Reproducibility of dopamine transporter density measured with 123 I-FPCIT SPECT in normal control and Parkinson s disease patients
|
|
|
- Andrew Hampton
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 18, No. 7, , 2004 Reproducibility of dopamine transporter density measured with 123 I-FPCIT SPECT in normal control and Parkinson s disease patients Tatsuro TSUCHIDA,* 1, * 3, * 7 James R. BALLINGER,* 1, * 3, * 5 Douglass VINES,* 1, * 4 Yun J. KIM,* 2, * 3 Keita UTSUNOMIYA,* 1, * 3, * 6 Anthony E. LANG* 2, * 3 and Masanori ICHISE* 1, * 3, * 4 * 1 Division of Nuclear Medicine, Department of Medical Imaging, Mount Sinai Hospital, * 2 Morton and Gloria Shulman Movement Disorders Center, * 3 University of Toronto, * 4 Molecular Imaging Branch, National Institute of Mental Health, * 5 Department of Nuclear Medicine, Guy s and St. Thomas Hospital, * 6 Department of Radiology, Osaka Medical College, and * 7 Department of Radiology, University of Fukui The objective of this study was to evaluate the reproducibility of 123 I-FPCIT SPECT by using whole striatal region of interest (ROI) and subdivided ROI in normal controls (NC) and Parkinson s disease (PD) patients. Methods: Ten NC and 6 PD received a SPECT scan for 6 hours postinjection of FPCIT. The distribution volume ratio (R V) and specific-nonspecific tissue activity ratio (R T) were measured as an outcome measure. The test/retest reproducibility of R V and R T was evaluated by calculating the test/retest difference, variability, and reliability. Results: There were no significant test/retest differences for any regions in either the NC or PD. The test/retest variability/reliability of R V was 5.53 ± 4.12%/0.89 in NC, 4.50 ± 5.31%/0.99 in PD with whole striatal ROI, 4.29 ± 0.78%/ 0.94 ± 0.03 in NC, and 6.87 ± 1.23 %/0.98 ± 0.01 in PD with subdivided ROI. The test/retest variability/reliability of R T was 11.1 ± 10.4%/0.59 in NC, 7.84 ± 8.94%/0.95 in PD with whole striatal ROI, 11.9 ± 1.22%/0.65 ± 0.06 in NC, and 12.2 ± 4.00%/0.95 ± 0.03 in PD with subdivided ROI. Conclusion: R V is highly reproducible and reliable compared with R T in both NC and PD as an outcome measure. Key words: 123 I-FPCIT, reproducibility, distribution volume ratio INTRODUCTION THE IMAGING of dopamine transporters using positron emission tomography (PET) or single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) has been introduced as a valuable tool to evaluate patients with movement disorders like Parkinson s disease (PD). 1,2 PET with 11 C- nomifensine or 11 C-labeled cocaine analogs showed a loss of striatal dopamine transporters in PD patients. 3,4 SPECT, which is more widely available than PET, with 123 I-labeled cocaine analogs, 123 I-2β-carbomethoxy-3β- (4-iodophenyl)tropane (β-cit), also showed a dramatic loss of striatal dopamine transporters in patients with PD with high signal-to-noise ratios. 2,5 8 However, the slow Received May 12, 2004, revision accepted July 8, For reprint contact: Tatsuro Tsuchida, M.D., Department of Radiology, University of Fukui, 23 3 Shimoaizuki, Matsuoka, Fukui , JAPAN. kinetics of 123 I-β-CIT is a serious drawback. A stable level of radioactivity in the striatum is only reached between 20 and 30 hr postinjection. 9 This indicates that optimal image acquisition can be performed only the day following the injection of [ 123 I]β-CIT (2-day protocol), which is highly inconvenient for outpatient evaluations. Moreover, due to the half-life of 123 I (13.2 hr), the counting statistics are considerably diminished at that time by physical decay. 123 I-N-ω-fluoropropyl-2β-carbomethoxy-3β-(4- iodophenyl)nortropane (FPCIT) is a new cocaine analog with a high affinity for dopamine transporter Previous studies have revealed that FPCIT SPECT allows the use of a 1-day protocol for imaging of dopamine transporters, due to the fast kinetics. 7,8,11,13,14 The demonstration of a reproducible SPECT outcome measure is critical and preliminary to the extension of FPCIT to clinical populations, including the serial monitoring of progressive disorders like PD, as has been revealed by other radiopharmaceuticals in normal Vol. 18, No. 7, 2004 Original Article 609
2 Table 1 Demographic characteristics of PD patients UPDRS* Patient Sex Age, y Disease Hoehn & Motor (contralateral/ no. duration, y Yahr stage Total ipsilateral) Medication (total daily dose in mg) 1 M (11.5/9) Sinemet (600), deprenyl (20), Bromocriptine (7.5) 2 F (13.5/1.5) None 3 M (3/0) None 4 F (7/4) Sinemet (500), Requip (5) 5 M (5/3) Sinemet CR (1200), Tolcapone (100) 6 M (13/11) Sinemet (200), Sinemet CR (1300) Mean (8.8/4.8) Permax (6), Amantadine (200) SD (4.4/4.3) * Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating Scale (Total: maximum possible score = 176; Motor: maximum possible score = 108; contralateral/ipsilateral motor; maximum possible score = 36) controls (NC) or PD Therefore, we undertook to evaluate the test/retest reproducibility of FPCIT SPECT imaging. MATERIALS AND METHODS Subjects We studied 10 NC subjects (6 men, 4 women; mean age 36.4 ± 15.9 y, range 25 to 70 y) with no current or past history of neuropsychiatric disorders or family history of movement disorders, and 6 PD patients (4 men, 2 women; mean age 58.0 ± 11.7 y, range 40 to 71 y), who were recruited from the Movement Disorder Clinic at The Toronto Hospital. The patients characteristics are described in detail in Table 1. The patients had mild PD, as assessed by the Hoehn and Yahr Scale 20 (1 stage I patient, and 5 stage II patients), and the Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) 21 (mean total UPDRS, score 32.1 ± 19.4, range 4 to 55.5). The diagnosis of PD was made according to the UK Parkinson s Disease Brain Bank clinical diagnosis criteria. 22 Four of the 6 patients took antiparkinsonian medication, which included L-dopa or dopamine agonists. Patients who were on treatment discontinued their drugs for at least 12 hours before the commencement of the SPECT studies and until their completion. All UPDRS scores were obtained before the SPECT studies, when the drug-treated patients had been off medication for at least 12 hours. All patients and controls gave written informed consent. The project was approved by the Human Subjects Review Committee of the University of Toronto. Preparation of 123 I-FPCIT FPCIT was prepared by a modification of the method of Zea-Ponce et al. 23 Fifty µg of the trimethylstannyl precursor supplied by Nihon Medi-Physics Co., Ltd. (Tokyo, Japan) was dissolved in 50 µl ethanol, and added to a vial containing 123 I sodium iodide (supplied by Nordion International, Ltd., Vancouver, BC, Canada) in 0.1 N NaOH ( MBq in µl). To the reaction mixture were added 50 µl 1 M phosphoric acid and 50 µl freshly-diluted 2.6% peracetic acid. After incubation for 30 minutes at room temperature, the reaction was quenched with 50 µl sodium metabisulfite (300 mg/ml) and 500 µl sodium bicarbonate (100 mg/ml), diluted with 5 ml sterile water and passed through a C-18 solid-phase extraction cartridge (Sep-Pak Classic). The cartridge was eluted with four fractions of 0.5 ml absolute ethanol. The hottest fractions were pooled, and diluted with 5 volumes of saline. After the addition of 100 µl ascorbic acid (1 mg/ml), the solution was sterilized through a low-protein-binding 0.22-microm membrane filter into a sterile 10 ml multidose vial. The radiochemical purity was checked using a C-18 extraction cartridge eluted with water. Retrospective sterility testing was negative. In 32 preparations, the yield was 68.5 ± 10.4% and the radiochemical purity was 99.2 ± 0.6%. SPECT imaging Imaging was performed using a triple-headed SPECT system (Prism 3000XP, Picker International, Inc., Cleveland, OH) equipped with ultra-high resolution fan beam collimators and interfaced to a dedicated computer (Odyssey VP; Picker International, Inc., Cleveland, OH). The NC subjects had a test/retest SPECT examination 1 wk apart, and the PD patients had it within 3 wks apart (13 ± 5 days). The FPCIT SPECT scans were acquired every 5 minutes at 0 120, , , and minutes postinjection. The injected doses of FPCIT were 351 ± 56 MBq for NC, and 365 ± 26 MBq for PD. For each scan, second projection images were obtained using 3 degree angle intervals on a matrix over 360 degrees by rotating each head 120 degrees. The radius of rotation was fixed at 13.5 cm. To identify the canthomeatal line (CML), fiducial markers containing 55.5 MBq of 99m Tc were taped on the outer canthus of the eye and over the external auditory meatus 610 Tatsuro Tsuchida, James R. Ballinger, Douglass Vines, et al Annals of Nuclear Medicine
3 Fig. 1 ROI template image. 2a 2b 2c Fig. 2 Test/retest time-activity curve (TAC) in representative cases in NC and PD. Six subdivided ROIs were averaged in each study, and their activities were normalized by an injected dose of 370 MBq in each study. Neither NC (2a, 23-year-old female) nor stage I PD (2b, 40-year-old male) show any apparent decline of striatal uptake. In contrast, in stage II PD (2c, 69-year-old female), a decline of the uptake in both striatum (closed circle) and the frontal cortex (open circle) was observed. Fig. 3 Test/retest FPCIT SPECT images in NC (53-year-old male, left) and PD (59-year-old male, right). The averaged variability of R V was 3.05 ± 2.46% in NC and 9.03 ± 1.86% in PD. The image intensity was adjusted so that the striatal uptake would reflect the mean striatal values of R V. Vol. 18, No. 7, 2004 Original Article 611
