The New Era of Finance: Neurofinance and Investment behavior
|
|
|
- Paul Atkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Available online at : pp. 47 ~ 56 Thomson Reuters ID: L The New Era of Finance: Neurofinance and Investment behavior Dr. Priya Jinda* Assistant Professor MMIM,MMU, Mullana Shilpa Bahl** Research Scholar MMIM,MMU, Mullana Article history: Abstract Received July 16 th, 2016; Approved July 25 th, 2016; Available online: Aug 2 st, Keyword : Human Mind, Investment Decision Making, Neurofinance, Neuroscience This paper highlight the effect of neurofinance which is the study of brain of humans and their financial decision making behavior which explains the cause why humans are not balanced as per the rules of the conventional theory of finance. We have tried to explain and present the literature review and fusion of the literature on neurofinance in this paper. Neuroscience is the subject which studies the functioning of human mind and how the financial decisions making process are influenced by the affective of neurological basis. When the neuroscience is studied with respect to investment environment, it is explained in form of Neurofinance. In this paper, role of important brain parts and enzymes like, Dopamine, Serotonin, Amygdala, Prefrontal Cortex etc at the events of loss, gain or volatility of stock price etc has been discussed Copyright 2016 The Author. Published by International Journal of Finance and Marketing. This is an open access article under the All rights reserved. Authors Correspondence : Shilpa Bahl* MMIM,MMU, Mullana Research Scholar 47
2 Introduction On a regular basis it has been found that, the decisions made by the investors are rational in nature. According to Markowitz (1952), he proposed the modern portfolio theory (MPT), which shows that when rational investors make a decision for selection of portfolio is mainly depend on the two categories, that is projected rewards and variations which helps to optimize their portfolios they should diversify them. MPT is based on the expected utility theory; the biggest disadvantage of this model is that it fails to explain how investors make their decision in reality, where individuals disobey the rules of expected utility. It can be clearer from this example as many investors are comfortable to invest in some category and do not diversify their portfolio and these types of investors are not risk averse. Therefore, to choose the optimal portfolio with the help of efficient deviations, gave rise to new era of finance i.e. behavioral finance and behavioral economics. According to Kahneman and Tversky s (1974, 1979), they work on behavioral finance studies, in which they discussed about the different biases, heuristics and prospect theory which tells about the investors behavior and decision making by them in indecisive and uncertain situations, they also enlighten the performance of the investor while making the financial decisions but they fail to clarify why and how these behaviors occur (Edwards, 2004; Tseng, 2006; Kuhnen, 2007; Sapra and Zak, 2008). The study of human brain gives the clarification why and how of financial decision making behaviors occurs. To understand the human financial decision making behaviour more enormously, it gave a rise the study of field called neurofinance. Neurofinance is the study of brain of humans and their financial decision making behavior which explains the cause why human s behavior are not balanced as per the rules of the conventional theory of finance. We have tried to explain and present the literature review and fusion of the literature on neurofinance in this paper. Neurofinance has developed out of neuroscience which tries to explain the working of the brain of the humans when decisions are taken by them. It also studies about the behavior of the investors prior to making the choice of the investment. With the help of neuroscience researchers, it helps to tell about the how affect influences the financial decision making and many psychological biases which also influence the decision choices. Neuroscience is the subject which studies the functioning of human mind and how the financial decisions making process are influenced by the affective of neurological basis. According to (Peterson, 2007a, b), in his research he emphasize on decision making process with the help of 48
3 innovative tools and knowledge available, it also observed the transform in the brain which can be experiential in real time which helps to understand the process of decision making. According to neuroscience, the human brain is categorized into three main parts. 1. The forebrain 2. Mid-brain 3. Hind-brain The largest and rational part of the brain is known as forebrain. The forebrain is also known as the cerebrums which consist of the cortex and the limbic system. According to (Morse, 2006; Peterson, 2007a, b), the cortex contain of the neopallium and the prefrontal cortex, is connected with advanced brain functions which includes thinking and action and because of it is also known as the balanced part of the brain. The limbic system is called as expressive brain which is consists in the handing out of the feeling and also carries the memories. The limbic system is the foundation of ancient inspirations and feelings which includes fear and enthusiasm, it also carries the insula and nucleus accumbens. The fore brain helps in while taking a financial decision and the expressive part of the brain, which is common between animal and human beings and is measured more ancient and the cognitive part of the brain, it is the part which is more energetic in the human beings, which is also taken as the superior brain, is of present origin. The function of body we do such as mental picture, hearing, eye movement and body movement is because of the mid-brain which consists of the tectumand tegmentum. The hind-brain consists of the cerebellum which is known as little brain, the pons and the medulla oblongata, which works simultaneously to maintain vital bodily processes. The main purpose of this paper is on development of neurofinance as a field of study to understand the behavior of the investor and the process of choice of the investment decision. Neurofinance: An Overview Neurofinance is an emerging field which provides lots of explanation of the investor s behavior by using the tool of Neuroscience. In other way, neurofinance can be explained as a discipline which attempts to give a better understanding of human decisions related to money by using brain science and economic theory. 49
4 Questions like, Role of emotion in decision making? What people think about an uncertain decision? People s feelings towards risk, are of interest for a wealth manager as well as a neuroeconomist. At the instance of investment decision making, investors encounters with the emotions like anxiety, fear, happiness, feeling of satisfaction or dissatisfaction with the returns generated by their investments. The above mentioned feelings are also associated with the risk component of the investment alternatives. Now we will discuss above mentioned feelings with reference to neurophysiology and their implication on investor behavior. Neurophysiology deals with the structures and secretion from brain responsible for investor behavior. Neurofinance has come forward as a derivation of neuroeconomics and field to the study and relevance of neuroscience while taking a investment decision making by the individual investors. The main purpose of the study of neurofinance is to concentrate on the monetary decision making while studying the execution of the brain when it stumble upon a financial decision choices. Techniques to determine the brain activity are various and comprise of functional magnetic resonance imaging (FMRI), positron emission tomography, EEG, eye tracking or blood pressure. Literature Review Kuhnen and Knutson (2005), they are the first one who develops the neurofinance study by using brain. In their study they present the function of sentiments in financial decision making. Their assessment of brain imaging studies analysis that affect suggest by the expectation of achieve and defeat may bear distinct neural signatures. Lo et al. (2005) also emphasize the function of sentiments method in financial decision making and also originate that the investors respond to both financial gains and losses, underneath the outlook 50
