Serum uric acid in England and Scotland
|
|
|
- Jocelyn Garrison
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, Serum uric acid in England and Scotland R. A. STURGE,1 J. T. SCOTT,' A. C. KENNEDY,2 D. P. HART,3 AND W. WATSON BUCHANAN2 From Charing Cross Hospital and Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology, London;' Centre for Rheumatic Diseases, Glasgow;2 and University of Birmingham3 SUMMARY Serum uric acid (SUA) was measured in 512 men and 254 women from two English regions and in 337 men from one Scottish region. Mean SUA levels were the same in the men (5-5 mg/100 ml) and similar in the women (3-9 and 4-1 mg/100 ml). The apparent rarity of gout in Scotsmen cannot be explained by regional differences in SUA levels or in the prevalence of hyperuricaemia (defined as SUA of 7.0 mg/100 ml or over) which was present in 6.6% of the English men and 8 of the Scots. SUA was positively correlated with weight and serum urea, and with age in women, but no variation was found with social class. Body weight was the most important predictor of SUA in both men and women and superior to measurements involving correction for height, such as ponderal index and calculated lean body mass. 'In Scotland gout is much less frequently met with than in England... and when it does occur it is generally in the upper classes of society and in larger cities, where wines and ales have been largely substituted for whisky.. Sir Robert Christison bears similar testimony, for he informed me that he had met with only two cases of gout in the (Edinburgh) infirmary, although physician to it for 30 years, and both subjects were fat and overfed English butlers'. A. B. Garrod in Gout and Rheumatic Gout, 3rd ed The prevalences of gout and of hyperuricaemia are known to vary considerably between population groups in different parts of the world (Healey and Hall, 1970). One hundred years ago A. B. Garrod wrote that gout was far less common in Scotland than in England, a view which continues to be held, though actual data on this are lacking. In the absence of recent hypouricaemic therapy, hyperuricaemia is a prerequisite for the diagnosis of gout; it was therefore decided to compare serum uric acid (SUA) levels between adults in England and Scotland. At the same time the opportunity was taken to investigate other factors which are possibly related to SUA levels, such as physique, blood urea, and social class. Accepted for publication May 2, 1977 Correspondence to Dr. J. T. Scott, Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology, Bute Gardens, Hammersmith, London W6 7DW Methods A total of 1103 subjects took part in the survey, comprising 341 male and 52 female employees of the Atomic Energy Research Establishment, Winfrith, Dorset, England; 171 male and 202 female blood donors attending the Regional Blood Transfusion Centre, Birmingham, England; and 337 male employees of three light industry establishments in the Glasgow, Scotland area. (The number of female subjects from Glasgow (6) was too small for statistical analysis.) Subjects were interviewed at either blood donor sessions (Winfrith and Birmingham) or routine medical examinations (Glasgow) and asked to donate 10 ml blood. A record was made of each subject's sex, height, weight, and occupation, the last being coded into social class according to the Registrar General's Classification of Occupations (1970). The serum was immediately separated from each blood sample and stored at -20 C. When all collections had been completed the sera were transported frozen to Charing Cross Hospital, London, for analysis. Mean storage time was 6 1 months. Serum urea and uric acid were measured colorimetrically on a Technicon autoanalyser (Technicon AA1-N30) in randomized batches of 30 sera for each run. The analysis sessions took place over three weekends and were carried out by the same senior technician and two assistants. Quality and drift control checks were carried out at frequent intervals throughout each session. As a final check three 420
2 samples from each run were carried over to the next run to exclude inter-batch variation. Daily means were calculated for each of the three regional gioups and showed no significant variation. Results COMPARABILITY OF REGIONAL GROUPS For the purpose of analysis the subjects were divided by sex and region of domicile. Mean ages, weights, and serum ureas for each group are given in Table 1. The ages were similar apart from those of the Winfrith men which were significantly higher than any of the other four groups (P<0 01). The Winfrith and Birmingham men were heavier than the Glasgow men (P<0 001) and the Birmingham women were heavier than the Winfrith women (P<0 05). The Birmingham men were taller than the Winfrith and Glasgow men (P <0 * 01) and the Birmingham women were taller than the Winfrith women (P<0 01). The Birmingham men had a lower mean serum urea than either of the other two males groups (P<0 001). Combining the regions the men were of similar age (mean 37 2 years) to the women (mean 36 4 years) but heavier (mean 74-9 kg and 62 6 kg respectively; P<0 001), taller (mean cm and cm respectively; P<0 001), and with a higher blood urea (mean 30-8 and 26-4 mg/100 ml (5-1 and 4-4 mmol/l) respectively; P<0 001). FREQUENCY DISTRIBUTION OF SUA* The SUA values were grouped into 0 5 mg/100 ml classes and plotted as a frequency distribution curve for each group (Fig. 1). The curves approximate a * When the study was undertaken, uric acid levels were expressed in gravimetric (mg/100 ml) rather than in SI (mmol/l) units, and frequency distribution curves were drawn in classes of gravimetric units. These are therefore retained in this paper, giving the additional advantage of easy comparison with previous epidemiological studies. To convert mg/100 ml to mmol/l, the figure should be multiplied by Table 1 Serum uric acid in England and Scotland 421 normal distribution, being slightly skewed towards the higher values, particularly in the women. No individual values were less than 1-3 mg/100 ml or greater than 8-9 mg/100 ml. Uric acid levels for men were identical in the three regional groups, with a modal class of mg/100 ml and a mean (±SD) of mg/100 ml. The modal class for the Winfrith women was mg/100 ml and for the Birmingham women mg/100 ml, the mean (±SD) being 4 1 ±0-8 and 3.9I0 8 mg/100 ml respectively. Combining the two female groups the modal class was mg/100 ml and the mean 3-9 mg/100 ml. AGE AND SUA The mean SUA values for each 5-year age class, separated by sex, are shown in Fig. 2. The regional groups have been combined as the individual group plots closely overlapped. For adult men there is no significant correlation between SUA and age. The slight terminal rise should be ignored as it represents only 4 subjects. In women, however, the levels fall slightly at age and thereafter gradually rise, more sharply after age 45-49, to reach a new higher level around age Overall there is a significantly positive correlation between the individual SUA values in women with age and there is a highly significant difference (t=4 176, P<0-001) between - the mean SUA in those under 50 (mean 3 8 mg/100 ml) and those 50 and over (mean 4-3 mg/100 ml). Analysis of variance confirmed that the differences between the age-specific mean SUA levels were unlikely to be due simply to sampling variations (F=2-756; degrees of freedom=9:244; P<0-01). Although there was considerable overlap between the individual male and female SUA values at most age groups, the mean values were all significantly different at the 1 % level or less, using the t test. WEIGHT AND SUA The mean SUA levels for each 10-kg weight class are shown in Fig. 3. The regional groups are combined as there were no significant differences in SUA Number of subjects from each region with mean age, weight, height, and blood urea Women Winfrith Birmingham Glasgow Winfrith Birmingham No. cf subjects Mean age (years) ±12 35±13 37±13 +SD Mean weight (kg) ± ±9-6 ±SD Mean height (cm) ± ±6*5 SD Mean serum urea ± (mg/100 ml)±sd Conversion: Traditional units to SI-Urea: 1 mg/100 ml mo- 166 mmol/l.
