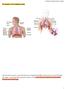
Anatomy. The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs.
|
|
|
- Marcia Copeland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Respiratory System
2 Anatomy The respiratory system starts from the nose, mouth, larynx, trachea, and the two lungs.
3
4
5
6
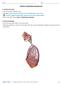
7 Within the lungs, the bronchi transport air with oxygen to the alveoli on inspiration and carry waste gases (e.g. carbon dioxide) away on expiration. The acinus is the gas exchange unit of the lung and consists of branching respiratory bronchioles leading to clusters of alveoli. Alveoli are tiny air sacs lined by flattened epithelial cells and covered in capillaries where gas exchanges occur
8 The alveoli and capillaries have extremely thin walls and come into very close contact (the alveolar capillary membrane) so gases can rapidly diffuse between them. There are approximately 300 million alveoli in each lung for gas exchange with a total surface area of meter square.
9 The lungs has two blood supplies(dual): 1) the bronchial arteries which arise from the aorta and supply oxygenated blood to the bronchial walls. 2) The pulmonary arteries which deliver deoxygenated blood to the capillaries surrounding the alveoli
10
11 Symptoms 1) Cough 2) Sputum production 3) Hemoptysis 4) Chest pain 5) Breathlessness
12 1 )Cough: Symptoms Is a forced expulsive maneuver against an initially closed glottis. Causing characteristic sound. Can be acute (less than 3 weeks) or chronic (more then 8 weeks) The most common cause is acute viral infections of the upper airway system
13 Cough (features) - Prolonged wheezy coughing: asthma, COPD. - Feeble non-explosive (bovine): lung cancer (paralysis of vocal cords), neuro-msucular disease causing respiratory muscle weakness - Moist cough: secretions from infection, bronchiectasis, chronic bronchitis. - Noctunral cough: asthma
14 Cough (causes) Acute: Viral respiratory tract infection Bronchitis Inhaled foreign body Inhalation of irritant dusts or fumes Pneumonia Acute extrinsic allergic alveolitis Chronic Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) Asthma Post bronchial hyper-activity Rhinitis/sinusitis Cigarette smoking Drugs, ACE inhibitors Irritant dusts/fumes Lung tumors TB, Interstitial lung disease Bronchiectasis
15 Symptoms 2) sputum production Amount Color Taste or smell Examples: COPD and chronic bronchitis: clear mucoid sputum if there is no infection Lower respiratory tract infection: yellowish sputum (presence of live neutrophils) Asthma: yellowish sputum (eosinophils) Bronchiectasis: large volumes of purulent sputum varying with posture Pulmonary edema: watery sputum with a pink tinge
16 Symptoms 3) Hemoptysis Amount and appearance Duration and frequency - intermittent with recurrent infections over years: bronchiectasis - Daily for a short periods (weeks) lung cancer, TB, abscess - Single episodes with chest pain: pulmonary infarction.
17 Hemoptysis (causes) - Infection: Bronchiectasis, Tuberculosis, lung abscess, cystic fibrosis - Tumours: Lung cancer, endobronchial metastasis, bronchial carcinoid. - Vascular: Pulmonary infarction, arteriovenous malformation - Vasculitis: - Trauma: Foreign body, iatrogenic
18 Hemoptysis (causes) Cardiac: Mitral Valve disease, acute left ventricular failure Hematological: Bleeding tendencies, anticoagulation
19 Symptoms 4) Chest pain: Pleural chest pain Chest wall pain Mediastinal chest pain
20 Pleural chest pain Is a sharp, stabbing pain and is identified by inspiration or coughing caused by irritation of the parietal pleura. Causes: Infection: pneumonia(involving pleura),bronchiectasis) Pneumothorax Pulmonary infarction Connective tissue disease
21 Chest wall pain Causes: Chornic cough/breathlessness Muscular pain Rib fractures Bony metastasis Thoracis shingles (herpes zoster)
22 Mediastinal chest pain Mediastinal chest pain is central, retrosternal and unrelated to respiration or cough. Causes: Massive pulmonary embolism Acute myocardial infarction Aortic dissection Infection, irritant dusts Eshophagitis Mediastinitis Lymphadenopathy
23 Symptoms 5) Breathlessness Shortness of breath, difficulty getting enough air. Mode of onset Minutes: pulmonary thromboembolism, pneumothorax, asthma, inhaled forein body Hours to days: pneumonia, asthma. Weeks to months: Anemia, Pleural effuion, neruomuscular disease. Months to years: COPD, pulmonary fibrosis, TB, Heart failure.