5 that two impetus forces are also part of the limbic system of the brain conduct the individual s decision under threat and ambiguity. Morse (2006), in his paper he stated that the more active the primeval, risk-anticipating brain area, the more risk reluctant the investors are. Peterson (2007a, b), in their research they present the two neurotransmitters namely dopamine and anterior insular. The dopamine (also called the delight element of the brain) which is linked with craving and serotonin which is linked with shyness. The anterior insular is linked with expressive experience and mindful thoughts, which includes feelings of hurt, rage, pleasure, repulsion, terror and irritation. Stenstrom and Saad (2011), in their analysis on testosterone, risk-taking and betting and establish that, high-testosterone investors have a higher craving for monetary risk-taking and are more probable to surrender to definite impulsivity-related pathologies. Objectives 1. To present a analysis and creation of the literature on neurofinance. 2. The relation between neurofinance and investment decision of the investors. 3. To present the difference between standard finance, behavioral finance and neurofinance. Neuro finance and Investment Decisions Usually we find that investor s behavior is affected by certain emotions. Optimistic expressive states such as enthusiasm leads to risk taking behavior and to be overconfident in their capacity to estimate investment choices as compare to pessimistic emotions such as nervousness have the contradictory effects like over investigation, framing etc. Beliefs also play important role in indentifying any decision making process. Beliefs are mental state which forces to continue a optimistic expressive state by overlook that piece of information which contradicts with individuals prior choices. Cognitive Dissonance is one behavioral bias developed because of beliefs and the discomfort developed at the time of contradiction of belief and the latest information. The physiological process of developing such cognitive dissonance in investment environment can be well explained in form of Neuroefinance. 51
6 Now we will discuss above mentioned feelings like overconfidence, risk aversion, mental accounting, anxiety etc with reference to neurophysiology and their implication on investor behavior. Neuroscience deals with the structures and secretion from brain responsible for investor behavior. Brain secretions responsible for Investor behavior Role of Dopamine Dopamine is a chemical secreted in brain at the time of a feeling of pleasure. More quantity of dopamine is secreted at the time of unexpected profits earned easily. At the same time when investors face an unexpected loss, the secretion of dopamine completely stops, and the person feels depressed. Suggestion on Investment Decisions As Dopamine is responsible for the feeling of pleasure and depression, dopamine influences the risk taking behavior of investors. Dopamine secretion rests on an increased level when the pred ictions made by investors are bringing gains to him, where as dopamine level reduces to a great extent if the predictions bring losses. Dopamine is responsible for behavioral biases like Herd Behavior, Overconfidence and Optimism in the investors. Role of Serotonin Serotonin is a transmitter available in central nervous system and digestive tract. Serotonin is responsible for the feelings of anxiety, depression and appetite. Suggestion on Investment Decisions Level of Serotonin reduces at the times of unfulfilled expectations like, investment losses. Such situations lead to depression, anxiety and loss of hunger in the investor. Under the influence of deep anxiety, investor may take erratic decisions to avoid losses and depression, but it may further lead to multiplied losses and high transaction costs. 52
7 Reduced levels of serotonin cause investors to sell winning positions too early.loss Aversion may be a result of reduced levels of serotonin. Take the money and run is the tendency developed because of reduced supply of serotonin. Brain structures responsible for Investor behavior Role of Amygdala Almond shaped body situated in brain s temporal medial lobe is responsible for feeling of emotions like fear, pleasure, developing phobia and post traumatic stress. Amygdala is responsible for fight or flight behavior of investors. Suggestion on Investment Decisions Selling behavior of investors in falling markets are due to functioning of amygdale. Investors want to flight away from the falling markets because of the feeling of fear, but actually it is the time to fight with the bear phase and add some fundamentally strong stocks at corrected value. Role of Prefrontal Cortex The prefrontal cortex of brain is responsible of complex cognitive decision making in social behavior and expression of personality. The prefrontal cortex is responsible for memorizing, analyzing and drawing conclusions from different situations. Suggestion on Investment Decisions Whenever investors commit cognitive errors, it means that prefrontal cortex does not have proper data in form of accurate, appropriate and update information for drawing decisions. Education in form of either self education or advice of professional advisor is required to provide proper data to prefrontal cortex to have a better decision making. Role of Nucleus Accumbens and Anterior Cingulate Nucleus Accumbens is a group of neurons located behind the ears of a human being. This group of neurons plays a role in developing addictive behavior. 53
8 Anterior Cingulate, which is the frontal portion of cingulated cortex plays important role in reward anticipation and decision amking. Together, the nucleus Accumbens and anterior cingulated help people to identify patterns and evaluate alternatives. Suggestion on Investment Decisions As the nucleus accumbens and anterior cingulate are responsible for patterns, they make investors to believe on trends without seeking any detailed explanations. For Example: if a company is declaring every quarter that they have increased their earnings estimates and with the response of this information the prices of stock increases in the market. Now after every quarter the above two parts of human brain will make a pattern that after every quarter the price of stock are going to show a jump, without making any detailed fundamental analysis about the stock. Also this has been observe that most of the investors commit the errors of pattern recognition in investment and prone to miss the investment opportunity in case of companies which have inconsistence earnings. Difference between Standard finance, behavioural finance and Neurofinance Standard Finance Behavioral Finance Neuro Finance Standard Finance believes in Behavioral Finance believe in Neurofinance studies the existence of Rational Markets existence of irrational markets investment behaviour of and Rational investors and irrational Investors people who were emotional were not rational. Standard helps in building a Behavioral finance helps in Neuro finance helps in rational portfolio Standard Finance theories rest on the assumptions that oversimplify the real market conditions building an optimal portfolio Explanations of behavioral finance are in light with the real problems associated with human psychology building an optimal portfolio. Neurofinance applies neurotechnology to recognize the behaviors of the financial market investors. Standard Finance explains how Behavioral Finance explains how Neuro finance explains how investor should behave does investor behave and why the investor behavior occurs. Standard Finance assumptions Behavioral finance assumptions Neurofinance helps to 54
