Structure. Lecture 4 Virology W3310/4310 Spring 2012
|
|
|
- Emily Pitts
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Structure Lecture 4 Virology W3310/4310 Spring 2012 In order to create something that func2ons properly - a container, a chair, a house - its essence has to be explored, for it should serve its purpose to perfec2on, i.e., it should be durable, inexpensive, and beau2ful. - Walter Gropius 1
2 Func)ons of virion proteins Protec)on of the genome - Assembly of a stable, protecave protein shell - Specific recogniaon and packaging of the nucleic acid genome - InteracAon with host cell membranes to form the envelope 2
3 Func)ons of virion proteins Delivery of the genome - Bind host cell receptors - UncoaAng of the genome - Fusion with cell membranes - Transport of genome to the appropriate site 3
4 Func)ons of virion proteins Other interac)ons with host - With cell components to ensure efficient infecaous cycle - With cell components for transport to sites of assembly - With the host immune system 4
5 Virus par)cles are not inert structures Virions are metastable structures: have not apained minimum free energy conformaaon Gained only when an unfavorable energy barrier is surmounted, following irreversible conformaaonal changes during apachment and entry Viruses are molecular machines that play acave role in delivery of genome 5
6 In other words... To be infecaous, the paracle must be metastable - Must protect the genome (stable) - Must come apart quickly on infecaon (unstable) An infecaous virion is a molecular machine - Has moving parts and does work 6
7 In other words... Virions are spring loaded to uncoat and deliver the genome if and only if the cell provides the proper signals - Energy is put into the structure upon assembly - That potenaal energy is used for disassembly 7
8 Virion structure and func)on Structure (the paracle; the virion) - Created by symmetrical arrangement of many idenacal proteins to provide maximal contact and non- covalent bonding FuncAon (genome delivery) - Structure is NOT permanently bonded together - Can be taken apart or loosened on infecaon to release or expose genome 8
9 Subunit - Single folded polypepade chain Structural unit (protomer, asymmetric unit) - Unit from which capsids or nucleocapsids are built; one or more subunits Capsid (coat) capsa is LaAn for box - Protein shell surrounding genome Nucleocapsid (core) - Nucleic acid - protein assembly within virion Envelope (viral membrane) - Virion - Host cell- derived lipid bilayer InfecAous viral paracle Defini)ons 9
10 PuAng virus par)cles into perspec)ve Nanometer: 10-9 meters Alpha helix in protein: 1 nm diameter DNA: 2 nm diameter Ribosome: 20 nm diameter Poliovirus: 30 nm Mimivirus: 750 nm 10
11 MOLECULAR MACHINERY: A Tour of the Protein Data Bank 3cyt Cytochrome c 1gcn Glucagon 2hiu Insulin 3hhr Human Growth Hormone 1fqy Aquaporin Cholesterol Phospholipid 1mbdMyoglobin 1hrs Ferritin 1e7i Serum Albumin 1msl Mechanosensitive Channel 1grm Gramicidin 2por Porin 1c17+1e79 ATP Synthase 1iat Phosphoglucose 1ald Aldolase Isomerase 1pfk Phosphofructokinase 1cza Hexokinase 1bgy Cytochrome b-c1 Complex 3pgk Phosphoglycerate Kinase 1oco Cytochrome c Oxidase 3gpd Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate Dehydrogenase 1rfb Interferon 1wsy Tryptophan Synthase 2dnj Deoxyribonuclease 1lz1 Lysozyme 2ptc Trypsin 4hhb Hemoglobin 1bl8 Potassium Channel 7tim Triosephosphate Isomerase 5enl Enolase 3pgmPhosphoglycerate Mutase 1a49 Pyruvate Kinase 1dhf Dihydrofolate Reductase 1f88 Rhodopsin 5rsa Ribonuclease 1smd Amylase 2ohx Alcohol Dehydrogenase 5pep Pepsin 2tsc Thymidylate Synthase 2gls Glutamine Synthetase 1poe Phospholipase 1pth Cyclooxygenase 1igt Antibody 1prc Photosynthetic Reaction Center 1kzu Light-Harvesting Complex 4at1 Aspartate Carbamoyltransferase 1rcx Ribulose Bisphosphate Carboxylase/Oxygenase 1gax Valyl-tRNA Synthetase 1qf6 Threonyl-tRNA Synthetase 1euq Glutaminyl-tRNA 1ttt Elongation Synthetase Factor Tu 1jb0 Photosystem I 4rhv Rhinovirus 1ffy Isoleucyl-tRNA Synthetase 1n2c Nitrogenase 1eiy Phenylalanyl-tRNA Synthetase 1asy Aspartyl-tRNA Synthetase 4tna Transfer RNA 1dar Elongation Factor G info@rcsb.org R ESEARCH C OLLABORATORY FOR STRUCTURAL B IOINFORMATICS RUTGERS, THE STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW JERSEY S AN DIEGO SUPERCOMPUTER CENTER N ATION AL INSTITUTE OF STANDARDS AND TECHNOLOGY 1efu Elongation Factor 1fjf+1jj2 Ribosome Tu and Ts 2cpl Proline cis/trans Isomerase 1fxk Prefoldin 1aon Chaperonin GroEL/ES 11
12 First recons)tu)on of a virion Purified TMV RNA and coat protein mixed, virus paracles formed spontaneously - TMV: first virus discovered - First virus crystallized - First demonstraaon that RNA serves as geneac material H. Fraenkel- Conrat and RC. Williams, ReconsAtuAon of AcAve Tobacco Mosaic Virus from Its InacAve Protein and Nucleic Acid Components PNAS 41:
13 The tools of viral structural biology Electron microscopy X- ray crystallography Cryo- electron microscopy Nuclear magneac resonance spectroscopy (NMR) Flint volume I, chapter 3, pp
14 Beginning of the era of modern structural virology 1940: Helmuth Ruska used an electron microscope to take the first pictures of virus paracles Ruska, H Die Sichtbarmachung der BakteriophagenLyse im Ubermikroskop. Naturwissenschaagen. 28:45-46). 14
15 Electron microscopy Biological materials have liple inherent contrast: need to be stained NegaAve staining with electron- dense material (uranyl acetate, phosphotungstate), scaper electrons (1959) ResoluAon Å (alpha helix 10 Å dia; 1 Å = 0.1 nm) Detailed structural interpretaaon impossible 15
16 16
17 Linda Stannard, University of Cape Town hpp://web.uct.ac.za/depts/mmi/stannard/linda.html 17
18 Cryo- electron microscopy ( Å) 18
19 Poliovirus + CD155 19
20 X- ray crystallography (2-3 Å for viruses) 20
21 1935: Wendell Stanley crystallized tobacco mosaic virus, showed it remained infecaous. First step towards describing virus structure. Nobel Prize,
22
23 Poliovirus,
24 Principles of building virions: Symmetry is key Watson and Crick did more than discover DNA structure : pointed out that most virus paracles were spherical or rod- shaped in the EM Knew paracles were made with many copies of few proteins (geneac economy) Viral proteins have structural properaes that permit regular and repeaave interacaons among them Their seminal contribuaon to virology: - - IdenAcal protein subunits are distributed with helical symmetry for rod- shaped viruses Platonic polyhedra symmetry for round viruses 24
25 The symmetry rules are elegant in their simplicity They provide rules for self- assembly Rule 1: Each subunit has idenacal bonding contacts with its neighbors - The repeated interacaon of chemically complementary surfaces at the subunit interfaces naturally leads to a symmetric arrangement Rule 2: These bonding contacts are usually non- covalent - The reversible formaaon of non- covalent bonds between properly folded subunits leads naturally to error- free assembly and minimizes free energy 25
