Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal transplant
|
|
|
- Emery Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7): /ISSN: /IJCEM Original Article High-resolution computed tomography features of Pneumocystis jirovecii infection in patients with renal transplant Qian Zhang, Xiaoling Xu Department of Respiratory Medicine, Anhui Provincial Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei, Anhui, China Received February 15, 2017; Accepted May 19, 2017; Epub July 15, 2017; Published July 30, 2017 Abstract: Objective: To describe the radiological and clinical features of Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) infection in patients who underwent renal transplantation. Subjects and methods: This retrospective analysis of 16 PJP infections in renal transplantation recipients was carried out at Anhui Provincial Hospital over a 5-year period. All patients underwent the same antimicrobial therapy. Between the onset of symptoms and the start of therapy, a series of early and late pulmonary high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) scans were evaluated. Results: The most common clinical features included fever (12/16, 75%), cough (8/16, 50%), and shortness of breath (8/16, 50%). Common HRCT findings were bilateral diffuse ground-glass opacity that was mostly distributed in the lung apices, emphysema, lymphadenopathy, air bronchogram, and pleural thickening. Conclusion: Renal transplantation patients with PJP appear to have a different pattern of infection than similar patients with immunosuppression caused by HIV infection. Analysis of HRCT features can enable an early diagnosis to be made, which would enable treatment to be started promptly to maximize prognosis. Keywords: Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, renal transplantation, HRCT, early diagnosis Introduction Pneumocystis jirovecii is a fungus normally found in humans and a variety of animals. P. jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) is the most common opportunistic infection in patients with impaired immune function and is the causative pathogen of Pneumocystis pneumonia [1-4]. The clinical symptoms of renal transplantation patients with PJP are more severe and atypical than those of HIV-infected patients [5]. Moreover, a delay in the diagnosis of PJP is associated with a high mortality rate caused by severe respiratory failure [1, 6-8]. Gruden et al. [9] previously showed that highresolution computed tomography (HRCT) is valuable in the evaluation and detection of clinically suspected PJP in AIDS patients with normal, equivocal, or nonspecific radiographic findings. However, to our knowledge, no data exist about the course, duration, and morphology of pulmonary changes depicted in HRCT in renal transplantation patients with PJP. This retrospective study therefore analyzed the clinical manifestations and HRCT characteristics of renal transplant recipients with PJP to better characterize their findings with the aim of providing an earlier correct diagnosis for a more effective treatment. Materials and methods Patients We collected clinical data from 348 living donor renal allograft recipients treated at the Anhui Provincial Hospital Transplantation Center from 2010 to All patients received the same immunotherapy after renal transplantation. A total of 16 (4.6%) patients had pulmonary infections with P. jirovecii. None of the PJP patients received specific prophylaxis prior to the onset of symptoms. All clinical records and imaging data were reviewed. Pathogenic diagnosis P. jirovecii is not readily cultured in the laboratory, so was diagnosed using microscopic anal-
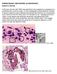
2 Results Clinical data Figure 1. Gomori methenamine silver staining. Typical pneumocystis cyst in a bronchoalveolar lavage specimen stained with Gomori methenamine (brown to black staining, 100 ). Thick cyst walls and some intracystic bodies are evident. ysis of respiratory secretions. A standard sample was initially obtained for examination. Sputum induction with hypertonic saline was performed if the initial specimen was negative for P. jirovecii (n = 6). Bronchoscopy with bronchoalveolar lavage was performed if the induced specimen was negative for P. jirovecii (n = 10) [4, 9]. Trophic and cystic forms of P. jirovecii were demonstrated using Gomori methenamine silver staining (Figure 1). HRCT protocol All patients underwent non-contrast HRCT imaging of the chest using Picker 6000 spiral CT (Philips Medical System, Best, the Netherlands), with a collimation of 2 or 5 mm. All images were viewed using standard mediastinal and lung windows. Every patient received follow-up HRCT imaging. All CT images were reviewed independently by two radiologists who were blinded to clinical data. Differences in CT reports were resolved by reviewer discussion. Treatment protocol All patients received sulfamethoxazole (SMZ) plus glucocorticoids after diagnosis [7, 10]. Third-generation cephalosporins were also administered to prevent bacterial infection. A total of 13 men and 3 women with a mean age of 33.1 ± 6.8 (SD) years (range: years) were diagnosed with PJP (Table 1). Common clinical features included fever (temperature >38 C; 12/16, 75%), cough (8/16, 50%), and shortness of breath (8/16, 50%; Table 1). All patients received long-term immunosuppressive treatment after renal transplantation with CellCept and prednisone. Nine patients also received cyclosporine and seven received tacrolimus (Table 2). The mean time from transplantation to diagnosis of PJP was ± days (range: days) for all patients. Patients treated with cyclosporine had a mean time to infection of days (range: days), while patients receiving tacrolimus had a mean time to infection of days (range: days). Thirteen (81.3%) patients improved with treatment and recovered by 150 days after the start of treatment, while three others died. One of these patients developed severe pulmonary infection and sepsis 2 months after hospital admission. The use of a non-invasive ventilator failed to improve oxygenation and family members gave up treatment. The second patient had hepatitis B-based disease and developed liver failure, hepatic encephalopathy, and multiple organ failure. The third patient had diabetes that was poorly controlled and pulmonary infection of Acinetobacter baumannii. This infection became difficult to control, leading to respiratory failure. All three women had received cyclosporine but no tacrolimus. Other clinical observations included the fact that patients older than 36 years suffered shortness of breath more often than younger patients (4/4 vs. 4/11, Chi square test, p = 0.029). All patients with PJP diagnosed before 120 days after transplantation had a cough compared with none diagnosed later than this (8/8 vs. 0/7, Chi square test, p < ). Patients treated with cyclosporine showed a trend toward a less frequent development of cough than patients treated with tacrolimus (6/8 vs. 2/7, Chi square test, p = 0.072) Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):