9 believe in idealized financial behavior believe in observed financial behavior understand the internal procedures that lead to the thinking that visible as an external action. Conclusion Homo sapiens are a collection of multifaceted structure which is prejudiced by diverse factors that affect their decision making choices. Neurofinance is an extremely new discipline in the era of finance. It aims to relate the brain functioning to the investment behaviour and one of the necessary conclusion of the field pertains to the essential role of sentiments in monetary decision making. Study of neurophysiology in form of neuroeconomics does not end with the limited study, but it is an upcoming field of modern finance, in which the study of human behavior and responses can be extended to the extent of study of neurology and neuroscience to seek the answers of biasness in the investor s behavior. References 1. Edwards, D. (2004), What is neurofinance?, August 9, available at: com/archives/2004/08/09/what_is_neurofinance.php. 2. Kuhnen, C.M. (2007), On money, risk and the brain, March 5, available at: northwestern.edu/faculty/kuhnen/htm/neuroeconreadinggroup/moneyriskbrain.pdf. 3. Kuhnen, C.M. and Knutson, B. (2005), The neural basis of financial risk taking, Neuron, Vol. 47, pp Kahneman, D. and Tversky, A. (1974), Judgment under uncertainty: heuristics and biases, Science, Vol. 185 No Kahneman, D. and Tversky, A. (1979), Prospect theory: an analysis of decision making under risk, Econometrica, Vol. 47 No Lo, A.W., Repin, D.V. and Steenbarger, B.N. (2005), Fear and greed in financial markets: a clinical study of day-traders,cognitiveneuroscientificfoundations of Behavior,Vol. 95No. 2, pp Markowitz, H.M. (1952), Portfolio selection, Journal of Finance, Vol. 7 No. 1, pp Morse, G. (2006), Decisions and desire, Harvard Business Review, January. 55
10 9. Tseng, K.C. (2006), Behavioral finance, bounded rationality, neuro-finance, and traditional finance, Investment Management and Financial Innovations, Vol. 3 No. 4, pp The IUP Journal of Behavioral Finance, IUP Publications, March & June 2010, Vol. VII, No. 1 & The IUP Journal of Behavioral Finance, IUP Publications, Sep 2010, Vol. VII, No Sapra, S.G. and Zak, P.J. (2008), Neurofinance: bridging psychology, neurology, and investor behavior, available at: Peterson, R.L. (2007a), Affect and financial decision-making: how neuroscience can inform market participants, The Journal of Behavioral Finance, Vol. 8 No. 2, pp Peterson, R.L. (2007b), Inside the Investor s Brain: The Power of Mind over Money, Wiley, Hoboken, NJ. 15. Stenstrom, E. and Saad, G. (2011), Testosterone, financial risk-taking, and pathological gambling, Journal of Neuroscience, Psychology, and Economics, Vol. 4 No. 4, pp
Academic year Lecture 16 Emotions LECTURE 16 EMOTIONS
 Course Behavioral Economics Academic year 2013-2014 Lecture 16 Emotions Alessandro Innocenti LECTURE 16 EMOTIONS Aim: To explore the role of emotions in economic decisions. Outline: How emotions affect
Course Behavioral Economics Academic year 2013-2014 Lecture 16 Emotions Alessandro Innocenti LECTURE 16 EMOTIONS Aim: To explore the role of emotions in economic decisions. Outline: How emotions affect
Inside the Investor s Brain: The Power of Mind Over Money
 Inside the Investor s Brain: The Power of Mind Over Money AAII Silicon Valley Sunnyvale, CA January 9, 2010 Richard L. Peterson, M.D. Managing Director MarketPsy Capital LLC (Asset Management) MarketPsych
Inside the Investor s Brain: The Power of Mind Over Money AAII Silicon Valley Sunnyvale, CA January 9, 2010 Richard L. Peterson, M.D. Managing Director MarketPsy Capital LLC (Asset Management) MarketPsych
INVESTOR S PSYCHOLOGY IN INVESTMENT DECISION MAKING: A BEHAVIORAL FINANCE APPROACH
 Volume 119 No. 7 2018, 1253-1261 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu INVESTOR S PSYCHOLOGY IN INVESTMENT DECISION MAKING: A BEHAVIORAL
Volume 119 No. 7 2018, 1253-1261 ISSN: 1311-8080 (printed version); ISSN: 1314-3395 (on-line version) url: http://www.ijpam.eu ijpam.eu INVESTOR S PSYCHOLOGY IN INVESTMENT DECISION MAKING: A BEHAVIORAL
Risk Tolerance and Behavioral Finance
 Risk Tolerance and Behavioral Finance September 11, 2017 by Michael Pompian of IMCA We have seen a powerful recovery in asset prices in the wake of the global financial crisis (GFC). We cannot forget,
Risk Tolerance and Behavioral Finance September 11, 2017 by Michael Pompian of IMCA We have seen a powerful recovery in asset prices in the wake of the global financial crisis (GFC). We cannot forget,
The Neural Basis of Financial Decision Making
 The Neural Basis of Financial Decision Making Camelia M. Kuhnen Kellogg School of Management Northwestern University University of Michigan - August 22, 2009 Dopamine predicts rewards Tobler et al. (2005)
The Neural Basis of Financial Decision Making Camelia M. Kuhnen Kellogg School of Management Northwestern University University of Michigan - August 22, 2009 Dopamine predicts rewards Tobler et al. (2005)
Impact of Cognitive Biases in Investment Decisions of Individual Investors in Stock Market
 Impact of Cognitive Biases in Investment Decisions of Individual Investors in Stock Market Dr. Joychen Manuel*, George Mathew.** *Associate Professor, Department of Business Administration, St.Berchmans.
Impact of Cognitive Biases in Investment Decisions of Individual Investors in Stock Market Dr. Joychen Manuel*, George Mathew.** *Associate Professor, Department of Business Administration, St.Berchmans.
Recap: Introduction & History of Motivation & Emotion (Lecture 01 - Ch 1 & 2, Reeve, 2009)
 Recap: Introduction & History of Motivation & Emotion (Lecture 01 - Ch 1 & 2, Reeve, 2009) 3 Learning outcomes 1. Drives and instincts 2. Theories of motivation, consciousness and volitional behaviour,
Recap: Introduction & History of Motivation & Emotion (Lecture 01 - Ch 1 & 2, Reeve, 2009) 3 Learning outcomes 1. Drives and instincts 2. Theories of motivation, consciousness and volitional behaviour,
Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse. Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver
 Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver NRSC January 28, 2010 Costs: Health, Crime, Productivity Costs in billions of dollars (2002) $400 $350 $400B legal
Brain Imaging studies in substance abuse Jody Tanabe, MD University of Colorado Denver NRSC January 28, 2010 Costs: Health, Crime, Productivity Costs in billions of dollars (2002) $400 $350 $400B legal
An Understanding of Role of Heuristic on Investment Decisions
 International Review of Business and Finance ISSN 0976-5891 Volume 9, Number 1 (2017), pp. 57-61 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com An Understanding of Role of Heuristic on Investment
International Review of Business and Finance ISSN 0976-5891 Volume 9, Number 1 (2017), pp. 57-61 Research India Publications http://www.ripublication.com An Understanding of Role of Heuristic on Investment
The UNDERLYING DYNAMICS of
 1 The UNDERLYING DYNAMICS of FINANCIAL DECISIONS Self Knowledge for Leading a Better Financial Life Josh Gilliam TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION THE ANATOMY OF A FINANCIAL DECISION Your Brain and Money
1 The UNDERLYING DYNAMICS of FINANCIAL DECISIONS Self Knowledge for Leading a Better Financial Life Josh Gilliam TABLE OF CONTENTS INTRODUCTION THE ANATOMY OF A FINANCIAL DECISION Your Brain and Money
Chapter 6 Section 1. The Nervous System: The Basic Structure
 Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Chapter 6 Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure Essential Question: How does studying the biology of the brain give us an understanding of our behavior? Draw or type 2 things you already know
