive therapy achieve significant reduction in limb volume (between 60% and 80%), improved cosmesis, softening of tissue and a return to near normal function. In addition to the interventions provided by physical therapists to decongest the swollen limb, lymphedema requires ongoing self-management whereby the patient must adhere to a life-long arduous maintenance routine. The role of the physical therapist is important in educating the patient and caregiver in proper self-care. Additional intermittent episodes of follow-up care with the physical therapist ensure appropriate self-care and comprehensive disease management. This model of care is consistent with the chronic disease management models espoused in the literature as efficacious for long-term disease management. It stands as reasonable to expect that the physical therapist, as a front-line provider for lymphedema management and care, should be engaged as the 10 Stout, Gergich, et al., Pfalzer LA, McGarvey C, Springer B, Gerber LH, Soballe P. Preoperative assessment enables the early diagnosis and successful treatment of lymphedema. Cancer 2008;112: Todd J, Scally A, Dodwell D, Horgan, K, Topping A. A randomized controlled trial of two programs of shoulder exercise following axillary node dissection for invasive breast cancer. Physiotherapy December 2008 (Vol. 94, Issue 4, Pages ) 12 Box RC, Reul-Hirche HM, Bullock-Saxton JE, Furnival CM. Shoulder movement after breast cancer surgery: results of a randomised controlled study of postoperative physiotherapy Breast Cancer Res Treat Sep;75(1): Lawenda B, Mondry T, Johnstone P. Lypmhedema: A primer on the identification and management of a chronic condition in oncologic treatment. A Cancer Journal for Clinicians. 2009; 59;
4 provider of choice for ongoing surveillance of those who are at high risk for developing lymphedema and for those with lymphedema to assure disease management. Patients who develop lymphedema and the providers, such as physical therapists, who care for them, face many obstacles. Lymphedema is often not diagnosed early enough and results in initial treatment being undertaken at an advanced stage when more intensive, costly therapy is required. There are several factors that can contribute to a delayed diagnosis. For instance, the physician may not recognize the signs or symptoms of lymphedema because his or her focus is treating the cancer, not its co-morbidities. In addition, lymphedema may be misdiagnosed as deep vein thrombosis or another condition. Coverage for services related to the treatment of lymphedema is limited as well, preventing timely or appropriate care. Delays in receiving care not only have implications for the patient s quality of life, but also take a financial toll on the overall health care system. As CMS and MEDCAC move forward with a potentially revised coverage decision for Medicare related to lymphedema, we respectfully request they consider the role of the physical therapist in the treatment of lymphedema. In this comment letter, we provide information in response to the questions developed in preparation for the MEDCAC meeting. Our responses focus specifically on the questions that relate to the efficacy of lymphedema treatment by physical therapists. We believe it is important that CMS and the MEDCAC consider all the evidence, including studies and expert clinical consensus, when determining whether sufficient evidence exists to provide coverage for lymphedema services. Of note is the extensive work done in the United Kingdom to develop consensus guidelines for the treatment of lymphedema. The consensus process commenced in 2002 and involved national patient support groups, patients with lymphedema, national professional lymphedema groups, clinical experts, and industry. The standards of practice recommended were made with several key concepts in mind including identification of people at risk for or with lymphedema and the provision of services that deliver high quality clinical care that is subject to continuous improvement and integrates community, hospital, and hospice based services. 14 This consensus document and best practice standard have been accepted in the UK by the National Health Service s National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence (NICE) and represents the standard of care for practice and reimbursement. The recommendations made in the consensus document are referenced throughout our comments as they related to the specific areas of concern identified by CMS to be addressed by MEDCAC. Diagnosis of Lymphedema The first question posed to the MEDCAC panel is whether certain diagnostic strategies can reliably identify and stratify the severity of secondary lymphedema. Appropriate diagnosis relies on standardized methodology and a diagnostic criteria that is sensitive to 14 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 4
5 identify the condition at its initial onset. One method identified to effectively diagnose lymphedema is pre- and post-operative measurements of both limbs (arms or legs as appropriate). A pre-operative limb volume measurement enables quantification of normal limb variance in volume. Interval surveillance, often in the absence of swelling, is recommended in order to identify and treat lymphedema at the earliest onset. 10 The initial onset of swelling may be sub-clinical in nature so the methodology for taking repeated measures is important. Without a methodology that involves pre-operative measurement and prospective surveillance the earliest onset of volume change will be missed. Validated clinical tools for diagnosing lymphedema include: circumferential measurements taken at consistent intervals along the length of the limb, water displacement, optoelectronic perometry, and bioelectrical impedance. Each technique is valid to assess limb volume associated with lymphedema; however the principle of consistent, repeated measures of both limbs through a surveillance program is necessary for these tools to effectively diagnose lymphedema. 15 We encourage MEDCAC to recognize that pre-operative assessment and prospective surveillance by a physical therapist is a diagnostic strategy that can reliably identify and stratify the severity of lymphedema. This methodology also potentiates prevention of disease progression and cost savings. 16 Staging of Lymphedema One of the questions posed to the MEDCAC panel relates to whether secondary lymphedema can be classified into prognostic stages of severity that are useful to guide choice of therapy or response to therapy. There is some consensus in the staging of lymphedema. 17 According to the International Society of Lymphology classification of lymphedema staging, there are four main stages, Stage 0-Stage III. Stage II is further subdivided to provide additional clarity. Stage 0 is the earliest stage of lymphedema where swelling is not evident but lymph transport is impaired. Stage I signifies the accumulation of tissue that is reduced with elevation of the affected limb. In the early period of Stage II, limb elevation alone is rarely effective and pitting is apparent. In the later phase of Stage II, pitting is less apparent as fibrous tissue is more evident. The final stage, Stage III, is defined as the stage in which tissue hardens and pitting is absent. The skin changes and becomes thicker, and skin folds, fat deposits, and warty overgrowths develop. 18 While the consensus document provides an increased level of detail when compared to other staging schemas, clear similarities exist in the classification of lymphedema into a system identified by stages. 15 Box RC, Reul-Hirche HM, Bullock-Saxton JE, Furnival CM. Physiotherapy after breast cancer surgery: results of a randomised controlled study to minimise lymphoedema. Breast Cancer Res Treat Sep;75(1): Shih YC, Xu Y, Cormier JN, Giordano S, Ridner SH, Buchholz TA, Perkins GH, Elting LS Incidence, treatment costs, and complications of lymphedema after breast cancer among women of working age: a 2- year follow-up study. J Clin Oncol Apr 20;27(12): Gordon K, Mortimer P. A Guide to Lymphedema. Expert Review of Dermatology. 2007; 2 (6). 18 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 5
6 One study categorized lymphedema according to three stages. Stage I was defined as the early accumulation of fluid relatively high in protein content which could subside with elevation of the limb. In Stage I, pitting may occur and an increase in proliferating cells may also be seen. Once lymphedema progresses to Stage II, elevation alone rarely reduces the tissue swelling and pitting is more pronounced. As Stage II progresses, pitting is less pronounced as excess fat and fibrosis become the dominant symptoms. By Stage III, pitting is largely absent and trophic skin changes such as acanthosis, further deposition of fat and fibrosis, and warty overgrowth have developed. 19 Although three stages were used in this study, similar characteristics appear to be attributed to the stages as those used in other studies and derived through consensus. CMS is also interested in determining if specific interventions are best suited for a particular stage of lymphedema. Again, there is some evidence and consensus on this topic. While details about the specific interventions are discussed in greater detail below, it is important to note what interventions are typically used for each stage of this disease. A standardized approach to education and risk reduction by a physical therapist may decrease the risk of developing lymphedema. 