Clinico-pathological conference
|
|
|
- Elinor Montgomery
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Genitourin Med 1992;68: Clinico-pathological conference Genitourinary Medicine, The London P French University College and Middlesex School of Medicine, The London, Department of Histopathology L Michaels Medicine R F Miller Thoracic Medicine, The Royal Free Hospital, London, NW3 2PF, UK M A Johnson Address for correspondence: Dr R F Miller, Department of Medicine, 5th Floor Jules Thorn Building, UCMSM, London, WIN 8AA, UK Accepted for publication 10 October 1991 Fulminant bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma P French, M A Johnson, L Michaels, R F Miller Case report (Dr P French) The patient was a 29 year old bisexual male dancer who first presented in January 1988 when he was found to be HIV-1 antibody positive and to have natural immunity to hepatitis B. Becuase of worsening nodulocystic acne he was treated with Roaccutane and ultraviolet B in early At this time his CD4 count was 500/mm3. Cutaneous lesions of Kaposi's sarcoma were first noted in June 1990, at which time the CD4 count had fallen to 130/mm3. The patient declined primary prophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and did not wish to take zidovudine. He was admitted to hospital in August 1990 with a one week history of progressive exertional dyspnoea, a dry cough and fever with sweats. He had several new lesions of Kaposi's sarcoma on the skin and there was a new lesion of Kaposi's sarcoma on the palate. A chest radiograph showed bilateral perihilar interstitial shadowing and widespread bilateral reticulo-nodular shadowing (fig 1). Arterial blood gases with the patient breathing air revealed a P02 of 9.4 kpa and at fibreoptic bronchoscopy two lesions of Kaposi's sarcoma were seen in the right main bronchus. Bronchoalveolar lavage was negative for acid and alcohol fast bacilli (AAFB) and also for Pneumocystis carinii. It was felt that he had pulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma but also possibly had Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), despite the negative bronchoalveolar lavage result. Treatment was begun with intravenous high dose co-trimoxazole, but this was discontinued after ten days because of diffuse macular rash. Two weeks after admission to hospital he remained unwell with dyspnoea and mild hypoxaemia. A gallium scan was performed and this showed no evidence of intrapulmonary accumulation of the radiotracer. He was noted to have cervical lymphadenopathy and biopsy of a right cervical lymph node revealed Kaposi's sarcoma. On the basis of his abnormal chest radiograph, mild hypoxaemia, the bronchoscopic appearances and the lesions on the palate together with the negative gallium scan it was thought that he had bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma. He was given chemotherapy with epirubicin administered intravenously once weekly for twelve weeks. On this regime there was resolution of symptoms and of the hypoxaemia within two weeks. The patient now agreed to have monthly PCP prophylaxis with inhaled pentamidine. In December 1990 he was really quite well and was able to work. He had only minimal dyspnoea on exertion, although a follow up chest radiograph showed no improvement in the pulmonary abnormalities (fig 2). He represented to the ward in mid-january 1991 with a two week history of dry cough, lethargy and a recurrence of his exertional dyspnoea. On examination at that time he was clearly unwell and was dyspnoeic at rest. He was apyrexial and had a dry cough. Examining the chest revealed a respiratory rate of 26 breaths per minute and there was widespread inspiratory wheeze which was not shifted by coughing. Apart from the cutaneous Kaposi's sarcoma lesions, which had progressed since completing chemotherapy, examination of the cardiovascular, gastrointestinal and nervous systems failed to detect any abnormalities. Arterial blood gases taken with the patient breathing air showed a PO2 of 7-5 kpa. Other investigations included, haemoglobin 12.5 g/dl, white blood count 2;7 x 109/1 (neutrophils 2.0 x 109/1, lymphocytes 0.4 x 109/l), platelets 227 x 109/l. Urea and electrolytes and liver function tests were normal. A chest radiograph was performed (fig 3) and showed widespread interstitial shadowing; the appearances had clearly deteriorated when compared to the chest radiograph taken three weeks previously at the end of the chemotherapy treatment. At this point the differential diagnosis lay between Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia or progressive bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma with or without a bacterial superinfection. Despite the urgency of his medical condition the patient declined admission and represented 48 hours later having deteriorated steadily. On examination he was markedly dyspnoeic and tachypnoeic at rest and his PO2 breathing room air was 7.0 kpa. Treatment was begun immediately for possible pneumocystis pneumonia; in view of the previous allergic reaction to high-dose cotrimoxazole he was given pentamidine 4 mg/kg daily by intravenous infusion and methylprednisolone was given in a pulse fashion 1 g daily for three days. On this regimen of treatment, over the next three days there was a steady improvement. The patient became less dyspnoeic and the PaO2 increased to 8 4 kpa on air. In view of the obvious improvement on specific treatment for
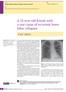
2 12 French, Johnson, Michaels, Miller Figure 1 Chest radiograph taken in August 1990 showing bilateral perihilar interstitial changes and widespread bilateral reticulo-nodular shadowing. Figure 2 Chest radiograph, December Despite a clinical improvement there is no improvement in the radiographic appearances. I M pneumocystis pneumonia bronchoscopy was not performed. Following this initial improvement there was a sudden deterioration in the patient's clinical condition. He became markedly tachypnoeic and the PaO2 fell to 6-0 kpa breathing room air. A chest radiograph (fig 4) showed worsening interstitial changes and areas of confluent alveolar consolidation. It was felt now that the patient was too ill to undergo bronchoscopy and bronchoalveolar lavage, but a sample of induced sputum was examined and was negative for P carinii, AAFB and bacteria. In the light of negative sputum results it was felt that progressive pulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma might explain his continuing deterioration. Vincristine 2 mg and bleomycin 30 mg were both given intravenously as a single dose. At this stage the patient declined further investigations and treatment, his condition steadily deteriorated and he died eight days after admission. Discussion (Dr R F Miller) We thought on his first presentation in August 1990 that he had bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma. We made this diagnosis on the basis of negative induced sputum and bronchoalveolar lavage findings and the fact that we saw lesions of Kaposi's sarcoma at bronchoscopy. We felt the chest radiograph (fig 1) was typical of bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma as was the fact that the gallium scan was negative. We know that gallium does not accumulate in lesions of Kaposi's sarcoma.' The presence of palatal