4 a b c d Fig. 4 The test/retest difference of R V in NC (a) and PD (b) and R T in NC (c) and PD (d). No significant difference was observed in any regions. WS; whole striatum, CCD; contralateral caudate head, CAP; contralateral anterior putamen, CPP; contralateral posterior putamen, ICD; ipsilateral caudate head, IAP; ipsilateral anterior putamen, IPP; ipsilateral posterior putamen. bilaterally throughout the imaging experiment. 24 Full width with half-maximum of this system was 9.1 mm in water at the center of the field of view. Before the SPECT study, each subject took 400 mg of potassium perchlorate orally for thyroid blocking. The SPECT images were reconstructed every 5 minutes for the first 30-minute data. Otherwise, they were reconstructed every 10 minutes. To obtain the template image of regions of interest (ROIs), the first 15-minute data were summed and used for reconstruction. Onepixel-thick transaxial slices from the vertex of the brain to the level of the CML, as identified by the fiducial markers, were reconstructed parallel to the CML using a threedimensional Butterworth postreconstruction filter (order 10, cutoff frequency 0.25 cycles/pixel) after applying a ramp back projection filter. Attenuation correction was performed (µ = 0.12 cm 1 ) within an ellipse drawn around the skull, as identified by the fiducial markers. Data analysis For NC, the contralateral side was assigned to the left side. For PD, the contralateral side was defined as the side contralateral to the most affected limbs. The ROIs used were three striatal subregions (subdivided ROI) caudate head (volume, 1.10 cm 3 ) anterior putamen (0.89 cm 3 ) and posterior putamen (1.23 cm 3 ) and six circular frontal cortex ROIs (total volume, 3.93 cm 3 ) shown in Figure 1. The ROIs placement depended on the visual identification of anatomic regions aided by the stereotaxic atlas and the early (first 15-minute) FPCIT image, which reflects mostly regional perfusion. In PD, as striatal perfusion is intact, this strategy facilitated placing striatal ROIs on the FPCIT images even after a long time postinjection. All ROIs were applied by one operator to eliminate interoperator variation. To obtain the whole striatal ROI value, six subdivided ROIs in each subject were averaged. For assessment of the time-activity curve (TAC), whole striatal ROI was used. The time-to-peak uptake in the striatum, the frontal cortex, and specific binding (striatum-frontal cortex) was quantified after fitting a sum of three exponentials to the regional time-activity data. The 612 Tatsuro Tsuchida, James R. Ballinger, Douglass Vines, et al Annals of Nuclear Medicine
5 time-to-peak uptake in the striatum and specific binding were used to evaluate the reproducibility of the TAC. The dopamine transporter binding was quantified as the distribution volume ratio (R V ) by using the multilinear regression technique 19 and the specific-nonspecific tissue activity ratio (R T ). The multilinear regression technique permits measurement of the binding potential, R V = V 3 / V 2, without blood data, according to the following equation: t 0 C ST (t)dt C ST(t) t 0 C ST (t)dt = ( a ) + ( ab ) C FC(t) + b (1) a C ST(t) a C ST (t) where C ST (t) represents the time-activity measurements in the striatum and C FC (t) represents the time-activity measurements in the frontal cortex, and a, a, b and b are constants. R V is related to the partial regression coefficient a/a in equation 1, as follows: R V = V 3 /V 2 = a/a 1 R T was calculated as follows; R T = (ST FC)/FC 1 where ST and FC represent the measured activity in the striatum and the frontal cortex. In this study, R T at 3-hour postinjection, which was reported to be a simple outcome measure by Booij et al., 14 was compared with R V in terms of variability and reliability. Statistical analysis All statistical analyses, including multilinear regression analysis, were implemented in STATISTICA (StatSoft, Inc., Tulsa, OK). For the assessment of the test/retest reproducibility of R V and R T in NC and PD, the test/retest differences, variability, and reliability were applied. Wilcoxon Matched-Pairs Signed Rank test was used for comparison between the test and retest measures. The test/retest variability in R V and R T was calculated as the absolute value of the difference between the two measurements, expressed as a percentage of the mean value of both measurements, and the rest/retest variability of R V and R T was also compared between the corresponding subdivided ROIs by means of Wilcoxon Matched-Pairs Signed Rank test. The reliability of the two measurements between the test and retest was assessed by calculating the intraclass correlation coefficient, according to the following equation. 25 MSBS MSWS ρ = (3) MSBS + (k 1)MSWS where MSBS and MSWS are the mean sum of squares between and within subjects, respectively, and k is the number of within-subject measurements, being 2 in the present study. This coefficient is an estimate of the reliability of the two sets of measurements, and varies from Table 2 Test/retest measures of R V Test Retest p NC WS 3.56 ± ± CCD 3.39 ± ± CAP 3.83 ± ± CPP 3.25 ± ± ICD 3.70 ± ± IAP 3.94 ± ± IPP 3.51 ± ± PD WS 1.22 ± ± CCD 1.36 ± ± CAP 1.29 ± ± CPP 0.79 ± ± ICD 1.52 ± ± IAP 1.41 ± ± IPP 0.99 ± ± WS; whole striatum, CCD; contralateral caudate head, CAP; contralateral anterior putamen, CPP; contralateral posterior putamen, ICD; ipsilateral caudate head, IAP;ipsilateral anterior putamen, IPP; ipsilateral posterior putamen Table 3 Test/retest measures of R T Test Retest p NC WS 3.67 ± ± CCD 3.53 ± ± CAP 3.89 ± ± CPP 3.34 ± ± ICD 3.82 ± ± IAP 3.95 ± ± IPP 3.50 ± ± PD WS 1.24 ± ± CCD 1.28 ± ± CAP 1.33 ± ± CPP 0.83 ± ± ICD 1.60 ± ± IAP 1.40 ± ± IPP 1.02 ± ± (no reliability) to 1 (total reliability). Statistical significance was defined as p < The summaries of study variables were expressed as mean ± s.d. RESULTS Of 20 SPECT studies in NC, the peak time of striatal uptake was not observed during a 6 hr scan in 1 study, and that of specific binding was not observed in 5 studies. In these studies, the peak time was assumed to be 6 hr postinjection for the convenience of statistical analysis. In PD, all studies showed the peak of striatal uptake and Vol. 18, No. 7, 2004 Original Article 613
6 Table 4 Test/retest variability (%) and reliability (ρ) between R V and R T R V Variability ρ Variability ρ p for variability NC WS 5.53 ± ± CCD 5.08 ± ± CAP 4.17 ± ± CPP 4.15 ± ± ICD 4.09 ± ± IAP 5.18 ± ± IPP 3.04 ± ± PD WS 4.50 ± ± CCD 4.86 ± ± CAP 7.03 ± ± CPP 7.98 ± ± ICD 6.49 ± ± IAP 6.53 ± ± IPP 8.30 ± ± NC + PD WS 5.08 ± ± CCD 5.00 ± ± CAP 5.25 ± ± CPP 5.59 ± ± ICD 4.99 ± ± IAP 5.69 ± ± IPP 5.01 ± ± R T specific binding within the end of the scan. The mean peak time of the striatal uptake in NC (222 ± 56 min) came later than that in PD (31 ± 30 min). The variability/reliability of the peak time of striatal uptake were 22.5 ± 12.9%/0.54 in NC and 16.4 ± 17.5%/0.29 in PD. The mean peak time of specific binding in NC (271 ± 57 min) was also reached later than in PD (123 ± 68 min). The variability/reliability of the peak time of specific binding were 18.9 ± 18.6%/ 0.50 in NC and 12.9 ± 14.5%/0.84 in PD. The test/retest TAC in NC, stage I PD (Patient 3), and stage II PD (Patient 4) are shown in Figures 2a, 2b, and 2c. The test/retest FPCIT SPECT images in NC and stage II PD (Patient 6) are shown in Figure 3. Figures 4a, 4b, 4c, and 4d show the test/retest differences of R V and R T in NC and PD. Test/retest measures are shown in Tables 2 and 3. There were no significant test/ retest differences of R V or R T in either NC or PD (p > 0.1). The test/retest variability and reliability of R V and R T in the whole striatal and subdivided ROI are shown in Table 4. A significant difference of variability between R V and R T was observed in the WS, CAP, CPP, ICD, and IPP of NC. When NC and PD data were combined, a significant difference was observed in all regions except WS and IAP. DISCUSSION In this study, the averaged variability and reliability of R V with FPCIT SPECT was 4.29%/0.94 in NC, and 6.87%/ 0.98 in PD when subdivided ROIs were used. In the previous reports, 26 the averaged variability/reliability of FPCIT SPECT was estimated as 7.25%/0.99 in NC and 7.9%/1.00 in PD. The averaged test/retest variability (%) and reliability in NC and PD on other PET/SPECT ligands are as follows: NC; 6.8/0.96 in 123 I β-cit, 18 and 3.3/0.73 in 18 F DOPA, 16 PD; 3/0.76 in 18 F DOPA. 17 In our study, we used both whole striatal and subdivided ROI to evaluate the test/retest reproducibility. In contrast, only whole striatal ROI was used for all other reproducibility studies. We used the subdivided ROI to determine if the reproducibility of FPCIT SPECT would be preserved or not in small or low count regions. The importance of estimating transporter binding in subdivided regions arises from the intrastriatal differences of dopaminergic function in PD. 27 In PD, the ventral portion of the substantia nigra pars compacta appears more susceptible to degeneration than the dorsal tier, 28 and more severe reduction in radiotracer binding can be observed in the posterior putamen. The uneven dopamine transporter deficit within the putamen is also known from postmortem findings, and from recent PET studies. 4,29 On the one hand, if whole striatal ROI is applied to estimate the dopamine transporter binding in 614 Tatsuro Tsuchida, James R. Ballinger, Douglass Vines, et al Annals of Nuclear Medicine
