Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men
|
|
|
- Agnes Phebe Williams
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
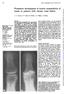
1 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1995; 54: Department of Community and Family Medicine, The Chinese University ofhong Kong, Hong Kong E M C Lau F Lin Orthopaedic and Traumatology Unit, Tuen Mun Hospital, Hong Kong D Lam Arthritis and Rheumatism Council Epidemiology Research Unit, University of Manchester, United Kingdom A Silman School of Postgraduate Medicine, University of Keele, Staffordshire, United Kingdom P Croft Correspondence to: Dr E M C Lau, Department of Community and Family Medicine, Lek Yuen Health Centre, Shatin, NT, Hong Kong. Accepted for publication 18 August 1995 Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men E M C Lau, F Lin, D Lam, A Silman, P Croft Abstract Objective-To estimate the prevalence of hip osteoarthritis (OA hip) and hip dysplasia in a sample of Hong Kong men who were unselected with respect to hip symptoms. Methods-The postmicturition films of 999 men aged 6-75 years, consecutive attenders for intravenous urography between 1987 and 199 at a regional hospital, were reviewed. OA hip was diagnosed as the occurrence of two or more features ofoa using a modified version of the Kellgren and Lawrence scale, or a minimal joint space of 1.5 mm or less. Hip dysplasia was defined as a centre-edge angle of less than 25, or an acetabular depth of less than 9 mm. The results were compared with British data obtained by similar methods. Results-In the Hong Kong sample, the proportion of men with two or more features of osteoarthritis in at least one hip was about 5% that of the men in the British study (5. 4% and 11.%, respectively). Severe joint space narrowing (of 1.5 mm or less) occurred in.7% of the hips in Hong Kong men, compared with 2% in the British men. The proportion of hips with centre-edge angles less than 25 was 4.5% in Hong Kong, compared with 3.6% in Britain, and the prevalence of shallow acetabular depth was greater in Chinese (14-5%) than in the British (2.1%). Radiographic measures of hip dysplasia were not associated with mni-mal joint space. Conclusions-Our results have confirmed the lower prevalence of radiographic hip osteoarthritis in Hong Kong men compared with British men. However, acetabular dysplasia was as prevalent among Chinese men as in the British sample. This is evidence against the hypothesis that variations in the frequency of hip osteoarthritis are caused by differences in the occurrence of hip dysplasia. (Ann Rheum Dis 1995; 54: ) Osteoarthritis of the hip (OA hip) is an important cause of pain and disability, especially in the elderly, but its aetiology remains poorly understood. Its prevalence appears to vary widely between different populations, from an estimated 1-4% of adult black populations to 7-24% of white people.' If the reasons for such geographical variation were identified, they would provide important clues to the aetiology of hip osteoarthritis. One study that highlighted such geographical differences was a hospital based investigation carried out in Hong Kong two decades ago.2 This estimated that only 1% of Hong Kong Chinese men and women aged 55 years and over had radiographically detectable hip osteoarthritis. The authors hypothesised that the low prevalence of OA hip was attributable either to the rarity of developmental abnormalities such as hip dysplasia, or to the preventive effect of the squatting position popular among the Chinese. It is difficult to compare prevalence estimates between studies from different countries because of contrasts in the selection of the study populations and in the definitions used for OA hip. We have therefore carried out a study to estimate the prevalence of hip osteoarthritris and hip dysplasia in a sample of Hong Kong men who were unselected with respect to hip symptoms, and to compare these estimates with results from a study carried out in 1987 in British men,3 which had used identical methods of sample selection and radiographic classification. Subjects and methods The study was carried out in a regional hospital in Hong Kong. From the radiograph register, we identified all 6-75 year old men who had attended for intravenous urograms during Their hip joints were then assessed from the control or postmicturition films. Radiographs were excluded if neither hip could be visualised adequately. Features of radiographic osteoarthritis were assessed using two methods: (i) A global qualitative score, modified from the Kellgren and Lawrence scheme,4 with a scale of -5 based on a count of the number of features present.3 This assessment was made by the same observer as performed the task in the earlier British study (PC). (ii) Ruler measurement of minimal joint space, defined as the shortest distance between the femoral head margin and the acetabulum. For purposes of this study, possible osteoarthritis of the hip was defined as a minimal joint space of 2-5 mm or less, and definite hip OA as a minimal joint space of 1-5 mm or less.3 The acetabular anatomy was assessed using two methods, illustrated in figure 1. The centre-edge angle was defined as the angle formed by a line from the centre of the femoral head to the lateral margin of the acetabular roof and a line perpendicular to that joining the centres of the two femoral heads. The centres of the femoral heads were located with the aid of a transparent plastic sheet marked with concentric circles. If the femoral head was
2 966 Lau, Lin Lam, Silman, Croft Figure 1 Measurements of acetabular dysplasia deformed, the plastic sheet was aligned in relation to the unaffected areas. In identifying the lateral margin of the acetabular roof, we took account of any osteophytosis, and followed Wlberg's rule of identifying the lateral end of the dense acetabular 'eyebrow' on the radiograph.5 The acetabular depth was defined using Murray's method: the greatest perpendicular distance from the acetabular roof to a line joining the lateral acetabular margin to the symphysis pubis on the same side.6 In the presence of acetabular dysplasia the centre-edge angle and the acetabular depth are both small. Dysplasia was defined in two separate ways: a centre-edge angle of less than 25, or an acetabular depth of less than 9 mm.6 Severe dysplasia was considered to be present if the centre-edge angle was 2 or less. The minimal joint space, centre-edge angle and acetabular depth were measured by one trained observer (FL). The results of these assessments were compared with results obtained from an earlier study of a sample of intravenous urograms in British men aged 6-75 years. This study had been carried out in The selection of films and methods of measurement were identical to those in the current study and were described in detail in an earlier publication.3 Repeatability was established both within and between observers using a subset of 4 Hong Kong hips. This subset was re-read after an interval of three months by the same observer (FL), and separately by the observer from the earlier British study (PC). In addition, a sample of the earlier British films were mixed with a sample of the Hong Kong films and re-read by the British observer (PC) in order to ensure that readings from the two studies were comparable. ANALYSIS The prevalence of osteoarthritis as defined by the overall grading was calculated by subject, a case being represented by involvement of one or both hips. All other analyses (minimal joint space, centre-edge angle, and acetabular depth) were by hip joint. Results Intravenous urograms showing the hip joints were available for 999 of the 197 men identified from the radiograph register. None of the 1998 hips was found to have been replaced, or deformed by Paget's disease. Most views were adequate for the measurement of minimal joint space (1996 hips), centreedge angle (1993 hips) or acetabular depth (1991 hips). The mean age of the Hong Kong men was 7 (SD 7) years; the mean age of men in the earlier British study was 67 (SD 4) years. PREVALENCE OF FEATURES OF OSTEOARTHRITIS Our results are presented alongside the data from the previous British study. Table 1 shows the distribution of overall qualitative grade. Isolated osteophytosis in at least one hip (grade 1) was as common in the Chinese as in the British men (14 8% compared with 129/9%, respectively). However, the proportion of men in the Hong Kong sample who had at least one hip showing two or more features of hip osteoarthritis (that is, grade 3 and above) was half that of the men in the British study (5 4% and 11 -%, respectively). There was a sixfold lower prevalence of osteoarthritis grade 4 and above among the Hong Kong men, representing an actual difference in prevalence between the two populations of 2-2% (95% confidence interval (CI) 1.3 to 3 1%). Minimal joint space measurement was distributed unimodally in the hips of Hong Kong men, with a mean of 3-4 mm, median 3-5 mm, and SD 7 mm. This was similar to the values obtained in Britain (mean 3-5 mm). The prevalence of possible osteoarthritis based on minimal joint space was 13 1% of all hips assessed in the Hong Kong sample (95% CI 11-6 to 14-6%); 14 hips had severe joint space narrowing (1.5 mm or less)-a prevalence for definite osteoarthritis of 7% (95% CI -3 to 1-1%) using this criterion. The corresponding figures in the British sample were 14'4% (95% CI 14'3 to 15-4%) and 2-% (95% CI 1.2 to 2-7%), respectively, for possible and definite OA based on minimal joint space. PREVALENCE OF ACETABULAR DYSPLASIA Centre-edge angle and acetabular depth were linearly related (correlation coefficient 75) (fig 2). Table 2 summarises their distribution Table 1 Prevalence ofradiographic osteoarthritis in at least one hip among 999 Chinese men (1987-9) and 1315 English men ( ) aged 6-75 years: overau qualitative assessment Grade Chinese men British ment (n = 999) (n = 1315) (v.) (%/) *Criteria for overall qualitative assessment of OA hip: = No osteoarthritic changes 1 = Osteophytosis only 2 = Joint space narrowing only 3 = Two of: osteophytosis, joint space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis, cyst formation 4 = Three of: osteophytosis, joint space narrowing, subchondral sclerosis, cyst formation 5 = As in grade 4, but with deformity of femoral head tbritish figures from reference 3.