3 Table 1. Clinical data # Gender Age (years) Δ (days) Cellcept Cyclosporine Tacrolimus Fever Cough Shortness of breath 1 M X X X X 2 M X X X X X X 3 M X X X X X 4 F X X X X 5 M X X X X 6 M X X X X X 7 F X X X X X 8 M X X X X 9 M X X X X X X 10 F X X X X X 11 M X X X X X 12 M X X X X X 13 M X X X X 14 M X X X X X 15 M X X X X 16 M X X X X X Δ (days) = days from transplantation; X = corresponding symptoms. HRCT of the chest HRCT of the chest identified three stages (Figure 2). Early-stage infection consisted of bilateral diffuse ground-glass opacities (GGO), typically in the apex of the upper lobe (n = 12) (Figure 3). Consolidation, represented by air bronchograms, was an uncommon manifestation (n = 1). Pleural effusion, cystic changes, and pneumothorax were not typically observed. Some patients had enlarged mediastinal lymph nodes (n = 4) or pleural thickening (n = 7; Table 2). Patients treated with trimethoprimsulfamethoxazole (TMP-SMZ) for at least 2 weeks showed markedly fewer GGO. Follow-up 1 month after the completion of treatment showed the complete resolution of lung findings with few residual fibrosis or cyst-like lesions. Discussion Pneumocystis pneumonia is a serious cause of sickness and death in immunocompromised individuals. Most reports of PJP have been in patients with HIV [4, 11-13]. However, patients undergoing solid organ transplantation are immunosuppressed by different mechanisms so have different clinical manifestations of PJP from those found in HIV patients [11, 14]. HRCT patterns in non-aids immunocompromised patients [12] were divided into three patterns. Early infections showed bilateral diffuse GGO, mid-stage had bilateral diffuse GGO and patchy consolidation, and late-stage had bilateral diffuse consolidations. Other manifestations included pleural effusions, small nodules, pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, pneumohypoderma, cystic lesions, and thickened lobular septa, consistent with previous reports [9, 12]. Common imaging findings of individuals with HIV-associated PJP were previously shown to include perihilar haze or GGO, scattered thinwalled lung cysts, and spontaneous pneumothorax. Uncommon manifestations include focal nodules or masses, focal consolidation, pleural effusion and organizing pneumonia [2, 8, 11]. The 16 treated patients could be divided into three stages on HRCT findings. The early stage was characterized by bilateral diffuse GGO, mainly in the mid and upper lobe distribution. Almost all patients had apex of the upper lobe involvement. Consolidation seen as air bronchograms was typical, but pleural effusion, cystic changes, and pneumothorax were rarely seen. A small number of patients had mediastinal lymph nodes or pleural thickening. The mid Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):
4 Table 2. Clinical symptoms and HRCT features Patient number/ sex/age (in yrs) Clinical symptoms Interval between transplantation and onset (days) Immunosuppressive agents 1/M/25 Fever for 1 day 140 Tacrolimus, CellCept, 2/M/41 Fever, cough and dyspnea for 7 days 81 Cyclosporine, CellCept, 3/M/31 Fever and dyspnea for 1 day 340 Tacrolimus, CellCept, 4/F/48 Cough and exertional dyspnea for more than 1 month 515 Cyclosporine, CellCept, 5/M/30 Fever for 3 days 90 Cyclosporine, CellCept, 6/M/30 7/F/25 8/M/31 9/M/35 10/F/36 Fever for 2 days, cough and expectoration for 10 days Fever for 1 day, cough for 4 days Cough and nonproductive cough for 1 day Fever, nonproductive cough and dyspnea for 3 days Fever and nonproductive cough for 10 days 348 Tacrolimus, CellCept, 114 Cyclosporine, CellCept, 94 Cyclosporine, CellCept, 89 Cyclosporine, CellCept, 73 Cyclosporine, CellCept, 11/M/36 Fever and cough for 5 days 87 Tacrolimus, CellCept, 12/M/26 Nonproductive cough, dyspnea and fatigue for 5 days 92 Cyclosporine, CellCept, 13/M/42 Dyspnea for 3 days 365 Tacrolimus, CellCept, 14/M/39 Fever for 3 days, dyspnea and fatigue for 10 days 160 Tacrolimus, CellCept, 15/M/27 Fever for 5 days 33 Cyclosporine, CellCept, 16/M/27 Fever, dyspnea and fatigue for 7 days ALF: bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. 270 Tacrolimus, CellCept, Microscopic examination/ sample Chest HRCT Bilateral diffuse ground-glass attenuation that was mostly distributed in the upper lobe Bilateral diffuse ground-glass attenuation that was mostly distributed in the right apex, combined with emphysema, consolidation in the left lower lobe, mediastinal lymphadenopathy, and pleural thickening Bilateral diffuse ground-glass attenuation, patchy consolidation in the right middle lobe; air bronchogram, pleural thickening, lesions resolved on follow-up CT scans Bilateral diffuse ground-glass attenuation that was mostly distributed in the right upper lobe Bilateral diffuse foggy shadow, ground-glass attenuation in apexes and more severe in the left lung, mediastinal lymphadenopathy; pleural thickening, large patchy consolidation on follow-up CT scans Bilateral diffuse ground-glass attenuation that was mostly distributed in the right upper lobe, combined with emphysema, consolidation in the right middle lobe, mediastinal lymphadenopathy Bilateral diffuse ground-glass attenuation that was mostly distributed in the apexes, consolidation in the left lingular lobe and lower lobe; patchy consolidation on follow-up CT scans Ground-glass attenuation in apexes, linear or reticular shadows in lower lobes Bilateral diffuse patchy shadow and ground-glass attenuation that were mostly distributed in apexes; lesions resolved on follow-up CT scans Bilateral diffuse linear or reticular, patchy shadow and ground-glass attenuation that were mostly distributed in the right apex;pleural thickening, mediastinal lymph nodes and lesions resolved on follow-up CT scans Bilateral diffuse ground-glass attenuation that was mostly distributed in the upper lobes Bilateral diffuse foggy shadow and ground-glass attenuation, linear or reticular shadows in left lower lobes Bilateral diffuse ground-glass attenuation that was mostly distributed in the upper lobes, pleural thickening in left lung, mediastinal lymphadenopathy Bilateral diffuse patchy shadow and ground-glass attenuation, combined with emphysema; pleural thickening, lesions resolved on follow-up CT scans Bilateral sporadic patchy shadow, sporadic ground-glass attenuation in apexes; lesions resolved on follow-up CT scans Bilateral diffuse patchy shadow and ground-glass attenuation, lymphadenopathy in lower lobes Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):
5 Figure 2. Serial chest CT imaging in a 36-year-old female patient with PJP 73 days after renal transplantation. A: Ten days after the onset of symptoms, CT shows diffuse ground-glass opacities in the upper lobe, mostly in the right apex. B: After 2 weeks of treatment, CT shows an obvious improvement in ground-glass opacity lesions. C: One month after treatment, CT shows that ground-glass opacities have been completely absorbed. Only residual fibrosis and a few cyst-like lesions remain. dle stage was seen after 2 weeks of TMP-SMZ treatment, and was associated with markedly fewer GGO. After about 1 month of treatment, the HRCT lesions were generally resolved with no residual pulmonary fibrosis or cyst-like lesions. PJP usually occurs in immunocompromised patients. Immune responses directed against PJP involve complex interactions between CD4+ T lymphocytes, CD8+ T lymphocytes, alveolar macrophages, neutrophils, and soluble mediators that facilitate the clearance of infection. The activity of CD4+ T cells is pivotal in the host s defense against PJP, and PJP usually occurs when the CD4+ count is below 200 cells/mm 3 in HIV patients [2, 4, 8, 11, 13, 14]. Patients with HIV and CD4+ counts below Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):