24 Breathlessness Causes: Non cardio-respiratory: Anemia, Obesity, Psychogenic, Metabolic acidosis. Cardiac: Heart failure, mitral valve disease, pericarditis, pericaridal effusion Respiratory: Foreign body, Ashtma, COPD, Bronchiectasis, Lung cancer, pulomnary fibrosis, Pneumonia, Tuberculosis, pulmonary thromboembolism, pulmonary hypertension, pneumothorax, kyphoscholiosis. Neumuscular disease.
25 will see you soon next year Thank you
Respiratory system. Applied Anatomy &Physiology
 Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Respiratory system Applied Anatomy &Physiology Anatomy The respiratory system consists of 1)The Upper airway : Nose, mouth and larynx 2)The Lower airways Trachea and the two lungs. Within the lungs,
Pulmonary Pathophysiology
 Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Pulmonary Pathophysiology 1 Reduction of Pulmonary Function 1. Inadequate blood flow to the lungs hypoperfusion 2. Inadequate air flow to the alveoli - hypoventilation 2 Signs and Symptoms of Pulmonary
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale. Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases
 Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Anatomy & Physiology 2 Canale Respiratory System: Exchange of Gases Why is it so hard to hold your breath for Discuss! : ) a long time? Every year carbon monoxide poisoning kills 500 people and sends another
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Biology 2201 Why do we breathe? Cells carry out the reactions of cellular respiration in order to produce ATP. ATP is used by the cells for energy. All organisms need
The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body.
 Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
Respiratory System The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply the blood with oxygen in order for the blood to deliver oxygen to all parts of the body. The respiratory system does this
LUNGS. Requirements of a Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
Respiratory System Requirements of a Respiratory System Gas exchange is the physical method that organisms use to obtain oxygen from their surroundings and remove carbon dioxide. Oxygen is needed for aerobic
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS
 CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
CARDIOVASCULAR AND RESPIRATORY SYSTEMS KEY TERMS: Cardiovascular System, cardio, vascular, blood vessels, valves, arteries, capillaries, veins, systemic circulation, pulmonary circulation Your Cardiovascular
Chapter 10. The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases. Copyright 2009 Pearson Education, Inc.
 Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Exchange of Gases http://www.encognitive.com/images/respiratory-system.jpg Human Respiratory System UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT LOWER RESPIRATORY TRACT Nose Passageway for
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
CHAPTER 7.1 STRUCTURES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 244-247 DO NOW What structures, do you think, are active participating in the breathing process? 2 WHAT ARE WE DOING IN TODAY S CLASS Finishing Digestion
Chapter 10 Respiration
 1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
1 Chapter 10 Respiration Introduction/Importance of the Respiratory System All eukaryotic organisms need oxygen to perform cellular respiration (production of ATP), either aerobically or anaerobically.
