48 HYPERTENSION VOL 7, No 1, JANUARY-FEBRUARY 1985
|
|
|
- Marjorie Daniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 48 HYPERTENSON VOL 7, No 1, JANUARY-FEBRUARY 1985 stricter responses were evoked by electrical stimulation of the renal nerves via platinum electrodes with the use of parameters that activate adrenergic nerves in this preparation 6 (0.5 to 5 Hz, 12 V, 1 msec, 10-second trains). Responses were also evoked by close intraartenal injection of norepinephrine (Sigma Chemical Company) (6.25 to 200 ng in 20 yi[ of saline). Responses were measured as the increase in perfusion pressure from the basal perfusion pressure immediately preceding the response. Dose and frequency response curves were repeated in the presence of epinephrine (Sigma Chemical) (10~ 9 M to 10~ 8 M), and these results were expressed as a percentage of the control vasoconstrictor response. The effect of epinephrine on vasoconstrictor responses was further examined after pretreatment with atenolol (Tenormin, C Pharmaceuticals, Macclesfield, England) (10-6 M),C (3 x 10-8 M), and cocaine (3 X 10-5 M) ' * * 10 2J> JJ) 4.0 Frrjutncycrf stiraulittxi (Hi) 1 3 H-Epinephrine Labeling of Kidneys After a 45-minute equilibration period, the kidneys were perfused with 3 H-epinephrine (5 x 10~ 9 M, 72.9 Ci/mmol) (New England Nuclear, Boston, MA) for 25 minutes, and a 10-minute washout period was allowed before stimulation of the renal nerves. Measurement of 3 H Efflux During a period of 45 minutes, the kidney was stimulated at 5-minute intervals (3 Hz, 12 V, 1 msec, 10- second trains). Prior to stimulation, two consecutive 12-second collections of perfusate were taken to determine basal tritium overflow. During and after stimulation, three consecutive 12-second collections were made to determine the efflux of 3 H evoked by electrical stimulation, as an indicator of the efflux of epinephrine. The experiment was repeated in kidneys perfused with Krebs solution containing cocaine (3 X 10" 5 M) or C (3 X 10" 8 M). These drugs were added 30 minutes before 3 H-epinephnne perfusion and were present for the duration of the experiment. Aquasol (New England Nuclear), a universal liquid scintillation cocktail, was added to aliquots (1.2 ml) of the perfusate, and a stiff gel formed after shaking. Radioactivity (counts/min/ahquot) was determined by liquid scintillation counting on a Phillips Liquid Scintillation Counter (Eindhoven, The Netherlands). The results were expressed as the total stimulusevoked increase in the efflux of radioactivity. Tissue Radioactivity Total tissue radioactivity was measured in the kidneys at the end of the experiment. The tissues were chopped, and 9 ml of xylene-based scintillation medium (P.C.S., Amersham nternational, Amersham, England) tissue solubilizer was added and allowed to stand at 37 C for 48 hours. Then 250 ^1 of the resulting solute was transferred to a counting vial, and 40 fi\ of a 1:3 dilution of concentrated HC1 plus 4 ml of P.C.S. (Amersham) liquid scintillant were added. To- FGURE 1 Effect of epinephrine on the amplitude of vasoconstrictor responses evoked by renal nerve stimulation in the isolated perfused rat kidney (n = 6) Epinephrine (10~ 9 M) = stippled bars at left, epinephrine (2.5 x 10~ 9 M) = crosshatched bars second from left; epinephrine (5 0 x 10~ 9 M) = diagonally ruled bars third from left; epinephrine (10~ s M) = open bars at the right. Vasoconstrictor responses were measured as the increase in perfusion pressure from the basal perfusion pressure immediately preceding the response 100% represents the amplitude of the vasoconstrictor response evoked in control solution (i e., in the absence of epinephrine) * p < 005;** = p<001;*** = p<0001. Vertical bars indicate SEM. tal radioactivity (counts/min) was determined by liquid scintillation counting. Statistical Methods Statistical analysis of data was by Student's paired and unpaired t tests, and by analysis of variance (ANOVA), as appropriate. Significance was accepted when/? < Results Effect of Epinephrine The amplitude of vasoconstrictor responses evoked by renal nerve stimulation and by exogenous norepinephrine was reproducible for the duration of the experiment. Continuous infusion of epinephrine (10~ 9 5 x 10~ 9 M) had no significant effect on basal perfusion pressure of the kidneys (72.6 ± 1.3mmHg, n = 24). However, a higher concentration of epinephrine (10~ 8 M) caused a significant (p < 0.05) increase in basal perfusion pressure to 80.6 ± 1.3 mm Hg (n = 6). Epinephrine infusion (2.5 X 10~ 9 to 10~ 8 M) caused a concentration-related enhancement of the amplitude of vasoconstrictor responses induced by renal nerve stimulation (Figure 1), while responses induced by exogenous norepinephrine were only slightly en-
3 EPNEPHRNE AND RENAL VASOCONSTRCTON/gwi et al. 49 _ 300 -i d e o - i A Nonpbwplul 50 Dots (ng) FGURE 2 Effect of epinephrine on the amplitude of vasoconstrictor responses evoked by intra-arterial injection ofnorepinephrine in the isolated perfused kidney of the rat (n = 6) Epinephrine (10~ 9 M) = stippled bars at left; epinephrine (2 5 x 10~ 9 M) = cross-hatched bars second from left, epinephrine (5 X 10~ 9 M) - diagonally ruled bars third from left; epinephrine (10~ s M) = open bars at the right Vasoconstrictor responses were measured as the increase in perfusion pressure from the basal pressure immediately preceding the response. 100% represents the amplitude of the vasoconstrictor response evoked in control solution (in the absence of epinephrine). * = p < 0.05; ** = p<0 01. Vertical bars indicate SEM hanced by the highest concentration of epinephrine (10" 8 M) used (Figure 2). The epinephrine-induced (5 x 10~ 9 M) enhancement of vasoconstrictor responses evoked by renal nerve stimulation was significantly attenuated 10 minutes after cessation of the epinephrine infusion. However, the amplitude of the responses remained significantly higher than those obtained prior to epinephrine infusion (Figure 3). Kidneys that had been perfused with 3 H-epinephrine (5 X 10~ 9 M) and then perfused for 60 minutes with normal Krebs solution accumulated significant amounts of radioactivity (Table 1). Stimulation of the renal nerves to these kidneys (3 Hz, 10-second train every 5 minutes) produced a consistent and significant increase in the efflux of radioactivity (Figure 4). Effect of Atenolol and C The presence of atenolol, a selective /3,-adrenergic receptorantagomst(10-6 M), orlc (3 X 10" 8 M), a selective /3 2 -adrenergic receptor antagonist, caused a slight enhancement of the vasoconstrictor responses to renal nerve stimulation and injected norepinephrine (Figures 5 and 6). The subsequent epinephrine-induced (5 X 10" 9 M) enhancement of vasoconstrictor responses evoked by renal nerve stimulation was unaffected in the presence of atenolol (Figure 5). The epinephrine-induced enhancement was abolished, however, in the presence of C (Figure 5). Epinephrine (5 X 10~ 9 M) had no effect on the amplitude of vasoconstrictor responses evoked by exogenous norepinephrine in the absence or presence of the /3-adrenergic-receptor-blocking drugs (Figure 6). The C (3 x 10" 8 M) had no significant effect on the accumulation of radioactivity in the kidneys that had been perfused with 3 H-epinephrine (Table 1). The efflux of radioactivity from these kidneys evoked by renal nerve stimulation was significantly reduced (p < 0.05) but not abolished by C (Figure 4) s Fraqumcy <* stfmuutton (Hz) FGURE 3 Effect of epinephrine (5 x O~ 9 M) on the amplitude of vasoconstrictor responses evoked by renal nerve stimulation in the isolated perfused rat kidney (n = 6) in the absence (Group ) and presence (Group 2) of cocaine (3 X O~ 5 M). Epinephrine (5 X lo' 9 M) = stippled bars at the left; 10 minutes after cessation of epinephrine infusion = crosshatched bars second from left, epinephrine (5 x lo' 9 M) infusion in the presence of cocaine (3 x 10~ 5 M) = diagonally ruled bars third from left; 10 minutes after cessation of epinephrine infusion (cocaine still present at 3 X 10~ 5 M) open bars at the right Vasoconstrictor responses were measured as the increase in perfusion pressure from the basal pressure immediately preceding the response Group 1: 100% represents the response evoked in control solution Group % represents the control response evoked in the presence of cocaine. = p< 0 05; ** = p < 0.01; *** = p < 0.00/. Vertical bars indicate SEM.