Kaposi's sarcoma lesions also strongly suggested the presence of parenchymal lung disease.2 In addition, the patient showed quite a rapid response to chemotherapy in terms of his symptoms. Looking back I just wonder whether we should have performed a transbronchial biopsy or even an open lung biopsy to absolutely confirm the diagnosis. Dr M Johnson When this man presented in August 1990 I am sure that he did have bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma. The only thing that was slightly atypical was the rapid presentation of symptoms. I think there was enough evidence on which to base your diagnosis. I would not have performed transbronchial biopsy, as Kaposi's sarcoma is a very patchy disease within the lung and this procedure has a relatively low yield for the diagnosis of Kaposi's sarcoma.34 I would be surprised if it would have added any information and indeed you actually saw lesions of Kaposi's at bronchoscopy. I too would have gone ahead and commenced chemotherapy. I am worried about whether it is appropriate to give prophylaxis for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia with nebulised pentamidine in somebody with bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma. There is always the worry that the aerosol of pentamidine will not penetrate completely to the terminal bronchioles and alveoli if there is obstruction by
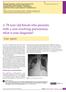
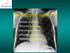
3 13 Fulminant bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma perhaps Figure 3 Chest radiograph, on representation, mid-january 1991, showing widesprea interstitial shadowing. The appearances have deteriorated, compared to fig 2. X... ~... 2?' A explains the subsequent rapid on discontinuation deterioration We methyl4 to 7 know that it mayoftake prednisolone. days for a patient with pneumocystis pneumonia to show any response to treatment with intravenous pentamidine.' Perhaps, despite the rash with the patient developed previously, I would have thought carefully about rechallenging this man with intravenous high-dose cotrimoxazole. The advantage of using this drug being a faster response time in patients with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia and in addition the broad spectrum of activity of the drug means that you would also cover for most bacterial pathogens.8 Radiographically the appearances during the second admission (figs 3 and 4) are entirely in keeping with progressive bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma.'910 The absence of pleural effusions does not worry me as only one third of patients with Kaposi's sarcoma involving the lung have effusions. I think this second admission to hospital was due to rapidly progressive Kaposi's sarcoma involvement of the lungs but I am concerned that there might have been a co-pathogen also, either Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia or a bacterium. Clinical diagnoses 1 Bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma. 2 Co-pathogen infection-pneumocystis carinii pneumonia? Bacterial pathogen? Figure 4 Chest radiograph following sudden deterioration in the patient's condition. There are worsened interstitial changes and areas of confluent alveolar consolidation. Pathology (Professor L Michaels) At autopsy the body was that of a thin Caucasian male. There were several lesions of Kaposi's sarcoma on the trunk. In addition lesions were evident on the palate, over the back of the tongue and on the epiglottis (fig 5). endobronchial lesions of Kaposi's sarcoma and associated oedema. Despite the rash after ten days of intravenous high dose co-trimoxazole I think I would have offered prophylaxis with oral co-trimoxazole, one double strength tablet three times a week. The events during his second admission are somewhat confusing. Despite the patient's initial reluctance to come in to hospital I would have been keen to do a fibreoptic bronchoscopy at the earliest opportunity. This would have told me whether there had been progression of the endobronchial Kaposi's sarcoma; bron_ choalveolar lavage could have been carried out and of course this technique is much more sensitive than examining sputum for confirming P carinii pneumonia or excluding alternativediagnosessuchasco-infection with M tuberculosis or bacterial pathogens.i Clearly the patient showed an initial response to the Figure Chest radiograph,treatment you began for presumed pneumocys. shad. Te a s he dtis pneumonia with intravenous pentamidine and methylprednisolone but when he subsequently deteriorated you had "missed the boat" and he was then too ill to bronchoscope. I think the initial response you saw was a nonspecific response to steroids and was not a response to the intravenous pentamidine and
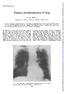
4 14 French, Johnson, Michaels, Miller Figure S Epiglottis and back of the tongue showing multiple lesions of Kaposi's sarcoma. The lungs were grossly abnormal. Both lungs were largely replaced by tumour, the tumour being Kaposi's sarcoma (fig 6). The main bronchi contained a little inpissated mucus. There were no obvious lesions of Kaposi's sarcoma within the trachea or main bronchi. The hilar lymph nodes were enlarged and macroscopically appeared to be involved with Kaposi's sarcoma. On closer examination the confluent areas of tumour appeared to be completely replacing the lung in some portions, in others the outlines of alveolar remnants were evident. Microscopically, in order to confirm a diagnosis of Kaposi's sarcoma we look for a tumour that is composed of blood vessels. Some of these blood vessels are quite normal in appearance. Others are more slit like. Secondly, the tumour is composed of large numbers of spindle cells. Immunohistochemical marker studies suggest that these spindle cells are probably endothelial in origin. ;t) I. 4Az Figure 6 Left lung showing massive tumour replacing normal lung tissue (arrows). The tumour is Kaposi's sarcoma. e _F a; i;w.;o s ~ v,,**..*. -.VIW! -, ~ ~ ~ ~ *o Figure 7 Kaposi's sarcoma around a blood vessel in the lung. There is a large quantity of blood surrounding the blood vessel. Magnification x 40 (haematoxylin and eosin). It is not clear whether they arise from lymphatic vessels or blood vessels or both. Thirdly, there may be evidence of small hyaline globules scattered throughout the tumour tissue. Turning now to this man and looking under the microscope at sections of tumour obtained from the lung we see the typical appearance I have just described-spindle cells with a large quantity of blood contained within blood vessels and also immediately around them (fig 7). The surprising thing about this tumour is that to a histopathologist there are absolutely no features ofmalignancy. Rarely one sees nuclear atypia or even mitosis but it is more usual to see, as in this case, appearances very similar to normal reactive fibrous tissue formation following injury. At higher power sections of this tumour show thet twere the sple cells there are vascular slits; many are not lined by endothelial cells (fig 8). Using periodic acid Figure 8 High power section of Kaposi's sarcoma tumour showing it to be composed of spindle cells, between which are vascular slits, many are not lined by endothelial cells. Magnification x 200 (haematoxylin and eosin).