Organization of the nervous system. The withdrawal reflex. The central nervous system. Structure of a neuron. Overview
 Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Overview The nervous system- central and peripheral The brain: The source of mind and self Neurons Neuron Communication Chemical messengers Inside the brain Parts of the brain Split Brain Patients Organization
Motivation, Conflict, Emotion. Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD; FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry
 Motivation, Conflict, Emotion Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD; FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry Motivation Motivation is the psychological feature that arouses an organism to action toward a desired goal and
Motivation, Conflict, Emotion Abdul-Monaf Al-Jadiry, MD; FRCPsych Professor of Psychiatry Motivation Motivation is the psychological feature that arouses an organism to action toward a desired goal and
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind
 Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
Name: Period: Chapter 2 Reading Guide The Biology of Mind The Nervous System (pp. 55-58) 1. What are nerves? 2. Complete the diagram below with definitions of each part of the nervous system. Nervous System
The Nervous System. Biological School. Neuroanatomy. How does a Neuron fire? Acetylcholine (ACH) TYPES OF NEUROTRANSMITTERS
 Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
Biological School The Nervous System It is all about the body!!!! It starts with an individual nerve cell called a NEURON. Synapse Neuroanatomy Neurotransmitters (chemicals held in terminal buttons that
biological psychology, p. 40 The study of the nervous system, especially the brain. neuroscience, p. 40
 biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
biological psychology, p. 40 The specialized branch of psychology that studies the relationship between behavior and bodily processes and system; also called biopsychology or psychobiology. neuroscience,
The Emotional Nervous System
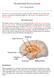 The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
The Emotional Nervous System Dr. C. George Boeree Emotion involves the entire nervous system, of course. But there are two parts of the nervous system that are especially significant: The limbic system
UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN TRINITY COLLEGE. Faculty of Arts Humanities and Social Sciences. School of Business
 UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN TRINITY COLLEGE Faculty of Arts Humanities and Social Sciences School of Business M.Sc. (Finance) Degree Examination Michaelmas 2011 Behavioural Finance Monday 12 th of December Luce
UNIVERSITY OF DUBLIN TRINITY COLLEGE Faculty of Arts Humanities and Social Sciences School of Business M.Sc. (Finance) Degree Examination Michaelmas 2011 Behavioural Finance Monday 12 th of December Luce
Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits
 Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits Brain electrical activity methods description and explanation of method state effects trait effects Positron emission tomography
Methods to examine brain activity associated with emotional states and traits Brain electrical activity methods description and explanation of method state effects trait effects Positron emission tomography
Sincerely, Ms. Paoloni and Mrs. Whitney
 Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Dear Students, Welcome to AP Psychology! We will begin our course of study focusing on the nervous system with a particular emphasis on how the brain and neurotransmitters influence our behaviors. In preparation
Myers Psychology for AP*
 Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Myers Psychology for AP* David G. Myers PowerPoint Presentation Slides by Kent Korek Germantown High School Worth Publishers, 2010 *AP is a trademark registered and/or owned by the College Board, which
Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6
 Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6 I. WHAT IS AN EMOTION? A. Three components (Oately & Jenkins, 1996) 1. caused by conscious or unconscious evaluation of an event as relevant to a goal that is important
Brain Mechanisms of Emotion 1 of 6 I. WHAT IS AN EMOTION? A. Three components (Oately & Jenkins, 1996) 1. caused by conscious or unconscious evaluation of an event as relevant to a goal that is important
Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom //
 Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom // http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/d/d_03/d_03_cl/d_03_cl_que/d_03_cl_que.html THE EVOLUTIONARY LAYERS OF THE HUMAN BRAIN The first time you observe the anatomy of the
Taken From The Brain Top to Bottom // http://thebrain.mcgill.ca/flash/d/d_03/d_03_cl/d_03_cl_que/d_03_cl_que.html THE EVOLUTIONARY LAYERS OF THE HUMAN BRAIN The first time you observe the anatomy of the
Mind over matter. Elio D Amato. An investors guide to remaining sane in an insane world. Chief Executive Officer Lincoln Indicators Pty Ltd
 Mind over matter An investors guide to remaining sane in an insane world Elio D Amato Chief Executive Officer Lincoln Indicators Pty Ltd Important Information This presentation is provided for educational
Mind over matter An investors guide to remaining sane in an insane world Elio D Amato Chief Executive Officer Lincoln Indicators Pty Ltd Important Information This presentation is provided for educational
DEMOGRAPHICS AND INVESTOR BIASES AT THE NAIROBI SECURITIES EXCHANGE, KENYA
 International Journal of Arts and Commerce Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 DEMOGRAPHICS AND INVESTOR BIASES AT THE NAIROBI SECURITIES EXCHANGE, KENYA Zipporah Nyaboke Onsomu 1, Prof. Erasmus Kaijage 2, Prof. Josiah
International Journal of Arts and Commerce Vol. 6 No. 5 July 2017 DEMOGRAPHICS AND INVESTOR BIASES AT THE NAIROBI SECURITIES EXCHANGE, KENYA Zipporah Nyaboke Onsomu 1, Prof. Erasmus Kaijage 2, Prof. Josiah
synapse neurotransmitters Extension of a neuron, ending in branching terminal fibers, through which messages pass to other neurons, muscles, or glands
 neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
neuron synapse The junction between the axon tip of a sending neuron and the dendrite of a receiving neuron Building block of the nervous system; nerve cell Chemical messengers that cross the synaptic
Psychology in Your Life
 Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
Sarah Grison Todd Heatherton Michael Gazzaniga Psychology in Your Life SECOND EDITION Chapter 2 The Role of Biology in Psychology 1 2016 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 2.1 How Do Our Nervous Systems Affect
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. The Brain & Spinal Cord
 THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM The Brain & Spinal Cord Review: Nervous System Parallel Distributed Processing Composition of the CNS Nuclei: Clusters of neurons in the CNS ( neighborhoods ) Fiber Tracts/Pathways:
Expanding Mindfulness as a Core Treatment Skill for Men and Women With Cognitive Deficits Thomas G. Beckers BS, LADC Vinland Center
 Expanding Mindfulness as a Core Treatment Skill for Men and Women With Cognitive Deficits Thomas G. Beckers BS, LADC Vinland Center What Are We Going to Cover? To gain understanding of the nature of addiction
Expanding Mindfulness as a Core Treatment Skill for Men and Women With Cognitive Deficits Thomas G. Beckers BS, LADC Vinland Center What Are We Going to Cover? To gain understanding of the nature of addiction
Have you ever noticed how easy it is to know when someone else is
 part one From the Outside Looking In Have you ever noticed how easy it is to know when someone else is making a bad decision a friend is impulsively quitting her job; a family member is buying a house