Respiratory System. Introduction. Atmosphere. Some Properties of Gases. Human Respiratory System. Introduction
 Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
Introduction Respiratory System Energy that we consume in our food is temporarily stored in the bonds of ATP (adenosine triphosphate) before being used by the cell. Cells use ATP for movement and to drive
The respiratory system structure and function
 Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
Name: Class: Date: Active reading 11A + Biology Gr11A The respiratory system structure and function The function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and eliminate carbon dioxide
The Respiratory System. Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi
 The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
The Respiratory System Dr. Ali Ebneshahidi Functions of The Respiratory System To allow gases from the environment to enter the bronchial tree through inspiration by expanding the thoracic volume. To allow
Respiratory Diseases and Disorders
 Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Chapter 9 Respiratory Diseases and Disorders Anatomy and Physiology Chest, lungs, and conducting airways Two parts: Upper respiratory system consists of nose, mouth, sinuses, pharynx, and larynx Lower
Respiratory Disease. Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician
 Respiratory Disease Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases Cardinal Symptoms Cough Sputum Hemoptysis Dyspnea Wheezes Chest pain Signs and Symptoms
Respiratory Disease Dr Amal Damrah consultant Neonatologist and Paediatrician Signs and Symptoms of Respiratory Diseases Cardinal Symptoms Cough Sputum Hemoptysis Dyspnea Wheezes Chest pain Signs and Symptoms
Respiratory System. Organization of the Respiratory System
 Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Respiratory System In addition to the provision of oxygen and elimination of carbon dioxide, the respiratory system serves other functions, as listed in (Table 15 1). Respiration has two quite different
Chapter Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages
 Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Chapter 18.1 Effects of Smoke on the Respiratory System Part 1 pages 412-416 ETS (Environmental Tobacco Smoke) Environmental Tobacco Smoke = ETS The smoke exhaled by active smokers. This smoke affects
Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of
 1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
1 2 3 4 5 Bio 1102 Lec. 7 (guided): Chapter 10 The Respiratory System Respiratory System Function: to supply blood with, and to rid the body of Oxygen: needed by cells to break down food in cellular respiration
Chapter 10. Respiratory System and Gas Exchange. Copyright 2005 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Benjamin Cummings
 Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
Chapter 10 Respiratory System and Gas Exchange Function of the Respiratory System To obtain oxygen (O 2 ) for all cells in the body. To rid the cells of waste gas (CO 2 ). Oxygen (O 2 ) is vital chemical
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
The Respiratory System Respiratory Anatomy Upper respiratory tract Nose Nasal passages Pharynx Larynx Respiratory Anatomy Functions of the upper respiratory tract: Provide entry for inhaled air Respiratory
Respiration.notebook March 07, Unit 3. Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium. Oct 11 3:27 PM. Hodgkin s Disease STSE
 Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
Unit 3 Maintaining Dynamic Equilibrium Review STSE overview Respiratory system Respiratory Disorders Challenge Conclusions Oct 11 3:27 PM Hodgkin s Disease STSE Lymphatic system Humans have two circulatory
B Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8
 The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
The Respiratory System Why do we breathe? B. 2201 Unit III Notes 6, 7 and 8 Respiratory System We know that our cells respire to produce ATP (energy). All organisms need energy to live, so that s why we
COUGH Dr. A m A it i e t sh A g A garwa w l Le L ctu t rer Departm t ent t o f f M e M dic i in i e
 COUGH Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Lecturer Department of Medicine Cough is an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign
COUGH Dr. Amitesh Aggarwal Lecturer Department of Medicine Cough is an explosive expiration that provides a normal protective mechanism for clearing the tracheobronchial tree of secretions and foreign
Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing
 Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Respiration Unconscious exchange of air between lungs and the external environment Breathing Two types External Exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen between the environment and the organism Internal Exchange
Function of the Respiratory System. Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration)
 Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Function of the Respiratory System Exchange CO2 (on expiration) for O2 (on inspiration) Upper Respiratory Tract Includes: Nose Mouth Pharynx Larynx Function: Warms and humidifies the inspired air Filters
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order. Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital
 Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
Tests Your Pulmonologist Might Order Center For Cardiac Fitness Pulmonary Rehab Program The Miriam Hospital BASIC ANATOMY OF THE LUNGS Lobes of Lung 3 lobes on the Right lung 2 lobes on the Left Blood
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. Pages and
 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM Pages 103-105 and 146-150 1 When the respiratory system is mentioned, people generally think of breathing, but breathing is only one of the activities of the respiratory system.