5 Fulminant bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma Schiffstain shows evidence ofhyaline globules. Elsewhere in the lung cytomegalovirus inclusions could be seen but there was no evidence of bacterial infection, AAFB nor Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia. Microscopically the hilar lymph nodes showed changes typical of Kaposi's sarcoma. Indeed the nodes were largely replaced by tumour. No lesions of Kaposi's sarcoma were seen on the visceral or parietal pleural surfaces of either lung. The only other pathological abnormality detected in this man was evidence of cytomegalovirus adrenalitis; this is a common finding and occurs in up to 70% ofpatients with AIDS at post mortem. Pathological diagnoses 1 Kaposi's sarcoma of the skin, tongue, palate and hypopharynx. 2 Parenchymal lung involvement with Kaposi's sarcoma. 3 Hilar lymph node involvement with Kaposi's sarcoma. 4 Cytomegalovirus adrenalitis. 1 Miller RF, Nuclear Medicine and AIDS. Eur J Nucl Med 1990;16: Moss F, Fleming J, Nelson J, Veale D, Peters B, Mitchell D. Pulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma. Thorax 1989;44:326P. 3 Meduri GU, Stover DE, Lee M, Myskowski PL, Caravelli JF, Zaman MB. Pulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Med 1986; 81: Griffiths MH, Kocjan G, Miller RF, Godfrey-Faussett P. Diagnosis of pulmonary disease in human immunodeficiency virus infection: role of transbronchial biopsy and bronchoalveolar lavage. Thorax 1989;44: Miller RF, Kocjan G, Buckland J, Holton J, Malin A, Semple SJG. Sputum induction for the diagnosis of pulmonary disease in HIV positive patients. J Infect 1991;23: Pitchenik AE, Ganjei P, Torres A, Evans DA, Rubin E, Baier H. Sputum examination for the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carimi pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am Rev Respir Dis 1986;133: Bigby TD, Margolskee D, Curtis JL, et al. The usefulness of induced sputum in the diagnosis of Pneumocystis carinii penumonia in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Am Rev Dis 1986;133: Sattler FR, Cowan R, Nielsen DM, Ruskin J. Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole compared with pentamidine for treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ann Intern Med 1981;109: SivitCJ,SchwartzAM,RockoffSD. Kaposi'ssarcomaofthe lung in AIDS: radiologic-pathologic correlation. AJR 1987;148: Davies SD, Henschke CI, Chamides BK, Westcott JL. Intrathoracic Kaposi's sarcoma in AIDS patients; radiographic-pathologic correlation. Radiology 1987; 163: is Genitourin Med: first published as /sti on 1 February Downloaded from on 10 January 2019 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Adult respiratory distress syndrome complicating Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia
 250 Genitourin Med 1991;67:250-255 Clinrico-pathological conference Adult respiratory distress syndrome complicating Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia A Scoular, J Moxham, S B Lucas, R F Miller Case report
250 Genitourin Med 1991;67:250-255 Clinrico-pathological conference Adult respiratory distress syndrome complicating Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia A Scoular, J Moxham, S B Lucas, R F Miller Case report
Bronchopulmonary Kaposi's sarcoma in patients
 Thorax 1992;47:721-725 Department of Medicine, University College and Middlesex School of Medicine R F Miller M C Tomlinson S J G Semple Meyerstein Institute of Clinical Oncology C P Cottrill M F Spittle
Thorax 1992;47:721-725 Department of Medicine, University College and Middlesex School of Medicine R F Miller M C Tomlinson S J G Semple Meyerstein Institute of Clinical Oncology C P Cottrill M F Spittle
Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma
 Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Article ID: WMC005047 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis
 Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Thorax (1965), 20, 385 Transient pulmonary infiltrations in cystic fibrosis due to allergic aspergillosis MARGARET MEARNS, WINIFRED YOUNG, AND JOHN BATTEN From the Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Hackney, and
Chapter 22. Pulmonary Infections
 Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Chapter 22 Pulmonary Infections Objectives State the incidence of pneumonia in the United States and its economic impact. Discuss the current classification scheme for pneumonia and be able to define hospital-acquired
Bronchopulmonary infection with Pseudomonas
 Genitourin Med 1995;71:73-77 Department of Medicine, University College London Medical School, Camden & Islington Community Services NHS Trust, Middlesex Hospital site, London W1N 8AA, UK NJ Ali R F Miller
Genitourin Med 1995;71:73-77 Department of Medicine, University College London Medical School, Camden & Islington Community Services NHS Trust, Middlesex Hospital site, London W1N 8AA, UK NJ Ali R F Miller
Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity
 Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Severe Nitrofurantoin-Induced Lung Toxicity Rami Jambeih, M.D. 1, John Flesher, M.D. 1,3, Joe J. Lin, M.D. 2,4 University of Kansas School of Medicine Wichita 1 Department of Internal Medicine 2 Department
Clinical Manifestations of HIV
 HIV Symptoms Diane Havlir, MD Professor of Medicine and Chief, HIV/AIDS Division University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) WorldMedSchool; July 2, 2013 1 Clinical Manifestations of HIV! Result from
HIV Symptoms Diane Havlir, MD Professor of Medicine and Chief, HIV/AIDS Division University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) WorldMedSchool; July 2, 2013 1 Clinical Manifestations of HIV! Result from
A 31-year-old female with a rare cause of recurrent lower lobar collapses
 Radhika Banka, Dayle Terrington, Ajay V. Kamath radhika.banka@gmail.com Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital, Norwich, UK. A 31-year-old female with a rare cause of recurrent
Radhika Banka, Dayle Terrington, Ajay V. Kamath radhika.banka@gmail.com Dept of Respiratory Medicine, Norfolk and Norwich University Hospital, Norwich, UK. A 31-year-old female with a rare cause of recurrent
Clinical syndromes: experience from the bedside. Professor Rob Miller University College Hospital, London
 Clinical syndromes: experience from the bedside Professor Rob Miller University College Hospital, London Presented at ECCMID Berlin April 30 th 2013 Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file