part one From the Outside Looking In Have you ever noticed how easy it is to know when someone else is making a bad decision a friend is impulsively quitting her job; a family member is buying a house
Altruistic Behavior: Lessons from Neuroeconomics. Kei Yoshida Postdoctoral Research Fellow University of Tokyo Center for Philosophy (UTCP)
 Altruistic Behavior: Lessons from Neuroeconomics Kei Yoshida Postdoctoral Research Fellow University of Tokyo Center for Philosophy (UTCP) Table of Contents 1. The Emergence of Neuroeconomics, or the Decline
Altruistic Behavior: Lessons from Neuroeconomics Kei Yoshida Postdoctoral Research Fellow University of Tokyo Center for Philosophy (UTCP) Table of Contents 1. The Emergence of Neuroeconomics, or the Decline
Organizational design and management have had, from the beginning, a principle based on the
 Emotional gap Organizational design and management have had, from the beginning, a principle based on the efficiency of the processes, but isolated from the dynamic context. This self-referential design
Emotional gap Organizational design and management have had, from the beginning, a principle based on the efficiency of the processes, but isolated from the dynamic context. This self-referential design
Neuroscience Optional Lecture. The limbic system the emotional brain. Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction
 Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Neuroscience Optional Lecture The limbic system the emotional brain Emotion, behaviour, motivation, long-term memory, olfaction Emotion Conscious experience intense mental activity and a certain degree
Whose Choice is it Anyway? Montague's Experimental Results
 Reference: McClure, SM, Li, J, Tomlin, D, Cypert, KS, Montague, LM, Montague, RM (2004) Neural correlates of behavioral preference for culturally familiar drinks. Neuron 44:379-387. The main goal of the
Reference: McClure, SM, Li, J, Tomlin, D, Cypert, KS, Montague, LM, Montague, RM (2004) Neural correlates of behavioral preference for culturally familiar drinks. Neuron 44:379-387. The main goal of the
Motivation represents the reasons for people's actions, desires, and needs. Typically, this unit is described as a goal
 Motivation What is motivation? Motivation represents the reasons for people's actions, desires, and needs. Reasons here implies some sort of desired end state Typically, this unit is described as a goal
Motivation What is motivation? Motivation represents the reasons for people's actions, desires, and needs. Reasons here implies some sort of desired end state Typically, this unit is described as a goal
ANALYSIS OF PROSPECT THEORY ON EQUITY INVESTMENT DECISION MAKING A BEHAVIOURAL PERSPECTIVE
 ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138 (Online) ANALYSIS OF PROSPECT THEORY ON EQUITY INVESTMENT DECISION MAKING A BEHAVIOURAL PERSPECTIVE D. VELUMONI 1 Assistant Professor, Sathyabama University, Chennai,
ISSN: 0976-2876 (Print) ISSN: 2250-0138 (Online) ANALYSIS OF PROSPECT THEORY ON EQUITY INVESTMENT DECISION MAKING A BEHAVIOURAL PERSPECTIVE D. VELUMONI 1 Assistant Professor, Sathyabama University, Chennai,
WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM?
 The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
The Nervous System WHAT ARE the COMPONENTS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM? The nervous system is made of: the brain & the spinal cord the nerves the senses There are lots of proteins and chemicals in your body
Neural Basis of Decision Making. Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Neural Basis of Decision Making Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Phineas Gage: Sept. 13, 1848 Working on the rail road Rod impaled his head. 3.5 x 1.25 13 pounds What happened
Neural Basis of Decision Making Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Phineas Gage: Sept. 13, 1848 Working on the rail road Rod impaled his head. 3.5 x 1.25 13 pounds What happened
Developing Leadership
 Developing Leadership Leadership Theory: the story over the last 100 years... In 20 minutes Great Man theories. Leaders are born great or have the appropriate character/traits. Ralph M. Stogdill Contingency
Developing Leadership Leadership Theory: the story over the last 100 years... In 20 minutes Great Man theories. Leaders are born great or have the appropriate character/traits. Ralph M. Stogdill Contingency
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology
 Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
Psychology Unit II: The Brain and Biology NATURE or NURTURE What are the effects of biochemistry on behavior? VOCABULARY Central Nervous System (CNS): The central nervous system is the part of the nervous
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION
 BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
BRAIN MECHANISMS OF REWARD AND ADDICTION TREVOR.W. ROBBINS Department of Experimental Psychology, University of Cambridge Many drugs of abuse, including stimulants such as amphetamine and cocaine, opiates
Behavioral Economics Lecture 1 An Introduction to Behavioral Economics
 Behavioral Economics Lecture 1 QIAO Zhilin( 乔志林 ) School of Economics & Finance Xi an Jiaotong University March, 2018 Richard Thaler Laureate of 2017 Nobel Prize in Economics University of Chicago Professor
Behavioral Economics Lecture 1 QIAO Zhilin( 乔志林 ) School of Economics & Finance Xi an Jiaotong University March, 2018 Richard Thaler Laureate of 2017 Nobel Prize in Economics University of Chicago Professor
Brain Based Change Management
 Brain Based Change Management PMI Mile Hi Chapter December 2, 2017 Vanita Bellen Executive Coach and Leadership Consultant True North Coaching and Facilitation Vanita Bellen, MHSc, PHR, SHRM-CP, PCC True
Brain Based Change Management PMI Mile Hi Chapter December 2, 2017 Vanita Bellen Executive Coach and Leadership Consultant True North Coaching and Facilitation Vanita Bellen, MHSc, PHR, SHRM-CP, PCC True
Profitability. Profitability. Trading Profits Mastery. Shifting the function of your amygdala from low order activity to high order activity
 Trading Profits Mastery Shifting the function of your amygdala from low order activity to high order activity 1 Profitability To become more profitable, you need to be able to learn, unlearn and relearn.
Trading Profits Mastery Shifting the function of your amygdala from low order activity to high order activity 1 Profitability To become more profitable, you need to be able to learn, unlearn and relearn.
the Global Financial Crisis and the Discipline of Economics by Adam Kessler
 Cognitive Dissonance the Global Financial Crisis and the Discipline of Economics by Adam Kessler Psychology has become a prominent field in the modern world, with psychology knowledge being applied in
Cognitive Dissonance the Global Financial Crisis and the Discipline of Economics by Adam Kessler Psychology has become a prominent field in the modern world, with psychology knowledge being applied in
International Journal of Economics And Business Management
 www.iaard.net IAARD Journals eissn:2455-4464 International Journal of Economics And Business Management IAARD-International Journal of Economics and Business Management, 2017, 3(1),17-22 Behavioral Finance:
www.iaard.net IAARD Journals eissn:2455-4464 International Journal of Economics And Business Management IAARD-International Journal of Economics and Business Management, 2017, 3(1),17-22 Behavioral Finance:
The Psychology of Trading Tools and Techniques for Minding the Markets by Dr. Brett Steenbarger
 The Psychology of Trading Tools and Techniques for Minding the Markets by Dr. Brett Steenbarger Success in the markets, as in life, depends on having a healthy and clear strategy for emotional risk management.
The Psychology of Trading Tools and Techniques for Minding the Markets by Dr. Brett Steenbarger Success in the markets, as in life, depends on having a healthy and clear strategy for emotional risk management.
