Brief Definitive Report
|
|
|
- Alannah Campbell
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Brief Definitive Report EOSINOPHILS AND RESISTANCE TO TRICHINELLA SPIRALIS* BY DAVID I. GROVE, ADEL A. F. MAHMOUD, AND KENNETH S. WARREN (From the Dw~smn of Geographic Medw~ne, Department of Medicine, Case Western Reserve Unwers~ty and Unwers~ty Hospitals, Cleveland, Ohm 44106) Although eosinophilia has long been associated with helminth infections, the function of the eosinophil granulocyte has remained obscure. Depletion of eosinophils by a recently developed monospecific anti-eosinophil serum (AES) (1) has provided a means by which the role of these cells might be elucidated. Schistosomiasis has been the only worm infection so far studied by this method. By using AES to eliminate eosinophils from the cells added to an in vitro assay of antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity, it was found that the absence of these cells prevented radiochromium release from tagged schistosomula (2). Of particular significance was the demonstration in vivo that the acquired resistance of mice with chronic schistosomiasis mansoni to challenge infection was abrogated by administration of AES (3). To verify these important observations and to extend them to another helminth infection, the present studies of trichinosis were undertaken. In trichinosis there are two phases in which eosinophils might affect the outcome of an infection. Firstly, after the ingestion of muscle larvae, adult worms develop in the intestines where they remain for approximately 2 wk and then are spontaneously eliminated. Secondly, first-stage larvae produced during this period penetrate the gut mucosa and pass via the bloodstream to the skeletal muscles where they mature into infective third-stage larvae over 3 wk. We have examined the effect of AES with its attendant marked depletion of circulating and tissue eosinophils on both the intestinal and muscle phases of a primary infection of mice with TrichineUa spiralis. Materials and Methods MonospeclfiC AES was prepared m rabbits lmmumzed with eoslnophils derived from mice infected with Schistosorna manson~ as previously described (1). 100 CFI Swiss albino mine (Carworth Farms, N. Y.), g in weight, were each infected by oral intubatlon with 350 larvae of T sp~ralis (from a stram originally supplied by Dr. W. C. Campbell, Merck Institute for Medical Research, N. J.) obtained by acid-pepsin digestion of infected mine (4). Each mouse was given 0.25 ml of AES or normal rabbit serum (NRS) by mtraperitoneal Injection twine weekly beginning on the 3rd day after refection. Groups of mice were killed at weekly intervals. Adult worms were recovered from the small intestine which was removed intact, chopped into 2-cm pieces, and then digested with 0 04% NaOH (5). Muscle larvae were obtained by homogenization of the whole carcass m a Warlng blendor followed by digestion m 1% acid-pepsin (4). Peripheral blood and bone marrow absolute eosmophil counts were performed (6). Biopmes of the hamstring muscles were stained with hematoxylin and eosm for measurement of muscle inflammation with a ~r MC particle measurement computer system (Millipore Corp., Bedford, Mass.) (7), while muscle and small intestinal biopsies were stained for tissue eosmophils using May-Grunwald stain (8). * Supported by a grant from the Rockefeller Foundation THE JOURNAL OF EXPERIMENTAL MEDICINE VOLUME 145,
2 756 GROVE ET AL. BRIEF DEFINITIVE REPORT 700 " (zi ~. 500 == 300 t00 O, x lo- b- 4. Weeks of Infechon Fm 1. Geometric mean absolute peripheral blood eosinophil counts and bone marrow eosinophils per femur in mice treated with NRS (e---e) and AES (e--e). Peripheral blood eosmophdla was suppressed by treatment with AES Bone marrow eosinophilia occurred earher in mine treated with AES. Results The peripheral eosinophilia which was observed between 17and 25 days after infection in mice treated with NRS was completely suppressed in animals treated with AES (Fig. 1). Mice treated with AES, which has no activity against immature eosinophils (6), showed significantly higher bone marrow eosinophil counts 2 wk after infection (P < 0.001, t test) than animals given NITS. 3 wk after infection, however, the bone marrow eosinophil counts were higher in mice given NRS (P < 0.01, t test). The moderate infiltration of the small intestinal mucosa by eosinophils in infected mice treated with NRS was markedly suppressed in the animals treated with AES. While the inflammatory infiltrate around muscle larvae in mice treated with NRS consisted of 10-20% eosinophils, eosinophils were reduced approximately fivefold in the animals treated with AES. There was a commensurate reduction in the area of inflammation around muscle larvae; the geometric mean area of inflammation around cysts in animals given NRS was 3,450 ftm ~ (range ,600) compared with 3,040 ftm 2 (450-20,500) in mice treated with AES, but this difference was not statistically significant. Intestinal worm counts at 1, 2, and 3 wk after infection were similar in mice treated with AES or NRS (Table I). Muscle larvae at 3 and 4 wk after infection in mice treated with AES, however, were almost double the number found in animals treated with NRS (P < 0.01 and 0.001, respectively) (Table I).