7 PD, the regional differences of the transporter binding might be obscured, and the sensitivity to detect subtle differences in the transporter density might decrease. On the other hand, if using subdivided ROI results in larger variability and lower reliability compared to using whole striatal ROI, the method would be of no use. Our results are thought to be comparable or superior to those of previous reports with respect to the values of variability and reliability, even though we used subdivided ROIs. Therefore, we think R V values are available for the estimation of transporter binding in subdivided regions. We speculated that our data showed excellent reproducibility because we used R V as outcome measures. Compared to R V which is estimated from multilinear regression analysis with multi point data, the specific to non-specifiic ratio (R T ), widely used for the estimation of transporter/receptor binding, 7,8,11,14,26,30 32 is obtained from one time point data. The variability reported by Booij et al. 26 is larger than that of our study, despite the fact that they used whole striatal ROI. This may mean that R T itself presents a risk of causing large variability. In our study, the larger variability of R T was observed in all subdivided ROIs. R T is a very simple index to calculate, and because of this, it might be suitable to use for routine study, but not of course if the index is unreliable. We think the selection of outcome measures depends on the situation in which they are used. For the discrimination of NC and PD, R T would be available, because PD shows a marked decrease of transporter density from the very early stage. Gutmann et al. 4 reported that even in very early PD, a 56% reduction of the transporter binding in the contralateral posterior putamen was observed with 11 C-RTI-32, and Marek et al. 33 reported a 53% reduction of contralateral striatal uptake with 123 I-β-CIT in patients with hemi-parkinson s disease. In contrast, to estimate the disease progression, a more reproducible method should be applied. Vingerhoets et al. 34 reported that the decline of striatal dopaminergic metabolic function in PD is 7.8% per decade, while an annual decline of 7% was reported by Morrish et al. 35 These changes are apparently smaller than the difference between NC and PD. Therefore, we think R V, rather than R T, should be applied for the estimation of disease progression, although R T is sufficient for diagnosing PD. The disadvantage to obtaining R V is that a dynamic scan is required. This is extremely inconvenient for the subjects. To make it easier for the subjects, the simplified method proposed by Ichise et al. 36 can be used. In conclusion, we reported the excellent reproducibility of R V in FPCIT SPECT with whole striatal and subdivided ROI. REFERENCES 1. Leenders KL, Salmon EP, Tyrrell P, Perani D, Brooks DJ, Sager H, et al. The nigrostriatal dopaminergic system assessed in vivo by positron emission tomography in healthy volunteer subjects and patients with Parkinson s disease. Arch Neurol 1990; 47: Innis RB, Seibyl JP, Scanley BE, Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, Wallece E, et al. Single photon emission computed tomographic imaging demonstrates loss of striatal dopamine transporters in Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1993; 90: Frost JJ, Rosier AJ, Reich SG, Smith JS, Ehlers MD, Snyder SH, et al. Positron emission tomographic imaging of the dopamine transporters with 11 C-WIN 35,428 reveals marked declines in mild Parkinson s disease. Ann Neurol 1993; 34: Guttman M, Burkholder J, Kish SJ, Hussey D, Wilson A, DaSilva J, et al. [ 11 C]RTI-32 PET studies of the dopamine transporters in early dopa-naive Parkinson s disease: implications for the symptomatic threshold. Neurology 1997; 48: Brücke T, Kohnhuber J, Angelberger P, Asenbaum S, Frassine H, Podreka I. SPECT imaging of dopamine and serotonin transporters with [ 123 I]β-CIT binding kinetics in human brain. J Neural Transm [GenSect] 1993; 94: Seibyl JP, Marek KL, Quinlan D, Sheff K, Zoghbi S, Zea- Ponce Y, et al. Decreased single-photon emission computed tomographic [ 123 I]β-CIT striatal uptake correlates with symptom severity in Parkinson s disease. Ann Neurol 1995; 38: Booij J, Tissingh G, Boer GJ, Speelman JD, Stoof JC, Janssen AGM, et al. [ 123 I]FP-CIT SPECT shows a pronounced decline of striatal dopamine transporter labelling in early and advanced Parkinson s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1997; 62: Booij J, Tissingh G, Winogrodzka A, Boer GJ, Stoof JC, Wolters EC, et al. Practical benefit of [ 123 I]FP-CIT SPET in the demonstration of the dopaminergic deficit in Parkinson s disease. Eur J Nucl Med 1997; 24: Laruelle M, Wallace E, Seibyl JP, Baldwin RM, Zea-Ponce Y, Zoghbi S, et al. Graphical, kinetic, and equilibrium analysis of in vivo [ 123 I]β-CIT binding to dopamine transporters in healthy human subjects. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1994; 14: Neumeyer JL, Wang S, Gao Y, Milius RA, Kula NS, Campbell A, et al. N-ω-fluoroalkyl analogs of (1R)-2βcarbomethoxy-3β-(4-iodophenyl)-tropane (β-cit): radiotracers for positron emission tomography and single photon emission computed tomography imaging of dopamine transporters. J Med Chem 1994; 37: Abi-Dargham A, Gandelman MS, DeErausquin GA, Zea- Ponce Y, Zoghbi SS, Baldwin RM, et al. SPECT imaging of dopamine transporters in human brain with iodine-123- fluoroalkyl analogs of β-cit. J Nucl Med 1996; 37: Scheffel U, Lever JR, Abraham P, Parham KR, Mathews WB, Kopajtic T, et al. N-substituted phenyltropanes as in vivo binding ligands for rapid imaging studies of the dopamine transporter. Synapse 1997; 25: Kuikka JT, Bergström KA, Ahonen A, Hiltunen J, Haukka J, Lansimies E, et al. Comparison of iodine-123 labelled 2β-carbomethoxy-3β-(4-iodophenyl)tropane and 2βcarbomethoxy-3β-(4-iodophenyl)-N-(3-fluoropropyl) Vol. 18, No. 7, 2004 Original Article 615
8 nortropane for imaging of the dopamine transporter in the living human brain. Eur J Nucl Med 1995; 22: Booij J, Hamelaar JTGM, Speelman JD, de Bruin K, Janssen AGM, van Royen EA. One-day protocol for imaging of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway in Parkinson s disease by [ 123 I]FPCIT SPECT. J Nucl Med 1999; 40: Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Wang GJ, Dewey SL, Schlyer D, MacGregor R, et al. Reproducibility of repeated measures of carbon-11-raclopride binding in the human brain. J Nucl Med 1993; 34: Vingerhoets FJG, Snow BJ, Schulzer M, Morrison S, Ruth TJ, Holden JE, et al. Reproducibility of fluorine fluorodopa positron emission tomography in normal human subjects. J Nucl Med 1994; 35: Vingerhoets FJG, Schulzer M, Ruth TJ, Holden JE, Snow BJ. Reproducibility and discriminating ability of fluorine fluoro-L-dopa PET in Parkinson s disease. J Nucl Med 1996; 37: Seibyl JP, Laruelle M, van Dyck CH, Wallace E, Baldwin RM, Zoghbi S, et al. Reproducibility of iodine-123-β-cit SPECT brain measurement of dopamine transporters. J Nucl Med 1996; 37: Ichise M, Ballinger JR, Vines D, Tsai S, Kung HF. Simplified quantification and reproducibility studies of dopamine D2- receptor binding with iodine-123-ibf SPECT in healthy subjects. J Nucl Med 1997; 38: Hoehn MM, Yahr MD. Parkinsonism: onset, progression, and mortality. Neurology 1967; 17: Lang AE, Fahn S. Assessment of Parkinson s disease. In: Munsat TL, ed. Quantification of Neurologic Deficit. Boston; Butterworths, 1989: Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L, Lees AJ. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson s disease: a clinicopathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1992; 55: Zea-Ponce Y, Baldwin RM, Laruelle M, Wang S, Neumeyer JL, Innis RB. Simplified multidose preparation of iodine- 123-β-CIT: a marker for dopamine transporters. J Nucl Med 1995; 36: Vines DC, Ivo BD, Ballinger JR, Ichise M. External radioactive reference markers in SPECT imaging of the dopamine system. J Nucl Med Technol 1999; 27: Snedecor GW, Cochran WG. Specific indices of interater reliability. In: Snedecor GW, Cochran WG, eds. Statistical Methods, 6th ed. Ames, IO; Iowa State University Press, 1989: Booij J, Habraken JBA, Bergmans P, Tissingh G, Winogrodzka A, Wolters EC, et al. Imaging of dopamine transporters with iodine-123-fp-cit SPECT in healthy controls and patients with Parkinson s disease. J Nucl Med 1998; 39: Brooks DJ, Ibanez V, Sawle GV, Quinn N, Lees AJ, Mathias CJ, et al. Differing patterns of striatal 18 F-dopa uptake in Parkinson s disease, multiple system atrophy, and progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 1990; 28: Gibb WR. Neuropathology of Parkinson s disease and related syndromes. Neurol Clin 1992; 10: Kish SJ, Shannak K, Hornykiewicz O. Uneven pattern of dopamine loss in the striatum of patients with idiopathic Parkinson s disease: pathophysiologic and clinical implications. N Engl J Med 1988; 318: Ishikawa T, Dhawan V, Kazumata K, Chaly T, Mandel F, Meumeyer J, et al. Comparative nigrostriatal dopaminergic imaging with iodine-123-βcit-fp/spect and fluorine- 18-FDOPA/PET. J Nucl Med 1996; 37: Seibyl JP, Marek K, Sheff K, Zoghbi S, Baldwin RM, Charney DS, et al. Iodine-123-β-CIT and iodine-123-fpcit SPECT measurement of dopamine transporters in healthy subjects and Parkinson s patients. J Nucl Med 1998; 39: Tissingh G, Booij J, Bergmans P, Winogrodzka A, Janssen AGM, van Royen EA, et al. Iodine-123-N-ω-fluoropropyl- 2β-carbomethoxy-3β-(4-iodophenyl)tropane SPECT in healthy controls and early-stage, drug-naive Parkinson s disease. J Nucl Med 1998; 39: Marek KL, Seibyl JP, Zoghbi SS, Zea-Ponce Y, Baldwin RM, Fussell B, et al. [ 123 I]β-CIT/SPECT imaging demonstrates bilateral loss of dopamine transporters in hemi- Parkinson s disease. Neurology 1996; 46: Vingerhoets FJG, Snow BJ, Lee CS, Schulzer M, Mak E, Calne DB. Longitudinal fluorodopa positron emission tomographic studies of the evolution of idiopathic parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 1994; 36: Morrish PK, Sawle GV, Brooks DJ. An [ 18 F]dopa-PET and clinical study of the rate of progression in Parkinson s disease. Brain 1996; 119: Ichise M, Ballinger JR, Golan H, Vines D, Luong A, Tsai S, Kung HF. Noninvasive quantification of dopamine D2 receptors with iodine-123-ibf SPECT. J Nucl Med 1996; 37: Tatsuro Tsuchida, James R. Ballinger, Douglass Vines, et al Annals of Nuclear Medicine
Short communication. dwk&:key words: Parkinson s disease Single-photon emission tomography Dopamine transporter imaging Aging. Materials and methods
 Short communication [ 123 I]β-CIT single-photon emission tomography in Parkinson s disease reveals a smaller decline in dopamine transporters with age than in controls G. Tissingh 1, P. Bergmans 1, J.