26 Regular structures form when iden)cal bonds are made between iden)cal subunits Aggregates, clumps, disordered complexes form when non- idenacal bonds form between idenacal subunits 26
27 The repe))on of these interac)ons among a limited number of proteins results in a regular structure Many capsid proteins can self assemble into virus- like paracles (VLPs) The HBV and HPV vaccines are VLPs made in yeast 27
28 TWiV
29 Helical symmetry Coat protein molecules engage in idenacal, equivalent interacaons with one another and with the viral genome to allow construcaon of a large, stable structure from a single protein subunit 29
30 30
31 31
32 32
33 Enveloped virions of RNA viruses with (- ) ssrna genomes with helical capsids Paramyxoviridae (measles virus, mumps virus) Rhabdoviridae (rabies virus) Orthomyxoviridae (influenza virus) Filoviridae (Ebola virus) These capsids are always called nucleocapsids - The nucleic acid- protein assembly that is packaged within the virion - The nucleocapsid is not the virion 33
34 How can you make a round capsid from proteins with irregular shapes? Clue 1: All round capsids have precise numbers of proteins; mulaples of 60 are common (60, 180, 240, 960) Clue 2: Spherical viruses come in many sizes, but capsid proteins are kda average 34
35 Caspar & Klug s 1962 solu)on They knew from Watson & Crick s work that round capsids are icosahedrons - no other Platonic solids were used Capsid subunits tended to be arranged as hexamers and pentamers The number of capsid subunits followed allowable values of T numbers: 60, 180, 240, 960; nothing in between 35
36 Icosahedral symmetry Icosahedron: solid with 20 faces, each an equilateral triangle Allows formaaon of a closed shell with smallest number (60) of idenacal subunits 36
37 Simple icosahedral capsids Made of 60 idenacal protein subunits The protein subunit is the structural unit InteracAons of all molecules with their neighbors are idenacal (head- to- head, tail- to- tail) 37
38 Adeno- associated virus 2 (parvovirus) 25 nm T=1 60 copies of a single capsid protein How are larger virions built? By adding more subunits 38
39 Triangula)on number, T The number of facets per triangular face of an icosahedron Each facet contains a capsid protein mulamer Combining several triangular facets allows assembly of larger face from same structural unit Capsids with T>1 have a 6-fold axis of symmetry 39
40 Quasiequivalence When a capsid contains more than 60 subunits, each occupies a quasiequivalent posiaon The noncovalent binding properaes of subunits in different structural environments are similar, but not idenacal 40
41 Three modes of subunit packing (orange, yellow, purple) Pentamers & hexamers Bonding interacaons are quasiequivalent: all engage tail- to- tail and head- to- head 180 idenacal protein subunits Figure
42 Nodamura virus nm T=3 180 copies of a single capsid protein 42
43 Poliovirus 30 nm pseudo T=3 60 copies X four capsid proteins 8- stranded anaparallel β- barrel - the structural moaf most commonly found in capsids 43
44 44
45 Structurally complex capsids Largest viruses; disanct components with different symmetries Presence of proteins devoted to specialized roles 45
46 Adenovirus Adenovirus 150 nm T=25 capsid, 240 subunits made of hexons, trimers of viral protein II Fibers at 12 veraces 46
47 Reoviruses T= nm two concentric shells Complex capsids with two icosahedral protein layers VP7 trimers, T=13 VP3 monomers, T=2 47
48 Capsids can be covered by host membranes: enveloped virions Envelope is a lipid bilayer derived from host cell - Viral genome does not encode lipid syntheac machinery Envelope acquired by budding of nucleocapsid through a cellular membrane - Can be any cell membrane, but is virus- specific Nucleocapsids inside the envelope may have helical or icosahedral symmetry 48
49 Viral envelope glycoproteins Integral membrane glycoproteins Ectodomain: apachment, anagenic sites, fusion Internal domain: assembly Oligomeric: spikes 49
50 50
51 Interac)on of viral proteins with viral envelope proteins 51
52 Structured envelopes: Sindbis virus The capsid has T=4 icosahedral symmetry (240 capsid proteins) The 80 envelope spikes (trimers of glycoproteins E1 and E2) ALSO are arranged with T=4 symmetry - anchored to the capsid under the membrane - a structured envelope The cytoplasmic tail of E2 contacts a cleg in the capsid protein, which gives rise to the symmetry in the membrane 52
53 Unstructured envelopes 53
54 Herpesviridae 80 viral genes, >50% encode proteins of 2,000 Å virions Envelope proteins (13) Icosahedral nucleocapsid surrounding DNA genome (4) Tegument (20) - delivery of proteins required early in infecaon 54
55 Herpes simplex capsid Holes for entry and exit of DNA The portal or opening for viral DNA is built at ONE of the 12, 5- fold ver2ces of the T=16 herpesvirus capsid 55
56 The TAILED VIRUSES The majority of bacterial viruses (bacteriophage) employ a molecular device called a tail for recogniaon and apachment to the host cell, penetraaon of the cell envelope, and for DNA transfer from the virus capsid into the host cell cytoplasm The tail is apached at one of the 12 veraces of the capsid (capsid has icosahedral symmetry). The tail is a complex rod - uses helical symmetry in many places - some tails are contrac2le 56
57 Complex virion structures are challenging viral structural biologists t=
58 Other virion components Enzymes - polymerases, integrases, associated proteins - proteases - poly(a) polymerase - capping enzymes - topoisomerase AcAvators, mrna degradaaon, required for efficient infecaon, mrnas Cellular components - histones, trnas, myristate, lipid, cyclophilin A, and many more 58
59 59
60 60
Structure of viruses
 Structure of viruses Lecture 4 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 In order to create something that functions properly - a container, a chair, a house - its essence has to be explored, for it should
Structure of viruses Lecture 4 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 In order to create something that functions properly - a container, a chair, a house - its essence has to be explored, for it should
Structure of viruses
 Structure of viruses Lecture 4 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2017 In order to create something that functions properly - a container, a chair, a house - its essence has to be explored, for it should
Structure of viruses Lecture 4 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2017 In order to create something that functions properly - a container, a chair, a house - its essence has to be explored, for it should
Virology. *Viruses can be only observed by electron microscope never by light microscope. The size of the virus: nm in diameter.