3 GROVE ET AL. BRIEF DEFINITIVE REPORT 757 TABLE I Intestinal Adult Worm Counts and Muscle Larvae Counts in Mice at Varying Periods after a Primary Infection with T. spiralis Numbers of am- Duration Treatment reals Mean SE Probablhty* Intestinal adult counts 1 wk AES i NRS i wk AES NRS wk AES NRS Muscle larval counts 3 wk AES 6 21,400 3,400 NRS 9 11, < wk AES 20 62,500 4,600 <0 001 NRS 20 32,700 1,800 Treatment wzth AES chd not mfluence the expulsion of adult worms from the gut, but lmpmred resmtance to the larval stages was ewdenced by increased numbers of muscle larvae * Student's t test Discussion As in other systemic helminth infections, eosinophilia is one of the hallmarks of trichinosis. The rise in peripheral eosinophils was shown by Basten and Beeson to be dependent upon an intact cellular immune system (9, 10). Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that lymphocytes obtained from animals with trichinosis when exposed to soluble Trichinella larval antigens secrete a lymphokine, eosinophil stimulation promoter (11). This substance may be one of the factors responsible for the migration of eosinophils into the major areas of inflammation observed in trichinosis: the intestinal mucosa where the adult worms reside between the columnar epithelial cells of the villi (12) and the muscles where the larvae undergo encystation. It has been suggested that the intestinal inflammation, of which eosinophils are a prominent component, is responsible for the expulsion of worms from the gut (13). The present study, however, indicates that eosinophils do not play a role in this response, as virtual elimination of these cells from the intestinal inflammatory infiltrate did not alter the rate of expulsion of the adult worms. It appears, though, that eosinophils are an important factor in resistance to the systemic phase of this infection as mice treated with AES had double the number of muscle larvae found in animals given NRS. Since the length of residence of adult worms in the gut, and hence the time available for larval production was identical in the two groups, the numbers of muscle larvae should have been similar. Although it is possible that the fecundity of the female worms in the eosinophilopenic animals could have been increased, it seems more likely that the increased number of muscle larvae in the AES-treated mice was related to facilitation of either the passage of the first-stage larvae through the gut mucosa and the bloodstream or of their development into mature larvae in the skeletal muscles. The small reduction in the area of inflammation around the muscle larvae was consistent with markedly decreased numbers of eosino-
4 758 GROVE ET AL. BRIEF DEFINITIVE REPORT phils in the lesions. These observations parallel those found in schistosomiasis where depletion of eosinophils with AES resulted in a corresponding decrease in the area of inflammation around schistosome eggs (6). Mahmoud et al. (3) showed that eosinophils are an essential factor in the resistance of mice with schistosomiasis mansoni to a challenge infection. The present experiments reveal that eosinophils play a role in resistance to the systemic phase of a primary T. spiralis infection in mice. Whether their effect is nonspecific or is related to the development of specific acquired immunity is as yet uncertain. Thus, the long-recognized association of eosinophils with helminth infections has been further defined. In a second helminthiasis, eosinophils have been shown to be an important factor in protection against infection. Summary Mice infected with Trich~nella spiralis were depleted of eosinophils by repeated administration of rabbit anti-mouse eosinophil serum. There was no effect on the spontaneous expulsion of adult worms from the small intestines, but the numbers of larvae in the muscles were almost doubled. It is concluded that eosinophils contribute to resistance to the systemic phase of trichinosis. Recewed for publication 8 December References 1. Mahmoud, A. A. F., K. S. Warren, and D L. Boros Production of a rabbit antimouse eosinophil serum with no cross-reactivity to neutrophils. J. Exp. Med. 137: Butterworth, A. E., R. F. Sturrock, V. Houba, A. A. F. Mahmoud, A. Sher, and P. H. Rees Eosinophils as mediators of antibody-dependent damage to schistosomula. Nature (Lond.). 256: Mahmoud, A. A. F., K. S. Warren, and P. A. Peters A role for the eosinophll m acqmred resistance to Sch~stosoma mansoni infection as determined by antieosinophil serum. J. Exp. Med. 142: Gould, S. E Trichinosis in man and animals. S. E. Gould, editor. Charles C Thomas, Publisher. Springfield, Ill Campbell, W. C Immunizing effect of enteral and enteral-parenteral infections of Tr~ch~nella sp~ralis in mice. J. Parasitol. 51: Mahmoud, A. A. F., K. S. Warren, and R. C. Graham, Jr Antmosinophil serum and the kinetics of eosinophilia in schistosomiasis mansoni. J. Exp. Med. 142: Grove, D. I., and K. S. Warren Effects on murine trichinosis of niridazole, a suppressant of cellular but not humoral immunological responses. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasztol. 70: Manual of hmtological and special staining technics of the armed forces institute of pathology, second edition McGraw-Hill Book Company, New York Basten, A., M. H. Boyer, and P. B. Beeson Mechanism of eosinophilia. I. Factors affecting the eosmophil response of rats to Trlchinella spiralls. J. Exp. Med. 131: Basten, A., and P. B. Beeson Mechanism of eoslnophiha. II. Role of the lymphocyte. J. Exp. Med. 131: Warren, K. S., R. Karp, R. P. Pelley, and A. A. F. Mahmoud The Eosinophil
5 GROVE ET AL. BRIEF DEFINITIVE REPORT 759 Stimulation Promoter test in murine and human Trichinella spiralis infection. J. Infect. D~s. 134: Race, G. J., J. E. Larsh, J. H. Martin, and N. F. Weatherly Light and electron mmroscopy of the intestinal tissue of mice parasitized by Tr~ch~nella spiralis. In Trichinellosis: Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Trichinosis. C. W. Kim, editor. Intext Educational Publishers, New York Larsh, J. E., and G. J. Race Allergic inflammation as a hypothesis for the expulsion of worms from tissues: a review. Exp. Parasitol. 37:251.
Effects of prednisolone on murine strongyloidiasis
 Parasitology (1981), 83, 401-409 With 2 figures in the text Effects of prednisolone on murine strongyloidiasis D. I. GROVE and H. J. S. DAWKINS Department of Medicine, University of Western Australia and
Parasitology (1981), 83, 401-409 With 2 figures in the text Effects of prednisolone on murine strongyloidiasis D. I. GROVE and H. J. S. DAWKINS Department of Medicine, University of Western Australia and
TRICHINELLOSIS. By: Christi Smykal
 TRICHINELLOSIS By: Christi Smykal Trichinellosis : Etiological agent: Trichinellosis is caused by a parasitic roundworm known as trichinella (7). Trichinella spiralis are found to be the causative agents
TRICHINELLOSIS By: Christi Smykal Trichinellosis : Etiological agent: Trichinellosis is caused by a parasitic roundworm known as trichinella (7). Trichinella spiralis are found to be the causative agents
Trichinellosis. By Michelle Randall
 Trichinellosis By Michelle Randall Disease Name: Trichinellosis Etiological Agent: Trichinella spiralis Transmission: People acquire Trichinellosis by consuming raw or undercooked meat infected with the
Trichinellosis By Michelle Randall Disease Name: Trichinellosis Etiological Agent: Trichinella spiralis Transmission: People acquire Trichinellosis by consuming raw or undercooked meat infected with the
STRONGYLOIDES RATTI INFECTIONS IN CONGENITALLY HYPOTHYMIC (NUDE) MICE
 Aust. J. Exp. Biul. Med. Sci., 0 (Pt.2) 181.18(1982) STRONGYLOIDES RATTI INFECTIONS IN CONGENITALLY HYPOTHYMIC (NUDE) MICE by H. J. S. DAWKINS, G. F. MITCHELL^' AND D. I. GROVE (From the Department of
Aust. J. Exp. Biul. Med. Sci., 0 (Pt.2) 181.18(1982) STRONGYLOIDES RATTI INFECTIONS IN CONGENITALLY HYPOTHYMIC (NUDE) MICE by H. J. S. DAWKINS, G. F. MITCHELL^' AND D. I. GROVE (From the Department of
Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases
 Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: Trichinosis Revised December 2014 Trichinosis 1.0 Provincial Reporting Confirmed and probable cases
Infectious Diseases Protocol Appendix B: Provincial Case Definitions for Reportable Diseases Disease: Trichinosis Revised December 2014 Trichinosis 1.0 Provincial Reporting Confirmed and probable cases
ALLERGY ARCHIVES THE EOSINOPHIL, A HISTORICAL RETROSPECTIVE: ANAPHYLAXIS AND ALLERGY
 Photomicrograph of guinea pig, 24 hours post anaphylactic shock, depicting massive peribronchial eosinophilia (originally published in Schlecht and Schwenker 1 ). Photomicrograph of skin from normal individual
Photomicrograph of guinea pig, 24 hours post anaphylactic shock, depicting massive peribronchial eosinophilia (originally published in Schlecht and Schwenker 1 ). Photomicrograph of skin from normal individual
Distribution of Trichinella spiralis Larvae in Tissues of Swine
 Proceedings of the Iowa Academy of Science Volume 68 Annual Issue Article 78 1961 Distribution of Trichinella spiralis Larvae in Tissues of Swine W. J. Zimmermann Iowa State University L. H. Schwarte Copyright
Proceedings of the Iowa Academy of Science Volume 68 Annual Issue Article 78 1961 Distribution of Trichinella spiralis Larvae in Tissues of Swine W. J. Zimmermann Iowa State University L. H. Schwarte Copyright
Eosinophils versus Neutrophils
 Eosinophils versus Neutrophils in Host Defense KILLING OF NEWBORN LARVAE OF TRICHINELLA SPIRALIS BY HUMAN GRANULOCYTES IN VITRO DAVID A. BASs and PAMELA SZEJDA, Department of Medicine, Bowman Gray School
Eosinophils versus Neutrophils in Host Defense KILLING OF NEWBORN LARVAE OF TRICHINELLA SPIRALIS BY HUMAN GRANULOCYTES IN VITRO DAVID A. BASs and PAMELA SZEJDA, Department of Medicine, Bowman Gray School
Immunological Tolerance
 Immunological Tolerance Definition: Making sure antibodies or T cells recognizing self components are either eliminated or brought under tight control. Failure of tolerance can lead to autoimmunity. (Also
Immunological Tolerance Definition: Making sure antibodies or T cells recognizing self components are either eliminated or brought under tight control. Failure of tolerance can lead to autoimmunity. (Also
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 9 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 9 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) An Alaskan hunter killed a bear. Subsequently, he prepared the meat for consumption, some fresh and some frozen (steaks, larger cuts, ground meat).
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 9 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) An Alaskan hunter killed a bear. Subsequently, he prepared the meat for consumption, some fresh and some frozen (steaks, larger cuts, ground meat).
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals. Taniawati Supali. Department of Parasitology
 Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Immunological Aspects of Parasitic Diseases in Immunocompromised Individuals Taniawati Supali Department of Parasitology 1 Defense mechanism in human Th17 (? ) Acute Chronic Th1 Th 2 Intracellular Treg
Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors
 PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
PowerPoint Lecture Slides for MICROBIOLOGY ROBERT W. BAUMAN Chapter 23 Parasitic Protozoa, Helminths, and Arthropod Vectors Helminthic Parasites of Humans Helminths are macroscopic, multicellular, eukaryotic
or basophils, although all of the granulocytes are
 Eosinophilopoietin A CIRCULATING LOW MOLECULAR WEIGHT PEPTIDE-LIKE SUBSTANCE WHICH STIMULATES THE PRODUCTION OF EOSINOPHILS IN MICE ADEL A. F. MAHMOUD, MARTA K. STONE, and ROBERT W. KELLERMEYER From the
Eosinophilopoietin A CIRCULATING LOW MOLECULAR WEIGHT PEPTIDE-LIKE SUBSTANCE WHICH STIMULATES THE PRODUCTION OF EOSINOPHILS IN MICE ADEL A. F. MAHMOUD, MARTA K. STONE, and ROBERT W. KELLERMEYER From the
Immunology. Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology)
 Host Defenses Overview and Nonspecific Defenses I Immunology Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology) The Nature of Host Defenses 2 3 4 1st line of defense - intact skin mucous membranes
Host Defenses Overview and Nonspecific Defenses I Immunology Prof. Nagwa Mohamed Aref (Molecular Virologist & Immunology) The Nature of Host Defenses 2 3 4 1st line of defense - intact skin mucous membranes
~Trichinella Spiralis:
 Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
Musculoskeletal System **Today we are going to talk about the parasites that affect the musculoskeletal system ~Trichinella Spiralis: It s a small nematode that measures to about 2-3mm in length. In general
1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity
 Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
Chapter 17A: Adaptive Immunity Part I 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity 2. T and B Cell Production 3. Antigens & Antigen Presentation 4. Helper T cells 1. Overview of Adaptive Immunity The Nature of Adaptive
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SURVEY OF TRICHINELLOSIS IN YUGOSLA VIA
 EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SURVEY OF TRICHINELLOSIS IN YUGOSLA VIA Albert Marinculic', Damir Rapic/, Janez Brglez', Nikola Dzakula', and Dagny Stojiljkovic' 'Veterinary Faculty, University of Zagreb, Yugoslavia;
EPIDEMIOLOGICAL SURVEY OF TRICHINELLOSIS IN YUGOSLA VIA Albert Marinculic', Damir Rapic/, Janez Brglez', Nikola Dzakula', and Dagny Stojiljkovic' 'Veterinary Faculty, University of Zagreb, Yugoslavia;
STUDIES ON BIOCHEMICAL PATHOLOGY IN TRICHINOSIS. 11. CHANGES IN LIVER AND MUSCLE GLYCOGEN AND SOME BLOOD CHEMICAL PARAMETERS IN MICE
 STUDIES ON BIOCHEMICAL PATHOLOGY IN TRICHINOSIS. 11. CHANGES IN LIVER AND MUSCLE GLYCOGEN AND SOME BLOOD CHEMICAL PARAMETERS IN MICE by George L. Stewart ABSTRACT Glycogen content of mouse diaphragm muscle
STUDIES ON BIOCHEMICAL PATHOLOGY IN TRICHINOSIS. 11. CHANGES IN LIVER AND MUSCLE GLYCOGEN AND SOME BLOOD CHEMICAL PARAMETERS IN MICE by George L. Stewart ABSTRACT Glycogen content of mouse diaphragm muscle
Parasitology Questions. Choose the best correct answer in the following statements
 Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Parasitology Questions Choose the best correct answer in the following statements ١. A.. is the larval stage of a fluke that is covered with cilia and swims about seeking out a snail to serve as an intermediate
Sushi Worms Diagnostic Challenges
 Department Medicine Diagnostic Centre Swiss TPH Winter Symposium 2017 Helminth Infection from Transmission to Control Sushi Worms Diagnostic Challenges Beatrice Nickel Fish-borne helminth infections Consumption
Department Medicine Diagnostic Centre Swiss TPH Winter Symposium 2017 Helminth Infection from Transmission to Control Sushi Worms Diagnostic Challenges Beatrice Nickel Fish-borne helminth infections Consumption
Extramedullar Proliferation of Eosinophil Granulocytes in Chronic Schistosomiasis Mansoni Is Mediated by a Factor Secreted by Inflammatory Macrophages
 INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 1990, p. 816-821 0019-9567/90/030816-06$02.00/0 Copyright C 1990, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 58, No. 3 Extramedullar Proliferation of Eosinophil Granulocytes in
INFECTION AND IMMUNITY, Mar. 1990, p. 816-821 0019-9567/90/030816-06$02.00/0 Copyright C 1990, American Society for Microbiology Vol. 58, No. 3 Extramedullar Proliferation of Eosinophil Granulocytes in
Cytokine Production in Hymenolepis Nana Infection
 ISSN 1735-1383 Iran. J. Immunol. December 2007, 4 (4), 236 240 Aboulghasem Ajami, Alireza Rafiei Cytokine Production in Hymenolepis Nana Infection Article Type: Research The Iranian Journal of Immunology
ISSN 1735-1383 Iran. J. Immunol. December 2007, 4 (4), 236 240 Aboulghasem Ajami, Alireza Rafiei Cytokine Production in Hymenolepis Nana Infection Article Type: Research The Iranian Journal of Immunology
Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica.
 TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
TREMATODES: INTRODUCTION: Ex. Schistosoma species (blood flukes) and Fasciola hepatica. The life cycle of trematodes involves a sexual cycle in humans and asexual reproduction in freshwater snails (intermediate
HISTOPATHOLOGICAL APPEARANCES IN PRIMARY AND SECONDARY INFECTIONS WITH STRONG YLOIDES RATTI IN MICE
 International Journnl for Parasitolog~v. Vol. Il. pp. 97-103. Prrpamon Press Ltd. 1981. Printed Great Britain. 0 Australian Society for Parasitology. OOZO-7519/81/010097-07$02.00/O HISTOPATHOLOGICAL APPEARANCES
International Journnl for Parasitolog~v. Vol. Il. pp. 97-103. Prrpamon Press Ltd. 1981. Printed Great Britain. 0 Australian Society for Parasitology. OOZO-7519/81/010097-07$02.00/O HISTOPATHOLOGICAL APPEARANCES
Immune system. Aims. Immune system. Lymphatic organs. Inflammation. Natural immune system. Adaptive immune system
 Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
Aims Immune system Lymphatic organs Inflammation Natural immune system Adaptive immune system Major histocompatibility complex (MHC) Disorders of the immune system 1 2 Immune system Lymphoid organs Immune
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and. Specific. (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell
 There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
There are 2 major lines of defense: Non-specific (Innate Immunity) and Specific (Adaptive Immunity) Photo of macrophage cell Development of the Immune System ery pl neu mφ nk CD8 + CTL CD4 + thy TH1 mye
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases
 محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
محاضرة مناعت مدرس المادة :ا.م. هدى عبدالهادي علي النصراوي Immunity to Infectious Diseases Immunity to infection depends on a combination of innate mechanisms (phagocytosis, complement, etc.) and antigen
PARASITOLOGICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RHESUS MONKEYS INFECTED WITH CHINESE MAINLAND STRAIN OF SCHISTOSOMA JAPONICUM
 PARASITOLOGICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RHESUS MONKEYS INFECTED WITH CHINESE MAINLAND STRAIN OF SCHISTOSOMA JAPONICUM He Yi-Xun, Yu Qi-Fang and Hu Ya-Qing Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese
PARASITOLOGICAL AND HISTOPATHOLOGICAL STUDIES ON RHESUS MONKEYS INFECTED WITH CHINESE MAINLAND STRAIN OF SCHISTOSOMA JAPONICUM He Yi-Xun, Yu Qi-Fang and Hu Ya-Qing Institute of Parasitic Diseases, Chinese
Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis. Hematopoiesis
 Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
Chapter. Cells and Organs of the Immune System Hematopoiesis Hematopoiesis- formation and development of WBC and RBC bone marrow. Hematopoietic stem cell- give rise to any blood cells (constant number,
The Nottingham eprints service makes this work by researchers of the University of Nottingham available open access under the following conditions.
 Behnke, Jerzy M (1975) Immune epulsion of the nematode Aspiculuris tetraptera from mice given primary and challenge infections International Journal for Parasitology, 5 pp 511-515 ISSN 0020-7519 Access
Behnke, Jerzy M (1975) Immune epulsion of the nematode Aspiculuris tetraptera from mice given primary and challenge infections International Journal for Parasitology, 5 pp 511-515 ISSN 0020-7519 Access
Immunology Lecture- 1
 Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
Immunology Lecture- 1 Immunology and Immune System Immunology: Study of the components and function of the immune system Immune System a network collected from cells, tissues organs and soluble factors
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE
 ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
ULTRASTRUCTURAL CHANGES IN THE INFECTIVE LARVAE OF NIPPOSTRONGYLUS BRASILIENSIS IN THE SKIN OF IMMUNE MICE by D. L. Lee ABSTRACT Infective stage larvae of Nippostrongylus brasiliensis are immobilized within
Trichinosis Table of Contents
 Subsection: Trichinosis Page 1 of 9 Trichinosis Table of Contents Trichinosis Trichinosis (Trichinellosis) Fact Sheet Investigation of Trichinosis Surveillance Case Report (CDC 54.7) Subsection: Trichinosis
Subsection: Trichinosis Page 1 of 9 Trichinosis Table of Contents Trichinosis Trichinosis (Trichinellosis) Fact Sheet Investigation of Trichinosis Surveillance Case Report (CDC 54.7) Subsection: Trichinosis
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response. Physiology Unit 3
 INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
INNATE IMMUNITY Non-Specific Immune Response Physiology Unit 3 Protection Against Infection The body has several defenses to protect itself from getting an infection Skin Mucus membranes Serous membranes
1. Specificity: specific activity for each type of pathogens. Immunity is directed against a particular pathogen or foreign substance.