3 Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men E 2- E :3 X 1- a, i O * es *... *...@ * * *@*** * * * ** * *- * * I Centre-edge angle (degrees) Figure 2 Association of acetabular depth and centre-edge angle in I Iong Kong Chinese (r = 175) I in the total sample and in relation to minimal joint space measurements. The mean centreedge angle (35.5) was similar to that observed in the British sample (36&2 ), and the prevalence of small angles (and by implication the prevalence of acetabular dysplasia) was similar in the two populations. The proportion of hips with angles of less than 25 was 4'5% in Hong Kong (95% CI 3-6 to 5 4%), compared with 3-6% in Britain (95% CI 3-4 to 3-8%); severe dysplasia (angles of 2 or less) affected 141% (95% CI 1.9 to 1.2%) of hips in Hong Kong, compared with 1-% in Britain (95% CI 3 to 1.7%). Dysplasia based on the measurement of acetabular depth presented a rather different picture. The mean depth in the Chinese men was less than the mean in the British sample (difference in means -2-6 mm, 95% CI -2-4 to -2-8 mm), and the prevalence of shallow acetabula with a depth less than 9 mm was consequently greater in the Chinese (difference in prevalence 12-4%, 95% CI 9 9 to 14.9%). RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN OSTEOARTHRITIS AND DYSPLASIA Table 3 shows the relationship between the measures of acetabular dysplasia and the Table 2 Distribution ofcentre-edge angle and acetabular depth in Hong Kong Chinese men compared with British men Chinese men British ment Centre-edge angle Number of hips Mean (deg) Median (deg) SD (deg) <25 (%) 89 (4 5) 94 (3-6) -2- (%/) 21 (1 1) 26 (1-) Number of hips Mean (mm) Median (mm) SD (mm) <9 mm (%) 289 (14-5) 54 (2-1) tbritish figures from reference 7. Table 3 Association between measures ofacetabular anatomy and minimaljoint space in Hong Kong Chinese men Minimaljoint space (hips) 34mm 15 mm Centre-edge angle Number of hips Mean (deg) Median (deg) SD (deg) <25 (/) 48 (7-2) () -2(%) 1 (1-5) () Number of hips Mean (mm) Median (mm) SD (mm) <9mm(%) 12(18) 1 (7-7) minimal joint space in Hong Kong men. The prevalence of dysplasia in the 14 hips with a minimal joint space of 1-5 mm or less was compared with that in the 667 hips with a minimal joint space of 4 mm or more (the upper third of the distribution of minimal joint space in the Hong Kong sample). There was little difference in the prevalence of dysplasia, whether measured by centre-edge angle or by acetabular depth, between hips with and without a narrowed joint space. This lack of a relationship was also reported in the study of British men.7 REPEATABILITY In the sample of Hong Kong films used to examine repeatability, the means of the differences between the observers were 1.6 for centre-edge angle, - 1 mm for acetabular depth, and -2 mm for minimal joint space. Such values indicate that there was little systematic error between observers. The within observer error in categorising films to grades 3-5, according to the modified Kellgren and Lawrence score, was similar to that observed in the original British study, unaffected by the presence of Hong Kong films in the mixed repeatability sample. Discussion We have found the prevalence of definite radiographic osteoarthritis in the hips of a sample of Hong Kong Chinese men aged 6 to 75 years to be 7% based on joint space measurement alone. The proportion of men with at least one hip showing three or more radiographic features of osteoarthritis was 5%. These frequencies were lower than those found in British men of the same age, selected and assessed in the same way. WEAKNESSES AND STRENGTHS OF THIS STUDY The study population was selected on the basis of gender, age, and presentation for an intravenous urogram. Our conclusions cannot be taken to represent osteoarthritis in younger adults or in women. However, it is likely that this age group is representative of older Hong Kong men in general, and these are the ages when hip osteoarthritis is most common.