11, 15 Utilizing basic principles of skin care, infection prevention and appropriate exercise precautions, the physical therapist is the optimal provider to guide patients in reducing risk associated with the development of lymphedema. When lymphedema is diagnosed at its earliest stage, a conservative compression intervention along with education and ongoing surveillance and education effectively manages the swelling and may prevent the condition from progressing to an advanced stage. Later stage (II and III) lymphedema requires intensive complex decongestive therapy. 20 Assessment of Measures of Improved Health Outcomes The panel is being asked whether an improvement in certain measures (e.g. affected limb circumference, affected limb volume) is associated with an improvement in health outcomes for the patient. As stated in one study by Kristiana Gordon and Peter Mortimer: A number of key issues need to be addressed for each patient: reduction in limb swelling, prevention of skin changes (such as brawny texture, prominent skin creases, hyperkeratosis, papillomatosis), prevent of infection and treatment of specific problems like lymphorrhea. These can be addressed through the four cornerstones of physical therapy. Treatment regimens should be considered as twofold: an initial intensive treatment phase aiming for limb- volume reduction, often combining external compression, exercise and massage therapies; followed by the long-term maintenance phase of utilizing compression hosiery to sustain manageable limb volume The Diagnosis and Treatment of Peripheral Lymphedema: 2009 Consensus Document of the International Society of Lymphedema. 2009; Mondry TE, Riffenburgh RH, Johnstone PA. Prospective trial of complete decongestive therapy for upper extremity lymphedema after breast cancer therapy. Cancer J Jan-Feb;10(1): Gordon K, Mortimer P. A Guide to Lymphedema. Expert Review of Dermatology. 2007; 2 (6). 6
7 Patients with lymphedema often suffer from skin infections or a break down in skin integrity. This is a result of reduced local immunity in the affected part of the body. As a result, an improvement in skin integrity and reduction in such infections could be seen as improving health outcomes in a patient. 22 In fact, lymphedema can cause ulceration, contact dermatitis, venous exczema, and fungal infections among other skin infections or conditions. Control of lymphedema is important to preventing these co-morbid skin conditions. 23 Lymphedema can also result in reduced limb function including strength, endurance, and range of motion. Assessment of limb function is considered a standard component of treatment of this condition. Included in an assessment of limb function as it pertains to lymphedema are the use of aides, range of joint motion, and the ability to carry out activities of daily living such as walking and dressing. 24 Effectiveness of Lymphedema Interventions CMS has asked MEDCAC to consider the evidence demonstrating the effectiveness and outcomes of the various treatment options for patients with secondary lymphedema, including compression bandaging and/or compression garments, pneumatic compression devices, exercise-based treatments, and massage-based treatment. The use of these interventions for the treatment of lymphedema has been analyzed in several studies, which have indicated the interventions are effective. Specifically, several studies have stated that a combination of these treatments, rather than a particular intervention provided in isolation, is often most effective in treating lymphedema. For example, elevation alone is rarely able to minimize the symptoms of lymphedema. 25 According to a report published by the Cochrane Collaboration in 2009, the standard treatment approach in Europe has involved a two-phased approach. In the first phase, multi-layer bandaging, care of the skin, manual lymph drainage, exercise, and pneumatic compression is employed. In the second phase, patients are required to wear strong compression hosiery to maintain the reduction in swelling, carry out regular daily exercise, and continue with regular manual lymph drainage whenever possible. 26 Current consensus literature also supports a multidisciplinary approach involving many services currently provided within the scope of practice of physical therapists. The exact 22 Preston N, Seers K, Mortimer P. Physical therapies for reducing and controlling lymphedema of the limbs. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2009; Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 24 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 25 Mergens A, Harris S. Physical Therapist Management of Lymphedema Following Treatment for Breast Cancer: A Critical Review of Its Effectiveness. Physical Therapy. 1998; 78 (12). 26 Preston N, Seers K, Mortimer P. Physical therapies for reducing and controlling lymphedema of the limbs. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2009; 3. 7
8 interventions are also determined by the site, stage, severity, and complexity of lymphedema. 27 Compression Bandaging/Compression Garments Several studies discuss the use, importance, and efficacy of compression garments and/or bandages. One such study stated that physical therapists had a responsibility to encourage their patients to consistently use compression garments over the long-term. 28 It is important to note that compression garments may be prefabricated or custom-made and are of varying degrees of elasticity. They lessen the amount of excess fluid that can enter an affected extremity by increasing interstitial hydrostatic pressure within the limb. 29 In fact, graded compression garments have been cited by some studies as a mainstay of lymphedema therapy. 30 In a study that used CT scanning to assess the effect of compression garment therapy, a significant decrease in the cross-sectional area of subcutaneous compartments was found. The mean decrease was 9% in the proximal portion and 26% in the distal portion of the limb. 31 The type of bandaging or garment used can vary based on the presentation of the patient and severity of the disease. When lymphedema is diagnosed at an early, sub-clinical stage, compression garments have been shown to be effective at reducing limb volume, possibly preventing the progression to a more advanced stage of lymphedema. Additionally, these authors found that with regular use of compression garments during exertional activities, patients were able to maintain their limb volume suggesting that this form of early compression intervention may have a long-term preventive effect. For patients with Stage II and more advanced lymphedema, one study recommended the use of elastic compression hosiery garments. This study also found that for patients with more advanced lymphedema, hosiery garments should be followed by the use of multilayer compression bandaging (CB). A randomized, controlled trial found that multiple-layer short stretch bandages were a superior initial treatment for Stage II and III lymphedema. 32 Regardless of the exact form of bandage or garment, many studies outline the efficacy of their use in the treatment of lymphedema. 33 While compression bandages have been determined to lead to reduction in lymphedema, those involved in developing consensus guidelines note the importance of coupling compression garment interventions with exercise, skin care, and elevation for early stage 27 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 28 Mergens A, Harris S. Physical Therapist Management of Lymphedema Following Treatment for Breast Cancer: A Critical Review of Its Effectiveness. Physical Therapy. 1998; 78 (12). 29 Mergens A, Harris S. Physical Therapist Management of Lymphedema Following Treatment for Breast Cancer: A Critical Review of Its Effectiveness. Physical Therapy. 1998; 78 (12). 30 Harris A, Hugi M, Olivotto I, Levine M. Clinical practice guidelines for the care and treatment of breast cancer: 11. Lymphedema. CMAJ. 2001; 164 (2). 31 Harris A, Hugi M, Olivotto I, Levine M. Clinical practice guidelines for the care and treatment of breast cancer: 11. Lymphedema. CMAJ. 2001; 164 (2). 32 Kerchner K, Fleischer A, Yosipovitch G. Lower extremity lymphedema update: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment guidelines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 4 (13). 33 Gordon K, Mortimer P. A Guide to Lymphedema. Expert Review of Dermatology. 2007; 2 (6). 8
9 lymphedema. When treating advanced stage lymphedema in the lower and upper limbs, strategies include compression bandaging, manual lymphatic drainage and therapeutic interventions including exercise, skin care, and elevation. Once limb decongestion has occurred, compression garments are the main compression intervention recommended for ongoing long-term care. Regular assessment of the patient using a compression garment should be conducted by the physical therapist at specified intervals. Garments should be replaced every three to six months depending on the needs of the patient and the elasticity of the garment. Compression garments have been found most effective for the treatment of patients with Stage I lymphedema while those in Stage II seem to garner best results with CB. Patients in Stages II and III benefit from a combination of skin care, exercise, elevation, and CB. 34 Multilayer compression bandaging is an important element of therapy related to the treatment of lymphedema. CB uses inelastic bandages that have low extensibility and produce high working pressures and lower resting pressures. CB restores shape to the limb and/or affected area, reduces skin changes, supports overstretched skin, and softens subcutaneous tissues. It is indicated when skin changes are marked or limb distortion and skin folds preclude compression garments. 35 Pneumatic Compression Devices Pneumatic compression consists of an electrical air compression pump attached to an inflatable garment that is placed over the affected limb. The garment is inflated and deflated over a set period of time. Pneumatic compression works by decreasing capillary function, and therefore lymph formation, rather than accelerating lymph return. Evidence suggests that it is most effective in non-obstructive edemas. 36 Studies have shown that pneumatic compression devices demonstrate promise in the treatment of lymphedema. Specifically, a study has found that sequential intermittent pneumatic compression has been shown to be beneficial in the treatment of lymphedema. This same study found that outcomes were improved when pneumatic compression devices were used in conjunction with compression therapy and comprehensive decongestive therapy. 37 A second study found that the reduction in lymphedema volume in patients treated with a pneumatic compression device was 18% greater than the 34 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 35 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 36 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 37 Kerchner K, Fleischer A, Yosipovitch G. Lower extremity lymphedema update: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment guidelines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 4 (13). 9