 L13: Acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity The resistance, which absent at the time of first exposure to a pathogen, but develops after being exposed to the pathogen is called acquired immunity. It
L13: Acquired or adaptive (specific) immunity The resistance, which absent at the time of first exposure to a pathogen, but develops after being exposed to the pathogen is called acquired immunity. It
Alberta Health and Wellness Public Health Notifiable Disease Management Guidelines August 2011
 August 2011 Trichinosis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 October 2005 Case Definition
August 2011 Trichinosis Revision Dates Case Definition Reporting Requirements Remainder of the Guideline (i.e., Etiology to References sections inclusive) August 2011 August 2011 October 2005 Case Definition
C. Incorrect! MHC class I molecules are not involved in the process of bridging in ADCC.
 Immunology - Problem Drill 13: T- Cell Mediated Immunity Question No. 1 of 10 1. During Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), the antibody acts like a bridge between the specific antigen
Immunology - Problem Drill 13: T- Cell Mediated Immunity Question No. 1 of 10 1. During Antibody-dependent cell mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), the antibody acts like a bridge between the specific antigen
2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory tract sweep out bacteria and particles.
 Chapter 39 Immunity I. Three Lines of Defense A. Surface Barriers to Invasion 1. is an important barrier. 2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory
Chapter 39 Immunity I. Three Lines of Defense A. Surface Barriers to Invasion 1. is an important barrier. 2. The normal of the gut, and vagina keep the growth of pathogens in check. 3. in the respiratory
By Lucy Simpson and Taylor Meyers
 By Lucy Simpson and Taylor Meyers Two Types of Immunity Innate immunity- Innate immunity consists of external barriers formed by the skin and mucous membranes, plus a set of internal cellular and chemical
By Lucy Simpson and Taylor Meyers Two Types of Immunity Innate immunity- Innate immunity consists of external barriers formed by the skin and mucous membranes, plus a set of internal cellular and chemical
8/11/16. Kevin Letz DNP, MSN, MBA, RN, CEN, CNE, FNP-C, PCPNP-BC, ANP-BC, FAANP
 Kevin Letz DNP, MSN, MBA, RN, CEN, CNE, FNP-C, PCPNP-BC, ANP-BC, FAANP Eosinophilia Eosinophilia refers to an absolute eosinophil count in the peripheral blood of 500 eosinophils/microl; this is considered
Kevin Letz DNP, MSN, MBA, RN, CEN, CNE, FNP-C, PCPNP-BC, ANP-BC, FAANP Eosinophilia Eosinophilia refers to an absolute eosinophil count in the peripheral blood of 500 eosinophils/microl; this is considered
Topics. Humoral Immune Response Part II Accessory cells Fc Receptors Opsonization and killing mechanisms of phagocytes NK, mast, eosynophils
 Topics Humoral Immune Response Part II Accessory cells Fc Receptors Opsonization and killing mechanisms of phagocytes NK, mast, eosynophils Immune regulation Idiotypic network 2/15/2005 MICR 415 / 515
Topics Humoral Immune Response Part II Accessory cells Fc Receptors Opsonization and killing mechanisms of phagocytes NK, mast, eosynophils Immune regulation Idiotypic network 2/15/2005 MICR 415 / 515
Reactivity and Specificity of Trichinella spiralis Fractions in
 JOURNAL OF CUNICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1977, p. 274-279 Copyright 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 6, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Reactivity and Specificity of Trichinella spiralis Fractions in
JOURNAL OF CUNICAL MICROBIOLOGY, Sept. 1977, p. 274-279 Copyright 1977 American Society for Microbiology Vol. 6, No. 3 Printed in U.S.A. Reactivity and Specificity of Trichinella spiralis Fractions in
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity. Lymphatic Pathways. Lymphatic Capillaries. network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids
 Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Chapter 16 Lymphatic System and Immunity network of vessels that assist in circulating fluids closely associated with the cardiovascular system transports excess fluid away from interstitial spaces transports
Giardia lamblia (flagellates)
 Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
Giardia lamblia (flagellates) Dr. Hala Al Daghistani Giardia lamblia (Giardia duodenalis or Giardia intestinalis) is the causative agent of giardiasis and is the only common pathogenic protozoan found
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions
 Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Chapter 23 Immunity Exam Study Questions 1. Define 1) Immunity 2) Neutrophils 3) Macrophage 4) Epitopes 5) Interferon 6) Complement system 7) Histamine 8) Mast cells 9) Antigen 10) Antigens receptors 11)
Pathophysiologic Basis of Autoimmune Disorders
 Pathophysiologic Basis of Autoimmune Disorders Linda Felver, Ph.D., R.N. Associate Professor School of Nursing Oregon Health & Science University The immune system has two arms: Adaptive (Acquired) Immune
Pathophysiologic Basis of Autoimmune Disorders Linda Felver, Ph.D., R.N. Associate Professor School of Nursing Oregon Health & Science University The immune system has two arms: Adaptive (Acquired) Immune
Outline. Animals: Immunity. Defenses Against Disease. Key Concepts:
 Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Animals: Immunity Defenses Against Disease Outline 1. Key concepts 2. Physical barriers: Skin, Mucus and HCL in stomach 3. Non-specific 4. Specific responses Immune System a. Components of Immune system
Trichinella Transmission and Control
 Trichinella Transmission and Control David Jenkins School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia djjenkins@csu.edu.au The generosity of Dr K Darwin Murelle
Trichinella Transmission and Control David Jenkins School of Animal and Veterinary Sciences, Charles Sturt University, Wagga Wagga, NSW, Australia djjenkins@csu.edu.au The generosity of Dr K Darwin Murelle
Introduction to Immunopathology
 MICR2209 Introduction to Immunopathology Dr Allison Imrie 1 Allergy and Hypersensitivity Adaptive immune responses can sometimes be elicited by antigens not associated with infectious agents, and this
MICR2209 Introduction to Immunopathology Dr Allison Imrie 1 Allergy and Hypersensitivity Adaptive immune responses can sometimes be elicited by antigens not associated with infectious agents, and this
Figure 2: Lymph node Cortical follicular (F) and paracortical (PC) atrophy, with narrowing of the cortex relative to the medulla (M).
 Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Figure 1: Lymph node Follicular hyperplasia, with expansion of the follicular germinal centres (F) by large blast cells. Paracortical hyperplasia, with expansion of the paracortex (PC) by small lymphocytes.