4 968 Lau, Lin Lam, Silman, Croft Dysplasia appears to be a more important influence on hip osteoarthritis presenting in young adults,8 but such patients form only a minority of all presenting cases of OA hip in Britain, and there is no evidence to suggest that this problem is common in young Hong Kong Chinese. Most intravenous urograms in Hong Kong men older than 6 years are performed to investigate prostatism, and there is no reason to suppose that such men are unrepresentative of other men of this age in the general population with respect to hip symptoms and osteoarthritis. A strength of the comparison with the British study is the identical methodology. Radiographic definitions of osteoarthritis are always arbitrary, but there is evidence to support the use of minimal joint space as the main criterion in large surveys.3 We did not study symptoms in the Hong Kong sample, and it is possible that symptoms and radiographs have a relationship different than that observed in Britain. However, this would not have affected the radiographic comparison that was the main focus of this study. COMPARISON WITH OTHER STUDIES: HIP OA A direct comparison with an earlier British study3 was possible because the age of the subjects, their method of selection, and the method of assessment were identical between the two studies. The mean minimal joint space and the prevalence of isolated osteophytosis were similar in the two populations, but the prevalence of osteoarthritis was lower in the Hong Kong men compared with the British men. A second comparison may be made with the earlier study of Hoaglund et al.2 They investigated 5 Hong Kong Chinese by identifying every fifth patient admitted to any service of a single hospital, including a minority who were attending as outpatients. Pelvic radiographs were then obtained of all patients. This study had the advantage that radiographs were taken specifically for purpose of the study, but the disadvantages that the population was highly selected (mostly confined to hospital) and the numbers in each age and sex grouping were relatively small. No direct comparison is possible with our study because of the different methods of radiographic assessment. The estimated prevalence of severe osteoarthritis in men aged years in the study by Hoaglund's group was 2.7%, rather less than the estimate based on global assessment of the presence of two or more radiographic features in our study. Nevertheless, the broad conclusion that the prevalence of hip osteoarthritis is lower in the Hong Kong Chinese than in British men of the same age is supported by both Hong Kong studies, despite their different methodologies. A study of 99 men from a rural population sample in Japan found no cases of hip osteoarthritis, defined as two or more radiographic features and using a method of qualitative grading identical to that described here.9 COMPARISON WITH OTHER STUDIES: ACETABULAR ANATOMY An association between OA hip and hip dysplasia has been described from radiological observations in patients admitted to hospital with OA hip6 8 1 and from follow up studies of subjects with dysplastic hips."1 However, the absence of a link between measures of acetabular dysplasia and joint space narrowing in our study of Hong Kong males attending for urography is similar to the finding from the parallel British study.7 In addition, the prevalence of dysplasia as measured by the centre-edge angle was remarkably similar in the two studies. The centre-edge angle measurements were also consistent with those reported in other studies. In the 74 men aged 6-74 years from Hoaglund's sample of Hong Kong Chinese,2 the mean centre-edge angle was 36 (SD 5 ). This is very close to the figures from both the current study and the British sample. The prevalence of angles less than 25 was 5%, again similar to that in the present study. The main reason for Murray's recommendation to use acetabular depth6 was the possibility that centre-edge angle measurements could be affected by osteophytosis and migration of the femoral head. However, the consistency of results for centre-edge angle across time and place in these three studies would lead us to conclude that there is no firm evidence that the prevalence of acetabular dysplasia is different in Hong Kong men compared with British men, and that the difference in the prevalence of hip OA in the two populations cannot be explained by corresponding differences in the occurrence of acetabular dysplasia. Indeed, evidence from Japan suggests that populations geographically closer to Hong Kong may actually have a higher prevalence of dysplasia, as measured by the centre-edge angle,9 despite a comparably low prevalence of hip osteoarthritis. In contrast, when the acetabular depth measurements were compared, acetabula in the Hong Kong Chinese sample were shallower than in British men. This might be an artefact of the positioning of the x ray tube relative to the hips; alternatively, acetabular configuration may be different in Chinese men. In the British intravenous urogram study, the data suggested that the relationship between acetabular depth and hip osteoarthritis was actually opposite to that hypothesised-that is, radiographic joint space narrowing was associated with a deep acetabulum. Such an acetabular shape may arise from developmental hip diseases other than dysplasia-slipped capital femoral epiphysis, for example. The twin observations of a smaller mean acetabular depth and a lesser prevalence of hip osteoarthritis in Chinese men raises the possibility that shallow acetabula may actually protect the hips from osteoarthritic changes later in life, perhaps because of altered mechanical loading. Our study cannot address whether other variations in acetabular anatomy might be linked to the different rates of hip osteoarthritis and whether the same lack of an association
5 Hip osteoarthritis and dysplasia in Chinese men 969 between osteoarthritis and centre-edge angles would be found in Chinese women living in Hong Kong. Conclusions Our results confirm the lower prevalence of radiographic hip osteoarthritis in Hong Kong men compared with British men. The study has provided no evidence of a lower prevalence of adult acetabular dysplasia among the Hong Kong Chinese men compared with British men, and this argues against the hypothesis that geographical variations in the frequency of hip osteoarthritis are caused by differences in the occurrence of dysplasia. It is possible that variations in the frequency of other conditions might explain the differences in the prevalence of hip OA. Rheumatoid arthritis is rare in Hong Kong compared with white populations,'2 although clinical rheumatoid arthritis explains only a very small proportion of cases of hip OA in the West. Anecdotal evidence suggests that slipped capital femoral epiphysis and Perthes disease are rare in the Chinese, and this might have a small influence on the prevalence of OA hip. Other host and lifestyle factors may contribute to the rarity of hip osteoarthritis in the Hong Kong Chinese. There is variable evidence for a link between obesity and radiographic hip osteoarthritis, although most studies suggest an association.'3 Obesity is much rarer in Chinese than in white populations,14 and this may partly account for the lower prevafence of hip osteoarthritis among the Hong Kong men in our study. A major risk for hip osteoarthritis in Europe is physical activity which places stress on the lower limbs: the excess of hip osteoarthritis in European farmers might be explained in this way.'5 It is difficult to suppose that the Chinese place any less stress on their hips, although it has been suggested that the squatting posture popular in former times (when this cohort of men were young adults) protected the hip cartilage against damage.'6 The possibility that some aspect of the lifestyle in the Chinese culture is protective of the hip remains an attractive one, whilst the influence of genetic differences on geographic variations in the occurrence of osteoarthritis remains to be explored. This work was supported by a project grant from The Arthritis and Rheumatism Council of Great Britain. The methodology for the study was developed at the Medical Research Council's Environmental Epidemiology Unit in Southampton by Drs David Coggon and Cyrus Cooper, who were principal investigators in the British urogram study. 1 Lawrence J S, Sebo M. The geography of osteoarthritis. In: Nuki G, ed. The aetiopathogenesis of osteoarthrosis. Baltimore: University Park Press, 198; Hoaglund F T, Yau A C M C, Wong W L. Osteoarthritis of the hip and other joints in Southern Chinese in Hong Kong. J7 Bonejoint SurgAm 1973; 55: Croft P, Cooper C, Wickham C, Coggon D. Defining osteoarthritis of the hip for epidemiologic studies. Am J Epidemiol 199; 132: Keligren J H, Lawrence J S. Radiological assessment of osteoarthrosis. Ann Rheum Dis 1957; 16: Wiberg G. Studies on dysplastic acetabula and congenital subluxation of the hip joint. Acta Chir Scand 1939; 58 (suppl): Murray R. The aetiology of primary osteoarthritis of the hip. BrJ Radiol 1965; 38: Croft P, Cooper C, Wickham C, Coggon D. Osteoarthritis of the hip and acetabular dysplasia. Ann Rheum Dis 1991; 5: Stulberg S D, Harris W H. Acetabular dysplasia and development of osteoarthritis of the hip. In: Harris W H, ed. The hip. Proceedings of the second open scientific meeting ofthe Hip Society. St Louis: Mosby, 1974; Yoshimura N, Campbell L, Cooper C, et al. Acetabular dysplasia in Britain and Japan. Br Jf Rheumatol 1994; 33 (suppl 1): Solomon L. Patterns of osteoarthritis of the hip. JBoneJoint Surg Br 1976; 58: Cooperman D R, Wallenstein R, Stulberg S D. Acetabular dysplasia in the adult. Clin Orthop 1983; 175: Lau E, Symmons D, Bankhead C, Macgregor A, Donnan S, Silman A. Low prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the urbanized Chinese of Hong Kong. J Rheumatol 1993; 2: Vingard E. Overweight predisposes to coxarthrosis. Acta Orthop Scand 1991; 62: Ho S C. Risk factors for obesity among Hong Kong youths. Public Health 199; 14: Croft P, Coggon D, Cruddas, Cooper C. Osteoarthritis of the hip: an occupational disease in farmers. BMJ 1992; 34: Gunn D R. Don't sit-squat! Clin Orthop 1974; 13: Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 December Downloaded from on 18 June 218 by guest. Protected by copyright.
Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 107-111 Primary osteoathrosis of the hip and Heberden's nodes J. S. MARKS, I. M. STEWART, AND K. HARDINGE From the Wrightington Hospital, Wigan, Lancs SUMMARY
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs
 Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
Assessment of primary hip osteoarthritis: comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs comparison of radiographic methods using colon radiographs Ingvarsson, T; Hägglund, Gunnar; Lindberg,
F. Birrell 1,3, M. Lunt 1, G. Macfarlane 2 and A. Silman 1
 Rheumatology 2005;44:337 341 Advance Access publication 9 November 2004 Association between pain in the hip region and radiographic changes of osteoarthritis: results from a population-based study F. Birrell
Rheumatology 2005;44:337 341 Advance Access publication 9 November 2004 Association between pain in the hip region and radiographic changes of osteoarthritis: results from a population-based study F. Birrell
Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not!
 Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
Circles are Pointless - Angles in the assessment of adult hip dysplasia are not! Poster No.: C-1964 Congress: ECR 2014 Type: Authors: Keywords: DOI: Educational Exhibit S. E. West, S. G. Cross, J. Adu,
OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORAL HEAD AND NECK
 908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
908 RDIOLOGIC VIGNETTE OSTEOPHYTOSIS OF THE FEMORL HED ND NECK DONLD RESNICK Osteophytes are frequently considered the most characteristic abnormality of degenerative joint disease. In patients with osteoarthritis,
Papers. Assessment of a genetic contribution to osteoarthritis of the hip: sibling study. Abstract. Participants and methods.
 Assessment of a genetic contribution to osteoarthritis of the hip: sibling study Peter Lanyon, Kenneth Muir, Sally Doherty, Michael Doherty Abstract Objectives To study the influence of genetics on the
Assessment of a genetic contribution to osteoarthritis of the hip: sibling study Peter Lanyon, Kenneth Muir, Sally Doherty, Michael Doherty Abstract Objectives To study the influence of genetics on the
S. Jacobsen and S. Sonne-Holm
 Rheumatology 2005;44:211 218 Advance Access publication 12 October 2004 Hip dysplasia: a significant risk factor for the development of hip osteoarthritis. A cross-sectional survey S. Jacobsen and S. Sonne-Holm
Rheumatology 2005;44:211 218 Advance Access publication 12 October 2004 Hip dysplasia: a significant risk factor for the development of hip osteoarthritis. A cross-sectional survey S. Jacobsen and S. Sonne-Holm
Hip osteoarthritis: influence of work with heavy lifting, climbing stairs or ladders, or combining kneeling/squatting with heavy lifting
 Correspondence to: Dr L K Jensen, Department of Occupational Medicine, Regionshospitalet Skive, Resenvej 25, DK-7800 Skive, Denmark; lilli.kirkeskov.jensen@ sygehusviborg.dk Accepted 18 June 2007 Published
Correspondence to: Dr L K Jensen, Department of Occupational Medicine, Regionshospitalet Skive, Resenvej 25, DK-7800 Skive, Denmark; lilli.kirkeskov.jensen@ sygehusviborg.dk Accepted 18 June 2007 Published
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View
 Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Radiographic Evaluation Of Dynamic Hip Instability In Lequesne s False Profile View Ryo Mori 1, Yuji Yasunaga 2, Takuma Yamasaki 1, Michio Hamanishi 1, Takeshi Shoji 1, Sotaro Izumi 1, Susumu Hachisuka
Periacetabular osteotomy: sporting, social and sexual activity 9-12 years post surgery
 Hip Int 2014; 24 ( 1) : 27-31 DOI: 10.5301/hipint.5000077 Original Article Periacetabular osteotomy: sporting, social and sexual activity 9-12 years post surgery Jakob Klit 1, Charlotte Hartig-Andreasen
Hip Int 2014; 24 ( 1) : 27-31 DOI: 10.5301/hipint.5000077 Original Article Periacetabular osteotomy: sporting, social and sexual activity 9-12 years post surgery Jakob Klit 1, Charlotte Hartig-Andreasen
Friday Teaching. Bones
 Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
Friday Teaching Bones Regarding slipped femoral capital epiphysis It represents Salter Harris type V injury 20% are bilateral There is slight widening of the joint space Slip is typically posteromedial
O steoarthritis (OA) of the hip is of particular interest as
 1427 EXTENDED REPORT Validity and reliability of three definitions of hip osteoarthritis: cross sectional and longitudinal approach M Reijman, J M W Hazes, H A P Pols, R M D Bernsen, B W Koes, S M A Bierma-Zeinstra...
1427 EXTENDED REPORT Validity and reliability of three definitions of hip osteoarthritis: cross sectional and longitudinal approach M Reijman, J M W Hazes, H A P Pols, R M D Bernsen, B W Koes, S M A Bierma-Zeinstra...
Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study
 Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Prague Medical Report / Vol. 106 (2005) No. 2, p. 159 166 159) Combined Pelvic Osteotomy in the Treatment of Both Deformed and Dysplastic Acetabulum Three Years Prospective Study Al Razi Orthopedic Hospital,
Radiographic patterns and associations of
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 1-1116 1111 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Doherty DepartmentofRadiology, University Hospital, Nottingham, United
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1992; 51: 1-1116 1111 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Nottingham, United Kingdom J Ledingham M Doherty DepartmentofRadiology, University Hospital, Nottingham, United
2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2003) 11, 328 334 2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s1063-4584(03)00023-2 The radiographic
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2003) 11, 328 334 2003 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/s1063-4584(03)00023-2 The radiographic
Pelvic orientation and assessment of hip dysplasia in adults
 Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Pelvic orientation and assessment of hip dysplasia in adults Steffen Jacobsen, Stig
Acta Orthopaedica Scandinavica ISSN: 0001-6470 (Print) (Online) Journal homepage: http://www.tandfonline.com/loi/iort19 Pelvic orientation and assessment of hip dysplasia in adults Steffen Jacobsen, Stig
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology
 Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology University of Rochester Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Raymond J. Kenney, MD P. Christopher Cook, MD Kelly
Combined Hip Arthroscopy and Periacetabular Osteotomy: Intra-Articular Pathology University of Rochester Department of Orthopaedics and Rehabilitation Raymond J. Kenney, MD P. Christopher Cook, MD Kelly
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes
 The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
The Birmingham Interlocking Pelvic Osteotomy (BIPO) for Acetabular Dysplasia: 13 to 21 Year Survival Outcomes Omer Mei-Dan, MD Dylan Jewell, BSc, MSc, FRCS Tigran Garabekyan, MD Jason Brockwell, FRCSEdOrth
The Factor Causing Poor Results in Late Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH)
 The Factor Causing Poor Results in Late Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamwong Saisamorn MD*, Tanatip Sisuchinthara MS* Thunchanok Jittivilai PN*, Kamolporn Keawpornsawan
The Factor Causing Poor Results in Late Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip (DDH) Perajit Eamsobhana MD*, Kamwong Saisamorn MD*, Tanatip Sisuchinthara MS* Thunchanok Jittivilai PN*, Kamolporn Keawpornsawan
Summary. Introduction. Materials and methods
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 303 308 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/040303+06 $35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.1999.0305, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2000) 8, 303 308 2000 OsteoArthritis Research Society International 1063 4584/00/040303+06 $35.00/0 doi:10.1053/joca.1999.0305, available online at http://www.idealibrary.com
Individual Risk Factors for Hip Osteoarthritis: Obesity, Hip Injury, and Physical Activity
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright C 1998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health AD rights reserved Vol. 147, No. 6 Printed In USA ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Individual
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright C 1998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health AD rights reserved Vol. 147, No. 6 Printed In USA ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTIONS Individual
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Bone Bangalore. Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal
 Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Degenerative arthritis of Hip Prof Sharath Rao Head, Dept. of Orthopaedics KMC Manipal Hip joint Classical Synovial joint Biomechanics of hip Force coincides with trabecular pattern Hip joint Acetabulum
Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule
 Pediatr Radiol (2017) 47:817 821 DOI 10.1007/s00247-017-3802-4 COMMENTARY Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule H. Theodore Harcke 1 & B. Pruszczynski 2 Received: 27 October 2016 /Revised:
Pediatr Radiol (2017) 47:817 821 DOI 10.1007/s00247-017-3802-4 COMMENTARY Hip ultrasound for developmental dysplasia: the 50% rule H. Theodore Harcke 1 & B. Pruszczynski 2 Received: 27 October 2016 /Revised:
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS
 HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
HIP DYSPLASIA WITHOUT DISLOCATION IN ONE-YEAR-OLD BOYS A. B. NEVELOS, p. R. J. BURCH From Leeds/Bradford Orthopaedic Training Schetne Six boys were examined during the second year of life, each with symptoms
ORIGINAL PAPER. Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Hamamatsu Medical Center ABSTRACT
 Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 71. 145 ~ 150, 2009 ORIGINAL PAPER AUTOGENOUS BULK STRUCTURAL BONE GRAFTING FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF THE ACETABLUM IN PRIMARY TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: AVERAGE 12-YEAR FOLLOW-UP TETSUO MASUI,
Nagoya J. Med. Sci. 71. 145 ~ 150, 2009 ORIGINAL PAPER AUTOGENOUS BULK STRUCTURAL BONE GRAFTING FOR RECONSTRUCTION OF THE ACETABLUM IN PRIMARY TOTAL HIP ARTHROPLASTY: AVERAGE 12-YEAR FOLLOW-UP TETSUO MASUI,
Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease
 Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 42-47 ORIGINAL STUDY Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease Robert P. BERG, Richard GALANTAY, Henk EIJER From the University of
Acta Orthop. Belg., 2010, 76, 42-47 ORIGINAL STUDY Retroversion of the contralateral adult acetabulum after previous Perthes disease Robert P. BERG, Richard GALANTAY, Henk EIJER From the University of
hands in patients with chronic renal failure
 378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
378 Annals ofthe Rheumatic Diseases 1990; 49: 378-382 Rheumatology Unit and "Renal Unit, The Queen Elizabeth Hospital, Woodville, South Australia 5011 I J S Duncan N P Hurst S C Milazzo l'a Disney Department
What is a Hip Dysplasia?