Neural Basis of Decision Making. Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD
 Neural Basis of Decision Making Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Phineas Gage: Sept. 13, 1848 Working on the rail road Rod impaled his head. 3.5 x 1.25 13 pounds What happened
Neural Basis of Decision Making Mary ET Boyle, Ph.D. Department of Cognitive Science UCSD Phineas Gage: Sept. 13, 1848 Working on the rail road Rod impaled his head. 3.5 x 1.25 13 pounds What happened
THE IMPORTANCE OF BEHAVIORAL ECONOMICS IN THE STUDY OF THE INVESTMENT PROCESS
 THE IMPORTANCE OF BEHAVIORAL ECONOMICS IN THE STUDY OF THE INVESTMENT PROCESS Ion Ignat, Prof., PhD and Andreea Grădinaru, PhD Candidate, Al. Ioan Cuza University of Iași Abstract: We live in a time when,
THE IMPORTANCE OF BEHAVIORAL ECONOMICS IN THE STUDY OF THE INVESTMENT PROCESS Ion Ignat, Prof., PhD and Andreea Grădinaru, PhD Candidate, Al. Ioan Cuza University of Iași Abstract: We live in a time when,
How do People Really Think about Climate Change?
 How do People Really Think about Climate Change? #LSESunstein Professor Cass Sunstein Robert Walmsley University Professor at Harvard Law School. Former Administrator of the White House Office of Information
How do People Really Think about Climate Change? #LSESunstein Professor Cass Sunstein Robert Walmsley University Professor at Harvard Law School. Former Administrator of the White House Office of Information
Nervous System and Brain Review. Bio 3201
 Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
Nervous System and Brain Review Bio 3201 Dont worry about: glial cells Oligodendrocytes Satelite cells etc Nervous System - Vital to maintaining homeostasis in organisms - Comprised of : brain, spinal
nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
 Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Nucleus accumbens From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia Brain: Nucleus accumbens Nucleus accumbens visible in red. Latin NeuroNames MeSH NeuroLex ID nucleus accumbens septi hier-259 Nucleus+Accumbens birnlex_727
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1
 Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Okami Study Guide: Chapter 2 1 Chapter in Review 1. The human nervous system is a complex biological system designed for nearly instantaneous communication among billions of neurons throughout the body.
Exploring Reflections and Conversations of Breaking Unconscious Racial Bias. Sydney Spears Ph.D., LSCSW
 Exploring Reflections and Conversations of Breaking Unconscious Racial Bias Sydney Spears Ph.D., LSCSW Race the Power of an Illusion: The Difference Between Us https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b7_yhur3g9g
Exploring Reflections and Conversations of Breaking Unconscious Racial Bias Sydney Spears Ph.D., LSCSW Race the Power of an Illusion: The Difference Between Us https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=b7_yhur3g9g
HD 101: Cognition and HD. Daniel O. Claassen, MD MS Assistant Professor of Neurology Director: HD and Chorea Clinic Vanderbilt University
 HD 101: Cognition and HD Daniel O. Claassen, MD MS Assistant Professor of Neurology Director: HD and Chorea Clinic Vanderbilt University The information provided by speakers in workshops, forums, sharing/networking
HD 101: Cognition and HD Daniel O. Claassen, MD MS Assistant Professor of Neurology Director: HD and Chorea Clinic Vanderbilt University The information provided by speakers in workshops, forums, sharing/networking
The Influence of Cranial Nerves on the Financial Risk Selection and Trading Behavior of Investors
 NeuroQuantology June 2018 Volume 16 Issue 6 Page 158-163 doi: 10.14704/nq.2018.16.6.1575 The Influence of Cranial Nerves on the Financial Risk Selection and Trading Behavior of Investors Huaquan Zhang*
NeuroQuantology June 2018 Volume 16 Issue 6 Page 158-163 doi: 10.14704/nq.2018.16.6.1575 The Influence of Cranial Nerves on the Financial Risk Selection and Trading Behavior of Investors Huaquan Zhang*
Activity Overview. A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity 1A. The Brain: It s All In Your Mind
 A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity Objectives: Using diagrams of the brain, students will be able to: Observe the basic anatomy of the brain and its components Identify the parts
A Piece of Your Mind: Brain Anatomy Teacher Pages Activity Objectives: Using diagrams of the brain, students will be able to: Observe the basic anatomy of the brain and its components Identify the parts
TABLE OF CONTINENTS. PSYC1002 Notes. Neuroscience.2. Cognitive Processes Learning and Motivation. 37. Perception Mental Abilities..
 TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
TABLE OF CONTINENTS Neuroscience.2 Cognitive Processes...21 Learning and Motivation. 37 Perception.....54 Mental Abilities.. 83 Abnormal Psychology....103 1 Topic 1: Neuroscience Outline 1. Gross anatomy
Chapter 6. Body and Behavior
 Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Chapter 6 Body and Behavior Section 1 The Nervous System: The Basic Structure How the nervous system works Central nervous system (CNS)- the brain and spinal cord Spinal cord- nerves that run up and down
Behavioral Finance? A Three-Part Model for Client Relationships
 Behavioral Finance? A Three-Part Model for Client Relationships July 14, 2009 by Susan B. Weiner, CFA Behavioral finance can deepen your client relationships during market turmoil, if you recognize your
Behavioral Finance? A Three-Part Model for Client Relationships July 14, 2009 by Susan B. Weiner, CFA Behavioral finance can deepen your client relationships during market turmoil, if you recognize your
Emotion Explained. Edmund T. Rolls
 Emotion Explained Edmund T. Rolls Professor of Experimental Psychology, University of Oxford and Fellow and Tutor in Psychology, Corpus Christi College, Oxford OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction:
Emotion Explained Edmund T. Rolls Professor of Experimental Psychology, University of Oxford and Fellow and Tutor in Psychology, Corpus Christi College, Oxford OXPORD UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents 1 Introduction:
fmri (functional MRI)
 Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
Lesion fmri (functional MRI) Electroencephalogram (EEG) Brainstem CT (computed tomography) Scan Medulla PET (positron emission tomography) Scan Reticular Formation MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) Thalamus
GUEN DONDÉ HEAD OF RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF BUSINESS ETHICS
 WHAT DOES ETHICS AT WORK MEAN TO EMPLOYEES? GUEN DONDÉ HEAD OF RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF BUSINESS ETHICS IBE 05/07/2018 1 ABOUT THE IBE The IBE was established in 1986 to promote high standards of business
WHAT DOES ETHICS AT WORK MEAN TO EMPLOYEES? GUEN DONDÉ HEAD OF RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF BUSINESS ETHICS IBE 05/07/2018 1 ABOUT THE IBE The IBE was established in 1986 to promote high standards of business
Psychotropic Drugs Critical Thinking - KEY
 Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
Open Your Class with This Tomorrow Chasing the Scream: The First and Last Days of the War on s Psychotropic s Critical Thinking - KEY Background: The blood-brain barrier is a network of tightly packed
Impact on our Mental Health. Biological Changes Psychological Changes Social Changes Professional Services Coping Skills
 Impact on our Mental Health Biological Changes Psychological Changes Social Changes Professional Services Coping Skills Biological Changes After a brain injury, biological impacts may affect mental health
Impact on our Mental Health Biological Changes Psychological Changes Social Changes Professional Services Coping Skills Biological Changes After a brain injury, biological impacts may affect mental health