10 reduction produced by elastic compression. 38 Pneumatic compression devices are widely used in the treatment of lymphedema. 39 Manual Lymphatic Drainage Manual lymphatic drainage is a technique that causes lymph conduits to contract more often and siphons lymphatic fluid away from congested regions and subsequently toward nearby functioning lymph basins. In other words it is designed to reduce swelling by encouraging lymph flow. 40 It is often used in the early, intensive phase of lymphedema therapy. 41 The use and effectiveness of manual lymphatic drainage is supported by expert clinical opinion. However, many believe that with few exceptions this intervention is not an effective treatment on its own and should be used in conjunction with compression therapy. 42 Manual lymphatic drainage is a specialized intervention involving specific hand placement and directionality of the treatment. Usually the therapist conducting MLD has specialty training in these techniques to facilitate improved fluid flow. Exercise-based Treatment Studies have shown that exercise is beneficial due to skeletal muscle activity aiding the extrinsic pumping mechanism of the lymphatic system. 43 Aerobic exercise increases intra-abdominal pressure which facilitates pumping of the thoracic duct. 44 In a document developed to provide clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of lymphedema related to breast cancer, exercise is reported as beneficial to controlling lymphedema. A recent study in the New England Journal of Medicine touts the benefits of resistive exercise in over 200 women with lymphedema. The study found that women with breast cancer related lymphedema performed exercise safely when they used compression garments during their exercise program Harris A, Hugi M, Olivotto I, Levine M. Clinical practice guidelines for the care and treatment of breast cancer: 11. Lymphedema. CMAJ. 2001; 164 (2). 39 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 40 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 41 Kerchner K, Fleischer A, Yosipovitch G. Lower extremity lymphedema update: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment guidelines. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008; 4 (13). 42 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 43 Mergens A, Harris S. Physical Therapist Management of Lymohedema Following Treatment for Breast Cancer: A Critical Review of Its Effectiveness. Physical Therapy. 1998; 78 (12). 44 Lymphedema Framework. Best Practice for the Management of Lymphedema. International consensus. 45 Schmitz KH, Ahmed RL, Troxel A, Cheville A, Smith R, Lewis-Grant L, Bryan CJ, Williams-Smith CT, Greene QP. Weight lifting in women with breast-cancer-related lymphedema. N Engl J Med Aug 13;361(7):
11 Conclusion In conclusion, I would like to again thank CMS and MEDCAC for the opportunity to comment on this important coverage issue. If you have additional questions, please contact Sarah Nicholls-Sharp, Assistant Director for Federal Payment and Regulatory Affairs at or sarahnicholls-sharp@apta.org. Sincerely, R. Scott Ward, PT, PhD President 11
Medical Policy Original Effective Date: 01/23/2019
 Page 1 of 12 Disclaimer Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans or the plan may have broader or more limited benefits
Page 1 of 12 Disclaimer Refer to the member s specific benefit plan and Schedule of Benefits to determine coverage. This may not be a benefit on all plans or the plan may have broader or more limited benefits
Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth
 Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth Paediatric lymphoedema A challenge for clinicians and families To receive an attendance certificate please complete your online evaluation at: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/paedlymphoedema
Welcome to Allied Health Telehealth Paediatric lymphoedema A challenge for clinicians and families To receive an attendance certificate please complete your online evaluation at: https://www.surveymonkey.com/s/paedlymphoedema
Submitted by: Date of request: 28 th October 2015
 Submitted by: Frank Vicini, MD, FACR Chief Medical Officer ImpediMed, Inc. 5900 Pasteur Court Suite 125 Carlsbad, CA 92008 Phone: 760 585 2100 Email: fvicini@impedimed.com Date of request: 28 th October
Submitted by: Frank Vicini, MD, FACR Chief Medical Officer ImpediMed, Inc. 5900 Pasteur Court Suite 125 Carlsbad, CA 92008 Phone: 760 585 2100 Email: fvicini@impedimed.com Date of request: 28 th October
Section: Durable Medical Equipment Last Reviewed Date: June Policy No: 82 Effective Date: September 1, 2014
 Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Date of Origin: April 2011 Section: Durable Medical Equipment Last Reviewed Date: June 2014 Policy No: 82 Effective
Medical Policy Manual Topic: Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Date of Origin: April 2011 Section: Durable Medical Equipment Last Reviewed Date: June 2014 Policy No: 82 Effective
EFFICACY OF DECONGESTIVE THERAPY AND INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH LYMPHEDEMA OF THE ARM AFTER BREAST CANCER TREATMENT
 EFFICACY OF DECONGESTIVE THERAPY AND INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH LYMPHEDEMA OF THE ARM AFTER BREAST CANCER TREATMENT Dragana Bojinović-Rodić MD, PhD Institute of Physical Medicine
EFFICACY OF DECONGESTIVE THERAPY AND INTERMITTENT PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION IN PATIENTS WITH LYMPHEDEMA OF THE ARM AFTER BREAST CANCER TREATMENT Dragana Bojinović-Rodić MD, PhD Institute of Physical Medicine
1. Skin care: Cleansing, lubrication, debriding and administration of antimicrobial therapy.
 Lymphedema Treatment Last Review Date: October 13, 2017 Number: MG.MM.ME.05aC9 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider
Lymphedema Treatment Last Review Date: October 13, 2017 Number: MG.MM.ME.05aC9 Medical Guideline Disclaimer Property of EmblemHealth. All rights reserved. The treating physician or primary care provider
The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations
 The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu
The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu
Priorities Forum Statement
 Priorities Forum Statement Number 5 Subject Lymphoedema Date of decision November 2015 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 GUIDANCE Lymphoedema is the result of accumulation of fluid
Priorities Forum Statement Number 5 Subject Lymphoedema Date of decision November 2015 Date refreshed March 2017 Date of review November 2018 GUIDANCE Lymphoedema is the result of accumulation of fluid
Catherine Holley, RN Operating Room Nurse Massachusetts General Hospital
 Operating Room Nurse Massachusetts General Hospital March 13, 2019 What is Lymphedema? Swelling (edema) that occurs due to injury or impairment of the lymphatic system Causes: Anything that disrupts the
Operating Room Nurse Massachusetts General Hospital March 13, 2019 What is Lymphedema? Swelling (edema) that occurs due to injury or impairment of the lymphatic system Causes: Anything that disrupts the
Please Provide Responses to the Fields Below Electronically to be Accepted
 Please Provide Responses to the Fields Below Electronically to be Accepted Medicare Red Tape Relief Project Submissions accepted by the Committee on Ways and Means, Subcommittee on Health Date: August
Please Provide Responses to the Fields Below Electronically to be Accepted Medicare Red Tape Relief Project Submissions accepted by the Committee on Ways and Means, Subcommittee on Health Date: August
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema
 2.01.82 Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection Effective Date January 30, 2015 Original Policy Date July 2, 2010 Next Review Date January 2015 Medical
2.01.82 Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Section 2.0 Medicine Subsection Effective Date January 30, 2015 Original Policy Date July 2, 2010 Next Review Date January 2015 Medical
Lymphedema 101. Andréa Leiserowitz, DPT, CLT. Oncology Physical Therapy;
 Lymphedema 101 Andréa Leiserowitz, DPT, CLT Oncology Physical Therapy; oncologypt@gmail.com Note: this information is the property of Dr. Leiserowitz and should not be copied, distributed, or otherwise
Lymphedema 101 Andréa Leiserowitz, DPT, CLT Oncology Physical Therapy; oncologypt@gmail.com Note: this information is the property of Dr. Leiserowitz and should not be copied, distributed, or otherwise
9 Day Certified Lymphedema & Wound Therapist (62.5 CE hrs On-line + 9 Days Live Training (8am 8pm *daily times vary; 153 CE hrs Total!