4 50 HYPERTENSON VOL 7, No 1, JANUARY-FEBRUARY 1985 TABLE 1. Total Tissue Radioactivity of Kidneys after Perfuswn with i H-Epinephrine (5 x lch 9 M) in the Absence or Presence of Cocaine or of 1C Total tissue radioactivity Treatment (counts x lovg/imn) Control C (3 Cocaine (3 X x 1(H M) 10-5 M) 651 ± ±0 17 2O7±O38* Significant difference (p < 0 001, analysis of variance) between the treated group (n = 6) and the control group (n = 6). Effect of Cocaine n the presence of cocaine (3 X 10~ 5 M), epinephrine(5 x 10~ 9 M) produced a significant enhancement of the amplitude of responses evoked by renal nerve stimulation (Figure 3). This potentiating effect of epinephrine was significantly less than that which occurred in the absence of cocaine (Figure 3). n the presence of cocaine, the potentiating effect of epinephrine was abolished 10 minutes after cessation of the perfusion with the catecholamine (Figure 3). Cocaine (3 x 10~ 5 M) significantly reduced the accumulation of radioactivity in kidneys that had been perfused with 3 H-epinephrine (Table 1). Stimulation of the renal nerves (3 Hz) in these kidneys did not evoke a significant increase in the efflux of radioactivity (Figure 4). Discussion The experiments described in this paper demonstrate that low concentrations of epinephrine increase the amplitude of vasoconstrictor responses evoked by adrenergic nerve stimulation. The degree of facilitation of neurogenic vasoconstrictor responses was related to the concentration of the amine used. The concentration required to cause a statistically significant enhancement was slightly above the normal plasma level in this strain of rat, 7 but within the range of concentrations that occur during acute stress. 8 Thus, it is likely that neurogenic vasoconstriction in the intact animal will be enhanced by circulating epinephrine during stress. The persistent nature of the facilitory effect of epinephrine in the kidney indicates that neurogenic vasoconstriction in vivo may remain enhanced after a stress-induced elevation of plasma epinephrine levels has subsided. This persistent effect appears to be due to the accumulation of epinephrine at some site in the kidney and its subsequent release during nerve stimulation. Since cocaine caused a marked reduction in the epinephrine content of the kidney, it is likely that most of the accumulation of the amine occurs via the neuronal uptake system. Both the release of tritium on nerve stimulation and the persistent enhancement of vasoconstrictor responses were abolished by cocaine. Thus, it appears that the persistent effect of epinephrine is due to the release of the catecholamine that has g i B! 1,500^ 1, o- 1 1 j Time (mln) after cessation of ^-adrenaline nfusion FGURE 4. Efflux of radioactivity induced by renal nerve stimulation (3Hz, 10-second train) from isolated perfused rat kidneys (n = 6)after infusion of 3 H-epinephrine. effect ofpretreatment with cocaine (3 x 0~ 5 M)or with C (3 x 10~ s M). Control efflux = stippled bars at the left; efflux from kidneys pretreated with cocaine (3 x 10~ 5 M) = cross-hatched bars in the center, efflux from kidneys pretreated with C (3 x 10~ s M) = diagonally ruled bars at the right n the presence ojcocaine (for the duration ofthe experiment), renal nerve stimulation did not evoke a significant increase in the efflux of radioactivity Significant difference from the efflux of radioactivity evoked by renal nerve stimulation in control conditions is indicated by * p < 0.05; ** p < Vertical bars indicate SEM
5 EPNEPHRNE AND RENAL VASOCONSTRCTON/0ui>m et al ^ CONTROL ATtN(XOl(10" 6 M C 118,551 (3 xlo"*m) " E O D JJ 0 U) S) U) J3 Fraqumcyot stimulation (Hz FGURE 5. Effect ofatenolol(k)- 6 M) and ofc (3 x 10~ 8 M) on the epmephrine-induced (5 x 1O~ 9 M) enhancement of vasoconstrictor responses evoked by renal nerve stimulation m the isolated perfused rat kidney (n = 6). Control frequency-response curve (O);frequency-responsecurve in the presence of epinephrine (5 X 10-9 M) ( ); * p < 0.01, * p < 0 OOl. Data are expressed as means ± SEM been stored in the adrenergic nerve terminals of the kidney. The facilitory effect of epinephrine in the perfused rat kidney may be mediated by a prejunctional /3- adrenergic receptor. A prejunctional site of action is suggested by the observation that low concentrations (2.5 5 x 10~ 9 M) of epinephrine enhanced the amplitude of neurogenic vasoconstrictor responses without affecting the basal perfusion pressure of the kidney or its responses to exogenous norepinephrine. The highest concentration of epinephrine (10~ 8 M) not only enhanced responses to nerve stimulation but also Control Ct (3 x 10-»M) enhanced those evoked by low doses of norepinephrine. This postjunctional effect may have accounted for the exaggerated enhancing effect of this concentration of epinephrine on the responses evoked by the lowest frequency of nerve stimulation used (0.5 Hz). The existence of a prejunctional facilitory /3-adrenergic receptor in the rat kidney has also been demonstrated by a study of the effects of salbutamol on the stimulus-evoked overflow of 3 H-norepinephrine. 9 The /3 2 -adrenergic-receptor-selective antagonist C abolished the facilitative effect of epinephrine on the amplitude of vasoconstrictor responses FGURE 6. Effect of atenolol (10~ 6 M) and of C (3 x 10-'M) on the amplitude of vasoconstrictor responses evoked by intra-arterial norepinephrine in the isolated perfused rat kidney (n = 6) in the absence and presence of epinephrine (5 x 10~ 9 M). Control doseresponse curve (o), dose-response curve in the presence of epinephrine (5 x 0-9 M) C) Data are expressed as means ± SEM.
6
PRESYNAPTIC cx-adrenoceptor BLOCKING PROPERTIES AMONG
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1979), 67, 511-517 PRESYNAPTIC cx-adrenoceptor BLOCKING PROPERTIES AMONG TRI- AND TETRA-CYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS BARBARA HARPER & I.E. HUGHES Department of Pharmacology, Medical and
Br. J. Pharmac. (1979), 67, 511-517 PRESYNAPTIC cx-adrenoceptor BLOCKING PROPERTIES AMONG TRI- AND TETRA-CYCLIC ANTIDEPRESSANT DRUGS BARBARA HARPER & I.E. HUGHES Department of Pharmacology, Medical and
RAPID COMMUNICATION. Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension
 Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Physiol. Res. 40:367-371,1991 RAPID COMMUNICATION Vascular Reactivity in Isolated Lungs of Rats with Spontaneous Systemic Hypertension V. HAMPL, J. HERGET Department of Physiology, 2nd Medical School,
Effects of Calcium-Antagonists on Norepinephrine Release from Sympathetic Nerve Endings in Rat Mesenteric Vasculature
 Effects of Calcium-Antagonists on Norepinephrine Release from Sympathetic Nerve Endings in Rat Mesenteric Vasculature Kazushi TSUDA, M.D., Masato KUCHII, M.D., Ichiro NISHIO, M.D., and Yoshiaki MASUYAMA,
Effects of Calcium-Antagonists on Norepinephrine Release from Sympathetic Nerve Endings in Rat Mesenteric Vasculature Kazushi TSUDA, M.D., Masato KUCHII, M.D., Ichiro NISHIO, M.D., and Yoshiaki MASUYAMA,
Prazosin-Induced Alterations in Renal a-adrenergic Receptor Function WILLIAM B. JEFFRIES, LEI-TING TAM, YUE WANG, DONALD D. AND WILLIAM A.