Short communication [ 123 I]β-CIT single-photon emission tomography in Parkinson s disease reveals a smaller decline in dopamine transporters with age than in controls G. Tissingh 1, P. Bergmans 1, J.
New semiquantitative assessment of 123 I-FP-CIT by an anatomical standardization method
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 20, No. 7, 477 484, 2006 New semiquantitative assessment of 123 I-FP-CIT by an anatomical standardization method Seiko TAKADA,* Mana YOSHIMURA,* Hiroaki
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 20, No. 7, 477 484, 2006 New semiquantitative assessment of 123 I-FP-CIT by an anatomical standardization method Seiko TAKADA,* Mana YOSHIMURA,* Hiroaki
T he main symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson s disease
 1211 PAPER How useful is [ 123 I]b-CIT SPECT in clinical practice? J Eerola, P J Tienari, S Kaakkola, P Nikkinen, J Launes... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Johanna
1211 PAPER How useful is [ 123 I]b-CIT SPECT in clinical practice? J Eerola, P J Tienari, S Kaakkola, P Nikkinen, J Launes... See end of article for authors affiliations... Correspondence to: Dr Johanna
Usefulness of a dopamine transporter PET ligand [ 18 F]β-CFT in assessing disability in Parkinson s disease
![Usefulness of a dopamine transporter PET ligand [ 18 F]β-CFT in assessing disability in Parkinson s disease Usefulness of a dopamine transporter PET ligand [ 18 F]β-CFT in assessing disability in Parkinson s disease](/thumbs/92/109717788.jpg) J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1999;67:737 741 737 Department of Neurology, University of Turku; Turku PET Centre, Turku, Finland J O Rinne H Ruottinen Department of Radiology, P Sonninen Radiochemistry
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 1999;67:737 741 737 Department of Neurology, University of Turku; Turku PET Centre, Turku, Finland J O Rinne H Ruottinen Department of Radiology, P Sonninen Radiochemistry
PET, especially with 6-18 F-fluoro-L-dopa ( 18 F-FDOPA)
 Journal of Nuclear Medicine, published on May 14, 2009 as doi:10.2967/jnumed.108.061572 Simple Ratio Analysis of F-Fluorodopa Uptake in Striatal Subregions Separates Patients with Early Parkinson Disease
Journal of Nuclear Medicine, published on May 14, 2009 as doi:10.2967/jnumed.108.061572 Simple Ratio Analysis of F-Fluorodopa Uptake in Striatal Subregions Separates Patients with Early Parkinson Disease
The current diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson s disease
 Sensitivity and Specificity of Tc-TRODAT-1 SPECT Imaging in Differentiating Patients with Idiopathic Parkinson s Disease from Healthy Subjects Yi-Hsin Weng, MD 1 ; Tzu-Chen Yen, PhD 2 ; Min-Chi Chen, PhD
Sensitivity and Specificity of Tc-TRODAT-1 SPECT Imaging in Differentiating Patients with Idiopathic Parkinson s Disease from Healthy Subjects Yi-Hsin Weng, MD 1 ; Tzu-Chen Yen, PhD 2 ; Min-Chi Chen, PhD
E123I]FP-CIT SPECT shows a pronounced decline of striatal dopamine transporter labelling in early and advanced Parkinson's disease
![E123I]FP-CIT SPECT shows a pronounced decline of striatal dopamine transporter labelling in early and advanced Parkinson's disease E123I]FP-CIT SPECT shows a pronounced decline of striatal dopamine transporter labelling in early and advanced Parkinson's disease](/thumbs/95/125312508.jpg) Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1997;62:133-14 Graduate School of Neurosciences Amsterdam, The Netherlands J Booij Department of Nuclear Medicine, Academic Medical Center, University
Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1997;62:133-14 Graduate School of Neurosciences Amsterdam, The Netherlands J Booij Department of Nuclear Medicine, Academic Medical Center, University
Radiotracer imaging of dopamine transporters and presynaptic dopamine synthesis in parkinsonian syndromes
 Radiotracer imaging of dopamine transporters and presynaptic dopamine synthesis in parkinsonian syndromes Nicolaas Paul L G Verhoeff PET Centre and Schizophrenia and Continuing care Division, Centre for
Radiotracer imaging of dopamine transporters and presynaptic dopamine synthesis in parkinsonian syndromes Nicolaas Paul L G Verhoeff PET Centre and Schizophrenia and Continuing care Division, Centre for
Clinical Study Serotonin Transporter Availability in Early Stage Parkinson s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy
 ISRN Neurology, Article ID 345132, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/345132 Clinical Study Serotonin Transporter Availability in Early Stage Parkinson s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy S. R. Suwijn,
ISRN Neurology, Article ID 345132, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/345132 Clinical Study Serotonin Transporter Availability in Early Stage Parkinson s Disease and Multiple System Atrophy S. R. Suwijn,
Jan Booij, Jos T.G.M. Hemelaar, Johannes D. Speelman, Kora de Bruin, Anton G.M. Janssen and Eric A. van Royen
 Downloaded from jnm.snmjournals.org by on March 5, 2014. For personal use only. Disease One-Day by Protocol [ 123 for Imaging of the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Pathway in Parkinson's I]FPCIT SPECT Jan
Downloaded from jnm.snmjournals.org by on March 5, 2014. For personal use only. Disease One-Day by Protocol [ 123 for Imaging of the Nigrostriatal Dopaminergic Pathway in Parkinson's I]FPCIT SPECT Jan
demonstrates loss of striatal dopamine transporters in Parkinson disease
 Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 9, Rp. 11965-11969, December 1993 Medical sciences Single photon emission computed tomographic imaging demonstrates loss of striatal dopamine transporters in Parkinson disease
Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA Vol. 9, Rp. 11965-11969, December 1993 Medical sciences Single photon emission computed tomographic imaging demonstrates loss of striatal dopamine transporters in Parkinson disease
Advanced brain dopamine transporter imaging in mice using small-animal SPECT/CT
 Pitkonen et al. EJNMMI Research 2012, 2:55 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Advanced brain dopamine transporter imaging in mice using small-animal SPECT/CT Miia Pitkonen 1, Eero Hippeläinen 2,5, Mari Raki
Pitkonen et al. EJNMMI Research 2012, 2:55 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Advanced brain dopamine transporter imaging in mice using small-animal SPECT/CT Miia Pitkonen 1, Eero Hippeläinen 2,5, Mari Raki
Idiopathic hyposmia as a preclinical sign of Parkinson s disease
 4 Idiopathic hyposmia as a preclinical sign of Parkinson s disease Mirthe Ponsen Diederick Stoffers Jan Booij Berthe van Eck-Smit Erik Wolters Henk Berendse Annals of Neurology 2004;56:173-181 Chapter
4 Idiopathic hyposmia as a preclinical sign of Parkinson s disease Mirthe Ponsen Diederick Stoffers Jan Booij Berthe van Eck-Smit Erik Wolters Henk Berendse Annals of Neurology 2004;56:173-181 Chapter
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lavalaye, J. (2001). SPECT imaging in young
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lavalaye, J. (2001). SPECT imaging in young
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication
 UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lavalaye, J. (2001). SPECT imaging in young
UvA-DARE (Digital Academic Repository) SPECT imaging in young patients with schizophrenia Lavalaye, J. Link to publication Citation for published version (APA): Lavalaye, J. (2001). SPECT imaging in young
Statistical parametric mapping with 18 F-dopa PET shows bilaterally reduced striatal and nigral dopaminergic function in early Parkinson s disease
 754 MRC Cyclotron Unit, Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK P K Morrish J S Rakshi T Uema D L Bailey D J Brooks Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London, UK J Ashburner K J Friston D J Brooks Department
754 MRC Cyclotron Unit, Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK P K Morrish J S Rakshi T Uema D L Bailey D J Brooks Institute of Neurology, Queen Square, London, UK J Ashburner K J Friston D J Brooks Department
doi: /brain/aws253 Brain 2012: 135; Left hemispheric predominance of nigrostriatal dysfunction in Parkinson s disease
 doi:10.1093/brain/aws253 Brain 2012: 135; 3348 3354 3348 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Left hemispheric predominance of nigrostriatal dysfunction in Parkinson s disease Christoph Scherfler, 1 Klaus Seppi,
doi:10.1093/brain/aws253 Brain 2012: 135; 3348 3354 3348 BRAIN A JOURNAL OF NEUROLOGY Left hemispheric predominance of nigrostriatal dysfunction in Parkinson s disease Christoph Scherfler, 1 Klaus Seppi,
Creation and validation of an I-123 FP-CIT template for statistical image analysis using high-resolution SPECT for parkinsonian patients
 Ann Nucl Med (2016) 30:477 483 DOI 10.1007/s12149-016-1085-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Creation and validation of an I- FP-CIT template for statistical image analysis using high-resolution SPECT for parkinsonian
Ann Nucl Med (2016) 30:477 483 DOI 10.1007/s12149-016-1085-8 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Creation and validation of an I- FP-CIT template for statistical image analysis using high-resolution SPECT for parkinsonian
D ementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is the second most
 134 PAPER Differentiation of dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer s disease using a dopaminergic presynaptic ligand Z Walker, D C Costa, RWHWalker, K Shaw, S Gacinovic, T Stevens, G Livingston, P Ince,
134 PAPER Differentiation of dementia with Lewy bodies from Alzheimer s disease using a dopaminergic presynaptic ligand Z Walker, D C Costa, RWHWalker, K Shaw, S Gacinovic, T Stevens, G Livingston, P Ince,
Dopamine transporter imaging 123 I-FP-CIT (DaTSCAN) SPET in differential diagnosis of dopa-responsive dystonia and young-onset Parkinson s disease
 Dopamine transporter imaging I-FP-CIT (DaTSCAN) SPET in differential diagnosis of dopa-responsive dystonia and young-onset Parkinson s disease Leposava D. Brajkovic 1 MD Marina V. Svetel 2, MD, PhD Vladimir
Dopamine transporter imaging I-FP-CIT (DaTSCAN) SPET in differential diagnosis of dopa-responsive dystonia and young-onset Parkinson s disease Leposava D. Brajkovic 1 MD Marina V. Svetel 2, MD, PhD Vladimir
SPECT Dopamin Transporter lmaging Agent
 SPECT Dopamin Transporter lmaging Agent Product Summary Product Name DATrace-123 Injection Active Ingredient Action Mechanism DATrace-123 is used as a radiopharmaceutical for the SPECT imaging of Dopamine
SPECT Dopamin Transporter lmaging Agent Product Summary Product Name DATrace-123 Injection Active Ingredient Action Mechanism DATrace-123 is used as a radiopharmaceutical for the SPECT imaging of Dopamine
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Dopamine Transporter Loss Visualized With FP-CIT SPECT in the Differential Diagnosis of Dementia With Lewy Bodies
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Dopamine Transporter Loss Visualized With FP-CIT SPECT in the Differential Diagnosis of Dementia With Lewy Bodies John T. O Brien, DM, MRCPysch; Sean Colloby, MPhil; John Fenwick,
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Dopamine Transporter Loss Visualized With FP-CIT SPECT in the Differential Diagnosis of Dementia With Lewy Bodies John T. O Brien, DM, MRCPysch; Sean Colloby, MPhil; John Fenwick,
years; baseline off-state Unified Parkinson s Disease Rating Scale (UPDRS) motor ratings 24.6 ± 6.8).