 Virology We are going to start with general introduction about viruses, they are everywhere around us; in food; within the environment; in direct contact to etc.. They may cause viral infection by itself
Virology We are going to start with general introduction about viruses, they are everywhere around us; in food; within the environment; in direct contact to etc.. They may cause viral infection by itself
Proteins and symmetry
 Proteins and symmetry Viruses (symmetry) Viruses come in many shapes, sizes and compositions All carry genomic nucleic acid (RNA or DNA) Structurally and genetically the simplest are the spherical viruses
Proteins and symmetry Viruses (symmetry) Viruses come in many shapes, sizes and compositions All carry genomic nucleic acid (RNA or DNA) Structurally and genetically the simplest are the spherical viruses
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES
 STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
STRUCTURE, GENERAL CHARACTERISTICS AND REPRODUCTION OF VIRUSES Introduction Viruses are noncellular genetic elements that use a living cell for their replication and have an extracellular state. Viruses
Structural biology of viruses
 Structural biology of viruses Biophysical Chemistry 1, Fall 2010 Coat proteins DNA/RNA packaging Reading assignment: Chap. 15 Virus particles self-assemble from coat monomers Virus Structure and Function
Structural biology of viruses Biophysical Chemistry 1, Fall 2010 Coat proteins DNA/RNA packaging Reading assignment: Chap. 15 Virus particles self-assemble from coat monomers Virus Structure and Function
Virus Structure. Characteristics of capsids. Virus envelopes. Virion assembly John Wiley & Sons, Inc. All rights reserved.
 Virus Structure Characteristics of capsids Virus envelopes Virion assembly Capsids package viral genomes and transmit them to a new host cell Capsid rigid, symmetrical container composed of viral protein
Virus Structure Characteristics of capsids Virus envelopes Virion assembly Capsids package viral genomes and transmit them to a new host cell Capsid rigid, symmetrical container composed of viral protein
General Virology I. Dr Esam Ibraheem Azhar (BSc, MSc, Ph.D Molecular Medical Virology) Asst. Prof. Medical Laboratory Technology Department
 General Virology I Dr Esam Ibraheem Azhar (BSc, MSc, Ph.D Molecular Medical Virology) Asst. Prof. Medical Laboratory Technology Department ١ General Virology I Lecture Outline Introduction istory Definition
General Virology I Dr Esam Ibraheem Azhar (BSc, MSc, Ph.D Molecular Medical Virology) Asst. Prof. Medical Laboratory Technology Department ١ General Virology I Lecture Outline Introduction istory Definition
Lecture 2: Virology. I. Background
 Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Lecture 2: Virology I. Background A. Properties 1. Simple biological systems a. Aggregates of nucleic acids and protein 2. Non-living a. Cannot reproduce or carry out metabolic activities outside of a
Some living things are made of ONE cell, and are called. Other organisms are composed of many cells, and are called. (SEE PAGE 6)
 Section: 1.1 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: We tend to only think of animals as living. However, there is a great diversity of organisms that we consider living
Section: 1.1 Question of the Day: Name: Review of Old Information: N/A New Information: We tend to only think of animals as living. However, there is a great diversity of organisms that we consider living
Overview of virus life cycle
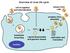 Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
Overview of virus life cycle cell recognition and internalization release from cells progeny virus assembly membrane breaching nucleus capsid disassembly and genome release replication and translation
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY
 PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY VIRUS - HISTORY In 1886, the Dutch Chemist Adolf Mayer showed TMD In 1892, the Russian Bactriologist Dimtri Iwanowski isolate
PHARMACEUTICAL MICROBIOLOGY JIGAR SHAH INSTITUTE OF PHARMACY NIRMA UNIVERSITY VIRUS - HISTORY In 1886, the Dutch Chemist Adolf Mayer showed TMD In 1892, the Russian Bactriologist Dimtri Iwanowski isolate
Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells
 Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Lec. 6 Dr. Ahmed K. Ali Attachment and entry of viruses into cells The aim of a virus is to replicate itself, and in order to achieve this aim it needs to enter a host cell, make copies of itself and
Unit 13.2: Viruses. Vocabulary capsid latency vaccine virion
 Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
Unit 13.2: Viruses Lesson Objectives Describe the structure of viruses. Outline the discovery and origins of viruses. Explain how viruses replicate. Explain how viruses cause human disease. Describe how
AP Biology. Viral diseases Polio. Chapter 18. Smallpox. Influenza: 1918 epidemic. Emerging viruses. A sense of size
 Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Hepatitis Viral diseases Polio Chapter 18. Measles Viral Genetics Influenza: 1918 epidemic 30-40 million deaths world-wide Chicken pox Smallpox Eradicated in 1976 vaccinations ceased in 1980 at risk population?