3 422 Sturge, Scott, Kennedy, Hart, Buchanan levels for each weight class. There is a trend for SUA to rise with weight and for individual values the correlation is significant at the 1 % level. Correlations were also drawn with Ponderal Index (PI), that is Ht/(3 V/Wt), and Lean Body Mass (LBM), calculated according to the formula of Hume and Weyers 0) Women 05~0 ~I * ~~~~~~~r= NS, E r-4 2 Woen.3 r22 b59,e2 P< year aqe classes Ov fer Fig. 2 Mean serum uric acid by 5-year age class. Numerals indicate number of subjects in each age class and stippled area represents 2 standard errors on either side of mean. Table 2 (1971), and the results are shown in Table 2. There was a significantly negative correlation with PI and a positive correlation with LBM but the correlation was no closer than that with weight. There was no correlation with height taken as a variable in its own right, in either sex. Winfrith Birminghom Glasgow be * E 85- E 40.7_ sz 3.- a u.- 2- E V) O-i 42 Fig. 1 Frequency distribution of serum uric acid levels for men and women. r = r= P<O-cxI P.<0o Women aover &over 10 kq weiqht classes Fig. 3 Mean serum uric acid by 10-kg weight class. Numerals indicate number of subjects in each weight class. Correlation coefficients for serum uric acid (SUA) with height, weight, ponderal index (P1), and lean body mass Height Weight P1 LBM r=0.55, P>0-1 r=0-216, P<0.001 r= , P<0 001 r=0-190, P<0.001 Women r= , P>0-1 r=0.319, P<0-001 r= , P<0.001 r=0. 146, P<0*01 46
4 SERUM UREA AND SUA The mean SUA values for each 10 mg/100 ml class in blood urea are shown in Fig. 4 for the combined men and combined women. There were again no significant differences between the regional groups in SUA levels at each urea class. There is a trend for SUA to rise with increasing serum urea; this takes place even within the generally accepted range for normal urea values. For individual values the correlation is significant at the 1 % level in men and 5 % level in women. HYPERURI CAEMIA Individual SUA values of 7 mg/100 ml or over were found in 19 Winfrith men (5 6%), 15 Birmingham men (8 * 8 Y.), and 27 Glasgow men (8 %), resulting in an overall prevalence of hyperuricaemia, defined in this way, of 7* 2 %. The regional differences were not significant using the X2 test with Yates's correction. Only one woman (0 4 %) from Birmingham was hyperuricaemic. Comparisons between the 788 normouricaemic and 61 hyperuricaemic men are shown in Table 3. The two groups were of similar age and PI but the Q 5-0' cr E a 0 j 2. E l L- Table 3 r=o 34 r =0 122 P<-,000 P<0.05 2Me Women Serum uric acid in England and Scotland 423 hyperuricaemic men were significantly heavier with a greater LBM and higher blood urea levels than the normouricaemic individuals. MULTIPLE REGRESSION A stepwise regression analysis was carried out to determine the relative contributions of each of the independent variables, shown previously to be significantly correlated, as predictors of SUA. The results are given in Table 4. Sex was by far the most important predictor of SUA, accounting for 33% of the total variation (percentage variation accounted for=r2 x 100), the other variables adding only another 6%, although with the exception of PI their contribution to the SUA of the combined sexes were all statistically significant. Taking the sexes separately the variables considered accounted for 14% of the variation of SUA in the women but only for 8 % in the men, with weight contributing 10% in the women and 5% in the men. PI and LBM were also more strongly correlated with SUA in the women than the men (Table 2) but only LBM in the women and PI in the men retained a significant contribution when entered Blood urea in Smq/lOOml classes c over Comparisons between normouricaemic and hyperuricaemic men Normouricaemic Hyperuricaemic t P Mean SUA+SD ± <0-001 (mg/100 ml) Mean agesd 37-3± ± NS (years) Mean urea+sd =0-01 (mg/100 ml) Mean heightsd 175-3± NS (cm) Mean weight+sd 74-6± ±12* <0-01 (kg) Mean PI+SD NS Mean LBM±SD <0.01 Fig. 4 Mean serum uric acid by S mg/100 ml serum urea class. Numerals indicate number of subjects in each urea class. Conversion: Traditional units to SI- Urea: I mg/100 mlk O 166 mmol/l.
5 424 Sturge, Scott, Kennedy, Hart, Buchanan Table 4 Stepwise regression of SUA with physique, blood urea, and age Women Both sexes Step Variable R R2 Variable R R2 Variable R R2 added added added 1 Weight* Weight* Sex* Urea* *064 LBMt Weight* Age* Urea Urea* PIt PI LBM* LBM Age Age* PI * P<0-01. t P<0-05. into the stepwise procedure; in neither case did this amount to more than 1 % of the total variation of SUA. Interestingly, age, because of its association with previously entered variables, became insignificant as a predictor of SUA in women but attained a significant contribution in men. Similarly serum urea lost its significance in women but retained it in men. SOCIAL CLASS AND SUA The mean SUA values for each social class group are shown in Table 5. As there was under-representation of social class V this was combined with social class IV. Many of the Birmingham women gave their occupation as 'housewife' and were excluded from the analysis as this does not adequately represent their social class. Only in the Birmingham men was a consistent trend shown of SUA to rise with decreasing social class. As social class cannot be considered to be continuously distributed, the Birmingham figures were tested for significance by analysis of variance. No significant variation of SUA between the class groups was found (F=1125; degrees of freedom 3:167). Discussion By separating the blood immediately, storing the sera in the frozen state, and analysing them in randomized batches over a limited number of sessions in one laboratory, the technical and interlaboratory errors which can reduce the validity of population comparisons (Bywaters and Holloway, Table 5 Social class and serum uric acid Mean SUA +SD for social class (numbers in parentheses) 1964) were minimized. The autoanalyser technique for measuring SUA is a colorimetric method and has been reported by most investigators to give readings 0 2 to 0 5 mg/100 ml higher than the more specific enzyme spectrophotometric method (Popert and Hewitt, 1962; O'Sullivan et al., 1965; Evans et al., 1969; Dodge and Mikkelsen, 1970). However, in our laboratory, comparison of the two methods gives a mean level of 0 3 mg/100 ml lower for the colorimetric method, as has been reported by other workers (Liddle et al., 1959), and an overall correlation coefficient of Storage should only improve the reliability of the method as it allows nonspecific chromogens to decay (Buchanan et al., 1965). Comparison of our findings with those of earlier surveys is difficult because of the above provisos and also because earlier nonautomated colorimetric procedures tend to give lower readings, of the order of 0 4 mg/100 ml, than the automated method (Finn et al., 1966). Nevertheless, it is interesting to compare the present survey with the findings of other surveys in Caucasian adults of a similar age range to our subjects. Table 6 gives the mean levels and the percentage of those with an SUA of 7 mg/100 ml or over in surveys including over 100 subjects. Mean levels in the present study are higher than those in the only previous large scale United Kingdom survey (Popert and Hewitt, 1962), a finding unlikely to be accounted for entirely by methodological differences. They are also higher in men than those in a Finnish survey (Isomaki and Takkunen, 1969). They are similar to those of two surveys in the USA (Mikkel- I II III IV& V Winfrithmen (106) (45) (133) 5.3±0.9 (58) Birmingham men 5.2±1-0 (20) (25) (111) (15) Glasgow men (10) (48) (109) 5.5±1.0 (170) Winfrith women (6) (2) 3-9±0.7 (34) (10) Birmingham women (16) (24) (101) 3.7±0-6 (17)
6 Table 6 Serum uric acid in England and Scotland 425 Mean SUA levels and percentage of hyperuricaemics in population surveys of over 100 subjects Author & year Location No. of Age range Mean SUA Percentage of subjects Method subjects (years) (mg/100 ml) with SUA 7-0 mg/100 ml or over Popert & Hewitt (1962) Wensleydale, UK Enzymatic Acheson (1969) Watford, UK 158 Adult 5.04 Mikkelsen et al. (1965) Tecumseh, USA Hall et al. (1967) Framingham, USA Colorimetric Acheson & O'Brien (1966) New Haven, USA 534 > Evans et al. (1969) Carterton, NZ 202 > Jeremy & Towson (1971) Sydney, Australia Garrick et al. (1972) Sydney, Australia (>8-3 mg/100 ml) Zalokar et al. (1972) Paris, France Adult Isomaki & Takkunen (1969) Saloinen, Finland 737 > Finn et al. (1966) Liverpool, UK 267 Adult Present study UK Women Popert & Hewitt (1962) Wensleydale, UK Enzymatic Acheson (1969) Watford, UK 163 Adult 4-20 Mikkelsen et al. (1965) Tecumseh, USA Hall et al. (1967) Framingham, USA Acheson & O'Brien (1966) New Haven, USA 679 > Colorimetric Evans et al. (1969) Carterton, NZ Garrick et al. (1972) Sydney, Australia Isomaki & Takkunen (1969) Saloinen, Finland Present study UK sen et al., 1965; Hall et al., 1967), a large French survey (Zalokar et al., 1972), and a smaller British study (Finn et al., 1966). They are considerably lower in both men and women than one other American survey (Acheson and O'Brien, 1966) and three Australasian surveys (Evans et al., 1969; Jeremy and Towson, 1971; Garrick et al., 1972). Comparison of their findings with those of earlier Australian studies led Jeremy and Towson to suggest that there had been a true increase in SUA levels in the population over the previous 10 to 15 years and the same argument might apply when the present findings are compared with those of Popert and Hewitt. This would be in accord with the view that 'the associates of a high uric acid are the associates of plenty' (Acheson and Chan, 1969). However, sampling variation probably plays a large part in the differences between various surveys, particularly where the subjects are selected on the basis of employment or attendance at blood donor sessions. For such reasons the subjects in this study may not have been completely representative of their regional population. However, when the regional groups were matched separately for age, physique, blood urea, and social class there were no significant differences in SUA levels between the groups (other than between the Winfrith and Birmingham women of social class IV/V). Indeed, the striking finding from this survey was the identical mean SUA level of the three male groups, and the closely similar levels in the two female groups. The apparent rarity of gout in Scotland is unlikely therefore to be explained by regional differences in SUA values. The prevalence of hyperuricaemia was a little lower, though not significantly so, in the combined English male groups (6 6%) than in the Scottish group (8 0%). It may be that Scotsmen are protected from the manifestations of gout in some other way; or, as we suspect, gout may have been uncommon in Scotland in the past but is less so today. In certain populations and ethnic groups gout is said to be on the increase (Shichikawa, 1968; Talbott, 1976) and it might be expected that this would be mirrored in an increased prevalence of hyperuricaemia. Our findings cannot be taken to support this concept as far as the UK as a whole is concerned since, although the prevalence of hyperuricaemia in the men (Table 6) was higher than in one previous survey (Popert and Hewitt, 1962), it was very close to that in the other English group (Finn et al., 1966). Selection factors may explain, at least in part, national and international differences, though much higher prevalence rates for hyperuricaemia were found in the French and one Australian study (Zalokar et al., 1972; Jeremy and Towson, 1971). Similar considerations apply to the women although here there appeared to be closer agreement. As expected, higher mean SUA levels were found in men than in women. The slight decrease in mean levels in women between the 3rd and 4th age decades is similar to that in other surveys and cannot be explained in terms of variations in obesity (Popert and Hewitt, 1962; Mikkelsen et al., 1965; Evans et al., 1969). The rise around the menopause has been