 1 9 Day Certified Lymphedema & Wound Therapist (62.5 CE hrs On-line + 9 Days Live Training (8am 8pm *daily times vary; 153 CE hrs Total!) On-Line COURSE OUTLINE/Overview of Topics (62.5hrs): Lymphatics
1 9 Day Certified Lymphedema & Wound Therapist (62.5 CE hrs On-line + 9 Days Live Training (8am 8pm *daily times vary; 153 CE hrs Total!) On-Line COURSE OUTLINE/Overview of Topics (62.5hrs): Lymphatics
Cancer Support V.I. Presents
 Cancer Support V.I. Presents Overview & Discussion of Manual Lymph Drainage/Complete Decongestive Therapy (MLD/CDT) Presented by: Christopher A. Borgesen, MS,OTR September 3 rd, 2008 Christopher A. Borgesen,
Cancer Support V.I. Presents Overview & Discussion of Manual Lymph Drainage/Complete Decongestive Therapy (MLD/CDT) Presented by: Christopher A. Borgesen, MS,OTR September 3 rd, 2008 Christopher A. Borgesen,
Catherine Holley, RN Operating Room Nurse Massachusetts General Hospital
 Operating Room Nurse Massachusetts General Hospital March 15, 2017 Background Nurse 34 years Operating room RN at Massachusetts General Hospital 1979 surgery to remove varicose veins right leg Strong family
Operating Room Nurse Massachusetts General Hospital March 15, 2017 Background Nurse 34 years Operating room RN at Massachusetts General Hospital 1979 surgery to remove varicose veins right leg Strong family
TREATING LOWER LIMB LYMPHOEDEMA WITH COMPRESSION BANDAGING
 TREATING LOWER LIMB LYMPHOEDEMA WITH COMPRESSION BANDAGING Debra Doherty is Senior Lecturer, Centre for Research and implementation of Clinical Practice, Thames Valley University Multilayer continues to
TREATING LOWER LIMB LYMPHOEDEMA WITH COMPRESSION BANDAGING Debra Doherty is Senior Lecturer, Centre for Research and implementation of Clinical Practice, Thames Valley University Multilayer continues to
Breast Cancer Treatment and Lymphedema
 Breast Cancer Treatment and Lymphedema Over the last decade, major advances have been made in the prevention and treatment of breast cancer in the United States, but minimal attention has been given to
Breast Cancer Treatment and Lymphedema Over the last decade, major advances have been made in the prevention and treatment of breast cancer in the United States, but minimal attention has been given to
PNEUMATIC COMPRESSION DEVICES IN THE HOME SETTING
 Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Medicine Policy Number: II-60 Effective Date: 05/19/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
Status Active Medical and Behavioral Health Policy Section: Medicine Policy Number: II-60 Effective Date: 05/19/2014 Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Minnesota medical policies do not imply that members should
5/28/ Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, All Rights Reserved Memorial Sloan-Kettering Cancer Center, All Rights Reserved.
 Sillerman Center for Rehabilitation The presenters have no conflict of interest to report regarding any commercial product/manufacturer that may be referenced during this presentation. 1 Key components
Sillerman Center for Rehabilitation The presenters have no conflict of interest to report regarding any commercial product/manufacturer that may be referenced during this presentation. 1 Key components
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment of Lymphedema and File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: pneumatic_compression_pumps_for _lymphedema_and_venous_ulcers
Corporate Medical Policy Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment of Lymphedema and File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: pneumatic_compression_pumps_for _lymphedema_and_venous_ulcers
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema
 Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Policy Number: 2.01.82 Last Review: 5/2018 Origination: 1/2011 Next Review: 5/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Policy Number: 2.01.82 Last Review: 5/2018 Origination: 1/2011 Next Review: 5/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Lymphoedema following treatment for breast cancer: a new approach to an old problem
 Lymphoedema following treatment for breast cancer: a new approach to an old problem Screening breast cancer patients for lymphoedema makes it possible to identify problems early and take action to halt
Lymphoedema following treatment for breast cancer: a new approach to an old problem Screening breast cancer patients for lymphoedema makes it possible to identify problems early and take action to halt
CaresiaTM. Off-the-Shelf Bandage Liners
 CaresiaTM M A N U F A C T U R E D B Y S O L A R I S Off-the-Shelf Bandage Liners Table of Contents 2 3 4 6 8 10 11 Contact Information About Caresia Upper Extremity Garments Lower Extremity Garments Donning
CaresiaTM M A N U F A C T U R E D B Y S O L A R I S Off-the-Shelf Bandage Liners Table of Contents 2 3 4 6 8 10 11 Contact Information About Caresia Upper Extremity Garments Lower Extremity Garments Donning
Liposuction for chronic lymphoedema
 NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Liposuction for chronic lymphoedema Chronic lymphoedema is the swelling and build-up of body fluid and fat,
NATIONAL INSTITUTE FOR HEALTH AND CARE EXCELLENCE Interventional procedure consultation document Liposuction for chronic lymphoedema Chronic lymphoedema is the swelling and build-up of body fluid and fat,
Intensive Decongestive Lymphatic Therapy for Non-Cancer Secondary Lymphoedema Criteria Based Access Protocol
 NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Intensive Decongestive Lymphatic Therapy for Non-Cancer Secondary Lymphoedema Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
NHS Dorset Clinical Commissioning Group Intensive Decongestive Lymphatic Therapy for Non-Cancer Secondary Lymphoedema Criteria Based Access Protocol Supporting people in Dorset to lead healthier lives
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema
 Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Policy Number: 2.01.82 Last Review: 5/2017 Origination: 1/2011 Next Review: 5/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Policy Number: 2.01.82 Last Review: 5/2017 Origination: 1/2011 Next Review: 5/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas City (Blue
Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment of Lymphedema and Venous Ulcers
 Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment of Lymphedema and Venous Ulcers Policy Number: 1.01.18 Last Review: 1/2019 Origination: 10/2000 Next Review: 1/2020 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment of Lymphedema and Venous Ulcers Policy Number: 1.01.18 Last Review: 1/2019 Origination: 10/2000 Next Review: 1/2020 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Treatment of lymphoedema surgical and conservative approaches
 Treatment of lymphoedema surgical and conservative approaches Nina Linnitt RN Clinical Manager medi UK Current Chair British Lymphology Society (BLS) What is lymphoedema? International Societie de Lymphologue
Treatment of lymphoedema surgical and conservative approaches Nina Linnitt RN Clinical Manager medi UK Current Chair British Lymphology Society (BLS) What is lymphoedema? International Societie de Lymphologue
CASE STUDY. Potential conflict of interest:
 CASE STUDY presented by MICHEL EID, Lymphedema therapist Vodder School Teacher Physio Extra 2014 1 Potential conflict of interest: Invited speaker for: Physio Extra Jobst Medi Valco 1 What is lymphedema?
CASE STUDY presented by MICHEL EID, Lymphedema therapist Vodder School Teacher Physio Extra 2014 1 Potential conflict of interest: Invited speaker for: Physio Extra Jobst Medi Valco 1 What is lymphedema?
Your Lymphatic System in Health & Disease
 Your Lymphatic System in Health & Disease Professor Neil Piller, Director, Lymphoedema Research Unit Flinders Medical Centre Dr Vaughan Keeley, Consultant in Palliative Medicine, Lymphoedema Clinic, Derby
Your Lymphatic System in Health & Disease Professor Neil Piller, Director, Lymphoedema Research Unit Flinders Medical Centre Dr Vaughan Keeley, Consultant in Palliative Medicine, Lymphoedema Clinic, Derby
A Patient Guide to Understanding and Managing Chronic Swelling
 A Patient Guide to Understanding and Managing Chronic Swelling WHAT IS CHRONIC SWELLING? As a normal part of your blood circulation, your vascular system leaks fluid into the surrounding tissues. Your
A Patient Guide to Understanding and Managing Chronic Swelling WHAT IS CHRONIC SWELLING? As a normal part of your blood circulation, your vascular system leaks fluid into the surrounding tissues. Your
A Patient Guide to Understanding and Managing Chronic Swelling
 A Patient Guide to Understanding and Managing Chronic Swelling WHAT IS LYMPHEDEMA? Most of us know the circulatory system pumps blood from the heart to the rest of the body. But many people are not aware
A Patient Guide to Understanding and Managing Chronic Swelling WHAT IS LYMPHEDEMA? Most of us know the circulatory system pumps blood from the heart to the rest of the body. But many people are not aware
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers. Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities. Evidence of healed ulcers. Dermatitis. Normal ABI.
 Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Venous Insufficiency Ulcers Patient Assessment: Superficial varicosities Evidence of healed ulcers Dermatitis Normal ABI Edema Eczematous skin changes 1. Scaling 2. Pruritus 3. Erythema 4. Vesicles Lipodermatosclerosis
Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment of Lymphedema and Venous Ulcers
 Last Review Status/Date: December 2015 Page: 1 of 9 Lymphedema and Venous Ulcers Description Description Pneumatic compression pumps are proposed as a treatment option for patients with lymphedema who
Last Review Status/Date: December 2015 Page: 1 of 9 Lymphedema and Venous Ulcers Description Description Pneumatic compression pumps are proposed as a treatment option for patients with lymphedema who
A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course
 2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
2014 Annual Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Healthcare Provider Event A Manual Therapy and Exercise Approach to Breast Cancer Rehabilitation Course November 7 th and 8 th, 2014 Mercer University, Atlanta,
LEVEL ONE COURSE CONTENT
 LEVEL ONE COURSE CONTENT Dear Health Practitioner, The level one lymphoedema training course offered by the ALERT program at Macquarie University is open to AHPRA registered health professionals only (such
LEVEL ONE COURSE CONTENT Dear Health Practitioner, The level one lymphoedema training course offered by the ALERT program at Macquarie University is open to AHPRA registered health professionals only (such
The impact of Lymphedema on occupational performance, an opportunity for Occupational Therapy. Byron Shier, MBA, B.Sc. OT, CLT-LANA, CHE.
 The impact of Lymphedema on occupational performance, an opportunity for Occupational Therapy Byron Shier, MBA, B.Sc. OT, CLT-LANA, CHE. CLR Healthcare Inc. Presentation at 2013 Canadian Association of
The impact of Lymphedema on occupational performance, an opportunity for Occupational Therapy Byron Shier, MBA, B.Sc. OT, CLT-LANA, CHE. CLR Healthcare Inc. Presentation at 2013 Canadian Association of
What is Lymphedema? Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels are not formed completely or malformed
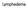 Lymphedema What is Lymphedema? Lymphedema is a chronic health condition which causes localized swelling. There are 2 types: Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels
Lymphedema What is Lymphedema? Lymphedema is a chronic health condition which causes localized swelling. There are 2 types: Primary lymphedema: a person is born with the condition where the lymphatic vessels
Lymphedema Myths Realities - Hope
 Lymphedema Myths Realities - Hope Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital of Dallas Lymphedema Therapy Department 214-345-7680 Lymphatic System Divided into sections - watersheds Lymph nodes act as filtration
Lymphedema Myths Realities - Hope Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital of Dallas Lymphedema Therapy Department 214-345-7680 Lymphatic System Divided into sections - watersheds Lymph nodes act as filtration
Improving best practices for diagnosing lymphedema
 Research Perspectives Improving best practices for diagnosing lymphedema A proposal to assess limbs according to segment Assessing limb segments can change the rate of diagnosis for lymphedema Introduction
Research Perspectives Improving best practices for diagnosing lymphedema A proposal to assess limbs according to segment Assessing limb segments can change the rate of diagnosis for lymphedema Introduction
Manipulative Therapy of Secondary Lymphedema in the Presence of Locoregional Tumors
 950 Manipulative Therapy of Secondary Lymphedema in the Presence of Locoregional Tumors Ximena A. Pinell, BA 1 Stephanie H. Kirkpatrick, MPT, clt-lana 1 Kennedy Hawkins, otr/l, CLT 2 Tammy E. Mondry, DPT,
950 Manipulative Therapy of Secondary Lymphedema in the Presence of Locoregional Tumors Ximena A. Pinell, BA 1 Stephanie H. Kirkpatrick, MPT, clt-lana 1 Kennedy Hawkins, otr/l, CLT 2 Tammy E. Mondry, DPT,
Expanding Lymphedema Prevention and Management Programs in Rural Health and Third World Countries: A Capstone Presentation
 Expanding Lymphedema Prevention and Management Programs in Rural Health and Third World Countries: A Capstone Presentation By: Cally Tejkl Pacific University July 2014 Objectives Define lymphedema Explain
Expanding Lymphedema Prevention and Management Programs in Rural Health and Third World Countries: A Capstone Presentation By: Cally Tejkl Pacific University July 2014 Objectives Define lymphedema Explain
Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association
 Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment Page 1 of 11 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See Also: Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment of Lymphedema
Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment Page 1 of 11 Medical Policy An independent licensee of the Blue Cross Blue Shield Association Title: See Also: Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment of Lymphedema
Utilizing Complete Decongestive Therapy to Treat Lymphedema: Evidence from Contemporary Literature
 Vol. 25, No. 3 July - September 2013 Article Reprints Utilizing Complete Decongestive Therapy to Treat Lymphedema: Evidence from Contemporary Literature By: Kathryn McKillip Thrift, BS, CLT-LANA and DeCourcy
Vol. 25, No. 3 July - September 2013 Article Reprints Utilizing Complete Decongestive Therapy to Treat Lymphedema: Evidence from Contemporary Literature By: Kathryn McKillip Thrift, BS, CLT-LANA and DeCourcy
MP Pneumatic Compression Pumps for Treatment of Lymphedema and Venous Ulcers
 Medical Policy MP 1.01.18 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 1.01.18 Last Review: 03/29/2018 Effective Date: 03/29/2018 Section: Durable Medical Equipment Related Policies 2.01.16 Recombinant and Autologous Platelet-Derived
Medical Policy MP 1.01.18 BCBSA Ref. Policy: 1.01.18 Last Review: 03/29/2018 Effective Date: 03/29/2018 Section: Durable Medical Equipment Related Policies 2.01.16 Recombinant and Autologous Platelet-Derived
When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA. John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA
 When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA Learning Objectives How to identify stages of lymphedema The Gold Standard of Treatment for Lymphedema
When is it lymphedema, when is it not lymphedema? UNDERSTANDING EDEMA John Mulligan, RMT/CLT-LANA Learning Objectives How to identify stages of lymphedema The Gold Standard of Treatment for Lymphedema
What is Lymphoedema? Incidence and Prevalence
 What is Lymphoedema? Incidence and Prevalence North of England Cancer Network Lymphoedema Conference - A problem shared 8 March 2013 Dr Andrew Hughes Consultant in Palliative Medicine Outline 1) What is
What is Lymphoedema? Incidence and Prevalence North of England Cancer Network Lymphoedema Conference - A problem shared 8 March 2013 Dr Andrew Hughes Consultant in Palliative Medicine Outline 1) What is
June 21, Harry Feliciano, MD, MPH Senior Medical Director Part A Policy Palmetto GBA PO Box (JM) AG-275 Columbia, SC 29202
 June 21, 2018 Harry Feliciano, MD, MPH Senior Medical Director Part A Policy Palmetto GBA PO Box 100238 (JM) AG-275 Columbia, SC 29202 Submitted electronically: A.Policy@PalmettoGBA.com RE: Proposed LCD
June 21, 2018 Harry Feliciano, MD, MPH Senior Medical Director Part A Policy Palmetto GBA PO Box 100238 (JM) AG-275 Columbia, SC 29202 Submitted electronically: A.Policy@PalmettoGBA.com RE: Proposed LCD
LYMPHEDEMA GOALS FOR TODAY WELL-INTENTIONED, BUT. the more you know TEDS. Diuretics. Prescribe compression garments without first reducing edema
 LYMPHEDEMA the more you know GOALS FOR TODAY WELL-INTENTIONED, BUT TEDS Recognize full Continuum of Lymphedema stages Identify Range of Lymphedema Diagnoses Differentiate Effective Treatment Options from
LYMPHEDEMA the more you know GOALS FOR TODAY WELL-INTENTIONED, BUT TEDS Recognize full Continuum of Lymphedema stages Identify Range of Lymphedema Diagnoses Differentiate Effective Treatment Options from