Chair of Medical Biology, Microbiology, Virology, and Immunology STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION AND PHYSIOLOGY OF VIRUSES
 Chair of Medical Biology, Microbiology, Virology, and Immunology STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION AND PHYSIOLOGY OF VIRUSES Viruses are small obligate intracellular parasites, which by definition contain either
Chair of Medical Biology, Microbiology, Virology, and Immunology STRUCTURE, CLASSIFICATION AND PHYSIOLOGY OF VIRUSES Viruses are small obligate intracellular parasites, which by definition contain either
Chapter 19: Viruses. 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction. 2. Bacteriophages. 3. Animal Viruses. 4. Viroids & Prions
 Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life
 Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Overview: Chapter 19 Viruses: A Borrowed Life Viruses called bacteriophages can infect and set in motion a genetic takeover of bacteria, such as Escherichia coli Viruses lead a kind of borrowed life between
Viruses defined acellular organisms genomes nucleic acid replicate inside host cells host metabolic machinery ribosomes
 The Viruses Viruses Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid, obligately replicate inside host cells using host metabolic machinery and ribosomes to form a pool
The Viruses Viruses Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid, obligately replicate inside host cells using host metabolic machinery and ribosomes to form a pool
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل
 Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Viral structure م.م رنا مشعل Viruses must reproduce (replicate) within cells, because they cannot generate energy or synthesize proteins. Because they can reproduce only within cells, viruses are obligate
Chapter 19: Viruses. 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction. What exactly is a Virus? 11/7/ Viral Structure & Reproduction. 2.
 Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Chapter 19: Viruses 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction 2. Bacteriophages 3. Animal Viruses 4. Viroids & Prions 1. Viral Structure & Reproduction Chapter Reading pp. 393-396 What exactly is a Virus? Viruses
Viral reproductive cycle
 Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Lecture 29: Viruses Lecture outline 11/11/05 Types of viruses Bacteriophage Lytic and lysogenic life cycles viruses viruses Influenza Prions Mad cow disease 0.5 µm Figure 18.4 Viral structure of capsid
Microbiology Chapter 7 Viruses
 Microbiology Chapter 7 Viruses 7:1 Viral Structure and Classification VIRUS: a biological particle composed of genetic material (DNA or RNA) encased in a protein coat CAPSID: protein coat surrounding a
Microbiology Chapter 7 Viruses 7:1 Viral Structure and Classification VIRUS: a biological particle composed of genetic material (DNA or RNA) encased in a protein coat CAPSID: protein coat surrounding a
LESSON 1.4 WORKBOOK. Viral sizes and structures. Workbook Lesson 1.4
 Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Eukaryotes organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles. Prokaryotes organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Viruses small, non-cellular (lacking a cell), infectious
Chapter 18. Viral Genetics. AP Biology
 Chapter 18. Viral Genetics 2003-2004 1 A sense of size Comparing eukaryote bacterium virus 2 What is a virus? Is it alive? DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat Viruses are not cells Extremely tiny electron
Chapter 18. Viral Genetics 2003-2004 1 A sense of size Comparing eukaryote bacterium virus 2 What is a virus? Is it alive? DNA or RNA enclosed in a protein coat Viruses are not cells Extremely tiny electron
LEC 2, Medical biology, Theory, prepared by Dr. AYAT ALI
 General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
General Characteristics, Structure and Taxonomy of Viruses Viruses A virus is non-cellular organisms made up of genetic material and protein that can invade living cells. They are considered both a living
Viral Capsids and Envelopes: Structure and Function
 Viral Capsids and Envelopes: Structure and Function William Lucas, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA David M Knipe, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA Virus particles contain
Viral Capsids and Envelopes: Structure and Function William Lucas, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA David M Knipe, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts, USA Virus particles contain
CONTENTS. 1. Introduction. 4. Virology. 2. Virus Structure. 5. Virus and Medicine. 3. Virus Replication. 6. Review
 CONTENTS 1. Introduction 4. Virology 2. Virus Structure 5. Virus and Medicine 3. Virus Replication 6. Review We have all gotten viruses from bacteria, plants to animals. Viruses cause colds, flu, warts
CONTENTS 1. Introduction 4. Virology 2. Virus Structure 5. Virus and Medicine 3. Virus Replication 6. Review We have all gotten viruses from bacteria, plants to animals. Viruses cause colds, flu, warts
Composition & Architecture of plant viruses. P.N. Sharma Department of Plant Pathology, CSK HPKV, Palampur (H.P.)
 Composition & Architecture of plant viruses P.N. Sharma Department of Plant Pathology, CSK HPKV, Palampur (H.P.) Plant Viruses Classification, Morphology, Genome, and Structure Importance Detailed knowledge
Composition & Architecture of plant viruses P.N. Sharma Department of Plant Pathology, CSK HPKV, Palampur (H.P.) Plant Viruses Classification, Morphology, Genome, and Structure Importance Detailed knowledge
Basic Properties of Viruses and Virus Cell Interaction
 WBV5 6/27/03 10:28 PM Page 49 Basic Properties of Viruses and Virus Cell Interaction II PART VIRUS STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION CLASSIFICATION SCHEMES THE BEGINNING AND END OF THE VIRUS REPLICATION CYCLE
WBV5 6/27/03 10:28 PM Page 49 Basic Properties of Viruses and Virus Cell Interaction II PART VIRUS STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATION CLASSIFICATION SCHEMES THE BEGINNING AND END OF THE VIRUS REPLICATION CYCLE
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses*
 Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Chapter 6- An Introduction to Viruses* *Lecture notes are to be used as a study guide only and do not represent the comprehensive information you will need to know for the exams. 6.1 Overview of Viruses
Introductory Virology. Ibrahim Jamfaru School of Medicine UHAS
 Introductory Virology Ibrahim Jamfaru School of Medicine UHAS Lecture outline Definition of viruses and general characteristics Structure of virus (virion) Chemical composition of viruses Virus morphology
Introductory Virology Ibrahim Jamfaru School of Medicine UHAS Lecture outline Definition of viruses and general characteristics Structure of virus (virion) Chemical composition of viruses Virus morphology
Herpesviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Herpesviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Enveloped icosahedral capsid (T=16), diameter 125 nm Diameter of enveloped virion 200 nm Capsid
Translation. Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation of eukaryotic translation involves many initiation factors
 Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