7 426 Sturge, Scott, Kennedy, Hart, Buchanan attributed to hormonal influences (Mikkelsen et al., 1965), though a recent study carefully matching pre- and postmenopausal women of the same age (menopause defined as no menstruation during the previous 6 months) disclosed no difference between the two groups (Bengtsson and Tibblin, 1974). This definition of the menopause may not however exclude a falling-off of menstrual blood loss, and hence a rising haemoglobin, which is itself positively correlated with SUA (Acheson and O'Brien, 1966). The known association of SUA with physique was also confirmed; it is of interest that there was a stronger correlation with body weight itself than with PI or LBM. Previous investigators have found a higher correlation with PI or relative body weight in men (Acheson and O'Brien, 1966; French et al., 1967), though our findings are in agreement to the extent that both weight and PI are more strongly correlated with SUA in women than in men. Although women have more adipose tissue per unit body weight than men, they also have less lean body mass and it seems that total weight is a better predictor of SUA than either of the other two physique calculations in both sexes. The association of SUA with serum urea levels, even within the normal range, is unexplained but has been noted before (Kennedy et al., 1975), as has an association with serum creatinine (Decker et al., 1968). Both renal and metabolic mechanisms could account for this; aging may contribute as highly significant correlations of serum urea with age were found in both men (r=0o 201) and women (r=0o 355). The very large contribution of sex to the total variation of SUA when compared with the other variables implies that other sex-associated factors which have not been taken into account, possibly hormonal (Nicholls and Scott, 1972), contribute significantly to the sex differences in SUA levels. Age and serum urea are seen to be less important than body weight as predictors of SUA in women, but retain their significance in men. However, the contribution of all these variables, apart from sex, is very small in practical terms. The absence of a significant relationship between SUA and social class is in keeping with earlier findings (Acheson, 1969), but true poverty was probably lacking in the groups studied by Acheson and ourselves. We are glad to acknowledge the technical assistance of Ian Moss and Peter Haisman; the collaboration of Dr. A. M. Laylee and Sister D. Newton at Winfrith; the kind collaboration of Dr. G. W. G. Bird, Director of the Regional Blood Transfusion Centre, Birmingham; and the statistical advice of Dr. K. Macrae in co-operation with Andrew Jenkins and staff of Charing Cross Hospital Medical School computer centre. The study was supported by the Arthritis and Rheumatism Council. References Acheson, R. M. (1969). Social class gradients in serum uric acid in males and females. British Medical Journal, 4, Acheson, R. M., and Chan, Y.-K. (1969). New Haven survey of joint diseases. The prediction of serum uric acid in a general population. Journal of Chronic Diseases, 21, Acheson, R. M., and O'Brien, W. M. (1966). Dependence of serum uric acid on haemoglobin and other factors in the general population. Lancet, 2, Bengtsson, C., and Tibblin, E. (1974). Serum uric acid levels in women. Acta Medica Scandinavica, 196, Buchanan, M. J., Isdale, I. C., and Rose, B. S. (1965). Serum uric acid estimations. Chemical and enzymatic methods compared. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 25, Bywaters, E. G. L., and Holloway, V. P. (1964). Measurement of serum uric acid in Great Britain in Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 23, Decker, J. L., Healey, L. A., and Skeith, M. D. (1968). Ethnic variations in serum uric acid: Filipino hyperuricaemia, the result of hereditary and environmental factors. Population Studies of the Rheumatic Diseases, pp Ed. by P. H. Bennett and P. H. N. Wood. International Congress Series, No Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam. Dodge, H. J., and Mikkelsen, W. M. (1970). Observations on the distribution of serum uric acid levels in participants of the Tecumseh, Michigan, community health studies. Journal of Chronic Diseases, 23, Evans, J. G., Prior, I. A. M., and Morrison, R. B. I. (1969). The Carterton study. 5. Serum uric acid levels of a sample of New Zealand European adults. New Zealand Medical Journal, 70, Finn, R., Jones, P. O., Tweedie, M. C. K., Hall, S. M., Dinsdale, 0. F., and Bourdillon, R. E. (1966). Frequency distribution curve of uric acid in the general population. Lancet, 2, Frencb, J. G., Dodge, H. J., Kjelsberg, M. O.. Mikkelsen, W. M., and Schull, W. J. (1967). A study of familial aggregation of serum uric acid levels in the population of Tecumseh, Michigan, American Journal of Epidemiology, 86, Garrick, R., Bauer, G. E., Ewan, C. E., and Neale, F. C. (1972). Serum uric acid in normal and hypertensive Australian subjects. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine, 4, Garrod, A. B. (1876). A Treatise on Gout and Rheumatic Gout (Rheumatoid Arthritis), 3rd ed., p Longmans/ Green, London. Hall, A. P., Barry, P. E., Dawber, T. R., and McNamara, P. M. (1967). The epidemiology of gout and hyperuricaemia. American Journal of Medicine, 42, Healey, L. A., and Hall, A. P. (1970). The epidemiology of hyperuricaemia. Bulletin on Rheumatic Diseases, 20, 600. Hume, R., and Weyers, E. (1971). Relationship between total body water and surface area in normal and obese subjects. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 24, Isomaki, H. A., and Takkunen, H. (1969). Gout and hyperuricaemia in a Finnish rural population. Acta Rheumatologica Scandinavica, 15, Jeremy, R., and Towson, J. (1971). Serum urate levels and gout in Australian males. Medical Journal of Australia, 1,
8 Kennedy, A. C., Brennan, J., Anderson, J., Brooks, P., Buchanan, W. W., and Dick, W. C. (1975). Serum uric acid-its relationship to lean body mass, sex, plasma urea, intracellular potassium and packed cell volume in a normal population group. Paper read to meeting of Heberden Society at Norwich, 14th March, Liddle, L., Seegmiller, J. E., and Laster, L. (1959). Enzymatic spectrophotometric method for determination of uric acid. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine, 54, Mikkelsen, W. M., Dodge, H. J., and Valkenburg, H. (1965). The distribution of serum uric acid values in a population unselected as to gout or hyperuricaemia. American Journal of Medicine, 39, Nicholls, A., and Scott, J. T. (1972). Effect of weight-loss on plasma and urinary levels of uric acid. Lancet, 2, O'Sullivan, J. B., Francis, J. O'S., and Kantor, N. (1975). Comparison of a colorimetric (automated) with an Serum uric acid in England and Scotland 427 enzymatic (manual) uric acid procedure. Clinical Chemistry, 11, Popert, A. J., and Hewitt, J. V. (1962). Gout and hyperuricaemia in rural and urban populations. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 21, Registrar General (1970). Classification of Occupations. HMSO, London. Shichikawa, K. (1968). The prevalence of gout in Japan. Population Studies of the Rheumatic Diseases, pp Ed. by P. H. Bennett and P. H. N. Wood. International Congress Series, No Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam. Talbott, J. H. (1976). It happened on the way to the XIII International Congress on Rheumatology in Kyoto and after I had arrived. Arthritis and Rheumatism, 18, Suppl., Zalokar, J., Lellouch, J., Claude, J. R., and Kuntz, D. (1972). Serum uric acid in 23,923 men and gout in a subsample of 427 men in France. Journal of Chronic Diseases, 25, Ann Rheum Dis: first published as /ard on 1 October Downloaded from on 9 December 2018 by guest. Protected by
The relationship between uric acid and potassium
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 333-338 The relationship between uric acid and potassium in normal subjects ALASTAIR C. KENNEDY, KEITH BODDY, PRISCILLA C. KING, JENNIFER BRENNAN, JOHN A. ANDERSON,
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 333-338 The relationship between uric acid and potassium in normal subjects ALASTAIR C. KENNEDY, KEITH BODDY, PRISCILLA C. KING, JENNIFER BRENNAN, JOHN A. ANDERSON,
The Prevalence of Gout in Three English Towns
 International Journal of Epidemiology Oxford University Press 82 Vol. 11, No. 1 Printed in Great Britain The Prevalence of Gout in Three English Towns M J GARDNER*. C POWER". D J P BARKER* and R PADDAY*
International Journal of Epidemiology Oxford University Press 82 Vol. 11, No. 1 Printed in Great Britain The Prevalence of Gout in Three English Towns M J GARDNER*. C POWER". D J P BARKER* and R PADDAY*
Serum uric acid in hypertensive patients
 British Heart Journal, 1975, 37, 1210-1215. Serum uric acid in hypertensive patients C. J. Bulpitt From the Department of Clinical Pharnacology, Royal Postgraduate Medical School; and Department of Medical
British Heart Journal, 1975, 37, 1210-1215. Serum uric acid in hypertensive patients C. J. Bulpitt From the Department of Clinical Pharnacology, Royal Postgraduate Medical School; and Department of Medical
Uric acid, joint morbidity, and streptococcal antibodies in Maori and European teenagers.