To understand AD, it is important to
 To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
To understand AD, it is important to know a bit about the brain. This part of Unraveling the Mystery gives an inside view of the normal brain, how it works, and what happens during aging. The brain is
Mindfulness at HFCS Information in this presentation was adapted from Dr. Bobbi Bennet & Jennifer Cohen Harper
 Mindfulness at HFCS 2015-2016 1 WHY Many children today are experiencing an increase in social and academic stress resulting in an over arousal of the sympathetic nervous system and a buildup of stress
Mindfulness at HFCS 2015-2016 1 WHY Many children today are experiencing an increase in social and academic stress resulting in an over arousal of the sympathetic nervous system and a buildup of stress
Neural plasticity in infants - relevance to baby swimming. Morten Overgaard
 Neural plasticity in infants - relevance to baby swimming Morten Overgaard Programme What is neuroscience? Totally superficial neuroanatomy Paradoxes of functional localization Mechanisms of neural plasticity
Neural plasticity in infants - relevance to baby swimming Morten Overgaard Programme What is neuroscience? Totally superficial neuroanatomy Paradoxes of functional localization Mechanisms of neural plasticity
Parts of the Brain. Hindbrain. Controls autonomic functions Breathing, Heartbeat, Blood pressure, Swallowing, Vomiting, etc. Upper part of hindbrain
 Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Parts of the Brain The human brain is made up of three main parts: 1) Hindbrain (or brainstem) Which is made up of: Myelencephalon Metencephalon 2) Midbrain Which is made up of: Mesencephalon 3) Forebrain
Instructions for use
 TitleA probabilistic choice model based Author(s) Takahashi, Taiki Citation Physica A: Statistical Mechanics an 335-338 Issue Date 2007-12-01 DOI Doc URLhttp://hdl.handle.net/2115/51261 Right Type article
TitleA probabilistic choice model based Author(s) Takahashi, Taiki Citation Physica A: Statistical Mechanics an 335-338 Issue Date 2007-12-01 DOI Doc URLhttp://hdl.handle.net/2115/51261 Right Type article
Ways we Study the Brain. Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI
 The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
The Brain Ways we Study the Brain Accidents Lesions CAT Scan PET Scan MRI Functional MRI Accidents Phineas Gage Story Personality changed after the accident. What this this tell us? That different part
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour
 Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Unit 3: The Biological Bases of Behaviour Section 1: Communication in the Nervous System Section 2: Organization in the Nervous System Section 3: Researching the Brain Section 4: The Brain Section 5: Cerebral
Introduction to Systems Neuroscience. Nov. 28, The limbic system. Daniel C. Kiper
 Introduction to Systems Neuroscience Nov. 28, 2017 The limbic system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html LIMBIC SYSTEM The term limbic system mean
Introduction to Systems Neuroscience Nov. 28, 2017 The limbic system Daniel C. Kiper kiper@ini.phys.ethz.ch http: www.ini.unizh.ch/~kiper/system_neurosci.html LIMBIC SYSTEM The term limbic system mean
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System
 The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
The Nervous System and the Endocrine System Neurons: The Building Blocks of the Nervous System Nervous System The electrochemical communication system of the body Sends messages from the brain to the
Putting Your Money Where Their Mouth Is: Financial Advisors Conflicts of Interest and the Limits of Disclosure
 Putting Your Money Where Their Mouth Is: Financial Advisors Conflicts of Interest and the Limits of Disclosure Sunita Sah, M.D., M.B.A., Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Business Ethics, Georgetown University
Putting Your Money Where Their Mouth Is: Financial Advisors Conflicts of Interest and the Limits of Disclosure Sunita Sah, M.D., M.B.A., Ph.D. Assistant Professor of Business Ethics, Georgetown University
1. Processes nutrients and provides energy for the neuron to function; contains the cell's nucleus; also called the soma.
 1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
1. Base of brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing 2. tissue destruction; a brain lesion is a naturally or experimentally caused destruction of brain tissue 3. A thick band of axons that connects the
Ch. 18. Brain Mechanisms of Emotion. Bear et al., Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3 rd ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006, pp
 Ch. 18. Brain Mechanisms of Emotion Bear et al., Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3 rd ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006, pp 564-583. WHAT IS EMOTION? Love, hate, disgust, joy, shame, envy, guilt,
Ch. 18. Brain Mechanisms of Emotion Bear et al., Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain, 3 rd ed., Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2006, pp 564-583. WHAT IS EMOTION? Love, hate, disgust, joy, shame, envy, guilt,
Neocortex. Hemispheres 9/22/2010. Psychology 472 Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs. Structures are divided into several section or lobes.
 Neocortex Psychology 472 Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs 1 Is the most developed in Humans Has many folds and fissures The folds of tissue are called gyri or a gyrus (single) The fissures or valleys
Neocortex Psychology 472 Pharmacology of Psychoactive Drugs 1 Is the most developed in Humans Has many folds and fissures The folds of tissue are called gyri or a gyrus (single) The fissures or valleys
Council on Chemical Abuse Annual Conference November 2, The Science of Addiction: Rewiring the Brain
 Council on Chemical Abuse Annual Conference November 2, 2017 The Science of Addiction: Rewiring the Brain David Reyher, MSW, CAADC Behavioral Health Program Director Alvernia University Defining Addiction
Council on Chemical Abuse Annual Conference November 2, 2017 The Science of Addiction: Rewiring the Brain David Reyher, MSW, CAADC Behavioral Health Program Director Alvernia University Defining Addiction
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas. Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template
 Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Regional and Lobe Parcellation Rhesus Monkey Brain Atlas Manual Tracing for Parcellation Template Overview of Tracing Guidelines A) Traces are performed in a systematic order they, allowing the more easily
Chapter 2 Knowledge Production in Cognitive Neuroscience: Tests of Association, Necessity, and Sufficiency
 Chapter 2 Knowledge Production in Cognitive Neuroscience: Tests of Association, Necessity, and Sufficiency While all domains in neuroscience might be relevant for NeuroIS research to some degree, the field
Chapter 2 Knowledge Production in Cognitive Neuroscience: Tests of Association, Necessity, and Sufficiency While all domains in neuroscience might be relevant for NeuroIS research to some degree, the field
Composed of gray matter and arranged in raised ridges (gyri), grooves (sulci), depressions (fissures).
 PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
PSYC1020 Neuro and Pysc Notes Structure Description Major Functions Brainstem Stemlike portion of the brain, continuous with diencephalon above and spinal cord below. Composed of midbrain, pons, medulla
Sleeping with the Enemy
 Sleeping with the Enemy May 25, 2010 by John W. Pfenenger II, CFA Advisor Perspectives welcomes guest contributions. The views presented here do not necessarily represent those of Advisor Perspectives.