GUIDELINES FOR SELF MANAGEMENT OF LYMPHOEDEMA. Nicole L. Stout DPT, CLT-LANA,
 GUIDELINES FOR SELF MANAGEMENT OF LYMPHOEDEMA Nicole L. Stout DPT, CLT-LANA, FAPTA nicole.stout@nih.gov @nicolestoutpt Self Management in Lymphedema Prevention and Risk Reduction Secondary Lymphedema
GUIDELINES FOR SELF MANAGEMENT OF LYMPHOEDEMA Nicole L. Stout DPT, CLT-LANA, FAPTA nicole.stout@nih.gov @nicolestoutpt Self Management in Lymphedema Prevention and Risk Reduction Secondary Lymphedema
Flexitouch System. Advanced Pneumatic Compression Therapy. An Effective At-Home Treatment for Chronic Swelling Associated with Lymphedema
 AT-HOME TREATMENT FOR LYMPHEDEMA Flexitouch System Advanced Pneumatic Compression Therapy An Effective At-Home Treatment for Chronic Swelling Associated with Lymphedema AT-HOME TREATMENT FOR LYMPHEDEMA
AT-HOME TREATMENT FOR LYMPHEDEMA Flexitouch System Advanced Pneumatic Compression Therapy An Effective At-Home Treatment for Chronic Swelling Associated with Lymphedema AT-HOME TREATMENT FOR LYMPHEDEMA
Lymphatic Facilitation for Athletic Injuries. Director of Instruction Discoverypoint School of Massage Seattle WA
 Lymphatic Facilitation for Athletic Injuries Pat Archer ATC, LMP Director of Instruction Discoverypoint School of Massage Seattle WA Lymphatic Facilitation A specific lymphatic technique proven as an easy
Lymphatic Facilitation for Athletic Injuries Pat Archer ATC, LMP Director of Instruction Discoverypoint School of Massage Seattle WA Lymphatic Facilitation A specific lymphatic technique proven as an easy
Supporting Information Leaflet (11): Managing Oedema and Circulatory Problems in Neuromuscular Disorders
 Supporting Information Leaflet (11): Managing Oedema and Circulatory Problems in Neuromuscular Disorders Oedema, sometimes known as Lymphoedema or fluid retention is the build up of fluid and other elements
Supporting Information Leaflet (11): Managing Oedema and Circulatory Problems in Neuromuscular Disorders Oedema, sometimes known as Lymphoedema or fluid retention is the build up of fluid and other elements
Lymphoedema Level One Course Content
 Lymphoedema Level One Course Content Dear Health Practitioner, The Level One lymphoedema training course offered by the ALERT Education at Macquarie University is open to AHPRA registered health professionals
Lymphoedema Level One Course Content Dear Health Practitioner, The Level One lymphoedema training course offered by the ALERT Education at Macquarie University is open to AHPRA registered health professionals
Use of a velcro wrap system in the management of lower limb lymphoedema/chronic oedema. Sue Lawrance
 Use of a velcro wrap system in the management of lower limb lymphoedema/chronic oedema Sue Lawrance Abstract Lymphoedema and chronic lower limb oedema are conventionally treated with multi-layer bandaging,
Use of a velcro wrap system in the management of lower limb lymphoedema/chronic oedema Sue Lawrance Abstract Lymphoedema and chronic lower limb oedema are conventionally treated with multi-layer bandaging,
VENIPUNCTURE AND LYMPHEDEMA
 VENIPUNCTURE AND LYMPHEDEMA AUTHOR: LYNN HADAWAY, M.ED., RN, BC, CRNI THE CLINICAL QUESTION Is it acceptable to perform venipuncture or VAD insertion on the ipsilateral arm after any type of breast cancer
VENIPUNCTURE AND LYMPHEDEMA AUTHOR: LYNN HADAWAY, M.ED., RN, BC, CRNI THE CLINICAL QUESTION Is it acceptable to perform venipuncture or VAD insertion on the ipsilateral arm after any type of breast cancer
Impact of BIS Technology
 Skilled nursing leaders know that the number of women surviving breast cancer is rising. While this is good news, survivorship care has grown more complex and challenging for clinicians in skilled nursing
Skilled nursing leaders know that the number of women surviving breast cancer is rising. While this is good news, survivorship care has grown more complex and challenging for clinicians in skilled nursing
Treatment. A Patient s Guide. Patient s Name. Clinician s Name
 Treatment A Patient s Guide Patient s Name Clinician s Name Introduction This booklet has been developed to help patients understand how the Huntleigh Healthcare LymphAssist machine can help in the management
Treatment A Patient s Guide Patient s Name Clinician s Name Introduction This booklet has been developed to help patients understand how the Huntleigh Healthcare LymphAssist machine can help in the management
REVIEW. Arm Edema in Breast Cancer Patients. Virginia S. Erickson, Marjorie L. Pearson, Patricia A. Ganz, John Adams, Katherine L.
 REVIEW Arm Edema in Breast Cancer Patients Virginia S. Erickson, Marjorie L. Pearson, Patricia A. Ganz, John Adams, Katherine L. Kahn The improvement in the life expectancy of women with breast cancer
REVIEW Arm Edema in Breast Cancer Patients Virginia S. Erickson, Marjorie L. Pearson, Patricia A. Ganz, John Adams, Katherine L. Kahn The improvement in the life expectancy of women with breast cancer
Lymphatic Research and Biology. Lymphatic Research and Biology:
 Lymphatic Research and Biology Lymphatic Research and Biology: http://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/lymphatic The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations Journal:
Lymphatic Research and Biology Lymphatic Research and Biology: http://mc.manuscriptcentral.com/lymphatic The Standard of Care for Lymphedema: Current Concepts and Physiological Considerations Journal:
Journal of Novel Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation. Hümeyra Kiloatar PT* Abstract. Introduction. Case Report ISSN
 Open Access Journal of Novel Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Case Report ISSN 2573-6264 The efficacy of complex Decongestive Physiotherapy in patients with Bilateral Primary Lower Extremity Lymphedema
Open Access Journal of Novel Physiotherapy and Rehabilitation Case Report ISSN 2573-6264 The efficacy of complex Decongestive Physiotherapy in patients with Bilateral Primary Lower Extremity Lymphedema
Programmable Intermittent Pneumatic Compression as a Component of Therapy. for Breast Cancer Treatment-Related Truncal and Arm Lymphedema
 Programmable Intermittent Pneumatic Compression as a Component of Therapy for Breast Cancer Treatment-Related Truncal and Arm Lymphedema Tina M. Hammond, PTA, CLT-LANA Washington Hospital Lymphedema Services
Programmable Intermittent Pneumatic Compression as a Component of Therapy for Breast Cancer Treatment-Related Truncal and Arm Lymphedema Tina M. Hammond, PTA, CLT-LANA Washington Hospital Lymphedema Services
COURSE INFORMATION. Professional Training in the Original Dr. Vodder Method of Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD) and Combined Decongestive Therapy (CDT)
 Professional Training in the Original Dr. Vodder Method of Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD) and Combined Decongestive Therapy (CDT) Post Graduate Certificate in MLD & CDT COURSE INFORMATION Jan Douglass CONTENTS
Professional Training in the Original Dr. Vodder Method of Manual Lymph Drainage (MLD) and Combined Decongestive Therapy (CDT) Post Graduate Certificate in MLD & CDT COURSE INFORMATION Jan Douglass CONTENTS
Translating Evidence into Practice: Primary Cutaneous Melanoma Guidelines. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
 American Academy of Dermatology 2018 Annual Meeting San Diego, CA, February 17, 2018 Translating Evidence into Practice: Primary Cutaneous Melanoma Guidelines. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Christopher Bichakjian,
American Academy of Dermatology 2018 Annual Meeting San Diego, CA, February 17, 2018 Translating Evidence into Practice: Primary Cutaneous Melanoma Guidelines. Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Christopher Bichakjian,
LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE
 LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y
LYMPHOEDEMA FAISAL GHANI SIDDIQUI MBBS; FCPS; PGDIP-BIOMEDICAL ETHICS; MCPS-HPE PROFESSOR OF SURGERY & DIRECTOR, PROFESSIONAL DEVELOPMENT CENTRE J I N N A H S I N D H M E D I C A L U N I V E R S I T Y
Combined Modality Treatment of Lymphedema using the ReidSleeve and the BioCompression/Optiflow System.