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 359 Uric acid, joint morbidity, and streptococcal antibodies in and teenagers Rotorua Lakes study 3 J. M. STANHOPE AND I. A. M. PRIOR From the Epidemiology Unit, Wellington
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1975), 34, 359 Uric acid, joint morbidity, and streptococcal antibodies in and teenagers Rotorua Lakes study 3 J. M. STANHOPE AND I. A. M. PRIOR From the Epidemiology Unit, Wellington
Occurrence of Gout in Copenhagen Males Aged 40-59
 International Journal of Epidemiology Oxford University Press 1976 Vol. 5, No. 2 Printed in Great Britain Occurrence of Gout in Copenhagen Males Aged 40-59 OVE B. SCHAFFALITZKY DE MUCKADELL 1 and FINN
International Journal of Epidemiology Oxford University Press 1976 Vol. 5, No. 2 Printed in Great Britain Occurrence of Gout in Copenhagen Males Aged 40-59 OVE B. SCHAFFALITZKY DE MUCKADELL 1 and FINN
The relationship between blood pressure and
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1976), 30, 158-162 The relationship between blood pressure and biochemical risk factors in a general population C. J. BULPITT, CHARLES HODES, AND M. G. EVERITT Chronic Disease
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1976), 30, 158-162 The relationship between blood pressure and biochemical risk factors in a general population C. J. BULPITT, CHARLES HODES, AND M. G. EVERITT Chronic Disease
AUSTRALIAN ABORIGINAL
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1969), 28, 150 SERUM URATE CONCENTRATIONS IN THE AUSTRALIAN ABORIGINAL BY B. T. EMMERSON,1 W. DOUGLAS,' R. L. DOHERTY,2 AND P. FEIGL3 From the University of Queensland Department of Medicine
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1969), 28, 150 SERUM URATE CONCENTRATIONS IN THE AUSTRALIAN ABORIGINAL BY B. T. EMMERSON,1 W. DOUGLAS,' R. L. DOHERTY,2 AND P. FEIGL3 From the University of Queensland Department of Medicine
Age- and sex-related reference ranges for eight plasma constituents derived from randomly selected adults in
 J Clin Pathol 19; 33: 3-385 Age- and sex-related reference ranges for eight plasma constituents derived from randomly selected adults in a Scottish new town MARY D GARDNER AND R SCOTT From the Departments
J Clin Pathol 19; 33: 3-385 Age- and sex-related reference ranges for eight plasma constituents derived from randomly selected adults in a Scottish new town MARY D GARDNER AND R SCOTT From the Departments
HEIGHTS AND WEIGHTS OF MEN VISITING A PUBLIC HEALTH EXHIBITION
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1972), 26, 180-185 HEIGHTS AND WEIGHTS OF MEN VISITING A PUBLIC HEALTH EXHIBITION R. E. WALLER AND A. G. F. BROOKS MRC Air Pollution Unit, St. Bartholomew's Hospital Medical College,
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1972), 26, 180-185 HEIGHTS AND WEIGHTS OF MEN VISITING A PUBLIC HEALTH EXHIBITION R. E. WALLER AND A. G. F. BROOKS MRC Air Pollution Unit, St. Bartholomew's Hospital Medical College,
symphysis in rheumatic disorders
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 529-534 A comparative radiological study of the pubic symphysis in rheumatic disorders D. L. SCOTT, C. J. EASTMOND, AND V. WRIGHT From the Rheumatism Research Unit,
Serum urate concentrations in homozygous sickle
 J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:965-969 Serum urate concentrations in homozygous sickle cell disease K DE CEULAER, AG MORGAN, E CHOO-KANG, WA WILSON, GR SERJEANT From the Department ofmedicine and the Medical Research
J Clin Pathol 1981 ;34:965-969 Serum urate concentrations in homozygous sickle cell disease K DE CEULAER, AG MORGAN, E CHOO-KANG, WA WILSON, GR SERJEANT From the Department ofmedicine and the Medical Research
Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Mathematics Level 3. Resource title: Sport Science. Investigate bivariate measurement data
 Exemplar for internal assessment resource Mathematics 3.9A for Achievement Standard 91581 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Mathematics Level 3 Resource title: Sport Science This exemplar supports
Exemplar for internal assessment resource Mathematics 3.9A for Achievement Standard 91581 Exemplar for Internal Assessment Resource Mathematics Level 3 Resource title: Sport Science This exemplar supports
Epidemiology of Hyperuricemia in the Elderly
 YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 74 (2001), pp. 151-157. Copyright 2001. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Epidemiology of Hyperuricemia in the Elderly Shih-Wei Laia, Chee-Keong Tana, and
YALE JOURNAL OF BIOLOGY AND MEDICINE 74 (2001), pp. 151-157. Copyright 2001. All rights reserved. ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Epidemiology of Hyperuricemia in the Elderly Shih-Wei Laia, Chee-Keong Tana, and
Population studies on Gilbert's syndrome
 Journal of Medical Genetics (1975). 12, 152. Population studies on Gilbert's syndrome D. OWENS and J. EVANS Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, University of Liverpool, Crown Street, Liverpool L69 3BX Summary.
Journal of Medical Genetics (1975). 12, 152. Population studies on Gilbert's syndrome D. OWENS and J. EVANS Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, University of Liverpool, Crown Street, Liverpool L69 3BX Summary.
PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF AGE OF ONSET IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 25 1 PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS DONITA B. SULLIVAN, JAMES T. CASSIDY, and ROSS E. PETTY An analysis of age of onset in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was performed in the
25 1 PATHOGENIC IMPLICATIONS OF IN JUVENILE RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS DONITA B. SULLIVAN, JAMES T. CASSIDY, and ROSS E. PETTY An analysis of age of onset in juvenile rheumatoid arthritis was performed in the
Uric acid clearance in and normal subjects
 nn. rheum. is. (1971), 3, 285 Uric acid clearance in and normal subjects patients with gout M. L. SNITH* N J. T. SCOTT Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology and West London Hospital, Hammersmith, London, W.6
nn. rheum. is. (1971), 3, 285 Uric acid clearance in and normal subjects patients with gout M. L. SNITH* N J. T. SCOTT Kennedy Institute of Rheumatology and West London Hospital, Hammersmith, London, W.6
Salt, soft drinks & obesity Dr. Feng He
 Salt, soft drinks & obesity Dr. Feng He Wolfson Institute of Preventive Medicine, Barts and The London School of Medicine & Dentistry, Queen Mary University of London, UK f.he@qmul.ac.uk BP Salt CVD Obesity
Salt, soft drinks & obesity Dr. Feng He Wolfson Institute of Preventive Medicine, Barts and The London School of Medicine & Dentistry, Queen Mary University of London, UK f.he@qmul.ac.uk BP Salt CVD Obesity
The Short NART: Cross-validation, relationship to IQ and some practical considerations
 British journal of Clinical Psychology (1991), 30, 223-229 Printed in Great Britain 2 2 3 1991 The British Psychological Society The Short NART: Cross-validation, relationship to IQ and some practical
British journal of Clinical Psychology (1991), 30, 223-229 Printed in Great Britain 2 2 3 1991 The British Psychological Society The Short NART: Cross-validation, relationship to IQ and some practical
Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 274 Osteoarthrosis in a rural South African Negro population L. SOLOMON, P. BEGHTON, AND J. S. LAWRENCE From the Epidemiological Research Unit, Department oforthopaedic Surgery,
hypothyroidism Growth in early treated congenital ORIGINAL ARTICLES
 464 Archives of Disease in Childhood 1994; 70: 464-468 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Institute of Child Health, London D B Grant Correspondence to: Dr D B Grant, Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London
464 Archives of Disease in Childhood 1994; 70: 464-468 ORIGINAL ARTICLES Institute of Child Health, London D B Grant Correspondence to: Dr D B Grant, Hospital for Sick Children, Great Ormond Street, London
Total body potassium in cor pulmonale
 Thorax (1976), 31, 708. Total body potassium in cor pulmonale A. D. HOWIE', A. I. PACK', K. BODDY2, and MAUREEN MAHAFFEY2 Centre for Respiratory Investigation, Glasgow Royal Infirmary, Glasgow G4 OSF1
Thorax (1976), 31, 708. Total body potassium in cor pulmonale A. D. HOWIE', A. I. PACK', K. BODDY2, and MAUREEN MAHAFFEY2 Centre for Respiratory Investigation, Glasgow Royal Infirmary, Glasgow G4 OSF1
Does Body Mass Index Adequately Capture the Relation of Body Composition and Body Size to Health Outcomes?
 American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 1998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 147, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A A BRIEF ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Does
American Journal of Epidemiology Copyright 1998 by The Johns Hopkins University School of Hygiene and Public Health All rights reserved Vol. 147, No. 2 Printed in U.S.A A BRIEF ORIGINAL CONTRIBUTION Does
Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy*
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1976), 35, 521 Chondrocalcinosis after parathyroidectomy* J. S. GLASS AND R. GRAHAME From Guy's Arthritis Research Unit, Guy's Hospital Medical School, London SE] 9RT Glass, J. S., and
Evaluation of the Cockroft Gault, Jelliffe and Wright formulae in estimating renal function in elderly cancer patients
 Original article Annals of Oncology 15: 291 295, 2004 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh079 Evaluation of the Cockroft Gault, Jelliffe and Wright formulae in estimating renal function in elderly cancer patients G.