Respiration. Chapter 37. Mader: Biology 8 th Ed.
 Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
Respiration Chapter 37 Gas Exchange Surfaces Respiration is the sequence of events that results in gas exchange between the body s cells and the environment. Ventilation External Respiration Internal Respiration
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY SESSION 12 THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM The Respiratory system is made up of organs that allow us to breathe. The primary function of the respiratory system is to supply oxygen to the
Pathogenesis of pulmonary symptoms Dr. Rehab F. Gwada
 Pathogenesis of pulmonary symptoms Dr. Rehab F. Gwada Objectives of the lectures Identify main symptoms of pulmonary diseases & their pathogeneses Outline the graded of dyspnea Differentiate between bronchial
Pathogenesis of pulmonary symptoms Dr. Rehab F. Gwada Objectives of the lectures Identify main symptoms of pulmonary diseases & their pathogeneses Outline the graded of dyspnea Differentiate between bronchial
Your Lungs and COPD. Patient Education Pulmonary Rehabilitation. A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs
 Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
Patient Education Your Lungs and COPD A guide to how your lungs work and how COPD affects your lungs Your lungs are organs that process every breath you take. They provide oxygen (O 2 ) to the blood and
5/5/2013. The Respiratory System. Chapter 16 Notes. The Respiratory System. Nasal Cavity. Sinuses
 The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
The Respiratory System Chapter 16 Notes The Respiratory System Objectives List the general functions of the respiratory system. Identify the organs of the respiratory system. Describe the functions of
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion
 Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
Chapter 13 Respiration & Excretion Breathing Did you know? Lungs are very spongy and elastic because of the millions of air sacs Lungs exchange about 10,000 L of air a day. Lungs would float like corks
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions. KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells.
 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions KEY CONCEPT The respiratory and circulatory systems bring oxygen and nutrients to the cells. 30.1 Respiratory and Circulatory Functions The respiratory and circulatory
Tuesday, December 13, 16. Respiratory System
 Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Respiratory System Trivia Time... What is the fastest sneeze speed? What is the surface area of the lungs? (hint... think of how large the small intestine was) How many breaths does the average person
Circulatory System. and. Respiratory System. Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song THE HEART LUNGS. Monday, May 23, 2011
 Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Human Anatomy Circulatory System and THE HEART Respiratory System LUNGS Ari Min, Yerim Lee and Min Ji Song Purpose of the Circulatory System Function of circulatory system: exchange gases with cardiovascular
Lung Cancer - Suspected
 Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
Lung Cancer - Suspected Shared Decision Making Lung Cancer: http://www.enhertsccg.nhs.uk/ Patient presents with abnormal CXR Lung cancer - clinical presentation History and Examination Incidental finding
The Human Respiration System
 The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
The Human Respiration System Nasal Passage Overall function is to filter, warm and moisten air as it enters the body. The nasal passages are the primary site of air movement we tend to be nose breathers.
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems. Chapter 37: Biology II
 Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Chapter 37: Biology II The Circulatory System Larger organisms cannot rely on diffusion to move oxygen, nutrients and wastes through cells The Circulatory System Closed
1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies 2 Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different Cause can be
 1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies 2 Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in hospital
1 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies 2 Respiratory Distress Patients often complain about. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in hospital
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
The Respiratory System By Mr. Danilo Villar Rogayan Jr. Instructor I, Department of Natural Sciences RMTU San Marcelino Introduction Function Move air in an out of lungs (ventilation) Delivers oxygen (O
Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to
 1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
1 Respiratory System 1. A function of the structure labelled X is to A. produce sound. B. exchange gases. C. carry air into and out of the lung. D. stimulate the breathing centre in the brain. 2. Identify
Respiratory System. Chapter 9
 Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
Respiratory System Chapter 9 Air Intake Air in the atmosphere is mostly Nitrogen (78%) Only ~21% oxygen Carbon dioxide is less than 0.04% Air Intake Oxygen is required for Aerobic Cellular Respiration
About the Respiratory System. Respiratory System. Human Respiratory System. Cellular Respiration. Nostrils. Label diagram
 Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
Respiratory System Human Respiratory System A system to deliver oxygen (O2) to body cells & get rid of carbon dioxide (CO2) as a waste through cellular respiration. Two systems involved: Respiratory &