Clinical syndromes: experience from the bedside Professor Rob Miller University College Hospital, London Presented at ECCMID Berlin April 30 th 2013 Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5,
 Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, Vol. 14, No. 5, 2008 1217 Case report Inappropriate use of steroid and Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia: report of two cases P. Tabarsi, 1 M. Mirsaeidi, 1 M. Amiri,
Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma
 Article ID: WMC005051 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
Article ID: WMC005051 ISSN 2046-1690 Bilateral Chest X-Ray Shadowing and Bilateral leg lesions - A case of Pulmonary Kaposi Sarcoma Peer review status: No Corresponding Author: Dr. Mohammad Fawad Khattak,
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
September 2014 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 57-year-old non-smoking woman presented to her physician as
New respiratory symptoms and lung imaging findings in a woman with polymyositis
 Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
Maria Bolaki 1, Konstantinos Karagiannis 1, George Bertsias 2, Ioanna Mitrouska 1, Nikolaos Tzanakis 1, Katerina M. Antoniou 1 kantoniou@uoc.gr 1 Dept of Thoracic Medicine, Heraklion University Hospital,
TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD
 TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
TB Nurse Case Management Salina, Kansas March 31-April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD April 1, 2010 TB Radiology for Nurses Highway Patrol Training Center Salina, KS April 1, 2010
medical monitoring: clinical monitoring and laboratory tests
 medical monitoring: clinical monitoring and laboratory tests Purpose of monitoring Check on the physical, psychological and emotional condition of the patient Detect other treatable conditions Identify
medical monitoring: clinical monitoring and laboratory tests Purpose of monitoring Check on the physical, psychological and emotional condition of the patient Detect other treatable conditions Identify
Differential diagnosis
 Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
Differential diagnosis Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is part of a large family of idiopathic interstitial pneumonias (IIP), one of four subgroups of interstitial lung disease (ILD). Differential
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses
 An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
An Introduction to Radiology for TB Nurses Garold O. Minns, MD September 14, 2017 TB Nurse Case Management September 12 14, 2017 EXCELLENCE EXPERTISE INNOVATION Garold O. Minns, MD has the following disclosures
Chapter 8. Other Important Tests and Procedures. Mosby items and derived items 2011, 2006 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Chapter 8 Other Important Tests and Procedures 1 Introduction Additional important diagnostic studies include: Sputum examination Skin tests Endoscopic examination Lung biopsy Thoracentesis Hematology,
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia
 Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Hospital-acquired Pneumonia Hospital-acquired pneumonia (HAP) Pneumonia that occurs at least 2 days after hospital admission. The second most common and the leading cause of death due to hospital-acquired
Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum
 Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
Ruth Sobala, Kevin Conroy, Hilary Tedd, Salem Elarbi kevin.peter.conroy@gmail.com Respiratory Dept, Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Gateshead, UK. Eosinophils and effusion: a clinical conundrum Case report A
11/19/2012. The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad.
 The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
The spectrum of pulmonary diseases in HIV-infected persons is broad. HIV-associated Opportunistic infections Neoplasms Miscellaneous conditions Non HIV-associated Antiretroviral therapy (ART)-associated
HIV-associated Pulmonary Disease. Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond QUESTION: HIV-associated Pulmonary Diseases
 Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond Laurence Huang, MD Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Chief, HIV/AIDS Chest Clinic Zuckerberg San Francisco General
Classic and Challenging Cases from the HIV/AIDS Clinic and Beyond Laurence Huang, MD Professor of Medicine University of California San Francisco Chief, HIV/AIDS Chest Clinic Zuckerberg San Francisco General
Professor Rob Miller
 BHIVA AUTUMN CONFERENCE 2013 Including CHIVA Parallel Sessions Professor Rob Miller University College London Medical School COMPETING INTEREST OF FINANCIAL VALUE > 1,000: Speaker Name Prof Rob Miller
BHIVA AUTUMN CONFERENCE 2013 Including CHIVA Parallel Sessions Professor Rob Miller University College London Medical School COMPETING INTEREST OF FINANCIAL VALUE > 1,000: Speaker Name Prof Rob Miller
Α 78-year-old female who presents with a non-resolving pneumonia: what is your diagnosis?
 Evangelia Panagiotidou 1, Serafeim-Chrysovalantis Kotoulas 1, Maria Kilmpasani 2, Nikoleta Pastelli 2, Sofia Akritidou 1, Evangelos Chatzopoulos 1, Vasilis Bikos 1, Vasilios Bagalas 1, Katalin Fekete-Passa
Evangelia Panagiotidou 1, Serafeim-Chrysovalantis Kotoulas 1, Maria Kilmpasani 2, Nikoleta Pastelli 2, Sofia Akritidou 1, Evangelos Chatzopoulos 1, Vasilis Bikos 1, Vasilios Bagalas 1, Katalin Fekete-Passa
Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia: Diagnosis
 THE JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES VOL. 157, NO.6. JUNE 1988 1988 by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved. 0022-1899/88/5706-0001$01.00 AIDS COMMENTARY Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia: Diagnosis
THE JOURNAL OF INFECTIOUS DISEASES VOL. 157, NO.6. JUNE 1988 1988 by The University of Chicago. All rights reserved. 0022-1899/88/5706-0001$01.00 AIDS COMMENTARY Pneumocystis carinii Pneumonia: Diagnosis
A 72-year-old male with worsening interstitial infiltrates and respiratory failure
 A 72-year-old male with worsening interstitial infiltrates and respiratory failure Case report On November 24, 2004, a 72-year-old male was admitted to the medical intensive care unit (ICU) with a history
A 72-year-old male with worsening interstitial infiltrates and respiratory failure Case report On November 24, 2004, a 72-year-old male was admitted to the medical intensive care unit (ICU) with a history
This resource was first published in 2014 and revised in 2017.