Translation Questions? 1) How does poliovirus shutoff eukaryotic translation? 2) If eukaryotic messages are not translated how can poliovirus get its message translated? Host Cell Shutoff 1) Initiation
19 Viruses BIOLOGY. Outline. Structural Features and Characteristics. The Good the Bad and the Ugly. Structural Features and Characteristics
 9 Viruses CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV Lecture Presentation
9 Viruses CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV Lecture Presentation
Lecture 5 (Ch6) - Viruses. Virus Characteristics. Viral Host Range
 Lecture 5 (Ch6) - Viruses Topics Characteristics Structure/Classification Multiplication Cultivation and replication Non-viral infectious agents Treatment 1 Virus Characteristics obligate intracellular
Lecture 5 (Ch6) - Viruses Topics Characteristics Structure/Classification Multiplication Cultivation and replication Non-viral infectious agents Treatment 1 Virus Characteristics obligate intracellular
Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage:
 Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Zeina Al-Momani Last time we talked about the few steps in viral replication cycle and the un-coating stage: Un-coating: is a general term for the events which occur after penetration, we talked about
Introduction to viruses. BIO 370 Ramos
 Introduction to viruses BIO 370 Ramos 1 2 General Structure of Viruses Size range most
Introduction to viruses BIO 370 Ramos 1 2 General Structure of Viruses Size range most
Viruses. CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani
 Viruses CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something smaller than bacteria could cause disease and they called it virion (Latin
Viruses CLS 212: Medical Microbiology Miss Zeina Alkudmani History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something smaller than bacteria could cause disease and they called it virion (Latin
11/15/2011. Outline. Structural Features and Characteristics. The Good the Bad and the Ugly. Viral Genomes. Structural Features and Characteristics
 Chapter 19 - Viruses Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV II. Prions The Good the Bad and the Ugly Viruses fit into the bad category
Chapter 19 - Viruses Outline I. Viruses A. Structure of viruses B. Common Characteristics of Viruses C. Viral replication D. HIV II. Prions The Good the Bad and the Ugly Viruses fit into the bad category
Genomes and Genetics
 Genomes and Genetics Lecture 3 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016...everywhere an interplay between nucleic acids and proteins; a spinning wheel in which the thread makes the spindle and the spindle
Genomes and Genetics Lecture 3 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016...everywhere an interplay between nucleic acids and proteins; a spinning wheel in which the thread makes the spindle and the spindle
BIOL*1090 Introduction To Molecular and Cellular Biology Fall 2014
 Last time... BIOL*1090 Introduction To Molecular and Cellular Biology Fall 2014 Lecture 3 - Sept. 15, 2014 Viruses Biological Membranes Karp 7th ed: Chpt. 4; sections 4-1, 4-3 to 4-7 1 2 VIRUS Non-cellular
Last time... BIOL*1090 Introduction To Molecular and Cellular Biology Fall 2014 Lecture 3 - Sept. 15, 2014 Viruses Biological Membranes Karp 7th ed: Chpt. 4; sections 4-1, 4-3 to 4-7 1 2 VIRUS Non-cellular
Viruses 101., and concluded that living organisms do not crystallize. In other words,.
 Viruses 101 In 1897, Dutch scientist called tiny particles in the liquid extracted from a plant disease, which is the Latin word for. In 1935, American biochemist isolated crystals of, and concluded that
Viruses 101 In 1897, Dutch scientist called tiny particles in the liquid extracted from a plant disease, which is the Latin word for. In 1935, American biochemist isolated crystals of, and concluded that
Chapter 25. 바이러스 (The Viruses)
 Chapter 25 바이러스 (The Viruses) Generalized Structure of Viruses 2 2 Virus Classification Classification based on numerous characteristics Nucleic acid type Presence or absence of envelope Capsid symmetry
Chapter 25 바이러스 (The Viruses) Generalized Structure of Viruses 2 2 Virus Classification Classification based on numerous characteristics Nucleic acid type Presence or absence of envelope Capsid symmetry
History of Virology. Russian Bacteriologist Dimitri Iwanowski TMD tobacco mosaic disease TMV isolated and purified
 Viruses & Prions Viruses Virus miniscule, acellular, infectious agent having one or several pieces of either DNA or RNA No cytoplasmic membrane, cytosol, organelles Cannot carry out any metabolic pathway
Viruses & Prions Viruses Virus miniscule, acellular, infectious agent having one or several pieces of either DNA or RNA No cytoplasmic membrane, cytosol, organelles Cannot carry out any metabolic pathway
Viruses and Prions (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus
 Viruses and Prions (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
Viruses and Prions (Chapter 13) Lecture Materials for Amy Warenda Czura, Ph.D. Suffolk County Community College Eastern Campus Primary Source for figures and content: Tortora, G.J. Microbiology An Introduction
Part I. Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents.
 Viruses Part I Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents. History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something
Viruses Part I Content: History of Viruses. General properties of viruses. Viral structure. Viral classifications. Virus-like agents. History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something
BIOLOGY. Viruses CAMPBELL. Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson. Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick TENTH EDITION
 CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 19 Viruses Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 19.1 Are the viruses (red) budding from this
CAMPBELL BIOLOGY TENTH EDITION Reece Urry Cain Wasserman Minorsky Jackson 19 Viruses Lecture Presentation by Nicole Tunbridge and Kathleen Fitzpatrick Figure 19.1 Are the viruses (red) budding from this
Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability
 Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability (Learning Objectives) Learn the types of DNA sequences present in the Human Genome other than genes coding for functional proteins. Review what you
Human Genome Complexity, Viruses & Genetic Variability (Learning Objectives) Learn the types of DNA sequences present in the Human Genome other than genes coding for functional proteins. Review what you
LESSON 1.4 WORKBOOK. Viral structures. Just how small are viruses? Workbook Lesson 1.4 1
 Eukaryotes- organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles Prokaryotes- organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles Viruses-small acellular (lacking a cell) infectious
Eukaryotes- organisms that contain a membrane bound nucleus and organelles Prokaryotes- organisms that lack a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles Viruses-small acellular (lacking a cell) infectious
Viruses. Rotavirus (causes stomach flu) HIV virus
 Viruses Rotavirus (causes stomach flu) HIV virus What is a virus? A virus is a microscopic, infectious agent that may infect any type of living cell. Viruses must infect living cells in order to make more