 Combined Modality Treatment of Lymphedema using the ReidSleeve and the BioCompression/Optiflow System. Renee Robinson, Lisa A Massa PT CLT, Jennifer Maddox, PT, Nancy Guillett, LMT, CLT- LANA, Katherine
Combined Modality Treatment of Lymphedema using the ReidSleeve and the BioCompression/Optiflow System. Renee Robinson, Lisa A Massa PT CLT, Jennifer Maddox, PT, Nancy Guillett, LMT, CLT- LANA, Katherine
Clinical Policy Title: Lymphedema garments
 Clinical Policy Title: Lymphedema garments Clinical Policy Number: 14.02.11 Effective Date: September 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: July 20, 2017 Most Recent Review Date: August 17, 2017 Next Review Date:
Clinical Policy Title: Lymphedema garments Clinical Policy Number: 14.02.11 Effective Date: September 1, 2017 Initial Review Date: July 20, 2017 Most Recent Review Date: August 17, 2017 Next Review Date:
AMERICAN JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN NURSING RESEARCH
 15 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN NURSING RESEARCH e - ISSN 2349-0691 Print ISSN - XXXX-XXXX Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajanr EXERCISES TO PREVENT ARM DYSFUNCTION IN WOMEN FOLLOWING MASTECTOMY
15 AMERICAN JOURNAL OF ADVANCES IN NURSING RESEARCH e - ISSN 2349-0691 Print ISSN - XXXX-XXXX Journal homepage: www.mcmed.us/journal/ajanr EXERCISES TO PREVENT ARM DYSFUNCTION IN WOMEN FOLLOWING MASTECTOMY
Lymphedema. Kelly Reichart, DNP, RN. About 246,660 women
 ADVANCED PRACTICE ASSOCIATE EDITOR DEBORAH "HUTCH" ALLEN, PhD, RN, CNS, FNP-BC, AOCNP Downloaded on 11 28 2018. Single-user license only. Copyright 2018 by the Oncology Nursing Society. For permission
ADVANCED PRACTICE ASSOCIATE EDITOR DEBORAH "HUTCH" ALLEN, PhD, RN, CNS, FNP-BC, AOCNP Downloaded on 11 28 2018. Single-user license only. Copyright 2018 by the Oncology Nursing Society. For permission
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Breast Brachytherapy for Accelerated Partial Breast Radiotherapy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: breast_brachytherapy_for_accelerated_partial_breast_radiotherapy
Corporate Medical Policy Breast Brachytherapy for Accelerated Partial Breast Radiotherapy File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: breast_brachytherapy_for_accelerated_partial_breast_radiotherapy
Taken into account multidiscilinary aspect of Vascular Compression
 The Vascular Center : A model to improve patient care Taken into account multidiscilinary aspect of Vascular Compression F. Vin C. Gardon-Mollard Compression Therapy is an efficient treatment for the management
The Vascular Center : A model to improve patient care Taken into account multidiscilinary aspect of Vascular Compression F. Vin C. Gardon-Mollard Compression Therapy is an efficient treatment for the management
AdvaMed Medtech Value Assessment Framework in Practice
 AdvaMed Medtech Value Assessment Framework in Practice Application of the Medtech Value Assessment Framework to Cymedica s e-vive System Value Framework Overview In response to the growing need to demonstrate
AdvaMed Medtech Value Assessment Framework in Practice Application of the Medtech Value Assessment Framework to Cymedica s e-vive System Value Framework Overview In response to the growing need to demonstrate
Lymphedema: Early Detection and Quantitative Assessment
 Lymphedema: Early Detection and Quantitative Assessment Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu Lymphedema Physiology
Lymphedema: Early Detection and Quantitative Assessment Harvey N. Mayrovitz PhD Professor of Physiology College of Medical Sciences Nova Southeastern University mayrovit@nova.edu Lymphedema Physiology
Economic Benefits of BIS-Aided Assessment of Post-BC Lymphedema in the United States
 n clinical n Economic Benefits of BIS-Aided Assessment of Post-BC Lymphedema in the United States Sara P. Bilir, MS; Mitchell P. DeKoven, MHSA; and Juliet Munakata, MS Objectives: To estimate the economic
n clinical n Economic Benefits of BIS-Aided Assessment of Post-BC Lymphedema in the United States Sara P. Bilir, MS; Mitchell P. DeKoven, MHSA; and Juliet Munakata, MS Objectives: To estimate the economic
Lexi Harlow, PT, DPT, CLT Seattle Cancer Care Alliance
 Lexi Harlow, PT, DPT, CLT Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Importance of Rehabilitation In Oncology Care Patient and family centered care Individualized treatment and management of side effects from cancer
Lexi Harlow, PT, DPT, CLT Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Importance of Rehabilitation In Oncology Care Patient and family centered care Individualized treatment and management of side effects from cancer
ONCOLOGY REHABILITATION AND SECONDARY LYMPHEDEMA THE PROSPECTIVE SURVEILLANCE MODEL
 ONCOLOGY REHABILITATION AND SECONDARY LYMPHEDEMA THE PROSPECTIVE SURVEILLANCE MODEL Nicole L. Stout DPT, CLT-LANA, FAPTA nicole.stout@nih.gov @nicolestoutpt Prospective Surveillance Model Diagnosis Pre-Operative
ONCOLOGY REHABILITATION AND SECONDARY LYMPHEDEMA THE PROSPECTIVE SURVEILLANCE MODEL Nicole L. Stout DPT, CLT-LANA, FAPTA nicole.stout@nih.gov @nicolestoutpt Prospective Surveillance Model Diagnosis Pre-Operative
The management of patients with lymphoedema
 Juxta-Fit compression garments in lymphoedema management Julie Mullings Julie Mullings, Tissue Viabilty Specialist Nurse, University Hospital of South Manchester - Community Services Email: Julie.mullings@uhsm.nhs.uk
Juxta-Fit compression garments in lymphoedema management Julie Mullings Julie Mullings, Tissue Viabilty Specialist Nurse, University Hospital of South Manchester - Community Services Email: Julie.mullings@uhsm.nhs.uk
Axillary Reverse Mapping to Reduce the Incidence of Lymphedema
 Axillary Reverse Mapping to Reduce the Incidence of Lymphedema Nathalie Johnson,MD,FACS Medical Director, Legacy Cancer Institute and Breast Health Centers Portland,Oregon Objectives for Learning Understand
Axillary Reverse Mapping to Reduce the Incidence of Lymphedema Nathalie Johnson,MD,FACS Medical Director, Legacy Cancer Institute and Breast Health Centers Portland,Oregon Objectives for Learning Understand
Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema
 Medical Policy Manual Durable Medical Equipment, Policy No. 82 Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Next Review: June 2018 Last Review: June 2017 Effective: August 1, 2017 IMPORTANT
Medical Policy Manual Durable Medical Equipment, Policy No. 82 Bioimpedance Devices for Detection and Management of Lymphedema Next Review: June 2018 Last Review: June 2017 Effective: August 1, 2017 IMPORTANT
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MANUAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE MASSAGE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI
 DOWNLOAD OR READ : MANUAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE MASSAGE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 manual lymphatic drainage massage manual lymphatic drainage massage pdf manual lymphatic drainage massage Manual Lymphatic
DOWNLOAD OR READ : MANUAL LYMPHATIC DRAINAGE MASSAGE PDF EBOOK EPUB MOBI Page 1 Page 2 manual lymphatic drainage massage manual lymphatic drainage massage pdf manual lymphatic drainage massage Manual Lymphatic
Early detection and prevention of lymphoedema
 Early detection and prevention of lymphoedema Katie Riches Senior Research Nurse Derby Hospitals NHSF Trust Background: Derby Lymphoedema Service Three lymphoedema services based in Acute Hospitals at
Early detection and prevention of lymphoedema Katie Riches Senior Research Nurse Derby Hospitals NHSF Trust Background: Derby Lymphoedema Service Three lymphoedema services based in Acute Hospitals at
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND COMPRESSION GARMENTS. POLICY NUMBER: CATEGORY: Equipment/ Supplies
 MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including
MEDICAL POLICY SUBJECT: SURGICAL STOCKINGS AND PAGE: 1 OF: 7 If a product excludes coverage for a service, it is not covered, and medical policy criteria do not apply. If a commercial product (including
Medical Policy. MP Surgical Treatments for Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema
 Medical Policy MP 7.01.162 Surgical Treatments for Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema BCBSA Ref. Policy: 7.01.162 Last Review: 07/25/2018 Effective Date: 10/30/2018 Section: Surgery Related Policies 1.01.18