Immune System AP SBI4UP
 Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immune System AP SBI4UP TYPES OF IMMUNITY INNATE IMMUNITY ACQUIRED IMMUNITY EXTERNAL DEFENCES INTERNAL DEFENCES HUMORAL RESPONSE Skin Phagocytic Cells CELL- MEDIATED RESPONSE Mucus layer Antimicrobial
Immunology 2011 Lecture 17 Lymphoid Tissue Architecture 13 October
 Immunology 2011 Lecture 17 Lymphoid Tissue Architecture 13 October TODAY Lymphoid Tissue Architecture, Chap. 16 APC Antigen processing (dendritic cells, MΦ et al.) Antigen "presentation" Ag/Ab complexes
Immunology 2011 Lecture 17 Lymphoid Tissue Architecture 13 October TODAY Lymphoid Tissue Architecture, Chap. 16 APC Antigen processing (dendritic cells, MΦ et al.) Antigen "presentation" Ag/Ab complexes
FALL IN IgE LEVELS AFTER TREATMENT FOR HOOKWORM
 Clin. exp. Immunol. (1974) 18, 565-569. FALL IN IgE LEVELS AFTER TREATMENT FOR HOOKWORM D. I. GROVE, T. 0. BURSTON AND I. J. FORBES Department of Medicine, University of Adelaide, South Australia, and
Clin. exp. Immunol. (1974) 18, 565-569. FALL IN IgE LEVELS AFTER TREATMENT FOR HOOKWORM D. I. GROVE, T. 0. BURSTON AND I. J. FORBES Department of Medicine, University of Adelaide, South Australia, and
Parasites List of Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis) Giardia ( Giardia lamblia Coccidia ( Cryptosporidium
 Parasites List of Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis) Pinworm, also known as seatworm or threadworm, is one of the most prevalent intestinal parasites in the United States, with approximately 40 million
Parasites List of Pinworm (Enterobius vermicularis) Pinworm, also known as seatworm or threadworm, is one of the most prevalent intestinal parasites in the United States, with approximately 40 million
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION
 PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
PARASITOLOGY INTRODUCTION DEFINITION Parasite means : one who eats at the table of another. Differs from bacteria and viruses in their complex life cycles, intermediate hosts and chronicity. Evolved to
Topics in Parasitology BLY Vertebrate Immune System
 Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Topics in Parasitology BLY 533-2008 Vertebrate Immune System V. Vertebrate Immune System A. Non-specific defenses against pathogens 1. Skin - physical barrier a. Tough armor protein KERATIN b. Surface
Introduction. Causes. Roundworms. Worms. Flatworms. How Flatworms are transmitted. Fast fact. Fast fact
 Module 5 Worms MODULE 5 INTRODUCTION Introduction Worms Worms or helminths are parasites that live on or in human or animal hosts and draw nutrients from their host 1. Worms are multi-cellular, have complex
Module 5 Worms MODULE 5 INTRODUCTION Introduction Worms Worms or helminths are parasites that live on or in human or animal hosts and draw nutrients from their host 1. Worms are multi-cellular, have complex
Immunobiology 7. The Humoral Immune Response
 Janeway Murphy Travers Walport Immunobiology 7 Chapter 9 The Humoral Immune Response Copyright Garland Science 2008 Tim Worbs Institute of Immunology Hannover Medical School 1 The course of a typical antibody
Janeway Murphy Travers Walport Immunobiology 7 Chapter 9 The Humoral Immune Response Copyright Garland Science 2008 Tim Worbs Institute of Immunology Hannover Medical School 1 The course of a typical antibody
12/10/2009. Department of Pathology, Case Western Reserve University. Mucosal Cytokine Network in IBD
 Cytokine-Mediated Inflammation in IBD Theresa T. Pizarro Department of Pathology, Case Western Reserve University Mucosal Cytokine Network in IBD Andoh, et al., 2008 1 Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Family Cytokine
Cytokine-Mediated Inflammation in IBD Theresa T. Pizarro Department of Pathology, Case Western Reserve University Mucosal Cytokine Network in IBD Andoh, et al., 2008 1 Interleukin-1 (IL-1) Family Cytokine
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19
 MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19 CHAPTER 16: NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES OF THE HOST I. THE FIRST LINE OF DEFENSE A. Mechanical Barriers (Physical
MONTGOMERY COUNTY COMMUNITY COLLEGE Department of Science LECTURE OUTLINE CHAPTERS 16, 17, 18 AND 19 CHAPTER 16: NONSPECIFIC DEFENSES OF THE HOST I. THE FIRST LINE OF DEFENSE A. Mechanical Barriers (Physical
What are bacteria? Microbes are microscopic(bacteria, viruses, prions, & some fungi etc.) How do the sizes of our cells, bacteria and viruses compare?
 7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
7.1 Microbes, pathogens and you Chp. 7 Lymphatic System & Immunity The interaction between microbes and humans? Microbes are very abundant in the environment and as well as in and on our bodies GOOD: We
EUROPEAN PROGRAMME FOR INTERVENTION EPIDEMIOLOGY TRAINING
 Epidem iol ogy EUROPEAN PROGRAMME FOR INTERVENTION EPIDEMIOLOGY TRAINING Lazareto de Mahón, Menorca, Spain 27 September 16 October 2004 An epidemic of Trichinosis in France Exercise Source : Thierry Ancelle,
Epidem iol ogy EUROPEAN PROGRAMME FOR INTERVENTION EPIDEMIOLOGY TRAINING Lazareto de Mahón, Menorca, Spain 27 September 16 October 2004 An epidemic of Trichinosis in France Exercise Source : Thierry Ancelle,
Page # Lecture 8: Immune Dysfunction - Immunopathology. Four Types of Hypersensitivity. Friend of Foe? Autoimmune disease Immunodeficiency
 Lecture 8: Immune Dysfunction - Immunopathology Autoimmune disease Immunodeficiency Allergy and Asthma Graft rejection and Lupus Friend of Foe? Four Types of Hypersensitivity Allergic Responses - Type
Lecture 8: Immune Dysfunction - Immunopathology Autoimmune disease Immunodeficiency Allergy and Asthma Graft rejection and Lupus Friend of Foe? Four Types of Hypersensitivity Allergic Responses - Type
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses ( )
 NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
NOTES: CH 43, part 1 The Immune System - Nonspecific & Specific Defenses (43.1-43.2) The lymphatic system is closely associated with the cardiovascular system. LYMPHATIC PATHWAYS Lymphatic capillaries
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Platyhelminthes
 Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Platyhelminthes Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Platyhelminthes Flat worms
Kingdom Animalia Subkingdom Eumetazoa Bilateria Phylum Platyhelminthes Professor Andrea Garrison Biology 3A Illustrations 2014 Cengage Learning unless otherwise noted Phylum Platyhelminthes Flat worms
Effector T Cells and
 1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
1 Effector T Cells and Cytokines Andrew Lichtman, MD PhD Brigham and Women's Hospital Harvard Medical School 2 Lecture outline Cytokines Subsets of CD4+ T cells: definitions, functions, development New
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM
 HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
HISTOLOGY VIRTUAL LABORATORY BLOOD AND LYMPHATICS SYSTEM Login: http://histopath.westernu.edu Histology Atlas AND Virtual Histology links. I. HEMATOLOGY - PERIPHERAL BLOOD Purpose: To be able to identify
Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells
 ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
ICI Basic Immunology course Effector mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity: Properties of effector, memory and regulatory T cells Abul K. Abbas, MD UCSF Stages in the development of T cell responses: induction
Diseases-causing agents, pathogens, can produce infections within the body.
 BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 16 Lecture: Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. LYMPHATIC and IMMUNE Systems Body Defenses Against
BIO 212: ANATOMY & PHYSIOLOGY II 1 CHAPTER 16 Lecture: Dr. Lawrence G. Altman www.lawrencegaltman.com Some illustrations are courtesy of McGraw-Hill. LYMPHATIC and IMMUNE Systems Body Defenses Against
Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems
 The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
The Chapter 13 Lymphatic and Immune Systems 1 The Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Organs Three functions contribute to homeostasis 1. Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream 2. Help defend the body against
Acquired Immunity Cells are initially and require before they can work Responds to individual microbes
 1 of 10 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM CHAPTER 43; PAGES 898 921 WHY DO WE NEED AN IMMUNE SYSTEM? It s a dirty, dirty world out there and we are vastly outnumbered Bacteria and parasites are everywhere The body has
1 of 10 THE IMMUNE SYSTEM CHAPTER 43; PAGES 898 921 WHY DO WE NEED AN IMMUNE SYSTEM? It s a dirty, dirty world out there and we are vastly outnumbered Bacteria and parasites are everywhere The body has
(From the Nu~eld Department of Clinical Medicine, University of Oxford, Oxford, England) Materials and Methods
 Published Online: 1 June, 1970 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.131.6.1288 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 13, 2018 MECHANISM OF EOSINOPHILIA II. ROLE OF THE LYMPHOCYTE* BY ANTONY BASTEN,~
Published Online: 1 June, 1970 Supp Info: http://doi.org/10.1084/jem.131.6.1288 Downloaded from jem.rupress.org on October 13, 2018 MECHANISM OF EOSINOPHILIA II. ROLE OF THE LYMPHOCYTE* BY ANTONY BASTEN,~
Trichuris muris system
 Trichuris muris system Analisis of IL-13 producing cells in intestine during nematodes infection 28 th September 28, 2012 Wenqi Wang(200910576) School of Life and Environmental Sciences College of Biological
Trichuris muris system Analisis of IL-13 producing cells in intestine during nematodes infection 28 th September 28, 2012 Wenqi Wang(200910576) School of Life and Environmental Sciences College of Biological
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 5 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia)
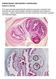 PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 5 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 47 year-old male presented with symptoms that were consistent with possible late adult-onset epilepsy (frequent headaches and occasional seizures).
PARASITOLOGY CASE HISTORY 5 (HISTOLOGY) (Lynne S. Garcia) A 47 year-old male presented with symptoms that were consistent with possible late adult-onset epilepsy (frequent headaches and occasional seizures).
BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY. White Blood Cells (WBC) Dr Nervana Mostafa
 BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY White Blood Cells (WBC) Dr Nervana Mostafa 1 Lecture content. 1 Eosinophils and Basophilophils formation, maturation and function. 2. 3. 4. 5 Monocytes and macrophage formation, maturation
BLOOD PHYSIOLOGY White Blood Cells (WBC) Dr Nervana Mostafa 1 Lecture content. 1 Eosinophils and Basophilophils formation, maturation and function. 2. 3. 4. 5 Monocytes and macrophage formation, maturation
TRICHINOSIS-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ASPECTS IN BIHOR COUNTY
 Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula: Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2010 TRICHINOSIS-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ASPECTS IN BIHOR COUNTY 1482 Mirela Indrieş * University of
Analele UniversităŃii din Oradea Fascicula: Ecotoxicologie, Zootehnie şi Tehnologii de Industrie Alimentară, 2010 TRICHINOSIS-EPIDEMIOLOGICAL ASPECTS IN BIHOR COUNTY 1482 Mirela Indrieş * University of
Warm-up. Parts of the Immune system. Disease transmission. Disease transmission. Why an immune system? Chapter 43 3/9/2012.
 Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
Warm-up Objective: Explain how antigens react with specific lymphocytes to induce immune response and immunological memory. Warm-up: Which of the following would normally contain blood with the least amount
Introduction to Multicellular Parasites
 Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Introduction to Multicellular Parasites Multicellular parasites are eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom Animalia (like us). Though
Harriet Wilson, Lecture Notes Bio. Sci. 4 - Microbiology Sierra College Introduction to Multicellular Parasites Multicellular parasites are eukaryotic organisms in the Kingdom Animalia (like us). Though
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens
 How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
How the Innate Immune System Profiles Pathogens Receptors on macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells for bacteria and viruses Broad specificity - Two main groups of bacteria: gram positive, gram-negative
The Immune System is the Third Line of Defense Against Infection. Components of Human Immune System
 Chapter 17: Specific Host Defenses: The Immune Response The Immune Response Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an organism to recognize and defend itself against specific pathogens or antigens. Immune
Chapter 17: Specific Host Defenses: The Immune Response The Immune Response Immunity: Free from burden. Ability of an organism to recognize and defend itself against specific pathogens or antigens. Immune
Trichinella Cat #
 DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
DIAGNOSTIC AUTOMATION, INC. 23961 Craftsman Road, Suite E/F, Calabasas, CA 91302 Tel: (818) 591-3030 Fax: (818) 591-8383 onestep@rapidtest.com technicalsupport@rapidtest.com www.rapidtest.com See external
THE ETIOLOGICAL FACTOR FOR EOSINOPHILIA AND HYPERGLOBULINEMIA E IN BRAZILIAN SCHOOL CHILDREN
 Jpn. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., Vol. 19 No. 2 1991, pp. 203-208 203 THE ETIOLOGICAL FACTOR FOR EOSINOPHILIA AND HYPERGLOBULINEMIA E IN BRAZILIAN SCHOOL CHILDREN ATSUO HAMADA1, NAOHIRO WATANABE1, MASASHI KOBAYASHI2,
Jpn. J. Trop. Med. Hyg., Vol. 19 No. 2 1991, pp. 203-208 203 THE ETIOLOGICAL FACTOR FOR EOSINOPHILIA AND HYPERGLOBULINEMIA E IN BRAZILIAN SCHOOL CHILDREN ATSUO HAMADA1, NAOHIRO WATANABE1, MASASHI KOBAYASHI2,
Regulation of Type 2 Immunity by Basophils Prof. Dr. David Voehringer
 Regulation of Type 2 Immunity by Basophils Department of Infection Biology Institute of Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Hygiene Outline of the presentation The concept of type 2 immunity Basophil
Regulation of Type 2 Immunity by Basophils Department of Infection Biology Institute of Clinical Microbiology, Immunology and Hygiene Outline of the presentation The concept of type 2 immunity Basophil
NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS
 LECTURE: 15 Title NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Determine the relative percentages in blood for the various types
LECTURE: 15 Title NEUTROPHIL, BASOPHIL, EOSINOPHIL, AND PLATELETS SURFACE RECEPTORS LEARNING OBJECTIVES: The student should be able to: Determine the relative percentages in blood for the various types
Trichinosis. Life Cycle
 Trichinosis Authors K. Darwin Murrell, USDA/ARS Peoria, Illinois George T. Woods, University of Illinois LeRoy G. Biehl, University of Illinois Reviewers Ray Gamble, USDA/ARS, Beltsville, Maryland Peter
Trichinosis Authors K. Darwin Murrell, USDA/ARS Peoria, Illinois George T. Woods, University of Illinois LeRoy G. Biehl, University of Illinois Reviewers Ray Gamble, USDA/ARS, Beltsville, Maryland Peter
Genetic relationships between indicator traits and parasitic nematode infection in sheep.