 Jourdain et al. 1 Supplemental Data Supplemental Methods Subjects We studied 28 PD subjects (20 men and 8 women; age 61.0 ± 9.6 (mean ± SD) years; duration 8.7 ± 9.6 years; baseline off-state Unified Parkinson
Jourdain et al. 1 Supplemental Data Supplemental Methods Subjects We studied 28 PD subjects (20 men and 8 women; age 61.0 ± 9.6 (mean ± SD) years; duration 8.7 ± 9.6 years; baseline off-state Unified Parkinson
Complementary PET studies of striatal neuronal function in the differential diagnosis between multiple system atrophy and Parkinson s disease
 Brain (1997), 120, 2187 2195 Complementary PET studies of striatal neuronal function in the differential diagnosis between multiple system atrophy and Parkinson s disease Angelo Antonini, 1 Klaus L. Leenders,
Brain (1997), 120, 2187 2195 Complementary PET studies of striatal neuronal function in the differential diagnosis between multiple system atrophy and Parkinson s disease Angelo Antonini, 1 Klaus L. Leenders,
responsiveness HMPAO SPECT in Parkinson's disease before and after levodopa: correlation with dopaminergic (SSmTc HMPAO) as a tracer in 21 patients
 18 1ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:18-185 Department of Neurology H S Markus A J Lees Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College and Middlesex School of Medicine, London,
18 1ournal of Neurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1994;57:18-185 Department of Neurology H S Markus A J Lees Institute of Nuclear Medicine, University College and Middlesex School of Medicine, London,
Parkinsonism in corticobasal syndrome may not be primarily due to presynaptic dopaminergic deficiency
 Neurology Asia 2015; 20(1) : 23 27 Parkinsonism in corticobasal syndrome may not be primarily due to presynaptic dopaminergic deficiency 1 Ji Young Yun MD, 2 Jong-Min Kim MD, PhD, 3 Han-Joon Kim MD PhD,
Neurology Asia 2015; 20(1) : 23 27 Parkinsonism in corticobasal syndrome may not be primarily due to presynaptic dopaminergic deficiency 1 Ji Young Yun MD, 2 Jong-Min Kim MD, PhD, 3 Han-Joon Kim MD PhD,
DND. 18F-FP-CIT Positron Emission Tomography for Correlating Motor and Cognitive Symptoms of Parkinson s Disease INTRODUCTION
 Print ISSN 1738-1495 / On-line ISSN 2384-0757 Dement Neurocogn Disord 2017;16(3):57-63 / https://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2017.16.3.57 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 18F-FP-CIT Positron Emission Tomography for Correlating
Print ISSN 1738-1495 / On-line ISSN 2384-0757 Dement Neurocogn Disord 2017;16(3):57-63 / https://doi.org/10.12779/dnd.2017.16.3.57 ORIGINAL ARTICLE 18F-FP-CIT Positron Emission Tomography for Correlating
Age-Related Decline in Dopamine Transporters. Analysis of Striatal Subregions, Nonlinear Effects, and Hemispheric Asymmetries
 Age-Related Decline in Dopamine Transporters Analysis of Striatal Subregions, Nonlinear Effects, and Hemispheric Asymmetries Christopher H. van Dyck, M.D., John P. Seibyl, M.D. Robert T. Malison, M.D.,
Age-Related Decline in Dopamine Transporters Analysis of Striatal Subregions, Nonlinear Effects, and Hemispheric Asymmetries Christopher H. van Dyck, M.D., John P. Seibyl, M.D. Robert T. Malison, M.D.,
Update on functional brain imaging in Movement Disorders
 Update on functional brain imaging in Movement Disorders Mario Masellis, MSc, MD, FRCPC, PhD Assistant Professor & Clinician-Scientist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre University of Toronto 53 rd CNSF
Update on functional brain imaging in Movement Disorders Mario Masellis, MSc, MD, FRCPC, PhD Assistant Professor & Clinician-Scientist Sunnybrook Health Sciences Centre University of Toronto 53 rd CNSF
Analysis of [ 11 C]L-deprenyl-D2 (DEP-D) brain PET studies
![Analysis of [ 11 C]L-deprenyl-D2 (DEP-D) brain PET studies Analysis of [ 11 C]L-deprenyl-D2 (DEP-D) brain PET studies](/thumbs/94/119609518.jpg) Turku PET Centre Modelling report TPCMOD0033 2006-05-26 Vesa Oikonen Analysis of [ 11 C]L-deprenyl-D2 (DEP-D) brain PET studies Introduction L-deprenyl and monoamine oxidase B Monoamine oxidase B (MAO
Turku PET Centre Modelling report TPCMOD0033 2006-05-26 Vesa Oikonen Analysis of [ 11 C]L-deprenyl-D2 (DEP-D) brain PET studies Introduction L-deprenyl and monoamine oxidase B Monoamine oxidase B (MAO
Corporate Medical Policy
 Corporate Medical Policy Dopamine Transporter Imaging with Single Photon Emission File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: dopamine_transporter_imaging_with_single_photon_emission_computed_tomography
Corporate Medical Policy Dopamine Transporter Imaging with Single Photon Emission File Name: Origination: Last CAP Review: Next CAP Review: Last Review: dopamine_transporter_imaging_with_single_photon_emission_computed_tomography
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed. Tomography
 Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Policy Number: 6.01.54 Last Review: 9/2018 Origination: 9/2015 Next Review: 9/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Policy Number: 6.01.54 Last Review: 9/2018 Origination: 9/2015 Next Review: 9/2019 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Dopaminergic Function and Dopamine Transporter Binding Assessed With Positron Emission Tomography in Parkinson Disease
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Dopaminergic Function and Dopamine Transporter Binding Assessed With Positron Emission Tomography in Parkinson Disease Maria-Joao Ribeiro, MD, PhD; Marie Vidailhet, MD; Christian
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Dopaminergic Function and Dopamine Transporter Binding Assessed With Positron Emission Tomography in Parkinson Disease Maria-Joao Ribeiro, MD, PhD; Marie Vidailhet, MD; Christian
Two multidisciplinary teams of investigators have
 Dopamine Cell Implantation in Parkinson s Disease: Long-Term Clinical and F-FDOPA PET Outcomes Yilong Ma 1,2, Chengke Tang 1, Thomas Chaly 1,2, Paul Greene 3, Robert Breeze 4, Stanley Fahn 3, Curt Freed
Dopamine Cell Implantation in Parkinson s Disease: Long-Term Clinical and F-FDOPA PET Outcomes Yilong Ma 1,2, Chengke Tang 1, Thomas Chaly 1,2, Paul Greene 3, Robert Breeze 4, Stanley Fahn 3, Curt Freed
Tc-TRODAT-1 SPECT Imaging in Early and Late Onset
 Tc-TRODAT-1 SPECT Imaging in Early and Late Onset Parkinson s Disease Payam Sasannezhad 1, Ali Ghabeli Juibary 1, Kayvan Sadri, Ramin Sadeghi, Mahsa Sabour, Vahid Reza Dabbagh Kakhki *, Hesam Alizadeh
Tc-TRODAT-1 SPECT Imaging in Early and Late Onset Parkinson s Disease Payam Sasannezhad 1, Ali Ghabeli Juibary 1, Kayvan Sadri, Ramin Sadeghi, Mahsa Sabour, Vahid Reza Dabbagh Kakhki *, Hesam Alizadeh
Structural Changes of the Substantia Nigra in Parkinson s Disease as Revealed by MR Imaging
 AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:697 701, April 2000 Structural Changes of the Substantia Nigra in Parkinson s Disease as Revealed by MR Imaging Michael Hutchinson and Ulrich Raff BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The possibility
AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:697 701, April 2000 Structural Changes of the Substantia Nigra in Parkinson s Disease as Revealed by MR Imaging Michael Hutchinson and Ulrich Raff BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: The possibility
Views and Reviews. [ 123 I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes ABSTRACT
![Views and Reviews. [ 123 I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes ABSTRACT Views and Reviews. [ 123 I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes ABSTRACT](/thumbs/76/73233066.jpg) Views and Reviews [ 123 I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes Robert A. Hauser, MD, Donald G. Grosset, MD From the Departments of Neurology, Molecular
Views and Reviews [ 123 I]FP-CIT (DaTscan) SPECT Brain Imaging in Patients with Suspected Parkinsonian Syndromes Robert A. Hauser, MD, Donald G. Grosset, MD From the Departments of Neurology, Molecular
Imaging of the dopaminergic system with SPECT has
 Clinical Testing of an Optimized Software Solution for an Automated, Observer-Independent Evaluation of Dopamine Transporter SPECT Studies Walter Koch, MD 1 ; Perry E. Radau, PhD 2 ; Christine Hamann,
Clinical Testing of an Optimized Software Solution for an Automated, Observer-Independent Evaluation of Dopamine Transporter SPECT Studies Walter Koch, MD 1 ; Perry E. Radau, PhD 2 ; Christine Hamann,