 Prazosin-Induced Alterations in Renal a-adrenergic Receptor Function WILLIAM B. JEFFRIES, LEI-TING TAM, YUE WANG, DONALD D. AND WILLIAM A. PETTINGER SMYTH, SUMMARY Chronic (3-day) treatment with prazosin
Prazosin-Induced Alterations in Renal a-adrenergic Receptor Function WILLIAM B. JEFFRIES, LEI-TING TAM, YUE WANG, DONALD D. AND WILLIAM A. PETTINGER SMYTH, SUMMARY Chronic (3-day) treatment with prazosin
Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 1-7 Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog B. N. DAVIES ADi P. G. WITHRINGTON Department of Physiology, Medical College of
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 41, 1-7 Actions of prostaglandin F20 on the splenic vascular and capsular smooth muscle in the dog B. N. DAVIES ADi P. G. WITHRINGTON Department of Physiology, Medical College of
Epinephrine Facilitates Neurogenic Vasoconstriction in Humans
 Epinephrine Facilitates Neurogenic Vasoconstriction in Humans John S. Floras, Philip E. Aylward, Ronald G. Victor, Allyn L. Mark, and Francois M. Abboud Cardiovascular Division ofthe Department ofnternal
Epinephrine Facilitates Neurogenic Vasoconstriction in Humans John S. Floras, Philip E. Aylward, Ronald G. Victor, Allyn L. Mark, and Francois M. Abboud Cardiovascular Division ofthe Department ofnternal
susceptibility of either the axons in the dorsal and ventral roots, or the intramedullary
 213 J. Physiol. (31958) I40, 2I3-2I9 THE SITE OF ACTION OF PROCAINE ON THE ISOLATED SPINAL CORD OF THE FROG BY M. HARMEL AND J. L. MALCOLM From the Department of Physiology, State University of New York,
213 J. Physiol. (31958) I40, 2I3-2I9 THE SITE OF ACTION OF PROCAINE ON THE ISOLATED SPINAL CORD OF THE FROG BY M. HARMEL AND J. L. MALCOLM From the Department of Physiology, State University of New York,
Platelet-induced Neurogenic Coronary Contractions Due to Accumulation of the False Neurotransmitter, 5-Hydroxytryptamine
 Platelet-induced Neurogenic Coronary Contractions Due to Accumulation of the False Neurotransmitter, 5-Hydroxytryptamine Richard A. Cohen With the technical assistance of Kevin Zitnay and Robert Weisbrod
Platelet-induced Neurogenic Coronary Contractions Due to Accumulation of the False Neurotransmitter, 5-Hydroxytryptamine Richard A. Cohen With the technical assistance of Kevin Zitnay and Robert Weisbrod
A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: INCREASED MAXIMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATIVE NORADREN- ALINE IN THE ISOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 171-176. A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: NCREASED MAXMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATVE NORADREN- ALNE N THE SOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS BY A. BARNETT, D. D. GREENHOUSE AND R..
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 171-176. A NEW TYPE OF DRUG ENHANCEMENT: NCREASED MAXMUM RESPONSE TO CUMULATVE NORADREN- ALNE N THE SOLATED RAT VAS DEFERENS BY A. BARNETT, D. D. GREENHOUSE AND R..
Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 48, 73-79. Action of drugs on denervated myoepithelial cells of salivary glands N. EMMELIN AND A. THULIN Institute of Physiology, University of Lund, Sweden Summary 1. The pressure
ACTIONS OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF [3H]-NORADRENALINE
![ACTIONS OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF [3H]-NORADRENALINE ACTIONS OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF [3H]-NORADRENALINE](/thumbs/74/71109260.jpg) Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1962), 18, 161-166. ACTIONS OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF [3H]-NORADRENALINE BY G. HERTTING,* J. AXELROD AND R. W. PATRICK From the Laboratory of Clinical
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1962), 18, 161-166. ACTIONS OF BRETYLIUM AND GUANETHIDINE ON THE UPTAKE AND RELEASE OF [3H]-NORADRENALINE BY G. HERTTING,* J. AXELROD AND R. W. PATRICK From the Laboratory of Clinical
to Regulation of the Brain Vessels
 Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 34,193-197,1984 The Relevance of Cardio-pulmonary-vascular Reflex to Regulation of the Brain Vessels Masatsugu NAKAI and Koichi OGINO Department of Cardiovascular
Short Communication Japanese Journal of Physiology, 34,193-197,1984 The Relevance of Cardio-pulmonary-vascular Reflex to Regulation of the Brain Vessels Masatsugu NAKAI and Koichi OGINO Department of Cardiovascular
Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria
 Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D., Yasuyuki FURUKAWA, M.D., and Hidehiko WATANABE, M.D. SUMMARY Using the isolated
Chronotropic and Inotropic Effects of 3 Kinds of Alpha-Adrenergic Blockers on the Isolated Dog Atria Shigetoshi CHIBA, M.D., Yasuyuki FURUKAWA, M.D., and Hidehiko WATANABE, M.D. SUMMARY Using the isolated
THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO
 Br. J. Anaesth. (1974), 46, 473 THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO M. R. WASSEF, H. LAL AND BARBARA J. PLEUVRY SUMMARY The cardiovascular effects
Br. J. Anaesth. (1974), 46, 473 THE CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS OF ERGOMETRINE IN THE EXPERIMENTAL ANIMAL IN VIVO AND IN VITRO M. R. WASSEF, H. LAL AND BARBARA J. PLEUVRY SUMMARY The cardiovascular effects
Mechanisms of Reflex Vasodilation:
 Mechanisms of Reflex Vasodilation: Assessment of the Role of Neural Reuptake of Norepinephrine and Release of Histamine GCALD GmCKc, ANDREw S. WECHSLER, and STEPHEN E. EPsTEIN with the technical assistance
Mechanisms of Reflex Vasodilation: Assessment of the Role of Neural Reuptake of Norepinephrine and Release of Histamine GCALD GmCKc, ANDREw S. WECHSLER, and STEPHEN E. EPsTEIN with the technical assistance
Trp7' 9 lo-sp. adrenoceptor antagonists in order to establish the nature of neurotransmitters
 Journal of Physiology (199), 43, pp. 77-86 77 With 5 figures Printed in Great Britain ALTERATIONS IN CAT KNEE JOINT BLOOD FLOW INDUCED BY ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF ARTICULAR AFFERENTS AND EFFERENTS BY
Journal of Physiology (199), 43, pp. 77-86 77 With 5 figures Printed in Great Britain ALTERATIONS IN CAT KNEE JOINT BLOOD FLOW INDUCED BY ELECTRICAL STIMULATION OF ARTICULAR AFFERENTS AND EFFERENTS BY
Autonomic Nervous System
 ANS..??? Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system CNS PNS Autonomic Somatic Symp Parasymp Enteric SOMATIC AUTONOMIC Organ supplied Skeletal muscle Other organs Distal most synapse Nerve fibre Peripheral
ANS..??? Autonomic Nervous System Nervous system CNS PNS Autonomic Somatic Symp Parasymp Enteric SOMATIC AUTONOMIC Organ supplied Skeletal muscle Other organs Distal most synapse Nerve fibre Peripheral
Increased forearm vascular resistance after dopamine blockade
 Br. J. clin. Pharnac. (1984), 17, 373-378 Increased forearm vascular resistance after dopamine blockade D. MANNERING, E.D. BENNE7T, N. MEHTA & F. KEMP Department of Medicine 1, St George's Hospital Medical
Br. J. clin. Pharnac. (1984), 17, 373-378 Increased forearm vascular resistance after dopamine blockade D. MANNERING, E.D. BENNE7T, N. MEHTA & F. KEMP Department of Medicine 1, St George's Hospital Medical
A CENTRAL NORADRENERGIC MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR MODULATION OF THE ARTERIAL BARORECEPTOR REFLEX IN CATS
 www.kopfinstruments.com A CENTRAL NORADRENERGIC MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR MODULATION OF THE ARTERIAL BARORECEPTOR REFLEX IN CATS V. S. EREMEEV, Ph.D. R. S. KHRUSTALEVA, Ph.D. V. A. TSYRLIN, Ph.D. Yu. I.
www.kopfinstruments.com A CENTRAL NORADRENERGIC MECHANISM RESPONSIBLE FOR MODULATION OF THE ARTERIAL BARORECEPTOR REFLEX IN CATS V. S. EREMEEV, Ph.D. R. S. KHRUSTALEVA, Ph.D. V. A. TSYRLIN, Ph.D. Yu. I.