2. List seven functions performed by the respiratory system?
 The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
The Respiratory System C23 Study Guide Tortora and Derrickson 1. In physiology we recognize that the word respiration has three meanings. What are the three different meanings of the word respiration as
10.1 The Pulmonary-Circulatory System
 pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
pulmonary system breathing lungs pneumonia suffocation asthma circulatory system atrium ventricle artery capillary vein heart attack stroke heart The Pulmonary System Our pulmonary system contains tissues
Respiratory System. December 20, 2011
 Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Respiratory System December 20, 2011 Nasal Cavity: Contains cilia (hair cells) to prevent particles from entering the respiratory tract Mucus does the same, in addition to warming and moistening the air
Chapter 16. Vocabulary. Name Class Date
 Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Chapter 16 Vocabulary plasma congenital larynx hemoglobin anemia bronchitis arteries leukemia pneumonia capillaries Hodgkin s disease pleurisy veins respiration asthma platelets diaphragm sinusitis lymph
Unit 9. Respiratory System 16-1
 Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
Unit 9 Respiratory System 16-1 Works together with the circulatory system Exchange of gases between atmosphere, blood, and cells If respiratory system and/or circulatory system fails, death will occur
The Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Structures of the Respiratory System Nose Sinuses
 CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
CH 14 D.E. Human Biology The Respiratory System The Respiratory System OUTLINE: Mechanism of Breathing Transport of Gases between the Lungs and the Cells Respiratory Centers in the Brain Function Provides
The Respiratory System
 130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
130 20 The Respiratory System 1. Define important words in this chapter 2. Explain the structure and function of the respiratory system 3. Discuss changes in the respiratory system due to aging 4. Discuss
In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body
 In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body. 1. 2. (2) Describe what gaseous exchange is and clearly state where it takes
In order for respiration to take place air must be taken in. Name two of the air passages which allow air to enter the body. 1. 2. (2) Describe what gaseous exchange is and clearly state where it takes
Chapter 11: Respiratory Emergencies
 29698_CH11_ANS_p001_005 4/12/05 2:02 PM Page 1 Answer Key Chapter 11 1 Chapter 11: Respiratory Emergencies Matching 1. B (page 373) 8. E (page 370) 2. D (page 369) 9. M(page 389) 3. H (page 370) 10. A
29698_CH11_ANS_p001_005 4/12/05 2:02 PM Page 1 Answer Key Chapter 11 1 Chapter 11: Respiratory Emergencies Matching 1. B (page 373) 8. E (page 370) 2. D (page 369) 9. M(page 389) 3. H (page 370) 10. A
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline" 5 minutes" "Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders " 10 minutes "Lecture:" 25 minutes "Lecture:" 15 minutes "Active study
Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems
 Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
Name Date Unit 1 Exam: Respiratory and Circulatory Systems Multiple Choice. Please make your best selection. 1. Respiration is the process of: (a) Sucking air into the lungs (b) Converting glucose into
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems Functions of the Respiratory System Warm, moisten, and filter incoming air Resonating chambers for speech and sound production Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide
Respiration. Chapter 35
 Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Respiration Chapter 35 Respiration Respiration is the exchange of gasses between an organism and its environment Gas exchange occurs between the environment and blood at the lungs, and the blood and cells
Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc...
 Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
Respiration Energy is needed for cell activities: growth,reproduction, repair, movement, etc... Metabolism refers to all of the chemical reactions in the body, where molecules are synthesized (anabolism)
61a A&P: Respiratory System!
 61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
61a A&P: Respiratory System! 61a A&P: Respiratory System! Class Outline 5 minutes Attendance, Breath of Arrival, and Reminders 10 minutes Lecture: 25 minutes Lecture: 15 minutes Active study skills: 60
-Rachel Naomi Remen. Respiratory System 1
 Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Life is known only by those who have found a way to be comfortable with change and the unknown. Given the nature of life, there may be no security, but only adventure. Respiratory System 1 -Rachel Naomi
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together
 Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 2: Human Body Systems Work Independently and Together 2.1 Body Systems Body systems Are made up of parts that work together as a whole Are connected to one or more other Will not function well
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
Chapter 10 Lecture Outline See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes. Copyright 2016 McGraw-Hill Education. Permission required for reproduction
The Respiratory System
 BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
BIOLOGY OF HUMANS Concepts, Applications, and Issues Fifth Edition Judith Goodenough Betty McGuire 14 The Respiratory System Lecture Presentation Anne Gasc Hawaii Pacific University and University of Hawaii
an inflammation of the bronchial tubes
 BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
BRONCHITIS DEFINITION Bronchitis is an inflammation of the bronchial tubes (or bronchi), which are the air passages that extend from the trachea into the small airways and alveoli. Triggers may be infectious
Exam 2 Respiratory Disorders
 Exam 2 Respiratory Disorders Common Cold Common Cold Pathology Common Cold Consequences Rhinosinusitis Rhinosinusitis Pathology Rhinosinusitis ostia can close due to Influenza (Flu) Influenza Pathology
Exam 2 Respiratory Disorders Common Cold Common Cold Pathology Common Cold Consequences Rhinosinusitis Rhinosinusitis Pathology Rhinosinusitis ostia can close due to Influenza (Flu) Influenza Pathology
The RESPIRATORY System. Unit 3 Transportation Systems
 The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
The RESPIRATORY System Unit 3 Transportation Systems The Respiratory System Functions of the Respiratory System Warms, moistens, and filters incoming air Nasal cavity Resonating chambers for speech and
Phases of Respiration
 Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
Phases of Respiration We get oxygen from the environment and it goes to our cells, there. Pulmonary ventilation External exchange of gases Internal exchange of gases Overview of respiration. In ventilation,
WF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. RESPIRATORY MEDICINE
 WF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. RESPIRATORY MEDICINE 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
WF RESPIRATORY SYSTEM. RESPIRATORY MEDICINE 1 Societies 11 History 13 Dictionaries. Encyclopaedias. Bibliographies Use for general works only. Classify with specific aspect where possible 15 Classification.