Morphological and functional imaging studies on the diagnosis and progression of Parkinson s disease
 J Neurol (2000) 247 [Suppl 2] : II/11 II/ Steinkopff Verlag 2000 David J. Brooks Morphological and functional imaging studies on the diagnosis and progression of Parkinson s disease D. J. Brooks ( ) MRC
J Neurol (2000) 247 [Suppl 2] : II/11 II/ Steinkopff Verlag 2000 David J. Brooks Morphological and functional imaging studies on the diagnosis and progression of Parkinson s disease D. J. Brooks ( ) MRC
Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson s disease
 3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Teaching Course 6 MDS-ES/EAN: Neuroimaging in movement disorders - Level 2 Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson
3 rd Congress of the European Academy of Neurology Amsterdam, The Netherlands, June 24 27, 2017 Teaching Course 6 MDS-ES/EAN: Neuroimaging in movement disorders - Level 2 Imaging biomarkers for Parkinson
Supplementary Online Content
 Supplementary Online Content Jauhar S, Nour MM, Veronese M, et al. A test of the transdiagnostic dopamine hypothesis of psychosis using positron emission tomographic imaging in bipolar affective disorder
Supplementary Online Content Jauhar S, Nour MM, Veronese M, et al. A test of the transdiagnostic dopamine hypothesis of psychosis using positron emission tomographic imaging in bipolar affective disorder
L ecografia cerebrale: accuratezza diagnostica Dr Patrizio Prati Neurologia CIDIMU Torino
 L ecografia cerebrale: accuratezza diagnostica Dr Patrizio Prati Neurologia CIDIMU Torino Ecografia cerebrale: l accuratezza diagnostica. Lo studio NOBIS Dr Patrizio Prati Neurologia CIDIMU Torinorin Normal
L ecografia cerebrale: accuratezza diagnostica Dr Patrizio Prati Neurologia CIDIMU Torino Ecografia cerebrale: l accuratezza diagnostica. Lo studio NOBIS Dr Patrizio Prati Neurologia CIDIMU Torinorin Normal
Chapter Four Reduced dopamine transporter binding predates impulse control disorders in Parkinson s disease
 Chapter Four Reduced dopamine transporter binding predates impulse control disorders in Parkinson s disease 4 Four Reduced dopamine transporter binding predates impulse control disorders in Parkinson's
Chapter Four Reduced dopamine transporter binding predates impulse control disorders in Parkinson s disease 4 Four Reduced dopamine transporter binding predates impulse control disorders in Parkinson's
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed. Tomography
 Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Policy Number: 6.01.54 Last Review: 9/2017 Origination: 9/2015 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Policy Number: 6.01.54 Last Review: 9/2017 Origination: 9/2015 Next Review: 9/2018 Policy Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Kansas
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics
 Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Reversible defect of 123 I-15-(p-iodophenyl)-9-(R,S)-methylpentadecanoic acid indicates residual viability within infarct-related area
 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 3, 183 187, 2002 Reversible defect of 123 I-15-(p-iodophenyl)-9-(R,S)-methylpentadecanoic acid indicates residual viability within infarct-related
ORIGINAL ARTICLE Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 16, No. 3, 183 187, 2002 Reversible defect of 123 I-15-(p-iodophenyl)-9-(R,S)-methylpentadecanoic acid indicates residual viability within infarct-related
D eep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus (STN
 PAPER Disease progression continues in patients with advanced Parkinson s disease and effective subthalamic nucleus stimulation R Hilker*, A T Portman*, J Voges, M J Staal, L Burghaus, T van Laar, A Koulousakis,
PAPER Disease progression continues in patients with advanced Parkinson s disease and effective subthalamic nucleus stimulation R Hilker*, A T Portman*, J Voges, M J Staal, L Burghaus, T van Laar, A Koulousakis,
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics
 Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Positron Emission Tomography: Tool to Facilitate Drug Development and to Study Pharmacokinetics Robert B. Innis, MD, PhD Molecular Imaging Branch National Institute Mental Health 1 Outline of Talk 1. PET
Brain neurotransmission SPECT is currently devoted
 Quantitative Accuracy of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission Imaging with I SPECT Marine Soret, MSc 1 ; Pierre Malick Koulibaly, PhD 2 ; Jacques Darcourt, MD, PhD 2 ;Sébastien Hapdey, PhD 1 ; and Irène Buvat,
Quantitative Accuracy of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission Imaging with I SPECT Marine Soret, MSc 1 ; Pierre Malick Koulibaly, PhD 2 ; Jacques Darcourt, MD, PhD 2 ;Sébastien Hapdey, PhD 1 ; and Irène Buvat,
PARKINSON DISEASE (PD) IS A
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Dopamine Transporter Brain Imaging to Assess the Effects of vs on arkinson Disease rogression arkinson Study Group ARKINSON DISEASE (D) IS A slow but relentlessly progressive neurodegenerative
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Dopamine Transporter Brain Imaging to Assess the Effects of vs on arkinson Disease rogression arkinson Study Group ARKINSON DISEASE (D) IS A slow but relentlessly progressive neurodegenerative
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta
 Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1792 (2009) 722 729 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbadis Review Imaging neurodegeneration
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1792 (2009) 722 729 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Biochimica et Biophysica Acta journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/bbadis Review Imaging neurodegeneration
Parkinsonian syndromes are a group of movement disorders
 REVIEW ARTICLE The Role of Functional Dopamine-Transporter SPECT Imaging in Parkinsonian Syndromes, Part 1 T.C. Booth, M. Nathan, A.D. Waldman, A.-M. Quigley, A.H. Schapira, and J. Buscombe ABSTRACT SUMMARY:
REVIEW ARTICLE The Role of Functional Dopamine-Transporter SPECT Imaging in Parkinsonian Syndromes, Part 1 T.C. Booth, M. Nathan, A.D. Waldman, A.-M. Quigley, A.H. Schapira, and J. Buscombe ABSTRACT SUMMARY:
Optimized, Automated Striatal Uptake Analysis Applied to SPECT Brain Scans of Parkinson s Disease Patients
 Optimized, Automated Striatal Uptake Analysis Applied to SPECT Brain Scans of Parkinson s Disease Patients I. George Zubal, Michele Early, Olive Yuan, Danna Jennings, Kenneth Marek, and John P. Seibyl
Optimized, Automated Striatal Uptake Analysis Applied to SPECT Brain Scans of Parkinson s Disease Patients I. George Zubal, Michele Early, Olive Yuan, Danna Jennings, Kenneth Marek, and John P. Seibyl
Dopamine Transporter Imaging with Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography
 Last Review Status/Date: September 2014 Page: 1 of 14 Photon Emission Computed Tomography Description Dopamine transporter imaging with single photon emission computed tomography (DAT-SPECT) is being evaluated
Last Review Status/Date: September 2014 Page: 1 of 14 Photon Emission Computed Tomography Description Dopamine transporter imaging with single photon emission computed tomography (DAT-SPECT) is being evaluated
Diagnostic Accuracy of Parkinson Disease by Support Vector Machine (SVM) Analysis of 123 I-FP-CIT Brain SPECT Data
 Diagnostic Accuracy of Parkinson Disease by Support Vector Machine (SVM) Analysis of 123 I-FP-CIT Brain SPECT Data Implications of Putaminal Findings and Age Barbara Palumbo, MD, Mario Luca Fravolini,
Diagnostic Accuracy of Parkinson Disease by Support Vector Machine (SVM) Analysis of 123 I-FP-CIT Brain SPECT Data Implications of Putaminal Findings and Age Barbara Palumbo, MD, Mario Luca Fravolini,
then a mechanism of reduced conversion and storage of administered levodopa as a cause for declining
 Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1989;52:72-76 Asymmetry of substantia nigra neuronal loss in Parkinson's disease and its relevance to the mechanism of levodopa related motor fluctuations.
Journal ofneurology, Neurosurgery, and Psychiatry 1989;52:72-76 Asymmetry of substantia nigra neuronal loss in Parkinson's disease and its relevance to the mechanism of levodopa related motor fluctuations.