 This resource was first published in 2014 and revised in 2017. 0 There is good evidence to suggest that patients eventually diagnosed with HIV infection have had contact with medical services, with symptoms
This resource was first published in 2014 and revised in 2017. 0 There is good evidence to suggest that patients eventually diagnosed with HIV infection have had contact with medical services, with symptoms
Respiratory Interactive Session. Elaine Borg
 Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
Respiratory Interactive Session Elaine Borg Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman Anterior mediastinal mass EBUS FNA Case 1 Respiratory Cytology 55 year old gentleman with anterior mediastinal
A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough
 Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Delphine Natali 1, Hai Tran Pham 1, Hung Nguyen The 2 delphinenatali@gmail.com Case report A Vietnamese woman with a 2-week history of cough A 52-year-old nonsmoker Vietnamese woman without any past medical
Five patients with AIDS in whom a lower respiratory. was wedged into the segmental bronchus that corresponded
 Thorax 1985;40: 166-170 Early experience and difficulties with bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial biopsy in the diagnosis of AIDS associated pneumonia in Britain CR SWINBURN, AL POZNIAK, S SUTHERLAND,
Thorax 1985;40: 166-170 Early experience and difficulties with bronchoalveolar lavage and transbronchial biopsy in the diagnosis of AIDS associated pneumonia in Britain CR SWINBURN, AL POZNIAK, S SUTHERLAND,
Histopathology: pulmonary pathology
 Histopathology: pulmonary pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
Histopathology: pulmonary pathology These presentations are to help you identify basic histopathological features. They do not contain the additional factual information that you need to learn about these
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE. Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018
 INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
INTERSTITIAL LUNG DISEASE Radhika Reddy MD Pulmonary/Critical Care Long Beach VA Medical Center January 5, 2018 Interstitial Lung Disease Interstitial Lung Disease Prevalence by Diagnosis: Idiopathic Interstitial
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Pneumocystis Pneumonia. Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine
 Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most
Pneumocystis Pneumonia Dr. Pradeep kumar II yr Pulmonary Medicine PNEUMOCYSTIS CARINII PNEUMONIA Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP), is commonly termed Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, is the 2 nd most
CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY
 Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
Thorax (1947), 2, 58 CAVERNOUS HAEMANGIOMA OF THE LUNG BY Leeds Cavernous haemangiomata of the lung are rare, and a survey of the French, American, and English literature on the subject has revealed only
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
Lung Cancer Case Study
 Lung Cancer Case Study Presented by s GP Education Programme 2 Part One Initial presentation 60 year old lady, presents with a 6 week history of right sided chest pain. The pain is like a dull ache, but
Lung Cancer Case Study Presented by s GP Education Programme 2 Part One Initial presentation 60 year old lady, presents with a 6 week history of right sided chest pain. The pain is like a dull ache, but
Clinico-pathological Conference. acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Disseminated histoplasmosis in patients with
 132 Clinico-pathological Conference Department of Medicine R F Miller Department of Histopathology, University College London Medical School, Middlesex Hospital, London, W1N 8AA S B Lucas Department of
132 Clinico-pathological Conference Department of Medicine R F Miller Department of Histopathology, University College London Medical School, Middlesex Hospital, London, W1N 8AA S B Lucas Department of
Pneumocystis. Pneumocystis BIOL Summer Introduction. Mycology. Introduction (cont.) Introduction (cont.)
 Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
Introduction Pneumocystis Disclaimer: This lecture slide presentation is intended solely for educational purposes. Many of the images contained herein are the property of the original owner, as indicated
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW. Financial Conflicts of Interest. Question #1: Question #1 (Cont.): None. Christopher H. Fanta, M.D.
 PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
PULMONARY MEDICINE BOARD REVIEW Christopher H. Fanta, M.D. Pulmonary and Critical Care Division Brigham and Women s Hospital Partners Asthma Center Harvard Medical School Financial Conflicts of Interest
Medical monitoring: tests available at central hospitals
 medial monitoring: tests available at central hospitals: 1 medical monitoring: tests available at central hospitals Medical monitoring: tests available at central hospitals medial monitoring: tests available
medial monitoring: tests available at central hospitals: 1 medical monitoring: tests available at central hospitals Medical monitoring: tests available at central hospitals medial monitoring: tests available
Radiological syndroms. Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome
 Radiological syndroms Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome Alveolar syndrome Pulmonary architecture : Morphological unit is the lobule 15-25mm
Radiological syndroms Alveolar syndrome Bronchial syndrome Interstitial syndrome Vascular syndrome Mediastinal Syndrome Alveolar syndrome Pulmonary architecture : Morphological unit is the lobule 15-25mm
Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach
 Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach Travis S Henry, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology Cardiac and Pulmonary Imaging Section University of California, San Francisco Large Middle Small 1 Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis: An Imaging Approach Travis S Henry, MD Associate Professor of Clinical Radiology Cardiac and Pulmonary Imaging Section University of California, San Francisco Large Middle Small 1 Bronchiectasis
Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia. Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia. Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia. Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia. 53 Year-Old Smoker
 Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia 53 Year-Old Smoker Emphysema Pink puffer Barrel chest Hyperinflation Trapped air
Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia Slide 120, Lobar Pneumonia Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia Slide 172, Interstitial Pneumonia 53 Year-Old Smoker Emphysema Pink puffer Barrel chest Hyperinflation Trapped air
HIV-related respiratory conditions
 HIV-related respiratory conditions 3 Rossana A. Ditangco Head, AIDS Research Group Department of Health, Research Institute for Tropical Medicine, Philippines The respiratory system is one of the most
HIV-related respiratory conditions 3 Rossana A. Ditangco Head, AIDS Research Group Department of Health, Research Institute for Tropical Medicine, Philippines The respiratory system is one of the most
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Financial disclosure COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT. High Res Chest HRCT. HRCT Pre test. I have no financial relationships to disclose. Anatomy Nomenclature
 Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Financial disclosure I have no financial relationships to disclose. Douglas Johnson D.O. Cardiothoracic Imaging Gaston Radiology COMMON DIAGNOSES IN HRCT High Res Chest Anatomy Nomenclature HRCT Sampling
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus
 Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Cryptogenic Organizing Pneumonia Diagnosis Approach Based on a Clinical-Radiologic-Pathologic Consensus Poster No.: C-1622 Congress: ECR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: C. Cordero Lares, E. Zorita
Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts
 Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
Nov 2003 Radiological Aspects of Pulmonary Tuberculosis in Immunocompetent Hosts Josh Rempell, Harvard Medical School Year III Tuberculosis: the captain of all (wo)men of death Overall, one third of the
* MILIARY MOTTLING --
 * MILIARY MOTTLING -- RARE CAUSE DR ARATHI SRINIVASAN FELLOW IN PEDIATRIC HEMATO ONCOLOGY DR A ANDAL DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS DR JULIUS XAVIER SCOTT DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRIC HEMATO ONCOLOGY KANCHI KAMAKOTI
* MILIARY MOTTLING -- RARE CAUSE DR ARATHI SRINIVASAN FELLOW IN PEDIATRIC HEMATO ONCOLOGY DR A ANDAL DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRICS DR JULIUS XAVIER SCOTT DEPARTMENT OF PEDIATRIC HEMATO ONCOLOGY KANCHI KAMAKOTI
Primary chondrosarcoma of lung
 Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
Thorax,(1970), 25, 366. Primary chondrosarcoma of lung G. M. REES Department of Surgery, Brompton Hospital, Lontdonl, S.W.3 A case of primary chondrosarcoma of the lung is described in a 64-year-old man.