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1
 BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
BIPN100 F15 Human Physiol I (Kristan) Lecture 14 Cardiovascular control mechanisms p. 1 Terms you should understand: hemorrhage, intrinsic and extrinsic mechanisms, anoxia, myocardial contractility, residual
rate of rat cerebral cortex neurones. They concluded that clonidine, as well as other 2-substituted imidazoline
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1981),74,709-713 FACILITATION BY CLONIDINE OF PURINE RELEASE INDUCED BY HIGH KC1 FROM THE RABBIT PULMONARY ARTERY TAKESHI KATSURAGI1 & CHE SU Department of Pharmacology, Southern Illinois
Br. J. Pharmac. (1981),74,709-713 FACILITATION BY CLONIDINE OF PURINE RELEASE INDUCED BY HIGH KC1 FROM THE RABBIT PULMONARY ARTERY TAKESHI KATSURAGI1 & CHE SU Department of Pharmacology, Southern Illinois
A Reduction in Some Vasodilator Responses
 Cardiovasc. Res., 1969, 3, 14-21. A Reduction in Some Vasodilator Responses in Free-standing Man J. G. MOSLEY" From the Department of Physiology, The Queen's University of Belfast, Northern Ireland AUTHOR'S
Cardiovasc. Res., 1969, 3, 14-21. A Reduction in Some Vasodilator Responses in Free-standing Man J. G. MOSLEY" From the Department of Physiology, The Queen's University of Belfast, Northern Ireland AUTHOR'S
less susceptible to blockade by prazosin than to blockade by either phentolamine or yohimbine (Drew & Whiting, 1979). In the latter study, NA was
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1984),83,889-898 Effects of reduced calcium ion concentration and of diltiazem on vasoconstrictor responses to noradrenaline and sympathetic nerve stimulation in rat isolated tail artery
Br. J. Pharmac. (1984),83,889-898 Effects of reduced calcium ion concentration and of diltiazem on vasoconstrictor responses to noradrenaline and sympathetic nerve stimulation in rat isolated tail artery
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION. Supplementary Figure 1
 SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION Supplementary Figure 1 The supralinear events evoked in CA3 pyramidal cells fulfill the criteria for NMDA spikes, exhibiting a threshold, sensitivity to NMDAR blockade, and all-or-none
Cardiovascular reactivity in the experimental hypertensive rat
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 42, 56-65. Cardiovascular reactivity in the experimental hypertensive rat L. FINCH* School of Studies in Pharmacology, University of Bradford, Bradford 7, Yot ks Summary 1. In pithed
Br. J. Pharmac. (1971), 42, 56-65. Cardiovascular reactivity in the experimental hypertensive rat L. FINCH* School of Studies in Pharmacology, University of Bradford, Bradford 7, Yot ks Summary 1. In pithed
Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches
 Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches during application of 500 µm Ca 2+ at the intracellular
Supplementary Figure 1: Steviol and stevioside potentiate TRPM5 in a cell-free environment. (a) TRPM5 currents are activated in inside-out patches during application of 500 µm Ca 2+ at the intracellular
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Supplementary Figure 1 Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold in capillaries from knockout animals. Relative expression of K IR2.1 transcript to enos was reduced 29-fold
Properties of Pressure
 OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
OBJECTIVES Overview Relationship between pressure and flow Understand the differences between series and parallel circuits Cardiac output and its distribution Cardiac function Control of blood pressure
CATION AND METABOLIC REQUIREMENTS FOR RETENTION OF METARAMINOL BY RAT UTERINE HORNS
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 277-286. CATION AND METABOLIC REQUIREMENTS FOR RETENTION OF METARAMINOL BY RAT UTERINE HORNS BY From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Alberta! Edmonton,
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 33, 277-286. CATION AND METABOLIC REQUIREMENTS FOR RETENTION OF METARAMINOL BY RAT UTERINE HORNS BY From the Department of Pharmacology, University of Alberta! Edmonton,
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS
 2. MATERIALS AND METHODS 2.1 Materials [ 3 H]-Digoxin (37Ci/mmol) was purchased from Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences Inc. (Boston, USA) and [U- 14 C]-Sucrose (660mCi/mmol) was purchased from Amersham Bioscience
2. MATERIALS AND METHODS 2.1 Materials [ 3 H]-Digoxin (37Ci/mmol) was purchased from Perkin-Elmer Life Sciences Inc. (Boston, USA) and [U- 14 C]-Sucrose (660mCi/mmol) was purchased from Amersham Bioscience
*Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
 HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GIAPREZA TM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GIAPREZA. GIAPREZA (angiotensin
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION These highlights do not include all the information needed to use GIAPREZA TM safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for GIAPREZA. GIAPREZA (angiotensin
Titrating Critical Care Medications
 Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Titrating Critical Care Medications Chad Johnson, MSN (NED), RN, CNCC(C), CNS-cc Clinical Nurse Specialist: Critical Care and Neurosurgical Services E-mail: johnsoc@tbh.net Copyright 2017 1 Learning Objectives
Norepinephrine (Levophed )
 Norepinephrine (Levophed ) Scope C3IFT CCT Generic Name: Norepinephrine Trade Name: Levophed Chemical Class: Therapeutic Class: Actions: Pharmacokinetics: Vasopressor Vasopressor Mechanism of Action: Norepinephrine
Norepinephrine (Levophed ) Scope C3IFT CCT Generic Name: Norepinephrine Trade Name: Levophed Chemical Class: Therapeutic Class: Actions: Pharmacokinetics: Vasopressor Vasopressor Mechanism of Action: Norepinephrine
A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 39, 748-754. A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs A. T. BIRMINGHAM*, G. PATRSON AND J. W6JCICKIt Department of Pharmacology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1970), 39, 748-754. A comparison of the sensitivities of innervated and denervated rat vasa deferentia to agonist drugs A. T. BIRMINGHAM*, G. PATRSON AND J. W6JCICKIt Department of Pharmacology,
Dopamine in Ube3a m-/p+ mice. Online Supplemental Material
 Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
Online Supplemental Material S1 Supplemental Figure 1. Schematic of rate-dependent intracranial self-stimulation (ICSS) (A) Mice implanted with monopolar stimulating electrodes to the medial forebrain
SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL. Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program)
 SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program) Scoring of Sleep Stages in Adults A. Stages of Sleep Stage W Stage
SLEEP STAGING AND AROUSAL Dr. Tripat Deep Singh (MBBS, MD, RPSGT, RST) International Sleep Specialist (World Sleep Federation program) Scoring of Sleep Stages in Adults A. Stages of Sleep Stage W Stage
-51mV 30s 3mV. n=14 n=4 p=0.4. Depolarization (mv) 3
 Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
Supplementary Figure 1 a optoβ 2 -AR b ChR2-51mV 30s 3mV -50mV 30s 3mV c 4 n=14 n=4 p=0.4 Depolarization (mv) 3 2 1 0 Both optogenetic actuators, optoβ 2 AR and ChR2, were effective in stimulating astrocytes
The removal of noradrenaline in the pulmonary circulation of rat isolated lungs
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 47, 325-331. The removal of noradrenaline in the pulmonary circulation of rat isolated lungs VALERIE A. ALABASTER AND Y. S. BAKHLE Departtent of Pharmacology, Institute of Basic
Br. J. Pharmac. (1973), 47, 325-331. The removal of noradrenaline in the pulmonary circulation of rat isolated lungs VALERIE A. ALABASTER AND Y. S. BAKHLE Departtent of Pharmacology, Institute of Basic
Supplementary Figure 1. SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn.
 Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary Figure 1 SybII and Ceb are sorted to distinct vesicle populations in astrocytes. (a) Exemplary images for cultured astrocytes co-immunolabeled with SybII and Ceb antibodies. SybII accumulates
Supplementary legends
 Supplementary legends Supplemental figure S1. Apelin-TAMRA is functional and induces apelin receptor internalization. HEK-293T cells transiently expressing YFP tagged APJ were incubated for 1 hour with:
Supplementary legends Supplemental figure S1. Apelin-TAMRA is functional and induces apelin receptor internalization. HEK-293T cells transiently expressing YFP tagged APJ were incubated for 1 hour with:
Supplemental Information Supplementary Table 1. Tph1+/+ Tph1 / Analyte Supplementary Table 2. Tissue Vehicle LP value
 Supplemental Information Supplementary Table. Urinary and adipose tissue catecholamines in Tph +/+ and Tph / mice fed a high fat diet for weeks. Tph +/+ Tph / Analyte ewat ibat ewat ibat Urine (ng/ml)
Supplemental Information Supplementary Table. Urinary and adipose tissue catecholamines in Tph +/+ and Tph / mice fed a high fat diet for weeks. Tph +/+ Tph / Analyte ewat ibat ewat ibat Urine (ng/ml)
(angiotensin II) injection for intravenous infusion
 ADMINISTERING GIAPREZA TM (angiotensin II) injection for intravenous infusion Visit www.giapreza.com INITIATE Recommended starting dose of GIAPREZA is 20 ng/kg/min, which is equivalent to 0.02 mcg/kg/min
ADMINISTERING GIAPREZA TM (angiotensin II) injection for intravenous infusion Visit www.giapreza.com INITIATE Recommended starting dose of GIAPREZA is 20 ng/kg/min, which is equivalent to 0.02 mcg/kg/min
THE ACTION OF GUANETHIDINE WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM
 Brit. J. Pharinacol. (1963), 20, 171-177. THE ACTION OF GUANETHIDINE WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM BY G. F. ABERCROMBIE AND B. N. DAVIES From the Department of Physiology,
Brit. J. Pharinacol. (1963), 20, 171-177. THE ACTION OF GUANETHIDINE WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO THE SYMPATHETIC NERVOUS SYSTEM BY G. F. ABERCROMBIE AND B. N. DAVIES From the Department of Physiology,
Direct Renal Vasodilatation Produced by Dopamine in the Dog
 Direct Renal Vasodilatation Produced by Dopamine in the Dog By John L. McNay, M.D., Robert H. McDonald, Jr., M.D., and Leon I. Goldberg, Ph.D., M.D. V/ith the technical assistance of Carolyn Davis We have
Direct Renal Vasodilatation Produced by Dopamine in the Dog By John L. McNay, M.D., Robert H. McDonald, Jr., M.D., and Leon I. Goldberg, Ph.D., M.D. V/ith the technical assistance of Carolyn Davis We have
prejunctional dopamine receptors in dog mesenteric
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1987), 91, 591-599 Dopamine released from nerve terminals activates prejunctional dopamine receptors in dog mesenteric arterial vessels P. Soares-da-Silva Laboratorio de Farmacolgia, Faculdade
Br. J. Pharmac. (1987), 91, 591-599 Dopamine released from nerve terminals activates prejunctional dopamine receptors in dog mesenteric arterial vessels P. Soares-da-Silva Laboratorio de Farmacolgia, Faculdade
INTERACTIONS BETWEEN COCAINE, TYRAMINE AND NORADRENALINE AT THE NORADRENALINE STORE
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 2, 54-549. INTERACTIONS BETWEEN COCAINE, TYRAMINE AND NORADRENALINE AT THE NORADRENALINE STORE BY J. FARRANT* From the Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, University
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 2, 54-549. INTERACTIONS BETWEEN COCAINE, TYRAMINE AND NORADRENALINE AT THE NORADRENALINE STORE BY J. FARRANT* From the Department of Pharmacology, School of Pharmacy, University
Effect of Nerve Stimulation on Precapillary Sphincters, Oxygen Extraction, and Hemodynamics in the Intestines of Cats
 32 Effect of Nerve Stimulation on Precapillary Sphincters, Oxygen Extraction, and Hemodynamics in the Intestines of Cats W. WAYNE LAUTT AND SHEILA A. GRAHAM SUMMARY The effect of stimulation of the nerves
32 Effect of Nerve Stimulation on Precapillary Sphincters, Oxygen Extraction, and Hemodynamics in the Intestines of Cats W. WAYNE LAUTT AND SHEILA A. GRAHAM SUMMARY The effect of stimulation of the nerves
AIRWAY RESPONSES TO LOW CONCENTRATIONS OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE IN NORMAL SUBJECTS
 Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology (1985) 70, 203-209 Printed in Great Britain AIRWAY RESPONSES TO LOW CONCENTRATIONS OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE IN NORMAL SUBJECTS K. E. BERKIN, G. C. INGLIS*,
Quarterly Journal of Experimental Physiology (1985) 70, 203-209 Printed in Great Britain AIRWAY RESPONSES TO LOW CONCENTRATIONS OF ADRENALINE AND NORADRENALINE IN NORMAL SUBJECTS K. E. BERKIN, G. C. INGLIS*,
Evidence for the Direct Effect of Adrenergic Drugs on the Cerebral Vascular Bed of the Unanesthetized Goat
 Evidence for the Direct Effect of Adrenergic Drugs on the Cerebral Vascular Bed of the Unanesthetized Goat BY SALVADOR LLUCH, M.D., CHARLES REIMANN, M.D., AND GERALD GLICK, M.D. Abstract: Evidence for
Evidence for the Direct Effect of Adrenergic Drugs on the Cerebral Vascular Bed of the Unanesthetized Goat BY SALVADOR LLUCH, M.D., CHARLES REIMANN, M.D., AND GERALD GLICK, M.D. Abstract: Evidence for
Nature Neuroscience: doi: /nn Supplementary Figure 1. Trial structure for go/no-go behavior
 Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
Supplementary Figure 1 Trial structure for go/no-go behavior a, Overall timeline of experiments. Day 1: A1 mapping, injection of AAV1-SYN-GCAMP6s, cranial window and headpost implantation. Water restriction
RESPONSES TO AMINES IN VASCULAR TISSUE
 Br. J. Pharmac. (197), 3, 267-277 ROLE OF EXTRANEURONAL MECHANISMS IN THE TERMINATION OF CONTRACTILE RESPONSES TO AMINES IN VASCULAR TISSUE S. KALSNER Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Br. J. Pharmac. (197), 3, 267-277 ROLE OF EXTRANEURONAL MECHANISMS IN THE TERMINATION OF CONTRACTILE RESPONSES TO AMINES IN VASCULAR TISSUE S. KALSNER Department of Pharmacology, Faculty of Medicine, University
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers
 Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Light-evoked hyperpolarization and silencing of neurons by conjugated polymers Paul Feyen 1,, Elisabetta Colombo 1,2,, Duco Endeman 1, Mattia Nova 1, Lucia Laudato 2, Nicola Martino 2,3, Maria Rosa Antognazza
Effects of Reboxetine on Sympathetic Neuroeffector
 JPET This Fast article Forward. has not been Published copyedited and on formatted. May 16, The 2003 final as version DOI:10.1124/jpet.103.052233 may differ from this version. JPET #52233 Effects of Reboxetine
JPET This Fast article Forward. has not been Published copyedited and on formatted. May 16, The 2003 final as version DOI:10.1124/jpet.103.052233 may differ from this version. JPET #52233 Effects of Reboxetine
Supplementary Figure 1
 Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
Supplementary Figure 1 Supplementary Figure 1. Short latency of the fepsp evoked in CA3 by electrical stimulation of perforant path inputs (a) Single and superimposed representative perforant pathway-ca3
Influence of Calcium-Entry Blockade on Vasoconstrictor Responses in Feline Mesenteric Vascular Bed
 570 Influence of Calcium-Entry Blockade on Vasoconstrictor Responses in Feline Mesenteric Vascular Bed Howard L. Lippton, William M. Armstead, Albert L. Hyman, and Philip J. Kadowitz The subtypes of postjunctional
570 Influence of Calcium-Entry Blockade on Vasoconstrictor Responses in Feline Mesenteric Vascular Bed Howard L. Lippton, William M. Armstead, Albert L. Hyman, and Philip J. Kadowitz The subtypes of postjunctional
Birmingham B15 2TJ. fi-adrenoreceptor influence of circulating catecholamines.