Viruses Rotavirus (causes stomach flu) HIV virus What is a virus? A virus is a microscopic, infectious agent that may infect any type of living cell. Viruses must infect living cells in order to make more
Genomes and Gene*cs. Lecture 3 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2015
 Genomes and Gene*cs Lecture 3 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2015...everywhere an interplay between nucleic acids and proteins; a spinning wheel in which the thread makes the spindle and the spindle
Genomes and Gene*cs Lecture 3 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2015...everywhere an interplay between nucleic acids and proteins; a spinning wheel in which the thread makes the spindle and the spindle
Viruses. Non-cellular organisms. Premedical - Biology
 Viruses Non-cellular organisms Premedical - Biology Size the smallest 20 nm and more Non-cellular: viruses are infectious particles plant, animal, bacterial = bacteriophages virion = nucleic acid + protein
Viruses Non-cellular organisms Premedical - Biology Size the smallest 20 nm and more Non-cellular: viruses are infectious particles plant, animal, bacterial = bacteriophages virion = nucleic acid + protein
number Done by Corrected by Doctor Ashraf
 number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
number 4 Done by Nedaa Bani Ata Corrected by Rama Nada Doctor Ashraf Genome replication and gene expression Remember the steps of viral replication from the last lecture: Attachment, Adsorption, Penetration,
Lesson 4. Molecular Virology
 Lesson 4 Molecular Virology 1. Introduction 1.1. Virus Definition Genetic elements made of living matter molecules, that are capable of growth and multiplication only in living cells DIFFERENCE WITH RESPECT
Lesson 4 Molecular Virology 1. Introduction 1.1. Virus Definition Genetic elements made of living matter molecules, that are capable of growth and multiplication only in living cells DIFFERENCE WITH RESPECT
Dr. Gary Mumaugh. Viruses
 Dr. Gary Mumaugh Viruses Viruses in History In 1898, Friedrich Loeffler and Paul Frosch found evidence that the cause of foot-and-mouth disease in livestock was an infectious particle smaller than any
Dr. Gary Mumaugh Viruses Viruses in History In 1898, Friedrich Loeffler and Paul Frosch found evidence that the cause of foot-and-mouth disease in livestock was an infectious particle smaller than any
Picornaviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Picornaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=1) Diameter of 30 nm Genome Linear single-stranded RNA, positive
Picornaviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=1) Diameter of 30 nm Genome Linear single-stranded RNA, positive
The Zombies of the Scientific Community Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents. Acellular Agents
 viruses protein and nucleic acid viroids RNA virusoids RNA prions proteins The Zombies of the Scientific Community Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents Acellular Agents Viruses major cause of
viruses protein and nucleic acid viroids RNA virusoids RNA prions proteins The Zombies of the Scientific Community Viruses and Other Acellular Infectious Agents Acellular Agents Viruses major cause of
VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION
 VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION Paulo Eduardo Brandão, PhD Department of Preventive Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health School of Veterinary Medicine University of São Paulo, Brazil I. VIRUS STRUCTURE
VIRUS TAXONOMY AND REPLICATION Paulo Eduardo Brandão, PhD Department of Preventive Veterinary Medicine and Animal Health School of Veterinary Medicine University of São Paulo, Brazil I. VIRUS STRUCTURE
VIROLOGY PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS WILEY. John B. Carter and Venetia A. Saunders
 VIROLOGY PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS John B. Carter and Venetia A. Saunders WILEY -urief Contents Preface to Second Edition xix Preface to First Edition xxi Abbreviations Used in This Book xxiii Greek
VIROLOGY PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS John B. Carter and Venetia A. Saunders WILEY -urief Contents Preface to Second Edition xix Preface to First Edition xxi Abbreviations Used in This Book xxiii Greek
Week 5 Section. Junaid Malek, M.D.
 Week 5 Section Junaid Malek, M.D. HIV: Anatomy Membrane (partiallystolen from host cell) 2 Glycoproteins (proteins modified by added sugar) 2 copies of RNA Capsid HIV Genome Encodes: Structural Proteins
Week 5 Section Junaid Malek, M.D. HIV: Anatomy Membrane (partiallystolen from host cell) 2 Glycoproteins (proteins modified by added sugar) 2 copies of RNA Capsid HIV Genome Encodes: Structural Proteins
2) What is the difference between a non-enveloped virion and an enveloped virion? (4 pts)
 Micro 260 SFCC Spring 2010 Name: All diagrams and drawings shall be hand drawn (do not photo-copied from a publication then cut and pasted into work sheet). Do not copy other student s answers. Para phase
Micro 260 SFCC Spring 2010 Name: All diagrams and drawings shall be hand drawn (do not photo-copied from a publication then cut and pasted into work sheet). Do not copy other student s answers. Para phase
Virus Entry/Uncoating
 Virus Entry/Uncoating Delivery of genome to inside of a cell Genome must be available for first step of replication The Problem--barriers to infection Virion Barriers: Non-enveloped viruses capsid Enveloped
Virus Entry/Uncoating Delivery of genome to inside of a cell Genome must be available for first step of replication The Problem--barriers to infection Virion Barriers: Non-enveloped viruses capsid Enveloped
Reoviruses. Virion. Genome. Genes and proteins. Viruses and hosts. Diseases. Distinctive characteristics
 Reoviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=13), diameter 60-85 nm Capsid consists of two or three concentric protein
Reoviruses Virion Genome Genes and proteins Viruses and hosts Diseases Distinctive characteristics Virion Naked icosahedral capsid (T=13), diameter 60-85 nm Capsid consists of two or three concentric protein
The protein stoichiometry of viral capsids via tiling theory
 The protein stoichiometry of viral capsids via tiling theory REIDUN TWAROCK Centre for Mathematical Science City University Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB UNITED KINGDOM Abstract: - A vital part of
The protein stoichiometry of viral capsids via tiling theory REIDUN TWAROCK Centre for Mathematical Science City University Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB UNITED KINGDOM Abstract: - A vital part of
Bacteriophage Reproduction
 Bacteriophage Reproduction Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles The following information is taken from: http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit3/index.html#charvir Bacteriophage Structure More complex
Bacteriophage Reproduction Lytic and Lysogenic Cycles The following information is taken from: http://student.ccbcmd.edu/courses/bio141/lecguide/unit3/index.html#charvir Bacteriophage Structure More complex
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology W3310/4310 Virology Spring 2016 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at
Virology Introduction. Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment.
 DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
DEVH Virology Introduction Definitions. Introduction. Structure of virus. Virus transmission. Classification of virus. DNA Virus. RNA Virus. Treatment. Definitions Virology: The science which study the
Lecture Readings. Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell
 October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
October 26, 2006 1 Vesicular Trafficking, Secretory Pathway, HIV Assembly and Exit from Cell 1. Secretory pathway a. Formation of coated vesicles b. SNAREs and vesicle targeting 2. Membrane fusion a. SNAREs
Virus Basics. General Characteristics of Viruses. Chapter 13 & 14. Non-living entities. Can infect organisms of every domain
 Virus Basics Chapter 13 & 14 General Characteristics of Viruses Non-living entities Not considered organisms Can infect organisms of every domain All life-forms Commonly referred to by organism they infect
Virus Basics Chapter 13 & 14 General Characteristics of Viruses Non-living entities Not considered organisms Can infect organisms of every domain All life-forms Commonly referred to by organism they infect
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions. Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroids, and Prions Biology 1009 Microbiology Johnson-Summer 2003 Viruses Virology-study of viruses Characteristics: acellular obligate intracellular parasites no ribosomes or means
Viruses. Picture from:
 Viruses Understand the structure of bacteriophages & human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Appreciate that viruses replicate in host cells (thereby destroying them) Picture from: http://eands.caltech.edu/articles/lxvii1/viruses.html
Viruses Understand the structure of bacteriophages & human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) Appreciate that viruses replicate in host cells (thereby destroying them) Picture from: http://eands.caltech.edu/articles/lxvii1/viruses.html
Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions SLOs What are the Characteristics
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University C H A P T E R 13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions SLOs What are the Characteristics
History electron microscopes
 Viruses History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something smaller than bacteria could cause disease and they called it virion (Latin word- poison) In the 1930s, after the invention of
Viruses History Through the 1800s, many scientists discovered that something smaller than bacteria could cause disease and they called it virion (Latin word- poison) In the 1930s, after the invention of
VIRUSES BC530 Fall Quarter 2014
 VIRUSES BC530 Fall Quarter 2014 Wim G. J. Hol http://www.bmsc.washington.edu/wimhol/ VIRUSES Are nucleo-protein or lipid-nucleo-protein complexes which use living cells for their proliferation. Affect
VIRUSES BC530 Fall Quarter 2014 Wim G. J. Hol http://www.bmsc.washington.edu/wimhol/ VIRUSES Are nucleo-protein or lipid-nucleo-protein complexes which use living cells for their proliferation. Affect
Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions 11/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Characteristics of Viruses Viruses Minuscule, acellular, infectious agent having either DNA or RNA Cause infections
Chapter13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions 11/20/2017 MDufilho 1 Characteristics of Viruses Viruses Minuscule, acellular, infectious agent having either DNA or RNA Cause infections
18.2. Viral Structure and Reproduction. Viruses differ in shape and in ways of entering
 18.2 Viral Structure and Reproduction VOCABULARY bacteriophage lytic infection lysogenic infection prophage compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role
18.2 Viral Structure and Reproduction VOCABULARY bacteriophage lytic infection lysogenic infection prophage compare the structures of viruses to cells, describe viral reproduction, and describe the role
19/06/2013. Viruses are not organisms (do not belong to any kingdom). Viruses are not made of cells, have no cytoplasm, and no membranes.
 VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
VIRUSES Many diseases of plants and animals are caused by bacteria or viruses that invade the body. Bacteria and viruses are NOT similar kinds of micro-organisms. Bacteria are classified as living organisms,
18.2 Viruses and Prions
 KEY CONCEPT Infections can be caused in several ways. Viruses, bacteria, viroids, and prions can all cause infection. Any disease-causing agent is called a pathogen. 1 nanometer (nm) = one billionth of
KEY CONCEPT Infections can be caused in several ways. Viruses, bacteria, viroids, and prions can all cause infection. Any disease-causing agent is called a pathogen. 1 nanometer (nm) = one billionth of
Virus Basics. General Characteristics of Viruses 5/9/2011. General Characteristics of Viruses. Chapter 13 & 14. Non-living entities
 Virus Basics Chapter 13 & 14 General Characteristics of Viruses Non-living entities Not considered organisms Can infect organisms of every domain All life-formsf Commonly referred to by organism they infect
Virus Basics Chapter 13 & 14 General Characteristics of Viruses Non-living entities Not considered organisms Can infect organisms of every domain All life-formsf Commonly referred to by organism they infect
Polyomaviridae. Spring
 Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Polyomaviridae Spring 2002 331 Antibody Prevalence for BK & JC Viruses Spring 2002 332 Polyoma Viruses General characteristics Papovaviridae: PA - papilloma; PO - polyoma; VA - vacuolating agent a. 45nm
Transcription and RNA processing
 Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Transcription and RNA processing Lecture 7 Biology 3310/4310 Virology Spring 2018 It is possible that Nature invented DNA for the purpose of achieving regulation at the transcriptional rather than at the
Intro II - Viral Replication. All living things survive in a sea of viruses
 Intro II - Viral Replication Prof. Vincent Racaniello Department of Microbiology Office: HHSC 1310B vrr1@columbia.edu All living things survive in a sea of viruses We eat and breathe billions of them regularly
Intro II - Viral Replication Prof. Vincent Racaniello Department of Microbiology Office: HHSC 1310B vrr1@columbia.edu All living things survive in a sea of viruses We eat and breathe billions of them regularly
Questions in Cell Biology
 Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
Name: Questions in Cell Biology Directions: The following questions are taken from previous IB Final Papers on the subject of cell biology. Answer all questions. This will serve as a study guide for the
Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids, and Prions
 PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University Modified by Ossi Turunen, Aalto University C H A P T E R 13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids,