parkinson s disease monitoring early diagnosis and disease progression
 parkinson s disease monitoring early diagnosis and disease progression Ania Winogrodzka Copyright: Hanna Winogrodzka, Amsterdam 2007 ISBN: 9789086591480 Typesetting: Michał Sławiński VRIJE UNIVERSITEIT
parkinson s disease monitoring early diagnosis and disease progression Ania Winogrodzka Copyright: Hanna Winogrodzka, Amsterdam 2007 ISBN: 9789086591480 Typesetting: Michał Sławiński VRIJE UNIVERSITEIT
A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging
 Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Editorial A Snapshot on Nuclear Cardiac Imaging Khalil, M. Department of Physics, Faculty of Science, Helwan University. There is no doubt that nuclear medicine scanning devices are essential tool in the
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging
 Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
Visualization and Quantification of the Striato pallidonigral Fibers in Parkinson's Disease Using Diffusion Tensor Imaging Yu Zhang, Katherine Wu, Shannon Buckley, Norbert Schuff On behalf of the Parkinson
Review Article SPECT Molecular Imaging in Parkinson s Disease
 Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology Volume 2012, Article ID 412486, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2012/412486 Review Article SPECT Molecular Imaging in Parkinson s Disease Ling Wang, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Qi Zhang,
Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology Volume 2012, Article ID 412486, 11 pages doi:10.1155/2012/412486 Review Article SPECT Molecular Imaging in Parkinson s Disease Ling Wang, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Qi Zhang,
Gender Differences in Age-Related Striatal Dopamine Depletion in Parkinson s Disease and in patients with PD. 8,11 The age-related decline
 JMD http://dx.doi.org/10.14802/jmd.15031 / J Mov Disord 2015;8(3):130-135 pissn 2005-940X / eissn 2093-4939 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gender Differences in Age-Related Striatal Dopamine Depletion in Parkinson s
JMD http://dx.doi.org/10.14802/jmd.15031 / J Mov Disord 2015;8(3):130-135 pissn 2005-940X / eissn 2093-4939 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Gender Differences in Age-Related Striatal Dopamine Depletion in Parkinson s
Research Article Pre- and Postsynaptic Dopamine SPECT in Idiopathic Parkinsonian Diseases: A Follow-Up Study
 BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 143532, 14 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/143532 Research Article Pre- and Postsynaptic Dopamine SPECT in Idiopathic Parkinsonian Diseases: A
BioMed Research International Volume 2013, Article ID 143532, 14 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2013/143532 Research Article Pre- and Postsynaptic Dopamine SPECT in Idiopathic Parkinsonian Diseases: A
Hallucinations and conscious access to visual inputs in Parkinson s disease
 Supplemental informations Hallucinations and conscious access to visual inputs in Parkinson s disease Stéphanie Lefebvre, PhD^1,2, Guillaume Baille, MD^4, Renaud Jardri MD, PhD 1,2 Lucie Plomhause, PhD
Supplemental informations Hallucinations and conscious access to visual inputs in Parkinson s disease Stéphanie Lefebvre, PhD^1,2, Guillaume Baille, MD^4, Renaud Jardri MD, PhD 1,2 Lucie Plomhause, PhD
CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM
 Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 HU-RO-DOCS CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM Part 3 Modern imaging methods SPECT, PET, nmri History of Nuclear Medicine Starts with the invention of the X-ray 1946: radioactive
Supported by: HURO/0901/069/2.3.1 HU-RO-DOCS CEREBRAL BLOOD FLOW AND METABOLISM Part 3 Modern imaging methods SPECT, PET, nmri History of Nuclear Medicine Starts with the invention of the X-ray 1946: radioactive
Impact of CT based attenuation correction on quantitative assessment of DaTSCAN ( 123 I-Ioflupane) imaging in diagnosis of extrapyramidal diseases
 Nuclear Medicine Review 2008 Vol. 11, No. 2, pp. 53 58 Copyright 2008 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Impact of CT based attenuation correction on quantitative assessment of DaTSCAN ( 123 I-Ioflupane) imaging
Nuclear Medicine Review 2008 Vol. 11, No. 2, pp. 53 58 Copyright 2008 Via Medica ISSN 1506 9680 Impact of CT based attenuation correction on quantitative assessment of DaTSCAN ( 123 I-Ioflupane) imaging
Citation for published version (APA): Portman, A. T. (2005). Parkinson's Disease: deep brain stimulation and FDOPA-PET Groningen: s.n.
 University of Groningen Parkinson's Disease Portman, Axel Tiddo IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
University of Groningen Parkinson's Disease Portman, Axel Tiddo IMPORTANT NOTE: You are advised to consult the publisher's version (publisher's PDF) if you wish to cite from it. Please check the document
Age-related changes of the [ 11 C]CFT binding to the striatal dopamine transporters in the Fischer 344 rats: a PET study
![Age-related changes of the [ 11 C]CFT binding to the striatal dopamine transporters in the Fischer 344 rats: a PET study Age-related changes of the [ 11 C]CFT binding to the striatal dopamine transporters in the Fischer 344 rats: a PET study](/thumbs/94/118542814.jpg) SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 17, No. 3, 249 253, 2003 Age-related changes of the [ 11 C]CFT binding to the striatal dopamine transporters in the Fischer 344 rats: a PET study Kazunori
SHORT COMMUNICATION Annals of Nuclear Medicine Vol. 17, No. 3, 249 253, 2003 Age-related changes of the [ 11 C]CFT binding to the striatal dopamine transporters in the Fischer 344 rats: a PET study Kazunori
PPMI Imaging Core Update
 PPMI Imaging Core Update John Seibyl, MD 7 May 2013 PPMI Imaging Core Update 1. PPMI status update: enrollment, demographics, compliance 2. DAT analyses -baseline and initial progression data -phantom
PPMI Imaging Core Update John Seibyl, MD 7 May 2013 PPMI Imaging Core Update 1. PPMI status update: enrollment, demographics, compliance 2. DAT analyses -baseline and initial progression data -phantom
Round table: Moderator; Fereshteh Sedaghat, MD, PhD Brain Mapping in Dementias and Non-invasive Neurostimulation
 Round table: Moderator; Fereshteh Sedaghat, MD, PhD Brain Mapping in Dementias and Non-invasive Neurostimulation 1. Reflection of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Dementias by Molecular Imaging, PET
Round table: Moderator; Fereshteh Sedaghat, MD, PhD Brain Mapping in Dementias and Non-invasive Neurostimulation 1. Reflection of Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) and Dementias by Molecular Imaging, PET
Transcranial sonography in movement disorders
 Transcranial sonography in movement disorders Uwe Walter 1st Residential Training of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics September 7-12, 2008 Bertinoro, Italy Department of
Transcranial sonography in movement disorders Uwe Walter 1st Residential Training of the European Society of Neurosonology and Cerebral Hemodynamics September 7-12, 2008 Bertinoro, Italy Department of
KEY SUMMARY. Mirapexin /Sifrol (pramipexole): What it is and how it works. What is Mirapexin /Sifrol (pramipexole)?
 KEY SUMMARY 1. Mirapexin /Sifrol (pramipexole*) is a selective non-ergot dopamine agonist approved as immediate release since 1997 for the treatment of the signs and symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson's
KEY SUMMARY 1. Mirapexin /Sifrol (pramipexole*) is a selective non-ergot dopamine agonist approved as immediate release since 1997 for the treatment of the signs and symptoms of idiopathic Parkinson's
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION. Cognitive Impairment and the Brain Dopaminergic System in Parkinson Disease
 ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Cognitive Impairment and the Brain Dopaminergic System in Parkinson Disease [ 18 F]Fluorodopa Positron Emission Tomographic Study Juha O. Rinne, MD, PhD; Raija Portin, PsychLic; Hanna
ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Cognitive Impairment and the Brain Dopaminergic System in Parkinson Disease [ 18 F]Fluorodopa Positron Emission Tomographic Study Juha O. Rinne, MD, PhD; Raija Portin, PsychLic; Hanna
Primary hyperparathyroidism (HPT) has an incidence of
 Dual-Phase Tc-Sestamibi Imaging: Its Utility in Parathyroid Hyperplasia and Use of Immediate/ Delayed Image Ratios to Improve Diagnosis of Hyperparathyroidism Leonie Gordon, MD; William Burkhalter, MD;
Dual-Phase Tc-Sestamibi Imaging: Its Utility in Parathyroid Hyperplasia and Use of Immediate/ Delayed Image Ratios to Improve Diagnosis of Hyperparathyroidism Leonie Gordon, MD; William Burkhalter, MD;
Basics of nuclear medicine
 Basics of nuclear medicine Prof. dr. Davor Eterović Prof. dr. Vinko Marković Radioisotopes are used both in diagnostics and in therapy Diagnostics gamma emitters are used since gamma rays can penetrate
Basics of nuclear medicine Prof. dr. Davor Eterović Prof. dr. Vinko Marković Radioisotopes are used both in diagnostics and in therapy Diagnostics gamma emitters are used since gamma rays can penetrate
With rapid advances in molecular medicine, the production
 A Technique for Standardized Central Analysis of 6- F-Fluoro-L-DOPA PET Data from a Multicenter Study Alan L. Whone, MRCP 1 ; Dale L. Bailey, PhD 2 ; Philippe Remy, PhD 3 ; Nicola Pavese, MD 1 ; and David
A Technique for Standardized Central Analysis of 6- F-Fluoro-L-DOPA PET Data from a Multicenter Study Alan L. Whone, MRCP 1 ; Dale L. Bailey, PhD 2 ; Philippe Remy, PhD 3 ; Nicola Pavese, MD 1 ; and David
Draft agreed by Scientific Advice Working Party 26 October Adopted by CHMP for release for consultation 09 November
 29 May 2018 EMA/CHMP/SAWP/765041/2017 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Qualification opinion on dopamine transporter imaging as an enrichment biomarker for Parkinson s disease clinical
29 May 2018 EMA/CHMP/SAWP/765041/2017 Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) Qualification opinion on dopamine transporter imaging as an enrichment biomarker for Parkinson s disease clinical
Fatigue in patients with Parkinson s disease
 103 Fatigue in patients with Parkinson s disease Kazuo Abe, Mayako Takanashi and Takehiko Yanagihara Department of Neurology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan Purpose: Fatigue is a complaint
103 Fatigue in patients with Parkinson s disease Kazuo Abe, Mayako Takanashi and Takehiko Yanagihara Department of Neurology, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan Purpose: Fatigue is a complaint
Many properties necessary for in vivo imaging of nicotinic
 I-5-IA-85380 SPECT Measurement of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Human Brain by the Constant Infusion Paradigm: Feasibility and Reproducibility Julie K. Staley, PhD 1 ; Christopher H. van Dyck, MD
I-5-IA-85380 SPECT Measurement of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptors in Human Brain by the Constant Infusion Paradigm: Feasibility and Reproducibility Julie K. Staley, PhD 1 ; Christopher H. van Dyck, MD