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS
 CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
CLINICAL FEATURES IN PULMONARY TUBERCULOSIS Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Department of Medicine Tuberculosis Captain of all the Men of Death Great White Plague devastating effect on society 100 years ago one in
Index No. All five (05) questions should be answered. All questions carry equal marks.
 POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN TUBERCULOSIS & CHEST DISEASES EXAMINATION - MAY 2016 Date :- 4 th May 2016 PAPER I CASE HISTORIES Time :- 9.00 a.m. -11.00
POSTGRADUATE INSTITUTE OF MEDICINE UNIVERSITY OF COLOMBO POSTGRADUATE DIPLOMA IN TUBERCULOSIS & CHEST DISEASES EXAMINATION - MAY 2016 Date :- 4 th May 2016 PAPER I CASE HISTORIES Time :- 9.00 a.m. -11.00
Pulmonary Aspergillosis
 May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
May 2005 Pulmonary Aspergillosis Nancy Wei, Harvard Medical School, Year III Overview Pulmonary aspergillosis background information Patient presentations Common radiographic findings for each type of
October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month. Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging. Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ
 October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 65-year-old non-smoking woman presented
October 2012 Imaging Case of the Month Michael B. Gotway, MD Associate Editor Imaging Department of Radiology Mayo Clinic Arizona Scottsdale, AZ Clinical History: A 65-year-old non-smoking woman presented
TB Intensive Houston, Texas
 TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
TB Intensive Houston, Texas October 15-17, 17 2013 Diagnosis of TB: Radiology Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP October 16, 2013 Rosa M Estrada-Y-Martin, MD MSc FCCP, has the following disclosures to
A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka
 A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka Author s Details: (1) Dushantha Madegedara (2) Asela Rasika Bandara (3) Sachini Seneviratne (4) Samadara Nakandala (5) Rathnayake R.M.D.H.M - (1) (2)
A Rare Case of Lymphangioleiomyomatosis in Sri Lanka Author s Details: (1) Dushantha Madegedara (2) Asela Rasika Bandara (3) Sachini Seneviratne (4) Samadara Nakandala (5) Rathnayake R.M.D.H.M - (1) (2)
Oncogenic Viruses in AIDS: Mechanisms of Disease and Intrathoracic Manifestations
 Burns et al. Oncogenic Viruses in IDS Chest Imaging Pictorial Essay Judah Burns 1 Rita Shaknovich 2 Jason Lau 3 Linda B. Haramati 1 Burns J, Shaknovich R, Lau J, Haramati LB Keywords: IDS, cancer, chest
Burns et al. Oncogenic Viruses in IDS Chest Imaging Pictorial Essay Judah Burns 1 Rita Shaknovich 2 Jason Lau 3 Linda B. Haramati 1 Burns J, Shaknovich R, Lau J, Haramati LB Keywords: IDS, cancer, chest
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Bronchospasm & SOB. Kim Kilmurray Senior Clinical Teaching Fellow
 Bronchospasm & SOB Kim Kilmurray Senior Clinical Teaching Fellow LEARNING OBJECTIVES Perform a comprehensive respiratory examination & link clinical signs to underlying pathology Identify the spectrum
Bronchospasm & SOB Kim Kilmurray Senior Clinical Teaching Fellow LEARNING OBJECTIVES Perform a comprehensive respiratory examination & link clinical signs to underlying pathology Identify the spectrum
Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP. Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital
 Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital Is this topic still relevant? Is this topic still relevant?
Adjunctive Options for Severe PCP Dr Erica Shaddock Division of Pulmonology and Critical Care Charlotte Maxeke Johannesburg Academic Hospital Is this topic still relevant? Is this topic still relevant?