Original article Annals of Oncology 15: 291 295, 2004 DOI: 10.1093/annonc/mdh079 Evaluation of the Cockroft Gault, Jelliffe and Wright formulae in estimating renal function in elderly cancer patients G.
SURVIVAL AFTER TRANSFUSION OF Rh-POSITIVE ERYTHROCYTES PREVIOUSLY INCUBATED
 J. clin. Path. (1949), 2, 109 SURVIVAL AFTER TRANSFUSION OF Rh-POSITIVE ERYTHROCYTES PREVIOUSLY INCUBATED WITH Rh ANTIBODY BY P. L. MOLLISON From the Medical Research Council Blood Transfusion Research
J. clin. Path. (1949), 2, 109 SURVIVAL AFTER TRANSFUSION OF Rh-POSITIVE ERYTHROCYTES PREVIOUSLY INCUBATED WITH Rh ANTIBODY BY P. L. MOLLISON From the Medical Research Council Blood Transfusion Research
Proposed new target height equations for use in Australian growth clinics
 doi:10.1111/j.1440-4.2008.01397.x ANNOTATION Proposed new target height equations for use in Australian growth clinics Ian P Hughes and Peter SW Davies The Children s Nutrition Research Centre, Discipline
doi:10.1111/j.1440-4.2008.01397.x ANNOTATION Proposed new target height equations for use in Australian growth clinics Ian P Hughes and Peter SW Davies The Children s Nutrition Research Centre, Discipline
An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report
 ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 1 Number 1 An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report M Jaibaji, M Chithriki Citation M Jaibaji, M Chithriki. An
ISPUB.COM The Internet Journal of Rheumatology Volume 1 Number 1 An Unusual Pattern Of Osteoarthritis Of The Fingers In A Nurse. A Case Report M Jaibaji, M Chithriki Citation M Jaibaji, M Chithriki. An
Proteinuria in rheumatoid arthritis-drug-induced or amyloid?
 Anna.'s of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 4, 24-244 Proteinuria in rheumatoid arthritis-drug-induced or amyloid? B. E. BOURKE, D. F. WOODROW, AND J. T. SCOTT From Charing Cross Hospital, London W6 SUMMARY
Anna.'s of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1981, 4, 24-244 Proteinuria in rheumatoid arthritis-drug-induced or amyloid? B. E. BOURKE, D. F. WOODROW, AND J. T. SCOTT From Charing Cross Hospital, London W6 SUMMARY
Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides
 Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 2, June 2003 Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides Abdurhman S Al-Arfaj, FRCPC, MRCP(UK), FACP, FACR* Objectives: In view of the many studies linking
Bahrain Medical Bulletin, Vol. 25, No. 2, June 2003 Radiographic Osteoarthritis and Serum Triglycerides Abdurhman S Al-Arfaj, FRCPC, MRCP(UK), FACP, FACR* Objectives: In view of the many studies linking
methods ofdata collection have been reported (Shaper
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (1986) 62, 11-16 Serum uric acid, serum glucose and diabetes: relationships in a population study Derek G. Cook', A.G. Shaper1, D.S. Thelle2 and T.P. Whitehead3 'Department
Postgraduate Medical Journal (1986) 62, 11-16 Serum uric acid, serum glucose and diabetes: relationships in a population study Derek G. Cook', A.G. Shaper1, D.S. Thelle2 and T.P. Whitehead3 'Department
Electroconvulsive Therapy Audit Report
 Electroconvulsive Therapy Audit Report Published in March 2005 by the Ministry of Health PO Box 5013, Wellington, New Zealand ISBN 0-478-28345-8 (Website) HP 3821 This document is available on the Ministry
Electroconvulsive Therapy Audit Report Published in March 2005 by the Ministry of Health PO Box 5013, Wellington, New Zealand ISBN 0-478-28345-8 (Website) HP 3821 This document is available on the Ministry
Main article An introduction to medical statistics for health care professionals: Describing and presenting data
 218 Musculoskeletal Care Volume 2 Number 4 Whurr Publishers 2004 Main article An introduction to medical statistics for health care professionals: Describing and presenting data Elaine Thomas PhD MSc BSc
218 Musculoskeletal Care Volume 2 Number 4 Whurr Publishers 2004 Main article An introduction to medical statistics for health care professionals: Describing and presenting data Elaine Thomas PhD MSc BSc
PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS*
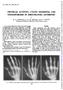 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 24, 522. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY B. A. CASTILLO, R. A. EL SALLAB, AND J. T. SCOTT Department of Medicine, Postgraduate
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1965), 24, 522. PHYSICAL ACTIVITY, CYSTIC EROSIONS, AND OSTEOPOROSIS IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS* BY B. A. CASTILLO, R. A. EL SALLAB, AND J. T. SCOTT Department of Medicine, Postgraduate
Chapter Two Renal function measures in the adolescent NHANES population
 0 Chapter Two Renal function measures in the adolescent NHANES population In youth acquire that which may restore the damage of old age; and if you are mindful that old age has wisdom for its food, you
0 Chapter Two Renal function measures in the adolescent NHANES population In youth acquire that which may restore the damage of old age; and if you are mindful that old age has wisdom for its food, you
PREVALENCE OF HYPERURICEMIA AMONG PEOPLE OF MORANG DISTRICT OF NEPAL
 PREVALENCE OF HYPERURICEMIA AMONG PEOPLE OF MORANG DISTRICT OF NEPAL Abstract Shrawan Kumar yadav, Niraj Nepal and DilliRam Niroula. refers to an elevation in the serum uric acid concentration. The blood
PREVALENCE OF HYPERURICEMIA AMONG PEOPLE OF MORANG DISTRICT OF NEPAL Abstract Shrawan Kumar yadav, Niraj Nepal and DilliRam Niroula. refers to an elevation in the serum uric acid concentration. The blood
SICKNESS ABSENCE BEFORE THE FIRST CLINICAL
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1954, 11, 20. SICKNESS ABSENCE BEFORE THE FIRST CLINICAL EPISODE OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE BY J. A. HEADY, J. N. MORRIS, F. J. LLOYD, and P. A. B. RAFFLE From the Social Medicine
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1954, 11, 20. SICKNESS ABSENCE BEFORE THE FIRST CLINICAL EPISODE OF CORONARY HEART DISEASE BY J. A. HEADY, J. N. MORRIS, F. J. LLOYD, and P. A. B. RAFFLE From the Social Medicine
Downloaded from:
 Ridler, C; Townsend, N; Dinsdale, H; Mulhall, C; Rutter, H (2009) National child measurement programme: detailed analysis of the 2007/08 national dataset. National Obesity Observatory, London. p. 41. Downloaded
Ridler, C; Townsend, N; Dinsdale, H; Mulhall, C; Rutter, H (2009) National child measurement programme: detailed analysis of the 2007/08 national dataset. National Obesity Observatory, London. p. 41. Downloaded
on maintenance therapy. Each curve represents a different Ofthe two patients on maintenance therapy, the one who 3 weeks earlier.
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 128 Serum gold 11. Levels in rheumatoid arthritis HRBRT M. RUBNSTN AND ALBRT A. DTZ From the Departments ofmedicine and Research, Veterans Administration Hospital, Hines, llinois
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 32, 128 Serum gold 11. Levels in rheumatoid arthritis HRBRT M. RUBNSTN AND ALBRT A. DTZ From the Departments ofmedicine and Research, Veterans Administration Hospital, Hines, llinois
RELATIVE ROLES OF GENETIC AND ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS IN THE CONTROL OF SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS IN NORMOURICAEMIC SUBJECTS
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1967), 26, 234 RELATIVE ROLES OF GENETIC AND ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS IN THE CONTROL OF SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS IN NORMOURICAEMIC SUBJECTS BY JAMES A. BOYLE, WILLIAM R. GREIG, MUKUNDRAI K.
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1967), 26, 234 RELATIVE ROLES OF GENETIC AND ENVIRONMENTAL FACTORS IN THE CONTROL OF SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS IN NORMOURICAEMIC SUBJECTS BY JAMES A. BOYLE, WILLIAM R. GREIG, MUKUNDRAI K.
Radioimmunoassay of serum digoxin in relation to digoxin intoxication
 British Heart journal, I975, 37, 6I9-623. Radioimmunoassay of serum digoxin in relation to digoxin intoxication R. B. Singh, A. N. Rai, K. P. Dube, D. K. Srivastav, P. N. Somani, and B. C. Katiyar From
British Heart journal, I975, 37, 6I9-623. Radioimmunoassay of serum digoxin in relation to digoxin intoxication R. B. Singh, A. N. Rai, K. P. Dube, D. K. Srivastav, P. N. Somani, and B. C. Katiyar From
Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 360-364 Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins C. J. EASTMOND* AND J. C. WOODROW From the Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 360-364 Discordance for ankylosing spondylitis in monozygotic twins C. J. EASTMOND* AND J. C. WOODROW From the Nuffield Unit of Medical Genetics, Department
Two-in-three are dieting or exercising In the Battle of the Bulge, More Soldiers Than Successes
 Two-in-three are dieting or exercising In the Battle of the Bulge, More Soldiers Than Successes EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE APRIL 25, 2006 Paul Taylor, Executive Vice President Cary Funk, Senior Project Director
Two-in-three are dieting or exercising In the Battle of the Bulge, More Soldiers Than Successes EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE APRIL 25, 2006 Paul Taylor, Executive Vice President Cary Funk, Senior Project Director
Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1978, 37, 19-194 Diagnostic value of sacroiliac joint scintigraphy with 99m technetium pyrophosphate in sacroiliitis H. BERGH, J. REMAN, L. DRIEKEN, L. KIEBOOM, AND J.