 What is a Hip Dysplasia? Hip dysplasia, developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)[1] or congenital dysplasia of the hip (CDH)[2] is a congenital or acquired deformation or misalignment of the hip joint.
What is a Hip Dysplasia? Hip dysplasia, developmental dysplasia of the hip (DDH)[1] or congenital dysplasia of the hip (CDH)[2] is a congenital or acquired deformation or misalignment of the hip joint.
Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult
 Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult STEPHEN B. MURPHY, M.D., PETER K. KIJEWSKI, PH.D.,* MICHAEL B. MILLIS, M.D., AND ANDREW HARLESS, A.B.* Hip dysplasia is a major cause of osteoarthrosis
Acetabular Dysplasia in the Adolescent and Young Adult STEPHEN B. MURPHY, M.D., PETER K. KIJEWSKI, PH.D.,* MICHAEL B. MILLIS, M.D., AND ANDREW HARLESS, A.B.* Hip dysplasia is a major cause of osteoarthrosis
Working conditions resulting in increased need for surgical treatment of knee osteoarthritis.
 Working conditions resulting in increased need for surgical treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Jonas Weidow, MD ; Anders Holmén, MSc ; Johan Kärrholm, MD, Professor. From Central Hospital, Halmstad, Sweden.
Working conditions resulting in increased need for surgical treatment of knee osteoarthritis. Jonas Weidow, MD ; Anders Holmén, MSc ; Johan Kärrholm, MD, Professor. From Central Hospital, Halmstad, Sweden.
Osteoarthritis of the Hip and Occupational Lifting
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright C 998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Hearth All rights reserved Vol. 7, No. 6 Printed in U.SA Osteoarthritis of the Hip and Occupational
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright C 998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Hearth All rights reserved Vol. 7, No. 6 Printed in U.SA Osteoarthritis of the Hip and Occupational
Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee.
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 344-349 Arthrographic study of the rheumatoid knee. Part 2. Articular cartilage and menisci KYOSUKE FUJIKAWA, YOSHINORI TANAKA, TSUNEYO MATSUBAYASHI, AND FUJIO
Ganzosteotomy Description and indications. Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout
 Ganzosteotomy Description and indications Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout Welcome Turnhout Flanders Cultural Capital 2012 Turnhout: Stad van m n hert Hip Dysplasia Natural history of HD without subluxation:
Ganzosteotomy Description and indications Dr. Jaak Roos - A.Z. Turnhout Welcome Turnhout Flanders Cultural Capital 2012 Turnhout: Stad van m n hert Hip Dysplasia Natural history of HD without subluxation:
A family with primary protrusio acetabuli
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 53-57 A family with primary protrusio acetabuli K. D'ARCY, B. M. ANSELL, AND E. G. L. BYWATERS From the Juvenile Rheumatism Unit, Canadian Red Cross Memorial
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 53-57 A family with primary protrusio acetabuli K. D'ARCY, B. M. ANSELL, AND E. G. L. BYWATERS From the Juvenile Rheumatism Unit, Canadian Red Cross Memorial
Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 6 Number 1 Total Hip Replacement in Diaphyseal Aclasis: A Case Report V Singh, S Carter Citation V Singh, S Carter.. The Internet Journal of
Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 14 No. 1 1999 Predicting the Position of the Femoral Head Center Nobuhiko Sugano, MD, Philip C. Noble, PhD, and Emir Kamaric, MS Abstract: To find an accurate method to
CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA. Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS
 CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS EDITOR IN CHIEF HIP INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF THESSALIA, LARISA HELLENIC REPUBLIC
CONGENITAL HIP DISEASE IN YOUNG ADULTS CLASSIFICATION AND TREATMENT WITH THA Th. KARACHALIOS, MD, DSc PROF IN ORTHOPAEDICS EDITOR IN CHIEF HIP INTERNATIONAL UNIVERSITY OF THESSALIA, LARISA HELLENIC REPUBLIC
Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update
 U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
U N I V E R S I T E T E T I B E R G E N Femoroacetabular impingement in adolescents and young adults an update Lene Bjerke Laborie, MD, PhD Paediatric Radiology Department, Haukeland University Hospital
Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review
 Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review, Sigurd Mikkelsen, Jane Frølund Thomsen Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine Bispebjerg Hospital, Copenhagen
Work-related risk factors in thumb carpometacarpal arthrosis a systematic review, Sigurd Mikkelsen, Jane Frølund Thomsen Department of Occupational and Environmental Medicine Bispebjerg Hospital, Copenhagen
the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 40, 109-114 A prospective study of the radiological changes in the cervical spine in early rheumatoid disease J. WINFIELD, D. COOKE,' A. S. BROOK,2 AND MARY CORBETT
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems?
 What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
What is FAI? And Why are we getting Hip Problems? Why is Hip pain so common NOW? Greater awareness More accurate imaging MRI Fashionable?? Geography Arthroscopy used to be OP now FAI! Why is Hip pain so
Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 9 Number 2 Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella R Gupta, S Canty, W Ryan Citation
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Orthopedic Surgery Volume 9 Number 2 Anterior knee pain following total knee replacement caused by isolated Paget's disease of patella R Gupta, S Canty, W Ryan Citation
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
OCCUPATIONAL PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES AND OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 7, July 2000, pp 1443 1449 2000, American College of Rheumatology 1443 OCCUPATIONAL PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES AND OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE DAVID COGGON, PETER CROFT, SAMANTHA
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 7, July 2000, pp 1443 1449 2000, American College of Rheumatology 1443 OCCUPATIONAL PHYSICAL ACTIVITIES AND OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE KNEE DAVID COGGON, PETER CROFT, SAMANTHA
THE HIP. Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness.
 THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
THE HIP Cooler than cool, the pinnacle of what is "it". Beyond all trends and conventional coolness. Objectives Hip anatomy Causes of hip pain Hip exam Anatomy Bones Ilium Anterior Superior Iliac Spine
DISEASES AND DISORDERS
 DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
DISEASES AND DISORDERS 9. 53 10. Rheumatoid arthritis 59 11. Spondyloarthropathies 69 12. Connective tissue diseases 77 13. Osteoporosis and metabolic bone disease 95 14. Crystal arthropathies 103 15.
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016
 Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
Femoral Acetabular Impingement 10/22/2016 Disclosures No Disclosures to report Questions Does FAI lead to early development of osteoarthritis? Is surgical correction an effective treatment for FAI? Who
International Cartilage Repair Society
 OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
OsteoArthritis and Cartilage (2006) 14, 496e500 ª 2005 OsteoArthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2005.12.001 Short communication
Dr. P.T. CHAN Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology, Tuen Mun Hospital. Dr. M.H. LEUNG Department of Medicine, Queen Elizabeth Hospital
 Second Announcement Date: 16 March 2012 Time: 08:45 17:00 Venue: H702, 7/F, Block H, Princess Margaret Hospital EARLY BIRD 29/02/2012 Dr. P.C. HO Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology, Prince of Wales
Second Announcement Date: 16 March 2012 Time: 08:45 17:00 Venue: H702, 7/F, Block H, Princess Margaret Hospital EARLY BIRD 29/02/2012 Dr. P.C. HO Department of Orthopaedics & Traumatology, Prince of Wales
Radiographic signs for detection of femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia should be carefully used in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip
 Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Radiographic signs for detection of femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia should be carefully used in patients
Ipach et al. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders 2014, 15:150 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Radiographic signs for detection of femoroacetabular impingement and hip dysplasia should be carefully used in patients
Incidence of femoro-acetabular impingement in adult Indian population on the basis of specific radiological findings: A prospective study
 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 24-11-2017 Accepted: 25-12-2017 Ansari Muqtadeer Abdul Aziz Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 ISSN: 2395-1958 IJOS 2018; 4(1): 1012-1017 2018 IJOS www.orthopaper.com Received: 24-11-2017 Accepted: 25-12-2017 Ansari Muqtadeer Abdul Aziz Associate Professor, Department of Orthopaedics,
Long-term outcomes of shelf acetabuloplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults: a minimum 20-year follow-up study
 J Orthop Sci (11) 16:698 73 DOI 1.7/s776-11-159-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term outcomes of shelf acetabuloplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults: a minimum -year follow-up study Shiro Hirose
J Orthop Sci (11) 16:698 73 DOI 1.7/s776-11-159-7 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Long-term outcomes of shelf acetabuloplasty for developmental dysplasia of the hip in adults: a minimum -year follow-up study Shiro Hirose
Prevalence of cartilage lesions in foot joints: a test of
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1987; 46, 515-519 Prevalence of cartilage lesions in foot joints: a test of the concept of limited and progressive lesions H R YOUNGMAN,' F COOPER,' AND PAUL BYERS2 From
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1987; 46, 515-519 Prevalence of cartilage lesions in foot joints: a test of the concept of limited and progressive lesions H R YOUNGMAN,' F COOPER,' AND PAUL BYERS2 From
Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt
 Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 806157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/806157 Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt Hiroyuki
Case Reports in Orthopedics, Article ID 806157, 4 pages http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2014/806157 Case Report Anterior Hip Subluxation due to Lumbar Degenerative Kyphosis and Posterior Pelvic Tilt Hiroyuki
Case 27 Clinical Presentation
 53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
53 Case 27 Clinical Presentation 40-year-old man presents with acute shoulder pain and normal findings on radiographs. 54 RadCases Musculoskeletal Radiology Imaging Findings (,) Coronal images of the shoulder
At least one slide latex test was performed on all 65. of them. there were more male cases but after 30 years the. female cases predominated (Fig. 1).
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1970), 29, 617 Rheumatoid arthritis in B. R. KANYEREZI Department of Medicine, Makerere University College Medical School, H. BADDELEY Department of Radiology, Mulago Hospital and Department
Low revision rate after total hip arthroplasty in patients with pediatric hip diseases
 6 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (5): x x 1 Low revision rate after total hip arthroplasty in patients with pediatric hip diseases Evaluation of 14,403 THAs due to DDH, SCFE, or Perthes disease and 288,435
6 Acta Orthopaedica 2012; 83 (5): x x 1 Low revision rate after total hip arthroplasty in patients with pediatric hip diseases Evaluation of 14,403 THAs due to DDH, SCFE, or Perthes disease and 288,435
Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty
 The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 23 No. 2 2008 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty 7135 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasties after Developmental Dysplasia of the
The Journal of Arthroplasty Vol. 23 No. 2 2008 Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip Good Results of Later Total Hip Arthroplasty 7135 Primary Total Hip Arthroplasties after Developmental Dysplasia of the
THE GENETIC CONTRIBUTION TO RADIOGRAPHIC HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS IN WOMEN
 2410 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 11, November 2000, pp 2410 2416 2000, American College of Rheumatology THE GENETIC CONTRIBUTION TO RADIOGRAPHIC HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS IN WOMEN Results of a Classic
2410 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 43, No. 11, November 2000, pp 2410 2416 2000, American College of Rheumatology THE GENETIC CONTRIBUTION TO RADIOGRAPHIC HIP OSTEOARTHRITIS IN WOMEN Results of a Classic
Fovea Alta on MR Images: Is It a Marker of Hip Dysplasia in Young Adults?
 Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Beltran et al. MRI of Fovea Alta Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Luis S. Beltran 1 Jason D. Mayo 2 Zehava S. Rosenberg 1 Maria Diaz De Tuesta 3 Olga
Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Beltran et al. MRI of Fovea Alta Musculoskeletal Imaging Original Research Luis S. Beltran 1 Jason D. Mayo 2 Zehava S. Rosenberg 1 Maria Diaz De Tuesta 3 Olga
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM
 ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM (3 Weeks) YEDİTEPE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology: Faik Altıntaş, MD Prof. Uğur Şaylı, MD Prof. Turhan Özler, MD
ORTHOPEDICS AND TRAUMATOLOGY TRAINING PROGRAM (3 Weeks) YEDİTEPE UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology: Faik Altıntaş, MD Prof. Uğur Şaylı, MD Prof. Turhan Özler, MD
The prevalence and history of knee osteoarthritis in general practice: a case control study
 The Author (2005). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org doi:10.1093/fampra/cmh700 Family Practice Advance Access
The Author (2005). Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oupjournals.org doi:10.1093/fampra/cmh700 Family Practice Advance Access
Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma
 Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1703.008 Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma King CKK, FRCS, Yung A, FRCS Department of Orthopaedics,
Doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.5704/moj.1703.008 Outcome of Treatment of Osteoarthritis with Arthroscopic Debridement and Autologous Conditioned Plasma King CKK, FRCS, Yung A, FRCS Department of Orthopaedics,
Summary. Introduction
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2010) 18, 312e316 ª 2009 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2009.11.004 Hip osteoarthritis and
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (2010) 18, 312e316 ª 2009 Osteoarthritis Research Society International. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved. doi:10.1016/j.joca.2009.11.004 Hip osteoarthritis and
Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip
 Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
Kathmandu University Medical Journal (2005) Vol. 3, No. 1, Issue 9, 6-10 Original Article Results of simultaneous open reduction and Salter innominate osteotomy for developmental dysplasia of the hip Banskota
Lack of support for the presence of an osteoarthritis susceptibility locus on chromosome 6p
 Lack of support for the presence of an osteoarthritis susceptibility locus on chromosome 6p Meenagh, G. K., McGibbon, D., Nixon, J., Wright, G. D., Doherty, M., & Hughes, A. (2005). Lack of support for
Lack of support for the presence of an osteoarthritis susceptibility locus on chromosome 6p Meenagh, G. K., McGibbon, D., Nixon, J., Wright, G. D., Doherty, M., & Hughes, A. (2005). Lack of support for
Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis in the community: definitions and normal joint space
 Ann Rheum Dis 99;:9 9 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG PB Correspondence to: Dr P Lanyon. Accepted for publication August 99 Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis
Ann Rheum Dis 99;:9 9 Rheumatology Unit, City Hospital, Hucknall Road, Nottingham NG PB Correspondence to: Dr P Lanyon. Accepted for publication August 99 Radiographic assessment of symptomatic knee osteoarthritis
Acta Medica Okayama JUNE 2009
 Acta Medica Okayama Volume 63, Issue 3 29 Article 1 JUNE 29 Radiographic Prediction of the Results of Long-term Treatment with the Pavlik Harness for Developmental Dislocation of the Hip Takao Ohmori Hirosuke
Acta Medica Okayama Volume 63, Issue 3 29 Article 1 JUNE 29 Radiographic Prediction of the Results of Long-term Treatment with the Pavlik Harness for Developmental Dislocation of the Hip Takao Ohmori Hirosuke
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF DYSPLASIA
 PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
PROBLEMS IN THE EARLY RECOGNITION OF HIP DYSPLASIA STUART J. M. DAVIES, GEOFFREY WALKER From Queen Mary s Hospitalfor Children, Carshalton Ten children who had clinically stable hips at birth were radiographed
O steoarthritis (OA) is the most common joint disorder1
 226 REVIEW Validity, reliability, and applicability of seven definitions of hip osteoarthritis used in epidemiological studies: a systematic appraisal M Reijman, J M W Hazes, B W Koes, A P Verhagen, S
226 REVIEW Validity, reliability, and applicability of seven definitions of hip osteoarthritis used in epidemiological studies: a systematic appraisal M Reijman, J M W Hazes, B W Koes, A P Verhagen, S
Analysis of Nonunion of the Superior Pubic Ramus Osteotomy Site After Curved Periacetabular Osteotomy
 福岡大医紀 (Med. Bull. Fukuoka Univ.):42(1),95 101,2015 Analysis of Nonunion of the Superior Pubic Ramus Osteotomy Site After Curved Periacetabular Osteotomy Tetsuya SAKAMOTO, Masatoshi NAITO Department of
福岡大医紀 (Med. Bull. Fukuoka Univ.):42(1),95 101,2015 Analysis of Nonunion of the Superior Pubic Ramus Osteotomy Site After Curved Periacetabular Osteotomy Tetsuya SAKAMOTO, Masatoshi NAITO Department of
THE DIRECT HEALTH COSTS OF INFLAMMATORY POLYARTHRITIS TEN YEARS AFTER DISEASE-ONSET: RESULTS FROM THE NORFOLK ARTHRITIS REGISTER
 THE DIRECT HEALTH COSTS OF INFLAMMATORY POLYARTHRITIS TEN YEARS AFTER DISEASE-ONSET: RESULTS FROM THE NORFOLK ARTHRITIS REGISTER Elena Nikiphorou 1,2, Charlotte Davies 3, Miranda Mugford 3, Nicola Cooper
THE DIRECT HEALTH COSTS OF INFLAMMATORY POLYARTHRITIS TEN YEARS AFTER DISEASE-ONSET: RESULTS FROM THE NORFOLK ARTHRITIS REGISTER Elena Nikiphorou 1,2, Charlotte Davies 3, Miranda Mugford 3, Nicola Cooper
We have observed damage to the labrum as a
 Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect A MRI-BASED QUANTITATIVE ANATOMICAL STUDY OF THE FEMORAL HEAD-NECK OFFSET K. Ito, M.-A. Minka-II, M. Leunig, S. Werlen, R.Ganz From the AO ASIF Research
Femoroacetabular impingement and the cam-effect A MRI-BASED QUANTITATIVE ANATOMICAL STUDY OF THE FEMORAL HEAD-NECK OFFSET K. Ito, M.-A. Minka-II, M. Leunig, S. Werlen, R.Ganz From the AO ASIF Research
Joint space width in dysplasia of the hip
 Joint space width in dysplasia of the hip CSE-CONTROL STUDY OF 81 DULTS FOLLOWED FOR TEN YERS S. Jacobsen, S. Sonne-Holm, K. Søballe, P. Gebuhr, B. Lund From Hvidovre University Hospital of Copenhagen,
Joint space width in dysplasia of the hip CSE-CONTROL STUDY OF 81 DULTS FOLLOWED FOR TEN YERS S. Jacobsen, S. Sonne-Holm, K. Søballe, P. Gebuhr, B. Lund From Hvidovre University Hospital of Copenhagen,
Sports Medicine and Radiology
 Sports Medicine and Radiology The judicious utilization of a thorough history and physical examination and appropriately applied imaging studies will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of athletic
Sports Medicine and Radiology The judicious utilization of a thorough history and physical examination and appropriately applied imaging studies will allow for accurate diagnosis and treatment of athletic
Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures
 Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Timothy Carey, DO 1 ; Christian Key, MD 2 ; David Oliver, MD 3
Prevalence of Radiographic Findings Consistent With Femoroacetabular Impingement in Military Personnel With Femoral Neck Stress Fractures Timothy Carey, DO 1 ; Christian Key, MD 2 ; David Oliver, MD 3
Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions. Claudio Mella, MD
 Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions Claudio Mella, MD Acetabular cartilage lesions are frequently found during hip arthroscopy. The arthroscopic view offers an exceptional perspective to assess
Classification of Acetabular Cartilage Lesions Claudio Mella, MD Acetabular cartilage lesions are frequently found during hip arthroscopy. The arthroscopic view offers an exceptional perspective to assess
25. PELVIC OSTEOTOMIES FOR THE TREATMENT OF HIP DYSPLASIA IN ADULTS
 Guidelines to be followed by centres, services and units in order to be designated as Reference Centres, Services and Units of the National Health System, as agreed by the Interterritorial Board 25. PELVIC
Guidelines to be followed by centres, services and units in order to be designated as Reference Centres, Services and Units of the National Health System, as agreed by the Interterritorial Board 25. PELVIC
Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo?
 Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery 2005;13(1):46-51 Does the self-centering mechanism of bipolar hip endoprosthesis really work in vivo? H Tsumura, N Kaku, T Torisu Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Oita University,
Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide Toacetabular Component Anteversion
 IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 65-69 www.iosrjournals.org Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide
IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-issn: 2279-0853, p-issn: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. I (Nov. 2015), PP 65-69 www.iosrjournals.org Transverse Acetabular Ligament A Guide
Nonspherical Femoral Head Shape (Pistol Grip Deformity), Neck Shaft Angle, and Risk of Hip Osteoarthritis
 ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 10, October 2008, pp 3172 3182 DOI 10.1002/art.23939 2008, American College of Rheumatology Nonspherical Femoral Head Shape (Pistol Grip Deformity), Neck Shaft Angle,
ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATISM Vol. 58, No. 10, October 2008, pp 3172 3182 DOI 10.1002/art.23939 2008, American College of Rheumatology Nonspherical Femoral Head Shape (Pistol Grip Deformity), Neck Shaft Angle,
Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults. Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p.
 Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
Title Axial alignment of the lower extremity in Chinese adults Author(s) Tang, WM; Zhu, YH; Chiu, KY Citation Journal Of Bone And Joint Surgery - Series A, 2000, v. 82 n. 11, p. 1603-1608 Issued Date 2000
The faux profil (oblique view) of the hip in the standing position. Contribution to the evaluation of osteoarthritis of the adult hip
 676 Department of Rheumatology, Léopold Bellan Teaching Hospital, Paris, France M G Lequesne Department of Radiology, Bone and Joint Imaging Unit, Lariboisière Hospital (Assistance Publique des Hôpitaux
676 Department of Rheumatology, Léopold Bellan Teaching Hospital, Paris, France M G Lequesne Department of Radiology, Bone and Joint Imaging Unit, Lariboisière Hospital (Assistance Publique des Hôpitaux
66 yr old female with groin and hip pain. Paul Jabour, MD
 66 yr old female with groin and hip pain Paul Jabour, MD 2 months later 12 months later 14 months after initial presentation Acetabular Insufficiency Fracture Pelvic stress fracture Fatigue
66 yr old female with groin and hip pain Paul Jabour, MD 2 months later 12 months later 14 months after initial presentation Acetabular Insufficiency Fracture Pelvic stress fracture Fatigue
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as /ard
 ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.038414 The relationship of Progressive Osteoarthritis of the Knee and Long-term Progression of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip and Lumbar
ARD Online First, published on October 11, 2005 as 10.1136/ard.2005.038414 The relationship of Progressive Osteoarthritis of the Knee and Long-term Progression of Osteoarthritis of the Hand, Hip and Lumbar
Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis Classification of Knee Arthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis Osteoarthritis of Knee
 1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
1 2 Evaluation and Treatment of Knee Arthritis John Zebrack, MD Reno Orthopaedic Clinic Classification of Knee Arthritis Non-inflammatory Osteoarthritis Primary Secondary Post-traumatic, dysplasia, neuropathic,
Factors Affecting Radiographic Progression of Knee Osteoarthritis
 IGINAL ARTICLE Factors Affecting Radiographic Progression of Knee Osteoarthritis Harry Isbagio ABSTRACT Aim: to determine factors affecting radiographic progression of knee OA. Methods: a cross sectional
IGINAL ARTICLE Factors Affecting Radiographic Progression of Knee Osteoarthritis Harry Isbagio ABSTRACT Aim: to determine factors affecting radiographic progression of knee OA. Methods: a cross sectional
Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement
 Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Original Article Efficacy of Osseous Abnormalities Correction with Arthroscopic Surgery in Femoroacetabular Impingement Cartilage 1(3) 233 237 The Author(s) 2010 Reprints and permission: sagepub.com/journalspermissions.nav
Bone Bangalore
 Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Dr Suresh Annamalai MBBS, MRCS(Edn), FRCS( Tr & Orth)(Edn), FEBOT(European Board), Young Hip and Knee Fellowship(Harrogate, UK) HOD & Consultant Arthroplasty and Arthroscopic Surgeon Manipal Hospital,
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, Osteoarthritis Research Society /95/ $08.00/0
 Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage (1995) 3, 205-209 1995 Osteoarthritis Research Society 1063-4584/95/030205 + 05 $08.00/0 OSTEOARTHRITIS and CARTILAGE Increased rate of hysterectomy in women undergoing surgery
Where to Draw the Line:
 Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
Where to Draw the Line: Anatomical Measurements Used to Evaluate Patellofemoral Instability Murray Grissom, MD 1 Bao Do, MD 2 Kathryn Stevens, MD 2 1 Santa Clara Valley Medical Center, San Jose, CA 2 Stanford
The surgical treatment of Perthes disease by
 Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in Perthes disease A REVIEW AT THE END OF GROWTH K. Daly, C. Bruce, A. Catterall From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore, England The surgical treatment of
Lateral shelf acetabuloplasty in Perthes disease A REVIEW AT THE END OF GROWTH K. Daly, C. Bruce, A. Catterall From the Royal National Orthopaedic Hospital, Stanmore, England The surgical treatment of
Radiological Sequelae of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a Review
 Radiological Sequelae of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a Review Poster No.: P-0037 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. G. Flanagan, J. Sarkodieh, K. Mcdonald, M. Ramachandran,
Radiological Sequelae of developmental dysplasia of the hip: a Review Poster No.: P-0037 Congress: ESSR 2012 Type: Scientific Exhibit Authors: S. G. Flanagan, J. Sarkodieh, K. Mcdonald, M. Ramachandran,
FAI syndrome with or without labral tear.
 Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
Case This 16-year-old female, soccer athlete was treated for pain in the right groin previously. Now has acute onset of pain in the left hip. The pain was in the groin that was worse with activities. Diagnosis
A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip
 A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
A Patient s Guide to Femoroacetabular Impingement (FAI) of the Hip 651 Old Country Road Plainview, NY 11803 Phone: 5166818822 Fax: 5166813332 p.lettieri@aol.com DISCLAIMER: The information in this booklet
VALGUS-EXTENSION OSTEOTOMY FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HIP
 VALGUS-EXTENSION OSTEOTOMY FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HIP INDICATIONS AND LONG-TERM RESULTS G. L. MAISTRELLI, M. GERUNDINI, U. FUSCO, R. BOMBELLI, M. BOMBELLI, A. AVAI From Busto Arsizio General Hospital,
VALGUS-EXTENSION OSTEOTOMY FOR OSTEOARTHRITIS OF THE HIP INDICATIONS AND LONG-TERM RESULTS G. L. MAISTRELLI, M. GERUNDINI, U. FUSCO, R. BOMBELLI, M. BOMBELLI, A. AVAI From Busto Arsizio General Hospital,
Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies
 Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies Organization Introduction Hip Biomechanics Principles of Osteotomy Femoral Osteotomies Pelvic Osteotomies Summary Inroduction Osteoarthritis is very prevalent Primary OA
Hip Biomechanics and Osteotomies Organization Introduction Hip Biomechanics Principles of Osteotomy Femoral Osteotomies Pelvic Osteotomies Summary Inroduction Osteoarthritis is very prevalent Primary OA
Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement
 Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hamamatsu University School of Medicine,
Radial center-edge angle calculated by acetabular coverage analysis software ACX dynamics in pincer type femoroacetabular impingement Department of Orthopaedic Surgery Hamamatsu University School of Medicine,
Case Developmental dysplasia of hip
 Case 13303 Developmental dysplasia of hip Hidayatullah Hamidi, Sahar Maroof French medical institute for children, Kabul, Afghanistan Email: Hedayatullah.hamidi@gmail.com Maroofsahar1@gmail.com French
Case 13303 Developmental dysplasia of hip Hidayatullah Hamidi, Sahar Maroof French medical institute for children, Kabul, Afghanistan Email: Hedayatullah.hamidi@gmail.com Maroofsahar1@gmail.com French