Sleeping with the Enemy May 25, 2010 by John W. Pfenenger II, CFA Advisor Perspectives welcomes guest contributions. The views presented here do not necessarily represent those of Advisor Perspectives.
DEFINING EMOTION 11/19/2009 THE BIOLOGY OF EMOTION & STRESS. A change in physiological arousal, ranging from slight to intense.
 DEFINING EMOTION Emotion A feeling that differs from a person s normal affective state; a biological function of the nervous system. A change in physiological arousal, ranging from slight to intense. An
DEFINING EMOTION Emotion A feeling that differs from a person s normal affective state; a biological function of the nervous system. A change in physiological arousal, ranging from slight to intense. An
NEUROSCIENCE. W1 Divisions of the nervous system PSYC1002 NOTES
 PSYC1002 NOTES NEUROSCIENCE W1 Divisions of the nervous system Nervous system: - CNS o Brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System o Sensory nerves o Motor nerves o Autonomic nervous system o Enteric
PSYC1002 NOTES NEUROSCIENCE W1 Divisions of the nervous system Nervous system: - CNS o Brain and spinal cord - Peripheral Nervous System o Sensory nerves o Motor nerves o Autonomic nervous system o Enteric
How rational are your decisions? Neuroeconomics
 How rational are your decisions? Neuroeconomics Hecke CNS Seminar WS 2006/07 Motivation Motivation Ferdinand Porsche "Wir wollen Autos bauen, die keiner braucht aber jeder haben will." Outline 1 Introduction
How rational are your decisions? Neuroeconomics Hecke CNS Seminar WS 2006/07 Motivation Motivation Ferdinand Porsche "Wir wollen Autos bauen, die keiner braucht aber jeder haben will." Outline 1 Introduction
Mental Health and Stress
 Mental Health and Stress Learning Objectives Ø Define mental health and discuss the characteristics of mentally healthy and selfactualized people Ø Describe the various mental disorders and appropriate
Mental Health and Stress Learning Objectives Ø Define mental health and discuss the characteristics of mentally healthy and selfactualized people Ø Describe the various mental disorders and appropriate
TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE. The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in
 1 NAME COURSE TITLE 2 TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in dopamine neurotransmitter, up-regulation
1 NAME COURSE TITLE 2 TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in dopamine neurotransmitter, up-regulation
Neural Basis of Motor Control
 Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Neural Basis of Motor Control Central Nervous System Skeletal muscles are controlled by the CNS which consists of the brain and spinal cord. Determines which muscles will contract When How fast To what
Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Name: The Brain Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most obvious difference between the human brain and the brain of a carp
Name: The Brain Multiple Choice Identify the letter of the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. The most obvious difference between the human brain and the brain of a carp
INTRODUCTION TO EDUCATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE
 INTRODUCTION TO EDUCATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE TRUE OR FALSE? We only use 10% of our brain. Ages zero-three years are more important than any other for learning. There are critical periods for learning important
INTRODUCTION TO EDUCATIONAL NEUROSCIENCE TRUE OR FALSE? We only use 10% of our brain. Ages zero-three years are more important than any other for learning. There are critical periods for learning important
Behavioral Finance 1-1. Chapter 5 Heuristics and Biases
 Behavioral Finance 1-1 Chapter 5 Heuristics and Biases 1 Introduction 1-2 This chapter focuses on how people make decisions with limited time and information in a world of uncertainty. Perception and memory
Behavioral Finance 1-1 Chapter 5 Heuristics and Biases 1 Introduction 1-2 This chapter focuses on how people make decisions with limited time and information in a world of uncertainty. Perception and memory
PRESENTER HORACIO SANCHEZ
 PRESENTER HORACIO SANCHEZ Self-regulation Self-regulation relies on the prefrontal cortex controlling the subcortical regions associated with reward and emotion Predictive o Emotional stability o Social
PRESENTER HORACIO SANCHEZ Self-regulation Self-regulation relies on the prefrontal cortex controlling the subcortical regions associated with reward and emotion Predictive o Emotional stability o Social
Acetylcholine (ACh) Action potential. Agonists. Drugs that enhance the actions of neurotransmitters.
 Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Acetylcholine (ACh) The neurotransmitter responsible for motor control at the junction between nerves and muscles; also involved in mental processes such as learning, memory, sleeping, and dreaming. (See
Adolescent Brain Development and Drug Abuse. Ken C. Winters, Ph.D. Professor, Department of Psychiatry, University of Minnesota
 Adolescent Brain Development and Drug Abuse New findings indicate that brain development still in progress during adolescence; immature brain structures may place teenagers at elevated risk of substance
Adolescent Brain Development and Drug Abuse New findings indicate that brain development still in progress during adolescence; immature brain structures may place teenagers at elevated risk of substance
Nervous Systems. Brain Development
 Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Nervous Systems Brain Development 2007-2008 Nervous system Central nervous system Peripheral nervous system Brain Spinal cord Sensory pathways Motor pathways Sympathetic arousal & energy production fight
Review of Lecture 01: Introduction (Ch 1) History (Ch 2) (Reeve, 2009)
 Review of Lecture 01: Introduction (Ch 1) History (Ch 2) (Reeve, 2009) 3 Two perennial questions What causes (starts, maintains, stops) behaviour? Why does behaviour vary in its intensity? 4 What is motivation?
Review of Lecture 01: Introduction (Ch 1) History (Ch 2) (Reeve, 2009) 3 Two perennial questions What causes (starts, maintains, stops) behaviour? Why does behaviour vary in its intensity? 4 What is motivation?
Annual Special Education Directors Conference 2013 Leading with the Brain in Mind
 Annual Special Education Directors Conference 2013 Leading with the Brain in Mind PJ Rooney, PhD pj.knowlton@gmail.com Overarching Organizing Principle MINIMIZE MAXIMIZE We crave comfort and security.
Annual Special Education Directors Conference 2013 Leading with the Brain in Mind PJ Rooney, PhD pj.knowlton@gmail.com Overarching Organizing Principle MINIMIZE MAXIMIZE We crave comfort and security.
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts
 CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
CNS composed of: Grey matter Unmyelinated axons Dendrites and cell bodies White matter Myelinated axon tracts The Brain: A Quick Tour Frontal Lobe Control of skeletal muscles Personality Concentration
Introduction to Consumer Neuroscience & Neuromarketing Copenhagen Business School (Coursera)
 Introduction to Consumer Neuroscience & Neuromarketing Copenhagen Business School (Coursera) Final Assignment: by Mark Jansen December 28, 2014 Final Score: 17/20 (peer graded) Case Procter & Gamble (P&G)
Introduction to Consumer Neuroscience & Neuromarketing Copenhagen Business School (Coursera) Final Assignment: by Mark Jansen December 28, 2014 Final Score: 17/20 (peer graded) Case Procter & Gamble (P&G)