 Journal of Physiology (1991), 436, pp. 499-510 499 With 2 figures Printed in Great Britain THE ROLES OF CATECHOLAMINES IN RESPONSES EVOKED IN ARTERIOLES AND VENULES OF RAT SKELETAL MUSCLE BY SYSTEMIC HYPOXIA
Journal of Physiology (1991), 436, pp. 499-510 499 With 2 figures Printed in Great Britain THE ROLES OF CATECHOLAMINES IN RESPONSES EVOKED IN ARTERIOLES AND VENULES OF RAT SKELETAL MUSCLE BY SYSTEMIC HYPOXIA
MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE
 Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 539-545. MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE BY K. SHIMAMOTO AND N. TODA From the Department
Br. J. Pharmac. Chemother. (1968), 32, 539-545. MODIFICATIONS BY PROPRANOLOL OF THE RESPONSE OF ISOLATED RABBIT ATRIA TO ENDOGENOUS AND EXOGENOUS NORADRENALINE BY K. SHIMAMOTO AND N. TODA From the Department
University of Groningen. Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan
 University of Groningen Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Melatonin on-line Drijfhout, Willem Jan IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
T HE value of the vasoconstrictor effect of epinephrine in angiography has now
 APRIL, 1969 CONTRAST-VASOCONSTRICTOR IN ANGIOGRAPHY* MIXTURES By PAUL C. KAHN, M.D. With the Technical Assistance of Joseph P. Zeppieri, A.B.,t and Gerald S. Lorch, B.S.t BOSTON, T HE value of the vasoconstrictor
APRIL, 1969 CONTRAST-VASOCONSTRICTOR IN ANGIOGRAPHY* MIXTURES By PAUL C. KAHN, M.D. With the Technical Assistance of Joseph P. Zeppieri, A.B.,t and Gerald S. Lorch, B.S.t BOSTON, T HE value of the vasoconstrictor
Cholinergic Inhibitory Response in the Bovine Iris Dilator Muscle
 Cholinergic Inhibitory Response in the Bovine Iris Dilator Muscle Ryo Suzuki,* Takuro Oso,f and Shunsaku Kobayashi* Isometric tension changes of the bovine iris dilator muscle were investigated in vitro.
Cholinergic Inhibitory Response in the Bovine Iris Dilator Muscle Ryo Suzuki,* Takuro Oso,f and Shunsaku Kobayashi* Isometric tension changes of the bovine iris dilator muscle were investigated in vitro.
Screening and bioassay of Sympatholytics. Dr. Magdy M. Awny Lecture 4
 Screening and bioassay of Sympatholytics by Dr. Magdy M. Awny Lecture 4 1 They are classified into: Sympatholytics = Antagonist of adrenergic activity Drugs that interfere with the activity of the sympathetic
Screening and bioassay of Sympatholytics by Dr. Magdy M. Awny Lecture 4 1 They are classified into: Sympatholytics = Antagonist of adrenergic activity Drugs that interfere with the activity of the sympathetic
Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology
 Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology Drugs act on Sympathetic NS (adrenergic system) Adrenergic Drugs (Sympathomimetics), adrenergic agonists, or alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists Antiadrenergic
Systemic Pharmacology Lecture 7: Neuropharmacology Drugs act on Sympathetic NS (adrenergic system) Adrenergic Drugs (Sympathomimetics), adrenergic agonists, or alpha- and beta-adrenergic agonists Antiadrenergic
EVIDENCE FOR AN INDIRECT CHOLINERGIC REGULATION OF BLOOD FLOW IN THE HYPOTHALAMUS OF CONSCIOUS RABBITS
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1979), 66, 217-221 EVIDENCE FOR AN INDIRECT CHOLINERGIC REGULATION OF BLOOD FLOW IN THE HYPOTHALAMUS OF CIOUS RABBITS K. KLUGMAN, G. MITCHELL & C. ROSENDORFF Department of Physiology,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1979), 66, 217-221 EVIDENCE FOR AN INDIRECT CHOLINERGIC REGULATION OF BLOOD FLOW IN THE HYPOTHALAMUS OF CIOUS RABBITS K. KLUGMAN, G. MITCHELL & C. ROSENDORFF Department of Physiology,
Influence of Prostaglandin E 2, Indomethacin, and Reserpine on Renal Vascular Responses to Nerve Stimulation, Pressor and Depressor Hormones
 72 Influence of Prostaglandin E 2, Indomethacin, and Reserpine on Renal Vascular Responses to Nerve Stimulation, Pressor and Depressor Hormones GREGORY D. FINK, BARRY M. CHAPNICK, MICHAEL R. GOLDBERG,
72 Influence of Prostaglandin E 2, Indomethacin, and Reserpine on Renal Vascular Responses to Nerve Stimulation, Pressor and Depressor Hormones GREGORY D. FINK, BARRY M. CHAPNICK, MICHAEL R. GOLDBERG,
HAAS and Goldblatt 1 reported that infusion
 Ability of Vasoconstrictor Drugs to Cause Adrenal Medullary Discharge after "Sensitization" by Ganglion Stimulating Agents By YOSHIIIIRO KAXEKO, M.D., JAMES W. MCCUBBIX, M.D., AXD IRVINE II. PAGE, M.D.
Ability of Vasoconstrictor Drugs to Cause Adrenal Medullary Discharge after "Sensitization" by Ganglion Stimulating Agents By YOSHIIIIRO KAXEKO, M.D., JAMES W. MCCUBBIX, M.D., AXD IRVINE II. PAGE, M.D.