6 Figure 3. Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PJP) in different renal transplant recipients. HRCT of different patients (A-C) shows diffuse ground-glass opacities typically in the apex of the upper lobe. Table 3. CD4+ and neutrophil counts CD4% N% N# 10 9 /L / / / Normal Range: CD4% (28.5, 60.5), N% (50, 70), N# (2, 7). CD4%: percentage of CD4+ T cells. N%: percentage of neutrophils; N#: absolute value of neutrophils. cells/mm 3 generally experience reconstitution of their immune system with highly active antiretroviral therapy. The CD4+ and neutrophil counts of patients we treated were within the normal range (Table 3). The CD4+ count decreased when TMP-SMZ was discontinued, but gradually normalized. Therefore, we hypothesized that PJP after renal transplantation is associated with severe inflammatory responses known as immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) [13, 15]. However, the development of IRIScan result in substantial pulmonary impairment. Renal transplant recipients experience a similar immune system reconstitution during en- graftment [4, 13], but those infected with PJP develop an intense T-cell-mediated inflammatory pulmonary response when immune reconstitution occurs [1, 4, 5, 16]. The biologic basis of IRIS in solid organ transplant recipients is believed to involve the change of anti-inflammatory responses into pro-inflammatory responses, which occurs with the withdrawal or reduction of immunosuppression. These findings are frequently observed in patients receiving immunosuppressive treatment consisting of tacrolimus, CellCept, and prednisone [13]. Because of the more rapid progression of PJP in non-aids immunosuppressed hosts, it is important to confirm the diagnosis of PJP at an early stage and begin specific anti-pjp therapy as soon as possible to reduce mortality and improve prognosis. We identified several factors in the present study that appeared to alter clinical presentation and may aid in the evaluation of PJP. Patients we treated that were aged over 36 years more frequently showed shortness of breath than younger patients, while all patients diagnosed with PJP before 120 days after transplantation had a cough, compared with none who were diagnosed later. The choice of cyclosporine or tacrolimus as an anti-suppressant may also affect the clinical presentation. This study was limited by the small number of patients with PJP. Conclusions High-resolution computed tomography is the first method of choice to diagnose PJP because of its high sensitivity, especially in lesions of the apex of the upper lobes. Imaging features Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):
7 can help achieve an early diagnosis and modify treatment. Different clinical parameters may affect the clinical presentation. Corroboration of these findings is needed in a larger group of patients. Acknowledgements This research was supported by grants from Anhui Provincial Natural Science Foundation (no mh216). We are grateful to Xiaoling Ma for help in preparing this manuscript and thank the numerous individuals who participated in this study. We also acknowledge the editors and reviewers for their insightful suggestions on this work. Disclosure of conflict of interest None. Address correspondence to: Xiaoling Xu, Department of Respiratory Medicine, Anhui Provincial Hospital of Anhui Medical University, No. 17 Lujiang Road, Hefei , Anhui, China. Tel: ; xxlahh08@163.com References [1] Goto N and Oka S. Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia in kidney transplantation. Transpl Infect Dis 2011; 13: [2] Guo F, Chen Y, Yang SL, Xia H, Li XW and Tong ZH. Pneumocystis pneumonia in HIV-infected and immunocompromised non-hiv infected patients: a retrospective study of two centers in China. PLoS One 2014; 9: e [3] Morris A, Lundgren JD, Masur H, Walzer PD, Hanson DL, Frederick T, Huang L, Beard CB and Kaplan JE. Current epidemiology of Pneumocystis pneumonia. Emerg Infect Dis 2004; 10: [4] Thomas CF Jr and Limper AH. Pneumocystis pneumonia. N Engl J Med 2004; 350: [5] Fishman JA. Infection in solid-organ transplant recipients. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: [6] Gilroy SA and Bennett NJ. Pneumocystis pneumonia. Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2011; 32: [7] Bourbigot B, Bensoussan T, Garo B, Islam MS, Hardy E, Moal MC and Garre M. CD4 T-lymphocyte counts as predictors of pneumonia after kidney transplantation. Transplant Proc 1993; 25: [8] Song T, Wei LP, Chen WJ, Liu P, Mai WW and Li ZZ. Imaging characteristics of pneumocystis pneumonia after renal transplantation. Ren Fail 2010; 32: [9] Vogel MN, Vatlach M, Weissgerber P, Goeppert B, Claussen CD, Hetzel J and Horger M. HRCTfeatures of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia and their evolution before and after treatment in non-hiv immunocompromised patients. Eur J Radiol 2012; 81: [10] Neff RT, Jindal RM, Yoo DY, Hurst FP, Agodoa LY and Abbott KC. Analysis of USRDS: incidence and risk factors for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia. Transplantation 2009; 88: [11] Hardak E, Brook O and Yigla M. Radiological features of Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia in immunocompromised patients with and without AIDS. Lung 2010; 188: [12] Mu XD, Jia P, Gao L, Su L, Zhang C, Wang RG and Wang GF. Relationship between radiological stages and prognoses of pneumocystis pneumonia in non-aids immunocompromised patients. Chin Med J (Engl) 2016; 129: [13] Sun HY and Singh N. Immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome in non-hiv immunocompromised patients. Curr Opin Infect Dis 2009; 22: [14] Crans CA Jr and Boiselle PM. Imaging features of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Crit Rev Diagn Imaging 1999; 40: [15] Tasaka S, Tokuda H, Sakai F, Fujii T, Tateda K, Johkoh T, Ohmagari N, Ohta H, Araoka H, Kikuchi Y, Yasui M, Inuzuka K and Goto H. Comparison of clinical and radiological features of pneumocystis pneumonia between malignancy cases and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome cases: a multicenter study. Intern Med 2010; 49: [16] Alangaden GJ, Thyagarajan R, Gruber SA, Morawski K, Garnick J, El-Amm JM, West MS, Sillix DH, Chandrasekar PH and Haririan A. Infectious complications after kidney transplantation: current epidemiology and associated risk factors. Clin Transplant 2006; 20: Int J Clin Exp Med 2017;10(7):
Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia: High-Resolution CT Findings in Patients With and Without HIV Infection
 Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Kanne et al. CT of Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey P. Kanne 1 Donald R. Yandow Cristopher. Meyer Kanne JP, Yandow
Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Kanne et al. CT of Pneumocystis jiroveci Pneumonia Cardiopulmonary Imaging Pictorial Essay Jeffrey P. Kanne 1 Donald R. Yandow Cristopher. Meyer Kanne JP, Yandow
Pneumocystis Pneumonia. Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine
 Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most
Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Pneumocystis jirovecci pneumonia: from mild disease to a real disaster. A pictorial review of the different radiologic patterns in acute settings
 Pneumocystis jirovecci pneumonia: from mild disease to a real disaster. A pictorial review of the different radiologic patterns in acute settings Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational
Pneumocystis jirovecci pneumonia: from mild disease to a real disaster. A pictorial review of the different radiologic patterns in acute settings Poster No.: C-1425 Congress: ECR 2017 Type: Educational
ARDS - a must know. Page 1 of 14
 ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
ARDS - a must know Poster No.: C-1683 Congress: ECR 2016 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit M. Cristian; Turda/RO Education and training, Edema, Acute, Localisation, Education, Digital radiography,
Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations
 08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
08/30/10 09/26/10 Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE): Pleuropulmonary Manifestations Camila Downey S. Universidad de Chile, School of Medicine, Year VII Harvard University, School of Medicine Sept 17,
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus
 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Community-Acquired Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia: Initial Chest Radiographic Findings and Follow-up CT Findings in Helping Predict Patient Outcome
 Community-Acquired Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia: Initial Chest Radiographic Findings and Follow-up CT Findings in Helping Predict Patient Outcome Jeong Joo Woo, Dong Hyun Lee, Jin Kyung An Department
Community-Acquired Acinetobacter baumannii Pneumonia: Initial Chest Radiographic Findings and Follow-up CT Findings in Helping Predict Patient Outcome Jeong Joo Woo, Dong Hyun Lee, Jin Kyung An Department
Case 1: Question. 1.1 What is the main pattern of this HRCT? 1. Intralobular line 2. Groundglass opacity 3. Perilymphatic nodule
 HRCT WORK SHOP Case 1 Case 1: Question 1.1 What is the main pattern of this HRCT? 1. Intralobular line 2. Groundglass opacity 3. Perilymphatic nodule Case 1: Question 1.2 What is the diagnosis? 1. Hypersensitivity
HRCT WORK SHOP Case 1 Case 1: Question 1.1 What is the main pattern of this HRCT? 1. Intralobular line 2. Groundglass opacity 3. Perilymphatic nodule Case 1: Question 1.2 What is the diagnosis? 1. Hypersensitivity
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Features of Pulmonary Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Non-HIV-Infected Patients
 Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC BACTERIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY Research Article Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Features of Pulmonary Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Non-HIV-Infected Patients Ehsan Shahverdi 1 *, Ashkan
Cronicon OPEN ACCESS EC BACTERIOLOGY AND VIROLOGY Research Article Computed Tomography (CT) Scan Features of Pulmonary Drug-Resistant Tuberculosis in Non-HIV-Infected Patients Ehsan Shahverdi 1 *, Ashkan
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Pneumocystis. Pneumocystis BIOL Summer Introduction. Mycology. Introduction (cont.) Introduction (cont.)
 Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Department of Anaesthesiology and Pain Medicine, Seonam University College of Medicine, Namwon, Korea
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.68.6.473 Rapid Progression of Metastatic Pulmonary Calcification and Alveolar Hemorrhage in a Patient with Chronic Renal Failure and Primary
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2013.68.6.473 Rapid Progression of Metastatic Pulmonary Calcification and Alveolar Hemorrhage in a Patient with Chronic Renal Failure and Primary
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5,
 Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY
 PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS RADIOLOGY RADIOLOGICAL MODALITIES Medical radiophotography Radiography Fluoroscopy Linear (conventional) tomography Computed tomography Pulmonary angiography, bronchography Ultrasonography,
11/10/2014. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Role of HRCT Diagnosis Fibrosis vs. inflammation Next step in management Response to treatment
5/9/2015. Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective. No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology
 Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
Multi-disciplinary Approach to Diffuse Lung Disease: The Imager s Perspective No, I am not a pulmonologist! Radiology Pathology Clinical 1 Everyone needs a CT Confidence in diagnosis Definitive HRCT +
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
imaging features, CD 4 + lymphocyte count, and plasma virus load were investigated. Materials and methods Study subjects
 Brief Report Correlation between imaging features of Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonitis (PCP), CD 4 T lymphocyte count, and plasma HIV viral load: A study in 50 consecutive AIDS patients Pu-Xuan Lu 1, Ying-Ying
Brief Report Correlation between imaging features of Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonitis (PCP), CD 4 T lymphocyte count, and plasma HIV viral load: A study in 50 consecutive AIDS patients Pu-Xuan Lu 1, Ying-Ying
Lung Allograft Dysfunction
 Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Lung Allograft Dysfunction Carlos S. Restrepo M.D. Ameya Baxi M.D. Department of Radiology University of Texas Health San Antonio Disclaimer: We do not have any conflict of interest or financial gain to
Acute and Chronic Lung Disease
 KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
KATHOLIEKE UNIVERSITEIT LEUVEN Faculty of Medicine Acute and Chronic Lung Disease W De Wever, JA Verschakelen Department of Radiology, University Hospitals Leuven, Belgium Clinical utility of HRCT To detect
Pulmonary Aspergillosis
 May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
New respiratory symptoms and lung imaging findings in a woman with polymyositis
 Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Respiratory Interactive Session. Elaine Borg
 Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Chest Imaging Findings for Evaluation HIV-related Pulmonary Diseases Comparing between Patients Receiving and Non-Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy
 Chest Imaging Findings for Evaluation HIV-related Pulmonary Diseases Comparing between Patients Receiving and Non-Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy Yutthaphan Wannasopha MD a, *, Natthaphong Nimitrungtavee
Chest Imaging Findings for Evaluation HIV-related Pulmonary Diseases Comparing between Patients Receiving and Non-Receiving Antiretroviral Therapy Yutthaphan Wannasopha MD a, *, Natthaphong Nimitrungtavee
Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation
 Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
Xiaohuan Pan 1,2 *, Xinguan Yang 1,2 *, Jingxu Li 1,2, Xiao Dong 1,2, Jianxing He 2,3, Yubao Guan 1,2. Original Article
 Original Article Is a 5-mm diameter an appropriate cut-off value for the diagnosis of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ on chest computed tomography and pathological examination?