Medical Policy MP 7.01.162 Surgical Treatments for Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema BCBSA Ref. Policy: 7.01.162 Last Review: 07/25/2018 Effective Date: 10/30/2018 Section: Surgery Related Policies 1.01.18
Phlebo Press. Use In: Phlebo Press
 Phlebo Press Use In: Phlebo Press is a sequential pneumatic compression system specially designed for efficient reduction and management of peripheral edema, such as lymphedema and ulceration associated
Phlebo Press Use In: Phlebo Press is a sequential pneumatic compression system specially designed for efficient reduction and management of peripheral edema, such as lymphedema and ulceration associated
A Proposed Exercise Pathway for Recovery. Enhancing the lymphatics during recovery. Understand how exercise can enhance lymphatic function
 A Proposed Exercise Pathway for Recovery Enhancing the lymphatics during recovery Review of the Lymphatic System Understand how exercise can enhance lymphatic function Finding your limits Evidence-based
A Proposed Exercise Pathway for Recovery Enhancing the lymphatics during recovery Review of the Lymphatic System Understand how exercise can enhance lymphatic function Finding your limits Evidence-based
30-31 March Organized by Women s Health Specialty Group, HKPA Limited Co-joint with the HEMAX Health Products Company Limited
 Advanced Course in Management of Lymphatic system and lymphedema 30-31 March 2013 Organized by Women s Health Specialty Group, HKPA Limited Co-joint with the HEMAX Health Products Company Limited Instructor
Advanced Course in Management of Lymphatic system and lymphedema 30-31 March 2013 Organized by Women s Health Specialty Group, HKPA Limited Co-joint with the HEMAX Health Products Company Limited Instructor
Lymphedema. Patient Education. Information for women with breast cancer. What is lymphedema? Surgical Specialties Center
 Patient Education Information for women with breast cancer This handout describes what lymphedema is, the steps you can take to lower your risk, and what signs to look for. Women who have been treated
Patient Education Information for women with breast cancer This handout describes what lymphedema is, the steps you can take to lower your risk, and what signs to look for. Women who have been treated
Exercise & Breast Cancer Recovery
 Exercise & Breast Cancer Recovery LEARNING OBJECTIVES Demonstrate an understanding of the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer Demonstrate an understanding of how breast cancer surgery and treatment
Exercise & Breast Cancer Recovery LEARNING OBJECTIVES Demonstrate an understanding of the diagnosis and treatment of breast cancer Demonstrate an understanding of how breast cancer surgery and treatment
Utilization of bioimpedance spectroscopy in the prevention of chronic breast cancer-related lymphedema
 Breast Cancer Res Treat (2017) 166:809 815 DOI 10.1007/s10549-017-4451-x CLINICAL TRIAL Utilization of bioimpedance spectroscopy in the prevention of chronic breast cancer-related lymphedema David I. Kaufman
Breast Cancer Res Treat (2017) 166:809 815 DOI 10.1007/s10549-017-4451-x CLINICAL TRIAL Utilization of bioimpedance spectroscopy in the prevention of chronic breast cancer-related lymphedema David I. Kaufman
ONS Putting Evidence into Practice Evidence Table: Lymphedema Literature updated through January 2011
 Page 1 of 60 Complete decongestive therapy: RECOMMENDED FOR PRACTICE Karadibak et al, 2008 Primary Aim: to evaluate the effects of kinesiophobia, quality of life, and home exercise programs on women with
Page 1 of 60 Complete decongestive therapy: RECOMMENDED FOR PRACTICE Karadibak et al, 2008 Primary Aim: to evaluate the effects of kinesiophobia, quality of life, and home exercise programs on women with
Soran, A., Ozmen, T. et al. Lymphat Res Biol 12(4):
 Early Detection and Treatment The importance of detection of subclinical lymphedema for the prevention of breast cancer-related clinical lymphedema after axillary lymph node dissection; a prospective observational
Early Detection and Treatment The importance of detection of subclinical lymphedema for the prevention of breast cancer-related clinical lymphedema after axillary lymph node dissection; a prospective observational
Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2)
 Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2) Definition Vascular surgery is the specialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of congenital and acquired diseases of the
Vascular Surgery Rotation Objectives for Junior Residents (PGY-1 and 2) Definition Vascular surgery is the specialty concerned with the diagnosis and management of congenital and acquired diseases of the
Measurement Issues in Anthropometric Measures of Limb Volume Change in Persons at Risk for and Living with Lymphedema: A Reliability Study
 J. Pers. Med. 2015, 5, 341-353; doi:10.3390/jpm5040341 Article OPEN ACCESS Journal of Personalized Medicine ISSN 2075-4426 www.mdpi.com/journal/jpm/ Measurement Issues in Anthropometric Measures of Limb
J. Pers. Med. 2015, 5, 341-353; doi:10.3390/jpm5040341 Article OPEN ACCESS Journal of Personalized Medicine ISSN 2075-4426 www.mdpi.com/journal/jpm/ Measurement Issues in Anthropometric Measures of Limb
Educational Goals and Objectives for Rotations on: Breast, Wound and Plastic Surgery
 Educational Goals and Objectives for Rotations on: Breast, Wound and Plastic Surgery Goal The goal of the Breast Surgery rotation is to develop the knowledge, skills and attitudes necessary to evaluate,
Educational Goals and Objectives for Rotations on: Breast, Wound and Plastic Surgery Goal The goal of the Breast Surgery rotation is to develop the knowledge, skills and attitudes necessary to evaluate,
CASE REPORT Blocking of the Lymphatic Vessel in Lymphedema
 CASE REPORT Blocking of the Lymphatic Vessel in Lymphedema Hisako Hara, MD, and Makoto Mihara, MD Department of Lymphatic and Reconstructive Surgery, Saiseikai Kawaguchi General Hospital, Saitama, Japan
CASE REPORT Blocking of the Lymphatic Vessel in Lymphedema Hisako Hara, MD, and Makoto Mihara, MD Department of Lymphatic and Reconstructive Surgery, Saiseikai Kawaguchi General Hospital, Saitama, Japan
December 18, Submitted Electronically
 December 18, 2017 Seema Verma, Administrator Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Department of Health and Human Services Attn: CMS-4182-P PO Box 8013 Baltimore, MD 21244-8013 Submitted Electronically
December 18, 2017 Seema Verma, Administrator Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services Department of Health and Human Services Attn: CMS-4182-P PO Box 8013 Baltimore, MD 21244-8013 Submitted Electronically
SUCTION ASSISTED PROTEIN LIPECTOMY (SAPL) EVEN FOR THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC FIBROTIC AND SCARIFIED LOWER EXTREMITY LYMPHEDEMA
 36 Lymphology 49 (2016) 36-41 SUCTION ASSISTED PROTEIN LIPECTOMY (SAPL) EVEN FOR THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC FIBROTIC AND SCARIFIED LOWER EXTREMITY LYMPHEDEMA M. Lee, L. Perry, J. Granzow Emory University
36 Lymphology 49 (2016) 36-41 SUCTION ASSISTED PROTEIN LIPECTOMY (SAPL) EVEN FOR THE TREATMENT OF CHRONIC FIBROTIC AND SCARIFIED LOWER EXTREMITY LYMPHEDEMA M. Lee, L. Perry, J. Granzow Emory University
A NOVEL, VALIDATED METHOD TO QUANTIFY BREAST CANCER-RELATED LYMPHEDEMA (BCRL) FOLLOWING BILATERAL BREAST SURGERY
 64 Lymphology 46 (2013) 64-74 A NOVEL, VALIDATED METHOD TO QUANTIFY BREAST CANCER-RELATED LYMPHEDEMA (BCRL) FOLLOWING BILATERAL BREAST SURGERY C.L. Miller, M.C. Specht, N. Horick, M.N. Skolny, L.S. Jammallo,
64 Lymphology 46 (2013) 64-74 A NOVEL, VALIDATED METHOD TO QUANTIFY BREAST CANCER-RELATED LYMPHEDEMA (BCRL) FOLLOWING BILATERAL BREAST SURGERY C.L. Miller, M.C. Specht, N. Horick, M.N. Skolny, L.S. Jammallo,
DOES DEEP TISSUE MASSAGE HAVE AN IMPACT ON DIMENSION IN THE HIPS AND THIGHS?
 DOES DEEP TISSUE MASSAGE HAVE AN IMPACT ON DIMENSION IN THE HIPS AND THIGHS? A Study Done By Charles W. Wiltsie III, LMT, NCBTMB INTRODUCTION Does deep tissue massage have an impact on the hips and thighs?
DOES DEEP TISSUE MASSAGE HAVE AN IMPACT ON DIMENSION IN THE HIPS AND THIGHS? A Study Done By Charles W. Wiltsie III, LMT, NCBTMB INTRODUCTION Does deep tissue massage have an impact on the hips and thighs?