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition
 Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Integrated Cardiopulmonary Pharmacology Third Edition Chapter 3 Pharmacology of the Autonomic Nervous System Multimedia Directory Slide 19 Slide 37 Slide 38 Slide 39 Slide 40 Slide 41 Slide 42 Slide 43
Long-term hypotensive effect of atenolol 4% eyedrops
 British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 287-291 Long-term hypotensive effect of atenolol 4% eyedrops R. F. BRENKMAN From the Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital, Leiden, The Netherlands
British Journal of Ophthalmology, 1978, 62, 287-291 Long-term hypotensive effect of atenolol 4% eyedrops R. F. BRENKMAN From the Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital, Leiden, The Netherlands
The Ventricular Evoked Response as Monitor for Adrenergic Stimulation
 216 June 1999 The Ventricular Evoked Response as Monitor for Adrenergic Stimulation I. DJAJADISASTRA, G. WEYERS, P. SCHWEIZER Evangelisches Krankenhaus, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany Summary We investigated
216 June 1999 The Ventricular Evoked Response as Monitor for Adrenergic Stimulation I. DJAJADISASTRA, G. WEYERS, P. SCHWEIZER Evangelisches Krankenhaus, Bergisch Gladbach, Germany Summary We investigated
The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that are stimulated by norepinephrine or epinephrine. Some adrenergic drugs act directly on the adrenergic
 Adrenergic drugs The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that are stimulated by norepinephrine or epinephrine. Some adrenergic drugs act directly on the adrenergic receptor (adrenoceptor) by activating it
Adrenergic drugs The adrenergic drugs affect receptors that are stimulated by norepinephrine or epinephrine. Some adrenergic drugs act directly on the adrenergic receptor (adrenoceptor) by activating it
Supplemental Figure 1. Vasoconstrictor responses of renal interlobular arteries to ATP. Responses of interlobular renal arterioles to ATP were
 Supplemental Figure 1. Vasoconstrictor responses of renal interlobular arteries to ATP. Responses of interlobular renal arterioles to ATP were compared in SS rats fed 1% salt diet (black circles) and WKY
Supplemental Figure 1. Vasoconstrictor responses of renal interlobular arteries to ATP. Responses of interlobular renal arterioles to ATP were compared in SS rats fed 1% salt diet (black circles) and WKY
Lai et al 2008 JCI RG-Revision 2
 Lai et al 2008 JCI 36612-RG-Revision 2 Suppmentary Table 1. Epitope specific dystrophin antibodies Name Epitope Dilution Source Dys-3* Hinge 1 1:20 Novocastra Dys-1 Repeats 6-8 1:100 Novocastra Mandys8
Lai et al 2008 JCI 36612-RG-Revision 2 Suppmentary Table 1. Epitope specific dystrophin antibodies Name Epitope Dilution Source Dys-3* Hinge 1 1:20 Novocastra Dys-1 Repeats 6-8 1:100 Novocastra Mandys8
Behavioral generalization
 Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
Supplementary Figure 1 Behavioral generalization. a. Behavioral generalization curves in four Individual sessions. Shown is the conditioned response (CR, mean ± SEM), as a function of absolute (main) or
EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1981), 73,829-835 EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE RESPONSES TO CHOLINOMIMETICS IN THE RAT ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE SHEILA A. DOGGRELL Department of Pharmacology & Clinical
Br. J. Pharmac. (1981), 73,829-835 EFFECT OF ANTIMUSCARINIC AGENTS ON THE CONTRACTILE RESPONSES TO CHOLINOMIMETICS IN THE RAT ANOCOCCYGEUS MUSCLE SHEILA A. DOGGRELL Department of Pharmacology & Clinical
a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline, isoprenaline, dopamine, dobutamine
 1 Adrenergic or sympathetic agonist: Are classified according to: I)- according to the chemical structure a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline,
1 Adrenergic or sympathetic agonist: Are classified according to: I)- according to the chemical structure a)-catecholamines // these are compounds which have the catechol nucleus as adrenaline, noradrenaline,
Hospital, London, W. 12
 J. Physiol. (1967), 19, pp. 221-228 221 With 3 text-figure8 Printed in Great Britain THE TIME COURSE OF THE EFFECT OF THYROID HORMONES UPON BSL OXYGEN CONSUMPTION ND PLSM CONCENTRTION OF FREE FTTY CID
J. Physiol. (1967), 19, pp. 221-228 221 With 3 text-figure8 Printed in Great Britain THE TIME COURSE OF THE EFFECT OF THYROID HORMONES UPON BSL OXYGEN CONSUMPTION ND PLSM CONCENTRTION OF FREE FTTY CID
Enhancement of Peripheral Alpha-Receptor Stimulation by Blockade of "Silent" Beta Receptors
 Enhancement of Peripheral Alpha-Receptor Stimulation by Blockade of "Silent" Beta Receptors By Thomas F. Burks, Ph.D., and Theodore Cooper, M.D., Ph.D. ABSTRACT Evidence is presented for the existence
Enhancement of Peripheral Alpha-Receptor Stimulation by Blockade of "Silent" Beta Receptors By Thomas F. Burks, Ph.D., and Theodore Cooper, M.D., Ph.D. ABSTRACT Evidence is presented for the existence
HISTAMINE RECEPTORS IN ESOPHAGEAL SMOOTH MUSCLE OF THE OPOSSUM
 GASTROENTEROLOGY 70:1071-1075, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 70, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. HISTAMINE RECEPTORS IN ESOPHAGEAL SMOOTH MUSCLE OF THE OPOSSUM DAVID J. DE CARLE, M.B.,
GASTROENTEROLOGY 70:1071-1075, 1976 Copyright 1976 by The Williams & Wilkins Co. Vol. 70, No.6 Printed in U.S.A. HISTAMINE RECEPTORS IN ESOPHAGEAL SMOOTH MUSCLE OF THE OPOSSUM DAVID J. DE CARLE, M.B.,
Function of Vascular Smooth Muscle and Its Sympathetic Innervation in the Newborn Dog *
 Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 44, No. 2, 1965 Function of Vascular Smooth Muscle and Its Sympathetic Innervation in the Newborn Dog * D. L. BOATMAN, R. A. SHAFFER, R. L. DIXON,t AND M. J. BRODY
Journal of Clinical Investigation Vol. 44, No. 2, 1965 Function of Vascular Smooth Muscle and Its Sympathetic Innervation in the Newborn Dog * D. L. BOATMAN, R. A. SHAFFER, R. L. DIXON,t AND M. J. BRODY
FAILURE IN PATIENTS WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION
 Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1982), 14, 187S-19lS BENEFICIAL EFFECTS OF CAPTOPRIL IN LEFT VENTRICULAR FAILURE IN PATIENTS WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION J.P. BOUNHOURE, J.G. KAYANAKIS, J.M. FAUVEL & J. PUEL Departments
Br. J. clin. Pharmac. (1982), 14, 187S-19lS BENEFICIAL EFFECTS OF CAPTOPRIL IN LEFT VENTRICULAR FAILURE IN PATIENTS WITH MYOCARDIAL INFARCTION J.P. BOUNHOURE, J.G. KAYANAKIS, J.M. FAUVEL & J. PUEL Departments
The Regulation of Liver Glucose Production and Uptake
 The Regulation of Liver Glucose Production and Uptake Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN USA Dale Edgerton, PhD An Organ Systems Approach to Experimental Targeting of the Metabolic Syndrome
The Regulation of Liver Glucose Production and Uptake Vanderbilt University Medical Center Nashville, TN USA Dale Edgerton, PhD An Organ Systems Approach to Experimental Targeting of the Metabolic Syndrome
The effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model
 (2002) 14, 251 255 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir The effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model N Ueno 1,
(2002) 14, 251 255 ß 2002 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0955-9930/02 $25.00 www.nature.com/ijir The effect of sildenafil on electrostimulation-induced erection in the rat model N Ueno 1,
SHOCK AETIOLOGY OF SHOCK (1) Inadequate circulating blood volume ) Loss of Autonomic control of the vasculature (3) Impaired cardiac function
 SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
SHOCK Shock is a condition in which the metabolic needs of the body are not met because of an inadequate cardiac output. If tissue perfusion can be restored in an expeditious fashion, cellular injury may
Venous / Arterial Compliance Ratio Calculation. Conflict of Interest
 Venous / Arterial Compliance Ratio Calculation Kirk H. Shelley, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Anesthesiology Yale University STA 13 Conflict of Interest Twenty plus year history of research on this and related
Venous / Arterial Compliance Ratio Calculation Kirk H. Shelley, M.D., Ph.D. Professor of Anesthesiology Yale University STA 13 Conflict of Interest Twenty plus year history of research on this and related
ALPHA-ADRENERGIC RECEPTORS IN HUMAN PROSTATE. Furuya, Seiji; Yokoyama, Eiji; Kuma Tsukamoto, Taiji. Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1983), 29(6):
 Title ALPHA-ADRENERGIC RECEPTORS IN HUMAN PROSTATE Author(s) Furuya, Seiji; Yokoyama, Eiji; Kuma Tsukamoto, Taiji Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1983), 29(6): 635-639 Issue Date 1983-06 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/120191
Title ALPHA-ADRENERGIC RECEPTORS IN HUMAN PROSTATE Author(s) Furuya, Seiji; Yokoyama, Eiji; Kuma Tsukamoto, Taiji Citation 泌尿器科紀要 (1983), 29(6): 635-639 Issue Date 1983-06 URL http://hdl.handle.net/2433/120191
Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l)
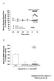 A 18 16 14 1 8 6 4 Vehicle BCTC (.8 mmol/l) Sensory deafferentation Time (min) Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l) N=3 4 * P
A 18 16 14 1 8 6 4 Vehicle BCTC (.8 mmol/l) Sensory deafferentation Time (min) Capsaicin (3.3 mmol/l) N=3 4 * P
RESPONSES TO SYMPATHETIC NERVE STIMULATION
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1975), 53, 517-524 THE EFFECT OF PROPRANOLOL ON VASCULAR RESPONSES TO SYMPATHETIC NERVE STIMULATION P.M. DAWES & D.C. FAULKNER Department of Pharmacology, I.C.I. Pharmaceuticals Division,
Br. J. Pharmac. (1975), 53, 517-524 THE EFFECT OF PROPRANOLOL ON VASCULAR RESPONSES TO SYMPATHETIC NERVE STIMULATION P.M. DAWES & D.C. FAULKNER Department of Pharmacology, I.C.I. Pharmaceuticals Division,
3/10/2009 VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD. Palpated Pulse. Figure 19.11
 VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD Palpated Pulse Figure 19.11 1 shows the common sites where the pulse is felt. 1. Temporal artery at the temple above and to the outer side of the eye 2. External maxillary
VESSELS PHYSIOLOGY D.HAMMOUDI.MD Palpated Pulse Figure 19.11 1 shows the common sites where the pulse is felt. 1. Temporal artery at the temple above and to the outer side of the eye 2. External maxillary
Birmingham B15 2TT. (Received 25 November 1992) hypoxia (breathing 8 or 6% 02 for 5 min).