Suicidal Behaviour among Young Adults (15-34 years)
 Scottish Needs Assessment Programme Suicidal Behaviour among Young Adults (15-34 years) Summary Progress Report SCOTTISH FORUM FOR PUBLIC HEALTH MEDICINE 69 Oakfield Avenue Glasgow G12 8QQ Tel - 0141 330
Scottish Needs Assessment Programme Suicidal Behaviour among Young Adults (15-34 years) Summary Progress Report SCOTTISH FORUM FOR PUBLIC HEALTH MEDICINE 69 Oakfield Avenue Glasgow G12 8QQ Tel - 0141 330
Myelotoxicity of D-penicillamine
 Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 232-236 Myelotoxicity of D-penicillamine APRIL G. L. KAY From the Arthritis and Rheumatism Council Epidemiology Research Unit and Guy's Arthritis Research Unit,
Annals of Rheumatic Diseases, 1979, 38, 232-236 Myelotoxicity of D-penicillamine APRIL G. L. KAY From the Arthritis and Rheumatism Council Epidemiology Research Unit and Guy's Arthritis Research Unit,
Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in healthy subjects and normoalbuminuric diabetic patients: validity of a new (MDRD) prediction equation
 Nephrol Dial Transplant (2002) 17: 1909 1913 Original Article Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in healthy subjects and normoalbuminuric diabetic patients: validity of a new () prediction equation
Nephrol Dial Transplant (2002) 17: 1909 1913 Original Article Assessment of glomerular filtration rate in healthy subjects and normoalbuminuric diabetic patients: validity of a new () prediction equation
Subject variability in short-term audiometric
 British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 271-275 Subject variability in short-term audiometric recording B. P. R. HARTLEY', R. W. HOWELL2, A. SINCLAIR,3 D. A. D. SLATTERY4 British Steel Corporation
British Journal of Industrial Medicine, 1973, 30, 271-275 Subject variability in short-term audiometric recording B. P. R. HARTLEY', R. W. HOWELL2, A. SINCLAIR,3 D. A. D. SLATTERY4 British Steel Corporation
Sickness absence after inguinal herniorrhaphy
 Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1979, 33, 121-126 Sickness absence after inguinal herniorrhaphy M. GRIFFITHS, W. E. WATERS, AND E. D. ACHESON From the Department of Community Medicine, University
Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1979, 33, 121-126 Sickness absence after inguinal herniorrhaphy M. GRIFFITHS, W. E. WATERS, AND E. D. ACHESON From the Department of Community Medicine, University
TRENDS IN SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS
 87 TRENDS IN SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS 1961-1980 ROBERT J. GLYNN. EDWARD W. CAMPION, and JEREMIAH E. SILBERT Uric acid levels of adult male volunteers in a longitudinal study of human aging rose steadily
87 TRENDS IN SERUM URIC ACID LEVELS 1961-1980 ROBERT J. GLYNN. EDWARD W. CAMPION, and JEREMIAH E. SILBERT Uric acid levels of adult male volunteers in a longitudinal study of human aging rose steadily
Chapter 2 The Link Between Obesity and Breast Cancer Risk: Epidemiological Evidence
 Chapter 2 The Link Between Obesity and Breast Cancer Risk: Epidemiological Evidence 2.1 BMI and Breast Cancer Risk BMI is routinely used to qualify an individual s adiposity, yet it is simply a measure
Chapter 2 The Link Between Obesity and Breast Cancer Risk: Epidemiological Evidence 2.1 BMI and Breast Cancer Risk BMI is routinely used to qualify an individual s adiposity, yet it is simply a measure
CHAPTER 9. Anthropometry and Body Composition
 CHAPTER 9 Anthropometry and Body Composition 9.1 INTRODUCTION Ageing is characterized by reduction in fat free mass (FFM), primarily via loss of muscle mass, loss of bone mineral in women, redistribution
CHAPTER 9 Anthropometry and Body Composition 9.1 INTRODUCTION Ageing is characterized by reduction in fat free mass (FFM), primarily via loss of muscle mass, loss of bone mineral in women, redistribution
Bringing prostate cancer education to regional and rural Australian communities
 Bringing prostate cancer education to regional and rural Australian communities Julie Sykes 1, Lisa Fodero 2, Nick Brook 3, Rachel Jenkin 4 1 Prostate Cancer Foundation of Australia; 2 Health Consult;
Bringing prostate cancer education to regional and rural Australian communities Julie Sykes 1, Lisa Fodero 2, Nick Brook 3, Rachel Jenkin 4 1 Prostate Cancer Foundation of Australia; 2 Health Consult;
. Time to transplant listing is dependent on. . In 2003, 9.1% of all prevalent transplant. . Patients with diabetes mellitus are less
 Chapter 5: Joint Analyses with UK Transplant in England and Wales; Access to the Renal Transplant Waiting List, Time to Listing, Diabetic Access to Transplantation and the Influence of Social Deprivation
Chapter 5: Joint Analyses with UK Transplant in England and Wales; Access to the Renal Transplant Waiting List, Time to Listing, Diabetic Access to Transplantation and the Influence of Social Deprivation
K.-H. Yu, S.-F. Luo, W.-P. Tsai and Y.-Y. Huang 1
 Rheumatology 2004;43:1541 1545 Advance Access publication 24 August 2004 Intermittent elevation of serum urate and 24-hour urinary uric acid excretion K.-H. Yu, S.-F. Luo, W.-P. Tsai and Y.-Y. Huang 1
Rheumatology 2004;43:1541 1545 Advance Access publication 24 August 2004 Intermittent elevation of serum urate and 24-hour urinary uric acid excretion K.-H. Yu, S.-F. Luo, W.-P. Tsai and Y.-Y. Huang 1
Carcinoma of the breast in East Anglia : a changing pattern of presentation?
 Journal oj'epidemiology and Community Health, 1978, 32, 178-182 Carcinoma of the breast in East Anglia 196-1975: a changing pattern of presentation? ANNE M. DE BONO AND E. M. KINGSLEY PILLERS From the
Journal oj'epidemiology and Community Health, 1978, 32, 178-182 Carcinoma of the breast in East Anglia 196-1975: a changing pattern of presentation? ANNE M. DE BONO AND E. M. KINGSLEY PILLERS From the
Chapter 6: Adequacy of haemodialysis (Urea reduction ratio)
 Chapter 6: Adequacy of haemodialysis (Urea reduction ratio) Summary In England & Wales a uniform method of measuring the post dialysis urea sample (as suggested in the 1 Renal Association standards document)
Chapter 6: Adequacy of haemodialysis (Urea reduction ratio) Summary In England & Wales a uniform method of measuring the post dialysis urea sample (as suggested in the 1 Renal Association standards document)
Math 124: Module 2, Part II
 , Part II David Meredith Department of Mathematics San Francisco State University September 15, 2009 What we will do today 1 Explanatory and Response Variables When you study the relationship between two
, Part II David Meredith Department of Mathematics San Francisco State University September 15, 2009 What we will do today 1 Explanatory and Response Variables When you study the relationship between two
and Peto (1976) all give values of the relative risk (RR) of death from IHD for a wide range of smoking
 Jourtial of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1979, 33, 243-247 Ischaemic heart disease mortality risks for smokers and non-smokers JOY L. TOWNSEND From the Department of Economics, University of Essex
Jourtial of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1979, 33, 243-247 Ischaemic heart disease mortality risks for smokers and non-smokers JOY L. TOWNSEND From the Department of Economics, University of Essex
Gout and its relation to lipid metabolism
 Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 3, 51 Gout and its relation to lipid metabolism 1. Serum uric acid, lipid, and lipoprotein levels in gout H. MIELANTS,* E. M. VEYS,* AND A. DE WEERDTt From the Department ofphysical
Ann. rheum. Dis. (1973), 3, 51 Gout and its relation to lipid metabolism 1. Serum uric acid, lipid, and lipoprotein levels in gout H. MIELANTS,* E. M. VEYS,* AND A. DE WEERDTt From the Department ofphysical
A COMPARISON OF THE EFFECTS OF CORTISONE AND PREDNISONE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS
 ORIGINAL PAPER A COMPARISON O THE EECTS O CORTISONE AND PREDNISONE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY C. P. INCH rom the Department of Physical Medicine and Regional Rheumatism Centre, The London Hospital THE
ORIGINAL PAPER A COMPARISON O THE EECTS O CORTISONE AND PREDNISONE IN RHEUMATOID ARTHRITIS BY C. P. INCH rom the Department of Physical Medicine and Regional Rheumatism Centre, The London Hospital THE
A mixed methods evaluation of a diabetes peer support scheme in an inner city London area
 A mixed methods evaluation of a diabetes peer support scheme in an inner city London area Introduction The diabetes mentor scheme was initiated across GP practices in an inner city London area covering
A mixed methods evaluation of a diabetes peer support scheme in an inner city London area Introduction The diabetes mentor scheme was initiated across GP practices in an inner city London area covering
DISTRIBUTION OF HAEMOGLOBIN LEVEL, PACKED CELL VOLUME, AND MEAN CORPUSCULAR HAEMOGLOBIN
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1964), 18, 81-87 DISTRIBUTION OF HAEMOGLOBIN LEVEL, PACKED CELL VOLUME, AND MEAN CORPUSCULAR HAEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRATION IN WOMEN IN THE COMMUNITY The definition of anaemia in most
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1964), 18, 81-87 DISTRIBUTION OF HAEMOGLOBIN LEVEL, PACKED CELL VOLUME, AND MEAN CORPUSCULAR HAEMOGLOBIN CONCENTRATION IN WOMEN IN THE COMMUNITY The definition of anaemia in most
Health care workers with serious communicable diseases who is being protected?