Basal ganglia motor circuit
 Parkinson s Disease Basal ganglia motor circuit 1 Direct pathway (gas pedal) 2 Indirect pathway (brake) To release or augment the tonic inhibition of GPi on thalamus Direct pathway There is a tonic inhibition
Parkinson s Disease Basal ganglia motor circuit 1 Direct pathway (gas pedal) 2 Indirect pathway (brake) To release or augment the tonic inhibition of GPi on thalamus Direct pathway There is a tonic inhibition
Volume Quantification of 123I-DaTSCAN Imaging by MatLab for the Differentiation and Grading of Parkinsonism and Essential Tremor
 Volume Quantification of 123I-DaTSCAN Imaging by MatLab for the Differentiation and Grading of Parkinsonism and Essential Tremor Maria Lyra, John Striligas, Maria Gavrilleli, Nefeli Lagopati Radiation
Volume Quantification of 123I-DaTSCAN Imaging by MatLab for the Differentiation and Grading of Parkinsonism and Essential Tremor Maria Lyra, John Striligas, Maria Gavrilleli, Nefeli Lagopati Radiation
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice Joseph W. Kable and Paul W. Glimcher a 10 0 b 10 0 10 1 10 1 Discount rate k 10 2 Discount rate k 10 2 10
Supplementary Information The neural correlates of subjective value during intertemporal choice Joseph W. Kable and Paul W. Glimcher a 10 0 b 10 0 10 1 10 1 Discount rate k 10 2 Discount rate k 10 2 10
Copyright 1999 by the American Neurological Association 723
 Presynaptic and Postsynaptic Dopaminergic Binding Densities in the Nigrostriatal and Mesocortical Systems in Early Parkinson s Disease: A Double-Tracer Positron Emission Tomography Study Yasuomi Ouchi,
Presynaptic and Postsynaptic Dopaminergic Binding Densities in the Nigrostriatal and Mesocortical Systems in Early Parkinson s Disease: A Double-Tracer Positron Emission Tomography Study Yasuomi Ouchi,
TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE. The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in
 1 NAME COURSE TITLE 2 TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in dopamine neurotransmitter, up-regulation
1 NAME COURSE TITLE 2 TO BE MOTIVATED IS TO HAVE AN INCREASE IN DOPAMINE The statement to be motivated is to have an increase in dopamine implies that an increase in dopamine neurotransmitter, up-regulation
TW Hamilton, EP Ficaro, TA Mitchell, JN Kritzman, JR Corbett University of Michigan Health System, Ann Arbor, MI
 Accuracy and Variability of of 3D-MSPECT for Estimating the Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction as as a Function of of Gating Frames and Reconstruction Filters TW Hamilton, EP Ficaro, TA Mitchell, JN Kritzman,
Accuracy and Variability of of 3D-MSPECT for Estimating the Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction as as a Function of of Gating Frames and Reconstruction Filters TW Hamilton, EP Ficaro, TA Mitchell, JN Kritzman,
Impulse control disorders in Parkinson s disease: decreased striatal dopamine transporter levels
 1 Department of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK 2 Behavioural and Clinical Neuroscience Institute, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK 3 Cambridgeshire and Peterborough NHS Foundation
1 Department of Psychiatry, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK 2 Behavioural and Clinical Neuroscience Institute, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK 3 Cambridgeshire and Peterborough NHS Foundation
GE Healthcare. Protocol Manual. Abnormal Scan. Normal Scan. Period-Shaped. Comma-Shaped
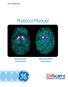 GE Healthcare Protocol Manual Normal Scan Comma-Shaped Abnormal Scan Period-Shaped 1 Contents Section 1: Introduction... 4 1.1 Scope 1.2 What is DaTscan? Section 2: Image Acquisition, Interpretation, and
GE Healthcare Protocol Manual Normal Scan Comma-Shaped Abnormal Scan Period-Shaped 1 Contents Section 1: Introduction... 4 1.1 Scope 1.2 What is DaTscan? Section 2: Image Acquisition, Interpretation, and
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography
 Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana,
Dopamine Transporter Imaging With Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography Applies to all products administered or underwritten by Blue Cross and Blue Shield of Louisiana and its subsidiary, HMO Louisiana,
Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
 International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (24), 7 (Supplement 1), S1 S5. Copyright f 24 CINP DOI : 1.117/S146114574411 Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology (24), 7 (Supplement 1), S1 S5. Copyright f 24 CINP DOI : 1.117/S146114574411 Do we still believe in the dopamine hypothesis? New data bring new evidence
Biomedical Technology Research Center 2011 Workshop San Francisco, CA
 Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Parkinson s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonism David E. Vaillancourt court1@uic.edu Associate Professor at UIC Departments t of Kinesiology i and Nutrition, Bioengineering, and
Diffusion Tensor Imaging: Parkinson s Disease and Atypical Parkinsonism David E. Vaillancourt court1@uic.edu Associate Professor at UIC Departments t of Kinesiology i and Nutrition, Bioengineering, and
The tracer 11 C-(1)-4-propyl-9-hydroxynaphthoxazine ( 11 C-
 Parametric Imaging and Test Retest Variability of C-(1)-PHNO BindingtoD 2 /D 3 Dopamine Receptors in Humans on the High-Resolution Research Tomograph PET Scanner Jean-Dominique Gallezot 1, Ming-Qiang Zheng
Parametric Imaging and Test Retest Variability of C-(1)-PHNO BindingtoD 2 /D 3 Dopamine Receptors in Humans on the High-Resolution Research Tomograph PET Scanner Jean-Dominique Gallezot 1, Ming-Qiang Zheng
Method Comparison for Interrater Reliability of an Image Processing Technique in Epilepsy Subjects
 22nd International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 3 to 8 December 2017 mssanz.org.au/modsim2017 Method Comparison for Interrater Reliability of an Image Processing Technique
22nd International Congress on Modelling and Simulation, Hobart, Tasmania, Australia, 3 to 8 December 2017 mssanz.org.au/modsim2017 Method Comparison for Interrater Reliability of an Image Processing Technique
Loss of thalamic serotonin transporters in early drug-naïve Parkinson s disease patients is associated with tremor: an [ 123 I]b-CIT SPECT study
![Loss of thalamic serotonin transporters in early drug-naïve Parkinson s disease patients is associated with tremor: an [ 123 I]b-CIT SPECT study Loss of thalamic serotonin transporters in early drug-naïve Parkinson s disease patients is associated with tremor: an [ 123 I]b-CIT SPECT study](/thumbs/71/66148846.jpg) J Neural Transm (2008) 115:721 729 DOI 10.1007/s00702-007-0015-2 PARKINSON S DISEASE AND ALLIED CONDITIONS - ORIGINAL ARTICLE Loss of thalamic serotonin transporters in early drug-naïve Parkinson s disease
J Neural Transm (2008) 115:721 729 DOI 10.1007/s00702-007-0015-2 PARKINSON S DISEASE AND ALLIED CONDITIONS - ORIGINAL ARTICLE Loss of thalamic serotonin transporters in early drug-naïve Parkinson s disease
Dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB) is the second most
 The F-FDG PET Cingulate Island Sign and Comparison to 123 I-b-CIT SPECT for Diagnosis of Dementia with Lewy Bodies Seok Ming Lim 1, Andrew Katsifis 2, Victor L. Villemagne 1,3, Rene Best 1, Gareth Jones
The F-FDG PET Cingulate Island Sign and Comparison to 123 I-b-CIT SPECT for Diagnosis of Dementia with Lewy Bodies Seok Ming Lim 1, Andrew Katsifis 2, Victor L. Villemagne 1,3, Rene Best 1, Gareth Jones
Philips Gemini TF camera (Philips, Cleveland OH), with an 18 cm coronal and a 57 cm axial
 Supplement Material 18 F-DCFBC PET/CT Imaging Protocol 18 F-DCFBC PET/CT imaging was performed on a 3D time of flight (TOF) mode Philips Gemini TF camera (Philips, Cleveland OH), with an 18 cm coronal
Supplement Material 18 F-DCFBC PET/CT Imaging Protocol 18 F-DCFBC PET/CT imaging was performed on a 3D time of flight (TOF) mode Philips Gemini TF camera (Philips, Cleveland OH), with an 18 cm coronal
Neuroimaging of Addiction
 Neuroimaging of Addiction Sang Eun Kim, MD, PhD Department of Nuclear Medicine Seoul National University College of Medicine Seoul, Korea SNUBH Preclinical and Clinical Molecular Imaging Center (SNUBH-MIC)
Neuroimaging of Addiction Sang Eun Kim, MD, PhD Department of Nuclear Medicine Seoul National University College of Medicine Seoul, Korea SNUBH Preclinical and Clinical Molecular Imaging Center (SNUBH-MIC)
function with dynamic chest planar imaging
 Suzuki et al. EJNMMI Research (2018) 8:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-018-0375-7 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Noninvasive quantitation of rat cerebral blood flow using 99m Tc-HMPAO assessment of input
Suzuki et al. EJNMMI Research (2018) 8:21 https://doi.org/10.1186/s13550-018-0375-7 ORIGINAL RESEARCH Open Access Noninvasive quantitation of rat cerebral blood flow using 99m Tc-HMPAO assessment of input
Brain SPECT has become an important diagnostic and
 CONTINUING EDUCATION Technical Overview of Brain SPECT Imaging: Improving Acquisition and Processing of Data* Gina N. Morano, CNMT, RT(N) 1 ; and John P. Seibyl, MD 2 1 Molecular NeuroImaging, LLC, New
CONTINUING EDUCATION Technical Overview of Brain SPECT Imaging: Improving Acquisition and Processing of Data* Gina N. Morano, CNMT, RT(N) 1 ; and John P. Seibyl, MD 2 1 Molecular NeuroImaging, LLC, New
The catechol-o-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor entacapone enhances the pharmacokinetic and clinical response to Sinemet CR in Parkinson s disease
 J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2;68:589 594 589 Department of Neurology, Imperial College, School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK P Piccini D J Brooks N Pavese Research Centre, Orion Pharma,
J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 2;68:589 594 589 Department of Neurology, Imperial College, School of Medicine, Hammersmith Hospital, London, UK P Piccini D J Brooks N Pavese Research Centre, Orion Pharma,
Understanding L-dopa L and Metabolism in the Human Brain
 Understanding L-dopa L Transport and Metabolism in the Human Brain Final Presentation for REU program August 3, 2006 Megan Mary Mekarski Advisor: Professor Linninger Dr. Libin Zhang Laboratory for Product
Understanding L-dopa L Transport and Metabolism in the Human Brain Final Presentation for REU program August 3, 2006 Megan Mary Mekarski Advisor: Professor Linninger Dr. Libin Zhang Laboratory for Product
TREATMENT-SPECIFIC ABNORMAL SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN EARLY PARKINSON S DISEASE
 TREATMENT-SPECIFIC ABNORMAL SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN EARLY PARKINSON S DISEASE Angel Lago-Rodriguez 1, Binith Cheeran 2 and Miguel Fernández-Del-Olmo 3 1. Prism Lab, Behavioural Brain Sciences, School of
TREATMENT-SPECIFIC ABNORMAL SYNAPTIC PLASTICITY IN EARLY PARKINSON S DISEASE Angel Lago-Rodriguez 1, Binith Cheeran 2 and Miguel Fernández-Del-Olmo 3 1. Prism Lab, Behavioural Brain Sciences, School of