Nontuberculous Mycobacteria (NTM) in Patients with Cystic Fibrosis
 Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/cystic-fibrosis-in-focus/nontuberculous-mycobacteria-ntm-in-patientswith-cystic-fibrosis/8337/
Transcript Details This is a transcript of an educational program accessible on the ReachMD network. Details about the program and additional media formats for the program are accessible by visiting: https://reachmd.com/programs/cystic-fibrosis-in-focus/nontuberculous-mycobacteria-ntm-in-patientswith-cystic-fibrosis/8337/
The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis
 www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN: 2161-2609 Article The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis Xin He, Chuanyu Zhang* Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
www.cancercellresearch.org ISSN: 2161-2609 Article The Imaging Analysis of Pulmonary Sarcodiosis Xin He, Chuanyu Zhang* Department of Radiology, Affiliated Hospital of Qingdao University, Qingdao, China
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia
 Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
Unit II Problem 2 Pathology: Pneumonia - Definition: pneumonia is the infection of lung parenchyma which occurs especially when normal defenses are impaired such as: Cough reflex. Damage of cilia in respiratory
GUIDELINES FOR CANCER IMAGING Lung Cancer
 GUIDELINES FOR CANCER IMAGING Lung Cancer Greater Manchester and Cheshire Cancer Network Cancer Imaging Cross-Cutting Group April 2010 1 INTRODUCTION This document is intended as a ready reference for
GUIDELINES FOR CANCER IMAGING Lung Cancer Greater Manchester and Cheshire Cancer Network Cancer Imaging Cross-Cutting Group April 2010 1 INTRODUCTION This document is intended as a ready reference for
Opportunistic Infections BHIVA Guidelines
 Opportunistic Infections BHIVA Guidelines Mark Nelson David Dockrell Simon Edwards I have.. 1. Read all of the BHIVA guidelines 12% 2. Read some of the BHIVA guidelines in their entirety 3. Browsed some
Opportunistic Infections BHIVA Guidelines Mark Nelson David Dockrell Simon Edwards I have.. 1. Read all of the BHIVA guidelines 12% 2. Read some of the BHIVA guidelines in their entirety 3. Browsed some
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Respiratory system. Applied Anatomy &Physiology
 Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Localised airway narrowing in sarcoidosis
 Thorax 1982;37:443-447 JW HADFIELD, RL PAGE, CDR FLOWER, JE STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard, Cambridge, and Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge ABSTRACr Four patients developed multiple narrowings
Thorax 1982;37:443-447 JW HADFIELD, RL PAGE, CDR FLOWER, JE STARK From Papworth Hospital, Papworth Everard, Cambridge, and Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge ABSTRACr Four patients developed multiple narrowings
P neumocystis jirovecii pneumonia (PCP) continues to be a
 716 RESPIRATORY INFECTION Improved survival for HIV infected patients with severe Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia is independent of highly active antiretroviral therapy R F Miller, E Allen, A Copas, M
716 RESPIRATORY INFECTION Improved survival for HIV infected patients with severe Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia is independent of highly active antiretroviral therapy R F Miller, E Allen, A Copas, M
Anatomy. The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs.
 Respiratory System Anatomy The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs. Within the lungs, the bronchi transport air with oxygen to the alveoli on inspiration
Respiratory System Anatomy The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs. Within the lungs, the bronchi transport air with oxygen to the alveoli on inspiration
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids
 Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
Treatment of Coccidioidomycosis-associated Eosinophilic Pneumonia with Corticosteroids Joshua Malo, MD Yuval Raz, MD Linda Snyder, MD Kenneth Knox, MD University of Arizona Medical Center Department of
ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH. Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch
 ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch AUTHOR HAS NOTHING TO DECLARE LEARNING OBJETIVES Understand the pathophysiology
ACUTE PULMNARY INFECTIONS: UNDERSTANDING THE CHEST RADIOGRAPH Leonard E. Swischuk, M.D. University of Texas Medical Branch AUTHOR HAS NOTHING TO DECLARE LEARNING OBJETIVES Understand the pathophysiology
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1).
 PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1). 1 Inform Consent Date: / / dd / Mmm / yyyy 2 Patient identifier: Please enter the 6 digit Patient identification number from your site patient log
PATIENT CHARACTERISTICS AND PREOPERATIVE DATA (ecrf 1). 1 Inform Consent Date: / / dd / Mmm / yyyy 2 Patient identifier: Please enter the 6 digit Patient identification number from your site patient log
Marc Bazot, MD; Jacques Cadranel, MD; Sylvie Benayoun, MD; Marc Tassart, MD; Jean Michel Bigot, MD; and Marie France Carette, MD
 Primary Pulmonary AIDS-Related Lymphoma* Radiographic and CT Findings Marc Bazot, MD; Jacques Cadranel, MD; Sylvie Benayoun, MD; Marc Tassart, MD; Jean Michel Bigot, MD; and Marie France Carette, MD Study
Primary Pulmonary AIDS-Related Lymphoma* Radiographic and CT Findings Marc Bazot, MD; Jacques Cadranel, MD; Sylvie Benayoun, MD; Marc Tassart, MD; Jean Michel Bigot, MD; and Marie France Carette, MD Study
Respiratory Medicine
 Respiratory Medicine This document is based on the handout from the Medicine for Finals course. The notes provided here summarise key aspects, focusing on areas that are popular in clinical examinations.
Respiratory Medicine This document is based on the handout from the Medicine for Finals course. The notes provided here summarise key aspects, focusing on areas that are popular in clinical examinations.
infection as a predictor for faster progression to
 Thorax 1993;48:481-485 Department of Respiratory Medicine R B Nieman J Fleming D M Mitchell Department of Genitourinary Medicine R J Coker J R W Harris St Mary's Hospital, London W2 INY Reprint requests
Thorax 1993;48:481-485 Department of Respiratory Medicine R B Nieman J Fleming D M Mitchell Department of Genitourinary Medicine R J Coker J R W Harris St Mary's Hospital, London W2 INY Reprint requests
Case Report Pulmonary Sarcoidosis following Etanercept Treatment
 Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 724013, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/724013 Case Report Pulmonary Sarcoidosis following Etanercept Treatment Kuljeet Bhamra and Richard Stevens Department
Case Reports in Rheumatology Volume 2012, Article ID 724013, 4 pages doi:10.1155/2012/724013 Case Report Pulmonary Sarcoidosis following Etanercept Treatment Kuljeet Bhamra and Richard Stevens Department
Chest radiograph of an. asymptomatic man. Case report. Case history
 Eleftheria Chaini 1, Niki Giannakou 2, Dimitra Haini 3, Anna Maria Athanassiadou 4, Angelos Tsipis 4, Nikolaos D. Hainis 5 elhaini@otenet.gr 1 Pulmonary Dept, Corfu General Hospital, Kontokali, Greece.
Eleftheria Chaini 1, Niki Giannakou 2, Dimitra Haini 3, Anna Maria Athanassiadou 4, Angelos Tsipis 4, Nikolaos D. Hainis 5 elhaini@otenet.gr 1 Pulmonary Dept, Corfu General Hospital, Kontokali, Greece.