 Health care workers with serious communicable diseases who is being protected? Dr Alison Rimmer Consultant Occupational Physician and Clinical Director Sheffield Occupational Health Service Serious communicable
Health care workers with serious communicable diseases who is being protected? Dr Alison Rimmer Consultant Occupational Physician and Clinical Director Sheffield Occupational Health Service Serious communicable
Cost-benefit analysis and prediction of 24-hour proteinuria from the spot urine proteincreatinine
 Cost-benefit analysis and prediction of 24-hour proteinuria from the spot urine proteincreatinine ratio Chitalia V C, Kothari J, Wells E J, Livesey J H, Robson R A, Searle M, Lynn K L Record Status This
Cost-benefit analysis and prediction of 24-hour proteinuria from the spot urine proteincreatinine ratio Chitalia V C, Kothari J, Wells E J, Livesey J H, Robson R A, Searle M, Lynn K L Record Status This
Scottish Parliament Region: North East Scotland. Case : Tayside NHS Board. Summary of Investigation
 Scottish Parliament Region: North East Scotland Case 201104213: Tayside NHS Board Summary of Investigation Category Health: General Surgical; communication Overview The complainant (Mrs C) raised concerns
Scottish Parliament Region: North East Scotland Case 201104213: Tayside NHS Board Summary of Investigation Category Health: General Surgical; communication Overview The complainant (Mrs C) raised concerns
by Springer-Verlag 1976
 Diabetologia 12, 47-52 (1976) Diabetologia @ by Springer-Verlag 1976 Diabetes, Prediabetes and Uricaemia J. B. Herman, J. H. Medalie and U. Goldbourt Hadassah Univ. Hospital, Jerusalem, and Dept. of Family
Diabetologia 12, 47-52 (1976) Diabetologia @ by Springer-Verlag 1976 Diabetes, Prediabetes and Uricaemia J. B. Herman, J. H. Medalie and U. Goldbourt Hadassah Univ. Hospital, Jerusalem, and Dept. of Family
Assessment of the SF-36 version 2 in the United Kingdom
 46 Health Services Research Unit, University of Oxford, Institute of Health Sciences, Headington, Oxford OX3 7LF Correspondence to: Dr C Jenkinson. Accepted for publication 15 June 1998 Assessment of the
46 Health Services Research Unit, University of Oxford, Institute of Health Sciences, Headington, Oxford OX3 7LF Correspondence to: Dr C Jenkinson. Accepted for publication 15 June 1998 Assessment of the
A.A. in the U.K. 1
 A.A. in the U.K. 1 London in 1947 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Ireland - 1946 1943 Conor F, an Irishman, gets sober in Philadelphia 1946 Conor F visits Ireland on holiday, resolves to create a group in Ireland before
A.A. in the U.K. 1 London in 1947 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Ireland - 1946 1943 Conor F, an Irishman, gets sober in Philadelphia 1946 Conor F visits Ireland on holiday, resolves to create a group in Ireland before
BYSSINOSIS IN THE COTTON INDUSTRY
 Brit. J. industr. Med., 1962, 19, 126. BYSSINOSIS IN THE COTTON INDUSTRY OF EGYPT BY MOSTAFA A. EL BATAWI From the Department of Occupational Health, High Institute of Public Health, Alexandria (RECEIVED
Brit. J. industr. Med., 1962, 19, 126. BYSSINOSIS IN THE COTTON INDUSTRY OF EGYPT BY MOSTAFA A. EL BATAWI From the Department of Occupational Health, High Institute of Public Health, Alexandria (RECEIVED
Nsambya Rubaga Jinja Source: National AIDS Programme, Figure 1. HIV infection rates among pregnant women. Selected sites
 ~ 6 A measure of success in Uganda These groups may have higher levels of infection than the population as a whole. Groups of blood donors, for example, may include injecting drug users who are selling
~ 6 A measure of success in Uganda These groups may have higher levels of infection than the population as a whole. Groups of blood donors, for example, may include injecting drug users who are selling
Karri Silventoinen University of Helsinki and Osaka University
 Karri Silventoinen University of Helsinki and Osaka University Childhood is an important phase of life and creates the base for all further life Childhood is the time of rapid physiological development
Karri Silventoinen University of Helsinki and Osaka University Childhood is an important phase of life and creates the base for all further life Childhood is the time of rapid physiological development
Duncan MacDonald photographed in Edinburgh
 Duncan MacDonald photographed in Edinburgh 48 SCOTS 52 1-112.indd 48 07/04/2011 10:38:10 Scotland s First Lady in America Described as a national treasure, Texan born Miss Duncan MacDonald works energetically
Duncan MacDonald photographed in Edinburgh 48 SCOTS 52 1-112.indd 48 07/04/2011 10:38:10 Scotland s First Lady in America Described as a national treasure, Texan born Miss Duncan MacDonald works energetically
myocardial infarction
 British Heart Journal, I9753 37, 790-794. Serum lipids in young female survivors of myocardial infarction J. I. Mann' and Margaret Thorogood with the technical assistance of R. Jelfs and G. R. Whiting
British Heart Journal, I9753 37, 790-794. Serum lipids in young female survivors of myocardial infarction J. I. Mann' and Margaret Thorogood with the technical assistance of R. Jelfs and G. R. Whiting
Plasma I25I-4abelled fibrinogen clearance in diagnosis of deep venous thrombosis after myocardial infarction
 British Heart Journal, I972, 34, 7II-7I6. Plasma I25I-4abelled fibrinogen clearance in diagnosis of deep venous after myocardial infarction Adrian V. Simmons', Margaret A. Sheppard, and Anthony F. Cox
British Heart Journal, I972, 34, 7II-7I6. Plasma I25I-4abelled fibrinogen clearance in diagnosis of deep venous after myocardial infarction Adrian V. Simmons', Margaret A. Sheppard, and Anthony F. Cox
rheumatica/giant cell arteritis on presentation and
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1989; 48: 667-671 Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C reactive protein in the assessment of polymyalgia rheumatica/giant cell arteritis on presentation and during follow
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases 1989; 48: 667-671 Erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C reactive protein in the assessment of polymyalgia rheumatica/giant cell arteritis on presentation and during follow
Summary of Results of a Survey of New Zealand Participants in IIMHL Exchanges 2003 to By Janet Peters
 Summary of Results of a Survey of New Zealand Participants in IIMHL Exchanges 2003 to 2007 By Janet Peters January 2008 2 Executive Summary After five years of New Zealand s participation in IIMHL leadership
Summary of Results of a Survey of New Zealand Participants in IIMHL Exchanges 2003 to 2007 By Janet Peters January 2008 2 Executive Summary After five years of New Zealand s participation in IIMHL leadership
Monitoring of nutritional status in hospitalized patients: the Australian experience (OP008)
 ESPEN Congress Barcelona 2012 Dietetic session Monitoring of nutritional status in hospitalized patients: the Australian experience (OP008) E. Agarwal (Australia) The Australasian Nutrition Care Day Survey:
ESPEN Congress Barcelona 2012 Dietetic session Monitoring of nutritional status in hospitalized patients: the Australian experience (OP008) E. Agarwal (Australia) The Australasian Nutrition Care Day Survey:
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and
 Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
Copyright is owned by the Author of the thesis. Permission is given for a copy to be downloaded by an individual for the purpose of research and private study only. The thesis may not be reproduced elsewhere
HYPERURICEMIA AND CORRELATES IN CORONARY HEART DISEASE
 HYPERURICEMIA AND CORRELATES IN CORONARY HEART DISEASE Pages with reference to book, From 90 To 94 Akhtar Parvaiz ( Department of Medicine, Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore. ) Akhtar Parvaiz, Hasan
HYPERURICEMIA AND CORRELATES IN CORONARY HEART DISEASE Pages with reference to book, From 90 To 94 Akhtar Parvaiz ( Department of Medicine, Allama Iqbal Medical College, Lahore. ) Akhtar Parvaiz, Hasan
Edinburgh Research Explorer
 Edinburgh Research Explorer Psychological distress as a risk factor for dementia death Citation for published version: Russ, TC, Hamer, M, Stamatakis, E, Starr, J & Batty, GD 2011, 'Psychological distress
Edinburgh Research Explorer Psychological distress as a risk factor for dementia death Citation for published version: Russ, TC, Hamer, M, Stamatakis, E, Starr, J & Batty, GD 2011, 'Psychological distress
The aim of the present study is to see the effect of obesity and urban-rural
 Journal Of Scientific Research in Allied Sciences ISSN NO. 2455-5800 Contents available at: www.jusres.com A STUDY OF AVOIDANT PERSONALITY DISORDER AMONG ADOLESCENT BOYS WITH RELATION TO GRADES OF BMI
Journal Of Scientific Research in Allied Sciences ISSN NO. 2455-5800 Contents available at: www.jusres.com A STUDY OF AVOIDANT PERSONALITY DISORDER AMONG ADOLESCENT BOYS WITH RELATION TO GRADES OF BMI
Guidelines for Gamma Irradiation of Blood Components
 AUSTRALIAN & NEW ZEALAND SOCIETY OF BLOOD TRANSFUSION INC. AUSTRALIAN RED CROSS BLOOD SERVICE NEW ZEALAND BLOOD SERVICE Guidelines for Gamma Irradiation of Blood Components Revised 2003 AN ZS B T Australian
AUSTRALIAN & NEW ZEALAND SOCIETY OF BLOOD TRANSFUSION INC. AUSTRALIAN RED CROSS BLOOD SERVICE NEW ZEALAND BLOOD SERVICE Guidelines for Gamma Irradiation of Blood Components Revised 2003 AN ZS B T Australian
2. Morbidity. Incidence
 2. Morbidity This chapter reports on country-level estimates of incidence, case fatality and prevalence of the following conditions: myocardial infarction (heart attack), stroke, angina and heart failure.