Original Article Is a 5-mm diameter an appropriate cut-off value for the diagnosis of atypical adenomatous hyperplasia and adenocarcinoma in situ on chest computed tomography and pathological examination?
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 10 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 46-year-old man with AIDS was admitted to the hospital for complaints of a persisting fever and dry cough. A chest radiograph showed bilateral
Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients. Immunocompromised patients
 Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
Value of CT in Early Pneumonia in Immunocompromised Patients Nantaka Kiranantawat, PSU Preventative Factors Phagocyts Cellular immunity Humoral immunity Predisposing Factors Infection, Stress, Poor nutrition,
HIV related pulmonary infections. A radiologic pictorial review.
 HIV related pulmonary infections. A radiologic pictorial review. Poster No.: C-0836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arcalis, P. Trallero, L. Berrocal Morales, S. Medrano, S. 1
HIV related pulmonary infections. A radiologic pictorial review. Poster No.: C-0836 Congress: ECR 2013 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: N. Arcalis, P. Trallero, L. Berrocal Morales, S. Medrano, S. 1
ESCMID Online Lecture Library. by author. CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel
 CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
CASE PRESENTATION ECCMID clinical grand round May 2014 Anat Stern, MD Rambam medical center Haifa, Israel An 18 years old Female, from Ukraine, diagnosed with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in 2003.
Marc Bazot, MD; Jacques Cadranel, MD; Sylvie Benayoun, MD; Marc Tassart, MD; Jean Michel Bigot, MD; and Marie France Carette, MD
 Primary Pulmonary AIDS-Related Lymphoma* Radiographic and CT Findings Marc Bazot, MD; Jacques Cadranel, MD; Sylvie Benayoun, MD; Marc Tassart, MD; Jean Michel Bigot, MD; and Marie France Carette, MD Study
Primary Pulmonary AIDS-Related Lymphoma* Radiographic and CT Findings Marc Bazot, MD; Jacques Cadranel, MD; Sylvie Benayoun, MD; Marc Tassart, MD; Jean Michel Bigot, MD; and Marie France Carette, MD Study
August 2018 Imaging Case of the Month: Dyspnea in a 55-Year-Old Smoker. Michael B. Gotway, MD
 August 2018 Imaging Case of the Month: Dyspnea in a 55-Year-Old Smoker Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ USA Clinical History: A 55 year old woman presented
August 2018 Imaging Case of the Month: Dyspnea in a 55-Year-Old Smoker Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ USA Clinical History: A 55 year old woman presented
TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than
 TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than PAP) BAL is not required as a diagnostic tool in patients
TBLB is not recommended as the initial biopsy option in cases of suspected IPF and is unreliable in the diagnosis of rare lung disease (other than PAP) BAL is not required as a diagnostic tool in patients
Interpretation of Chest Radiographs Paul Christensen, MD 10/21/09. Diagnostic Evaluation. Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation.
 Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
Diagnostic Evaluation Medical Evaluation & CXR Interpretation University of Michigan TB Consultant Washtenaw County Medical history Physical examination Testing for TB exposure (previously covered) Radiologic
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus Infection: A Case Report of Serial Computed Tomographic Findings in a Young Male Patient
 Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.1.166 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2016;17(1):166-170 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus Infection: A Case
Case Report Thoracic Imaging http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2016.17.1.166 pissn 1229-6929 eissn 2005-8330 Korean J Radiol 2016;17(1):166-170 Middle East Respiratory Syndrome-Coronavirus Infection: A Case
and localized ground glass opacities, or bronchiolar focal or multifocal micronodules;
 E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
E1 Chest CT scan and Pneumoniae_YE Claessens et al- Supplementary methods Level of CAP probability according to CT scan - definite CAP: systematic alveolar condensation, or alveolar condensation with peripheral
Progression pattern of restrictive allograft syndrome after lung transplantation
 http://www.jhltonline.org FEATURED ARTICLES Progression pattern of restrictive allograft syndrome after lung transplantation Masaaki Sato, MD, PhD, a,b David M. Hwang, MD, PhD, a Thomas K. Waddell, MD,
http://www.jhltonline.org FEATURED ARTICLES Progression pattern of restrictive allograft syndrome after lung transplantation Masaaki Sato, MD, PhD, a,b David M. Hwang, MD, PhD, a Thomas K. Waddell, MD,
Department of Radiology, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea 2
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2018;79(5):276-281 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.79.5.276 Sequential CT Findings in Two Cases of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Lung Disease:
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 J Korean Soc Radiol 2018;79(5):276-281 https://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2018.79.5.276 Sequential CT Findings in Two Cases of Immunoglobulin G4-Related Lung Disease:
Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Mimicking DILD:
 Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Mimicking DILD: A Case Report 1 Ju Young Lee, M.D., In Jae Lee, M.D., Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. 2, Soo Kee Min, M.D. 3, Min-Jeong Kim, M.D., Sung Il Hwang, M.D., Yul Lee, M.D., Sang
Bronchioloalveolar Carcinoma Mimicking DILD: A Case Report 1 Ju Young Lee, M.D., In Jae Lee, M.D., Dong Gyu Kim, M.D. 2, Soo Kee Min, M.D. 3, Min-Jeong Kim, M.D., Sung Il Hwang, M.D., Yul Lee, M.D., Sang