 Journal of Physiology (1993), 47, pp. 463-472 463 With 4 figures Printed in Great Britain THE ROLE OF VASOPRESSIN IN THE REGIONAL VASCULAR RESPONSES EVOKED IN THE SPONTANEOUSLY BREATHING RAT BY SYSTEMIC
Journal of Physiology (1993), 47, pp. 463-472 463 With 4 figures Printed in Great Britain THE ROLE OF VASOPRESSIN IN THE REGIONAL VASCULAR RESPONSES EVOKED IN THE SPONTANEOUSLY BREATHING RAT BY SYSTEMIC
Physiology and Pharmacology
 Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake Vasoactivity Local
Pharmacokinetics Physiology and Pharmacology Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics Uptake Oral Route Topical Route Injection Distribution Metabolism (Biotransformation) Excretion Uptake Vasoactivity Local
Stimulation of Active K + Transport by Anti-L Antibodies in Trypsin-Treated Low Potassium Sheep Erythrocytes
 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Stimulation of Active K + Transport by Anti-L Antibodies in Trypsin-Treated Low Potassium Sheep Erythrocytes Dear Sir: In this letter we attempt to resolve a discrepancy on the effect
LETTER TO THE EDITOR Stimulation of Active K + Transport by Anti-L Antibodies in Trypsin-Treated Low Potassium Sheep Erythrocytes Dear Sir: In this letter we attempt to resolve a discrepancy on the effect
Evidence that Serotonin Receptors Mediate the Cutaneous Vasoconstriction Produced by 5-Hydroxytryptamine in Canine Forelimbs
 473 Evidence that Serotonin Receptors Mediate the Cutaneous Vasoconstriction Produced by 5-Hydroxytryptamine in Canine Forelimbs David E. Dobbins, Stan W. Adamski, Mustafa F. Lokhandwala, and George J.
473 Evidence that Serotonin Receptors Mediate the Cutaneous Vasoconstriction Produced by 5-Hydroxytryptamine in Canine Forelimbs David E. Dobbins, Stan W. Adamski, Mustafa F. Lokhandwala, and George J.
THE EFFECT OF ESERINE ON THE RESPONSE OF THE VAS DEFERENS TO HYPOGASTRIC NERVE STIMULATION
 Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 20, 74-82. THE EFFECT OF ESERINE ON THE RESPONSE OF THE VAS DEFERENS TO HYPOGASTRIC NERVE STIMULATION BY J. H. BURN AND D. F. WEETMAN From the Biological Research Laboratories,
Brit. J. Pharmacol. (1963), 20, 74-82. THE EFFECT OF ESERINE ON THE RESPONSE OF THE VAS DEFERENS TO HYPOGASTRIC NERVE STIMULATION BY J. H. BURN AND D. F. WEETMAN From the Biological Research Laboratories,
Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC
 1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
1 2 1 3 Supplementary figure 1: LII/III GIN-cells show morphological characteristics of MC 4 5 6 7 (a) Reconstructions of LII/III GIN-cells with somato-dendritic compartments in orange and axonal arborizations
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
 doi:10.1038/nature10776 Supplementary Information 1: Influence of inhibition among blns on STDP of KC-bLN synapses (simulations and schematics). Unconstrained STDP drives network activity to saturation
doi:10.1038/nature10776 Supplementary Information 1: Influence of inhibition among blns on STDP of KC-bLN synapses (simulations and schematics). Unconstrained STDP drives network activity to saturation
EFFECT OF MUSCARINE ON RELEASE OF CATECHOLAMINES
 Br. J. Pharmac. (1982), 77, 455-46 EFFECT OF MUSCARINE ON RELEASE OF CATECHOLAMINES FROM THE PERFUSED ADRENAL GLAND OF THE CAT S.M. KIRPEKAR, J.C. PRAT & M.T. SCHIAVONE Department of Pharmacology, Downstate
Br. J. Pharmac. (1982), 77, 455-46 EFFECT OF MUSCARINE ON RELEASE OF CATECHOLAMINES FROM THE PERFUSED ADRENAL GLAND OF THE CAT S.M. KIRPEKAR, J.C. PRAT & M.T. SCHIAVONE Department of Pharmacology, Downstate
When Fluids are Not Enough: Inopressor Therapy
 When Fluids are Not Enough: Inopressor Therapy Problems in Neonatology Neonatal problem: hypoperfusion Severe sepsis Hallmark of septic shock Secondary to neonatal encephalopathy Vasoplegia Syndrome??
When Fluids are Not Enough: Inopressor Therapy Problems in Neonatology Neonatal problem: hypoperfusion Severe sepsis Hallmark of septic shock Secondary to neonatal encephalopathy Vasoplegia Syndrome??
Mechanism of Norepinephrine Depletion in Experimental Heart Failure Produced by Aortic Constriction in the Guinea Pig
 Mechanism of Norepinephrine Depletion in Experimental Heart Failure Produced by Aortic Constriction in the Guinea Pig By James F. Spann, Jr., M.D., Charles A. Chidsey, M.D., Peter E. Pool, M.D., and Eugene
Mechanism of Norepinephrine Depletion in Experimental Heart Failure Produced by Aortic Constriction in the Guinea Pig By James F. Spann, Jr., M.D., Charles A. Chidsey, M.D., Peter E. Pool, M.D., and Eugene
PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker
 PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
PACKAGE INSERT Pr PHENTOLAMINE MESYLATE INJECTION SANDOZ STANDARD 5 mg/ ml THERAPEUTIC CLASSIFICATION Alpha-adrenoreceptor Blocker ACTIONS AND CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY Phentolamine produces an alpha-adrenergic
Noradrenaline improves the tumour to normal blood ow ratio and drug delivery in a model of liver metastases
 Original article Noradrenaline improves the tumour to normal blood ow ratio and drug delivery in a model of liver metastases A. Shankar, M. Loizidou, G. Burnstock* and I. Taylor Department of Surgery and
Original article Noradrenaline improves the tumour to normal blood ow ratio and drug delivery in a model of liver metastases A. Shankar, M. Loizidou, G. Burnstock* and I. Taylor Department of Surgery and
Veins. VENOUS RETURN = PRELOAD = End Diastolic Volume= Blood returning to heart per cardiac cycle (EDV) or per minute (Venous Return)
 Veins Venous system transports blood back to heart (VENOUS RETURN) Capillaries drain into venules Venules converge to form small veins that exit organs Smaller veins merge to form larger vessels Veins
Veins Venous system transports blood back to heart (VENOUS RETURN) Capillaries drain into venules Venules converge to form small veins that exit organs Smaller veins merge to form larger vessels Veins