 Genetic relationships between indicator traits and parasitic nematode infection in sheep. G. Davies* 1,2, M.J. Stear 2 and S.C. Bishop 1 1 Roslin Institute (Edinburgh), Roslin, Midlothian EH25 9PS UK,
Genetic relationships between indicator traits and parasitic nematode infection in sheep. G. Davies* 1,2, M.J. Stear 2 and S.C. Bishop 1 1 Roslin Institute (Edinburgh), Roslin, Midlothian EH25 9PS UK,
LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY
 Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Introduction to immunology. LESSON 2: THE ADAPTIVE IMMUNITY Today we will get to know: The adaptive immunity T- and B-cells Antigens and their recognition How T-cells work 1 The adaptive immunity Unlike
Station A: YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament. Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5.
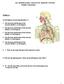 YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled 5 on the diagram. 2. Give the
YR3 -RESPIRATORY, DIGESTIVE, IMMUNE SYSTEM Sample Tournament Station A: Use the diagram in answering Questions 1-5. 1. Give the name and functions of the structure labeled 5 on the diagram. 2. Give the
Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit.
 Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. Intended Use For the qualitative screening of serum IgG antibodies to Trichinella using an Enzyme Linked Immunoabsorbant Assay
Please use only the valid version of the package insert provided with the kit. Intended Use For the qualitative screening of serum IgG antibodies to Trichinella using an Enzyme Linked Immunoabsorbant Assay
Supplementary Information
 Supplementary Information TABLE S1. SUBJECT CHARACTERISTICS* Normal Control Subjects Subjects with Asthma p Value Number 23 48 Age (years) 35±10 35±10 0.75 Sex, M:F (% F) 9:12 (57) 17:26 (60) 0.76 FEV1
Supplementary Information TABLE S1. SUBJECT CHARACTERISTICS* Normal Control Subjects Subjects with Asthma p Value Number 23 48 Age (years) 35±10 35±10 0.75 Sex, M:F (% F) 9:12 (57) 17:26 (60) 0.76 FEV1
Immunity. Innate & Adaptive
 Immunity Innate & Adaptive Immunity Innate: response to attack is always the same Mechanical mechanisms Chemical mediators Cellular response Inflammatory response Adaptive: response to attack improves
Immunity Innate & Adaptive Immunity Innate: response to attack is always the same Mechanical mechanisms Chemical mediators Cellular response Inflammatory response Adaptive: response to attack improves
The Adaptive Immune Response. B-cells
 The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
The Adaptive Immune Response B-cells The innate immune system provides immediate protection. The adaptive response takes time to develop and is antigen specific. Activation of B and T lymphocytes Naive
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research ISSN:
 International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Mast Cells in Appendicitis Dr. Jyoti Sharma 1*, Dr. Nitin Chaudhary 2*, Dr. Sunita
International Journal of Health Sciences and Research www.ijhsr.org ISSN: 2249-9571 Original Research Article Role of Mast Cells in Appendicitis Dr. Jyoti Sharma 1*, Dr. Nitin Chaudhary 2*, Dr. Sunita
Immunology of Asthma. Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph. Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine
 Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline Consensus characteristics/incidence data Immune/inflammatory basis Etiology/Genetic basis Hygiene
Immunology of Asthma Kenneth J. Goodrum,Ph Ph.D. Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Outline Consensus characteristics/incidence data Immune/inflammatory basis Etiology/Genetic basis Hygiene
Analysis of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte populations in experimental Trichinella spiralis infection of mice
 FOLIA PARASITOLOGICA 47: 55-59, 2000 Analysis of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte populations in experimental Trichinella spiralis infection of mice Frane Božić 1, Albert Marinculić 2 and Emir Duraković
FOLIA PARASITOLOGICA 47: 55-59, 2000 Analysis of intestinal intraepithelial lymphocyte populations in experimental Trichinella spiralis infection of mice Frane Božić 1, Albert Marinculić 2 and Emir Duraković
Chapter Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs
 Chapter 22.2 Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs Lymphatic Cells These are the cells that play a key roll in the structure and function of the immune system. We have already introduced
Chapter 22.2 Lymphatic Cells, Lymphatic Tissues, and Lymphatic Organs Lymphatic Cells These are the cells that play a key roll in the structure and function of the immune system. We have already introduced
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy
 Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
Advances in Cancer Immunotherapy Immunology 101 for the Non-Immunologist Arnold H. Zea, PhD azea@lsuhsc.edu Disclosures No relevant financial relationships to disclose This presentation does not contain
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System
 Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Chapter 12: The Lymphatic System Immune System Composed of many nonspecific and specific defenses Lymphatic System also plays an important role in establishing immunity Lymphatic System Major components
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1
 Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Prelab #4 BLOOD; BONE MARROW; RESPIRATORY; INTEGUEMENT Page 1 Blood Slide 101 This a classic slide of blood cells using a Wright stain. Inspect red blood cells and their appearance. Note the approximate
Title: Public Health Reporting and National Notification for Trichinellosis
 09-ID-64 Committee: Infectious Title: Public Health Reporting and National Notification for Trichinellosis I. Statement of the Problem CSTE position statement 07-EC-02 recognized the need to develop an
09-ID-64 Committee: Infectious Title: Public Health Reporting and National Notification for Trichinellosis I. Statement of the Problem CSTE position statement 07-EC-02 recognized the need to develop an