Case Report pissn / eissn J Korean Soc Radiol 2016;75(2):
 Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.2.151 Thoracic Air-Leakage Syndrome in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients as a Late Complication of Chronic
Case Report pissn 1738-2637 / eissn 2288-2928 http://dx.doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2016.75.2.151 Thoracic Air-Leakage Syndrome in Allogeneic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients as a Late Complication of Chronic
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT
 Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Thoracic lung involvement in rheumatoid arthritis: Findings on HRCT Poster No.: C-2488 Congress: ECR 2015 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: R. E. Correa Soto, M. J. Martín Sánchez, J. M. Fernandez 1 1
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases. Punnarerk Thongcharoen
 Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Surgical indications: Non-malignant pulmonary diseases Punnarerk Thongcharoen Non-malignant Malignant as a pathological term: Cancer Non-malignant = not cancer Malignant as an adjective: Disposed to cause
Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2
 Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2 The Committee for Management of CT-screening-detected Pulmonary Nodules 2009-2011 The Japanese Society of CT Screening
Low-dose CT Lung Cancer Screening Guidelines for Pulmonary Nodules Management Version 2 The Committee for Management of CT-screening-detected Pulmonary Nodules 2009-2011 The Japanese Society of CT Screening
Web Chapter 3. Image Gallery: Lesion detection on low dose chest CT
 Web Chapter 3 Image Gallery: Lesion detection on low dose chest CT Sarabjeet Singh, MD Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD *Eugene J. Mark, MD *James Stone, MD James H. Thrall, MD Department of Radiology and *Department
Web Chapter 3 Image Gallery: Lesion detection on low dose chest CT Sarabjeet Singh, MD Mannudeep K. Kalra, MD *Eugene J. Mark, MD *James Stone, MD James H. Thrall, MD Department of Radiology and *Department
All I Need Is The Air That I Breathe: A Case Study of Immunotherapy and Severe Pneumonitis
 All I Need Is The Air That I Breathe: A Case Study of Immunotherapy and Severe Pneumonitis Presenter Disclosure Faculty/Speaker: Dr. Brett Finney BSc MD CCFP Relationships with financial sponsors: Grants/Research
All I Need Is The Air That I Breathe: A Case Study of Immunotherapy and Severe Pneumonitis Presenter Disclosure Faculty/Speaker: Dr. Brett Finney BSc MD CCFP Relationships with financial sponsors: Grants/Research
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell lymphocyte proliferative disease
 Du et al. Respiratory Research (2018) 19:247 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0941-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell
Du et al. Respiratory Research (2018) 19:247 https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0941-6 LETTER TO THE EDITOR Pleural effusion as an initial manifestation in a patient with primary pulmonary monoclonal B-cell
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page
 The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1135-1140 Role of High Resolution Computed Tomography in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases in Patients with Collagen Diseases
The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine (July 2017) Vol.68 (2), Page 1135-1140 Role of High Resolution Computed Tomography in Diagnosis of Interstitial Lung Diseases in Patients with Collagen Diseases
HIV-related respiratory conditions
 HIV-related respiratory conditions 3 Rossana A. Ditangco Head, AIDS Research Group Department of Health, Research Institute for Tropical Medicine, Philippines The respiratory system is one of the most
HIV-related respiratory conditions 3 Rossana A. Ditangco Head, AIDS Research Group Department of Health, Research Institute for Tropical Medicine, Philippines The respiratory system is one of the most
Reverse Halo Sign in Pulmonary Mucormyosis
 QJM Advance Access published February 6, 2014 Reverse Halo Sign in Pulmonary Mucormyosis Yu-Hsiang Juan MD 1,2, Sachin S Saboo, MD FRCR 1, Yu-Ching Lin MD 2, James R. Conner MD, Ph.D 3, Francine L. Jacobson
QJM Advance Access published February 6, 2014 Reverse Halo Sign in Pulmonary Mucormyosis Yu-Hsiang Juan MD 1,2, Sachin S Saboo, MD FRCR 1, Yu-Ching Lin MD 2, James R. Conner MD, Ph.D 3, Francine L. Jacobson
Ruijin robotic thoracic surgery: S segmentectomy of the left upper lobe
 Case Report Page 1 of 5 Ruijin robotic thoracic surgery: S 1+2+3 segmentectomy of the left upper lobe Han Wu, Su Yang, Wei Guo, Runsen Jin, Yajie Zhang, Xingshi Chen, Hailei Du, Dingpei Han, Kai Chen,
Case Report Page 1 of 5 Ruijin robotic thoracic surgery: S 1+2+3 segmentectomy of the left upper lobe Han Wu, Su Yang, Wei Guo, Runsen Jin, Yajie Zhang, Xingshi Chen, Hailei Du, Dingpei Han, Kai Chen,
Severe adenovirus community-acquired pneumonia in immunocompetent adults: chest radiographic and CT findings
 Original Article Severe adenovirus community-acquired pneumonia in immunocompetent adults: chest radiographic and CT findings Dingyu Tan 1 *, Yangyang Fu 1 *, Jun Xu 1 *, Zhiwei Wang 2, Jian Cao 2, Joseph
Original Article Severe adenovirus community-acquired pneumonia in immunocompetent adults: chest radiographic and CT findings Dingyu Tan 1 *, Yangyang Fu 1 *, Jun Xu 1 *, Zhiwei Wang 2, Jian Cao 2, Joseph
A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma
 August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
August 2001 A Case of Pediatric Plasma Cell Granuloma Nii Tetteh, Harvard Medical School Year IV Our Patient 8 year old male with history of recurrent left lower lobe and lingular pneumonias since 1994.
Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity
 Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma
 July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
July 2016 New lung lesion in a 55 year-old male treated with chemoradiation for non-small cell lung carcinoma Contributed by: Laurel Rose, MD, Resident Physician, Indiana University School of Medicine,
Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in
 Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Infection & Sepsis Symposium Porto, April 1-3, 2009 Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis in Non-Immunocompromised Patients Stijn BLOT, PhD General Internal Medicine & Infectious Diseases Ghent University Hospital,
Outline Definition of Terms: Lexicon. Traction Bronchiectasis
 HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
HRCT OF IDIOPATHIC INTERSTITIAL PNEUMONIAS Disclosures Genentech, Inc. Speakers Bureau Tadashi Allen, MD University of Minnesota Assistant Professor Diagnostic Radiology 10/29/2016 Outline Definition of
Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining
 Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining of PBMCs. Forward scatter area (FSC-A) versus side scatter area (SSC-A) was used to select lymphocytes followed
Supplemental Figure 1. Gating strategies for flow cytometry and intracellular cytokinestaining of PBMCs. Forward scatter area (FSC-A) versus side scatter area (SSC-A) was used to select lymphocytes followed
10/17/2016. Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology. Objectives. Techniques
 Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
Nuts and Bolts of Thoracic Radiology October 20, 2016 Carleen Risaliti Objectives Understand the basics of chest radiograph Develop a system for interpreting chest radiographs Correctly identify thoracic
HIV-associated Pulmonary Disease. Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond QUESTION: HIV-associated Pulmonary Diseases
 Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond Laurence Huang, MD Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Chief, HIV/AIDS Chest Clinic Zuckerberg San Francisco General
Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond Laurence Huang, MD Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Chief, HIV/AIDS Chest Clinic Zuckerberg San Francisco General
Role of Chest Low-dose Computed Tomography in Elderly Patients with Suspected Acute Pulmonary Infection in the Emergency Room
 Role of Chest Low-dose Computed Tomography in Elderly Patients with Suspected Acute Pulmonary Infection in the Emergency Room Poster No.: C-1461 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Role of Chest Low-dose Computed Tomography in Elderly Patients with Suspected Acute Pulmonary Infection in the Emergency Room Poster No.: C-1461 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Scientific
Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma
 Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Pediatric High-Resolution Chest CT
 Pediatric High-Resolution Chest CT Alan S. Brody, MD Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Chief, Thoracic Imaging Cincinnati Children s s Hospital Cincinnati, Ohio, USA Pediatric High-Resolution CT Short
Pediatric High-Resolution Chest CT Alan S. Brody, MD Professor of Radiology and Pediatrics Chief, Thoracic Imaging Cincinnati Children s s Hospital Cincinnati, Ohio, USA Pediatric High-Resolution CT Short
Case Presentations in ILD. Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco
 Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
Case Presentations in ILD Harold R. Collard, MD Department of Medicine University of California San Francisco Outline Overview of diagnosis in ILD Definition/Classification High-resolution CT scan Multidisciplinary
CT findings of pulmonary nocardiosis: a report of 9 cases
 Original Article on Quantitative Imaging of Thoracic Diseases CT findings of pulmonary nocardiosis: a report of 9 cases Baoliang Liu 1, Yuanlong Zhang 1,2, Jingshan Gong 2, Shubing Jiang 1, Yunkai Huang
Original Article on Quantitative Imaging of Thoracic Diseases CT findings of pulmonary nocardiosis: a report of 9 cases Baoliang Liu 1, Yuanlong Zhang 1,2, Jingshan Gong 2, Shubing Jiang 1, Yunkai Huang
A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka
 A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka Author s Details: (1) Dushantha Madegedara (2) Asela Rasika Bandara (3) Sachini Seneviratne (4) Samadara Nakandala (5) Rathnayake R.M.D.H.M - (1) (2)
A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka Author s Details: (1) Dushantha Madegedara (2) Asela Rasika Bandara (3) Sachini Seneviratne (4) Samadara Nakandala (5) Rathnayake R.M.D.H.M - (1) (2)
Thin-Section CT Findings in 32 Immunocompromised Patients with Cytomegalovirus Pneumonia Who Do Not Have AIDS
 Tomás Franquet 1,2 Kyung S. Lee 3 Nestor L. Müller 1 Received January 27, 2003; accepted after revision April 21, 2003. 1 Department of Radiology, Vancouver Hospital and Health Sciences Center and University
Tomás Franquet 1,2 Kyung S. Lee 3 Nestor L. Müller 1 Received January 27, 2003; accepted after revision April 21, 2003. 1 Department of Radiology, Vancouver Hospital and Health Sciences Center and University
Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
 Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A. Lynch, MB Disclosures Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A Lynch, MB Consultant: t Research support: Perceptive Imaging Boehringer Ingelheim
Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A. Lynch, MB Disclosures Progress in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis David A Lynch, MB Consultant: t Research support: Perceptive Imaging Boehringer Ingelheim
ARDS during Neutropenia. D Mokart DAR IPC GRRRRROH 2010
 ARDS during Neutropenia D Mokart DAR IPC GRRRRROH 2010 Definitions Neutropenia is a decrease in circulating neutrophil white cells in the peripheral blood. neutrophil count of 1,000 1,500 cells/ml = mild
ARDS during Neutropenia D Mokart DAR IPC GRRRRROH 2010 Definitions Neutropenia is a decrease in circulating neutrophil white cells in the peripheral blood. neutrophil count of 1,000 1,500 cells/ml = mild
An Image Repository for Chest CT
 An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
An Image Repository for Chest CT Francesco Frajoli for the Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group An Image Repository for Chest CT he Chest CT in Antibody Deficiency Group is an international and interdisciplinary
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Case 1 : Question. 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random
 Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Interesting case Case 1 Case 1 : Question 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular 2. Perilymphatic 3. Random Case 1: Answer 1.1 What is the intralobular distribution? 1. Centrilobular
Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates
 Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates Maria Elena Vega, M.D Assistant Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Nothing to
Connective Tissue Disorder- Associated Interstitial Lung Disease (CTD-ILD) and Updates Maria Elena Vega, M.D Assistant Professor of Medicine Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University Nothing to
Tuberculosis - clinical forms. Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases
 Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