The Circulatory System
 The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
The Circulatory System Single-celled organisms do not need a circulatory system. They are in direct contact with their environment, so transport of materials occurs by diffusion and osmosis. Larger organisms
Chapter 13. Respiratory Emergencies
 Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies Introduction Patients often complain about dyspnea. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different conditions Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in
Chapter 13 Respiratory Emergencies Introduction Patients often complain about dyspnea. Shortness of breath Symptom of many different conditions Cause can be difficult to determine. Even for physician in
Chapter 16. Respiratory System
 Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 16 Respiratory System Introduction Respiration = the entire process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and body cells 1. Ventilation 2. Gas exchange 3. Gas transport : 4. Cellular respiration
Chapter 11 The Respiratory System
 Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
Biology 12 Name: Respiratory System Per: Date: Chapter 11 The Respiratory System Complete using BC Biology 12, page 342-371 11.1 The Respiratory System pages 346-350 1. Distinguish between A. ventilation:
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING. Compiled by. Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives --()--
 IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
IRIDOLOGY BREATHING Compiled by Campbell M Gold (2006) CMG Archives http://campbellmgold.com Introduction The respiratory tract, which is also called respiratory system, is the complex of organs and structures
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals
 Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Notes to complete gas exchange in mammals Mass flow of air to respiratory surface this is achieved through the mechanics of ventilation (breathing). This ensures a regular supply of air into and out of
Level 2 Anatomy and Physiology Bite size revision. Respiratory System. The order of the passage of oxygen into the body (inhalation/inspiration) is: -
 Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
Respiratory System Function of the respiratory system The lungs are located in the chest cavity and their function is to intake oxygen and remove carbon dioxide from the body. Structure of the respiratory
CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY
 pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
pulmonary ventilation move air external respiration exchange gases transportation of gases internal respiration exchange gases CHAPTER 22 RESPIRATORY in / out lungs air - blood blood - cells cell respiration
? Pulmonary Respiratory System
 The Structure of The Respiratory System The respiratory system is composed of groups of organelles that filters and transports air into the lungs. The organs comprising of the respiratory system include
The Structure of The Respiratory System The respiratory system is composed of groups of organelles that filters and transports air into the lungs. The organs comprising of the respiratory system include
Phases of Respiration. Chapter 18: The Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System. Structures of the Respiratory System
 Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Phases of Respiration Chapter 18: The Respiratory System Respiration Process of obtaining oxygen from environment and delivering it to cells Phases of Respiration 1. Pulmonary ventilation between air and
Biology. A Guide to the Natural World. Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath. Fifth Edition.
 Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Biology A Guide to the Natural World Chapter 30 Lecture Outline Transport and Exchange 1: Blood and Breath Fifth Edition David Krogh 30.1 The Cardiovascular System The Cardiovascular System The human cardiovascular
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System
 Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Unit Nine - The Respiratory System I. Introduction A. Definition: the respiratory system consists of the nose, nasal cavity, (throat), (voice box), (windpipe), bronchi and lungs (which contain the alveoli).
Chapter 16. The Respiratory System. Mosby items and derived items 2010, 2006, 2002, 1997, 1992 by Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc.
 Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Chapter 16 The Respiratory System Objectives Discuss the generalized functions of the respiratory system List the major organs of the respiratory system and describe the function of each Compare, contrast,
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab
 Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
Activity 1: Respiratory System Lab Launch Human Anatomy Atlas. Navigate to Quizzes/Lab Activities, find the Respiratory Lab section. Don t have AR? Select view 1. Respiratory System. 2. Fill in the blanks.
The Respiratory System
 I. Organization of the Respiratory System The Respiratory System The respiratory system allows the circulation of air and the gas exchange between the body and the outside environment. It consists of the
I. Organization of the Respiratory System The Respiratory System The respiratory system allows the circulation of air and the gas exchange between the body and the outside environment. It consists of the
Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs
 The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
The lungs consist of right and left sides. The right lung has three lobes: Upper lobe, Middle lobe, Lower lobe The left lung has two lobes: Upper lobe, Lower lobe Anatomy and Physiology of the Lungs The
Structural Plan. Respiratory System. ose. Upper Respiratory Tract. Upper Respiratory Tract ose, nasopharynx, oropharynx, laryngopharynx, and larynx
 Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
Respiratory System By: Mrs. Bailey Functions Air distributor and gas exchanger so that oxygen may be supplied to and carbon dioxide removed from the body s cells Filters, warms, and humidifies the air
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing
 Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
Chronic inflammation of the airways Hyperactive bronchi Shortness of breath Tightness in chest Coughing Wheezing Components of the respiratory system Nasal cavity Pharynx Trachea Bronchi Bronchioles Lungs
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS
 FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
FROM FOOD TO NUTRIENTS NUTRITION It s the incorporation and transformation of matter and energy of the medium to carry out our vital functions. Living beings obtain from food the nutrients necessary for
GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES
 October 4-7, 2004 Respiratory GOALS: GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES By the end of the week, the first quarter student will have an in-depth understanding of the diagnoses listed under Primary Diagnoses
October 4-7, 2004 Respiratory GOALS: GOALS AND INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES By the end of the week, the first quarter student will have an in-depth understanding of the diagnoses listed under Primary Diagnoses
The Respiratory System
 13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
13 PART A The Respiratory System PowerPoint Lecture Slide Presentation by Jerry L. Cook, Sam Houston University ESSENTIALS OF HUMAN ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY EIGHTH EDITION ELAINE N. MARIEB Organs of the Respiratory
Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number.
 Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
Name: Grade: ANATOMY TEST Questions 1-3 refer to the following diagram. Indicate the plane labeled by the corresponding question number. 1. Plane #1 is the... 2. Plane #2 is the... 3. Plane #3 is the...
COPD Management in LTC: Presented By: Jessica Denney RRT
 COPD Management in LTC: Presented By: Jessica Denney RRT Sponsored by Z & D Medical Services, Diamond Sponsor Seizing Opportunities to Provide Individualized Treatment and Device Selection for your COPD
COPD Management in LTC: Presented By: Jessica Denney RRT Sponsored by Z & D Medical Services, Diamond Sponsor Seizing Opportunities to Provide Individualized Treatment and Device Selection for your COPD
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks. Cards 1A
 Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
Geography of Pulmo Park: Landmarks Cards 1A Directions: Cut out the cards, fold and laminate and then hand out to students (one each). If you have more cards than students, some students will have more
The Respiratory System
 The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
The Respiratory System Cells continually use O2 & release CO2 Respiratory system designed for gas exchange Cardiovascular system transports gases in blood Failure of either system rapid cell death from
Respiratory System. Respiratory System Overview. Component 3/Unit 11. Health IT Workforce Curriculum Version 2.0/Spring 2011
 Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 11-Respiratory System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health and
Component 3-Terminology in Healthcare and Public Health Settings Unit 11-Respiratory System This material was developed by The University of Alabama at Birmingham, funded by the Department of Health and
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems
 The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
The Human Body: Circulatory and Respiratory Systems Lesson 1: What is a Body System? Cells - smallest parts - billions in the body - can have special jobs Tissues - similar cells grouped together - muscle
What is lung cancer? Contents
 13 11 20 Information and support What is lung cancer? Contents About the lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Different types of lung cancer Causes Symptoms Information reviewed by About the lungs
13 11 20 Information and support What is lung cancer? Contents About the lungs What is lung cancer? How common is it? Different types of lung cancer Causes Symptoms Information reviewed by About the lungs
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 3: CHRONIC BRNCHITIS AND BRONCHIECTASIS
 DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 3: CHRONIC BRNCHITIS AND BRONCHIECTASIS INTRDUCTION In the last lecture we discussed the difference between restrictive and obstructive lung
DISEASES OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 2018 DR HEYAM AWAD LECTURE 3: CHRONIC BRNCHITIS AND BRONCHIECTASIS INTRDUCTION In the last lecture we discussed the difference between restrictive and obstructive lung
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 14b Lab Activity
 HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 14b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Respiratory Distress Respiratory distress is a broad medical term that applies to any type of breathing difficulty and the associated
HASPI Medical Anatomy & Physiology 14b Lab Activity Name(s): Period: Date: Respiratory Distress Respiratory distress is a broad medical term that applies to any type of breathing difficulty and the associated
The Respiratory System
 Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology Elaine N. Marieb Seventh Edition Chapter 13 The Respiratory System Slides 13.1 13.30 Lecture Slides in PowerPoint by Jerry L. Cook Copyright 2003 Pearson Education,
Respiratory Physiology
 Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
Respiratory Physiology Dr. Aida Korish Associate Prof. Physiology KSU The main goal of respiration is to 1-Provide oxygen to tissues 2- Remove CO2 from the body. Respiratory system consists of: Passages