Pulmonary And Central Nervous System Involvement In Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Vasculopathy And/Or Steroids As Causative Agents - A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 Pulmonary And Central Nervous System Involvement In Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Vasculopathy And/Or Steroids As Causative Agents - A Case Report
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Radiology Volume 4 Number 1 Pulmonary And Central Nervous System Involvement In Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Vasculopathy And/Or Steroids As Causative Agents - A Case Report
Lung Cancer. This reference summary will help you better understand lung cancer and the treatment options that are available.
 Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
Lung Cancer Introduction Lung cancer is the number one cancer killer of men and women. Over 165,000 people die of lung cancer every year in the United States. Most cases of lung cancer are related to cigarette
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum
 The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
The McMaster at night Pediatric Curriculum Community Acquired Pneumonia Based on CPS Practice Point Pneumonia in healthy Canadian children and youth and the British Thoracic Society Guidelines on CAP Objectives
Management of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS)
 Management of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS) Adult Clinical Guideline from the New York State Department of Health AIDS Institute www.hivguidelines.org Purpose of the IRIS Guideline
Management of Immune Reconstitution Inflammatory Syndrome (IRIS) Adult Clinical Guideline from the New York State Department of Health AIDS Institute www.hivguidelines.org Purpose of the IRIS Guideline
Bronchogenic Carcinoma
 A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
A 55-year-old construction worker has smoked 2 packs of ciggarettes daily for the past 25 years. He notes swelling in his upper extremity & face, along with dilated veins in this region. What is the most
generalised lymphadenopathy presenting with shortness of breath and infiltrates on chest
 Abhishek Biswas 1, Herman Gaztambide 1, Dara N. Wakefield 2, Peruvemba S. Sriram 1 abiswas@ufl.edu 1 University of Florida, Division of Pulmonary Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, Gainesville, FL, USA.
Abhishek Biswas 1, Herman Gaztambide 1, Dara N. Wakefield 2, Peruvemba S. Sriram 1 abiswas@ufl.edu 1 University of Florida, Division of Pulmonary Critical Care and Sleep Medicine, Gainesville, FL, USA.
Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation
 Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Original Research Article Pulmonary Sarcoidosis - Radiological Evaluation Jayesh Shah 1, Darshan Shah 2*, C. Raychaudhuri 3 1 Associate Professor, 2 1 st Year Resident, 3 Professor and HOD Radiology Department,
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
TB in Children. Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012
 TB in Children Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012 Contents Epidemiology Transmission and pathogenesis Diagnosis of TB TB and HIV Management Epidemiology The year 2000 8.3 million new TB cases diagnosed
TB in Children Rene De Gama Block 10 Lectures 2012 Contents Epidemiology Transmission and pathogenesis Diagnosis of TB TB and HIV Management Epidemiology The year 2000 8.3 million new TB cases diagnosed
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis. Dr: Salah Ahmed
 Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pathology of pulmonary tuberculosis Dr: Salah Ahmed Is a chronic granulomatous disease, caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (hominis) Usually it involves lungs but may affect any organ or tissue Transmission:
Pneumocystis carinii infection: current treatment and prevention
 Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1996) 37, Suppl. B, 33-53 Pneumocystis carinii infection: current treatment and prevention Robert F. Miller***, Jo Le Noury*, Elizabeth L. Corbetf, J. Mark Felton'
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy (1996) 37, Suppl. B, 33-53 Pneumocystis carinii infection: current treatment and prevention Robert F. Miller***, Jo Le Noury*, Elizabeth L. Corbetf, J. Mark Felton'
Common things are common, but not always the answer
 Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Kevin Conroy, Joe Mackenzie, Stephen Cowie kevin.conroy@nhs.net Respiratory Dept, Darlington Memorial Hospital, Darlington, UK. Common things are common, but not always the answer Case report Cite as:
Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema
 Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema Poster No.: P-0025 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Lee, C.-K. Park; Guri/KR Keywords: Neoplasia, Biopsy, PET-CT, CT, Thorax, Lung DOI:
Lung cancer in patients with chronic empyema Poster No.: P-0025 Congress: ESTI 2015 Type: Scientific Poster Authors: Y. Lee, C.-K. Park; Guri/KR Keywords: Neoplasia, Biopsy, PET-CT, CT, Thorax, Lung DOI:
Care of the Patient with a Respiratory Disorder
 Care of the Patient with a Respiratory Disorder 1 Slide 1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology External respiration Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lung and the environment Internal respiration
Care of the Patient with a Respiratory Disorder 1 Slide 1 Overview of Anatomy and Physiology External respiration Exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the lung and the environment Internal respiration
ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA
 ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 302 Mohammad Zaman ( Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Asthmatic pulmonary
ASTHMATIC PULMONARY EOSINOPHILIA Pages with reference to book, From 300 To 302 Mohammad Zaman ( Department of Pulmonary Medicine, Pakistan Institute of Medical Sciences, Islamabad. ) Asthmatic pulmonary
Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference
 Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference CASE 1: A 59-year-old female Housekeeper Live in Phuket, Thailand Progressive dyspnea for 1 year Present illness 1 year PTA : She developed dyspnea on exertion
Clinical Radiological Pathological Conference CASE 1: A 59-year-old female Housekeeper Live in Phuket, Thailand Progressive dyspnea for 1 year Present illness 1 year PTA : She developed dyspnea on exertion
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Pages and
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
manifestations are uncommon. Initial descriptions of the disease (Rosai and Dorfman, 1969) specifically
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 521-525 Diffuse cutaneous involvement and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy A. A. WOODCOCK B.Sc., M.B., Ch.B., M.R.C.P. Summary Severe skin involvement
Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1980) 56, 521-525 Diffuse cutaneous involvement and sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy A. A. WOODCOCK B.Sc., M.B., Ch.B., M.R.C.P. Summary Severe skin involvement
Making the Right Call With. Pneumonia. Community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is a. Community-Acquired. What exactly is CAP?
 Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
Making the Right Call With Community-Acquired Pneumonia In this article: By Thomas J. Marrie, MD The case of Allyson Allyson, 32, presented to the emergency department with a 48-hour history of anorexia,