Tuberculosis - clinical forms Dr. A.Torossian,, M.D., Ph. D. Department of Respiratory Diseases 1 TB DISEASE Primary Post-primary (Secondary) Common primary forms Primary complex Tuberculosis of the intrathoracic
MRSA pneumonia mucus plug burden and the difficult airway
 Case report Crit Care Shock (2016) 19:54-58 MRSA pneumonia mucus plug burden and the difficult airway Ann Tsung, Brian T. Wessman An 80-year-old female with a past medical history of chronic obstructive
Case report Crit Care Shock (2016) 19:54-58 MRSA pneumonia mucus plug burden and the difficult airway Ann Tsung, Brian T. Wessman An 80-year-old female with a past medical history of chronic obstructive
Pulmonary CT Findings of Visceral Larva Migrans due to Ascaris suum
 Pulmonary CT Findings of Visceral Larva Migrans due to Ascaris suum Poster No.: E-0038 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Honda, F. Okada, Y. Ando, A. Ono, S. Matsumoto, H. Mori;
Pulmonary CT Findings of Visceral Larva Migrans due to Ascaris suum Poster No.: E-0038 Congress: ESTI 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: K. Honda, F. Okada, Y. Ando, A. Ono, S. Matsumoto, H. Mori;
Outcomes of Moderate-to-Severe Pneumocystis Pneumonia Treated with Adjunctive Steroid in Non-HIV-Infected Patients
 ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Oct. 2011, p. 4613 4618 Vol. 55, No. 10 0066-4804/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.00669-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Outcomes
ANTIMICROBIAL AGENTS AND CHEMOTHERAPY, Oct. 2011, p. 4613 4618 Vol. 55, No. 10 0066-4804/11/$12.00 doi:10.1128/aac.00669-11 Copyright 2011, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved. Outcomes
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP
 Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Liebow and Carrington's original classification of IIP-- 1969 Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington UIP Usual interstitial pneumonia DIP Desquamative interstitial pneumonia BIP Bronchiolitis obliterans
Interesting Cases. Pulmonary
 Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
Interesting Cases Pulmonary 54M with prior history of COPD, hep B/C, and possible history of TB presented with acute on chronic dyspnea, and productive cough Hazy opacity overlying the left hemithorax
The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis
 www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN: 2161-2609 Article The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis Xin He, Chuanyu Zhang* Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN: 2161-2609 Article The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis Xin He, Chuanyu Zhang* Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference. Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2
 June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
June 2013 Pulmonary Case of the Month: Diagnosis Makes a Difference Lewis J. Wesselius, MD 1 Henry D. Tazelaar, MD 2 Departments of Pulmonary Medicine 1 and Laboratory Medicine and Pathology 2 Mayo Clinic
American College of Radiology ACR Appropriateness Criteria
 American College of Radiology ACR Criteria Radiologic Management of Thoracic Nodules and Masses Variant 1: Middle-aged patient (35 60 years old) with an incidental 1.5-cm lung nodule. The lesion was smooth.
American College of Radiology ACR Criteria Radiologic Management of Thoracic Nodules and Masses Variant 1: Middle-aged patient (35 60 years old) with an incidental 1.5-cm lung nodule. The lesion was smooth.
2009 H1N1 Influenza Infection: Spectrum Of Chest CT Findings, With Radiologic- Pathologic Correlation
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 2009 H1N1 Influenza Infection: Spectrum Of Chest CT Findings, With Radiologic- Pathologic Correlation A Nachiappan, E Weihe, B Akkanti, V
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 12 Number 2 2009 H1N1 Influenza Infection: Spectrum Of Chest CT Findings, With Radiologic- Pathologic Correlation A Nachiappan, E Weihe, B Akkanti, V
CT findings in multifocal or diffuse non-mucinous bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC)
 CT findings in multifocal or diffuse non-mucinous bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC) Poster No.: C-2192 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Sandu, A. R. Popita, I.-A. Brumboiu; Cluj-Napoca/RO
CT findings in multifocal or diffuse non-mucinous bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC) Poster No.: C-2192 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Sandu, A. R. Popita, I.-A. Brumboiu; Cluj-Napoca/RO
CT findings in multifocal or diffuse non-mucinous bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC)
 CT findings in multifocal or diffuse non-mucinous bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC) Poster No.: C-2192 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Sandu, A. R. Popita, I.-A. Brumboiu; Cluj-Napoca/RO
CT findings in multifocal or diffuse non-mucinous bronchioloalveolar carcinoma (BAC) Poster No.: C-2192 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: I. Sandu, A. R. Popita, I.-A. Brumboiu; Cluj-Napoca/RO
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping. Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington
 Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Imaging Small Airways Diseases: Not Just Air trapping Eric J. Stern MD University of Washington What we are discussing SAD classification SAD imaging with MDCT emphasis What is a small airway? Airway with
Pulmonary Complications after Bone Marrow Transplantation in paediatric patients - pathological findings on high-resolution CT
 Pulmonary Complications after Bone Marrow Transplantation in paediatric patients - pathological findings on high-resolution CT Poster No.: C-2359 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C.
Pulmonary Complications after Bone Marrow Transplantation in paediatric patients - pathological findings on high-resolution CT Poster No.: C-2359 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Educational Exhibit Authors: C.
Daria Manos RSNA 2016 RC 401. https://medicine.dal.ca/departments/depar tment-sites/radiology/contact/faculty/dariamanos.html
 Daria Manos RSNA 2016 RC 401 https://medicine.dal.ca/departments/depar tment-sites/radiology/contact/faculty/dariamanos.html STEP1: Is this fibrotic lung disease? STEP 2: Is this a UIP pattern? If yes:
Daria Manos RSNA 2016 RC 401 https://medicine.dal.ca/departments/depar tment-sites/radiology/contact/faculty/dariamanos.html STEP1: Is this fibrotic lung disease? STEP 2: Is this a UIP pattern? If yes:
Radiological and clinical characteristics of plastic bronchitis complicated with H1N1 influenza viral pneumonia in children
 Radiological and clinical characteristics of plastic bronchitis complicated with H1N1 influenza viral pneumonia in children Poster No.: C-1727 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: H. Fujisawa,
Radiological and clinical characteristics of plastic bronchitis complicated with H1N1 influenza viral pneumonia in children Poster No.: C-1727 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: H. Fujisawa,
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW
 SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
SCLERODERMA LUNG DISEASE: WHAT THE PATIENT SHOULD KNOW Lung disease can be a serious complication of scleroderma. The two most common types of lung disease in patients with scleroderma are interstitial