PowerPoint Lecture Presentations prepared by Mindy Miller-Kittrell, North Carolina State University Modified by Ossi Turunen, Aalto University C H A P T E R 13 Characterizing and Classifying Viruses, Viroids,
Medical Virology. Herpesviruses, Orthomyxoviruses, and Retro virus. - Herpesviruses Structure & Composition: Herpesviruses
 Medical Virology Lecture 2 Asst. Prof. Dr. Dalya Basil Herpesviruses, Orthomyxoviruses, and Retro virus - Herpesviruses Structure & Composition: Herpesviruses Enveloped DNA viruses. All herpesviruses have
Medical Virology Lecture 2 Asst. Prof. Dr. Dalya Basil Herpesviruses, Orthomyxoviruses, and Retro virus - Herpesviruses Structure & Composition: Herpesviruses Enveloped DNA viruses. All herpesviruses have
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology
 علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
علم األحياء الدقيقة Microbiology Introduction to Virology & Immunology What is a virus? Viruses may be defined as acellular organisms whose genomes consist of nucleic acid (DNA or RNA), and which obligatory
19 2 Viruses Slide 1 of 34
 1 of 34 What Is a Virus? What Is a Virus? Viruses are particles of nucleic acid, protein, and in some cases, lipids. Viruses can reproduce only by infecting living cells. 2 of 34 What Is a Virus? Viruses
1 of 34 What Is a Virus? What Is a Virus? Viruses are particles of nucleic acid, protein, and in some cases, lipids. Viruses can reproduce only by infecting living cells. 2 of 34 What Is a Virus? Viruses
VIRUSES BC530. Fall Quarter 2011 (Slide set # 2)
 VIRUSES BC530 Fall Quarter 2011 (Slide set # 2) Wim G. J. Hol http://www.bmsc.washington.edu/wimhol/ http://depts.washington.edu/biowww/faculty/hol-wim/ VIRUSES Are nucleo-protein or lipid-nucleo-protein
VIRUSES BC530 Fall Quarter 2011 (Slide set # 2) Wim G. J. Hol http://www.bmsc.washington.edu/wimhol/ http://depts.washington.edu/biowww/faculty/hol-wim/ VIRUSES Are nucleo-protein or lipid-nucleo-protein
Size nm m m
 1 Viral size and organization Size 20-250nm 0.000000002m-0.000000025m Virion structure Capsid Core Acellular obligate intracellular parasites Lack organelles, metabolic activities, and reproduction Replicated
1 Viral size and organization Size 20-250nm 0.000000002m-0.000000025m Virion structure Capsid Core Acellular obligate intracellular parasites Lack organelles, metabolic activities, and reproduction Replicated
Discovery of. 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes. 1931: first images of viruses obtained using
 Discovery of (1884: invention of the Chamberland filter with pores smaller than bacteria) 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes a paper in which shows that extracts from diseased tobacco plants
Discovery of (1884: invention of the Chamberland filter with pores smaller than bacteria) 1892: Russian biologist Dmitri Ivanovsky publishes a paper in which shows that extracts from diseased tobacco plants
J. A. Sands, 21 October 2013 Lehigh University
 J. A. Sands, 21 October 2013 Lehigh University Cryptococcus, Candidiasis, Aspergillosis Tuberculosis Cholera Plague Bact. Meningitis Salmonella Listeria Leptospirosis Staph. (MRSA) E. coli Clostridium
J. A. Sands, 21 October 2013 Lehigh University Cryptococcus, Candidiasis, Aspergillosis Tuberculosis Cholera Plague Bact. Meningitis Salmonella Listeria Leptospirosis Staph. (MRSA) E. coli Clostridium
Virus. Landmarks in Virology. Introduction to Virology. Landmarks in Virology. Definitions. Definitions. Latin for slimy liquid or poison
 Landmarks in Virology Introduction to Virology Scott M. Hammer, M.D. Introduction of concept of filterable agents for plant pathogens (Mayer, Ivanofsky, Beijerinck in late 1880 s) First filterable agent
Landmarks in Virology Introduction to Virology Scott M. Hammer, M.D. Introduction of concept of filterable agents for plant pathogens (Mayer, Ivanofsky, Beijerinck in late 1880 s) First filterable agent
Rama Abbady. Odai Bani-Monia. Diala Abu-Hassan
 5 Rama Abbady Odai Bani-Monia Diala Abu-Hassan Lipid Rafts Lipid rafts are aggregates (accumulations) of sphingolipids. They re semisolid clusters (10-200 nm) of cholesterol and sphingolipids (sphingomyelin
5 Rama Abbady Odai Bani-Monia Diala Abu-Hassan Lipid Rafts Lipid rafts are aggregates (accumulations) of sphingolipids. They re semisolid clusters (10-200 nm) of cholesterol and sphingolipids (sphingomyelin
Principles of Molecular Virology STAGE / YEAR: 3 CREDITS: 10. PROGRAMME COMMITTEE: Biomedical Sciences. VERSION: 4th March 2015
 MODULE: MODULE NUMBER: JACS CODE: Principles of Molecular Virology BIO00041H C540 STAGE / YEAR: 3 CREDITS: 10 ORGANISER: Nathalie Signoret PROGRAMME COMMITTEE: Biomedical Sciences VERSION: 4th March 2015
MODULE: MODULE NUMBER: JACS CODE: Principles of Molecular Virology BIO00041H C540 STAGE / YEAR: 3 CREDITS: 10 ORGANISER: Nathalie Signoret PROGRAMME COMMITTEE: Biomedical Sciences VERSION: 4th March 2015
Viruses Tomasz Kordula, Ph.D.
 Viruses Tomasz Kordula, Ph.D. Resources: Alberts et al., Molecular Biology of the Cell, pp. 295, 1330, 1431 1433; Lehninger CD Movie A0002201. Learning Objectives: 1. Understand parasitic life cycle of
Viruses Tomasz Kordula, Ph.D. Resources: Alberts et al., Molecular Biology of the Cell, pp. 295, 1330, 1431 1433; Lehninger CD Movie A0002201. Learning Objectives: 1. Understand parasitic life cycle of
Lecture Guide Viruses (CH13)
 Lecture Guide Viruses (CH13) This chapter is on the general characteristics of viruses and focuses on both bacterial and animal viruses and their life cycles. Let s start with a quick look at the history
Lecture Guide Viruses (CH13) This chapter is on the general characteristics of viruses and focuses on both bacterial and animal viruses and their life cycles. Let s start with a quick look at the history
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses
 Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Chapter 21: Prokaryotes & Viruses Microorganisms Single-celled organisms that are too small to be seen without a microscope Bacteria are the smallest living organisms Viruses are smaller but are not alive
Chapter 13. Viruses, Viroides and Prions
 Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroides and Prions 1 A GLIMPSE OF HISTORY Tobacco mosaic disease (1890s) D. M. Iwanowsky, Martinus Beijerinck determined caused by filterable virus too small to be seen with light
Chapter 13 Viruses, Viroides and Prions 1 A GLIMPSE OF HISTORY Tobacco mosaic disease (1890s) D. M. Iwanowsky, Martinus Beijerinck determined caused by filterable virus too small to be seen with light
Viruses. and Prions. ct o, ni, 21. Viruses. Table 2. Essential Questions
 ct o, ni, 21 Essential Questions ;1 What is the general structure of a virus? What are similarities and differences in the lytic cycle, the lysogenic cycle, and retroviral replication? I What is the relationship
ct o, ni, 21 Essential Questions ;1 What is the general structure of a virus? What are similarities and differences in the lytic cycle, the lysogenic cycle, and retroviral replication? I What is the relationship