2. Morbidity This chapter reports on country-level estimates of incidence, case fatality and prevalence of the following conditions: myocardial infarction (heart attack), stroke, angina and heart failure.
HIV in the UK: Changes and Challenges; Actions and Answers The People Living With HIV Stigma Survey UK 2015 Scotland STIGMA SURVEY UK 2015
 HIV in the UK: Changes and Challenges; Actions and Answers The People Living With HIV Stigma Survey UK 2015 Scotland STIGMA SURVEY UK 2015 SCOTLAND The landscape for people living with HIV in the United
HIV in the UK: Changes and Challenges; Actions and Answers The People Living With HIV Stigma Survey UK 2015 Scotland STIGMA SURVEY UK 2015 SCOTLAND The landscape for people living with HIV in the United
abcdefghijklmnopqrstu
 Health Workforce Directorate Employment and Retention Division Dear Colleague Best Practice Guidance Hepatitis B infected healthcare workers and antiviral therapy abcdefghijklmnopqrstu CEL 38 (2009) Date
Health Workforce Directorate Employment and Retention Division Dear Colleague Best Practice Guidance Hepatitis B infected healthcare workers and antiviral therapy abcdefghijklmnopqrstu CEL 38 (2009) Date
ribonucleoprotein in SLE and other connective tissue
 Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 442-447 Frequency and clinical significance of antibodies to ribonucleoprotein in SLE and other connective tissue disease subgroups D. M. GRENNAN, C. BUNN, G.
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 1977, 36, 442-447 Frequency and clinical significance of antibodies to ribonucleoprotein in SLE and other connective tissue disease subgroups D. M. GRENNAN, C. BUNN, G.
Potassium status of patients with cirrhosis
 Gut, 1976, 17, 152-157 Potassium status of patients with cirrhosis N. G. SOLER1, S. JAIN, H. JAMES, AND A. PATON From the Dudley Road Hospital, Birmingham, and the Department of Experimental Pathology,
Gut, 1976, 17, 152-157 Potassium status of patients with cirrhosis N. G. SOLER1, S. JAIN, H. JAMES, AND A. PATON From the Dudley Road Hospital, Birmingham, and the Department of Experimental Pathology,
Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic
 Thorax 1984;39:340-344 Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma RICHARD F WILLEY, RONALD J FERGUSSON, DAVID J GODDEN, GRAHAM K CROMPTON,
Thorax 1984;39:340-344 Comparison of oral prednisolone and intramuscular depot triamcinolone in patients with severe chronic asthma RICHARD F WILLEY, RONALD J FERGUSSON, DAVID J GODDEN, GRAHAM K CROMPTON,
Dietary intake in male and female smokers, ex-smokers, and never smokers: The INTERMAP Study
 (2003) 17, 641 654 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dietary intake in male and female smokers, ex-smokers, and never smokers: The
(2003) 17, 641 654 & 2003 Nature Publishing Group All rights reserved 0950-9240/03 $25.00 www.nature.com/jhh ORIGINAL ARTICLE Dietary intake in male and female smokers, ex-smokers, and never smokers: The
Relationship between Twenty-four Hour Urinary Creatinine Excretion and Weight, or Weight and Height of Japanese Children
 J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol., 33, 185-193, 1987 Relationship between Twenty-four Hour Urinary Creatinine Excretion and Weight, or Weight and Height of Japanese Children Masaki MORIYAMA, Hiroshi SAITO,1 and
J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol., 33, 185-193, 1987 Relationship between Twenty-four Hour Urinary Creatinine Excretion and Weight, or Weight and Height of Japanese Children Masaki MORIYAMA, Hiroshi SAITO,1 and
The reliability and validity of the Index of Complexity, Outcome and Need for determining treatment need in Dutch orthodontic practice
 European Journal of Orthodontics 28 (2006) 58 64 doi:10.1093/ejo/cji085 Advance Access publication 8 November 2005 The Author 2005. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Orthodontics
European Journal of Orthodontics 28 (2006) 58 64 doi:10.1093/ejo/cji085 Advance Access publication 8 November 2005 The Author 2005. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Orthodontics
New global report highlights silent epidemic of kidney disease and neglect of treatment and prevention in all countries
 New global report highlights silent epidemic of kidney disease and neglect of treatment and prevention in all countries An estimated 1 in 10 people worldwide have chronic kidney disease **Embargo: 18:00H
New global report highlights silent epidemic of kidney disease and neglect of treatment and prevention in all countries An estimated 1 in 10 people worldwide have chronic kidney disease **Embargo: 18:00H
during and after the second world war
 Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1986, 40, 37-44 Diet and coronary heart disease in England and Wales during and after the second world war D J P BARKER AND C OSMOND From the MRC Environmental
Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health, 1986, 40, 37-44 Diet and coronary heart disease in England and Wales during and after the second world war D J P BARKER AND C OSMOND From the MRC Environmental
PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA AND SOCIAL CLASS
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1964), 18, 157-162 PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA AND SOCIAL CLASS BY From the Department of Social Medicine, University of Aberdeen It has been known for many years that death rates from
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1964), 18, 157-162 PROSTATIC HYPERPLASIA AND SOCIAL CLASS BY From the Department of Social Medicine, University of Aberdeen It has been known for many years that death rates from
ARTERIAL PRESSURE, PHYSIQUE, AND OCCUPATION
 Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1964), 18, 115-124 ARTERIAL PRESSURE, PHYSIQUE, AND OCCUPATION BY C. R. LOWE Department of Social and Occupational Medicine, Welsh National School of Medicine, and Department
Brit. J. prev. soc. Med. (1964), 18, 115-124 ARTERIAL PRESSURE, PHYSIQUE, AND OCCUPATION BY C. R. LOWE Department of Social and Occupational Medicine, Welsh National School of Medicine, and Department
Implementing Recovery in Mental Health Services What can we learn from the UK experience?
 Implementing Recovery in Mental Health Services What can we learn from the UK experience? Montreal, Wednesday 13 th April 2011 Dr. Jed Boardman, Consultant Psychiatrist, South London & Maudsley NHS Trust
Implementing Recovery in Mental Health Services What can we learn from the UK experience? Montreal, Wednesday 13 th April 2011 Dr. Jed Boardman, Consultant Psychiatrist, South London & Maudsley NHS Trust
THE PLASMA LIPIDS IN CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE
 THE PLASMA LIPIDS IN CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE BY M. F. OLIVER* AND G. S. BOYDt From the Dept. of Cardiology, Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh, and the Dept. of Biochemistry, Received June 8, 1953 University of
THE PLASMA LIPIDS IN CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE BY M. F. OLIVER* AND G. S. BOYDt From the Dept. of Cardiology, Royal Infirmary, Edinburgh, and the Dept. of Biochemistry, Received June 8, 1953 University of
Relationship between serum urate concentration and clinically evident incident gout: an individual participant data analysis
 This site uses cookies. More info Home / Online First Article Text Article menu Clinical and epidemiological research Concise report Relationship between serum urate concentration and clinically evident
This site uses cookies. More info Home / Online First Article Text Article menu Clinical and epidemiological research Concise report Relationship between serum urate concentration and clinically evident
insulin, lipid and lipoprotein levels in twenty-five patients suffering from peripheral arterial disease. Subjects
 Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1972) 48, 409-413. The effect of fenfluramine on glucose tolerance, insulin, lipid and lipoprotein levels in patients with peripheral arterial disease B. P. BLISS M.S.,
Postgraduate Medical Journal (July 1972) 48, 409-413. The effect of fenfluramine on glucose tolerance, insulin, lipid and lipoprotein levels in patients with peripheral arterial disease B. P. BLISS M.S.,
